
- Why Does Water Expand When It Freezes
- Gold Foil Experiment
- Faraday Cage
- Oil Drop Experiment
- Magnetic Monopole
- Why Do Fireflies Light Up
- Types of Blood Cells With Their Structure, and Functions
- The Main Parts of a Plant With Their Functions
- Parts of a Flower With Their Structure and Functions
- Parts of a Leaf With Their Structure and Functions
- Why Does Ice Float on Water
- Why Does Oil Float on Water
- How Do Clouds Form
- What Causes Lightning
- How are Diamonds Made
- Types of Meteorites
- Types of Volcanoes
- Types of Rocks

Photosynthesis
What is photosynthesis.
It is the process by which green plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy that is used to make glucose. The word ‘photosynthesis’ is derived from the Greek word phōs, meaning ‘light’ and synthesis meaning ‘combining together.’
Jan Ingenhousz, the Dutch-born British physician and scientist, discovered the process of photosynthesis.
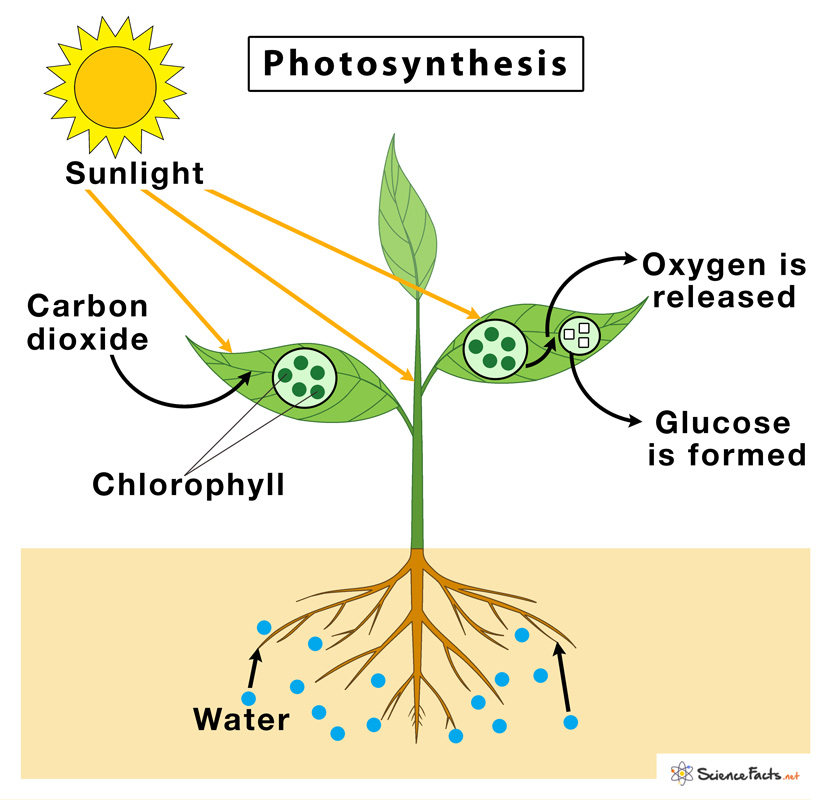
Where does Photosynthesis Occur
Photosynthesis takes place mainly in the leaves of green plants and also in the stems of herbaceous plants as they also contain chlorophyll. Sometimes it also occurs in roots that contain chlorophyll like in water chestnut and Heart-leaved moonseed. Apart from plants, photosynthesis is also found to occur in blue-green algae.
What Happens During Photosynthesis
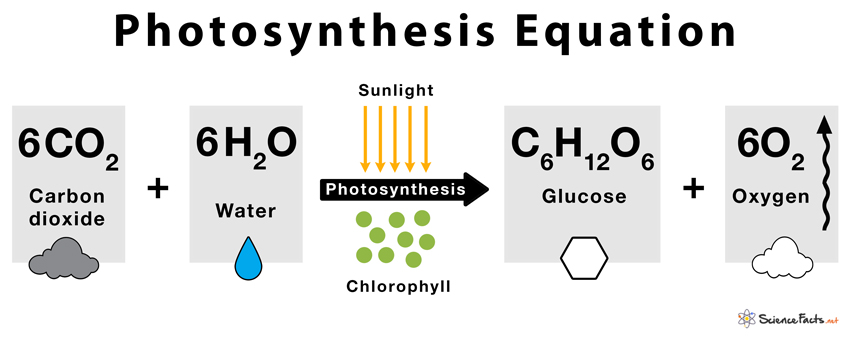
It involves a chemical reaction where water, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, and solar energy are utilized as raw materials (inputs) to produce glucose, oxygen, and water (outputs).
Stages of the Process
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages:
1) The Light-dependent Reaction
- Takes place in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts only during the day in the presence of sunlight
- High-energy phosphate molecules adenosine triphosphate ( ATP ) and the reducing agent NADPH are produced with the help of electron transport chain
2) The Light-independent or Dark Reaction ( Calvin cycle )
- Takes place in the stroma of chloroplast in the absence of light that helps to fix carbon
- ATP and NADPH produced in the light reaction are utilized along with carbon dioxide to produce sugar in the form of glucose
Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis
- Intensity of Light: The higher intensity of light increases the rate of photosynthesis
- Temperature: Warmer the temperature, higher the rate of photosynthesis. The rate is highest between the temperatures of 25° to 35° C, after which it starts to decrease
- Concentration of Carbon dioxide: Higher concentration of carbon dioxide increases the rate of photosynthesis until it reaches a certain point, beyond which no further effects are found
Although all the above factors together interact to affect the rate of photosynthesis, each of them individually is also capable of directly influencing the process without the other factors and thus called limiting factors.
Importance of Photosynthesis
It serves two main purposes that are essential to support life on earth:
- Producing food for organisms that depend on others for their nutrition such as humans along with all other animals
- Synthesizing oxygen by replacing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Ans. Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction because it absorbs the heat of the sun to carry out the process.
Ans. The oxygen in photosynthesis comes from splitting the water molecules.
Ans. Chlorophyll is the main light-absorbing pigment in photosynthesis.
Ans. The role of water is to provide oxygen in the form of oxygen gas to the atmosphere.
Ans. Sunlight is the source of energy that drives photosynthesis.
Ans. The easiest way to measure the rate of photosynthesis is to quantify the carbon dioxide or oxygen levels using a data logger. The rate of photosynthesis can also be measured by determining the increase in the plant ’s biomass (weight).
Ans. Photosynthesis is an energy-requiring process occurring only in green plants, algae, and certain bacteria that utilizes carbon dioxide and water to produce food in the form of carbohydrates. In contrast, cellular respiration is an energy-releasing process found in all living organisms where oxygen and glucose are utilized to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Ans. Glucose produced in photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration to make ATP.
Article was last reviewed on Tuesday, April 21, 2020

Related articles
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Popular Articles

Join our Newsletter
Fill your E-mail Address
Related Worksheets
- Privacy Policy
© 2024 ( Science Facts ). All rights reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part without permission is prohibited.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Biology Wise
A Step-by-step Guide to Understand the Process of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis helps plants to generate glucose, carbohydrates, and oxygen by using carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. In this article, we attempt to answer all your queries about this process.
Like it? Share it!

The foremost thing that one needs to understand is that photosynthesis is important for all lifeforms on the Earth and not just plants. There is no questioning the fact that it occurs in plants, algae, and some species of bacteria, but indirectly, it helps all the organisms which cannot produce their own food, including humans.

Plants, algae, and species of bacteria that can produce their own food are known as photoautotrophs. These organisms―the plants in particular―resort to photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide into organic compounds by using the energy derived from the Sun. The process is also known as carbon fixation process, as it produces carbon compounds which store chemical energy meant to be used in cell growth.
Photosynthesis Process Step by Step
By definition, photosynthesis is a process by which photoautotrophs convert the energy derived from the Sun into usable chemical energy. Light, water, chlorophyll, and carbon dioxide are the basic requirements for this process.
Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere enters the plant leaf through stomata, i.e., minute epidermal pores in the leaves and stem of plants which facilitate the transfer of various gases and water vapor.
Water enters the leaves, primarily through the roots. These roots are especially designed to draw the ground water and transport it to the leaves through the stem.
As sunlight falls on the leaf surface, the chlorophyll, i.e., the green pigment present in the plant leaf, traps the energy in it. Interestingly, the green color of the leaf is also attributed to presence of chlorophyll.
Then hydrogen and oxygen are produced by converting water using the energy derived from the Sun. Hydrogen is combined with carbon dioxide in order to make food for the plant, while oxygen is released through the stomata. Similarly, even algae and bacteria use carbon dioxide and hydrogen to prepare food, while oxygen is let out as a waste product.

The electrons from the chlorophyll molecules and protons from the water molecules facilitate chemical reactions in the cell. These reactions produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which provides energy for cellular reactions, and NADP (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide diphosphate), essential in plant metabolism.
The entire process can be explained by a single chemical formula.
6CO 2 +12H 2 O + Light → C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 + 6H 2 O
While we take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide to produce energy, plants take in carbon dioxide and give out oxygen to produce energy.

Photosynthesis has several benefits, not just for the photoautotrophs, but also for humans and animals. The chemical energy stored in plants is transferred to animals and humans when they consume plant matter. It also helps in maintaining a normal level of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Almost all the oxygen present in the atmosphere can be attributed to this process, which also means that respiration and photosynthesis go together.

Get Updates Right to Your Inbox
Privacy overview.
