
Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research

How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
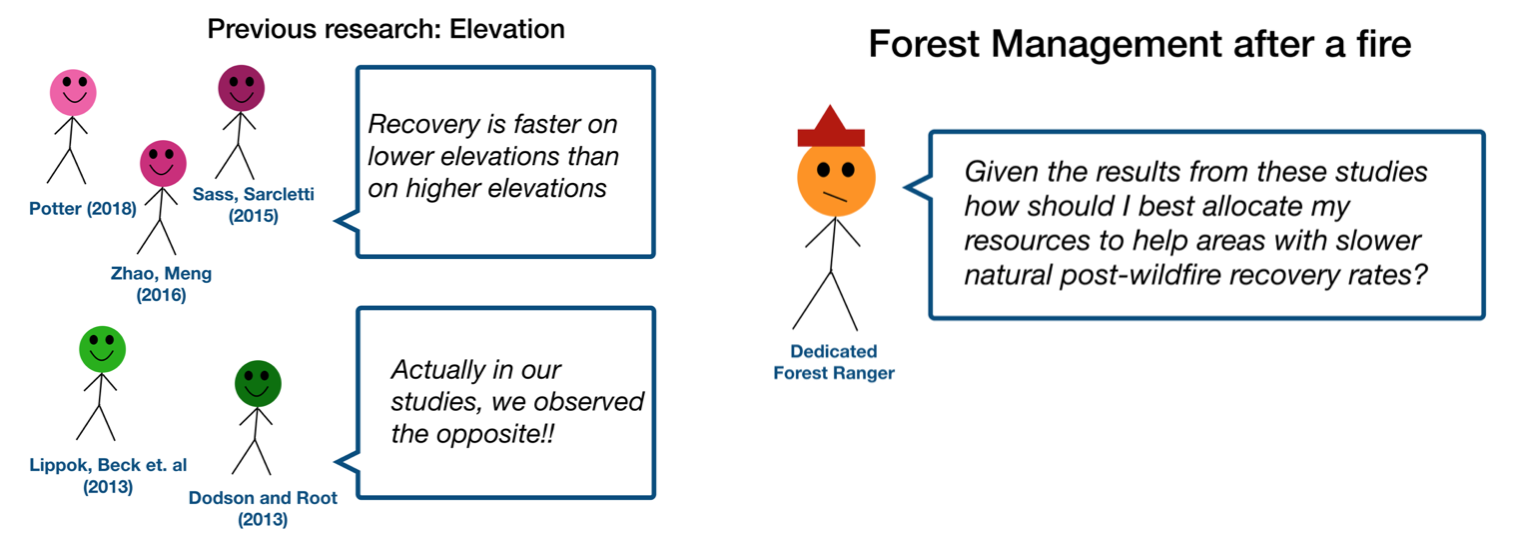
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

- Google Slides Presentation Design
- Pitch Deck Design
- Powerpoint Redesign
- Other Design Services
- Guide & How to's
- How to present a research paper in PPT: best practices
A research paper presentation is frequently used at conferences and other events where you have a chance to share the results of your research and receive feedback from colleagues. Although it may appear as simple as summarizing the findings, successful examples of research paper presentations show that there is a little bit more to it.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the basic outline and steps to create a good research paper presentation. We’ll also explain what to include and what not to include in your presentation of research paper and share some of the most effective tips you can use to take your slides to the next level.
Research paper PowerPoint presentation outline
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves organizing and summarizing your key findings, methodology, and conclusions in a way that encourages your audience to interact with your work and share their interest in it with others. Here’s a basic research paper outline PowerPoint you can follow:
1. Title (1 slide)
Typically, your title slide should contain the following information:
- Title of the research paper
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of presentation
2. Introduction (1-3 slides)
On this slide of your presentation, briefly introduce the research topic and its significance and state the research question or objective.
3. Research questions or hypothesis (1 slide)
This slide should emphasize the objectives of your research or present the hypothesis.
4. Literature review (1 slide)
Your literature review has to provide context for your research by summarizing relevant literature. Additionally, it should highlight gaps or areas where your research contributes.
5. Methodology and data collection (1-2 slides)
This slide of your research paper PowerPoint has to explain the research design, methods, and procedures. It must also Include details about participants, materials, and data collection and emphasize special equipment you have used in your work.
6. Results (3-5 slides)
On this slide, you must present the results of your data analysis and discuss any trends, patterns, or significant findings. Moreover, you should use charts, graphs, and tables to illustrate data and highlight something novel in your results (if applicable).
7. Conclusion (1 slide)
Your conclusion slide has to summarize the main findings and their implications, as well as discuss the broader impact of your research. Usually, a single statement is enough.
8. Recommendations (1 slide)
If applicable, provide recommendations for future research or actions on this slide.
9. References (1-2 slides)
The references slide is where you list all the sources cited in your research paper.
10. Acknowledgments (1 slide)
On this presentation slide, acknowledge any individuals, organizations, or funding sources that contributed to your research.
11. Appendix (1 slide)
If applicable, include any supplementary materials, such as additional data or detailed charts, in your appendix slide.
The above outline is just a general guideline, so make sure to adjust it based on your specific research paper and the time allotted for the presentation.
Steps to creating a memorable research paper presentation
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves several critical steps needed to convey your findings and engage your audience effectively, and these steps are as follows:
Step 1. Understand your audience:
- Identify the audience for your presentation.
- Tailor your content and level of detail to match the audience’s background and knowledge.
Step 2. Define your key messages:
- Clearly articulate the main messages or findings of your research.
- Identify the key points you want your audience to remember.
Step 3. Design your research paper PPT presentation:
- Use a clean and professional design that complements your research topic.
- Choose readable fonts, consistent formatting, and a limited color palette.
- Opt for PowerPoint presentation services if slide design is not your strong side.
Step 4. Put content on slides:
- Follow the outline above to structure your presentation effectively; include key sections and topics.
- Organize your content logically, following the flow of your research paper.
Step 5. Final check:
- Proofread your slides for typos, errors, and inconsistencies.
- Ensure all visuals are clear, high-quality, and properly labeled.
Step 6. Save and share:
- Save your presentation and ensure compatibility with the equipment you’ll be using.
- If necessary, share a copy of your presentation with the audience.
By following these steps, you can create a well-organized and visually appealing research paper presentation PowerPoint that effectively conveys your research findings to the audience.
What to include and what not to include in your presentation
In addition to the must-know PowerPoint presentation recommendations, which we’ll cover later in this article, consider the following do’s and don’ts when you’re putting together your research paper presentation:
- Focus on the topic.
- Be brief and to the point.
- Attract the audience’s attention and highlight interesting details.
- Use only relevant visuals (maps, charts, pictures, graphs, etc.).
- Use numbers and bullet points to structure the content.
- Make clear statements regarding the essence and results of your research.
Don’ts:
- Don’t write down the whole outline of your paper and nothing else.
- Don’t put long, full sentences on your slides; split them into smaller ones.
- Don’t use distracting patterns, colors, pictures, and other visuals on your slides; the simpler, the better.
- Don’t use too complicated graphs or charts; only the ones that are easy to understand.
- Now that we’ve discussed the basics, let’s move on to the top tips for making a powerful presentation of your research paper.
8 tips on how to make research paper presentation that achieves its goals
You’ve probably been to a presentation where the presenter reads word for word from their PowerPoint outline. Or where the presentation is cluttered, chaotic, or contains too much data. The simple tips below will help you summarize a 10 to 15-page paper for a 15 to 20-minute talk and succeed, so read on!
Tip #1: Less is more
You want to provide enough information to make your audience want to know more. Including details but not too many and avoiding technical jargon, formulas, and long sentences are always good ways to achieve this.
Tip #2: Be professional
Avoid using too many colors, font changes, distracting backgrounds, animations, etc. Bullet points with a few words to highlight the important information are preferable to lengthy paragraphs. Additionally, include slide numbers on all PowerPoint slides except for the title slide, and make sure it is followed by a table of contents, offering a brief overview of the entire research paper.
Tip #3: Strive for balance
PowerPoint slides have limited space, so use it carefully. Typically, one to two points per slide or 5 lines for 5 words in a sentence are enough to present your ideas.
Tip #4: Use proper fonts and text size
The font you use should be easy to read and consistent throughout the slides. You can go with Arial, Times New Roman, Calibri, or a combination of these three. An ideal text size is 32 points, while a heading size is 44.
Tip #5: Concentrate on the visual side
A PowerPoint presentation is one of the best tools for presenting information visually. Use graphs instead of tables and topic-relevant illustrations instead of walls of text. Keep your visuals as clean and professional as the content of your presentation.
Tip #6: Practice your delivery
Always go through your presentation when you’re done to ensure a smooth and confident delivery and time yourself to stay within the allotted limit.
Tip #7: Get ready for questions
Anticipate potential questions from your audience and prepare thoughtful responses. Also, be ready to engage in discussions about your research.
Tip #8: Don’t be afraid to utilize professional help
If the mere thought of designing a presentation overwhelms you or you’re pressed for time, consider leveraging professional PowerPoint redesign services . A dedicated design team can transform your content or old presentation into effective slides, ensuring your message is communicated clearly and captivates your audience. This way, you can focus on refining your delivery and preparing for the presentation.
Lastly, remember that even experienced presenters get nervous before delivering research paper PowerPoint presentations in front of the audience. You cannot know everything; some things can be beyond your control, which is completely fine. You are at the event not only to share what you know but also to learn from others. So, no matter what, dress appropriately, look straight into the audience’s eyes, try to speak and move naturally, present your information enthusiastically, and have fun!
If you need help with slide design, get in touch with our dedicated design team and let qualified professionals turn your research findings into a visually appealing, polished presentation that leaves a lasting impression on your audience. Our experienced designers specialize in creating engaging layouts, incorporating compelling graphics, and ensuring a cohesive visual narrative that complements content on any subject.
- Presenting techniques
- 50 tips on how to improve PowerPoint presentations in 2022-2023 [Updated]
- Present financial information visually in PowerPoint to drive results
- Keynote VS PowerPoint
Guide to Research Methods
About the guide
This guide will
- Introduce you to a range of research methods
- Help you think about the value and limitations of different research methods
- Identify when to use alternative research methods
You should use the guide
- After or while you establish your research questions (See the Guide to Research Questions )
- When you are completing your Research Design Framework
- When you are thinking about who you want to talk to and why (See the Guide to Sampling )
You should print or read this guide
These slides are set up so that they can be printed back to back (two/four sided) to give:
- A short hand overview about when to use each method
- A summary of the method, what it’s good for and limitations (linking to other slides in this pack)
Choosing research methods
When you need to think about which method is best in theory and in practice
Choosing Research Methods
Providing a rationale for the methods you choose to use and how you employ them.
- What are your research goals? If you are looking to influence experts or policy makers, quantitative approaches will add weight to your findings. If you are looking to understand problems, inform innovation or develop a prototype, look at qualitative methods or user research
- What are your research questions? If they begin with ‘explore’ or ‘what’ look at qualitative methods (talking). If they begin with ‘identify’ or ‘why’ look at quantitative (see guide to research questions )
- What research traditions exist? You may choose to follow or challenge them. Think about whether you want your research to be noted for its quality and robustness or creative approach and unique insights
- What are your/your teams skills? You may not be an expert in the most appropriate method so consider asking for other team members or commissioning out research
- Who are you research participants? Think about your relationship to participants (especially if you are doing qualitative research) and how they will respond to you and the method. Consider if they are often consulted or surveyed and whether if could be helpful or unhelpful to stick with their comfort zone or not.
Using online tools
When you need to decide which tools to use for research
What to think about when choosing a tool to conduct research
- What’s the cost to the research quality ? Most tools are ‘freemium’, use a basic version for free. BUT these are designed to annoy you to pay to do good research. Consider privacy settings, data access, storage and value for money. Survey tools will have no option to filter participants (if yes/no answer this q), a 10Q limit, no branding. Mapping/visualisations are published online and open source tools aren’t always user friendly
- Start with user needs, understand the context and think about everyone. Consider what technology they have, how they will access the tool and what they need to do this. Do they have internet, data, time?
- Be creative: Online tools may not be designed for research, but Google Forms, Trello, Workflowy and Slack are all valuable collaboration tools. Twitter and Facebook polls may increase participation in research. However, think about what they are missing, what they can’t do and pilot your analysis approach first
- See what’s out there: This online sheet of Applied Social Research Guides and Resources includes a list of online tools for research and evaluation to test. Those widely used for your research method or sector are likely to be the best starting point. Some tools allow you to do research (see Tags for Twitter data capture), analyse it or present it in new ways (see Raw Graph s for data visualisation)
Contents: Methods summary
- Structured Interviews : When you want to gain a broad range of perspectives about specific questions
- Semi-Structured Interviews : When you want to gain in-depth insights about broad questions
- Unstructured Interviews : When you want to gain in-depth insights about a complex research topics
- Telephone Interviews : A tool for when you want to interview people quickly and easily
- Guerilla Interviews : When you want to carry out user research or explore general perspectives quickly
- Contextual Interviews : When you want to understand actions and particular experiences indepth and in context
- Focus Groups : When you want to understand shared experiences and different perspectives
- Participant Observation : When you want to ‘learn by doing’ or observe social interactions and behaviour
- Ethnography : When you want to experience social practices, interactions and behaviour with minimal influence
- Surveys: When you want to generate numerical data about the scale of people’s opinions and feelings
- Mixed Methods: When one method cannot fully answer your main research question
- User Research : When you want to learn about the behaviours and motivations of your target audience
- Service Design Research : When you want to design a service to meet people’s needs.
- Content Analysis : When you want to understand public discourse through secondary or online data
- Workshops : When you want to engage stakeholders in research, generate ideas or codesign solutions
- Usability tests : When you want to test prototypes or learn about problems with an existing service
Find out more
How to do good…
- Applied social research: A curated online sheet of Applied Social Research Guides and Resources
- Surveys : Guide to creating questions here and here , build on existing data/questions , analysis guide
- Interviews : A nice overview here which includes how to structure an interview
- User research : The GDS for intro guides and DisAmbiguity blog
- Service design: This is Service Design Doing has great tools and formats for workshops
Inspiration for emerging research methods and creative formats for research
- Ethnography and mixed methods presented well: Ikea At Home Report
- User mapping techniques as a social research method NPC Report
- User Research to understand domestic abuse experiences and the potential for technology Tech Vs Abuse
- Using Twitter data for social research Demos
- Data visualisation as a tool for research communication - Nesta data visualisation and Women’s Aid Map
- Data journalism and data storytelling - Guardian reading the riots
- An online games to shift perspective on a social problem - Financial Times Uber Story
- Content analysis to map trends - Nesta analysed creative skills in job adverts
- Issue mapping online - networks of websites and people on Twitter - Warwick University Issue Mapping
Structured Interviews
When you want to gain a broad range of perspectives about specific questions
Also consider
Semi-structured interviews
A conversation with a set structure (a script of fixed questions) and specific purpose. Can be a method to undertake a survey or called a ‘directed’ interview.
- Asking standardised questions across many participants makes data easier to analyse and compare
- Giving participants a clear guide about what you want to learn from them
- Topics that would be too complex to capture in a questionnaire tick box/short response
- Respondents with limited time, who want to consider responses in advance or do not want to write
- The quality of the interview is less dependent on the interviewer and their rapport with the interviewee
Limitations (and how to avoid or what to consider instead)
- The structure prevents participants from bringing in other ideas (consider semi-structured interviews )
- Whilst quicker to conduct and analyse than semi-structured interviews, they are still resource intensive and only possible to do with limited numbers of people (consider questionnaires online - see surveys )
Semi-Structured Interviews
When you want to gain in-depth insights about broad questions
Participant Observation
User research
Focus groups
Semi-Structured interviews
Conversation with a structure (set of open questions) and clear purpose. Also called directed interviews.
- Exploring a range of perspectives on research questions, engaging experts and getting buy-in to research
- Gaining in-depth insights about how people feel or interpret complex issues
- Topics which are sensitive, difficult to express in writing or to articulate views about in a survey
- Allowing participants to respond in their words, framing what they see as important
Limitations
- Quality can depend on interviewer skills and put people on the spot (consider setting topics in advance)
- The set-up affects the quality of engagement and discussion (consider location, relationship with the interviewee and whether you should do a face to face or Telephone/Online interview )
- Time consuming to do, analyse and compare (consider Structured Interviews or Focus groups )
- Can lack validity as evidence (consider Surveys )
- Explore what people say, think and remember, not what they actually do (consider Participant Observation contextual interviews or User Research ) or shared perspectives (consider Focus groups )
- Easy to provide too much structure and prevent open exploration of a topic (see unstructured interviews )
Unstructured Interviews
When you want to gain in-depth insights about a complex research topics
Contextual interviews
Unstructured interviews
A loosely structured open conversation guided by research topics (also called non-directed interviews)
- Very exploratory research and broad research questions
- Letting the participant guide the interview according to their priorities and views
- In-depth and broad discussion about a person's expertise, experiences and opinions
- Participant can feel like the they are not saying the ‘right’ thing (explain technique and rationale well)
- Whilst useful for expert interviews, an unstructured approach can give the impression that the interviewer is unprepared, lacks knowledge or the research purpose is unclear (consider semi-structured interviews )
- Interviews are longer, resource intensive and only smaller numbers are possible (consider focus groups )
- Generates in-depth insights that are difficult to analyse and compare
- A lack of structure can encourage participants to focus in-depth on one thing they are positive about or know very well in-depth (consider using desk research to inform the interview topics)
Guerilla Interviews
When you want to carry out user research or explore general perspectives quickly and easily
An ‘impromptu’ approach to interviewing, often talking to real people on the street or at a key site
- Gaining immediate responses to a tool or design and insights into a problem
- Informal method means participants can be more relaxed and open
- Speaking to a lot of people, simply, quickly and cheaply about one key question
- User research and user experience of interacting with digital products
- Speaking to people for convenience (users are available in a single place and time) introduces sample bias (but you can add more targeting and profiling of participants, see the Guide to Sampling )
- The lack of formal structure can mean that you miss important questions or insights
- Findings are often unreliable and not generalisable because they rely on a single type of user
- Difficult to understand complexity or gain contextual insights
Telephone / online interviews
A tool for when you want to interview people quickly and easily
Telephone or Online interviews
A tool to conduct an interview (it is not a method in itself) which is not in person/ face to face
- Conducting interviews without the costs of travel and meeting time (often shorter)
- Expert and stakeholder interviews, when you already know the participant well or they are short of time
- Taking notes and looking up information whilst interviewing is less disruptive than in person, easy to record
- Sending informed consent information and interview questions in advance
- Can be difficult to undertake an engaging interview (hard to build rapport on the phone)
- Often need to be shorter and put alongside other meetings
What method are you using?
- Structured interviews : When you want to gain a broad range of perspectives about specific questions
- Semi-structured interviews : When you want to gain in-depth insights about broad questions
- Unstructured interviews : When you want to gain in-depth insights about a complex research topics
Further guides to Interviews : A nice overview here , including how to structure an interview
Contextual Interview
When you want to understand actions and particular experiences in-depth and in context
Ethnography
Interviews conducted with people in a situational context relevant to the research question; also known as contextual inquiry.
- Understanding what happens, experiences and emotions whilst interacting with a tool, service or event.
- Easier for research participants to show rather than explain, participants are active and engaged
- Uncover what happens, what people do, how they behave in the moment, rather than how they remember this and give meaning to these responses later.
- Open and flexible method giving depth of insights about a tool or specific interaction
- Time and resource intensive for the researcher
- Each context is unique - making it difficult to generalise from or to answer broader research questions about experiences (consider semi-structured interviews )
- The researcher influences the interactions and events (consider ethnography or participant observation )
When you want to understand shared experiences and different perspectives
Focus Groups
An organised discussion with a group of participants, led by a facilitator around a few key topics
- Gaining several perspectives about the same topic quickly
- Research contexts and topics where familiarity between participants can generate discussion about similar experiences (or different ones) which may not arise in a one to one interview
- When attitudes, feelings and beliefs are more likely to be revealed in social gathering and interactions
- Including tasks and creative methods to elicit views (e.g. shared ranking of importance of statements)
- Difficult to identify the individual view from the group view (consider semi-structured interviews )
- Group dynamics will affect the conversation focus and participation levels of different members
- The role of the moderator is very significant. Good levels of group leadership and interpersonal skill are required to moderate a group successfully.
- The group set-up is an ‘artificial’ social setting and discussion (consider Participant Observation )
Participant observation
When you want to ‘learn by doing’ and observe social interactions and behaviour
Participant observation/ shadowing
The researcher immerses themselves in lives of participants as an ‘observer’ of their behaviours, practices and interactions. A type of ethnography. The people being observed know about the research.
- Understanding everyday behaviours, interactions and practice in the context that they occur
- Gaining an intuitive understanding of what happens in practice and what this means for those involved
- Allowing research participants to show you what they do, when they can’t describe and remember this well
- Establishing topics for further investigation through more structured or focused research methods
- If explicit (shadowing for example) the research situation is still ‘artificial’
- Your audience may not respect it and can be difficult to generalise from (consider mixed methods)
- The quality of the data is dependent on the researchers’ skills and relationships with participants
When you want to experience social practices, interactions and behaviour with minimal influence on what happens
The systematic study of a group of people or cultures to understand behaviours and interactions. The researcher becomes an ‘insider’. It is a way of presenting research findings, as well as a method, which can include participant observation, document analysis and visual methods.
- When you need to be an ‘insider’ to fully access the research context (such as organisational cultures)
- Presenting how everyday behaviours, interactions and practice occur in context
- Gaining an in-depth knowledge of your research context, participants and social relationships
- When little is known about a research context or topic
- If covert (at a conference or workplace for example) it has implications for informed consent
- If explicit (shadowing for example) the researcher’s presence can affect the interactions and findings
Example use case : Ikea At Home research study to understand how people feel about their home
When you want to generate numerical data about the scale of people’s opinions and feelings
Mixed Methods
A process of systematically collecting information from a large number of different people. Responses are summarised as statistics (online surveys automate this analysis for you).
- Targeting specific types of research participant and providing data about their views
- If designed well, they can be quick, simple and non intrusive for research participants
- Findings can have more credibility than other methods because of their breadth
- Describing, measuring and understanding (a basic questionnaire)
- Statistical analysis, modelling cause and effect (large scale survey designed to represent the population)
- Can raise more questions about what happens and why, lack depth of insight (consider mixed methods )
- Hard to design well and require a lot of time upfront and data skills to analyse the results
- Low completion rates and people feel ‘over surveyed’ (consider incentives )
- Assumes people will be honest and sufficiently aware of the research context to provide credible answers.
Further information: A great guide to creating questions here and here , build on existing data/questions here
When one research method cannot fully answer your main research question
Mixed methods
Combining different methods to answer your research questions, can be a mix of quantitative or qualitative methods or both. It may mean working with different types of data, research designs or being part of a research team (covering different research disciplines)
- Overcoming the limitation of relying on a single research method or approach
- Triangulating findings (i.e. using an additional method) can give them more validity
- Accessing different types of research participants
- A more holistic understanding about how, why and the extent to which something happens
- Answering different types of research questions about frequency and perceptions
- Giving findings more validity and influence because of the range of data and insights
- Requires a broader range of skills and more time to deliver, analyse and report on
- Research design must have strong sequencing (when each method is used and analysed , why) to make the most of a mixed methods approach - not always possible in a tight timescale or short research project
User Research
When you want to learn about people’s needs, behaviours and motivations for using a service
Service Design
S emi-Structured Interviews
Usability testing
A research approach employed to understand users and their needs, motivations and behaviours, primarily to inform service design.
- User-centered design processes which look to ensure services meet the needs of their audience
- Gaining specific insights into how a person interacts with a digital tool or service
- Exploring general needs, behaviours and motivations for a specific target group using a range of services
- Focus on a tool or service can prevent wider analysis, relevance and applicability
- Research can lack credibility due to small numbers, set up, documentation (often highly specific focus)
- Can overlook those who do not use a service for a whole range of reasons
What method?
- User research involves any method which looks at who users are, the problems they face, what they are trying to do and how they use existing services. This can create user personas, user journeys and user experience maps. It largely includes qualitative research methods.
When you want to design a service to meet people’s needs, including planning, organising, infrastructure, communication and components)
A research approach employed in the activity of planning and organising of people, infrastructure, communication and material components of a service, in order to improve quality and interaction.
- Gaining a holistic picture of all components (infrastructure, people, organisations, culture) affecting how a person interacts with a service
- Service design often begins with user research but participants in research include all those involved in delivering (not just using) a service, such as employees and stakeholders in an organisation as well as looking at the context and system which affect how a service works and its effectiveness
Content analysis
When you want to understand public discourse through secondary or online data
A systematic process of classifying and interpreting documents, text or images to analyse key discourses (their meaning) or to quantify patterns (such as word frequencies). This can be done manually or it can be automated.
- Exploring the focus of messages, text or imagery and change over time
- Secondary data sources, such as archives, online social media data (such as Tweets) and news articles
- Gaining a qualitative or quantitative insights about key messages
- Focuses on public and documented interpretations of events and experiences
- Documents are not exhaustive and not all are accessible (or available online/freely)
- Qualitative coding is time intensive to manually classify, reliant on researcher interpretation
- Automated coding for key words can miss nuances and difficult to produce meaningful findings
When you want to engage stakeholders in research, generate ideas or codesign solutions
Also consider:
A tool to undertake research. It is an interactive session, often taking a full day, in which research participants sor stakeholders work intensively on an issue or question. The process can combine elements of qualitative research, brainstorming or problem solving.
- Engaging stakeholders - building empathy with and understanding of research findings
- Understanding problems or prototyping solutions, linked to user research and service design approaches
- Participatory research, allowing participants to shape agendas and outcomes
- Creative, collaborative and engaging activities to build rapport and understanding with participants
- Participatory design, enabling participants to co-design solutions which work for them
- Highly dependent on the right people attending and the facilitation skills
- Can be a lot of time and effort to coordinate a workshop effectively and analyse findings
- The immersive and collaborative environment makes it difficult to document effectively
- Collaborative solutions may duplicate existing problems or solutions
When you want to test prototypes or learn about problems with an existing service
A user research method where you watch participants try to complete specific tasks using your service. Moderated testing involve interaction with the research participant, asking them to explain what they are doing, thinking and feeling. Unmoderated testing is completed alone by the participant.
- Identify any usability issues with a digital service - for example, problems with the language or layout
- Seeing if users understand what they need to do in order to complete designated tasks
- Generating ideas to improve a prototype of existing digital service
- Assessing user experience
- Focus is not on ‘natural’ use (consider contextual interviews , participant observation , ethnography )
- Data is about a specific design and interaction with a tool at that moment
- Findings cannot be generalised or applicable more broadly to understand users and behaviours

- Step 1: Sections in a Research Paper
- Step 2: Order for Preparation
- Step 3: Conceptualizing an Attractive Title
- Step 4: Effectively Reviewing Literature
- Step 5: Drafting the Abstract
- Step 6: Drafting Introduction
- Step 7: Drafting Materials and Methods
- Step 8: Drafting Results
- Step 9: Drafting Discussion
- Step 10: Drafting the Conclusion
- Step 11: Citing and Referencing
- Step 12: Preparing Figures
- Step 13: Preparing Tables
- Step 14: Assigning Authorship
- Step 15: Acknowledgements Section
- Step 16: Checking the Author Guidelines
- Step 17: Proofreading and Editing
- Step 18: Pre-submission Peer-Review
- Step 1: How to Structure a Research Paper?
- Step 3: How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
- Step 4: How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
- Step 5: How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
- Step 6: How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
- Step 7: How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
- Step 8: How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
- Step 9: How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
- Step 10: How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
- Step 15: How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
How to Write a Research Paper – A to Z of Academic Writing
Part of a scientist’s job is to publish research. In fact, some would argue that your experiment is only complete once you have published the results. This makes it available to the scientific community for authentication and the advancement of science. In addition, publishing is essential for a researcher’s career as it validates the research and opens doors for funding and employment. In this section, we give you a step-by-step guide to help you write an effective research paper. So, remember to set aside half an hour each day to write. This habit will make your writing manageable and keep you focused.
There are different types of research papers. The most common ones include:
Original research paper, rapid communication or letter, review article, meeting abstract, paper, and proceedings.
This is a full report written by researchers covering the analysis of their experimental study from start to finish. It is the most common type research manuscript that is published in academic journals. Original articles are expected to follow the IMRAD format.
These are usually written to publish results urgently in rapidly changing or highly competitive fields. They will be brief and may not be separated by headings.It consists of original preliminary results that are likely to have a significant impact in the respective field.
This is a comprehensive summary of a certain topic. It is usually requested by a journal editor and written by a leader in the field. It includes current assessment, latest findings, and future directions of the field. It is a massive undertaking in which approximately 100 research articles are cited. Uninvited reviews are published too, but it is best to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor first.
This is mostly used in the medical field to report interesting occurrences such as previously unknown or emerging pathologies. It could be a report of a single case or multiple cases and will include a short introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
This is a brief report of research presented at an organized meeting such as a conference. These range from an abstract to a full report of the research. It needs to be focused and clear in explaining your topic and the main points of the study that will be shared with the audience.
- STEP 1: How to Structure a Research Paper?
- STEP 2: Order for Preparation of the Manuscript
- STEP 3: How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
- STEP 4: How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
- STEP 5: How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
- STEP 6: How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
- STEP 7: How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 8: How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 9: How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
- STEP 10: How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
- STEP 11: Effectively Citing and Referencing Your Sources
- STEP 12: Preparing Figures
- STEP 13: Preparing Tables
- STEP 14: Assigning Authorship
- STEP 15: How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
- STEP 16: Checking the Author Guidelines Before Preparing the Manuscript
- STEP 17: Proofreading and Editing Your Manuscript
- STEP 18: Pre-submission Peer-Review
How to Structure a Research Paper?
Your research paper should tell a story of how you began your research, what you found, and how it advances your research field. It is important to structure your research paper so that editors and readers can easily find information. The widely adopted structure that research papers mostly follow is the IMRaD format . IMRaD stands for Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion. Additional requirements from journals include an abstract, keywords, acknowledgements, and references. This format helps scientists to tell their story in an organized manner. Authors often find it easier to write the IMRaD sections in a different order. However, the final paper should be collated in the IMRaD format as follows:

Case studies follow a slightly different format to the traditional IMRAD format. They include the following extra sections:
- History and physical examination: Details of the patient’s history. It provides the story of when a patient first sought medical care.
- Diagnostic focus and assessment : Describe the steps taken that lead to a diagnosis and any test results.
- Therapeutic focus and assessment: Explain therapies tried and any other recommendations from consultants. Assess the efficacy of the treatments given.
- Follow-up and outcome: Provide results and state the patient adhered to treatment. Include any side effects.
- Patient perspective: Describe the patient’s experience.
- Patient consent: State that informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Order for Preparation of the Manuscript
As mentioned above, most research publications follow the IMRAD format. However, it is often easier to write each section in a different order than that of the final paper.
Authors recommend you organize the data first and then write the sections as follows:
- Figures and tables: Decide how your data should be presented. You can use graphics, tables or describe it in the text.
- Methods: It is important that anyone can use your methods to reproduce your experiments.
- Results: Here you write only what the results of your experiments were. You do not discuss them here.
- Discussion: This section requires analysis, thought, and a thorough understanding of the literature. You need to discuss your results without repeating the results section.
- Conclusion: This section can either be under a sub-heading or the last paragraph of the discussion. It should inform the reader how your results advance the field.
- Introduction: Now that you have thought about your results in the context of the literature, you can write your introduction.
- Abstract: This is an overview of your paper. Give a concise background of the problem and how you tried to solve it. Next state your main findings.
- Title: As discussed above, this needs to be concise as well as informative. Ensure that it makes sense.
- Keywords: These are used for indexing. Keywords need to be specific. Often you are not allowed to use words that appear in the journal name. Use abbreviations with care and only well-established ones.
- Acknowledgements: This section is to thank anyone involved in the research that does not qualify as an author.
- References: Check the “Guide for authors” for the formatting style. Be accurate and do not include unnecessary references.
How to Conceptualize an Attractive Research Paper Title?
Your research title is the first impression of your paper. A good research paper title is a brief description of the topic, method, sample, and results of your study. A useful formula you could use is:

There are different ways to write a research paper title :
Declarative
State the main conclusions. Example: Mixed strains of probiotics improve antibiotic associated diarrhea.
Descriptive
Describe the subject. Example: Effects of mixed strains of probiotics on antibiotic associated diarrhea.
Interrogative
Use a question for the subject. Example: Do mixed strains of probiotics improve antibiotic associated diarrhea?
We recommend the following five top tips to conceptualize an attractive research title:
- Be descriptive
- Use a low word count (5-15 words)
- Check journal guidelines
- Avoid jargon and symbols
How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review
The process of conducting a literature review can be overwhelming. However, if you start with a clear research question, you can stay focused.
- Literature search: Search for articles related to your research question. Keep notes of the search terms and keywords you use. A list of databases to search and notes of the ones you have searched will prevent duplicate searches.
- What is their research question?
- Are there potential conflicts of interest such as funders who may want a particular result?
- Are their methods sufficient to test the objectives?
- Can you identify any flaws in the research?
- Do their results make sense, or could there be other reasons for their conclusion?
- Are the authors respected in the field?
- Has the research been cited?
- Introduction: Here you introduce the topic. The introduction describes the problem and identifies gaps in knowledge. It also rationalizes your research.
- Discussion: Here you support and compare your results. Use the literature to put your research in context with the current state of knowledge. Furthermore, show how your research has advanced the field.
How to Write a Good Research Paper Abstract
The importance of research paper abstracts cannot be emphasized enough.
- They are used by online databases to index large research works. Therefore, critical keywords must be used.
- Editors and reviewers read an abstract to decide whether an article is worth considering for publication.
- Readers use an abstract to decide whether the research is relevant to them.
A good research paper abstract is a concise and appealing synopsis of your research. There are two ways to write an abstract: structured and unstructured research abstracts . The author guidelines of the journal you are submitting your research to will tell you the format they require.
- The structured abstract has distinct sections with headings. This style enables a reader to easily find the relevant information under clear headings (objective, methods, results, and conclusion). Think of each section as a question and provide a concise but detailed answer under each heading.
- The unstructured abstract is a narrative paragraph of your research. It is similar to the structured abstract but does not contain headings. It gives the context, findings, conclusion, and implications of your paper.
How to Write a Compelling Introduction for a Research Paper
The Introduction section of your research paper introduces your research in the context of the knowledge in the field. First introduce the topic including the problem you are addressing, the importance of solving this problem, and known research and gaps in the knowledge. Then narrow it down to your research questions and hypothesis.
Tips to write an effective introduction for your research paper :
- Give broad background information about the problem.
- Write it in a logical manner so that the reader can follow your thought process.
- Focus on the problem you intend to solve with your research
- Note any solutions in the literature thus far.
- Propose your solution to the problem with reasons.
Done with drafting your research paper?
With enago’s english editing & proofreading service your success is just a step away.

How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper
When writing the Materials and Methods section of a research paper, you need to give enough detail in your methods so that others can reproduce your experiments. However, there is no need to detail established experiments. Readers can find these details in the previously published references you refer to in the methods. Follow these tips to write the Materials and Methods section of your research paper: :
- Write in the past tense because you are reporting on procedures you carried out.
- Avoid unnecessary details that disrupts the flow.
- Materials and equipments should be mentioned throughout the procedure, rather than listed at the beginning of a section.
- Detail any ethics or consent requirements if your study included humans or animal subjects.
- Use standard nomenclature and numbers.
- Ensure you have the correct control experiments.
- Methods should be listed logically.
- Detail statistical methods used to analyze your data.
Here is a checklist of things that should be in your Materials and Methods:
- References of previously published methods.
- Study settings : If the research involves studying a population, give location and context of the site.
- Cell lines : Give their source and detail any contamination tests performed.
- Antibodies : Give details such as catalogue numbers, citations, dilutions used, and batch numbers.
- Animal models : Species, age, and sex of animals as well as ethical compliance information.
- Human subjects : Ethics committee requirements and a statement confirming you received informed consent. If relevant, clinical trial registration numbers and selection criteria.
- Data accession codes for data you deposited in a repository.
- Software : Where you obtained the programs and their version numbers.
- Statistics : Criteria for including or excluding samples or subjects, randomisation methods, details of investigator blinding to avoid bias, appropriateness of statistical tests used for your study.
- Timeframes if relevant.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
Some journals combine the results and discussion section, whereas others have separate headings for each section. If the two sections are combined, you state the results of your research and discuss them immediately afterwards, before presenting your next set of results. The challenge is to present your data in a way that is logical and accurate. Set out your results in the same order as you set out your methods.
When writing the Results section of your research paper remember to include:
- Control group data.
- Relevant statistical values such as p-values.
- Visual illustrations of your results such as figures and tables.
Things that do not belong in the results section:
- Speculation or commentary about the results.
- References – you are reporting your own data.
- Do not repeat data in text if it has been presented in a table or graph.
Keep the discussion section separate . Keep explanations, interpretations, limitations, and comparisons to the literature for the discussion.
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of your research paper answers several questions such as: did you achieve your objectives? How do your results compare to other studies? Were there any limitations to your research? Start discussing your data specifically and then broaden out to how it furthers your field of interest.
Questions to get you started:
- How do your results answer your objectives?
- Why do you think your results are different to published data?
- Do you think further research would help clarify any issues with your data?
The aim is to tell the reader what your results mean. Structure the discussion section of your research paper in a logical manner. Start with an introductory paragraph where you set out the context and main aims of the study. Do this without repeating the introduction. Some authors prefer starting with the major findings first to keep the readers interested.
The next paragraph should discuss what you found, how it compares to other studies, any limitations, your opinion, and what they mean for the field.
The concluding paragraph should talk about the major outcomes of the study. Be careful not to write your conclusion here. Merely highlight the main themes emerging from your data.
Tips to write an effective discussion:
- It is not a literature review. Keep your comments relevant to your results.
- Interpret your results.
- Be concise and remove unnecessary words.
- Do not include results not presented in the result section.
- Ensure your conclusions are supported by your data.
How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper
While writing the conclusion for your research paper, give a summary of your research with emphasis on your findings. Again, structuring the conclusion section of your research paper will make it easier to draft this section. Here are some tips when writing the conclusion of your paper:
- State what you set out to achieve.
- Tell the reader what your major findings were.
- How has your study contributed to the field?
- Mention any limitations.
- End with recommendations for future research.
Having difficulties with understanding concepts on academic writing?
Enago learn can guide you through the manuscript preparation process and help you achieve success.

Effectively Citing and Referencing Your Sources
You need to acknowledge the original work that you talk about in your write-up. There are two reasons for this. First, cite someone’s idea to avoid plagiarism. Plagiarism is when you use words or ideas of others without acknowledging them and this is a serious offence. Second, readers will be able to source the literature you cited easily.
This is done by citing works in your text and providing the full reference for this citation in a reference list at the end of your document.
Tips for effective refencing/citations:
- Keep a detailed list of your references including author(s), publication, year of publication, title, and page numbers.
- Insert a citation (either a number or author name) in-text as you write.
- List the full reference in a reference list according to the style required by the publication.
- Pay attention to details as mistakes will misdirect readers.
Try referencing software tools “cite while you write”. Examples of such referencing software programs include: Mendeley , Endnote , Refworks and Zotero .
Preparing Figures
Some quick tips about figures:
- Legends of graphs and tables must be self-explanatory.
- Use easily distinguishable symbols.
- Place long tables of data in the supplementary material.
- Include a scale bar in photographs.
Preparing Tables
Important pointers for tables:
- Check the author guidelines for table formatting requirements.
- Tables do not have vertical lines in publications.
- Legends must be self-explanatory.
Assigning Authorship
To qualify as an author on a paper, an individual must:
- Make substantial contributions to all stages of the research.
- Draft or revise the manuscript.
- Approve the final version of the article.
- Be accountable for the accuracy and integrity of the research.
Unethical and unprofessional authorships have emerged over the years. These include:
- Gift authorship : An individual is listed as a co-author in lieu of funding or supervision.
- Ghost authorship : An author is paid to write an article but does not contribute to the article in any other way.
- Guest authorship : An individual who is given authorship because they are well known and respected in the field, or they are senior members of staff.
These authors pose a threat to research. Readers may override their concerns with an article if it includes a well-respected co-author. This is especially problematic when decisions about medical interventions are concerned.
How to Write an Acknowledgment Section for a Research Paper
Those who do not qualify as authors but have contributed to the research should be given credit in the acknowledgements section of your research paper . These include funders, supervisors, administrative supporters, writing, editing, and proofreading assistance .
The contributions made by these individuals should be stated and sometimes their written permission to be acknowledged is required by editors.
Has your target journal's author guidelines left you confused?
With enago consult you can talk to our experts through live 1-to-1 video calls.

Points to Note from the Author Instructions Before Preparing the Manuscript
Check the author guidelines for your chosen publication before submission. Publishers mostly have a “House Style” that ensures all their manuscripts are consistent with regards to language, formatting, and style. For example, these guidelines will tell you whether to use UK or US English, which abbreviations are allowed, and how to format figures and tables. They are also especially important for the references section as each journal has their own style.
Proofreading/Editing your Manuscript
Ensure that your manuscript is structured correctly, clearly written, contains the correct technical language, and supports your claims with proper evidence. To ensure the structure is correct, it is essential to edit your paper .
Once you are happy with the manuscript, proofread for small errors. These could be spelling, consistency, spacing, and so forth. Importantly, check that figures and tables include all the necessary data and statistical values. Seek assistance from colleagues or professional editing companies to edit and proofread your manuscript too.
Pre-submission Peer-Review of Your Manuscript
A pre-submission peer-review could improve the quality of articles submitted to journals in general. The benefits include:
- A fresh eye to spot gaps or errors.
- Receiving constructive feedback on your work and writing.
- Improves the clarity of your paper.
You could ask experienced colleagues, supervisors or even professional editing services to review your article.
- Reporting Research
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Open Access Week 2024
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What factors would influence the future of open access (OA) publishing?
Please log in to save materials. Log in
- Resource Library
- Research Methods
- VIVA Grant Recipients
- Vgr-social-work-research
Education Standards
Radford university.
Learning Domain: Social Work
Standard: Basic Research Methodology
Lesson 10: Sampling in Qualitative Research
Lesson 11: qualitative measurement & rigor, lesson 12: qualitative design & data gathering, lesson 1: introduction to research, lesson 2: getting started with your research project, lesson 3: critical information literacy, lesson 4: paradigm, theory, and causality, lesson 5: research questions, lesson 6: ethics, lesson 7: measurement in quantitative research, lesson 8: sampling in quantitative research, lesson 9: quantitative research designs, powerpoint slides: sowk 621.01: research i: basic research methodology.
The twelve lessons for SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University. Dr. DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant.
The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at Radford University.
Version History
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .

Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved October 15, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Introduction to Research
Published by Conrad Stokes Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Introduction to Research"— Presentation transcript:

Critical Reading Strategies: Overview of Research Process

What is research? Lecture 2 INFO61003 Harold Somers.

Introduction to Research Methodology

RESEARCH METHODS Introduction to Research Lecture 1:

Chapter 1 Conducting & Reading Research Baumgartner et al Chapter 1 Nature and Purpose of Research.

Research problem, Purpose, question

RESEARCH DESIGN.

Chapter 3 An Overview of Quantitative Research

MODULE 3 INVESTIGATING HUMAN AND SOCIL DEVELOPMENT IN THE CARIBBEAN.

What is Research ? Research Methodology CHP400:

Educational Research: Competencies for Analysis and Application, 9 th edition. Gay, Mills, & Airasian © 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.

RSBM: Introduction to Research Business School Introduction to Research Dr Gill Green.

What is research? Based on Ranjit Kumar “Research methodology: a step-by-step guide for beginners”, 2005.

Conducting and Reading Research in Health and Human Performance.

Copyright © Allyn & Bacon 2008 Intelligent Consumer Chapter 14 This multimedia product and its contents are protected under copyright law. The following.

CSD 5100 Introduction to Research Methods in CSD Where To Begin?? Selecting the Research Problem Identification of a topic Framing a research problem Research.

Research Tools and Techniques The Research Process: Step 3 & 4 Lecture 8.

Introduction to Research. Purpose of Research Evidence-based practice Validate clinical practice through scientific inquiry Scientific rational must exist.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Download Free PDF
Guidelines to Scientific Paper Writing.pptx

Related papers
Zebrafish, 2012
Journal of Universal College of Medical Sciences, 2021
INTRODUCTION A research paper is a part of academic writing where there is a gathering of information from different sources. It is multistep process. Selection of title is the most important part of research writing. The title which is interesting should be chosen for the research purpose. All the related information is gathered and the title for research is synthesized. After thorough understanding and developing the title, the preliminary outline is made which maintains the logical path for its exploration. After preliminary research, proper research work is started with collection of previous resources which is then organized and important points are noted. Then research paper is written by referring to outlines, notes, articles, journals and books. The research paper should be well structured containing core parts like introduction, material and methods, results and disscussion and important additional parts like title, abstract, references.
A scientific paper is a written report describing original research results whose format has been defined by centuries of developing tradition, editorial practice, scientific ethics and the interplay with printing and publishing services. The result of this process is that virtually every scientific paper has a title, abstract, introduction, materials and methods, results and discussion.
Problems of Education in the 21st Century, ISSN 1822-7864, 2020
Scientific (academic) writing is continuous activity of every scientist (researcher), and therefore needs to be regularly advanced. Thus, it should be wrong to assume that writing proficiency is achieved once and for all. The skills of academic writing are essential for the independent acquisition of scientific knowledge and for disseminating the acquired information, i.e. sharing knowledge with others. On these grounds, it is worth remembering that a fully completed research paper, the clear results of the conducted research and specific and valid conclusions act as prerequisites for writing a good scientific article etc. Another trivial but important point is that writing an article (or other research paper) is barely a study itself, but only the presentation, dissemination and publicity of the findings. Consequently, even properly carried out research (exploration, examination etc.) and the obtained significant results may fail to be appropriately presented, and the importance of the produced results may simply ‘disappear’ in a poor description.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
Tips on How to Write Scientific Papers, 2019
Journal of Fine Arts Campus
Annals of Forestry, 1993
IAA Journal of Applied Sciences, 2023
Vìsnik Žitomirsʹkogo deržavnogo unìversitetu ìmenì Ìvana Franka, 2021
Microsurgery, 2012
ANZ Journal of Surgery, 2013
Related topics
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Got any suggestions?
We want to hear from you! Send us a message and help improve Slidesgo
Top searches
Trending searches

fall pumpkin
61 templates

15 templates

dia de muertos
24 templates

9 templates

38 templates

thanksgiving
50 templates
Research Presentation templates
Customize our free themes and templates for google slides or powerpoint and explain what your research is about. these designs are easy to edit, so that will speed things up.
- Calendar & Weather
- Infographics
- Marketing Plan
- Project Proposal
- Social Media
- Thesis Defense
- Black & White
- Craft & Notebook
- Floral & Plants
- Illustration
- Interactive & Animated
- Professional
- Instagram Post
- Instagram Stories

It seems that you like this template!

Register for free and start downloading now
Formal research paper slideshow.
Have you seen these slides? They are perfect for presenting your research paper! First of all, because we have included all the necessary sections of this type of work, such as hypothesis, objectives, methodology, analysis and the conclusions of the paper. The second reason is that the formal style will...

Elegant Black & White Thesis Defense
Present your research findings with grace and assertiveness through this template. Available for Google Slides and PowerPoint, this design set offers minimalistic charm with its simple, gray scale elegance. The template not only provides a polished platform to showcase your thesis but also ensures seamless and efficient delivery of your...

Premium template
Unlock this template and gain unlimited access
3D Style Research Poster
Wow, this poster is going to amaze everyone! We've created a poster design for you to include everything about your latest research and present it to those who want to know what you've discovered. We have organized the poster with sections so that you can include an introduction, the basis...

Data Collection and Analysis - Master of Science in Community Health and Prevention Research
Download the "Data Collection and Analysis - Master of Science in Community Health and Prevention Research" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the...

Economics Thesis
If numbers, exchange rates, money and trading are your forte, odds are you’re already working on an economics thesis for your master’s degree. Defending your dissertation is the last step and the most difficult one, but Slidesgo can help you. Here’s our new free presentation template with a focus on...

Muslim Festivities and Celebrations Thesis
Download the Muslim Festivities and Celebrations Thesis presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase your research in the best...

Create your presentation Create personalized presentation content
Writing tone, number of slides, taking care of heart diseases.
Download the "Taking Care of Heart Diseases" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Taking care of yourself and of those around you is key! By learning about various illnesses and how they are spread, people can get a better understanding of them and make informed decisions about eating, exercise, and...

Data Analysis for Business
Download the Data Analysis for Business presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and start impressing your audience with a creative and original design. Slidesgo templates like this one here offer the possibility to convey a concept, idea or topic in a clear, concise and visual way, by using different graphic...

AP Research Defense for High School
AP, or Advanced Placement, is a North American educational program that offers a rigorous course designed to challenge and prepare high school students for their future careers and academic pursuits. It requires students to conduct independent research, write a lengthy academic paper, and present their findings to a panel of...
SWOT Analysis Infographics
Discover the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats of your own company performing a SWOT analysis. Use this basic strategic planning to evaluate your position with these new infographics created by Slidesgo.
Project Research Infographics
Download the "Project Research Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics like this set...

Data Analysis and Statistics - 5th Grade
Download the "Data Analysis and Statistics - 5th Grade" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides and easily edit it to fit your own lesson plan! Designed specifically for elementary school education, this eye-catching design features engaging graphics and age-appropriate fonts; elements that capture the students' attention and make the learning...

Research Methodologies - Master of Arts in English
Master the art of research methodologies with this expertly designed presentation template. Nervous about introducing complex theories? Not a problem! Tailored for Google Slides and PowerPoint, this user-friendly template helps deliver a digestible summary of English literature analytical techniques in a straightforward manner. It's fully customizable and fashioned in a...

Data Analysis for Marketing Strategies
With the amount of data available through various digital platforms, it's easier than ever to determine the trends and preferences of your target audience. By collecting and analyzing data, marketers can create highly personalized campaigns that align with the exact needs and wants of their customers. If you're trying to...

Formulating a Research Problem for University Students
Download the "Formulating a Research Problem for University Students" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. As university curricula increasingly incorporate digital tools and platforms, this template has been designed to integrate with presentation software, online learning management systems, or referencing software, enhancing the overall efficiency and effectiveness of student work....

Vintage French Literature Thesis
Download the Vintage French Literature Thesis presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase your research in the best way...

Cellular Respiration and its Impact on Health Research Thesis Defense
Download the "Cellular Respiration and its Impact on Health Research Thesis Defense" presentation for PowerPoint or Google Slides. Congratulations, you have finally finished your research and made it to the end of your thesis! But now comes the big moment: the thesis defense. You want to make sure you showcase...

Research Proposal for College Students
Research proposals can be both exciting and overwhelming for college students. It's an opportunity to explore a topic they are passionate about and potentially make a valuable contribution to their field of study! If you have some tips and recommendations for college students so that they learn the best way...
- Page 1 of 105
Register for free and start editing online

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor's standpoint.
Creating a PowerPoint presentation for a research paper involves several critical steps needed to convey your findings and engage your audience effectively, and these steps are as follows: Step 1. Understand your audience: Identify the audience for your presentation. Tailor your content and level of detail to match the audience's background ...
Create a focus that fully analyzes your topic. (creates a cause/effect relationship) i.e. John Keats's poetry exhibits many melancholy and gothic characteristics because he wrote most of his work while dying. 5 Step 4: Gather Information That Supports Your Focus Continue to research Begin to refine your focus- remember-it's ok if it changes ...
1. Your outline should be written before you start your paper and after you finish researching. It organizes your thoughts and creates a plan so you know how your paper will look. 2. Your introduction or thesis statement tells the audience what you will explain in your paper. It will let the audience know what to expect from reading your paper. 3.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
This guide will. Introduce you to a range of research methods. Help you think about the value and limitations of different research methods. Identify when to use alternative research methods. You should use the guide. After or while you establish your research questions (See the Guide to Research Questions) When you are completing your Research ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
STEP 7: How to Write the Materials and Methods Section of a Research Paper. STEP 8: How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper. STEP 9: How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper. STEP 10: How to Write the Conclusion of a Research Paper. STEP 11: Effectively Citing and Referencing Your Sources.
A COURSE IN RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 2018.pptx. Naimi AMARA. This teaching paper is an introdcution to the field of research methodology as it enables beginners (students) to understand basic things about research, research techniques , research design and research procedure. The general aim behind this teaching paper is to facilitate the task of ...
Dr. DeCarlo and his team developed a complete package of materials that includes a textbook, ancillary materials, and a student workbook as part of a VIVA Open Course Grant. The PowerPoint slides associated with the twelve lessons of the course, SOWK 621.01: Research I: Basic Research Methodology, as previously taught by Dr. Matthew DeCarlo at ...
When you write a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to: Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context; Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
What is Research? Definition: An organised, systematic, data-based critical scientific inquiry or investigation into a specific problem, undertaken with the objective of finding answers or solutions to it. Outcome: Information that enables managers to make decisions to rectify problems. Data : Primary (first-hand) or Secondary (readily available); Quantitative or Qualitative
Journal of Universal College of Medical Sciences, 2021. INTRODUCTION A research paper is a part of academic writing where there is a gathering of information from different sources. It is multistep process. Selection of title is the most important part of research writing. The title which is interesting should be chosen for the research purpose.
Features of this template. Contains easy-to-edit graphics such as graphs, maps, tables, timelines and mockups. Includes 500+ icons and Flaticon's extension for customizing your slides. Designed to be used in Google Slides, Canva, and Microsoft PowerPoint. 16:9 widescreen format suitable for all types of screens.
Download the "Project Research Infographics" template for PowerPoint or Google Slides and discover the power of infographics. An infographic resource gives you the ability to showcase your content in a more visual way, which will make it easier for your audience to understand your topic. Slidesgo infographics like this set...