Classroom Q&A
With larry ferlazzo.
In this EdWeek blog, an experiment in knowledge-gathering, Ferlazzo will address readers’ questions on classroom management, ELL instruction, lesson planning, and other issues facing teachers. Send your questions to [email protected]. Read more from this blog.

What Students Are Really Thinking About Online Learning

- Share article
Today, several students from my classes “wrap things up” in the final post of this series.
“The temptations are REAL!”
Lee Xiong is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
School has been tough. Transferring to all online learning has been the biggest challenge this year for me. As a student, I’d say I’ve usually kept up with all my work for all my classes. The biggest change I’ve seen in myself is becoming less focused with my school work.
Being in a physical classroom is tremendously different from learning online. In a classroom, most of your focus is there, unlike virtually, the temptations are REAL! Yes, self-discipline is good to learn, but when having all this thrown at you, you can’t blame the student for not wanting to work... at least that’s my opinion.
This online learning has affected me personally because during this time, I found myself turning in assignments weeks late. It wasn’t because I was having trouble, it was because I had no motivation and energy to do them. This isn’t the norm for me. Without a routine schedule, I felt lost. That makes me sound like a robot, but I think it’s because it’s been that way since we were so small, change this big is affecting me to the max.
This has taught me that online learning will not be for me in the future! Maybe for one or two classes, but overall I plan for my school life to be set in a physical classroom for the most part. Although this has been a challenging time for school and out in the real world, remembering to stand tall will get us through this together.

“Learning at school is best for me”
Evelynn Vang is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
The online learning experience as a student for me has been fine. I sometimes find myself not interested in doing my assignments and I feel like I’m lazy. I still do the assignments, but I sometimes end up turning in my assignments late. It’s like I’ll do the assignments whenever I feel like doing it.
I can say that there is a reason for this, and that is where I am doing my school work. My home is not a learning environment like at school, where there are teachers, other students, learning tools, desks/tables, chairs, a library, lots of space, and those who you can get support from. At home is like a sleeping or resting environment. In a classroom, I can focus more on my assignments/work and get engaged in the subject. Whenever I’m in a classroom, I feel prepared to learn and get my brain pumped; at home, I feel like it’s very hard to be prepared because I’m always getting distracted. Whenever I need help, my teachers or classmates are there for me. When I have a question at home, I have to wait for a response.
I do have to say that whenever I’m at school, I always feel nervous in class. Now that I’m at home learning, I don’t feel nervous. From my online learning experience right now, I would not choose more online learning in the future because in a school, a classroom is a learning environment. Also, I feel like it’s easier to communicate with my classmates/groups for projects, teachers, counselors, and principal. Learning at a school is best for me.

“I have many responsibilities at home”
Diana Lopez is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
As a student, my online learning experience hasn’t been great. This new learning system has its perks, such as more time to do assignments in the comfort of your home, not having to wake up so early to go to school, and ensuring the safety of the staff as well as the students. Despite these benefits, there are downsides of this method of learning. For example, I have many responsibilities at home, such as taking care of my younger siblings, cooking meals, cleaning up after them, etc. I also find it harder to have any motivation when I’m doing school assignments. When I’m surrounded by all these other temptations like my phone or other electronics, I lose any will to do work.
The environment at home is different from the workspace students have at school. A classroom provides a quiet academic place to do work while a household can be loud and cause students to lose concentration or not even work at all. Additionally, I find that simply reading the instructions for an assignment or lesson isn’t as engaging as when it’s explained by a teacher. The information is much easier to retain when heard rather than simply rushing to read the directions. If I could choose, in the future I would not like to do more online learning because I like having a teacher physically there to help me when I need it. Having a teacher presence helps me focus more on school work, engages me into learning, and the teachers help guide me through the work and are there for any questions I have.

“Online learning has been difficult”
Isabella Sandoval is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
Online learning has been difficult. I feel pressured to try and hurry to finish and turn in all of my assignments on time. Most of my assignments are due at the same time, and a lot of them are time- consuming.
Though, for the most part it’s difficult to adapt to since I’ve had my education in person with my teachers and classmates, I like how I can do the assignments on my own time. I could divide the day and time I complete my work, I can sleep in a little longer, and overall just be comfortable while in my own home. I feel that online learning is nothing compared to physical learning. With physical learning, I can talk to my teachers one on one and visually see and interact with everything. Whereas online, when I have a question, I either have to email or text my teachers, and sometimes they don’t see my message and/or take forever to respond.
In the future, I honestly would not mind doing online learning. Just for a little bit though, because it’s not that bad, it’s just the fact that I can’t physically talk to my teachers in person when I need help or have questions. Communicating with teachers online is what I feel is the most difficult part about online learning.

“My online experience has been interesting”
Brenda Hernandez is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
As a student, my online experience has been interesting. What I like about this experience is that I have more time to talk to my family and call or text some friends. I get to do school work from home and I have time for self-care. I like that I kind of get to choose which classes I should work on first and which I could wait to do after.
What I don’t like about it is that I am on a screen all day. I like electronics, but school has kept me from staring at a screen for hours. I also don’t like that I have more distractions at home. I live in a small apartment with five other people and four dogs.
This experience is different from being in a physical classroom because I socialize less now. In school, I get to hear the opinions and ideas of my friends and classmates. Some of my teachers would tell us to talk to the people around us about the lesson. Now, not everyone’s online at the same time. I have anxiety, which prevents me from texting some friends and some of my classmates. And if I did, they’d take a while to respond. Same with communicating with teachers.
In the future, if I could choose, I’d like to do a bit of online learning and the rest in an actual classroom. Although it depends on the class. I have noticed that some of the classes I’ve been able to complete at home since there isn’t anyone asking questions or reading the directions to stall me from beginning my work. In other classes, it has been more difficult since I’m more of a visual learner for that subject, and my teachers keep me on task.

“My online learning experience hasn’t been the best but not worst experience”
Laitak Briand is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
Being an engaging student during quarantine has been difficult. There have been a lot things that happened during the first weeks since school was canceled. Stores began to close down, parks being shut down, and people told to stay in the house 24-7 unless they needed their necessities.
What I liked about it, though, is that I have more time to do things that I said I wanted to do if I only had time. Now I have time to do things like spend time with family and resting. What I don’t like about online learning is that I have to still do homework even though we are in a pandemic and can’t leave the house.
The experience from doing online learning and going to school physically are vastly different. With online classes, if you need help you have to ask your parents or google. But when you go to school, there is a teacher that can help you. Also, my friends I can’t physically see them when I’m at home, but if I went to school, I could. In the future, if I had to choose to continue online learning or not, I’d choose not because I like to be somewhere I can ask someone near me for help and see if I did something right or wrong. In conclusion, my online learning experience hasn’t been the best but not worst experience I have ever had.

“There is nothing that I liked about it besides how supportive the teachers have been”
Na Lee Her is a junior at Luther Burbank High School:
My experience with online learning is very stressful and hard. I felt this way because of how hard it is for me to understand the assignments and having to not be able to check with your teacher face to face if you are doing it correctly or not. It doesn’t make me confident because I want to make sure that I am actually doing the assignment correctly in order to deserve the credit for it.
Not only that, but having time to do the assignments is another problem. At home, there are many things to take care of, and it makes it hard for me to be able to do my assignments. This makes me turn in the assignment late or not turn it in at all. Last but not least, it is the lack of motivation that makes online learning hard. Not being able to be face to face with friends and teachers gives me no motivation and makes me unhappy about this. I am unable to get ideas from them, and it makes me lose hope because I don’t know what I will do to be able to complete the assignment and meet its requirement. It just makes me very worried and anxious to know that I may have done things wrong or to not know what to do.
During this time of online learning, there is nothing that I liked about it besides how supportive the teachers have been. If I were to choose online learning or learning face to face, I would rather choose learning face to face. I choose this because it is much easier and I get my questions answered right away. Not only that, but I can also get suggestions/ideas from my peers as well.

Thanks to Lee, Evelynn, Diana, Isabella, Brenda, Laitak, and Na Lee for their contributions!
(This is the final post in a multipart series. You can see Part One here , Part Two here , and Part Three here .)
Here is the new question-of-the-week:
What has your online learning experience been as a student? What did you like about it? What didn’t you like about it? How does it compare with your experience as a student in a physical classroom? In the future, if you could choose, would you want to do more online learning? If so, why? If not, why not?
In Part One , five students from the high school where I teach in Sacramento, Calif., shared their reflections.
In Part Two , contributions come from students in Austin Green’s 1st grade class in Utah and others connected with the Kansas State School for the Blind.
In Part Three , contributors came from my class; Ryan Jakacki’s class in Plymouth, Minn.; and Anne Magnin’s class in France.
Consider contributing a question to be answered in a future post. You can send one to me at [email protected] . When you send it in, let me know if I can use your real name if it’s selected or if you’d prefer remaining anonymous and have a pseudonym in mind.
You can also contact me on Twitter at @Larryferlazzo .
Education Week has published a collection of posts from this blog, along with new material, in an e-book form. It’s titled Classroom Management Q&As: Expert Strategies for Teaching .
If you missed any of the highlights from the first eight years of this blog, you can see a categorized list below. The list doesn’t include ones from this current year.
This Year’s Most Popular Q&A Posts
Race & Gender Challenges
Classroom-Management Advice
Best Ways to Begin the School Year
Best Ways to End the School Year
Implementing the Common Core
Student Motivation & Social-Emotional Learning
Teaching Social Studies
Cooperative & Collaborative Learning
Using Tech in the Classroom
Parent Engagement in Schools
Teaching English-Language Learners
Reading Instruction
Writing Instruction
Education Policy Issues
Differentiating Instruction
Math Instruction
Science Instruction
Advice for New Teachers
Author Interviews
Entering the Teaching Profession
The Inclusive Classroom
Learning & the Brain
Administrator Leadership
Teacher Leadership
Relationships in Schools
Professional Development
Instructional Strategies
Best of Classroom Q&A
Professional Collaboration
Classroom Organization
Mistakes in Education
Project-Based Learning
I am also creating a Twitter list including all contributors to this column .
The opinions expressed in Classroom Q&A With Larry Ferlazzo are strictly those of the author(s) and do not reflect the opinions or endorsement of Editorial Projects in Education, or any of its publications.
Sign Up for EdWeek Tech Leader
How does virtual learning impact students in higher education?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, stephanie riegg cellini stephanie riegg cellini nonresident senior fellow - governance studies , brown center on education policy.
August 13, 2021
In 2020, the pandemic pushed millions of college students around the world into virtual learning. As the new academic year begins, many colleges in the U.S. are poised to bring students back to campus, but a large amount of uncertainty remains. Some institutions will undoubtedly continue to offer online or hybrid classes, even as in-person instruction resumes. At the same time, low vaccination rates, new coronavirus variants, and travel restrictions for international students may mean a return to fully online instruction for some U.S. students and many more around the world.
Public attention has largely focused on the learning losses of K-12 students who shifted online during the pandemic. Yet, we may have reason to be concerned about postsecondary students too. What can we expect from the move to virtual learning? How does virtual learning impact student outcomes? And how does it compare to in-person instruction at the postsecondary level?
Several new papers shed light on these issues, building on previous work in higher education and assessing the efficacy of online education in new contexts. The results are generally consistent with past research: Online coursework generally yields worse student performance than in-person coursework. The negative effects of online course-taking are particularly pronounced for less-academically prepared students and for students pursuing bachelor’s degrees. New evidence from 2020 also suggests that the switch to online course-taking in the pandemic led to declines in course completion. However, a few new studies point to some positive effects of online learning, too. This post discusses this new evidence and its implications for the upcoming academic year.
Evaluating online instruction in higher education
A number of studies have assessed online versus in-person learning at the college level in recent years. A key concern in this literature is that students typically self-select into online or in-person programs or courses, confounding estimates of student outcomes. That is, differences in the characteristics of students themselves may drive differences in the outcome measures we observe that are unrelated to the mode of instruction. In addition, the content, instructor, assignments, and other course features might differ across online and in-person modes as well, which makes apples-to-apples comparisons difficult.
The most compelling studies of online education draw on a random assignment design (i.e., randomized control trial or RCT) to isolate the causal effect of online versus in-person learning. Several pathbreaking studies were able to estimate causal impacts of performance on final exams or course grades in recent years. Virtually all of these studies found that online instruction resulted in lower student performance relative to in-person instruction; although in one case , students with hybrid instruction performed similarly to their in-person peers. Negative effects of online course-taking were particularly pronounced for males and less-academically prepared students.
A new paper by Kofoed and co-authors adds to this literature looking specifically at online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in a novel context: the U.S. Military Academy at West Point. When many colleges moved classes completely online or let students choose their own mode of instruction at the start of the pandemic, West Point economics professors arranged to randomly assign students to in-person or online modes of learning. The same instructors taught one online and one in-person economics class each, and all materials, exams, and assignments were otherwise identical, minimizing biases that otherwise stand in the way of true comparisons. They find that online education lowered a student’s final grade by about 0.2 standard deviations. Their work also confirms the results of previous papers, finding that the negative effect of online learning was driven by students with lower academic ability. A follow-up survey of students’ experiences suggests that online students had trouble concentrating on their coursework and felt less connected to both their peers and instructors relative to their in-person peers.
Cacault et al. (2021) also use an RCT to assess the effects of online lectures in a Swiss university. The authors find that having access to a live-streamed lecture in addition to an in-person option improves the achievement of high-ability students, but lowers the achievement of low-ability students. The key to understanding this two-pronged effect is the counterfactual: When streamed lectures substitute for no attendance (e.g., if a student is ill), they can help students, but when streaming lectures substitute for in-person attendance, they can hurt students.
Broader impacts of online learning
One drawback of RCTs is that these studies are typically limited to a single college and often a single course within that college, so it is not clear if the results generalize to other contexts. Several papers in the literature draw on larger samples of students in non-randomized settings and mitigate selection problems with various econometric methods. These papers find common themes: Students in online courses generally get lower grades, are less likely to perform well in follow-on coursework, and are less likely to graduate than similar students taking in-person classes.
In a recent paper , my co-author Hernando Grueso and I add to this strand of the literature, expanding it to a very different context. We draw on data from the country of Colombia, where students take a mandatory exit exam when they graduate. Using these data, we can assess test scores as an outcome, rather than (more subjective) course grades used in other studies. We can also assess performance across a wide range of institutions, degree programs, and majors.
We find that bachelor’s degree students in online programs perform worse on nearly all test score measures—including math, reading, writing, and English—relative to their counterparts in similar on-campus programs. Results for shorter technical certificates, however, are more mixed. While online students perform significantly worse than on-campus students on exit exams in private institutions, they perform better in SENA, the main public vocational institution in the country, suggesting substantial heterogeneity across institutions in the quality of online programming. Interviews with SENA staff indicate that SENA’s approach of synchronous learning and real-world projects may be working for some online students, but we cannot definitively call this causal evidence, particularly because we can only observe the students who graduate.
A new working paper by Fischer et al. pushes beyond near-term outcomes, like grades and scores, to consider longer-term outcomes, like graduation and time-to-degree, for bachelor’s degree-seeking students in a large public university in California. They find reason to be optimistic about online coursework: When students take courses required for their major online, they are more likely to graduate in four years and see a small decrease in time-to-degree relative to students taking the requirements in-person.
On the other hand, new work considering course completion during the pandemic is less promising. Looking at student outcomes in spring 2020 in Virginia’s community college system, Bird et al. find that the switch to online instruction resulted in an 8.5% reduction in course completion. They find that both withdrawals and failures rose. They also confirm findings in the literature that negative impacts are more extreme among less-academically-prepared students.
Online learning in the fall and beyond
Much more research on virtual learning will undoubtedly be forthcoming post-pandemic. For now, college professors and administrators should consider that college students pushed online may be less prepared for future follow-on classes, their GPAs may be lower, course completion may suffer, and overall learning may have declined relative to in-person cohorts in previous years. These results seem particularly problematic for students with less academic preparation and those in bachelor’s degree programs.
The research is less clear on the impact of virtual instruction on college completion. Although course completion rates appear to be lower for online courses relative to in-person, the evidence is mixed on the impact of virtual instruction on graduation and time-to-degree. The negative learning impacts, reduced course completion, and lack of connection with other students and faculty in a virtual environment could ultimately reduce college completion rates. On the other hand, there is also evidence that the availability of online classes may allow students to move through their degree requirement more quickly.
As the fall semester approaches, colleges will need to make critical choices about online, hybrid, and in-person course offerings. Maintaining some of the most successful online courses will enhance flexibility at this uncertain time and allow some students to continue to make progress on their degrees if they get sick or cannot return to campus for other reasons. For those transitioning back to campus, administrators might consider additional in-person programming, review sessions, tutoring, and other enhanced supports as students make up for learning losses associated with the virtual instruction of the past year.
Related Content
Stephanie Riegg Cellini, Kathryn J. Blanchard
July 22, 2021
Daphna Bassok, Lauren Bauer, Stephanie Riegg Cellini, Helen Shwe Hadani, Michael Hansen, Douglas N. Harris, Brad Olsen, Richard V. Reeves, Jon Valant, Kenneth K. Wong
March 12, 2021
Education Policy Higher Education
Governance Studies
Brown Center on Education Policy
Kelli Bird, Ben Castleman
April 23, 2024
Phillip Levine
April 12, 2024
Hannah C. Kistler, Shaun M. Dougherty
April 9, 2024
These 3 charts show the global growth in online learning

More than 20 million new learners registered for online learning in 2021. Image: UNSPLASH/Glenn Carstens-Peters
.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo{-webkit-transition:all 0.15s ease-out;transition:all 0.15s ease-out;cursor:pointer;-webkit-text-decoration:none;text-decoration:none;outline:none;color:inherit;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:hover,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-hover]{-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;}.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo:focus,.chakra .wef-1c7l3mo[data-focus]{box-shadow:0 0 0 3px rgba(168,203,251,0.5);} Johnny Wood

.chakra .wef-9dduvl{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-9dduvl{font-size:1.125rem;}} Explore and monitor how .chakra .wef-15eoq1r{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-size:1.25rem;color:#F7DB5E;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-15eoq1r{font-size:1.125rem;}} COVID-19 is affecting economies, industries and global issues

.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;color:#2846F8;font-size:1.25rem;}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-1nk5u5d{font-size:1.125rem;}} Get involved with our crowdsourced digital platform to deliver impact at scale
Stay up to date:.
Listen to the article
- People are increasingly accessing online courses to help them navigate today’s ever changing labour market.
- Online learning platform Coursera recorded 20 million new student registrations in 2021.
- The highest rate of new learner growth online came from emerging economies.
- Online learning is an important tool helping to close the widening global skills gap.
The number of students accessing its online courses now exceeds pre-pandemic levels, a leading global online learning platform reports. Following the COVID-19-induced shift to remote working, people are increasingly looking to digital learning to develop the skills to navigate today’s constantly evolving world of work.
Online learning platform Coursera has released its 2021 Impact Report, which shows more than 20 million new learners registered for courses in the year - equivalent to total growth in the three years pre-pandemic. The increase continues an upward trend that predates the pandemic but has since gained momentum.
The upward trend in online learning
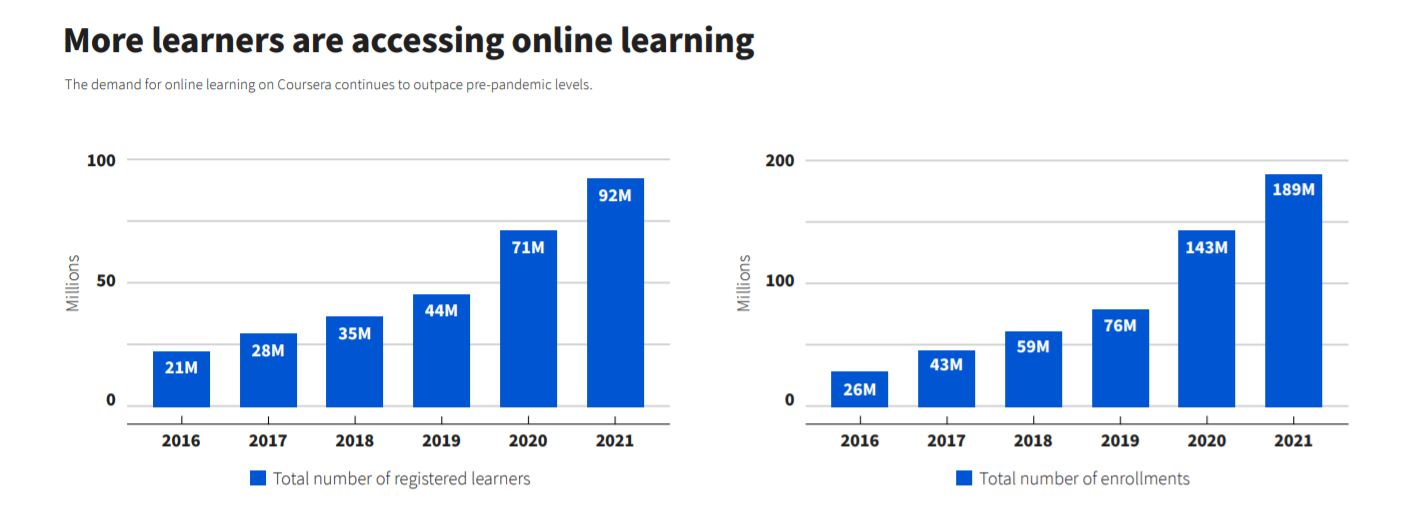
In 2016, 21 million students registered for Coursera’s online courses, a number that increased annually by around 7 million over the next two years. But the switch to remote working as the pandemic hit triggered a three-fold increase in new registrations, bringing the figure to 71 million in 2020, and 92 million in 2021. Course enrolments for online learning followed a similar pattern, with pre-pandemic gains overshadowed by huge spikes. Enrolment numbers more than doubled in 2020 and increased by 32% the following year, peaking at 189 million. These increases reflect growing global acceptance of online teaching, including increases in remote learners taking higher education courses and those from vulnerable or remote communities.
Where do most online learners call home?
Regionally, Asia Pacific saw the biggest student presence on the learning platform, with 28 million new online learners enrolling for 68 million courses, followed by North America, Europe and Latin America. By comparison, just 3 million online learners came from Africa, joining 5 million courses. However, Africa saw the highest growth in both student registrations (up 43%) and course enrolments (up 50%).

At the country level, the US topped the standings with more than 17 million people getting enrolled in online learning, followed by India with 13.6 million. A sizable gap separated these two nations from Mexico with almost 5 million, with Brazil and China completing the top five list.

The highest rate of new learner growth came from emerging economies however, led by Paraguay with 98% growth totalling 110,000 learners.
Lebanon saw 97% growth in learners, with 158,000 in total. Although the Philippines saw 85% learner growth, the South East Asian nation registered 1.3 million learners in total. Other emerging nations with high student totals that saw more than 50% growth in 2021 include Indonesia, Kenya, Vietnam and Kazakhstan.
Have you read?
The future of jobs report 2023, how to follow the growth summit 2023, reskilling for the future.
Access to quality online learning is an important step in helping people future-proof their skills and seek new opportunities for growth and development. The pandemic has accelerated an already fast-changing world, where technologies like AI and automation continue to disrupt labour markets and bring structural change. This creates an uncertain future for many.
Today’s rate of technological change is expected to continue or accelerate in some areas, the Forum’s The Future of Jobs Report 2020 predicts . Cloud computing, big data and e-commerce look set to remain focal points for big business, along with advances in digital encryption, non-humanoid robots and AI.
For many, the future of work is already here. And, although the total number of jobs lost in the technical revolution will be outnumbered by the ‘jobs of tomorrow’ it creates, the immediate impact could displace many workers and leave them without the skills needed to perform new and more technical roles. But disruption also creates new opportunities requiring new skills. And the increased focus on reskilling among both companies and individuals offers a solution. On average, 66% of employers surveyed for the report expect to get a return on investment within a year of upskilling and reskilling employees. There has been a five-fold increase in employer provision of online learning opportunities for employees, a four-fold increase in individuals independently seeking online learning opportunities, and a nine-fold increase in online learning opportunities created through government programmes.
In this environment, the World Economic Forum’s Reskilling Revolution initiative aims to provide one billion people with better education, work skills and employment opportunities by 2030 .
COVID-19 has exposed digital inequities globally and exacerbated the digital divide. Most of the world lives in areas covered by a mobile broadband network, yet more than one-third (2.9 billion people) are still offline. Cost, not coverage, is the barrier to connectivity.
At The Davos Agenda 2021 , the World Economic Forum launched the EDISON Alliance , the first cross-sector alliance to accelerate digital inclusion and connect critical sectors of the economy.
Through the 1 Billion Lives Challenge , the EDISON Alliance aims to improve 1 billion lives globally through affordable and accessible digital solutions across healthcare, financial services and education by 2025.
Read more about the EDISON Alliance’s work in our Impact Story.
The COVID-19 pandemic has changed education forever. This is how
Here's how we can improve online learning for deaf students, digital learning can help us close the global education gap. this is how, don't miss any update on this topic.
Create a free account and access your personalized content collection with our latest publications and analyses.
License and Republishing
World Economic Forum articles may be republished in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International Public License, and in accordance with our Terms of Use.
The views expressed in this article are those of the author alone and not the World Economic Forum.
Related topics:
The agenda .chakra .wef-n7bacu{margin-top:16px;margin-bottom:16px;line-height:1.388;font-weight:400;} weekly.
A weekly update of the most important issues driving the global agenda
.chakra .wef-1dtnjt5{display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;} More on Health and Healthcare Systems .chakra .wef-nr1rr4{display:-webkit-inline-box;display:-webkit-inline-flex;display:-ms-inline-flexbox;display:inline-flex;white-space:normal;vertical-align:middle;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:0.75rem;border-radius:0.25rem;font-weight:700;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;line-height:1.2;-webkit-letter-spacing:1.25px;-moz-letter-spacing:1.25px;-ms-letter-spacing:1.25px;letter-spacing:1.25px;background:none;padding:0px;color:#B3B3B3;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;box-decoration-break:clone;-webkit-box-decoration-break:clone;}@media screen and (min-width:37.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:0.875rem;}}@media screen and (min-width:56.5rem){.chakra .wef-nr1rr4{font-size:1rem;}} See all

This Earth Day we consider the impact of climate change on human health
Shyam Bishen and Annika Green
April 22, 2024

Scientists have invented a method to break down 'forever chemicals' in our drinking water. Here’s how
Johnny Wood
April 17, 2024

Young people are becoming unhappier, a new report finds

Promoting healthy habit formation is key to improving public health. Here's why
Adrian Gore
April 15, 2024

What's 'biophilic design' and how can it benefit neurodivergent people?
Fatemeh Aminpour, Ilan Katz and Jennifer Skattebol
Why stemming the rise of antibiotic resistance will be an historic achievement
Carel du Marchie Sarvaas
April 11, 2024
Online schooling is not just for lockdowns. Could it work for your child?
Associate Professor of Education (Adjunct) & Senior Manager (BCE), Charles Sturt University
Senior Lecturer in Health and Physical Education, University of Tasmania
Disclosure statement
Brendon Hyndman is Senior Manager - Research, Innovation and Impact with Brisbane Catholic Education.
Vaughan Cruickshank does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
Charles Sturt University and University of Tasmania provide funding as members of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
During COVID almost all Australian students and their families experienced online learning. But while schools have long since gone back to in-person teaching, online learning has not gone away.
What are online schools doing now? What does the research say? And how do you know if they might be a good fit for your child?
Online learning in Australia
Online learning for school students has been around in basic form since the 1990s with the School of the Air and other government-run distance education schools for students who are geographically isolated or can’t attend regular school.
But until the pandemic, online schooling was largely considered a special-case scenario. For example, for students who are in hospital or training as an elite athlete.
While learning in COVID lockdowns was extremely tough, it also showed schools, students and parents the potential benefits of online learning for a wider range of students. This can include greater accessibility (learning from any location) and flexibility (personalised, self-paced learning).
Students who have mental health challenges or who are neurodiverse particularly found learning from home suited them better. There is also less hassle with transport and uniforms.
This has prompted an expansion of online learning options in Australia.
Primary and high school options
Some schools have been developing online subjects and options to sit alongside in-person classes. For example, in New South Wales, Queensland and the Australian Capital Territory, some Catholic schools are using online classes to widen subject choices.
Some private schools have also begun fully online or blended online/in-person programs in the recognition some students prefer to learn largely from home.
There are also specialist courses. For example, Monash University has a free virtual school with revision sessions for Year 12 students.

Read more: Australia has a new online-only private school: what are the options if the mainstream system doesn't suit your child?
What about academic outcomes?
Research on the academic outcomes of distance education students is inconclusive.
For example, a 2019 US study of around 200,000 full-time online primary and secondary students showed they had less learning growth in maths and reading compared to their face-to-face peers.
A 2017 study of primary and high school students in Ohio found reduced academic progress in reading, maths, history and science. Another 2017 US study also found online students had lower graduation rates than their in-person peers.
Research has also found it is difficult to authentically teach practical subjects online such as visual arts, design and technology and physical education.
But a lot of research has been limited to a specific context or has not captured whether online learning principles have been followed. Online teaching approaches need to be different from traditional face-to-face methods.
These include ensuring there is an adequate number of teachers allocated and personalised attention for students, and ways to ensure collaboration between students and parental engagement with the school.
What about wellbeing?
Online schooling approaches are still catching up with the support services provided by in-person schools. This includes access to specialists such as psychologists, nurses and social workers.
Some research has noted concerns about online student engagement , social isolation , sense of belonging and social and emotional development .
But COVID showed schools could address these by starting the school day with wellbeing check-ins or supporting mental health through meditation, deep listening journals and taking nature photos.
Online approaches now also include having mentor teachers or summer programs to meet in-person as well as online clubs for students to socialise with each other.

Read more: As homeschooling numbers keep rising in Australia, is more regulation a good idea?
Is online learning a good fit for your child?
Traditional schooling might still be the best option for families who do not have good internet access, or the flexibility or financial freedom to work from home and support your child.
However, if certain subjects are unavailable, or health, elite sport and distance to school make in-person learning difficult, learning online could be a viable option to consider.
Because online learning tends to be a mix of live lessons and self-paced learning, online students need to be independent, motivated and organised to succeed.
The best online learning programs to look out for are those that provide a lot of opportunities for students to learn from each other.
Online learning should also include an active teacher presence, wellbeing support, and quality, interactive digital resources. There should also be flexible approaches to learning and assessment.
- Secondary education
- Primary school
- distance education

Associate Professor, Occupational Therapy

Operations Manager

Project Offier - Diversity & Inclusion

Senior Lecturer - Earth System Science

Sydney Horizon Educators (Identified)

The pros and cons of online learning
What to look for in an online course.
By: MIT xPRO
If you’re at a point in your life where you’re considering continuing your education, you may wonder if online learning is the right path for you.
Taking an online course requires a notable investment of time, effort, and money, so it’s important to feel confident about your decision before moving forward. While online learning works incredibly well for some people, it’s not for everyone.
We recently sat down with MIT xPRO Senior Instructional Designer and Program Manager Luke Hobson to explore the pros and cons of online learning and what to look for in an online course. If you’re waiting for a sign about whether or not to enroll in that course you’ve been eying, you just might find it here.
Pros of Online Learning
First, let’s take a look at the true value of online learning by examining some of the benefits:
1. Flexibility
Online learning’s most significant advantage is its flexibility. It’s the reason millions of adults have chosen to continue their education and pursue certificates and degrees.
Asynchronous courses allow learners to complete work at their own pace, empowering them to find the optimal time to consume the content and submit assignments.
Some people are more attentive, focused, and creative in the mornings compared to the evenings and vice versa. Whatever works best for the learners should be the priority of the learning experience.
2. Community
When Luke asks people about their main reason for enrolling in a course, a common answer is networking and community.
Learners crave finding like-minded individuals who are going through the same experiences and have the same questions. They want to find a place where they belong. Being in the company of others who understand what they’re going through can help online learners who are looking for support and motivation during challenging times and times that are worth celebrating.
Some learners have created study groups and book clubs that have carried on far beyond the end of the course-it’s amazing what can grow from a single post on a discussion board!
3. Latest information
“Speed is a massive benefit of online learning,” and according to Luke, it often doesn’t get the attention it deserves.
“When we say speed, we don’t mean being quick with learning. We mean actual speed to market. There are so many new ideas evolving within technical spaces that it’s impossible to keep courses the way they were originally designed for a long period of time.”
Luke notes that a program on Additive Manufacturing , Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality , or Nanotechnology must be checked and updated frequently. More formal learning modalities have difficulty changing content at this rapid pace. But within the online space, it’s expected that the course content will change as quickly as the world itself does.
Cons of Online Learning
Now that we’ve looked at some of the biggest pros of online learning, let’s examine a few of the drawbacks:
1. Learning environment
While many learners thrive in an asynchronous learning environment, others struggle. Some learners prefer live lessons and an instructor they can connect with multiple times a week. They need these interactions to feel supported and to persist.
Most learners within the online space identify themselves as self-directed learners, meaning they can learn on their own with the right environment, guidance, materials, and assignments. Learners should know themselves first and understand their preferences when it comes to what kind of environment will help them thrive.
2. Repetition
One drawback of online courses is that the structure can be repetitive: do a reading, respond to two discussion posts, submit an essay, repeat. After a while, some learners may feel disengaged from the learning experience.
There are online courses that break the mold and offer multiple kinds of learning activities, assessments, and content to make the learning experience come alive, but it may take some research to find them-more on what to look for in an online course later in this article! Luke and his colleagues at MIT xPRO are mindful of designing courses that genuinely engage learners from beginning to end.
3. Underestimation
Luke has noticed that some learners underestimate how much work is required in an online course. They may mistakenly believe that online learning is somehow “easier” compared to in-person learning.
For those learners who miscalculate how long they will need to spend online or how challenging the assignments can be, changing that mindset is a difficult process. It’s essential to set aside the right amount of time per week to contribute to the content, activities, and assignments. Creating personal deadlines and building a study routine are two best practices that successful online learners follow to hold themselves accountable.
Experience the Value of Online Learning: What to Look For in an Online Course
You’ve probably gathered by now that not all online courses are created equal. On one end of the spectrum, there are methods of online learning that leave learners stunned by what a great experience they had. On the other end of the spectrum, some online learning courses are so disappointing that learners regret their decision to enroll.
If you want to experience the value of online learning, it’s essential to pick the right course. Here’s a quick list of what to look for:
- Feedback and connection to peers within the course platform. Interacting regularly with other learners makes a big difference. Luke and the MIT xPRO team use peer-reviewed feedback to give learners the opportunity to engage with each other’s work.
- Proof of hard work. In the online learning space, proof of hard work often comes in the form of Continuing Education Units (CEUs) or specific certifications. MIT xPRO course participants who successfully complete one or more courses are eligible to receive CEUs , which many employers, licensing agencies, and professional associations accept as evidence of a participant’s serious commitment to their professional development.
Online learning isn’t for everyone, but with the right approach, it can be a valuable experience for many people. Now that you know what to look for in an online course, see what Luke and the MIT xPRO instructional design team have to offer by checking out the latest MIT xPRO courses and programs .
Originally published at http://curve.mit.edu on August 8th, 2022.
The pros and cons of online learning was originally published in MIT Open Learning on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Open Learning newsletter
161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples
🏆 best research title examples about online class, 💡 most interesting online learning topics to write about, 📚 good online education topics for presentation, 🌐 catchy titled for online learning essay, 💻 online class research titles, ❓ research topics about online classes.
- Online Classes Vs. Traditional Classes Essay The essay shall endeavor to examine the differences between online classes and the traditional classes, with a preference for the later.
- Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay The thesis statement for this study is: “online learning has positive impact on the learners, teachers and the institution offering these courses” Online learning or E learning is a term used to describe various learning […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Benefits of Online Learning This knowledge and skill one gains from online help the person to intermingle with others in a better way, progress their profession, or develop their business successfully.
- Comparison of Stress Level Among Traditional Learning and Online Learning College Students The distance learners have been perceived to be enjoying a suitable environment of learning as opposed to the traditional classroom learners who experience high levels of stress.
- Traditional vs. Distance Learning Systems On the other hand, in online learning, the students partake learning individually, and in some cases, students doing the same course in the same college do not even get to know each other.
- How to Succeed in Online Classes The time you attend the class has to coincide with the time of day when your brain is also most receptive to the information it receives.
- Virtual Learning: Yes and No Argumentation The argument stems from the quality of the education that can be received via the internet and what the drawbacks are once there is no physical contact between students and the professors.
- Online Learning and Classroom Learning Combining the two concepts then, we can define e-learning “as a learning environment that exists solely in the form of digital content that is stored, accessed and exchanged through networked computer and information systems” The […]
- Personal Reflections for the MBA Distance Learning I was able to concentrate on various subjects, complete assignments, and liaise with different instructors throughout the learning process. The approach made the learning process desirable and capable of supporting my aims.
- The Importance of Online Learning For this purpose, it is possible to conduct classes in real-time, when they can ask and receive the opinion of others.
- Distance Learning: Advantages and Limitations All three articles cover the topic of distance learning in the context of the coronavirus and everyday practice. Speaking of the advantages of distance learning, the author suggests that remote learning may not be ideal […]
- Learning Objectives Implementation With the advent of the internet, online courses have sprouted resulting in the debate on the two options, traditional class setting, and the online class.
- Distance Learning and Its Evolution Definitions of distance education are varied and diverse, but the main concept of distance learning can be summarized from the situation wherein the student and the educator are separated by distance and time and the […]
- Changes in Learning and Motivation With the Advent of Online Learning Institutions of learning have introduced online learning through improvement of infrastructure, incorporation of new technologies in learning, recruitment of professionals who are conversant with new technologies, and revision of curriculums in order to accommodate new […]
- The Importance of Virtual Learning Communities The learning communities enable the instructors and the students to volunteer their questions. The virtual learning communities enable online degree programs to give students autonomy over the learning process.
- Online Learning Is a Superior Form of Education This paper will argue that online learning is a superior form of education since it helps students and learning institutes to overcome limitations imposed by the traditional learning environment.
- Zoom for Online Learning Updates During the pandemic, the zoom was and is still the most downloaded App in the USA and globally compared to others.
- The Roles of Families in Virtual Learning By analyzing the various roles that families play in virtual learning, the authors demonstrate that family involvement and support are critical to the success of their children The authors begin by discussing the impact of […]
- Distance Learning During the COVID-19 Pandemic The radical transition from the traditional system of obtaining knowledge to virtual education actualizes research related to the analysis of the specifics and dysfunctions of distance learning.
- The Need for Online Learning at St. Francis Elementary School This has led to the need to design an online learning platform suitable for interactive and critical learning experiences by the tutors and their learners.
- Online Learning Perception and Effectiveness While the solution allowed students to access information and continue their studies, there was apprehension in regard to the efficacy of online learning and the outcomes such shifts have on students’ academic performances.
- Distance Learning of Forest Management Considering that the goal of the research was to analyze the results and implications of a practical approach to the forest management course engagement and e-learning development, most information was derived from the expert team […]
- The Impact of Distance Learning on the Mental State The argument of the supporters of the first perspective is based on the fact that online education reduces the ability of students to concentrate and deteriorates overall motivation.
- A Distance Learning Program: Strategies for Successful Starting or Expanding An institution has to identify the most appropriate communication tools and media to be used by students and teachers in a distance learning program.
- Starting and Expanding Distance Learning Program Therefore, decision-makers must grapple with the problem of distant learning planning, as institutions are caught between the desire to serve students online and the requirement to maintain traditional student services.
- Factors for Teachers’ Motivation in Distance Learning Efficient communication with the administration of an institution is a crucial factor that affects the motivation of teachers in distance learning.
- Strengths and Weaknesses of Online Learning Amidst that confusion, it would be important to take a deep look into the subject and see the disadvantages and the advantages of online learning.
- Pros and Cons of Distance Education On the one hand, modernization of education allows it to expand the usual boundaries of transmitting and receiving information in the educational process while retaining all the integral components.
- Rhetorical Analysis of the Distance Education The essay can be addressed both to the children and parents for whom the issues of health and psychology are important.
- Distance Learning Experiences of In-Service Music Teachers From Puerto Rico The study explores the experiences of in-service music teachers in distance learning. This paper examines the motivations of in-service teachers in distance learning.
- Design Thinking for Online Learning Project In this paper, attention will be paid to the problem of a lack of engagement with online learning and a reflection on design thinking as its solution.
- Maximizing the Effectiveness of Online Learning Flipped learning allows the teacher to provide the greatest amount of time for direct interaction with students, which is especially important in the framework of online learning.
- New Online Learning Platform: Market Analysis The goal of online education is to enhance the knowledge of people who want to pursue a particular career for a fee that is lesser when compared to offline studies in Universities.
- Software Engineering Online Learning Center However, it is not easy to tell what the website is promoting just by the look of the homepage and thus, visitors with less time might not be interested to click to the sub-sections and […]
- Distance Education Problem Overview Generally, distance education can be evaluated as a binary prospect: on one hand, it presents a row of advantages for the people who are busy with their work and family duties, and on the other […]
- Negotiation: Distance Learning and Social Change The conflict that arises, in this case, is that the Pirates are demanding ransom money from the owners of the tanker in order to release it and its crew. The essay has given a detailed […]
- Online Learning in Jordan Universities: Effectiveness and Obstruction For the quality learning process, e-learning has been developed to use different approaches to ease the process of learning. E-learning is a novel idea in most of the Arab world and it has come with […]
- Online Learning Institutions and Courses This account allows you to access the online learning institutions library. Which are the most reliable online learning institutions?
- Professional Development Methods: Distance Education Technologies Professional development at universities has included methods to assist faculty in improving course design and educational methods, as well as in becoming familiar with and applying educational technologies, such as distance education tools. These centers […]
- Why Distance Education Can Fulfill the Purpose of a True Education? The only reason I can see for professors to frown upon distance education is that it has removed their infallibility in the eyes of the students.
- Earning a Degree Through Distance Education Though both foreign and traditional education institutions provide knowledge and skills to students in order to enable them become competent in their profession, the institutions vary in the quality of degree courses they provide to […]
- Online Learning in Vocational Education and Training There are different variations in the process of learning on the basis of the types of combination and integration with the other technologies used for the teaching and learning process.
- Distance Learning Fulfilling Education Purpose Distance learning mode of education, which is a kind of education that takes place when the teachers and the students are separated by space and time, does not entirely serve the purpose of education. The […]
- Distributed and Distance Learning Systems It is a system that can be of great impact to the researchers this is because one is able to get information that will help him or her get a cue for that group that […]
- Social Constructivism in Cooperative and Distance Learning As opposed to the behaviorist view of learning which gives more importance to the imitation aspects of the learner in the learning process, this constructivist theory gives greater room for the active interaction of the […]
- Online Learning and Learning Behaviours In such a way, the main reason for the creation of this project is the increased popularity of online learning and the need for the in-depth investigation of this phenomenon because of its increased demand.
- Nurses and Virtual Learning Environments: Understanding Limits in Nursing Education Despite the expected benefits and improvements in nursing education due to the use of virtual learning environments, this practice may create a number of challenges for students and teachers.
- Online Learning Design Specifications The rapid rise of technologies and the evolution of communication means resulted in the appearance of new approaches to the learning process.
- Innovative Social Networking in Online High School The preparedness of the school is also critical towards the success of this innovative technology. The school should also examine the benefits and bottlenecks of the new technology.
- Online Class and Its Outcome Measurement The focus of the paper will be on the aspect of public evaluation while considering what was involved while evaluating the impact on the class. Therefore, these are some of the outcome measures that can […]
- Online Classes for High School Students I wish to submit to you that the need for extra input in terms of study has caused many parents to enroll their children in online study classes to supplement the knowledge they get from […]
- Online Learning Environments The questions will be posted to the group by the instructor. The learners are likely to face a number of challenges in the course of the module.
- Evaluating Online Learning Tools The learners can be referred to reliable wikis and blogs to integrate the ideas learnt from the class. In this manner, the desires of people to learn are not limited by distance and time.
- Online Learning Principles and Objectives In this way, the students will not only argue the purposes and significance of the course to their life, but also create an interactive session among the students and their instructor. As the instructor, I […]
- Online Learning Space Creating Process On the other hand, a community of practice has been known to mean a crowd of people who are in the same career or share the same interest.
- Distance Learning and Virtual High School This implies that district schools in lines with virtual High school are of much importance to both the educators and students.
- Distance Education: Best Practices and Approaches The study with the use of a case-based learning system undertaken by Cifuentes, Mercer, Alverez, and Bettati in 2010 demonstrated that students could remotely participate in the learning process without the need to be physically […]
- Online Learning and Innovations in Pedagogy On the other hand, computer-based learning can be understood as a learning environment in which computers are used to mediate between learners and content without necessarily being online.
- Efficient Interaction in Distance Learning Classroom The problem is that the number of enrolments in the online form of education is augmenting, even as the knowledge regarding the factors that influence the effectiveness of distance education continues to be scarce.
- Virtual Learning Environments: Effective Use Tutors often face the challenge of effective delivery of lessons in the classroom given the diverse categories of students. Learning objects basically refer to blocks of content that can be interlinked to produce a course.
- Using Wikis to Encourage Online Classes Collaborative Work The problem is that the entire process seems to ignore the relevance of enabling students to interact and share their ideas in the learning environment.
- Technology Acceptance Model of Online Learning The findings of the study demonstrate the effectiveness of external variables related to online learning environments in predicting the ability of users to adopt online learning community.
- Formulating an Online Learning Course Reviewing is done from the student side where a person analyzes the content and readability of the information contained in the online learning program.
- Tone Impact in Distance Education Thus, in this paper, the tone will refer to the tone the instructor implies in the text material and the tone of conversations between the instructors and the students.
- Ethical Issues in Online Learning The online assessment methods should consider the ethical issues arising from the learning process. The assessment methods should be able to prevent all forms of dishonesty during the learning process.
- Virtual Learning Environment: Concord Consortium The problem is that this capitalization can be perceived as sign of rudeness, and it can make reluctant to take part in the discussion. Provided that a teacher can promote the involvement of students, they […]
- High School of Virtual Learning Environment The aim will be to see incorporation of the system, the opportunities, and the challenges faced while using Virtual Learning Environment.
- Transition From Traditional Education to Online Learning The speed of information transfer at any time and anywhere through the internet makes online learning relatively cheap compared to the traditional education system.
- Distance Learning OL and Interactive Video in Higher Education The two-way communication systems as well as the need to interact ‘physically’ between and among the participants are what propelled the adoption of this mode of learning.
- Distance Learning Foundational Concepts Another problem that arises as a result of distance learning is the lack of face to face or one on one contact between teachers or instructors and their students.
- Convenience and Flexibility of the Online Classes The advantage of online courses for full or part-time employed individuals is that you can plan how you take your courses. Online classes also introduce students to a variety of web-based tools and techniques that […]
- Concept of Distance Learning in Modern Education System The accessibility of the distance learning courses mainly depend on the awareness of the instructor to the accessibility issues and how the instructor can best handle the course with consideration of accessibility.
- Creating Student Engagement in Online Learning Environment To contribute to creating and stimulating student engagement in online learning environments, it is important to focus on such factors as the increase of students’ motivation, focus on independent and inquiry-based learning, the active role […]
- Administrative Progressivism in Relation to Online Learning The main idea of the discussion is to consider online learning from the perspective of administrative progressivism with identifying the advantages and disadvantages of using the mentioned approach along with the chosen method of study.
- Contrasting an Online Class to a Traditional Class In most cases, the traditional class syllabus is usually a bit wider hence offering the trainee much more as opposed to online classes where there is lack of provisions for diversification of the subject.
- Comparison of Online Learning and Traditional Learning
- Historical and Socio Cultural Analysis of Online Learning
- Analysis of Using Online Video Lecture on Learning Outcome: The Mediating Role of Student Interaction and Student Engagement
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Synchronous and Asynchronous Learning in an Online Class
- Analysis of the Cyber School as an Institution With Online Methods of Learning
- Benefits & Issues of Online Learning
- Swot Analyis for Online Learning
- Comparing the Effectiveness of Classroom and Online Learning
- How Does Prior Knowledge Impact Students Online Learning Behaviors?
- How Learning Online Works?
- How Technology Can Improve Online Learning?
- Is Face For Face Learning Better Then Online Learning?
- Online Classes: A Successful Learning Environment
- Online Learning For Students With Disabilities
- Pros And Disadvantages of Online Education
- Should Online Learning Be Encouraged?
- Knowledge Gradient Algorithm for a General Class of Online Learning Problems
- Three Online Learning Strategies
- Virtual Learning Environment and Online Education
- What Factors Promote Sustained Online Discussions and Collaborative Learning in a Web-Based Course?
- Adult Learning in an Online Environment
- Analysis on Early Design for Online Learning
- Assessment of Conflict Resolution Strategies Within an Online Learning Team
- Compare and Contrast Online Learning vs Traditional Classroom Learning
- Examining the Factors that Influence how Instructors Provide Feedback in Online Learning Environments
- False Concepts Surrounding The Online Learning Environment
- Generalized Feature Embedding for Supervised, Unsupervised, and Online Learning Tasks
- Implementing Comprehensive Interventions to Support Student Success in Online Learning
- Learning Management Systems (LMS) and Online Education
- Managing Online Learning In Collabrative Group
- Managing the Online Learning Revolution in an MBA course: Quality Assurance through Strategic Development
- Online Education Is a Type of Distance Learning
- Online Learning: High School Students For College
- Online Learning: Stochastic Approximation
- Planning Strategies And Time Management Essential in Online Learning
- Development of Online Technology and the Advantages of E-Learning
- Effectiveness of Online Learning
- Reasons Why Older Students Have a Difficult Time Adjusting to Online Classes
- How Does Online Classes Work
- Why Online Learning Is Not Common Among Primary School Students
- Reasons for Taking Online Classes
- Online Classes Are More Flexible Than Conventional Education
- Online Classes Are Less Effective Than Regular Classroom Classes
- The Four Coursera Online Classes
- The Pros and Cons of Online Classes
- The Advocacy for Online Classes According to Todd Gilman
- Online Classes and Face With Face Classes
- Are Online Classes Beneficial To Students
- The Benefits and Drawbacks of Traditional and Online Classes
- Online Classes Are Becoming A Trend for College Campuses
- Online Classes Should Not Reduce Students’ Options and Opportunities
- Why Are More Students Taking Online Classes
- Online Classes vs. Traditional Classroom Learning
- The Demand for Online Classes
- Online Courses and the Impact of Weaker Interpersonal Connections in Online Classes
- The Similarities Between Online Classes and Traditional Classes
- Comparision Between Traditional Classes and Online Classes
- Online Classes Are Becoming More and More Relevant Now
- Online Classes and Oral Presentation Challenges
- The Primary Difference Between Classroom and Online Classes
- What Is the Newest Innovation in Online Learning?
- What Are Some Good Websites for Online Learning?
- Will Online Learning Will Replace Face to Face Teaching?
- Do Students Appreciate Online Learning?
- What Are the Benefits and Drawbacks of Online Learning?
- Which Is the Best Online Learning Platform?
- Which Machine Learning Algorithms for Classification Support Online Learning?
- How Much Does It Cost to Set up an Online Learning Management System?
- How Is Online Learning More Convenient Over the Traditional Classroom?
- Is Online Learning Becoming More Interactive With the Passage of Time?
- What Is the Relation Between Reinforcement Learning and Online Learning?
- What Are the Issues Related to Online Learning and Teaching?
- Why Do Students Struggle With Online Learning?
- What Problems and Issues Are Seen in Online Learning Communities?
- What Are the Disadvantages of Online Learning?
- What Opportunities Does Online Learning Give?
- What Are the Benefits and Challenges of Online Learning?
- What Is the Difference Between Distance Learning and Online Learning?
- Where Do Online Learning Sites Keep Videos?
- Why Do Many People Find Online Learning Really Hard?
- Is It Possible to Do Online Learning With LSTM?
- Why Do Online Learning Sites Use So Much Handwriting?
- How Effective Is Online Learning in Higher Education?
- Is SMC University a Credible Online Learning Institution?
- What Is Online Learning and Its Types?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/
"161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "161 Online Education Topics and Essay Examples." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/online-learning-essay-topics/.
- College Students Research Ideas
- Distance Education Topics
- Internet Research Ideas
- Classroom Management Essay Topics
- Philosophy of Education Paper Topics
- Study Abroad Research Topics
- Academic Dishonesty Research Ideas
- Bilingual Education Essay Ideas
- Brain-Based Learning Essay Titles
- Computers Essay Ideas
- Performance Indicators Essay Topics
- Learning Styles Essay Topics
- Online Community Essay Topics
- Cheating Questions
- Plagiarism Research Ideas
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley - PMC COVID-19 Collection

Online and face‐to‐face learning: Evidence from students’ performance during the Covid‐19 pandemic
Carolyn chisadza.
1 Department of Economics, University of Pretoria, Hatfield South Africa
Matthew Clance
Thulani mthembu.
2 Department of Education Innovation, University of Pretoria, Hatfield South Africa
Nicky Nicholls
Eleni yitbarek.
This study investigates the factors that predict students' performance after transitioning from face‐to‐face to online learning as a result of the Covid‐19 pandemic. It uses students' responses from survey questions and the difference in the average assessment grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown at a South African university. We find that students' performance was positively associated with good wifi access, relative to using mobile internet data. We also observe lower academic performance for students who found transitioning to online difficult and who expressed a preference for self‐study (i.e. reading through class slides and notes) over assisted study (i.e. joining live lectures or watching recorded lectures). The findings suggest that improving digital infrastructure and reducing the cost of internet access may be necessary for mitigating the impact of the Covid‐19 pandemic on education outcomes.
1. INTRODUCTION
The Covid‐19 pandemic has been a wake‐up call to many countries regarding their capacity to cater for mass online education. This situation has been further complicated in developing countries, such as South Africa, who lack the digital infrastructure for the majority of the population. The extended lockdown in South Africa saw most of the universities with mainly in‐person teaching scrambling to source hardware (e.g. laptops, internet access), software (e.g. Microsoft packages, data analysis packages) and internet data for disadvantaged students in order for the semester to recommence. Not only has the pandemic revealed the already stark inequality within the tertiary student population, but it has also revealed that high internet data costs in South Africa may perpetuate this inequality, making online education relatively inaccessible for disadvantaged students. 1
The lockdown in South Africa made it possible to investigate the changes in second‐year students' performance in the Economics department at the University of Pretoria. In particular, we are interested in assessing what factors predict changes in students' performance after transitioning from face‐to‐face (F2F) to online learning. Our main objectives in answering this study question are to establish what study materials the students were able to access (i.e. slides, recordings, or live sessions) and how students got access to these materials (i.e. the infrastructure they used).
The benefits of education on economic development are well established in the literature (Gyimah‐Brempong, 2011 ), ranging from health awareness (Glick et al., 2009 ), improved technological innovations, to increased capacity development and employment opportunities for the youth (Anyanwu, 2013 ; Emediegwu, 2021 ). One of the ways in which inequality is perpetuated in South Africa, and Africa as a whole, is through access to education (Anyanwu, 2016 ; Coetzee, 2014 ; Tchamyou et al., 2019 ); therefore, understanding the obstacles that students face in transitioning to online learning can be helpful in ensuring more equal access to education.
Using students' responses from survey questions and the difference in the average grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown, our findings indicate that students' performance in the online setting was positively associated with better internet access. Accessing assisted study material, such as narrated slides or recordings of the online lectures, also helped students. We also find lower academic performance for students who reported finding transitioning to online difficult and for those who expressed a preference for self‐study (i.e. reading through class slides and notes) over assisted study (i.e. joining live lectures or watching recorded lectures). The average grades between pre‐lockdown and post‐lockdown were about two points and three points lower for those who reported transitioning to online teaching difficult and for those who indicated a preference for self‐study, respectively. The findings suggest that improving the quality of internet infrastructure and providing assisted learning can be beneficial in reducing the adverse effects of the Covid‐19 pandemic on learning outcomes.
Our study contributes to the literature by examining the changes in the online (post‐lockdown) performance of students and their F2F (pre‐lockdown) performance. This approach differs from previous studies that, in most cases, use between‐subject designs where one group of students following online learning is compared to a different group of students attending F2F lectures (Almatra et al., 2015 ; Brown & Liedholm, 2002 ). This approach has a limitation in that that there may be unobserved characteristics unique to students choosing online learning that differ from those choosing F2F lectures. Our approach avoids this issue because we use a within‐subject design: we compare the performance of the same students who followed F2F learning Before lockdown and moved to online learning during lockdown due to the Covid‐19 pandemic. Moreover, the study contributes to the limited literature that compares F2F and online learning in developing countries.
Several studies that have also compared the effectiveness of online learning and F2F classes encounter methodological weaknesses, such as small samples, not controlling for demographic characteristics, and substantial differences in course materials and assessments between online and F2F contexts. To address these shortcomings, our study is based on a relatively large sample of students and includes demographic characteristics such as age, gender and perceived family income classification. The lecturer and course materials also remained similar in the online and F2F contexts. A significant proportion of our students indicated that they never had online learning experience before. Less than 20% of the students in the sample had previous experience with online learning. This highlights the fact that online education is still relatively new to most students in our sample.
Given the global experience of the fourth industrial revolution (4IR), 2 with rapidly accelerating technological progress, South Africa needs to be prepared for the possibility of online learning becoming the new norm in the education system. To this end, policymakers may consider engaging with various organizations (schools, universities, colleges, private sector, and research facilities) To adopt interventions that may facilitate the transition to online learning, while at the same time ensuring fair access to education for all students across different income levels. 3
1.1. Related literature
Online learning is a form of distance education which mainly involves internet‐based education where courses are offered synchronously (i.e. live sessions online) and/or asynchronously (i.e. students access course materials online in their own time, which is associated with the more traditional distance education). On the other hand, traditional F2F learning is real time or synchronous learning. In a physical classroom, instructors engage with the students in real time, while in the online format instructors can offer real time lectures through learning management systems (e.g. Blackboard Collaborate), or record the lectures for the students to watch later. Purely online courses are offered entirely over the internet, while blended learning combines traditional F2F classes with learning over the internet, and learning supported by other technologies (Nguyen, 2015 ).
Moreover, designing online courses requires several considerations. For example, the quality of the learning environment, the ease of using the learning platform, the learning outcomes to be achieved, instructor support to assist and motivate students to engage with the course material, peer interaction, class participation, type of assessments (Paechter & Maier, 2010 ), not to mention training of the instructor in adopting and introducing new teaching methods online (Lundberg et al., 2008 ). In online learning, instructors are more facilitators of learning. On the other hand, traditional F2F classes are structured in such a way that the instructor delivers knowledge, is better able to gauge understanding and interest of students, can engage in class activities, and can provide immediate feedback on clarifying questions during the class. Additionally, the designing of traditional F2F courses can be less time consuming for instructors compared to online courses (Navarro, 2000 ).
Online learning is also particularly suited for nontraditional students who require flexibility due to work or family commitments that are not usually associated with the undergraduate student population (Arias et al., 2018 ). Initially the nontraditional student belonged to the older adult age group, but with blended learning becoming more commonplace in high schools, colleges and universities, online learning has begun to traverse a wider range of age groups. However, traditional F2F classes are still more beneficial for learners that are not so self‐sufficient and lack discipline in working through the class material in the required time frame (Arias et al., 2018 ).
For the purpose of this literature review, both pure online and blended learning are considered to be online learning because much of the evidence in the literature compares these two types against the traditional F2F learning. The debate in the literature surrounding online learning versus F2F teaching continues to be a contentious one. A review of the literature reveals mixed findings when comparing the efficacy of online learning on student performance in relation to the traditional F2F medium of instruction (Lundberg et al., 2008 ; Nguyen, 2015 ). A number of studies conducted Before the 2000s find what is known today in the empirical literature as the “No Significant Difference” phenomenon (Russell & International Distance Education Certificate Center (IDECC), 1999 ). The seminal work from Russell and IDECC ( 1999 ) involved over 350 comparative studies on online/distance learning versus F2F learning, dating back to 1928. The author finds no significant difference overall between online and traditional F2F classroom education outcomes. Subsequent studies that followed find similar “no significant difference” outcomes (Arbaugh, 2000 ; Fallah & Ubell, 2000 ; Freeman & Capper, 1999 ; Johnson et al., 2000 ; Neuhauser, 2002 ). While Bernard et al. ( 2004 ) also find that overall there is no significant difference in achievement between online education and F2F education, the study does find significant heterogeneity in student performance for different activities. The findings show that students in F2F classes outperform the students participating in synchronous online classes (i.e. classes that require online students to participate in live sessions at specific times). However, asynchronous online classes (i.e. students access class materials at their own time online) outperform F2F classes.
More recent studies find significant results for online learning outcomes in relation to F2F outcomes. On the one hand, Shachar and Yoram ( 2003 ) and Shachar and Neumann ( 2010 ) conduct a meta‐analysis of studies from 1990 to 2009 and find that in 70% of the cases, students taking courses by online education outperformed students in traditionally instructed courses (i.e. F2F lectures). In addition, Navarro and Shoemaker ( 2000 ) observe that learning outcomes for online learners are as effective as or better than outcomes for F2F learners, regardless of background characteristics. In a study on computer science students, Dutton et al. ( 2002 ) find online students perform significantly better compared to the students who take the same course on campus. A meta‐analysis conducted by the US Department of Education finds that students who took all or part of their course online performed better, on average, than those taking the same course through traditional F2F instructions. The report also finds that the effect sizes are larger for studies in which the online learning was collaborative or instructor‐driven than in those studies where online learners worked independently (Means et al., 2010 ).
On the other hand, evidence by Brown and Liedholm ( 2002 ) based on test scores from macroeconomics students in the United States suggest that F2F students tend to outperform online students. These findings are supported by Coates et al. ( 2004 ) who base their study on macroeconomics students in the United States, and Xu and Jaggars ( 2014 ) who find negative effects for online students using a data set of about 500,000 courses taken by over 40,000 students in Washington. Furthermore, Almatra et al. ( 2015 ) compare overall course grades between online and F2F students for a Telecommunications course and find that F2F students significantly outperform online learning students. In an experimental study where students are randomly assigned to attend live lectures versus watching the same lectures online, Figlio et al. ( 2013 ) observe some evidence that the traditional format has a positive effect compared to online format. Interestingly, Callister and Love ( 2016 ) specifically compare the learning outcomes of online versus F2F skills‐based courses and find that F2F learners earned better outcomes than online learners even when using the same technology. This study highlights that some of the inconsistencies that we find in the results comparing online to F2F learning might be influenced by the nature of the course: theory‐based courses might be less impacted by in‐person interaction than skills‐based courses.
The fact that the reviewed studies on the effects of F2F versus online learning on student performance have been mainly focused in developed countries indicates the dearth of similar studies being conducted in developing countries. This gap in the literature may also highlight a salient point: online learning is still relatively underexplored in developing countries. The lockdown in South Africa therefore provides us with an opportunity to contribute to the existing literature from a developing country context.
2. CONTEXT OF STUDY
South Africa went into national lockdown in March 2020 due to the Covid‐19 pandemic. Like most universities in the country, the first semester for undergraduate courses at the University of Pretoria had already been running since the start of the academic year in February. Before the pandemic, a number of F2F lectures and assessments had already been conducted in most courses. The nationwide lockdown forced the university, which was mainly in‐person teaching, to move to full online learning for the remainder of the semester. This forced shift from F2F teaching to online learning allows us to investigate the changes in students' performance.
Before lockdown, classes were conducted on campus. During lockdown, these live classes were moved to an online platform, Blackboard Collaborate, which could be accessed by all registered students on the university intranet (“ClickUP”). However, these live online lectures involve substantial internet data costs for students. To ensure access to course content for those students who were unable to attend the live online lectures due to poor internet connections or internet data costs, several options for accessing course content were made available. These options included prerecorded narrated slides (which required less usage of internet data), recordings of the live online lectures, PowerPoint slides with explanatory notes and standard PDF lecture slides.
At the same time, the university managed to procure and loan out laptops to a number of disadvantaged students, and negotiated with major mobile internet data providers in the country for students to have free access to study material through the university's “connect” website (also referred to as the zero‐rated website). However, this free access excluded some video content and live online lectures (see Table 1 ). The university also provided between 10 and 20 gigabytes of mobile internet data per month, depending on the network provider, sent to students' mobile phones to assist with internet data costs.
Sites available on zero‐rated website
Note : The table summarizes the sites that were available on the zero‐rated website and those that incurred data costs.
High data costs continue to be a contentious issue in Africa where average incomes are low. Gilbert ( 2019 ) reports that South Africa ranked 16th of the 45 countries researched in terms of the most expensive internet data in Africa, at US$6.81 per gigabyte, in comparison to other Southern African countries such as Mozambique (US$1.97), Zambia (US$2.70), and Lesotho (US$4.09). Internet data prices have also been called into question in South Africa after the Competition Commission published a report from its Data Services Market Inquiry calling the country's internet data pricing “excessive” (Gilbert, 2019 ).
3. EMPIRICAL APPROACH
We use a sample of 395 s‐year students taking a macroeconomics module in the Economics department to compare the effects of F2F and online learning on students' performance using a range of assessments. The module was an introduction to the application of theoretical economic concepts. The content was both theory‐based (developing economic growth models using concepts and equations) and skill‐based (application involving the collection of data from online data sources and analyzing the data using statistical software). Both individual and group assignments formed part of the assessments. Before the end of the semester, during lockdown in June 2020, we asked the students to complete a survey with questions related to the transition from F2F to online learning and the difficulties that they may have faced. For example, we asked the students: (i) how easy or difficult they found the transition from F2F to online lectures; (ii) what internet options were available to them and which they used the most to access the online prescribed work; (iii) what format of content they accessed and which they preferred the most (i.e. self‐study material in the form of PDF and PowerPoint slides with notes vs. assisted study with narrated slides and lecture recordings); (iv) what difficulties they faced accessing the live online lectures, to name a few. Figure 1 summarizes the key survey questions that we asked the students regarding their transition from F2F to online learning.

Summary of survey data
Before the lockdown, the students had already attended several F2F classes and completed three assessments. We are therefore able to create a dependent variable that is comprised of the average grades of three assignments taken before lockdown and the average grades of three assignments taken after the start of the lockdown for each student. Specifically, we use the difference between the post‐ and pre‐lockdown average grades as the dependent variable. However, the number of student observations dropped to 275 due to some students missing one or more of the assessments. The lecturer, content and format of the assessments remain similar across the module. We estimate the following equation using ordinary least squares (OLS) with robust standard errors:
where Y i is the student's performance measured by the difference between the post and pre‐lockdown average grades. B represents the vector of determinants that measure the difficulty faced by students to transition from F2F to online learning. This vector includes access to the internet, study material preferred, quality of the online live lecture sessions and pre‐lockdown class attendance. X is the vector of student demographic controls such as race, gender and an indicator if the student's perceived family income is below average. The ε i is unobserved student characteristics.
4. ANALYSIS
4.1. descriptive statistics.
Table 2 gives an overview of the sample of students. We find that among the black students, a higher proportion of students reported finding the transition to online learning more difficult. On the other hand, more white students reported finding the transition moderately easy, as did the other races. According to Coetzee ( 2014 ), the quality of schools can vary significantly between higher income and lower‐income areas, with black South Africans far more likely to live in lower‐income areas with lower quality schools than white South Africans. As such, these differences in quality of education from secondary schooling can persist at tertiary level. Furthermore, persistent income inequality between races in South Africa likely means that many poorer black students might not be able to afford wifi connections or large internet data bundles which can make the transition difficult for black students compared to their white counterparts.
Descriptive statistics
Notes : The transition difficulty variable was ordered 1: Very Easy; 2: Moderately Easy; 3: Difficult; and 4: Impossible. Since we have few responses to the extremes, we combined Very Easy and Moderately as well as Difficult and Impossible to make the table easier to read. The table with a full breakdown is available upon request.
A higher proportion of students reported that wifi access made the transition to online learning moderately easy. However, relatively more students reported that mobile internet data and accessing the zero‐rated website made the transition difficult. Surprisingly, not many students made use of the zero‐rated website which was freely available. Figure 2 shows that students who reported difficulty transitioning to online learning did not perform as well in online learning versus F2F when compared to those that found it less difficult to transition.

Transition from F2F to online learning.
Notes : This graph shows the students' responses to the question “How easy did you find the transition from face‐to‐face lectures to online lectures?” in relation to the outcome variable for performance
In Figure 3 , the kernel density shows that students who had access to wifi performed better than those who used mobile internet data or the zero‐rated data.

Access to online learning.
Notes : This graph shows the students' responses to the question “What do you currently use the most to access most of your prescribed work?” in relation to the outcome variable for performance
The regression results are reported in Table 3 . We find that the change in students' performance from F2F to online is negatively associated with the difficulty they faced in transitioning from F2F to online learning. According to student survey responses, factors contributing to difficulty in transitioning included poor internet access, high internet data costs and lack of equipment such as laptops or tablets to access the study materials on the university website. Students who had access to wifi (i.e. fixed wireless broadband, Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL) or optic fiber) performed significantly better, with on average 4.5 points higher grade, in relation to students that had to use mobile internet data (i.e. personal mobile internet data, wifi at home using mobile internet data, or hotspot using mobile internet data) or the zero‐rated website to access the study materials. The insignificant results for the zero‐rated website are surprising given that the website was freely available and did not incur any internet data costs. However, most students in this sample complained that the internet connection on the zero‐rated website was slow, especially in uploading assignments. They also complained about being disconnected when they were in the middle of an assessment. This may have discouraged some students from making use of the zero‐rated website.
Results: Predictors for student performance using the difference on average assessment grades between pre‐ and post‐lockdown
Coefficients reported. Robust standard errors in parentheses.
∗∗∗ p < .01.
Students who expressed a preference for self‐study approaches (i.e. reading PDF slides or PowerPoint slides with explanatory notes) did not perform as well, on average, as students who preferred assisted study (i.e. listening to recorded narrated slides or lecture recordings). This result is in line with Means et al. ( 2010 ), where student performance was better for online learning that was collaborative or instructor‐driven than in cases where online learners worked independently. Interestingly, we also observe that the performance of students who often attended in‐person classes before the lockdown decreased. Perhaps these students found the F2F lectures particularly helpful in mastering the course material. From the survey responses, we find that a significant proportion of the students (about 70%) preferred F2F to online lectures. This preference for F2F lectures may also be linked to the factors contributing to the difficulty some students faced in transitioning to online learning.
We find that the performance of low‐income students decreased post‐lockdown, which highlights another potential challenge to transitioning to online learning. The picture and sound quality of the live online lectures also contributed to lower performance. Although this result is not statistically significant, it is worth noting as the implications are linked to the quality of infrastructure currently available for students to access online learning. We find no significant effects of race on changes in students' performance, though males appeared to struggle more with the shift to online teaching than females.
For the robustness check in Table 4 , we consider the average grades of the three assignments taken after the start of the lockdown as a dependent variable (i.e. the post‐lockdown average grades for each student). We then include the pre‐lockdown average grades as an explanatory variable. The findings and overall conclusions in Table 4 are consistent with the previous results.
Robustness check: Predictors for student performance using the average assessment grades for post‐lockdown
As a further robustness check in Table 5 , we create a panel for each student across the six assignment grades so we can control for individual heterogeneity. We create a post‐lockdown binary variable that takes the value of 1 for the lockdown period and 0 otherwise. We interact the post‐lockdown dummy variable with a measure for transition difficulty and internet access. The internet access variable is an indicator variable for mobile internet data, wifi, or zero‐rated access to class materials. The variable wifi is a binary variable taking the value of 1 if the student has access to wifi and 0 otherwise. The zero‐rated variable is a binary variable taking the value of 1 if the student used the university's free portal access and 0 otherwise. We also include assignment and student fixed effects. The results in Table 5 remain consistent with our previous findings that students who had wifi access performed significantly better than their peers.
Interaction model
Notes : Coefficients reported. Robust standard errors in parentheses. The dependent variable is the assessment grades for each student on each assignment. The number of observations include the pre‐post number of assessments multiplied by the number of students.
6. CONCLUSION
The Covid‐19 pandemic left many education institutions with no option but to transition to online learning. The University of Pretoria was no exception. We examine the effect of transitioning to online learning on the academic performance of second‐year economic students. We use assessment results from F2F lectures before lockdown, and online lectures post lockdown for the same group of students, together with responses from survey questions. We find that the main contributor to lower academic performance in the online setting was poor internet access, which made transitioning to online learning more difficult. In addition, opting to self‐study (read notes instead of joining online classes and/or watching recordings) did not help the students in their performance.
The implications of the results highlight the need for improved quality of internet infrastructure with affordable internet data pricing. Despite the university's best efforts not to leave any student behind with the zero‐rated website and free monthly internet data, the inequality dynamics in the country are such that invariably some students were negatively affected by this transition, not because the student was struggling academically, but because of inaccessibility of internet (wifi). While the zero‐rated website is a good collaborative initiative between universities and network providers, the infrastructure is not sufficient to accommodate mass students accessing it simultaneously.
This study's findings may highlight some shortcomings in the academic sector that need to be addressed by both the public and private sectors. There is potential for an increase in the digital divide gap resulting from the inequitable distribution of digital infrastructure. This may lead to reinforcement of current inequalities in accessing higher education in the long term. To prepare the country for online learning, some considerations might need to be made to make internet data tariffs more affordable and internet accessible to all. We hope that this study's findings will provide a platform (or will at least start the conversation for taking remedial action) for policy engagements in this regard.
We are aware of some limitations presented by our study. The sample we have at hand makes it difficult to extrapolate our findings to either all students at the University of Pretoria or other higher education students in South Africa. Despite this limitation, our findings highlight the negative effect of the digital divide on students' educational outcomes in the country. The transition to online learning and the high internet data costs in South Africa can also have adverse learning outcomes for low‐income students. With higher education institutions, such as the University of Pretoria, integrating online teaching to overcome the effect of the Covid‐19 pandemic, access to stable internet is vital for students' academic success.
It is also important to note that the data we have at hand does not allow us to isolate wifi's causal effect on students' performance post‐lockdown due to two main reasons. First, wifi access is not randomly assigned; for instance, there is a high chance that students with better‐off family backgrounds might have better access to wifi and other supplementary infrastructure than their poor counterparts. Second, due to the university's data access policy and consent, we could not merge the data at hand with the student's previous year's performance. Therefore, future research might involve examining the importance of these elements to document the causal impact of access to wifi on students' educational outcomes in the country.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The authors acknowledge the helpful comments received from the editor, the anonymous reviewers, and Elizabeth Asiedu.
Chisadza, C. , Clance, M. , Mthembu, T. , Nicholls, N. , & Yitbarek, E. (2021). Online and face‐to‐face learning: Evidence from students’ performance during the Covid‐19 pandemic . Afr Dev Rev , 33 , S114–S125. 10.1111/afdr.12520 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
1 https://mybroadband.co.za/news/cellular/309693-mobile-data-prices-south-africa-vs-the-world.html .
2 The 4IR is currently characterized by increased use of new technologies, such as advanced wireless technologies, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, robotics, among others. This era has also facilitated the use of different online learning platforms ( https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-fourth-industrialrevolution-and-digitization-will-transform-africa-into-a-global-powerhouse/ ).
3 Note that we control for income, but it is plausible to assume other unobservable factors such as parental preference and parenting style might also affect access to the internet of students.
- Almatra, O. , Johri, A. , Nagappan, K. , & Modanlu, A. (2015). An empirical study of face‐to‐face and distance learning sections of a core telecommunication course (Conference Proceedings Paper No. 12944). 122nd ASEE Annual Conference and Exposition, Seattle, Washington State.
- Anyanwu, J. C. (2013). Characteristics and macroeconomic determinants of youth employment in Africa . African Development Review , 25 ( 2 ), 107–129. [ Google Scholar ]
- Anyanwu, J. C. (2016). Accounting for gender equality in secondary school enrolment in Africa: Accounting for gender equality in secondary school enrolment . African Development Review , 28 ( 2 ), 170–191. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arbaugh, J. (2000). Virtual classroom versus physical classroom: An exploratory study of class discussion patterns and student learning in an asynchronous internet‐based MBA course . Journal of Management Education , 24 ( 2 ), 213–233. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arias, J. J. , Swinton, J. , & Anderson, K. (2018). On‐line vs. face‐to‐face: A comparison of student outcomes with random assignment . e‐Journal of Business Education and Scholarship of Teaching, , 12 ( 2 ), 1–23. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bernard, R. M. , Abrami, P. C. , Lou, Y. , Borokhovski, E. , Wade, A. , Wozney, L. , Wallet, P. A. , Fiset, M. , & Huang, B. (2004). How does distance education compare with classroom instruction? A meta‐analysis of the empirical literature . Review of Educational Research , 74 ( 3 ), 379–439. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown, B. , & Liedholm, C. (2002). Can web courses replace the classroom in principles of microeconomics? American Economic Review , 92 ( 2 ), 444–448. [ Google Scholar ]
- Callister, R. R. , & Love, M. S. (2016). A comparison of learning outcomes in skills‐based courses: Online versus face‐to‐face formats . Decision Sciences Journal of Innovative Education , 14 ( 2 ), 243–256. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coates, D. , Humphreys, B. R. , Kane, J. , & Vachris, M. A. (2004). “No significant distance” between face‐to‐face and online instruction: Evidence from principles of economics . Economics of Education Review , 23 ( 5 ), 533–546. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coetzee, M. (2014). School quality and the performance of disadvantaged learners in South Africa (Working Paper No. 22). University of Stellenbosch Economics Department, Stellenbosch
- Dutton, J. , Dutton, M. , & Perry, J. (2002). How do online students differ from lecture students? Journal of Asynchronous Learning Networks , 6 ( 1 ), 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emediegwu, L. (2021). Does educational investment enhance capacity development for Nigerian youths? An autoregressive distributed lag approach . African Development Review , 32 ( S1 ), S45–S53. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fallah, M. H. , & Ubell, R. (2000). Blind scores in a graduate test. Conventional compared with web‐based outcomes . ALN Magazine , 4 ( 2 ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Figlio, D. , Rush, M. , & Yin, L. (2013). Is it live or is it internet? Experimental estimates of the effects of online instruction on student learning . Journal of Labor Economics , 31 ( 4 ), 763–784. [ Google Scholar ]
- Freeman, M. A. , & Capper, J. M. (1999). Exploiting the web for education: An anonymous asynchronous role simulation . Australasian Journal of Educational Technology , 15 ( 1 ), 95–116. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert, P. (2019). The most expensive data prices in Africa . Connecting Africa. https://www.connectingafrica.com/author.asp?section_id=761%26doc_id=756372
- Glick, P. , Randriamamonjy, J. , & Sahn, D. (2009). Determinants of HIV knowledge and condom use among women in Madagascar: An analysis using matched household and community data . African Development Review , 21 ( 1 ), 147–179. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gyimah‐Brempong, K. (2011). Education and economic development in Africa . African Development Review , 23 ( 2 ), 219–236. [ Google Scholar ]
- Johnson, S. , Aragon, S. , Shaik, N. , & Palma‐Rivas, N. (2000). Comparative analysis of learner satisfaction and learning outcomes in online and face‐to‐face learning environments . Journal of Interactive Learning Research , 11 ( 1 ), 29–49. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundberg, J. , Merino, D. , & Dahmani, M. (2008). Do online students perform better than face‐to‐face students? Reflections and a short review of some empirical findings . Revista de Universidad y Sociedad del Conocimiento , 5 ( 1 ), 35–44. [ Google Scholar ]
- Means, B. , Toyama, Y. , Murphy, R. , Bakia, M. , & Jones, K. (2010). Evaluation of evidence‐based practices in online learning: A meta‐analysis and review of online learning studies (Report No. ed‐04‐co‐0040 task 0006). U.S. Department of Education, Office of Planning, Evaluation, and Policy Development, Washington DC.
- Navarro, P. (2000). Economics in the cyber‐classroom . Journal of Economic Perspectives , 14 ( 2 ), 119–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Navarro, P. , & Shoemaker, J. (2000). Performance and perceptions of distance learners in cyberspace . American Journal of Distance Education , 14 ( 2 ), 15–35. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neuhauser, C. (2002). Learning style and effectiveness of online and face‐to‐face instruction . American Journal of Distance Education , 16 ( 2 ), 99–113. [ Google Scholar ]
- Nguyen, T. (2015). The effectiveness of online learning: Beyond no significant difference and future horizons . MERLOT Journal of Online Teaching and Learning , 11 ( 2 ), 309–319. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paechter, M. , & Maier, B. (2010). Online or face‐to‐face? Students' experiences and preferences in e‐learning . Internet and Higher Education , 13 ( 4 ), 292–297. [ Google Scholar ]
- Russell, T. L. , & International Distance Education Certificate Center (IDECC) (1999). The no significant difference phenomenon: A comparative research annotated bibliography on technology for distance education: As reported in 355 research reports, summaries and papers . North Carolina State University. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shachar, M. , & Neumann, Y. (2010). Twenty years of research on the academic performance differences between traditional and distance learning: Summative meta‐analysis and trend examination . MERLOT Journal of Online Learning and Teaching , 6 ( 2 ), 318–334. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shachar, M. , & Yoram, N. (2003). Differences between traditional and distance education academic performances: A meta‐analytic approach . International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning , 4 ( 2 ), 1–20. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tchamyou, V. S. , Asongu, S. , & Odhiambo, N. (2019). The role of ICT in modulating the effect of education and lifelong learning on income inequality and economic growth in Africa . African Development Review , 31 ( 3 ), 261–274. [ Google Scholar ]
- Xu, D. , & Jaggars, S. S. (2014). Performance gaps between online and face‐to‐face courses: Differences across types of students and academic subject areas . The Journal of Higher Education , 85 ( 5 ), 633–659. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paragraph Writing
- Paragraph on Online Classes
Paragraph on Online Classes - Check Samples for Various Word Limits
Online classes have existed in our society for some time now, but the importance of online classes was fully realised only during the lockdowns on account of the pandemic. The online classes were very helpful to all students, teachers, and institutions. They are also beneficial to students who wish to pursue long-distance courses.
You can refer to the sample paragraphs on online classes given below to learn more about them.
Table of Contents
Paragraph on online classes in 100 words, paragraph on online classes in 150 words, paragraph on online classes in 200 words, paragraph on online classes in 250 words, frequently asked questions on online classes.
Even with the advances in science and technology, many people lagged behind and were not able to cope with the pace of growth in many places around the world. Most were unaware of the benefits of online education or of the existence of online classes in various countries. Just like every coin has two sides, there are two sides to online classes as well. Online classes are beneficial to continue our education despite various barriers. But online activities have the chance to digress into other addictive online activities at times when it comes to kids. Excess of anything is dangerous; therefore, investing too much time can harm the kids. Thus, parents should be responsible enough to take care of their children during online classes.
E-learning and ed-tech companies are the new beginnings that will revolutionise the whole education process. Online learning has become more convenient with the use of advanced science and technology. In this changing world, online classes have become more accessible. Online classes have made our learning process more manageable with our busy schedules. Online classes have been beneficial to students who do not have access to proper schooling and quality education. Ed-tech platforms are now helping students as well as teachers with different study materials, various online courses, etc., at a very reasonable cost so that education can be accessible and available to all grades of students. Online classes help students and teachers excel academically even better than offline classes because they get their own space for learning. They can learn in their own comfort zone. During the pandemic, online classes have been beneficial to the students and their parents to keep the children engaged with their studies.
Online classes have been the best possible solution for educational institutions as well as students during the pandemic. Online education or online classes were not a new concept, but online classes’ prominence was seen only during the pandemic. The online class provides a flexible and quick learning option. Its adaptability and efficiency made it more popular during the pandemic’s early days. It lowers the distance between learning locations. There are a lot of advantages as well as disadvantages to online classes. It is a versatile method of learning which helps connect with people from various parts of the globe, which was not possible in offline classes. Students were given their comfort zone to study, resulting in better performance and productivity. It reduced a lot of paperwork, ultimately saving mother earth. Many renowned institutions have changed their learning methods to online methods because it made education more accessible. There are also a few disadvantages, like, as a lot of students misuse these benefits and get addicted to different games and social media. But it all depends on the individual and if they want to make their career bright. Therefore it is essential to know the limitations of everything.
Online classes are the new modes of learning which have brought about a revolution in the education system. Online classes have been existing in various countries, but their importance increased only during the pandemic. A lot of colleges and universities never accepted a degree certificate that was earned after attending classes online, but now, with the changing time, many renowned colleges and universities have accepted online courses and have shifted to the online method of learning. Online classes have been more accessible and accepted by students as well as teachers. We connect with different people from around the world through online classes, which makes students more competent and engaging. Students have become smarter and technologically sound with online classes, and it has also helped teachers to be more technologically sound. With the growing demand for online classes, education has become more comforting and more satisfying. Even with a hundred barriers, people have accepted online learning methods to continue their education. It has been noticed that student’s performance has improved due to online classes, which is why most students have accepted online learning methods. There was a time when girls were not allowed to go to college to attend classes, and there were many restrictions to choosing a course, but with the increasing demand for online classes, there are no more limitations to education. The students now have all the freedom to choose any course of their choice and build their careers as per their choice. Therefore, online education has been a great help and revolution in today’s learning system.
How do I write a paragraph on online classes?
While writing a paragraph on online classes, you can write about the growing importance of it and how it has changed learning patterns. You can write about the advantages and disadvantages of online classes that you have gone through during the Covid-19 pandemic.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of online classes?
The advantages and disadvantages vary depending on the individual. If a student misuses online classes and takes advantage of them, they will be misusing their phones or computers for other purposes. Online classes can be helpful in various ways as it gives the comfort zone for students and teachers to study, connect with people from around the world, become more competent, etc.
Are the online course certificates accepted?
Yes, with time, people have understood the importance of online classes, and the certificates are now being accepted by various organisations.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


Online Education Essay in English (200-250) Words Paragraph & PDF
Online Education Essay in English: Online education is one of the major changes in the global education industry after COVID hits the country. Read Online Education Essay from here only.

Table of Contents
Online education is a type of learning in which students get instructional content via the internet. It is a flexible and convenient method of learning that has grown in popularity in recent years.
Online Education Essay
Online education is one of the major changes in the global education industry after COVID hits the country. The internet is used for this type of learning. This form of learning has been made easier with new and improved technologies. Higher education institutions favour online learning as well. In short and extended articles about online education, this article will inform students of its benefits and outcomes.
Education spans a range more than just attending classes and reading books to learn things. It exceeds all restrictions. Learning extends beyond the pages of a book. We are fortunate to live in a time where learning is accessible online. Yes! We can educate our kids and ourselves while sitting in our own homes. Online education is a good option for doing this. All needy kids who are unable to enroll in local schools now have access to education thanks to online learning.

Online Education Essay PDF
Download Online Education Essay PDF: Online Education Essay in English

Online Education Essay in English (200-250) words
Today’s Essay on Online Education covers an important subject. There are different types of essays about online education in English for students and children in this post.

Here we, at adda247 are providing 10 lines essays, short essays, and long essays on online education.
- Online education is the process of acquiring education using the internet.
- The Internet is the foundation of online learning.
- Online education was an idea that existed years back.
- It protects students’ sensitive time and money.
- It provides students with a range of courses while sitting at their homes.
- It helped in achieving a balance between safety and education during the pandemic.
- However, it may be shown that it is bad for students’ health.
- In areas with poor network connectivity, studying online is challenging.
- There are numerous online learning resources, including Adda247,Coursera, Udemy etc.
- Online learning features including texts, videos, and animations aid in student comprehension.

Online Education Essay in Paragraph 200-250 Words
These days, technology has impacted every industry, including education. The most recent method of getting an education through the internet is online education. Utilizing your smartphones, laptops, or tablets for learning is a fun and productive method. Both teachers and students can benefit greatly from it, but there are also many drawbacks. Learning from anywhere is flexible with online education.
Non-time-boundness is another advantageous property. You don’t have to sit from morning until lunch like in a typical school. Depending on your preference, you can study online day or night. There is no upper age limit for learning online, in addition to the flexibility of time and location. You can pick the subjects and skills you want to learn by using online education. There are numerous institutions that provide their degrees and courses online. As a result, it is a more practical option to educate yourself without physically visiting schools or universities. Additionally, it helps you save money on transportation and other expenses.
People who reside in areas with poor internet connectivity, however, struggle with online learning. The core of online education is the internet. Your health may suffer if you spend more time in front of devices. Only those with the ability to discipline themselves should consider it.

Online Education Essay in 500-1000 words for UPSC
Introduction: Online education is a flexible method of providing instruction that includes all online learning. Online learning helps students who need to do their work on their own time and at their own speed and gives teachers access to students who may not be able to enroll in a regular classroom course.
The modern method of education, known as online education, differs greatly from the traditional method of learning. For a better comprehension of the students, the instructor or mentor employs a variety of techniques, including texts, audios, films, animations, etc.
Every field is experiencing a rapid increase in the amount of distant learning and the awarding of online degrees. The number of institutions and schools that provide online education is likewise increasing. Students who are seeking degrees online need to be careful in making sure that they finish their coursework through a reputable and recognized university.
Synchronization is a well-known benefit of online learning. Here, the chosen format allows for lively dialogue between the students and the teachers. Sources are exchanged through these communications, and a synergy that is open-ended develops as a result of a learning process. It helps the learner learn more when each person shares their point of view or opinion through conversations and comments on others’ work. This unique advantage can only be achieved through online learning, which creates a virtual learning environment focused on the needs of the students.
We don’t need to commute over long distances or travel to different place because we can take classes online. While pursuing a degree online to advance our careers, we can remain where we are and keep our current jobs. Digital nomads—those who advocate a technologically enabled or location-independent lifestyle—are also helped by online schooling. No matter where we are, we may finish our schoolwork and view lectures.
The online education experience offers a lot more reasonable schedule, whether we are full-time or part-time students. The low cost of online education has contributed to its popularity. Online courses are less expensive than those provided at schools or colleges because of this. While attending a university, we might need to pay for things like transportation, lodging, and meals; however, online education might not.
The inherent flexibility of online learning is one of its key benefits, but there is a catch: one needs to be very self-motivated. The top online learners use a variety of strategies for maintaining their assignments. Setting aside time each week for studying and designing a workspace with few distractions can both be highly beneficial.
Conclusion: Increased educational access, high-quality learning opportunities, improved student outcomes and abilities, and more educational options are some of the possible benefits of online education. Because of online education, variables like location, time, and quality are no longer taken into account when looking for degree programmes or higher education.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Education for Essay
Advantages of online education.
Save time and money: Students who pursue their education online do so at a considerable time and financial savings. It cuts down on both the cost and time of transportation. Accessible to All : Everyone has access to online schooling. Online education is available to students of all backgrounds and ages. For students who have physical disabilities, this is one of the main benefits. They can receive an education from the comfort of their own home without having to travel anyplace. No Time Limit : Students have a lot of freedom with online education. Anytime, students can seek knowledge. There is no time limit like there is in the traditional learning method.
Choice : Online education offers a wide range of courses. Students can study skills like personality development and other things that are typically challenging to master offline in addition to course material.
Disadvantages of Online Education
Dependency : Online learning is beneficial for those who can study independently. Kids and other students cannot effectively study online without help. Self-concentration is necessary for this kind of study. Lack of Resources : Online education requires computers or mobile devices as well as strong internet connectivity. Online study is not possible for those without computers or in places with network problems. Disengagement from Society : Spending a lot of time in front of a screen could be bad for your health. The students’ physical growth is also impacted by it. They will grow apart from their friends and society if they don’t attend school.
Online vs Offline Education Comparision
- Time management: Unlike online education, where you can choose a time slot that best suits your needs, offline education has a set timetable.
- Cost-Effectiveness : Online learning is significantly less expensive than traditional learning. Transportation costs are just one of the numerous costs associated with the existing educational system. Students require appropriate uniforms as well as a number of other items.
- Online learning presents new challenges for students, but it also has the potential to cut them off from their surroundings. Children’s physical and mental development are both aided by attending school. They enjoy spending time with their friends and teachers.
- Choice: In an online classroom, students are allowed to select the subject they want to learn about. They can view it multiple times for better comprehension. Students have no options in offline schooling.
- Knowledge Outside the Books: In an offline setting, students physically interact. They also learn other manners, such as self-control, appropriate behaviour, and other related abilities. These competencies are not produced by offline schooling.
Online Education Essay in Hindi
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा पर आज का निबंध एक महत्वपूर्ण विषय को शामिल करता है। इस पोस्ट में छात्रों और बच्चों के लिए अंग्रेजी में ऑनलाइन शिक्षा के बारे में विभिन्न प्रकार के निबंध हैं।
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा पर 10 पंक्तियों के निबंध, लघु निबंध और लंबे निबंध प्रदान कर रहे हैं।
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा इंटरनेट का उपयोग करके शिक्षा प्राप्त करने की प्रक्रिया है। इंटरनेट ऑनलाइन सीखने का आधार है। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा एक ऐसा विचार था जो वर्षों पहले अस्तित्व में था। यह छात्रों के संवेदनशील समय और धन की रक्षा करता है। यह छात्रों को उनके घरों पर बैठकर कई तरह के पाठ्यक्रम प्रदान करता है। इसने महामारी के दौरान सुरक्षा और शिक्षा के बीच संतुलन हासिल करने में मदद की। हालांकि, यह दिखाया जा सकता है कि यह छात्रों के स्वास्थ्य के लिए खराब है। खराब नेटवर्क कनेक्टिविटी वाले क्षेत्रों में, ऑनलाइन अध्ययन करना चुनौतीपूर्ण है। Adda247, Coursera, Udemy आदि सहित कई ऑनलाइन शिक्षण संसाधन हैं। टेक्स्ट, वीडियो और एनिमेशन सहित ऑनलाइन सीखने की विशेषताएं छात्र की समझ में सहायता करती हैं। 250-300 शब्दों में ऑनलाइन शिक्षा निबंध
इन दिनों, प्रौद्योगिकी ने शिक्षा सहित हर उद्योग को प्रभावित किया है। इंटरनेट के माध्यम से शिक्षा प्राप्त करने का सबसे हालिया तरीका ऑनलाइन शिक्षा है। सीखने के लिए अपने स्मार्टफोन, लैपटॉप या टैबलेट का उपयोग करना एक मजेदार और उत्पादक तरीका है। इससे शिक्षक और छात्र दोनों ही काफी लाभान्वित हो सकते हैं, लेकिन कई कमियां भी हैं। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा के साथ कहीं से भी सीखना लचीला है।
गैर-समयबद्धता एक और लाभप्रद संपत्ति है। आपको एक ठेठ स्कूल की तरह सुबह से दोपहर के भोजन तक बैठने की ज़रूरत नहीं है। आप अपनी पसंद के आधार पर दिन हो या रात ऑनलाइन पढ़ाई कर सकते हैं। समय और स्थान के लचीलेपन के अलावा, ऑनलाइन सीखने के लिए कोई ऊपरी आयु सीमा नहीं है। आप ऑनलाइन शिक्षा का उपयोग करके उन विषयों और कौशलों को चुन सकते हैं जिन्हें आप सीखना चाहते हैं। ऐसे कई संस्थान हैं जो अपनी डिग्री और पाठ्यक्रम ऑनलाइन प्रदान करते हैं। नतीजतन, शारीरिक रूप से स्कूलों या विश्वविद्यालयों का दौरा किए बिना खुद को शिक्षित करना एक अधिक व्यावहारिक विकल्प है। इसके अतिरिक्त, यह आपको परिवहन और अन्य खर्चों पर पैसे बचाने में मदद करता है।
हालांकि, जो लोग खराब इंटरनेट कनेक्टिविटी वाले क्षेत्रों में रहते हैं, उन्हें ऑनलाइन सीखने में कठिनाई होती है। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा का मूल इंटरनेट है। यदि आप उपकरणों के सामने अधिक समय बिताते हैं तो आपका स्वास्थ्य खराब हो सकता है। केवल उन्हें ही इस पर विचार करना चाहिए जो स्वयं को अनुशासित करने की क्षमता रखते हैं।
यूपीएससी के लिए 500-1000 शब्दों में ऑनलाइन शिक्षा निबंध
परिचय: ऑनलाइन शिक्षा निर्देश प्रदान करने का एक लचीला तरीका है जिसमें सभी ऑनलाइन शिक्षण शामिल हैं। ऑनलाइन सीखने से उन छात्रों को मदद मिलती है जिन्हें अपना काम अपने समय पर और अपनी गति से करने की आवश्यकता होती है और शिक्षकों को उन छात्रों तक पहुंच प्रदान करता है जो नियमित कक्षा पाठ्यक्रम में नामांकन करने में सक्षम नहीं हो सकते हैं।
शिक्षा की आधुनिक पद्धति, जिसे ऑनलाइन शिक्षा के रूप में जाना जाता है, सीखने की पारंपरिक पद्धति से बहुत अलग है। छात्रों की बेहतर समझ के लिए, प्रशिक्षक या संरक्षक कई तरह की तकनीकों का इस्तेमाल करते हैं, जिनमें टेक्स्ट, ऑडियो, फिल्म, एनिमेशन आदि शामिल हैं।
हर क्षेत्र दूरस्थ शिक्षा और ऑनलाइन डिग्री प्रदान करने की मात्रा में तेजी से वृद्धि का अनुभव कर रहा है। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा प्रदान करने वाले संस्थानों और स्कूलों की संख्या भी बढ़ रही है। ऑनलाइन डिग्री चाहने वाले छात्रों को यह सुनिश्चित करने में सावधानी बरतने की जरूरत है कि वे एक प्रतिष्ठित और मान्यता प्राप्त विश्वविद्यालय के माध्यम से अपना शोध कार्य पूरा करें।
तुल्यकालन ऑनलाइन सीखने का एक प्रसिद्ध लाभ है। यहां, चुना गया प्रारूप छात्रों और शिक्षकों के बीच जीवंत संवाद की अनुमति देता है। इन संचारों के माध्यम से स्रोतों का आदान-प्रदान किया जाता है, और एक सीखने की प्रक्रिया के परिणामस्वरूप एक तालमेल विकसित होता है। यह शिक्षार्थी को अधिक जानने में मदद करता है जब प्रत्येक व्यक्ति बातचीत और दूसरों के काम पर टिप्पणियों के माध्यम से अपनी बात या राय साझा करता है। यह अनूठा लाभ केवल ऑनलाइन सीखने के माध्यम से प्राप्त किया जा सकता है, जो छात्रों की जरूरतों पर केंद्रित एक आभासी सीखने का माहौल बनाता है।
हमें लंबी दूरी तय करने या अलग-अलग जगहों की यात्रा करने की आवश्यकता नहीं है क्योंकि हम ऑनलाइन कक्षाएं ले सकते हैं। अपने करियर को आगे बढ़ाने के लिए ऑनलाइन डिग्री का पीछा करते हुए, हम जहां हैं वहीं रह सकते हैं और अपनी वर्तमान नौकरी रख सकते हैं। डिजिटल खानाबदोश – जो तकनीकी रूप से सक्षम या स्थान-स्वतंत्र जीवन शैली की वकालत करते हैं – को भी ऑनलाइन स्कूली शिक्षा से मदद मिलती है। चाहे हम कहीं भी हों, हम अपना स्कूल का काम पूरा कर सकते हैं और व्याख्यान देख सकते हैं।
ऑनलाइन शिक्षा का अनुभव बहुत अधिक उचित कार्यक्रम प्रदान करता है, चाहे हम पूर्णकालिक या अंशकालिक छात्र हों। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा की कम लागत ने इसकी लोकप्रियता में योगदान दिया है। इस वजह से स्कूलों या कॉलेजों में प्रदान किए जाने वाले ऑनलाइन पाठ्यक्रमों की तुलना में ऑनलाइन पाठ्यक्रम कम खर्चीले हैं। विश्वविद्यालय में भाग लेने के दौरान, हमें परिवहन, आवास और भोजन जैसी चीज़ों के लिए भुगतान करना पड़ सकता है; हालाँकि, ऑनलाइन शिक्षा नहीं हो सकती है।
ऑनलाइन सीखने का अंतर्निहित लचीलापन इसके प्रमुख लाभों में से एक है, लेकिन एक पकड़ है: किसी को बहुत आत्म-प्रेरित होने की आवश्यकता है। शीर्ष ऑनलाइन शिक्षार्थी विभिन्न प्रकार की रणनीतियों का उपयोग करते हैं
अपने कार्यों को बनाए रखने के लिए। अध्ययन के लिए हर हफ्ते समय अलग करना और कुछ ध्यान भटकाने वाले कार्यक्षेत्र को डिजाइन करना दोनों ही अत्यधिक फायदेमंद हो सकते हैं।
निष्कर्ष: बढ़ी हुई शैक्षिक पहुंच, उच्च गुणवत्ता वाले सीखने के अवसर, बेहतर छात्र परिणाम और क्षमताएं, और अधिक शैक्षिक विकल्प ऑनलाइन शिक्षा के कुछ संभावित लाभ हैं। ऑनलाइन शिक्षा के कारण, डिग्री प्रोग्राम या उच्च शिक्षा की तलाश में स्थान, समय और गुणवत्ता जैसे चरों को ध्यान में नहीं रखा जाता है।
Found this article helpful?
Let’s connect via chat or call our senior expert counselor at +91-9625869989 to learn more about the different streams and options available. We would love it if we could add some of your insights. If you have a definite goal of scoring the highest marks, then you can resolve your doubts via our app/quizzes and youtube class assistance ( https://www.youtube.com/c/Adda247School )
Related Post:
- Cow Essay- 10 Lines In English/Hindi For Class 1 & 3
- Teachers Day
- What Is National Income
Essay on Online Education- FAQs
Q.Are online learning and distance learning the same?
Ans. Online learning follows a school learning format and provides students more campus-like feel. Students have a formal or informal interactions with the teachers as well as their peers. But in distance learning, there is no interaction with teachers or classmates.
Q. What are some benefits of online classes?
- Flexibility.
- Reduced Costs.
- More Free Time.
- Increased Course Variety.
- Career Advancement Opportunities.
Q. How does online education affect students?
Ans.Online learning has helped students to become independent learners before they make their way into the real world.
Q. Are online classes good for students?
Ans. The importance of online classes are that they are much more convenient and flexible as compared to traditional learning platforms.
Q. Why do students prefer online learning?
Ans. Online courses are easily accessible on much smaller budgets . In addition to the convenience and the cost, a large number of students are turning to online learning courses because they have become a better way to learn.
Sharing is caring!
Are online learning and distance learning the same?
Online learning follows a school learning format and provides students more campus-like feel. Students have a formal or informal interactions with the teachers as well as their peers. But in distance learning, there is no interaction with teachers or classmates.

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trending Articles
- TS Inter Results 2024 Link
- TS Inter Topper List 2024

CBSE Board Exam 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Previous Year Papers
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Previous Year paper
- CUET Participating College & Universities
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main Syllabus 2024
- JEE Main Exam Analysis 2023
- NEET 2024
- NEET Syllabus 2024
- NEET State wise Cut off
- NEET Rank Predictor
- NEET OMR Sheet
- NEET College Predictor
Recent Posts
Important exams, ncert solutions.
- NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT Class 10
- NCERT Class 9
NCERT Books
School syllabus.
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 9
- JEE Mains 2024
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Adda Malayalam
- Adda Punjab
- Current Affairs
- Defence Adda
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School

Get all your queries solved in one single place. We at Adda247 school strive each day to provide you the best material across the online education industry. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Best Online Writing Courses: 18 Top Options (2024)
Discover the best online writing courses to help you take your career and craft to the next level.
I spent a year taking a traditional in-person writing class. We covered topics like writing short stories and personal essays. It was fun to meet other writers, but a conventional writing class involves traveling to a location at a set time each week. It’s often hard to do this with a job and family commitments.
New and experienced writers can choose from a plethora of online writing classes. You can learn a specific topic related to the craft at your own pace. No matter what you write, write books, articles, blog posts, and so on, there’s an online writing course for you.
Online writing courses provide valuable lessons for new and established writers. No matter your skill level, you can continually improve and build new skills with the help of industry experts. Some of my most valuable skills have been gained from online classes.
Using online writing courses can open up opportunities to further your career. This could include launching your online blog with articles, publishing your non-fiction or fiction book, beginning a copywriting career, or delving into journalism. Whatever your passion is, online courses are a great way to develop your skills and start your next adventure.
Learn from the world's best teachers and instructors about writing, business, creative pursuits and more. It's affordable and includes dozens of hours of high-quality lessons that you can't get anywhere else. It costs just $10 per month.

Establish Your Goals for an Online Writing Course
Set your course budget, the best online writing courses , 1. the successful writers’ club, 2. masterclass, 3. the novelry, 4. creativelive, 6. storylogue, 7. writers village university, 8. your first 10k readers, 9. self-publishing formula/ads for authors, 10. authority pub-academy, 11. brandon sanderson’s writing lectures at brigham young university, 12. accelerated program for six-figure copywriting, 13. skillshare, 14. coursera, 15. writer’s digest university, 16. bookfox, 17. grammar lion, 18. litreactor, why you can trust us, best online writing courses: the final word, do creative writing courses help, are writing-intensive courses hard, are writing courses worth it, masterclass resources.

What to Do Before Starting a Writing Course?

The first step towards improving your writing skills is to understand online writing classes vary widely in price, content, and theme. Before picking a class, decide what part of the writing process you want to learn more about and your budget.
Before spending money on a course, it’s a good idea to reflect on what you write, who it’s for, and your ideal learning goal. For example, a non-fiction writer probably has different creative goals than a novelist. The former may want more clients, whereas the latter may be interested in world-building. So here are several questions to ask yourself before handing over your credit card details:
- Are you a new writer looking for something to inspire you to start writing?
- Do you need help with writer’s block?
- Are you trying to hone your writing style?
- Would you like to write your first book?
- Or perhaps you want to pen and publish a personal essay?
- Do you need help with novel writing?
- Do you want to increase revenue by self-publishing your book on Amazon?
- Are you a freelance writer who wants to develop better business writing skills?
- Would you like to improve your brand storytelling skills?
- Or do you want to hone everyday writing skills, like self-editing ?
- Do you need help launching and marketing a potential best-seller?
Online writing courses exist for all types of creative and business pursuits! These courses can help you improve several aspects of your writing skills. Some of these classes are available today, whereas others only open their doors several times a year.
Next, you must determine how much you are willing to invest in a course. For example, if you are new to online learning, you might want to try free online courses like Brandon Sanderson’s lectures for genre fiction writers.
You can check out affordable courses like Udemy or The Successful Writers’s Club. Then, once you have covered the absolute basics of the writing format through free online courses – step up to a more advanced paid class like Masterclass.
Remember, set your budget for what you can afford now and what is suited to your skill set. You can always note down interesting courses and add them to your wishlist to revisit at a later time. It is better to start small and build up to more comprehensive courses than pay for something above your skill level out of pocket.

I teach new writers how to share their stories, make an impact and get paid to write. With a plethora of experience, I share my insights into what makes a great book and how you can achieve your writing goals. By pulling from my writing, I share skills that will help you write online, get paid and make an impact. I also delve into popular topics like publishing a book, blogging and SEO for writers. The club comprises a series of mini-courses for writers and comes with a 30-day money back guarantee.
Key Concepts:
I cover topics like
- What it takes to go from the blank page to a finished book
- Conquering writer’s block once and for all
- Editing that messy first draft like a pro!
- Getting paid as a freelance writer
- How to find readers using blogging and SEO
- Lots more… I record new mini courses regularly
Instructor(s): Yours truly
Course Schedule: Self-paced
Recommended for: This course is suitable for bloggers, aspiring non-fiction authors, and freelance writers.
Pricing: It only costs $20 per month

With thousands of courses to choose from, Masterclass provides a professional platform for acclaimed experts to share their knowledge. In addition, Masterclass offers writing classes focusing on the craft and theory of fiction and non-fiction writing. Where else will you find talented authors talking about their writing process and style in such great detail? Click here to read our detailed Masterclass review .
Each lesson is between five and ten minutes long, and you can watch them on your mobile or desktop. They also come with downloadable materials like PDF worksheets and notes. You can also engage with other writers and students. If you’re lucky, one of the celebrity tutors may even workshop your piece!
Instructor(s): Masterclass superstar writing tutors include: James Patterson, Malcolm Gladwell, Margaret Atwood, and David Mamet. You might want to consider Patterson’s class if you write fiction and Gladwell if you write non-fiction. In addition, students can pick from over a dozen Masterclass courses for writers .
Course Schedule: The course is self-paced.
Recommended for: From fiction to creative non-fiction to script-writing – Masterclass has courses for every kind of writer, including novelists, bloggers, and aspiring authors. You’ll learn about everything from character development to getting published.
Pricing: These classes are relatively affordable and cost approximately $100. You can access digestible materials from great writers who are usually inaccessible.

The Novelry supports writers from the twinkling of an idea to submission to their literary agency partners. In addition, the Novelry offers online creative writing courses for the budding author keen to complete a novel. Founded by award-winning Booker-listed novelist Louise Dean, The Novelry supports writers from the twinkling of an idea to submission to their literary agency partners. I recently interviewed Louise Dean for my podcast, and she has a great approach that helps writers finish a draft in 90 days.
Course Schedule: Self-paced.
Recommended for: Fiction writers. Aspiring novelists.

CreativeLive is an exciting alternative to Masterclass. Rather than featuring celebrity writers and authors, many of CreativeLive instructors are entrepreneurs, bloggers, and online personalities.
Having taken several of these classes, I found them more practical than Masterclass offers. However, if Masterclass provides the theory, CreativeLive provides the steps you must take to succeed at blogging or book writing.
Click here to read my detailed CreativeLive review .
These writing classes are recorded in a live studio by instructors teaching or presenting to other writers. It’s an exciting way to learn because you can see the audience’s reactions and get ideas from their questions for the writing instructors.
Again, the materials are readily digestible. With some exceptions, the lessons are between five and 15-minutes long. The CreativeLive writing classes also include downloadable PDFs, exercises, and worksheets. You can watch the materials on your desktop or through the CreativeLive app on your mobile device.
If you’re unsure where to start, consider Wired for Story: How to Become a Story Genius by Lisa Cron.
Instructors: Notable instructors include New York Times best-selling authors Ramit Sethi and Tim Ferriss.
Recommended for: CreativeLive has classes for bloggers and fiction and non-fiction writers.
Pricing: The cost varies depending on the class. Classes start from $20.
Master your craft, your passion, or something new
with creative classes taught by the world’s best.

These Udemy classes cover everything from critical concepts like basic grammar and punctuation to freelance writing, self-publishing, and blogging. Udemy is the supermarket of online learning. It also has courses on hundreds of topics other than writing. You can choose from dozens of different writing classes of varying standards. These Udemy classes cover everything from critical concepts like basic grammar and punctuation to f reelance writing , self-publishing, and blogging.
Typically, these writing classes involve the instructor recording a video from their office, sometimes supported by a PowerPoint presentation. However, the quality of the lesson materials varies widely from class to class, so make sure you read the reviews before buying one. In addition, consider taking the Secret Sauce of Great Writing by former Wall Street Journal editor Shani Raja. His other course writing with flair is popular.
Instructors: Many of the instructors on Udemy are less well-known than CreativeLive or Masterclass.
Recommended for: Udemy is an excellent place to start if you’re new to online learning, as the classes don’t cost much, and you can buy them anytime.
Pricing: Udemy online writing classes are cheap to start with and often sold at a discount . The cost varies depending on the class. Classes start from $9.99.

Run by screenwriter, author, and creative instructor Robert McKee, Storylogue is one of the lesser-known online writing classes available today. It’s based on what McKee teaches in person and his excellent book Storynomics.
Robert McKee’s in-person workshops cost several hundred to several thousand dollars, depending on where and when you take them. However, the online writing class Storylogue distills what McKee knows about storytelling, emphasizing screenwriting and business writing. These lessons typically involve McKee speaking straight to the camera from his office.
The materials aren’t as well-organized as those in a Masterclass or CreativeLive. I had to use the search feature to find suitable lessons. They’ve updated the user interface since I was a member. The slight emphasis on screenwriting may also deter some writers.
Instructor(s): Robert McKee is an author, lecturer, and story consultant. He consulted on business storytelling for companies like Microsoft, Nike, Hewlett-Packard, Time Warner, and Siemens. I attended Robert McKee’s in-person business writing class several years ago in Kerry. He was an engaging and inspiring instructor. At one point, McKee became so passionate about a story that his eyes watered.
Recommended for: This course is suitable for screenwriters, content marketers , and anyone who wants to improve their storytelling skills.
Pricing: You get access to all lessons for $19.97 (paid monthly) or $197 (paid annually).

Writer’s Village University is a popular online writing class and community aimed at fiction writers. The emphasis here is on the community. So consider Writer’s Village University, an online version of your local creative writing group. It’s been around since 1995, too, making it the oldest writing class in this review. I joined for two months out of curiosity, even though I don’t write much fiction.
The website contains an active forum. There are over 200 different short classes you can take at your pace. They cover topics like writing poetry, crafting thrillers, essay writing , and more. There’s less emphasis on video learning than in other classes featured in this review. Instead, you receive a series of writing assignments via email.
You can then submit your homework assignments to your online writing tutor and other students to the workshop. I joined this website for three months before moving on. That said, it struck me as a valuable resource for fiction writers who hunger for a community.
Instructor(s): It is a community of writers.
Course Schedule: Click here for more upcoming courses.
Recommended for: These courses are suitable for fiction writers who want the support of other writers.
Pricing: It costs $30 for a 30-day trial. After the trial period, a one-year Writers’ Village University membership costs $99.
Try Writers’ Village University

This online writing class is aimed at fiction and non-fiction authors who want to self-publish and sell more books. The instructor is Nick Stephenson, an author from the United Kingdom. Self-publishing is an underrated pathway to becoming a successful author. Nowadays, self-publishing has become the new normal. With the influx of social media, it is possible to self-publish, self-promote, and self-market.
I took this course in 2017. It walks you through some basic and more advanced book marketing strategies that work. For example – It teaches you the process of self-publishing a short book that you offer for free. This book serves as an introduction to your series or a reader magnet. The goal of this free book is to encourage people to buy your next book.
Instructor(s): The course is offered by British indie author Nick Stephenson, known for his thriller novels.
Course Schedule: Stephenson only opens this course several times a year, so you’ll need to join his email list first.
Recommended for: This course suits authors who want to earn money from self-publishing books.
Pricing: This course, in its entirety, costs around $595. However, you can sign up for a free training session.

Both of these courses are taught by bestselling author Mark Dawson, a noted indie author from the United Kingdom. He’s also an expert in book marketing through paid advertising.
Self Publishing Formula teaches the basics of writing, publishing, and promoting a book on Amazon and other stores. Dawson’s second course, Ads for Authors , will help you sell more copies of your book. He explains how to use various ads to sell your books, including Facebook, YouTube, and Amazon ads. In 2016 and early 2017, I struggled to earn a profit from selling my books on Amazon. But, thanks to Dawson’s second course, I learned how to run profitable Amazon ads, making me an excellent monthly return on my books.
Instructor(s): Mark Dawson is a British thriller author. He has reportedly earned $450,000 a year by publishing books on Amazon!
Course Schedule: Dawson only opens the doors to his courses a few times a year, so join his email list first.
Recommended for: This course is suitable for aspiring indie authors or established authors who want to increase their profits.
Pricing: This course, in its entirety, costs around $497.

Authority Pub-Academy is an online learning class run by noted indie authors and entrepreneurs Steve Barrie and Barrie Davenport over at Authority Pub .
I haven’t taken this writing class, but many other indie authors recommend it. I have browsed the curriculum, and it’s similar to what Bolt, Dawson, and Stephenson teach. In other words, this course walks you through the basics of writing and self-publishing a book that sells. The course contains six lessons, with multiple lessons in each one. Some lessons include:
- The Current State of Self-Publishing
- How to Research and Pick A Winning Niche
- How to Create A Bestselling Topic
- Ten-Day Free Book Launch Strategy
- How to Create a Facebook Ad For Your Books
This writing course has been around for nearly ten years, which is encouraging. I will update this online writing course review when I take it.
Instructor(s): Steve Barrie and Barrie Davenport have published nearly 100 books.
Recommended for: It’s suitable for aspiring writers who want to learn about self-publishing.
Pricing: The course, in its entirety, costs around $797.

In 2016, Brandon Sanderson recorded a course focused on writing fantasy books. Then, he uploaded these classes and published them as a YouTube playlist . Now, you can take Sanderson’s curriculum online in the same sequence as his students.
I don’t write fantasy stories (at least, not anymore), but I watched nearly a dozen of Sanderson’s writing classes. I was fascinated to hear him describe his world-building techniques and genre fiction writing.
Some of the classes are hard to follow because of background noise. Also, the classes were typically between 30 and 60 minutes long, and it took me a long time to go through them. Still, Sanderson’s classes are free and an excellent introduction to learning online for aspiring fiction authors.
Instructor(s): Brandon Sanderson is a famous American fiction author specializing in fantasy. Notable works of his include the Mistborn series and his conclusion to the Wheel of Time series.
Course Schedule: You can watch all of his videos at your leisure.
Recommended for: These lectures are a great introduction to online writing courses. It is suitable for fiction writers (specifically fantasy).
Pricing: You can watch all of his lectures for free!

Copywriting is a specialism for non-fiction writers that involves writing words that sell. In the past, I’ve taken several types of copywriting classes and enjoyed reading many books about this art. Accelerated Program for Six-Figure Copywriting is the most popular online writing class for copywriters. Many noted online writers recommend it.
I haven’t taken this online writing class yet, but it’s on my list. I will update this writing class review with more information when I complete this class.
Instructor(s): American Writers & Artists, various copywriters
Recommended for: Suitable for bloggers, freelance writers, and copywriters who want to improve business writing skills.
Pricing: The course in its entirety costs $497.

Students can take a class on almost anything by participating in nearly 30,000 classes. You can watch unlimited lessons while your subscription lasts, but when it expires, you lose access. With unlimited access, this course is brilliant if you want to scale up your skillset in multiple ways. Read our Skillshare review
Key Concepts: Writing, coding, graphic design
Instructors : Varies
Recommended for: This course is suitable for bloggers, freelance writers, and creative entrepreneurs.
Pricing : Free trial available
Explore your creativity with classes in illustration, photography, design, content writing and more.

By partnering with established colleges and universities, you can gain access to valuable certificates by completing specializations.
Key Concepts: The Creative Writing specialization contains multiple courses you can participate in, including short stories, narrative essays, and memoirs. Coursera is a fantastic option for writers seeking official qualifications and certificates and learning from industry leaders.
Instructors: Coursera’s Creative Writing course includes Brando Skyhors (Visiting Assistant professor of Creative Writing), Amy Bloom (Distinguished University Writer in Residence and Director of the Shapiro Centre for Creative writing, Amity Gaige (Visiting Scholar in Creative Writing), and Salvator Scibons (Frank B. Weeks Visiting Professor of English).
Course Schedule : This course is self-paced and lasts 3-6 months.
Recommended for: Those who want to get a headstart on their writing career or to achieve college-level coursework and qualifications
Pricing: $49 per month

Writer’s Digest University provides a creative writing crash course for those beginning their writing career. With a fantastic reputation of being an established magazine since 1920, you can get the best start to begin your first exciting writing project.
Key Concepts: The class teaches common concerns, such as deciding on the point of view and beating writer’s block.
Instructors: Ran Walker, winner of the 2019 National Undie Author of the Year Award.
Course Schedule: This is a 12-week course
Recommended for: Those who are ready to take the next to begin their writing career.
Pricing: $579.99

Bookfox is created by John Matthew Fox, a former college professor, editor, and writer. His course is packed with helpful information for writers looking to create an excellent children’s book. This course has 14 lessons, which take as long as you want as it is self-paced.
Key Concepts:
The content provides you with everything you need to know to write and publish your book. This includes writing, proofreading, editing, finding an illustrator and agent, and getting your book on the shelves! It’s a must-have course for serious writers.
Instructor: John Matthew Fox
Course Schedule: This course is self-paced
Recommended for: Children’s book writers
Pricing: $149

This Grammar Lion course is perfect for those looking to upgrade their grammar skills or learn the art of proofreading and copyediting. The course material involves:
- Identifying parts of speech.
- Reviewing sentence structure.
- Discovering different verb forms.
- Learning about the different tenses.
This course allows one-on-one discussions with the lecturer to learn new skills. As well as this, you have access to 12 comprehensive lessons, each delving into a different topic that will improve your grammar.
Instructor: Ellen Field
Course Schedule: This course is self-paced and lasts 12 weeks.
Recommended for: Beginners looking to elevate their grammar schools
Pricing: $67

With interesting elements weaved into the coursework, this writing experience is like no other. For example, the course “Writing the Weird” features assignments that look at surreal and bizarre literature to find and examine the writing within these novels that makes them stand out.
Key Concepts: This course examines humanity, structure, setting, and resolution within a story’s plot.
Instructor: J.S. Breukelaar (finalist for the Ladies of Horror Fiction Award).
Course Schedule: 4-week schedule that you can work through at your leisure.
Recommended for: Writers within niche genres.
Price : $350
I’ve written and published dozens of articles for newspapers, magazines, and online publications, including Forbes and Lifehacker. I’m also a best-selling non-fiction author, a trained journalist, and a copywriter.
I’ve spent thousands of dollars taking writing courses in college and online. I consider writing courses a crucial part of my development as a writer. I also sometimes commission other writers to review these courses to get another point of view.
What other online writing classes would you like me to feature in this review? How do you plan to develop your English writing skills? Please let me know in the comments section below.
Please note the cost of some of these writing classes varies depending on when they are launched.
FAQs on The Best Online Writing Courses
Creative writing courses help if you complete the course and also write and share your short stories or pieces. In addition, it helps if you can take a course alongside other students and an experienced teacher.
If you haven’t written much before, they can be a challenge as you’ll have to cultivate a regular writing habit and adapt to getting feedback from other writers, even if it’s negative.
They are if you pick a course from a reputable instructor that solves a particular problem. For example, I took a book marketing course that doubled my book sales and earnings over time.
Masterclass Review
David Lynch Masterclass Review
Neil Gaiman’s Masterclass Review
Margaret Atwood Masterclass Review
Joyce Carol Oates Masterclass Review
James Patterson Masterclass Review
Steve Martin Masterclass Review
Judy Blume Masterclass Review
Salman Rushdie Masterclass Review
Werner Herzog Masterclass Review
Neil deGrasse Tyson Masterclass Review
David Baldacci Masterclass Review
Malcolm Gladwell Masterclass Review
The Best Online Writing Courses
The Best Masterclass Courses In 2022
How To Watch Masterclass On TV: Step-By-Step

Meet Rachael, the editor at Become a Writer Today. With years of experience in the field, she is passionate about language and dedicated to producing high-quality content that engages and informs readers. When she's not editing or writing, you can find her exploring the great outdoors, finding inspiration for her next project.
View all posts
Choose The Best Online Writing Classes Today

Online education does more good than harm

I’m on my school’s debate team and, this being one of our topics, decided to get some help by creating a new debate here. Things like statistics, real life stories (with sources!), or any point really, help out tremendously. Thank you!
All the Yes points:
Online education is great, all the no points:, does not encourage activity, social life, and is distracting., a mature adult is capable of choosing a great online school., yes because….
I think online classes are great. In my opinion it teaches people (mostly kids) responsibility by making them get up and take the initiative to go online and do the work without people having to remind or be on them for it. It’s also good because their is no mandatory time for you to go on in the day. You can still work and then come online and do your work and if you happen to finish early you can actually leave unlike in a real class.
No because…
Yes, online education can be beneficial, but at school you actually move around, whereas on a computer, you sit and do nothing. With obesity on the rise in America, we should be pushing for more healthy things. Also, it doesn’t encourage a social life. It can also be very distracting because it’s the internet. Sure, no bullying, no hiring teachers, etc. but a face to face education is extremely important. The issue at hand would be the complete segregation of a child from their peers, sure the bullying would stop, but would a child who sits potentially in the house all day have the appropriate skills for the wider working world in adult life? Probably not… If you wanted to grow a generation of WOW style MMO gamers this might well be your option, but without face to face interaction with teachers and other children the social skills of the children would quickly become very self-centered.. and distant compared to face to face interaction.
When it boils down to the points of activity, social life, and is distracting, we must observe several things; 1: Kids will be sitting as much in regular class as during online schools. Peninsula Press posted in an article called “High school students sit for too long, new health research suggests.” Within this article it is quoted that “In a traditional class, the teacher stands and talks, and the kids sit,” Josh Maisel said. “But a lot of us know that that’s not good teaching.” Expanding on this, the article provides a Stanford University study showing the affects of sitting to long, including diabetes, heart disease and obesity. Online school is task based oriented, for example “read four chapters in two days.” Rather than everything being then and there, online education encourages students to not only finish work but also encourage work in other means such as play because it is task based oriented. 2: The fact of the matter is that the world is slowly changing to lives on computers. Life we know could not exist without computers. For example, in the industry of Drafting and Design, the complex building would be impossible difficult and extremely time consuming. Auto-CAD is a type of design program manufacturer and without their innovations in design, a skyscraper would not take a month to design but perhaps many years. Helium posted in an article called “Are computers necessary in today’s society?” that in society today that computers are necessary for their many uses such as instant access to information and uses of social interaction. Without online education, the transition into the computer world we’re slowly becoming would be very difficult. 3: The fact of distracting students is not nearly as tempting as in regular social environments. The urge to talk to friends, draw, sleep or day-dream is not nearly as strong as the urge to use the internet. Not only is internet limited within schools, but internet access is prohibited. For example, in my Algebra II class on FL-VS (Florida Virtual School), I am monitored not only by administrators working close by, but also by my teacher. If I use inappropriate access, I would either be stopped or swayed back into work. Furthermore, as I stated in #1, online education is task based oriented, allowing students to work and play at different times, encouraging working and playing at separate times. 4: The comment made that “no hiring teachers” is extremely false. All the time I am personally emailed by my FL-VS teacher. Secondly, if a person is taking a physical education class, they are required to either receive calls from the teacher to their parents or Face Time the teacher during exercise. And Lastly, the student to teacher ratio is closer to 8:1 or 10:1 rather than the common 25:1 or upwards of 45:1 in some large class experiences. In fact, because the ratio is better, the education quality of the students is significantly better, furthering education. So as you can see, their is every reason to vote in Affirmation while none remaining to vote in negation. -VotedForMcCain
I realize I’ve added a caveat, in that a MATURE adult is capable of choosing a great online school. My husband is a case in point. He is obtaining a Master’s degree online, from an accredited university, and has only to complete his thesis before graduating from the program. Certainly there are bogus programs out there, but the fault does not lie in whether or not a particular online program may be bogus. There are many things on the internet that may do more harm than good, but the ultimate responsibility lies with the person using the internet. If that person is underage, then the responsibilty lies with the parents or guardians of the underage person. As in the case of my husband, it is up to the user of a particular online education program to thoroughly investigate any online education program. It would also help if people would report programs to the authorities that are bogus and may have damaged them in some way. But to do away with all online education programs would do a great disservice to people like my husband. Mature, adult perople are capable of taking in information, investigating it, then making choices about whether or not the information is true or valid, and following through with a mature, informed decision. This applies to any site we may visit on the internet, not just online education sites.
I think another point that can be added is that online education saves infrastructural costs that are associated with physical classes( electricity, maintainenance of school, etc). The school saves this money, and can redirect it to hiring better faculty and overall improving the quality of Education to the students/
The online education is very bad for our eyes as we use mobile phone computers and laptop for online classes and it is not good for our eyes.
Get glasses or upgrade your monitor, there are people out there who code and are on the computer screen for hours
Online classes good for student in period of covid 19
it is bad also due to it causes many health problems like social isolatiom
We would love to hear what you think – please leave a comment!
Yes , I”m in the favour of online teaching because urng these unusual times Without Online Learning it can’ be managed to teach childrens………..
Free tools to make your students better writers and readers .
Quill.org, a non-profit, provides free literacy activities that build reading comprehension, writing, and language skills for elementary, middle, and high school students.
Writing Across the Curriculum: Quill's nonprofit mission is to now build both reading and writing skills through free, OER content across the curriculum. Over the coming years, we will be building a library of free ELA, social studies, and science activities that engage students in deeper thinking through writing prompts that provide immediate feedback.
9 million students have written 2 billion sentences on Quill.
Quill Reading for Evidence
Provide your students with nonfiction texts paired with AI-powered writing prompts, instead of multiple-choice questions, to enable deeper thinking.
Students read a nonfiction text and build their comprehension through writing prompts, supporting a series of claims with evidence sourced from the text. Quill challenges students to write responses that are precise, logical, and based on textual evidence, with Quill coaching the student through custom, targeted feedback on each revision so that students strengthen their reading comprehension and hone their writing skills.
Video not supported
Culture & Society Topics

"Should Schools Have Grade Requirements for Student Athletes?"
Science Topics

"How Does Eating Meat Impact Global Warming?"
Social Studies Topics

U.S. History
World History
Under Development, Coming 2023
Quill Connect
Help your students advance from fragmented and run-on sentences to complex and well structured ones.
Using the evidence-based strategy of sentence combining, students combine multiple ideas into a single sentence. They then receive instant feedback designed to help them improve their clarity and precision.
Quill Lessons
The Quill Lessons tool enables teachers to lead whole-class and small-group writing instruction.
Teachers control interactive slides that contain writing prompts, and the entire class responds to each prompt. Each Quill Lessons activity provides a lesson plan, writing prompts, discussion topics, and a follow up independent practice activity.
Quill Diagnostic
Quickly determine which skills your students need to work on with our diagnostics.
The diagnostics cover vital sentence construction skills and generate personalized learning plans based on the student’s performance.

Quill Proofreader
Proofreader teaches your students editing skills by having them proofread passages.
Students edit passages and receive personalized exercises based on their results. With over 100 expository passages, Proofreader gives students the practice they need to spot common grammatical errors.
Quill Grammar
Students practice basic grammar skills, from comma placement to parallel structure.
Quill Grammar has over 150 sentence writing activities to help your students. Our activities are designed to be completed in 10 minutes so you have the freedom to use them in the way that works best for your classroom.
How Quill Works
Set up your classroom, without it.
You can quickly and easily set up your classroom in Quill by inputting student names or providing students with a unique code. If you use Google Classroom or Clever, you can automatically set up your classroom with one click.
Choose activities
Decide if you want your students to proofread passages, combine sentences, or complete a diagnostic. Use our ten minute activities as building blocks during your classroom instruction.
Use easy-to-consume reporting
Use our reporting to spot trends and identify growth opportunities. Monitor comprehension on specific writing standards.
Get immediate feedback for your students
Save time grading and watch your students correct their mistakes instantly.
Intervene where students struggle
See exactly where your students need intervention with our comprehensive reports.
Differentiate learning to meet the needs of all students
Assign specific activities for ELLs and students with learning differences.
Engage students with adaptive activities
Challenge students with questions that automatically adapt based on their previous responses.
Align with the Common Core Standards
Easily meet Common Core language standards with our aligned activities.
Easily sign up with Google Classroom
With one click all of your students and classes will be imported.
Over 100 concepts totaling 50 hours of quality curriculum.
Teacher stories
Quill in the classroom.
ROXANNA BUTKUS, RANGEVIEW ELEMENTARY
SARA ANGEL, KIPP LA
COLETTE KANG, EAST BAY INNOVATION ACADEMY
DANIEL SCIBIENSKI, PRINCETON PUBLIC SCHOOLS
3rd Grade ELA
5th Grade ELA
6th Grade ELA
8th Grade ELA & ELL
Join over 2,000 schools using Quill to advance student writing.
Quill Premium
Quill Premium's advanced reporting features are the best way to support teachers at the school or district level.

ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Online poetry writing at school – comparing lower secondary students’ experiences between individual and collaborative poetry writing provisionally accepted.

- 1 University of Helsinki, Finland
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
This study investigates how seventh-grade students experience online collaborative writing, its support in writing poems, and how collaboratively and individually written poems differ. The educational design research method was used in this mixed-methods study, which was conducted in natural classroom settings to investigate students' individual and collaborative poetry writing. The quantitative analysis of questionnaires and qualitative thematic analysis of post-experimental interviews show that the students enjoyed collaborative writing more and found it more accessible than individual writing. They experienced that it supported them in writing better poems and increased their writing confidence. They also appreciated the support of teamwork, although individual writing gave them more liberty to explore various aspects of poetry and express their feelings. From a pedagogical point of view, the students need to be provided with opportunities for collaborative poetry writing to make the writing process easier and more enjoyable. Online collaborative writing supports the process of poetry writing.
Keywords: Digital tool, technology in education, online poetry writing, collaborative writing Online Poetry Writing at School -Comparing Lower Secondary Students' Experiences between Individual and Collaborative Poetry Writing, poetry writing
Received: 02 Feb 2024; Accepted: 22 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Kangasharju, Ilomäki and Toom. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Mx. Arja Kangasharju, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland
People also looked at
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
About 1 in 5 U.S. teens who’ve heard of ChatGPT have used it for schoolwork

Roughly one-in-five teenagers who have heard of ChatGPT say they have used it to help them do their schoolwork, according to a new Pew Research Center survey of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17. With a majority of teens having heard of ChatGPT, that amounts to 13% of all U.S. teens who have used the generative artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot in their schoolwork.
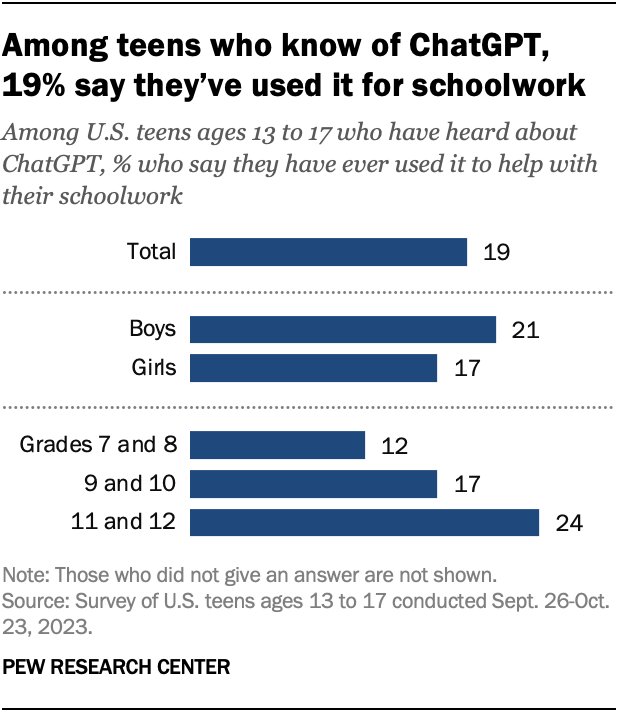
Teens in higher grade levels are particularly likely to have used the chatbot to help them with schoolwork. About one-quarter of 11th and 12th graders who have heard of ChatGPT say they have done this. This share drops to 17% among 9th and 10th graders and 12% among 7th and 8th graders.
There is no significant difference between teen boys and girls who have used ChatGPT in this way.
The introduction of ChatGPT last year has led to much discussion about its role in schools , especially whether schools should integrate the new technology into the classroom or ban it .
Pew Research Center conducted this analysis to understand American teens’ use and understanding of ChatGPT in the school setting.
The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. Ipsos recruited the teens via their parents, who were part of its KnowledgePanel . The KnowledgePanel is a probability-based web panel recruited primarily through national, random sampling of residential addresses. The survey was weighted to be representative of U.S. teens ages 13 to 17 who live with their parents by age, gender, race and ethnicity, household income, and other categories.
This research was reviewed and approved by an external institutional review board (IRB), Advarra, an independent committee of experts specializing in helping to protect the rights of research participants.
Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
Teens’ awareness of ChatGPT
Overall, two-thirds of U.S. teens say they have heard of ChatGPT, including 23% who have heard a lot about it. But awareness varies by race and ethnicity, as well as by household income:
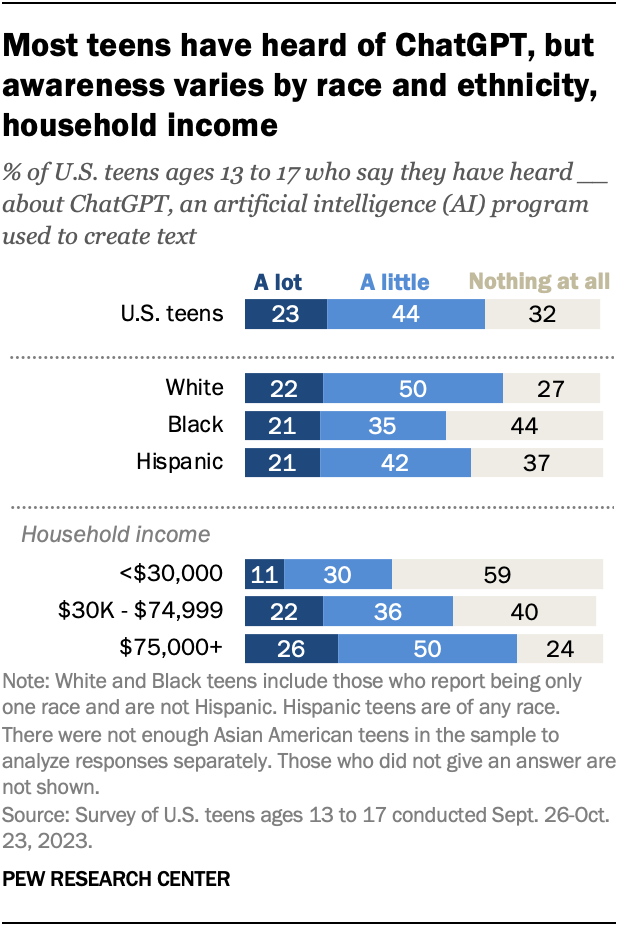
- 72% of White teens say they’ve heard at least a little about ChatGPT, compared with 63% of Hispanic teens and 56% of Black teens.
- 75% of teens living in households that make $75,000 or more annually have heard of ChatGPT. Much smaller shares in households with incomes between $30,000 and $74,999 (58%) and less than $30,000 (41%) say the same.
Teens who are more aware of ChatGPT are more likely to use it for schoolwork. Roughly a third of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT (36%) have used it for schoolwork, far higher than the 10% among those who have heard a little about it.
When do teens think it’s OK for students to use ChatGPT?
For teens, whether it is – or is not – acceptable for students to use ChatGPT depends on what it is being used for.
There is a fair amount of support for using the chatbot to explore a topic. Roughly seven-in-ten teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use when they are researching something new, while 13% say it is not acceptable.
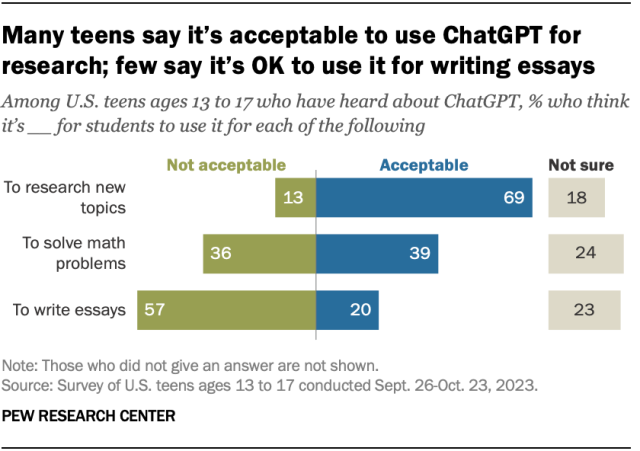
However, there is much less support for using ChatGPT to do the work itself. Just one-in-five teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to write essays, while 57% say it is not acceptable. And 39% say it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT to solve math problems, while a similar share of teens (36%) say it’s not acceptable.
Some teens are uncertain about whether it’s acceptable to use ChatGPT for these tasks. Between 18% and 24% say they aren’t sure whether these are acceptable use cases for ChatGPT.
Those who have heard a lot about ChatGPT are more likely than those who have only heard a little about it to say it’s acceptable to use the chatbot to research topics, solve math problems and write essays. For instance, 54% of teens who have heard a lot about ChatGPT say it’s acceptable to use it to solve math problems, compared with 32% among those who have heard a little about it.
Note: Here are the questions used for this analysis , along with responses, and its methodology .
- Artificial Intelligence
- Technology Adoption
- Teens & Tech

Olivia Sidoti is a research assistant focusing on internet and technology research at Pew Research Center

Jeffrey Gottfried is an associate director focusing on internet and technology research at Pew Research Center
Many Americans think generative AI programs should credit the sources they rely on
Americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, q&a: how we used large language models to identify guests on popular podcasts, striking findings from 2023, what the data says about americans’ views of artificial intelligence, most popular.
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
Welcome to the United Nations

30 years on, South Africa still dismantling racism and apartheid’s legacy
Get monthly e-newsletter.
Rethabile Ratsomo said it’s the little things that remind her of her perceived “place” in South African society.
There are the verbal slights and side-eye in workspaces, where she’s been viewed as a B-BBEE hire (The Broad-Based Black Economic Empowerment programme in South African that seeks to advance and transform the participation of black people in the country’s economy) and therefore not capable of doing the work. There are the passive-aggressive comments from colleagues, constantly complimenting her on how well she speaks English. She has lived through the daily microaggressions that form part of her life.
“I am a born-free and despite being born after the advent of democracy in South Africa, my race continues to play a huge role in my being, as a South African,” Ratsomo said, 29, who currently works at the Anti-Racism Network and the Ahmed Kathrada Foundation. “Many people continue to normalise racial discrimination and perpetuate harmful behaviours. Racism remains rife.”
Thirty years since the end of Apartheid, South Africa still grapples with its legacy. Unequal access to education, unequal pay, segregated communities and massive economic disparities persists, much of it is reinforced by existing institutions and attitudes. How is it that racism and its accompanying discrimination continues to hold such sway in this, majority Black populated and Black governed nation?
Racism has deep roots in the economic, spatial and social fabric of this country. It reflects the legacy of oppression and subjugation from apartheid and colonialism. While progress has been made to eliminate the scourge of racism it requires everyone to do their part for it be eliminated, said Abigail Noko, Representative for UN Human Rights Regional Office of Southern Africa (OHCHR ROSA)
“Dismantling such entrenched racist and discriminatory systems requires commitment, leadership, dialogue and advocacy to put in place anti-racist policies that implement human rights norms and provide a framework to help address and rectify these injustices and promote equality,” she added.
Free your mind and the rest will follow
The project of dismantling racist systems in a place like South Africa, must go hand in hand with the process of decolonization – both at an institutional and an individual level, said Professor Tshepo Madlingozi, a Commissioner at the South African Human Rights Commission (SAHRC).

“History has shown that unless you have decolonized your mind, you are going to step into the shoes of the oppressor and oppress other people over and over again,” he said.
Madlingozi’s comments were part of a panel discussion on dismantling racist systems in South Africa, which took place during the Human Rights Festival in Johannesburg in March, which aligns with national Human Rights Day and the International Day for the Elimination of Racial Discrimination. The discussion, sponsored by OHCHR ROSA, had three panellists providing their answers to the overarching question, how can racism present in the “rainbow nation” be dismantled to bring about freedom, equality, and justice for all?
Samkelo Mkhomi, a social justice and equality activist in her 20s, agreed that an internal mindset change was needed, especially among young people. She said she noticed that many of her born-free peers, i.e., someone who was born after the advent of democracy in South Africa, harbour suspicious and distrustful attitudes toward other races. She mentioned a friend who has a distrust of all white people. When Mkhomi asked why, he told her “because of what they did in the past.” She called this deliberate lack of understanding among her peers as hereditary and a big stumbling block in moving forward.
“We have set perceptions and stereotypes that we've inherited from family, from social experiences, experiences that are not our own,” Mkhomi said. “And we've used that as a blueprint to view other people. Once you can get rid of that as young people, I feel like we can start moving on and dismantling racism.”
Madlingozi suggested one way to do this could be to not only focus on individual racist incidences, but also to bring more awareness, and push for policies in institutions that deconstruct current ways of working.
“What matters is, have we dismantled the institutions, the cultures that perpetuate racism,” he said. “Because unless you do that, you’ll have Black people, you will have a Black government that will continue to perpetuate racism because that is the nature of institutionalised racism. So yes, let’s focus on individual human rights. Let’s focus on social justice, but where it matters the most is structural institutionalized oppression.”
Casting a long shadow

The scars of Apartheid run deep, leaving a legacy of segregation, discrimination and inequality. This is evidenced by the stark economic disparities in the country. A 2022 World Bank report on inequality in southern Africa gave South Africa the unfortunate distinction of being the most unequal country in the world.
The report stated that 80 percent of the country’s wealth was in the hands of 10 percent of the population. And it is the Black population who factor the most into the poorest category. The report places the blame for the income disparities directly on race.
“The legacy of colonialism and Apartheid rooted in racial and spatial segregation continues to reinforce inequality,” the report states.
The spatial divide mirrors the economic one.
The evil genius of Apartheid was the segregation project, as it allowed the Government to not only separate people based on arbitrary categorisations, but through this create material differences between the communities to reinforce the idea of actual racial differences, said Tessa Dooms. These racial classifications also encouraged the idea that the different groups needed to compete for basic human rights, dignity and economic opportunities, she added.
“The Apartheid government didn’t just give people categories, they gave real live material meaning to those categories,” said Dooms, Director of Programmes for Rivonia Circle during the panel discussion. “As long as those categories mean something in the world, we still have work to do, to undo Apartheid, to undo colonialism, to decolonize.”
To do this, Dooms recommended practical vision as to what a decolonized South Africa would look like, being very specific about the results wanted. She also called on the privileged groups to do the heavy lifting of helping to create more equality. Until those with privileges work to broaden access to them, the cycle will continue, Dooms added.
“We cannot leave creating a more just world to the people who are most affected by injustice,” she said. “It’s not fair, it’s not right and it won’t work.”
Taking concrete action
Globally, South Africa’s post-Apartheid long walk to freedom has garnered an international reputation as a leader in global efforts to combat racism. In 2001, South Africa hosted the World Conference Against Racism, Racial Discrimination, Xenophobia and Related Intolerance (WCAR), which resulted in the Durban Declaration and Programme of Action (DDPA). The DDPA is a roadmap, providing concrete measures for States to combat racism, discrimination and xenophobia and related intolerance.

One of the big recommendations was to have each country create its own National Action Plan (NAP). The plan is a means through which governments locally codify their commitment to taking action, with concrete steps on how they will combat racism. South Africa launched its plan in 2019, with OHCHR ROSA providing technical assistance. This assistance took many forms including participation in the consultations that led up to the final NAP and helping to set up support structures for its implementation, and support for research and other work to help develop systems for data collection on issues related to the NAP.
“Human rights play crucial role in dismantling racism by providing a framework for addressing and rectifying historical injustices, promoting equality, and ensuring that all individuals are treated fairly and with dignity,” Noko said
Various other sectors have pioneered innovative approaches to chip away at Apartheid’s remnants. Corporate and governmental diversity programmes, such as B-BBEE, and the Employment Equity Amendment Bill of 2020, aim to promote diversity and equity in the workplace.
Ratsomo of the Ahmed Kathrada Foundation said these and other efforts to address the underlying issue of what to do about that still exists in the country are key to taking it down. Everyone must learn, speak up, and act on racism, racial discrimination and related intolerances, she said.
“The beginning point to tackle and dismantle systemic racism is to understand that being anti-racist does not only mean being against racism,” she said. “It also means being active and speaking out against racism whenever you see it happen. The more we understand racism, the easier it becomes to identify when it happens, which allows us to speak out and act against it when we see it happening.”
Also in this issue

We must do more to prevent genocide

Football saved me from genocide; now I promote peace with it

Kwibuka30: Learning from the past, safeguarding the future against genocide

Streamlining Egypt’s food value chain through technology

Lessons post the 1994 genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda: we must speak out against discrimination and prejudice

Creating credible carbon market in Africa

REMEMBER.UNITE.RENEW.

Breaking gender barriers through education

Claver Irakoze: Bridging Generations Through the Memory of the 1994 Genocide against the Tutsi in Rwanda

Sudan: Horrific violations and abuses as fighting spreads - report
More from africa renewal.

Hate is taught: it can be fought

Two years after the killing of George Floyd, urgency to end racial inequalities and discrimination beckons

Homophobia: The Violence of Intolerance
ONLY AVAILABLE FOR SUBSCRIBERS
The Tampa Bay Times e-Newspaper is a digital replica of the printed paper seven days a week that is available to read on desktop, mobile, and our app for subscribers only. To enjoy the e-Newspaper every day, please subscribe.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
7. You might save money compared to in-person learning. Beyond tuition and fees, there are a lot of costs associated with attending college or university—or a workshop, course, or certificate program—in person. With online learning, you tend to benefit from lower overall costs because there's less overhead associated with operating each ...
So, almost certainly, online classes sometimes benefit students. In comparisons of online and in-person classes, however, online classes aren't as effective as in-person classes for most ...
Lyna Nguyen is a junior at Luther Burbank High School in Sacramento, Calif. My online learning experience as a student this fall has been great. What's working for me is I like the 40 minutes in ...
Online Tutoring. Online tutoring is a subset of online learning that pairs individual students with tutors. Tutoring is a process wherein an expert in a particular subject offers targeted support ...
Diana Lopez is a junior at Luther Burbank High School: As a student, my online learning experience hasn't been great. This new learning system has its perks, such as more time to do assignments ...
In either case, the advantages of virtual learning can be clearly seen on a resume. 6. Increased Collaboration. Online students have better opportunities to collaborate with classmates through virtual group work and meetings. One of the benefits of online courses are the message boards and grouping tools that allow students to post their ...
Online writing course curriculum. With online writing courses, any learner can master the skills needed to become a strong writer. Start with the fundamentals in an online grammar course, where you can learn about the different parts of speech, punctuation, conjugation, and sentence structure. Or more advanced writers can practice their ...
A new paper by Kofoed and co-authors adds to this literature looking specifically at online learning during the COVID-19 pandemic in a novel context: the U.S. Military Academy at West Point. When ...
On online learning platforms, it's easier for kids with social anxiety or shyness to participate. One of Gardner's students with social anxiety participated far more in virtual settings and chats. ... Before the pandemic, she was behind academically, but by guiding her own learning—writing poems, reading books, playing outside with her ...
Regionally, Asia Pacific saw the biggest student presence on the learning platform, with 28 million new online learners enrolling for 68 million courses, followed by North America, Europe and Latin America. By comparison, just 3 million online learners came from Africa, joining 5 million courses. However, Africa saw the highest growth in both ...
Online learning should also include an active teacher presence, wellbeing support, and quality, interactive digital resources. ... Write an article and join a growing community of more than ...
First, let's take a look at the true value of online learning by examining some of the benefits: 1. Flexibility. Online learning's most significant advantage is its flexibility. It's the reason millions of adults have chosen to continue their education and pursue certificates and degrees. Asynchronous courses allow learners to complete ...
Online learning has many benefits for high-tech companies: As the companies use different methods to design, transport, select, manage and extend their business, etc. online teaching process is instrumental for them. They can give valuable guidance, pieces of training for their employees without the need for them to be absent for long which ...
The article presents some challenges faced by teachers and learners, supplemented with the recommendations to remove them. JEL Code: A20. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to an expansion in the demand for online teaching and learning across the globe. Online teaching and learning is attracting many students for enhanced learning experiences.
Impact of Online Classes on Students Essay. The thesis statement for this study is: "online learning has positive impact on the learners, teachers and the institution offering these courses" Online learning or E learning is a term used to describe various learning […] We will write.
1.1. Related literature. Online learning is a form of distance education which mainly involves internet‐based education where courses are offered synchronously (i.e. live sessions online) and/or asynchronously (i.e. students access course materials online in their own time, which is associated with the more traditional distance education).
With online learning, an instructor can write down notes on a digital whiteboard or even assign a student to write real-time notes that students can easily download after the class. Online classes unlock more learning opportunities ... Online education must support the social aspect of learning to match the effectiveness of traditional classes.
Online Education Outline Online and traditional education may share numerous academic techniques, but online education better assists students by proposing format according to their skills, interests and requirements. Online and traditional education can offer student-centered, teacher-facilitated learning opportunities. Students can work independently or in groups on projects and assignments.
Online education or online classes were not a new concept, but online classes' prominence was seen only during the pandemic. The online class provides a flexible and quick learning option. ... While writing a paragraph on online classes, you can write about the growing importance of it and how it has changed learning patterns. You can write ...
nayanshi Published On June 18th, 2023. Table of Contents. Online Education Essay. Online Education Essay PDF. Online Education Essay in English (200-250) words. Online Education Essay in Paragraph 200-250 Words. Online Education Essay in 500-1000 words for UPSC. Advantages and Disadvantages of Online Education for Essay.
Recommended for: Udemy is an excellent place to start if you're new to online learning, as the classes don't cost much, and you can buy them anytime. Pricing: Udemy online writing classes are cheap to start with and often sold at a discount. The cost varies depending on the class. Classes start from $9.99.
Without online education, the transition into the computer world we're slowly becoming would be very difficult. 3: The fact of distracting students is not nearly as tempting as in regular social environments. The urge to talk to friends, draw, sleep or day-dream is not nearly as strong as the urge to use the internet. ...
The Quill Lessons tool enables teachers to lead whole-class and small-group writing instruction. Teachers control interactive slides that contain writing prompts, and the entire class responds to each prompt. Each Quill Lessons activity provides a lesson plan, writing prompts, discussion topics, and a follow up independent practice activity.
As Clay Shirky, vice provost for AI and technology in education at NYU, told me: "A full-service OPM buys you a bundle of competencies. If you go with an OPM, you get less change at your own institution. If you do it yourself, you take the longer road, adapting to online learning."
Motivational research identifies utility value, or the importance of a learning task to future goals, as central to motivation to learn. This study analyzed survey data (N = 86) collected from adult literacy learners to examine their utility value of writing improvement in grammar and spelling skills, word processing skills, and planning, drafting, and revising skills.
Liz Simmons has been writing for various online publications about career development, higher education and college affordability for nearly a decade. Her articles demystify the college ...
This study investigates how seventh-grade students experience online collaborative writing, its support in writing poems, and how collaboratively and individually written poems differ. The educational design research method was used in this mixed-methods study, which was conducted in natural classroom settings to investigate students' individual and collaborative poetry writing.
The Center conducted an online survey of 1,453 U.S. teens from Sept. 26 to Oct. 23, 2023, via Ipsos. ... Just one-in-five teens who have heard of ChatGPT say it's acceptable to use it to write essays, while 57% say it is not acceptable. And 39% say it's acceptable to use ChatGPT to solve math problems, while a similar share of teens (36% ...
Unequal access to education, unequal pay, segregated communities and massive economic disparities persists, much of it is reinforced by existing institutions and attitudes. How is it that racism ...
Respond to the Tampa Bay Times' coverage and state and local discussions. Submit your letters to the editor.