Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, coherence – how to achieve coherence in writing.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
Coherence refers to a style of writing where ideas, themes, and language connect logically, consistently, and clearly to guide the reader's understanding. By mastering coherence , alongside flow , inclusiveness , simplicity, and unity , you'll be well-equipped to craft professional or academic pieces that engage and inform effectively. Acquire the skills to instill coherence in your work and discern it in the writings of others.


What is Coherence?
Coherence in writing refers to the logical connections and consistency that hold a text together, making it understandable and meaningful to the reader. Writers create coherence in three ways:
- logical consistency
- conceptual consistency
- linguistic consistency.
What is Logical Consistency?
- For instance, if they argue, “If it rains, the ground gets wet,” and later state, “It’s raining but the ground isn’t wet,” without additional explanation, this represents a logical inconsistency.
What is Conceptual Consistency?
- For example, if you are writing an essay arguing that regular exercise has multiple benefits for mental health, each paragraph should introduce and discuss a different benefit of exercise, all contributing to your main argument. Including a paragraph discussing the nutritional value of various foods, while interesting, would break the conceptual consistency, as it doesn’t directly relate to the benefits of exercise for mental health.
What is Linguistic Consistency?
- For example, if a writer jumps erratically between different tenses or switches point of view without clear demarcation, the reader might find it hard to follow the narrative, leading to a lack of linguistic coherence.
Related Concepts: Flow ; Given to New Contract ; Grammar ; Organization ; Organizational Structures ; Organizational Patterns ; Sentence Errors
Why Does Coherence Matter?
Coherence is crucial in writing as it ensures that the text is understandable and that the ideas flow logically from one to the next. When writing is coherent, readers can easily follow the progression of ideas, making the content more engaging and easier to comprehend. Coherence connects the dots for the reader, linking concepts, arguments, and details in a clear, logical manner.
Without coherence, even the most interesting or groundbreaking ideas can become muddled and lose their impact. A coherent piece of writing keeps the reader’s attention, demonstrates the writer’s control over their subject matter, and can effectively persuade, inform, or entertain. Thus, coherence contributes significantly to the effectiveness of writing in achieving its intended purpose.
How Do Writers Create Coherence in Writing?
- Your thesis statement serves as the guiding star of your paper. It sets the direction and focus, ensuring all subsequent points relate back to this central idea.
- Acknowledge and address potential counterarguments to strengthen your position and add depth to your writing.
- Use the genres and organizational patterns appropriate for your rhetorical situation . A deductive structure (general to specific) is often effective, guiding the reader logically through your argument. Yet different disciplines may privilege more inductive approaches , such as law and philosophy.
- When following a given-to-new order, writers move from what the reader already knows to new information. In formal or persuasive contexts, writers are careful to vet new information for the reader following information literacy laws and conventions .
- Strategic repetition of crucial terms and your thesis helps your readers follow your main ideas and evidence for claims
- While repetition is useful, varying language with synonyms can prevent redundancy and keep the reader engaged.
- Parallelism in sentences can provide rhythm and clarity, making complex ideas easier to follow.
- Consistent use of pronouns avoids confusion and helps in maintaining a clear line of thought.
- Arrange your ideas in a sequence that naturally builds from one point to the next, ensuring each paragraph flows smoothly into the next .
- Signposting , or using phrases that indicate what’s coming next or what just happened, can help orient the reader within your argument.
- Don’t bother repeating your argument in your conclusion. Prioritize conciseness. Yet end with a call to action or appeal to kairos and ethos .
Recommended Resources
- Organization
- Organizational Patterns

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Pasco-Hernando State College
- Unity and Coherence in Essays
- The Writing Process
- Paragraphs and Essays
- Proving the Thesis/Critical Thinking
- Appropriate Language
Test Yourself
- Essay Organization Quiz
- Sample Essay - Fairies
- Sample Essay - Modern Technology
Related Pages
- Proving the Thesis
Unity is the idea that all parts of the writing work to achieve the same goal: proving the thesis. Just as the content of a paragraph should focus on a topic sentence, the content of an essay must focus on the thesis. The introduction paragraph introduces the thesis, the body paragraphs each have a proof point (topic sentence) with content that proves the thesis, and the concluding paragraph sums up the proof and restates the thesis. Extraneous information in any part of the essay which is not related to the thesis is distracting and takes away from the strength of proving the thesis.
An essay must have coherence. The sentences must flow smoothly and logically from one to the next as they support the purpose of each paragraph in proving the thesis. .
Just as the last sentence in a paragraph must connect back to the topic sentence of the paragraph, the last paragraph of the essay should connect back to the thesis by reviewing the proof and restating the thesis.
Example of Essay with Problems of Unity and Coherence
Here is an example of a brief essay that includes a paragraph that does not support the thesis “Many people are changing their diets to be healthier.”
People are concerned about pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics in the food they eat. Many now shop for organic foods since they don’t have the pesticides used in conventionally grown food. Meat from chicken and cows that are not given steroids or antibiotics are gaining in popularity even though they are much more expensive. More and more, people are eliminating pesticides, steroids, and antibiotics from their diets.
Eating healthier also is beneficial to the environment since there are less pesticides poisoning the earth. Pesticides getting into the waterways is creating a problem with drinking water. Historically, safe drinking water has been a problem. It is believed the Ancient Egyptians drank beer since the water was not safe to drink. Brewing beer killed the harmful organisms and bacteria in the water from the Nile.
There is a growing concern about eating genetically modified foods, and people are opting for non-GMO diets. Some people say there are more allergic reactions and other health problems resulting from these foods. Others are concerned because there are no long-term studies which clearly show no adverse health effects such as cancers or other illnesses. Avoiding GMO food is another way people are eating healthier food.
See how just one paragraph can take away from the effectiveness of the essay in showing how people are changing to healthier food since the unity and coherence are affected. There is no longer unity among all the paragraphs. The thought pattern is disjointed and the essay loses its coherence.
Transitions and Logical Flow of Ideas
Transitions are words, groups of words, or sentences that connect one sentence to another or one paragraph to another.
They promote a logical flow from one idea to the next and overall unity and coherence.
While transitions are not needed in every sentence or at the end of every paragraph, they are missed when they are omitted since the flow of thoughts becomes disjointed or even confusing.
There are different types of transitions:
Time – before, after, during, in the meantime, nowadays
Space – over, around, under
Examples – for instance, one example is
Comparison – on the other hand, the opposing view
Consequence – as a result, subsequently
These are just a few examples. The idea is to paint a clear, logical connection between sentences and between paragraphs.
- Printer-friendly version

- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Coherently
I. What is Coherence?
Coherence describes the way anything, such as an argument (or part of an argument) “hangs together.” If something has coherence, its parts are well-connected and all heading in the same direction. Without coherence, a discussion may not make sense or may be difficult for the audience to follow. It’s an extremely important quality of formal writing.
Coherence is relevant to every level of organization, from the sentence level up to the complete argument. However, we’ll be focused on the paragraph level in this article. That’s because:
- Sentence-level coherence is a matter of grammar, and it would take too long to explain all the features of coherent grammar.
- Most people can already write a fairly coherent sentence, even if their grammar is not perfect.
- When you write coherent paragraphs, the argument as a whole will usually seem coherent to your readers.
Although coherence is primarily a feature of arguments, you may also hear people talk about the “coherence” of a story, poem, etc. However, in this context the term is extremely vague, so we’ll focus on formal essays for the sake of simplicity.
Coherence is, in the end, a matter of perception. This means it’s a completely subjective judgement. A piece of writing is coherent if and only if the reader thinks it is.
II. Examples of Coherence
There are many distinct features that help create a sense of coherence. Let’s look at an extended example and go through some of the features that make it seem coherent. Most people would agree that this is a fairly coherent paragraph:
Credit cards are convenient , but dangerous . People often get them in order to make large purchases easily without saving up lots of money in advance. This is especially helpful for purchases like cars, kitchen appliances, etc., that you may need to get without delay . However, this convenience comes at a high price : interest rates. The more money you put on your credit card, the more the bank or credit union will charge you for that convenience . If you’re not careful, credit card debt can quickly break the bank and leave you in very dire economic circumstances!
- Topic Sentence . The paragraph starts with a very clear, declarative topic sentence, and the rest of the paragraph follows that sentence. Everything in the paragraph is tied back to the statement in the beginning.
- Key terms . The term “credit card” appears repeatedly in this short paragraph. This signals the reader that the whole paragraph is about the subject of credit cards. Similarly, the word convenience (and related words) are also peppered throughout. In addition, the key term “ danger ” appears in the topic sentence and is then explained fully as the paragraph goes on.
- Defined terms . For most readers, the terms in this paragraph will be quite clear and will not need to be defined. Some readers, however, might not understand the term “interest rates,” and they would need an explanation. To these readers, the paragraph will seem less coherent !
Clear transitions . Each sentence flows into the next quite easily, and readers can follow the line of logic without too much effort.
III. The Importance of Coherence
Say you’re reading a piece of academic writing – maybe a textbook. As you read, you find yourself drifting off, having to read the same sentence over and over before you understand it. Maybe, after a while, you get frustrated and give up on the chapter. What happened?
Nine times out of ten, this is a symptom of incoherence. Your brain is unable to find a unified argument or narrative in the book. This may become frustrating and often happens when a book is above your current level of understanding. To someone else, the writing might seem perfectly coherent, because they understand the concepts involved. But from your perspective, the chapter seems incoherent. And as a result, you don’t get as much out of it as you otherwise would.
How can you avoid this in your own writing? How can you make sure that readers don’t misunderstand you (or just give up altogether)? The answer is to work on coherent writing. Coherence is perhaps the most important feature of argumentative writing. Without it, everything falls apart. If an argument is not coherent, it doesn’t matter how good the evidence is, or how beautiful the writing is: an incoherent argument will never persuade anyone or even hold their attention.
V. Examples in Literature and Scholarship
Since coherence is subjective, people will disagree about the examples. This is especially true in scholarly fields , where authors are writing for a very specific audience of experts; anyone outside that audience is likely to see the work as incoherent. For example, the various fields of analytic philosophy are a great place to look for coherence in scholarly work. Analytic philosophers are trained to write very carefully, with all the steps in the argument carefully laid out ahead of time. So their arguments usually have a remarkable internal coherence. However, analytic philosophy is a very obscure topic, and very few people are trained to understand the terms these scholars use! Thus, ironically, some of the most coherent writers in academia (from an expert perspective) usually come across as incoherent to the majority of readers.
For writing Indian Schools: a Nation’s Neglect , journalist Jill Burcum was nominated for a Pulitzer Prize in the editorial writing category. An excellent example of coherence in journalistic writing, the editorial deals with the shabby federal schools that are meant for Native Americans on reservations. The essay’s paragraphs are much shorter than they would be in an essay. Yet each one still revolves around a single, tightly focused set of ideas. You can find key concepts (such as “neglect”) that run as themes throughout the piece. The whole editorial is also full of smooth and clear transitions.
VI. Examples in Media and Pop Culture
You can often see something like argumentative coherence in political satire. Good satire always focuses on a single question and lampoons it in a highly coherent manner. Watch, for example, Jon Stewart’s opening monologues on The Daily Show. Whatever your opinion on Stewart’s politics, it’s hard to argue with the fact that he uses terms carefully. He transitions smoothly and focuses on a single, tightly controlled set of concepts in each monologue.
Sports debates can also provide a good example of coherence. When you watch a show about sports (like SportsCenter or First Take), pay attention to the attributes of coherence. How do the hosts and guests use their terms? Do they repeat key terms? Do they start each monologue with a “topic sentence”? Do they stick to one topic, or do they go off on tangents?
VII. Related Terms
“Cogency” sounds like “coherence,” but means convincing or persuasive . The two terms are related, though: an argument cannot be cogent if it’s not coherent, because coherence is essential to persuasion. However, an argument could be coherent but not cogent (i.e. it’s clear, unified, and easy to read, but the argument does not persuade its reader).
Focus is also related to coherence. Often, coherence problems emerge when the focus is too broad. When the focus is broad, there are just too many parts to cover all at once, and writers struggle to maintain coherence.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

Cohesion And Coherence In Essay Writing
Table of contents, introduction.
Coherent essays are identified by relevance to the central topic. They communicate a meaningful message to a specific audience and maintain pertinence to the main focus. In a coherent essay, the sentences and ideas flow smoothly and, as a result, the reader can follow the ideas developed without any issues.
To achieve coherence in an essay, writers use lexical and grammatical cohesive devices. Examples of these cohesive devices are repetition, synonymy, antonymy, meronymy, substitutions , and anaphoric or cataphoric relations between sentences. We will discuss these devices in more detail below.
This article will discuss how to write a coherent essay. We will be focusing on the five major points.
- We will start with definitions of coherence and cohesion.
- Then, we will give examples of how a text can achieve cohesion.
- We will see how a text can be cohesive but not coherent.
- The structure of a coherent essay will also be discussed.
- Finally, we will look in detail at ways to improve cohesion and write a coherent essay.

Before illustrating how to write coherent essays, let us start with the definitions of coherence and cohesion and list the ways we can achieve cohesion in a coherent text.
Definitions Cohesion and Coherence
In general, coherence and cohesion refer to how a text is structured so that the elements it is constituted of can stick together and contribute to a meaningful whole. In coherent essays, writers use grammatical and lexical cohesive techniques so that ideas can flow meaningfully and logically.
What is coherence?
Coherence refers to the quality of forming a unified consistent whole. We can describe a text as being coherent if it is semantically meaningful, that is if the ideas flow logically to produce an understandable entity.
If a text is coherent it is logically ordered and connected. It is clear, consistent, and understandable.
Coherence is related to the macro-level features of a text which enable it to have a sense as a whole.
What is cohesion?
Cohesion is commonly defined as the grammatical and lexical connections that tie a text together, contributing to its meaning (i.e. coherence.)
While coherence is related to the macro-level features of a text, cohesion is concerned with its micro-level – the words, the phrases, and the sentences and how they are connected to form a whole.
If the elements of a text are cohesive, they are united and work together or fit well together.
To summarize, coherence refers to how the ideas of the text flow logically and make a text semantically meaningful as a whole. Cohesion is what makes the elements (e.g. the words, phrases, clauses, and sentences) of a text stick together to form a whole.
How to Achieve Cohesion And Coherence In Essay Writing
There are two types of cohesion: lexical and grammatical. Writers connect sentences and ideas in their essays using both lexical and grammatical cohesive devices.
Lexical cohesion
We can achieve cohesion through lexical cohesion by using these techniques:
- Repetition.
Now let’s look at these in more detail.
Repeating words may contribute to cohesion. Repetition creates cohesive ties within the text.
- Birds are beautiful. I like birds.
You can use a word or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word to achieve cohesion.
- Paul saw a snake under the mattress. The serpent was probably hiding there for a long time.
Antonymy refers to the use of a word of opposite meaning. This is often used to create links between the elements of a text.
- Old movies are boring, the new ones are much better.
This refers to the use of a word that denotes a subcategory of a more general class.
- I saw a cat . The animal was very hungry and looked ill.
Relating a superordinate term (i.e. animal) to a corresponding subordinate term (i.e. cat) may create more cohesiveness between sentences and clauses.
Meronymy is another way to achieve cohesion. It refers to the use of a word that denotes part of something but which is used to refer to the whole of it for instance faces can be used to refer to people as in “I see many faces here”. In the following example, hands refer to workers.
- More workers are needed. We need more hands to finish the work.
Grammatical cohesion
Grammatical cohesion refers to the grammatical relations between text elements. This includes the use of:
- Cataphora .
- Substitutions.
- Conjunctions and transition words.
Let us illustrate the above devices with some examples.
Anaphora is when you use a word referring back to another word used earlier in a text or conversation.
- Jane was brilliant. She got the best score.
The pronoun “she” refers back to the proper noun “Jane”.
Cataphora is the opposite of anaphora. Cataphora refers to the use of a word or phrase that refers to or stands for a following word or phrase.
- Here he comes our hero. Please, welcome John .
The pronoun “he” refers back to the proper noun “John”.
Ellipsis refers to the omission from speech or writing of a word or words that are superfluous or able to be understood from contextual clues.
- Liz had some chocolate bars, and Nancy an ice cream.
In the above example, “had” in “Nancy an ice cream” is left because it can be understood (or presupposed) as it was already mentioned previously in the sentence.
Elliptic elements can be also understood from the context as in:
- A: Where are you going?
Substitutions
Substitutions refer to the use of a word to replace another word.
- A: Which T-shirt would you like?
- B: I would like the pink one .
Conjunctions transition words
Conjunctions and transition words are parts of speech that connect words, phrases, clauses, or sentences.
- Examples of conjunctions: but, or, and, although, in spite of, because,
- Examples of transition words: however, similarly, likewise, specifically, consequently, for this reason, in contrast to, accordingly, in essence, chiefly, finally.
Here are some examples:
- I called Tracy and John.
- He was tired but happy.
- She likes neither chocolates nor cookies.
- You can either finish the work or ask someone to do it for you.
- He went to bed after he had done his homework.
- Although she is very rich, she isn’t happy.
- I was brought up to be responsible. Similarly , I will try to teach my kids how to take responsibility for their actions.
Cohesive but not coherent texts
Sometimes, a text may be cohesively connected, yet may still be incoherent.
Learners may wrongly think that simply linking sentences together will lead to a coherent text.
Here is an example of a text in which sentences are cohesively connected, yet the overall coherence is lacking:
The player threw the ball toward the goalkeeper. Balls are used in many sports. Most balls are spheres, but American football is an ellipsoid. Fortunately, the goalkeeper jumped to catch the ball. The crossbar in the soccer game is made of iron. The goalkeeper was standing there.
The sentences and phrases in the above text are decidedly cohesive but not coherent.
There is a use of:
- Repetition of: the ball, goalkeeper, the crossbar.
- Conjunctions and transition words: but, fortunately.
The use of the above cohesive devices does not result in a meaningful and unified whole. This is because the writer presents material that is unrelated to the topic. Why should a writer talk about what the crossbar is made of? And is talking about the form balls in sports relevant in this context? What is the central focus of the text?
A coherent essay has to be cohesively connected and logically expressive of the central topic.
How to write a coherent essay?
1. start with an outline.
An outline is the general plan of your essays. It contains the ideas you will include in each paragraph and the sequence in which these ideas will be mentioned.
It is important to have an outline before starting to write. Spending a few minutes on the outline can be rewarding. An outline will organize your ideas and the end product can be much more coherent.
Here is how you can outline your writing so that you can produce a coherent essay:
- Start with the thesis statement – the sentence that summarizes the topic of your writing.
- Brainstorm the topic for a few minutes. Write down all the ideas related to the topic.
- Sift the ideas brainstormed in the previous step to identify only the ideas worth including in your essay.
- Organize ideas in a logical order so that your essay reflects the unified content that you want to communicate.
- Each idea has to be treated in a separate paragraph.
- Think of appropriate transitions between the different ideas.
- Under each idea/paragraph, write down enough details to support your idea.
After identifying and organizing your ideas into different paragraphs, they have to fit within the conventional structure of essays.

2. Structure your essay
It is also important to structure your essay so that you the reader can identify the organization of the different parts of your essay and how each paragraph leads to the next one.
Here is a structure of an essay
3. Structure your paragraphs
Paragraphs have to be well-organized. The structure of each paragraph should have:
- A topic sentence that is usually placed at the beginning,
- Supporting details that give further explanation of the topic sentence,
- And a concluding sentence that wraps up the content of the paragraph.
The supporting sentences in each paragraph must flow smoothly and logically to support the purpose of the topic sentence. Similarly, each paragraph has to serve the thesis statement, the main topic of the essay.
4. Relevance to the main topic
No matter how long the essay is, we should make sure that we stick to the topic we want to talk about. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly to create unity. So, sentences and ideas must be relevant to the central thesis statement.
The writer has to maintain the flow of ideas to serve the main focus of the essay.
5. Stick to the purpose of the type of essay you’re-writing
Essays must be clear and serve a purpose and direction. This means that the writer’s thoughts must not go astray in developing the purpose of the essay.
Essays are of different types and have different purposes. Accordingly, students have to stick to the main purpose of each genre of writing.
- An expository essay aims to inform, describe, or explain a topic, using essential facts to teach the reader about a topic.
- A descriptive essay intends to transmit a detailed description of a person, event, experience, or object. The aim is to make the reader perceive what is being described.
- A narrative essay attempts to tell a story that has a purpose. Writers use storytelling techniques to communicate an experience or an event.
- In argumentative essays, writers present an objective analysis of the different arguments about a topic and provide an opinion or a conclusion of positive or negative implications. The aim is to persuade the reader of your point.
6. Use cohesive devices and signposting phrases
Sentences should be connected using appropriate cohesive devices as discussed above:
Cohesive devices such as conjunctions and transition words are essential in providing clarity to your essay. But we can add another layer of clarity to guide the reader throughout the essay by using signpost signals.
What is signposting in writing?
Signposting refers to the use of phrases or words that guide readers to understand the direction of your essay. An essay should take the reader on a journey throughout the argumentation or discussion. In that journey, the paragraphs are milestones. Using signpost signals assists the reader in identifying where you want to guide them. Signposts serve to predict what will happen, remind readers of where they are at important stages along the process, and show the direction of your essay.
Essay signposting phrases
The following are some phrases you can use to signpost your writing:
It should be noted though that using cohesive devices or signposting language may not automatically lead to a coherent text. Some texts can be highly cohesive but remain incoherent. Appropriate cohesion and signposting are essential to coherence but they are not enough. To be coherent, an essay has to follow, in addition to using appropriate cohesive devices, all the tips presented in this article.
7. Draft, revise, and edit
After preparing the ground for the essay, students produce their first draft. This is the first version of the essay. Other subsequent steps are required.
The next step is to revise the first draft to rearrange, add, or remove paragraphs, ideas, sentences, or words.
The questions that must be addressed are the following:
- Is the essay clear? Is it meaningful? Does it serve the thesis statement (the main topic)?
- Are there sufficient details to convey ideas?
- Are there any off-topic ideas that you have to do without?
- Have you included too much information? Does your writing stray off-topic?
- Do the ideas flow in a logical order?
- Have you used appropriate cohesive devices and transition words when needed?
Once the revision is done, it is high time for the editing stage. Editing involves proofreading and correcting mistakes in grammar and mechanics. Pay attention to:
- Verb tense.
- Subject-verb agreement.
- Sentence structure. Have you included a subject a verb and an object (if the verb is transitive.)
- Punctuation.
- Capitalization.
Coherent essays are identified by relevance to the thesis statement. The ideas and sentences of coherent essays flow smoothly. One can follow the ideas discussed without any problems. Lexical and grammatical cohesive devices are used to achieve coherence. However, these devices are not sufficient. To maintain relevance to the main focus of the text, there is a need for a whole process of collecting ideas, outlining, reviewing, and editing to create a coherent whole.
More writing lessons are here .
Related Pages:
- Figures of speech
- Articles about writing

Definition of Coherence
Coherence is a Latin word, meaning “to stick together.” In a composition, coherence is a literary technique that refers to logical connections, which listeners or readers perceive in an oral or written text. In other words, it is a written or spoken piece that is not only consistent and logical, but also unified and meaningful. It makes sense when read or listened to as a whole. The structure of a coherent paragraph could be general to particular and particular to general or any other format.
Types of Coherence
- Local Level Coherent Text In this type of text, coherence occurs within small portions of a passage or a text.
- Global level Coherent Text In this type of text, coherence takes place within the whole text of a story or essay , rather than in its few parts.
Examples of Coherence in Literature
Example #1: one man’s meat (by e.b. white).
“Scientific agriculture, however sound in principle, often seems strangely unrelated to, and unaware of, the vital, grueling job of making a living by farming. Farmers sense this quality in it as they study their bulletins, just as a poor man senses in a rich man an incomprehension of his own problems. The farmer of today knows, for example, that manure loses some of its value when exposed to the weather … But he knows also that to make hay he needs settled weather – better weather than you usually get in June.”
This is a global level coherent text passage in which White has wonderfully unified the sentences to make it a whole. He has started the passage with a general topic, scientific agriculture, but moved it to a specific text about farmers and their roles.
Example #2: A Tale of Two Cities (by Charles Dickens)
“The wine was red wine, and had stained the ground of the narrow street in the suburb of Saint Antoine, in Paris, where it was spilled. It had stained many hands, too, and many faces, and many naked feet, and many wooden shoes. The hands of the man who sawed the wood, left red marks on the billets; and the forehead of the woman who nursed her baby, was stained with the stain of the old rag she wound about her head again. Those who had been greedy with the staves of the cask … scrawled upon a wall with his finger dipped in muddy wine-lees—BLOOD.”
Taken from the novel , A Tale of Two Cities , this passage’s emphasis is on the idea of staining, and scrawling the word “blood,” which further brings coherence into the lines. The connection is thus made through the appearance of Wood-Sawyer, a man who scares Lucie later. This is how it achieves coherence.
Example #3: Animal Farm (by George Orwell)
“ Now , comrades, what is the nature of this life of ours? Let us face it: our lives are miserable, laborious, and short. We are born, we are given just so much food as will keep the breath in our bodies, and those of us who are capable of it are forced to work to the last atom of our strength … “No animal in England knows the meaning of happiness or leisure after he is a year old. The life of an animal is misery and slavery: that is the plain truth.”
Through the speech of the Old Major, Orwell starts the passage about the miserable nature of the life of animals on the animal farm , and then he inspires them to think about how to safeguard their interests on the farm. The entire paragraph is an example of coherent speech.
Example #4: Unpopular Essays (by Bertrand Russell)
“The word “philosophy” is one of which the meaning is by no means fixed. Like the word “religion,” it has one sense when used to describe certain features of historical cultures, and another when used to denote a study or an attitude of mind which is considered desirable in the present day. Philosophy, as pursued in the universities of the Western democratic world, is, at least in intention, part of the pursuit of knowledge, aiming at the same kind of detachment as is sought in science …”
See how brilliantly Russell has connected the ideas of philosophy and politics, by moving from a general to a specific topic, with sentences connecting one to another, creating coherence.
Coherence links the sentences of a work with one another. This may be done with paragraphs, making sure that each statement logically connects with the one preceding it, making the text easier for the readers to understand and follow. Also, ordering thoughts in a sequence helps the reader to move from one point to the next smoothly. As all of the sentences relate back to the topic, the thoughts and ideas flow smoothly.
Post navigation

Achieving coherence
“A piece of writing is coherent when it elicits the response: ‘I follow you. I see what you mean.’ It is incoherent when it elicits the response: ‘I see what you're saying here, but what has it got to do with the topic at hand or with what you just told me above?’ ” - Johns, A.M
Transitions
Parallelism, challenge task, what is coherence.
Coherence in a piece of writing means that the reader can easily understand it. Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly. The reader can see that everything is logically arranged and connected, and relevance to the central focus of the essay is maintained throughout.

Repetition in a piece of writing does not always demonstrate cohesion. Study these sentences:
So, how does repetition as a cohesive device work?
When a pronoun is used, sometimes what the pronoun refers to (ie, the referent) is not always clear. Clarity is achieved by repeating a key noun or synonym . Repetition is a cohesive device used deliberately to improve coherence in a text.
In the following text, decide ifthe referent for the pronoun it is clear. Otherwise, replace it with the key noun English where clarity is needed.
Click here to view the revised text.
Suggested improvement
English has almost become an international language. Except for Chinese, more people speak it (clear reference; retain) than any other language. Spanish is the official language of more countries in the world, but more countries have English ( it is replaced with a key noun) as their official or unofficial second language. More than 70% of the world's mail is written in English ( it is replaced with a key noun). It (clear reference; retain) is the primary language on the Internet.
Sometimes, repetition of a key noun is preferred even when the reference is clear. In the following text, it is clear that it refers to the key noun gold , but when used throughout the text, the style becomes monotonous.
Improved text: Note where the key noun gold is repeated. The deliberate repetition creates interest and adds maturity to the writing style.
Gold , a precious metal, is prized for two important characteristics. First of all, gold has a lustrous beauty that is resistant to corrosion. Therefore, it is suitable for jewellery, coins and ornamental purposes. Gold never needs to be polished and will remain beautiful forever. For example, a Macedonian coin remains as untarnished today as the day it was made 23 centuries ago. Another important characteristic of gold is its usefulness to industry and science. For many years, it has been used in hundreds of industrial applications. The most recent use of gold is in astronauts’ suits. Astronauts wear gold -plated shields when they go outside spaceships in space. In conclusion, gold is treasured not only for its beauty but also its utility.
Pronoun + Repetition of key noun
Sometimes, greater cohesion can be achieved by using a pronoun followed by an appropriate key noun or synonym (a word with a similar meaning).
Transitions are like traffic signals. They guide the reader from one idea to the next. They signal a range of relationships between sentences, such as comparison, contrast, example and result. Click here for a more comprehensive list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) .

Test yourself: How well do you understand transitions?
Which of the three alternatives should follow the transition or logical organiser in capital letters to complete the second sentence?
Using transitions/logical organisers
Improve the coherence of the following paragraph by adding transitions in the blank spaces. Use the italicised hint in brackets to help you choose an apporpriate transition for each blank. If you need to, review the list of Transitions (Logical Organisers) before you start.
Using transitions
Choose the most appropriate transition from the options given to complete the article:
Overusing transitions
While the use of appropriate transitions can improve coherence (as the previous practice activity shows), it can also be counterproductive if transitions are overused. Use transitions carefully to enhance and clarify the logical connection between ideas in extended texts. Write a range of sentences and vary sentence openings.
Study the following examples:
Identifying cohesive devices

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility

- WRITING SKILLS
Coherence in Writing
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Writing Skills:
- A - Z List of Writing Skills
The Essentials of Writing
- Common Mistakes in Writing
- Introduction to Grammar
- Improving Your Grammar
- Active and Passive Voice
- Punctuation
- Clarity in Writing
- Writing Concisely
- Gender Neutral Language
- Figurative Language
- When to Use Capital Letters
- Using Plain English
- Writing in UK and US English
- Understanding (and Avoiding) Clichés
- The Importance of Structure
- Know Your Audience
- Know Your Medium
- Formal and Informal Writing Styles
- Note-Taking from Reading
- Note-Taking for Verbal Exchanges
- Creative Writing
- Top Tips for Writing Fiction
- Writer's Voice
- Writing for Children
- Writing for Pleasure
- Writing for the Internet
- Journalistic Writing
- Technical Writing
- Academic Writing
- Editing and Proofreading
Writing Specific Documents
- Writing a CV or Résumé
- Writing a Covering Letter
- Writing a Personal Statement
- Writing Reviews
- Using LinkedIn Effectively
- Business Writing
- Study Skills
- Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Have you ever read a piece of writing and wondered what point the writer was trying to make? If so, that piece of writing probably lacked coherence. Coherence is an important aspect of good writing—as important as good grammar or spelling. However, it is also rather harder to learn how to do it, because it is not a matter of simple rules.
Coherent writing moves smoothly between ideas. It guides the reader through an argument or series of points using signposts and connectors. It generally has a clear structure and consistent tone, with little or no repetition. Coherent writing feels planned —usually because it is. This page provides some tips to help you to develop your ability to write coherently.
Defining Coherence
Dictionary definition of coherence
cohere , v. to stick together, to be consistent, to fit together in a consistent, orderly whole.
coherence , a sticking together, consistency.
Source: Chambers English Dictionary, 1989 edition.
The dictionary definition of coherence is clear enough—but what does that mean in practical terms for writers?
Once you have achieved coherence in your writing, you will find that:
Your sentences and ideas are connected and flow together;
Readers can move easily through the text from one sentence, paragraph or idea to the next; and
Readers will be able to follow the ideas and main points of the text.
On the other hand, a text that is NOT coherent jumps between ideas without making clear connections between them. It is often hard to follow the argument. Readers may find themselves unclear about the point of particular paragraphs or even whole sections. There may be odd sentences that do not fit well with the previous or following sentence, or paragraphs that repeat earlier ideas.
All these issues provide pointers for how to develop coherence.
Elements of Coherence
There are several different elements that contribute to coherence, or are closely linked to the concept.
They include:
Cohesion , or whether ideas are linked within and between sentences.
Unity , or the extent to which a sentence, paragraph or section focuses on a single idea or group or ideas. In any given paragraph, every sentence should be relevant to a single focus.
A joint effort
Together, cohesion and unity mean that sentences and paragraphs are connected around a central theme.
- Flow , or how the reader is led through the text. Some of this is about the ordering of ideas, but it also takes into account issues like phrasing, rhythm and style. Some people define flow as the quality that makes writing engaging and easy to read.
Levels of Coherence
We can consider coherence at several different levels. These include:
Within sentences. A sentence is coherent when it flows naturally, and uses correct grammar , spelling and punctuation . Coherence also includes the use of the most appropriate words, and avoidance of redundancy.
Between sentences . Coherence between sentences means that each sentence flows logically and naturally from the previous one. Connections are made between them so that readers can see the flow of ideas, and how each sentence is linked to the previous one.
Within paragraphs . This is a logical extension of coherence between sentences. Coherence within a paragraph means that the sentences within the paragraph work together as a whole to present a complete thesis or idea.
Why single-sentence paragraphs don’t work
This definition of ‘within paragraph’ coherence explains why you should (almost) never use single-sentence paragraphs. A single sentence is (almost) never going to be able to provide a complete summary of your thesis or idea.
Between paragraphs . For most pieces of writing, you will also need to consider how the paragraphs fit together. Each paragraph covers an idea or thesis—and must then be connected logically to the next paragraph, so that your overall thesis is built step-by-step.
Between subsections or sections . This final level of coherence is only really important for longer documents. You must create a logical flow between different sections, to guide your reader from one to the next so that they can follow the development of your ideas.
Techniques to Improve Coherence
The first step to improving coherence is to plan your writing in advance.
Decide on the main point that you want to make, and the ideas that will lead your reader towards your point. It is also helpful to consider your planned audience, and what they want from your text.
There is more about this in our page on Know Your Audience . You may also find it helpful to read our page on Know Your Medium , to check whether there is anything about your publishing medium that you need to consider ahead of starting to write.
There are some techniques that you can use to help improve coherence within your writing. These include:
Using transitional expressions and phrases to signal connections
Words and phrases like ‘however’, ‘because’, ‘therefore’, ‘additionally’, and ‘on the one hand... on the other’ can be used to signal connections between sentences and paragraphs.
WARNING! Real connections needed!
Transitional phrases and words should only be used where the ideas really are connected.
Just inserting transitional expressions will not connect your ideas. Instead, you need to create a reasonable progression of ideas through a paragraph or section.
You also need to use transitional expressions sparingly. Not all ideas need an obvious link—and sometimes putting one in can seem awkward and contrived.
Using repeating forms or parallel structures to emphasise links between ideas
Generally speaking, repetition of words and phrases is unadvisable.
However, used sparingly, you may be able to harness repetition as a way to signal connections between sentences or ideas.
For example, many research papers have a section setting out the limitations of the study. These limitations can often be quite diverse, which makes for a rather disjointed section. To overcome this issue, writers often use the form ‘First... Second... Finally...’ to demonstrate the links between the disparate ideas.
Using pronouns and synonyms to eliminate unnecessary repetition
Repetition is often the enemy of coherence because it interrupts your movement through the writing. You tend to get distracted by the repeated words, and lose the thread of the argument or idea.
Pronouns and synonyms are a good way to avoid repeating words and phrases. However, care is needed when using them, to avoid ambiguity. It is advisable NOT to use pronouns following a sentence with two elements that might take the same pronoun.
For example:
John was sure that Tom was wrong. He had made the same argument last week.
Who made the same argument last week? John or Tom?
It is better to use at least one name again than create ambiguity.
TOP TIP! Come back later
It is often hard to detect ambiguity in your own writing because you know what you wanted to say.
It is therefore a good idea to leave any piece of writing overnight, and read it again in the morning. This will often identify problems such as ambiguous pronouns, and give you a chance to revise them.
Revisit, Revise and Review
Alongside planning, the single most important thing that you can do to improve the coherence of a piece of writing is to review and revise it with the reader’s needs in mind.
When you have finished a piece of writing, put it aside for a while. Overnight is ideal, but longer is fine. Once you have had a chance to forget precisely what you meant, read it over again as if you were coming to it for the first time.
As you start to read, consider the focus of your text: the main point that you want to make.
With that in mind, consciously examine whether the ideas flow clearly through your sentences, paragraphs and sections. Can the reader grasp your argument and follow it through the text? Is there an obvious conclusion?
While you are reading, you should also consider whether there are any very long sentences. If so, shorten them, using transitional words or phrases to link them together effectively. This will make your writing easier to read, and it will naturally flow better.
A Final Thought
It is not always easy to know how to create more coherent writing.
The best way to do so is to plan your writing, and then review it carefully. You should particularly consider your focus, and your readers’ needs. In doing so, you may find it helpful to use some of the techniques described on this page—but they will not, in themselves, be sufficient without the planning and review.
Continue to: Writing Concisely Using Plain English
See also: The Importance of Structure in Writing Editing and Proofreading Copywriting
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11 Unity & Coherence
Preserving unity.
Academic essays need unity, which means that all of the ideas in an essay need to relate to the thesis, and all of the ideas in a paragraph need to relate to the paragraph’s topic. It can be easy to get “off track” and start writing about an idea that is somewhat related to your main idea, but does not directly connect to your main point.

All of the sentences in a paragraph should stay “on track;” that is, they should connect to the topic. One way to preserve unity in a paragraph is to start with a topic sentence that shows the main idea of the paragraph. Then, make sure each sentence in the paragraph relates to that main idea.
If you find a sentence that goes off track, perhaps you need to start a separate paragraph to write more about that different idea. Each paragraph should generally have only one main idea.
As you pre-write and draft an essay, try to pause occasionally. Go back to the assignment prompt and re-read it to make sure you are staying on topic. Use the prompt to guide your essay; make sure you are addressing all of the questions. Do not just re-state the words in the prompt. Instead, respond to the questions with your own ideas, in your own words, and make sure everything connects to the prompt and your thesis.
Activity A ~ Finding Breaks in Unity
Consider the following paragraphs. Is there a topic sentence? If so, do all of the other sentences relate to the topic sentence? Can you find any sentences that don’t relate?
The planned community of Columbia, Maryland, was designed as a city open to all, regardless of race, level of income, or religion. When Columbia began in 1967, many cities in the U.S. did not allow people of certain races to rent or buy homes. Its developer, James W. Rouse, wanted to build a new city that had fair and open housing options for everyone. HCC has a building named for James W. Rouse. Today, the city’s nearly 100,000 remain diverse, as shown by recent census data. *****
College can be expensive and difficult. Critical thinking is a very important skill for college students to develop so that they can be successful in their careers. Employers look for graduates who can understand information, analyze data, and solve problems. They also want employees who can think creatively and communicate their ideas clearly. College students need to practice these skills in all of their classes so that they can demonstrate their abilities to potential employers. ***** Bananas are one of Americans’ favorite types of fruit. The Cavendish variety, grown in Central and South America, is the most commonly sold here in the U.S. Recent problems with a fungus called Panama disease (or TR4), however, have led to a shortage of Cavendish bananas. Similar problems occurred a few years ago in parts of Asia and the Middle East. Because the fungus kills the crop and contaminates the soil, scientists are concerned that the popular Cavendish banana could be completely eradicated. Bananas contain many nutrients, including potassium and Vitamin B6. *****
Whether you choose to include a topic sentence or not, all of the sentences in your paragraph need to relate to the one main idea of the paragraph.
Another way to think about unity in a paragraph is to imagine your family tree. Draw a quick sketch of your family tree in your notebook. If you were writing an essay about your family, you might write a paragraph about close family members first. Next, you might branch out into another paragraph to write about more distant relatives. You might even include a paragraph about very close family friends, or pets. Each paragraph would have just one main idea (immediate family, more distant relatives, close family friends), and every sentence in each paragraph would relate to that main idea.
Activity B ~ Preserving Unity in Your Own Writing
Examine a composition that you have written for this class. Do all of your paragraphs have unity? Can you find any sentences that don’t relate to the topic of each paragraph? Exchange papers with a partner to peer review.
Ensuring Coherence
There are several ways to create connections between ideas in your essay. Here are some suggestions:
1. Repeat key words and phrases. This can be a powerful way to make a point. Consider this excerpt from Rev. Martin Luther King’s famous “I Have a Dream” speech at the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom, in which he uses parallel structure :
I say to you today, my friends, so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.” I have a dream that one day on the red hills of Georgia, the sons of former slaves and the sons of former slave owners will be able to sit down together at the table of brotherhood. I have a dream that one day even the state of Mississippi, a state sweltering with the heat of injustice, sweltering with the heat of oppression, will be transformed into an oasis of freedom and justice. I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character. I have a dream today.
2. Use synonyms , as in this example, where King uses both repetition (“Let freedom ring”) and synonyms (for “mountains”):
And if America is to be a great nation, this must become true. So let freedom ring from the prodigious hilltops of New Hampshire. Let freedom ring from the mighty mountains of New York. Let freedom ring from the heightening Alleghenies of Pennsylvania. Let freedom ring from the snow-capped Rockies of Colorado. Let freedom ring from the curvaceous slopes of California. But not only that: Let freedom ring from Stone Mountain of Georgia. Let freedom ring from Lookout Mountain of Tennessee. Let freedom ring from every hill and molehill of Mississippi. From every mountainside, let freedom ring.
3. Use pronouns to refer to antecedents , as King does here; this can be more elegant than just repeating the key words and phrases:
I have a dream that my four little children will one day live in a nation where they will not be judged by the color of their skin but by the content of their character.
4. Use demonstratives ( this, that, these, those ) as adjectives or pronouns, as King does here:
I say to you today, my friends, so even though we face the difficulties of today and tomorrow, I still have a dream. It is a dream deeply rooted in the American dream. I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed: “We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal.”…. This is our hope. This is the faith that I go back to the South with. With this faith we will be able to hew out of the mountain of despair a stone of hope. With this faith we will be able to transform the jangling discords of our nation into a beautiful symphony of brotherhood.
Questions to Ponder
Pause for a moment here to think about the examples above. Think about audience, purpose, and context of an academic essay. Would you use the techniques for coherence in the same way that Dr. King did in his speech, or would you use the techniques in a different way? Discuss with a small group.
5. Use transitions. Transition words and phrases will help you to make sure your essay has coherence. Also called signal words/phrases or signposts, these help to guide your readers.
Transitions connect your related ideas; they can also show your reader that you are starting a new topic, giving an example, adding information, explaining causes and effects, and so on. Using the correct transition word or phrase in a sentence can make your writing much clearer. Try the activity below to think of possible transitions.
Activity C ~ Transition Words & Phrases
With your partner, brainstorm a list of transition words and phrases for each of the categories below.
Can you think of other transition words and phrases? What other categories do they belong to?
After you have completed these activities with your partner, consult Transition Words & Phrases ~ Useful Lists for more on compare/contrast, addition, cause/effect, and other transitions to try.
Activity D ~ Ensuring Coherence in Your Own Writing
Examine a composition that you have written for this class for coherence. Find and mark examples of places where you used repetition, synonyms, pronouns or demonstratives to build connections between ideas.
Underline your transition words and phrases. Did you use the strongest signal words? Can you find examples where you need to add a transition? Or, did you use too many transitions? Exchange papers with a partner to peer review.
Consult our chapter on Transitions for more inspiration on achieving coherence and cohesion in your writing. Challenge yourself to use some new transitions in your next composition.
Is this chapter:
…about right, but you would like more examples? –> Read “ Cohesion and Coherence ” from George Mason University’s Writing Center.
…too easy, or you would like more examples? –> Read “ ESL: Coherence and Cohesion ” from the Writing & Communication Center at the University of Washington/Bothell
Note: links open in new tabs.
King, Martin Luther, Jr. “I Have a Dream.” March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom. 28 August 1963. Washington, D.C. Speech.
to start to do something different
short piece or sample, for example a direct quote in writing or a few measures of a musical composition
to think about
ENGLISH 087: Academic Advanced Writing Copyright © 2020 by Nancy Hutchison is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- I nfographics
- Show AWL words
- Subscribe to newsletter
- What is academic writing?
- Academic Style
- What is the writing process?
- Understanding the title
- Brainstorming
- Researching
- First draft
- Proofreading
- Report writing
- Compare & contrast
- Cause & effect
- Problem-solution
- Classification
- Essay structure
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Book review
- Research proposal
- Thesis/dissertation
What is cohesion?
- Cohesion vs coherence
Transition signals
- What are references?
- In-text citations
- Reference sections
- Reporting verbs
- Band descriptors
Show AWL words on this page.
Levels 1-5: grey Levels 6-10: orange
Show sorted lists of these words.
Any words you don't know? Look them up in the website's built-in dictionary .
Choose a dictionary . Wordnet OPTED both
Cohesion How to make texts stick together
Cohesion and coherence are important features of academic writing. They are one of the features tested in exams of academic English, including the IELTS test and the TOEFL test . This page gives information on what cohesion is and how to achieve good cohesion. It also explains the difference between cohesion and coherence , and how to achieve good coherence. There is also an example essay to highlight the main features of cohesion mentioned in this section, as well as some exercises to help you practise.
For another look at the same content, check out YouTube or Youku , or the infographic .
It is important for the parts of a written text to be connected together. Another word for this is cohesion . This word comes from the verb cohere , which means 'to stick together'. Cohesion is therefore related to ensuring that the words and sentences you use stick together.
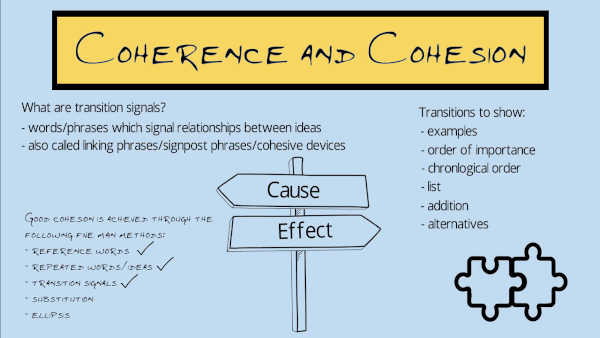
Good cohesion is achieved through the following five main methods, each of which is described in more detail below:
- repeated words/ideas
- reference words
- transition signals
- substitution
Two other ways in which cohesion is achieved in a text, which are covered less frequently in academic English courses, are shell nouns and thematic development . These are also considered below.
Repeated words/ideas

Check out the cohesion infographic »
One way to achieve cohesion is to repeat words, or to repeat ideas using different words (synonyms). Study the following example. Repeated words (or synonyms) are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing . It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report . You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
In this example, the word cohesion is used several times, including as a verb ( coheres ). It is important, in academic writing, to avoid too much repetition, so using different word forms or synonyms is common. The word writing is also used several times, including the phrase essay or report , which is a synonym for writing . The words important features are also repeated, again using synonyms: key feature , important aspect .
Reference words
Reference words are words which are used to refer to something which is mentioned elsewhere in the text, usually in a preceding sentence. The most common type is pronouns, such as 'it' or 'this' or 'these'. Study the previous example again. This time, the reference words are shown in bold.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features. The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
The words it , which and these are reference words. The first two of these, it and which , both refer to 'cohesion' used in the preceding sentence. The final example, these , refers to 'important features', again used in the sentence that precedes it.
Transition signals, also called cohesive devices or linking words, are words or phrases which show the relationship between ideas. There are many different types, the most common of which are explained in the next section on transition signals . Some examples of transition signals are:
- for example - used to give examples
- in contrast - used to show a contrasting or opposite idea
- first - used to show the first item in a list
- as a result - used to show a result or effect
Study the previous example again. This time, the transition signals are shown in bold. Here the transition signals simply give a list, relating to the five important features: first , second , third , fourth , and final .
Substitution
Substitution means using one or more words to replace (substitute) for one or more words used earlier in the text. Grammatically, it is similar to reference words, the main difference being that substitution is usually limited to the clause which follows the word(s) being substituted, whereas reference words can refer to something far back in the text. The most common words used for substitution are one , so , and auxiliary verbs such as do, have and be . The following is an example.
- Drinking alcohol before driving is illegal in many countries, since doing so can seriously impair one's ability to drive safely.
In this sentence, the phrase 'doing so' substitutes for the phrase 'drinking alcohol before driving' which appears at the beginning of the sentence.
Below is the example used throughout this section. There is just one example of substitution: the word one , which substitutes for the phrase 'important features'.
Ellipsis means leaving out one or more words, because the meaning is clear from the context. Ellipsis is sometimes called substitution by zero , since essentially one or more words are substituted with no word taking their place.
Below is the example passage again. There is one example of ellipsis: the phrase 'The fourth is', which means 'The fourth [important feature] is', so the words 'important feature' have been omitted.
Shell nouns
Shell nouns are abstract nouns which summarise the meaning of preceding or succeeding information. This summarising helps to generate cohesion. Shell nouns may also be called carrier nouns , signalling nouns , or anaphoric nouns . Examples are: approach, aspect, category, challenge, change, characteristics, class, difficulty, effect, event, fact, factor, feature, form, issue, manner, method, problem, process, purpose, reason, result, stage, subject, system, task, tendency, trend, and type . They are often used with pronouns 'this', 'these', 'that' or 'those', or with the definite article 'the'. For example:
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods , however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals.
- An increasing number of overseas students are attending university in the UK. This trend has led to increased support networks for overseas students.
In the example passage used throughout this section, the word features serves as a shell noun, summarising the information later in the passage.
Cohesion is an important feature of academic writing. It can help ensure that your writing coheres or 'sticks together', which will make it easier for the reader to follow the main ideas in your essay or report. You can achieve good cohesion by paying attention to five important features . The first of these is repeated words. The second key feature is reference words. The third one is transition signals. The fourth is substitution. The final important aspect is ellipsis.
Thematic development
Cohesion can also be achieved by thematic development. The term theme refers to the first element of a sentence or clause. The development of the theme in the rest of the sentence is called the rheme . It is common for the rheme of one sentence to form the theme of the next sentence; this type of organisation is often referred to as given-to-new structure, and helps to make writing cohere.
Consider the following short passage, which is an extension of the first example above.
- Virus transmission can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals. These methods, however, are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals. It is important for such health workers to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening.
Here we have the following pattern:
- Virus transmission [ theme ]
- can be reduced via frequent washing of hands, use of face masks, and isolation of infected individuals [ rheme ]
- These methods [ theme = rheme of preceding sentence ]
- are not completely effective and transmission may still occur, especially among health workers who have close contact with infected individuals [ rheme ]
- health workers [ theme, contained in rheme of preceding sentence ]
- [need to] to pay particular attention to transmission methods and undergo regular screening [ rheme ]
Cohesion vs. coherence
The words 'cohesion' and 'coherence' are often used together with a similar meaning, which relates to how a text joins together to make a unified whole. Although they are similar, they are not the same. Cohesion relates to the micro level of the text, i.e. the words and sentences and how they join together. Coherence , in contrast, relates to the organisation and connection of ideas and whether they can be understood by the reader, and as such is concerned with the macro level features of a text, such as topic sentences , thesis statement , the summary in the concluding paragraph (dealt with in the essay structure section), and other 'bigger' features including headings such as those used in reports .
Coherence can be improved by using an outline before writing (or a reverse outline , which is an outline written after the writing is finished), to check that the ideas are logical and well organised. Asking a peer to check the writing to see if it makes sense, i.e. peer feedback , is another way to help improve coherence in your writing.
Example essay
Below is an example essay. It is the one used in the persuasion essay section. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different cohesive aspects in this essay, i.e. repeated words/ideas, reference words, transition signals, substitution and ellipsis.
Title: Consider whether human activity has made the world a better place.
History shows that human beings have come a long way from where they started. They have developed new technologies which means that everybody can enjoy luxuries they never previously imagined. However , the technologies that are temporarily making this world a better place to live could well prove to be an ultimate disaster due to , among other things, the creation of nuclear weapons , increasing pollution , and loss of animal species . The biggest threat to the earth caused by modern human activity comes from the creation of nuclear weapons . Although it cannot be denied that countries have to defend themselves, the kind of weapons that some of them currently possess are far in excess of what is needed for defence . If these [nuclear] weapons were used, they could lead to the destruction of the entire planet . Another harm caused by human activity to this earth is pollution . People have become reliant on modern technology, which can have adverse effects on the environment . For example , reliance on cars causes air and noise pollution . Even seemingly innocent devices, such as computers and mobile phones, use electricity, most of which is produced from coal-burning power stations, which further adds to environmental pollution . If we do not curb our direct and indirect use of fossil fuels, the harm to the environment may be catastrophic. Animals are an important feature of this earth and the past decades have witnessed the extinction of a considerable number of animal species . This is the consequence of human encroachment on wildlife habitats, for example deforestation to expand cities. Some may argue that such loss of [animal] species is natural and has occurred throughout earth's history. However , the current rate of [animal] species loss far exceeds normal levels [of animal species loss] , and is threatening to become a mass extinction event. In summary , there is no doubt that current human activities such as the creation of nuclear weapons , pollution , and destruction of wildlife , are harmful to the earth . It is important for us to see not only the short-term effects of our actions, but their long-term ones as well. Otherwise , human activities will be just another step towards destruction .
Aktas, R.N. and Cortes, V. (2008), 'Shell nouns as cohesive devices in published and ESL student writing', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 7 (2008) 3-14.
Alexander, O., Argent, S. and Spencer, J. (2008) EAP Essentials: A teacher's guide to principles and practice . Reading: Garnet Publishing Ltd.
Gray, B. (2010) 'On the use of demonstrative pronouns and determiners as cohesive devices: A focus on sentence-initial this/these in academic prose', Journal of English for Academic Purposes , 9 (2010) 167-183.
Halliday, M. A. K., and Hasan, R. (1976). Cohesion in English . London: Longman.
Hinkel, E. (2004). Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Inc Publishers.
Hyland, K. (2006) English for Academic Purposes: An advanced resource book . Abingdon: Routledge.
Thornbury, S. (2005) Beyond the Sentence: Introducing discourse analysis . Oxford: Macmillan Education.

GET FREE EBOOK
Like the website? Try the books. Enter your email to receive a free sample from Academic Writing Genres .
Below is a checklist for essay cohesion and coherence. Use it to check your own writing, or get a peer (another student) to help you.
Next section
Find out more about transition signals in the next section.
- Transitions
Previous section
Go back to the previous section about paraphrasing .
- Paraphrasing
Exercises & Activities Some ways to practise this area of EAP
You need to login to view the exercises. If you do not already have an account, you can register for free.
- Register
- Forgot password
- Resend activiation email

Author: Sheldon Smith ‖ Last modified: 03 February 2022.
Sheldon Smith is the founder and editor of EAPFoundation.com. He has been teaching English for Academic Purposes since 2004. Find out more about him in the about section and connect with him on Twitter , Facebook and LinkedIn .
Compare & contrast essays examine the similarities of two or more objects, and the differences.
Cause & effect essays consider the reasons (or causes) for something, then discuss the results (or effects).
Discussion essays require you to examine both sides of a situation and to conclude by saying which side you favour.
Problem-solution essays are a sub-type of SPSE essays (Situation, Problem, Solution, Evaluation).
Transition signals are useful in achieving good cohesion and coherence in your writing.
Reporting verbs are used to link your in-text citations to the information cited.
Coherence in Composition
Guiding the Reader to Understand a Piece of Writing or Speech
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
In composition , coherence refers to the meaningful connections that readers or listeners perceive in a written or oral text , often called linguistic or discourse coherence, and can occur on either the local or global level, depending on the audience and writer.
Coherence is directly increased by the amount of guidance a writer provides to the reader, either through context clues or through direct use of transitional phrases to direct the reader through an argument or narrative.
Word choice and sentence and paragraph structure influence the coherence of a written or spoken piece, but cultural knowledge, or understanding of the processes and natural orders on the local and global levels, can also serve as cohesive elements of writing.
Guiding the Reader
It is important in composition to maintain the coherence of a piece by leading the reader or listener through the narrative or process by providing cohesive elements to the form. In "Marking Discourse Coherence," Uta Lenk states that the reader or listener's understanding of coherence "is influenced by the degree and kind of guidance given by the speaker: the more guidance is given, the easier it is for the hearer to establish the coherence according to the speaker's intentions."
Transitional words and phrases like "therefore," "as a result," "because" and the like serve to move connect one posit to the next, either through cause and effect or correlation of data, while other transitional elements like combining and connecting sentences or repetition of keywords and structures can similarly guide the reader to make connections in tandem with their cultural knowledge of the topic.
Thomas S. Kane describes this cohesive element as "flow" in "The New Oxford Guide to Writing," wherein these "invisible links which bind the sentences of a paragraph can be established in two basic ways." The first, he says, is to establish a plan in the first of the paragraph and introduce each new idea with a word marking its place in this plan while the second concentrates on the successive linking of sentences to develop the plan through connecting each sentence to the one before it.
Constructing Coherence Relations
Coherence in composition and constructionist theory relies on a readers' local and global understanding of the written and spoken language, inferring the binding elements of text that help guide them through understanding the author's intentions.
As Arthur C. Graesser, Peter Wiemer-Hasting and Katka Wiener-Hastings put it in "constructing Inferences and Relations During Text Comprehension," local coherence "is achieved if the reader can connect the incoming sentence to information in the previous sentence or to the content in working memory." On the other hand, global coherence comes from the major message or point of the structure of the sentence or from an earlier statement in the text.
If not driven by these global or local understanding, the sentence is typically given coherence by explicit features like anaphoric references, connectives, predicates, signaling devices and transitional phrases.
In any case, coherence is a mental process and the Coherence Principle accounts for "the fact that we do not communicate by verbal means only," according to Edda Weigand's "Language as Dialogue: From Rules to Principles." Ultimately, then, it comes down to the listener or leader's own comprehension skills, their interaction with the text, that influences the true coherence of a piece of writing.
- What Is Cohesion in Composition?
- What Is World Knowledge (Regarding Language Studies)?
- Paragraph Length in Compositions and Reports
- High School English Curricula Explained
- Definition and Examples of Body Paragraphs in Composition
- What Is Composition? Definition, Types, and Examples
- Making Inferences to Improve Reading Comprehension
- Definition and Examples of Text Linguistics
- Paragraph Transition: Definition and Examples
- What Is Textuality?
- AP English Exam: 101 Key Terms
- Definition and Examples of Paragraphing in Essays
- The Drafting Stage of the Writing Process
- Unity in Composition
- Definition and Examples of a Transition in Composition
- Ways of Achieving Emphasis in Writing and in Speech
Cohesion and Coherence

Introduction
Every writer wishes to make their points clearly to their readers, with pieces of writing that are are easy to read and have logical links between the various points made. This coherence , this clarity of expression , is created by grammar and vocabulary (lexis) through cohesion . This is the “glue” that joins your ideas together to form a cohesive whole.
In this Learning Object we are going to focus on how this is done, in order to assist you when you come to write your next assignments and in your reading. In reading, if you understand how the author makes connections within the text, you gain a better understanding of his or her message. As regards your writing, after analysing the texts in this Learning Object, you should analyse your own writing in the same way. This will help you to realise which techniques you could use more to benefit your reader.
Before starting the activities, you can obtain an overview of how best to use this Learning Object, using a Screencast (with audio), by following this link Overview
- To raise awareness of how cohesion contributes to coherence in text
- To raise awareness of how cohesion is created through: reference, conjunction, ellipsis, substitution and lexis , including cohesive nouns .
- To raise your awareness of cohesion at paragraph level and how punctuation plays a crucial role in this
Activity 1: Ways of creating cohesion in text
According to the writers Halliday and Hasan (1976), there are six main ways that cohesion is created in a text. These they called: Reference , Substitution , Ellipsis , Lexical Chains , Cohesive Nouns and Conjunction .
Open this Cohesion Presentation PDF document that shows you examples of each of them.
For the following six ways of creating cohesion, select each one to read detailed explanations and examples:

This way of creating cohesion uses:
- determiners (e.g. "this" , "that" , "these" and "those" );
- pronouns (e.g. "him" , "them" , "me" );
- possessive pronouns (e.g. "your" , "their" , "hers" );
- relative pronouns (e.g. "which" , "who" , "whose" ).
- This type of cohesion can also be achieved comparatively with expressions like: "similarly" , "likewise" , "less" .

In this way of creating cohesion you can use:
- synonyms (e.g. "beautiful" for "lovely" );
- hyponyms and superordinates (e.g. "daffodil" , "rose" and "daisy" , are all hyponyms of the superordinate "flower" ).
- Lexical chains are created in a text by using words in the same lexical set (e.g. "army" , "soldiers" , "barracks" , "weapons" ).
These techniques allow for the central themes to be reiterated in a way that avoids monotony for the reader.

These words are a kind of lexical reference.
- They can summarise many words in one (e.g. "attitude" , "solution" , "difficulty" ), and have been called 'umbrella' nouns for this reason (Bailey 2006:150).
- They are used to signal what is to come (e.g. "the problem to be discussed..." ), or can refer back (e.g. "The issue mentioned above..." ).

This method of creating cohesion uses one word/phrase to replace a word/phrase used earlier. For example,
- "the one(s)" and "the same" can be used to replace nouns (e.g. "I'll have the same." ).
- Verbs can be replaced by "do" (e.g. "The authorities said they had acted , but nobody believed they had done .").
- In speaking, whole clauses can be replaced by, "so" or "not" (e.g. "I hope so/not." ).

In this way of creating cohesion, words are omitted because they are understood from the context. e.g.
- " John can type and I can [type] too! ";
- " I don't want to go out, do you? [want to go out] ."

This type of cohesion includes:
- listing words (e.g. "firstly" , "next" , "lastly" );
- linkers for addition (e.g. " moreover" , "and" , "also" );
- concession (e.g. "but" , "however" , "despite" ); and
- cause and effect (e.g. "so" , "because" , "as a result" ).
Then try this Cohesion quiz to test your memory of the terms.
Activity 2: Highlighting cohesion in a text
For this activity you are going to read the short narrative text below, which is a piece of creative writing about a student, and then complete an exercise in highlighting the cohesive words, using colour codes. First, read the text quickly and try to think of a title for it.
The student sighed as she handed in the assignment, at last it was finished. This was the most difficult piece of writing which she had been set, but she had completed it. The ‘magnum opus’ was 10,000 words long. This project, though not quite a dissertation, was still the longest piece of academic writing she had ever written. She had thought she would never complete it and it had taken all her strength to do so.
Her achievement made her elated, but had left her exhausted. When she had read the title of the task, she knew it was not going to be just another essay, not an easy one at all. Finally, the completed work lay on the counter of the reception [and was] beautifully bound. She would sleep easy at night, [and she would be] no longer troubled by thoughts of its accusing blank pages – the nightmare was over!
Instruction
Now try this colour coding exercise to highlight the 6 different ways of creating cohesion.
--> Show feedback Hide feedback
The original title of the piece of writing was “The Assignment” .
Now try this interactive exercise to colour-code the words and phrases that create cohesion in the 6 different ways using the six colours.
You can download this Feedback 1 PDF for a summary of the answers to the task.
Activity 3: Cohesion in a discursive text
In this exercise you are going to see how the 6 ways of creating cohesion are used in a short text arguing in favour of working in groups as a way to learn better in class. Before you read the text, you might like to predict what the arguments might be in favour of and against classes being organised to work together in this way.
To do a series of exercises to raise awareness of different forms of cohesion used in academic writing, try these interactive cloze exercises .
Activity 4: Colour coding the cohesion in the discursive text
Now, we are going to use the same text to see how your awareness of cohesion is improving.
Read this longer discursive text about working in groups. As you read, notice the different forms of cohesion that are used in the text. After you’ve read it, move on to the colour-coding exercise that follows.
“Working in groups is a bad idea because it encourages weak students to let the others do the work.” Discuss
The idea that working in groups is a bad thing is fundamentally mistaken because, overall, the advantages of this way of configuring the class outweigh the potential disadvantages [of this way of configuring the class]. In groups there is the opportunity for peer teaching, which can often be invaluable. In addition, lessons organised in this way become less teacher-centred. Moreover, in life today, team-working is a feature of every workplace and one of the roles of university education is to provide a preparation for students’ future careers.
Firstly, peer teaching can contribute to effective learning in most classroom situations. Many students (especially in large classes) can benefit from this approach. Weaker students are often less afraid of making mistakes and taking risks in front of their peers, than in close contact with their teacher or in front of the whole class. Also, with regard to the stronger students, a perfect way to consolidate their learning is to transmit that knowledge to others. Furthermore, most pedagogic approaches today concur that a lesson that is focused on the teacher at all times, is one from which the students are unlikely to benefit. Certainly, some classroom activities, like project work for example, are best conducted in small groups. The teacher as the source of all wisdom standing at the front of the class, the ‘jug and mug’ model of education, is not only antiquated, but also ineffective.
A further benefit of group-teaching is the preparation it provides for working in teams. In a great variety of careers today, the employees are asked to, and are judged on their ability to work in teams. Group working in class represents basically the same concept. The same skills are being tested and developed – interpersonal skills and emotional intelligence, to mention just two. In business today, the ability to lead effectively and to support one’s peers is prized almost above all other skills.
In conclusion then, while it may sometimes be true that the weak students may ‘take it easy’ sometimes in groups, allowing others to work hard to compensate for their laziness, if the lesson materials are interesting and the teacher motivating, this is a rare occurrence. As outlined above, there are so many ‘pros’ to this method of classroom configuration that these easily outweigh this somewhat questionable ‘con’.
Now try these Cohesion colour-coding exercies , using the 6 different colours.
Show feedback Hide feedback
You can download this Feedback 2 PDF document for a summary of the answers to the task.
Activity 5: Cohesive nouns, reference and substitution
For more exercises to practise cohesive nouns, reference and substitution try this Reference and Substitution cloze exercise .
Activity 6: Cohesion and coherence at paragraph level
Cohesion has a strong connection to coherence (logic and meaning). In fact, cohesion is the grammatical and lexical realisation of coherence at a profound level within the text. It is what makes a text more than just a jumbled mixture of sentences.
In this exercise, you will use your understanding of cohesion and punctuation, and your understanding of the underlying meaning of paragraphs, to put them into the most logical order. Now try these Paragraph Cohesion Activities .
Would you like to review the main points?
Show review Hide review
To review the way we create cohesion in texts follow this link The 6 Ways of Creating Cohesion
For websites with more information and exercises to raise your awareness of cohesion and the way we organise information following a ‘given-to-new’ pattern, we recommend the following websites:
- The Grammar of English Ideas
- Academic Writing in English
References:
Batstone, R. (1994). Grammar. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Cook, G. (1996). Discourse. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Halliday, M. A. K. and R. Hasan (1976). Cohesion in English. London: Longman UK Group Limited.
Lubelska, D. (1991). “An approach to teaching cohesion to improve in reading” in Reading in a Foreign Language, 7 (2)
© William Tweddle, Queen Mary, University of London, 2010, visual created by the author using a Smartboard and Jing
Module 8: Revising a Research Paper
Writing coherently, learning objectives.
- Define coherence in terms of writing
- Identify strategies to revise your argument for coherence
The term “coherence” comes from the verb “to cohere,” which means “to be united,” “to form a whole,” or “to be logically consistent”.
Coherence in writing refers to the big picture of a text. How can you construct an essay or research paper to create a united, logically consistent whole?
The USDA’s controversial and now deprecated food pyramid.
Consider this example:
Micronutrients play a vital role in the maintenance of healthy skin and immune function. Of course, nothing is better for healthy skin than sleep and proper hydration. Many Americans drink too little water every day. There has been a good deal of debate about the 8-glasses-of-water advice that many of us remember from growing up. Will this advice go the way of the food pyramid? As it turns out, the food pyramid does not represent a medically ideal diet. A number of health organizations have criticized the food pyramid’s advice, and some have even suggested that the food industry had far too great a role in its creation. It certainly wouldn’t be the first time the food industry has intervened in public health policy.
This passage is cohesive, meaning that one sentence flows from the next. But it’s not coherent. Why?
- The topics of the individual sentences vary widely. We go from hearing about micronutrients to sleep and hydration to recommended water intake to the food pyramid. If sentences (and paragraphs) in a piece of writing don’t share common topics and ideas, how is the reader supposed to understand what the piece is about?
- The paragraph lacks a topic sentence signaling its main idea or purpose. The first sentence sounds like it could be a topic sentence, but the paragraph doesn’t stay with micronutrients for long.
Overall, this paragraph illustrates the pitfalls of associative organization (healthy skin → water → nutrition advice→ food pyramid) and topic sentences that fail to live up to the promise they make to readers. Your reader will become disoriented, fail to see your point (if you have one), and walk away frustrated.
Revising for Coherence
A coherent text needs a strong, logical structure. To revise for coherence, you must first check the logic and flow of your draft to ensure readers can see the big picture you are trying to create.
Reverse Outlining
Let’s face it: the process of writing a draft can be hectic, messy, and confusing. Sometimes we don’t really know what we’ve written until the dust settles. Reverse outlining can help us see the overall structure of the draft, which often differs significantly from what we set out to write!
To write a reverse outline,
- Number each paragraph in your draft (write in the margin or use the comment feature in Docs or Word).
- In a separate document, write down these numbers, one per line.
- If you have trouble figuring out what the paragraph is about, make a note for yourself that the paragraph needs to be reworked.
- If the paragraph is has more than one main idea, make a note for yourself that it needs to be split in two.
- If you find a redundant paragraph that repeats a point made in another paragraph using different words, make a note to combine or differentiate the two paragraphs.
- If a paragraph doesn’t relate to the overall argument, make a note to revise or remove this paragraph.
- How does this sequence of topics help you achieve your purpose (or not)?
- Are any topics unnecessary or redundant?
- Are there any extended side-notes or rabbit-holes that risk confusing the reader?
- How could you revise and reorder paragraph topics to better accomplish your goals?
Compare the sequence of points in your reverse outline with your original outline (if you have one) to see where you diverged from your plan. Finally, you can create a new outline that represents the best possible sequence of points and revise your draft accordingly.
The following video describes reverse outlining, its benefits, and a technique you can use to reverse outline your draft.
Question Outlining
If you’re still not sure about the overall order of your argument, you can try writing an outline of questions:
- Create a new list of numbers corresponding to the paragraphs of your paper.
- For each paragraph, think about what question this paragraph is answering.
- Write this question down from the point of view of the audience.
- Does this sequence of questions reflect how a reasonable person might seek answers about your topic?
- How do the questions connect to one another?
- Does it make sense to answer some before others?
- Would it be beneficial to have these questions follow a more logical pattern of development (general to specific, or specific to general)?
- Food Pyramid. Provided by : USDA. Located at : https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_pyramid_(nutrition)#/media/File:USDA_Food_Pyramid.gif . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Writing Coherently. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

Paragraph Unity, Coherence, and Development
In each paragraph of an essay, one particular idea or topic is developed and explained. In order to successfully do so, however, it is essential that the paragraph be written in a unified and coherent manner.
A unified paragraph must follow the idea mentioned in the topic sentence and must not deviate from it. For a further explanation on topic sentences, see the Write Right on Topic Sentences .
A coherent paragraph has sentences that all logically follow each other; they are not isolated thoughts. Coherence can be achieved in several ways. First, using transitions helps connect ideas from one sentence to the next. For more on transitions, see the Write Right on Transitions . Second, ordering thoughts in numerical sequence helps to direct the reader from one point to the next. Third, structuring each paragraph according to one of the following patterns helps to organize sentences: general to particular; particular to general; whole to parts; question to answer; or effect to cause.
Remember that a paragraph should have enough sentences so that the main idea of the topic sentence is completely developed. Generalizations should be supported with examples or illustrations. Also, details and descriptions help the reader to understand what you mean. Don't ever assume that the reader can read your mind: be specific enough to develop your ideas thoroughly, but avoid repetition
An effective paragraph might look like this:
It is commonly recognized that dogs have an extreme antagonism toward cats. This enmity between these two species can be traced back to the time of the early Egyptian dynasties. Archaeologists in recent years have discovered Egyptian texts in which there are detailed accounts of canines brutally mauling felines. Today this type of cruelty between these two domestic pets can be witnessed in regions as close as your own neighborhood. For example, when dogs are walked by their masters (and they happen to catch sight of a stray cat), they will pull with all their strength on their leash until the master is forced to yield; the typical result is that a feline is chased up a tree. The hatred between dogs and cats has lasted for many centuries, so it is unlikely that this conflict will ever end.
This paragraph is effective for the following reasons:
- The paragraph shows unity. All the sentences effectively relate back to the topic sentence at the beginning of the paragraph.
- The paragraph shows coherence. There is a flow of thoughts and ideas among the sentences in this paragraph. There are good transitions employed in the paragraph. The writer also presents her sub-topics in an orderly fashion that the reader can follow easily.
- The paragraph is developed. The writer gives herself enough space to develop the topic. She gives us at least two reasons to accept her argument and incorporates some examples in order to give those reasons more validity.
Reference: Strunk, Wiliam Jr., and E. B. White. The Elements of Style . 4th ed., Allyn and Bacon, 2000.
Copyright © 2009 Wheaton College Writing Center
British Council Malaysia
- English schools
- myClass Login
- Show search Search Search Close search
How to write a cohesive essay

When it comes to writing, people usually emphasise the importance of good grammar and proper spelling. However, there is a third element that actually helps authors get their thoughts across to readers, that is cohesiveness in writing.
In writing, cohesiveness is the quality that makes it easier for people to read and understand an essay’s content. A cohesive essay has all its parts (beginning, middle, and end) united, supporting each other to inform or convince the reader.
Unfortunately, this is an element that even intermediate or advanced writers stumble on. While the writer’s thoughts are in their compositions, all too often readers find it difficult to understand what is being said because of the poor organisation of ideas. This article provides tips on how you can make your essay cohesive.
1. Identify the thesis statement of your essay
A thesis statement states what your position is regarding the topic you are discussing. To make an essay worth reading, you will need to make sure that you have a compelling stance.
However, identifying the thesis statement is only the first step. Each element that you put in your essay should be included in a way that supports your argument, which should be the focus of your writing. If you feel that some of the thoughts you initially included do not contribute to strengthening your position, it might be better to take them out when you revise your essay to have a more powerful piece.
2. Create an outline
One of the common mistakes made by writers is that they tend to add a lot of details to their essay which, while interesting, may not really be relevant to the topic at hand. Another problem is jumping from one thought to another, which can confuse a reader if they are not familiar with the subject.
Preparing an outline can help you avoid these difficulties. List the ideas you have in mind for your essay, and then see if you can arrange these thoughts in a way that would make it easy for your readers to understand what you are saying.
While discursive essays do not usually contain stories, the same principle still applies. Your writing should have an introduction, a discussion portion and a conclusion. Again, make sure that each segment supports and strengthens your thesis statement.
As a side note, a good way to write the conclusion of your essay is to mention the points that you raised in your introduction. At the same time, you should use this section to summarise main ideas and restate your position to drive the message home to your readers.
3. Make sure everything is connected
In connection to the previous point, make sure that each section of your essay is linked to the one after it. Think of your essay as a story: it should have a beginning, middle, and end, and the way that you write your piece should logically tie these elements together in a linear manner.
4. Proofread before submitting your essay
Make sure to review your composition prior to submission. In most cases, the first draft may be a bit disorganised because this is the first time that your thoughts have been laid out on paper. By reviewing what you have written, you will be able to see which parts need editing, and which ones can be rearranged to make your essay more easily understood by your readers. Try to look at what you wrote from the point of view of your audience. Will they be able to understand your train of thought, or do you need to reorganise some parts to make it easier for them to appreciate what you are saying? Taking another look at your essay and editing it can do wonders for how your composition flows.
Writing a cohesive essay could be a lot easier than you think – especially when you follow these steps. Don’t forget that reading complements writing: try reading essays on various topics and see if each of their parts supports their identified goal or argument.

Words and Phrases to Build Up Coherent Text

If you are a long-time writer, you are likely to know the most popular problem in writing is scarcity of coherence since most texts students hand their professors over feature a broken cause and effect relationship. Coherence is the direct clue to correct understanding of information. If absent, there is a tiny likelihood readers will grasp the very point you tried to express. Our edit essay service is the leader in providing writing services of all kinds. We can manage college essay editing on any subject . Our admission essay editing ensures you will entry a desired institution. Our fast thesis editing can save your time and let you enjoy solely your research work. At last, our best-quality essay rewriting is a guarantee your essay work will be the most original and unique. We can teach you amazing techniques to create fascinating texts on multifarious subjects. You do not need to waste all days and nights long in search of effective and quick methods to improve your writing abilities. Our writers have already discovered these secrets and are waiting to share them with people, who truly deserve it. If you aim high, you will find our collaboration fruitful. If you are doubtful, here are all the merits you will benefit from once you have let us come into your life:
- Our support agents are in touch at any time to assist you in any issues.
- Our writer staff is well-qualified and capable of finding an especial approach to each task.
- Our services are available to all people regardless of their age and social position owing to low prices.
- Our realm of interests is vast enough to involve all people seeking for personal development.
- Our reputation speaks for itself. You will never find a more reliable and devoted partner to entrust.
Have curiosity grasped your mind? If it is so, you are welcome to get to know us closer. Visit our paper editing website to look into all the services we render . Do not forget that we encourage team work and are open to overcome numerous hurdles jointly.
Also in this section:
- Easy Revision – Perfect Paper Is As Easy As ABC Now
- English Proofreading On-line. Magic Wand for Foreign Student
- Dissertation Proofreading: Where to Find a Good Editor
- What Essay Proofreading Company to Choose?
- Papers Editing Services Teach How to Outdo Oneself
But let’s get down to business. Today, the issue on the agenda is how essential coherence is in writing. Well, at first, it would be better to define what it is? ‘ Coherence ’ derives from the Latin language and denotes “ to stick together ”. Coherence, which is also often called cohesion , is a way to make phrases or sentences logically connected and flow smoothly one after another. Lack of coherence is usually a proof of poor language and an inability to organize thoughts in a clear manner. Coherence allows combining several ideas or assertions so as to form a unique text that makes sense. In fact, coherence has to do with both oral and written language. It does not matter in what form information is presented, it matters in what manner. In addition, coherence is examined on two textual levels:
- Local Level Coherent Text : coherence occurs on the level of some parts of a text.
- Global Level Coherent Text : coherence occurs on the level of the entire text (for example, a novel or monograph).
In general, coherence is an art of turning single sentences into one integral text. The simple way to make a text coherent is to arrange your thoughts in logical order , which is a paramount feature of any good essay. No text can be easy to understand without this condition. There exist different types of logical order, but the common ones are contrast, importance, and chronology. Chronology refers to time and means that events are described according to the time of their occurrence. In this case, tense agreement plays not less an important role since it is obligatory to use time markers and proper tenses to show readers time relations between events discussed. For this reason, you cannot do without learning Future Perfect Tense or advancing Future Perfect Continuous . Importance anticipates that ideas are stated according to their level of significance. The crucial ones are elucidated above all. At last, contrast is a way to arrange idea by comparing or posing them.
There are different cohesive devices of achieving coherence. They can be applied individually or jointly to get a better results. There is nothing uncanny about them. You are sure to have been using at least one of them even being unaware of it.
1. Repetition
Any text features key words, which constitute the ground for a main idea. Regular repetition of key phrases or words is a sure method to connect parts of information. But there is such a blurred line between redundancy and coherence. As a rule, it is nouns to be repeated since they reflect the main notions of any discussion. Repetition is sometimes regarded as a music motive since it keeps in an audience’s mind the right melody. The following fragment (Oshima & Hogue, 2006) serves a good example of how repetition may contribute to coherence:
Ankara , the capital of the Republic of Turkey, has a unique and stunning history. In the past, Ankara was an ordinary commercial city situated on the crossroads of trade routes. For this reason, it was famous for honey, Muscat grapes and pearls. Later, after the decadence of the Ottoman Empire Ankara replaced the former Turkish capital Istanbul and took the role of the leading city in 1923. Today, Ankara is the second most populous city in the country.
As you see, repetition of the word ‘gold’ here is not lack of a writer’s vocabulary but a tool to stick to the main subject of discussion. There is no fixed rule of how many key words should be used in one paragraph. You should rely on your own feeling of sufficiency.
To be sure your essay is not spoiled by redundancy but coherent owing to key words, turn to our essay proofreading service where the most proficient editors are waiting to help you.
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are a natural way to substitute nouns in texts. Their first function is to note objects or people without naming them. It is an easy way to avoid excessive wordiness or improper repetition. No text can do without pronoun; otherwise, repetition is inevitable. Moreover, it is usually intelligible from a context what is hidden behind a pronoun. If it is impossible for readers to catch what an author’s implies by some pronoun, it is a proof of insufficient clarity of the text. Let’s turn to our familiar fragment:
In the past, Ankara was an ordinary commercial city situated on the crossroads of trade routes. For this reason, it was famous for honey, Muscat grapes and pearls.
It is not a big deal to unveil what IT denotes, isn’t it? Hence, pronoun usage is a powerful method of coherence if applied in the right place and at the right time. By the way, you may find these facts about noun in English useful for your further writing.
3. Linking words
Linking words, or so-called transition tags, is a widely applied cohesive device to connect various ideas and maintain logical order in a text. These are used to organize paragraphs and fix cause and effect relationship, which allows readers to follow what is going on in the text smoothly. Transition words are an intensifying tool of coherence and consistent. They include conjunctions, conjunctive adverbs, and transitional expressions. On our site you can read the definition of an adverb , and what role it plays in a sentence. It is much easier to catch on information if it is arranged by means of logical markers, for example:
Many students believe they cannot write a good essay because they are not writers. However , as they keep on writing and working on developing their writing skills, most students gain the needed confidence to start believing they are writers.
You can find plenty of transition words, and they vary from one to another, but their general purpose remains the same – to ensure textual coherence. In general, most linkers are essential for compound sentences. For this reason, you cannot do without knowing of what English relative clauses are , their types and divergences.
Transition tags are divided into classes based on functions. This will facilitate you choosing a right one. Here is the list of the most widespread transitional markers you are likely to need in writing:
One more problem about dealing with transitional words is ignorance of their right meaning. Putting a linker in a wrong context will only aggravate the situation. None wants to be misunderstood, so it is better to abstain from taking some transitional tag at all or look up its meaning each time you are unsure of its relevance. If you are in dread of making a mistake all the time, we can help you by revealing what errors students mostly do and how to forget about grammar mistakes once and forever.
You do not need to memorize all these words since you can always find them here. Moreover, a usual 250-word essay might require 5 examples at the most. It is reasonable to learn only a dozen of linkers, which you could use for your exam essay, for example. It is important not to get obsessed with using transitional signals since their redundancy can make reading perplexing. The same is about their absence. If your text has none of them, it will be challenging for others to grip what you meant. Our essay editing online service is providing support at any hour, so if this task is not up to you, we are free to collaborate.
If you are truly interested in this topic, there are plenty of amazing ways to get skillful in it. First, you need to get used to everyday reading. There is no better way to learn new words and see the context of their relevant usage. Half an hour every day suffices to make your vocabulary advanced. Have a pen at hand to write all important phrases. If you are an assiduous person, there is one more efficient technique for you. Try to practice writing regularly. This will involve your brain activity and foster development of your writing skills. You can read our service blog publishing useful writing information weekly: https://edit-it.org/blog/choose-the-help-of-a-paper-proofreader-for-excellent-effect ; or you may ask our team of experienced and academic editors to help you at any time if some difficulties arise.
4. Parallelism
Parallel constructions are another cohesive device to keep a text coherent. It consists in a deliberate repetition of phrases or sentences, which have similar grammatical forms. This technique works like ordinary repetition. The only difference is that it is not only one word that is regularly repeated but the whole sentence, not literally but at the grammatical level. By the way, you can find out more about parallelisms from our writers: https://edit-it.org/blog/uk-proofreading-services-help-get-rid-of-study-problems
But for now, let’s examine the brilliant example of parallelism usage – a famous speech of Abraham Lincoln at Gettysburg. Let’s examine one of the parallelisms he used:
But, in a larger sense, we cannot dedicate – we cannot consecrate – we cannot hallow – this ground.
This parallelism serves an emphasis on the idea by means of which the American president is striving to inspire his people. You can find many other instances of parallelisms in political speeches. It is regarded as a powerful figure of speech, which is widely used in both press and belles-lettres, which have the main purpose – to affect audience’s mind. If you got stuck and have no idea how to apply parallelisms in your essay, just mail us ‘ proofread my essay within 24 hours ’, and the work will be ready.
As you see, coherence is a complex phenomenon. It encompasses numerous aspects, each of them is aimed at making a text logical and intelligible for a target audience. This is not only about academic writing but writing as a whole. It is impossible for your listeners to get what you mean if your message is deprived of clarity. If we are talking about the ways coherence is achieved in language, it is closely bound to grammar and vocabulary. Our experts are masterful in writing. You can follow our blog to boost your writing abilities: https://edit-it.org/blog/get-the-best-proofreading-service-with-us
We have mentioned the most efficient techniques to “glue” sentences between each other. If you are eager to find out more about cohesive devices, you can always benefit from our blog where you can have at your disposal vast information on writing development: https://edit-it.org/blog/students-choose-services-to-proofread-paper-online
In addition, our qualified essay editing service is working twenty-four hours a day to be always within call for you. Our experts, who have ample experience in providing services of all kinds, from qualified dissertation writing services to college paper proofreading services . Thus, whatever your activity is, it is for sure they have something to share with you. There is no limit to imperfection, do not you think so? If you agree, then you cannot but find our possible friendship profitable only. The more opportunities you take, the more roads are open for you. Do not miss this one, and if we are here for you , let us assist in achieving new laurels on your academic path. There are numerous grateful feedbacks from customers we helped and have been collaborating up to date. We are not only one-time urgent aid but a reliable partner for mutual development . Your success is part of our success!
More popular topics:
- Essay Editing Services: How to Improve Writing
- Online Proofreading Service: Get Professional Help!
- Dissertation Editor: Main Role and Functions
- What Should You Know About The Complex Object?
Calculate Your Price
Having doubts?
Try our service for FREE!
Recent posts
- Best Cheapest Proofreading Cost from Our Writing Service
- English Proofreading Online: Best Service for Students
- Secrets of Implicit and Explicit Memory at Edit-it.org
- Let Professional Rate My Paper With Regard to Requirements
- Copy Editing Fees Affordable for Everyone
The Concept of Manifest Destiny: its Definition and Impact on U.S. History
This essay about Manifest Destiny examines the complex and controversial role it played in shaping American history. It discusses the origins, ideological underpinnings, and historical consequences of this doctrine, which justified the expansion from coast to coast. The text explores both the positive impacts, such as economic growth and national unity, and the negative repercussions, including the displacement of Native Americans and the exacerbation of slavery issues, culminating in the Civil War and America’s later imperialist ventures.
How it works
In the vast tapestry of American history, few ideas carry the weight and controversy of Manifest Destiny. This ideological current, born in the turbulent cauldron of 19th-century America, drove the nation westward, imprinting its identity, politics, and trajectory with an indelible mark. Manifest Destiny was not merely a slogan but a potent force that animated America’s territorial ambitions, spanning from coast to coast. Coined in the 1840s, it embodied the prevailing notion that America was fated, even obligated, to expand its dominion from sea to shining sea, carrying democracy, civilization, and Protestant Christianity in its wake.
Rooted in centuries-old ideals of American exceptionalism and territorial expansion, it blossomed into a compelling narrative of expansionism, profoundly shaping American society.
The genesis of Manifest Destiny can be traced back to the earliest days of European colonization in America. The Puritans envisioned a “city upon a hill,” a beacon of righteousness to illuminate the world. Thomas Jefferson’s vision of an agrarian republic foreshadowed the desire for a vast expanse of land for future generations of American pioneers. These ideals laid the groundwork for Manifest Destiny, but it was the tumultuous 19th century that provided the fertile ground for its growth.
The Louisiana Purchase of 1803 served as the spark for westward expansion, effectively doubling the size of the fledgling nation and sparking dreams of a continental empire. The Lewis and Clark expedition, venturing into the uncharted territories of the West, captivated the imagination of a nation hungry for adventure and opportunity. As settlers pushed further into the frontier, encountering Native American tribes, Mexican territories, and foreign powers, Manifest Destiny provided the ideological justification for their conquests, legitimizing their actions as part of a divine mandate.
The impact of Manifest Destiny on U.S. history was profound and multifaceted, leaving an enduring mark on the American landscape. On one hand, it fueled economic growth, spurred innovation, and united a fractured nation. The promise of fertile land, abundant resources, and limitless opportunity attracted millions of immigrants seeking a better life in the “land of the free.” The construction of the transcontinental railroad, the passage of the Homestead Act, and the migration along the Oregon Trail stand as testaments to America’s unyielding drive for westward expansion.
However, this westward expansion came at a steep cost. For Native American tribes, Manifest Destiny spelled devastation, leading to displacement, dispossession, and cultural genocide on an unprecedented scale. Treaties were disregarded, wars were waged, and entire civilizations were decimated in the name of progress. The Trail of Tears, the Massacre at Wounded Knee, and the imposition of the reservation system serve as painful reminders of the human toll exacted by Manifest Destiny.
Similarly, Manifest Destiny fueled tensions with Mexico, culminating in the Mexican-American War of 1846-1848. The annexation of Texas and the dispute over the territories of the Southwest ignited conflict over the rightful borders of the expanding nation. Though the war ended with American victory and the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, it left a legacy of imperialism and exploitation, sowing seeds of resentment that endure to this day.
Moreover, Manifest Destiny exacerbated existing divisions over slavery, pushing the nation to the brink of civil war. The question of whether to extend slavery into the newly acquired territories tore at the fabric of American society, exposing the deep-rooted contradictions at its core. The Compromise of 1850 and the Kansas-Nebraska Act of 1854 attempted to placate these divisions, but they only served to inflame tensions further, ultimately leading to the bloodshed of the Civil War.
In the aftermath of the Civil War, Manifest Destiny experienced a resurgence as America turned its gaze outward to the global stage. The doctrine of “American exceptionalism” took hold, justifying interventions in Latin America, the Caribbean, and the Pacific. The Spanish-American War of 1898, with its rallying cry of “Remember the Maine!,” marked the pinnacle of American imperialism as the nation acquired colonies in Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines.
Yet, even as Manifest Destiny propelled America to new heights of power and influence, it faced growing criticism from within. Voices such as Henry David Thoreau and Frederick Douglass denounced the hypocrisy of a nation that preached freedom and democracy abroad while denying it to its own citizens. The anti-imperialist movement of the late 19th and early 20th centuries challenged the morality and legality of America’s overseas ventures, advocating for a return to the principles of self-determination and non-interventionism.
In the 20th century, Manifest Destiny gradually receded from the forefront of American consciousness, supplanted by new ideologies and challenges. The Great Depression, World War II, and the Cold War shifted the nation’s focus away from territorial expansion toward economic prosperity and global leadership. Nevertheless, echoes of Manifest Destiny linger in America’s national psyche, influencing its foreign policy, shaping its sense of identity, and informing its place in the world.
In conclusion, Manifest Destiny stands as a pivotal chapter in U.S. history, a testament to the power of ideology to shape the course of nations. Its definition as a belief in America’s divine right to expand across the continent captures the audacity and ambition of a young nation on the rise. Its impact, from westward expansion to imperial conquest, leaves an enduring legacy, reminding us of the complex interplay between ideology, power, and destiny in the American experience. As America grapples with its past and charts its future, the legacy of Manifest Destiny serves as a poignant reminder of the enduring consequences of our collective aspirations and actions.
Cite this page
The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History. (2024, May 21). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/
"The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History." PapersOwl.com , 21 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/ [Accessed: 21 May. 2024]
"The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History." PapersOwl.com, May 21, 2024. Accessed May 21, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/
"The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History," PapersOwl.com , 21-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/. [Accessed: 21-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Concept of Manifest Destiny: Its Definition and Impact on U.S. History . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-concept-of-manifest-destiny-its-definition-and-impact-on-u-s-history/ [Accessed: 21-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Linguistic coherence refers to the clear and logical arrangement of words, phrases, and sentences in a piece of writing to ensure the message is understood as intended. It involves the use of grammatically correct sentences, appropriate use of conjunctions, pronouns and transitional phrases, correct sequencing of ideas, and maintaining the same ...
An essay must have coherence. The sentences must flow smoothly and logically from one to the next as they support the purpose of each paragraph in proving the thesis. . Just as the last sentence in a paragraph must connect back to the topic sentence of the paragraph, the last paragraph of the essay should connect back to the thesis by reviewing ...
Coherence describes the way anything, such as an argument (or part of an argument) "hangs together.". If something has coherence, its parts are well-connected and all heading in the same direction. Without coherence, a discussion may not make sense or may be difficult for the audience to follow. It's an extremely important quality of ...
Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly to create unity. So, sentences and ideas must be relevant to the central thesis statement. The writer has to maintain the flow of ideas to serve the main focus of the essay. 5. Stick to the purpose of the type of essay you're-writing.
Coherence is a Latin word, meaning "to stick together.". In a composition, coherence is a literary technique that refers to logical connections, which listeners or readers perceive in an oral or written text. In other words, it is a written or spoken piece that is not only consistent and logical, but also unified and meaningful.
Coherence is about making everything flow smoothly. The reader can see that everything is logically arranged and connected, and relevance to the central focus of the essay is maintained throughout. Two key aspects of coherence. Cohesion: This relates to the linking of ideas within a sentence, the linking of sentences (the ties between sentences ...
Cohesion and Coherence. A well-organized paper uses techniques to build cohesion and coherence between and within paragraphs to guide the reader through the paper by connecting ideas, building details, and strengthening the argument. Although transitions are the most obvious way to display the relationship between ideas, consider some of the ...
Coherence is an important aspect of good writing—as important as good grammar or spelling. However, it is also rather harder to learn how to do it, because it is not a matter of simple rules. Coherent writing moves smoothly between ideas. It guides the reader through an argument or series of points using signposts and connectors.
Coherence is achieved when sentences and ideas are connected and flow together smoothly. An essay without coherence can inhibit a reader's ability to understand the ideas and main points of the essay. Coherence allows the reader to move easily throughout the essay from one idea to the next, from one sentence to the next, and from one ...
Coherence is built into the paper from the bottom up - from the sentence, to the paragraph, to the essay as whole - by creating patterns of language, syntax, sound, images, and relationships that occur throughout the paper. Below are a few strategies for constructing these patterns. Let's begin with the first few sentences from ...
See the AXES Handout for more information on this approach. COHERENCE - Coherence refers to the overall sense of unity among your ideas and clarity of your writing structure. It consists of linking together the key claims you are making in each sentence, each paragraph, and finally in your paper as a whole. Think of this as the macro level of ...
Preserving Unity. Academic essays need unity, which means that all of the ideas in an essay need to relate to the thesis, and all of the ideas in a paragraph need to relate to the paragraph's topic. It can be easy to get "off track" and start writing about an idea that is somewhat related to your main idea, but does not directly connect ...
Asking a peer to check the writing to see if it makes sense, i.e. peer feedback, is another way to help improve coherence in your writing. Example essay. Below is an example essay. It is the one used in the persuasion essay section. Click on the different areas (in the shaded boxes to the right) to highlight the different cohesive aspects in ...
In composition, coherence refers to the meaningful connections that readers or listeners perceive in a written or oral text, often called linguistic or discourse coherence, and can occur on either the local or global level, depending on the audience and writer. Coherence is directly increased by the amount of guidance a writer provides to the ...
This coherence, this clarity of expression, is created by grammar and vocabulary (lexis) through cohesion. This is the "glue" that joins your ideas together to form a cohesive whole. In this Learning Object we are going to focus on how this is done, in order to assist you when you come to write your next assignments and in your reading.
Paragraph coherence: Decide on an order for your sentences that will best develop the paragraph's main idea. Your supporting sentences are raw materials. They will not make sense to a reader unless they are put in order. This order could be based on several factors: Chronological sequence. This is useful for describing a sequence of events.
Coherence • Coherence refers to the overall sense of unity in a passage, including both the main point of sentences and the main point of each paragraph. • Coherence focuses the reader's attention on the specific people, things, and events you are writing about To Improve Cohesion For Cohesion in Sentence Beginnings . . . Put the OLD FIRST
Define coherence in terms of writing. Identify strategies to revise your argument for coherence. The term "coherence" comes from the verb "to cohere," which means "to be united," "to form a whole," or "to be logically consistent". Coherence in writing refers to the big picture of a text. How can you construct an essay or ...
Coherence in written text is a complex concept, involving a multitude of reader- and text-based features. Perhaps because of this, we writing instructors and the textbooks we use often discuss coherence in a vague or incomplete manner. This article reviews current coherence literature, defines coherence in broad terms,
In each paragraph of an essay, one particular idea or topic is developed and explained. In order to successfully do so, however, it is essential that the paragraph be written in a unified and coherent manner.. A unified paragraph must follow the idea mentioned in the topic sentence and must not deviate from it. For a further explanation on topic sentences, see the Write Right on Topic Sentences.
3. Make sure everything is connected. In connection to the previous point, make sure that each section of your essay is linked to the one after it. Think of your essay as a story: it should have a beginning, middle, and end, and the way that you write your piece should logically tie these elements together in a linear manner. 4.
Academic writing is a kind of formal style of writing practiced mainly in the universities and in. publications. Cohesion a nd coherence, which refer to intra-text connectedness, and the c ...
Global Level Coherent Text: coherence occurs on the level of the entire text (for example, a novel or monograph). In general, coherence is an art of turning single sentences into one integral text. The simple way to make a text coherent is to arrange your thoughts in logical order, which is a paramount feature of any good essay. No text can be ...
Definition Essay; Informative Essay; Topic Ideas. Narrative Essay Topics; Argumentative Essay Topics; ... Looking at the appendix in paper definition, one can swiftly understand its importance. Therefore, you should think about the data you would like to include in your appendix for research paper or appendix in report to make it 10/10 ...
Essay Example: In the nascent years of the 19th century, a profound stirring gripped the heart of America, shaking the foundations of society and ushering in a spiritual renaissance known as the Second Great Awakening. This epochal wave of revivalism was not merely a resurgence of religious
Essay Example: In the vast tapestry of American history, few ideas carry the weight and controversy of Manifest Destiny. This ideological current, born in the turbulent cauldron of 19th-century America, drove the nation westward, imprinting its identity, politics, and trajectory with an indelible ... Its definition as a belief in America's ...
"The movie was a patriotic rallying cry that affirmed a sense of national purpose," wrote Cristóbal S. Berry-Cabán in an essay. "The film emphasized group effort and the value of ...