

4 Types of Market Research + 6 New Ways to Do It Smarter

In June this year, 500 business leaders shared their favorite types of market research with me via a direct external survey.
Astonishingly, 83% of people said the same thing: favoring qualitative research ( specifically market research surveys ) over anything else.
Having a favorite is all good and well, but as we know, variety is the spice of life. By avoiding dependency on any single type of market research, you get a relevant, unbiased view of your market and opportunities at all times.
Spoiler alert The types of market research I outline in this post will speed up your time to insight significantly. Instead of a process that spans days and weeks, certain tasks can be done and dusted in a few hours at most.

To help you stay on top of your game, I’m outlining the different types of market research, their benefits, and how to use them. As a bonus, I’m sharing six modern ways to do market research using digital research intelligence tools (like Similarweb).
The 4 types of market research
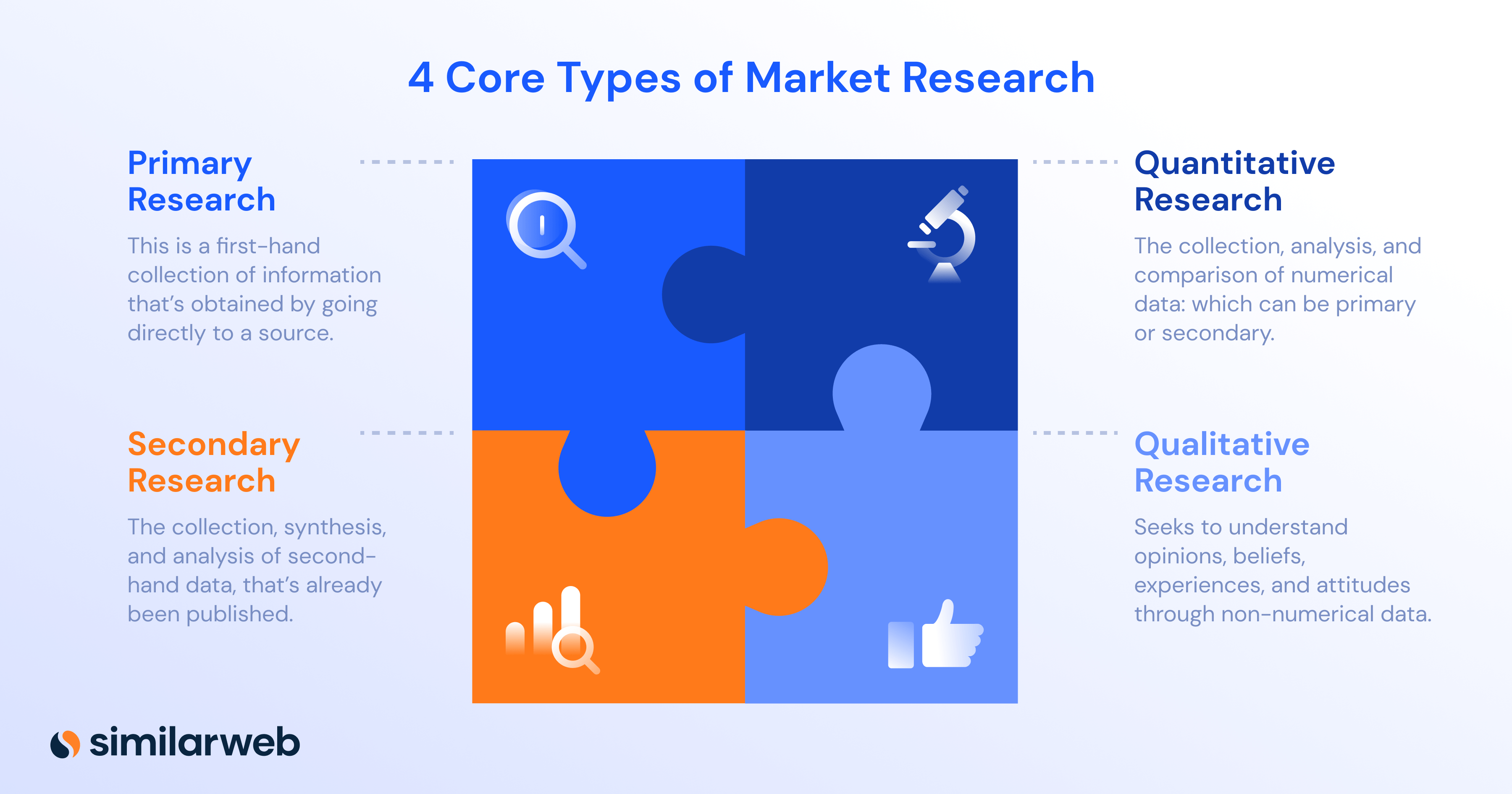
1. Primary research
Primary research is the first-hand collection of data. You go directly to a source instead of relying on existing information. It’s also known as field research.
Who is it for? Doing primary research involves collecting information relevant to a specific research context. For instance, if data is required about the shifting needs of a target market , primary research methods are a great way to explore this.
How to collect the data? Usually, an individual will go into the marketplace (field) to find the information they need.
Benefits of primary research
- You get more control over the research methodologies.
- The information is up-to-date.
- Because data is relevant, it reveals current trends, not outdated ones.
- Most primary research addresses the individual market instead of the mass market.
- The data collector retains ownership of the data.

Types of primary research
The right research method depends on the goal of the research and the resources available. Here are five of the best ways to do primary research.
- Ethnographic or observational research
- Trials or experiments
- Focus groups
2. Secondary research
Secondary research collates existing information or research for analysis. Essentially, it’s a type of market research that uses second-hand data.
Who is it for? Secondary research is ideal for start-ups and small businesses, needing a type of market research that’s low-cost and quick to undertake.
How to collect the data? Secondary data is collected from various places but always comes from existing third-party information.
Benefits of secondary research
- A low-cost type of research
- It’s quick to conduct
- Data is easy to access
- Initial findings can help shape any longer-term investment in primary research
- Anybody can do it; there’s no professional training required
- Gives you a broad understanding of a topic quickly

Types of secondary research
Most secondary market research methods can be done for free. It’s also called desk research . Here are some of the most popular places to obtain that data.
- Internet search engines
- Trade associations
- Research companies
- Media outlets
- Industry experts
- Government and non-government agencies
- Digital intelligence platforms (like Similarweb)
- Educational institutions
- Company reports
- Academic journals
- Public libraries
- Competitor websites
3. Qualitative research
Qualitative research aims to understand opinions, beliefs, experiences, attitudes, and interactions by collecting and analyzing non-numerical data. It helps researchers understand why things are so, through observation or unstructured questioning.
Compared to quantitative methods, this is more of a touchy-feely type of market research. It’s more about emotions and opinions than crunching numbers.
Who is it for? Any business or start-up can use (and benefit from) qualitative research. To understand the sentiment of a target audience or market in detail, this type of research uncovers key insights that help shape and develop products, services, and strategies.
How to collect the data? You can conduct qualitative research remotely or in person. What’s key is that the data is collected first-hand, directly from an individual or group of people.
Benefits of qualitative research
- Captures shifting attitudes or sentiments within a target group.
- Can uncover key insights that numbers alone couldn’t reveal.
- More targeted research, is often more concentrated compared to quantitative research.
- Cost and speed can be managed more effectively with smaller groups.
- Promotes authenticity in discussions as responses aren’t formed by pre-set constraints.
- Greater flexibility than other research methods as questions can be adapted over time.
Types of qualitative research
- Participant observation
- Ethnography
- Case Studies
- Grounded theory (using research to generate a theory)
- Thematic analysis (looks to identify or interpret patterns and their connected meanings)
- Open-ended surveys
- Diary or Journal logging
- Phenomenological study (where you take a customer or individual, and examine things from their perspective)
Read More: 83 Qualitative Research Questions & Examples
4. Quantitative research
Quantitative research is focused on collecting, analyzing, and comparing numerical data. It’s predominantly used to make predictions, spot trends , find patterns, and establish averages. It deals with primary and secondary data, as long as it is represented in numerical form.
Who is it for? Quantitative research provides data that can shed light on statistical information about a market or business. It’s useful for start-ups and established companies and can help with forecasting, market sizing , market validation , and more.
How to collect the data? Using various methods, quantitative research is systematically collected and recorded to do analysis in a database through graphics, charts, and tables.
Benefits of quantitative research
- Data can be analyzed reliably and consistently.
- Studies can be easily replicated in the future or a different market.
- It’s possible to do a broader study with large sample sizes.
- Fewer variables are involved as data is often close-ended.
- Automation makes data collection quicker and easier to conduct.
- More cost-effective than qualitative research.
Types of quantitative research
Due to the often complex nature of this type of market research, I’ve added a quick explainer.
- Experimental research Also referred to as true experimentation, this relies on theory. In most cases, multiple theories that have not yet been proven. An analysis is carried out to prove or disprove the theory.
- Descriptive research This is used better to understand a specific situation, population, or phenomenon. It seeks only to measure (not manipulate) variables through observation to investigate them thoroughly.
- Survey research Quite simply, this uses a range of online or offline polls to understand what customers or a group of people think about products, services, and more.
- Quasi-experimental research Similar to experimental research, it aims to evaluate a cause-and-effect relationship amongst variables. However, it’s a dependent and independent variable in this case.
- Correlational research This is typically undertaken to determine a relationship between two closely related entities. It explores how each entity impacts the other and examines key changes.
Read More: 98 Quantitative Market Research Questions & Examples
Mixed-method research approach
Discover a better way to do market research.
Get the data you need to adapt to market changes and industry trends in an instant.
6 modern types of market research
Outside the four core types of market research, there are modern ways to discover valuable information that can leverage better insights. If you’re looking for new types of research that’ll help you quickly find new opportunities to go after, read on.
1. Competitor research
In-depth competitor analysis allows you to quickly find growth opportunities, by taking a detailed look at what is and isn’t working for your rivals. What’s more, it can help you spot emerging trends and shifts, so you can take action when and where it matters most.
These are some of the things you can expect to uncover with competitive market research:
- Understand how to track and target your competitors’ audiences.
- Discover the best traffic sources to see where rivals are gaining referrals from.
- Establish a clear view of rival’s market share across any industry.
- See traffic changes over time amongst industry leaders and emerging players.
- Find out which channels are working best for competitors.
- Benchmark your business against others in your space.
- Track a customized list of players in your sector to see gains and losses.
2. Audience research
Consumer insights are fundamental to the success of any organization, regardless of size or sector. Through the analysis of consumer behavior, you can drive better engagement, discover new digital strategies , and develop a more detailed understanding of your prospects and customers.
Here are just a few examples of how doing audience-based research can help:
- Better understand audience interests relative to an industry or your rivals.
- Measure audience loyalty .
- See where they spend their time online.
- Build a picture of an audience layered with insights from real-world browsing habits.
- Uncover key demographics , interests, and geographies of an audience.
To help you get started, here are four audience analysis examples .
3. Content and keyword research
At the last count, there were roughly 1.93 billion websites online, and I’m not even going to get into how many social media accounts there are. But with so many digital channels, you must ensure your content and company can be easily found online. This is where ( and why ) content and keyword-based market research deliver immense value.
Get it right, and you’ll reap the benefits through more visitors, leads, conversions, and revenue. The golden nugget you uncover with keyword and content research is a greater understanding of an audience. Although most people would associate keyword research with SEO, it serves a dual purpose.
To get started, do a competitive content analysis within your market.
4. Campaign effectiveness
Knowing how effective a specific type of advertising channel, message, or format is for a target audience can quickly help you determine where’s best to spend your marketing dollars. By researching the effectiveness of ads in your space, you can more easily see the best places to invest your time and effort.
This type of market research helps you:
- Find out if paid advertising is working or not.
- Discover the highest-converting ads.
- See what types of creatives work best for your target audience.
- Look at competitors’ total spend in a specific channel.
- View social media referrals and their impact on website traffic.
- Drill-down into top-performing ads to see messaging, visuals, and more.
5. Mobile app market research
Mobile-first consumer habits have seen industries turned on their heads overnight. For most, it’s not a question of ‘if’ but ‘when’ mobile apps will infiltrate their market. In any industry, seeing the impact of apps in your space is vital. The need to see a complete view of the digital landscape is rising fast.
Some of the key things you can uncover through app intelligence -focused research include:
- Find trending apps in any sector, specifically looking at growth/decline.
- App usage and engagement metrics across multiple markets.
- Analyze an app’s ranking over time.
- Identify underserved markets and spot opportunities to break into new spaces.
- Evaluate iOS vs. Android stats to determine which platform is optimal for an audience.
- View the performance of competitors’ apps over time.
- Compare app performance metrics directly against desktop or mobile web channels.
- Determine whether or not to invest in a mobile app for your business.

6. Market segmentation
Understanding whole market trends are useful. But the real pearls of wisdom can be found when you slice and dice a market into manageable portions. Market segmentation is important for businesses to identify and target specific customer groups, tailor their products and services, and measure their performance. This type of market research helps you:
- Deliver personalized marketing
- Identify market shifts
- Find opportunities for growth in specific segments of a market
- Improve targeting
- Allocate resources more efficiently
- Improve customer engagement and loyalty
- Increase return on investment by identifying opportunity segments

Choosing the right type of market research
Whatever your industry, role, or experience, the type of market research you choose will influence key decisions in your business. With rapid shifts in consumer behavior and emerging threats now virtually an everyday thing, you need a broad and relevant view of the landscape. No single type of market research alone gives a complete picture.
Organizations must keep a finger on the pulse to stay relevant, adapt, and compete. While using traditional types of market research is key, you can gain key insights much quicker, often for a much lower cost, using modern tools like Similarweb Research Intelligence .
Why not take it for a trial run today? For free.
What’s the difference between qualitative and quantitative research? Quantitative research is based on numbers and seeks to explain theories or hypotheses. In contrast, qualitative research is more about understanding the ‘how’ and ‘why’ things happen.
Should I use more than one market research method at a time? Yes, it’s important to take a balanced approach when choosing the best type of research. While it’s vital to clearly understand what is happening, you also need to consider the ‘why’ things happen.
What type of market research is best for start-ups? Most start-ups use secondary research as it’s quick and affordable. However, there are many benefits to conducting first-hand primary research as well.
What types of market research can you do for free? Most secondary research is free to conduct. If you have access to a list of subjects or prospects, you can also use market research surveys to conduct primary market research for free.
Is quantitative research primary or secondary? It can be both. Secondary and primary data can be quantitative (number-based) or qualitative (verbal or opinion-based).
Related Posts

What is Quantitative Data? Your Guide to Data-Driven Success

Demand Forecasting 101: How to Predict Future Demand For Your Products

US Financial Outlook: Top Trends to Watch in 2024

Top Economic Trends in Australia to Watch in 2024

What Is Data Management and Why Is It Important?

What is a Niche Market? And How to Find the Right One
Wondering what similarweb can do for your business.
Give it a try or talk to our insights team — don’t worry, it’s free!

- Services ›
- Business Services
Market research in U.S. - statistics & facts
The market research industry includes any organized activity to gather information about a specific target market or group of customers. It includes traditional methods of information gathering such as surveys, as well as newer methods of data analytics that have emerged with the increasing digitization of society. In 2019, in the United States, market research companies generated over 47 billion U.S. dollars in revenue, more than half of the total revenue of the market research industry globally . The vast majority of money spent on market research in the U.S. in 2019 was for quantitative research , which accounted for 64 percent of the market. Within the quantitative segment, online research and phone interviews were the most dominant research methods, while face-to-face interviews accounted for only two percent of spending. Customer satisfaction investigations were the main type of project conducted in 2019, constituting 20 percent of of revenue received by market research companies. The next largest source of revenue was media audience measurement, which accounted for 16 percent of revenue. Within the U.S., the market leader was Nielsen Holdings, who reported 3.9 billion U.S. dollars in domestic revenue for 2019. There is a significant difference in revenue to the next largest company in the U.S. market, IQVIA , which reported approximately 2.2 billion U.S. dollars in revenue for the same period. However, this gap is not surprising given IQVIA specializes in research for the healthcare sector, while Nielson provide services regarding goods, consumers. and the media across a broad range of sectors. Other leaders in the U.S. market research industry include Kantar , Information Resources Inc , and Ipsos , each of which generated under one billion of U.S. revenue in that year. This text provides general information. Statista assumes no liability for the information given being complete or correct. Due to varying update cycles, statistics can display more up-to-date data than referenced in the text. Show more - Description Published by Statista Research Department , Dec 19, 2023
Key insights
Detailed statistics
Revenue of the market research industry worldwide 2008-2023
Distribution of global market research revenue by region 2022
Market research revenue in the U.S. 2009-2022 with 2023 forecast
Editor’s Picks Current statistics on this topic
Market Research
Leading market research companies by U.S. research revenue in 2021
Further recommended statistics
Market overview.
- Premium Statistic Revenue of the market research industry worldwide 2008-2023
- Premium Statistic Distribution of global market research revenue by region 2022
- Premium Statistic Market research revenue in the U.S. 2009-2022 with 2023 forecast
- Premium Statistic Market research revenue in the U.S. by segment 2013-2018
- Premium Statistic Full-time U.S. employees of the leading market research companies 2005-2020
- Premium Statistic Market research companies leading client sectors in the U.S. 2022
- Premium Statistic Leading market research companies by U.S. research revenue in 2021
- Premium Statistic Number of full-time employees at the leading U.S. market research companies in 2020
Revenue of the market research industry worldwide from 2008 to 2023 with a forecast for 2024 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Distribution of global market research revenue in 2022, by region
Revenue of market research companies in the United States from 2009 to 2022, with a forecast for 2023 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Market research revenue in the U.S. by segment 2013-2018
Revenue of market research companies in the United States from 2013 to 2018, by segment (in billion U.S. dollars)
Full-time U.S. employees of the leading market research companies 2005-2020
Number of full-time employees in the United States of the leading market research companies from 2005 to 2020
Market research companies leading client sectors in the U.S. 2022
Leading client sectors of market research companies in the United States in 2022, by share of research sales
Leading market research companies in 2021, by U.S. research revenue (in million U.S. dollars)
Number of full-time employees at the leading U.S. market research companies in 2020
Number of full-time employees at the leading market research companies in the United States in 2020
U.S. market leaders
- Premium Statistic Market research revenue of Nielsen in the U.S. 2013-2021
- Premium Statistic Market research revenue of IQVIA in the U.S. 2013-2021
- Basic Statistic Market research revenue of Kantar in the U.S. 2013-2021
- Premium Statistic Information Resources Inc. market research revenue in the U.S. 2013-2021
- Premium Statistic Ipsos's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
- Premium Statistic GfK's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
- Premium Statistic Westat's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Nielsen in the U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Nielsen Holdings in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Market research revenue of IQVIA in the U.S. 2013-2021
Research revenue of IQVIA in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in billion U.S. dollars)
Market research revenue of Kantar in the U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Kantar in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in million U.S. dollars)
Information Resources Inc. market research revenue in the U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Information Resources Inc. (IRI) in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in million U.S. dollars)
Ipsos's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Ipsos in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in million U.S. dollars)
GfK's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of GfK in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in million U.S. dollars)
Westat's market research revenue U.S. 2013-2021
Market research revenue of Westat in the United States from 2013 to 2021 (in million U.S. dollars)
Market research methods
- Premium Statistic Market research spend in the U.S. by research project type 2022
- Premium Statistic Market research spend in the U.S. by method of survey 2022
- Premium Statistic Market research spend in the U.S. by research method 2022
- Premium Statistic Market research spend in the U.S. by research design 2022
Market research spend in the U.S. by research project type 2022
Distribution of market research spend in the United States in 2022, by research project type
Market research spend in the U.S. by method of survey 2022
Distribution of market research spending in the United States in 2022, by method of survey
Market research spend in the U.S. by research method 2022
Share of market research spend in the United States in 2022, by research method
Market research spend in the U.S. by research design 2022
Distribution of market research spend in the United States in 2022, by research design
Further reports
Get the best reports to understand your industry.
- Advertising worldwide
- Mobile advertising and marketing in the U.S.
- Market research industry
- Email marketing worldwide
Mon - Fri, 9am - 6pm (EST)
Mon - Fri, 9am - 5pm (SGT)
Mon - Fri, 10:00am - 6:00pm (JST)
Mon - Fri, 9:30am - 5pm (GMT)
Market Research: A How-To Guide and Template
Discover the different types of market research, how to conduct your own market research, and use a free template to help you along the way.

MARKET RESEARCH KIT
5 Research and Planning Templates + a Free Guide on How to Use Them in Your Market Research

Updated: 02/21/24
Published: 02/21/24
Today's consumers have a lot of power. As a business, you must have a deep understanding of who your buyers are and what influences their purchase decisions.
Enter: Market Research.
![market research industry type → Download Now: Market Research Templates [Free Kit]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/6ba52ce7-bb69-4b63-965b-4ea21ba905da.png)
Whether you're new to market research or not, I created this guide to help you conduct a thorough study of your market, target audience, competition, and more. Let’s dive in.
Table of Contents
What is market research?
Primary vs. secondary research, types of market research, how to do market research, market research report template, market research examples.
Market research is the process of gathering information about your target market and customers to verify the success of a new product, help your team iterate on an existing product, or understand brand perception to ensure your team is effectively communicating your company's value effectively.
Market research can answer various questions about the state of an industry. But if you ask me, it's hardly a crystal ball that marketers can rely on for insights on their customers.
Market researchers investigate several areas of the market, and it can take weeks or even months to paint an accurate picture of the business landscape.
However, researching just one of those areas can make you more intuitive to who your buyers are and how to deliver value that no other business is offering them right now.
How? Consider these two things:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. It‘s very possible that your immediate resources are, in many ways, equal to those of your competition’s immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your customers don't represent the attitudes of an entire market. They represent the attitudes of the part of the market that is already drawn to your brand.
The market research services market is growing rapidly, which signifies a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from roughly $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025 .
.png)
Free Market Research Kit
- SWOT Analysis Template
- Survey Template
- Focus Group Template
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Why do market research?
Market research allows you to meet your buyer where they are.
As our world becomes louder and demands more of our attention, this proves invaluable.
By understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired solutions, you can aptly craft your product or service to naturally appeal to them.
Market research also provides insight into the following:
- Where your target audience and current customers conduct their product or service research
- Which of your competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- What's trending in your industry and in the eyes of your buyer
- Who makes up your market and what their challenges are
- What influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Whether there‘s demand for the business initiatives you’re investing in
- Unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be flipped into selling opportunity
- Attitudes about pricing for a particular product or service
Ultimately, market research allows you to get information from a larger sample size of your target audience, eliminating bias and assumptions so that you can get to the heart of consumer attitudes.
As a result, you can make better business decisions.
To give you an idea of how extensive market research can get , consider that it can either be qualitative or quantitative in nature — depending on the studies you conduct and what you're trying to learn about your industry.
Qualitative research is concerned with public opinion, and explores how the market feels about the products currently available in that market.
Quantitative research is concerned with data, and looks for relevant trends in the information that's gathered from public records.
That said, there are two main types of market research that your business can conduct to collect actionable information on your products: primary research and secondary research.
Primary Research
Primary research is the pursuit of first-hand information about your market and the customers within your market.
It's useful when segmenting your market and establishing your buyer personas.
Primary market research tends to fall into one of two buckets:
- Exploratory Primary Research: This kind of primary market research normally takes place as a first step — before any specific research has been performed — and may involve open-ended interviews or surveys with small numbers of people.
- Specific Primary Research: This type of research often follows exploratory research. In specific research, you take a smaller or more precise segment of your audience and ask questions aimed at solving a suspected problem.
Secondary Research
Secondary research is all the data and public records you have at your disposal to draw conclusions from (e.g. trend reports, market statistics, industry content, and sales data you already have on your business).
Secondary research is particularly useful for analyzing your competitors . The main buckets your secondary market research will fall into include:
- Public Sources: These sources are your first and most-accessible layer of material when conducting secondary market research. They're often free to find and review — like government statistics (e.g., from the U.S. Census Bureau ).
- Commercial Sources: These sources often come in the form of pay-to-access market reports, consisting of industry insight compiled by a research agency like Pew , Gartner , or Forrester .
- Internal Sources: This is the market data your organization already has like average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other historical data that can help you draw conclusions on buyer needs.
- Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
- Observation-Based Research
- Buyer Persona Research
- Market Segmentation Research
- Pricing Research
- Competitive Analysis Research
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
- Brand Awareness Research
- Campaign Research
1. Interviews
Interviews allow for face-to-face discussions so you can allow for a natural flow of conversation. Your interviewees can answer questions about themselves to help you design your buyer personas and shape your entire marketing strategy.
2. Focus Groups
Focus groups provide you with a handful of carefully-selected people that can test out your product and provide feedback. This type of market research can give you ideas for product differentiation.
3. Product/Service Use Research
Product or service use research offers insight into how and why your audience uses your product or service. This type of market research also gives you an idea of the product or service's usability for your target audience.
4. Observation-Based Research
Observation-based research allows you to sit back and watch the ways in which your target audience members go about using your product or service, what works well in terms of UX , and which aspects of it could be improved.
5. Buyer Persona Research
Buyer persona research gives you a realistic look at who makes up your target audience, what their challenges are, why they want your product or service, and what they need from your business or brand.
6. Market Segmentation Research
Market segmentation research allows you to categorize your target audience into different groups (or segments) based on specific and defining characteristics. This way, you can determine effective ways to meet their needs.
7. Pricing Research
Pricing research helps you define your pricing strategy . It gives you an idea of what similar products or services in your market sell for and what your target audience is willing to pay.
8. Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses give you a deep understanding of the competition in your market and industry. You can learn about what's doing well in your industry and how you can separate yourself from the competition .
9. Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Customer satisfaction and loyalty research gives you a look into how you can get current customers to return for more business and what will motivate them to do so (e.g., loyalty programs , rewards, remarkable customer service).
10. Brand Awareness Research
Brand awareness research tells you what your target audience knows about and recognizes from your brand. It tells you about the associations people make when they think about your business.
11. Campaign Research
Campaign research entails looking into your past campaigns and analyzing their success among your target audience and current customers. The goal is to use these learnings to inform future campaigns.
- Define your buyer persona.
- Identify a persona group to engage.
- Prepare research questions for your market research participants.
- List your primary competitors.
- Summarize your findings.
1. Define your buyer persona.
You have to understand who your customers are and how customers in your industry make buying decisions.
This is where your buyer personas come in handy. Buyer personas — sometimes referred to as marketing personas — are fictional, generalized representations of your ideal customers.
Use a free tool to create a buyer persona that your entire company can use to market, sell, and serve better.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

26 Tools & Resources for Conducting Market Research

What is a Competitive Analysis — and How Do You Conduct One?
![market research industry type SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/marketingplan_20.webp)
SWOT Analysis: How To Do One [With Template & Examples]

TAM SAM SOM: What Do They Mean & How Do You Calculate Them?
![market research industry type How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Google%20Drive%20Integration/how%20to%20do%20a%20competitor%20analysis_122022.jpeg)
How to Run a Competitor Analysis [Free Guide]
![market research industry type 5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/challenges%20marketers%20face%20in%20understanding%20the%20customer%20.png)
5 Challenges Marketers Face in Understanding Audiences [New Data + Market Researcher Tips]

Causal Research: The Complete Guide

Total Addressable Market (TAM): What It Is & How You Can Calculate It

What Is Market Share & How Do You Calculate It?
![market research industry type 3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-data-privacy-benefits-marketers_1.webp)
3 Ways Data Privacy Changes Benefit Marketers [New Data]
Free Guide & Templates to Help Your Market Research
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
Quick links
- Case Studies
- White Papers
Send Inquiry
Market Research Definition, Types, Tools and Benefits

Published on Jul 01, 2022
More than doubling in size from 2008 to 2021, the market research sector brought in over $76.4 (Statista) billion worldwide in 2021.
What is Market Research?
Market research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market, about the product or service to be offered for sale in that market. It is also about the previous, current, and potential customers for the product or service.
Data collection, analysis, and interpretation are the three main steps in any successful market research project. The data could pertain to a certain demographic, general consumers, rival businesses, or the entire market. This is the cornerstone of any thriving business. The findings can be used for anything from discovering a fresh opportunity to entering the market to developing an entirely new product or service.
Small business owners can benefit greatly from conducting market research. It can eliminate uncertainty in the creative process and direct energy and funding toward the most promising ideas and initiatives. Many types of market research are conducted by businesses at many different stages.
Market Research for Businesses
Accurate and comprehensive data gives a plethora of information on potential and existing customers, competitors, and the industry as a whole, making it the bedrock of any successful commercial endeavor. It helps entrepreneurs weigh the odds of success before sinking a lot of money into a new firm.
.jpg)
An essential aspect of every successful business plan is conducting market research to gather data that can be used to address potential marketing obstacles. In reality, it is not viable to develop tactics like market segmentation (identifying distinct groups within a market) and product differentiation (establishing a unique selling proposition for a product or service that distinguishes it from the competition) without conducting market research.
Types of Market Research
1. quantitative research .
The results of quantitative studies are typically presented using numerical and graphic representations. It's the gold standard for verifying or disproving hypotheses. It is possible to establish broad, overarching truths about a subject by conducting this kind of study. Experiments, numerically recorded observations, and surveys with a limited number of predetermined answer choices are all examples of common quantitative approaches.
2. Qualitative research
Words are the currency of qualitative inquiry. It's a tool for making sense of things like ideas and experiences. Using this method, you can learn more about a topic from every angle, which is very useful for researching controversial or poorly understood subjects. Open-ended interviews, written descriptions of observations, and in-depth analyses of the existing literature are all examples of common qualitative techniques.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research
Quantitative research focuses on numerical and statistical facts, while qualitative research examines concepts and interpretations. Both are necessary to learn various things. Comparatively, qualitative research draws its conclusions from interviews and documents rather than statistics and reasoning. Quantitative studies typically report their findings numerically or graphically, while qualitative studies report their findings verbally.
3. Primary Research
Primary data refers to a study that seeks to collect firsthand information from real-world participants. Primary research is data collected by the researcher themselves through various techniques of approaching the target audience directly. You have full legal and ethical rights to the data set you to create. Primary research can be challenging due to the time, money, resources, and familiarity with the topic that it demands.
4. Secondary Research
Secondary research is a study that is done after primary research has already been conducted, and it consists of analyzing, interpreting, and summarizing the results of the primary research. A more precise definition of secondary research would be any study that makes use of publicly available data. When conducting secondary research, scholars refer to information that has already been gathered, processed, and made public (and therefore, you do not own this data). Since the accessible data has already been evaluated and interpreted, the researcher just needs to determine the data he wants to use, i.e., the data that is necessary for his project.
Primary Research vs. Secondary Research
Research that involves the collection of new information, or "primary" research, is distinguished from secondary research by the fact that it is conducted for the first time on a particular topic. Instead, secondary research makes use of information that has previously been gathered through primary research. The fundamental dividing line between primary and secondary research is whether the research has been done before.
5. Market Research
Market research on branding can help a business develop, launch, and sustain its brand. This may involve the firm's ethos, branding, visuals, ideals, or very name. Interviews, focus groups, and surveys are all viable options for conducting research.
6. Customer Research
Market research on customers is learning what factors most strongly affect your demographic of interest and what adjustments may be made to better attract and retain them as paying customers. The objective of this study is to acquire an intimate understanding of your consumer base and their habits and preferences as they relate to your business.
7. Competitor Research
Conducting market research on your competitors entails learning about their businesses and assessing how they stack up against your own. Your competitive product in the market or how to break into a new market could also be a topic of discussion. The study's overarching goal is to help your company prepare for the future by identifying methods to set itself apart from competitors and by learning from customers' opinions and suggestions.
8. Product Research
Conducting market research on your items is essential to ensuring they will sell successfully once they hit the shelves. Finding out how people feel about your product and if they feel it's valuable and functioning properly is the goal of this study. The ability to think creatively about enhancements and new features is another benefit.
Benefits of Market Research
According to a survey, the market research business is expected to increase at a rate of 12-14% (The Economic Times) per year through FY26, at which point it would have surpassed the $4 billion mark.

The following is a list of the most important reasons and benefits of marketing research:
It's a great tool for boosting companies' standing. The ability to think critically and act on that thinking is the key to success. You can keep your business one step ahead of the competition by conducting market research to expand your knowledge of your market or target audience.
Reduces the potential for loss on an investment. This is a basic point to think about, but it is often crucial to the success of a firm. When starting a firm, it makes sense to spend what amounts to a negligible amount on research and testing the market, product, concept, or idea.
Possible dangers and benefits are highlighted. Insurance against these two glaring pitfalls lies in both primary research (fieldwork) and secondary research (desk research). Opportunities or red flags may be uncovered through the combination of this with qualitative research for further investigation.
You can learn more about the advantages and disadvantages of your own business and of your competitors. To achieve entirely objective reporting, it is generally recommended to collaborate with a market research agency. Take advantage of what you've learned from study to improve in areas where you're weak and to gain an edge over the competition.
Strategic preparation is helped by this. Where do you stand with the core principles of your company plan? If it's supported by data, and you've put in the time and effort to do your own (hopefully continuous) research, you can rest assured that you're giving yourself the best chance of success in your commercial endeavors.
This aids in the identification of developing tendencies. Being the first, the best, or coming up with the idea that nobody else has is typically what it takes to stay ahead in business. Taking the pulse of your industry on a regular basis is an important habit. You can learn more about the tools available to you to identify and capitalize on these trends by consulting with a research firm or expert.
Helpful for firms in keeping up with the competition. Being the best calls for an insatiable need for knowledge and a propensity to experiment. The key to success, and the ability to maintain that success, is knowing how to effectively apply the information gleaned from market research, audience research, and data research.
It includes forecasts for future income. One of the most important parts of any market study is a forecast, which looks into the future and predicts the size, makeup, and trends of the market you're interested in. This allows for the categorization of prospective clients. You should prioritize the market that is the best fit for your business rather than the largest or fastest-growing.
It's geared toward meeting the wants and desires of its patrons. Many things in business, including research, benefit from keeping clients front and center. By reaching out to individuals through online panels, web forums, telephone surveys, in-depth interviews, and focus groups, market researchers can learn where their business's ideas, services, and products can be strengthened.
Using this method, one can measure the progress of one's company against predetermined standards. Utilize data gathered from the market to study the competition, gauge employee enthusiasm, identify knowledge or skill shortages, and identify development opportunities. This will allow you to consider novel approaches, ideas, and resources for boosting your company's efficiency.

Market Research Tools
In order to better understand your market and target audience, you need to use market research techniques. It's fundamental to every company's success, and in today's more crowded marketplace, a thorough familiarity with your target market is more important than ever. Good news: you don't have to be an "insights genius" to get started collecting the data you need, owing to the proliferation of market research tools. Some of the best and most widely used methods of market research include:
- Answer the Public
- Attest
- Google Trends
- Social Mention
- Remesh
- Heartbeat Ai
- Think With Google
- Spyfu
- Latana
- BuzzSumo
- Statista
- Typeform
- Otter.ai
- Dimensions.ai
How to Conduct Research for Your Business: Market Research Strategies
Despite their different objectives, market research and marketing research should use the same framework for gathering and analyzing information about your company's target audiences. These help in primary research as well as secondary research.
Clearly identify the problem at stake. Establish an initial research topic. Having a clear research question in mind will allow you to better organize your findings.
Start by figuring out your financial and time constraints. How much money do you have to put into your study? When do you anticipate finishing data collection? Research, like any other tactic for expanding your company, should be carried out within your means. Nonetheless, it may be worthwhile to spend more money to receive the most comprehensive results available, especially if the questions you are answering are time-sensitive.
Planning your approach and requirements. Find out what information needs to be gathered and figure out how to get it. Observation, surveys, phone calls, and focus groups are among the alternatives. Consult a professional research agency if you are unsure of how to organize your data collection.
Pick a way to sample the data. I need to know how you plan on picking people to take part in your study. You may require a cross-section of the consumer population at large, a subset of the population who share a particular characteristic of their way of life, or just the opinions of those who are already familiar with your brand. Develop a plan for tracking down and contacting the persons who will take part in your research.
Prepare a data analysis strategy. Think about the methods you'll use to examine the data. Do you require numbers for statistical analysis, or can you get a sense of things from qualitative, observable data? Spend some time learning about the many types of analysis so you can pick the one that will yield the most useful results for your study.
Gathering information. The next step is data collection, which may begin once you have settled on a research question and developed a strategy for answering it within the bounds of your time and money. Research is often outsourced to professional firms or consultants by many corporations.
Examining the information. It is important to apply certain methods of analysis to make sense of your data, no matter how simple it may appear at first. Which analytical techniques you employ are most suited to your data is a function of the information you've gathered. Also, this is the time to double-check for any mistakes that might have crept into your data gathering, analysis, or sampling.

Make the report you need. Concluding your research with a written report is the next to last stage. From formulating a problem statement to discussing the findings of your data study, your report should include it all.
Why is Market Research Important?
Over 44,000 businesses across the United States provide some form of market research. Their total annual income is around $23 billion (QuestionPro).
The importance of Market Research is the following -
1. Identifies new products or services
By conducting market research, a business can learn what consumers want and how to best meet their demands. Identifying the major challenges associated with creating a product or service can help you save money. It's useful for figuring out what customers value most and how to implement that into your product or service offering.
2. Identifies potential customers
You may learn more about your clientele by analyzing demographic information like their gender, age, income, occupation, and interests. You'll have a better idea of who to target with your future advertising efforts if you have a clear picture of your current clientele. When a product is marketed to the wrong demographic, sales suffer.
3. Establishes viability of a product or service
If your organization is considering introducing a novel product or service to consumers, you should find out if there is a need for it. Do people need this product? Do the people you plan to sell to actually want this product? Does it have any chance of succeeding, and does it even have a chance of being a viable trend?
4. Anticipates and discovers future market trends
If you are familiar with your market and the tendencies that are just beginning to emerge, you will be better prepared to build tactics to combat any negative tendencies that may threaten your company. As a result, you can use rising tendencies to your advantage and propel your company forward.
5. Keeps your company ahead of competitors
Examining your company's performance in relation to that of its rivals is a prime use for comparative research. If they're much ahead of you, it's a fantastic chance to figure out what you're doing wrong. It is possible to devise business plans that will help you surpass the competition.
6. Decide the best marketing strategy
Conducting research is helpful for pinpointing the optimal distribution platform for reaching your target audience. If you find out that a large portion of your audience prefers one form of communication over another, it makes sense to concentrate your efforts there. Because of the scarcity of these resources, it only makes sense to direct them toward endeavors with a high probability of success.
7. Reduces risk and increases profitability
The ability to assess the value of potential risks in light of past performance and anticipated future market behavior is a crucial business skill. The success or failure of a business idea depends heavily on the results of market research. Understanding your consumers and their habits is another crucial step in risk reduction. Taking less risk leads to greater financial rewards.
8. Identifies threats and opportunities
The SWOT analysis is likely familiar to many of you. The acronym SWOT refers to a company's "strengths," "weaknesses," and "All four of them can be figured out with the use of market research . While a lot of data can be collected through market research, not all of it needs to be used. Use only information that is directly related to your major objective (which you will have established in advance).
9. Helps to understand existing customers
By conducting market research, you can learn more about your current clientele. Because of this complexity, you can't assume that you know what your clients require. If you want to be successful, you need to take the temperature of your clientele on a frequent basis. Satisfaction levels among customers can also be measured with the help of surveys. You can find out what is bothering them and make adjustments if necessary. If they are already rather high, you can examine the factors that led to this success and implement changes to maintain it.
10. Assists in realistic goal setting
Goals that are more realistic can be established with the support of up-to-the-minute information on your market and customer base. Knowing what to expect and how to realistically expand growth over time is greatly aided by establishing a growth pattern throughout time. Setting objectives that are too lofty will cause you to waste time and energy trying to achieve something that is impossible.
.jpg)
How Efficient is Market Research?
You should only invest time, energy, and money into market research if you expect to see a favorable return on that investment. Because it is so worthwhile, market research continues to play a significant role in the success of any organization. Market research won't ensure your company's success on its own, but it will arm you with the data you need to make the moves that will.
Many of the advantages of this type of study were examined, but the drawbacks were also taken into account. If you don't conduct market research, you run the danger of losing clients to the competition, missing out on growth prospects, being more susceptible to hazards, making bad business decisions, and more. Some companies succeed without first doing their homework, but those situations are unusual. To build your firm and avoid typical errors, conduct market research.
Market Research Methods
Although there are a variety of approaches to conducting market research, the majority of companies opt to utilize one of the following five fundamental approaches: surveys, focus groups, personal interviews, observation, and field trials. Which strategies you decide to implement for your company will depend on the kinds of data you require as well as the amount of money you are ready to pay. Some of the major methods of market research are following -
1. Surveys
Surveys ask participants questions. They can use numerous survey methods. Surveys are a cost-effective technique to collect data for the study. Written surveys may encourage truthful responses since participants feel like they're speaking privately.
2. Discussions
Focus groups are moderated discussions. Companies assemble consumers to conduct focus groups, pose questions, and record replies. Participants' replies may reveal what consumers want in a firm or a product because they represent a broad group. Focus groups offer longer participant interaction than surveys.
3. Interviews
An interview combines focus group and one-on-one survey aspects. It includes recording one participant's comments at a time. Open-ended questions elicit in-depth answers from the interviewee. Researchers can ask follow-up questions and let interviewees ask their own.
4. Social media listening
Social media users routinely discuss corporations and their products. Researchers can search for discussion topics and measure consumer sentiment through social media listening.
5. Observations
Observation in market research means studying how consumers shop. Filming shoppers in a store and studying their shopping habits is common. This strategy can reveal their natural selves if they are ignorant of the observation.
6. Experiments
In a field trial, a corporation lets participants use a product under typical conditions and collects data. Participants' feedback was used to improve the product.
7. Competitive analysis
Competitive analysis is a secondary market research process where companies acquire and analyze competition information. It entails identifying primary and secondary rivals and analyzing their offerings, revenues, and marketing methods.
8. Statistics
Public data entails seeking and evaluating public market data. This research is often free online or in libraries. Research centers, polls, or government databases may provide this information. Public data is often used to confirm or compare primary market research.
9. Purchased data
Companies without the time or resources to perform their own market research can buy it. Several market research companies sell database subscriptions. Small and medium-sized businesses that can't afford primary market research may benefit from this approach.
10. Analysis of sales data
Competition analysis is just one way that may be used in tandem with sales data analysis to show how different business tactics affect revenue. It can also reveal consumers' buying behavior and consumer trends.
Functions of Marketing Research
The following are the main functions of Marketing Research -
Description: Marketing research details customers. Age, sex, education, income, etc., are listed. It describes the market and competitors. This description helps marketing decision-makers and problem-solvers.
Evaluation: Marketing research evaluates firm performance. It evaluates production and marketing policies. It measures customer reactions to product quality, price, packaging, advertising, sales, and promotions. If consumers dislike the company's policies, they must alter them. It contrasts company and rival policies.

Explanation: Marketing research answers all marketing questions. It explains why sales are declining, why retailers are unhappy, etc. It explains the problem's causes. It gives a solution.
Prediction: Marketing research forecasts. Predictions are future forecasts. It predicts sales, market prospects, dangers, marketing environment, customer behavior, etc. All predictions may be wrong. Predictions help the organization create plans and policies. It helps seize possibilities. It prevents future hazards.
Decision Making: Marketing research aids decision-makers. It gives decision-making data. Decision-making involves choosing between options. Decision-making requires accurate data. MR helps the marketer decide. It gives decision-making data. It offers alternatives. It compares each option's pros and cons. It helps marketing managers choose the right action.
Conclusion
The world's markets are changing at a dizzying rate, making it more important than ever for companies to adapt quickly enough to be competitive. One method is to conduct market research. The results of your market research and analysis will provide you with a thorough understanding of your target audience's wants and needs, as well as your competitors' strengths and weaknesses.
The key to making your business successful in the face of intense competition is identifying and fixing your deficiencies. The right market research tools will aid you in doing just that! The time to begin expanding your company is now.
With a presence in New York, San Francisco, Austin, Seattle, Toronto, London, Zurich, Pune, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, SG Analytics, a pioneer in Research and Analytics, offers tailor-made services to enterprises worldwide.
A leader in Market research services , SG Analytics enables organizations to achieve actionable insights into products, technology, customers, competition, and the marketplace to make insight-driven decisions. Contact us today if you are an enterprise looking to make critical data-driven decisions to prompt accelerated growth and breakthrough performance.
Our Services
Investment Insights
Market Research
Data Analytics
ESG Services
Data Solutions
ESG Data Services
Technology Services
Investment Banking
Private Equity and Venture Capital
Private Equity/VC
ESG Data and Research
Marketing Analytics
Advanced Analytics
Customer Analytics
Hedge Fund Services
Market Intelligence
Equity Research
Recent Blogs

The Importance of Sustainable Data Centers in the Age of AI

Harnessing the Power of Data for Data-driven Decision-Making and Business Growth

Where Data Meets Dominance: Unleashing the Power of Data

Exploring ESG Investment Options: Ways Your Business Portfolio Can Save the Planet

Nurturing an Inclusive Workplace: Strategies to Foster Diversity, Equity, & Inclusion

NAB 2024 Key Trends

A Shift toward Sustainable Media Consumption Imminent

ESG Global Enterprise Pulse Survey 2023: Key Findings
Future Trends and Technological Advances in Vaccine and Disease Prevention

SGA Knowledge Team
We are a dynamic team of subject matter experts who create informative, relevant and...
START YOUR ECOMMERCE BUSINESS FOR JUST $1
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
A magazine for young entrepreneurs
The best advice in entrepreneurship
Subscribe for exclusive access, the complete guide to market research: what it is, why you need it, and how to do it.

Written by Mary Kate Miller | June 1, 2021
Comments -->

Get real-time frameworks, tools, and inspiration to start and build your business. Subscribe here
Market research is a cornerstone of all successful, strategic businesses. It can also be daunting for entrepreneurs looking to launch a startup or start a side hustle . What is market research, anyway? And how do you…do it?
We’ll walk you through absolutely everything you need to know about the market research process so that by the end of this guide, you’ll be an expert in market research too. And what’s more important: you’ll have actionable steps you can take to start collecting your own market research.
What Is Market Research?
Market research is the organized process of gathering information about your target customers and market. Market research can help you better understand customer behavior and competitor strengths and weaknesses, as well as provide insight for the best strategies in launching new businesses and products. There are different ways to approach market research, including primary and secondary research and qualitative and quantitative research. The strongest approaches will include a combination of all four.
“Virtually every business can benefit from conducting some market research,” says Niles Koenigsberg of Real FiG Advertising + Marketing . “Market research can help you piece together your [business’s] strengths and weaknesses, along with your prospective opportunities, so that you can understand where your unique differentiators may lie.” Well-honed market research will help your brand stand out from the competition and help you see what you need to do to lead the market. It can also do so much more.
The Purposes of Market Research
Why do market research? It can help you…
- Pinpoint your target market, create buyer personas, and develop a more holistic understanding of your customer base and market.
- Understand current market conditions to evaluate risks and anticipate how your product or service will perform.
- Validate a concept prior to launch.
- Identify gaps in the market that your competitors have created or overlooked.
- Solve problems that have been left unresolved by the existing product/brand offerings.
- Identify opportunities and solutions for new products or services.
- Develop killer marketing strategies .
What Are the Benefits of Market Research?
Strong market research can help your business in many ways. It can…
- Strengthen your market position.
- Help you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
- Help you identify your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimize risk.
- Center your customers’ experience from the get-go.
- Help you create a dynamic strategy based on market conditions and customer needs/demands.
What Are the Basic Methods of Market Research?
The basic methods of market research include surveys, personal interviews, customer observation, and the review of secondary research. In addition to these basic methods, a forward-thinking market research approach incorporates data from the digital landscape like social media analysis, SEO research, gathering feedback via forums, and more. Throughout this guide, we will cover each of the methods commonly used in market research to give you a comprehensive overview.
Primary vs. Secondary Market Research
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own.
This approach is limited, however. It’s likely that the research objectives of these secondary data points differ from your own, and it can be difficult to confirm the veracity of their findings.
Primary Market Research
Primary research is more labor intensive, but it generally yields data that is exponentially more actionable. It can be conducted through interviews, surveys, online research, and your own data collection. Every new business should engage in primary market research prior to launch. It will help you validate that your idea has traction, and it will give you the information you need to help minimize financial risk.
You can hire an agency to conduct this research on your behalf. This brings the benefit of expertise, as you’ll likely work with a market research analyst. The downside is that hiring an agency can be expensive—too expensive for many burgeoning entrepreneurs. That brings us to the second approach. You can also do the market research yourself, which substantially reduces the financial burden of starting a new business .
Secondary Market Research
Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be beneficial to start your market research with secondary sources because it’s widely available and often free-to-access. This information will help you gain a broad overview of the market conditions for your new business.
Identify Your Goals and Your Audience
Before you begin conducting interviews or sending out surveys, you need to set your market research goals. At the end of your market research process, you want to have a clear idea of who your target market is—including demographic information like age, gender, and where they live—but you also want to start with a rough idea of who your audience might be and what you’re trying to achieve with market research.
You can pinpoint your objectives by asking yourself a series of guiding questions:
- What are you hoping to discover through your research?
- Who are you hoping to serve better because of your findings?
- What do you think your market is?
- Who are your competitors?
- Are you testing the reception of a new product category or do you want to see if your product or service solves the problem left by a current gap in the market?
- Are you just…testing the waters to get a sense of how people would react to a new brand?
Once you’ve narrowed down the “what” of your market research goals, you’re ready to move onto how you can best achieve them. Think of it like algebra. Many math problems start with “solve for x.” Once you know what you’re looking for, you can get to work trying to find it. It’s a heck of a lot easier to solve a problem when you know you’re looking for “x” than if you were to say “I’m gonna throw some numbers out there and see if I find a variable.”

How to Do Market Research
This guide outlines every component of a comprehensive market research effort. Take into consideration the goals you have established for your market research, as they will influence which of these elements you’ll want to include in your market research strategy.
Secondary Data
Secondary data allows you to utilize pre-existing data to garner a sense of market conditions and opportunities. You can rely on published market studies, white papers, and public competitive information to start your market research journey.
Secondary data, while useful, is limited and cannot substitute your own primary data. It’s best used for quantitative data that can provide background to your more specific inquiries.
Find Your Customers Online
Once you’ve identified your target market, you can use online gathering spaces and forums to gain insights and give yourself a competitive advantage. Rebecca McCusker of The Creative Content Shop recommends internet recon as a vital tool for gaining a sense of customer needs and sentiment. “Read their posts and comments on forums, YouTube video comments, Facebook group [comments], and even Amazon/Goodreads book comments to get in their heads and see what people are saying.”
If you’re interested in engaging with your target demographic online, there are some general rules you should follow. First, secure the consent of any group moderators to ensure that you are acting within the group guidelines. Failure to do so could result in your eviction from the group.
Not all comments have the same research value. “Focus on the comments and posts with the most comments and highest engagement,” says McCusker. These high-engagement posts can give you a sense of what is already connecting and gaining traction within the group.
Social media can also be a great avenue for finding interview subjects. “LinkedIn is very useful if your [target customer] has a very specific job or works in a very specific industry or sector. It’s amazing the amount of people that will be willing to help,” explains Miguel González, a marketing executive at Dealers League . “My advice here is BE BRAVE, go to LinkedIn, or even to people you know and ask them, do quick interviews and ask real people that belong to that market and segment and get your buyer persona information first hand.”
Market research interviews can provide direct feedback on your brand, product, or service and give you a better understanding of consumer pain points and interests.
When organizing your market research interviews, you want to pay special attention to the sample group you’re selecting, as it will directly impact the information you receive. According to Tanya Zhang, the co-founder of Nimble Made , you want to first determine whether you want to choose a representative sample—for example, interviewing people who match each of the buyer persona/customer profiles you’ve developed—or a random sample.
“A sampling of your usual persona styles, for example, can validate details that you’ve already established about your product, while a random sampling may [help you] discover a new way people may use your product,” Zhang says.
Market Surveys
Market surveys solicit customer inclinations regarding your potential product or service through a series of open-ended questions. This direct outreach to your target audience can provide information on your customers’ preferences, attitudes, buying potential, and more.
Every expert we asked voiced unanimous support for market surveys as a powerful tool for market research. With the advent of various survey tools with accessible pricing—or free use—it’s never been easier to assemble, disseminate, and gather market surveys. While it should also be noted that surveys shouldn’t replace customer interviews , they can be used to supplement customer interviews to give you feedback from a broader audience.
Who to Include in Market Surveys
- Current customers
- Past customers
- Your existing audience (such as social media/newsletter audiences)
Example Questions to Include in Market Surveys
While the exact questions will vary for each business, here are some common, helpful questions that you may want to consider for your market survey. Demographic Questions: the questions that help you understand, demographically, who your target customers are:
- “What is your age?”
- “Where do you live?”
- “What is your gender identity?”
- “What is your household income?”
- “What is your household size?”
- “What do you do for a living?”
- “What is your highest level of education?”
Product-Based Questions: Whether you’re seeking feedback for an existing brand or an entirely new one, these questions will help you get a sense of how people feel about your business, product, or service:
- “How well does/would our product/service meet your needs?”
- “How does our product/service compare to similar products/services that you use?”
- “How long have you been a customer?” or “What is the likelihood that you would be a customer of our brand?
Personal/Informative Questions: the deeper questions that help you understand how your audience thinks and what they care about.
- “What are your biggest challenges?”
- “What’s most important to you?”
- “What do you do for fun (hobbies, interests, activities)?”
- “Where do you seek new information when researching a new product?”
- “How do you like to make purchases?”
- “What is your preferred method for interacting with a brand?”
Survey Tools
Online survey tools make it easy to distribute surveys and collect responses. The best part is that there are many free tools available. If you’re making your own online survey, you may want to consider SurveyMonkey, Typeform, Google Forms, or Zoho Survey.
Competitive Analysis
A competitive analysis is a breakdown of how your business stacks up against the competition. There are many different ways to conduct this analysis. One of the most popular methods is a SWOT analysis, which stands for “strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.” This type of analysis is helpful because it gives you a more robust understanding of why a customer might choose a competitor over your business. Seeing how you stack up against the competition can give you the direction you need to carve out your place as a market leader.
Social Media Analysis
Social media has fundamentally changed the market research landscape, making it easier than ever to engage with a wide swath of consumers. Follow your current or potential competitors on social media to see what they’re posting and how their audience is engaging with it. Social media can also give you a lower cost opportunity for testing different messaging and brand positioning.
SEO Analysis and Opportunities
SEO analysis can help you identify the digital competition for getting the word out about your brand, product, or service. You won’t want to overlook this valuable information. Search listening tools offer a novel approach to understanding the market and generating the content strategy that will drive business. Tools like Google Trends and Awario can streamline this process.
Ready to Kick Your Business Into High Gear?
Now that you’ve completed the guide to market research you know you’re ready to put on your researcher hat to give your business the best start. Still not sure how actually… launch the thing? Our free mini-course can run you through the essentials for starting your side hustle .

About Mary Kate Miller
Mary Kate Miller writes about small business, real estate, and finance. In addition to writing for Foundr, her work has been published by The Washington Post, Teen Vogue, Bustle, and more. She lives in Chicago.
Related Posts

How to Create a Marketing Plan In 2024 (Template + Examples)
What Is UGC and Why It’s a Must-Have for Your Brand

Ad Expert Phoenix Ha on How to Make Creative Ads without Breaking Your Budget
14 Punchy TikTok Marketing Strategies to Amplify Your Growth

How to Grow Your YouTube Channel and Gain Subscribers Quickly

How to Get More Views on Snapchat with These 12 Tactics

12 Instagram Growth Hacks For More Engaged Followers (Without Running Ads)

Create Viral Infographics That Boost Your Organic Traffic
How to Create a Video Sales Letter (Tips and Tricks from a 7-Figure Copywriter)

How to Write a Sales Email That Converts in 2024

What Is a Media Kit: How to Make One in 2024 (With Examples)

Namestorming: How to Choose a Brand Name in 20 Minutes or Less

10 Ways to Increase Brand Awareness without Increasing Your Budget

What Is a Content Creator? A Deep Dive Into This Evolving Industry

Content Creator vs Influencer: What’s the Difference?
FREE TRAINING FROM LEGIT FOUNDERS
Actionable Strategies for Starting & Growing Any Business.
Don't Miss Out! Get Instant Access to foundr+ for Just $1!
1000+ lessons. customized learning. 30,000+ strong community..

- Entrepreneurs
- News About Crunchbase
- New Features
- Partnerships

The Types of Market Research [+10 Market Research Methods]
- Market research
Jaclyn Robinson, Senior Manager of Content Marketing at Crunchbase
Market research can help startups understand where they should be placing their resources and time. It can tell you everything from how people are perceiving your company, as well as which features to drop or continue developing. And while there are plenty of ways to conduct market research, not every market research method is right for every situation.
Search less. Close more.
Grow your revenue with all-in-one prospecting solutions powered by the leader in private-company data.
Market research can help play a major role in developing your product, marketing, and overall business strategy. Understanding the different market research methods can be the difference between wasting months of engineering time or exceeding your ambitious revenue targets.
We review the types of market research as well as the market research methods you can pursue based on your primary objectives and business goals.
The 2 types of market research
All market research falls under two distinct categories: primary research and secondary research.
Primary research looks at any data you collect yourself (or someone you pay). It encompasses analyzing current sales, metrics, and customers. It also takes into account the effectiveness of current practices, while taking competitors into account.
Secondary research looks at data that has already been published by others. It includes reports and studies from other companies, government organizations, and others in your industry.
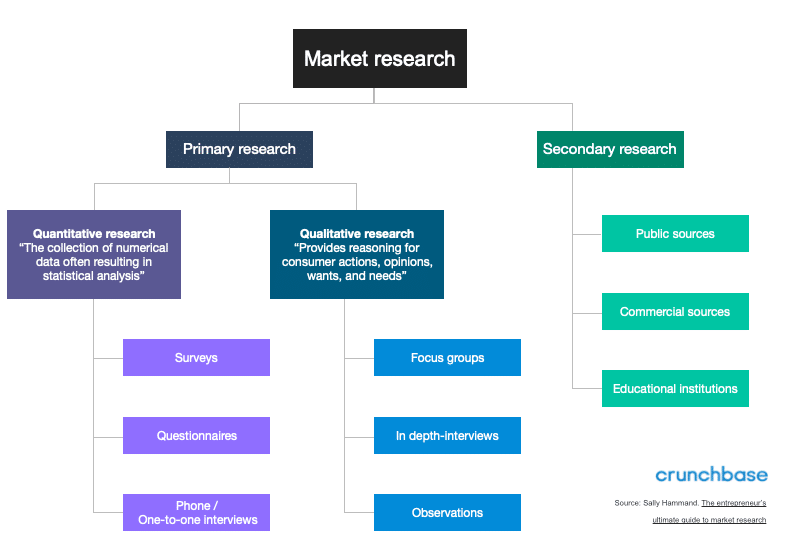
10 market research methods
The type of data you need will decide which market research technique to use. Here are the most commonly used market research methods:
Primary research methods
These primary research methods will help you identify both qualitative and quantitative data. Qualitative data is information that cannot be measured while qualitative data is taken from a large sample size and is a statistically significant mathematical analysis.
1. Interviews
Great for: expert advice
Consisting of one-on-one discussions, interviews are a great source of qualitative data. You can either perform interviews by telephone, video conference, or face-to-face. Interviews are great for an in-depth look for target audience insights.
In-depth interviews are great when expert advice is needed or when discussing highly complex or sensitive topics. Interviews are usually 10 to 30 minutes long with 25 to 75 respondents.
Great for: understanding brand awareness, satisfaction and loyalty analysis, pricing research, and market segmentation .
One of the most commonly used market research methods, Surveys are an easy way to understand your target audience and allow you to test a large sample size to determine if findings are true across a larger segment of your customers.
3. Questionnaires
Great for: Customer feedback and satisfaction surveys (NPS surveys), and when you want more detail on your target audience and customer base.
Do not confuse questionnaires for surveys ! While surveys are aggregated for statistical analysis, questionnaires are a set of written questions used for collecting information.
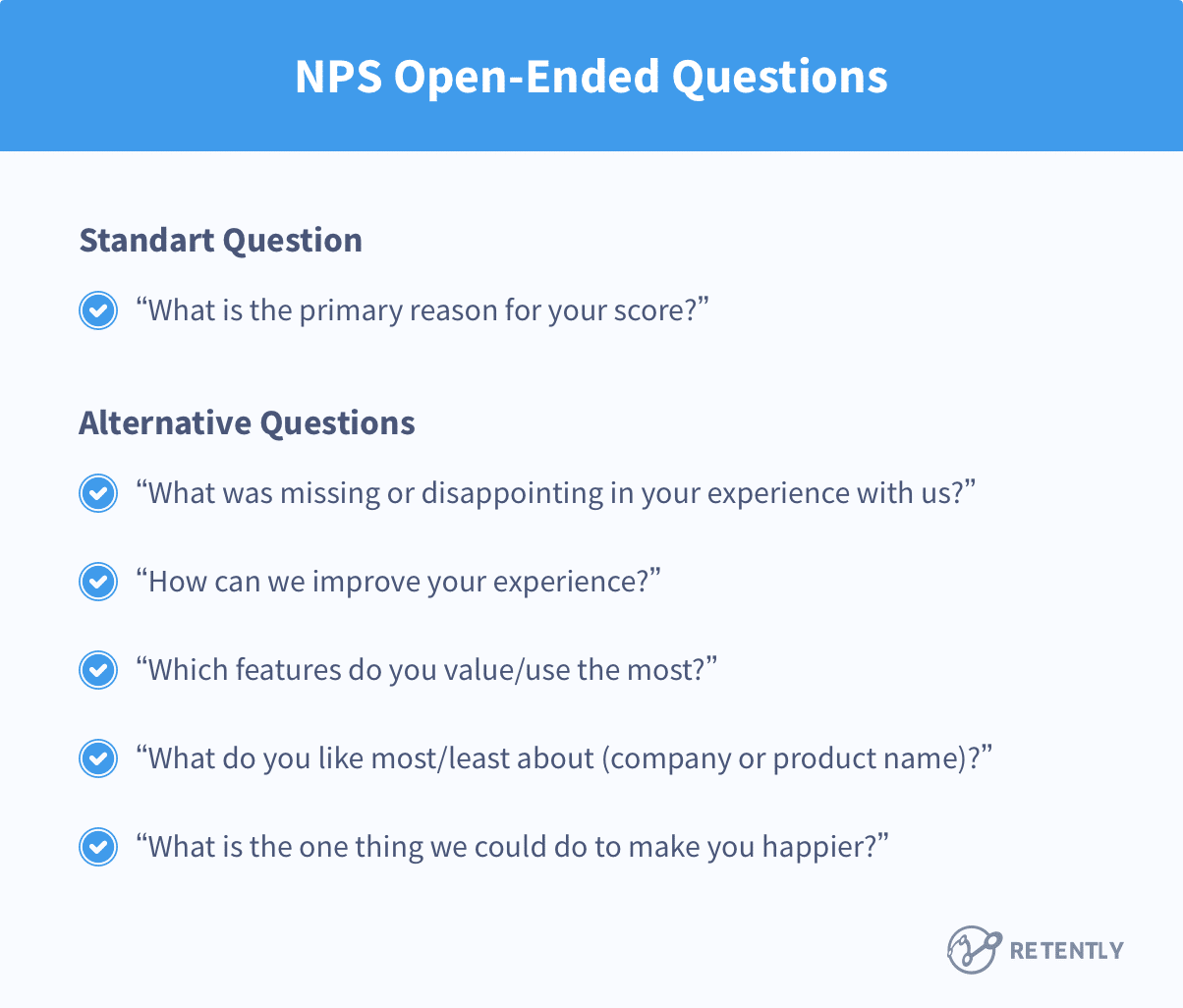
Questionnaires are used to collect information rather than draw a conclusion. Surveys can include a questionnaire, but a survey must aggregate and analyze the responses to the questions.
When writing questionnaires for market research, keep the number of questions in mind.
In one study, SurveyMonkey found that questionnaires with 40 questions have about a 10% lower response rate than questionnaires with 10 questions . The more questions, the less likely people will finish your questionnaire.
4. Focus groups
Great for: Price testing, advertising concepts, product/messaging testing
Even with the rise of big data, focus groups have remained an integral part of how companies build their products, strategy, and messaging. Focus groups are intentionally compromised by a group of purposefully selected individuals. Above all, the collaborative setting ensures that members of the group are able to interact and influence each other.
Typically these open and interactive groups are composed of around five to 12 screened individuals . Make sure that your participants are diverse so you can get a range of opinions and you have enough representation from several segments of your market.
Many smaller startups will conduct DIY focus groups and will use video conferencing technology, which is one of the most cost-effective and time-efficient market research methods.
This is a great resource to see some good questions to ask your focus groups as well as what topics focus groups should touch on.
5. User groups
Great for: Feature testing, UX and web design feedback
User groups are used to gather UX data and provide insight for website design. User groups usually meet regularly to discuss their experience with a product, while researchers capture their comments.
Here’s a great guide on how to format questions for user groups .
6. Test markets
Great for: Testing new marketing campaigns
Test markets represent a larger market. Using a test group as well as a control group can show you the success of a new landing page, messaging copy, or CTA button. We particularly like the free version of Google Optimize to get quantitative data on how your experiment is performing based on a specific goal.
Secondary research methods
Secondary research can help establish a starting point prior to diving into more expensive primary research techniques. While there is a lot of data on the web regarding basic statistics, you may have to purchase a distinct data provider for a more in-depth look at your market.
Crunchbase Pro and Marketplace partners are a great and inexpensive way to start your secondary research directly on Crunchbase.com.
7. Competitor benchmarks
Great for: Understanding your revenue, churn, operating costs, sales, profit margin, and burn rate.
Competitor benchmarks are the most valuable and widely used of the secondary research methods. Moreover, competitor benchmarks measure specific growth metrics or key performance indicators in comparison to business within the same industry and of a similar size.
You can use Crunchbase Pro to find how much companies in a certain industry are raising and who are the leading players with our global coverage on companies ranging from pre-seed to late-stage. So, as one of the most informative of the market research methods, competitive benchmarks are a great way to inform your business strategy.
Free Crunchbase registered users have access to revenue estimates as well as web traffic data.
8. Sales data
Great for: Understanding your audience and where to place marketing efforts.
Taking a look at internal sales data not only reveals profitability but also helps market researchers segment customer trends.
However, taking a look at competitive sales data is a great way to make sure that you’re meeting the numbers you should be targeting as well as capturing the full potential of the market
9. Government publications and statistics
Great for: General demographic information and larger trends
The U.S. Census Bureau is a great resource of national demographic data. You can also review patents as a preview of industry trends and future innovation.
Also, you can find additional data and research from Data.gov , The World Bank , as well as the Pew Research Center to help inform your market research decisions.
10. Commercial data
Great for: Greater insight into industry trends and reports
If you’re interested in purchasing secondary market research, commercial data is available. For comprehensive reports, Mintel and IBISWorld are both traditional market research companies that provide commercial data.
Additionally, to choose which type of market research method is best for your goal, follow this graph from Relevant Insights. Begin with the metric you’re trying to move and then backtrack into a targeted market research method.
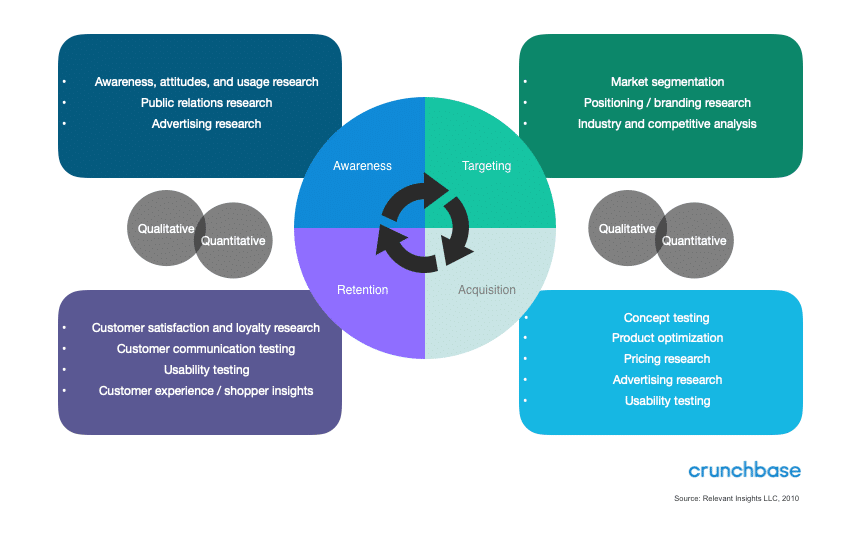
How can Crunchbase help with my market research?
Crunchbase gives market researchers flexible access to Crunchbase’s complete company data. Innovative teams and leaders in market research rely on Crunchbase’s live company data to build powerful internal databases and research insights in respective industries. Learn more about how Crunchbase can help you with your market research .

- Originally published March 14, 2019, updated April 26, 2023
You may also like

- 10 min read
How to Do Market Research for a Startup: Tips for Success

Eastern Europe Industry Review: Russia-Connected SPACs, New VC Darlings, Food Delivery Disruption
By Adrien Henni, Chief Editor, East-West Digital News

Women In Russian VC: How Gender Stereotypes Hinder Investment
Daria Zharkova, Senior Research Manager at Dsight
The all-in-one prospecting solution
- Find the right companies
- Identify the right contacts
- Connect with decision-makers
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
Market research definition
Market research – in-house or outsourced, market research in the age of data, when to use market research.
- Types of market research
Different types of primary research
How to do market research (primary data), how to do secondary market research, communicating your market research findings, choose the right platform for your market research, try qualtrics for free, the ultimate guide to market research: how to conduct it like a pro.
27 min read Wondering how to do market research? Or even where to start learning about it? Use our ultimate guide to understand the basics and discover how you can use market research to help your business.
Market research is the practice of gathering information about the needs and preferences of your target audience – potential consumers of your product.
When you understand how your target consumer feels and behaves, you can then take steps to meet their needs and mitigate the risk of an experience gap – where there is a shortfall between what a consumer expects you to deliver and what you actually deliver. Market research can also help you keep abreast of what your competitors are offering, which in turn will affect what your customers expect from you.
Market research connects with every aspect of a business – including brand , product , customer service , marketing and sales.
Market research generally focuses on understanding:
- The consumer (current customers, past customers, non-customers, influencers))
- The company (product or service design, promotion, pricing, placement, service, sales)
- The competitors (and how their market offerings interact in the market environment)
- The industry overall (whether it’s growing or moving in a certain direction)
Free eBook: 2024 market research trends report
Why is market research important?
A successful business relies on understanding what like, what they dislike, what they need and what messaging they will respond to. Businesses also need to understand their competition to identify opportunities to differentiate their products and services from other companies.
Today’s business leaders face an endless stream of decisions around target markets, pricing, promotion, distribution channels, and product features and benefits . They must account for all the factors involved, and there are market research studies and methodologies strategically designed to capture meaningful data to inform every choice. It can be a daunting task.
Market research allows companies to make data-driven decisions to drive growth and innovation.
What happens when you don’t do market research?
Without market research, business decisions are based at best on past consumer behavior, economic indicators, or at worst, on gut feel. Decisions are made in a bubble without thought to what the competition is doing. An important aim of market research is to remove subjective opinions when making business decisions. As a brand you are there to serve your customers, not personal preferences within the company. You are far more likely to be successful if you know the difference, and market research will help make sure your decisions are insight-driven.
Traditionally there have been specialist market researchers who are very good at what they do, and businesses have been reliant on their ability to do it. Market research specialists will always be an important part of the industry, as most brands are limited by their internal capacity, expertise and budgets and need to outsource at least some aspects of the work.
However, the market research external agency model has meant that brands struggled to keep up with the pace of change. Their customers would suffer because their needs were not being wholly met with point-in-time market research.
Businesses looking to conduct market research have to tackle many questions –
- Who are my consumers, and how should I segment and prioritize them?
- What are they looking for within my category?
- How much are they buying, and what are their purchase triggers, barriers, and buying habits?
- Will my marketing and communications efforts resonate?
- Is my brand healthy ?
- What product features matter most?
- Is my product or service ready for launch?
- Are my pricing and packaging plans optimized?
They all need to be answered, but many businesses have found the process of data collection daunting, time-consuming and expensive. The hardest battle is often knowing where to begin and short-term demands have often taken priority over longer-term projects that require patience to offer return on investment.
Today however, the industry is making huge strides, driven by quickening product cycles, tighter competition and business imperatives around more data-driven decision making. With the emergence of simple, easy to use tools , some degree of in-house market research is now seen as essential, with fewer excuses not to use data to inform your decisions. With greater accessibility to such software, everyone can be an expert regardless of level or experience.
How is this possible?
The art of research hasn’t gone away. It is still a complex job and the volume of data that needs to be analyzed is huge. However with the right tools and support, sophisticated research can look very simple – allowing you to focus on taking action on what matters.
If you’re not yet using technology to augment your in-house market research, now is the time to start.
The most successful brands rely on multiple sources of data to inform their strategy and decision making, from their marketing segmentation to the product features they develop to comments on social media. In fact, there’s tools out there that use machine learning and AI to automate the tracking of what’s people are saying about your brand across all sites.
The emergence of newer and more sophisticated tools and platforms gives brands access to more data sources than ever and how the data is analyzed and used to make decisions. This also increases the speed at which they operate, with minimal lead time allowing brands to be responsive to business conditions and take an agile approach to improvements and opportunities.
Expert partners have an important role in getting the best data, particularly giving access to additional market research know-how, helping you find respondents , fielding surveys and reporting on results.
How do you measure success?
Business activities are usually measured on how well they deliver return on investment (ROI). Since market research doesn’t generate any revenue directly, its success has to be measured by looking at the positive outcomes it drives – happier customers, a healthier brand, and so on.
When changes to your products or your marketing strategy are made as a result of your market research findings, you can compare on a before-and-after basis to see if the knowledge you acted on has delivered value.
Regardless of the function you work within, understanding the consumer is the goal of any market research. To do this, we have to understand what their needs are in order to effectively meet them. If we do that, we are more likely to drive customer satisfaction , and in turn, increase customer retention .
Several metrics and KPIs are used to gauge the success of decisions made from market research results, including
- Brand awareness within the target market
- Share of wallet
- CSAT (customer satisfaction)
- NPS (Net Promoter Score)
You can use market research for almost anything related to your current customers, potential customer base or target market. If you want to find something out from your target audience, it’s likely market research is the answer.
Here are a few of the most common uses:
Buyer segmentation and profiling
Segmentation is a popular technique that separates your target market according to key characteristics, such as behavior, demographic information and social attitudes. Segmentation allows you to create relevant content for your different segments, ideally helping you to better connect with all of them.
Buyer personas are profiles of fictional customers – with real attributes. Buyer personas help you develop products and communications that are right for your different audiences, and can also guide your decision-making process. Buyer personas capture the key characteristics of your customer segments, along with meaningful insights about what they want or need from you. They provide a powerful reminder of consumer attitudes when developing a product or service, a marketing campaign or a new brand direction.
By understanding your buyers and potential customers, including their motivations, needs, and pain points, you can optimize everything from your marketing communications to your products to make sure the right people get the relevant content, at the right time, and via the right channel .
Attitudes and Usage surveys
Attitude & Usage research helps you to grow your brand by providing a detailed understanding of consumers. It helps you understand how consumers use certain products and why, what their needs are, what their preferences are, and what their pain points are. It helps you to find gaps in the market, anticipate future category needs, identify barriers to entry and build accurate go-to-market strategies and business plans.
Marketing strategy
Effective market research is a crucial tool for developing an effective marketing strategy – a company’s plan for how they will promote their products.
It helps marketers look like rock stars by helping them understand the target market to avoid mistakes, stay on message, and predict customer needs . It’s marketing’s job to leverage relevant data to reach the best possible solution based on the research available. Then, they can implement the solution, modify the solution, and successfully deliver that solution to the market.
Product development
You can conduct market research into how a select group of consumers use and perceive your product – from how they use it through to what they like and dislike about it. Evaluating your strengths and weaknesses early on allows you to focus resources on ideas with the most potential and to gear your product or service design to a specific market.
Chobani’s yogurt pouches are a product optimized through great market research . Using product concept testing – a form of market research – Chobani identified that packaging could negatively impact consumer purchase decisions. The brand made a subtle change, ensuring the item satisfied the needs of consumers. This ability to constantly refine its products for customer needs and preferences has helped Chobani become Australia’s #1 yogurt brand and increase market share.
Pricing decisions
Market research provides businesses with insights to guide pricing decisions too. One of the most powerful tools available to market researchers is conjoint analysis, a form of market research study that uses choice modeling to help brands identify the perfect set of features and price for customers. Another useful tool is the Gabor-Granger method, which helps you identify the highest price consumers are willing to pay for a given product or service.
Brand tracking studies
A company’s brand is one of its most important assets. But unlike other metrics like product sales, it’s not a tangible measure you can simply pull from your system. Regular market research that tracks consumer perceptions of your brand allows you to monitor and optimize your brand strategy in real time, then respond to consumer feedback to help maintain or build your brand with your target customers.
Advertising and communications testing
Advertising campaigns can be expensive, and without pre-testing, they carry risk of falling flat with your target audience. By testing your campaigns, whether it’s the message or the creative, you can understand how consumers respond to your communications before you deploy them so you can make changes in response to consumer feedback before you go live.
Finder, which is one of the world’s fastest-growing online comparison websites, is an example of a brand using market research to inject some analytical rigor into the business. Fueled by great market research, the business lifted brand awareness by 23 percent, boosted NPS by 8 points, and scored record profits – all within 10 weeks.
Competitive analysis
Another key part of developing the right product and communications is understanding your main competitors and how consumers perceive them. You may have looked at their websites and tried out their product or service, but unless you know how consumers perceive them, you won’t have an accurate view of where you stack up in comparison. Understanding their position in the market allows you to identify the strengths you can exploit, as well as any weaknesses you can address to help you compete better.
Customer Story
See How Yamaha Does Product Research
Types of market research
Although there are many types market research, all methods can be sorted into one of two categories: primary and secondary.
Primary research
Primary research is market research data that you collect yourself. This is raw data collected through a range of different means – surveys , focus groups, , observation and interviews being among the most popular.
Primary information is fresh, unused data, giving you a perspective that is current or perhaps extra confidence when confirming hypotheses you already had. It can also be very targeted to your exact needs. Primary information can be extremely valuable. Tools for collecting primary information are increasingly sophisticated and the market is growing rapidly.
Historically, conducting market research in-house has been a daunting concept for brands because they don’t quite know where to begin, or how to handle vast volumes of data. Now, the emergence of technology has meant that brands have access to simple, easy to use tools to help with exactly that problem. As a result, brands are more confident about their own projects and data with the added benefit of seeing the insights emerge in real-time.
Secondary research
Secondary research is the use of data that has already been collected, analyzed and published – typically it’s data you don’t own and that hasn’t been conducted with your business specifically in mind, although there are forms of internal secondary data like old reports or figures from past financial years that come from within your business. Secondary research can be used to support the use of primary research.
Secondary research can be beneficial to small businesses because it is sometimes easier to obtain, often through research companies. Although the rise of primary research tools are challenging this trend by allowing businesses to conduct their own market research more cheaply, secondary research is often a cheaper alternative for businesses who need to spend money carefully. Some forms of secondary research have been described as ‘lean market research’ because they are fast and pragmatic, building on what’s already there.
Because it’s not specific to your business, secondary research may be less relevant, and you’ll need to be careful to make sure it applies to your exact research question. It may also not be owned, which means your competitors and other parties also have access to it.
Primary or secondary research – which to choose?
Both primary and secondary research have their advantages, but they are often best used when paired together, giving you the confidence to act knowing that the hypothesis you have is robust.
Secondary research is sometimes preferred because there is a misunderstanding of the feasibility of primary research. Thanks to advances in technology, brands have far greater accessibility to primary research, but this isn’t always known.
If you’ve decided to gather your own primary information, there are many different data collection methods that you may consider. For example:
- Customer surveys
- Focus groups
- Observation
Think carefully about what you’re trying to accomplish before picking the data collection method(s) you’re going to use. Each one has its pros and cons. Asking someone a simple, multiple-choice survey question will generate a different type of data than you might obtain with an in-depth interview. Determine if your primary research is exploratory or specific, and if you’ll need qualitative research, quantitative research, or both.
Qualitative vs quantitative
Another way of categorizing different types of market research is according to whether they are qualitative or quantitative.
Qualitative research
Qualitative research is the collection of data that is non-numerical in nature. It summarizes and infers, rather than pin-points an exact truth. It is exploratory and can lead to the generation of a hypothesis.
Market research techniques that would gather qualitative data include:
- Interviews (face to face / telephone)
- Open-ended survey questions
Researchers use these types of market research technique because they can add more depth to the data. So for example, in focus groups or interviews, rather than being limited to ‘yes’ or ‘no’ for a certain question, you can start to understand why someone might feel a certain way.
Quantitative research
Quantitative research is the collection of data that is numerical in nature. It is much more black and white in comparison to qualitative data, although you need to make sure there is a representative sample if you want the results to be reflective of reality.
Quantitative researchers often start with a hypothesis and then collect data which can be used to determine whether empirical evidence to support that hypothesis exists.
Quantitative research methods include:
- Questionnaires
- Review scores
Exploratory and specific research
Exploratory research is the approach to take if you don’t know what you don’t know. It can give you broad insights about your customers, product, brand, and market. If you want to answer a specific question, then you’ll be conducting specific research.
- Exploratory . This research is general and open-ended, and typically involves lengthy interviews with an individual or small focus group.
- Specific . This research is often used to solve a problem identified in exploratory research. It involves more structured, formal interviews.
Exploratory primary research is generally conducted by collecting qualitative data. Specific research usually finds its insights through quantitative data.
Primary research can be qualitative or quantitative, large-scale or focused and specific. You’ll carry it out using methods like surveys – which can be used for both qualitative and quantitative studies – focus groups, observation of consumer behavior, interviews, or online tools.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
Research topics could include:
- Product features
- Product or service launch
- Understanding a new target audience (or updating an existing audience)
- Brand identity
- Marketing campaign concepts
- Customer experience
Step 2: Draft a research hypothesis
A hypothesis is the assumption you’re starting out with. Since you can disprove a negative much more easily than prove a positive, a hypothesis is a negative statement such as ‘price has no effect on brand perception’.
Step 3: Determine which research methods are most effective
Your choice of methods depends on budget, time constraints, and the type of question you’re trying to answer. You could combine surveys, interviews and focus groups to get a mix of qualitative and quantitative data.
Step 4: Determine how you will collect and analyze your data.
Primary research can generate a huge amount of data, and when the goal is to uncover actionable insight, it can be difficult to know where to begin or what to pay attention to.
The rise in brands taking their market research and data analysis in-house has coincided with the rise of technology simplifying the process. These tools pull through large volumes of data and outline significant information that will help you make the most important decisions.
Step 5: Conduct your research!
This is how you can run your research using Qualtrics CoreXM
- Pre-launch – Here you want to ensure that the survey/ other research methods conform to the project specifications (what you want to achieve/research)
- Soft launch – Collect a small fraction of the total data before you fully launch. This means you can check that everything is working as it should and you can correct any data quality issues.
- Full launch – You’ve done the hard work to get to this point. If you’re using a tool, you can sit back and relax, or if you get curious you can check on the data in your account.
- Review – review your data for any issues or low-quality responses. You may need to remove this in order not to impact the analysis of the data.
A helping hand
If you are missing the skills, capacity or inclination to manage your research internally, Qualtrics Research Services can help. From design, to writing the survey based on your needs, to help with survey programming, to handling the reporting, Research Services acts as an extension of the team and can help wherever necessary.
Secondary market research can be taken from a variety of places. Some data is completely free to access – other information could end up costing hundreds of thousands of dollars. There are three broad categories of secondary research sources:
- Public sources – these sources are accessible to anyone who asks for them. They include census data, market statistics, library catalogs, university libraries and more. Other organizations may also put out free data from time to time with the goal of advancing a cause, or catching people’s attention.
- Internal sources – sometimes the most valuable sources of data already exist somewhere within your organization. Internal sources can be preferable for secondary research on account of their price (free) and unique findings. Since internal sources are not accessible by competitors, using them can provide a distinct competitive advantage.
- Commercial sources – if you have money for it, the easiest way to acquire secondary market research is to simply buy it from private companies. Many organizations exist for the sole purpose of doing market research and can provide reliable, in-depth, industry-specific reports.
No matter where your research is coming from, it is important to ensure that the source is reputable and reliable so you can be confident in the conclusions you draw from it.
How do you know if a source is reliable?
Use established and well-known research publishers, such as the XM Institute , Forrester and McKinsey . Government websites also publish research and this is free of charge. By taking the information directly from the source (rather than a third party) you are minimizing the risk of the data being misinterpreted and the message or insights being acted on out of context.
How to apply secondary research
The purpose and application of secondary research will vary depending on your circumstances. Often, secondary research is used to support primary research and therefore give you greater confidence in your conclusions. However, there may be circumstances that prevent this – such as the timeframe and budget of the project.
Keep an open mind when collecting all the relevant research so that there isn’t any collection bias. Then begin analyzing the conclusions formed to see if any trends start to appear. This will help you to draw a consensus from the secondary research overall.
Market research success is defined by the impact it has on your business’s success. Make sure it’s not discarded or ignored by communicating your findings effectively. Here are some tips on how to do it.
- Less is more – Preface your market research report with executive summaries that highlight your key discoveries and their implications
- Lead with the basic information – Share the top 4-5 recommendations in bullet-point form, rather than requiring your readers to go through pages of analysis and data
- Model the impact – Provide examples and model the impact of any changes you put in place based on your findings
- Show, don’t tell – Add illustrative examples that relate directly to the research findings and emphasize specific points
- Speed is of the essence – Make data available in real-time so it can be rapidly incorporated into strategies and acted upon to maximize value
- Work with experts – Make sure you’ve access to a dedicated team of experts ready to help you design and launch successful projects
Trusted by 8,500 brands for everything from product testing to competitor analysis, Our Strategic Research software is the world’s most powerful and flexible research platform . With over 100 question types and advanced logic, you can build out your surveys and see real-time data you can share across the organization. Plus, you’ll be able to turn data into insights with iQ, our predictive intelligence engine that runs complicated analysis at the click of a button.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
The Ultimate Guide to Market Research: Types, Benefits, and Real-World Examples
Team Fratzke

Today's consumers hold a lot of power when making purchase decisions. With a quick inquiry in a search engine or search bar within a social media platform, they can access genuine reviews from their peers without relying on sales reps.
Considering this shift in consumer behavior, adjusting your marketing strategy so it caters to the modern-day buying process is essential . To achieve this, you must thoroughly understand your target audience, the market you operate in, and the factors influencing their decision-making.
This is where market research can be leveraged so you stay current with your audience and industry.
Article Overview
In this article, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about how to conduct market research, including:
- Why market research is essential for understanding your target audience, the market you operate in, and factors influencing decision-making
- What are the different types of market research, such as primary and secondary market research
- How to collect information about your customers and target market to determine the success of a new or existing product, improve your brand, and communicate your company's value
- Real-world examples of companies leveraging market research

What is market research?
Market research is a necessary process that involves collecting and documenting information about your target market and customers. This helps you determine the success of a new product, improve an existing one, or understand how your brand is perceived. You can then turn this research into profits by developing marketing strategies and campaigns to effectively communicate your company's value .
While market research can provide insights into various aspects of an industry, it is not a crystal ball that can predict everything about your customers. Market researchers typically explore multiple areas of the market, which can take several weeks or even months to get a complete picture of the business landscape.
Even by researching just one of those areas, you can gain better insights into who your buyers are and what unique value proposition you can offer them that no other business currently provides.
Of course, you can simply use your industry experience and existing customer insights to make sound judgment calls. However, it's important to note that market research provides additional benefits beyond these strategies. There are two things to consider:
- Your competitors also have experienced individuals in the industry and a customer base. Your immediate resources may equal those of your competition's immediate resources. Seeking a larger sample size for answers can provide a better edge.
- Your brand's customers do not represent the entire market's attitudes, only those who are attracted to your brand.
The market research services industry is experiencing rapid growth , indicating a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from approximately $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 5%.
Your competitors have highly skilled individuals within the industry, meaning your available personnel resources are likely similar to those of your competitors. So what are you going to do to get ahead?
You’re going to do thorough market research, which is why seeking answers from a larger sample size is essential. Remember that your customers represent only a portion of the market already attracted to your brand, and their attitudes may not necessarily reflect those of the entire market. You could be leaving money on the table by leaving out untapped customers .
Why do market research?
Market research helps you meet your buyers where they are. Understanding your buyer's problems, pain points, and desired outcomes is invaluable as our world becomes increasingly noisy and demanding. This knowledge will help you tailor your product or service to appeal to them naturally.
What’s even better is when you're ready to grow your business, market research can also guide you in developing an effective market expansion strategy.
Market research provides valuable insights into factors that impact your profits and can help you to :

- Identify where your target audience and current customers are conducting their product or service research
- Determine which competitors your target audience looks to for information, options, or purchases
- Keep up with the latest trends in your industry and understand what your buyers are interested in
- Understand who makes up your market and what challenges they are facing
- Determine what influences purchases and conversions among your target audience
- Analyze consumer attitudes about a particular topic, pain, product, or brand
- Assess the demand for the business initiatives you're investing in
- Identify unaddressed or underserved customer needs that can be turned into selling opportunities
- Understand consumer attitudes about pricing for your product or service.
Market research provides valuable information from a larger sample size of your target audience, enabling you to obtain accurate consumer attitudes. By eliminating any bias or assumptions you have about your target audience, you can make better business decisions based on the bigger picture.
As you delve deeper into your market research, you will come across two types of research: primary and secondary market research . Simply put, think of two umbrellas beneath market research - one for primary and one for secondary research. In the next section, we will discuss the difference between these two types of research. That way, if you work with a market who wants to use them, you’ll be ready with an understanding of how they can each benefit your business.
Primary vs. Secondary Research
Both primary and secondary research are conducted to collect actionable information on your product. That information can then be divided into two types: qualitative and quantitative research. Qualitative research focuses on public opinion and aims to determine how the market feels about the products currently available. On the other hand, quantitative research seeks to identify relevant trends in the data gathered from public records.
Let's take a closer look at these two types.

Primary Research
Primary research involves gathering first-hand information about your market and its customers. It can be leveraged to segment your market and create focused buyer personas . Generally, primary market research can be categorized into exploratory and specific studies.
Exploratory Primary Research
This type of primary market research is not focused on measuring customer trends; instead, it is focused on identifying potential problems worth addressing as a team. It is usually conducted as an initial step before any specific research is done and may involve conducting open-ended interviews or surveys with a small group of people.
Specific Primary Research
After conducting exploratory research, businesses may conduct specific primary research to explore issues or opportunities they have identified as necessary. Specific research involves targeting a smaller or more precise audience segment and asking questions aimed at solving a suspected problem. Specific primary research reveals problems that are unique to your audience so you can then offer a unique (and valuable) solution.
Secondary Research
Secondary research refers to collecting and analyzing data that has already been published or made available in public records. This may include market statistics, trend reports, sales data, and industry content you already can access. Secondary research really shines when you go to your competitors . The most commonly used sources of secondary market research include:
- Public sources
- Commercial sources
- Internal sources
Public Sources
When conducting secondary market research, the first and most accessible sources of information are usually free . That’s right–these public sources are free and at your fingertips so there’s no reason for you to not be checking them out and leveraging them for your own gain.
One of the most common types of public sources is government statistics. According to Entrepreneur, two examples of public market data in the United States are the U.S. Census Bureau and the Bureau of Labor & Statistics. These sources offer helpful information about the state of various industries nationwide including:
Commercial Sources
Research agencies such as Pew, Fratzke, Gartner, or Forrester often provide market reports containing industry insights from their own in-depth studies . These reports usually come at a cost if you want to download and obtain the information, but these agencies are experts at what they do, so the research is most likely valuable.
Internal Sources
Internal sources of market data can include average revenue per sale, customer retention rates, and other data on the health of old and new accounts. They are often overlooked when it comes to conducting market research because of how specific the data is; however, these sources can be valuable as they provide information on the organization's historical data.
By analyzing this information, you can gain insights into what your customers want now . In addition to these broad categories, there are various ways to conduct market research. Let’s talk about them.
Types of Market Research
- Interviews (in-person or remote)
Focus Groups
- Product/ Service Use Research
Observation-Based Research
Buyer persona research, market segmentation research, pricing research.
- Competitive Analysis Research
Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty Research
Brand awareness research, campaign research.

Interviews can be conducted face-to-face or virtually, allowing for a natural conversation flow while observing the interviewee's body language. By asking questions about themselves, the interviewee can help you create buyer personas , which are made by using information about the ideal customer, such as:
- Family size
- Challenges faced at work or in life
And other aspects of their lifestyle. This buyer profile can shape your entire marketing strategy , from the features you add to your product to the content you publish on your website. Your target audience will feel that the marketing was made just for them and will be drawn to your product or service.
Focus groups are market research involving a few carefully selected individuals who can test your product, watch a demonstration, offer feedback, and answer specific questions. This research can inspire ideas for product differentiation or highlight the unique features of your product or brand that set it apart from others in the market. This is a great market research option to gain specific feedback, which you can use to improve your services .

Product/Service Use Research
Product or service usage research provides valuable insights into how and why your target audience uses your product or service. This research can help in various ways including:
- Identifying specific features of your offering that appeal to your audience.
- Allowing you to assess the usability of your product or service for your target audience.
According to a report published in 2020, usability testing was rated the most effective method for discovering user insights, with a score of 8.7 out of 10. In comparison, digital analytics scored 7.7, and user surveys scored 6.4.
Observation-based research is a process that involves observing how your target audience members use your product or service. The way that you intended your product or service to be used may not be the actual way that it is used. Observation-based research helps you understand what works well in terms of customer experience (CX) and user experience (UX), what problems they face, and which aspects of your product or service can be improved to make it easier for them to use.
To better understand how your potential customers make purchasing decisions in your industry, it is essential to know who they are. This is where buyer persona research comes in handy. Buyer or marketing personas are fictional yet generalized representations of your ideal customers. They give you someone to whom you want your marketing efforts to empathize and move, even though they don’t really exist.
Gathering survey data and additional research to correctly identify your buyer personas will help you to visualize your audience so you can streamline your communications and inform marketing strategy . Key characteristics to include in a buyer persona are:
- Job title(s)
- Family size
- Major challenges

Market segmentation research enables you to classify your target audience into various groups or segments based on specific and defining characteristics. This method allows you to understand their needs, pain points, expectations, and goals more effectively.
Pricing research can provide valuable insights about the prices of similar products or services in your market. It can help you understand what your target audience expects to pay for your offerings and what would be a reasonable price for you to set. Correct pricing is important because if you set it too high, consumers will go to your cheaper competitor; but if you set it too low, your consumers may become suspicious of your product or service and still end up with your competitor. This information allows you to develop a solid pricing strategy aligning with your business goals and objectives.
Competitive Analysis
Competitive analyses are incredibly valuable as they provide a deep understanding of your market and industry competition. Through these analyses, you can gain insights like:
- What works well in your industry
- What your target audience is already interested in regarding products like yours
- Which competitors you should work to keep up with and surpass
- How you can differentiate yourself from the competition
Understanding customer satisfaction and loyalty is crucial to encouraging repeat business and identifying what drives customers to return (such as loyalty programs, rewards, and exceptional customer service). Researching this area will help you determine the most effective methods to keep your customers coming back again and again. If you have a CRM system, consider further utilizing automated customer feedback surveys to improve your understanding of their needs and preferences.
Brand awareness research helps you understand the level of familiarity your target audience has with your brand. It provides insights into your audience members' perceptions and associations when they think about your business.This type of research reveals what they believe your brand represents. This information is valuable for developing effective marketing strategies, improving your brand's reputation, and increasing customer loyalty .
To improve your marketing campaigns, you need to research by analyzing the success of your past campaigns among your target audience and current customers. This requires experimentation and thoroughly examining the elements that resonate with your audience. By doing so, you can identify the aspects of your campaigns that matter most to your audience and use them as a guide for future campaigns.
Now that you understand the different market research categories and types let's look at how to conduct your market research. Using our expertise and experience, we’ve created a step-by-step guide to conducting market research.
How to Do Market Research (Detailed Roadmap)
- Define the problem or objective of the research.
- Determine the type of data needed.
- Identify the sources of data.
- Collect the data.
- Analyze the data.
- Interpret the results.
- Report the findings.
- Take action based on the findings.

1. Define the problem or objective of the research
Defining the problem or objective of the research is the first step in conducting market research. This involves identifying the specific issue that the research is trying to address. It is essential to be clear and specific about the research problem or objective, as it will guide the entire research process.
2. Determine the type of data needed
After defining the research problem or objective, the next step is determining the data type needed to address the issue. This involves deciding whether to collect primary or secondary data. Primary data is collected directly from the source, while secondary data is collected from existing sources such as government reports or market research studies.
3. Identify the sources of data
Once the data type has been determined, the next step is identifying the data sources. This involves identifying potential sources of primary and secondary data that can be used to address the research problem or objective. Primary data sources can include surveys, focus groups, and interviews, while secondary data sources can include government reports, industry publications, and academic journals.
4. Collect the data
After identifying the data sources, the next step is to collect the data. This involves designing and implementing a data collection plan consistent with the research problem or objective. The data collection plan should specify the methods and procedures for collecting data, sample size, and sampling method.
5. Analyze the data
Once the data has been collected, the next step is to analyze the data. This involves organizing, summarizing, and interpreting the data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. The research problem or objective should guide the data analysis process and be conducted using appropriate statistical methods and software.
6. Interpret the results
After analyzing the data, the next step is to interpret the results. This involves drawing conclusions from the data analysis and using the results to address the research problem or objective. It is essential to analyze the results objectively and to avoid making assumptions or drawing conclusions that are not supported by the data.
7. Report the findings
Try identifying common themes to create a story and action items.To make the process easier, use your favorite presentation software to create a report, as it will make it easy to add quotes, diagrams, or call clips.
Feel free to add your flair, but the following outline should help you craft a clear summary:
- Background: What are your goals, and why did you conduct this study?
- Participants: Who you talked to? A table works well to break groups down by persona and customer/prospect.
- Executive Summary: What were the most exciting things you learned? What do you plan to do about it?
- Key Findings: Identify the key findings using data visualizations and emphasize key points.
- Recommendations + Action Plan: Your analysis will uncover actionable insights to fuel strategies and campaigns you can run to get your brand in front of buyers earlier and more effectively. Provide your list of priorities, action items , a timeline, and its impact on your business.
8. Take action based on the findings
The final step in conducting market research is to take action based on the findings. This involves using the results to make informed decisions about the marketing strategy, product development, or other business decisions. It is important to use the findings to drive action and to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the action taken continuously.
How to Prepare for Market Research Projects
Identify a persona group to engage, prepare research questions for your market research participants, list your primary competitors.
The idea is to use your persona as a reference point for understanding and reaching out to your industry's audience members. Your business might cater to more than one persona, and that's completely acceptable! However, you must be mindful of each persona while strategizing and planning your content and campaigns.
How to Identify the Right People to Engage for Market Research
When selecting a group on which to conduct market research , it is essential to consider individuals with the same characteristics as your target audience.
If you need to research multiple target audiences, recruit separate groups for each one. Select people who have recently interacted with you by looking through social media for post interactions or seeing if they’ve made recent purchases from you.
If you are planning to conduct an evaluation, it is recommended that you focus on people who have completed it within the last six months. However, if you have a longer sales cycle or a specific market, you can extend the period up to a year. It is crucial to ask detailed questions during the evaluation, so the participants' experience must be fresh.
Gather a mix of participants
If you want to expand your customer base, you’re going to want to get viewpoints of your product or service from every angle. Consider getting this mix by recruiting individuals who have already purchased your product, those who have bought a competitor's product, and those who haven't purchased anything. While targeting your existing customers may be the easiest option, gathering information from non-customers can help you gain a more balanced market perspective .
We recommend taking the following steps to select a mix of participants:
- Create a list of customers who made a recent purchase . This is usually the most accessible group to recruit. If you have a CRM system with list segmentation capabilities, run a report of deals that closed within the past six months and filter it for the characteristics you're looking for. Otherwise, work with your sales team to get them a list of appropriate accounts.
- Create a list of customers who were in an active evaluation but didn't make a purchase. You should get a mix of buyers who either purchased from a competitor or decided not to purchase. Again, you can obtain this list from your CRM or your Sales team's system to track deals.
- Use social media to call for participants. Try reaching out to people who follow you on social media but decided not to buy from you. Some may be willing to talk to you and explain why they did not purchase your product.
- Leverage your network . Spread the word that you're conducting a study to your coworkers, former colleagues, and LinkedIn connections. Even if your direct connections don't qualify, some will likely have a coworker, friend, or family member who does.
- Choose an incentive to motivate participants to spend time on your study. If you're on a tight budget , you can reward participants for free by giving them exclusive access to content.
Related Resources:
- Digital Marketing Strategy: Keep It Simple
- 5 Marketing Predictions for the Looming Recession
- Recession Proof Marketing Strategies for Your Business
- Marketing Operations Framework - The Five Ps
- Biggest Marketing Challenges Leaders Face
- Digital Marketing Benchmarks & KPIs - How To Compare Your Performance
Preparation is key when conducting research in hopes of gaining productive and informative conversations. This involves creating a discussion guide, whether it is for a focus group, an online survey, or a phone interview. The guide should help you cover all the relevant topics and manage your time efficiently.
The discussion guide should be in an outline format, with an allocated time and open-ended questions for each section. All the questions must be open-ended, as asking closed questions may lead the interviewee to respond with a simple "yes" or "no" answer. You may need more detailed answers to make informed decisions, so be sure to ask follow-up questions as necessary. Also leave out any leading questions as they may unintentionally influence the interviewee's response, skewing your research results.
It's essential to identify your competitors accurately and you may even have some hidden in plain sight. There are some instances where your company's business division might compete with your main product or service, even though that company's brand might have a different focus. Take a look at Apple: the company is known primarily for its laptops and mobile devices, but Apple Music competes with Spotify over its music streaming service.
From a content perspective, you might compete with a blog, YouTube channel, or similar publication for inbound website visitors — even though their products don't overlap with yours. An example of this is when a toothpaste company might compete with publications like Health.com or Prevention on specific blog topics related to health and hygiene, even though the magazines don't sell oral care products.
Here are a few ways to build your competitor list:
- Check your industry quadrant on G2 Crowd: This is a significant first step for secondary market research in some industries. G2 Crowd aggregates user ratings and social data to create "quadrants" that show companies as contenders, leaders, niche players, or high performers in their respective industries. G2 Crowd specializes in digital content, IT services, HR, e-commerce, and related business services.
- Download a market report: Companies like Forrester and Gartner offer free and gated market forecasts yearly on the vendors leading their industry. On Forrester's website, for example, you can select "Latest Research" from the navigation bar and browse Forrester's latest material using a variety of criteria to narrow your search. These reports are good assets to save on your computer.
- Use social media : Social networks can be excellent company directories if you use the search bar correctly. On LinkedIn, for example, select the search bar and enter the name of the industry you're pursuing. Then, under "More," select "Companies" to narrow your results to the businesses that include this or a similar industry term on their LinkedIn profile.
Identifying Content Competitors
Search engines can be beneficial when it comes to secondary market research . To identify the online publications competing with your business, start with the overarching industry term you identified earlier, and then come up with more specific industry terms that are related to your company . For example, if you run a catering business, you might consider yourself a "food service" company, as well as a vendor in "event catering," "cake catering," "baked goods," and so on.
Once you have this list, follow these steps:
- Google it: Running a search on Google for the industry terms that describe your company can be very beneficial. You may come across a mix of product developers, blogs, magazines, and other websites.
- Compare your search results against your buyer persona: Remember the persona you created during the primary research stage? You can use it to evaluate whether a publication you found through Google could steal website traffic from you. If the website's content aligns with what your buyer persona would want to see, it is a potential competitor and should be added to your list of competitors.
After a series of similar Google searches for the industry terms you identify with, look for repetition in the website domains that have come up.
When searching, examine the first two or three pages of results. These websites are considered reputable sources of content in your industry and should be monitored closely as you create your collection of videos, reports, web pages, and blog posts.

Market Research Examples
Mcdonald's focus on customer feedback and profiling.
McDonald's invests in developing a detailed consumer profile to attract and retain customers, including parents of young children who appreciate the family-friendly atmosphere and menus. The brand seeks feedback from customers through surveys and questionnaires in stores, social media, and its mobile app. It also monitors customer feedback on digital channels.
Nike's Extensive Research and Collaboration for Running Shoes Development
Nike invests heavily in creating running shoes that cater to the needs of its customers, which it determines through extensive market research and customer surveys. The brand goes to great lengths to understand its customers' preferences, such as the type of running surface, the distance they run, and their running style, to develop shoes that meet their specific needs.
In addition to customer surveys, Nike also collaborates with athletes to develop shoes that cater to their specific requirements. This research helps Nike improve its existing running shoe models and innovate new ones, ensuring that the brand stays ahead of the competition.
Disney employs focus groups that specifically cater to children to test out their new characters and ideas.
The Walt Disney Company invests millions of dollars in creating captivating stories tested for their effectiveness with children, the intended audience. Disney executives hold focus groups with preschoolers and kindergartners several times a year to gather their opinions and feedback on TV episodes, Disney characters, and more.
This market research strategy is effective because children are the ultimate audience that Disney aims to please. The collected feedback helps the company improve existing content to meet the preferences of its audience and ensure continued success as a multi-billion dollar enterprise.
KFC tested its meatless product in specific markets before launching it nationwide.
In 2019, KFC began developing and testing a meatless version of its famous chicken. However, instead of immediately launching the product nationwide, they decided to test it in select stores in the Atlanta, Georgia area.
This is an innovative and practical approach to market research, as it allows the company to determine the product's sales performance on a smaller scale before committing too many resources to it. If the meatless chicken fails to gain popularity in Georgia, KFC can make the necessary changes to the product before introducing it to the broader market.
Yamaha conducted a survey to determine whether to use knobs or sliding faders on the Montage keyboard.
Yamaha is a Japanese corporation that produces various products, from motorcycles to golf cars to musical instruments. When it began developing its new Montage keyboard, the team was unsure whether to use knobs or sliding faders on the product.
To address this dilemma, Yamaha used Qualtrics to send a survey to their customers. Within just a few hours , they received 400 responses. By using survey feedback, Yamaha ensured that it was designing a product that would perfectly meet the preferences of its audiences.
The Body Shop used social listening to determine how to reposition brand campaigns based on customer feedback.
The Body Shop is a well-known brand that offers ethically sourced and natural products. They take pride in their core value of sustainability. The Body Shop team tracked conversations to understand the sustainability subtopics that were most important to their audiences.
They found that their customers cared a lot about refills. Based on this information, the Body Shop team confidently relaunched their Refill Program across 400 stores globally in 2021, with plans to add another 400 in 2022. Market research confirmed that their refill concept was on the right track and also highlighted the need for increased efforts to demonstrate how much the Body Shop cares about its customers' values .
VideoTranscript
The takeaway.
Fratzke Consulting offers a comprehensive suite of market research services to help brands gain valuable insights into their target market, competitors, and industry trends. Our expert team utilizes various primary and secondary research methods to gather accurate and unbiased data, including surveys, competitive research, and industry reports. With Fratzke Consulting, you'll have the tools to succeed in today's rapidly evolving business landscape.
Interested in learning more? Book a free audit consultation today.
Stay in the know
Get the latest insights sent directly to your inbox.
Related Posts
Fractional CMO: What is it and Why Your Brand May Need One
Learn about fractional CMOs, their responsibilities, and why your business might benefit from hiring one. With a fractional CMO, you can get expert marketing strategy and leadership without the cost of a full-time CMO.
100 of the Best Website Designs to Inspire You in 2024 (A-Z)
100 inspiring website designs that can fuel your next web project in 2024. From visually stunning e-commerce sites to user-friendly SaaS platforms, Fratzke Consulting showcases our favorite designs.
What Is an SEO Consultant, and Do You Need One?
Discover the importance of hiring an SEO consultant for your business and the different types of SEO consultants. Learn More.
201 Harbor Blvd. Suite 203 Fullerton, CA, 92832 Phone: (714) 614-2881 Hours: Monday - Friday 8AM-6PM
Stay in the loop
© 2024 by Fratzke
- Solutions Corporate Market Analysis Customer Experience Product Lifecycle Brand Strategy Research & Insights Higher Education Enrollment Management Academic Program Development Student Success Operations & Finance Advancement Marketing Grants Research & Insights K-12 Education Curriculum and Instruction Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Academic Program Planning and Impact Strategic Planning Teacher Recruitment and Retention Operational Planning School Climate Research & Insights
- Data Analysis
- Qualitative Research
- Strategic Advising
- Benchmarking & Best Practices
- Market Modeling
- Research & Insights By Industry Corporate Higher Education K–12 Education By Type Insights Blog Reports & Briefs Case Studies Webinars All Research & Insights
- Client Testimonials
- Careers Overview
- Current Openings
- Recruitment Process
- Social Impact
- Careers in Research
- Careers in Sales and Account Management
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Client Login
Table of Contents
Everything you want to know about market research.
Nearly 80% of businesses conduct market research to gather targeted insights into their performance, customers, industry, and competition.
While market research offers a variety of benefits, it can be challenging to identify what research to conduct, and when to ensure you get accurate and actionable data for your business decisions.
To cut through information overload and discover how market research can help you, we are breaking down the basics of market research, including what it is, what you can learn, potential benefits, and how to get started.
What is market research?
Market research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about your target market, competitors, and industry. Market research spans a wide range of topics, uncovering insights on various elements that can impact a business.
Some common subjects of market research include:
- Customer needs, preferences, and behaviors
- Market trends, competitors, and growth opportunities
- Brand awareness, perception, and evaluation amongst competitors
- Product performance, strengths and weaknesses, and customer evaluations
Why do companies conduct market research?
There is a wealth of insights and benefits provided by market research, but at its core, the purpose and value of market research is that it helps you make informed decisions by:
Understanding the Market
Market research provides in-depth insights, allowing companies to better understand the market, identify customers’ needs and preferences, discover how their brand is perceived in the market, and measure the impact of investments and strategies.
Identifying Opportunities
Market research spots untapped opportunities for companies to focus on, including how to improve their brand status, identify new customer bases and markets to sell to, and provide insights to help senior leadership prioritize investment opportunities.
Uncovering Risks
Market research also reveals potential risks that, if ignored, can cause considerable damage. This includes insight into competitors, the impact of major challenges or economic influences (i.e., COVID-19, heightened regulatory concerns), and negative perceptions of the company and its brands.
What types of companies use market research?
All types of businesses use market research, Including B2B ( 77% of companies ), B2C (82%), and B2B2C (83%).
While they conduct research at similar rates, the types of questions they ask are driven by the unique challenges each type of business faces. For example, over half of B2B companies conducted a market share analysis last year, while B2C and B2B2C companies’ top project was evaluating customer satisfaction.
Find out how Hanover can help collect and analyze the data you need for better business decisions.
- Hanover Research Corporate Solutions
What can you learn from market research?
Anything. One of the biggest values of market research is how you can customize your research to gather the insights you need most. Below are some common examples of insights you can learn through market research.
Understand the Market
- Identify and prioritize markets for exploration and entry.
- Identify and build in-depth comparative profiles for your biggest competitors in the market.
- Understand market dynamics and identify potential factors, innovations, and trends that might impact your company.
Optimize Products and Services
- Generate new product ideas or optimize existing products.
- Develop an optimized pricing strategy.
- Evaluate how customers perceive and use your products and services.
- Identify any sales and service gaps or unmet customer needs.
Strengthen Brand Strategy
- Measure and track the strength of your brand and competing brands.
- Measure and improve brand health.
- Evaluate marketing and sales approaches to align with customer needs and preferences.
Understand Customers
- Understand the needs and preferences of your target customers.
- Identify crucial components of the customer experience. including unmet needs, pain points and levels of satisfaction.
- Differentiate customers into targetable segments based on behavioral, attitudinal, demographic, and psychographic data.
What are the most common market research projects?
The most popular market research projects can vary slightly over time, often reflecting market, economic, and societal shifts that impact company performance. Last year, with a focus on expanding to new markets and obtaining new customers, leading projects were analyzing customer satisfaction and needs , evaluating the market and identifying current and upcoming market trends , and measuring the strength of their brand equity .
This year, with inflation affecting customers’ buying power and increased production and resource costs, companies have expressed increased interest in price sensitivity research , making it the fifth-most common market research project. Increased uncertainty has also prompted companies to evaluate sales and renewal performance with win loss analysis projects increasing by 19%.
Most Common Research Projects

How do you know you need market research?
With endless possibilities for insights, it can be hard to figure out where to start. To identify the type of market research you need, examine your top business priorities and determine if they could benefit from new data and insights.
Ask yourself these two questions.
- Do you have the information you need to accomplish your goals?
- Is that data comprehensive and recent?
If the answer to either is no, your strategies will benefit from updated research insights.
Need help convincing your executive team to invest in market research?
You can find more stats on the use and impact of market research in our recent study.
- The State of Market Research
When should you conduct market research?
Companies usually conduct market research for one of three reasons: In response to a triggering event, to evaluate past performance, or to measure changes over time and quickly respond to declined performance.
Market Research Triggers
There are a variety of triggering events that prompt businesses to conduct research. Some common situations include:
- Evaluating the impact of external influences (economic factors, political shifts, etc.,)
- Understanding and adjusting to shifting customer needs
- Entering new markets
- New or increased competition
- Developing new products or features
- Merging or acquiring a new company
Evaluating Past Performance
In addition to conducting research to inform upcoming strategies or overcome pressing challenges, companies also conduct market research to evaluate the success of recent strategies or determine the reason for recent declines in performance. Market research allows companies to measure performance and identify areas of improvement. This can include anything from evaluating the performance of recent product launches, assessing the impact of recent sales and marketing strategies, or measuring the impact of recent pricing or service changes.
Recurring Assessments
The final instance of market research is recurring research. Companies conduct recurring research to ensure data is relevant, to evaluate performance over time, and to quickly identify and respond to changes in performance. For example, some companies periodically measure their brand health including brand awareness, perception, and evaluation against their competitors. By consistently assessing their brand health, these companies have updated insights into their presence in the industry, how customers evaluate them, and potential threats from competitors.
How often should you conduct market research?
How much research you should conduct depends on your unique business needs and strategies. Often, the amount you conduct is determined by the market research triggers we mention above. If you are launching a new product, breaking into a new market or customer base, or have noticed a decline in performance, you should conduct market research to address these needs as they arise.
Most businesses conduct multiple market research projects a year depending on their needs and resources. Over 80% of companies conduct market research frequently, and 79% conduct at least five market research projects a year.
Get customized research, expert support, and targeted insights to solve your organization’s needs.
- Hanover Research Expertise
Value of market research
What roi can you expect from market research.
In addition to successful key initiatives, companies that conduct market research say it provides an ROI of over four times the cost.

What challenges does market research address?
The insights market research provides are directly related to businesses’ biggest challenges. In our State of Market Research report , we asked respondents what their company’s biggest challenges were. In addition, we also asked respondents how their companies have benefited from market research findings.
We found that the benefits they attributed to market research directly addressed their biggest reported challenges. Even those who did not report having a specific challenge reported market research insights helped them accomplish their goals.

What are the benefits of effective market research?
There are a variety of benefits of market research depending on the specific research you conduct.
Market research can benefit your company by helping you:

Companies that leverage market research insights into their strategies are also able to accomplish their goals at a higher rate than those without market research insights.
Companies that conduct market research are:

Discover how Rheem leveraged customer insights to build its sustainability strategy.
- Rheem Measures Homeowner and Contractor Demand for Sustainability
Market research KPIs
Some common KPIs based on the focus of the research can include:
Brand-focused
- Brand recall and recognition
- Brand perception
- Brand preference
- Net promoter score (NPS)
Customer-focused
- Customer retention and churn
- Customer satisfaction (CSAT)
- Cost per acquisition
Product-focused
- Product appeal
- Willingness to pay
- Future purchase consideration
- Post-purchase satisfaction
Market-focused
- Share of market
- Competitive benchmarks
- Total addressable market
- Market demand
How do you evaluate the success of market research?
Market research is successful if the resulting data is accurate, representative, and informative. Accurate data means the data has been cleaned and is a valid response to the study questions. Representative means that the data reflects the target market and is comprehensive. Finally, informative means the data provides insight and is actionable.
See how market research can help you with these key market research stats.
- Market Research Stats You Need to Know
How to perform market research
What are the common market research methods .
There are four main types of market research.
Quantitative Data Analysis
Data analytics involves collecting and analyzing large sets of existing data to uncover patterns and predict future outcomes. These data sets can include information like customer behavior data or historical sales data that allows companies to analyze their current performance and model potential scenarios and outcomes.
By leveraging existing data, data analytics provides companies with an objective view of the situation, allowing them to identify gaps and discern trends.
Quantitative Survey Research
Surveys pose a set of questions to a targeted group of people. The survey measures the opinions, preferences, perceptions, and experiences of a desired audience and can collect self-reported demographic and geographic data.
With surveys, companies get an aggregate but statistically valid picture that they can leverage to make decisions. Surveys also offer the ability to segment and further analyze the answers to determine key drivers of behaviors.
Qualitative Primary Research
Qualitative research focuses on targeted insights around concepts, opinions, and preferences. Unlike quantitative methods, these market research methodologies leverage a smaller set of data and respondents but allow for more in-depth answers.
There are two common types of qualitative primary research: in-depth Interviews and focus groups.
- In-depth Interviews In-depth interviews involve one-on-one conversations between interviewers and those from the target audience. The interview follows a pre-determined set of questions, or guide, to reveal sentiment, decision-making processes, and unmet needs.
- Focus Groups Focus groups are facilitator-led group discussions reveal perceptions of or reception to a concept or idea. While the facilitator guides the meeting, the direction of the conversation is determined by the participants creating organic responses that stem from participant perception and reactions.
Secondary Research
Secondary research, also known as desk research, is leveraging data that already exists to answer questions. It can be used to understand what others in the market are doing, identify potential markets for growth or expansion, or allow companies to compare their organization to others on key performance indicators.
What is the market research process?
There are five stages to the market research process.
- Determine your Area of Focus To determine the focus of your market research, look at your goals objectively and determine if you have accurate and effective data to accomplish these goals. Once you have identified your goal, the next thing is to determine what you need to learn to support it. This could be anything from external information like market trends and competitors or internal information like customer satisfaction with your brand and offerings.

- Gather Your Data With your focus and methodology determined, the next step is to start collecting data. Each methodology has its own methods of data collection. Methods like surveys and interviews require researchers to gather feedback data from a select sample of their intended audience. Data analysis and secondary research entail gathering existing internal or external data related to the primary research focus.
- Analyze the Results Once the data is collected, the next step is to clean and analyze the results. It is essential that data is verified and accessed to ensure the data is valid and is sufficient to provide accurate results. Once the data has been cleaned it should be reviewed for general findings, evaluated against your initial questions, and benchmarked against past performance or competitors.
- Leverage Findings to Inform Your Business Strategies After conducting your initial research, it’s time to reassess your strategies. Look at the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats that your research has uncovered to see how it might impact your business and existing strategies. Is there a way to enhance your current strategies with the new data? Do you need to alter your strategies and resources to address an uncovered threat?
Leverage your findings to inform your strategy and determine your next steps, whether they indicate you should stay the course, pivot to tackle a more pressing challenge, or even conduct new research to further understand your recent findings.
Why use both quantitative and qualitative research?
Leveraging both quantitative and qualitative research can provide a more holistic view of a situation. For example, quantitative data analysis offers relevant findings but can sometimes lack context. If it is followed up by qualitative in-depth interviews, companies can gather feedback to understand the factors that lead to the data analysis findings and identify potential solutions or untapped opportunities.
Interviews can help businesses identify customers’ thoughts and opinions and then that feedback can inform a survey that is sent to a wider audience for measurable insights. Companies can also use secondary desktop research to identify market trends and industry benchmarks and combine it with data analysis or surveys to evaluate the company’s performance in the market.
What is a sample in market research?
A sample in research refers to a small but representative group of people whose answers are extrapolated to a larger population.
For example, if a company wants to identify their brand awareness, they will survey a sample of people that have similar characteristics to their target audience. The survey’s findings will then provide a general understanding of how well known the brand is and directions on how to improve their brand’s presence in the market.
Start conducting your own research with this step-by-step guide.
- The Ultimate Guide to Market Research
How companies conduct market research
How can you get market research.
There are three main ways companies can get market research insights.
- Internal non-dedicated research Some companies conduct research with no real dedicated resource, requiring members in the marketing, product, strategy, and business intelligence departments to conduct research themselves. While initially low-cost, this option consumes internal resources and time, can produce incomplete, inaccurate, and biased results, and is often not shared company wide.
- Dedicated internal research team Some companies are big enough or require extensive market research and have therefore invested in building an internal research department. This option produces more accurate and strategic results than the first option. However, it requires a long-term investment and the amount of research and insights you can collect will be limited depending on the amount and expertise of the analysts employed.
- External market research company Many companies partner with an external research company to gain access to research experts, technology, and advice for actionable insights. The price for this option depends on the type and amount of research you do, but it can be less of a burden than maintaining an internal department while still providing the value of research expertise.
What are the types of market research firms?
A market research company is a firm that specializes in conducting research. There are a few different types of market research firms based on the services they provide.
- Custom research providers Custom research companies (like Hanover) design and conduct research centered around client’s unique needs. They often specialize in all four research methodologies to develop research that answers clients’ focus questions and provide findings that connect the data back to the intent of the research.
- Syndicated research providers Syndicated research companies do not conduct client-specific research. Instead, these companies conduct widespread research to offer data such as industry statistics, current best practices, or recent trends. Businesses can then buy this research to gather perspectives on their performance and identify areas where custom research can help provide more insight.
- Self-service platforms Self-service companies provide research technology for companies to conduct their own research. It allows companies to design and administer their own research and analyze and assess the results.
Should you use a market research firm?
Market research companies provide valuable benefits, making them an effective partner for your research needs. In addition to the research they provide, they have added benefits like:
- Removing the influence of preconceived opinions and personal or company bias
- Access to sophisticated analysis software and research methods
- Offering expert insights to help design research that results in accurate and relevant findings
- Offloading time-intensive research and analysis enabling companies to focus internal resources on strategic work
- Access to expert researchers without having to hire a full-time employees
How much does market research cost?
The cost of market research varies based on how you conduct your research. Conducting research in-house vs hiring a research company might be cheaper (but less effective). The type of methodology you use can affect the cost, for example, in-depth interviews can become quite expensive depending on the incentives you offer to participate. Price can also vary depending on the level of service you need, for example some companies will work with you to identify your focus and mythology, conduct the research, and present findings and recommendations while others will only conduct research and deliver the results.
Don’t make the mistake of focusing on costs by itself. Opting for cheaper or quick research can provide you with skewed data that can do more harm than good.
Good research is worth the investment. Over 85% of companies say market research ROI is over four times the investment. The insights and impact market research provides has also led 69% of businesses to increase their investment in market research this year.
Find out how Baltimore Aircoil successfully entered an international market with targeted insights
- Baltimore Aircoil Company Develops HVAC Purchasing Strategy for New International Market
What are some tips for making market research effective?
Market research is instrumental in building effective data-driven strategies. But only if done right. As you begin to plan out your market research and business strategies, keep the following tips in mind.
- Refresh your data to ensure it is accurate and relevant
- Tailor research to your unique needs and challenges
- Use the correct methodology to accurately answer your questions
- Incorporate research findings into your strategies
- Share insights across the company to ensure everyone is operating off the same data
- Leverage outside expertise when you need it
By implementing these tips, you can enhance the quality and effectiveness of your market research efforts, enabling data-driven decision-making and strategic planning that aligns with your business objectives.
Start gathering targeted insights
Research & Insights
Receive industry-leading insights directly in your inbox.
If you have difficulty accessing any part of this website or the products or services offered by Hanover Research, please contact us at [email protected] for support.
Become a client
Access the best custom research to help hit your organization’s goals . Request your custom consult below and a member of our team will be in touch.
Have questions? Please visit our contact page .
Let us come to you!
Receive industry insights directly in your inbox.
Our newsletters are packed with helpful tips, industry guides, best practices, case studies, and more. Enter your email address below to opt in:
How To Do Market Research: Definition, Types, Methods
Jan 2, 2024
11 min. read
Market research isn’t just collecting data. It’s a strategic tool that allows businesses to gain a competitive advantage while making the best use of their resources. Research reveals valuable insights into your target audience about their preferences, buying habits, and emerging demands — all of which help you unlock new opportunities to grow your business.
When done correctly, market research can minimize risks and losses, spur growth, and position you as a leader in your industry.
Let’s explore the basic building blocks of market research and how to collect and use data to move your company forward:
Table of Contents
What Is Market Research?
Why is market research important, market analysis example, 5 types of market research, what are common market research questions, what are the limitations of market research, how to do market research, improving your market research with radarly.
Market Research Definition: The process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a market or audience.

Market research studies consumer behavior to better understand how they perceive products or services. These insights help businesses identify ways to grow their current offering, create new products or services, and improve brand trust and brand recognition .
You might also hear market research referred to as market analysis or consumer research .
Traditionally, market research has taken the form of focus groups, surveys, interviews, and even competitor analysis . But with modern analytics and research tools, businesses can now capture deeper insights from a wider variety of sources, including social media, online reviews, and customer interactions. These extra layers of intel can help companies gain a more comprehensive understanding of their audience.
With consumer preferences and markets evolving at breakneck speeds, businesses need a way to stay in touch with what people need and want. That’s why the importance of market research cannot be overstated.
Market research offers a proactive way to identify these trends and make adjustments to product development, marketing strategies , and overall operations. This proactive approach can help businesses stay ahead of the curve and remain agile as markets shift.
Market research examples abound — given the number of ways companies can get inside the minds of their customers, simply skimming through your business’s social media comments can be a form of market research.
A restaurant chain might use market research methods to learn more about consumers’ evolving dining habits. These insights might be used to offer new menu items, re-examine their pricing strategies, or even open new locations in different markets, for example.
A consumer electronics company might use market research for similar purposes. For instance, market research may reveal how consumers are using their smart devices so they can develop innovative features.
Market research can be applied to a wide range of use cases, including:
- Testing new product ideas
- Improve existing products
- Entering new markets
- Right-sizing their physical footprints
- Improving brand image and awareness
- Gaining insights into competitors via competitive intelligence
Ultimately, companies can lean on market research techniques to stay ahead of trends and competitors while improving the lives of their customers.
Market research methods take different forms, and you don’t have to limit yourself to just one. Let’s review the most common market research techniques and the insights they deliver.
1. Interviews
3. Focus Groups
4. Observations
5. AI-Driven Market Research
One-on-one interviews are one of the most common market research techniques. Beyond asking direct questions, skilled interviewers can uncover deeper motivations and emotions that drive purchasing decisions. Researchers can elicit more detailed and nuanced responses they might not receive via other methods, such as self-guided surveys.

Interviews also create the opportunity to build rapport with customers and prospects. Establishing a connection with interviewees can encourage them to open up and share their candid thoughts, which can enrich your findings. Researchers also have the opportunity to ask clarifying questions and dig deeper based on individual responses.
Market research surveys provide an easy entry into the consumer psyche. They’re cost-effective to produce and allow researchers to reach lots of people in a short time. They’re also user-friendly for consumers, which allows companies to capture more responses from more people.
Big data and data analytics are making traditional surveys more valuable. Researchers can apply these tools to elicit a deeper understanding from responses and uncover hidden patterns and correlations within survey data that were previously undetectable.
The ways in which surveys are conducted are also changing. With the rise of social media and other online channels, brands and consumers alike have more ways to engage with each other, lending to a continuous approach to market research surveys.
3. Focus groups
Focus groups are “group interviews” designed to gain collective insights. This interactive setting allows participants to express their thoughts and feelings openly, giving researchers richer insights beyond yes-or-no responses.

One of the key benefits of using focus groups is the opportunity for participants to interact with one another. They spark discussions while sharing diverse viewpoints. These sessions can uncover underlying motivations and attitudes that may not be easily expressed through other research methods.
Observing your customers “in the wild” might feel informal, but it can be one of the most revealing market research techniques of all. That’s because you might not always know the right questions to ask. By simply observing, you can surface insights you might not have known to look for otherwise.
This method also delivers raw, authentic, unfiltered data. There’s no room for bias and no potential for participants to accidentally skew the data. Researchers can also pick up on non-verbal cues and gestures that other research methods may fail to capture.
5. AI-driven market research
One of the newer methods of market research is the use of AI-driven market research tools to collect and analyze insights on your behalf. AI customer intelligence tools and consumer insights software like Meltwater Radarly take an always-on approach by going wherever your audience is and continuously predicting behaviors based on current behaviors.
By leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning, and big data analysis , AI enables companies to uncover deep-seated patterns and correlations within large datasets that would be near impossible for human researchers to identify. This not only leads to more accurate and reliable findings but also allows businesses to make informed decisions with greater confidence.
Tip: Learn how to use Meltwater as a research tool , how Meltwater uses AI , and learn more about consumer insights and about consumer insights in the fashion industry .
No matter the market research methods you use, market research’s effectiveness lies in the questions you ask. These questions should be designed to elicit honest responses that will help you reach your goals.
Examples of common market research questions include:
Demographic market research questions
- What is your age range?
- What is your occupation?
- What is your household income level?
- What is your educational background?
- What is your gender?
Product or service usage market research questions
- How long have you been using [product/service]?
- How frequently do you use [product/service]?
- What do you like most about [product/service]?
- Have you experienced any problems using [product/service]?
- How could we improve [product/service]?
- Why did you choose [product/service] over a competitor’s [product/service]?
Brand perception market research questions
- How familiar are you with our brand?
- What words do you associate with our brand?
- How do you feel about our brand?
- What makes you trust our brand?
- What sets our brand apart from competitors?
- What would make you recommend our brand to others?
Buying behavior market research questions
- What do you look for in a [product/service]?
- What features in a [product/service] are important to you?
- How much time do you need to choose a [product/service]?
- How do you discover new products like [product/service]?
- Do you prefer to purchase [product/service] online or in-store?
- How do you research [product/service] before making a purchase?
- How often do you buy [product/service]?
- How important is pricing when buying [product/service]?
- What would make you switch to another brand of [product/service]?
Customer satisfaction market research questions
- How happy have you been with [product/service]?
- What would make you more satisfied with [product/service]?
- How likely are you to continue using [product/service]?
Bonus Tip: Compiling these questions into a market research template can streamline your efforts.
Market research can offer powerful insights, but it also has some limitations. One key limitation is the potential for bias. Researchers may unconsciously skew results based on their own preconceptions or desires, which can make your findings inaccurate.
- Depending on your market research methods, your findings may be outdated by the time you sit down to analyze and act on them. Some methods struggle to account for rapidly changing consumer preferences and behaviors.
- There’s also the risk of self-reported data (common in online surveys). Consumers might not always accurately convey their true feelings or intentions. They might provide answers they think researchers are looking for or misunderstand the question altogether.
- There’s also the potential to miss emerging or untapped markets . Researchers are digging deeper into what (or who) they already know. This means you might be leaving out a key part of the story without realizing it.
Still, the benefits of market research cannot be understated, especially when you supplement traditional market research methods with modern tools and technology.
Let’s put it all together and explore how to do market research step-by-step to help you leverage all its benefits.
Step 1: Define your objectives
You’ll get more from your market research when you hone in on a specific goal : What do you want to know, and how will this knowledge help your business?
This step will also help you define your target audience. You’ll need to ask the right people the right questions to collect the information you want. Understand the characteristics of the audience and what gives them authority to answer your questions.
Step 2: Select your market research methods
Choose one or more of the market research methods (interviews, surveys, focus groups, observations, and/or AI-driven tools) to fuel your research strategy.
Certain methods might work better than others for specific goals . For example, if you want basic feedback from customers about a product, a simple survey might suffice. If you want to hone in on serious pain points to develop a new product, a focus group or interview might work best.
You can also source secondary research ( complementary research ) via secondary research companies , such as industry reports or analyses from large market research firms. These can help you gather preliminary information and inform your approach.

Step 3: Develop your research tools
Prior to working with participants, you’ll need to craft your survey or interview questions, interview guides, and other tools. These tools will help you capture the right information , weed out non-qualifying participants, and keep your information organized.
You should also have a system for recording responses to ensure data accuracy and privacy. Test your processes before speaking with participants so you can spot and fix inefficiencies or errors.
Step 4: Conduct the market research
With a system in place, you can start looking for candidates to contribute to your market research. This might include distributing surveys to current customers or recruiting participants who fit a specific profile, for example.
Set a time frame for conducting your research. You might collect responses over the course of a few days, weeks, or even months. If you’re using AI tools to gather data, choose a data range for your data to focus on the most relevant information.
Step 5: Analyze and apply your findings
Review your findings while looking for trends and patterns. AI tools can come in handy in this phase by analyzing large amounts of data on your behalf.
Compile your findings into an easy-to-read report and highlight key takeaways and next steps. Reports aren’t useful unless the reader can understand and act on them.
Tip: Learn more about trend forecasting , trend detection , and trendspotting .
Meltwater’s Radarly consumer intelligence suite helps you reap the benefits of market research on an ongoing basis. Using a combination of AI, data science, and market research expertise, Radarly scans multiple global data sources to learn what people are talking about, the actions they’re taking, and how they’re feeling about specific brands.

Our tools are created by market research experts and designed to help researchers uncover what they want to know (and what they don’t know they want to know). Get data-driven insights at scale with information that’s always relevant, always accurate, and always tailored to your organization’s needs.
Learn more when you request a demo by filling out the form below:
Continue Reading

What Are Consumer Insights? Meaning, Examples, Strategy

How Coca-Cola Collects Consumer Insights

Market Intelligence 101: What It Is & How To Use It
9 Top Consumer Insights Tools & Companies
Send us an email
How to do market research: The complete guide for your brand
Written by by Jacqueline Zote
Published on April 13, 2023
Reading time 10 minutes
Blindly putting out content or products and hoping for the best is a thing of the past. Not only is it a waste of time and energy, but you’re wasting valuable marketing dollars in the process. Now you have a wealth of tools and data at your disposal, allowing you to develop data-driven marketing strategies . That’s where market research comes in, allowing you to uncover valuable insights to inform your business decisions.
Conducting market research not only helps you better understand how to sell to customers but also stand out from your competition. In this guide, we break down everything you need to know about market research and how doing your homework can help you grow your business.
Table of contents:
What is market research?
Why is market research important, types of market research, where to conduct market research.
- Steps for conducting market research
- Tools to use for market research
Market research is the process of gathering information surrounding your business opportunities. It identifies key information to better understand your audience. This includes insights related to customer personas and even trends shaping your industry.
Taking time out of your schedule to conduct research is crucial for your brand health. Here are some of the key benefits of market research:
Understand your customers’ motivations and pain points
Most marketers are out of touch with what their customers want. Moreover, these marketers are missing key information on what products their audience wants to buy.
Simply put, you can’t run a business if you don’t know what motivates your customers.
And spoiler alert: Your customers’ wants and needs change. Your customers’ behaviors today might be night and day from what they were a few years ago.
Market research holds the key to understanding your customers better. It helps you uncover their key pain points and motivations and understand how they shape their interests and behavior.
Figure out how to position your brand
Positioning is becoming increasingly important as more and more brands enter the marketplace. Market research enables you to spot opportunities to define yourself against your competitors.
Maybe you’re able to emphasize a lower price point. Perhaps your product has a feature that’s one of a kind. Finding those opportunities goes hand in hand with researching your market.
Maintain a strong pulse on your industry at large
Today’s marketing world evolves at a rate that’s difficult to keep up with.
Fresh products. Up-and-coming brands. New marketing tools. Consumers get bombarded with sales messages from all angles. This can be confusing and overwhelming.
By monitoring market trends, you can figure out the best tactics for reaching your target audience.
Not everyone conducts market research for the same reason. While some may want to understand their audience better, others may want to see how their competitors are doing. As such, there are different types of market research you can conduct depending on your goal.
Interview-based market research allows for one-on-one interactions. This helps the conversation to flow naturally, making it easier to add context. Whether this takes place in person or virtually, it enables you to gather more in-depth qualitative data.
Buyer persona research
Buyer persona research lets you take a closer look at the people who make up your target audience. You can discover the needs, challenges and pain points of each buyer persona to understand what they need from your business. This will then allow you to craft products or campaigns to resonate better with each persona.
Pricing research
In this type of research, brands compare similar products or services with a particular focus on pricing. They look at how much those products or services typically sell for so they can get more competitive with their pricing strategy.
Competitive analysis research
Competitor analysis gives you a realistic understanding of where you stand in the market and how your competitors are doing. You can use this analysis to find out what’s working in your industry and which competitors to watch out for. It even gives you an idea of how well those competitors are meeting consumer needs.
Depending on the competitor analysis tool you use, you can get as granular as you need with your research. For instance, Sprout Social lets you analyze your competitors’ social strategies. You can see what types of content they’re posting and even benchmark your growth against theirs.
Brand awareness research
Conducting brand awareness research allows you to assess your brand’s standing in the market. It tells you how well-known your brand is among your target audience and what they associate with it. This can help you gauge people’s sentiments toward your brand and whether you need to rebrand or reposition.
If you don’t know where to start with your research, you’re in the right place.
There’s no shortage of market research methods out there. In this section, we’ve highlighted research channels for small and big businesses alike.
Considering that Google sees a staggering 8.5 billion searches each day, there’s perhaps no better place to start.
A quick Google search is a potential goldmine for all sorts of questions to kick off your market research. Who’s ranking for keywords related to your industry? Which products and pieces of content are the hottest right now? Who’s running ads related to your business?
For example, Google Product Listing Ads can help highlight all of the above for B2C brands.

The same applies to B2B brands looking to keep tabs on who’s running industry-related ads and ranking for keyword terms too.

There’s no denying that email represents both an aggressive and effective marketing channel for marketers today. Case in point, 44% of online shoppers consider email as the most influential channel in their buying decisions.
Looking through industry and competitor emails is a brilliant way to learn more about your market. For example, what types of offers and deals are your competitors running? How often are they sending emails?

Email is also invaluable for gathering information directly from your customers. This survey message from Asana is a great example of how to pick your customers’ brains to figure out how you can improve your quality of service.

Industry journals, reports and blogs
Don’t neglect the importance of big-picture market research when it comes to tactics and marketing channels to explore. Look to marketing resources such as reports and blogs as well as industry journals
Keeping your ear to the ground on new trends and technologies is a smart move for any business. Sites such as Statista, Marketing Charts, AdWeek and Emarketer are treasure troves of up-to-date data and news for marketers.
And of course, there’s the Sprout Insights blog . And invaluable resources like The Sprout Social Index™ can keep you updated on the latest social trends.
Social media
If you want to learn more about your target market, look no further than social media. Social offers a place to discover what your customers want to see in future products or which brands are killin’ it. In fact, social media is become more important for businesses than ever with the level of data available.
It represents a massive repository of real-time data and insights that are instantly accessible. Brand monitoring and social listening are effective ways to conduct social media research . You can even be more direct with your approach. Ask questions directly or even poll your audience to understand their needs and preferences.

The 5 steps for how to do market research
Now that we’ve covered the why and where, it’s time to get into the practical aspects of market research. Here are five essential steps on how to do market research effectively.
Step 1: Identify your research topic
First off, what are you researching about? What do you want to find out? Narrow down on a specific research topic so you can start with a clear idea of what to look for.
For example, you may want to learn more about how well your product features are satisfying the needs of existing users. This might potentially lead to feature updates and improvements. Or it might even result in new feature introductions.
Similarly, your research topic may be related to your product or service launch or customer experience. Or you may want to conduct research for an upcoming marketing campaign.
Step 2: Choose a buyer persona to engage
If you’re planning to focus your research on a specific type of audience, decide which buyer persona you want to engage. This persona group will serve as a representative sample of your target audience.
Engaging a specific group of audience lets you streamline your research efforts. As such, it can be a much more effective and organized approach than researching thousands (if not millions) of individuals.
You may be directing your research toward existing users of your product. To get even more granular, you may want to focus on users who have been familiar with the product for at least a year, for example.
Step 3: Start collecting data
The next step is one of the most critical as it involves collecting the data you need for your research. Before you begin, make sure you’ve chosen the right research methods that will uncover the type of data you need. This largely depends on your research topic and goals.
Remember that you don’t necessarily have to stick to one research method. You may use a combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches. So for example, you could use interviews to supplement the data from your surveys. Or you may stick to insights from your social listening efforts.
To keep things consistent, let’s look at this in the context of the example from earlier. Perhaps you can send out a survey to your existing users asking them a bunch of questions. This might include questions like which features they use the most and how often they use them. You can get them to choose an answer from one to five and collect quantitative data.
Plus, for qualitative insights, you could even include a few open-ended questions with the option to write their answers. For instance, you might ask them if there’s any improvement they wish to see in your product.
Step 4: Analyze results
Once you have all the data you need, it’s time to analyze it keeping your research topic in mind. This involves trying to interpret the data to look for a wider meaning, particularly in relation to your research goal.
So let’s say a large percentage of responses were four or five in the satisfaction rating. This means your existing users are mostly satisfied with your current product features. On the other hand, if the responses were mostly ones and twos, you may look for opportunities to improve. The responses to your open-ended questions can give you further context as to why people are disappointed.
Step 5: Make decisions for your business
Now it’s time to take your findings and turn them into actionable insights for your business. In this final step, you need to decide how you want to move forward with your new market insight.
What did you find in your research that would require action? How can you put those findings to good use?
The market research tools you should be using
To wrap things up, let’s talk about the various tools available to conduct speedy, in-depth market research. These tools are essential for conducting market research faster and more efficiently.
Social listening and analytics
Social analytics tools like Sprout can help you keep track of engagement across social media. This goes beyond your own engagement data but also includes that of your competitors. Considering how quickly social media moves, using a third-party analytics tool is ideal. It allows you to make sense of your social data at a glance and ensure that you’re never missing out on important trends.

Email marketing research tools
Keeping track of brand emails is a good idea for any brand looking to stand out in its audience’s inbox.
Tools such as MailCharts , Really Good Emails and Milled can show you how different brands run their email campaigns.
Meanwhile, tools like Owletter allow you to monitor metrics such as frequency and send-timing. These metrics can help you understand email marketing strategies among competing brands.
Content marketing research
If you’re looking to conduct research on content marketing, tools such as BuzzSumo can be of great help. This tool shows you the top-performing industry content based on keywords. Here you can see relevant industry sites and influencers as well as which brands in your industry are scoring the most buzz. It shows you exactly which pieces of content are ranking well in terms of engagements and shares and on which social networks.

SEO and keyword tracking
Monitoring industry keywords is a great way to uncover competitors. It can also help you discover opportunities to advertise your products via organic search. Tools such as Ahrefs provide a comprehensive keyword report to help you see how your search efforts stack up against the competition.

Competitor comparison template
For the sake of organizing your market research, consider creating a competitive matrix. The idea is to highlight how you stack up side-by-side against others in your market. Use a social media competitive analysis template to track your competitors’ social presence. That way, you can easily compare tactics, messaging and performance. Once you understand your strengths and weaknesses next to your competitors, you’ll find opportunities as well.
Customer persona creator
Finally, customer personas represent a place where all of your market research comes together. You’d need to create a profile of your ideal customer that you can easily refer to. Tools like Xtensio can help in outlining your customer motivations and demographics as you zero in on your target market.

Build a solid market research strategy
Having a deeper understanding of the market gives you leverage in a sea of competitors. Use the steps and market research tools we shared above to build an effective market research strategy.
But keep in mind that the accuracy of your research findings depends on the quality of data collected. Turn to Sprout’s social media analytics tools to uncover heaps of high-quality data across social networks.
- Marketing Disciplines
- Team Collaboration
How to build a marketing tech stack that scales your business
- Customer Experience
Brand trust: What it is and why it matters
- Leveling Up
The 43 best marketing resources we recommend in 2024
Executing a successful demand generation strategy [with examples]
- Now on slide
Build and grow stronger relationships on social
Sprout Social helps you understand and reach your audience, engage your community and measure performance with the only all-in-one social media management platform built for connection.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Market Research: What it Is, Methods, Types & Examples

Would you like to know why, how, and when to apply market research? Do you want to discover why your consumers are not buying your products? Are you interested in launching a new product, service, or even a new marketing campaign, but you’re not sure what your consumers want?
LEARN ABOUT: Market research vs marketing research
To answer the questions above, you’ll need help from your consumers. But how will you collect that data? In this case and in many other situations in your business, market research is the way to get all the answers you need.
In this ultimate guide about market research, you’ll find the definition, advantages, types of market research, and some examples that will help you understand this type of research. Don’t forget to download the free ebook available at the end of this guide!
LEARN ABOUT: Perceived Value
Content Index
Three key objectives of market research
Why is market research important.
- Types of Market Research: Methods and Examples
Steps for conducting Market Research
Benefits of an efficient market research, 5 market research tips for businesses, why does every business need market research, free market research ebook, what is market research.
Market research is a technique that is used to collect data on any aspect that you want to know to be later able to interpret it and, in the end, make use of it for correct decision-making.
Another more specific definition could be the following:
Market research is the process by which companies seek to collect data systematically to make better decisions. Still, its true value lies in the way in which all the data obtained is used to achieve a better knowledge of the market consumer.
The process of market research can be done through deploying surveys , interacting with a group of people, also known as a sample , conducting interviews, and other similar processes.
The primary purpose of conducting market research is to understand or examine the market associated with a particular product or service to decide how the audience will react to a product or service. The information obtained from conducting market research can be used to tailor marketing/ advertising activities or determine consumers’ feature priorities/service requirement (if any).
LEARN ABOUT: Consumer Surveys
Conducting research is one of the best ways of achieving customer satisfaction , reducing customer churn and elevating business. Here are the reasons why market research is important and should be considered in any business:
- Valuable information: It provides information and opportunities about the value of existing and new products, thus, helping businesses plan and strategize accordingly.
- Customer-centric: It helps to determine what the customers need and want. Marketing is customer-centric and understanding the customers and their needs will help businesses design products or services that best suit them. Remember that tracing your customer journey is a great way to gain valuable insights into your customers’ sentiments toward your brand.
- Forecasts: By understanding the needs of customers, businesses can also forecast their production and sales. Market research also helps in determining optimum inventory stock.
- Competitive advantage: To stay ahead of competitors market research is a vital tool to carry out comparative studies. Businesses can devise business strategies that can help them stay ahead of their competitors.
LEARN ABOUT: Data Analytics Projects
Types of Market Research: Market Research Methods and Examples
Whether an organization or business wishes to know the purchase behavior of consumers or the likelihood of consumers paying a certain cost for a product segmentation , market research helps in drawing meaningful conclusions.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting
Depending on the methods and tools required, the following are the types:
1. Primary Market Research (A combination of both Qualitative and Quantitative Research):
Primary market research is a process where organizations or businesses get in touch with the end consumers or employ a third party to carry out relevant studies to collect data. The data collected can be qualitative data (non-numerical data) or quantitative data (numerical or statistical data).
While conducting primary market research, one can gather two types of information: Exploratory and Specific. Exploratory research is open-ended, where a problem is explored by asking open ended questions in a detailed interview format usually with a small group of people, also known as a sample. Here the sample size is restricted to 6-10 members. Specific research, on the other hand, is more pinpointed and is used to solve the problems that are identified by exploratory research.
LEARN ABOUT: Marketing Insight
As mentioned earlier, primary market research is a combination of qualitative market research and quantitative market research. Qualitative market research study involves semi-structured or unstructured data collected through some of the commonly used qualitative research methods like:
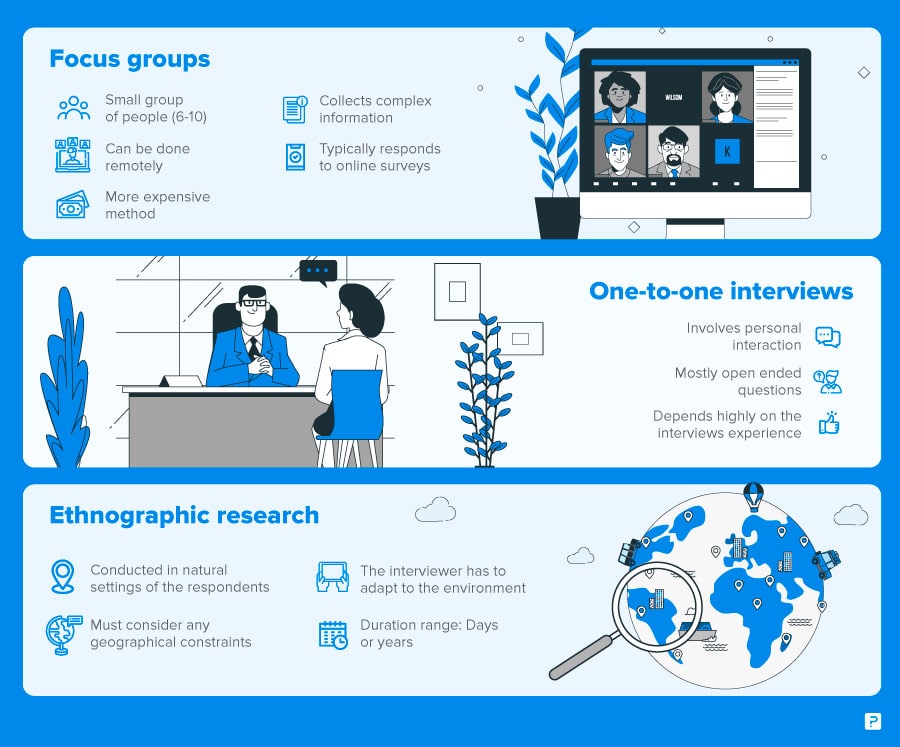
Focus groups :
Focus group is one of the commonly used qualitative research methods. Focus group is a small group of people (6-10) who typically respond to online surveys sent to them. The best part about a focus group is the information can be collected remotely, can be done without personally interacting with the group members. However, this is a more expensive method as it is used to collect complex information.
One-to-one interview:
As the name suggests, this method involves personal interaction in the form of an interview, where the researcher asks a series of questions to collect information or data from the respondents. The questions are mostly open-ended questions and are asked to facilitate responses. This method heavily depends on the interviewer’s ability and experience to ask questions that evoke responses.
Ethnographic research :
This type of in-depth research is conducted in the natural settings of the respondents. This method requires the interviewer to adapt himself/herself to the natural environment of the respondents which could be a city or a remote village. Geographical constraints can be a hindering market research factor in conducting this kind of research. Ethnographic research can last from a few days to a few years.
Organizations use qualitative research methods to conduct structured market research by using online surveys , questionnaires , and polls to gain statistical insights to make informed decisions.
LEARN ABOUT: Qualitative Interview
This method was once conducted using pen and paper. This has now evolved to sending structured online surveys to the respondents to gain actionable insights. Researchers use modern and technology-oriented survey platforms to structure and design their survey to evoke maximum responses from respondents.
Through a well-structured mechanism, data is easily collected and reported, and necessary action can be taken with all the information made available firsthand.
Learn more: How to conduct quantitative research
2. Secondary Market Research:
Secondary research uses information that is organized by outside sources like government agencies, media, chambers of commerce etc. This information is published in newspapers, magazines, books, company websites, free government and nongovernment agencies and so on. The secondary source makes use of the following:
- Public sources: Public sources like library are an awesome way of gathering free information. Government libraries usually offer services free of cost and a researcher can document available information.
- Commercial sources: Commercial source although reliable are expensive. Local newspapers, magazines, journal, television media are great commercial sources to collect information.
- Educational Institutions: Although not a very popular source of collecting information, most universities and educational institutions are a rich source of information as many research projects are carried out there than any business sector.
Learn more: Market Research Example with Types and Methods
A market research project may usually have 3 different types of objectives.
- Administrative : Help a company or business development, through proper planning, organization, and both human and material resources control, and thus satisfy all specific needs within the market, at the right time.
- Social : Satisfy customers’ specific needs through a required product or service. The product or service should comply with a customer’s requirements and preferences when consumed.
- Economical : Determine the economical degree of success or failure a company can have while being new to the market, or otherwise introducing new products or services, thus providing certainty to all actions to be implemented.
LEARN ABOUT: Test Market Demand
Knowing what to do in various situations that arise during the investigation will save the researcher time and reduce research problems . Today’s successful enterprises use powerful market research survey software that helps them conduct comprehensive research under a unified platform, providing actionable insights much faster with fewer problems.
LEARN ABOUT: Market research industry
Following are the steps to conduct effective market research.
Step #1: Define the Problem
Having a well-defined subject of research will help researchers when they ask questions. These questions should be directed to solve problems and must be adapted to the project. Make sure the questions are written clearly and that the respondents understand them. Researchers can conduct a marketing test with a small group to know if the questions are going to know whether the asked questions are understandable and if they will be enough to gain insightful results.
Research objectives should be written in a precise way and should include a brief description of the information that is needed and the way in which it will obtain it. They should have an answer to this question “why are we doing the research?”
Learn more: Interview Questions
Step #2: Define the Sample
To carry out market research, researchers need a representative sample that can be collected using one of the many sampling techniques . A representative sample is a small number of people that reflect, as accurately as possible, a larger group.
- An organization cannot waste their resources in collecting information from the wrong population. It is important that the population represents characteristics that matter to the researchers and that they need to investigate, are in the chosen sample.
- Take into account that marketers will always be prone to fall into a bias in the sample because there will always be people who do not answer the survey because they are busy, or answer it incompletely, so researchers may not obtain the required data.
- Regarding the size of the sample, the larger it is, the more likely it is to be representative of the population. A larger representative sample gives the researcher greater certainty that the people included are the ones they need, and they can possibly reduce bias. Therefore, if they want to avoid inaccuracy in our surveys, they should have representative and balanced samples.
- Practically all the surveys that are considered in a serious way, are based on a scientific sampling, based on statistical and probability theories.
There are two ways to obtain a representative sample:
- Probability sampling : In probability sampling , the choice of the sample will be made at random, which guarantees that each member of the population will have the same probability of selection bias and inclusion in the sample group. Researchers should ensure that they have updated information on the population from which they will draw the sample and survey the majority to establish representativeness.
- Non-probability sampling : In a non-probability sampling , different types of people are seeking to obtain a more balanced representative sample. Knowing the demographic characteristics of our group will undoubtedly help to limit the profile of the desired sample and define the variables that interest the researchers, such as gender, age, place of residence, etc. By knowing these criteria, before obtaining the information, researchers can have the control to create a representative sample that is efficient for us.
When a sample is not representative, there can be a margin of error . If researchers want to have a representative sample of 100 employees, they should choose a similar number of men and women.
The sample size is very important, but it does not guarantee accuracy. More than size, representativeness is related to the sampling frame , that is, to the list from which people are selected, for example, part of a survey.
LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Research If researchers want to continue expanding their knowledge on how to determine the size of the sample consult our guide on sampling here.
Step #3: Carry out data collection
First, a data collection instrument should be developed. The fact that they do not answer a survey, or answer it incompletely will cause errors in research. The correct collection of data will prevent this.
Step #4: Analyze the results
Each of the points of the market research process is linked to one another. If all the above is executed well, but there is no accurate analysis of the results, then the decisions made consequently will not be appropriate. In-depth analysis conducted without leaving loose ends will be effective in gaining solutions. Data analysis will be captured in a report, which should also be written clearly so that effective decisions can be made on that basis.
Analyzing and interpreting the results is to look for a wider meaning to the obtained data. All the previous phases have been developed to arrive at this moment. How can researchers measure the obtained results? The only quantitative data that will be obtained is age, sex, profession, and number of interviewees because the rest are emotions and experiences that have been transmitted to us by the interlocutors. For this, there is a tool called empathy map that forces us to put ourselves in the place of our clientele with the aim of being able to identify, really, the characteristics that will allow us to make a better adjustment between our products or services and their needs or interests. When the research has been carefully planned, the hypotheses have been adequately defined and the indicated collection method has been used, the interpretation is usually carried out easily and successfully. What follows after conducting market research?
Learn more: Types of Interviews
Step #5: Make the Research Report
When presenting the results, researchers should focus on: what do they want to achieve using this research report and while answering this question they should not assume that the structure of the survey is the best way to do the analysis. One of the big mistakes that many researchers make is that they present the reports in the same order of their questions and do not see the potential of storytelling.

To make good reports, the best analysts give the following advice: follow the inverted pyramid style to present the results, answering at the beginning the essential questions of the business that caused the investigation. Start with the conclusions and give them fundamentals, instead of accumulating evidence. After this researchers can provide details to the readers who have the time and interest.
Step #6: Make Decisions
An organization or a researcher should never ask “why do market research”, they should just do it! Market research helps researchers to know a wide range of information, for example, consumer purchase intentions, or gives feedback about the growth of the target market. They can also discover valuable information that will help in estimating the prices of their product or service and find a point of balance that will benefit them and the consumers.
Take decisions! Act and implement.
Learn more: Quantitative Research
- Make well-informed decisions: The growth of an organization is dependent on the way decisions are made by the management. Using market research techniques, the management can make business decisions based on obtained results that back their knowledge and experience. Market research helps to know market trends, hence to carry it out frequently to get to know the customers thoroughly.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
- Gain accurate information: Market research provides real and accurate information that will prepare the organization for any mishaps that may happen in the future. By properly investigating the market, a business will undoubtedly be taking a step forward, and therefore it will be taking advantage of its existing competitors.
- Determine the market size: A researcher can evaluate the size of the market that must be covered in case of selling a product or service in order to make profits.
- Choose an appropriate sales system: Select a precise sales system according to what the market is asking for, and according to this, the product/service can be positioned in the market.
- Learn about customer preferences: It helps to know how the preferences (and tastes) of the clients change so that the company can satisfy preferences, purchasing habits, and income levels. Researchers can determine the type of product that must be manufactured or sold based on the specific needs of consumers.
- Gather details about customer perception of the brand: In addition to generating information, market research helps a researcher in understanding how the customers perceive the organization or brand.
- Analyze customer communication methods: Market research serves as a guide for communication with current and potential clients.
- Productive business investment: It is a great investment for any business because thanks to it they get invaluable information, it shows researchers the way to follow to take the right path and achieve the sales that are required.
LEARN ABOUT: Total Quality Management
The following tips will help businesses with creating a better market research strategy.
Tip #1: Define the objective of your research.
Before starting your research quest, think about what you’re trying to achieve next with your business. Are you looking to increase traffic to your location? Or increase sales? Or convert customers from one-time purchasers to regulars? Figuring out your objective will help you tailor the rest of your research and your future marketing materials. Having an objective for your research will flesh out what kind of data you need to collect.
Tip #2: Learn About Your Target Customers.
The most important thing to remember is that your business serves a specific kind of customer. Defining your specific customer has many advantages like allowing you to understand what kind of language to use when crafting your marketing materials, and how to approach building relationships with your customer. When you take time to define your target customer you can also find the best products and services to sell to them.
You want to know as much as you can about your target customer. You can gather this information through observation and by researching the kind of customers who frequent your type of business. For starters, helpful things to know are their age and income. What do they do for a living? What’s their marital status and education level?
Learn more: Customer Satisfaction
Tip #3: Recognize that knowing who you serve helps you define who you do not.
Let’s take a classic example from copywriting genius Dan Kennedy. He says that if you’re opening up a fine dining steakhouse focused on decadent food, you know right off the bat that you’re not looking to attract vegetarians or dieters. Armed with this information, you can create better marketing messages that speak to your target customers.
It’s okay to decide who is not a part of your target customer base. In fact, for small businesses knowing who you don’t cater to can be essential in helping you grow. Why? Simple, if you’re small your advantage is that you can connect deeply with a specific segment of the market. You want to focus your efforts on the right customer who already is compelled to spend money on your offer.
If you’re spreading yourself thin by trying to be all things to everyone, you will only dilute your core message. Instead, keep your focus on your target customer. Define them, go deep, and you’ll be able to figure out how you can best serve them with your products and services.
Tip #4: Learn from your competition.
This works for brick-and-mortar businesses as well as internet businesses because it allows you to step into the shoes of your customer and open up to a new perspective of your business. Take a look around the internet and around your town. If you can, visit your competitor’s shops. For example, if you own a restaurant specializing in Italian cuisine, dine at the other Italian place in your neighborhood or in the next township.
As you experience the business from the customer’s perspective, look for what’s being done right and wrong.
Can you see areas that need attention or improvement? How are you running things in comparison? What’s the quality of their product and customer service ? Are the customers here pleased? Also, take a close look at their market segment. Who else is patronizing their business? Are they the same kinds of people who spend money with you? By asking these questions and doing in-person research, you can dig up a lot of information to help you define your unique selling position and create even better offers for your customers.
Tip #5: Get your target customers to open up and tell you everything.
A good customer survey is one of the most valuable market research tools because it gives you the opportunity to get inside your customer’s head. However, remember that some feedback may be harsh, so take criticism as a learning tool to point you in the right direction.
Creating a survey is simple. Ask questions about what your customer thinks you’re doing right and what can be improved. You can also prompt them to tell you what kinds of products and services they’d like to see you add, giving you fantastic insight into how to monetize your business more. Many customers will be delighted to offer feedback. You can even give customers who fill out surveys a gift like a special coupon for their next purchase.
Bonus Tip: Use an insight & research repository
An insight & research repository is a consolidated research management platform to derive insights about past and ongoing market research. With the use of such a tool, you can leverage past research to get to insights faster, build on previously done market research and draw trendlines, utilize research techniques that have worked in the past, and more.
Market research is one of the most effective ways to gain insight into your customer base , competitors , and the overall market. The goal of conducting market research is to equip your company with the information you need to make informed decisions.
It is especially important when small businesses are trying to determine whether a new business idea is viable, looking to move into a new market, or are launching a new product or service. Read below for a more in-depth look at how market research can help small businesses.
- COMPETITION According to a study conducted by Business Insider, 72% of small businesses focus on increasing revenue. Conducting research helps businesses gain insight into competitor behavior. By learning about your competitor’s strengths and weaknesses, you can learn how to position your product or offering. In order to be successful, small businesses need to have an understanding of what products and services competitors are offering, and their price point.
Learn more: Trend Analysis
- CUSTOMERS Many small businesses feel they need to understand their customers, only to conduct market research and learn they had the wrong assumptions. By researching, you can create a profile of your average customer and gain insight into their buying habits, how much they’re willing to spend, and which features resonate with them. Additionally, and perhaps more importantly, you can learn what will make someone use your product or service over a competitor.
Learn more: Customer Satisfaction Survey
- OPPORTUNITIES Potential opportunities, whether they are products or services, can be identified by conducting market research. By learning more about your customers, you can gather insights into complementary products and services. Consumer needs change over time, influenced by new technology and different conditions, and you may find new needs that are not being met, which can create new opportunities for your business.
Learn more: SWOT Analysis
- FORECAST A small business is affected by the performance of the local and national economy, as are its’ customers. If consumers are worried, then they will be more restrained when spending money, which affects the business. By conducting research with consumers, businesses can get an idea of whether they are optimistic or apprehensive about the direction of the economy, and make adjustments as necessary. For example, a small business owner may decide to postpone a new product launch if it appears the economic environment is turning negative.
Learn more: 300+ Market Research Survey Questionnaires
Market research and market intelligence may be as complex as the needs that each business or project has. The steps are usually the same. We hope this ultimate guide helps you have a better understanding of how to make your own market research project to gather insightful data and make better decisions.
LEARN ABOUT: Projective Techniques
We appreciate you taking the time to read this ultimate guide. We hope it was helpful!
You can now download our free ebook that will guide you through a market research project, from the planning stage to the presentation of the outcomes and their analysis.
Sign up now, and download our free ebook: The Hacker’s Guide to Advanced Research Methodologies
DOWNLOAD NOW
MORE LIKE THIS

Why Multilingual 360 Feedback Surveys Provide Better Insights
Jun 3, 2024

Raked Weighting: A Key Tool for Accurate Survey Results
May 31, 2024

Top 8 Data Trends to Understand the Future of Data
May 30, 2024

Top 12 Interactive Presentation Software to Engage Your User
May 29, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- UNC Libraries
- Subject Research
- Market Research Basics
- What is Market Research?
Market Research Basics: What is Market Research?
- Accessing Information
- Advanced Web Searching
- Definitions of Source Types
- Industry Codes
- Self-Check #1
- Track Down "Who Cares"
- Finding Trade Publications
- Finding Industry Reports
- Self-Check #2
- Finding Competitors
- Self-Check #3
- How to Size a Market
- Finding Demographic Data
- Finding Psychographic Data
- SimplyAnalytics
- Wrapping Up
Doing market research is like a cross between a scavenger hunt and a jigsaw puzzle.

There's no one magic information source that has all the answers. And sometimes, the information or data you're looking for may not even exist. Don't get discouraged! There are often alternate places to look or ways to search.
What is a market research definition?
Market research is " The process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a market, about a product or service to be offered for sale in that market, and about the past, present and potential customers for the product or service; research into the characteristics, spending habits, location and needs of your business's target market, the industry as a whole, and the particular competitors you face " ( source ).
Essentially, it helps you answer some of the following questions:
- What is the size of my market?
- Who are my competitors?
- Which market is best suited for my product or service?
- How much will customers pay for my product or service?
- What are the emerging trends in an industry?
These questions can be roughly divided into two categories, Industry Questions, and Market Sizing & Customer Discovery.
The best market research is a combination of primary and secondary information.
Primary information: research you compile yourself or hire someone to gather for you.
Secondary information : This type of research is already compiled and organized for you. Examples of secondary information include reports and studies by government agencies, trade associations or other businesses within your industry.( source )
This module focuses on secondary research.
The next section defines the information sources you will likely use in researching your market.
Business Research Consultant/Librarian

- << Previous: Advanced Web Searching
- Next: Definitions of Source Types >>
- Last Updated: Jan 22, 2024 2:24 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.unc.edu/market-research-tutorial
- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
Building an effective business launch plan
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Conducting Market Research
Crafting a business plan, reviewing funding options, understanding legal requirements, implementing marketing strategies, the bottom line.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Headshot-4c571aa3d8044192bcbd7647dd137cf1.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps CURRENT ARTICLE
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Starting a business in the United States involves a number of different steps spanning legal considerations, market research, creating a business plan, securing funding, and developing a marketing strategy. It also requires decisions about a business’ location, structure, name, taxation, and registration. Here are the key steps involved in starting a business, as well as important aspects of the process for entrepreneurs to consider.
Key Takeaways
- Entrepreneurs should start by conducting market research to understand their industry space, competition, and target customers.
- The next step is to write a comprehensive business plan, outlining the company’s structure, vision, and strategy.
- Securing funding in the form of grants, loans, venture capital, and/or crowdfunded money is crucial if you’re not self-funding.
- When choosing a venue, be aware of local regulations and requirements.
- Design your business structure with an eye to legal aspects, such as taxation and registration.
- Make a strategic marketing plan that addresses the specifics of the business, industry, and target market.
Before starting a business, entrepreneurs should conduct market research to determine their target audience, competition, and market trends. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) breaks down common market considerations as follows:
- Demand : Is there a need for this product or service?
- Market size : How many people might be interested?
- Economic indicators : What are the income, employment rate, and spending habits of potential customers?
- Location : Are the target market and business well situated for each other?
- Competition : What is the market saturation ? Who and how many are you going up against?
- Pricing : What might a customer be willing to pay?
Market research should also include an analysis of market opportunities, barriers to market entry, and industry trends, as well as the competition’s strengths, weaknesses, and market share .
There are various methods for conducting market research, and these will vary depending on the nature of the industry and potential business. Data can come from a variety of places, including statistical agencies, economic and financial institutions, and industry sources, as well as direct consumer research through focus groups, interviews, surveys, and questionnaires.
A comprehensive business plan is like a blueprint. It lays the foundation for business development and affects decision-making, day-to-day operations, and growth. Potential investors or partners may want to review and assess it in advance of agreeing to work together. Financial institutions often request business plans as part of an application for a loan or other forms of capital.
Business plans will differ according to the needs and nature of the company and should only include what makes sense for the business in question. As such, they can vary in length and structure. They can generally be divided into two formats: traditional and lean start-up. The latter is less common and more useful for simple businesses or those that expect to rework their traditional business plan frequently. It provides a vivid snapshot of the company through a small number of elements.
The process of funding a business depends on its needs and the vision and financial situation of its owner. The first step is to calculate the start-up costs . Identify a list of expenses and put a dollar amount to each of them through research and requesting quotes. The SBA has a start-up costs calculator for small businesses that includes common types of business expenses.
The next step is to determine how to get the money. Common methods include:
- Self-funding , also known as “ bootstrapping ”
- Finding investors willing to contribute to your venture capital
- Raising money online by crowdfunding
- Securing a business loan from a bank, an online lender, or a credit union
- Winning a business grant from a donor, usually a government, foundation, charity, or corporation
Different methods suit different businesses, and it’s important to consider the obligations associated with any avenue of funding. For example, investors generally want a degree of control for their money, while self-funding puts business owners fully in charge. Of course, investors also mitigate risk; self-funding does not.
Availability is another consideration. Loans are easier to get than grants, which don’t have to be paid back. Additionally, the federal government doesn’t provide grants for the purposes of starting or growing a business, although private organizations may. However, the SBA does guarantee several categories of loans , accessing capital that may not be available through traditional lenders. No matter the funding method(s), it’s essential to detail how the money will be used and lay out a future financial plan for the business, including sales projections and loan repayments .
Businesses operating in the U.S. are legally subject to regulations at the local, county, state, and federal level involving taxation, business IDs, registrations, and permits.
Choosing a Business Location
Where a business operates will dictate such things as taxes, zoning laws (for brick-and-mortar locations), licenses, and permits. Other considerations when choosing a location might include:
- Human factors : These include target audience and the preferences of business owners and partners regarding convenience, knowledge of the area, and commuting distance.
- Regulations : Government at every level will assert its authority.
- Regionally specific expenses : Examples are average salaries (including required minimum wages), property or rental prices, insurance rates, utilities, and government fees and licensing.
- The tax and financial environment : Tax types include income, sales, corporate, and property, as well as tax credits; available investment incentives and loan programs may also be geographically determined.
Picking a Business Structure
The structure of a business should reflect the desired number of owners, liability characteristics, and tax status. Because these have legal and tax compliance implications , it’s important to understand them fully. If necessary, consult a business counselor, a lawyer, and/or an accountant.
Common business structures include:
- Sole proprietorship : A sole proprietorship is an unincorporated business that has just one owner, who pays personal income tax on its profits.
- Partnership : Partnership options include a limited partnership (LP) and a limited liability partnership (LLP) .
- Limited liability company (LLC) : An LLC protects its owners from personal responsibility for the company’s debts and liabilities.
- Corporation : The different types of corporations include C corp , S corp , B corp , closed corporation , and nonprofit .
Getting a Tax ID Number
A tax ID number is the equivalent of a Social Security number for a business. Whether or not a state and/or federal tax ID number is required will depend on the nature of the business and the location in which it’s registered.
A federal tax ID, also known as an employer identification number (EIN) , is required if a business:
- Operates as a corporation or partnership
- Pays federal taxes
- Has employees
- Files employment, excise, alcohol, tobacco, or firearms tax returns
- Has a Keogh plan
- Withholds taxes on non-wage income to nonresident aliens
- Is involved with certain types of organizations, including trusts, estates, real estate mortgage investment conduits, nonprofits, farmers’ cooperatives, and plan administrators
An EIN can also be useful if you want to open a business bank account, offer an employer-sponsored retirement plan, or apply for federal business licenses and permits. You can get one online from the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) . State websites will do the same for a state tax ID.
Registering a Business
How you register a business will depend on its location, nature, size, and business structure. For example, a small business may not require any steps beyond registering its business name with local and state governments, and business owners whose business name is their own legal name might not need to register at all.
That said, registration can provide personal liability protection, tax-exempt status, and trademark protection, so it can be beneficial even if it’s not strictly required. Overall registration requirements, costs, and documentation will vary depending on the governing jurisdictions and business structure.
Most LLCs, corporations, partnerships, and nonprofits are required to register at the state level and will need a registered agent to file on their behalf. Determining which state to register with can depend on factors such as:
- Whether the business has a physical presence in the state
- If the business often conducts in-person client meetings in the state
- If a large portion of business revenue comes from the state
- Whether the business has employees working in the state
If a business operates in more than one state, it may need to file for foreign qualification in other states in which it conducts business. In this case the business would register in the state in which it was formed (this would be considered the domestic state) and file for foreign qualification in any additional states.
Obtaining Permits
Filing for the applicable government licenses and permits will depend on the industry and nature of the business and might include submitting an application to a federal agency, state, county, and/or city. The SBA lists federally regulated business activities alongside the corresponding license-issuing agency, while state, county, and city regulations can be found on the official government websites for each region.
Every business should have a marketing plan that outlines an overall strategy and the day-to-day tactics used to execute it. A successful marketing plan will lay out tactics for how to connect with customers and convince them to buy what the company is selling.
Marketing plans will vary according to the specifics of the industry, target market, and business, but they should aim to include descriptions of and strategies for the following:
- A target customer : Including market size, demographics, traits, and relevant trends
- Value propositions or business differentiators : An overview of the company’s competitive advantage with regard to employees, certifications, and offerings
- A sales and marketing plan : Including methods, channels, and a customer’s journey through interacting with the business
- Goals : Should cover different aspects of the marketing and sales strategy, such as social media follower growth, public relations opportunities, and sales targets
- An execution plan : Should detail tactics and break down higher-level goals into specific actions
- A budget : Detailing how much different marketing projects and activities will cost
How Much Does It Cost to Start a Business?
Business start-up costs will vary depending on the industry, business activity, and product or service offered. Home-based online businesses will usually cost less than those that require an office setting to meet with customers. The estimated cost can be calculated by first identifying a list of expenses and then researching and requesting quotes for each one. Use the SBA’s start-up costs calculator for common types of expenses associated with starting a small business.
What Should I Do Before Starting a Business?
Entrepreneurs seeking to start their own business should fully research and understand all the legal and funding considerations involved, conduct market research, and create marketing and business plans. They will also need to secure any necessary permits, licenses, funding, and business bank accounts.
What Types of Funding Are Available to Start a Business?
Start-up capital can come in the form of loans, grants, crowdfunding, venture capital, or self-funding. Note that the federal government does not provide grant funding for the purposes of starting a business, although some private sources do.
Do You Need to Write a Business Plan?
Business plans are comprehensive documents that lay out the most important information about a business. They reference its growth, development, and decision-making processes, and financial institutions and potential investors and partners generally request to review them in advance of agreeing to provide funding or to collaborate.
Starting a business is no easy feat, but research and preparation can help smooth the way. Having a firm understanding of your target market, competition, industry, goals, company structure, funding requirements, legal regulations, and marketing strategy, as well as conducting research and consulting experts where necessary, are all things that entrepreneurs can do to set themselves up for success.
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Calculate Your Startup Costs ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Fund Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Grants .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Loans .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Pick Your Business Location .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Choose a Business Structure .”
Internal Revenue Service. “ Do You Need an EIN? ”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Get Federal and State Tax ID Numbers .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Register Your Business .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Apply for Licenses and Permits .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Marketing and Sales .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1421562920-d5cf7a5a92204c579da450389c6b01a5.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- Ask a Librarian
ENTR Certificate: Market and Industry Research Reports
Market and industry research reports.
- Investors and Trending Markets
- Consumer and Location Research
- Company Research
Key Takeaways
- The terms "market research reports" and "industry reports" are somewhat interchangeable - this guide lists both types available at Purdue.
- Generally speaking, industry reports cover information about competitors within an industry, while market research reports focus on customers. However, industry and market reports typically contain both types of information.
Return to ENTR Certificate
Return to Landing Page
Tutorial Icons

Wide Coverage
Consumer Products and Services Focus
International Market Research Focus
IT/Digital/Ecommerce Focus
- Gartner This link opens in a new window Access the latest technology research and information. Provides timely, real-world examples and content about technology, applicable to many facets of education. West Lafayette students, faculty and staff can access the Gartner database using their Purdue Career Account credentials at no cost.
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Investors and Trending Markets >>
- Last Edited: May 28, 2024 12:14 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.purdue.edu/entr-cert
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 17 October 2023
The impact of founder personalities on startup success
- Paul X. McCarthy 1 , 2 ,
- Xian Gong 3 ,
- Fabian Braesemann 4 , 5 ,
- Fabian Stephany 4 , 5 ,
- Marian-Andrei Rizoiu 3 &
- Margaret L. Kern 6
Scientific Reports volume 13 , Article number: 17200 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
60k Accesses
2 Citations
305 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Human behaviour
- Information technology
An Author Correction to this article was published on 07 May 2024
This article has been updated
Startup companies solve many of today’s most challenging problems, such as the decarbonisation of the economy or the development of novel life-saving vaccines. Startups are a vital source of innovation, yet the most innovative are also the least likely to survive. The probability of success of startups has been shown to relate to several firm-level factors such as industry, location and the economy of the day. Still, attention has increasingly considered internal factors relating to the firm’s founding team, including their previous experiences and failures, their centrality in a global network of other founders and investors, as well as the team’s size. The effects of founders’ personalities on the success of new ventures are, however, mainly unknown. Here, we show that founder personality traits are a significant feature of a firm’s ultimate success. We draw upon detailed data about the success of a large-scale global sample of startups (n = 21,187). We find that the Big Five personality traits of startup founders across 30 dimensions significantly differ from that of the population at large. Key personality facets that distinguish successful entrepreneurs include a preference for variety, novelty and starting new things (openness to adventure), like being the centre of attention (lower levels of modesty) and being exuberant (higher activity levels). We do not find one ’Founder-type’ personality; instead, six different personality types appear. Our results also demonstrate the benefits of larger, personality-diverse teams in startups, which show an increased likelihood of success. The findings emphasise the role of the diversity of personality types as a novel dimension of team diversity that influences performance and success.
Similar content being viewed by others

Predicting success in the worldwide start-up network
The personality traits of self-made and inherited millionaires
The nexus of top executives’ attributes, firm strategies, and outcomes: Large firms versus SMEs
Introduction.
The success of startups is vital to economic growth and renewal, with a small number of young, high-growth firms creating a disproportionately large share of all new jobs 1 , 2 . Startups create jobs and drive economic growth, and they are also an essential vehicle for solving some of society’s most pressing challenges.
As a poignant example, six centuries ago, the German city of Mainz was abuzz as the birthplace of the world’s first moveable-type press created by Johannes Gutenberg. However, in the early part of this century, it faced several economic challenges, including rising unemployment and a significant and growing municipal debt. Then in 2008, two Turkish immigrants formed the company BioNTech in Mainz with another university research colleague. Together they pioneered new mRNA-based technologies. In 2020, BioNTech partnered with US pharmaceutical giant Pfizer to create one of only a handful of vaccines worldwide for Covid-19, saving an estimated six million lives 3 . The economic benefit to Europe and, in particular, the German city where the vaccine was developed has been significant, with windfall tax receipts to the government clearing Mainz’s €1.3bn debt and enabling tax rates to be reduced, attracting other businesses to the region as well as inspiring a whole new generation of startups 4 .
While stories such as the success of BioNTech are often retold and remembered, their success is the exception rather than the rule. The overwhelming majority of startups ultimately fail. One study of 775 startups in Canada that successfully attracted external investment found only 35% were still operating seven years later 5 .
But what determines the success of these ‘lucky few’? When assessing the success factors of startups, especially in the early-stage unproven phase, venture capitalists and other investors offer valuable insights. Three different schools of thought characterise their perspectives: first, supply-side or product investors : those who prioritise investing in firms they consider to have novel and superior products and services, investing in companies with intellectual property such as patents and trademarks. Secondly, demand-side or market-based investors : those who prioritise investing in areas of highest market interest, such as in hot areas of technology like quantum computing or recurrent or emerging large-scale social and economic challenges such as the decarbonisation of the economy. Thirdly, talent investors : those who prioritise the foundation team above the startup’s initial products or what industry or problem it is looking to address.
Investors who adopt the third perspective and prioritise talent often recognise that a good team can overcome many challenges in the lead-up to product-market fit. And while the initial products of a startup may or may not work a successful and well-functioning team has the potential to pivot to new markets and new products, even if the initial ones prove untenable. Not surprisingly, an industry ‘autopsy’ into 101 tech startup failures found 23% were due to not having the right team—the number three cause of failure ahead of running out of cash or not having a product that meets the market need 6 .
Accordingly, early entrepreneurship research was focused on the personality of founders, but the focus shifted away in the mid-1980s onwards towards more environmental factors such as venture capital financing 7 , 8 , 9 , networks 10 , location 11 and due to a range of issues and challenges identified with the early entrepreneurship personality research 12 , 13 . At the turn of the 21st century, some scholars began exploring ways to combine context and personality and reconcile entrepreneurs’ individual traits with features of their environment. In her influential work ’The Sociology of Entrepreneurship’, Patricia H. Thornton 14 discusses two perspectives on entrepreneurship: the supply-side perspective (personality theory) and the demand-side perspective (environmental approach). The supply-side perspective focuses on the individual traits of entrepreneurs. In contrast, the demand-side perspective focuses on the context in which entrepreneurship occurs, with factors such as finance, industry and geography each playing their part. In the past two decades, there has been a revival of interest and research that explores how entrepreneurs’ personality relates to the success of their ventures. This new and growing body of research includes several reviews and meta-studies, which show that personality traits play an important role in both career success and entrepreneurship 15 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 , that there is heterogeneity in definitions and samples used in research on entrepreneurship 16 , 18 , and that founder personality plays an important role in overall startup outcomes 17 , 19 .
Motivated by the pivotal role of the personality of founders on startup success outlined in these recent contributions, we investigate two main research questions:
Which personality features characterise founders?
Do their personalities, particularly the diversity of personality types in founder teams, play a role in startup success?
We aim to understand whether certain founder personalities and their combinations relate to startup success, defined as whether their company has been acquired, acquired another company or listed on a public stock exchange. For the quantitative analysis, we draw on a previously published methodology 20 , which matches people to their ‘ideal’ jobs based on social media-inferred personality traits.
We find that personality traits matter for startup success. In addition to firm-level factors of location, industry and company age, we show that founders’ specific Big Five personality traits, such as adventurousness and openness, are significantly more widespread among successful startups. As we find that companies with multi-founder teams are more likely to succeed, we cluster founders in six different and distinct personality groups to underline the relevance of the complementarity in personality traits among founder teams. Startups with diverse and specific combinations of founder types (e. g., an adventurous ‘Leader’, a conscientious ‘Accomplisher’, and an extroverted ‘Developer’) have significantly higher odds of success.
We organise the rest of this paper as follows. In the Section " Results ", we introduce the data used and the methods applied to relate founders’ psychological traits with their startups’ success. We introduce the natural language processing method to derive individual and team personality characteristics and the clustering technique to identify personality groups. Then, we present the result for multi-variate regression analysis that allows us to relate firm success with external and personality features. Subsequently, the Section " Discussion " mentions limitations and opportunities for future research in this domain. In the Section " Methods ", we describe the data, the variables in use, and the clustering in greater detail. Robustness checks and additional analyses can be found in the Supplementary Information.
Our analysis relies on two datasets. We infer individual personality facets via a previously published methodology 20 from Twitter user profiles. Here, we restrict our analysis to founders with a Crunchbase profile. Crunchbase is the world’s largest directory on startups. It provides information about more than one million companies, primarily focused on funding and investors. A company’s public Crunchbase profile can be considered a digital business card of an early-stage venture. As such, the founding teams tend to provide information about themselves, including their educational background or a link to their Twitter account.
We infer the personality profiles of the founding teams of early-stage ventures from their publicly available Twitter profiles, using the methodology described by Kern et al. 20 . Then, we correlate this information to data from Crunchbase to determine whether particular combinations of personality traits correspond to the success of early-stage ventures. The final dataset used in the success prediction model contains n = 21,187 startup companies (for more details on the data see the Methods section and SI section A.5 ).
Revisions of Crunchbase as a data source for investigations on a firm and industry level confirm the platform to be a useful and valuable source of data for startups research, as comparisons with other sources at micro-level, e.g., VentureXpert or PwC, also suggest that the platform’s coverage is very comprehensive, especially for start-ups located in the United States 21 . Moreover, aggregate statistics on funding rounds by country and year are quite similar to those produced with other established sources, going to validate the use of Crunchbase as a reliable source in terms of coverage of funded ventures. For instance, Crunchbase covers about the same number of investment rounds in the analogous sectors as collected by the National Venture Capital Association 22 . However, we acknowledge that the data source might suffer from registration latency (a certain delay between the foundation of the company and its actual registration on Crunchbase) and success bias in company status (the likeliness that failed companies decide to delete their profile from the database).
The definition of startup success
The success of startups is uncertain, dependent on many factors and can be measured in various ways. Due to the likelihood of failure in startups, some large-scale studies have looked at which features predict startup survival rates 23 , and others focus on fundraising from external investors at various stages 24 . Success for startups can be measured in multiple ways, such as the amount of external investment attracted, the number of new products shipped or the annual growth in revenue. But sometimes external investments are misguided, revenue growth can be short-lived, and new products may fail to find traction.
Success in a startup is typically staged and can appear in different forms and times. For example, a startup may be seen to be successful when it finds a clear solution to a widely recognised problem, such as developing a successful vaccine. On the other hand, it could be achieving some measure of commercial success, such as rapidly accelerating sales or becoming profitable or at least cash positive. Or it could be reaching an exit for foundation investors via a trade sale, acquisition or listing of its shares for sale on a public stock exchange via an Initial Public Offering (IPO).
For our study, we focused on the startup’s extrinsic success rather than the founders’ intrinsic success per se, as its more visible, objective and measurable. A frequently considered measure of success is the attraction of external investment by venture capitalists 25 . However, this is not in and of itself a good measure of clear, incontrovertible success, particularly for early-stage ventures. This is because it reflects investors’ expectations of a startup’s success potential rather than actual business success. Similarly, we considered other measures like revenue growth 26 , liquidity events 27 , 28 , 29 , profitability 30 and social impact 31 , all of which have benefits as they capture incremental success, but each also comes with operational measurement challenges.
Therefore, we apply the success definition initially introduced by Bonaventura et al. 32 , namely that a startup is acquired, acquires another company or has an initial public offering (IPO). We consider any of these major capital liquidation events as a clear threshold signal that the company has matured from an early-stage venture to becoming or is on its way to becoming a mature company with clear and often significant business growth prospects. Together these three major liquidity events capture the primary forms of exit for external investors (an acquisition or trade sale and an IPO). For companies with a longer autonomous growth runway, acquiring another company marks a similar milestone of scale, maturity and capability.
Using multifactor analysis and a binary classification prediction model of startup success, we looked at many variables together and their relative influence on the probability of the success of startups. We looked at seven categories of factors through three lenses of firm-level factors: (1) location, (2) industry, (3) age of the startup; founder-level factors: (4) number of founders, (5) gender of founders, (6) personality characteristics of founders and; lastly team-level factors: (7) founder-team personality combinations. The model performance and relative impacts on the probability of startup success of each of these categories of founders are illustrated in more detail in section A.6 of the Supplementary Information (in particular Extended Data Fig. 19 and Extended Data Fig. 20 ). In total, we considered over three hundred variables (n = 323) and their relative significant associations with success.
The personality of founders
Besides product-market, industry, and firm-level factors (see SI section A.1 ), research suggests that the personalities of founders play a crucial role in startup success 19 . Therefore, we examine the personality characteristics of individual startup founders and teams of founders in relationship to their firm’s success by applying the success definition used by Bonaventura et al. 32 .
Employing established methods 33 , 34 , 35 , we inferred the personality traits across 30 dimensions (Big Five facets) of a large global sample of startup founders. The startup founders cohort was created from a subset of founders from the global startup industry directory Crunchbase, who are also active on the social media platform Twitter.
To measure the personality of the founders, we used the Big Five, a popular model of personality which includes five core traits: Openness to Experience, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness, and Emotional stability. Each of these traits can be further broken down into thirty distinct facets. Studies have found that the Big Five predict meaningful life outcomes, such as physical and mental health, longevity, social relationships, health-related behaviours, antisocial behaviour, and social contribution, at levels on par with intelligence and socioeconomic status 36 Using machine learning to infer personality traits by analysing the use of language and activity on social media has been shown to be more accurate than predictions of coworkers, friends and family and similar in accuracy to the judgement of spouses 37 . Further, as other research has shown, we assume that personality traits remain stable in adulthood even through significant life events 38 , 39 , 40 . Personality traits have been shown to emerge continuously from those already evident in adolescence 41 and are not significantly influenced by external life events such as becoming divorced or unemployed 42 . This suggests that the direction of any measurable effect goes from founder personalities to startup success and not vice versa.
As a first investigation to what extent personality traits might relate to entrepreneurship, we use the personality characteristics of individuals to predict whether they were an entrepreneur or an employee. We trained and tested a machine-learning random forest classifier to distinguish and classify entrepreneurs from employees and vice-versa using inferred personality vectors alone. As a result, we found we could correctly predict entrepreneurs with 77% accuracy and employees with 88% accuracy (Fig. 1 A). Thus, based on personality information alone, we correctly predict all unseen new samples with 82.5% accuracy (See SI section A.2 for more details on this analysis, the classification modelling and prediction accuracy).
We explored in greater detail which personality features are most prominent among entrepreneurs. We found that the subdomain or facet of Adventurousness within the Big Five Domain of Openness was significant and had the largest effect size. The facet of Modesty within the Big Five Domain of Agreeableness and Activity Level within the Big Five Domain of Extraversion was the subsequent most considerable effect (Fig. 1 B). Adventurousness in the Big Five framework is defined as the preference for variety, novelty and starting new things—which are consistent with the role of a startup founder whose role, especially in the early life of the company, is to explore things that do not scale easily 43 and is about developing and testing new products, services and business models with the market.
Once we derived and tested the Big Five personality features for each entrepreneur in our data set, we examined whether there is evidence indicating that startup founders naturally cluster according to their personality features using a Hopkins test (see Extended Data Figure 6 ). We discovered clear clustering tendencies in the data compared with other renowned reference data sets known to have clusters. Then, once we established the founder data clusters, we used agglomerative hierarchical clustering. This ‘bottom-up’ clustering technique initially treats each observation as an individual cluster. Then it merges them to create a hierarchy of possible cluster schemes with differing numbers of groups (See Extended Data Fig. 7 ). And lastly, we identified the optimum number of clusters based on the outcome of four different clustering performance measurements: Davies-Bouldin Index, Silhouette coefficients, Calinski-Harabas Index and Dunn Index (see Extended Data Figure 8 ). We find that the optimum number of clusters of startup founders based on their personality features is six (labelled #0 through to #5), as shown in Fig. 1 C.
To better understand the context of different founder types, we positioned each of the six types of founders within an occupation-personality matrix established from previous research 44 . This research showed that ‘each job has its own personality’ using a substantial sample of employees across various jobs. Utilising the methodology employed in this study, we assigned labels to the cluster names #0 to #5, which correspond to the identified occupation tribes that best describe the personality facets represented by the clusters (see Extended Data Fig. 9 for an overview of these tribes, as identified by McCarthy et al. 44 ).
Utilising this approach, we identify three ’purebred’ clusters: #0, #2 and #5, whose members are dominated by a single tribe (larger than 60% of all individuals in each cluster are characterised by one tribe). Thus, these clusters represent and share personality attributes of these previously identified occupation-personality tribes 44 , which have the following known distinctive personality attributes (see also Table 1 ):
Accomplishers (#0) —Organised & outgoing. confident, down-to-earth, content, accommodating, mild-tempered & self-assured.
Leaders (#2) —Adventurous, persistent, dispassionate, assertive, self-controlled, calm under pressure, philosophical, excitement-seeking & confident.
Fighters (#5) —Spontaneous and impulsive, tough, sceptical, and uncompromising.
We labelled these clusters with the tribe names, acknowledging that labels are somewhat arbitrary, based on our best interpretation of the data (See SI section A.3 for more details).
For the remaining three clusters #1, #3 and #4, we can see they are ‘hybrids’, meaning that the founders within them come from a mix of different tribes, with no one tribe representing more than 50% of the members of that cluster. However, the tribes with the largest share were noted as #1 Experts/Engineers, #3 Fighters, and #4 Operators.
To label these three hybrid clusters, we examined the closest occupations to the median personality features of each cluster. We selected a name that reflected the common themes of these occupations, namely:
Experts/Engineers (#1) as the closest roles included Materials Engineers and Chemical Engineers. This is consistent with this cluster’s personality footprint, which is highest in openness in the facets of imagination and intellect.
Developers (#3) as the closest roles include Application Developers and related technology roles such as Business Systems Analysts and Product Managers.
Operators (#4) as the closest roles include service, maintenance and operations functions, including Bicycle Mechanic, Mechanic and Service Manager. This is also consistent with one of the key personality traits of high conscientiousness in the facet of orderliness and high agreeableness in the facet of humility for founders in this cluster.
Founder-Level Factors of Startup Success. ( A ), Successful entrepreneurs differ from successful employees. They can be accurately distinguished using a classifier with personality information alone. ( B ), Successful entrepreneurs have different Big Five facet distributions, especially on adventurousness, modesty and activity level. ( C ), Founders come in six different types: Fighters, Operators, Accomplishers, Leaders, Engineers and Developers (FOALED) ( D ), Each founder Personality-Type has its distinct facet.
Together, these six different types of startup founders (Fig. 1 C) represent a framework we call the FOALED model of founder types—an acronym of Fighters, Operators, Accomplishers, Leaders, Engineers and D evelopers.
Each founder’s personality type has its distinct facet footprint (for more details, see Extended Data Figure 10 in SI section A.3 ). Also, we observe a central core of correlated features that are high for all types of entrepreneurs, including intellect, adventurousness and activity level (Fig. 1 D).To test the robustness of the clustering of the personality facets, we compare the mean scores of the individual facets per cluster with a 20-fold resampling of the data and find that the clusters are, overall, largely robust against resampling (see Extended Data Figure 11 in SI section A.3 for more details).
We also find that the clusters accord with the distribution of founders’ roles in their startups. For example, Accomplishers are often Chief Executive Officers, Chief Financial Officers, or Chief Operating Officers, while Fighters tend to be Chief Technical Officers, Chief Product Officers, or Chief Commercial Officers (see Extended Data Fig. 12 in SI section A.4 for more details).
The ensemble theory of success
While founders’ individual personality traits, such as Adventurousness or Openness, show to be related to their firms’ success, we also hypothesise that the combination, or ensemble, of personality characteristics of a founding team impacts the chances of success. The logic behind this reasoning is complementarity, which is proposed by contemporary research on the functional roles of founder teams. Examples of these clear functional roles have evolved in established industries such as film and television, construction, and advertising 45 . When we subsequently explored the combinations of personality types among founders and their relationship to the probability of startup success, adjusted for a range of other factors in a multi-factorial analysis, we found significantly increased chances of success for mixed foundation teams:
Initially, we find that firms with multiple founders are more likely to succeed, as illustrated in Fig. 2 A, which shows firms with three or more founders are more than twice as likely to succeed than solo-founded startups. This finding is consistent with investors’ advice to founders and previous studies 46 . We also noted that some personality types of founders increase the probability of success more than others, as shown in SI section A.6 (Extended Data Figures 16 and 17 ). Also, we note that gender differences play out in the distribution of personality facets: successful female founders and successful male founders show facet scores that are more similar to each other than are non-successful female founders to non-successful male founders (see Extended Data Figure 18 ).
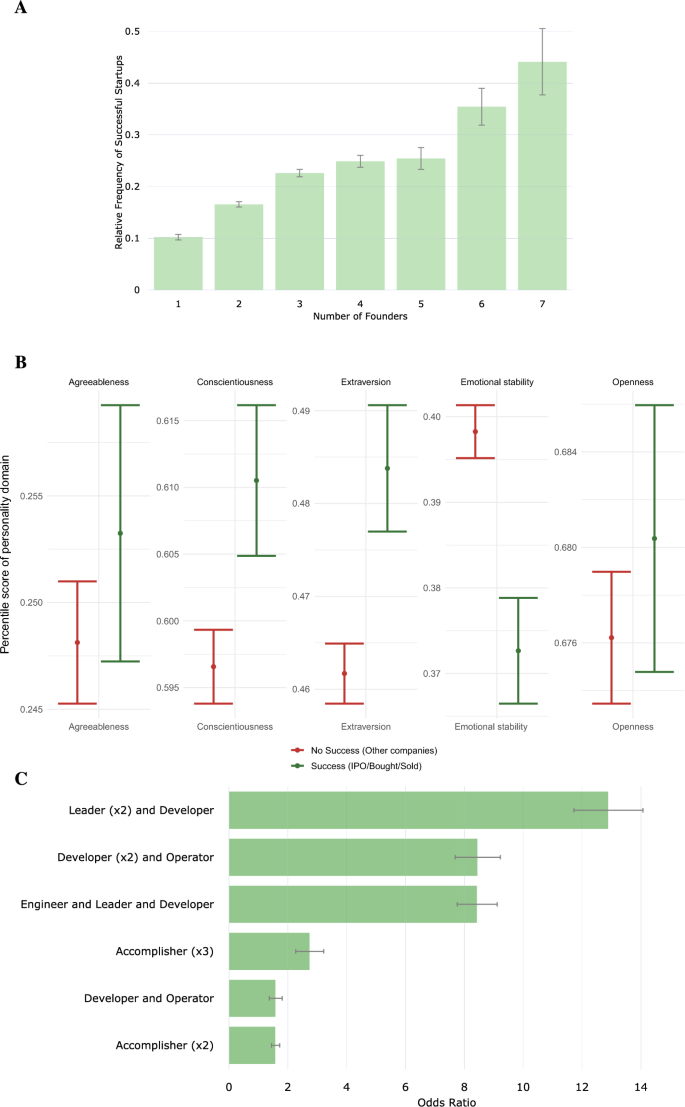
The Ensemble Theory of Team-Level Factors of Startup Success. ( A ) Having a larger founder team elevates the chances of success. This can be due to multiple reasons, e.g., a more extensive network or knowledge base but also personality diversity. ( B ) We show that joint personality combinations of founders are significantly related to higher chances of success. This is because it takes more than one founder to cover all beneficial personality traits that ‘breed’ success. ( C ) In our multifactor model, we show that firms with diverse and specific combinations of types of founders have significantly higher odds of success.
Access to more extensive networks and capital could explain the benefits of having more founders. Still, as we find here, it also offers a greater diversity of combined personalities, naturally providing a broader range of maximum traits. So, for example, one founder may be more open and adventurous, and another could be highly agreeable and trustworthy, thus, potentially complementing each other’s particular strengths associated with startup success.
The benefits of larger and more personality-diverse foundation teams can be seen in the apparent differences between successful and unsuccessful firms based on their combined Big Five personality team footprints, as illustrated in Fig. 2 B. Here, maximum values for each Big Five trait of a startup’s co-founders are mapped; stratified by successful and non-successful companies. Founder teams of successful startups tend to score higher on Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, and Agreeableness.
When examining the combinations of founders with different personality types, we find that some ensembles of personalities were significantly correlated with greater chances of startup success—while controlling for other variables in the model—as shown in Fig. 2 C (for more details on the modelling, the predictive performance and the coefficient estimates of the final model, see Extended Data Figures 19 , 20 , and 21 in SI section A.6 ).
Three combinations of trio-founder companies were more than twice as likely to succeed than other combinations, namely teams with (1) a Leader and two Developers , (2) an Operator and two Developers , and (3) an Expert/Engineer , Leader and Developer . To illustrate the potential mechanisms on how personality traits might influence the success of startups, we provide some examples of well-known, successful startup founders and their characteristic personality traits in Extended Data Figure 22 .
Startups are one of the key mechanisms for brilliant ideas to become solutions to some of the world’s most challenging economic and social problems. Examples include the Google search algorithm, disability technology startup Fingerwork’s touchscreen technology that became the basis of the Apple iPhone, or the Biontech mRNA technology that powered Pfizer’s COVID-19 vaccine.
We have shown that founders’ personalities and the combination of personalities in the founding team of a startup have a material and significant impact on its likelihood of success. We have also shown that successful startup founders’ personality traits are significantly different from those of successful employees—so much so that a simple predictor can be trained to distinguish between employees and entrepreneurs with more than 80% accuracy using personality trait data alone.
Just as occupation-personality maps derived from data can provide career guidance tools, so too can data on successful entrepreneurs’ personality traits help people decide whether becoming a founder may be a good choice for them.
We have learnt through this research that there is not one type of ideal ’entrepreneurial’ personality but six different types. Many successful startups have multiple co-founders with a combination of these different personality types.
To a large extent, founding a startup is a team sport; therefore, diversity and complementarity of personalities matter in the foundation team. It has an outsized impact on the company’s likelihood of success. While all startups are high risk, the risk becomes lower with more founders, particularly if they have distinct personality traits.
Our work demonstrates the benefits of personality diversity among the founding team of startups. Greater awareness of this novel form of diversity may help create more resilient startups capable of more significant innovation and impact.
The data-driven research approach presented here comes with certain methodological limitations. The principal data sources of this study—Crunchbase and Twitter—are extensive and comprehensive, but there are characterised by some known and likely sample biases.
Crunchbase is the principal public chronicle of venture capital funding. So, there is some likely sample bias toward: (1) Startup companies that are funded externally: self-funded or bootstrapped companies are less likely to be represented in Crunchbase; (2) technology companies, as that is Crunchbase’s roots; (3) multi-founder companies; (4) male founders: while the representation of female founders is now double that of the mid-2000s, women still represent less than 25% of the sample; (5) companies that succeed: companies that fail, especially those that fail early, are likely to be less represented in the data.
Samples were also limited to those founders who are active on Twitter, which adds additional selection biases. For example, Twitter users typically are younger, more educated and have a higher median income 47 . Another limitation of our approach is the potentially biased presentation of a person’s digital identity on social media, which is the basis for identifying personality traits. For example, recent research suggests that the language and emotional tone used by entrepreneurs in social media can be affected by events such as business failure 48 , which might complicate the personality trait inference.
In addition to sampling biases within the data, there are also significant historical biases in startup culture. For many aspects of the entrepreneurship ecosystem, women, for example, are at a disadvantage 49 . Male-founded companies have historically dominated most startup ecosystems worldwide, representing the majority of founders and the overwhelming majority of venture capital investors. As a result, startups with women have historically attracted significantly fewer funds 50 , in part due to the male bias among venture investors, although this is now changing, albeit slowly 51 .
The research presented here provides quantitative evidence for the relevance of personality types and the diversity of personalities in startups. At the same time, it brings up other questions on how personality traits are related to other factors associated with success, such as:
Will the recent growing focus on promoting and investing in female founders change the nature, composition and dynamics of startups and their personalities leading to a more diverse personality landscape in startups?
Will the growth of startups outside of the United States change what success looks like to investors and hence the role of different personality traits and their association to diverse success metrics?
Many of today’s most renowned entrepreneurs are either Baby Boomers (such as Gates, Branson, Bloomberg) or Generation Xers (such as Benioff, Cannon-Brookes, Musk). However, as we can see, personality is both a predictor and driver of success in entrepreneurship. Will generation-wide differences in personality and outlook affect startups and their success?
Moreover, the findings shown here have natural extensions and applications beyond startups, such as for new projects within large established companies. While not technically startups, many large enterprises and industries such as construction, engineering and the film industry rely on forming new project-based, cross-functional teams that are often new ventures and share many characteristics of startups.
There is also potential for extending this research in other settings in government, NGOs, and within the research community. In scientific research, for example, team diversity in terms of age, ethnicity and gender has been shown to be predictive of impact, and personality diversity may be another critical dimension 52 .
Another extension of the study could investigate the development of the language used by startup founders on social media over time. Such an extension could investigate whether the language (and inferred psychological characteristics) change as the entrepreneurs’ ventures go through major business events such as foundation, funding, or exit.
Overall, this study demonstrates, first, that startup founders have significantly different personalities than employees. Secondly, besides firm-level factors, which are known to influence firm success, we show that a range of founder-level factors, notably the character traits of its founders, significantly impact a startup’s likelihood of success. Lastly, we looked at team-level factors. We discovered in a multifactor analysis that personality-diverse teams have the most considerable impact on the probability of a startup’s success, underlining the importance of personality diversity as a relevant factor of team performance and success.
Data sources
Entrepreneurs dataset.
Data about the founders of startups were collected from Crunchbase (Table 2 ), an open reference platform for business information about private and public companies, primarily early-stage startups. It is one of the largest and most comprehensive data sets of its kind and has been used in over 100 peer-reviewed research articles about economic and managerial research.
Crunchbase contains data on over two million companies - mainly startup companies and the companies who partner with them, acquire them and invest in them, as well as profiles on well over one million individuals active in the entrepreneurial ecosystem worldwide from over 200 countries and spans. Crunchbase started in the technology startup space, and it now covers all sectors, specifically focusing on entrepreneurship, investment and high-growth companies.
While Crunchbase contains data on over one million individuals in the entrepreneurial ecosystem, some are not entrepreneurs or startup founders but play other roles, such as investors, lawyers or executives at companies that acquire startups. To create a subset of only entrepreneurs, we selected a subset of 32,732 who self-identify as founders and co-founders (by job title) and who are also publicly active on the social media platform Twitter. We also removed those who also are venture capitalists to distinguish between investors and founders.
We selected founders active on Twitter to be able to use natural language processing to infer their Big Five personality features using an open-vocabulary approach shown to be accurate in the previous research by analysing users’ unstructured text, such as Twitter posts in our case. For this project, as with previous research 20 , we employed a commercial service, IBM Watson Personality Insight, to infer personality facets. This service provides raw scores and percentile scores of Big Five Domains (Openness, Conscientiousness, Extraversion, Agreeableness and Emotional Stability) and the corresponding 30 subdomains or facets. In addition, the public content of Twitter posts was collected, and there are 32,732 profiles that each had enough Twitter posts (more than 150 words) to get relatively accurate personality scores (less than 12.7% Average Mean Absolute Error).
The entrepreneurs’ dataset is analysed in combination with other data about the companies they founded to explore questions about the nature and patterns of personality traits of entrepreneurs and the relationships between these patterns and company success.
For the multifactor analysis, we further filtered the data in several preparatory steps for the success prediction modelling (for more details, see SI section A.5 ). In particular, we removed data points with missing values (Extended Data Fig. 13 ) and kept only companies in the data that were founded from 1990 onward to ensure consistency with previous research 32 (see Extended Data Fig. 14 ). After cleaning, filtering and pre-processing the data, we ended up with data from 25,214 founders who founded 21,187 startup companies to be used in the multifactor analysis. Of those, 3442 startups in the data were successful, 2362 in the first seven years after they were founded (see Extended Data Figure 15 for more details).
Entrepreneurs and employees dataset
To investigate whether startup founders show personality traits that are similar or different from the population at large (i. e. the entrepreneurs vs employees sub-analysis shown in Fig. 1 A and B), we filtered the entrepreneurs’ data further: we reduced the sample to those founders of companies, which attracted more than US$100k in investment to create a reference set of successful entrepreneurs (n \(=\) 4400).
To create a control group of employees who are not also entrepreneurs or very unlikely to be of have been entrepreneurs, we leveraged the fact that while some occupational titles like CEO, CTO and Public Speaker are commonly shared by founders and co-founders, some others such as Cashier , Zoologist and Detective very rarely co-occur seem to be founders or co-founders. To illustrate, many company founders also adopt regular occupation titles such as CEO or CTO. Many founders will be Founder and CEO or Co-founder and CTO. While founders are often CEOs or CTOs, the reverse is not necessarily true, as many CEOs are professional executives that were not involved in the establishment or ownership of the firm.
Using data from LinkedIn, we created an Entrepreneurial Occupation Index (EOI) based on the ratio of entrepreneurs for each of the 624 occupations used in a previous study of occupation-personality fit 44 . It was calculated based on the percentage of all people working in the occupation from LinkedIn compared to those who shared the title Founder or Co-founder (See SI section A.2 for more details). A reference set of employees (n=6685) was then selected across the 112 different occupations with the lowest propensity for entrepreneurship (less than 0.5% EOI) from a large corpus of Twitter users with known occupations, which is also drawn from the previous occupational-personality fit study 44 .
These two data sets were used to test whether it may be possible to distinguish successful entrepreneurs from successful employees based on the different patterns of personality traits alone.
Hierarchical clustering
We applied several clustering techniques and tests to the personality vectors of the entrepreneurs’ data set to determine if there are natural clusters and, if so, how many are the optimum number.
Firstly, to determine if there is a natural typology to founder personalities, we applied the Hopkins statistic—a statistical test we used to answer whether the entrepreneurs’ dataset contains inherent clusters. It measures the clustering tendency based on the ratio of the sum of distances of real points within a sample of the entrepreneurs’ dataset to their nearest neighbours and the sum of distances of randomly selected artificial points from a simulated uniform distribution to their nearest neighbours in the real entrepreneurs’ dataset. The ratio measures the difference between the entrepreneurs’ data distribution and the simulated uniform distribution, which tests the randomness of the data. The range of Hopkins statistics is from 0 to 1. The scores are close to 0, 0.5 and 1, respectively, indicating whether the dataset is uniformly distributed, randomly distributed or highly clustered.
To cluster the founders by personality facets, we used Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering (AHC)—a bottom-up approach that treats an individual data point as a singleton cluster and then iteratively merges pairs of clusters until all data points are included in the single big collection. Ward’s linkage method is used to choose the pair of groups for minimising the increase in the within-cluster variance after combining. AHC was widely applied to clustering analysis since a tree hierarchy output is more informative and interpretable than K-means. Dendrograms were used to visualise the hierarchy to provide the perspective of the optimal number of clusters. The heights of the dendrogram represent the distance between groups, with lower heights representing more similar groups of observations. A horizontal line through the dendrogram was drawn to distinguish the number of significantly different clusters with higher heights. However, as it is not possible to determine the optimum number of clusters from the dendrogram, we applied other clustering performance metrics to analyse the optimal number of groups.
A range of Clustering performance metrics were used to help determine the optimal number of clusters in the dataset after an apparent clustering tendency was confirmed. The following metrics were implemented to evaluate the differences between within-cluster and between-cluster distances comprehensively: Dunn Index, Calinski-Harabasz Index, Davies-Bouldin Index and Silhouette Index. The Dunn Index measures the ratio of the minimum inter-cluster separation and the maximum intra-cluster diameter. At the same time, the Calinski-Harabasz Index improves the measurement of the Dunn Index by calculating the ratio of the average sum of squared dispersion of inter-cluster and intra-cluster. The Davies-Bouldin Index simplifies the process by treating each cluster individually. It compares the sum of the average distance among intra-cluster data points to the cluster centre of two separate groups with the distance between their centre points. Finally, the Silhouette Index is the overall average of the silhouette coefficients for each sample. The coefficient measures the similarity of the data point to its cluster compared with the other groups. Higher scores of the Dunn, Calinski-Harabasz and Silhouette Index and a lower score of the Davies-Bouldin Index indicate better clustering configuration.
Classification modelling
Classification algorithms.
To obtain a comprehensive and robust conclusion in the analysis predicting whether a given set of personality traits corresponds to an entrepreneur or an employee, we explored the following classifiers: Naïve Bayes, Elastic Net regularisation, Support Vector Machine, Random Forest, Gradient Boosting and Stacked Ensemble. The Naïve Bayes classifier is a probabilistic algorithm based on Bayes’ theorem with assumptions of independent features and equiprobable classes. Compared with other more complex classifiers, it saves computing time for large datasets and performs better if the assumptions hold. However, in the real world, those assumptions are generally violated. Elastic Net regularisation combines the penalties of Lasso and Ridge to regularise the Logistic classifier. It eliminates the limitation of multicollinearity in the Lasso method and improves the limitation of feature selection in the Ridge method. Even though Elastic Net is as simple as the Naïve Bayes classifier, it is more time-consuming. The Support Vector Machine (SVM) aims to find the ideal line or hyperplane to separate successful entrepreneurs and employees in this study. The dividing line can be non-linear based on a non-linear kernel, such as the Radial Basis Function Kernel. Therefore, it performs well on high-dimensional data while the ’right’ kernel selection needs to be tuned. Random Forest (RF) and Gradient Boosting Trees (GBT) are ensembles of decision trees. All trees are trained independently and simultaneously in RF, while a new tree is trained each time and corrected by previously trained trees in GBT. RF is a more robust and straightforward model since it does not have many hyperparameters to tune. GBT optimises the objective function and learns a more accurate model since there is a successive learning and correction process. Stacked Ensemble combines all existing classifiers through a Logistic Regression. Better than bagging with only variance reduction and boosting with only bias reduction, the ensemble leverages the benefit of model diversity with both lower variance and bias. All the above classification algorithms distinguish successful entrepreneurs and employees based on the personality matrix.
Evaluation metrics
A range of evaluation metrics comprehensively explains the performance of a classification prediction. The most straightforward metric is accuracy, which measures the overall portion of correct predictions. It will mislead the performance of an imbalanced dataset. The F1 score is better than accuracy by combining precision and recall and considering the False Negatives and False Positives. Specificity measures the proportion of detecting the true negative rate that correctly identifies employees, while Positive Predictive Value (PPV) calculates the probability of accurately predicting successful entrepreneurs. Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (AUROC) determines the capability of the algorithm to distinguish between successful entrepreneurs and employees. A higher value means the classifier performs better on separating the classes.
Feature importance
To further understand and interpret the classifier, it is critical to identify variables with significant predictive power on the target. Feature importance of tree-based models measures Gini importance scores for all predictors, which evaluate the overall impact of the model after cutting off the specific feature. The measurements consider all interactions among features. However, it does not provide insights into the directions of impacts since the importance only indicates the ability to distinguish different classes.
Statistical analysis
T-test, Cohen’s D and two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test are introduced to explore how the mean values and distributions of personality facets between entrepreneurs and employees differ. The T-test is applied to determine whether the mean of personality facets of two group samples are significantly different from one another or not. The facets with significant differences detected by the hypothesis testing are critical to separate the two groups. Cohen’s d is to measure the effect size of the results of the previous t-test, which is the ratio of the mean difference to the pooled standard deviation. A larger Cohen’s d score indicates that the mean difference is greater than the variability of the whole sample. Moreover, it is interesting to check whether the two groups’ personality facets’ probability distributions are from the same distribution through the two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. There is no assumption about the distributions, but the test is sensitive to deviations near the centre rather than the tail.
Privacy and ethics
The focus of this research is to provide high-level insights about groups of startups, founders and types of founder teams rather than on specific individuals or companies. While we used unit record data from the publicly available data of company profiles from Crunchbase , we removed all identifiers from the underlying data on individual companies and founders and generated aggregate results, which formed the basis for our analysis and conclusions.
Data availability
A dataset which includes only aggregated statistics about the success of startups and the factors that influence is released as part of this research. Underlying data for all figures and the code to reproduce them are available on GitHub: https://github.com/Braesemann/FounderPersonalities . Please contact Fabian Braesemann ( [email protected] ) in case you have any further questions.
Change history
07 may 2024.
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-61082-7
Henrekson, M. & Johansson, D. Gazelles as job creators: A survey and interpretation of the evidence. Small Bus. Econ. 35 , 227–244 (2010).
Article Google Scholar
Davila, A., Foster, G., He, X. & Shimizu, C. The rise and fall of startups: Creation and destruction of revenue and jobs by young companies. Aust. J. Manag. 40 , 6–35 (2015).
Which vaccine saved the most lives in 2021?: Covid-19. The Economist (Online) (2022). noteName - AstraZeneca; Pfizer Inc; BioNTech SE; Copyright - Copyright The Economist Newspaper NA, Inc. Jul 14, 2022; Last updated - 2022-11-29.
Oltermann, P. Pfizer/biontech tax windfall brings mainz an early christmas present (2021). noteName - Pfizer Inc; BioNTech SE; Copyright - Copyright Guardian News & Media Limited Dec 27, 2021; Last updated - 2021-12-28.
Grant, K. A., Croteau, M. & Aziz, O. The survival rate of startups funded by angel investors. I-INC WHITE PAPER SER.: MAR 2019 , 1–21 (2019).
Google Scholar
Top 20 reasons start-ups fail - cb insights version (2019). noteCopyright - Copyright Newstex Oct 21, 2019; Last updated - 2022-10-25.
Hochberg, Y. V., Ljungqvist, A. & Lu, Y. Whom you know matters: Venture capital networks and investment performance. J. Financ. 62 , 251–301 (2007).
Fracassi, C., Garmaise, M. J., Kogan, S. & Natividad, G. Business microloans for us subprime borrowers. J. Financ. Quantitative Ana. 51 , 55–83 (2016).
Davila, A., Foster, G. & Gupta, M. Venture capital financing and the growth of startup firms. J. Bus. Ventur. 18 , 689–708 (2003).
Nann, S. et al. Comparing the structure of virtual entrepreneur networks with business effectiveness. Proc. Soc. Behav. Sci. 2 , 6483–6496 (2010).
Guzman, J. & Stern, S. Where is silicon valley?. Science 347 , 606–609 (2015).
Article ADS CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Aldrich, H. E. & Wiedenmayer, G. From traits to rates: An ecological perspective on organizational foundings. 61–97 (2019).
Gartner, W. B. Who is an entrepreneur? is the wrong question. Am. J. Small Bus. 12 , 11–32 (1988).
Thornton, P. H. The sociology of entrepreneurship. Ann. Rev. Sociol. 25 , 19–46 (1999).
Eikelboom, M. E., Gelderman, C. & Semeijn, J. Sustainable innovation in public procurement: The decisive role of the individual. J. Public Procure. 18 , 190–201 (2018).
Kerr, S. P. et al. Personality traits of entrepreneurs: A review of recent literature. Found. Trends Entrep. 14 , 279–356 (2018).
Hamilton, B. H., Papageorge, N. W. & Pande, N. The right stuff? Personality and entrepreneurship. Quant. Econ. 10 , 643–691 (2019).
Salmony, F. U. & Kanbach, D. K. Personality trait differences across types of entrepreneurs: A systematic literature review. RMS 16 , 713–749 (2022).
Freiberg, B. & Matz, S. C. Founder personality and entrepreneurial outcomes: A large-scale field study of technology startups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 120 , e2215829120 (2023).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kern, M. L., McCarthy, P. X., Chakrabarty, D. & Rizoiu, M.-A. Social media-predicted personality traits and values can help match people to their ideal jobs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 116 , 26459–26464 (2019).
Article ADS CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dalle, J.-M., Den Besten, M. & Menon, C. Using crunchbase for economic and managerial research. (2017).
Block, J. & Sandner, P. What is the effect of the financial crisis on venture capital financing? Empirical evidence from us internet start-ups. Ventur. Cap. 11 , 295–309 (2009).
Antretter, T., Blohm, I. & Grichnik, D. Predicting startup survival from digital traces: Towards a procedure for early stage investors (2018).
Dworak, D. Analysis of founder background as a predictor for start-up success in achieving successive fundraising rounds. (2022).
Hsu, D. H. Venture capitalists and cooperative start-up commercialization strategy. Manage. Sci. 52 , 204–219 (2006).
Blank, S. Why the lean start-up changes everything (2018).
Kaplan, S. N. & Lerner, J. It ain’t broke: The past, present, and future of venture capital. J. Appl. Corp. Financ. 22 , 36–47 (2010).
Hallen, B. L. & Eisenhardt, K. M. Catalyzing strategies and efficient tie formation: How entrepreneurial firms obtain investment ties. Acad. Manag. J. 55 , 35–70 (2012).
Gompers, P. A. & Lerner, J. The Venture Capital Cycle (MIT Press, 2004).
Shane, S. & Venkataraman, S. The promise of entrepreneurship as a field of research. Acad. Manag. Rev. 25 , 217–226 (2000).
Zahra, S. A. & Wright, M. Understanding the social role of entrepreneurship. J. Manage. Stud. 53 , 610–629 (2016).
Bonaventura, M. et al. Predicting success in the worldwide start-up network. Sci. Rep. 10 , 1–6 (2020).
Schwartz, H. A. et al. Personality, gender, and age in the language of social media: The open-vocabulary approach. PLoS ONE 8 , e73791 (2013).
Plank, B. & Hovy, D. Personality traits on twitter-or-how to get 1,500 personality tests in a week. In Proceedings of the 6th workshop on computational approaches to subjectivity, sentiment and social media analysis , pp 92–98 (2015).
Arnoux, P.-H. et al. 25 tweets to know you: A new model to predict personality with social media. In booktitleEleventh international AAAI conference on web and social media (2017).
Roberts, B. W., Kuncel, N. R., Shiner, R., Caspi, A. & Goldberg, L. R. The power of personality: The comparative validity of personality traits, socioeconomic status, and cognitive ability for predicting important life outcomes. Perspect. Psychol. Sci. 2 , 313–345 (2007).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Youyou, W., Kosinski, M. & Stillwell, D. Computer-based personality judgments are more accurate than those made by humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 112 , 1036–1040 (2015).
Soldz, S. & Vaillant, G. E. The big five personality traits and the life course: A 45-year longitudinal study. J. Res. Pers. 33 , 208–232 (1999).
Damian, R. I., Spengler, M., Sutu, A. & Roberts, B. W. Sixteen going on sixty-six: A longitudinal study of personality stability and change across 50 years. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 117 , 674 (2019).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Rantanen, J., Metsäpelto, R.-L., Feldt, T., Pulkkinen, L. & Kokko, K. Long-term stability in the big five personality traits in adulthood. Scand. J. Psychol. 48 , 511–518 (2007).
Roberts, B. W., Caspi, A. & Moffitt, T. E. The kids are alright: Growth and stability in personality development from adolescence to adulthood. J. Pers. Soc. Psychol. 81 , 670 (2001).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Cobb-Clark, D. A. & Schurer, S. The stability of big-five personality traits. Econ. Lett. 115 , 11–15 (2012).
Graham, P. Do Things that Don’t Scale (Paul Graham, 2013).
McCarthy, P. X., Kern, M. L., Gong, X., Parker, M. & Rizoiu, M.-A. Occupation-personality fit is associated with higher employee engagement and happiness. (2022).
Pratt, A. C. Advertising and creativity, a governance approach: A case study of creative agencies in London. Environ. Plan A 38 , 1883–1899 (2006).
Klotz, A. C., Hmieleski, K. M., Bradley, B. H. & Busenitz, L. W. New venture teams: A review of the literature and roadmap for future research. J. Manag. 40 , 226–255 (2014).
Duggan, M., Ellison, N. B., Lampe, C., Lenhart, A. & Madden, M. Demographics of key social networking platforms. Pew Res. Center 9 (2015).
Fisch, C. & Block, J. H. How does entrepreneurial failure change an entrepreneur’s digital identity? Evidence from twitter data. J. Bus. Ventur. 36 , 106015 (2021).
Brush, C., Edelman, L. F., Manolova, T. & Welter, F. A gendered look at entrepreneurship ecosystems. Small Bus. Econ. 53 , 393–408 (2019).
Kanze, D., Huang, L., Conley, M. A. & Higgins, E. T. We ask men to win and women not to lose: Closing the gender gap in startup funding. Acad. Manag. J. 61 , 586–614 (2018).
Fan, J. S. Startup biases. UC Davis Law Review (2022).
AlShebli, B. K., Rahwan, T. & Woon, W. L. The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration. Nat. Commun. 9 , 1–10 (2018).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Żbikowski, K. & Antosiuk, P. A machine learning, bias-free approach for predicting business success using crunchbase data. Inf. Process. Manag. 58 , 102555 (2021).
Corea, F., Bertinetti, G. & Cervellati, E. M. Hacking the venture industry: An early-stage startups investment framework for data-driven investors. Mach. Learn. Appl. 5 , 100062 (2021).
Chapman, G. & Hottenrott, H. Founder personality and start-up subsidies. Founder Personality and Start-up Subsidies (2021).
Antoncic, B., Bratkovicregar, T., Singh, G. & DeNoble, A. F. The big five personality-entrepreneurship relationship: Evidence from slovenia. J. Small Bus. Manage. 53 , 819–841 (2015).
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Gary Brewer from BuiltWith ; Leni Mayo from Influx , Rachel Slattery from TeamSlatts and Daniel Petre from AirTree Ventures for their ongoing generosity and insights about startups, founders and venture investments. We also thank Tim Li from Crunchbase for advice and liaison regarding data on startups and Richard Slatter for advice and referrals in Twitter .
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Data Science Institute, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Paul X. McCarthy
School of Computer Science and Engineering, UNSW Sydney, Sydney, NSW, Australia
Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, University of Technology Sydney, Sydney, Australia
Xian Gong & Marian-Andrei Rizoiu
Oxford Internet Institute, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK
Fabian Braesemann & Fabian Stephany
DWG Datenwissenschaftliche Gesellschaft Berlin, Berlin, Germany
Melbourne Graduate School of Education, The University of Melbourne, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Margaret L. Kern
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors designed research; All authors analysed data and undertook investigation; F.B. and F.S. led multi-factor analysis; P.M., X.G. and M.A.R. led the founder/employee prediction; M.L.K. led personality insights; X.G. collected and tabulated the data; X.G., F.B., and F.S. created figures; X.G. created final art, and all authors wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Fabian Braesemann .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The original online version of this Article was revised: The Data Availability section in the original version of this Article was incomplete, the link to the GitHub repository was omitted. Full information regarding the corrections made can be found in the correction for this Article.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary information., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
McCarthy, P.X., Gong, X., Braesemann, F. et al. The impact of founder personalities on startup success. Sci Rep 13 , 17200 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41980-y
Download citation
Received : 15 February 2023
Accepted : 04 September 2023
Published : 17 October 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-41980-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines . If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing: AI and Robotics newsletter — what matters in AI and robotics research, free to your inbox weekly.
The state of AI in early 2024: Gen AI adoption spikes and starts to generate value
If 2023 was the year the world discovered generative AI (gen AI) , 2024 is the year organizations truly began using—and deriving business value from—this new technology. In the latest McKinsey Global Survey on AI, 65 percent of respondents report that their organizations are regularly using gen AI, nearly double the percentage from our previous survey just ten months ago. Respondents’ expectations for gen AI’s impact remain as high as they were last year , with three-quarters predicting that gen AI will lead to significant or disruptive change in their industries in the years ahead.
About the authors
This article is a collaborative effort by Alex Singla , Alexander Sukharevsky , Lareina Yee , and Michael Chui , with Bryce Hall , representing views from QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and McKinsey Digital.
Organizations are already seeing material benefits from gen AI use, reporting both cost decreases and revenue jumps in the business units deploying the technology. The survey also provides insights into the kinds of risks presented by gen AI—most notably, inaccuracy—as well as the emerging practices of top performers to mitigate those challenges and capture value.
AI adoption surges
Interest in generative AI has also brightened the spotlight on a broader set of AI capabilities. For the past six years, AI adoption by respondents’ organizations has hovered at about 50 percent. This year, the survey finds that adoption has jumped to 72 percent (Exhibit 1). And the interest is truly global in scope. Our 2023 survey found that AI adoption did not reach 66 percent in any region; however, this year more than two-thirds of respondents in nearly every region say their organizations are using AI. 1 Organizations based in Central and South America are the exception, with 58 percent of respondents working for organizations based in Central and South America reporting AI adoption. Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Also, responses suggest that companies are now using AI in more parts of the business. Half of respondents say their organizations have adopted AI in two or more business functions, up from less than a third of respondents in 2023 (Exhibit 2).
Gen AI adoption is most common in the functions where it can create the most value
Most respondents now report that their organizations—and they as individuals—are using gen AI. Sixty-five percent of respondents say their organizations are regularly using gen AI in at least one business function, up from one-third last year. The average organization using gen AI is doing so in two functions, most often in marketing and sales and in product and service development—two functions in which previous research determined that gen AI adoption could generate the most value 3 “ The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier ,” McKinsey, June 14, 2023. —as well as in IT (Exhibit 3). The biggest increase from 2023 is found in marketing and sales, where reported adoption has more than doubled. Yet across functions, only two use cases, both within marketing and sales, are reported by 15 percent or more of respondents.
Gen AI also is weaving its way into respondents’ personal lives. Compared with 2023, respondents are much more likely to be using gen AI at work and even more likely to be using gen AI both at work and in their personal lives (Exhibit 4). The survey finds upticks in gen AI use across all regions, with the largest increases in Asia–Pacific and Greater China. Respondents at the highest seniority levels, meanwhile, show larger jumps in the use of gen Al tools for work and outside of work compared with their midlevel-management peers. Looking at specific industries, respondents working in energy and materials and in professional services report the largest increase in gen AI use.
Investments in gen AI and analytical AI are beginning to create value
The latest survey also shows how different industries are budgeting for gen AI. Responses suggest that, in many industries, organizations are about equally as likely to be investing more than 5 percent of their digital budgets in gen AI as they are in nongenerative, analytical-AI solutions (Exhibit 5). Yet in most industries, larger shares of respondents report that their organizations spend more than 20 percent on analytical AI than on gen AI. Looking ahead, most respondents—67 percent—expect their organizations to invest more in AI over the next three years.
Where are those investments paying off? For the first time, our latest survey explored the value created by gen AI use by business function. The function in which the largest share of respondents report seeing cost decreases is human resources. Respondents most commonly report meaningful revenue increases (of more than 5 percent) in supply chain and inventory management (Exhibit 6). For analytical AI, respondents most often report seeing cost benefits in service operations—in line with what we found last year —as well as meaningful revenue increases from AI use in marketing and sales.
Inaccuracy: The most recognized and experienced risk of gen AI use
As businesses begin to see the benefits of gen AI, they’re also recognizing the diverse risks associated with the technology. These can range from data management risks such as data privacy, bias, or intellectual property (IP) infringement to model management risks, which tend to focus on inaccurate output or lack of explainability. A third big risk category is security and incorrect use.
Respondents to the latest survey are more likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider inaccuracy and IP infringement to be relevant to their use of gen AI, and about half continue to view cybersecurity as a risk (Exhibit 7).
Conversely, respondents are less likely than they were last year to say their organizations consider workforce and labor displacement to be relevant risks and are not increasing efforts to mitigate them.
In fact, inaccuracy— which can affect use cases across the gen AI value chain , ranging from customer journeys and summarization to coding and creative content—is the only risk that respondents are significantly more likely than last year to say their organizations are actively working to mitigate.
Some organizations have already experienced negative consequences from the use of gen AI, with 44 percent of respondents saying their organizations have experienced at least one consequence (Exhibit 8). Respondents most often report inaccuracy as a risk that has affected their organizations, followed by cybersecurity and explainability.
Our previous research has found that there are several elements of governance that can help in scaling gen AI use responsibly, yet few respondents report having these risk-related practices in place. 4 “ Implementing generative AI with speed and safety ,” McKinsey Quarterly , March 13, 2024. For example, just 18 percent say their organizations have an enterprise-wide council or board with the authority to make decisions involving responsible AI governance, and only one-third say gen AI risk awareness and risk mitigation controls are required skill sets for technical talent.
Bringing gen AI capabilities to bear
The latest survey also sought to understand how, and how quickly, organizations are deploying these new gen AI tools. We have found three archetypes for implementing gen AI solutions : takers use off-the-shelf, publicly available solutions; shapers customize those tools with proprietary data and systems; and makers develop their own foundation models from scratch. 5 “ Technology’s generational moment with generative AI: A CIO and CTO guide ,” McKinsey, July 11, 2023. Across most industries, the survey results suggest that organizations are finding off-the-shelf offerings applicable to their business needs—though many are pursuing opportunities to customize models or even develop their own (Exhibit 9). About half of reported gen AI uses within respondents’ business functions are utilizing off-the-shelf, publicly available models or tools, with little or no customization. Respondents in energy and materials, technology, and media and telecommunications are more likely to report significant customization or tuning of publicly available models or developing their own proprietary models to address specific business needs.
Respondents most often report that their organizations required one to four months from the start of a project to put gen AI into production, though the time it takes varies by business function (Exhibit 10). It also depends upon the approach for acquiring those capabilities. Not surprisingly, reported uses of highly customized or proprietary models are 1.5 times more likely than off-the-shelf, publicly available models to take five months or more to implement.
Gen AI high performers are excelling despite facing challenges
Gen AI is a new technology, and organizations are still early in the journey of pursuing its opportunities and scaling it across functions. So it’s little surprise that only a small subset of respondents (46 out of 876) report that a meaningful share of their organizations’ EBIT can be attributed to their deployment of gen AI. Still, these gen AI leaders are worth examining closely. These, after all, are the early movers, who already attribute more than 10 percent of their organizations’ EBIT to their use of gen AI. Forty-two percent of these high performers say more than 20 percent of their EBIT is attributable to their use of nongenerative, analytical AI, and they span industries and regions—though most are at organizations with less than $1 billion in annual revenue. The AI-related practices at these organizations can offer guidance to those looking to create value from gen AI adoption at their own organizations.
To start, gen AI high performers are using gen AI in more business functions—an average of three functions, while others average two. They, like other organizations, are most likely to use gen AI in marketing and sales and product or service development, but they’re much more likely than others to use gen AI solutions in risk, legal, and compliance; in strategy and corporate finance; and in supply chain and inventory management. They’re more than three times as likely as others to be using gen AI in activities ranging from processing of accounting documents and risk assessment to R&D testing and pricing and promotions. While, overall, about half of reported gen AI applications within business functions are utilizing publicly available models or tools, gen AI high performers are less likely to use those off-the-shelf options than to either implement significantly customized versions of those tools or to develop their own proprietary foundation models.
What else are these high performers doing differently? For one thing, they are paying more attention to gen-AI-related risks. Perhaps because they are further along on their journeys, they are more likely than others to say their organizations have experienced every negative consequence from gen AI we asked about, from cybersecurity and personal privacy to explainability and IP infringement. Given that, they are more likely than others to report that their organizations consider those risks, as well as regulatory compliance, environmental impacts, and political stability, to be relevant to their gen AI use, and they say they take steps to mitigate more risks than others do.
Gen AI high performers are also much more likely to say their organizations follow a set of risk-related best practices (Exhibit 11). For example, they are nearly twice as likely as others to involve the legal function and embed risk reviews early on in the development of gen AI solutions—that is, to “ shift left .” They’re also much more likely than others to employ a wide range of other best practices, from strategy-related practices to those related to scaling.
In addition to experiencing the risks of gen AI adoption, high performers have encountered other challenges that can serve as warnings to others (Exhibit 12). Seventy percent say they have experienced difficulties with data, including defining processes for data governance, developing the ability to quickly integrate data into AI models, and an insufficient amount of training data, highlighting the essential role that data play in capturing value. High performers are also more likely than others to report experiencing challenges with their operating models, such as implementing agile ways of working and effective sprint performance management.
About the research
The online survey was in the field from February 22 to March 5, 2024, and garnered responses from 1,363 participants representing the full range of regions, industries, company sizes, functional specialties, and tenures. Of those respondents, 981 said their organizations had adopted AI in at least one business function, and 878 said their organizations were regularly using gen AI in at least one function. To adjust for differences in response rates, the data are weighted by the contribution of each respondent’s nation to global GDP.
Alex Singla and Alexander Sukharevsky are global coleaders of QuantumBlack, AI by McKinsey, and senior partners in McKinsey’s Chicago and London offices, respectively; Lareina Yee is a senior partner in the Bay Area office, where Michael Chui , a McKinsey Global Institute partner, is a partner; and Bryce Hall is an associate partner in the Washington, DC, office.
They wish to thank Kaitlin Noe, Larry Kanter, Mallika Jhamb, and Shinjini Srivastava for their contributions to this work.
This article was edited by Heather Hanselman, a senior editor in McKinsey’s Atlanta office.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Moving past gen AI’s honeymoon phase: Seven hard truths for CIOs to get from pilot to scale

A generative AI reset: Rewiring to turn potential into value in 2024

Implementing generative AI with speed and safety

- Asia Pacific
- Hong Kong SAR, China
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- Taiwan, China
- Czech Republic
- Netherlands
- Saudi Arabia
- South Africa
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- El Salvador
- United States
- Investor Relations
U.S. Industrial Market Outlook Report | Q1 2024

U.S. Industrial Demand Fell in Q1 but Will Build as New Supply Falls

Related Experts

Craig Hurvitz
Director, National Industrial Research
Chicago - Rosemont
Craig brings 17 years of commercial real estate research experience to his role as Director, National Industrial Research for Colliers' national team. Utilizing his strong background in statistics, analytics, marketing, and real estate development, Craig is instrumental in growing and supporting Colliers' national industrial real estate business. He is responsible for partnering with local research teams to produce innovative, thought-provoking research and analysis of industrial trends for use in market reports, trend studies, presentations, and custom research projects. In addition, Craig develops and delivers compelling national thought leadership pieces, perspectives on industrial trends to the media, and contributes to significant client-facing business development initiatives. Prior to his current role, Craig led a five-person research team in Colliers' Chicago and Rosemont offices for eight years, and built from the ground up or enhanced research departments at three additional commercial real estate firms in the Chicago market where he managed proprietary databases to track property inventory, contact, transaction, and comparable details among tens of thousands of buildings in Chicago’s market. Born and raised in the Chicago area, Craig is a graduate of Tulane University in New Orleans and currently resides with his family in Lake County, Illinois.

Stephanie Rodriguez
National Director, Industrial Services | U.S. and Executive Managing Director – Florida
As National Director of Industrial Services for the U.S., Stephanie focuses on the overall growth of Colliers’ industrial business, including establishing new client relationships and expanding existing affiliations. She promotes talent recruitment and retention to support Colliers’ best-in-class Industrial Services team as they accelerate client success.
Drawing on her 25 years of commercial real estate experience, Stephanie leads Colliers’ Industrial platform, especially in providing thought leadership, research, and marketing. She brings extensive experience in acquisitions, lease transactions and negotiations, asset management, and development projects.
As the Executive Managing Director of Colliers Florida, Stephanie is responsible for all aspects of Colliers’ operations in the Florida region, focusing on financial management, human capital development, and new business generation. She leads a team of brokers and support staff advising clients who wish to sell, purchase, or lease retail, office, medical, industrial, land, and multifamily assets. Stephanie also collaborates with the firm’s Real Estate Management Services and Valuation and Advisory divisions on identifying and sourcing new business opportunities.
Before joining Colliers, Stephanie spent nearly 15 years at Duke Realty Corporation, where she rose to the level of Regional Senior Vice President, overseeing leasing for a multi-market, multi-million-square-foot portfolio in Central and South Florida in addition to leading property management, development, and marketing of the firm’s industrial portfolio in the region. Before her time at Duke, she held progressively more senior roles at Trammell Crow Company and CBRE.
Fill out the form to download the report

COMMENTS
The next market research types can be defined as qualitative and quantitative research types: 3. Qualitative research. Qualitative market research is the collection of primary or secondary data that is non-numerical in nature, and therefore hard to measure. Researchers collect this market research type because it can add more depth to the data.
Market research is the process of assessing the viability of a new good or service through research conducted directly with the consumer which allows a company to ...
Market research is defined as the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of data about a specific market, industry, or consumer segment. Learn more about market research methods, types, process with examples and best practices.
These benefits make it a huge industry; the global market research services market is expected to grow from $76.37 billion in 2021 to $108.57 billion in 2026. Now, let's dig into the different types of market research that can help you achieve these benefits.
The global revenue of the market research industry exceeded 84 billion U.S. dollars in 2023 and has grown more than twofold since 2008. In 2022, North America generated the largest share of market ...
Choosing the right type of market research. Whatever your industry, role, or experience, the type of market research you choose will influence key decisions in your business. With rapid shifts in consumer behavior and emerging threats now virtually an everyday thing, you need a broad and relevant view of the landscape.
In 2019, in the United States, market research companies generated over 47 billion U.S. dollars in revenue, more than half of the total revenue of the market research industry globally . The vast ...
The market research stats and trends favor the U.S. According to a recent report by First Research Inc., the market research industry globally produces $45 billion in revenue each year. Europe and the United States lead the industry overall. Other countries such as China, Brazil, Russia, and India are experiencing increasing demand for market ...
June 3, 2021 28 min read. Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
Market Research Report. 2021 Market Research Global Trends. For market researchers, COVID-19 accelerated a transformation that's been a decade in the making — and it will completely reshape the industry in the coming years. In our first annual study into the state of the market research industry, we surveyed more than 2,000 market research ...
Download HubSpot's free, editable market research report template here. 1. Five Forces Analysis Template. Use Porter's Five Forces Model to understand an industry by analyzing five different criteria and how high the power, threat, or rivalry in each area is — here are the five criteria: Competitive rivalry.
Many types of market research are conducted by businesses at many different stages. Market Research for Businesses . Accurate and comprehensive data gives a plethora of information on potential and existing customers, competitors, and the industry as a whole, making it the bedrock of any successful commercial endeavor. ...
Customer Decision-Making. Customer journey or decision-making research tells why customers make purchases and why they don't. More specifically, this research speaks to their. • Purchasing ...
Primary and secondary are the two main types of market research you can do. The latter relies on research conducted by others. Primary research, on the other hand, refers to the fact-finding efforts you conduct on your own. ... Secondary research includes resources like government databases and industry-specific data and publications. It can be ...
2. Surveys. Great for: understanding brand awareness, satisfaction and loyalty analysis, pricing research, and market segmentation. One of the most commonly used market research methods, Surveys are an easy way to understand your target audience and allow you to test a large sample size to determine if findings are true across a larger segment ...
The competitors (and how their market offerings interact in the market environment) The industry overall (whether it's growing or moving in a certain direction) Free eBook: 2024 market research trends report ... Although there are many types market research, all methods can be sorted into one of two categories: primary and secondary. ...
The market research services industry is experiencing rapid growth, indicating a strong interest in market research as we enter 2024. The market is expected to grow from approximately $75 billion in 2021 to $90.79 billion in 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 5%. ... 11 types of market research Interviews. Interviews can be conducted ...
Market research is the process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about your target market, competitors, and industry. Market research spans a wide range of topics, uncovering insights on various elements that can impact a business. Some common subjects of market research include:
Step 4: Conduct the market research. With a system in place, you can start looking for candidates to contribute to your market research. This might include distributing surveys to current customers or recruiting participants who fit a specific profile, for example. Set a time frame for conducting your research.
Not everyone conducts market research for the same reason. While some may want to understand their audience better, others may want to see how their competitors are doing. As such, there are different types of market research you can conduct depending on your goal. Interviews. Interview-based market research allows for one-on-one interactions.
Types of Market Research: Market Research Methods and Examples. Whether an organization or business wishes to know the purchase behavior of consumers or the likelihood of consumers paying a certain cost for a product segmentation, market research helps in drawing meaningful conclusions. LEARN ABOUT: Behavioral Targeting.
Market research is "The process of gathering, analyzing and interpreting information about a market, about a product or service to be offered for sale in that market, and about the past, present and potential customers for the product or service; research into the characteristics, spending habits, location and needs of your business's target market, the industry as a whole, and the particular ...
Starting a business in the United States involves a number of different steps spanning legal considerations, market research, creating a business plan, securing funding, and developing a marketing ...
The terms "market research reports" and "industry reports" are somewhat interchangeable - this guide lists both types available at Purdue. Generally speaking, industry reports cover information about competitors within an industry, while market research reports focus on customers. However, industry and market reports typically contain both ...
New research into B2B content marketing trends for 2024 reveals specifics of AI implementation, social media use, and budget forecasts, plus content success factors. Marketers talk AI, common challenges, best results, and more in the 14th annual B2B Content Marketing Benchmarks, Budgets, and Trends: Outlook for 2024.
Besides product-market, industry, and firm-level factors (see SI section A.1), research suggests that the personalities of founders play a crucial role in startup success 19.
Eighty-two percent use thought leadership e-books/white papers, 81% use long articles/posts, 63% use data visualizations/visual content, 62% use product/technical data sheets, and 56% use research reports. Less than half of technology marketers use brochures (45%), interactive content (35%), livestreaming content (34%), and audio content (31%).
Looking by industry, the biggest increase in adoption can be found in professional services. 2 Includes respondents working for organizations focused on human resources, legal services, management consulting, market research, R&D, tax preparation, and training.
Industrial construction completions outstripped tenant demand for the seventh quarter in a row, pushing the U.S. average vacancy rate up 50 basis points, to 6.1% during the first quarter of 2024 — the highest since early 2015. Vacancy was highest in the South region at 7.4%, 68 basis points higher during the quarter, and increased in 61 of ...
1. Medical and health services manager. Median annual salary (BLS.gov): $101,340. Job outlook (projected growth from 2020-2030): 32%. As a medical or health service manager you work behind the scenes at a hospital, doctor's office, or other care facility to keep it running safely and efficiently.