How to Write a Perfect Assignment: Step-By-Step Guide
Table of contents
- 1 How to Structure an Assignment?
- 2.1 The research part
- 2.2 Planning your text
- 2.3 Writing major parts
- 3 Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
- 4 Will I succeed with my assignments?
- 5 Conclusion

How to Structure an Assignment?
To cope with assignments, you should familiarize yourself with the tips on formatting and presenting assignments or any written paper, which are given below. It is worth paying attention to the content of the paper, making it structured and understandable so that ideas are not lost and thoughts do not refute each other.
If the topic is free or you can choose from the given list — be sure to choose the one you understand best. Especially if that could affect your semester score or scholarship. It is important to select an engaging title that is contextualized within your topic. A topic that should captivate you or at least give you a general sense of what is needed there. It’s easier to dwell upon what interests you, so the process goes faster.
To construct an assignment structure, use outlines. These are pieces of text that relate to your topic. It can be ideas, quotes, all your thoughts, or disparate arguments. Type in everything that you think about. Separate thoughts scattered across the sheets of Word will help in the next step.
Then it is time to form the text. At this stage, you have to form a coherent story from separate pieces, where each new thought reinforces the previous one, and one idea smoothly flows into another.
Main Steps of Assignment Writing
These are steps to take to get a worthy paper. If you complete these step-by-step, your text will be among the most exemplary ones.
The research part
If the topic is unique and no one has written about it yet, look at materials close to this topic to gain thoughts about it. You should feel that you are ready to express your thoughts. Also, while reading, get acquainted with the format of the articles, study the details, collect material for your thoughts, and accumulate different points of view for your article. Be careful at this stage, as the process can help you develop your ideas. If you are already struggling here, pay for assignment to be done , and it will be processed in a split second via special services. These services are especially helpful when the deadline is near as they guarantee fast delivery of high-quality papers on any subject.
If you use Google to search for material for your assignment, you will, of course, find a lot of information very quickly. Still, the databases available on your library’s website will give you the clearest and most reliable facts that satisfy your teacher or professor. Be sure you copy the addresses of all the web pages you will use when composing your paper, so you don’t lose them. You can use them later in your bibliography if you add a bit of description! Select resources and extract quotes from them that you can use while working. At this stage, you may also create a request for late assignment if you realize the paper requires a lot of effort and is time-consuming. This way, you’ll have a backup plan if something goes wrong.
Planning your text
Assemble a layout. It may be appropriate to use the structure of the paper of some outstanding scientists in your field and argue it in one of the parts. As the planning progresses, you can add suggestions that come to mind. If you use citations that require footnotes, and if you use single spacing throughout the paper and double spacing at the end, it will take you a very long time to make sure that all the citations are on the exact pages you specified! Add a reference list or bibliography. If you haven’t already done so, don’t put off writing an essay until the last day. It will be more difficult to do later as you will be stressed out because of time pressure.
Writing major parts
It happens that there is simply no mood or strength to get started and zero thoughts. In that case, postpone this process for 2-3 hours, and, perhaps, soon, you will be able to start with renewed vigor. Writing essays is a great (albeit controversial) way to improve your skills. This experience will not be forgotten. It will certainly come in handy and bring many benefits in the future. Do your best here because asking for an extension is not always possible, so you probably won’t have time to redo it later. And the quality of this part defines the success of the whole paper.
Writing the major part does not mean the matter is finished. To review the text, make sure that the ideas of the introduction and conclusion coincide because such a discrepancy is the first thing that will catch the reader’s eye and can spoil the impression. Add or remove anything from your intro to edit it to fit the entire paper. Also, check your spelling and grammar to ensure there are no typos or draft comments. Check the sources of your quotes so that your it is honest and does not violate any rules. And do not forget the formatting rules.
with the right tips and guidance, it can be easier than it looks. To make the process even more straightforward, students can also use an assignment service to get the job done. This way they can get professional assistance and make sure that their assignments are up to the mark. At PapersOwl, we provide a professional writing service where students can order custom-made assignments that meet their exact requirements.
Expert Tips for your Writing Assignment
Want to write like a pro? Here’s what you should consider:
- Save the document! Send the finished document by email to yourself so you have a backup copy in case your computer crashes.
- Don’t wait until the last minute to complete a list of citations or a bibliography after the paper is finished. It will be much longer and more difficult, so add to them as you go.
- If you find a lot of information on the topic of your search, then arrange it in a separate paragraph.
- If possible, choose a topic that you know and are interested in.
- Believe in yourself! If you set yourself up well and use your limited time wisely, you will be able to deliver the paper on time.
- Do not copy information directly from the Internet without citing them.
Writing assignments is a tedious and time-consuming process. It requires a lot of research and hard work to produce a quality paper. However, if you are feeling overwhelmed or having difficulty understanding the concept, you may want to consider getting accounting homework help online . Professional experts can assist you in understanding how to complete your assignment effectively. PapersOwl.com offers expert help from highly qualified and experienced writers who can provide you with the homework help you need.
Will I succeed with my assignments?
Anyone can learn how to be good at writing: follow simple rules of creating the structure and be creative where it is appropriate. At one moment, you will need some additional study tools, study support, or solid study tips. And you can easily get help in writing assignments or any other work. This is especially useful since the strategy of learning how to write an assignment can take more time than a student has.
Therefore all students are happy that there is an option to order your paper at a professional service to pass all the courses perfectly and sleep still at night. You can also find the sample of the assignment there to check if you are on the same page and if not — focus on your papers more diligently.
So, in the times of studies online, the desire and skill to research and write may be lost. Planning your assignment carefully and presenting arguments step-by-step is necessary to succeed with your homework. When going through your references, note the questions that appear and answer them, building your text. Create a cover page, proofread the whole text, and take care of formatting. Feel free to use these rules for passing your next assignments.
When it comes to writing an assignment, it can be overwhelming and stressful, but Papersowl is here to make it easier for you. With a range of helpful resources available, Papersowl can assist you in creating high-quality written work, regardless of whether you’re starting from scratch or refining an existing draft. From conducting research to creating an outline, and from proofreading to formatting, the team at Papersowl has the expertise to guide you through the entire writing process and ensure that your assignment meets all the necessary requirements.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Study Skills
How to Start an Assignment
Last Updated: January 29, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michelle Golden, PhD . Michelle Golden is an English teacher in Athens, Georgia. She received her MA in Language Arts Teacher Education in 2008 and received her PhD in English from Georgia State University in 2015. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 107,013 times.
Getting started on an assignment or homework can often times be the hardest step. Putting off the assignment can make the problem worse, reducing the time you have to complete the task and increasing stress. By learning how to get started and overcome the urge to procrastinate, you can get your assignments done on schedule and with less stress, opening up more free time.
Restructuring Your Assignment

- For example, you might research areas of a report that you find most interesting before moving on to other areas.
- If your math assignment has different types of questions, try doing those that you enjoy the most before moving on to the others.
- You might also try tackling smaller or easier tasks first so you can cross a few items off your list. Seeing that you've already made progress may help you feel motivated to continue.

- Promise yourself that you will meet your goal of working for five minutes on the assignment.
- Once you get started, you may find that you don't want to stop working. Otherwise, you can take a break and come back to the assignment, knowing you're at least five minutes closer to finishing than you were before.

- Try to set reasonable periods of time that you know you can meet. For example, you might set aside two hours on a Friday to dedicate to your assignment. If you don't have that much time all at once, try to carve out a few 20- or 30-minute blocks.
- You may or may not wish to continue working after your time limit has gone by.
- Have a realistic understanding of how fast you can write and plan your schedule accordingly.

- It can help to read the assignment as soon as you get it and then ask any questions you might have.
- If you're not sure if you understand the assignment, try rewriting it in your own words or explaining it to someone else. If you find you can't or have a lot of questions, you may need more information.
- You should have an overview of the assignment, understand the main task, and understand the technical and stylistic requirements.
- Look for important words in the instructions to understand the assignment. These words might include define, explain, compare, relate, or prove.
- Keep your audience in mind and write a paper that would best deliver information to them.

- Goals that are too big or not well defined can be difficult to start working towards.
- Smaller and well defined goals can seem easier to achieve than larger ones.
- For example, you could break a research paper down into several smaller tasks: 1) do preliminary research, 2) write an outline, 3) draft an introduction, 4) draft body paragraphs, 5) write conclusion, 6) revise. Each of these is much more do-able on its own.
Changing Your Focus

- You might want to go for a quick walk after working for a set amount of time.
- Try reading a website or book that you enjoy for a few minutes after working.
- Alternatively, try a quick burst of exercise before setting to work. Exercise releases feel-good chemicals called endorphins and can also help boost your memory. [8] X Research source

- Instead of dreading your work, focus on how good it will feel to make progress. You won't have it hanging over your head. You can actually enjoy the weekend instead of feeling guilty.
- Keeping your eye on long-term rewards can help you stay motivated to finish your assignment.

- Avoid moving your workspace constantly.
- Don't get lost on tangential research.
- Don't take constant breaks to get a snack.

- For every hour you waste procrastinating, you can limit how much television you watch that night.
- If you waste too much time procrastinating, you might deny yourself a favorite snack later on.

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/solving-unsolvable-problems/201408/4-steps-stop-procrastinating
- ↑ https://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/friendship-20/201405/the-surefire-first-step-stop-procrastinating
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/procrastination/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/homework.html
- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/understanding-assignments/
- ↑ https://open.alberta.ca/dataset/ab22ff64-3358-4387-9761-8c58878a6b84/resource/3ee38320-17e4-46f9-b24f-c95f9f345eb9/download/ipp7.pdf
- ↑ http://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2013/08/07/how-exercise-can-help-us-learn/
- ↑ https://kidshealth.org/en/teens/happy-life.html
About This Article

To start an assignment, try working on the most enjoyable or easiest parts of the assignment first to get the ball rolling. Even if no part of the assignment seems enjoyable or easy, set a timer and try to make yourself work for at least 5 minutes, which is usually enough time to build momentum and overcome procrastination. You can also try breaking your assignment up into smaller, more manageable tasks and scheduling yourself regular breaks so it doesn't seem as overwhelming. To learn how to stay positive and avoid procrastination while working on your homework, scroll down! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Faith Wanjiku
Dec 7, 2018
Did this article help you?
Winnie Wong
May 18, 2016
Turab Ahamad
Oct 23, 2016
Sofia Madrid
Sep 5, 2016
Doha Elabbasi
Sep 27, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
- Utility Menu
GA4 Tracking Code
fa51e2b1dc8cca8f7467da564e77b5ea
- Make a Gift
- Join Our Email List
How to Write an Effective Assignment
At their base, all assignment prompts function a bit like a magnifying glass—they allow a student to isolate, focus on, inspect, and interact with some portion of your course material through a fixed lens of your choosing.
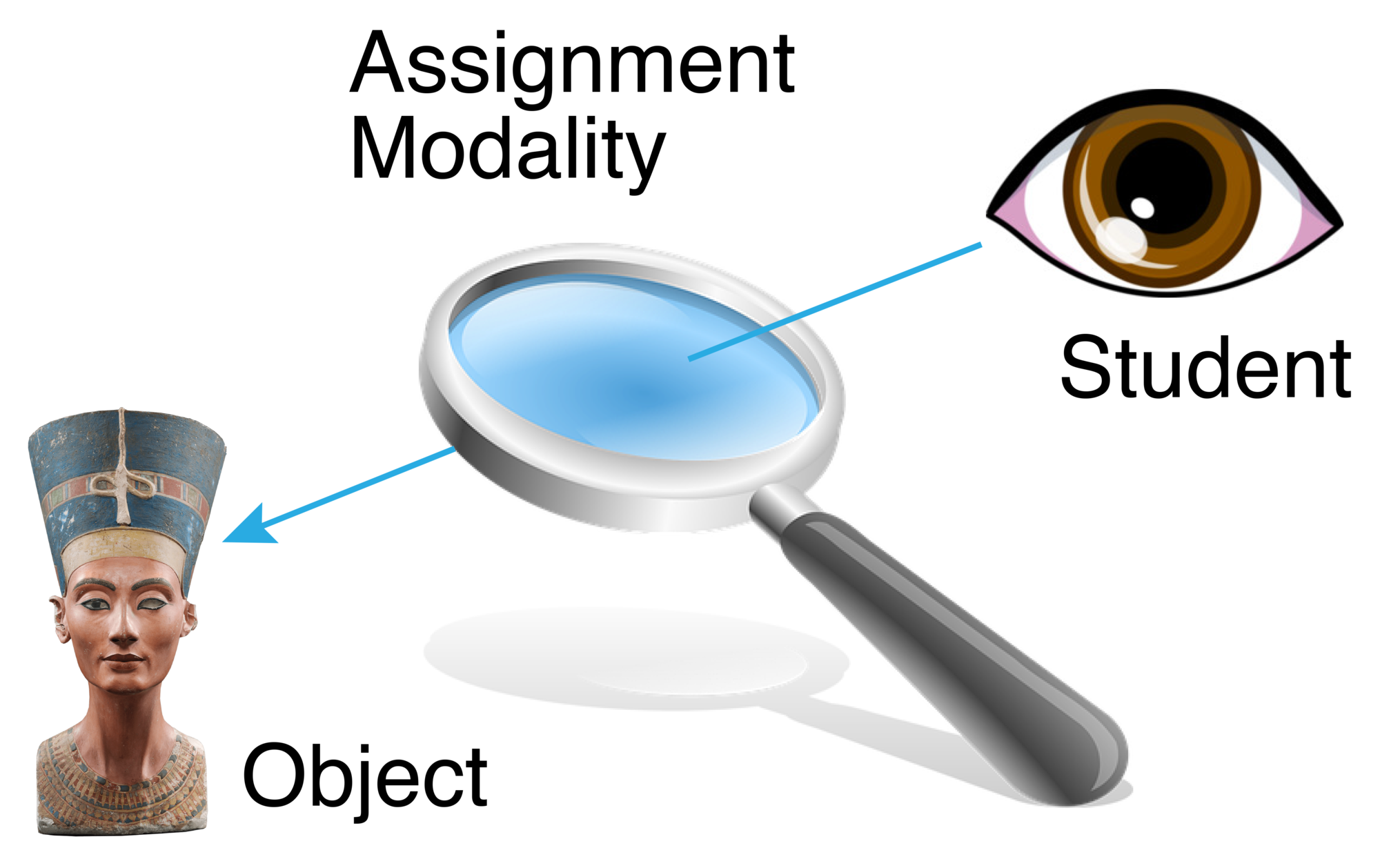
The Key Components of an Effective Assignment Prompt
All assignments, from ungraded formative response papers all the way up to a capstone assignment, should include the following components to ensure that students and teachers understand not only the learning objective of the assignment, but also the discrete steps which they will need to follow in order to complete it successfully:
- Preamble. This situates the assignment within the context of the course, reminding students of what they have been working on in anticipation of the assignment and how that work has prepared them to succeed at it.
- Justification and Purpose. This explains why the particular type or genre of assignment you’ve chosen (e.g., lab report, policy memo, problem set, or personal reflection) is the best way for you and your students to measure how well they’ve met the learning objectives associated with this segment of the course.
- Mission. This explains the assignment in broad brush strokes, giving students a general sense of the project you are setting before them. It often gives students guidance on the evidence or data they should be working with, as well as helping them imagine the audience their work should be aimed at.
- Tasks. This outlines what students are supposed to do at a more granular level: for example, how to start, where to look, how to ask for help, etc. If written well, this part of the assignment prompt ought to function as a kind of "process" rubric for students, helping them to decide for themselves whether they are completing the assignment successfully.
- Submission format. This tells students, in appropriate detail, which stylistic conventions they should observe and how to submit their work. For example, should the assignment be a five-page paper written in APA format and saved as a .docx file? Should it be uploaded to the course website? Is it due by Tuesday at 5:00pm?
For illustrations of these five components in action, visit our gallery of annotated assignment prompts .
For advice about creative assignments (e.g. podcasts, film projects, visual and performing art projects, etc.), visit our Guidance on Non-Traditional Forms of Assessment .
For specific advice on different genres of assignment, click below:
Response Papers
Problem sets, source analyses, final exams, concept maps, research papers, oral presentations, poster presentations.
- Learner-Centered Design
- Putting Evidence at the Center
- What Should Students Learn?
- Start with the Capstone
- Gallery of Annotated Assignment Prompts
- Scaffolding: Using Frequency and Sequencing Intentionally
- Curating Content: The Virtue of Modules
- Syllabus Design
- Catalogue Materials
- Making a Course Presentation Video
- Teaching Teams
- In the Classroom
- Getting Feedback
- Equitable & Inclusive Teaching
- Advising and Mentoring
- Teaching and Your Career
- Teaching Remotely
- Tools and Platforms
- The Science of Learning
- Bok Publications
- Other Resources Around Campus
Search form
How to write the best college assignments.
By Lois Weldon
When it comes to writing assignments, it is difficult to find a conceptualized guide with clear and simple tips that are easy to follow. That’s exactly what this guide will provide: few simple tips on how to write great assignments, right when you need them. Some of these points will probably be familiar to you, but there is no harm in being reminded of the most important things before you start writing the assignments, which are usually determining on your credits.
The most important aspects: Outline and Introduction
Preparation is the key to success, especially when it comes to academic assignments. It is recommended to always write an outline before you start writing the actual assignment. The outline should include the main points of discussion, which will keep you focused throughout the work and will make your key points clearly defined. Outlining the assignment will save you a lot of time because it will organize your thoughts and make your literature searches much easier. The outline will also help you to create different sections and divide up the word count between them, which will make the assignment more organized.
The introduction is the next important part you should focus on. This is the part that defines the quality of your assignment in the eyes of the reader. The introduction must include a brief background on the main points of discussion, the purpose of developing such work and clear indications on how the assignment is being organized. Keep this part brief, within one or two paragraphs.
This is an example of including the above mentioned points into the introduction of an assignment that elaborates the topic of obesity reaching proportions:
Background : The twenty first century is characterized by many public health challenges, among which obesity takes a major part. The increasing prevalence of obesity is creating an alarming situation in both developed and developing regions of the world.
Structure and aim : This assignment will elaborate and discuss the specific pattern of obesity epidemic development, as well as its epidemiology. Debt, trade and globalization will also be analyzed as factors that led to escalation of the problem. Moreover, the assignment will discuss the governmental interventions that make efforts to address this issue.
Practical tips on assignment writing
Here are some practical tips that will keep your work focused and effective:
– Critical thinking – Academic writing has to be characterized by critical thinking, not only to provide the work with the needed level, but also because it takes part in the final mark.
– Continuity of ideas – When you get to the middle of assignment, things can get confusing. You have to make sure that the ideas are flowing continuously within and between paragraphs, so the reader will be enabled to follow the argument easily. Dividing the work in different paragraphs is very important for this purpose.
– Usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ – According to the academic writing standards, the assignments should be written in an impersonal language, which means that the usage of ‘you’ and ‘I’ should be avoided. The only acceptable way of building your arguments is by using opinions and evidence from authoritative sources.
– Referencing – this part of the assignment is extremely important and it takes a big part in the final mark. Make sure to use either Vancouver or Harvard referencing systems, and use the same system in the bibliography and while citing work of other sources within the text.
– Usage of examples – A clear understanding on your assignment’s topic should be provided by comparing different sources and identifying their strengths and weaknesses in an objective manner. This is the part where you should show how the knowledge can be applied into practice.
– Numbering and bullets – Instead of using numbering and bullets, the academic writing style prefers the usage of paragraphs.
– Including figures and tables – The figures and tables are an effective way of conveying information to the reader in a clear manner, without disturbing the word count. Each figure and table should have clear headings and you should make sure to mention their sources in the bibliography.
– Word count – the word count of your assignment mustn’t be far above or far below the required word count. The outline will provide you with help in this aspect, so make sure to plan the work in order to keep it within the boundaries.
The importance of an effective conclusion
The conclusion of your assignment is your ultimate chance to provide powerful arguments that will impress the reader. The conclusion in academic writing is usually expressed through three main parts:
– Stating the context and aim of the assignment
– Summarizing the main points briefly
– Providing final comments with consideration of the future (discussing clear examples of things that can be done in order to improve the situation concerning your topic of discussion).
Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE /* Style Definitions */ table.MsoNormalTable {mso-style-name:"Table Normal"; mso-tstyle-rowband-size:0; mso-tstyle-colband-size:0; mso-style-noshow:yes; mso-style-priority:99; mso-style-parent:""; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt; mso-para-margin:0in; mso-para-margin-bottom:.0001pt; mso-pagination:widow-orphan; font-size:11.0pt; font-family:"Calibri","sans-serif"; mso-ascii-font-family:Calibri; mso-ascii-theme-font:minor-latin; mso-hansi-font-family:Calibri; mso-hansi-theme-font:minor-latin;}
Lois Weldon is writer at Uk.bestdissertation.com . Lives happily at London with her husband and lovely daughter. Adores writing tips for students. Passionate about Star Wars and yoga.
7 comments on “How To Write The Best College Assignments”
Extremely useful tip for students wanting to score well on their assignments. I concur with the writer that writing an outline before ACTUALLY starting to write assignments is extremely important. I have observed students who start off quite well but they tend to lose focus in between which causes them to lose marks. So an outline helps them to maintain the theme focused.
Hello Great information…. write assignments
Well elabrated
Thanks for the information. This site has amazing articles. Looking forward to continuing on this site.
This article is certainly going to help student . Well written.
Really good, thanks
Practical tips on assignment writing, the’re fantastic. Thank you!
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Utility Menu
- Writing Center
- Writing Program
- Designing Essay Assignments
by Gordon Harvey
Students often do their best and hardest thinking, and feel the greatest sense of mastery and growth, in their writing. Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount:
1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it
However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you’re inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit. Having satisfied yourself, as you should, that what you’re asking is doable, with dignity, by writers just learning the material, try to anticipate in your prompt or discussions of the assignment the following queries:
- What is the purpose of this? How am I going beyond what we have done, or applying it in a new area, or practicing a key academic skill or kind of work?
- To what audience should I imagine myself writing?
- What is the main task or tasks, in a nutshell? What does that key word (e.g., analyze, significance of, critique, explore, interesting, support) really mean in this context or this field?
- What will be most challenging in this and what qualities will most distinguish a good paper? Where should I put my energy? (Lists of possible questions for students to answer in a paper are often not sufficiently prioritized to be helpful.)
- What misconceptions might I have about what I’m to do? (How is this like or unlike other papers I may have written?) Are there too-easy approaches I might take or likely pitfalls? An ambitious goal or standard that I might think I’m expected to meet but am not?
- What form will evidence take in my paper (e.g., block quotations? paraphrase? graphs or charts?) How should I cite it? Should I use/cite material from lecture or section?
- Are there some broad options for structure, emphasis, or approach that I’ll likely be choosing among?
- How should I get started on this? What would be a helpful (or unhelpful) way to take notes, gather data, discover a question or idea? Should I do research?
2. Take time in class to prepare students to succeed at the paper
Resist the impulse to think of class meetings as time for “content” and of writing as work done outside class. Your students won’t have mastered the art of paper writing (if such a mastery is possible) and won’t know the particular disciplinary expectations or moves relevant to the material at hand. Take time in class to show them:
- discuss the assignment in class when you give it, so students can see that you take it seriously, so they can ask questions about it, so they can have it in mind during subsequent class discussions;
- introduce the analytic vocabulary of your assignment into class discussions, and take opportunities to note relevant moves made in discussion or good paper topics that arise;
- have students practice key tasks in class discussions, or in informal writing they do in before or after discussions;
- show examples of writing that illustrates components and criteria of the assignment and that inspires (class readings can sometimes serve as illustrations of a writing principle; so can short excerpts of writing—e.g., a sampling of introductions; and so can bad writing—e.g., a list of problematic thesis statements);
- the topics of originality and plagiarism (what the temptations might be, how to avoid risks) should at some point be addressed directly.
3. Build in process
Ideas develop over time, in a process of posing and revising and getting feedback and revising some more. Assignments should allow for this process in the following ways:
- smaller assignments should prepare for larger ones later;
- students should do some thinking and writing before they write a draft and get a response to it (even if only a response to a proposal or thesis statement sent by email, or described in class);
- for larger papers, students should write and get response (using the skills vocabulary of the assignment) to a draft—at least an “oral draft” (condensed for delivery to the class);
- if possible, meet with students individually about their writing: nothing inspires them more than feeling that you care about their work and development;
- let students reflect on their own writing, in brief cover letters attached to drafts and revisions (these may also ask students to perform certain checks on what they have written, before submitting);
- have clear and firm policies about late work that nonetheless allow for exception if students talk to you in advance.
- Pedagogy Workshops
- Responding to Student Writing
- Commenting Efficiently
- Vocabulary for Discussing Student Writing
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- HarvardWrites Instructor Toolkit
- Additional Resources for Teaching Fellows

Understanding Assignments
What this handout is about.
The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms and practices into meaningful clues to the type of writing your instructor expects. See our short video for more tips.
Basic beginnings
Regardless of the assignment, department, or instructor, adopting these two habits will serve you well :
- Read the assignment carefully as soon as you receive it. Do not put this task off—reading the assignment at the beginning will save you time, stress, and problems later. An assignment can look pretty straightforward at first, particularly if the instructor has provided lots of information. That does not mean it will not take time and effort to complete; you may even have to learn a new skill to complete the assignment.
- Ask the instructor about anything you do not understand. Do not hesitate to approach your instructor. Instructors would prefer to set you straight before you hand the paper in. That’s also when you will find their feedback most useful.
Assignment formats
Many assignments follow a basic format. Assignments often begin with an overview of the topic, include a central verb or verbs that describe the task, and offer some additional suggestions, questions, or prompts to get you started.
An Overview of Some Kind
The instructor might set the stage with some general discussion of the subject of the assignment, introduce the topic, or remind you of something pertinent that you have discussed in class. For example:
“Throughout history, gerbils have played a key role in politics,” or “In the last few weeks of class, we have focused on the evening wear of the housefly …”
The Task of the Assignment
Pay attention; this part tells you what to do when you write the paper. Look for the key verb or verbs in the sentence. Words like analyze, summarize, or compare direct you to think about your topic in a certain way. Also pay attention to words such as how, what, when, where, and why; these words guide your attention toward specific information. (See the section in this handout titled “Key Terms” for more information.)
“Analyze the effect that gerbils had on the Russian Revolution”, or “Suggest an interpretation of housefly undergarments that differs from Darwin’s.”
Additional Material to Think about
Here you will find some questions to use as springboards as you begin to think about the topic. Instructors usually include these questions as suggestions rather than requirements. Do not feel compelled to answer every question unless the instructor asks you to do so. Pay attention to the order of the questions. Sometimes they suggest the thinking process your instructor imagines you will need to follow to begin thinking about the topic.
“You may wish to consider the differing views held by Communist gerbils vs. Monarchist gerbils, or Can there be such a thing as ‘the housefly garment industry’ or is it just a home-based craft?”
These are the instructor’s comments about writing expectations:
“Be concise”, “Write effectively”, or “Argue furiously.”
Technical Details
These instructions usually indicate format rules or guidelines.
“Your paper must be typed in Palatino font on gray paper and must not exceed 600 pages. It is due on the anniversary of Mao Tse-tung’s death.”
The assignment’s parts may not appear in exactly this order, and each part may be very long or really short. Nonetheless, being aware of this standard pattern can help you understand what your instructor wants you to do.
Interpreting the assignment
Ask yourself a few basic questions as you read and jot down the answers on the assignment sheet:
Why did your instructor ask you to do this particular task?
Who is your audience.
- What kind of evidence do you need to support your ideas?
What kind of writing style is acceptable?
- What are the absolute rules of the paper?
Try to look at the question from the point of view of the instructor. Recognize that your instructor has a reason for giving you this assignment and for giving it to you at a particular point in the semester. In every assignment, the instructor has a challenge for you. This challenge could be anything from demonstrating an ability to think clearly to demonstrating an ability to use the library. See the assignment not as a vague suggestion of what to do but as an opportunity to show that you can handle the course material as directed. Paper assignments give you more than a topic to discuss—they ask you to do something with the topic. Keep reminding yourself of that. Be careful to avoid the other extreme as well: do not read more into the assignment than what is there.
Of course, your instructor has given you an assignment so that they will be able to assess your understanding of the course material and give you an appropriate grade. But there is more to it than that. Your instructor has tried to design a learning experience of some kind. Your instructor wants you to think about something in a particular way for a particular reason. If you read the course description at the beginning of your syllabus, review the assigned readings, and consider the assignment itself, you may begin to see the plan, purpose, or approach to the subject matter that your instructor has created for you. If you still aren’t sure of the assignment’s goals, try asking the instructor. For help with this, see our handout on getting feedback .
Given your instructor’s efforts, it helps to answer the question: What is my purpose in completing this assignment? Is it to gather research from a variety of outside sources and present a coherent picture? Is it to take material I have been learning in class and apply it to a new situation? Is it to prove a point one way or another? Key words from the assignment can help you figure this out. Look for key terms in the form of active verbs that tell you what to do.
Key Terms: Finding Those Active Verbs
Here are some common key words and definitions to help you think about assignment terms:
Information words Ask you to demonstrate what you know about the subject, such as who, what, when, where, how, and why.
- define —give the subject’s meaning (according to someone or something). Sometimes you have to give more than one view on the subject’s meaning
- describe —provide details about the subject by answering question words (such as who, what, when, where, how, and why); you might also give details related to the five senses (what you see, hear, feel, taste, and smell)
- explain —give reasons why or examples of how something happened
- illustrate —give descriptive examples of the subject and show how each is connected with the subject
- summarize —briefly list the important ideas you learned about the subject
- trace —outline how something has changed or developed from an earlier time to its current form
- research —gather material from outside sources about the subject, often with the implication or requirement that you will analyze what you have found
Relation words Ask you to demonstrate how things are connected.
- compare —show how two or more things are similar (and, sometimes, different)
- contrast —show how two or more things are dissimilar
- apply—use details that you’ve been given to demonstrate how an idea, theory, or concept works in a particular situation
- cause —show how one event or series of events made something else happen
- relate —show or describe the connections between things
Interpretation words Ask you to defend ideas of your own about the subject. Do not see these words as requesting opinion alone (unless the assignment specifically says so), but as requiring opinion that is supported by concrete evidence. Remember examples, principles, definitions, or concepts from class or research and use them in your interpretation.
- assess —summarize your opinion of the subject and measure it against something
- prove, justify —give reasons or examples to demonstrate how or why something is the truth
- evaluate, respond —state your opinion of the subject as good, bad, or some combination of the two, with examples and reasons
- support —give reasons or evidence for something you believe (be sure to state clearly what it is that you believe)
- synthesize —put two or more things together that have not been put together in class or in your readings before; do not just summarize one and then the other and say that they are similar or different—you must provide a reason for putting them together that runs all the way through the paper
- analyze —determine how individual parts create or relate to the whole, figure out how something works, what it might mean, or why it is important
- argue —take a side and defend it with evidence against the other side
More Clues to Your Purpose As you read the assignment, think about what the teacher does in class:
- What kinds of textbooks or coursepack did your instructor choose for the course—ones that provide background information, explain theories or perspectives, or argue a point of view?
- In lecture, does your instructor ask your opinion, try to prove their point of view, or use keywords that show up again in the assignment?
- What kinds of assignments are typical in this discipline? Social science classes often expect more research. Humanities classes thrive on interpretation and analysis.
- How do the assignments, readings, and lectures work together in the course? Instructors spend time designing courses, sometimes even arguing with their peers about the most effective course materials. Figuring out the overall design to the course will help you understand what each assignment is meant to achieve.
Now, what about your reader? Most undergraduates think of their audience as the instructor. True, your instructor is a good person to keep in mind as you write. But for the purposes of a good paper, think of your audience as someone like your roommate: smart enough to understand a clear, logical argument, but not someone who already knows exactly what is going on in your particular paper. Remember, even if the instructor knows everything there is to know about your paper topic, they still have to read your paper and assess your understanding. In other words, teach the material to your reader.
Aiming a paper at your audience happens in two ways: you make decisions about the tone and the level of information you want to convey.
- Tone means the “voice” of your paper. Should you be chatty, formal, or objective? Usually you will find some happy medium—you do not want to alienate your reader by sounding condescending or superior, but you do not want to, um, like, totally wig on the man, you know? Eschew ostentatious erudition: some students think the way to sound academic is to use big words. Be careful—you can sound ridiculous, especially if you use the wrong big words.
- The level of information you use depends on who you think your audience is. If you imagine your audience as your instructor and they already know everything you have to say, you may find yourself leaving out key information that can cause your argument to be unconvincing and illogical. But you do not have to explain every single word or issue. If you are telling your roommate what happened on your favorite science fiction TV show last night, you do not say, “First a dark-haired white man of average height, wearing a suit and carrying a flashlight, walked into the room. Then a purple alien with fifteen arms and at least three eyes turned around. Then the man smiled slightly. In the background, you could hear a clock ticking. The room was fairly dark and had at least two windows that I saw.” You also do not say, “This guy found some aliens. The end.” Find some balance of useful details that support your main point.
You’ll find a much more detailed discussion of these concepts in our handout on audience .
The Grim Truth
With a few exceptions (including some lab and ethnography reports), you are probably being asked to make an argument. You must convince your audience. It is easy to forget this aim when you are researching and writing; as you become involved in your subject matter, you may become enmeshed in the details and focus on learning or simply telling the information you have found. You need to do more than just repeat what you have read. Your writing should have a point, and you should be able to say it in a sentence. Sometimes instructors call this sentence a “thesis” or a “claim.”
So, if your instructor tells you to write about some aspect of oral hygiene, you do not want to just list: “First, you brush your teeth with a soft brush and some peanut butter. Then, you floss with unwaxed, bologna-flavored string. Finally, gargle with bourbon.” Instead, you could say, “Of all the oral cleaning methods, sandblasting removes the most plaque. Therefore it should be recommended by the American Dental Association.” Or, “From an aesthetic perspective, moldy teeth can be quite charming. However, their joys are short-lived.”
Convincing the reader of your argument is the goal of academic writing. It doesn’t have to say “argument” anywhere in the assignment for you to need one. Look at the assignment and think about what kind of argument you could make about it instead of just seeing it as a checklist of information you have to present. For help with understanding the role of argument in academic writing, see our handout on argument .
What kind of evidence do you need?
There are many kinds of evidence, and what type of evidence will work for your assignment can depend on several factors–the discipline, the parameters of the assignment, and your instructor’s preference. Should you use statistics? Historical examples? Do you need to conduct your own experiment? Can you rely on personal experience? See our handout on evidence for suggestions on how to use evidence appropriately.
Make sure you are clear about this part of the assignment, because your use of evidence will be crucial in writing a successful paper. You are not just learning how to argue; you are learning how to argue with specific types of materials and ideas. Ask your instructor what counts as acceptable evidence. You can also ask a librarian for help. No matter what kind of evidence you use, be sure to cite it correctly—see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial .
You cannot always tell from the assignment just what sort of writing style your instructor expects. The instructor may be really laid back in class but still expect you to sound formal in writing. Or the instructor may be fairly formal in class and ask you to write a reflection paper where you need to use “I” and speak from your own experience.
Try to avoid false associations of a particular field with a style (“art historians like wacky creativity,” or “political scientists are boring and just give facts”) and look instead to the types of readings you have been given in class. No one expects you to write like Plato—just use the readings as a guide for what is standard or preferable to your instructor. When in doubt, ask your instructor about the level of formality they expect.
No matter what field you are writing for or what facts you are including, if you do not write so that your reader can understand your main idea, you have wasted your time. So make clarity your main goal. For specific help with style, see our handout on style .
Technical details about the assignment
The technical information you are given in an assignment always seems like the easy part. This section can actually give you lots of little hints about approaching the task. Find out if elements such as page length and citation format (see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial ) are negotiable. Some professors do not have strong preferences as long as you are consistent and fully answer the assignment. Some professors are very specific and will deduct big points for deviations.
Usually, the page length tells you something important: The instructor thinks the size of the paper is appropriate to the assignment’s parameters. In plain English, your instructor is telling you how many pages it should take for you to answer the question as fully as you are expected to. So if an assignment is two pages long, you cannot pad your paper with examples or reword your main idea several times. Hit your one point early, defend it with the clearest example, and finish quickly. If an assignment is ten pages long, you can be more complex in your main points and examples—and if you can only produce five pages for that assignment, you need to see someone for help—as soon as possible.
Tricks that don’t work
Your instructors are not fooled when you:
- spend more time on the cover page than the essay —graphics, cool binders, and cute titles are no replacement for a well-written paper.
- use huge fonts, wide margins, or extra spacing to pad the page length —these tricks are immediately obvious to the eye. Most instructors use the same word processor you do. They know what’s possible. Such tactics are especially damning when the instructor has a stack of 60 papers to grade and yours is the only one that low-flying airplane pilots could read.
- use a paper from another class that covered “sort of similar” material . Again, the instructor has a particular task for you to fulfill in the assignment that usually relates to course material and lectures. Your other paper may not cover this material, and turning in the same paper for more than one course may constitute an Honor Code violation . Ask the instructor—it can’t hurt.
- get all wacky and “creative” before you answer the question . Showing that you are able to think beyond the boundaries of a simple assignment can be good, but you must do what the assignment calls for first. Again, check with your instructor. A humorous tone can be refreshing for someone grading a stack of papers, but it will not get you a good grade if you have not fulfilled the task.
Critical reading of assignments leads to skills in other types of reading and writing. If you get good at figuring out what the real goals of assignments are, you are going to be better at understanding the goals of all of your classes and fields of study.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

- All Articles
- Before You Start
- How To Get In
- Being a Student
- Good To Know
Most Effective Tips for Writing an Impressive Assignment

When in college, you have to accomplish all of your assignments as part of your education. One of the most common assignments is written essays that will contribute to your grade at the end of your course.
But you might feel apprehensive when you receive such an assignment, especially if it's your first time. You might not feel like you have the necessary skills to write a good essay. But there are certain tips you can use to write a good assignment and lay your apprehensions to rest.
Research and plan
When you take on a course, you will receive a reading list. Familiarize yourself with it right away because your professors will choose texts from this list that will specifically help you with your tasks and assignments. Reading what's on your list will provide you with valuable insight into the topics you have to write about. It will make life easier for you when you need to write an assignment.
After researching, you should make a schedule for writing your assignments. Stick to your schedule. Also, double-check your deadline so you won't have to feel overwhelmed when you realize that your deadline is right around the corner. Break down your time and tasks into more manageable chunks so that you will always be on top of your work. Make a schedule that consists of mini-deadlines. Knowing that you have completed a task will keep you motivated.
Understand your assignment and take notes
Before starting your assignment, make sure that you understand it because writing an essay that contains irrelevant information or isn't coherent will prove disastrous. You should always know what you're doing and what you need to convey. If needed, rereading the instructions will help you understand what's expected of you. Moreover, you also need to determine how long the essay should be and how you will proceed with it.
Note-taking is another important aspect of writing. Before you start, you must collect various materials and resources relevant to your topic. You should also create an outline that will guide you. Go through various research materials, then take down notes on the most crucial information that you can include in your work. The writing process will become more manageable when you have all of the information you need.
Assignment writing by professionals
As a student in college, you have the option to ask for help when you need to complete an assignment and you have no time to do it. Since written tasks are an unavoidable aspect of college education, the best thing you can do is to seek assistance when you need it. The writers at AssignmentBro helped with my assignment writing in college. Thanks to their professional writers, I still had plenty of time to study and tackle my other responsibilities.
Use various resources
Aside from the deadlines and instructions that your professor will provide, they might also recommend some resources to you. Sadly, this is something that many students tend to overlook. For instance, for you to understand how your professor will grade your assignment, you will need to examine their rubric. This is a chart that provides information on what you must do. You will also learn about the objectives of the assignments or the learning outcomes.
Other resources you might receive include reading lists, lecture recordings, discussion boards, and sample assignments. Usually, you will find all of these resources in an online platform known as a Learning Management System (LMS). Research has shown that students who use LMS tend to get higher grades. If you still have any questions, you can ask your professor either online or offline.
Determine the objective and structure of your assignment
The next thing you need to do is to define the objectives of your written work and its structure. This is where you will determine the pattern of a well-written assignment. You want to make your work look impressive in the eyes of your reader. One way to accomplish this is to include more theoretical content and details in your essay.
Make sure all of your paragraphs flow smoothly
It's not enough for the essay writing project assigned to you to provide enough information. It's also important to remain coherent. You must link each paragraph to each other.
This will keep your reader connected with the content . To achieve this, you need to go back to your plan for your assignment, then search for significant concepts that will help you connect the paragraphs smoothly. Here's an easy tip to do this - include phrases or words that will attract the eyes of your readers while supporting the context of your written assignment.
University life is full of challenges. One of which is the writing of assignments that will require higher communication, critical thinking, and information gathering skills that you may have practiced in high school. Instead of feeling daunted because of your assignments, use the tips you learned to make things easier for you.
Share with friends:
You might like to know more about.


5 tips on writing better university assignments
Lecturer in Student Learning and Communication Development, University of Sydney
Disclosure statement
Alexandra Garcia does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Sydney provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
University life comes with its share of challenges. One of these is writing longer assignments that require higher information, communication and critical thinking skills than what you might have been used to in high school. Here are five tips to help you get ahead.
1. Use all available sources of information
Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often overlook these.
For example, to understand how your assignment will be graded, you can examine the rubric . This is a chart indicating what you need to do to obtain a high distinction, a credit or a pass, as well as the course objectives – also known as “learning outcomes”.
Other resources include lecture recordings, reading lists, sample assignments and discussion boards. All this information is usually put together in an online platform called a learning management system (LMS). Examples include Blackboard , Moodle , Canvas and iLearn . Research shows students who use their LMS more frequently tend to obtain higher final grades.
If after scrolling through your LMS you still have questions about your assignment, you can check your lecturer’s consultation hours.
2. Take referencing seriously
Plagiarism – using somebody else’s words or ideas without attribution – is a serious offence at university. It is a form of cheating.

In many cases, though, students are unaware they have cheated. They are simply not familiar with referencing styles – such as APA , Harvard , Vancouver , Chicago , etc – or lack the skills to put the information from their sources into their own words.
To avoid making this mistake, you may approach your university’s library, which is likely to offer face-to-face workshops or online resources on referencing. Academic support units may also help with paraphrasing.
You can also use referencing management software, such as EndNote or Mendeley . You can then store your sources, retrieve citations and create reference lists with only a few clicks. For undergraduate students, Zotero has been recommended as it seems to be more user-friendly.
Using this kind of software will certainly save you time searching for and formatting references. However, you still need to become familiar with the citation style in your discipline and revise the formatting accordingly.
3. Plan before you write
If you were to build a house, you wouldn’t start by laying bricks at random. You’d start with a blueprint. Likewise, writing an academic paper requires careful planning: you need to decide the number of sections, their organisation, and the information and sources you will include in each.
Research shows students who prepare detailed outlines produce higher-quality texts. Planning will not only help you get better grades, but will also reduce the time you spend staring blankly at the screen thinking about what to write next.

During the planning stage, using programs like OneNote from Microsoft Office or Outline for Mac can make the task easier as they allow you to organise information in tabs. These bits of information can be easily rearranged for later drafting. Navigating through the tabs is also easier than scrolling through a long Word file.
4. Choose the right words
Which of these sentences is more appropriate for an assignment?
a. “This paper talks about why the planet is getting hotter”, or b. “This paper examines the causes of climate change”.
The written language used at university is more formal and technical than the language you normally use in social media or while chatting with your friends. Academic words tend to be longer and their meaning is also more precise. “Climate change” implies more than just the planet “getting hotter”.
To find the right words, you can use SkELL , which shows you the words that appear more frequently, with your search entry categorised grammatically. For example, if you enter “paper”, it will tell you it is often the subject of verbs such as “present”, “describe”, “examine” and “discuss”.
Another option is the Writefull app, which does a similar job without having to use an online browser.
5. Edit and proofread
If you’re typing the last paragraph of the assignment ten minutes before the deadline, you will be missing a very important step in the writing process: editing and proofreading your text. A 2018 study found a group of university students did significantly better in a test after incorporating the process of planning, drafting and editing in their writing.

You probably already know to check the spelling of a word if it appears underlined in red. You may even use a grammar checker such as Grammarly . However, no software to date can detect every error and it is not uncommon to be given inaccurate suggestions.
So, in addition to your choice of proofreader, you need to improve and expand your grammar knowledge. Check with the academic support services at your university if they offer any relevant courses.
Written communication is a skill that requires effort and dedication. That’s why universities are investing in support services – face-to-face workshops, individual consultations, and online courses – to help students in this process. You can also take advantage of a wide range of web-based resources such as spell checkers, vocabulary tools and referencing software – many of them free.
Improving your written communication will help you succeed at university and beyond.
- College assignments
- University study
- Writing tips
- Essay writing
- Student assessment

Case Management Specialist

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer - Marketing

Assistant Editor - 1 year cadetship

Executive Dean, Faculty of Health

Lecturer/Senior Lecturer, Earth System Science (School of Science)
- Steps for writing assignments
- Information and services
- Student support
- Study skills and learning advice
- Study skills and learning advice overview
- Assignment writing
Follow this step-by-step guide to assignment writing to help you to manage your time and produce a better assignment.
This is a general guide. It's primarily for research essays, but can be used for all assignments. The specific requirements for your course may be different. Make sure you read through any assignment requirements carefully and ask your lecturer or tutor if you're unsure how to meet them.
- Analysing the topic
- Researching and note-taking
- Planning your assignment
- Writing your assignment
- Editing your assignment
1. Analysing the topic
Before you start researching or writing, take some time to analyse the assignment topic to make sure you know what you need to do.
Understand what you need to do
Read through the topic a few times to make sure you understand it. Think about the:
- learning objectives listed in the course profile – understand what you should be able to do after completing the course and its assessment tasks
- criteria you'll be marked on – find out what you need to do to achieve the grade you want
- questions you need to answer – try to explain the topic in your own words.
Identify keywords
Identify keywords in the topic that will help guide your research, including any:
- task words – what you have to do (usually verbs)
- topic words – ideas, concepts or issues you need to discuss (often nouns)
- limiting words – restrict the focus of the topic (e.g. to a place, population or time period).
If you're writing your own topic, include task words, topic words and limiting words to help you to focus on exactly what you have to do.
Example keyword identification - text version
Topic: Evaluate the usefulness of a task analysis approach to assignment writing, especially with regard to the writing skill development of second language learners in the early stages of university study in the Australian university context. Task words: Evaluate Topic words: task analysis approach, assignment writing, writing skill development Limiting words : second language learners (population), early stages of university (time period), Australian university (place)
Brainstorm your ideas
Brainstorm information about the topic that you:
- already know
- will need to research to write the assignment.
When you brainstorm:
- use 'Who? What? When? Where? Why? and How?' questions to get you thinking
- write down all your ideas – don't censor yourself or worry about the order
- try making a concept map to capture your ideas – start with the topic in the centre and record your ideas branching out from it.
- Assignment types
- How to write a literature review
Learning Advisers
Our advisers can help undergraduate and postgraduate students in all programs clarify ideas from workshops, help you develop skills and give feedback on assignments.
How a Learning Adviser can help
Further support
Workshops Find a proofreader

9 Awesome Assignment Writing Tips to Get Better Marks!
There are some things that are common among every student in the universe: they do not like getting up early, they hate it when their best friend is absent, and they absolutely despise writing assignments.
Well, we can’t solve the first two problems (because it’s between you, your parents and your best friend) – we can definitely solve the third one – writing assignments.
We know that the word ‘assignment’ usually sends shivers down your spine. You have got a blank page, a ticking clock, and probably your best buddy – procrastination. Those are enough things to send you into panic mode.
So what if we tell you that writing those dreadful assignments can be a really fun and easy process? All you need is some assignment writing tips up your sleeve, and we’re going to give you just that.
Yes, in this blog, we’ll be sharing 9 tips that will completely transform your assignment writing process (and get you an A Grade.) Ready? Let’s go!
List of 9 Tips That Will Help You Write Awesome Assignments
1. understand what exactly you need to do.
Yes, we can use the “just swing it” method while doing a lot of things in life. But, it’s not very wise to practice it while writing assignments. (Unless you want to face the wrath of your teacher.)
Basically, even if there is even one tiny thing that you don’t get about the assignment, clarify it with your teacher or classmates BEFORE starting the assignment.
Otherwise, you’d end up working on something that wasn’t even supposed to be done, and all your effort and time would go down the drain, along with a good grade.
Moral of the story: If you want to ace the assignment, you’ve to be very, very clear about what you need to work on. Don’t be afraid to ask questions – because it’s always worth it.
2. Plan Your Time Well
Sometimes, we all wish there were more than 24 hours in a day. That way, we’d have so much more time to do assignments and meet the deadlines, right?
Well, you can still write great assignments on time. All you need to do is plan your time well. As soon as you get your assignment, create a solid schedule and follow it religiously until the deadline.
For example, you can set a deadline yourself for each sub-topic in the assignment, OR you can create a time-table and allot a few hours of the day to writing that assignment.

If you want to know more about how you can manage your time well and beat the procrastination monster, you can check out our comprehensive list of time management strategies.
3. Always Start With Research
First things first, gather as much knowledge as you can about the topic of your assignment. Read all the pre-existing material. In fact, take a deep dive into it.
After that, note down all the important points that you came across. Once that’s done, start working on your assignment using the knowledge you gained.
This way, you will be able to hand in a much more solid assignment because 1) the assignment would be more detailed and comprehensive, and 2) You do better when you know better.
Read more: How To Make Class Notes Worth Reading?
4. Prepare a Structure Beforehand
Even though all those inspirational quotes ask us to ‘go with the flow’, it’s not the right thing to do while writing assignments. Assignment writing isn’t a piece of cake, so it’s better to be prepared.
Before writing the content of your assignment, first lay down the structure you’re going to follow. This will make your assignment writing process a lot smoother.
For example, if you need to write about what buyer persona is, you should first divide your assignment into different subtopics like the definition, importance, steps to create one, and so on.
5. Write a Classy Introduction

Your introduction is going to set the tone for the rest of your assignment, so you need to make it awesome. Write an intro that makes the reader feel like you know what you’re talking about.
Also, don’t keep the introduction too long. Cut to the chase and get to the meat of your assignment quickly. Remember, your introduction needs to hook the readers and grab their attention in a matter of seconds!
At the end of the intro, write a little about everything that you’ve included in the assignment. You can include a little background information about the topic to establish the context.
6. Don’t Use Slang Words
This isn’t a chat room. This isn’t an extra paper you’re scribbling on to pass time. This is an assignment – a professional thing that needs to be written professionally.
Even though you might have the habit of using slang words while talking or texting, you absolutely can’t use them while writing your assignment. As simple as that.
For example, you can’t write, “LOL girl, that was hilarious” to describe a funny anecdote or “Damn, that was dope” to describe an incredible thing that happened. 🙂
7. Proofread, Proofread & Proofread
Don’t just hand over the assignment to your teacher the minute your write the last word. Proofread it at least three times. Read it out loud. Check for spellings, punctuations, and other grammatical mistakes.
No matter how great your assignment is and how hard you worked on it, if the teacher comes across tons of mistakes in the assignment, it won’t be able to leave a good impression.
So, if you don’t want your effort to go down the drain, have some patience and proofread your assignment until you’re sure that there are no more mistakes.
Read more: Study Guide: What is it & How to Create an Amazing One?
8. Cite Your References

When you’ll write your assignment, it’s natural that you’ll refer to books and other materials related to the topic. After all, as we said, research is the key to writing great assignments.
So, if you’re using a few lines, phrases, or stats from SOMEONE else’s work in YOUR assignment, don’t forget to cite the reference. Here’s why you need to do it:
First, if you cite the source of the information, your work won’t seem copied and it won’t be termed as ‘plagiarised’. Secondly, it’d give the impression that you researched thoroughly before writing the assignment!
9. Use Bit.ai
Last but definitely not least on our list of assignment writing tips is: use Bit.ai . This nifty platform simplifies and automates your entire documentation process.
See, you’ve spent hours working on the assignment. You did all the research, you compiled all the information, and you wrote the assignment really well.
But, between all this, you might overlook the presentation aspect of your assignment, which matters as much as the content of your assignment.
We totally understand. The deadline is lingering upon you, so you don’t have the time to care about the format of your assignment. But that doesn’t change the fact that a clumsy-looking assignment never works.
Luckily, Bit solves that problem for you by automating the design aspect of your documents for you. 😎 With over 90+ fully responsive and gorgeous templates , Bit has made the process of writing assignments super smooth.
With just one click, you can change the look of your entire assignment. You can even change the layout of the theme and update the color of your assignment too. How great is that?
Before you go!
Our team at bit.ai has created a few awesome education templates to make your processes more efficient. Make sure to check them out before you go, y ou might need them!
- Class Notes Template
- Lesson Plan Template
- Letter of Recommendation Template
- Recommended Reading Template
- Research Paper Template
- Thesis Template
- Checklist Template
- To-Do List Template
- White Paper Template
- eBook Template
Start Writing Efficient Assignments Today!
If you made it this far, we’re sure you’re going to ace your next assignment. Just follow all the tips we’ve given, use Bit.ai, and you’d end up with an assignment you could be proud of.
Remember, assignment writing doesn’t have to be a dreadful task. Just do thorough research on the topic first, prepare a structure beforehand, and you’ll be on your way to writing a great assignment.
If you’ve got any other assignment writing tips that worked for you, let us know by tweeting us @bit_docs. We’d be more than happy to include it on our list. Good luck!
Further reads:
11 Grammarly Alternatives and Competitors You Must Know!
8 Different Types of Writing Styles (And How to Improve Your Own)
Top 9 Writing Checkers Every Writer Should Use!
9 Best Paraphrasing Tools In 2022 (Free & Paid)
Collaborative Teaching: What is it & How to Do it the Right Way?
12 Best Student Tools for Better Learning in 2022
Student Collaboration: What, Why, and Tools!
Lesson plan: What is it & How to Create an Effective One? (Free template)
Learning Objectives: What are they & How to Write them?

Thesis Statement: Definition, Importance, Steps & Tips!
9 Powerful Mind Mapping Software & Tools for Business!
Related posts
Project scope: what is it and how to write it, 13 social media post ideas for interesting content, top 9 wunderlist alternatives that are worth checking out, periodic report: what is it and how to create it, top 9 hr software and tools for human resource departments, 50 best team building activities for collaboration.

About Bit.ai
Bit.ai is the essential next-gen workplace and document collaboration platform. that helps teams share knowledge by connecting any type of digital content. With this intuitive, cloud-based solution, anyone can work visually and collaborate in real-time while creating internal notes, team projects, knowledge bases, client-facing content, and more.
The smartest online Google Docs and Word alternative, Bit.ai is used in over 100 countries by professionals everywhere, from IT teams creating internal documentation and knowledge bases, to sales and marketing teams sharing client materials and client portals.
👉👉Click Here to Check out Bit.ai.
Recent Posts
Personal user manual: enhance professional profile & team productivity, 9 document management trends every business should know, ai for social media marketing: tools & tactics to boost engagement, a guide to building a client portal for your online course, knowledge management vs document management, 11 must-try ai tools for market research in 2024.
- Do My Essay
- Assignment Help
- Coursework Help
- Dissertation Help
- Do My Homework
- How it works
How to Write an Assignment
- Dissertation Topics
- Essay Samples
- Essay Topics

Write an Assignment – Easy-to-Follow Guide
Our article focuses on how to write an assignment effectively, highlighting the challenges students face in navigating complex tasks. It emphasizes the need to alleviate these struggles by demystifying the process and empowering students to approach tasks with confidence and competence.
The article promises a comprehensive step-by-step guide from experts in the field, providing both theoretical advice and practical tips from seasoned writers and educators who have successfully navigated the intricacies of assignments.
This structured approach dismantles the complexities of assignment writing, making the process more manageable and rewarding. The guide is based on real-world experience and academic wisdom, ensuring readers can benefit from the insights gained from those who have mastered the art of assignment writing.
Prewriting Stage
Before starting the writing process, it is essential to understand how to write an assignment prompt. This involves identifying key instructions, determining the purpose of the task, and identifying any specific requirements. By breaking down the language and expectations, writers can establish a solid foundation for the whole writing process. Practical examples and strategies are provided to help writers approach complex prompts with clarity and confidence.
Next, writers must research and gather relevant information. Effective research strategies include using academic databases, libraries, and online resources. Critical evaluation of sources is crucial to ensure the information is relevant and contributes to a well-informed discussion.
A well-defined thesis statement is at the core of any well-crafted assignment, encapsulating the main argument or purpose. This part of the prewriting process guides writers in formulating a clear statement that aligns with the assignment prompt and reflects their understanding of the subject matter.
Importance of Writing an Assignment
Assignment writing is crucial for academic success as it allows students to explore subject matter and apply theoretical knowledge to real-world scenarios. It influences grades and cultivates a deeper understanding of the subject matter, laying the groundwork for long-term academic success.
Effective assignment writing is connected to comprehensive learning as it fosters deeper engagement with course content, encourages independent exploration, and enhances research, analytical, and communication skills. This symbiotic relationship between mastering assignment writing and achieving a more comprehensive and enduring understanding of academic material is undeniable, as it helps students develop a deeper understanding of the material and reinforces learning objectives.
Assignment Writing Structure Nuances
Developing a strong introduction, organizing an influential body, and providing a captivating conclusion are essential skills for anyone starting an assignment writing journey. We dissect the craft of each section in this brief manual, offering useful advice on how to write an assignment. Together, let’s examine the intricate procedure.
Introduction
The introduction of an assignment is an important element that sets the stage for a captivating performance. It should capture the reader’s attention from the very first sentence, using techniques such as thought-provoking questions, relevant quotes, or compelling anecdotes. This section aims to equip writers with the tools to create introductions that grab attention and establish the tone and context for the entire assignment.
A well-crafted introduction should also serve as a roadmap, providing the reader with a clear understanding of the assignment’s purpose and scope. It is crucial to articulate the assignment’s objectives succinctly, whether it involves analyzing a specific topic, presenting an argument, or exploring a particular theme. By incorporating examples and breaking down the components of purpose and scope, writers can navigate the fine balance between providing enough information to orient the reader and maintaining intrigue that propels them further into the assignment. The emphasis is on clarity and conciseness, setting the stage for a well-structured and purposeful piece of writing.
The body of an assignment is the intellectual core, where ideas unfold, arguments develop, and concepts are explored in depth. It provides strategies for dividing content logically, such as dividing discussions based on key themes, chronological order, or contrasting perspectives. This helps students in writing an assignment that is structured and reader-friendly.
The strength of any academic assignment lies in its ability to present a compelling and logically sound argument. This section focuses on constructing coherent and logical arguments that address the assignment prompt and contribute to a robust and persuasive narrative. It examines examples of effective argumentation and provides step-by-step guidelines to empower writers with the skills needed to construct a compelling academic discourse.
Writers learn how to write an assignment judiciously and incorporate scholarly sources, data, and real-world examples to bolster their arguments. Comprehending the balance between quantity and quality of evidence enhances the persuasiveness of their arguments, fostering deeper engagement with the reader and establishing credibility within the academic discourse.
The conclusion of an assignment is a reflection of the main ideas and findings presented throughout the body. It serves as a synthesis of these ideas, offering a clear understanding of the key points discussed. This section focuses on summarizing key findings effectively, distilling complex information into concise yet impactful statements.
It emphasizes identifying the assignment’s core takeaways, ensuring the reader leaves with a clear understanding. By providing examples and practical guidelines, this subsection empowers writers for writing an assignment conclusion that resonates with the overall purpose of the assignment, leaving a lasting impression on the reader. The conclusion is not only a summary but also a reinforcement of the assignment’s central argument. It guides writers in restating the thesis and reinforcing the main points, ensuring the reader is left with a lasting impression of the assignment’s core arguments.
The Best Way to Write Assignment Projects
To know how to write an assignment effectively, you should avoid common pitfalls such as vague language, excessive wordiness, and unclear expressions. By understanding these pitfalls and learning strategies, writers can enhance the impact of their writing assignments, ensuring their ideas resonate with the reader effectively.
Clarity and coherence in sentences and paragraphs are crucial for well-crafted writing. Techniques to ensure meaningful contributions to the narrative and seamless paragraph flow are explored. By organizing ideas logically, employing effective transitions, and structuring sentences for maximum impact, clear and coherent writing enhances understanding and showcases a writer’s mastery of the subject matter.
Incorporating appropriate academic language is essential for effective communication in scholarly writing. By understanding how to write good assignments with precise vocabulary and navigating academic tone conventions, writers can tailor their language to the expectations of their audience. By incorporating discipline-specific terminology and adhering to established writing conventions, writers can convey their ideas with authority and credibility, contributing to the overall effectiveness of their academic communication.
Writing an Assignment Following Citation Styles
The foundational principle of accurate and ethical citation is crucial in academic writing to avoid plagiarism. This principle involves understanding various methods of attribution, such as in-text citations and footnotes, to integrate others’ ideas into one’s work while giving due credit. By mastering paraphrasing and quoting, writers can maintain academic integrity and contribute responsibly to the scholarly conversation.
Academic disciplines often follow specific citation styles, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, which ensure clarity, consistency, and demonstrate a writer’s commitment to scholarly standards. The ultimate goal of proper citation practices is the creation of a comprehensive bibliography or works cited page, which includes a list of sources consulted during the research and writing assignment process. This comprehensive bibliography provides a comprehensive and accurate list of references, adding a layer of professionalism to understanding how to write an assignment.
Final Words on Writing and Editing
The process of editing and proofreading is crucial for ensuring the clarity and coherence of a university assignment . It involves systematically reviewing the work, focusing on the flow of ideas and logical progression, and ensuring each paragraph contributes to the assignment’s central theme. Reputable essay writing services can provide valuable support in this process, employing professional editors who specialize in refining academic writing. These services can help writers enhance the structure and coherence of their work, leading to a polished final product.
The credibility of an assignment writing is also crucial, and it is essential to check for grammatical and spelling errors. Writers learn essential proofreading techniques to identify and rectify common language mistakes, enhancing the professionalism of the work and contributing to the writer’s reputation as a skilled communicator.
Proofreading services often teach how to write assignments, proofread, and identify and correct grammatical and spelling errors, providing an additional layer of assurance for a polished final draft.
Collaboration and feedback are essential in the refinement process, and assignment help services can offer additional layers of feedback through their review and critique services. Experienced professionals provide constructive comments on the content, structure, and style of the university assignment , offering valuable perspectives for enhancement. Engaging with such services allows writers to benefit from expert evaluations, further refining their work before submission.

Teaching, Learning, & Professional Development Center
- Teaching Resources
- TLPDC Teaching Resources
How Do I Create Meaningful and Effective Assignments?
Prepared by allison boye, ph.d. teaching, learning, and professional development center.
Assessment is a necessary part of the teaching and learning process, helping us measure whether our students have really learned what we want them to learn. While exams and quizzes are certainly favorite and useful methods of assessment, out of class assignments (written or otherwise) can offer similar insights into our students' learning. And just as creating a reliable test takes thoughtfulness and skill, so does creating meaningful and effective assignments. Undoubtedly, many instructors have been on the receiving end of disappointing student work, left wondering what went wrong… and often, those problems can be remedied in the future by some simple fine-tuning of the original assignment. This paper will take a look at some important elements to consider when developing assignments, and offer some easy approaches to creating a valuable assessment experience for all involved.
First Things First…
Before assigning any major tasks to students, it is imperative that you first define a few things for yourself as the instructor:
- Your goals for the assignment . Why are you assigning this project, and what do you hope your students will gain from completing it? What knowledge, skills, and abilities do you aim to measure with this assignment? Creating assignments is a major part of overall course design, and every project you assign should clearly align with your goals for the course in general. For instance, if you want your students to demonstrate critical thinking, perhaps asking them to simply summarize an article is not the best match for that goal; a more appropriate option might be to ask for an analysis of a controversial issue in the discipline. Ultimately, the connection between the assignment and its purpose should be clear to both you and your students to ensure that it is fulfilling the desired goals and doesn't seem like “busy work.” For some ideas about what kinds of assignments match certain learning goals, take a look at this page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons.
- Have they experienced “socialization” in the culture of your discipline (Flaxman, 2005)? Are they familiar with any conventions you might want them to know? In other words, do they know the “language” of your discipline, generally accepted style guidelines, or research protocols?
- Do they know how to conduct research? Do they know the proper style format, documentation style, acceptable resources, etc.? Do they know how to use the library (Fitzpatrick, 1989) or evaluate resources?
- What kinds of writing or work have they previously engaged in? For instance, have they completed long, formal writing assignments or research projects before? Have they ever engaged in analysis, reflection, or argumentation? Have they completed group assignments before? Do they know how to write a literature review or scientific report?
In his book Engaging Ideas (1996), John Bean provides a great list of questions to help instructors focus on their main teaching goals when creating an assignment (p.78):
1. What are the main units/modules in my course?
2. What are my main learning objectives for each module and for the course?
3. What thinking skills am I trying to develop within each unit and throughout the course?
4. What are the most difficult aspects of my course for students?
5. If I could change my students' study habits, what would I most like to change?
6. What difference do I want my course to make in my students' lives?
What your students need to know
Once you have determined your own goals for the assignment and the levels of your students, you can begin creating your assignment. However, when introducing your assignment to your students, there are several things you will need to clearly outline for them in order to ensure the most successful assignments possible.
- First, you will need to articulate the purpose of the assignment . Even though you know why the assignment is important and what it is meant to accomplish, you cannot assume that your students will intuit that purpose. Your students will appreciate an understanding of how the assignment fits into the larger goals of the course and what they will learn from the process (Hass & Osborn, 2007). Being transparent with your students and explaining why you are asking them to complete a given assignment can ultimately help motivate them to complete the assignment more thoughtfully.
- If you are asking your students to complete a writing assignment, you should define for them the “rhetorical or cognitive mode/s” you want them to employ in their writing (Flaxman, 2005). In other words, use precise verbs that communicate whether you are asking them to analyze, argue, describe, inform, etc. (Verbs like “explore” or “comment on” can be too vague and cause confusion.) Provide them with a specific task to complete, such as a problem to solve, a question to answer, or an argument to support. For those who want assignments to lead to top-down, thesis-driven writing, John Bean (1996) suggests presenting a proposition that students must defend or refute, or a problem that demands a thesis answer.
- It is also a good idea to define the audience you want your students to address with their assignment, if possible – especially with writing assignments. Otherwise, students will address only the instructor, often assuming little requires explanation or development (Hedengren, 2004; MIT, 1999). Further, asking students to address the instructor, who typically knows more about the topic than the student, places the student in an unnatural rhetorical position. Instead, you might consider asking your students to prepare their assignments for alternative audiences such as other students who missed last week's classes, a group that opposes their position, or people reading a popular magazine or newspaper. In fact, a study by Bean (1996) indicated the students often appreciate and enjoy assignments that vary elements such as audience or rhetorical context, so don't be afraid to get creative!
- Obviously, you will also need to articulate clearly the logistics or “business aspects” of the assignment . In other words, be explicit with your students about required elements such as the format, length, documentation style, writing style (formal or informal?), and deadlines. One caveat, however: do not allow the logistics of the paper take precedence over the content in your assignment description; if you spend all of your time describing these things, students might suspect that is all you care about in their execution of the assignment.
- Finally, you should clarify your evaluation criteria for the assignment. What elements of content are most important? Will you grade holistically or weight features separately? How much weight will be given to individual elements, etc? Another precaution to take when defining requirements for your students is to take care that your instructions and rubric also do not overshadow the content; prescribing too rigidly each element of an assignment can limit students' freedom to explore and discover. According to Beth Finch Hedengren, “A good assignment provides the purpose and guidelines… without dictating exactly what to say” (2004, p. 27). If you decide to utilize a grading rubric, be sure to provide that to the students along with the assignment description, prior to their completion of the assignment.
A great way to get students engaged with an assignment and build buy-in is to encourage their collaboration on its design and/or on the grading criteria (Hudd, 2003). In his article “Conducting Writing Assignments,” Richard Leahy (2002) offers a few ideas for building in said collaboration:
• Ask the students to develop the grading scale themselves from scratch, starting with choosing the categories.
• Set the grading categories yourself, but ask the students to help write the descriptions.
• Draft the complete grading scale yourself, then give it to your students for review and suggestions.
A Few Do's and Don'ts…
Determining your goals for the assignment and its essential logistics is a good start to creating an effective assignment. However, there are a few more simple factors to consider in your final design. First, here are a few things you should do :
- Do provide detail in your assignment description . Research has shown that students frequently prefer some guiding constraints when completing assignments (Bean, 1996), and that more detail (within reason) can lead to more successful student responses. One idea is to provide students with physical assignment handouts , in addition to or instead of a simple description in a syllabus. This can meet the needs of concrete learners and give them something tangible to refer to. Likewise, it is often beneficial to make explicit for students the process or steps necessary to complete an assignment, given that students – especially younger ones – might need guidance in planning and time management (MIT, 1999).
- Do use open-ended questions. The most effective and challenging assignments focus on questions that lead students to thinking and explaining, rather than simple yes or no answers, whether explicitly part of the assignment description or in the brainstorming heuristics (Gardner, 2005).
- Do direct students to appropriate available resources . Giving students pointers about other venues for assistance can help them get started on the right track independently. These kinds of suggestions might include information about campus resources such as the University Writing Center or discipline-specific librarians, suggesting specific journals or books, or even sections of their textbook, or providing them with lists of research ideas or links to acceptable websites.
- Do consider providing models – both successful and unsuccessful models (Miller, 2007). These models could be provided by past students, or models you have created yourself. You could even ask students to evaluate the models themselves using the determined evaluation criteria, helping them to visualize the final product, think critically about how to complete the assignment, and ideally, recognize success in their own work.
- Do consider including a way for students to make the assignment their own. In their study, Hass and Osborn (2007) confirmed the importance of personal engagement for students when completing an assignment. Indeed, students will be more engaged in an assignment if it is personally meaningful, practical, or purposeful beyond the classroom. You might think of ways to encourage students to tap into their own experiences or curiosities, to solve or explore a real problem, or connect to the larger community. Offering variety in assignment selection can also help students feel more individualized, creative, and in control.
- If your assignment is substantial or long, do consider sequencing it. Far too often, assignments are given as one-shot final products that receive grades at the end of the semester, eternally abandoned by the student. By sequencing a large assignment, or essentially breaking it down into a systematic approach consisting of interconnected smaller elements (such as a project proposal, an annotated bibliography, or a rough draft, or a series of mini-assignments related to the longer assignment), you can encourage thoughtfulness, complexity, and thoroughness in your students, as well as emphasize process over final product.
Next are a few elements to avoid in your assignments:
- Do not ask too many questions in your assignment. In an effort to challenge students, instructors often err in the other direction, asking more questions than students can reasonably address in a single assignment without losing focus. Offering an overly specific “checklist” prompt often leads to externally organized papers, in which inexperienced students “slavishly follow the checklist instead of integrating their ideas into more organically-discovered structure” (Flaxman, 2005).
- Do not expect or suggest that there is an “ideal” response to the assignment. A common error for instructors is to dictate content of an assignment too rigidly, or to imply that there is a single correct response or a specific conclusion to reach, either explicitly or implicitly (Flaxman, 2005). Undoubtedly, students do not appreciate feeling as if they must read an instructor's mind to complete an assignment successfully, or that their own ideas have nowhere to go, and can lose motivation as a result. Similarly, avoid assignments that simply ask for regurgitation (Miller, 2007). Again, the best assignments invite students to engage in critical thinking, not just reproduce lectures or readings.
- Do not provide vague or confusing commands . Do students know what you mean when they are asked to “examine” or “discuss” a topic? Return to what you determined about your students' experiences and levels to help you decide what directions will make the most sense to them and what will require more explanation or guidance, and avoid verbiage that might confound them.
- Do not impose impossible time restraints or require the use of insufficient resources for completion of the assignment. For instance, if you are asking all of your students to use the same resource, ensure that there are enough copies available for all students to access – or at least put one copy on reserve in the library. Likewise, make sure that you are providing your students with ample time to locate resources and effectively complete the assignment (Fitzpatrick, 1989).
The assignments we give to students don't simply have to be research papers or reports. There are many options for effective yet creative ways to assess your students' learning! Here are just a few:
Journals, Posters, Portfolios, Letters, Brochures, Management plans, Editorials, Instruction Manuals, Imitations of a text, Case studies, Debates, News release, Dialogues, Videos, Collages, Plays, Power Point presentations
Ultimately, the success of student responses to an assignment often rests on the instructor's deliberate design of the assignment. By being purposeful and thoughtful from the beginning, you can ensure that your assignments will not only serve as effective assessment methods, but also engage and delight your students. If you would like further help in constructing or revising an assignment, the Teaching, Learning, and Professional Development Center is glad to offer individual consultations. In addition, look into some of the resources provided below.
Online Resources
“Creating Effective Assignments” http://www.unh.edu/teaching-excellence/resources/Assignments.htm This site, from the University of New Hampshire's Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning, provides a brief overview of effective assignment design, with a focus on determining and communicating goals and expectations.
Gardner, T. (2005, June 12). Ten Tips for Designing Writing Assignments. Traci's Lists of Ten. http://www.tengrrl.com/tens/034.shtml This is a brief yet useful list of tips for assignment design, prepared by a writing teacher and curriculum developer for the National Council of Teachers of English . The website will also link you to several other lists of “ten tips” related to literacy pedagogy.
“How to Create Effective Assignments for College Students.” http:// tilt.colostate.edu/retreat/2011/zimmerman.pdf This PDF is a simplified bulleted list, prepared by Dr. Toni Zimmerman from Colorado State University, offering some helpful ideas for coming up with creative assignments.
“Learner-Centered Assessment” http://cte.uwaterloo.ca/teaching_resources/tips/learner_centered_assessment.html From the Centre for Teaching Excellence at the University of Waterloo, this is a short list of suggestions for the process of designing an assessment with your students' interests in mind. “Matching Learning Goals to Assignment Types.” http://teachingcommons.depaul.edu/How_to/design_assignments/assignments_learning_goals.html This is a great page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons, providing a chart that helps instructors match assignments with learning goals.
Additional References Bean, J.C. (1996). Engaging ideas: The professor's guide to integrating writing, critical thinking, and active learning in the classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Fitzpatrick, R. (1989). Research and writing assignments that reduce fear lead to better papers and more confident students. Writing Across the Curriculum , 3.2, pp. 15 – 24.
Flaxman, R. (2005). Creating meaningful writing assignments. The Teaching Exchange . Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008 from http://www.brown.edu/Administration/Sheridan_Center/pubs/teachingExchange/jan2005/01_flaxman.pdf
Hass, M. & Osborn, J. (2007, August 13). An emic view of student writing and the writing process. Across the Disciplines, 4.
Hedengren, B.F. (2004). A TA's guide to teaching writing in all disciplines . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's.
Hudd, S. S. (2003, April). Syllabus under construction: Involving students in the creation of class assignments. Teaching Sociology , 31, pp. 195 – 202.
Leahy, R. (2002). Conducting writing assignments. College Teaching , 50.2, pp. 50 – 54.
Miller, H. (2007). Designing effective writing assignments. Teaching with writing . University of Minnesota Center for Writing. Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008, from http://writing.umn.edu/tww/assignments/designing.html
MIT Online Writing and Communication Center (1999). Creating Writing Assignments. Retrieved January 9, 2008 from http://web.mit.edu/writing/Faculty/createeffective.html .
Contact TTU
Communication Across the Disciplines
10 tips for writing assignments.
- Clarify the task. Don't let questions about the task encourage procrastination.
- Do the research early. Collecting and absorbing the material will help you meditate on what you will write, even if you don't get to work on the writing immediately.
- Leave a strong paper trail. Frequently, the lack of good note taking doesn't register until you are in the throes of the final preparation of your project, when deadlines loom, and materials are difficult to recover. This is because one often reads and discards materials as not being relevant during the research process, only to discover later, during the writing process, that they are.
- Brainstorm, make notes, jot down ideas as they occur, and begin by writing the stuff you do know. Most writing will be complex and you can't do all of the stages--brainstorming, drafting, revising, editing, proofreading--in one fell swoop. Breaking the process into smaller steps makes it more manageable, and lets you make progress even when you don't have large chunks of time to devote to writing.
- Get feedback. It's difficult to anticipate the gaps, confusion, and potential misinterpretations that complex writing can generate. You need to have at least one outside reader to help you.
- Allow time for revising and editing. Once the ideas are drafted, you'll usually find that you need to go back and re-read, re-search, re-organize, and re-think what you have said.
- Make the organization apparent. Use paragraphs, subheadings, and spatial divisions (layout) to indicate clearly changes in subject matter, focus, and depth. Sometimes this is a good time to prepare an outline, to make sure that your organization makes sense.
- Write the introduction last. A good introduction must point forward to what the writing contains. It is a promise to the reader, and should be accurate. The best introductions will be prepared after you know what you will say and how you will say it.
- Check for accuracy. Research-based writing is often complex and it is easy to overlook a mistake made while drafting. Check your sources, read carefully through your quotations, citations, and documentation.
- Proofread carefully. This is often a step left out in the crunch to finish by a deadline, and yet, it is often little mistakes (typos, errors of punctuation and grammar) which communicate to your reader a sense of carelessness or inability to write.
- Forgive yourself for what is not perfect. We never stop learning how to write. No draft is ever perfect, but the deadline requires that you do your best and then send it out into the world of the reader.
Created by Susan Wyche
Thanks for helping us improve csumb.edu. Spot a broken link, typo, or didn't find something where you expected to? Let us know. We'll use your feedback to improve this page, and the site overall.
12 Professional Tips on How to Write an Assignment for University

- Post author By admin
- September 2, 2022
How to Write an Assignment? Assignment writing is not an easy task because it requires knowledge in a particular field. For writing a perfect assignment your grammar and writing skills should be excellent.
Before starting to write an assignment, you should understand you have the subject knowledge or not. If not so, first learn to gain knowledge about the subject before writing assignments.
Once you have the required knowledge then start collecting information and reference sources. With the reference sources and citation, start gathering necessary information, data, and other related elements.
There are many other things that should be keep in mind while writing an assignment. Here we provide 12 professional tips to write a good assignment.
Table of Contents
Plan : How to Write an Assignment
Writing a good assignment needs a great plan. Plan about paragraphs: like the main idea of writing that paragraph and listing main point describing problems and solution etc.
- How many paragraphs and points should need in the assignment?
- Draw a timeline for the key stages in order to make your task measurable.
- Main three parts we should take care of is introduction, body and, conclusion.
Understand the topic:
If you have the freedom to choose your topic, then go ahead and select your assignment topic which holds your interest. Choosing an interesting topic will not only help you in developing an interesting assignment. It also helps you in making it more descriptive and informative.
Collect Information:
A good way to start collecting information is to recollect your books, and lecture notes. During the search, you need to find the key concepts, principles, ideas, and theories that would relate well to the assignment topic.
- You can collect information from the internet.
- Go to the library and collect the informational book. You also take help from the librarian.
Research and Read the collected information:
Read the collected data and once you start finding key ideas and concepts then start making notes. You can search online, go to the library, search for an academic database, or read newspapers.
- Research can definitely give you a better understanding of the broader issue of your topic.
- This will also give you plenty of innovative ideas which you can apply on your assignment.
- Analyze the topic in-depth, identifying all relevant issues.
- You can also consider journal articles. Because journals are updated and have a particular focus on the topic.
Read More: Is Homework Good or Bad
Create an outline
- Writing an outline is an important part for assignment. It also saves your time.
- Outline contains the main points and divides the assignment into sections.
- It makes easy for you to organize their ideas or points.
Start with Introduction
- Introduction is an important feature that shows the reader about the further discussion.
- Keep the introduction short. It is necessary to keep the word count in control, but it doesn’t mean that you make the introduction boring.
- You need to make the introduction interesting and attractive.
The main body
The main body is starting where you will discuss the concepts in brief. The basic guidelines about the main body are:
- When you start to discuss a new idea, start a new paragraph.
- Always refer to the question to keep the main body of your assignment on track.
- This is your closing paragraph. It is a summary of what you have discussed.
- Don’t introduce new topics or ideas in your conclusion that you haven’t discussed in your main essay.
Referencing
References play an important role in assignments. The primary concern of reference is to acknowledge the source of information and ideas in the body of assignment.
Referencing are usually considered in two forms:
- End-texting referencing:
It appears at the end of the writing section.
- In-texting referencing:
It appears on the body of assignments with authors name and date of the source.
Some important tips for referencing:
- Arrange the references in an alphabetical list at the end of the assignment.
- If your teacher does not specify a significant referencing style. You can use the APA style of referencing for your assignment.
- APA, MLA, Harvard, and Chicago are the various referencing styles used in university.
Revise and Proofread
- After completing your assignment firstly you need to revise your assignment.
- Check your assignment is complete or not.
- Also check your assignment structure, title, and introduction
- Always check any grammatical and spelling error.
- If you have any error in your assignment then you can easily remove these.
Get online help
- You can also get help from any homework help provider website. There are many websites, you can choose anyone.
- They complete your assignment within the deadline and give you 100% unique solution.
- You can save your time by taking online homework help service.
Submit the Assignment
After completing the assignment again you need to revise it. If there is no error in an assignment then you should go and submit it.
In this article we try to show you how to write an assignment and if any student follows these steps he will write an amazing assignment and for your future we will pray you do good in your academics and your journey will be safe and secure. For more wonderful and helpful content follow the Course Mentor and stay tuned with us.
How Do You Start an Assignment?
In your first line, you should introduce your main point, give some background, and talk about the main points of the question. You should then talk about how you plan to answer the question. Some people find it easier to write their introduction after they’ve finished the rest of their task.
What is the Format of Assignment File?
Depending on the OS, an assignment file is an ASCII or EBCDIC text file with the extension.asn. Any ASCII file editor can be used to make or change assignment files.
What is the Format of a University Essay?
Proper Format for Your Academic Writing
Most academic essays are written in the standard format of five paragraphs: an opening, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Also, each part will have its own structure on the inside.
- Tags How to Write an Assignment
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (276)
- General (75)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts

- How it works

How to Write an Assignment – 10 Tips for Pro-Level Writing
Published by Ellie Cross at January 26th, 2023 , Revised On October 11, 2023
Writing an assignment is not a simple task. It requires extensive research, critical thinking and strategic planning. However, it is an opportunity to demonstrate your understanding of the subject matter and to develop your analytical skills.
When you’re given an assignment, your first thought “ how to write an assignment ” or “what do I need to write?” But before you begin writing, consider the following things.
How to Start an Assignment?
There are many ways to start an assignment , but here is a list of some of the most common methods.
Write an introduction – This is where you introduce yourself and your topic. It should be about a paragraph long and should include your assignment topic.
Provide background information – The next step after writing an introduction is providing background information to support your assignment. This can include definitions, examples and anecdotes.
Make an argument – Now that you have provided background information, it is time to make your argument! First, you need to explain why you believe what you believe and why others should agree with you (or not).
What is the Assignment Format?
The assignment format is a standardised way of writing out assignments. The assignment format aims to ensure that all students have a clear understanding of what the assignment entails and the expectations of their work.
The assignment format may vary depending on the type of assignment and the purpose for which it is being written.
Assignment Guidelines Example
The assignment format is based on the number of pages or words you have written. the assignment should be double-spaced, with 1-inch margins and a 12-point font size. the first page should include a title page, abstract, table of contents (with page numbers), introduction, conclusion, main body paragraphs and any references used in your paper., hire an expert writer.
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

Dissertation blogs: Dissertation writing guidelines , How to write dissertation introduction , Abbreviation list in dissertation .
Assignment Writing Tips
Assignments are a big part of your studies, but they can also be one of the most stressful aspects. If you’re not sure how to write an assignment that gets a good grade, here are some assignment-writing tips prepared through evaluating multiple professional assignment writing services available online.
Planning the Assignment
Before you start working on an assignment, it’s important to plan it out. Ask yourself these questions:
How much time do I have?
What resources are available? (e.g., library , internet, friends)
What type of assignment is it? (e.g., essay , report)
What am I being asked to do? (e.g., compare/contrast two novels)
Once you know what you need to do and how long you have to do it, you can start planning your work more effectively.
You Can’t Write an Assignment Without Knowing What you’re Supposed to do .
The first step is to find out what you’re supposed to write about and how long you have to do it. Find out from your lecturer, the course notes, the textbook, your friends, the internet, or whatever. Then write down what you need to know about the topic so you don’t forget anything.
Know your Audience
This is good advice for any writer, but it’s especially important when writing an assignment. Because if you don’t know who will be reading it, how do you know whether they’ll understand it?
Get Started as soon as Possible
Many students find it difficult to start writing assignments because they are unsure exactly what they should write about. This can lead to procrastination and missed deadlines.
Use a Planning Sheet Before Starting an Assignment
This helps you organise your thoughts and make sure that everything is in place before you start writing up your final product.
Read it Carefully
Read through the assignment instructions carefully to know exactly what is required of you. Then, ensure you understand all the requirements before beginning work on any aspect of the assignment.
Ask Questions if Necessary.
Ask questions if there is anything you do not understand or ambiguities in the instructions provided by your tutor or professor.
Write Clearly
Use short sentences and paragraphs. Avoid passive voice (except in case of official documents like reports); avoid long sentences with multiple clauses if possible; use personal pronouns (“I”, “we”, etc.) instead of the third person (“he”, “she”, etc.) when referring to yourself; use action verbs rather than adjectives; avoid using too many adjectives or adverbs in one sentence or paragraph (too many modifiers will make your writing unclear). It’s best to stick to one adjective per noun or verb phrase (“The blue car” vs “The small blue car”).
Check for Spelling Mistakes and Grammar Errors.
Use spelling, grammar, and punctuation checkers before submitting your assignment. It will not only make your answers easier to read, but it will also help prove that you’ve done your research properly.
Pay Attention to the Structure.
Always pay attention to structure: introduction, body paragraphs, conclusion, etc.
Be Organised and Use the Heading.
Use headings, subheadings, and bullets where appropriate (but don’t overdo them). This makes it easier for them to follow along with your ideas without missing any important details or losing interest.
Use Simple Language
Use simple language that everyone can understand. Avoid jargon or technical terms whenever possible. Don’t use slang or informal expressions that are not suitable for academic papers or formal writing style in general (e.g., “I think” vs “In my opinion”).
Check your Sources
Make sure the information you use is from reliable sources (such as books, journals and websites). It’s also important to acknowledge all of the people whose ideas or research you used in your assignment.
Set yourself a Deadline
Set yourself a deadline for when your assignment must be completed by, and stick to it! If your professor gives no deadline, consider setting one yourself – even if it’s just one day before.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write an assignment.
To write an assignment, start by understanding the task, researching, outlining, drafting, and revising. Use credible sources, follow guidelines, and proofread for clarity and correctness.
You May Also Like
Here are the five most popular degrees in Australia based on the interest shown by the students and student bodies.
Students around the globe always make sure to run assignments or other academic work through an online plagiarism checker. Still, the question arises over here,
Discover the factors influencing dissertation length and find guidance on typical page ranges for shorter, average, and longer dissertations.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Welcome to GoodWritingHelp.com!
- How to Write an Assignment
How to Write a Good Assignment
Homework and assignments make the educational process a solid and complicated flow of questions that have to be solved. Good Writing Help is more then just a summarize of good assignment writing tips, we tell students how to prepare themselves for writing and how to manage their time for the most productive work. In this article students of all levels (high-school, college and university) can find an interesting tips for every academic assignment: how to write a good assignment . Whatever academic paper you do – use our instructions as additional supporting information for creating a good writing.
Step one: Assignment
First of all do not start writing just after you were assigned a paper. If you want to do a good assignment – do not hurry at all. If this kind of assignment is new for you or even if you have a previous experience – start with learning more about a certain academic paper. It goes without saying that every writing has it’s own specific and numerous nuances that students should know well in order to create something worthy. The easiest way to start – is to search for additional information on your paper in the web. Find the purpose and main requirements that are pretty the same for every institution.
Step two: Topic research
When you have learned enough about your paper you can go the step two that is a research related to the topic. Start a research using a literature and Internet, do not forget to note the names of the books as far as every assignment should has a bibliography. If you are assigned to write a paper that requires from student to read the only one book (book review or book report), concentrate on noting the details. Usually, good performed research work helps a lot in writing the last part of paper.
Step three: Drafts
Write your draft. Do not afraid of making mistakes – you can always correct them. Read your draft and ask yourself what sounds the worst? Take that part away and completely rewrite it. Continue doing the same way until your draft will look good. Also organize everything in topics and sub-topics – that will help you to understand the structure of your paper and how to make an outline better.
Step four: Double-check
Ask your friends or relatives to read your draft and tell you their honest opinion. They can give you a good advice or find a few grammar mistakes. Doing this way you can reach really good results because your paper is checked twice before submitting.
Step five: Did you answer the question?
Every type of academic paper has it’s own questions to be answered during writing an assignment. When you have everything written well – just check if you have an answer in your writing. The person that read a paper should have a clear understanding of the subject. Questions that need to be answered you can easily find in our writing tips and guidelines articles. Good Writing Help hopes you do your study well and wish you a good writing!

How to Write a Good:
- Research Paper
- Dissertation
- Book Report
- Book Review
- Personal Statement
- Research Proposal
- PowerPoint Presentation
- Reaction Paper
- Annotated Bibliography
- Grant Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Movie Review
- Creative Writing
- Critical Thinking
- Article Critique
- Literature Review
- Research Summary
- English Composition
- Short Story
- Poem Analysis
- Reflection Paper
- Disciplines
Test Grade Calculator
How to calculate test score, test grade calculator – how to use it, test grade calculator – advanced mode options.
This test grade calculator is a must if you're looking for a tool to help set a grading scale . Also known as test score calculator or teacher grader , this tool quickly finds the grade and percentage based on the number of points and wrong (or correct) answers. Moreover, you can change the default grading scale and set your own. Are you still wondering how to calculate test scores? Scroll down to find out – or simply experiment with this grading scale calculator.
If this test grade calculator is not the tool you're exactly looking for, check out our other grading calculators like the grade calculator .
Prefer watching rather than reading? We made a video for you! Check it out below:
To calculate the percentile test score, all you need to do is divide the earned points by the total points possible . In other words, you're simply finding the percentage of good answers:
percentage score = (#correct / #total) × 100
As #correct + #wrong = #total , we can write the equation also as:
percentage score = 100 × (#total - #wrong) / #total
Then, all you need to do is convert the percentage score into a letter grade . The default grading scale looks as in the table below:
If you don't like using the +/- grades, the scale may look like:
- An A is 90% to 100%;
- A B is 80% to 89%;
- A C is 70% to 79%;
- A D is 60% to 69%; and finally
- F is 59% and below – and it's not a passing grade
Above, you can find the standard grading system for US schools and universities. However, the grading may vary among schools, classes, and teachers. Always check beforehand which system is used in your case.
Sometimes the border of passing score is not 60%, but, e.g., 50 or 65%. What then? We've got you covered – you can change the ranges of each grade! Read more about it in the last section of this article: Advanced mode options .
🙋 You might also be interested in our semester grade calculator and the final grade calculator .
Our test score calculator is a straightforward and intuitive tool!
Enter the number of questions/points/problems in the student's work (test, quiz, exam – anything). Assume you've prepared the test with 18 questions.
Type in the number the student got wrong . Instead – if you prefer – you can enter the number of gained points. Let's say our exemplary student failed to answer three questions.
Here we go! Teacher grader tool shows the percentage and grade for that score. For our example, the student scored 83.33% on a test, which corresponds to a B grade.
Underneath you'll find a full grading scale table . So to check the score for the next students, you can type in the number of questions they've got wrong – or just use this neat table.
That was a basic version of the test grade calculator. But our teacher grader is a much more versatile and flexible tool!
You can choose more options to customize this test score calculator. Just hit the Advanced mode button below the tool, and two more options will appear:
Increment by box – Here, you can change the look of the table you get as a result. The default value is 1, meaning the student can get an integer number of points. But sometimes it's possible to get, e.g., half-points – then you can use this box to declare the increment between the next scores.
Percentage scale – In this set of boxes, you can change the grading scale from the default one. For example, assume that the test was challenging and you'd like to change the scale so that getting 50% is already a passing grade (usually, it's 60% or even 65%). Change the last box, Grade D- ≥ value, from default 60% to 50% to reach the goal. You can also change the other ranges if you want to.
And what if I don't need +/- grades ? Well, then just ignore the signs 😄
How do I calculate my test grade?
To calculate your test grade:
- Determine the total number of points available on the test.
- Add up the number of points you earned on the test.
- Divide the number of points you earned by the total number of points available.
- Multiply the result by 100 to get a percentage score.
That's it! If you want to make this easier, you can use Omni's test grade calculator.
Is 27 out of 40 a passing grade?
This depends mainly on the grading scale that your teacher is using. If a passing score is defined as 60% (or a D-), then 27 out of 40 would correspond to a 67.5% (or a D+), which would be a passing grade. However, depending on your teacher’s scale, the passing score could be higher or lower.
What grade is 7 wrong out of 40?
This is a B-, or 82.5% . To get this result:
Use the following percentage score formula: percentage score = 100 × (#total - #wrong) / #total
Here, #total represents the total possible points, and #wrong , the number of incorrect answers.
Substitute your values: percentage score = 100 × (40 - 7) / 40 percentage score = 82.5%
Convert this percentage into a letter grade. In the default grading scale, 82.5% corresponds to a B-. However, grading varies — make sure to clarify with teachers beforehand.
Is 75 out of 80 an A?
Yes , a score of 75 out of 80 is an A according to the default grading scale. This corresponds to a percentage score of 93.75%.
- Poker Odds Calculator
- RAID Calculator
Coffee kick
Flat vs. round earth.
- Biology (100)
- Chemistry (100)
- Construction (144)
- Conversion (295)
- Ecology (30)
- Everyday life (262)
- Finance (570)
- Health (440)
- Physics (510)
- Sports (105)
- Statistics (184)
- Other (183)
- Discover Omni (40)

How students’ GenAI skills and reflection affect assignment instructions
The ability to use generative AI is akin to time management or other learning skills that students need practice to master. Here, Vincent Spezzo and Ilya Gokhman offer tips to make sure instructions land equally no matter students’ level of AI experience
Vincent Spezzo
.css-76pyzs{margin-right:0.25rem;} ,, ilya gokhman.
Created in partnership with

You may also like

Popular resources
.css-1txxx8u{overflow:hidden;max-height:81px;text-indent:0px;} Rather than restrict the use of AI, embrace the challenge
Emotions and learning: what role do emotions play in how and why students learn, leveraging llms to assess soft skills in lifelong learning, how hard can it be testing ai detection tools, a diy guide to starting your own journal.
November 2022: ChatGPT rapidly emerges as the next big disruptor in higher education. On campuses across the US, the primary feelings are scepticism and fear of cheating, but pushing past that is the notion that this technology could be harnessed to benefit education.
Spring 2023: At Georgia Institute of Technology, our conversations and workshops on generative AI (GenAI) focus on how faculty can use it in course design, assignment creation, personalised learning efforts and more. Fear and scepticism still exist but don’t obstruct brainstorming efforts. In the summer, we see instructors’ responses range from dipping toes into the AI water and using it to create rubrics, case studies and other standard course content to diving in headfirst and using GenAI to produce entire courses.
Fall 2023: Many employers of future graduates want students to gain knowledge and experience using GenAI tools while in their degree programmes. Thinking shifts from students wanting to use GenAI to cheat to students needing to learn about GenAI to succeed. The professors at our institution are beginning to embrace the idea that they should support the correct usage of GenAI in their classrooms.
- AI can help fix student evaluations
- How can we teach AI literacy skills?
- Resource collection: How to build data literacy on campus
Here lies the challenge: how much direction should you include in GenAI-inclusive assignments? Previously, instructors had to balance assignment guidelines with student creativity, so students could create a unique submission while remaining within the assignment objectives. Now the additional task is finding the right amount of guidance to ensure students can effectively use GenAI beyond simply copying and pasting predefined prompts.
Creating GenAI assignments
How to create assignments using GenAI is one of the questions that co-authors Ilya Gokhman and Vincent Spezzo have addressed. Students in Gokhman’s public policy course worked in groups of four to complete project-based tasks and provide peer feedback to their team members at four points during the semester. The idea was to have students use GenAI as a leadership and collaboration coach to help them process and reflect on peer feedback. GenAI was used in three of the four feedback phases (students completed the first reflection unassisted). For the remaining phases, students were: 1) instructed to use GenAI with no further guidance, 2) given detailed instructions on how to use GenAI, including suggested prompts, and 3) instructed to use GenAI how they wanted, whether that was to use the instructors suggested prompts or their own.
Students divided on using GenAI
Students were surveyed on a six-point Likert scale to determine their experience using GenAI in their assignments and how it impacted their learning (see list below). This included a self-rating on their prior experience using GenAI that included options of “a lot”, “some”, “little” and “none”. From the 72 participants, several novel insights were gleaned. The most significant finding was a clear division in students’ experiences using GenAI for assignments between the two groups at opposite ends of the prior-usage spectrum. Those students who had the most prior experience rated several items significantly higher than those who came into the class never having used GenAI before. This was true despite very detailed instructions and prompt examples being added to the third and fourth assignments.
- I would rather use GenAI than complete feedback review with another person: A lot M=4.7, None M=2.78
- I felt using GenAI helped me in learning the course material: A lot M=4.8, None M=3.06
- I felt using GenAI increased my motivation to complete assignments: A lot M=4.8, None M=2.83
- Overall, I felt using GenAI had a positive impact on my course experience: A lot M=5.4, None M=3.89
Two things worth noting are: 1) while students with more experience rated items significantly higher, students with no prior experience generally still rated items around a three on the six-point scale, and 2) students who fell into the two middle groupings were not shown to be significantly different from the two extremes on almost all questions.
Students also responded to open-ended questions, with 30 per cent stating that the assignments could be improved by more frequent GenAI usage, 25 per cent commented that GenAI was useful in generating ideas and expanding their perspectives, and 20 per cent indicated a desire for more detailed instructions on using GenAI for the assignment.
Addressing students’ differences in experience using GenAI
Results pointed to a difference in instructional needs between students with no GenAI experience and those with a lot of experience. One could mistakenly assume the number of students with little or no experience will decrease as use of these technologies becomes more widespread. However, the ability to use GenAI is likely more akin to time management, studying and a host of other learning skills that students need support and practice with before mastering. Coupling this with the current lack of adoption at K-12 , it is very likely that inequity with prior usage of GenAI will exist for some time. Two actionable practices that can address this inequality:
- Include more detailed instruction and prompt examples for assignments. While not all students need this, at least 20 per cent of the students surveyed indicated they wanted even more direction than was provided, and there was no indication that the additional instructions negatively impacted students with prior experience. Part of an equitable framework is to ensure that those who need the additional support have it available, so including optional additional guidelines may be the way to go with GenAI assignments for now.
- Create and include a lesson or optional module for teaching students how to use GenAI effectively within your course or discipline. From this study, it seems that simply including more examples and instructions was not enough for some students. To address the gap of experience, students seem to need support and exposure to the basics of using GenAI that goes beyond creating good prompts. There is already discussion of including such experiences in freshmen seminar courses, but until then it will be up to instructors to help bridge the gap for students who have yet to learn how to use GenAI in ways that will benefit their education.
By using these practices, the intent is that students coming into a course with little or no prior GenAI experience can be brought up to speed and benefit at near the same level as those who have had a lot of experience using the tools. Conducting a start-of-semester survey is a good way to identify students who need additional resources and ensure they are directed to access them. While this means yet another task for instructors, the benefits to student learning and the expectations of future employers make this worth taking on.
Vincent Spezzo is assistant director of teaching and learning online in the Center for Teaching and Learning, and Ilya Gokhman is faculty lead for grand challenges in the Office of Leadership Education and Development, both at Georgia Institute of Technology.
If you would like advice and insight from academics and university staff delivered direct to your inbox each week, sign up for the Campus newsletter .
Rather than restrict the use of AI, embrace the challenge
Let’s think about assessments and ai in a different way, how students’ genai skills affect assignment instructions, how not to land a job in academia, contextual learning: linking learning to the real world, three steps to unearth the hidden curriculum of networking.
Register for free
and unlock a host of features on the THE site

Orioles designate reliever Mike Baumann for assignment, activate Grayson Rodriguez from IL to start Saturday vs. Mariners
Mike Baumann is too good to be designated for assignment, but that’s the Orioles’ new reality.
Baltimore made the move Saturday morning to make room on its 26-man roster for Grayson Rodriguez, who was reinstated off the injured list to start the club’s late afternoon game against the Seattle Mariners. Rodriguez was placed on the 15-day IL on April 30 with right shoulder inflammation , but the injury was minor enough that he did not need to pitch in rehabilitation games before rejoining the Orioles’ rotation.
Baumann was one of several pitchers in Baltimore’s bullpen with no more minor league options, decreasing the club’s roster flexibility and making the decision on how to create space for Rodriguez a challenging one.
“It’s been a really tough morning,” manager Brandon Hyde said before Saturday’s game. “Mike has been with us for a while. Think about the first half he had for us last year, how many games he helped us win, how good he was. He threw the ball really well last night. On top of all those things, just the incredible person he was, unbelievable teammate, first-class pro in every single way and so well-liked by guys in our clubhouse.
“It’s been a gloomy morning.”
It’s not a surprise that Baumann was the odd man out given the success of the Orioles’ other relievers and the decision to likely move to a six-man rotation soon . But with a veteran relief corps on one of baseball’s best teams — the Orioles (28-14) are on pace to win 108 games — comes challenging choices such as letting Baumann go.
Baltimore will hope to pass him through waivers — or trade him before that process begins — but it’s almost certain his next outing is in a different uniform.
“It’s the hardest part of this game,” reliever Danny Coulombe said. “Me and Mikey are really close. I think we all know how talented he is. There’s no doubt in my mind that there might be better opportunities out there for him. I wouldn’t be shocked in two or three weeks if he’s closing for somebody, you just never know. It’s tough to see, a huge loss to us in the clubhouse and on the field, too.
“He’s a great pitcher, but this is the business we’re in.”
The right-hander has been in the organization since they drafted him in the third round in 2017, pitching 127 1/3 innings with the Orioles since his MLB debut in 2021. He was one of Hyde’s most-trusted relievers last season after the club transitioned him from a starting pitcher into a bullpen arm. He appeared in 60 games last year — fourth most on the team behind Yennier Cano, Coulombe and Cionel Pérez — despite spending a month in the minors to recharge after his heavy workload. Baumann’s 10 relief wins were most by an Oriole since Brad Brach in 2016.
After posting a 3.76 ERA in 2023, the 28-year-old has experienced an up-and-down season so far, although his 3.44 ERA is more than respectable. What made the decision additionally difficult was the fact that Baumann has found his groove recently, recording a 1.04 ERA over his past 8 2/3 innings. With a plus curveball and a mid-90s mph fastball, Baumann matched up well against right-handed batters. Now, the Orioles’ bullpen has four left-handers, potentially posing a challenge against right-handed heavy lineups.
But there were seemingly no other options than to DFA him. Craig Kimbrel, Jacob Webb, Albert Suárez, Cole Irvin, Pérez and Coulombe aren’t able to be sent to the minors, while Cano (2.14 ERA) and Keegan Akin (2.84 ERA) are pitching too well to option.
“It’s going to be tough,” Hyde said on managing the bullpen without flexibility like the organization has had in the past. “It made a decision like this morning very, very hard. Just the way the rules are in place with only being able to carry 13 pitches, having guys that are out of options — you have to make tough decisions.”
Rodriguez carried his strong second half of 2023 into 2024 before his minor shoulder injury, winning four of his six starts with a 3.71 ERA. His start Saturday will be his first since April 29, and Hyde said the fireballer will have a “shorter leash” Saturday with Suárez and Irvin available in long relief. Irvin will likely rejoin the rotation later this month when the club moves to a six-man rotation.
Related Articles
- Baltimore Orioles | Orioles game Saturday vs. Mariners at Camden Yards delayed because of rain
- Baltimore Orioles | Orioles outfielder Austin Hays knows ‘things turn around quick.’ His return so far is promising.
- Baltimore Orioles | Even with 6-man rotation, Orioles plan to keep Corbin Burnes on schedule
- Baltimore Orioles | Orioles explode for 5 runs in 1st inning to beat Mariners, 9-2, in John Means’ first home win since 2021
- Baltimore Orioles | Orioles prospect Coby Mayo placed on injured list with fractured rib, will miss several weeks
Hyde has largely managed his bullpen this season in a similar way to last year despite the lack of flexibility. The large number of days off have allowed that, but now that the club is in the infancy of a 43-game in 45-day stretch, Hyde expects to alter the way he handles his relievers.
“You definitely have to keep in mind recovery, times that they get up, all those types of things I’m very conscious of. I am already, but especially when you roll into a long stretch,” he said. “You want to keep as many people as fresh as possible [and] a 6-man [rotation] makes it even harder. Not having optionable guys and wanting to keep this group together through this stretch, I’m going to be very aware of usage.”
Hyde hopes to be able to lean on his starters more once the Orioles move to a six-man rotation with each starter receiving an extra day of rest between starts, but he won’t risk their health to do so.
“I’m never going to sacrifice anything to try to get them through an extra inning if we feel like it’s not going to be responsible for them or putting them in harm’s way in any single way,” he said. “A lot goes into pulling a starter — from pitches to stressful innings all those type of things.”
©2024 Baltimore Sun. Visit baltimoresun.com. Distributed by Tribune Content Agency, LLC.


NBA Draft Lottery 2024 live updates: Hawks win top pick with just a 3 percent chance
50 New Updates
The NBA lottery results
The Atlanta Hawks , despite having a three percent chance, have won the 2024 NBA Draft lottery. Here is the full draft order.
- Atlanta Hawks
- Washington Wizards
- Houston Rockets
- San Antonio Spurs
- Detroit Pistons
- Charlotte Hornets
- Portland Trail Blazers
- San Antonio Spurs ( via Toronto Raptors )
- Memphis Grizzlies
- Chicago Bulls
- Oklahoma City Thunder (via Houston Rockets )
- Sacramento Kings
- Portland Trail Blazers (via Golden State Warriors )
The Pistons and Wizards had the best shot of earning the No. 1 pick. Detroit moves down for the third straight season.

2024 NBA Draft Lottery: Hawks win No. 1 pick after having 3 percent chance to claim top spot

Don't count out Castle
Throughout the season, Stephon Castle consistently took on the toughest assignment on the perimeter and wing defensively for Connecticut, a top-five defense in the country, and found success. Need someone to chase potential first-rounder Baylor Scheierman around screens? Castle can do it. Need someone to defend at the point of attack? Castle can do that. What about a big wing creator? Castle will do that, too, and shut off his water, just like he did in the Elite Eight against Illinois’ Terrence Shannon Jr.
Shannon came into that game averaging 27.2 points over his prior 15 games. Castle held him to eight points on 2-of-12 shooting. In the Final Four, he took on the Mark Sears assignment at point guard. Sears scored 24 but only nine of those points came on Castle, and four of those nine came on heavily contested attempts that Sears maneuvered around or shot over the top of to make. He made life miserable for one of the best guards in the country this season and made him work for every bucket. Against Purdue in the title game, Castle took long swaths of time on Braden Smith, who only scored two points when being guarded by Castle.
If that’s all he did, he’d be worth a first-round pick. But Castle also was quite good on offense. He averaged 12.5 points, nearly six rebounds and three assists while posting a 2-to-1 assist-to-turnover ratio. He had 21 points in the Final Four against Alabama and was the team’s best offensive player, then followed it up with 15 against Purdue. I thought he had a real case as Most Outstanding Player at the Final Four, especially when accounting for the defensive job he did on Sears and Smith.

2024 NBA Draft Big Board: Stephon Castle, Donovan Clingan rise into Top 5 after title run
Advertisement

Pistons could add some S(t)arr power

(Photo: Colin Murty / Getty)
Alexandre Sarr has the highest upside of any prospect in this class and has improved greatly this season playing overseas. Defensively, Sarr has a chance to be special. He covers well in space for his size. He flies around the court and can stay in front of small players. At the rim, Sarr is an intimidating presence because of his length. And if he’s not blocking shots, he’s likely disrupting them.
Offensively, there has been some fun, intriguing stuff from Sarr with the ball in his hands in both transition and a half-court setting. I also believe he’s shown good-enough touch to be a legitimate shooting threat at some point in his career.
Ultimately though, Detroit would be selecting Sarr for who he could become on defense. This franchise desperately needs elite rim protection in the frontcourt, and I’m not sure there is a better prospect in this class who could both check that box and grow into more than just a lob threat on the offensive side of the floor.
My biggest questions with Sarr are about his current level of competition. That stuff is always hard to gauge, particularly with someone of Sarr’s age. He’s also not a great defensive rebounder. He’ll need a more punishing big man next to him at the NBA level, I believe, to have success sooner rather than later.
Yet, if the majority of this stuff ends up clicking, Detroit could end up with a very special player. I’m just not sure, with how fragile the franchise is right now, that it can afford to take a gamble on a prospect if there is legitimate trade interest in the No. 1 pick that could yield proven, good NBA players.ge

2024 NBA mock draft: Should the Pistons draft Alexandre Sarr if they get the No. 1 pick?
It’s the morning of the NBA Draft Lottery, and I woke up feeling like the Pistons, who have had the best odds at the No. 1 pick the last four years and only got it once in 2021, will win it this year, when there is no hyped-up prospect.
Which lottery teams have traded their picks?
Five of the 14 picks in the NBA Draft Lottery have been traded by their original teams. Here's the breakdown:
- No. 6: The Toronto Raptors dealt this pick to the San Antonio Spurs in a 2023 deal for Jakob Poeltl, but the selection is top-six protected. If it stays in the top six, Toronto will retain the pick, but if it winds up at No. 7 or below, San Antonio receives it.
- No. 8: Currently belongs to the Utah Jazz, who have a top-10 protection on the pick. But it lands outside the top 10, it will go to the Oklahoma City Thunder as part of a 2022 trade for Derrick Favors.
- No. 9: The Brooklyn Nets originally owned this selection, but it will go to the Houston Rockets thanks to the 2021 James Harden deal.
- No. 12: This pick was originally Houston's, but it will go to the Oklahoma City Thunder from the 2019 Russell Westbrook trade. However, Houston does have a top-four protection on it, so they have some chance to keep the pick.
- No. 14: Originally the Golden State Warriors' pick, this selection was sent to the Portland Trail Blazers by way of the Boston Celtics' 2023 Jrue Holiday trade. Boston had acquired the pick from Memphis in the 2023 Marcus Smart trade, and the Grizzlies had acquired the pick from Golden State in the 2019 Andre Iguodala trade. The pick is top-four protected, so if it lands that high, it will stay with the Warriors.
How do the 2025 and 2026 draft classes project?
The 2025 and 2026 classes are seen as drastically better drafts at the top than the 2024 draft. Those classes will unlikely be seen as worse than the 2024 NBA Draft in terms of pick-by-pick value. The top of the 2025 class, particularly, is seen as very strong, with Cooper Flagg, Ace Bailey and Khaman Maluach. There is also thought to be a solid amount of depth for young talent in those classes.

Raptors draft needs, Spurs pick, tournament viewing and more: Koreen and Vecenie
To trade or not to trade

(Photo: Bill Streicher / USA Today)
Assuming the Pistons land the No.1 pick, one way they can add more proven, NBA talent — which is needed and also more realistic than adding a star at this stage — is by trading it.
Consider this proposal: The Pistons trade their 2024 first-round pick (No. 1), Jaden Ivey and Jalen Duren to the Brooklyn Nets for Mikal Bridges, Dorian Finney-Smith and a 2025 first-round pick (via Phoenix Suns, top-14 protected).
Parting ways with both Ivey and Duren is risky, as both are very young and still have upside despite rocky sophomore seasons, but this is the situation Detroit finds itself in. It has to make an aggressive moves in order to make serious strides. Cade Cunningham, who has the highest trade value on the team, isn’t going anywhere. Ivey and Duren both have value around the league, and while this free-agency class is meh, Detroit can address both positions in the open market.
In this scenario, the Pistons address a significant need on the wing, getting one of the better 3-and-D wings in the NBA in Bridges and a very solid 3-and-D wing in Finney-Smith. Both players have multiple years left on their respective contracts. Having those two with Ausar Thompson, Simone Fontecchio and Quentin Grimes would mean Detroit being legitimately set at the wing rotation for several years. As for the Nets, who had a disappointing season and appears to have a real ceiling as constructed, they should start rebuilding around youth, and the No. 1 pick in the 2024 draft and two recent lottery picks in Ivey and Duren is a really good way to begin that process.
Furthermore in this trade scenario, the Pistons still will have roughly $34 million to use in free agency, while this deal opens up about $15 million in cap space for the Nets (after they sign the No. 1 pick).

How the Detroit Pistons can improve their roster through trades and NBA free agency

Draft lottery luck could come in various forms for Raptors
Due to the Jakob Poeltl trade in February 2023, the Raptors enter the lottery in one of the most intellectually interesting spots in recent memory. As part of the deal with the San Antonio Spurs, they will surrender their pick this year if it falls outside the top six. They finished the season with the sixth-worst record in the league, giving them a 45.8 percent chance of keeping it.
If the pick does not convey this year, the same protections carry over into 2025. In that scenario, if the Raptors kept the pick next season, the protections would carry over one final year. If the Raptors haven’t sent their pick to San Antonio by 2026, they would owe two second-round picks to the Spurs to complete the trade.
“I think either way it plays out well for us,” Raptors president Masai Ujiri said in April at his end-of-season media availability. “We get a high pick this year (and) next year we play ball and see where we stand. If you’re not picking high next year, then your team is good, or your team is progressing the right way.”

Can the Wizards make some magic in a weak NBA Draft?
Wizards general manager Will Dawkins insists he doesn’t agree with the conventional wisdom that this year’s draft class lacks talent at the top.
“I think people hold their cards tight to their vests strategically, so I definitely don’t agree with the narrative,” Dawkins said in an interview with The Athletic . “I think people realize how good this draft is, and in any draft, I’d rather have the power of choice to make the decision than be left with other players on the board that I might not feel as good about. So for me and the Wizards, we’re ones that would always want the highest pick possible if you have an option to choose a player. As we’ve shown in last year’s draft, we don’t draft necessarily off mock drafts. We find the right person first, and if they connect with everything that we have going on in the long term, we’re going to do our best to go get that person.”
A list of top prospects the Wizards may go after includes 7-foot-1 big man Alexandre Sarr, who played in Australia this season; 6-6 wing Stephon Castle of the University of Connecticut; 6-8 wing/forward Zaccharie Risacher, who is playing in France; 6-10 wing/forward Matas Buzelis of G League Ignite; 6-6 point guard Nikola Topić from Serbia; and 6-8 wing Cody Williams of the University of Colorado.
Read more here.
Possible Pistons picks

The Pistons have the best odds of landing the No. 1 pick for the fourth consecutive year, but this draft class has been labeled as one of the worst in recent memory , as many executives and scouts don’t believe there is real star power at the top. So who will Detroit pick? A few names and scenarios to consider:
If Detroit lands the No. 1 pick...
Alexandre Sarr | 7-foot-1 big | 19 years old | Perth Wildcats
While Sarr isn’t the unanimous No. 1 pick at this point, he seems to be the favorite. I think he’d definitely be the top choice for the Pistons if the ping-pong balls are kind.
Sarr has the highest upside of any prospect in this class, in my opinion, and has improved greatly this season playing overseas. Defensively, Sarr has a chance to be special. He defends well in space for his size. He flies around the court and can stay in front of small players. At the rim, Sarr is an intimidating presence because of his length. And if he’s not blocking shots, he’s likely disrupting them.
If Detroit lands picks 2-3...
Stephon Castle | 6-foot-6 wing | 19 years old | Connecticut
For a roster that needs more defense on the wing and high-IQ players, Castle makes too much sense for Detroit in this range. Oh, and he’s already a winner.
Castle is a guard/wing hybrid who somewhat reminds me of the Orlando Magic’s Anthony Black with his IQ, size, defensive versatility and tenacity. I see him more of a secondary ballhandler than a lead guard at the NBA level, which is perfect for the Pistons, who have Cade Cunningham running the offense. One of Detroit’s biggest issues is it doesn’t currently have a wing-sized secondary playmaker with guard skills. Ausar Thompson will get there one day, but his handle isn’t tight enough yet to be a lead ballhandler for large sections of games. Castle would help fill that void for Detroit.
Matas Buzelis | 6-foot-9 wing | 19 years old | G League Ignite
Buzelis is a weird one because I’d view him as a late-lottery prospect in most classes. As I’m not in love with anyone in this class and the Ignite season was a mess, I can talk myself into his upside as a top-five pick.
He’s got great size and length for a wing, is athletic and doesn’t need the ball to be impactful. If he’s going to play alongside Cunningham, being able to be effective in an off-ball role is important. In watching film, I like what I’ve seen defensively from Buzelis off the ball but do have questions how he’ll hold up on the ball at the NBA level, especially early on.
On-stage representatives for each team
Here are the people the viewers will see on TV when the lottery results are unveiled at 3 p.m. ET on ABC.
- Atlanta Hawks: Landry Fields, general manager
- Charlotte Hornets: Brandon Miller, player
- Chicago Bulls: Julian Phillips, player
- Detroit Pistons: Ausar Thompson, player
- Golden State Warriors: Brandin Podziemski, player
- Houston Rockets: Ime Udoka, coach
- Memphis Grizzlies: Tayshaun Prince, vice president of basketball affairs
- Portland Trail Blazers: Scoot Henderson, player
- Sacramento Kings: Keegan Murray, player
- San Antonio Spurs: Brian Wright, general manager
- Toronto Raptors: Scottie Barnes, player
- Utah Jazz: Thurl Bailey, former Jazz player and current broadcaster
- Washington Wizards: Bilal Coulibaly
Who's had the most lottery appearances?

(Bobby Clay / The Athletic)
The Sacramento Kings lead all franchises with 27 total appearances in the draft lottery, while the Golden State Warriors and Charlotte Hornets (23 times apiece) are the only other teams to appear more than 20 times.
For all of their chances over the years, the Kings have only walked away with the No. 1 pick on one occasion: 1989, when they picked Pervis Ellison.

Evolutions of the draft lottery
Since its institution in 1984, the draft lottery has undergone multiple changes.
The NBA had unweighted draft lottery odds from 1985 through 1989 and then implemented the weighted system in 1990. Back then there were 66 “chances” for winning the No. 1 pick. The team with the worst record had 11 out of 66. The team with the second-worst record had 10 out of 66. And so on, and so forth. We saw the 41-41 Seattle SuperSonics move up to the second pick with just a 3.03 percent chance of getting the top spot, and they took Hall of Famer Gary Payton.
After the Orlando Magic won back-to-back No. 1 overall picks in 1992 (15.15 percent chance, second-best odds) and 1993 (1.52 percent chance, worst odds), the NBA decided to overreact and change things to an even more unevenly weighted system. The worst record went from a 16.7 percent chance of grabbing the top pick to a 25.0 percent chance. The teams with the lowest odds dropped even more, to a 0.5 percent chance. It pretty much stayed that way until 2019, when the NBA decided to legislate against the “Trust the Process” 76ers to make the lottery system less severe for odds to win it.
Now, the teams with the three worst records each have a 14.0 percent chance of obtaining the top pick in the draft. The fourth-worst record has a 12.5 percent chance of getting it. Then, with each subsequently better record from the regular season, the odds continue to drop
Read my piece from 2022 on the new NBA Draft lottery odds.
A weak draft class

Trying to parse through this class has been dreadfully difficult at the top. I do not have a Tier One or Tier Two player in this class. I’m not even sure how many Tier Three players I will have by the end of the process.
In some capacity, all of the players ranked in my top 10 have a non-zero chance to go No. 1 overall if things break right in terms of the draft lottery and they have a strong pre-draft process. There are players there who have a much better chance to go No. 1 than others, to be sure, but NBA teams are all over the map in this class. It does not have a sure-fire guy, so teams are doing their due diligence across the spectrum. I cannot remember a class in which the lottery will have such a significant impact on how the top will be selected.
Because there’s no sure-fire All-Star, decision-makers have many questions to ponder: What do you value in prospects? What skill sets are most important to you? What translates best in your mind? Or in many cases, what are the skill deficiencies players in this class have that are most fixable to you?
By the law of averages, multiple players will be All-Stars from this draft, even with it being a below-average one, and it’ll be because they improved something in their game substantially.

How does the NBA Draft Lottery work?
In the current lottery setup, 14 ping pong balls are placed in a lottery machine and four are drawn out at a time. There are 1,001 possible combinations of the four balls (regardless of order), and 1,000 of those combinations are assigned to the 14 teams. The number of assigned combinations is in alignment with the team’s odds to win the lottery. For example, the teams with the worst, second-worst and third-worst records have 140 assigned combinations (aligning with their 14 percent chance to win the lottery).
After being placed in the machine, the balls are mixed for 20 seconds, then the first ball is taken out. Then the remaining balls are mixed for another 10 seconds before the second ball is taken out, which repeats for the third and fourth balls. The team with that assigned combination of four balls will receive the No. 1 pick.
The process then repeats with the same balls for picks No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4. If the one unassigned combination is drawn, the result of that drawing is discarded and the balls are drawn again.
After the fourth pick is drawn for, draft slots five through 14 are assigned in inverse order of regular-season record. Thus, a team with the worst record can’t select lower than fifth, the second-worst record can’t select lower than sixth and so on.
As the broadcast announces the draft order from 14 to one, any reveal that a team has slipped back in the draft is a sign that another team has leaped up.
Read the rest of our explainer from last season here.
Each team’s odds to win No. 1 pick

- Detroit Pistons: 14 percent
- Washington Wizards: 14 percent
- Charlotte Hornets: 13.3 percent
- Portland Trail Blazers: 13.2 percent
- San Antonio Spurs: 10.5 percent
- Toronto Raptors: 9 percent
- Memphis Grizzlies: 7.5 percent
- Utah Jazz: 6 percent
- Houston Rockets (via Brooklyn Nets): 4.5 percent
- Atlanta Hawks: 3 percent
- Chicago Bulls: 2 percent
- Rockets: 1.5 percent
- Sacramento Kings: 0.8 percent
- Golden State Warriors: 0.7 percent

Looking to follow along the NBA Draft Lottery live? Here's what you need to know:
- Date: Sunday, May 12
- Time: 3 p.m. ET
- Location: Chicago
- Broadcast: ABC
The Detroit Pistons and Washington Wizards, the NBA's two worst teams, each have a 14-percent chance to earn the No. 1 pick. Here are the odds for each team.
Here's the latest big board from The Athletic's NBA Draft expert Sam Vecenie.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To construct an assignment structure, use outlines. These are pieces of text that relate to your topic. It can be ideas, quotes, all your thoughts, or disparate arguments. Type in everything that you think about. Separate thoughts scattered across the sheets of Word will help in the next step. Then it is time to form the text.
7. Structure your argument. As you write the body of your assignment, make sure that each point you make has some supporting evidence. Use statistics or quotes you gathered during your reading to support your argument, or even as something to argue against. Expert tip: If you're using a lot of different sources, it's easy to forget to add ...
For example, you could break a research paper down into several smaller tasks: 1) do preliminary research, 2) write an outline, 3) draft an introduction, 4) draft body paragraphs, 5) write conclusion, 6) revise. Each of these is much more do-able on its own. Method 2.
The diagram above represents an assignment prompt which is functioning well. For one thing, the presence of the assignment prompt/magnifying glass (which might, in this case, take the form of an ekphrastic essay) is enabling the student to see and describe qualities or features of the course material (in this case, an Egyptian bust) better than they could were the glass to be absent.
Dividing the work in different paragraphs is very important for this purpose. - Usage of 'you' and 'I' - According to the academic writing standards, the assignments should be written in an impersonal language, which means that the usage of 'you' and 'I' should be avoided. The only acceptable way of building your arguments ...
Courses and assignments should be planned with this in mind. Three principles are paramount: 1. Name what you want and imagine students doing it. However free students are to range and explore in a paper, the general kind of paper you're inviting has common components, operations, and criteria of success, and you should make these explicit ...
What this handout is about. The first step in any successful college writing venture is reading the assignment. While this sounds like a simple task, it can be a tough one. This handout will help you unravel your assignment and begin to craft an effective response. Much of the following advice will involve translating typical assignment terms ...
It's also important to remain coherent. You must link each paragraph to each other. This will keep your reader connected with the content. To achieve this, you need to go back to your plan for your assignment, then search for significant concepts that will help you connect the paragraphs smoothly. Here's an easy tip to do this - include phrases ...
Here are five tips to help you get ahead. 1. Use available sources of information. Beyond instructions and deadlines, lecturers make available an increasing number of resources. But students often ...
Make sure you read through any assignment requirements carefully and ask your lecturer or tutor if you're unsure how to meet them. Analysing the topic. Researching and note-taking. Planning your assignment. Writing your assignment. Editing your assignment. 1. Analysing the topic. Before you start researching or writing, take some time to ...
As simple as that. For example, you can't write, "LOL girl, that was hilarious" to describe a funny anecdote or "Damn, that was dope" to describe an incredible thing that happened. 7. Proofread, Proofread & Proofread. Don't just hand over the assignment to your teacher the minute your write the last word.
Our article focuses on how to write an assignment effectively, highlighting the challenges students face in navigating complex tasks. It emphasizes the need to alleviate these struggles by demystifying the process and empowering students to approach tasks with confidence and competence. The article promises a comprehensive step-by-step guide ...
It is also a good idea to define the audience you want your students to address with their assignment, if possible - especially with writing assignments. Otherwise, students will address only the instructor, often assuming little requires explanation or development (Hedengren, 2004; MIT, 1999). ... "A good assignment provides the purpose ...
10 Tips for Writing Assignments. Clarify the task. Don't let questions about the task encourage procrastination. Do the research early. Collecting and absorbing the material will help you meditate on what you will write, even if you don't get to work on the writing immediately. Leave a strong paper trail.
If you have any doubts, clarify them with your instructor. 2. RESEARCH THOROUGHLY. When it comes to writing an assignment for academic success, in-depth research is one of the most crucial steps ...
clear and that your sentences make sense. Get your draft assignment written Once you've written a draft or first version of your essay / report, it's best to stop working on it for a while. Hopefully you haven't left your assignment to the last minute and have time to ignore it overnight or even for a couple of days.
End-texting referencing: It appears at the end of the writing section. In-texting referencing: It appears on the body of assignments with authors name and date of the source. Some important tips for referencing: Arrange the references in an alphabetical list at the end of the assignment. If your teacher does not specify a significant ...
Learn the steps for writing an assignment for school, college or university.
Write an introduction - This is where you introduce yourself and your topic. It should be about a paragraph long and should include your assignment topic. Provide background information - The next step after writing an introduction is providing background information to support your assignment. This can include definitions, examples and ...
04. Create graphs and charts people want to look at. Graphs and charts tend to draw someone's eye. If you see a page full of text, or a presentation full of bullet points, these picture representations of your work tend to be where people look first. Sometimes, they even set the tone for what someone is about to read.
Step one: Assignment. First of all do not start writing just after you were assigned a paper. If you want to do a good assignment - do not hurry at all. If this kind of assignment is new for you or even if you have a previous experience - start with learning more about a certain academic paper. It goes without saying that every writing has ...
How to make an assignment on MS Word on PC or Laptop easily.To make an assignment attractive, good & acceptable you must have to follow these simple steps.1....
#Assignment #bestassignment #perfectassignment #uniAssignment Welcome to Ls techno Advice.We provide a quality-Not quantity.Thanks for reaching out.For Quest...
In other words, you're simply finding the percentage of good answers: percentage score = (#correct / #total) × 100. As #correct + #wrong = #total, we can write the equation also as: percentage score = 100 × (#total - #wrong) / #total. Then, all you need to do is convert the percentage score into a letter grade. The default grading scale looks ...
Creating GenAI assignments. How to create assignments using GenAI is one of the questions that co-authors Ilya Gokhman and Vincent Spezzo have addressed. Students in Gokhman's public policy course worked in groups of four to complete project-based tasks and provide peer feedback to their team members at four points during the semester.
Mike Baumann is too good to be designated for assignment, but that's the Orioles' new reality. Baltimore made the move Saturday morning to make room on its 26-man roster for Grayson Rodriguez ...
The 4 C's in a proposal refer to the key components that should be included to make a winning proposal. Customer-focused: A good proposal should be customer-focused, meaning it should be tailored to meet the specific needs and requirements of the customer. Clear: The proposal should be clear and concise, with a well-defined structure and ...
TikTok video from BlockTheVote2024 (@blockthevote2024): "Day 2 of exposing our leaders who hold us down - your next assignment is to support the opponent of Nanette Barragán. Yesterday I asked you to block the candidate, but I'm also a strong believer in sunlight being the best disinfectant, and some commenters felt the same. So today, your assignment is different.
Throughout the season, Stephon Castle consistently took on the toughest assignment on the perimeter and wing defensively for Connecticut, a top-five defense in the country, and found success. Need ...