Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology

Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 20 March 2023.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall aims and approach
- The type of research design you’ll use
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, frequently asked questions.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities – start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types. Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships, while descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends, and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analysing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study – plants, animals, organisations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region, or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalise your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study, your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalise to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question.
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviours, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews.
Observation methods
Observations allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviours, or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected – for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are reliable and valid.
Operationalisation
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalisation means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in – for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced , while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method, you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample – by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method, it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method, how will you avoid bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organising and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymise and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well organised will save time when it comes to analysing them. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings.
On their own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyse the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarise your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarise your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analysing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
Operationalisation means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioural avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalise the variables that you want to measure.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, March 20). Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Qualitative Research: Characteristics, Design, Methods & Examples
Lauren McCall
MSc Health Psychology Graduate
MSc, Health Psychology, University of Nottingham
Lauren obtained an MSc in Health Psychology from The University of Nottingham with a distinction classification.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
“Not everything that can be counted counts, and not everything that counts can be counted“ (Albert Einstein)
Qualitative research is a process used for the systematic collection, analysis, and interpretation of non-numerical data (Punch, 2013).
Qualitative research can be used to: (i) gain deep contextual understandings of the subjective social reality of individuals and (ii) to answer questions about experience and meaning from the participant’s perspective (Hammarberg et al., 2016).
Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on gathering and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis, qualitative research focuses on thematic and contextual information.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Reality is socially constructed.
Qualitative research aims to understand how participants make meaning of their experiences – individually or in social contexts. It assumes there is no objective reality and that the social world is interpreted (Yilmaz, 2013).
The primacy of subject matter
The primary aim of qualitative research is to understand the perspectives, experiences, and beliefs of individuals who have experienced the phenomenon selected for research rather than the average experiences of groups of people (Minichiello, 1990).
Variables are complex, interwoven, and difficult to measure
Factors such as experiences, behaviors, and attitudes are complex and interwoven, so they cannot be reduced to isolated variables , making them difficult to measure quantitatively.
However, a qualitative approach enables participants to describe what, why, or how they were thinking/ feeling during a phenomenon being studied (Yilmaz, 2013).
Emic (insider’s point of view)
The phenomenon being studied is centered on the participants’ point of view (Minichiello, 1990).
Emic is used to describe how participants interact, communicate, and behave in the context of the research setting (Scarduzio, 2017).
Why Conduct Qualitative Research?
In order to gain a deeper understanding of how people experience the world, individuals are studied in their natural setting. This enables the researcher to understand a phenomenon close to how participants experience it.
Qualitative research allows researchers to gain an in-depth understanding, which is difficult to attain using quantitative methods.
An in-depth understanding is attained since qualitative techniques allow participants to freely disclose their experiences, thoughts, and feelings without constraint (Tenny et al., 2022).
This helps to further investigate and understand quantitative data by discovering reasons for the outcome of a study – answering the why question behind statistics.
The exploratory nature of qualitative research helps to generate hypotheses that can then be tested quantitatively (Busetto et al., 2020).
To design hypotheses, theory must be researched using qualitative methods to find out what is important in order to begin research.
For example, by conducting interviews or focus groups with key stakeholders to discover what is important to them.
Examples of qualitative research questions include:
- How does stress influence young adults’ behavior?
- What factors influence students’ school attendance rates in developed countries?
- How do adults interpret binge drinking in the UK?
- What are the psychological impacts of cervical cancer screening in women?
- How can mental health lessons be integrated into the school curriculum?
Collecting Qualitative Data
There are four main research design methods used to collect qualitative data: observations, interviews, focus groups, and ethnography.
Observations
This method involves watching and recording phenomena as they occur in nature. Observation can be divided into two types: participant and non-participant observation.
In participant observation, the researcher actively participates in the situation/events being observed.
In non-participant observation, the researcher is not an active part of the observation and tries not to influence the behaviors they are observing (Busetto et al., 2020).
Observations can be covert (participants are unaware that a researcher is observing them) or overt (participants are aware of the researcher’s presence and know they are being observed).
However, awareness of an observer’s presence may influence participants’ behavior.
Interviews give researchers a window into the world of a participant by seeking their account of an event, situation, or phenomenon. They are usually conducted on a one-to-one basis and can be distinguished according to the level at which they are structured (Punch, 2013).
Structured interviews involve predetermined questions and sequences to ensure replicability and comparability. However, they are unable to explore emerging issues.
Informal interviews consist of spontaneous, casual conversations which are closer to the truth of a phenomenon. However, information is gathered using quick notes made by the researcher and is therefore subject to recall bias.
Semi-structured interviews have a flexible structure, phrasing, and placement so emerging issues can be explored (Denny & Weckesser, 2022).
The use of probing questions and clarification can lead to a detailed understanding, but semi-structured interviews can be time-consuming and subject to interviewer bias.
Focus groups
Similar to interviews, focus groups elicit a rich and detailed account of an experience. However, focus groups are more dynamic since participants with shared characteristics construct this account together (Denny & Weckesser, 2022).
A shared narrative is built between participants to capture a group experience shaped by a shared context.
The researcher takes on the role of a moderator, who will establish ground rules and guide the discussion by following a topic guide to focus the group discussions.
Typically, focus groups have 4-10 participants as a discussion can be difficult to facilitate with more than this, and this number allows everyone the time to speak.
Ethnography
Ethnography is a methodology used to study a group of people’s behaviors and social interactions in their environment (Reeves et al., 2008).
Data are collected using methods such as observations, field notes, or structured/ unstructured interviews.
The aim of ethnography is to provide detailed, holistic insights into people’s behavior and perspectives within their natural setting. In order to achieve this, researchers immerse themselves in a community or organization.
Due to the flexibility and real-world focus of ethnography, researchers are able to gather an in-depth, nuanced understanding of people’s experiences, knowledge and perspectives that are influenced by culture and society.
In order to develop a representative picture of a particular culture/ context, researchers must conduct extensive field work.
This can be time-consuming as researchers may need to immerse themselves into a community/ culture for a few days, or possibly a few years.
Qualitative Data Analysis Methods
Different methods can be used for analyzing qualitative data. The researcher chooses based on the objectives of their study.
The researcher plays a key role in the interpretation of data, making decisions about the coding, theming, decontextualizing, and recontextualizing of data (Starks & Trinidad, 2007).
Grounded theory
Grounded theory is a qualitative method specifically designed to inductively generate theory from data. It was developed by Glaser and Strauss in 1967 (Glaser & Strauss, 2017).
This methodology aims to develop theories (rather than test hypotheses) that explain a social process, action, or interaction (Petty et al., 2012). To inform the developing theory, data collection and analysis run simultaneously.
There are three key types of coding used in grounded theory: initial (open), intermediate (axial), and advanced (selective) coding.
Throughout the analysis, memos should be created to document methodological and theoretical ideas about the data. Data should be collected and analyzed until data saturation is reached and a theory is developed.
Content analysis
Content analysis was first used in the early twentieth century to analyze textual materials such as newspapers and political speeches.
Content analysis is a research method used to identify and analyze the presence and patterns of themes, concepts, or words in data (Vaismoradi et al., 2013).
This research method can be used to analyze data in different formats, which can be written, oral, or visual.
The goal of content analysis is to develop themes that capture the underlying meanings of data (Schreier, 2012).
Qualitative content analysis can be used to validate existing theories, support the development of new models and theories, and provide in-depth descriptions of particular settings or experiences.
The following six steps provide a guideline for how to conduct qualitative content analysis.
- Define a Research Question : To start content analysis, a clear research question should be developed.
- Identify and Collect Data : Establish the inclusion criteria for your data. Find the relevant sources to analyze.
- Define the Unit or Theme of Analysis : Categorize the content into themes. Themes can be a word, phrase, or sentence.
- Develop Rules for Coding your Data : Define a set of coding rules to ensure that all data are coded consistently.
- Code the Data : Follow the coding rules to categorize data into themes.
- Analyze the Results and Draw Conclusions : Examine the data to identify patterns and draw conclusions in relation to your research question.
Discourse analysis
Discourse analysis is a research method used to study written/ spoken language in relation to its social context (Wood & Kroger, 2000).
In discourse analysis, the researcher interprets details of language materials and the context in which it is situated.
Discourse analysis aims to understand the functions of language (how language is used in real life) and how meaning is conveyed by language in different contexts. Researchers use discourse analysis to investigate social groups and how language is used to achieve specific communication goals.
Different methods of discourse analysis can be used depending on the aims and objectives of a study. However, the following steps provide a guideline on how to conduct discourse analysis.
- Define the Research Question : Develop a relevant research question to frame the analysis.
- Gather Data and Establish the Context : Collect research materials (e.g., interview transcripts, documents). Gather factual details and review the literature to construct a theory about the social and historical context of your study.
- Analyze the Content : Closely examine various components of the text, such as the vocabulary, sentences, paragraphs, and structure of the text. Identify patterns relevant to the research question to create codes, then group these into themes.
- Review the Results : Reflect on the findings to examine the function of the language, and the meaning and context of the discourse.
Thematic analysis
Thematic analysis is a method used to identify, interpret, and report patterns in data, such as commonalities or contrasts.
Although the origin of thematic analysis can be traced back to the early twentieth century, understanding and clarity of thematic analysis is attributed to Braun and Clarke (2006).
Thematic analysis aims to develop themes (patterns of meaning) across a dataset to address a research question.
In thematic analysis, qualitative data is gathered using techniques such as interviews, focus groups, and questionnaires. Audio recordings are transcribed. The dataset is then explored and interpreted by a researcher to identify patterns.
This occurs through the rigorous process of data familiarisation, coding, theme development, and revision. These identified patterns provide a summary of the dataset and can be used to address a research question.
Themes are developed by exploring the implicit and explicit meanings within the data. Two different approaches are used to generate themes: inductive and deductive.
An inductive approach allows themes to emerge from the data. In contrast, a deductive approach uses existing theories or knowledge to apply preconceived ideas to the data.
Phases of Thematic Analysis
Braun and Clarke (2006) provide a guide of the six phases of thematic analysis. These phases can be applied flexibly to fit research questions and data.
Template analysis
Template analysis refers to a specific method of thematic analysis which uses hierarchical coding (Brooks et al., 2014).
Template analysis is used to analyze textual data, for example, interview transcripts or open-ended responses on a written questionnaire.
To conduct template analysis, a coding template must be developed (usually from a subset of the data) and subsequently revised and refined. This template represents the themes identified by researchers as important in the dataset.
Codes are ordered hierarchically within the template, with the highest-level codes demonstrating overarching themes in the data and lower-level codes representing constituent themes with a narrower focus.
A guideline for the main procedural steps for conducting template analysis is outlined below.
- Familiarization with the Data : Read (and reread) the dataset in full. Engage, reflect, and take notes on data that may be relevant to the research question.
- Preliminary Coding : Identify initial codes using guidance from the a priori codes, identified before the analysis as likely to be beneficial and relevant to the analysis.
- Organize Themes : Organize themes into meaningful clusters. Consider the relationships between the themes both within and between clusters.
- Produce an Initial Template : Develop an initial template. This may be based on a subset of the data.
- Apply and Develop the Template : Apply the initial template to further data and make any necessary modifications. Refinements of the template may include adding themes, removing themes, or changing the scope/title of themes.
- Finalize Template : Finalize the template, then apply it to the entire dataset.
Frame analysis
Frame analysis is a comparative form of thematic analysis which systematically analyzes data using a matrix output.
Ritchie and Spencer (1994) developed this set of techniques to analyze qualitative data in applied policy research. Frame analysis aims to generate theory from data.
Frame analysis encourages researchers to organize and manage their data using summarization.
This results in a flexible and unique matrix output, in which individual participants (or cases) are represented by rows and themes are represented by columns.
Each intersecting cell is used to summarize findings relating to the corresponding participant and theme.
Frame analysis has five distinct phases which are interrelated, forming a methodical and rigorous framework.
- Familiarization with the Data : Familiarize yourself with all the transcripts. Immerse yourself in the details of each transcript and start to note recurring themes.
- Develop a Theoretical Framework : Identify recurrent/ important themes and add them to a chart. Provide a framework/ structure for the analysis.
- Indexing : Apply the framework systematically to the entire study data.
- Summarize Data in Analytical Framework : Reduce the data into brief summaries of participants’ accounts.
- Mapping and Interpretation : Compare themes and subthemes and check against the original transcripts. Group the data into categories and provide an explanation for them.
Preventing Bias in Qualitative Research
To evaluate qualitative studies, the CASP (Critical Appraisal Skills Programme) checklist for qualitative studies can be used to ensure all aspects of a study have been considered (CASP, 2018).
The quality of research can be enhanced and assessed using criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, co-coding, and member-checking.
Co-coding
Relying on only one researcher to interpret rich and complex data may risk key insights and alternative viewpoints being missed. Therefore, coding is often performed by multiple researchers.
A common strategy must be defined at the beginning of the coding process (Busetto et al., 2020). This includes establishing a useful coding list and finding a common definition of individual codes.
Transcripts are initially coded independently by researchers and then compared and consolidated to minimize error or bias and to bring confirmation of findings.
Member checking
Member checking (or respondent validation) involves checking back with participants to see if the research resonates with their experiences (Russell & Gregory, 2003).
Data can be returned to participants after data collection or when results are first available. For example, participants may be provided with their interview transcript and asked to verify whether this is a complete and accurate representation of their views.
Participants may then clarify or elaborate on their responses to ensure they align with their views (Shenton, 2004).
This feedback becomes part of data collection and ensures accurate descriptions/ interpretations of phenomena (Mays & Pope, 2000).
Reflexivity in qualitative research
Reflexivity typically involves examining your own judgments, practices, and belief systems during data collection and analysis. It aims to identify any personal beliefs which may affect the research.
Reflexivity is essential in qualitative research to ensure methodological transparency and complete reporting. This enables readers to understand how the interaction between the researcher and participant shapes the data.
Depending on the research question and population being researched, factors that need to be considered include the experience of the researcher, how the contact was established and maintained, age, gender, and ethnicity.
These details are important because, in qualitative research, the researcher is a dynamic part of the research process and actively influences the outcome of the research (Boeije, 2014).
Reflexivity Example
Who you are and your characteristics influence how you collect and analyze data. Here is an example of a reflexivity statement for research on smoking. I am a 30-year-old white female from a middle-class background. I live in the southwest of England and have been educated to master’s level. I have been involved in two research projects on oral health. I have never smoked, but I have witnessed how smoking can cause ill health from my volunteering in a smoking cessation clinic. My research aspirations are to help to develop interventions to help smokers quit.
Establishing Trustworthiness in Qualitative Research
Trustworthiness is a concept used to assess the quality and rigor of qualitative research. Four criteria are used to assess a study’s trustworthiness: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility in Qualitative Research
Credibility refers to how accurately the results represent the reality and viewpoints of the participants.
To establish credibility in research, participants’ views and the researcher’s representation of their views need to align (Tobin & Begley, 2004).
To increase the credibility of findings, researchers may use data source triangulation, investigator triangulation, peer debriefing, or member checking (Lincoln & Guba, 1985).
Transferability in Qualitative Research
Transferability refers to how generalizable the findings are: whether the findings may be applied to another context, setting, or group (Tobin & Begley, 2004).
Transferability can be enhanced by giving thorough and in-depth descriptions of the research setting, sample, and methods (Nowell et al., 2017).
Dependability in Qualitative Research
Dependability is the extent to which the study could be replicated under similar conditions and the findings would be consistent.
Researchers can establish dependability using methods such as audit trails so readers can see the research process is logical and traceable (Koch, 1994).
Confirmability in Qualitative Research
Confirmability is concerned with establishing that there is a clear link between the researcher’s interpretations/ findings and the data.
Researchers can achieve confirmability by demonstrating how conclusions and interpretations were arrived at (Nowell et al., 2017).
This enables readers to understand the reasoning behind the decisions made.
Audit Trails in Qualitative Research
An audit trail provides evidence of the decisions made by the researcher regarding theory, research design, and data collection, as well as the steps they have chosen to manage, analyze, and report data.
The researcher must provide a clear rationale to demonstrate how conclusions were reached in their study.
A clear description of the research path must be provided to enable readers to trace through the researcher’s logic (Halpren, 1983).
Researchers should maintain records of the raw data, field notes, transcripts, and a reflective journal in order to provide a clear audit trail.
Discovery of unexpected data
Open-ended questions in qualitative research mean the researcher can probe an interview topic and enable the participant to elaborate on responses in an unrestricted manner.
This allows unexpected data to emerge, which can lead to further research into that topic.
Flexibility
Data collection and analysis can be modified and adapted to take the research in a different direction if new ideas or patterns emerge in the data.
This enables researchers to investigate new opportunities while firmly maintaining their research goals.
Naturalistic settings
The behaviors of participants are recorded in real-world settings. Studies that use real-world settings have high ecological validity since participants behave more authentically.
Limitations
Time-consuming .
Qualitative research results in large amounts of data which often need to be transcribed and analyzed manually.
Even when software is used, transcription can be inaccurate, and using software for analysis can result in many codes which need to be condensed into themes.
Subjectivity
The researcher has an integral role in collecting and interpreting qualitative data. Therefore, the conclusions reached are from their perspective and experience.
Consequently, interpretations of data from another researcher may vary greatly.
Limited generalizability
The aim of qualitative research is to provide a detailed, contextualized understanding of an aspect of the human experience from a relatively small sample size.
Despite rigorous analysis procedures, conclusions drawn cannot be generalized to the wider population since data may be biased or unrepresentative.
Therefore, results are only applicable to a small group of the population.
Extraneous variables
Qualitative research is often conducted in real-world settings. This may cause results to be unreliable since extraneous variables may affect the data, for example:
- Situational variables : different environmental conditions may influence participants’ behavior in a study. The random variation in factors (such as noise or lighting) may be difficult to control in real-world settings.
- Participant characteristics : this includes any characteristics that may influence how a participant answers/ behaves in a study. This may include a participant’s mood, gender, age, ethnicity, sexual identity, IQ, etc.
- Experimenter effect : experimenter effect refers to how a researcher’s unintentional influence can change the outcome of a study. This occurs when (i) their interactions with participants unintentionally change participants’ behaviors or (ii) due to errors in observation, interpretation, or analysis.
What sample size should qualitative research be?
The sample size for qualitative studies has been recommended to include a minimum of 12 participants to reach data saturation (Braun, 2013).
Are surveys qualitative or quantitative?
Surveys can be used to gather information from a sample qualitatively or quantitatively. Qualitative surveys use open-ended questions to gather detailed information from a large sample using free text responses.
The use of open-ended questions allows for unrestricted responses where participants use their own words, enabling the collection of more in-depth information than closed-ended questions.
In contrast, quantitative surveys consist of closed-ended questions with multiple-choice answer options. Quantitative surveys are ideal to gather a statistical representation of a population.
What are the ethical considerations of qualitative research?
Before conducting a study, you must think about any risks that could occur and take steps to prevent them. Participant Protection : Researchers must protect participants from physical and mental harm. This means you must not embarrass, frighten, offend, or harm participants. Transparency : Researchers are obligated to clearly communicate how they will collect, store, analyze, use, and share the data. Confidentiality : You need to consider how to maintain the confidentiality and anonymity of participants’ data.
What is triangulation in qualitative research?
Triangulation refers to the use of several approaches in a study to comprehensively understand phenomena. This method helps to increase the validity and credibility of research findings.
Types of triangulation include method triangulation (using multiple methods to gather data); investigator triangulation (multiple researchers for collecting/ analyzing data), theory triangulation (comparing several theoretical perspectives to explain a phenomenon), and data source triangulation (using data from various times, locations, and people; Carter et al., 2014).
Why is qualitative research important?
Qualitative research allows researchers to describe and explain the social world. The exploratory nature of qualitative research helps to generate hypotheses that can then be tested quantitatively.
In qualitative research, participants are able to express their thoughts, experiences, and feelings without constraint.
Additionally, researchers are able to follow up on participants’ answers in real-time, generating valuable discussion around a topic. This enables researchers to gain a nuanced understanding of phenomena which is difficult to attain using quantitative methods.
What is coding data in qualitative research?
Coding data is a qualitative data analysis strategy in which a section of text is assigned with a label that describes its content.
These labels may be words or phrases which represent important (and recurring) patterns in the data.
This process enables researchers to identify related content across the dataset. Codes can then be used to group similar types of data to generate themes.
What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative research?
Qualitative research involves the collection and analysis of non-numerical data in order to understand experiences and meanings from the participant’s perspective.
This can provide rich, in-depth insights on complicated phenomena. Qualitative data may be collected using interviews, focus groups, or observations.
In contrast, quantitative research involves the collection and analysis of numerical data to measure the frequency, magnitude, or relationships of variables. This can provide objective and reliable evidence that can be generalized to the wider population.
Quantitative data may be collected using closed-ended questionnaires or experiments.
What is trustworthiness in qualitative research?
Trustworthiness is a concept used to assess the quality and rigor of qualitative research. Four criteria are used to assess a study’s trustworthiness: credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability.
Credibility refers to how accurately the results represent the reality and viewpoints of the participants. Transferability refers to whether the findings may be applied to another context, setting, or group.
Dependability is the extent to which the findings are consistent and reliable. Confirmability refers to the objectivity of findings (not influenced by the bias or assumptions of researchers).
What is data saturation in qualitative research?
Data saturation is a methodological principle used to guide the sample size of a qualitative research study.
Data saturation is proposed as a necessary methodological component in qualitative research (Saunders et al., 2018) as it is a vital criterion for discontinuing data collection and/or analysis.
The intention of data saturation is to find “no new data, no new themes, no new coding, and ability to replicate the study” (Guest et al., 2006). Therefore, enough data has been gathered to make conclusions.
Why is sampling in qualitative research important?
In quantitative research, large sample sizes are used to provide statistically significant quantitative estimates.
This is because quantitative research aims to provide generalizable conclusions that represent populations.
However, the aim of sampling in qualitative research is to gather data that will help the researcher understand the depth, complexity, variation, or context of a phenomenon. The small sample sizes in qualitative studies support the depth of case-oriented analysis.
Boeije, H. (2014). Analysis in qualitative research. Sage.
Braun, V., & Clarke, V. (2006). Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qualitative research in psychology , 3 (2), 77-101. https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Brooks, J., McCluskey, S., Turley, E., & King, N. (2014). The utility of template analysis in qualitative psychology research. Qualitative Research in Psychology , 12 (2), 202–222. https://doi.org/10.1080/14780887.2014.955224
Busetto, L., Wick, W., & Gumbinger, C. (2020). How to use and assess qualitative research methods. Neurological research and practice , 2 (1), 14-14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42466-020-00059-z
Carter, N., Bryant-Lukosius, D., DiCenso, A., Blythe, J., & Neville, A. J. (2014). The use of triangulation in qualitative research. Oncology nursing forum , 41 (5), 545–547. https://doi.org/10.1188/14.ONF.545-547
Critical Appraisal Skills Programme. (2018). CASP Checklist: 10 questions to help you make sense of a Qualitative research. https://casp-uk.net/images/checklist/documents/CASP-Qualitative-Studies-Checklist/CASP-Qualitative-Checklist-2018_fillable_form.pdf Accessed: March 15 2023
Clarke, V., & Braun, V. (2013). Successful qualitative research: A practical guide for beginners. Successful Qualitative Research , 1-400.
Denny, E., & Weckesser, A. (2022). How to do qualitative research?: Qualitative research methods. BJOG : an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology , 129 (7), 1166-1167. https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.17150
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (2017). The discovery of grounded theory. The Discovery of Grounded Theory , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203793206-1
Guest, G., Bunce, A., & Johnson, L. (2006). How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods, 18 (1), 59-82. doi:10.1177/1525822X05279903
Halpren, E. S. (1983). Auditing naturalistic inquiries: The development and application of a model (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Indiana University, Bloomington.
Hammarberg, K., Kirkman, M., & de Lacey, S. (2016). Qualitative research methods: When to use them and how to judge them. Human Reproduction , 31 (3), 498–501. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dev334
Koch, T. (1994). Establishing rigour in qualitative research: The decision trail. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 19, 976–986. doi:10.1111/ j.1365-2648.1994.tb01177.x
Lincoln, Y., & Guba, E. G. (1985). Naturalistic inquiry. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Mays, N., & Pope, C. (2000). Assessing quality in qualitative research. BMJ, 320(7226), 50–52.
Minichiello, V. (1990). In-Depth Interviewing: Researching People. Longman Cheshire.
Nowell, L. S., Norris, J. M., White, D. E., & Moules, N. J. (2017). Thematic Analysis: Striving to Meet the Trustworthiness Criteria. International Journal of Qualitative Methods, 16 (1). https://doi.org/10.1177/1609406917733847
Petty, N. J., Thomson, O. P., & Stew, G. (2012). Ready for a paradigm shift? part 2: Introducing qualitative research methodologies and methods. Manual Therapy , 17 (5), 378–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2012.03.004
Punch, K. F. (2013). Introduction to social research: Quantitative and qualitative approaches. London: Sage
Reeves, S., Kuper, A., & Hodges, B. D. (2008). Qualitative research methodologies: Ethnography. BMJ , 337 (aug07 3). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.a1020
Russell, C. K., & Gregory, D. M. (2003). Evaluation of qualitative research studies. Evidence Based Nursing, 6 (2), 36–40.
Saunders, B., Sim, J., Kingstone, T., Baker, S., Waterfield, J., Bartlam, B., Burroughs, H., & Jinks, C. (2018). Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Quality & quantity , 52 (4), 1893–1907. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-017-0574-8
Scarduzio, J. A. (2017). Emic approach to qualitative research. The International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods, 1–2 . https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118901731.iecrm0082
Schreier, M. (2012). Qualitative content analysis in practice / Margrit Schreier.
Shenton, A. K. (2004). Strategies for ensuring trustworthiness in qualitative research projects. Education for Information, 22 , 63–75.
Starks, H., & Trinidad, S. B. (2007). Choose your method: a comparison of phenomenology, discourse analysis, and grounded theory. Qualitative health research , 17 (10), 1372–1380. https://doi.org/10.1177/1049732307307031
Tenny, S., Brannan, J. M., & Brannan, G. D. (2022). Qualitative Study. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing.
Tobin, G. A., & Begley, C. M. (2004). Methodological rigour within a qualitative framework. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 48, 388–396. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03207.x
Vaismoradi, M., Turunen, H., & Bondas, T. (2013). Content analysis and thematic analysis: Implications for conducting a qualitative descriptive study. Nursing & health sciences , 15 (3), 398-405. https://doi.org/10.1111/nhs.12048
Wood L. A., Kroger R. O. (2000). Doing discourse analysis: Methods for studying action in talk and text. Sage.
Yilmaz, K. (2013). Comparison of Quantitative and Qualitative Research Traditions: epistemological, theoretical, and methodological differences. European journal of education , 48 (2), 311-325. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12014
Related Articles

Research Methodology
What Is a Focus Group?

Cross-Cultural Research Methodology In Psychology

What Is Internal Validity In Research?

Research Methodology , Statistics
What Is Face Validity In Research? Importance & How To Measure

Criterion Validity: Definition & Examples
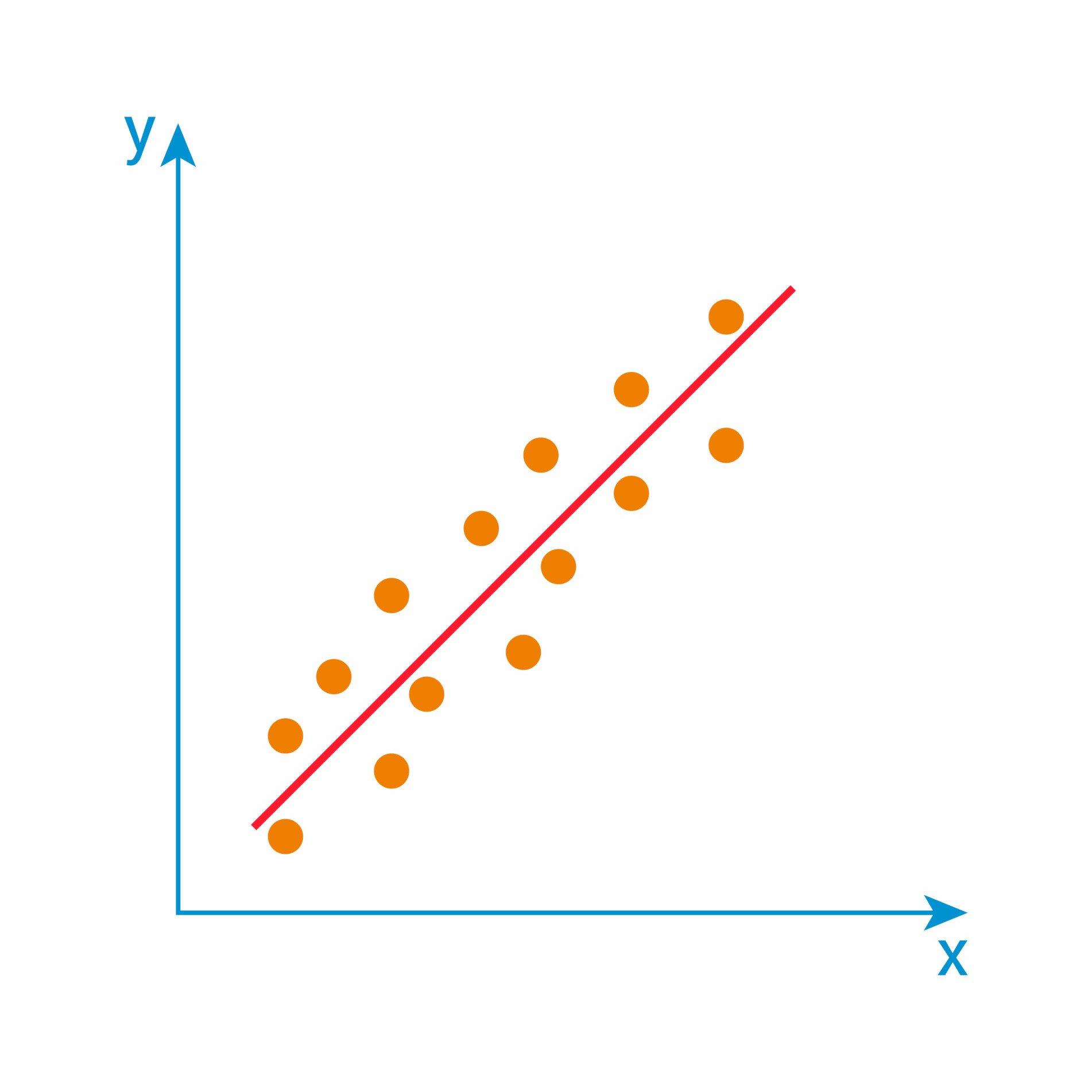
Convergent Validity: Definition and Examples

Research Design in Qualitative Research
Throughout March we will explore research design, with a focus on theory and conceptual frameworks. Find the unfolding series here . This post is from this month’s Mentor in Residence, Sharon Ravitch.
Qualitative research design is, most basically, the way that you, as a researcher, articulate, plan for, and set up the doing of your study. Research design is the overall approach to how a researcher (or research team) bridges theory and concepts with the development of research questions and the design of data collection and analysis methods for a specific study. A research design is based on an integration of the theories, concepts, goals, contexts, beliefs, and sets of relationships that shape a specific topic. In addition, it is shaped by responding to the realities and perspectives of participants and contexts of a study. In a solid qualitative research design, framing theory and key constructs are clearly explicated, and methods are built out of theory in ways that reflect prior learning. This theoretical examination of core concepts/constructs in the study sets the stage for a rigorous, systematic process of gathering and analyzing data. Every aspect of a study, from early development of guiding research questions to selection of setting and participants to the micro and macro contexts that shape all of this, interacts in dynamic ways that reflect the lived complexity and intersectionality of human beings in the social world.
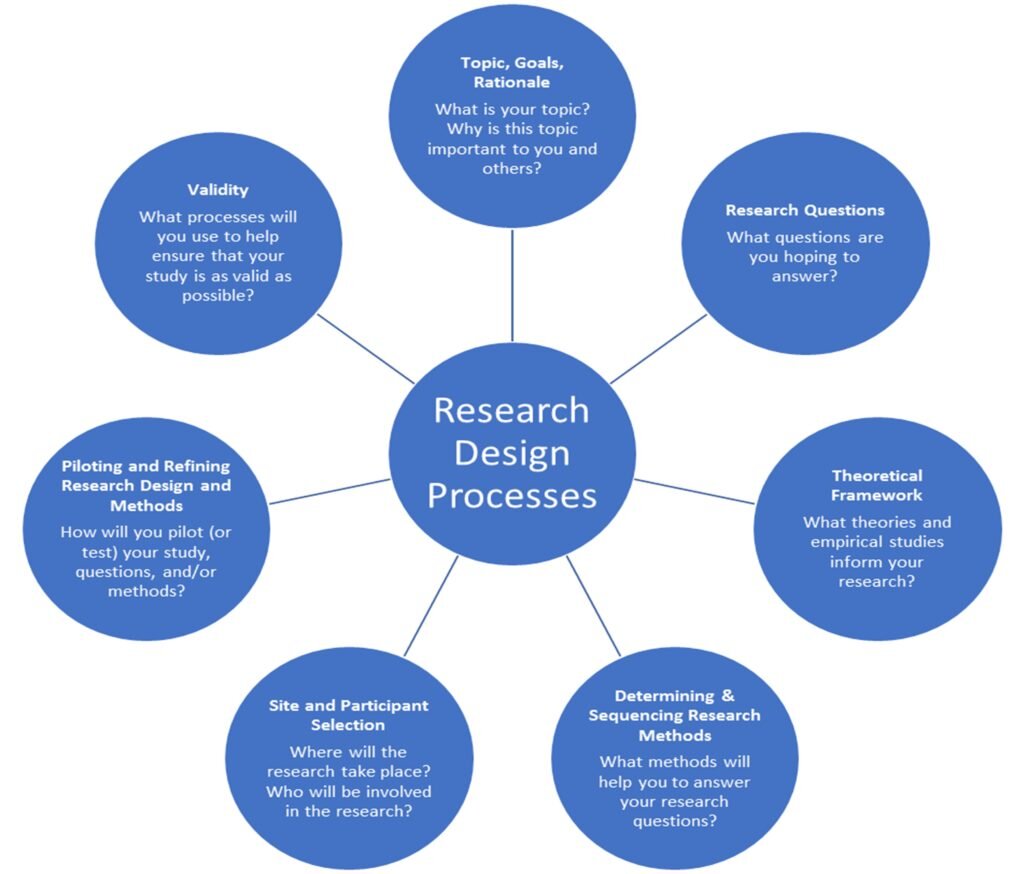
As illustrated in Figure above, the qualitative research design process begins with your research topic. Sometimes, this can be determined by a setting, group of people, or phenomenon that you are interested in studying. Once you have determined what you want to study, you explore fields, concepts, contexts, and theories that help you to understand what you want to know more about and what is already known about this topic. The guiding research questions, which are cultivated through structured processes of learning, reflecting, and engaging in dialogue with a range of thought partners, are central to all aspects of research design. The centrality of research questions to every facet of the research is the reason why it is vitally important to understand each of the core constructs of your research questions. Furthermore, because researchers are responsive to phenomena, realities, and contexts of a study, research questions may get refined over time. This requires a mindset that allows you to not only work hard to refine a set of research questions and a matching research design early on, but also to adopt an approach to research that is ongoingly flexible about, and responsive to, the realities in the setting once the study begins.
As with research questions, the overall research design process is inductive so that data collection and analysis processes can evolve to reflect real-time learning. This can include making changes to data collection methods. It can also mean that data analysis is not only summative, or at the end of data collection (as is commonly the case), but is employed as a generative design tool that begins with formative analysis early on that shapes subsequent data collection and continues throughout a study. As data are collected and analyzed, aspects of the research design may change to respond to emerging learnings and contextual realities.
Data collection and analysis should not be seen as two separate phases in the research process; they are iterative and integral to all aspects of qualitative research design. The notion of the “inseparability of methods and findings” (Emerson, Fretz, & Shaw, 1995) [i] means that how a study is structured and how data are collected are directly related to the nature and quality of the data and therefore the analyses and findings that emerge from the research. This is an important example of how connected all aspects of the research process are. This connected aspect of the qualitative research process highlights the need for flexible research design. Qualitative research design ideally involves simultaneous processes of “collecting and analyzing data, developing and modifying theory, elaborating or refocusing the research questions, and identifying and addressing validity threats” (Maxwell, 2013, p. 2). Qualitative research design is fluid, flexible, interactive, and reflexive (Maxwell, 2013; Ravitch & Carl, 2019). Your role, as a researcher, is to connect (and reconnect) the dots between all of these intersecting parts (not as a lone researcher or sole interpreter, but with thought partners and through participant validation ).
New Resource: "Doing Fieldwork In A Pandemic"
16 answers to your questions about teaching online.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.

StatPearls [Internet].
Qualitative study.
Steven Tenny ; Janelle M. Brannan ; Grace D. Brannan .
Affiliations
Last Update: September 18, 2022 .
- Introduction
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems. [1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences, perceptions, and behavior. It answers the hows and whys instead of how many or how much. It could be structured as a standalone study, purely relying on qualitative data, or part of mixed-methods research that combines qualitative and quantitative data. This review introduces the readers to some basic concepts, definitions, terminology, and applications of qualitative research.
Qualitative research, at its core, asks open-ended questions whose answers are not easily put into numbers, such as "how" and "why." [2] Due to the open-ended nature of the research questions, qualitative research design is often not linear like quantitative design. [2] One of the strengths of qualitative research is its ability to explain processes and patterns of human behavior that can be difficult to quantify. [3] Phenomena such as experiences, attitudes, and behaviors can be complex to capture accurately and quantitatively. In contrast, a qualitative approach allows participants themselves to explain how, why, or what they were thinking, feeling, and experiencing at a particular time or during an event of interest. Quantifying qualitative data certainly is possible, but at its core, qualitative data is looking for themes and patterns that can be difficult to quantify, and it is essential to ensure that the context and narrative of qualitative work are not lost by trying to quantify something that is not meant to be quantified.
However, while qualitative research is sometimes placed in opposition to quantitative research, where they are necessarily opposites and therefore "compete" against each other and the philosophical paradigms associated with each other, qualitative and quantitative work are neither necessarily opposites, nor are they incompatible. [4] While qualitative and quantitative approaches are different, they are not necessarily opposites and certainly not mutually exclusive. For instance, qualitative research can help expand and deepen understanding of data or results obtained from quantitative analysis. For example, say a quantitative analysis has determined a correlation between length of stay and level of patient satisfaction, but why does this correlation exist? This dual-focus scenario shows one way in which qualitative and quantitative research could be integrated.
Qualitative Research Approaches
Ethnography
Ethnography as a research design originates in social and cultural anthropology and involves the researcher being directly immersed in the participant’s environment. [2] Through this immersion, the ethnographer can use a variety of data collection techniques to produce a comprehensive account of the social phenomena that occurred during the research period. [2] That is to say, the researcher’s aim with ethnography is to immerse themselves into the research population and come out of it with accounts of actions, behaviors, events, etc, through the eyes of someone involved in the population. Direct involvement of the researcher with the target population is one benefit of ethnographic research because it can then be possible to find data that is otherwise very difficult to extract and record.
Grounded theory
Grounded Theory is the "generation of a theoretical model through the experience of observing a study population and developing a comparative analysis of their speech and behavior." [5] Unlike quantitative research, which is deductive and tests or verifies an existing theory, grounded theory research is inductive and, therefore, lends itself to research aimed at social interactions or experiences. [3] [2] In essence, Grounded Theory’s goal is to explain how and why an event occurs or how and why people might behave a certain way. Through observing the population, a researcher using the Grounded Theory approach can then develop a theory to explain the phenomena of interest.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is the "study of the meaning of phenomena or the study of the particular.” [5] At first glance, it might seem that Grounded Theory and Phenomenology are pretty similar, but the differences can be seen upon careful examination. At its core, phenomenology looks to investigate experiences from the individual's perspective. [2] Phenomenology is essentially looking into the "lived experiences" of the participants and aims to examine how and why participants behaved a certain way from their perspective. Herein lies one of the main differences between Grounded Theory and Phenomenology. Grounded Theory aims to develop a theory for social phenomena through an examination of various data sources. In contrast, Phenomenology focuses on describing and explaining an event or phenomenon from the perspective of those who have experienced it.
Narrative research
One of qualitative research’s strengths lies in its ability to tell a story, often from the perspective of those directly involved in it. Reporting on qualitative research involves including details and descriptions of the setting involved and quotes from participants. This detail is called a "thick" or "rich" description and is a strength of qualitative research. Narrative research is rife with the possibilities of "thick" description as this approach weaves together a sequence of events, usually from just one or two individuals, hoping to create a cohesive story or narrative. [2] While it might seem like a waste of time to focus on such a specific, individual level, understanding one or two people’s narratives for an event or phenomenon can help to inform researchers about the influences that helped shape that narrative. The tension or conflict of differing narratives can be "opportunities for innovation." [2]
Research Paradigm
Research paradigms are the assumptions, norms, and standards underpinning different research approaches. Essentially, research paradigms are the "worldviews" that inform research. [4] It is valuable for qualitative and quantitative researchers to understand what paradigm they are working within because understanding the theoretical basis of research paradigms allows researchers to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the approach being used and adjust accordingly. Different paradigms have different ontologies and epistemologies. Ontology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of reality,” whereas epistemology is defined as the "assumptions about the nature of knowledge" that inform researchers' work. [2] It is essential to understand the ontological and epistemological foundations of the research paradigm researchers are working within to allow for a complete understanding of the approach being used and the assumptions that underpin the approach as a whole. Further, researchers must understand their own ontological and epistemological assumptions about the world in general because their assumptions about the world will necessarily impact how they interact with research. A discussion of the research paradigm is not complete without describing positivist, postpositivist, and constructivist philosophies.
Positivist versus postpositivist
To further understand qualitative research, we must discuss positivist and postpositivist frameworks. Positivism is a philosophy that the scientific method can and should be applied to social and natural sciences. [4] Essentially, positivist thinking insists that the social sciences should use natural science methods in their research. It stems from positivist ontology, that there is an objective reality that exists that is wholly independent of our perception of the world as individuals. Quantitative research is rooted in positivist philosophy, which can be seen in the value it places on concepts such as causality, generalizability, and replicability.
Conversely, postpositivists argue that social reality can never be one hundred percent explained, but could be approximated. [4] Indeed, qualitative researchers have been insisting that there are “fundamental limits to the extent to which the methods and procedures of the natural sciences could be applied to the social world,” and therefore, postpositivist philosophy is often associated with qualitative research. [4] An example of positivist versus postpositivist values in research might be that positivist philosophies value hypothesis-testing, whereas postpositivist philosophies value the ability to formulate a substantive theory.
Constructivist
Constructivism is a subcategory of postpositivism. Most researchers invested in postpositivist research are also constructivist, meaning they think there is no objective external reality that exists but instead that reality is constructed. Constructivism is a theoretical lens that emphasizes the dynamic nature of our world. "Constructivism contends that individuals' views are directly influenced by their experiences, and it is these individual experiences and views that shape their perspective of reality.” [6] constructivist thought focuses on how "reality" is not a fixed certainty and how experiences, interactions, and backgrounds give people a unique view of the world. Constructivism contends, unlike positivist views, that there is not necessarily an "objective"reality we all experience. This is the ‘relativist’ ontological view that reality and our world are dynamic and socially constructed. Therefore, qualitative scientific knowledge can be inductive as well as deductive.” [4]
So why is it important to understand the differences in assumptions that different philosophies and approaches to research have? Fundamentally, the assumptions underpinning the research tools a researcher selects provide an overall base for the assumptions the rest of the research will have. It can even change the role of the researchers. [2] For example, is the researcher an "objective" observer, such as in positivist quantitative work? Or is the researcher an active participant in the research, as in postpositivist qualitative work? Understanding the philosophical base of the study undertaken allows researchers to fully understand the implications of their work and their role within the research and reflect on their positionality and bias as it pertains to the research they are conducting.
Data Sampling
The better the sample represents the intended study population, the more likely the researcher is to encompass the varying factors. The following are examples of participant sampling and selection: [7]
- Purposive sampling- selection based on the researcher’s rationale for being the most informative.
- Criterion sampling selection based on pre-identified factors.
- Convenience sampling- selection based on availability.
- Snowball sampling- the selection is by referral from other participants or people who know potential participants.
- Extreme case sampling- targeted selection of rare cases.
- Typical case sampling selection based on regular or average participants.
Data Collection and Analysis
Qualitative research uses several techniques, including interviews, focus groups, and observation. [1] [2] [3] Interviews may be unstructured, with open-ended questions on a topic, and the interviewer adapts to the responses. Structured interviews have a predetermined number of questions that every participant is asked. It is usually one-on-one and appropriate for sensitive topics or topics needing an in-depth exploration. Focus groups are often held with 8-12 target participants and are used when group dynamics and collective views on a topic are desired. Researchers can be participant-observers to share the experiences of the subject or non-participants or detached observers.
While quantitative research design prescribes a controlled environment for data collection, qualitative data collection may be in a central location or the participants' environment, depending on the study goals and design. Qualitative research could amount to a large amount of data. Data is transcribed, which may then be coded manually or using computer-assisted qualitative data analysis software or CAQDAS such as ATLAS.ti or NVivo. [8] [9] [10]
After the coding process, qualitative research results could be in various formats. It could be a synthesis and interpretation presented with excerpts from the data. [11] Results could also be in the form of themes and theory or model development.
Dissemination
The healthcare team can use two reporting standards to standardize and facilitate the dissemination of qualitative research outcomes. The Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research or COREQ is a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. [12] The Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) is a checklist covering a more comprehensive range of qualitative research. [13]
Applications
Many times, a research question will start with qualitative research. The qualitative research will help generate the research hypothesis, which can be tested with quantitative methods. After the data is collected and analyzed with quantitative methods, a set of qualitative methods can be used to dive deeper into the data to better understand what the numbers truly mean and their implications. The qualitative techniques can then help clarify the quantitative data and also help refine the hypothesis for future research. Furthermore, with qualitative research, researchers can explore poorly studied subjects with quantitative methods. These include opinions, individual actions, and social science research.
An excellent qualitative study design starts with a goal or objective. This should be clearly defined or stated. The target population needs to be specified. A method for obtaining information from the study population must be carefully detailed to ensure no omissions of part of the target population. A proper collection method should be selected that will help obtain the desired information without overly limiting the collected data because, often, the information sought is not well categorized or obtained. Finally, the design should ensure adequate methods for analyzing the data. An example may help better clarify some of the various aspects of qualitative research.
A researcher wants to decrease the number of teenagers who smoke in their community. The researcher could begin by asking current teen smokers why they started smoking through structured or unstructured interviews (qualitative research). The researcher can also get together a group of current teenage smokers and conduct a focus group to help brainstorm factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke (qualitative research).
In this example, the researcher has used qualitative research methods (interviews and focus groups) to generate a list of ideas of why teens start to smoke and factors that may have prevented them from starting to smoke. Next, the researcher compiles this data. The research found that, hypothetically, peer pressure, health issues, cost, being considered "cool," and rebellious behavior all might increase or decrease the likelihood of teens starting to smoke.
The researcher creates a survey asking teen participants to rank how important each of the above factors is in either starting smoking (for current smokers) or not smoking (for current nonsmokers). This survey provides specific numbers (ranked importance of each factor) and is thus a quantitative research tool.
The researcher can use the survey results to focus efforts on the one or two highest-ranked factors. Let us say the researcher found that health was the primary factor that keeps teens from starting to smoke, and peer pressure was the primary factor that contributed to teens starting smoking. The researcher can go back to qualitative research methods to dive deeper into these for more information. The researcher wants to focus on keeping teens from starting to smoke, so they focus on the peer pressure aspect.
The researcher can conduct interviews and focus groups (qualitative research) about what types and forms of peer pressure are commonly encountered, where the peer pressure comes from, and where smoking starts. The researcher hypothetically finds that peer pressure often occurs after school at the local teen hangouts, mostly in the local park. The researcher also hypothetically finds that peer pressure comes from older, current smokers who provide the cigarettes.
The researcher could further explore this observation made at the local teen hangouts (qualitative research) and take notes regarding who is smoking, who is not, and what observable factors are at play for peer pressure to smoke. The researcher finds a local park where many local teenagers hang out and sees that the smokers tend to hang out in a shady, overgrown area of the park. The researcher notes that smoking teenagers buy their cigarettes from a local convenience store adjacent to the park, where the clerk does not check identification before selling cigarettes. These observations fall under qualitative research.
If the researcher returns to the park and counts how many individuals smoke in each region, this numerical data would be quantitative research. Based on the researcher's efforts thus far, they conclude that local teen smoking and teenagers who start to smoke may decrease if there are fewer overgrown areas of the park and the local convenience store does not sell cigarettes to underage individuals.
The researcher could try to have the parks department reassess the shady areas to make them less conducive to smokers or identify how to limit the sales of cigarettes to underage individuals by the convenience store. The researcher would then cycle back to qualitative methods of asking at-risk populations their perceptions of the changes and what factors are still at play, and quantitative research that includes teen smoking rates in the community and the incidence of new teen smokers, among others. [14] [15]
Qualitative research functions as a standalone research design or combined with quantitative research to enhance our understanding of the world. Qualitative research uses techniques including structured and unstructured interviews, focus groups, and participant observation not only to help generate hypotheses that can be more rigorously tested with quantitative research but also to help researchers delve deeper into the quantitative research numbers, understand what they mean, and understand what the implications are. Qualitative research allows researchers to understand what is going on, especially when things are not easily categorized. [16]
- Issues of Concern
As discussed in the sections above, quantitative and qualitative work differ in many ways, including the evaluation criteria. There are four well-established criteria for evaluating quantitative data: internal validity, external validity, reliability, and objectivity. Credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability are the correlating concepts in qualitative research. [4] [11] The corresponding quantitative and qualitative concepts can be seen below, with the quantitative concept on the left and the qualitative concept on the right:
- Internal validity: Credibility
- External validity: Transferability
- Reliability: Dependability
- Objectivity: Confirmability
In conducting qualitative research, ensuring these concepts are satisfied and well thought out can mitigate potential issues from arising. For example, just as a researcher will ensure that their quantitative study is internally valid, qualitative researchers should ensure that their work has credibility.
Indicators such as triangulation and peer examination can help evaluate the credibility of qualitative work.
- Triangulation: Triangulation involves using multiple data collection methods to increase the likelihood of getting a reliable and accurate result. In our above magic example, the result would be more reliable if we interviewed the magician, backstage hand, and the person who "vanished." In qualitative research, triangulation can include telephone surveys, in-person surveys, focus groups, and interviews and surveying an adequate cross-section of the target demographic.
- Peer examination: A peer can review results to ensure the data is consistent with the findings.
A "thick" or "rich" description can be used to evaluate the transferability of qualitative research, whereas an indicator such as an audit trail might help evaluate the dependability and confirmability.
- Thick or rich description: This is a detailed and thorough description of details, the setting, and quotes from participants in the research. [5] Thick descriptions will include a detailed explanation of how the study was conducted. Thick descriptions are detailed enough to allow readers to draw conclusions and interpret the data, which can help with transferability and replicability.
- Audit trail: An audit trail provides a documented set of steps of how the participants were selected and the data was collected. The original information records should also be kept (eg, surveys, notes, recordings).
One issue of concern that qualitative researchers should consider is observation bias. Here are a few examples:
- Hawthorne effect: The effect is the change in participant behavior when they know they are being observed. Suppose a researcher wanted to identify factors that contribute to employee theft and tell the employees they will watch them to see what factors affect employee theft. In that case, one would suspect employee behavior would change when they know they are being protected.
- Observer-expectancy effect: Some participants change their behavior or responses to satisfy the researcher's desired effect. This happens unconsciously for the participant, so it is essential to eliminate or limit the transmission of the researcher's views.
- Artificial scenario effect: Some qualitative research occurs in contrived scenarios with preset goals. In such situations, the information may not be accurate because of the artificial nature of the scenario. The preset goals may limit the qualitative information obtained.
- Clinical Significance
Qualitative or quantitative research helps healthcare providers understand patients and the impact and challenges of the care they deliver. Qualitative research provides an opportunity to generate and refine hypotheses and delve deeper into the data generated by quantitative research. Qualitative research is not an island apart from quantitative research but an integral part of research methods to understand the world around us. [17]
- Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Qualitative research is essential for all healthcare team members as all are affected by qualitative research. Qualitative research may help develop a theory or a model for health research that can be further explored by quantitative research. Much of the qualitative research data acquisition is completed by numerous team members, including social workers, scientists, nurses, etc. Within each area of the medical field, there is copious ongoing qualitative research, including physician-patient interactions, nursing-patient interactions, patient-environment interactions, healthcare team function, patient information delivery, etc.
- Review Questions
- Access free multiple choice questions on this topic.
- Comment on this article.
Disclosure: Steven Tenny declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Janelle Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
Disclosure: Grace Brannan declares no relevant financial relationships with ineligible companies.
This book is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ), which permits others to distribute the work, provided that the article is not altered or used commercially. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal.
- Cite this Page Tenny S, Brannan JM, Brannan GD. Qualitative Study. [Updated 2022 Sep 18]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-.
In this Page
Bulk download.
- Bulk download StatPearls data from FTP
Related information
- PMC PubMed Central citations
- PubMed Links to PubMed
Similar articles in PubMed
- Suicidal Ideation. [StatPearls. 2024] Suicidal Ideation. Harmer B, Lee S, Rizvi A, Saadabadi A. StatPearls. 2024 Jan
- Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. [Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022] Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas. Crider K, Williams J, Qi YP, Gutman J, Yeung L, Mai C, Finkelstain J, Mehta S, Pons-Duran C, Menéndez C, et al. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1; 2(2022). Epub 2022 Feb 1.
- Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). [Phys Biol. 2013] Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012). Foffi G, Pastore A, Piazza F, Temussi PA. Phys Biol. 2013 Aug; 10(4):040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2.
- Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics [ 2014] Review Evidence Brief: The Effectiveness Of Mandatory Computer-Based Trainings On Government Ethics, Workplace Harassment, Or Privacy And Information Security-Related Topics Peterson K, McCleery E. 2014 May
- Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. [Campbell Syst Rev. 2021] Review Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Mugellini G, Della Bella S, Colagrossi M, Isenring GL, Killias M. Campbell Syst Rev. 2021 Jun; 17(2):e1173. Epub 2021 May 24.
Recent Activity
- Qualitative Study - StatPearls Qualitative Study - StatPearls
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers

Chapter 1. Introduction
“Science is in danger, and for that reason it is becoming dangerous” -Pierre Bourdieu, Science of Science and Reflexivity
Why an Open Access Textbook on Qualitative Research Methods?
I have been teaching qualitative research methods to both undergraduates and graduate students for many years. Although there are some excellent textbooks out there, they are often costly, and none of them, to my mind, properly introduces qualitative research methods to the beginning student (whether undergraduate or graduate student). In contrast, this open-access textbook is designed as a (free) true introduction to the subject, with helpful, practical pointers on how to conduct research and how to access more advanced instruction.
Textbooks are typically arranged in one of two ways: (1) by technique (each chapter covers one method used in qualitative research); or (2) by process (chapters advance from research design through publication). But both of these approaches are necessary for the beginner student. This textbook will have sections dedicated to the process as well as the techniques of qualitative research. This is a true “comprehensive” book for the beginning student. In addition to covering techniques of data collection and data analysis, it provides a road map of how to get started and how to keep going and where to go for advanced instruction. It covers aspects of research design and research communication as well as methods employed. Along the way, it includes examples from many different disciplines in the social sciences.
The primary goal has been to create a useful, accessible, engaging textbook for use across many disciplines. And, let’s face it. Textbooks can be boring. I hope readers find this to be a little different. I have tried to write in a practical and forthright manner, with many lively examples and references to good and intellectually creative qualitative research. Woven throughout the text are short textual asides (in colored textboxes) by professional (academic) qualitative researchers in various disciplines. These short accounts by practitioners should help inspire students. So, let’s begin!
What is Research?
When we use the word research , what exactly do we mean by that? This is one of those words that everyone thinks they understand, but it is worth beginning this textbook with a short explanation. We use the term to refer to “empirical research,” which is actually a historically specific approach to understanding the world around us. Think about how you know things about the world. [1] You might know your mother loves you because she’s told you she does. Or because that is what “mothers” do by tradition. Or you might know because you’ve looked for evidence that she does, like taking care of you when you are sick or reading to you in bed or working two jobs so you can have the things you need to do OK in life. Maybe it seems churlish to look for evidence; you just take it “on faith” that you are loved.
Only one of the above comes close to what we mean by research. Empirical research is research (investigation) based on evidence. Conclusions can then be drawn from observable data. This observable data can also be “tested” or checked. If the data cannot be tested, that is a good indication that we are not doing research. Note that we can never “prove” conclusively, through observable data, that our mothers love us. We might have some “disconfirming evidence” (that time she didn’t show up to your graduation, for example) that could push you to question an original hypothesis , but no amount of “confirming evidence” will ever allow us to say with 100% certainty, “my mother loves me.” Faith and tradition and authority work differently. Our knowledge can be 100% certain using each of those alternative methods of knowledge, but our certainty in those cases will not be based on facts or evidence.
For many periods of history, those in power have been nervous about “science” because it uses evidence and facts as the primary source of understanding the world, and facts can be at odds with what power or authority or tradition want you to believe. That is why I say that scientific empirical research is a historically specific approach to understand the world. You are in college or university now partly to learn how to engage in this historically specific approach.
In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries in Europe, there was a newfound respect for empirical research, some of which was seriously challenging to the established church. Using observations and testing them, scientists found that the earth was not at the center of the universe, for example, but rather that it was but one planet of many which circled the sun. [2] For the next two centuries, the science of astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry emerged and became disciplines taught in universities. All used the scientific method of observation and testing to advance knowledge. Knowledge about people , however, and social institutions, however, was still left to faith, tradition, and authority. Historians and philosophers and poets wrote about the human condition, but none of them used research to do so. [3]
It was not until the nineteenth century that “social science” really emerged, using the scientific method (empirical observation) to understand people and social institutions. New fields of sociology, economics, political science, and anthropology emerged. The first sociologists, people like Auguste Comte and Karl Marx, sought specifically to apply the scientific method of research to understand society, Engels famously claiming that Marx had done for the social world what Darwin did for the natural world, tracings its laws of development. Today we tend to take for granted the naturalness of science here, but it is actually a pretty recent and radical development.
To return to the question, “does your mother love you?” Well, this is actually not really how a researcher would frame the question, as it is too specific to your case. It doesn’t tell us much about the world at large, even if it does tell us something about you and your relationship with your mother. A social science researcher might ask, “do mothers love their children?” Or maybe they would be more interested in how this loving relationship might change over time (e.g., “do mothers love their children more now than they did in the 18th century when so many children died before reaching adulthood?”) or perhaps they might be interested in measuring quality of love across cultures or time periods, or even establishing “what love looks like” using the mother/child relationship as a site of exploration. All of these make good research questions because we can use observable data to answer them.
What is Qualitative Research?
“All we know is how to learn. How to study, how to listen, how to talk, how to tell. If we don’t tell the world, we don’t know the world. We’re lost in it, we die.” -Ursula LeGuin, The Telling
At its simplest, qualitative research is research about the social world that does not use numbers in its analyses. All those who fear statistics can breathe a sigh of relief – there are no mathematical formulae or regression models in this book! But this definition is less about what qualitative research can be and more about what it is not. To be honest, any simple statement will fail to capture the power and depth of qualitative research. One way of contrasting qualitative research to quantitative research is to note that the focus of qualitative research is less about explaining and predicting relationships between variables and more about understanding the social world. To use our mother love example, the question about “what love looks like” is a good question for the qualitative researcher while all questions measuring love or comparing incidences of love (both of which require measurement) are good questions for quantitative researchers. Patton writes,
Qualitative data describe. They take us, as readers, into the time and place of the observation so that we know what it was like to have been there. They capture and communicate someone else’s experience of the world in his or her own words. Qualitative data tell a story. ( Patton 2002:47 )
Qualitative researchers are asking different questions about the world than their quantitative colleagues. Even when researchers are employed in “mixed methods” research ( both quantitative and qualitative), they are using different methods to address different questions of the study. I do a lot of research about first-generation and working-college college students. Where a quantitative researcher might ask, how many first-generation college students graduate from college within four years? Or does first-generation college status predict high student debt loads? A qualitative researcher might ask, how does the college experience differ for first-generation college students? What is it like to carry a lot of debt, and how does this impact the ability to complete college on time? Both sets of questions are important, but they can only be answered using specific tools tailored to those questions. For the former, you need large numbers to make adequate comparisons. For the latter, you need to talk to people, find out what they are thinking and feeling, and try to inhabit their shoes for a little while so you can make sense of their experiences and beliefs.
Examples of Qualitative Research
You have probably seen examples of qualitative research before, but you might not have paid particular attention to how they were produced or realized that the accounts you were reading were the result of hours, months, even years of research “in the field.” A good qualitative researcher will present the product of their hours of work in such a way that it seems natural, even obvious, to the reader. Because we are trying to convey what it is like answers, qualitative research is often presented as stories – stories about how people live their lives, go to work, raise their children, interact with one another. In some ways, this can seem like reading particularly insightful novels. But, unlike novels, there are very specific rules and guidelines that qualitative researchers follow to ensure that the “story” they are telling is accurate , a truthful rendition of what life is like for the people being studied. Most of this textbook will be spent conveying those rules and guidelines. Let’s take a look, first, however, at three examples of what the end product looks like. I have chosen these three examples to showcase very different approaches to qualitative research, and I will return to these five examples throughout the book. They were all published as whole books (not chapters or articles), and they are worth the long read, if you have the time. I will also provide some information on how these books came to be and the length of time it takes to get them into book version. It is important you know about this process, and the rest of this textbook will help explain why it takes so long to conduct good qualitative research!
Example 1 : The End Game (ethnography + interviews)
Corey Abramson is a sociologist who teaches at the University of Arizona. In 2015 he published The End Game: How Inequality Shapes our Final Years ( 2015 ). This book was based on the research he did for his dissertation at the University of California-Berkeley in 2012. Actually, the dissertation was completed in 2012 but the work that was produced that took several years. The dissertation was entitled, “This is How We Live, This is How We Die: Social Stratification, Aging, and Health in Urban America” ( 2012 ). You can see how the book version, which was written for a more general audience, has a more engaging sound to it, but that the dissertation version, which is what academic faculty read and evaluate, has a more descriptive title. You can read the title and know that this is a study about aging and health and that the focus is going to be inequality and that the context (place) is going to be “urban America.” It’s a study about “how” people do something – in this case, how they deal with aging and death. This is the very first sentence of the dissertation, “From our first breath in the hospital to the day we die, we live in a society characterized by unequal opportunities for maintaining health and taking care of ourselves when ill. These disparities reflect persistent racial, socio-economic, and gender-based inequalities and contribute to their persistence over time” ( 1 ). What follows is a truthful account of how that is so.
Cory Abramson spent three years conducting his research in four different urban neighborhoods. We call the type of research he conducted “comparative ethnographic” because he designed his study to compare groups of seniors as they went about their everyday business. It’s comparative because he is comparing different groups (based on race, class, gender) and ethnographic because he is studying the culture/way of life of a group. [4] He had an educated guess, rooted in what previous research had shown and what social theory would suggest, that people’s experiences of aging differ by race, class, and gender. So, he set up a research design that would allow him to observe differences. He chose two primarily middle-class (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly White) and two primarily poor neighborhoods (one was racially diverse and the other was predominantly African American). He hung out in senior centers and other places seniors congregated, watched them as they took the bus to get prescriptions filled, sat in doctor’s offices with them, and listened to their conversations with each other. He also conducted more formal conversations, what we call in-depth interviews, with sixty seniors from each of the four neighborhoods. As with a lot of fieldwork , as he got closer to the people involved, he both expanded and deepened his reach –
By the end of the project, I expanded my pool of general observations to include various settings frequented by seniors: apartment building common rooms, doctors’ offices, emergency rooms, pharmacies, senior centers, bars, parks, corner stores, shopping centers, pool halls, hair salons, coffee shops, and discount stores. Over the course of the three years of fieldwork, I observed hundreds of elders, and developed close relationships with a number of them. ( 2012:10 )
When Abramson rewrote the dissertation for a general audience and published his book in 2015, it got a lot of attention. It is a beautifully written book and it provided insight into a common human experience that we surprisingly know very little about. It won the Outstanding Publication Award by the American Sociological Association Section on Aging and the Life Course and was featured in the New York Times . The book was about aging, and specifically how inequality shapes the aging process, but it was also about much more than that. It helped show how inequality affects people’s everyday lives. For example, by observing the difficulties the poor had in setting up appointments and getting to them using public transportation and then being made to wait to see a doctor, sometimes in standing-room-only situations, when they are unwell, and then being treated dismissively by hospital staff, Abramson allowed readers to feel the material reality of being poor in the US. Comparing these examples with seniors with adequate supplemental insurance who have the resources to hire car services or have others assist them in arranging care when they need it, jolts the reader to understand and appreciate the difference money makes in the lives and circumstances of us all, and in a way that is different than simply reading a statistic (“80% of the poor do not keep regular doctor’s appointments”) does. Qualitative research can reach into spaces and places that often go unexamined and then reports back to the rest of us what it is like in those spaces and places.
Example 2: Racing for Innocence (Interviews + Content Analysis + Fictional Stories)
Jennifer Pierce is a Professor of American Studies at the University of Minnesota. Trained as a sociologist, she has written a number of books about gender, race, and power. Her very first book, Gender Trials: Emotional Lives in Contemporary Law Firms, published in 1995, is a brilliant look at gender dynamics within two law firms. Pierce was a participant observer, working as a paralegal, and she observed how female lawyers and female paralegals struggled to obtain parity with their male colleagues.
Fifteen years later, she reexamined the context of the law firm to include an examination of racial dynamics, particularly how elite white men working in these spaces created and maintained a culture that made it difficult for both female attorneys and attorneys of color to thrive. Her book, Racing for Innocence: Whiteness, Gender, and the Backlash Against Affirmative Action , published in 2012, is an interesting and creative blending of interviews with attorneys, content analyses of popular films during this period, and fictional accounts of racial discrimination and sexual harassment. The law firm she chose to study had come under an affirmative action order and was in the process of implementing equitable policies and programs. She wanted to understand how recipients of white privilege (the elite white male attorneys) come to deny the role they play in reproducing inequality. Through interviews with attorneys who were present both before and during the affirmative action order, she creates a historical record of the “bad behavior” that necessitated new policies and procedures, but also, and more importantly , probed the participants ’ understanding of this behavior. It should come as no surprise that most (but not all) of the white male attorneys saw little need for change, and that almost everyone else had accounts that were different if not sometimes downright harrowing.
I’ve used Pierce’s book in my qualitative research methods courses as an example of an interesting blend of techniques and presentation styles. My students often have a very difficult time with the fictional accounts she includes. But they serve an important communicative purpose here. They are her attempts at presenting “both sides” to an objective reality – something happens (Pierce writes this something so it is very clear what it is), and the two participants to the thing that happened have very different understandings of what this means. By including these stories, Pierce presents one of her key findings – people remember things differently and these different memories tend to support their own ideological positions. I wonder what Pierce would have written had she studied the murder of George Floyd or the storming of the US Capitol on January 6 or any number of other historic events whose observers and participants record very different happenings.
This is not to say that qualitative researchers write fictional accounts. In fact, the use of fiction in our work remains controversial. When used, it must be clearly identified as a presentation device, as Pierce did. I include Racing for Innocence here as an example of the multiple uses of methods and techniques and the way that these work together to produce better understandings by us, the readers, of what Pierce studied. We readers come away with a better grasp of how and why advantaged people understate their own involvement in situations and structures that advantage them. This is normal human behavior , in other words. This case may have been about elite white men in law firms, but the general insights here can be transposed to other settings. Indeed, Pierce argues that more research needs to be done about the role elites play in the reproduction of inequality in the workplace in general.
Example 3: Amplified Advantage (Mixed Methods: Survey Interviews + Focus Groups + Archives)
The final example comes from my own work with college students, particularly the ways in which class background affects the experience of college and outcomes for graduates. I include it here as an example of mixed methods, and for the use of supplementary archival research. I’ve done a lot of research over the years on first-generation, low-income, and working-class college students. I am curious (and skeptical) about the possibility of social mobility today, particularly with the rising cost of college and growing inequality in general. As one of the few people in my family to go to college, I didn’t grow up with a lot of examples of what college was like or how to make the most of it. And when I entered graduate school, I realized with dismay that there were very few people like me there. I worried about becoming too different from my family and friends back home. And I wasn’t at all sure that I would ever be able to pay back the huge load of debt I was taking on. And so I wrote my dissertation and first two books about working-class college students. These books focused on experiences in college and the difficulties of navigating between family and school ( Hurst 2010a, 2012 ). But even after all that research, I kept coming back to wondering if working-class students who made it through college had an equal chance at finding good jobs and happy lives,
What happens to students after college? Do working-class students fare as well as their peers? I knew from my own experience that barriers continued through graduate school and beyond, and that my debtload was higher than that of my peers, constraining some of the choices I made when I graduated. To answer these questions, I designed a study of students attending small liberal arts colleges, the type of college that tried to equalize the experience of students by requiring all students to live on campus and offering small classes with lots of interaction with faculty. These private colleges tend to have more money and resources so they can provide financial aid to low-income students. They also attract some very wealthy students. Because they enroll students across the class spectrum, I would be able to draw comparisons. I ended up spending about four years collecting data, both a survey of more than 2000 students (which formed the basis for quantitative analyses) and qualitative data collection (interviews, focus groups, archival research, and participant observation). This is what we call a “mixed methods” approach because we use both quantitative and qualitative data. The survey gave me a large enough number of students that I could make comparisons of the how many kind, and to be able to say with some authority that there were in fact significant differences in experience and outcome by class (e.g., wealthier students earned more money and had little debt; working-class students often found jobs that were not in their chosen careers and were very affected by debt, upper-middle-class students were more likely to go to graduate school). But the survey analyses could not explain why these differences existed. For that, I needed to talk to people and ask them about their motivations and aspirations. I needed to understand their perceptions of the world, and it is very hard to do this through a survey.
By interviewing students and recent graduates, I was able to discern particular patterns and pathways through college and beyond. Specifically, I identified three versions of gameplay. Upper-middle-class students, whose parents were themselves professionals (academics, lawyers, managers of non-profits), saw college as the first stage of their education and took classes and declared majors that would prepare them for graduate school. They also spent a lot of time building their resumes, taking advantage of opportunities to help professors with their research, or study abroad. This helped them gain admission to highly-ranked graduate schools and interesting jobs in the public sector. In contrast, upper-class students, whose parents were wealthy and more likely to be engaged in business (as CEOs or other high-level directors), prioritized building social capital. They did this by joining fraternities and sororities and playing club sports. This helped them when they graduated as they called on friends and parents of friends to find them well-paying jobs. Finally, low-income, first-generation, and working-class students were often adrift. They took the classes that were recommended to them but without the knowledge of how to connect them to life beyond college. They spent time working and studying rather than partying or building their resumes. All three sets of students thought they were “doing college” the right way, the way that one was supposed to do college. But these three versions of gameplay led to distinct outcomes that advantaged some students over others. I titled my work “Amplified Advantage” to highlight this process.
These three examples, Cory Abramson’s The End Game , Jennifer Peirce’s Racing for Innocence, and my own Amplified Advantage, demonstrate the range of approaches and tools available to the qualitative researcher. They also help explain why qualitative research is so important. Numbers can tell us some things about the world, but they cannot get at the hearts and minds, motivations and beliefs of the people who make up the social worlds we inhabit. For that, we need tools that allow us to listen and make sense of what people tell us and show us. That is what good qualitative research offers us.
How Is This Book Organized?
This textbook is organized as a comprehensive introduction to the use of qualitative research methods. The first half covers general topics (e.g., approaches to qualitative research, ethics) and research design (necessary steps for building a successful qualitative research study). The second half reviews various data collection and data analysis techniques. Of course, building a successful qualitative research study requires some knowledge of data collection and data analysis so the chapters in the first half and the chapters in the second half should be read in conversation with each other. That said, each chapter can be read on its own for assistance with a particular narrow topic. In addition to the chapters, a helpful glossary can be found in the back of the book. Rummage around in the text as needed.
Chapter Descriptions
Chapter 2 provides an overview of the Research Design Process. How does one begin a study? What is an appropriate research question? How is the study to be done – with what methods ? Involving what people and sites? Although qualitative research studies can and often do change and develop over the course of data collection, it is important to have a good idea of what the aims and goals of your study are at the outset and a good plan of how to achieve those aims and goals. Chapter 2 provides a road map of the process.
Chapter 3 describes and explains various ways of knowing the (social) world. What is it possible for us to know about how other people think or why they behave the way they do? What does it mean to say something is a “fact” or that it is “well-known” and understood? Qualitative researchers are particularly interested in these questions because of the types of research questions we are interested in answering (the how questions rather than the how many questions of quantitative research). Qualitative researchers have adopted various epistemological approaches. Chapter 3 will explore these approaches, highlighting interpretivist approaches that acknowledge the subjective aspect of reality – in other words, reality and knowledge are not objective but rather influenced by (interpreted through) people.
Chapter 4 focuses on the practical matter of developing a research question and finding the right approach to data collection. In any given study (think of Cory Abramson’s study of aging, for example), there may be years of collected data, thousands of observations , hundreds of pages of notes to read and review and make sense of. If all you had was a general interest area (“aging”), it would be very difficult, nearly impossible, to make sense of all of that data. The research question provides a helpful lens to refine and clarify (and simplify) everything you find and collect. For that reason, it is important to pull out that lens (articulate the research question) before you get started. In the case of the aging study, Cory Abramson was interested in how inequalities affected understandings and responses to aging. It is for this reason he designed a study that would allow him to compare different groups of seniors (some middle-class, some poor). Inevitably, he saw much more in the three years in the field than what made it into his book (or dissertation), but he was able to narrow down the complexity of the social world to provide us with this rich account linked to the original research question. Developing a good research question is thus crucial to effective design and a successful outcome. Chapter 4 will provide pointers on how to do this. Chapter 4 also provides an overview of general approaches taken to doing qualitative research and various “traditions of inquiry.”
Chapter 5 explores sampling . After you have developed a research question and have a general idea of how you will collect data (Observations? Interviews?), how do you go about actually finding people and sites to study? Although there is no “correct number” of people to interview , the sample should follow the research question and research design. Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research involves nonprobability sampling. Chapter 5 explains why this is so and what qualities instead make a good sample for qualitative research.
Chapter 6 addresses the importance of reflexivity in qualitative research. Related to epistemological issues of how we know anything about the social world, qualitative researchers understand that we the researchers can never be truly neutral or outside the study we are conducting. As observers, we see things that make sense to us and may entirely miss what is either too obvious to note or too different to comprehend. As interviewers, as much as we would like to ask questions neutrally and remain in the background, interviews are a form of conversation, and the persons we interview are responding to us . Therefore, it is important to reflect upon our social positions and the knowledges and expectations we bring to our work and to work through any blind spots that we may have. Chapter 6 provides some examples of reflexivity in practice and exercises for thinking through one’s own biases.
Chapter 7 is a very important chapter and should not be overlooked. As a practical matter, it should also be read closely with chapters 6 and 8. Because qualitative researchers deal with people and the social world, it is imperative they develop and adhere to a strong ethical code for conducting research in a way that does not harm. There are legal requirements and guidelines for doing so (see chapter 8), but these requirements should not be considered synonymous with the ethical code required of us. Each researcher must constantly interrogate every aspect of their research, from research question to design to sample through analysis and presentation, to ensure that a minimum of harm (ideally, zero harm) is caused. Because each research project is unique, the standards of care for each study are unique. Part of being a professional researcher is carrying this code in one’s heart, being constantly attentive to what is required under particular circumstances. Chapter 7 provides various research scenarios and asks readers to weigh in on the suitability and appropriateness of the research. If done in a class setting, it will become obvious fairly quickly that there are often no absolutely correct answers, as different people find different aspects of the scenarios of greatest importance. Minimizing the harm in one area may require possible harm in another. Being attentive to all the ethical aspects of one’s research and making the best judgments one can, clearly and consciously, is an integral part of being a good researcher.
Chapter 8 , best to be read in conjunction with chapter 7, explains the role and importance of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) . Under federal guidelines, an IRB is an appropriately constituted group that has been formally designated to review and monitor research involving human subjects . Every institution that receives funding from the federal government has an IRB. IRBs have the authority to approve, require modifications to (to secure approval), or disapprove research. This group review serves an important role in the protection of the rights and welfare of human research subjects. Chapter 8 reviews the history of IRBs and the work they do but also argues that IRBs’ review of qualitative research is often both over-inclusive and under-inclusive. Some aspects of qualitative research are not well understood by IRBs, given that they were developed to prevent abuses in biomedical research. Thus, it is important not to rely on IRBs to identify all the potential ethical issues that emerge in our research (see chapter 7).
Chapter 9 provides help for getting started on formulating a research question based on gaps in the pre-existing literature. Research is conducted as part of a community, even if particular studies are done by single individuals (or small teams). What any of us finds and reports back becomes part of a much larger body of knowledge. Thus, it is important that we look at the larger body of knowledge before we actually start our bit to see how we can best contribute. When I first began interviewing working-class college students, there was only one other similar study I could find, and it hadn’t been published (it was a dissertation of students from poor backgrounds). But there had been a lot published by professors who had grown up working class and made it through college despite the odds. These accounts by “working-class academics” became an important inspiration for my study and helped me frame the questions I asked the students I interviewed. Chapter 9 will provide some pointers on how to search for relevant literature and how to use this to refine your research question.
Chapter 10 serves as a bridge between the two parts of the textbook, by introducing techniques of data collection. Qualitative research is often characterized by the form of data collection – for example, an ethnographic study is one that employs primarily observational data collection for the purpose of documenting and presenting a particular culture or ethnos. Techniques can be effectively combined, depending on the research question and the aims and goals of the study. Chapter 10 provides a general overview of all the various techniques and how they can be combined.
The second part of the textbook moves into the doing part of qualitative research once the research question has been articulated and the study designed. Chapters 11 through 17 cover various data collection techniques and approaches. Chapters 18 and 19 provide a very simple overview of basic data analysis. Chapter 20 covers communication of the data to various audiences, and in various formats.
Chapter 11 begins our overview of data collection techniques with a focus on interviewing , the true heart of qualitative research. This technique can serve as the primary and exclusive form of data collection, or it can be used to supplement other forms (observation, archival). An interview is distinct from a survey, where questions are asked in a specific order and often with a range of predetermined responses available. Interviews can be conversational and unstructured or, more conventionally, semistructured , where a general set of interview questions “guides” the conversation. Chapter 11 covers the basics of interviews: how to create interview guides, how many people to interview, where to conduct the interview, what to watch out for (how to prepare against things going wrong), and how to get the most out of your interviews.
Chapter 12 covers an important variant of interviewing, the focus group. Focus groups are semistructured interviews with a group of people moderated by a facilitator (the researcher or researcher’s assistant). Focus groups explicitly use group interaction to assist in the data collection. They are best used to collect data on a specific topic that is non-personal and shared among the group. For example, asking a group of college students about a common experience such as taking classes by remote delivery during the pandemic year of 2020. Chapter 12 covers the basics of focus groups: when to use them, how to create interview guides for them, and how to run them effectively.
Chapter 13 moves away from interviewing to the second major form of data collection unique to qualitative researchers – observation . Qualitative research that employs observation can best be understood as falling on a continuum of “fly on the wall” observation (e.g., observing how strangers interact in a doctor’s waiting room) to “participant” observation, where the researcher is also an active participant of the activity being observed. For example, an activist in the Black Lives Matter movement might want to study the movement, using her inside position to gain access to observe key meetings and interactions. Chapter 13 covers the basics of participant observation studies: advantages and disadvantages, gaining access, ethical concerns related to insider/outsider status and entanglement, and recording techniques.
Chapter 14 takes a closer look at “deep ethnography” – immersion in the field of a particularly long duration for the purpose of gaining a deeper understanding and appreciation of a particular culture or social world. Clifford Geertz called this “deep hanging out.” Whereas participant observation is often combined with semistructured interview techniques, deep ethnography’s commitment to “living the life” or experiencing the situation as it really is demands more conversational and natural interactions with people. These interactions and conversations may take place over months or even years. As can be expected, there are some costs to this technique, as well as some very large rewards when done competently. Chapter 14 provides some examples of deep ethnographies that will inspire some beginning researchers and intimidate others.
Chapter 15 moves in the opposite direction of deep ethnography, a technique that is the least positivist of all those discussed here, to mixed methods , a set of techniques that is arguably the most positivist . A mixed methods approach combines both qualitative data collection and quantitative data collection, commonly by combining a survey that is analyzed statistically (e.g., cross-tabs or regression analyses of large number probability samples) with semi-structured interviews. Although it is somewhat unconventional to discuss mixed methods in textbooks on qualitative research, I think it is important to recognize this often-employed approach here. There are several advantages and some disadvantages to taking this route. Chapter 16 will describe those advantages and disadvantages and provide some particular guidance on how to design a mixed methods study for maximum effectiveness.
Chapter 16 covers data collection that does not involve live human subjects at all – archival and historical research (chapter 17 will also cover data that does not involve interacting with human subjects). Sometimes people are unavailable to us, either because they do not wish to be interviewed or observed (as is the case with many “elites”) or because they are too far away, in both place and time. Fortunately, humans leave many traces and we can often answer questions we have by examining those traces. Special collections and archives can be goldmines for social science research. This chapter will explain how to access these places, for what purposes, and how to begin to make sense of what you find.
Chapter 17 covers another data collection area that does not involve face-to-face interaction with humans: content analysis . Although content analysis may be understood more properly as a data analysis technique, the term is often used for the entire approach, which will be the case here. Content analysis involves interpreting meaning from a body of text. This body of text might be something found in historical records (see chapter 16) or something collected by the researcher, as in the case of comment posts on a popular blog post. I once used the stories told by student loan debtors on the website studentloanjustice.org as the content I analyzed. Content analysis is particularly useful when attempting to define and understand prevalent stories or communication about a topic of interest. In other words, when we are less interested in what particular people (our defined sample) are doing or believing and more interested in what general narratives exist about a particular topic or issue. This chapter will explore different approaches to content analysis and provide helpful tips on how to collect data, how to turn that data into codes for analysis, and how to go about presenting what is found through analysis.
Where chapter 17 has pushed us towards data analysis, chapters 18 and 19 are all about what to do with the data collected, whether that data be in the form of interview transcripts or fieldnotes from observations. Chapter 18 introduces the basics of coding , the iterative process of assigning meaning to the data in order to both simplify and identify patterns. What is a code and how does it work? What are the different ways of coding data, and when should you use them? What is a codebook, and why do you need one? What does the process of data analysis look like?
Chapter 19 goes further into detail on codes and how to use them, particularly the later stages of coding in which our codes are refined, simplified, combined, and organized. These later rounds of coding are essential to getting the most out of the data we’ve collected. As students are often overwhelmed with the amount of data (a corpus of interview transcripts typically runs into the hundreds of pages; fieldnotes can easily top that), this chapter will also address time management and provide suggestions for dealing with chaos and reminders that feeling overwhelmed at the analysis stage is part of the process. By the end of the chapter, you should understand how “findings” are actually found.
The book concludes with a chapter dedicated to the effective presentation of data results. Chapter 20 covers the many ways that researchers communicate their studies to various audiences (academic, personal, political), what elements must be included in these various publications, and the hallmarks of excellent qualitative research that various audiences will be expecting. Because qualitative researchers are motivated by understanding and conveying meaning , effective communication is not only an essential skill but a fundamental facet of the entire research project. Ethnographers must be able to convey a certain sense of verisimilitude , the appearance of true reality. Those employing interviews must faithfully depict the key meanings of the people they interviewed in a way that rings true to those people, even if the end result surprises them. And all researchers must strive for clarity in their publications so that various audiences can understand what was found and why it is important.
The book concludes with a short chapter ( chapter 21 ) discussing the value of qualitative research. At the very end of this book, you will find a glossary of terms. I recommend you make frequent use of the glossary and add to each entry as you find examples. Although the entries are meant to be simple and clear, you may also want to paraphrase the definition—make it “make sense” to you, in other words. In addition to the standard reference list (all works cited here), you will find various recommendations for further reading at the end of many chapters. Some of these recommendations will be examples of excellent qualitative research, indicated with an asterisk (*) at the end of the entry. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words. A good example of qualitative research can teach you more about conducting research than any textbook can (this one included). I highly recommend you select one to three examples from these lists and read them along with the textbook.
A final note on the choice of examples – you will note that many of the examples used in the text come from research on college students. This is for two reasons. First, as most of my research falls in this area, I am most familiar with this literature and have contacts with those who do research here and can call upon them to share their stories with you. Second, and more importantly, my hope is that this textbook reaches a wide audience of beginning researchers who study widely and deeply across the range of what can be known about the social world (from marine resources management to public policy to nursing to political science to sexuality studies and beyond). It is sometimes difficult to find examples that speak to all those research interests, however. A focus on college students is something that all readers can understand and, hopefully, appreciate, as we are all now or have been at some point a college student.
Recommended Reading: Other Qualitative Research Textbooks
I’ve included a brief list of some of my favorite qualitative research textbooks and guidebooks if you need more than what you will find in this introductory text. For each, I’ve also indicated if these are for “beginning” or “advanced” (graduate-level) readers. Many of these books have several editions that do not significantly vary; the edition recommended is merely the edition I have used in teaching and to whose page numbers any specific references made in the text agree.
Barbour, Rosaline. 2014. Introducing Qualitative Research: A Student’s Guide. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A good introduction to qualitative research, with abundant examples (often from the discipline of health care) and clear definitions. Includes quick summaries at the ends of each chapter. However, some US students might find the British context distracting and can be a bit advanced in some places. Beginning .
Bloomberg, Linda Dale, and Marie F. Volpe. 2012. Completing Your Qualitative Dissertation . 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Specifically designed to guide graduate students through the research process. Advanced .
Creswell, John W., and Cheryl Poth. 2018 Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing among Five Traditions . 4th ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a classic and one of the go-to books I used myself as a graduate student. One of the best things about this text is its clear presentation of five distinct traditions in qualitative research. Despite the title, this reasonably sized book is about more than research design, including both data analysis and how to write about qualitative research. Advanced .
Lareau, Annette. 2021. Listening to People: A Practical Guide to Interviewing, Participant Observation, Data Analysis, and Writing It All Up . Chicago: University of Chicago Press. A readable and personal account of conducting qualitative research by an eminent sociologist, with a heavy emphasis on the kinds of participant-observation research conducted by the author. Despite its reader-friendliness, this is really a book targeted to graduate students learning the craft. Advanced .
Lune, Howard, and Bruce L. Berg. 2018. 9th edition. Qualitative Research Methods for the Social Sciences. Pearson . Although a good introduction to qualitative methods, the authors favor symbolic interactionist and dramaturgical approaches, which limits the appeal primarily to sociologists. Beginning .
Marshall, Catherine, and Gretchen B. Rossman. 2016. 6th edition. Designing Qualitative Research. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. Very readable and accessible guide to research design by two educational scholars. Although the presentation is sometimes fairly dry, personal vignettes and illustrations enliven the text. Beginning .
Maxwell, Joseph A. 2013. Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach . 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced .
Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002. Qualitative Research and Evaluation Methods . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. This is a comprehensive text that served as my “go-to” reference when I was a graduate student. It is particularly helpful for those involved in program evaluation and other forms of evaluation studies and uses examples from a wide range of disciplines. Advanced .
Rubin, Ashley T. 2021. Rocking Qualitative Social Science: An Irreverent Guide to Rigorous Research. Stanford : Stanford University Press. A delightful and personal read. Rubin uses rock climbing as an extended metaphor for learning how to conduct qualitative research. A bit slanted toward ethnographic and archival methods of data collection, with frequent examples from her own studies in criminology. Beginning .
Weis, Lois, and Michelle Fine. 2000. Speed Bumps: A Student-Friendly Guide to Qualitative Research . New York: Teachers College Press. Readable and accessibly written in a quasi-conversational style. Particularly strong in its discussion of ethical issues throughout the qualitative research process. Not comprehensive, however, and very much tied to ethnographic research. Although designed for graduate students, this is a recommended read for students of all levels. Beginning .
Patton’s Ten Suggestions for Doing Qualitative Research
The following ten suggestions were made by Michael Quinn Patton in his massive textbooks Qualitative Research and Evaluations Methods . This book is highly recommended for those of you who want more than an introduction to qualitative methods. It is the book I relied on heavily when I was a graduate student, although it is much easier to “dip into” when necessary than to read through as a whole. Patton is asked for “just one bit of advice” for a graduate student considering using qualitative research methods for their dissertation. Here are his top ten responses, in short form, heavily paraphrased, and with additional comments and emphases from me:
- Make sure that a qualitative approach fits the research question. The following are the kinds of questions that call out for qualitative methods or where qualitative methods are particularly appropriate: questions about people’s experiences or how they make sense of those experiences; studying a person in their natural environment; researching a phenomenon so unknown that it would be impossible to study it with standardized instruments or other forms of quantitative data collection.
- Study qualitative research by going to the original sources for the design and analysis appropriate to the particular approach you want to take (e.g., read Glaser and Straus if you are using grounded theory )
- Find a dissertation adviser who understands or at least who will support your use of qualitative research methods. You are asking for trouble if your entire committee is populated by quantitative researchers, even if they are all very knowledgeable about the subject or focus of your study (maybe even more so if they are!)
- Really work on design. Doing qualitative research effectively takes a lot of planning. Even if things are more flexible than in quantitative research, a good design is absolutely essential when starting out.
- Practice data collection techniques, particularly interviewing and observing. There is definitely a set of learned skills here! Do not expect your first interview to be perfect. You will continue to grow as a researcher the more interviews you conduct, and you will probably come to understand yourself a bit more in the process, too. This is not easy, despite what others who don’t work with qualitative methods may assume (and tell you!)
- Have a plan for analysis before you begin data collection. This is often a requirement in IRB protocols , although you can get away with writing something fairly simple. And even if you are taking an approach, such as grounded theory, that pushes you to remain fairly open-minded during the data collection process, you still want to know what you will be doing with all the data collected – creating a codebook? Writing analytical memos? Comparing cases? Having a plan in hand will also help prevent you from collecting too much extraneous data.
- Be prepared to confront controversies both within the qualitative research community and between qualitative research and quantitative research. Don’t be naïve about this – qualitative research, particularly some approaches, will be derided by many more “positivist” researchers and audiences. For example, is an “n” of 1 really sufficient? Yes! But not everyone will agree.
- Do not make the mistake of using qualitative research methods because someone told you it was easier, or because you are intimidated by the math required of statistical analyses. Qualitative research is difficult in its own way (and many would claim much more time-consuming than quantitative research). Do it because you are convinced it is right for your goals, aims, and research questions.
- Find a good support network. This could be a research mentor, or it could be a group of friends or colleagues who are also using qualitative research, or it could be just someone who will listen to you work through all of the issues you will confront out in the field and during the writing process. Even though qualitative research often involves human subjects, it can be pretty lonely. A lot of times you will feel like you are working without a net. You have to create one for yourself. Take care of yourself.
- And, finally, in the words of Patton, “Prepare to be changed. Looking deeply at other people’s lives will force you to look deeply at yourself.”
- We will actually spend an entire chapter ( chapter 3 ) looking at this question in much more detail! ↵
- Note that this might have been news to Europeans at the time, but many other societies around the world had also come to this conclusion through observation. There is often a tendency to equate “the scientific revolution” with the European world in which it took place, but this is somewhat misleading. ↵
- Historians are a special case here. Historians have scrupulously and rigorously investigated the social world, but not for the purpose of understanding general laws about how things work, which is the point of scientific empirical research. History is often referred to as an idiographic field of study, meaning that it studies things that happened or are happening in themselves and not for general observations or conclusions. ↵
- Don’t worry, we’ll spend more time later in this book unpacking the meaning of ethnography and other terms that are important here. Note the available glossary ↵
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
In contrast to methodology, methods are more simply the practices and tools used to collect and analyze data. Examples of common methods in qualitative research are interviews , observations , and documentary analysis . One’s methodology should connect to one’s choice of methods, of course, but they are distinguishable terms. See also methodology .
A proposed explanation for an observation, phenomenon, or scientific problem that can be tested by further investigation. The positing of a hypothesis is often the first step in quantitative research but not in qualitative research. Even when qualitative researchers offer possible explanations in advance of conducting research, they will tend to not use the word “hypothesis” as it conjures up the kind of positivist research they are not conducting.
The foundational question to be addressed by the research study. This will form the anchor of the research design, collection, and analysis. Note that in qualitative research, the research question may, and probably will, alter or develop during the course of the research.
An approach to research that collects and analyzes numerical data for the purpose of finding patterns and averages, making predictions, testing causal relationships, and generalizing results to wider populations. Contrast with qualitative research .
Data collection that takes place in real-world settings, referred to as “the field;” a key component of much Grounded Theory and ethnographic research. Patton ( 2002 ) calls fieldwork “the central activity of qualitative inquiry” where “‘going into the field’ means having direct and personal contact with people under study in their own environments – getting close to people and situations being studied to personally understand the realities of minutiae of daily life” (48).
The people who are the subjects of a qualitative study. In interview-based studies, they may be the respondents to the interviewer; for purposes of IRBs, they are often referred to as the human subjects of the research.
The branch of philosophy concerned with knowledge. For researchers, it is important to recognize and adopt one of the many distinguishing epistemological perspectives as part of our understanding of what questions research can address or fully answer. See, e.g., constructivism , subjectivism, and objectivism .
An approach that refutes the possibility of neutrality in social science research. All research is “guided by a set of beliefs and feelings about the world and how it should be understood and studied” (Denzin and Lincoln 2005: 13). In contrast to positivism , interpretivism recognizes the social constructedness of reality, and researchers adopting this approach focus on capturing interpretations and understandings people have about the world rather than “the world” as it is (which is a chimera).
The cluster of data-collection tools and techniques that involve observing interactions between people, the behaviors, and practices of individuals (sometimes in contrast to what they say about how they act and behave), and cultures in context. Observational methods are the key tools employed by ethnographers and Grounded Theory .
Research based on data collected and analyzed by the research (in contrast to secondary “library” research).
The process of selecting people or other units of analysis to represent a larger population. In quantitative research, this representation is taken quite literally, as statistically representative. In qualitative research, in contrast, sample selection is often made based on potential to generate insight about a particular topic or phenomenon.
A method of data collection in which the researcher asks the participant questions; the answers to these questions are often recorded and transcribed verbatim. There are many different kinds of interviews - see also semistructured interview , structured interview , and unstructured interview .
The specific group of individuals that you will collect data from. Contrast population.
The practice of being conscious of and reflective upon one’s own social location and presence when conducting research. Because qualitative research often requires interaction with live humans, failing to take into account how one’s presence and prior expectations and social location affect the data collected and how analyzed may limit the reliability of the findings. This remains true even when dealing with historical archives and other content. Who we are matters when asking questions about how people experience the world because we, too, are a part of that world.
The science and practice of right conduct; in research, it is also the delineation of moral obligations towards research participants, communities to which we belong, and communities in which we conduct our research.
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Research, according to US federal guidelines, that involves “a living individual about whom an investigator (whether professional or student) conducting research: (1) Obtains information or biospecimens through intervention or interaction with the individual, and uses, studies, or analyzes the information or biospecimens; or (2) Obtains, uses, studies, analyzes, or generates identifiable private information or identifiable biospecimens.”
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A form of interview that follows a standard guide of questions asked, although the order of the questions may change to match the particular needs of each individual interview subject, and probing “follow-up” questions are often added during the course of the interview. The semi-structured interview is the primary form of interviewing used by qualitative researchers in the social sciences. It is sometimes referred to as an “in-depth” interview. See also interview and interview guide .
A method of observational data collection taking place in a natural setting; a form of fieldwork . The term encompasses a continuum of relative participation by the researcher (from full participant to “fly-on-the-wall” observer). This is also sometimes referred to as ethnography , although the latter is characterized by a greater focus on the culture under observation.
A research design that employs both quantitative and qualitative methods, as in the case of a survey supplemented by interviews.
An epistemological perspective that posits the existence of reality through sensory experience similar to empiricism but goes further in denying any non-sensory basis of thought or consciousness. In the social sciences, the term has roots in the proto-sociologist August Comte, who believed he could discern “laws” of society similar to the laws of natural science (e.g., gravity). The term has come to mean the kinds of measurable and verifiable science conducted by quantitative researchers and is thus used pejoratively by some qualitative researchers interested in interpretation, consciousness, and human understanding. Calling someone a “positivist” is often intended as an insult. See also empiricism and objectivism.
A place or collection containing records, documents, or other materials of historical interest; most universities have an archive of material related to the university’s history, as well as other “special collections” that may be of interest to members of the community.
A method of both data collection and data analysis in which a given content (textual, visual, graphic) is examined systematically and rigorously to identify meanings, themes, patterns and assumptions. Qualitative content analysis (QCA) is concerned with gathering and interpreting an existing body of material.
A word or short phrase that symbolically assigns a summative, salient, essence-capturing, and/or evocative attribute for a portion of language-based or visual data (Saldaña 2021:5).
Usually a verbatim written record of an interview or focus group discussion.
The primary form of data for fieldwork , participant observation , and ethnography . These notes, taken by the researcher either during the course of fieldwork or at day’s end, should include as many details as possible on what was observed and what was said. They should include clear identifiers of date, time, setting, and names (or identifying characteristics) of participants.
The process of labeling and organizing qualitative data to identify different themes and the relationships between them; a way of simplifying data to allow better management and retrieval of key themes and illustrative passages. See coding frame and codebook.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
A detailed description of any proposed research that involves human subjects for review by IRB. The protocol serves as the recipe for the conduct of the research activity. It includes the scientific rationale to justify the conduct of the study, the information necessary to conduct the study, the plan for managing and analyzing the data, and a discussion of the research ethical issues relevant to the research. Protocols for qualitative research often include interview guides, all documents related to recruitment, informed consent forms, very clear guidelines on the safekeeping of materials collected, and plans for de-identifying transcripts or other data that include personal identifying information.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
What is Qualitative Research Design? Definition, Types, Methods and Best Practices
By Nick Jain
Published on: July 7, 2023
Table of Contents
What is Qualitative Research Design?
Types of qualitative research design, qualitative research design methods, qualitative research design process: 9 key steps, top 12 best practices for qualitative research design.
Qualitative research design is defined as a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding complex phenomena and the meanings attributed to them by individuals or groups. It is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, anthropology, and other fields where subjective experiences and interpretations are of interest.
Qualitative research is concerned with capturing the richness and depth of human experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. It aims to go beyond simple statistical analysis and uncover insights that quantitative research may not be able to capture.
Qualitative research design typically involves gathering data through methods such as interviews, observations, focus groups , and analysis of documents or artifacts. These methods allow researchers to collect detailed, descriptive information about participants’ perspectives, experiences, and contexts.
Key characteristics of qualitative research design include:
- Exploratory nature: Qualitative research often begins with an open-ended approach to allow for the discovery of new insights and patterns.
- Contextual understanding: It emphasizes understanding phenomena within their social, cultural, and historical contexts, as these factors shape individuals’ experiences.
- Subjectivity and reflexivity: Qualitative researchers acknowledge the influence of their own perspectives and biases and often engage in reflexivity to critically examine their role in shaping the research process and outcomes.
- Small and purposive sampling: Rather than aiming for large representative samples, qualitative research often involves selecting participants who can provide rich and diverse information relevant to the research question.
- In-depth data collection: Researchers spend considerable time with participants, collecting detailed and nuanced data, often through open-ended interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Iterative data analysis: Qualitative analysis involves coding, categorizing, and interpreting data to identify patterns, themes, and relationships. This process is often iterative, with researchers revisiting and refining their analysis as new insights emerge.
There are several types of qualitative research designs, each with its own specific characteristics and purposes. Here are some common types:
- Phenomenological Research
This design aims to understand the essence and meaning of human experiences related to a particular phenomenon. Researchers explore participants’ subjective experiences through in-depth interviews or observations to uncover the underlying structures and patterns of their lived experiences.
- Ethnographic Research
Ethnography involves studying and understanding the culture, beliefs, practices, and social interactions of a specific group or community. Researchers immerse themselves in the participants’ natural environment for an extended period, often conducting participant observation, interviews, and document analysis to gain an in-depth understanding of the culture.
- Grounded Theory
Grounded theory is an approach where researchers aim to develop theories or conceptual frameworks grounded in the data. Through constant comparison and analysis of collected data, researchers identify categories, concepts, and relationships to generate a theory that explains the phenomenon under investigation.
Case study research involves an in-depth examination of a single individual, group, organization, or specific context. Researchers collect multiple sources of data such as interviews, observations, and documents to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and to draw insights that may have broader implications.
- Narrative Research
Narrative research focuses on understanding and analyzing the stories and personal narratives shared by individuals. Researchers examine the structure, content, and context of these narratives to gain insights into how individuals construct meaning and make sense of their experiences.
- Participatory Action Research (PAR)
PAR is a collaborative approach that involves researchers working closely with participants or communities to identify and address social issues or problems. The aim is to empower participants and generate actionable knowledge through a cyclical process of reflection, action, and change.
- Constructivist/Interpretive Research
This design emphasizes the importance of understanding multiple subjective realities and interpretations of social phenomena. Researchers explore the different meanings and perspectives attributed to a phenomenon, often using interviews, focus groups , or textual analysis to uncover the complexities of individuals’ interpretations.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Market Research?
Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or new to the field, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the tools and techniques needed to conduct impactful qualitative research.
- Interviews: Gain In-Depth Insights Discover the nuances of conducting interviews, from structured to unstructured approaches. Learn how to ask the right questions, build rapport with participants, and extract valuable insights into their experiences, beliefs, and attitudes.
- Observations: Decode Human Behavior Explore the world of observational research and learn how to systematically observe and record human behavior in natural or controlled settings. From participant to non-participant observation, uncover the secrets to decoding social interactions and contextual factors.
- Focus Groups: Harness Collective Wisdom Harness the power of group dynamics with focus groups. Delve into the process of facilitating discussions, eliciting diverse perspectives, and uncovering shared insights that drive actionable outcomes.
- Case Studies: Unravel Complex Phenomena Embark on an in-depth exploration of single cases to unravel complex phenomena. Dive deep into the world of case studies, gathering multiple data sources to provide a comprehensive understanding within real-world contexts.
- Ethnography: Immerse Yourself in Culture Immerse yourself in the cultural context of your research subjects with ethnographic methods. From participant observation to in-depth interviews, learn how to capture the essence of cultural practices and social interactions.
- Visual Methods: Enhance Understanding Elevate your research with visual methods, from photography to video recordings. Explore how visual data can complement traditional methods, providing additional insights and documentation of participants’ experiences.
- Textual Analysis: Uncover Hidden Patterns Master the art of textual analysis and uncover hidden patterns and meanings within written or verbal data. From coding techniques to thematic analysis, unlock the secrets buried within the text.
Armed with a newfound understanding of qualitative research methods, you’re ready to embark on a journey of discovery. Whether you’re exploring new territories or refining existing practices, our guide will empower you to navigate the complexities of human behavior and unlock insights that drive meaningful change.
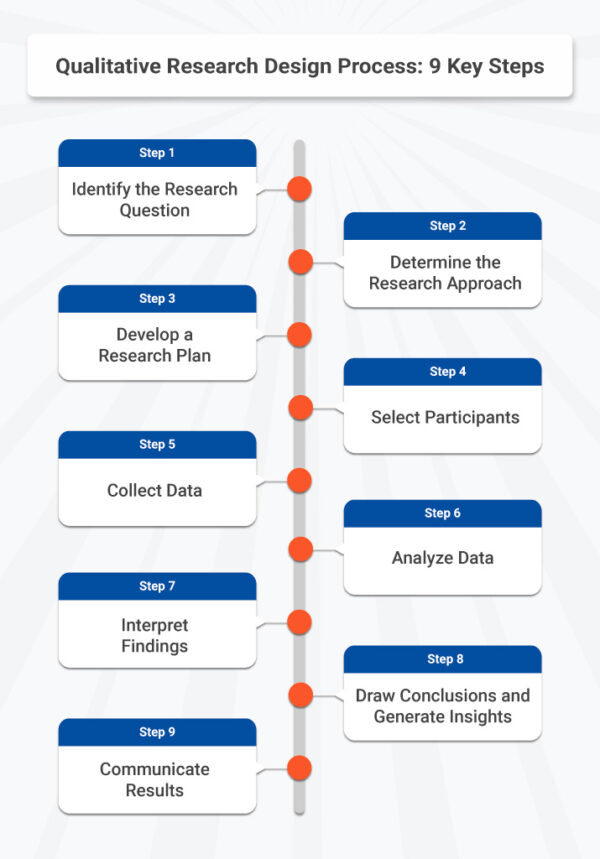
The qualitative research design process typically involves several key steps. While the specific details may vary depending on the research context and methodology, here is a general overview of the steps involved:
1. Identify the Research Question
Start by providing a concise and unambiguous statement that outlines your research question or objective. What do you want to explore or understand through your qualitative research ? Ensure that the question is specific, focused, and relevant to your field of study.
2. Determine the Research Approach
Select the most appropriate qualitative research approach or design based on your research question and objectives. Consider the different types of qualitative research designs (such as phenomenology, ethnography, and grounded theory) and choose one that aligns with your research goals.
3. Develop a Research Plan
Create a research plan that outlines the steps, procedures, and timeline for your study. Identify the target population or participants, data collection methods, and data analysis techniques you intend to use.
4. Select Participants
Determine the criteria for selecting participants who can provide valuable insights related to your research question. Consider factors such as demographics, expertise, experiences, or specific characteristics relevant to your study. Choose a sampling method (e.g., purposive sampling, snowball sampling) to recruit participants.
5. Collect Data
Conduct data collection using the chosen qualitative methods . This may involve conducting interviews, observations, focus groups , or document analysis. To maintain ethical standards, it is crucial to adhere to ethical guidelines and ensure that participants provide informed consent. Consider audio or video recording to ensure accurate data capture.
6. Analyze Data
Engage in data analysis to identify patterns, themes, and insights from the collected data. This may involve coding, categorizing, and organizing the data using qualitative analysis software or manual techniques. Use iterative and reflexive processes to refine and deepen your analysis.
7. Interpret Findings
Interpret the findings based on the analysis of your data. Explore the emerging themes, relationships, and meanings that have emerged from the data. Consider how the findings relate to your research question and existing literature in your field.
8. Draw Conclusions and Generate Insights
Summarize the key findings of your study and draw conclusions based on your interpretation of the data. Reflect on the implications and significance of your findings for theory, practice, or future research. Identify any limitations or potential biases in your study.
9. Communicate Results
Prepare a report or manuscript to communicate your research findings. Present your qualitative data, analysis, interpretations, and conclusions in a clear and organized manner. Consider sharing your findings through presentations, publications, or other appropriate dissemination channels.
Learn more: What is Quantitative Market Research?
When conducting qualitative research , it is important to follow best practices to ensure the rigor, validity, and trustworthiness of your study. Here are some top best practices for qualitative research design:
1. Clearly Define Research Questions: Begin by clearly defining your research questions or objectives. Make sure they are specific, focused, and aligned with the purpose of your study. Clearly articulating your research questions will guide your entire research design.
2. Use a Theoretical Framework: Situate your research within a relevant theoretical framework or existing body of literature. This provides a foundation for understanding the context and helps you generate insights that contribute to theory development or refinement.
3. Select an Appropriate Research Design: Choose a qualitative research design that best suits your research questions and objectives. Consider the different approaches available, such as phenomenology, ethnography, or grounded theory, and select the one that aligns with your research goals.
4. Use Rigorous Sampling Techniques: Select participants or cases using rigorous sampling techniques. Consider purposeful sampling, where participants are chosen based on specific criteria relevant to your research question. Aim for diversity and seek saturation, where data collection reaches a point of redundancy and further data collection does not yield significant new insights.
5. Establish Trustworthiness and Credibility: Enhance the trustworthiness of your research findings by employing strategies such as member checking, where participants review and validate your interpretations, or peer debriefing, where colleagues provide feedback on your analysis and interpretations. Triangulation, or the use of multiple data sources or methods, can also strengthen the credibility of your findings.
6. Maintain Reflexivity: Be aware of your own biases, assumptions, and preconceptions throughout the research process. Engage in reflexivity by regularly reflecting on how your own perspectives may influence data collection, analysis, and interpretation. Documenting and acknowledging your own role and potential impact on the research process is essential.
7. Plan and Conduct Ethical Research: Adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants. Ensure participant confidentiality, anonymity, and privacy. Seek ethics approval from relevant institutional review boards or ethics committees.
8. Use Clear and Consistent Data Collection Methods: Follow established protocols and guidelines for data collection methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis. Develop interview guides or observation protocols to ensure consistency and standardization across participants or cases.
9. Maintain Detailed Documentation: Keep comprehensive records of your research process, including field notes, transcripts, or analysis memos. Thorough documentation allows for transparency, traceability, and the potential for independent audit or replication of your study.
10. Engage in Iterative Data Analysis: Conduct data analysis iteratively throughout the research process. Use coding techniques, thematic analysis, or other appropriate qualitative research methods to identify patterns, themes, and relationships in the data. Allow for revisions, refinements, and further exploration of emerging insights.
11. Ensure Researcher Independence and Objectivity: Be mindful of your own biases and maintain researcher independence throughout the research process. Strive for objectivity by critically examining your interpretations, seeking alternative explanations, and engaging in peer debriefing or external review.
12. Communicate Findings Effectively: Clearly communicate your research findings, including the methodology, data analysis, interpretations, and limitations. Provide rich and detailed descriptions to support your arguments and conclusions. Consider presenting findings in a way that resonates with your intended audience, whether it be academic researchers, practitioners, or policymakers.
Learn more: What is Qualitative Observation?
Enhance Your Research
Collect feedback and conduct research with IdeaScale’s award-winning software
Elevate Research And Feedback With Your IdeaScale Community!
IdeaScale is an innovation management solution that inspires people to take action on their ideas. Your community’s ideas can change lives, your business and the world. Connect to the ideas that matter and start co-creating the future.
Copyright © 2024 IdeaScale
Privacy Overview
- Top Courses
- Online Degrees
- Find your New Career
- Join for Free

Qualitative Research Design
This course is part of Qualitative Research Design and Methods for Public Health Specialization
Taught in English
Some content may not be translated

Instructor: Karen Andes, PhD
Financial aid available
13,529 already enrolled

(105 reviews)
What you'll learn
Design a qualitative research project to respond to specific public health problems/questions.
Design strategies and instruments for qualitative data collection linked to study objectives and appropriate for the population of interest.
Address ethical concerns in qualitative research design and implementation.
Details to know

Add to your LinkedIn profile
See how employees at top companies are mastering in-demand skills

Build your subject-matter expertise
- Learn new concepts from industry experts
- Gain a foundational understanding of a subject or tool
- Develop job-relevant skills with hands-on projects
- Earn a shareable career certificate

Earn a career certificate
Add this credential to your LinkedIn profile, resume, or CV
Share it on social media and in your performance review

There are 6 modules in this course
This course introduces qualitative research, compares and contrasts qualitative and quantitative research approaches, and provides an overview of qualitative methods for data collection. It outlines a step-by-step approach to qualitative research design that begins by identifying a public health topic of interest, works to hone in on a specific research problem, and then specifies research questions, objectives, and specific aims. The course emphasizes the iterative nature of research design in qualitative inquiry and highlights the importance of specifying a population of interest, an appropriate sampling strategy, and potential approaches to recruitment. It introduces the relationship between these considerations and key concepts such as saturation and transferability in qualitative research. Finally, the course considers ethical concerns specific to qualitative research and potential solutions. Learners of this course will not only be able to put what they learn into practice, but they'll also develop a portfolio of qualitative research materials for career advancement.
Introduction to Qualitative Research
In this first week, you'll get the chance to explore characteristics and approaches of both qualitative and quantitative research, understand their differences, and acknowledge how both are complementary.
What's included
6 videos 4 readings 1 quiz 1 peer review
6 videos • Total 20 minutes
- Welcome to the Course! • 2 minutes • Preview module
- What Is Research? • 2 minutes
- What Is Qualitative Research? • 3 minutes
- How Is Qualitative Different From Quantitative? • 4 minutes
- Five Basic Approaches to Qualitative Research • 4 minutes
- Qualitative and Quantitative As Complementary Methods • 3 minutes
4 readings • Total 145 minutes
- Course Outline and Grading Information • 5 minutes
- Introduction to Qualitative Research • 20 minutes
- Qualitative Inquiry • 90 minutes
- Mixed Methods Design • 30 minutes
1 quiz • Total 20 minutes
- Practice • 20 minutes
1 peer review • Total 60 minutes
- Week 1: Comparing Quantitative and Qualitative Studies • 60 minutes
Qualitative Methods
This week, we'll look at two types of data that can be collected and dive into the three main data collection methods used in qualitative studies. Finally, we'll wrap up by discussing the concept of saturation and consider the lingering question, "how much data is enough?"
6 videos 2 readings 1 quiz 1 peer review
6 videos • Total 15 minutes
- A Look at This Week • 2 minutes • Preview module
- Types of Data • 1 minute
- Observation • 4 minutes
- Interviews • 3 minutes
- Focus Group Discussions • 2 minutes
- Saturation: How Much Data to Collect? • 2 minutes
2 readings • Total 135 minutes
- Data Collection • 90 minutes
- Saturation Point • 45 minutes
- Week 2: Exploring Qualitative Methods • 60 minutes
Objective-Driven Design
In our third week, we'll discuss how to develop a problem statement from a topic of interest, craft research questions and aims, and discuss how this process all relates to objective-driven design.
5 videos 2 readings 1 quiz 1 peer review
5 videos • Total 21 minutes
- A Look at This Week • 3 minutes • Preview module
- What Is Objective-Driven Design? • 1 minute
- Uncovering a Problem • 6 minutes
- Developing & Refining a Problem Statement • 3 minutes
- Developing Research Questions & Specific Aims • 6 minutes
2 readings • Total 75 minutes
- Setting Up a Qualitative Project • 30 minutes
- Resources for Developing Your Research Problem & Question • 45 minutes
- Week 3: Identifying Your Research Problem • 60 minutes
Methods, Population, Sampling, & Recruitment
For our fourth week, we'll take a look at how to choose data collection methods that are best suited for your aims, explore the various sampling and recruitment strategies to select participants, and finally consider how research design is an iterative process.
- A Look at This Week • 1 minute • Preview module
- Aligning Methods with Aims • 2 minutes
- Identifying a Setting and Honing in on a Population • 2 minutes
- Sampling Strategies • 6 minutes
- Recruitment Strategies • 2 minutes
- Iterative Design • 0 minutes
2 readings • Total 95 minutes
- Resources for Selecting Appropriate Methods • 35 minutes
- Resources for Identifying Your Strategies • 60 minutes
1 quiz • Total 30 minutes
- Practice • 30 minutes
- Week 4: Identifying Your Methods, Population, Sampling, & Recruitment Strategies • 60 minutes
Research Ethics
Our fifth week is all about ethical considerations in qualitative research. As researchers, we need to be aware and take precautions to ensure our work with human subjects is never exploitative, deceitful, or harmful. We'll go over the key ethical principles to keep in mind when beginning a qualitative study.
4 videos 3 readings 1 quiz 1 peer review 1 discussion prompt
4 videos • Total 12 minutes
- Overview of Research Ethics • 4 minutes
- Key Issues and Benefits of Qualitative Research • 5 minutes
- Strategies for IRBs and Ethics Committees • 1 minute
3 readings • Total 130 minutes
- CITI Certification for Human Subjects Research • 10 minutes
- Studies with Questionable Ethics • 30 minutes
- Resources for Ethics in Qualitative Research • 90 minutes
- Week 5: Considering Ethics in Research • 60 minutes
1 discussion prompt • Total 10 minutes
- Ethics Around the World • 10 minutes
Course Project and Design Examples
In this final week, you'll combine all items of your research design for a final submission. We'll also review real cases of graduates in the MPH program to see the different approaches that can be taken.
5 videos 2 readings 1 peer review
5 videos • Total 47 minutes
- Elements of Research Design: An Example (from Tamar Goldenberg's MPH Thesis Research) • 5 minutes
- Candace Girod: Menstrual Hygiene Management at Schools in Nairobi, Kenya • 13 minutes
- Wendy Avila: Exclusive Breast-Feeding among Women in Managua, Nicaragua • 15 minutes
- Jasmine Kelly: Maternal & Child Nutrition in Rural Tanzania • 11 minutes
2 readings • Total 60 minutes
- Interview Series • 30 minutes
- Preparing Your Research Design • 30 minutes
- Week 6: Your Qualitative Research Design • 60 minutes
Instructor ratings
We asked all learners to give feedback on our instructors based on the quality of their teaching style.

Emory University, located in Atlanta, Georgia, is one of the world's leading research universities. Its mission is to create, preserve, teach and apply knowledge in the service of humanity.
Recommended if you're interested in Health Informatics

Emory University
Qualitative Data Collection Methods

University of Michigan

Translating Research to Communities

Qualitative Data Analysis with MAXQDA Software
Qualitative Research Design and Methods for Public Health
Specialization
Why people choose Coursera for their career

Learner reviews
Showing 3 of 105
105 reviews
Reviewed on Oct 2, 2023
It was really a difficult nut to crack but a very useful and descriptive course for those people who wants to do research
Reviewed on Feb 4, 2021
highly productive and a good source of learning. Thank you very much for organizing this professional platform for learners of enhancing their skills and knowledge.
Reviewed on Jul 15, 2021
Excellent Course. Improved my understanding of Qualitative Research Design through actually doing it for my research.
New to Health Informatics? Start here.

Open new doors with Coursera Plus
Unlimited access to 7,000+ world-class courses, hands-on projects, and job-ready certificate programs - all included in your subscription
Advance your career with an online degree
Earn a degree from world-class universities - 100% online
Join over 3,400 global companies that choose Coursera for Business
Upskill your employees to excel in the digital economy
Frequently asked questions
When will i have access to the lectures and assignments.
Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the Certificate experience, during or after your audit. If you don't see the audit option:
The course may not offer an audit option. You can try a Free Trial instead, or apply for Financial Aid.
The course may offer 'Full Course, No Certificate' instead. This option lets you see all course materials, submit required assessments, and get a final grade. This also means that you will not be able to purchase a Certificate experience.
What will I get if I subscribe to this Specialization?
When you enroll in the course, you get access to all of the courses in the Specialization, and you earn a certificate when you complete the work. Your electronic Certificate will be added to your Accomplishments page - from there, you can print your Certificate or add it to your LinkedIn profile. If you only want to read and view the course content, you can audit the course for free.
What is the refund policy?
If you subscribed, you get a 7-day free trial during which you can cancel at no penalty. After that, we don’t give refunds, but you can cancel your subscription at any time. See our full refund policy Opens in a new tab .
Is financial aid available?
Yes. In select learning programs, you can apply for financial aid or a scholarship if you can’t afford the enrollment fee. If fin aid or scholarship is available for your learning program selection, you’ll find a link to apply on the description page.
More questions

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.4 Types of qualitative research designs
Learning objectives.
- Define focus groups and outline how they differ from one-on-one interviews
- Describe how to determine the best size for focus groups
- Identify the important considerations in focus group composition
- Discuss how to moderate focus groups
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of focus group methodology
- Describe case study research, ethnography, and phenomenology.
There are various types of approaches to qualitative research. This chapter presents information about focus groups, which are often used in social work research. It also introduces case studies, ethnography, and phenomenology.
Focus Groups
Focus groups resemble qualitative interviews in that a researcher may prepare a guide in advance and interact with participants by asking them questions. But anyone who has conducted both one-on-one interviews and focus groups knows that each is unique. In an interview, usually one member (the research participant) is most active while the other (the researcher) plays the role of listener, conversation guider, and question-asker. Focus groups , on the other hand, are planned discussions designed to elicit group interaction and “obtain perceptions on a defined area of interest in a permissive, nonthreatening environment” (Krueger & Casey, 2000, p. 5). In focus groups, the researcher play a different role than in a one-on-one interview. The researcher’s aim is to get participants talking to each other, to observe interactions among participants, and moderate the discussion.

There are numerous examples of focus group research. In their 2008 study, for example, Amy Slater and Marika Tiggemann (2010) conducted six focus groups with 49 adolescent girls between the ages of 13 and 15 to learn more about girls’ attitudes towards’ participation in sports. In order to get focus group participants to speak with one another rather than with the group facilitator, the focus group interview guide contained just two questions: “Can you tell me some of the reasons that girls stop playing sports or other physical activities?” and “Why do you think girls don’t play as much sport/physical activity as boys?” In another focus group study, Virpi Ylanne and Angie Williams (2009) held nine focus group sessions with adults of different ages to gauge their perceptions of how older characters are represented in television commercials. Among other considerations, the researchers were interested in discovering how focus group participants position themselves and others in terms of age stereotypes and identities during the group discussion. In both examples, the researchers’ core interest in group interaction could not have been assessed had interviews been conducted on a one-on-one basis, making the focus group method an ideal choice.
Who should be in your focus group?
In some ways, focus groups require more planning than other qualitative methods of data collection, such as one-on-one interviews in which a researcher may be better able to the dialogue. Researchers must take care to form focus groups with members who will want to interact with one another and to control the timing of the event so that participants are not asked nor expected to stay for a longer time than they’ve agreed to participate. The researcher should also be prepared to inform focus group participants of their responsibility to maintain the confidentiality of what is said in the group. But while the researcher can and should encourage all focus group members to maintain confidentiality, she should also clarify to participants that the unique nature of the group setting prevents her from being able to promise that confidentiality will be maintained by other participants. Once focus group members leave the research setting, researchers cannot control what they say to other people.

Group size should be determined in part by the topic of the interview and your sense of the likelihood that participants will have much to say without much prompting. If the topic is one about which you think participants feel passionately and will have much to say, a group of 3–5 could make sense. Groups larger than that, especially for heated topics, can easily become unmanageable. Some researchers say that a group of about 6–10 participants is the ideal size for focus group research (Morgan, 1997); others recommend that groups should include 3–12 participants (Adler & Clark, 2008). The size of the focus group is ultimately the decision of the researcher. When forming groups and deciding how large or small to make them, take into consideration what you know about the topic and participants’ potential interest in, passion for, and feelings about the topic. Also consider your comfort level and experience in conducting focus groups. These factors will help you decide which size is right in your particular case.
It may seem counterintuitive, but in general, it is better to form focus groups consisting of participants who do not know one another than to create groups consisting of friends, relatives, or acquaintances (Agar & MacDonald, 1995). The reason is that group members who know each other may not share some taken-for-granted knowledge or assumptions. In research, it is precisely the taken-for-granted knowledge that is often of interest; thus, the focus group researcher should avoid setting up interactions where participants may be discouraged to question or raise issues that they take for granted. However, group members should not be so different from one another that participants will be unlikely to feel comfortable talking with one another.
Focus group researchers must carefully consider the composition of the groups they put together. In his text on conducting focus groups, Morgan (1997) suggests that “homogeneity in background and not homogeneity in attitudes” (p. 36) should be the goal, since participants must feel comfortable speaking up but must also have enough differences to facilitate a productive discussion. Whatever composition a researcher designs for her focus groups, the important point to keep in mind is that focus group dynamics are shaped by multiple social contexts (Hollander, 2004). Participants’ silences as well as their speech may be shaped by gender, race, class, sexuality, age, or other background characteristics or social dynamics—all of which might be suppressed or exacerbated depending on the composition of the group. Hollander (2004) suggests that researchers must pay careful attention to group composition, must be attentive to group dynamics during the focus group discussion, and should use multiple methods of data collection in order to “untangle participants’ responses and their relationship to the social contexts of the focus group” (p. 632).
The role of the moderator
In addition to the importance of group composition, focus groups also require skillful moderation. A moderator is the researcher tasked with facilitating the conversation in the focus group. Participants may ask each other follow-up questions, agree or disagree with one another, display body language that tells us something about their feelings about the conversation, or even come up with questions not previously conceived of by the researcher. It is just these sorts of interactions and displays that are of interest to the researcher. A researcher conducting focus groups collects data on more than people’s direct responses to her question, as in interviews.
The moderator’s job is not to ask questions to each person individually, but to stimulate conversation between participants. It is important to set ground rules for focus groups at the outset of the discussion. Remind participants you’ve invited them to participate because you want to hear from all of them. Therefore, the group should aim to let just one person speak at a time and avoid letting just a couple of participants dominate the conversation. One way to do this is to begin the discussion by asking participants to briefly introduce themselves or to provide a brief response to an opening question. This will help set the tone of having all group members participate. Also, ask participants to avoid having side conversations; thoughts or reactions to what is said in the group are important and should be shared with everyone.
As the focus group gets rolling, the moderator will play a less active role as participants talk to one another. There may be times when the conversation stagnates or when you, as moderator, wish to guide the conversation in another direction. In these instances, it is important to demonstrate that you’ve been paying attention to what participants have said. Being prepared to interject statements or questions such as “I’d really like to hear more about what Sunil and Joe think about what Dominick and Jae have been saying” or “Several of you have mentioned X. What do others think about this?” will be important for keeping the conversation going. It can also help redirect the conversation, shift the focus to participants who have been less active in the group, and serve as a cue to those who may be dominating the conversation that it is time to allow others to speak. Researchers may choose to use multiple moderators to make managing these various tasks easier.
Moderators are often too busy working with participants to take diligent notes during a focus group. It is helpful to have a note-taker who can record participants’ responses (Liamputtong, 2011). The note-taker creates, in essence, the first draft of interpretation for the data in the study. They note themes in responses, nonverbal cues, and other information to be included in the analysis later on. Focus groups are analyzed in a similar way as interviews; however, the interactive dimension between participants adds another element to the analytical process. Researchers must attend to the group dynamics of each focus group, as “verbal and nonverbal expressions, the tactical use of humour, interruptions in interaction, and disagreement between participants” are all data that are vital to include in analysis (Liamputtong, 2011, p. 175). Note-takers record these elements in field notes, which allows moderators to focus on the conversation.
Strengths and weaknesses of focus groups
Focus groups share many of the strengths and weaknesses of one-on-one qualitative interviews. Both methods can yield very detailed, in-depth information; are excellent for studying social processes; and provide researchers with an opportunity not only to hear what participants say but also to observe what they do in terms of their body language. Focus groups offer the added benefit of giving researchers a chance to collect data on human interaction by observing how group participants respond and react to one another. Like one-on-one qualitative interviews, focus groups can also be quite expensive and time-consuming. However, there may be some savings with focus groups as it takes fewer group events than one-on-one interviews to gather data from the same number of people. Another potential drawback of focus groups, which is not a concern for one-on-one interviews, is that one or two participants might dominate the group, silencing other participants. Careful planning and skillful moderation on the part of the researcher are crucial for avoiding, or at least dealing with, such possibilities. The various strengths and weaknesses of focus group research are summarized in Table 91.
Grounded Theory
Grounded theory has been widely used since its development in the late 1960s (Glaser & Strauss, 1967). Largely derived from schools of sociology, grounded theory involves emersion of the researcher in the field and in the data. Researchers follow a systematic set of procedures and a simultaneous approach to data collection and analysis. Grounded theory is most often used to generate rich explanations of complex actions, processes, and transitions. The primary mode of data collection is one-on-one participant interviews. Sample sizes tend to range from 20 to 30 individuals, sampled purposively (Padgett, 2016). However, sample sizes can be larger or smaller, depending on data saturation. Data saturation is the point in the qualitative research data collection process when no new information is being discovered. Researchers use a constant comparative approach in which previously collected data are analyzed during the same time frame as new data are being collected. This allows the researchers to determine when new information is no longer being gleaned from data collection and analysis — that data saturation has been reached — in order to conclude the data collection phase.
Rather than apply or test existing grand theories, or “Big T” theories, grounded theory focuses on “small t” theories (Padgett, 2016). Grand theories, or “Big T” theories, are systems of principles, ideas, and concepts used to predict phenomena. These theories are backed up by facts and tested hypotheses. “Small t” theories are speculative and contingent upon specific contexts. In grounded theory, these “small t” theories are grounded in events and experiences and emerge from the analysis of the data collected.
One notable application of grounded theory produced a “small t” theory of acceptance following cancer diagnoses (Jakobsson, Horvath, & Ahlberg, 2005). Using grounded theory, the researchers interviewed nine patients in western Sweden. Data collection and analysis stopped when saturation was reached. The researchers found that action and knowledge, given with respect and continuity led to confidence which led to acceptance. This “small t” theory continues to be applied and further explored in other contexts.
Case study research
Case study research is an intensive longitudinal study of a phenomenon at one or more research sites for the purpose of deriving detailed, contextualized inferences and understanding the dynamic process underlying a phenomenon of interest. Case research is a unique research design in that it can be used in an interpretive manner to build theories or in a positivist manner to test theories. The previous chapter on case research discusses both techniques in depth and provides illustrative exemplars. Furthermore, the case researcher is a neutral observer (direct observation) in the social setting rather than an active participant (participant observation). As with any other interpretive approach, drawing meaningful inferences from case research depends heavily on the observational skills and integrative abilities of the researcher.
Ethnography
The ethnographic research method, derived largely from the field of anthropology, emphasizes studying a phenomenon within the context of its culture. The researcher must be deeply immersed in the social culture over an extended period of time (usually 8 months to 2 years) and should engage, observe, and record the daily life of the studied culture and its social participants within their natural setting. The primary mode of data collection is participant observation, and data analysis involves a “sense-making” approach. In addition, the researcher must take extensive field notes, and narrate her experience in descriptive detail so that readers may experience the same culture as the researcher. In this method, the researcher has two roles: rely on her unique knowledge and engagement to generate insights (theory), and convince the scientific community of the trans-situational nature of the studied phenomenon.
The classic example of ethnographic research is Jane Goodall’s study of primate behaviors, where she lived with chimpanzees in their natural habitat at Gombe National Park in Tanzania, observed their behaviors, interacted with them, and shared their lives. During that process, she learnt and chronicled how chimpanzees seek food and shelter, how they socialize with each other, their communication patterns, their mating behaviors, and so forth. A more contemporary example of ethnographic research is Myra Bluebond-Langer’s (1996)14 study of decision making in families with children suffering from life-threatening illnesses, and the physical, psychological, environmental, ethical, legal, and cultural issues that influence such decision-making. The researcher followed the experiences of approximately 80 children with incurable illnesses and their families for a period of over two years. Data collection involved participant observation and formal/informal conversations with children, their parents and relatives, and health care providers to document their lived experience.
Phenomenology
Phenomenology is a research method that emphasizes the study of conscious experiences as a way of understanding the reality around us. Phenomenology is concerned with the systematic reflection and analysis of phenomena associated with conscious experiences, such as human judgment, perceptions, and actions, with the goal of (1) appreciating and describing social reality from the diverse subjective perspectives of the participants involved, and (2) understanding the symbolic meanings (“deep structure”) underlying these subjective experiences. Phenomenological inquiry requires that researchers eliminate any prior assumptions and personal biases, empathize with the participant’s situation, and tune into existential dimensions of that situation, so that they can fully understand the deep structures that drives the conscious thinking, feeling, and behavior of the studied participants.
Some researchers view phenomenology as a philosophy rather than as a research method. In response to this criticism, Giorgi and Giorgi (2003) developed an existential phenomenological research method to guide studies in this area. This method can be grouped into data collection and data analysis phases. In the data collection phase, participants embedded in a social phenomenon are interviewed to capture their subjective experiences and perspectives regarding the phenomenon under investigation. Examples of questions that may be asked include “can you describe a typical day” or “can you describe that particular incident in more detail?” These interviews are recorded and transcribed for further analysis. During data analysis, the researcher reads the transcripts to: (1) get a sense of the whole, and (2) establish “units of significance” that can faithfully represent participants’ subjective experiences. Examples of such units of significance are concepts such as “felt space” and “felt time,” which are then used to document participants’ psychological experiences. For instance, did participants feel safe, free, trapped, or joyous when experiencing a phenomenon (“felt-space”)? Did they feel that their experience was pressured, slow, or discontinuous (“felt-time”)? Phenomenological analysis should take into account the participants’ temporal landscape (i.e., their sense of past, present, and future), and the researcher must transpose herself in an imaginary sense in the participant’s situation (i.e., temporarily live the participant’s life). The participants’ lived experience is described in form of a narrative or using emergent themes. The analysis then delves into these themes to identify multiple layers of meaning while retaining the fragility and ambiguity of subjects’ lived experiences.
Key Takeaways
- In terms of focus group composition, homogeneity of background among participants is recommended while diverse attitudes within the group are ideal.
- The goal of a focus group is to get participants to talk with one another rather than the researcher.
- Like one-on-one qualitative interviews, focus groups can yield very detailed information, are excellent for studying social processes, and provide researchers with an opportunity to observe participants’ body language; they also allow researchers to observe social interaction.
- Focus groups can be expensive and time-consuming, as are one-on-one interviews; there is also the possibility that a few participants will dominate the group and silence others in the group.
- Other types of qualitative research include case studies, ethnography, and phenomenology.
- Data saturation – the point in the qualitative research data collection process when no new information is being discovered
- Focus groups- planned discussions designed to elicit group interaction and “obtain perceptions on a defined area of interest in a permissive, nonthreatening environment” (Krueger & Casey, 2000, p. 5)
- Moderator- the researcher tasked with facilitating the conversation in the focus group
Image attributions
target group by geralt CC-0
workplace team by Free-Photos CC-0
Foundations of Social Work Research Copyright © 2020 by Rebecca L. Mauldin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Quantitative Research – Methods, Types and...

Qualitative Research Methods

Explanatory Research – Types, Methods, Guide
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts
- Jeremy Segrott ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6215-0870 1 ,
- Sue Channon 2 ,
- Amy Lloyd 4 ,
- Eleni Glarou 2 , 3 ,
- Josie Henley 5 ,
- Jacqueline Hughes 2 ,
- Nina Jacob 2 ,
- Sarah Milosevic 2 ,
- Yvonne Moriarty 2 ,
- Bethan Pell 6 ,
- Mike Robling 2 ,
- Heather Strange 2 ,
- Julia Townson 2 ,
- Qualitative Research Group &
- Lucy Brookes-Howell 2
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 323 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Background/aims
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
We held group discussions on the work of the Qualitative Research Group (QRG) within CTR. The content of these discussions, materials for a presentation in CTR, and documents relating to the development of the QRG were interpreted at a workshop attended by group members. Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) was used to structure analysis. A writing group prepared a document for input from members of CTR, forming the basis of this paper.
Actions to integrate qualitative research comprised: its inclusion in Centre strategies; formation of a QRG with dedicated funding/roles; embedding of qualitative research within operating systems; capacity building/training; monitoring opportunities to include qualitative methods in studies; maximising the quality of qualitative research and developing methodological innovation. Facilitators of these actions included: the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial/study design and its promotion of the value of qualitative research; and close physical proximity of CTR qualitative staff/students allowing sharing of methodological approaches. Introduction of innovative qualitative methods generated interest among other staff groups. Challenges included: pressure to under-resource qualitative components of research, preference for a statistical stance historically in some research areas and funding structures, and difficulties faced by qualitative researchers carving out individual academic profiles when working across trials/studies.
Conclusions
Given that CTUs are pivotal to the design and conduct of RCTs and related study types across multiple disciplines, integrating qualitative research into trials units is crucial if its contribution is to be fully realised. We have made explicit one trials unit’s experience of embedding qualitative research and present this to open dialogue on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. NPT provides a valuable framework with which to theorise these processes, including the importance of sense-making and legitimisation when introducing new practices within organisations.
Peer Review reports
The value of using qualitative methods within randomised control trials (RCTs) is widely recognised [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Qualitative research generates important evidence on factors affecting trial recruitment/retention [ 4 ] and implementation, aiding interpretation of quantitative data [ 5 ]. Though RCTs have traditionally been viewed as sitting within a positivist paradigm, recent methodological innovations have developed new trial designs that draw explicitly on both quantitative and qualitative methods. For instance, in the field of complex public health interventions, realist RCTs seek to understand the mechanisms through which interventions generate hypothesised impacts, and how interactions across different implementation contexts form part of these mechanisms. Proponents of realist RCTs—which integrate experimental and realist paradigms—highlight the importance of using quantitative and qualitative methods to fully realise these aims and to generate an understanding of intervention mechanisms and how context shapes them [ 6 ].
A need for guidance on how to conduct good quality qualitative research is being addressed, particularly in relation to feasibility studies for RCTs [ 7 ] and process evaluations embedded within trials of complex interventions [ 5 ]. There is also guidance on the conduct of qualitative research within trials at different points in the research cycle, including development, conduct and reporting [ 8 , 9 ].
A high proportion of trials are based within or involve clinical trials units (CTUs). In the UK the UKCRC Registered CTU Network describes them as:
… specialist units which have been set up with a specific remit to design, conduct, analyse and publish clinical trials and other well-designed studies. They have the capability to provide specialist expert statistical, epidemiological, and other methodological advice and coordination to undertake successful clinical trials. In addition, most CTUs will have expertise in the coordination of trials involving investigational medicinal products which must be conducted in compliance with the UK Regulations governing the conduct of clinical trials resulting from the EU Directive for Clinical Trials.
Thus, CTUs provide the specialist methodological expertise needed for the conduct of trials, and in the case of trials of investigational medicinal products, their involvement may be mandated to ensure compliance with relevant regulations. As the definition above suggests, CTUs also conduct and support other types of study apart from RCTs, providing a range of methodological and subject-based expertise.
However, despite their central role in the conduct and design of trials, (and other evaluation designs) little has been written about how CTUs have integrated qualitative work within their organisation at a time when such methods are, as stated above, now recognised as an important aspect of RCTs and evaluation studies more generally. This is a significant gap, since integration at the organisational level arguably shapes how qualitative research is integrated within individual studies, and thus it is valuable to understand how CTUs have approached the task. There are different ways of involving qualitative work in trials units, such as partnering with other departments (e.g. social science) or employing qualitative researchers directly. Qualitative research can be imagined and configured in different ways—as a method that generates data to inform future trial and intervention design, as an embedded component within an RCT or other evaluation type, or as a parallel strand of research focusing on lived experiences of illness, for instance. Understanding how trials units have integrated qualitative research is valuable, as it can shed light on which strategies show promise, and in which contexts, and how qualitative research is positioned within the field of trials research, foregrounding the value of qualitative research. However, although much has been written about its use within trials, few accounts exist of how trials units have integrated qualitative research within their systems and structures.
This paper discusses the process of embedding qualitative research within the work of one CTU—Cardiff University’s Centre for Trials Research (CTR). It highlights facilitators of this process and identifies challenges to integration. We use the Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) as a framework to structure our experience and approach. The key gap addressed by this paper is the implementation of strategies to integrate qualitative research (a relatively newly adopted set of practices and processes) within CTU systems and structures. We acknowledge from the outset that there are multiple ways of approaching this task. What follows therefore is not a set of recommendations for a preferred or best way to integrate qualitative research, as this will comprise diverse actions according to specific contexts. Rather, we examine the processes through which integration occurred in our own setting and highlight the potential value of these insights for others engaged in the work of promoting qualitative research within trials units.
Background to the integration of qualitative research within CTR
The CTR was formed in 2015 [ 10 ]. It brought together three existing trials units at Cardiff University: the South East Wales Trials Unit, the Wales Cancer Trials Unit, and the Haematology Clinical Trials Unit. From its inception, the CTR had a stated aim of developing a programme of qualitative research and integrating it within trials and other studies. In the sections below, we map these approaches onto the framework offered by Normalisation Process Theory to understand the processes through which they helped achieve embedding and integration of qualitative research.
CTR’s aims (including those relating to the development of qualitative research) were included within its strategy documents and communicated to others through infrastructure funding applications, annual reports and its website. A Qualitative Research Group (QRG), which had previously existed within the South East Wales Trials Unit, with dedicated funding for methodological specialists and group lead academics, was a key mechanism through which the development of a qualitative portfolio was put into action. Integration of qualitative research within Centre systems and processes occurred through the inclusion of qualitative research in study adoption processes and representation on committees. The CTR’s study portfolio provided a basis to track qualitative methods in new and existing studies, identify opportunities to embed qualitative methods within recently adopted studies (at the funding application stage) and to manage staff resources. Capacity building and training were an important focus of the QRG’s work, including training courses, mentoring, creation of an academic network open to university staff and practitioners working in the field of healthcare, presentations at CTR staff meetings and securing of PhD studentships. Standard operating procedures and methodological guidance on the design and conduct of qualitative research (e.g. templates for developing analysis plans) aimed to create a shared understanding of how to undertake high-quality research, and a means to monitor the implementation of rigorous approaches. As the QRG expanded its expertise it sought to develop innovative approaches, including the use of visual [ 11 ] and ethnographic methods [ 12 ].
Understanding implementation—Normalisation Process Theory (NPT)
Normalisation Process Theory (NPT) provides a model with which to understand the implementation of new sets of practices and their normalisation within organisational settings. The term ‘normalisation’ refers to how new practices become routinised (part of the everyday work of an organisation) through embedding and integration [ 13 , 14 ]. NPT defines implementation as ‘the social organisation of work’ and is concerned with the social processes that take place as new practices are introduced. Embedding involves ‘making practices routine elements of everyday life’ within an organisation. Integration takes the form of ‘sustaining embedded practices in social contexts’, and how these processes lead to the practices becoming (or not becoming) ‘normal and routine’ [ 14 ]. NPT is concerned with the factors which promote or ‘inhibit’ attempts to embed and integrate the operationalisation of new practices [ 13 , 14 , 15 ].
Embedding new practices is therefore achieved through implementation—which takes the form of interactions in specific contexts. Implementation is operationalised through four ‘generative mechanisms’— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring [ 14 ]. Each mechanism is characterised by components comprising immediate and organisational work, with actions of individuals and organisations (or groups of individuals) interdependent. The mechanisms operate partly through forms of investment (i.e. meaning, commitment, effort, and comprehension) [ 14 ].
Coherence refers to how individuals/groups make sense of, and give meaning to, new practices. Sense-making concerns the coherence of a practice—whether it ‘holds together’, and its differentiation from existing activities [ 15 ]. Communal and individual specification involve understanding new practices and their potential benefits for oneself or an organisation. Individuals consider what new practices mean for them in terms of tasks and responsibilities ( internalisation ) [ 14 ].
NPT frames the second mechanism, cognitive participation , as the building of a ‘community of practice’. For a new practice to be initiated, individuals and groups within an organisation must commit to it [ 14 , 15 ]. Cognitive participation occurs through enrolment —how people relate to the new practice; legitimation —the belief that it is right for them to be involved; and activation —defining which actions are necessary to sustain the practice and their involvement [ 14 ]. Making the new practices work may require changes to roles (new responsibilities, altered procedures) and reconfiguring how colleagues work together (changed relationships).
Third, Collective Action refers to ‘the operational work that people do to enact a set of practices’ [ 14 ]. Individuals engage with the new practices ( interactional workability ) reshaping how members of an organisation interact with each other, through creation of new roles and expectations ( relational interaction ) [ 15 ]. Skill set workability concerns how the work of implementing a new set of practices is distributed and the necessary roles and skillsets defined [ 14 ]. Contextual integration draws attention to the incorporation of a practice within social contexts, and the potential for aspects of these contexts, such as systems and procedures, to be modified as a result [ 15 ].
Reflexive monitoring is the final implementation mechanism. Collective and individual appraisal evaluate the value of a set of practices, which depends on the collection of information—formally and informally ( systematisation ). Appraisal may lead to reconfiguration in which procedures of the practice are redefined or reshaped [ 14 , 15 ].
We sought to map the following: (1) the strategies used to embed qualitative research within the Centre, (2) key facilitators, and (3) barriers to their implementation. Through focused group discussions during the monthly meetings of the CTR QRG and in discussion with the CTR senior management team throughout 2019–2020 we identified nine types of documents (22 individual documents in total) produced within the CTR which had relevant information about the integration of qualitative research within its work (Table 1 ). The QRG had an ‘open door’ policy to membership and welcomed all staff/students with an interest in qualitative research. It included researchers who were employed specifically to undertake qualitative research and other staff with a range of study roles, including trial managers, statisticians, and data managers. There was also diversity in terms of career stage, including PhD students, mid-career researchers and members of the Centre’s Executive team. Membership was therefore largely self-selected, and comprised of individuals with a role related to, or an interest in, embedding qualitative research within trials. However, the group brought together diverse methodological perspectives and was not solely comprised of methodological ‘champions’ whose job it was to promote the development of qualitative research within the centre. Thus whilst the group (and by extension, the authors of this paper) had a shared appreciation of the value of qualitative research within a trials centre, they also brought varied methodological perspectives and ways of engaging with it.
All members of the QRG ( n = 26) were invited to take part in a face-to-face, day-long workshop in February 2019 on ‘How to optimise and operationalise qualitative research in trials: reflections on CTR structure’. The workshop was attended by 12 members of staff and PhD students, including members of the QRG and the CTR’s senior management team. Recruitment to the workshop was therefore inclusive, and to some extent opportunistic, but all members of the QRG were able to contribute to discussions during regular monthly group meetings and the drafting of the current paper.
The aim of the workshop was to bring together information from the documents in Table 1 to generate discussion around the key strategies (and their component activities) that had been adopted to integrate qualitative research into CTR, as well as barriers to, and facilitators of, their implementation. The agenda for the workshop involved four key areas: development and history of the CTR model; mapping the current model within CTR; discussing the structure of other CTUs; and exploring the advantages and disadvantages of the CTR model.
During the workshop, we discussed the use of NPT to conceptualise how qualitative research had been embedded within CTR’s systems and practices. The group produced spider diagrams to map strategies and actions on to the four key domains (or ‘generative mechanisms’ of NPT) summarised above, to aid the understanding of how they had functioned, and the utility of NPT as a framework. This is summarised in Table 2 .
Detailed notes were made during the workshop. A core writing group then used these notes and the documents in Table 1 to develop a draft of the current paper. This was circulated to all members of the CTR QRG ( n = 26) and stored within a central repository accessible to them to allow involvement and incorporate the views of those who were not able to attend the workshop. This draft was again presented for comments in the monthly CTR QRG meeting in February 2021 attended by n = 10. The Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence 2.0 (SQUIRE) guidelines were used to inform the structure and content of the paper (see supplementary material) [ 16 ].
In the following sections, we describe the strategies CTR adopted to integrate qualitative research. These are mapped against NPT’s four generative mechanisms to explore the processes through which the strategies promoted integration, and facilitators of and barriers to their implementation. A summary of the strategies and their functioning in terms of the generative mechanisms is provided in Table 2 .
Coherence—making sense of qualitative research
In CTR, many of the actions taken to build a portfolio of qualitative research were aimed at enabling colleagues, and external actors, to make sense of this set of methodologies. Centre-level strategies and grant applications for infrastructure funding highlighted the value of qualitative research, the added benefits it would bring, and positioned it as a legitimate set of practices alongside existing methods. For example, a 2014 application for renewal of trials unit infrastructure funding stated:
We are currently in the process of undertaking […] restructuring for our qualitative research team and are planning similar for trial management next year. The aim of this restructuring is to establish greater hierarchical management and opportunities for staff development and also provide a structure that can accommodate continuing growth.
Within the CTR, various forms of communication on the development of qualitative research were designed to enable staff and students to make sense of it, and to think through its potential value for them, and ways in which they might engage with it. These included presentations at staff meetings, informal meetings between project teams and the qualitative group lead, and the visibility of qualitative research on the public-facing Centre website and Centre committees and systems. For instance, qualitative methods were included (and framed as a distinct set of practices) within study adoption forms and committee agendas. Information for colleagues described how qualitative methods could be incorporated within funding applications for RCTs and other evaluation studies to generate new insights into questions research teams were already keen to answer, such as influences on intervention implementation fidelity. Where externally based chief investigators approached the Centre to be involved in new grant applications, the existence of the qualitative team and group lead enabled the inclusion of qualitative research to be actively promoted at an early stage, and such opportunities were highlighted in the Centre’s brochure for new collaborators. Monthly qualitative research network meetings—advertised across CTR and to external research collaborators, were also designed to create a shared understanding of qualitative research methods and their utility within trials and other study types (e.g. intervention development, feasibility studies, and observational studies). Training events (discussed in more detail below) also aided sense-making.
Several factors facilitated the promotion of qualitative research as a distinctive and valuable entity. Among these was the influence of the broader methodological landscape within trial design which was promoting the value of qualitative research, such as guidance on the evaluation of complex interventions by the Medical Research Council [ 17 ], and the growing emphasis placed on process evaluations within trials (with qualitative methods important in understanding participant experience and influences on implementation) [ 5 ]. The attention given to lived experience (both through process evaluations and the move to embed public involvement in trials) helped to frame qualitative research within the Centre as something that was appropriate, legitimate, and of value. Recognition by research funders of the value of qualitative research within studies was also helpful in normalising and legitimising its adoption within grant applications.
The inclusion of qualitative methods within influential methodological guidance helped CTR researchers to develop a ‘shared language’ around these methods, and a way that a common understanding of the role of qualitative research could be generated. One barrier to such sense-making work was the varying extent to which staff and teams had existing knowledge or experience of qualitative research. This varied across methodological and subject groups within the Centre and reflected the history of the individual trials units which had merged to form the Centre.
Cognitive participation—legitimising qualitative research
Senior CTR leaders promoted the value and legitimacy of qualitative research. Its inclusion in centre strategies, infrastructure funding applications, and in public-facing materials (e.g. website, investigator brochures), signalled that it was appropriate for individuals to conduct qualitative research within their roles, or to support others in doing so. Legitimisation also took place through informal channels, such as senior leadership support for qualitative research methods in staff meetings and participation in QRG seminars. Continued development of the QRG (with dedicated infrastructure funding) provided a visible identity and equivalence with other methodological groups (e.g. trial managers, statisticians).
Staff were asked to engage with qualitative research in two main ways. First, there was an expansion in the number of staff for whom qualitative research formed part of their formal role and responsibilities. One of the three trials units that merged to form CTR brought with it a qualitative team comprising methodological specialists and a group lead. CTR continued the expansion of this group with the creation of new roles and an enlarged nucleus of researchers for whom qualitative research was the sole focus of their work. In part, this was linked to the successful award of projects that included a large qualitative component, and that were coordinated by CTR (see Table 3 which describes the PUMA study).
Members of the QRG were encouraged to develop their own research ideas and to gain experience as principal investigators, and group seminars were used to explore new ideas and provide peer support. This was communicated through line management, appraisal, and informal peer interaction. Boundaries were not strictly demarcated (i.e. staff located outside the qualitative team were already using qualitative methods), but the new team became a central focus for developing a growing programme of work.
Second, individuals and studies were called upon to engage in new ways with qualitative research, and with the qualitative team. A key goal for the Centre was that groups developing new research ideas should give more consideration in general to the potential value and inclusion of qualitative research within their funding applications. Specifically, they were asked to do this by thinking about qualitative research at an early point in their application’s development (rather than ‘bolting it on’ after other elements had been designed) and to draw upon the expertise and input of the qualitative team. An example was the inclusion of questions on qualitative methods within the Centre’s study adoption form and representation from the qualitative team at the committee which reviewed new adoption requests. Where adoption requests indicated the inclusion of qualitative methods, colleagues were encouraged to liaise with the qualitative team, facilitating the integration of its expertise from an early stage. Qualitative seminars offered an informal and supportive space in which researchers could share initial ideas and refine their methodological approach. The benefits of this included the provision of sufficient time for methodological specialists to be involved in the design of the proposed qualitative component and ensuring adequate costings had been drawn up. At study adoption group meetings, scrutiny of new proposals included consideration of whether new research proposals might be strengthened through the use of qualitative methods where these had not initially been included. Meetings of the QRG—which reviewed the Centre’s portfolio of new studies and gathered intelligence on new ideas—also helped to identify, early on, opportunities to integrate qualitative methods. Communication across teams was useful in identifying new research ideas and embedding qualitative researchers within emerging study development groups.
Actions to promote greater use of qualitative methods in funding applications fed through into a growing number of studies with a qualitative component. This helped to increase the visibility and legitimacy of qualitative methods within the Centre. For example, the PUMA study [ 12 ], which brought together a large multidisciplinary team to develop and evaluate a Paediatric early warning system, drew heavily on qualitative methods, with the qualitative research located within the QRG. The project introduced an extensive network of collaborators and clinical colleagues to qualitative methods and how they could be used during intervention development and the generation of case studies. Further information about the PUMA study is provided in Table 3 .
Increasing the legitimacy of qualitative work across an extensive network of staff, students and collaborators was a complex process. Set within the continuing dominance of quantitative methods with clinical trials, there were variations in the extent to which clinicians and other collaborators embraced the value of qualitative methods. Research funding schemes, which often continued to emphasise the quantitative element of randomised controlled trials, inevitably fed through into the focus of new research proposals. Staff and external collaborators were sometimes uncertain about the added value that qualitative methods would bring to their trials. Across the CTR there were variations in the speed at which qualitative research methods gained legitimacy, partly based on disciplinary traditions and their influences. For instance, population health trials, often located within non-health settings such as schools or community settings, frequently involved collaboration with social scientists who brought with them experience in qualitative methods. Methodological guidance in this field, such as MRC guidance on process evaluations, highlighted the value of qualitative methods and alternatives to the positivist paradigm, such as the value of realist RCTs. In other, more clinical areas, positivist paradigms had greater dominance. Established practices and methodological traditions across different funders also influenced the ease of obtaining funding to include qualitative research within studies. For drugs trials (CTIMPs), the influence of regulatory frameworks on study design, data collection and the allocation of staff resources may have played a role. Over time, teams gained repeated experience of embedding qualitative research (and researchers) within their work and took this learning with them to subsequent studies. For example, the senior clinician quoted within the PUMA case study (Table 3 below) described how they had gained an appreciation of the rigour of qualitative research and an understanding of its language. Through these repeated interactions, embedding of qualitative research within studies started to become the norm rather than the exception.
Collective action—operationalising qualitative research
Collective action concerns the operationalisation of new practices within organisations—the allocation and management of the work, how individuals interact with each other, and the work itself. In CTR the formation of a Qualitative Research Group helped to allocate and organise the work of building a portfolio of studies. Researchers across the Centre were called upon to interact with qualitative research in new ways. Presentations at staff meetings and the inclusion of qualitative research methods in portfolio study adoption forms were examples of this ( interactive workability ). It was operationalised by encouraging study teams to liaise with the qualitative research lead. Development of standard operating procedures, templates for costing qualitative research and methodological guidance (e.g. on analysis plans) also helped encourage researchers to interact with these methods in new ways. For some qualitative researchers who had been trained in the social sciences, working within a trials unit meant that they needed to interact in new and sometimes unfamiliar ways with standard operating procedures, risk assessments, and other trial-based systems. Thus, training needs and capacity-building efforts were multidirectional.
Whereas there had been a tendency for qualitative research to be ‘bolted on’ to proposals for RCTs, the systems described above were designed to embed thinking about the value and design of the qualitative component from the outset. They were also intended to integrate members of the qualitative team with trial teams from an early stage to promote effective integration of qualitative methods within larger trials and build relationships over time.
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs), formal and informal training, and interaction between the qualitative team and other researchers increased the relational workability of qualitative methods within the Centre—the confidence individuals felt in including these methods within their studies, and their accountability for doing so. For instance, study adoption forms prompted researchers to interact routinely with the qualitative team at an early stage, whilst guidance on costing grants provided clear expectations about the resources needed to deliver a proposed set of qualitative data collection.
Formation of the Qualitative Research Group—comprised of methodological specialists, created new roles and skillsets ( skill set workability ). Research teams were encouraged to draw on these when writing funding applications for projects that included a qualitative component. Capacity-building initiatives were used to increase the number of researchers with the skills needed to undertake qualitative research, and for these individuals to develop their expertise over time. This was achieved through formal training courses, academic seminars, mentoring from experienced colleagues, and informal knowledge exchange. Links with external collaborators and centres engaged in building qualitative research supported these efforts. Within the Centre, the co-location of qualitative researchers with other methodological and trial teams facilitated knowledge exchange and building of collaborative relationships, whilst grouping of the qualitative team within a dedicated office space supported a collective identity and opportunities for informal peer support.
Some aspects of the context in which qualitative research was being developed created challenges to operationalisation. Dependence on project grants to fund qualitative methodologists meant that there was a continuing need to write further grant applications whilst limiting the amount of time available to do so. Similarly, researchers within the team whose role was funded largely by specific research projects could sometimes find it hard to create sufficient time to develop their personal methodological interests. However, the cultivation of a methodologically varied portfolio of work enabled members of the team to build significant expertise in different approaches (e.g. ethnography, discourse analysis) that connected individual studies.
Reflexive monitoring—evaluating the impact of qualitative research
Inclusion of questions/fields relating to qualitative research within the Centre’s study portfolio database was a key way in which information was collected ( systematisation ). It captured numbers of funding applications and funded studies, research design, and income generation. Alongside this database, a qualitative resource planner spreadsheet was used to link individual members of the qualitative team with projects and facilitate resource planning, further reinforcing the core responsibilities and roles of qualitative researchers within CTR. As with all staff in the Centre, members of the qualitative team were placed on ongoing rather than fixed-term contracts, reflecting their core role within CTR. Planning and strategy meetings used the database and resource planner to assess the integration of qualitative research within Centre research, identify opportunities for increasing involvement, and manage staff recruitment and sustainability of researcher posts. Academic meetings and day-to-day interaction fulfilled informal appraisal of the development of the group, and its position within the Centre. Individual appraisal was also important, with members of the qualitative team given opportunities to shape their role, reflect on progress, identify training needs, and further develop their skillset, particularly through line management systems.
These forms of systematisation and appraisal were used to reconfigure the development of qualitative research and its integration within the Centre. For example, group strategies considered how to achieve long-term integration of qualitative research from its initial embedding through further promoting the belief that it formed a core part of the Centre’s business. The visibility and legitimacy of qualitative research were promoted through initiatives such as greater prominence on the Centre’s website. Ongoing review of the qualitative portfolio and discussion at academic meetings enabled the identification of areas where increased capacity would be helpful, both for qualitative staff, and more broadly within the Centre. This prompted the qualitative group to develop an introductory course to qualitative methods open to all Centre staff and PhD students, aimed at increasing understanding and awareness. As the qualitative team built its expertise and experience it also sought to develop new and innovative approaches to conducting qualitative research. This included the use of visual and diary-based methods [ 11 ] and the adoption of ethnography to evaluate system-level clinical interventions [ 12 ]. Restrictions on conventional face-to-face qualitative data collection due to the COVID-19 pandemic prompted rapid adoption of virtual/online methods for interviews, observation, and use of new internet platforms such as Padlet—a form of digital note board.
In this paper, we have described the work undertaken by one CTU to integrate qualitative research within its studies and organisational culture. The parallel efforts of many trials units to achieve these goals arguably come at an opportune time. The traditional designs of RCTs have been challenged and re-imagined by the increasing influence of realist evaluation [ 6 , 18 ] and the widespread acceptance that trials need to understand implementation and intervention theory as well as assess outcomes [ 17 ]. Hence the widespread adoption of embedded mixed methods process evaluations within RCTs. These broad shifts in methodological orthodoxies, the production of high-profile methodological guidance, and the expectations of research funders all create fertile ground for the continued expansion of qualitative methods within trials units. However, whilst much has been written about the importance of developing qualitative research and the possible approaches to integrating qualitative and quantitative methods within studies, much less has been published on how to operationalise this within trials units. Filling this lacuna is important. Our paper highlights how the integration of a new set of practices within an organisation can become embedded as part of its ‘normal’ everyday work whilst also shaping the practices being integrated. In the case of CTR, it could be argued that the integration of qualitative research helped shape how this work was done (e.g. systems to assess progress and innovation).
In our trials unit, the presence of a dedicated research group of methodological specialists was a key action that helped realise the development of a portfolio of qualitative research and was perhaps the most visible evidence of a commitment to do so. However, our experience demonstrates that to fully realise the goal of developing qualitative research, much work focuses on the interaction between this ‘new’ set of methods and the organisation into which it is introduced. Whilst the team of methodological specialists was tasked with, and ‘able’ to do the work, the ‘work’ itself needed to be integrated and embedded within the existing system. Thus, alongside the creation of a team and methodological capacity, promoting the legitimacy of qualitative research was important to communicate to others that it was both a distinctive and different entity, yet similar and equivalent to more established groups and practices (e.g. trial management, statistics, data management). The framing of qualitative research within strategies, the messages given out by senior leaders (formally and informally) and the general visibility of qualitative research within the system all helped to achieve this.
Normalisation Process Theory draws our attention to the concepts of embedding (making a new practice routine, normal within an organisation) and integration —the long-term sustaining of these processes. An important process through which embedding took place in our centre concerned the creation of messages and systems that called upon individuals and research teams to interact with qualitative research. Research teams were encouraged to think about qualitative research and consider its potential value for their studies. Critically, they were asked to do so at specific points, and in particular ways. Early consideration of qualitative methods to maximise and optimise their inclusion within studies was emphasised, with timely input from the qualitative team. Study adoption systems, centre-level processes for managing financial and human resources, creation of a qualitative resource planner, and awareness raising among staff, helped to reinforce this. These processes of embedding and integration were complex and they varied in intensity and speed across different areas of the Centre’s work. In part this depended on existing research traditions, the extent of prior experience of working with qualitative researchers and methods, and the priorities of subject areas and funders. Centre-wide systems, sometimes linked to CTR’s operation as a CTU, also helped to legitimise and embed qualitative research, lending it equivalence with other research activity. For example, like all CTUs, CTR was required to conform with the principles of Good Clinical Practice, necessitating the creation of a quality management system, operationalised through standard operating procedures for all areas of its work. Qualitative research was included, and became embedded, within these systems, with SOPs produced to guide activities such as qualitative analysis.
NPT provides a helpful way of understanding how trials units might integrate qualitative research within their work. It highlights how new practices interact with existing organisational systems and the work needed to promote effective interaction. That is, alongside the creation of a team or programme of qualitative research, much of the work concerns how members of an organisation understand it, engage with it, and create systems to sustain it. Embedding a new set of practices may be just as important as the quality or characteristics of the practices themselves. High-quality qualitative research is of little value if it is not recognised and drawn upon within new studies for instance. NPT also offers a helpful lens with which to understand how integration and embedding occur, and the mechanisms through which they operate. For example, promoting the legitimacy of a new set of practices, or creating systems that embed it, can help sustain these practices by creating an organisational ambition and encouraging (or requiring) individuals to interact with them in certain ways, redefining their roles accordingly. NPT highlights the ways in which integration of new practices involves bi-directional exchanges with the organisation’s existing practices, with each having the potential to re-shape the other as interaction takes place. For instance, in CTR, qualitative researchers needed to integrate and apply their methods within the quality management and other systems of a CTU, such as the formalisation of key processes within standard operating procedures, something less likely to occur outside trials units. Equally, project teams (including those led by externally based chief investigators) increased the integration of qualitative methods within their overall study design, providing opportunities for new insights on intervention theory, implementation and the experiences of practitioners and participants.
We note two aspects of the normalisation processes within CTR that are slightly less well conceptualised by NPT. The first concerns the emphasis within coherence on identifying the distinctiveness of new practices, and how they differ from existing activities. Whilst differentiation was an important aspect of the integration of qualitative research in CTR, such integration could be seen as operating partly through processes of de-differentiation, or at least equivalence. That is, part of the integration of qualitative research was to see it as similar in terms of rigour, coherence, and importance to other forms of research within the Centre. To be viewed as similar, or at least comparable to existing practices, was to be legitimised.
Second, whilst NPT focuses mainly on the interaction between a new set of practices and the organisational context into which it is introduced, our own experience of introducing qualitative research into a trials unit was shaped by broader organisational and methodological contexts. For example, the increasing emphasis placed upon understanding implementation processes and the experiences of research participants in the field of clinical trials (e.g. by funders), created an environment conducive to the development of qualitative research methods within our Centre. Attempts to integrate qualitative research within studies were also cross-organisational, given that many of the studies managed within the CTR drew together multi-institutional teams. This provided important opportunities to integrate qualitative research within a portfolio of studies that extended beyond CTR and build a network of collaborators who increasingly included qualitative methods within their funding proposals. The work of growing and integrating qualitative research within a trials unit is an ongoing one in which ever-shifting macro-level influences can help or hinder, and where the organisations within which we work are never static in terms of barriers and facilitators.
The importance of utilising qualitative methods within RCTs is now widely recognised. Increased emphasis on the evaluation of complex interventions, the influence of realist methods directing greater attention to complexity and the widespread adoption of mixed methods process evaluations are key drivers of this shift. The inclusion of qualitative methods within individual trials is important and previous research has explored approaches to their incorporation and some of the challenges encountered. Our paper highlights that the integration of qualitative methods at the organisational level of the CTU can shape how they are taken up by individual trials. Within CTR, it can be argued that qualitative research achieved high levels of integration, as conceptualised by Normalisation Process Theory. Thus, qualitative research became recognised as a coherent and valuable set of practices, secured legitimisation as an appropriate focus of individual and organisational activity and benefitted from forms of collective action which operationalised these organisational processes. Crucially, the routinisation of qualitative research appeared to be sustained, something which NPT suggests helps define integration (as opposed to initial embedding). However, our analysis suggested that the degree of integration varied by trial area. This variation reflected a complex mix of factors including disciplinary traditions, methodological guidance, existing (un)familiarity with qualitative research, and the influence of regulatory frameworks for certain clinical trials.
NPT provides a valuable framework with which to understand how these processes of embedding and integration occur. Our use of NPT draws attention to the importance of sense-making and legitimisation as important steps in introducing a new set of practices within the work of an organisation. Integration also depends, across each mechanism of NPT, on the building of effective relationships, which allow individuals and teams to work together in new ways. By reflecting on our experiences and the decisions taken within CTR we have made explicit one such process for embedding qualitative research within a trials unit, whilst acknowledging that approaches may differ across trials units. Mindful of this fact, and the focus of the current paper on one trials unit’s experience, we do not propose a set of recommendations for others who are working to achieve similar goals. Rather, we offer three overarching reflections (framed by NPT) which may act as a useful starting point for trials units (and other infrastructures) seeking to promote the adoption of qualitative research.
First, whilst research organisations such as trials units are highly heterogenous, processes of embedding and integration, which we have foregrounded in this paper, are likely to be important across different contexts in sustaining the use of qualitative research. Second, developing a plan for the integration of qualitative research will benefit from mapping out the characteristics of the extant system. For example, it is valuable to know how familiar staff are with qualitative research and any variations across teams within an organisation. Thirdly, NPT frames integration as a process of implementation which operates through key generative mechanisms— coherence , cognitive participation , collective action and reflexive monitoring . These mechanisms can help guide understanding of which actions help achieve embedding and integration. Importantly, they span multiple aspects of how organisations, and the individuals within them, work. The ways in which people make sense of a new set of practices ( coherence ), their commitment towards it ( cognitive participation ), how it is operationalised ( collective action ) and the evaluation of its introduction ( reflexive monitoring ) are all important. Thus, for example, qualitative research, even when well organised and operationalised within an organisation, is unlikely to be sustained if appreciation of its value is limited, or people are not committed to it.
We present our experience of engaging with the processes described above to open dialogue with other trials units on ways to operationalise and optimise qualitative research in trials. Understanding how best to integrate qualitative research within these settings may help to fully realise the significant contribution which it makes the design and conduct of trials.
Availability of data and materials
Some documents cited in this paper are either freely available from the Centre for Trials Research website or can be requested from the author for correspondence.
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Hewison J. What can qualitative research do for randomised controlled trials? A systematic mapping review. BMJ Open. 2013;3(6):e002889.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Thomas KJ, Drabble SJ, Rudolph A, Goode J, Hewison J. Maximising the value of combining qualitative research and randomised controlled trials in health research: the QUAlitative Research in Trials (QUART) study – a mixed methods study. Health Technol Assess. 2014;18(38):1–197.
Clement C, Edwards SL, Rapport F, Russell IT, Hutchings HA. Exploring qualitative methods reported in registered trials and their yields (EQUITY): systematic review. Trials. 2018;19(1):589.
Hennessy M, Hunter A, Healy P, Galvin S, Houghton C. Improving trial recruitment processes: how qualitative methodologies can be used to address the top 10 research priorities identified within the PRioRiTy study. Trials. 2018;19:584.
Moore GF, Audrey S, Barker M, Bond L, Bonell C, Hardeman W, et al. Process evaluation of complex interventions: Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2015;350(mar19 6):h1258.
Bonell C, Fletcher A, Morton M, Lorenc T, Moore L. Realist randomised controlled trials: a new approach to evaluating complex public health interventions. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(12):2299–306.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
O’Cathain A, Hoddinott P, Lewin S, Thomas KJ, Young B, Adamson J, et al. Maximising the impact of qualitative research in feasibility studies for randomised controlled trials: guidance for researchers. Pilot Feasibility Stud. 2015;1:32.
Cooper C, O’Cathain A, Hind D, Adamson J, Lawton J, Baird W. Conducting qualitative research within Clinical Trials Units: avoiding potential pitfalls. Contemp Clin Trials. 2014;38(2):338–43.
Rapport F, Storey M, Porter A, Snooks H, Jones K, Peconi J, et al. Qualitative research within trials: developing a standard operating procedure for a clinical trials unit. Trials. 2013;14:54.
Cardiff University. Centre for Trials Research. Available from: https://www.cardiff.ac.uk/centre-for-trials-research . Accessed 10 May 2024.
Pell B, Williams D, Phillips R, Sanders J, Edwards A, Choy E, et al. Using visual timelines in telephone interviews: reflections and lessons learned from the star family study. Int J Qual Methods. 2020;19:160940692091367.
Thomas-Jones E, Lloyd A, Roland D, Sefton G, Tume L, Hood K, et al. A prospective, mixed-methods, before and after study to identify the evidence base for the core components of an effective Paediatric Early Warning System and the development of an implementation package containing those core recommendations for use in th. BMC Pediatr. 2018;18:244.
May C, Finch T, Mair F, Ballini L, Dowrick C, Eccles M, et al. Understanding the implementation of complex interventions in health care: the normalization process model. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007;7:148.
May C, Finch T. Implementing, embedding, and integrating practices: an outline of normalization process theory. Sociology. 2009;43(3):535–54.
Article Google Scholar
May CR, Mair F, Finch T, Macfarlane A, Dowrick C, Treweek S, et al. Development of a theory of implementation and integration: normalization process theory. Implement Sci. 2009;4:29.
Ogrinc G, Davies L, Goodman D, Batalden PB, Davidoff F, Stevens D. SQUIRE 2.0 (Standards for QUality Improvement Reporting Excellence): Revised publication guidelines from a detailed consensus process. BMJ Quality and Safety. 2016;25:986-92.
Craig P, Dieppe P, Macintyre S, Michie S, Nazareth I, Petticrew M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ. 2008;337:a1655.
Jamal F, Fletcher A, Shackleton N, Elbourne D, Viner R, Bonell C. The three stages of building and testing mid-level theories in a realist RCT: a theoretical and methodological case-example. Trials. 2015;16(1):466.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Members of the Centre for Trials Research (CTR) Qualitative Research Group were collaborating authors: C Drew (Senior Research Fellow—Senior Trial Manager, Brain Health and Mental Wellbeing Division), D Gillespie (Director, Infection, Inflammation and Immunity Trials, Principal Research Fellow), R Hale (now Research Associate, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University), J Latchem-Hastings (now Lecturer and Postdoctoral Fellow, School of Healthcare Sciences, Cardiff University), R Milton (Research Associate—Trial Manager), B Pell (now PhD student, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University), H Prout (Research Associate—Qualitative), V Shepherd (Senior Research Fellow), K Smallman (Research Associate), H Stanton (Research Associate—Senior Data Manager). Thanks are due to Kerry Hood and Aimee Grant for their involvement in developing processes and systems for qualitative research within CTR.
No specific grant was received to support the writing of this paper.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Trials Research, DECIPHer Centre, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Jeremy Segrott
Centre for Trials Research, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Sue Channon, Eleni Glarou, Jacqueline Hughes, Nina Jacob, Sarah Milosevic, Yvonne Moriarty, Mike Robling, Heather Strange, Julia Townson & Lucy Brookes-Howell
Division of Population Medicine, School of Medicine, Cardiff University, Neuadd Meirionnydd, Heath Park, Cardiff, CF14 4YS, UK
Eleni Glarou
Wales Centre for Public Policy, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, King Edward VII Avenue, Cardiff, CF10 3WA, UK
Josie Henley
DECIPHer Centre, School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, Sbarc I Spark, Maindy Road, Cardiff, CF24 4HQ, UK
Bethan Pell
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Qualitative Research Group
- , D. Gillespie
- , J. Latchem-Hastings
- , R. Milton
- , V. Shepherd
- , K. Smallman
- & H. Stanton
Contributions
JS contributed to the design of the work and interpretation of data and was responsible for leading the drafting and revision of the paper. SC contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. AL contributed to the design of the work, the acquisition of data and the drafting and revision of the paper. EG contributed to a critical review of the manuscript and provided additional relevant references. JH provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. JHu provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. NG provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. SM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. YM was involved in the acquisition and analysis of data and provided a critical review of the manuscript. MR was involved in the interpretation of data and critical review and revision of the paper. HS contributed to the conception and design of the work, the acquisition and analysis of data, and the revision of the manuscript. JT provided feedback on initial drafts of the paper and contributed to subsequent revisions. LB-H made a substantial contribution to the design and conception of the work, led the acquisition and analysis of data, and contributed to the drafting and revision of the paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Jeremy Segrott .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was not sought as no personal or identifiable data was collected.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
All authors are or were members of staff or students in the Centre for Trials Research. JS is an associate editor of Trials .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Segrott, J., Channon, S., Lloyd, A. et al. Integrating qualitative research within a clinical trials unit: developing strategies and understanding their implementation in contexts. Trials 25 , 323 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Download citation
Received : 20 October 2023
Accepted : 17 April 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08124-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative research
- Qualitative methods
- Trials units
- Normalisation Process Theory
- Randomised controlled trials
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

New Content From Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
- Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Meta-Analysis
- Methodology
- Preregistration
- Reproducibility

A Practical Guide to Conversation Research: How to Study What People Say to Each Other Michael Yeomans, F. Katelynn Boland, Hanne Collins, Nicole Abi-Esber, and Alison Wood Brooks
Conversation—a verbal interaction between two or more people—is a complex, pervasive, and consequential human behavior. Conversations have been studied across many academic disciplines. However, advances in recording and analysis techniques over the last decade have allowed researchers to more directly and precisely examine conversations in natural contexts and at a larger scale than ever before, and these advances open new paths to understand humanity and the social world. Existing reviews of text analysis and conversation research have focused on text generated by a single author (e.g., product reviews, news articles, and public speeches) and thus leave open questions about the unique challenges presented by interactive conversation data (i.e., dialogue). In this article, we suggest approaches to overcome common challenges in the workflow of conversation science, including recording and transcribing conversations, structuring data (to merge turn-level and speaker-level data sets), extracting and aggregating linguistic features, estimating effects, and sharing data. This practical guide is meant to shed light on current best practices and empower more researchers to study conversations more directly—to expand the community of conversation scholars and contribute to a greater cumulative scientific understanding of the social world.
Open-Science Guidance for Qualitative Research: An Empirically Validated Approach for De-Identifying Sensitive Narrative Data Rebecca Campbell, McKenzie Javorka, Jasmine Engleton, Kathryn Fishwick, Katie Gregory, and Rachael Goodman-Williams
The open-science movement seeks to make research more transparent and accessible. To that end, researchers are increasingly expected to share de-identified data with other scholars for review, reanalysis, and reuse. In psychology, open-science practices have been explored primarily within the context of quantitative data, but demands to share qualitative data are becoming more prevalent. Narrative data are far more challenging to de-identify fully, and because qualitative methods are often used in studies with marginalized, minoritized, and/or traumatized populations, data sharing may pose substantial risks for participants if their information can be later reidentified. To date, there has been little guidance in the literature on how to de-identify qualitative data. To address this gap, we developed a methodological framework for remediating sensitive narrative data. This multiphase process is modeled on common qualitative-coding strategies. The first phase includes consultations with diverse stakeholders and sources to understand reidentifiability risks and data-sharing concerns. The second phase outlines an iterative process for recognizing potentially identifiable information and constructing individualized remediation strategies through group review and consensus. The third phase includes multiple strategies for assessing the validity of the de-identification analyses (i.e., whether the remediated transcripts adequately protect participants’ privacy). We applied this framework to a set of 32 qualitative interviews with sexual-assault survivors. We provide case examples of how blurring and redaction techniques can be used to protect names, dates, locations, trauma histories, help-seeking experiences, and other information about dyadic interactions.
Impossible Hypotheses and Effect-Size Limits Wijnand van Tilburg and Lennert van Tilburg
Psychological science is moving toward further specification of effect sizes when formulating hypotheses, performing power analyses, and considering the relevance of findings. This development has sparked an appreciation for the wider context in which such effect sizes are found because the importance assigned to specific sizes may vary from situation to situation. We add to this development a crucial but in psychology hitherto underappreciated contingency: There are mathematical limits to the magnitudes that population effect sizes can take within the common multivariate context in which psychology is situated, and these limits can be far more restrictive than typically assumed. The implication is that some hypothesized or preregistered effect sizes may be impossible. At the same time, these restrictions offer a way of statistically triangulating the plausible range of unknown effect sizes. We explain the reason for the existence of these limits, illustrate how to identify them, and offer recommendations and tools for improving hypothesized effect sizes by exploiting the broader multivariate context in which they occur.
It’s All About Timing: Exploring Different Temporal Resolutions for Analyzing Digital-Phenotyping Data Anna Langener, Gert Stulp, Nicholas Jacobson, Andrea Costanzo, Raj Jagesar, Martien Kas, and Laura Bringmann
The use of smartphones and wearable sensors to passively collect data on behavior has great potential for better understanding psychological well-being and mental disorders with minimal burden. However, there are important methodological challenges that may hinder the widespread adoption of these passive measures. A crucial one is the issue of timescale: The chosen temporal resolution for summarizing and analyzing the data may affect how results are interpreted. Despite its importance, the choice of temporal resolution is rarely justified. In this study, we aim to improve current standards for analyzing digital-phenotyping data by addressing the time-related decisions faced by researchers. For illustrative purposes, we use data from 10 students whose behavior (e.g., GPS, app usage) was recorded for 28 days through the Behapp application on their mobile phones. In parallel, the participants actively answered questionnaires on their phones about their mood several times a day. We provide a walk-through on how to study different timescales by doing individualized correlation analyses and random-forest prediction models. By doing so, we demonstrate how choosing different resolutions can lead to different conclusions. Therefore, we propose conducting a multiverse analysis to investigate the consequences of choosing different temporal resolutions. This will improve current standards for analyzing digital-phenotyping data and may help combat the replications crisis caused in part by researchers making implicit decisions.
Calculating Repeated-Measures Meta-Analytic Effects for Continuous Outcomes: A Tutorial on Pretest–Posttest-Controlled Designs David R. Skvarc, Matthew Fuller-Tyszkiewicz
Meta-analysis is a statistical technique that combines the results of multiple studies to arrive at a more robust and reliable estimate of an overall effect or estimate of the true effect. Within the context of experimental study designs, standard meta-analyses generally use between-groups differences at a single time point. This approach fails to adequately account for preexisting differences that are likely to threaten causal inference. Meta-analyses that take into account the repeated-measures nature of these data are uncommon, and so this article serves as an instructive methodology for increasing the precision of meta-analyses by attempting to estimate the repeated-measures effect sizes, with particular focus on contexts with two time points and two groups (a between-groups pretest–posttest design)—a common scenario for clinical trials and experiments. In this article, we summarize the concept of a between-groups pretest–posttest meta-analysis and its applications. We then explain the basic steps involved in conducting this meta-analysis, including the extraction of data and several alternative approaches for the calculation of effect sizes. We also highlight the importance of considering the presence of within-subjects correlations when conducting this form of meta-analysis.
Reliability and Feasibility of Linear Mixed Models in Fully Crossed Experimental Designs Michele Scandola, Emmanuele Tidoni
The use of linear mixed models (LMMs) is increasing in psychology and neuroscience research In this article, we focus on the implementation of LMMs in fully crossed experimental designs. A key aspect of LMMs is choosing a random-effects structure according to the experimental needs. To date, opposite suggestions are present in the literature, spanning from keeping all random effects (maximal models), which produces several singularity and convergence issues, to removing random effects until the best fit is found, with the risk of inflating Type I error (reduced models). However, defining the random structure to fit a nonsingular and convergent model is not straightforward. Moreover, the lack of a standard approach may lead the researcher to make decisions that potentially inflate Type I errors. After reviewing LMMs, we introduce a step-by-step approach to avoid convergence and singularity issues and control for Type I error inflation during model reduction of fully crossed experimental designs. Specifically, we propose the use of complex random intercepts (CRIs) when maximal models are overparametrized. CRIs are multiple random intercepts that represent the residual variance of categorical fixed effects within a given grouping factor. We validated CRIs and the proposed procedure by extensive simulations and a real-case application. We demonstrate that CRIs can produce reliable results and require less computational resources. Moreover, we outline a few criteria and recommendations on how and when scholars should reduce overparametrized models. Overall, the proposed procedure provides clear solutions to avoid overinflated results using LMMs in psychology and neuroscience.
Understanding Meta-Analysis Through Data Simulation With Applications to Power Analysis Filippo Gambarota, Gianmarco Altoè
Meta-analysis is a powerful tool to combine evidence from existing literature. Despite several introductory and advanced materials about organizing, conducting, and reporting a meta-analysis, to our knowledge, there are no introductive materials about simulating the most common meta-analysis models. Data simulation is essential for developing and validating new statistical models and procedures. Furthermore, data simulation is a powerful educational tool for understanding a statistical method. In this tutorial, we show how to simulate equal-effects, random-effects, and metaregression models and illustrate how to estimate statistical power. Simulations for multilevel and multivariate models are available in the Supplemental Material available online. All materials associated with this article can be accessed on OSF ( https://osf.io/54djn/ ).
Feedback on this article? Email [email protected] or login to comment.
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.
Privacy Overview
- Open access
- Published: 09 May 2024
Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – how women with persistent health problems due to severe perineal trauma experience encounters with healthcare services: a qualitative study
- Katharina Tjernström 1 ,
- Inger Lindberg 1 ,
- Maria Wiklund 2 &
- Margareta Persson 1
BMC Health Services Research volume 24 , Article number: 610 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
102 Accesses
Metrics details
During the first year postpartum, about 25 per cent of Swedish women with severe perineal trauma (SPT), i.e., a third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration at childbirth, are unsatisfied with their healthcare contacts. Further, there is a lack of research on the more long-term experiences of healthcare encounters among women with persistent SPT-related health problems. This study explores how women with self-reported persistent SPT-related health problems experience their contact with healthcare services 18 months to five years after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
In this descriptive qualitative study, a purposive sample of twelve women with self-reported persistent health problems after SPT were individually interviewed from November 2020 – February 2022. The data was analysed using inductive qualitative content analysis.
Our results showed a paradoxical situation for women with persistent health problems due to SPT. They struggled with their traumatised body, but healthcare professionals rejected their health problems as postpartum normalities. This paradox highlighted the women’s difficulties in accessing postpartum healthcare, rehabilitation, and sick leave, which left them with neglected healthcare needs, diminished emotional well-being, and loss of financial and social status. Our results indicated that these health problems did not diminish over time. Consequently, the women had to search relentlessly for a ‘key person’ in healthcare who acknowledged their persistent problems as legitimate to access needed care, rehabilitation, and sick leave, thus feeling empowered.
Conclusions
Our study revealed that women with persistent SPT-related health problems experienced complex health challenges. Additionally, their needs for medical care, rehabilitation, and sick leave were largely neglected. Thus, the study highlights an inequitable provision of SPT-related healthcare services in Sweden, including regional disparities in access to care. Hence, the authors suggest that Swedish national guidelines for SPT-related care need to be developed and implemented, applying a woman-centered approach, to ensure equitable, effective, and accessible healthcare.
Peer Review reports
Intrapartum and postpartum healthcare should ideally be high-quality, evidence-based, and a positive experience stemming from woman-centred care with a holistic approach based on human rights [ 1 ]. This approach acknowledges each woman’s articulated needs and expectations in her social, emotional, physical, spiritual, and cultural context [ 2 ]. Nevertheless, during the first year postpartum, about one in four Swedish women with severe perineal trauma (SPT) [ 3 ], i.e., a third- or fourth-degree perineal laceration involving the anal sphincter muscle and anorectal mucosa at vaginal childbirth [ 4 ], are dissatisfied with their care and one in three women report ongoing health problems related to their SPT. Women with SPT may suffer from various physiological and psychological consequences such as pain [ 5 , 6 ] , incontinence [ 7 ], defecation problems [ 8 ], vaginal prolapse [ 5 ], sexual dysfunction [ 9 ] or depression and anxiety [ 10 , 11 , 12 ].
Reducing physical symptoms is essential to support emotional and social recovery after any perineal trauma [ 13 , 14 ]. Women with SPT emphasise that professional, competent, and respectful attitudes from healthcare professionals (HCPs), including individual and adapted information, facilitate, and promote their postpartum recovery. Thus, the HCPs’ competence and knowledge of treatment options is a prerequisite for women to access needed care [ 15 ]. An additional problem in the Swedish context is the lack of national recommendations or guidelines, which enables each of the 21 regions to develop own regional and local guidelines. An audit of the existing regional and local guidelines for prevention and care of SPT shows an unexpected diversity or lack of evidence-based recommendations [ 16 ]. However, dissatisfaction with access to healthcare has been expressed by women with persistent, i.e., beyond one year postpartum, SPT-related health problems [ 6 , 17 ]. Furthermore, women criticise inadequate or absent support [ 6 , 18 ], poor information and education [ 6 , 10 , 18 ], and lack of follow-up care regarding SPT and its potential psychological and social consequences [ 6 , 10 ]. Postpartum care focuses more on the baby than the mother’s well-being [ 18 , 19 ]. Also, the available treatment options are perceived as limited and outdated by those with access to needed care [ 17 , 18 ]. Moreover, women with SPT describe that some HCPs tend to normalise their SPT-related problems [ 10 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ], and women are met in unprofessional and disrespectful ways [ 17 , 23 ], where HCPs are perceived as ignorant, nonchalant, and questioning women’s symptoms [ 10 , 17 ]. Previous research [ 24 ] indicates an institutional objectification of women with SPT by Swedish healthcare providers hindering access to healthcare, sick leave, and occupational rehabilitation after SPT. In contrast, women also report being acknowledged and liberated when HCPs have a professional and empathic approach and provide continuity of care that enables access to care for persistent SPT-related health problems [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 25 ]. Thus, several women who sustained an SPT during childbirth do not experience access to needed and necessary care, a fact that needs further exploration.
Globally, sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) are crucial for individual health and gender equality [ 26 ]. Current issues within SRHR and midwifery are controlled by the institutional power in health institutions, i.e., medical power [ 27 ], connected to the still-existing economic and educational disadvantages of women globally, which are also feminist issues [ 26 , 28 ]. As midwife stands for ‘with woman’ [ 28 ], gender or feminist approaches are used in advancing midwifery theory [ 27 , 29 ] and various aspects of SRHR topics such as breastfeeding promotion [ 30 ], birth plans [ 31 ] and attitudes towards contraceptives [ 32 ]. In midwifery and feminist approaches, the biological material body and the socially constructed gendered body are viewed as intertwined [ 33 ]. Moreover, midwifery care is recommended to be woman-centred [ 1 , 2 ], focusing on the individual woman’s needs and transferring control from the institution to the woman herself. However, despite the different organisations of sexual and reproductive healthcare between countries, international research shows similar results regarding women’s diverging experiences with postpartum SPT-related healthcare [ 6 , 15 , 17 , 18 ].
In sum, there is growing evidence showing that many women with persisting health problems caused by SPT are often, but not always, met with mistrust and ignorance when seeking care for their problems. Even though there may be national, regional, or local protocols or guidelines for care after SPT, women with persistent SPT-related problems still raise their voices about the difficulty of getting access to competent quality care. This indicates a potential gender bias [ 34 ] and a need for gender theoretical perspectives in midwifery [ 28 ], as utilized in this study. Additionally, few studies explore the care-seeking experience among this group of women in a longer time perspective after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
The aim of this study is to explore how women with self-reported persistent SPT-related health problems experience their contact with healthcare services 18 months to five years after childbirth when the SPT occurred.
Study design and context
The present study is part of a larger research project investigating the long-term consequences of SPT on quality of life, working life, and healthcare contacts. This study had an inductive qualitative interview study design applying qualitative content analysis to analyse data [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. This method searches for patterns, e.g., by identifying similarities and differences in the data. The researchers obtain an in-depth understanding of the studied phenomenon through abstraction and interpretation [ 36 ]; thus, an appropriate method to apply to capture women’s experiences of their healthcare encounters when seeking medical help and support. Throughout the research process, the recommendations for qualitative research according to ‘Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research’ (COREQ) were followed [ 38 ].
Sweden has 21 partly independent regions primarily responsible for providing healthcare services to the population. Healthcare services are tax-funded, and the regions have extensive autonomy to decide upon the healthcare services within each region based on the frameworks of the Health and Medical Service Act [ 39 ]. Additionally, within the Swedish social security system, 480 days of paid parental leave are allocated to each child in Sweden and can be utilised by their legal guardian(s) until the child is twelve years old. Of these 480 days, 60 days are specifically assigned to each parent, and the remaining days are split between parents as desired. The financial compensation is based on the parent’s income and is financed by taxes [ 40 ].
In Sweden, midwives are the primary care providers to women with normal pregnancies, births, and postpartum care. In case of complications to pregnancy and childbirth, midwives collaborate with other medical professionals, especially obstetricians. For example, midwives suture first- and second-degree perineal lacerations, while obstetricians are responsible for all SPT repairs [ 41 ]. Generally, in Sweden, women who sustain an SPT during childbirth are offered a check-up with the obstetrician responsible for the repair before discharge and should also have a follow-up with an obstetrician or sometimes a physiotherapist within the postnatal period. Thereafter, women with no mayor initial healing problems are advised to contact relevant healthcare services if any health issues related to the SPT should arise in the future. Women presenting with complicated healing are treated accordingly. Additionally, women with second- to fourth-degree perineal lacerations are assessed with questionnaires three times during the first year postpartum by the National Perineal Laceration Register. However, there are no recommendations in Sweden for prolonged check-ups for women with SPT after the postnatal period and no guidelines on organised check-ups for women with prolonged symptoms due to SPT exist [ 42 , 43 ].
Women with persistent SPT-related health problems and characteristics were purposively recruited to achieve a heterogeneous sample reflecting multiple experiences. An overview of inclusion and exclusion criteria can be found in Table 1 .
The closed Swedish Facebook community ‘Förlossningsskadad? Du är inte ensam!’ [‘Injured at childbirth? You are not alone!’] functioned as a recruitment platform for a national sample of women reporting persistent SPT-related health problems. The Facebook community is secluded to women with SPT and started in 2014. During the data collection period (Nov 2020 – Feb 2022), the group had over 7,600 members; today, the community has grown to include over 9,500 members [ 44 ].
In late November 2020, the administrators of the Facebook community pinned a digital poster with study information and a link to the study homepage in the group feed. The study homepage contained written information on the research project and contact details for the research group if any women wanted additional information about the study. Interested potential participants contacted the research group via a contact form on the homepage, and the first author (KT) confirmed that the potential participants met the inclusion criteria via telephone. Thirteen participants from different parts of Sweden showed interest in participating and left their contact information. One woman never responded to our efforts to reach her. The remaining twelve women fulfilled the inclusion criteria and were invited to an interview. Before the interview, the women answered a digital survey on background data (such as demographic data, education, employment, sick leave, and childbirth history) distributed via REDCap ® , a web-based application to create secure online questionnaires and research databases [ 45 ]. The interviews were finalised in February 2022.
Data collection
We collected data via individual open-ended interviews [ 46 ], supported by a semi-structured interview guide [see Additional file 1 ]. The interview guide, developed by KT and MP with input from MW and IL, was based on literature reviews, our awareness of gender as a social construct [ 33 ], and the clinical pre-understanding within the research group. After a pilot interview conducted by KT (not included in the data), minor adjustments were made to the interview guide. The final interview guide covered the topics of everyday life experiences, work, and general functioning. However, despite the mentioned interview topics, the emergent study design and the ability to speak freely about what was perceived as important for their daily functioning, the contacts with healthcare services was brought up in vivid and extensive narratives by all participants as part of their descriptions of their challenges in everyday life and their ability to function at work. Hence, the experiences the women made of the healthcare services played an important role for the women in their daily management of SPT-related health problems.
As data collection occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic, all participants were interviewed digitally via Zoom ® [ 47 , 48 ]. With the participant’s consent, the interviews were audio-recorded via Zoom ® and a separate digital recorder (as backup). Any Zoom video files automatically generated were deleted directly after the termination of the interview to protect participants’ identities. The first author interviewed all women; in two interviews, co-authors (IL or MW) also attended. The authors had no professional or personal affiliation with the enrolled participants . Detailed interviews ranging from 29 – 112 minutes (median: 61.5 minutes) gave extensive data. All interviews were performed in Swedish and transcribed verbatim. After that, the first author validated the transcripts for accuracy by reviewing the text while listening to the recordings.
Authors’ pre-understanding and theoretical positionality
The research group comprises three midwives (KT, IL, MP) and one physiotherapist (MW). We all have extensive professional experiences from clinical practice in primary and in-patient care, where three authors (KT, IL, MP) have specific professional experiences of caring for women with SPT. Additionally, we are women, feminists, and mothers with various birth experiences. Further, the group holds expertise in gender studies and qualitative research within midwifery science, such as perineal trauma and medical sociology. Hence, we stem from a social constructivist research standpoint and utilise ourselves as co-constructors in the analysis process. As feminist researchers, we apply a gender theoretical lens to the data.
Data analysis
The interviews were analysed using qualitative content analysis with an inductive and stepwise approach focusing on the manifest and latent content [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. The interviews, transcripts, and analysis steps were performed in Swedish.
The analytical procedure started with reading the transcripts multiple times while highlighting text, meaning units, with content relevant to the aim of this study. Then, identified meaning units were condensed, focusing on preserving their core meaning and labelled with manifest codes [ 35 , 36 , 37 ]. Initially, KT coded one interview and triangulated those codes with the principal investigator (MP). KT then coded the rest of the interviews. In the next step, similar codes were clustered, forming subcategories based on the manifest content. Moving towards an interpretation of the content, categories were created by the abstraction of subcategories. This was done by KT and MP separately and then triangulated to identify significant concepts. Next, the preliminary categories and subcategories were triangulated with the whole research group until a consensus was obtained. To answer the question of ‘what?’ and ‘how?’ within the data, the latent content and thread of meaning were identified by clustering and abstracting the emerging findings to form subthemes and a theme [ 36 , 37 ]. The emerging findings were also peer-reviewed and discussed at a research seminar. The finalisation of the analysis resulted in an overarching theme and four subthemes. The translation of categories, subthemes, theme and inserted citations from Swedish into English was performed as a last step. The translation and choice of words were discussed between authors (all knowledgeable in English) to reach a consensus and minimise translation bias.
During the coding process, the researchers used MAXQDA ® [ 49 ], a software for organising, transcribing, analysing, and visualising qualitative research data, and Microsoft Excel ® [ 50 ] as aids to organise the codes.
Demographics of included participants
The background characteristics of the twelve participants in the final sample are presented in Table 2 .
The participants identified themselves as cis women, i.e., their gender identity matched their sex assigned at birth [ 51 ], and are thus referred to as ‘women’ in this paper. All women were in a partner relationship. The women reported a broad spectrum of physical and phycological health problems following the SPT at childbirth, e.g., urine or anal incontinence, pain in the lower abdomen, sexual dysfunction, and depression. Thirty per cent of the women had full-time employment, and the proportion of parental leave varied from 12% to 100% (three women had an ongoing parental leave with subsequent children at the interview). Further, 60% of the women had a sedentary occupation. Five women had been on sick leave after reconstructive surgery, and five reported sick leave for other reasons than their SPT.
The analysis resulted in one theme, ‘Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body’, with related subthemes ‘Questioning whether it’s all in my head’, ‘Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land’, ‘Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight’, and ‘Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system’. An overview of the findings is presented in Table 3 . The findings are presented as an overarching theme and thereafter, the related subthemes and categories. Citations from the participants illustrate the findings. All women have been allocated pseudonyms in the result presentation.
Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body
The latent theme ‘Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – living the paradox of a normalised but traumatised postpartum body’ represented the women’s experiences of healthcare encounters covering HCPs’ diminishing attitudes towards women’s persistent SPT-related health problems and the women’s difficulties accessing healthcare and sick leave. We interpreted that the women were assessed by the HCPs’ ‘obstetric gaze’, i.e., a medical gaze in postpartum healthcare normalising their persistent health problems and judging the women’s lower abdomen as ‘fine’ by their looks. The obstetric gaze put the women in a paradoxical situation where HCPs normalised tangible symptoms to be a natural part of childbirth. With no medical legitimacy of the health problems, the women also felt labelled as ‘hysterical’ (exaggerating health problems) by the HCPs. As a result, on the one hand, they had to continue facing persistent and tangible health problems such as incontinence, pain or prolapses. On the other hand, no acknowledgement by HCPs of their health problems led them to question whether their problems were merely a product of their imagination and, thus, only existed ‘in their head’. The theme also comprised women’s struggle for legitimacy in a gendered healthcare system - a no-(wo)man's land. They experienced that healthcare services and social insurance systems were challenging to access and demanded a tenacious and extensive fight to obtain legitimacy for their health problems. Consequently, the women had to put up with neglected healthcare needs, negatively impacting their physical and emotional well-being, and financial and social status when no medical help or rehabilitation was available. However, some women had encountered an HCP who was empathic and understanding, hence not guided by the obstetric gaze. Such encounters legitimised persistent problems and were crucial for accessing needed care, sick leave, and rehabilitation.
Questioning whether it’s all in my head
The subtheme ‘Questioning whether it’s all in my head’ focused on the women’s experiences of facing ignoration and no confirmation of perceived health problems and thus being labelled as a hysterical woman. The related categories referred to a normalisation process that the women experienced in their encounters with HCPs, which made them question their bodily perceptions. Furthermore, the women felt accused of exaggerating symptoms because their persistent SPT-related health problems did not match HPCs’ views of acceptable postpartum symptoms. Thus, it could be understood that the women found themselves in a paradox of suffering from tangible physical consequences after SPT, which were normalised by HCPs and their ‘obstetric gaze’.
Facing HCP's ignoration of perceived problems
The women experienced the HCPs defining their persistent health problems after the SPT as ‘normal’. The HCPs assured the women that their problems would disappear with time or that transient motherhood-related aspects, such as breastfeeding or fragile vaginal mucosa, were the cause of the problem. One woman expressed:
“Then I felt, ‘It should not feel like this; this is something wrong’, and I sought medical attention and was seen by multiple physicians […] They thought my vaginal mucous membrane was not ready for intercourse. I was still breastfeeding, so they thought I should stop breastfeeding. Then maybe the mucous membrane would be restored, which was causing me the pain. I was not listened to at all. I was treated very poorly by one physician in particular, and despite second opinions and so on, nobody… nobody took me seriously.” (Linda)
Consequently, the women perceived that their concerns were ignored. They also learned that the HCPs saw their prolonged physical problems after SPT as an inevitable part of childbirth, which the women should accept. One woman resigned:
“But then [the physician] says something like this: ’Well, that's completely normal’, but I felt like, ‘Yes, but it doesn't feel normal'.” (Emma)
After the genital and pelvic floor examinations, the HCPs often guaranteed the women that ‘everything looked fine’, i.e., reinforcing the normality of the genital area. Although the women described to the HCPs that they struggled with SPT-related problems, their concerns were met with a comment on the physical appearance rather than a comprehensive examination of the pelvic floor's functionality.
One woman responded:
“They think ‘everything looks fine’ and ‘everything looks good and repaired’. I still have problems. I was also referred to a surgeon, who did a rectoscopy, and ‘it looked so nice’. Then, I was referred to a urotherapist to learn how to pinch my muscles because ‘everything would be so good’. She helped me get a second opinion in XX [town], where they discovered that there was still damage." (Jin)
Another woman expressed:
”I couldn’t care less what it [genital area] looks like. Nobody will be down there watching. I only need it [genital area] to function as intended.” (Anna)
Consequently, the women felt ignored and unheard in their contact with healthcare services. They perceived that HCPs did not listen to them, leaving them feeling invisible, sometimes even having severe health problems.
“I was hospitalised with sepsis before someone listened to me.” (Josefin)
Being labelled as a hysterical woman
The women also experienced being labelled as the ‘hysterical woman’ who exaggerated their persistent symptoms and had mental health problems. The women described how the HCPs accused them of imagining their SPT-related health problems. One woman indignantly revealed that the HCP she encountered said, 'These problems only exist in your head’ (Joanna), i.e., suggesting that the perceived symptoms did not exist and rejecting the health concerns. Hence, this attitude made some women believe their problems were a product of their imagination and sometimes made them even question their sanity.
Moreover, the HCPs’ condescending attitudes towards the women made them feel dismissed and devalued. For example, the women shared that HCPs laughed at them or were rough or cold during the examination. Moreover, HCPs expressed that they had ‘seen worse’ (Amanda). Some women also conveyed that they were advised ‘to drink some wine to feel better’ (Elin) when discussing painful intercourses due to their SPT-related health problems.
“You are constantly dismissed, ‘No, but everything looks fine, you have no problems’. Then you start to think you’re imagining things. And then you may not dare to talk about the injuries.” (Jin)
Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land
The subtheme ‘Fighting persistently for access and legitimacy in no (wo)man's-land’ referred to the women’s experience of gender constructs related to inaccessible healthcare services and their often year-long struggles to access this gendered healthcare and linked social insurance systems. The difficulties in accessing care created negative attitudes towards the healthcare services, making the women wish for general improvements in women’s healthcare.
Struggling to access the gendered healthcare and social insurance systems
The women pointed out that after giving birth, they needed more extensive information on their injury, precautions, available help (follow-up care or re-operation), and sick leave. To overcome the lack of required information, they had to request or actively search for it on their own, which also led to uncertainty about where and when to seek further help if needed.
“I was sent home with a brochure and a pat on the shoulder.” (Amanda)
The women also experienced a lack of adequate healthcare services targeted at their SPT-related health problems. For example, many women did not have access to a pelvic floor clinic or had to travel long distances to see specialists. Hence, their place of residence decided the quality of care the women received. Moreover, some women problematised the organisation of postpartum care as they missed out on follow-up care and even, in some cases, were denied follow-up care or referrals to specialised care were lost. As a result, some women had no opportunity to talk to the operating physician or experienced no follow-up care, although they requested it.
“They said it can take up to a year to get better. So, when that year had passed, and before starting to work again, I called different places in the hospital and asked: What should I do now? […] It took several months before I got an appointment with the surgeon for an assessment. And then I had to get a second opinion. So, it took like seven months before I got an appointment at [a specialist clinic].” (Hawa)
For the women, access to healthcare services, sick leave certificates, and HCPs’ dismissive attitudes were perceived as gender-related, i.e., difficulties in obtaining help from women’s healthcare services would not exist if the services were more women-oriented. One woman illustrated this by expressing: ‘If men gave birth to babies, the situation would not be like this’ (Joanna). Moreover, they perceived that women’s healthcare services were not prioritised. They explicitly stated that the absence of sick leave certificates and benefits was related to their gender. The women were expected to cope without sick leave benefits because vaginal and perineal lacerations of any scope were viewed as a natural part of childbirth, a normal process of a woman’s body. Thus, sequelae thereof did not exist or were taboo in society.
“Everything that happens during and after childbirth and related injuries has been a taboo discussion topic, so it has been completely ‘normal’ to suffer from persistent pain.” (Anna)
“I have applied for compensation from the national patient insurance. I got rejection after rejection; nothing has gone wrong. I was told: 'You simply must expect these things in childbirth. And a caesarean section is not less risky'.” (Hawa)
Thus, the women argued that society and the government did not invest needed resources in women’s healthcare. In addition, those few women receiving a short period of sick cash benefits had it immediately after giving birth or after re-operation, but not for prolonged problems. Further, the women noted that they were not offered sick leave certificates due to persistent physical SPT-related health problems but instead due to mental issues, such as depression or anxiety.
“I've heard about women who have been mentally unwell and have hurt their children. So maybe physicians get cautious and put women on sick leave if they say, ‘I'm not feeling mentally well’. Then they act quickly because they think it's so important. But they don't think about the physical injuries because that's part of [childbirth].” (Jenny)
However, the women shared how they fought long and hard for acknowledgement and care and made demands; for many, this process had covered years. They had to repeatedly insist that something was wrong and felt pressure to prove their health problems to the HCPs. In some women, this led to their persistent problems being diagnosed and acknowledged after several years of delay. The struggle for care involved countless visits and referrals to different HCPs, demanding much strength and persistence, which exhausted them. Sometimes, the sequelae had to develop into an acute health situation, or some women decided to pay for private care to access the proper treatment and rehabilitation. Further, with time, they also became explicit about their demands for sick leave certificates and benefits.
“Well, it [short sick leave period because of birth traumas] just feels like scorn. To me, it is not a sufficient length of sick leave.” (Elin)
Wishing for improvement in women's healthcare
The perceived lack of adequate care and rehabilitation, access to sick leave benefits, and HCPs’ attitude negatively influenced the women’s opinions on healthcare services, especially postpartum healthcare. In addition, the women perceived many HCPs as unprofessional, indifferent, and unstructured. As a result, the women mistrusted the HCPs and lost hope in healthcare services. Thus, they were reluctant to seek further care and were anxious about receiving proper treatment or that HCPs would miss important things.
“I am not being listened to in women's healthcare. This is partly why I feel so disappointed.” (Linda) “You just don't trust the healthcare system. […] Some people have been struggling with their injuries for like 18 years. But the [specialist clinic] – I finally received fantastic treatment, and what if it could be available everywhere [in Sweden]?” (Hawa)
Moreover, the women described a struggle for their rights when deciding whether to report the HCPs to the authorities and pointed out the need to improve women’s healthcare. Reporting HCPs was perceived as complicated as the women did not want to blame specific individuals. The women saw that the major problem lay within the healthcare system and with individual HCPs.
“In the end, I met a fantastic person [healthcare professional]. She wanted me to report the mistreatment when I eventually had the strength. Because no one listened when I said I was ill. So, she has offered to help me if I want to, but I don't know if I have the strength to file a complaint.” (Josefin)
A wish to improve women’s healthcare services was articulated, especially regarding personal follow-up care beyond one year postpartum and the possibility of full-time or part-time sick leave certificates and benefits for persistent problems on equal terms. This wish also strengthened their decision not to give up searching for help and to raise their voices to help themselves and other women.
“I received physiotherapy and the follow-up surveys [the Perineal Laceration Register] during the first year, but thereafter I would have liked to have an annual follow-up for the next years to ensure the status and potential re-operations. […] I can google, but I want to have that information in dialog with a living person, but you do not get that.” (Jenny)
Partaking in developing educational material for HCPs or starting a career within women’s healthcare were some women’s ways to contribute and increase competency in persistent SPT-related health problems.
“One of my strategies since I got the injury is also to try to influence. Being able to be involved and influence what postpartum care should consist of.” (Jin)
Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight
The subtheme ‘Facing multidimensional losses when no help in sight’ covered physical and mental health consequences and the financial and social losses the participating women faced when no support or access to needed care and rehabilitation was provided.
Being physically victimised by HCP's malpractice
The women’s experiences covered either being misdiagnosed during the suturing after birth or in the following years when seeking help for persistent SPT-related health problems. Further, they shared how physicians had incorrectly sutured vaginal and perineal muscles after childbirth, leading the women to live with incontinence, pain, prolapses, or sexual dysfunction if their vaginas were sutured too tight. They also described how they endured infections, wound ruptures, sepsis, necrosis, and re-operations. Additionally, the women perceived a general lack of competency regarding communication and persistent SPT-related health problems, including problems related to sex life and sexual functioning, besides a more specific lack regarding suturing techniques and ultrasound examinations.
“I was referred to a specialist clinic. And they found out that all the muscles were separated, the internal and external sphincters were torn, and my pinching ability was kind of weak. So, it was quite the opposite, really, quite the opposite. None of what the other physician had said was true [laughs]. Absolutely incredible. And she is supposed to be a specialist.” (Hawa)
Aching inside
Living with troubled postpartum bodies and the absence of HCPs’ legitimation of the women´s problems made them struggle mentally, feeling speechless and silenced. This neglect reinforced irritation, anger, distress, bitterness, and disappointment towards the HCPs and the healthcare services. One woman illustrated the emotional struggle in this way:
“It's just that the health services don’t believe you, which makes you feel terrible. It's a big deal that no one listens.” (Josefin)
Moreover, the women felt uncertain about their health status due to a default medical diagnosis with concerns for their future and which staff to trust. Consequently, some had to bite the bullet, put up with their situation, and try to think positively. Other women were denying or diminishing their SPT-related health problems, accepting that their symptoms would improve, even disappear or that their condition was ‘normal’ as they had been told. Further, the women described despair because their neglected health problems caused by their SPT made them feel exposed, unsure, and hopeless. In some, this desperation resulted in a mental breakdown, a fear of losing custody of their child due to mental illness or suicidal thoughts.
“Something broke inside of me that day. I felt entirely omitted; I was close to leaving my son and committing suicide. Nobody understood how bad everything was.” (Elin)
Additionally, the women suffered emotionally when motherhood was crushed. Their partner had to take the primary responsibility for the family, and the children had to come in second place as the mothers suffered from various physical and mental health problems. As a result, the women felt they missed their children’s development and could not use their parental social security benefits as desired.
“I feel devasted because people tell me, ‘You are on maternity leave’. I’m not on maternity leave; I’m sick. I should be on sick leave.” (Jaanika)
Suffering financial and societal losses
Moreover, the women suffered financially and societally due to persistent health problems. Some women were denied financial compensation from Patient Insurance (a national insurance system where patients can seek compensation for care injuries). The Social Security Agency and the HCPs were perceived as obstacles to receiving sick cash benefits. They noted that ‘extensive’ health problems were required to receive sick cash benefits and that their health problems paradoxically were not seen as extensive or even a problem per se by the HCPs; hence, no sick leave certificates were issued.
“He [the physician] tried to argue and clarify my pain situation in the sick leave certificate to meet the requirements for a sick leave benefit at the Social Security Agency. I was in so much pain and had to lie down to breastfeed. But, no, ‘If you can manage to hold the baby when breastfeeding, then you are on maternity leave, not sick leave benefit’ [mimicking the official at the Social Security Agency who rejected the certificate and consequently also the sick cash benefit]”. (Jaanika)
Furthermore, the women were set back financially and societally because they could not work full-time due to their persistent health problems. Therefore, some women chose to compensate for their work absence with part-time parental benefits to diminish their working hours and cover their inability to work due to persistent SPT-related health problems. Without a sick leave certificate, i.e., the physicians or the officials at the Social Security Agency’s acknowledgement of a ‘true’ health problem, partners or other relatives were obliged to adjust their work schedules to support or unburden the woman’s suffering and inability to work full-time. This reduction in working hours for the SPT-affected women and, in some cases, their partners was expressed to potentially negatively affect their upcoming careers and pensions. As a result, the women experienced being caught between stools in the social insurance systems:
“[…] You end up in a position where you are neither on sick leave nor unemployment benefits and at the same time cannot perform any offered work [due to persistent problems]. But multiple societal bodies demand and expect you to be a part of the working force, and nobody really listens.” (Elin)
Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system
The last subtheme, ‘Depending on other’s advocacy to navigate an arbitrary system’, highlights the women’s experiences of, often by chance, finding a single devoted professional, i.e., a ‘key person’, to access needed care and rehabilitation. Such a ‘key person’ was vital to recognising persistent problems, legitimating symptoms, and enabling access to needed care, sick leave, and rehabilitation. The women who finally had legitimation for their health problems described that the medical diagnosis also came with a feeling of sanity and empowerment, relieving them of their paradoxical situation.
Encountering a ‘key person’ to receive needed care
A support system was a prerequisite for enduring their health problems and finding the strength to fight for access to care. This system could be a partner, other family members, or friends who gave the women power and courage, but most importantly – encountering a professional who saw their problems and provided referrals or other options to obtain the needed help and support. In most cases, women would search for years for competent HCPs, such as midwives, physicians, or physiotherapists, who would listen and acknowledge persistent problems. This ‘key person’ showed empathy and trustworthiness, creating relief and security. Further, the ‘key person’ was portrayed as competent, attentive, professional, and respectful. The ‘key persons’ also shared women’s outrage at the mistreatment and default healthcare they endured. Additionally, these ‘key persons’ were surprised that the women were not on sick cash benefits due to their symptoms and that they had to compensate for their financial situation with parental benefits or reduced working hours and lower salaries. Consequently, finding this ‘key person’, often by chance or word of mouth, was crucial for accessing care and marked a significant turning point in the women’s recovery.
“I sought help from another midwife, as I felt something was wrong. This midwife referred me to the physiotherapist, who referred me to a specialist, who then referred me to surgery and rehabilitation.” (Malin)
Some women received follow-up care for their persistent SPT-related health problems during the first year postpartum. If persistent problems occurred and were acknowledged, the women were offered different surgical approaches with various outcomes, consultations by colon specialists, physiotherapy, and psychiatric care. They were grateful for the help they received but felt more comprehensive care was needed.
Feeling sane and empowered
Confirmation of persistent SPT-related health problems was expressed as liberating, strengthening and, as one woman put it, a ‘win’ (Elin). Receiving a medical diagnosis and appurtenant treatment was relieving because the medical confirmation of the symptoms released a considerable burden. These women described being acknowledged, and the diagnosis proved that health problems existed, and the struggles were not in vain. Furthermore, it explicitly stated to everyone, including themselves, that they were not ‘crazy’, ‘imagining things’ or ‘hysterical’.
“So, my laceration has been classified as an injury caused by the healthcare services. This was somehow a confirmation. It's not just that it's in my head, but it has been established that it is a medical injury, and it could have been avoided.” (Jin)
Alongside feelings of sanity and being legitimised, the women experienced empowerment. The women felt supported and confident. Thus, finding an agency to address the taboo of their SPT by talking openly about it and helping others in the same situation was also seen as therapeutic. Further, the legitimation of the sequelae and access to appropriate care gave them time to heal and process their trauma. Receiving sick leave certificates and benefits was seen as a part of the empowerment and legitimacy of their persistent SPT-related health problems, reducing stress, and easing the financial burden. Furthermore, access to occupational rehabilitation and understanding at work became available. Thus, the women who had received the help they needed after a struggle to obtain it were hopeful about the future and possible recovery.
“I have regained my authority to speak up. It [SPT-related health problems] should be out in the open, not withheld.” (Jaanika)
Our main finding was that women with persistent health problems due to SPT at childbirth were caught in a paradox of living in a normalised but traumatised body, and their health problems were rejected as postpartum normalities. Furthermore, our results elucidated the difficulties in accessing postpartum healthcare, rehabilitation, and sick leave benefits. Therefore, the women struggled with neglected healthcare needs, diminished emotional well-being, and loss of financial and social status. Our study highlighted experiences up to 5 years after sustaining SPT, which showed that some women’s SPT-related health problems do not diminish with time. They faced challenges functioning in daily life, at work, and in society. In contrast, finding a ‘key person’, i.e., a professional who acknowledged the women’s persistent problems as legitimate, was a prerequisite for accessing all the needed care and sick leave and enhancing empowerment for the women. Thus, this ‘key person’ was not blinded by the obstetric gaze and instead used their agency and advocacy as support.
In the following, we will discuss our findings related to other empirical studies and problematise them with theoretical reflections.
The paradox of normalising the postpartum body
In our findings, the paradox arose when the HCPs dismissed physical health problems after SPT despite women’s perceived symptoms. Central in this context was a normalisation process where health problems were regarded as ‘normal’ by HCPs, a phenomenon also found in prior research on SPT [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 ]. The HCPs’ normalisation of women’s health problems can also be found regarding other medical conditions affecting women, such as pelvic organ prolapse [ 52 ], menstrual pain [ 53 ], endometriosis [ 54 ] or nausea and vomiting during pregnancy [ 55 ]. In light of the medicalisation of women’s healthcare, where the medical field has sought to pathologise natural bodily processes such as pregnancy and childbirth [ 33 ], actual medical conditions such as persistent SPT-related health problems are paradoxically normalised. Our findings, therefore, highlight the need to challenge HCPs’ views of what constitutes a ‘normal postpartum body’ or ‘normal postpartum symptoms’ after sustaining SPT.
The key to healthcare
In the context of denied legitimacy of health problems and neglected needs, it appeared that the women became dependent on the goodwill of a ‘key person’, personified as the respectful, competent, and empathetic HCP. Prior research on SPT has also found women struggling with accessing healthcare [ 6 , 17 ] and specific HCPs as enablers of care [ 12 ]. The dependency on a ‘key person’ to access adequate care might highlight a structural problem within the provision of postpartum SPT-related healthcare. Globally, there are a few national guidelines on SPT management and prevention [ 56 ]. Additionally, no national guidelines regarding postpartum care of SPT exist in Sweden, and pelvic floor teams are only available in some Swedish regions [ 16 ]. In our study, the women lacked information, and competent HCPs were hard to find or located far away. Other studies have shown poor patient information and education as a postpartum problem [ 6 , 10 , 18 ], indicating a need to develop targeted oral and written information on wound healing and recovery. Further, women in Australia describe similar challenges to accessing SPT-related healthcare when having persistent SPT-related health problems [ 18 ]. The absence of national Australian guidelines may have led to inconsistent care, failing to meet women’s healthcare needs. Further, women from rural areas have had additional difficulties accessing needed care. In 2021, a clinical standard for SPT was implemented in Australia, comprising care standards for follow-up [ 57 ]. Thus, to improve the national situation in Sweden, more research and resources must be allocated to develop evidence-based recommendations, preferably internationally accepted guidelines [ 56 ]. Moreover, the accessibility of SPT-related healthcare, such as pelvic floor clinics, needs to be expanded so that women can easily meet their ‘key person’ if required.
Woman-(de)centred care?
We found that HCPs were obstructed by their obstetric gaze when assessing women with persistent SPT-related health problems. Obstetric gaze derives from the medical gaze notions [ 58 ], suggesting a gaze that splits the individual from the body, constructing the care-seeker as a medical object or condition instead of an individual with a social context. This gaze blinded HCPs who normalised obvious health problems. Recent advances in women’s healthcare in industrial countries and midwifery research show development towards continuity of care models with a woman-centred approach in different caseload-midwifery projects and informed choice regarding place of childbirth [ 28 , 59 , 60 , 61 ]. Wom e n-centred care [ 2 ] is a widespread care philosophy within midwifery that advocates for providing individualised care to women. Further, wom a n-centred care emphasises the individual woman’s healthcare needs and situation, incorporating the concepts of choice, control, continuity of caregiver, and self-determination. It can be argued that the obstetric gaze obstructed HCPs in providing wom a n-centred care because they did not acknowledge the women’s healthcare needs. Consequently, the women did not have control over their health situation. Making women feel empowered [ 2 , 62 ] is crucial in woman-centred care. Hence, the ‘key persons’ in our study managed to provide wom a n-centred care where acknowledgement of problems as real medical problems and access to care made the women experience empowerment. Therefore, we argue that guidelines regarding follow-up care after SPT should ideally be developed with wom a n-centred care as its core.
Everything looks fine
The biomedical model has traditionally focused on normality and abnormality rather than health [ 63 ]. Theoretically, the ‘obstetric gaze’ is closely tied to the ‘medical gaze’ and the ‘male gaze’, referring to the biomedical paradigm and its power [ 27 , 58 ]. In our study, the obstetric gaze judged the women’s persistent health problems due to SPT as ‘normal’ and the appearance of their genital area as ‘fine’, which created a paradoxical situation regarding the legitimacy of their ongoing health problems after SPT. Generally, the healthcare sector is critiqued for reducing the body to only incorporating organs and tissue, i.e., focusing on physical symptoms [ 27 ].
The women in our study, of which most showed more than one significant symptom after SPT, noted that HCPs would comment on the physical appearance of the perineal area rather than its functionality by telling them that ‘everything looked fine’. The focus on looks rather than functionality regarding SPT-related health problems aligns with the findings presented by others [ 17 ]. Having women describe how their persistent physical pelvic floor problems after SPT during childbirth are trivialised, normalised, questioned, and labelled as mental health issues is of utmost concern. This implies the need for rapid improvements in HCPs’ knowledge and organisation of care but also raises the question of what is considered a normal status and recovery after any perineal laceration in the short- and long-term perspective. A similar discursive focus on women’s appearance instead of their health problems has also been found among HCPs when women seek care for chronic pain [ 64 ]. The sentence ‘Everything looks fine’ can be interpreted as an objectifying, gendered discourse in an obstetric context. This discourse may reinforce the obstetric gaze and, in the broader sense, the medical gaze [ 58 ]. The Swedish Health and Medical Care Act [ 39 ] advocates for the respectful treatment of patients. Hence, it is noteworthy that the women experienced being judged by the looks of their genital area in their medical encounters rather than HCPs addressing the functionality. Such treatment does not align with the legislation and calls for a discourse analysis of the attitudes of HCPs towards women with persistent SPT-related health problems and their experiences of providing care for affected women.
Being subjected to obstetric gaslighting
In light of the women’s perception of their dismissal as dramatic, illegitimate, and irrational patients, we argue that they faced so-called ‘gaslighting’ in an obstetric context [ 65 , 66 ]. Thus, the women experienced being offered sick leave for mental problems instead of their perceived physical health problems, depicting them as hysterical women who exaggerated their condition. Gaslighting is a concept used in medicine in general [ 66 ] and in obstetrics regarding traumatic childbirth experiences [ 65 ]. The concept of hysteria, i.e., a prior medical diagnosis and historical concept theoretically linked to femininity [ 67 , 68 ] and ‘obstetric gaslighting’ [ 65 ], has also been found in research on women’s chronic pain [ 64 ] and endometriosis [ 69 ]. Men with chronic pain are perceived as brave, and women in pain are hysterical, emotional, whining, malingering, or imagining pain [ 64 ]. Further, women with endometriosis are viewed as ‘reproductive bodies’ with a proneness for hysteria [ 69 ]. Obstetric gaslighting, enforced by the normalisation of SPT-related health problems and the gendered stereotype of women as hysterical patients, puts women with SPT in an inferior position towards HCPs and can, therefore, be interpreted as a demonstration of institutional power [ 65 ]. Hence, being overlooked by the obstetric gaze might constitute a form of obstetric gaslighting, a concept that has not been applied to SPT before.
Implications and significance
Our study indicated that women continue to have problems accessing healthcare for persistent SPT-related health problems several years postpartum. Additionally, women with persistent SPT-related health problems often depended on a ‘key person’ with the competence to open the doors to comprehensive care, as shown in our findings. The Swedish Government launched a multi-million project from 2015 to 2022 to improve and promote women’s health [ 70 ]. Despite this investment, the depicted experiences of the included women reflect upon remaining structural and clinical problems within Swedish healthcare, which need further attention, investigation, and actions. Additionally, there are considerable differences in reported satisfaction and prevalence of complications at the one-year follow-up between the regions [ 3 ], indicating that there are suboptimal healthcare services. With a significant variation in satisfaction and recovery at one year, there are reasons to believe that women with prolonged problems may experience problems getting access to needed care.
Our study also showed that SPT-related healthcare services are not available on equal terms to women with persistent SPT-related health problems. In general, many women within this group had problems accessing care and sick leave for years. However, depending on where the women reside, not all women have access to specialised care. This inequity may be explained by Sweden having 21 self-governing health regions, and in the absence of national guidelines regarding SPT care and follow-up, the healthcare provision for affected women varies. To secure access to postpartum care for women with SPT in general and those with different prerequisites within this group, implementation studies are needed to develop and evaluate the effect of national guidelines for follow-up care regarding SPT.
Strengths and limitations
This study has strengths and limitations that need to be addressed. A significant strength, enhancing credibility and transferability, was providing a clear context and thick descriptions of our results, where we thoroughly portrayed the women’s voices using quotations [ 35 ]. Further, our detailed account of the study context, data collection, and data analysis process facilitated the transferability of our study. Including three women born outside of Sweden added to the variety of the sample and thus improved credibility because qualitative research often overlooks immigrants' experiences. However, the migrant women spoke Swedish well enough to participate in an interview, indicating that they have been living in Sweden for some time and might be familiar with the healthcare system. Finally, the credibility and dependability of this study were also strengthened by the frequent use of interdisciplinary triangulation between the authors throughout data analysis and the writing process, as well as peer review at a research seminar.
A potential limitation was that this study may not have fully explored the situation of women with fourth-degree lacerations or those with lower education, as most participants had third-degree perineal lacerations and higher education. Further, we could not include non-binary persons and same-sex or single parents, which may be a weakness; consequently, future studies should focus on the under-represented participant groups and migrant women needing an interpreter. Additionally, all women responded voluntarily to the study invitation. Thus, our participants might be particularly outspoken about their problems or interested in raising their voices or experiences. However, they represented a variety of persistent SPT-related health problems of various severity, and some had been able to get access to medical help, whereas others had not. Additionally, our findings cohered to similar studies [ 12 , 17 ] covering shorter periods after the SPT, which may indicate that the experiences of the challenging search for needed help remain over time. Therefore, our findings may reflect other women’s experiences seeking care for SPT-related health problems and may be transferable to other women’s experiences with persistent health problems of a rare condition.
The data for this study was comprehensive and rich. Information power in qualitative research is an ongoing discussion, and the number of participants and their representativity can be seen as a limitation of credibility and transferability [ 71 , 72 ]. Graneheim, Lindgren and Lundman [ 36 ] argue that sample size should be determined by the study’s aim and the data’s quality so that variations in experiences can be captured. They do, therefore, not recommend a specific number of participants, but others do [ 71 ]. With this in mind, the authors believe that the women’s detailed descriptions of the included concepts and the extensive length of the conducted interviews enabled us to achieve sufficient information power based on the richness of the data [ 72 ].
By qualitatively exploring how women with persistent SPT-related health problems experienced their healthcare encounters, we interpreted that they faced a paradox of being reassured of normality by HCPs despite reporting sequelae symptoms. Thus, women’s needs for medical care, rehabilitation, and sick leave were largely neglected. Further, our study might indicate a structural problem within women’s postpartum healthcare, indicating that access to care depended on encountering a ‘key person’, a professional who acknowledged persistent problems as real symptoms. Access to quality care provided with a professional attitude was essential for the future well-being of women with persistent SPT-related health problems. Thus, it should not depend on meeting a single ‘key person’. Therefore, national guidelines for long-term postpartum care of persistent SPT-related health problems must be developed in Sweden. Additionally, to ensure that healthcare services meet the individual needs of women with persistent SPT-related health problems, it is crucial to consider arranging the organisation and availability of quality care for these women from a woman-centred perspective.
Availability of data and materials
The original recordings and transcripts from the current study are not publicly available due to securing the individual privacy and confidentiality of the participants. Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Healthcare professionals
Interquartile range
Strategic Research Area Health Care Science
- Severe perineal trauma
Sexual and reproductive health and rights
World Health Organisation
World Health Organization (WHO). WHO recommendations: Intrapartum care for a positive childbirth experience. Geneva: WHO; 2018. Cited 2024 Feb 14. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241550215 .
Leap N. Woman-centred or women-centred care: does it matter? Br J Midwifery. 2009;17(1):12–6.
Article Google Scholar
Uustal E. Bristning vid förlossning grad 3 - 4. Årsrapport från GynOp-registret avseende operationer utförda år 2022. [Laceration at childbirth, grade 3 - 4, Annual Report of surgeries 2022]. Umeå: The Swedish National Quality Register of Gynecological Surgery; 2023. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.gynop.se/rapporter/arsrapporter/ .
World Health Organization (WHO). International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems (ICD) 10th revision. Geneva: WHO; 2019. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://icd.who.int/browse10/2019/en .
d’Almeida I. Women’s experiences following obstetric anal sphincter injury. J Pelvic Obstet Gynaecol Physiother. 2020;127:39–50.
Google Scholar
Darmody E, Bradshaw C, Atkinson S. Women’s experience of obstetric anal sphincter injury following childbirth: An integrated review. Midwifery. 2020;91:102820.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
LaCross A, Groff M, Smaldone A. Obstetric anal sphincter injury and anal incontinence following vaginal birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Midwifery Women’s Health. 2015;60(1):37–47.
Samarasekera DN, Bekhit MT, Wright Y, Lowndes RH, Stanley KP, Preston JP, et al. Long-term anal continence and quality of life following postpartum anal sphincter injury. Colorectal Dis. 2008;10(8):793–9.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Andreucci CB, Bussadori JC, Pacagnella RC, Chou D, Filippi V, Say L, et al. Sexual life and dysfunction after maternal morbidity: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2015;15:307.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Beck CT. Effects of fourth-degree perineal lacerations on women’s physical and mental health. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs. 2021;50(2):133–42.
Keighley MR, Perston Y, Bradshaw E, Hayes J, Keighley DM, Webb S. The social, psychological, emotional morbidity and adjustment techniques for women with anal incontinence following Obstetric Anal Sphincter Injury: use of a word picture to identify a hidden syndrome. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16(1):275.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Lindqvist M, Lindberg I, Nilsson M, Uustal E, Persson M. “Struggling to settle with a damaged body” - A Swedish qualitative study of women’s experiences one year after obstetric anal sphincter muscle injury (OASIS) at childbirth. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2019;19:36–41.
Shoorab NJ, Taghipour A, Mirteimouri M, Roudsari RL. Social recovery: a neglected dimension of caring for women with perineal trauma in Iran. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2020;25(4):333–40.
Jahani Shoorab N, Mirteimouri M, Taghipour A, Latifnejad Roudsari R. Women’s experiences of emotional recovery from childbirth-related perineal trauma: a qualitative content analysis. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2019;7(3):181–91.
PubMed Google Scholar
Swedish Agency for Health Technology Assessment and Assessment of Social Services. Practices to improve detection of perineal tears and women’s views and experiences of healthcare providers following sustained perineal tear. A systematic review. 2021. Report No.: 323.
Persson M, Lindberg I, Ohman A. Regional and clinical guidelines for prevention and care of obstetric anal sphincter injuries - A critical frame analysis. Midwifery. 2023;119:103608.
Huber M, Tunon K, Lindqvist M. “From hell to healed” - A qualitative study on women’s experience of recovery, relationships and sexuality after severe obstetric perineal injury. Sex Reprod Healthc. 2022;33:100736.
Priddis HS, Schmied V, Kettle C, Sneddon A, Dahlen HG. “A patchwork of services”–caring for women who sustain severe perineal trauma in New South Wales–from the perspective of women and midwives. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2014;14:236.
Priddis H, Schmied V, Dahlen H. Women’s experiences following severe perineal trauma: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health. 2014;14(1):32.
Williams A, Lavender T, Richmond DH, Tincello DG. Women’s experiences after a third-degree obstetric anal sphincter tear: a qualitative study. Birth. 2005;32(2):129–36.
Herron-Marx S, Williams A, Hicks C. A Q methodology study of women’s experience of enduring postnatal perineal and pelvic floor morbidity. Midwifery. 2007;23(3):322–34.
Crookall R, Fowler G, Wood C, Slade P. A systematic mixed studies review of women’s experiences of perineal trauma sustained during childbirth. J Adv Nurs. 2018;74(9):2038–52.
Priddis H, Dahlen H, Schmied V. Women’s experiences following severe perineal trauma: a meta-ethnographic synthesis. J Adv Nurs. 2013;69(4):748–59.
Tjernström K, Lindberg I, Wiklund M, Persson M. Negotiating the ambiguity of an (in)authentic working life: a grounded theory study into severe perineal trauma. BMC Women’s Health. 2023;23(1):47.
Lindqvist M, Persson M, Nilsson M, Uustal E, Lindberg I. “A worse nightmare than expected” - a Swedish qualitative study of women’s experiences two months after obstetric anal sphincter muscle injury. Midwifery. 2018;61:22–8.
United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2022. New York City: United Nations; 2022. Cited 2024 Feb 24. Available from: https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2022/ .
Fahy K, Foureur M, Hastie C. Birth territory and midwifery guardianship : theory for practice, education, and research. Edinburgh: Books for Midwives; 2008.
Walsh D, Christianson M, Stewart M. Why midwives should be feminists. Midirs Midwifery Digest. 2015;25(2):154–60.
Buchanan K, Newnham E, Geraghty S, Whitehead L. Navigating midwifery solidarity: a feminist participatory action research framework. Women Birth. 2023;36(1):e169–74.
Benoit B, Goldberg L, Campbell-Yeo M. Infant feeding and maternal guilt: The application of a feminist phenomenological framework to guide clinician practices in breast feeding promotion. Midwifery. 2016;34:58–65.
Westergren A, Edin K, Walsh D, Christianson M. Autonomous and dependent-The dichotomy of birth: a feminist analysis of birth plans in Sweden. Midwifery. 2019;68:56–64.
Alspaugh A, Barroso J, Reibel M, Phillips S. Women’s contraceptive perceptions, beliefs, and attitudes: an integrative review of qualitative research. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2020;65(1):64–84.
Davis DL, Walker K. Re-discovering the material body in midwifery through an exploration of theories of embodiment. Midwifery. 2010;26(4):457–62.
Govender V, Penn-Kekana L. Gender biases and discrimination: a review of health care interpersonal interactions. Global Public Health. 2008;3(sup1):90–103.
Graneheim UH, Lundman B. Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ Today. 2004;24(2):105–12.
Graneheim UH, Lindgren BM, Lundman B. Methodological challenges in qualitative content analysis: a discussion paper. Nurse Educ Today. 2017;56:29–34.
Lindgren BM, Lundman B, Graneheim UH. Abstraction and interpretation during the qualitative content analysis process. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;108:103632.
Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007;19(6):349–57.
Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Hälso- och sjukvårdslag (2017:30) [Health and Medical Care Act]. Stockholm: The Swedish Riksdag; 2017. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.riksdagen.se/sv/dokument-och-lagar/dokument/svensk-forfattningssamling/halso-och-sjukvardslag-201730_sfs-2017-30/ .
The Swedish Social Insurance Agency. Parental benefits. 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.forsakringskassan.se/english/parents/when-the-child-is-born/parental-benefit .
The Swedish Association of Midwives. Kompetensbeskrivning för legitimerad barnmorska [Description of competences for registered midwives]. Stockholm: The Swedish Association of Midwives; 2018. Updated 2019 Jan. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://storage.googleapis.com/barnmorskeforbundet-se/uploads/2020/04/Kompetensbeskrivning-for-legitimerad-barnmorska.pdf .
Bäckenbottenutbildning [Pelvic floor education]. Utbildningsmaterial: Uppföljning [Educational material: Follow-up]. 2022. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://backenbottenutbildning.se/index.php/utbildningsmaterial/uppfoljning .
GynOp [The Swedish National Quality Register of Gynecological Surgery]. About GynOp. 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.gynop.se/home/about-gynop/ .
Öhman H, Schesny S, Bearth L, Löwendahl J. Förlossningsskadad? Du är inte ensam! [Injured at childbirth? You are not alone!’]. 2014. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.facebook.com/groups/forlossningsskadad/ .
Vanderbilt University. About REDCap. Nashville: Vanderbilt; 2023. Updated 2023. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://projectredcap.org/about/ .
Kvale S, Brinkmann S. Interviews: learning the craft of qualitative research interviewing. 2nd ed. Los Angeles: Sage Publications; 2009.
Keen S, Lomeli-Rodriguez M, Joffe H. From challenge to opportunity: virtual qualitative research during COVID-19 and beyond. Int J Qual Methods. 2022;21:16094069221105076.
Thunberg S, Arnell L. Pioneering the use of technologies in qualitative research - A research review of the use of digital interviews. Int J Soc Res Methodol. 2022;25(6):757–68.
MAXQDA. Why MAXQDA? Berlin: VERBI Software GmbH; 2024. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.maxqda.com/why-maxqda .
Microsoft. Microsoft Excel. Redmond: Microsoft; 2024. Cited 2024 Maj 8. Available from: https://www.microsoft.com/sv-se/microsoft-365/excel?market=se .
Griffin GA. Dictionary of Gender Studies. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Abhyankar P, Uny I, Semple K, Wane S, Hagen S, Wilkinson J, et al. Women’s experiences of receiving care for pelvic organ prolapse: a qualitative study. BMC Womens Health. 2019;19(1):45.
Scott KD, Hintz EA, Harris TM. “Having pain is normal”: How talk about chronic pelvic and genital pain reflects messages from menarche. Health Commun. 2022;37(3):296–306.
Pettersson A, Bertero CM. How women with endometriosis experience health care encounters. Womens Health Rep (New Rochelle). 2020;1(1):529–42.
Heitmann K, Svendsen HC, Sporsheim IH, Holst L. Nausea in pregnancy: attitudes among pregnant women and general practitioners on treatment and pregnancy care. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2016;34(1):13–20.
Roper JC, Amber N, Wan OYK, Sultan AH, Thakar R. Review of available national guidelines for obstetric anal sphincter injury. Int Urogynecol J. 2020;31(11):2247–59.
The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care. Third and Fourth Degree Perineal Tears Clinical Care Standard. Sydney: The Australian Commission on Safety and Quality in Health Care; 2021. Cited 2024 Feb 20. Available from: https://www.safetyandquality.gov.au/standards/clinical-care-standards/third-and-fourth-degree-perineal-tears-clinical-care-standard .
Foucault M, Sheridan A. The birth of the clinic: an archaeology of medical perception. 3rd ed. London: Routledge; 2003.
Scarf VL, Rossiter C, Vedam S, Dahlen HG, Ellwood D, Forster D, et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes by planned place of birth among women with low-risk pregnancies in high-income countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Midwifery. 2018;62:240–55.
Offerhaus P, Jans S, Hukkelhoven C, de Vries R, Nieuwenhuijze M. Women’s characteristics and care outcomes of caseload midwifery care in the Netherlands: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020;20(1):517.
Forster DA, McLachlan HL, Davey MA, Biro MA, Farrell T, Gold L, et al. Continuity of care by a primary midwife (caseload midwifery) increases women’s satisfaction with antenatal, intrapartum and postpartum care: results from the COSMOS randomised controlled trial. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:28.
Brady S, Lee N, Gibbons K, Bogossian F. Woman-centred care: an integrative review of the empirical literature. Int J Nurs Stud. 2019;94:107–19.
Findlay D. The medical gaze: medical models, power, and women’s health. Atlantis. 1992;18(1&2):104–24.
Samulowitz A, Gremyr I, Eriksson E, Hensing G. “Brave Men” and “Emotional Women”: a theory-guided literature review on gender bias in health care and gendered norms towards patients with chronic pain. Pain Res Manag. 2018;2018:6358624.
Fielding-Singh P, Dmowska A. Obstetric gaslighting and the denial of mothers’ realities. Soc Sci Med (1982). 2022;301:114938.
Sebring JCH. Towards a sociological understanding of medical gaslighting in western health care. Sociol Health Ill. 2021;43(9):1951–64.
Jones CE. Wandering wombs and “female troubles”: the hysterical origins, symptoms, and treatments of endometriosis. Women Stud. 2015;44(8):1083–113.
Tasca C, Rapetti M, Carta MG, Fadda B. Women and hysteria in the history of mental health. Clin Pract Epidemiol Ment Health. 2012;8:110–9.
Young K, Fisher J, Kirkman M. “Do mad people get endo or does endo make you mad?”: Clinicians’ discursive constructions of Medicine and women with endometriosis. Fem Psychol. 2019;29(3):337–56.
The Swedish Ministry of Health and Social Affairs. Överenskommelse om en förbättrad förlossningsvård och insatser för kvinnors hälsa [Agreement on improving maternity care and women's health] [Internet]. Stockholm: The Swedish Government; 2015. S2015/07777/FS. [cited 2024 Maj 8]. Available from: https://www.regeringen.se/overenskommelser-och-avtal/2015/12/overenskommelse-om-en-forbattrad-forlossningsvard-och-insatser-for-kvinnors-halsa/ .
Boddy CR. Sample size for qualitative research. Qual Mark Res. 2016;19(4):426–32.
Malterud K, Siersma VD, Guassora AD. Sample size in qualitative interview studies: guided by information power. Qual Health Res. 2016;26(13):1753–60.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We want to thank the participating women for generously sharing their experiences.
Open access funding provided by Umea University. This work was supported by the Research Lift (SWE: Forskningslyftet) and Strategic Research Area Health Care Science (SFO-V), Umeå University. The funders had no specific role in the conceptualisation, design, data collection, analysis, publication decision, or manuscript preparation.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Umeå University, 901 87, Umeå, Sweden
Katharina Tjernström, Inger Lindberg & Margareta Persson
Department of Community Medicine and Rehabilitation, Section of Physiotherapy, Umeå University, 901 87, Umeå, Sweden
Maria Wiklund
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
KT: conceptualisation; data curation; formal analysis; investigation; methodology; validation; visualisation; writing - original draft; writing - review & editing. IL: conceptualisation; methodology; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. MW: conceptualisation; methodology; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. MP: conceptualisation; data curation; funding acquisition; methodology; project administration; supervision; visualisation; writing - review & editing. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Katharina Tjernström .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The Swedish Ethical Review Authority approved the study. An amendment to the original ethical approval of the research project to further explore the experiences of encounters with healthcare services was obtained (Dnr: 2020-035410908 and Dnr: 2022-02784-02). The study was undertaken in compliance with research ethics guidelines. All participation was voluntary, and participants received oral and written information about the study and provided written informed consent before the interviews. No interview questions were mandatory, and the women decided if and how detailed they wanted to share their experiences.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
12913_2024_11037_moesm1_esm.pdf.
Additional file 1. Semi-structured interview guide for individual interviews; contains interview questions aimed at highlighting the experience of everyday life and working life after suffering 3 rd or 4 th degree perineal laceration at childbirth (i.e., severe perineal trauma [SPT]).
Additional file 2. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative studies (COREQ): 32-item checklist.
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tjernström, K., Lindberg, I., Wiklund, M. et al. Overlooked by the obstetric gaze – how women with persistent health problems due to severe perineal trauma experience encounters with healthcare services: a qualitative study. BMC Health Serv Res 24 , 610 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11037-5
Download citation
Received : 11 September 2023
Accepted : 23 April 2024
Published : 09 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-024-11037-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Persistent health problems
- Qualitative content analysis
- Healthcare encounters
- Postpartum healthcare
- Normalisation
- Access to care
- Empowerment
BMC Health Services Research
ISSN: 1472-6963
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Chapter 2. Research Design Getting Started. When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a "research proposal" that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
Step 2: Choose a type of research design. Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research. Types of quantitative research designs. Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
The qualitative researcher today faces a baffling array of options for con-ducting qualitative research. Numerous inquiry strategies (Denzin & Lincoln, 2005), inquiry traditions (Creswell, 1998), qualitative approaches (Miller & Crabtree, 1992), and design types (Creswell, 2007) are available for selec-tion. What criteria should govern whether ...
Qualitative research is a method of inquiry used in various disciplines, including social sciences, education, and health, to explore and understand human behavior, experiences, and social phenomena. It focuses on collecting non-numerical data, such as words, images, or objects, to gain in-depth insights into people's thoughts, feelings, motivations, and perspectives.
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...
A research design is based on an integration of the theories, concepts, goals, contexts, beliefs, and sets of relationships that shape a specific topic. In addition, it is shaped by responding to the realities and perspectives of participants and contexts of a study. In a solid qualitative research design, framing theory and key constructs are ...
that the research design of a qualitative study differs from that of a study that starts with an understanding to be tested, where often the hypothesis literally dictates the form, quantity, and scope of required data. This sort of design preempts other ways of looking at the research question. Qualitative research is usually not preemptive ...
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervene or introduce treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypotheses as well as further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants ...
Qualitative Research Design: An Interactive Approach. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE. A short and accessible introduction to qualitative research design, particularly helpful for graduate students contemplating theses and dissertations. This has been a standard textbook in my graduate-level courses for years. Advanced. Patton, Michael Quinn. 2002.
3. It provides a model for the structure of a proposal for a qualitative study, one. that clearly communicates and justifies the major design decisions and the. connections among these (see ...
When conducting qualitative research, it is important to follow best practices to ensure the rigor, validity, and trustworthiness of your study. Here are some top best practices for qualitative research design: 1. Clearly Define Research Questions: Begin by clearly defining your research questions or objectives.
It outlines a step-by-step approach to qualitative research design that begins by identifying a public health topic of interest, works to hone in on a specific research problem, and then specifies research questions, objectives, and specific aims. The course emphasizes the iterative nature of research design in qualitative inquiry and ...
the comparison of research design procedures in Qualitative and Quantitative Research. By tradition, introductory textbooks on social science research compare ... in a survey, you would rely on well-defined samples and carefully constructed variables so your results will represent equivalent variables in larger popula-tions. Similarly, in ...
Learn how to get started with research design for qualitative studies, including dissertations, theses and research projects. We explain what research design...
This will guide your research design and help you select appropriate methods. Select a research design: There are many different research designs to choose from, including experimental, survey, case study, and qualitative designs. Choose a design that best fits your research question and objectives.
Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples. Published on June 20, 2019 by Shona McCombes.Revised on June 22, 2023. When you start planning a research project, developing research questions and creating a research design, you will have to make various decisions about the type of research you want to do.. There are many ways to categorize different types of research.
The burden of offering adequate sample sizes in research has been one of. the major criticisms against qualitative s tudies. One of the most acceptable standards in qualitative research is to ...
Sample sizes tend to range from 20 to 30 individuals, sampled purposively (Padgett, 2016). However, sample sizes can be larger or smaller, depending on data saturation. Data saturation is the point in the qualitative research data collection process when no new information is being discovered. Researchers use a constant comparative approach in ...
Research design is the key that unlocks before the both the researcher and the audience all the primary elements of the research—the purpose of the research, the research questions, the type of case study research to be carried out, the sampling method to be adopted, the sample size, the techniques of data collection to be adopted and the ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH PAPER 45 population sample, so your study is limited by the number of participants, or that you used a convenience sample. Summary Then the author would wrap up the chapter with the summarization of the chapter and a transition to the next chapter as described above. Notice that this section started with a
Most qualitative data analysis programs include a code and retrieve function. We argue that onscreen coding and the retrieval of coded segments, or snapshots, can result in researchers missing ...
The lack of a definite standard for determining the sample size in qualitative research leaves the research process to the initiative of the researcher, and this situation overshadows the scientificity of the research. ... homogeneity, information strength, drilling ability, triangulation and research design, are used as inputs. A total of 20 ...
Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches. Sage. ... Blyth K., Coates S., Pearson S., Cavalheri V. (2021). An evaluation of research capacity and culture in a sample of western Australian allied health professionals. Tasman Medical Journal, 3(1), 23-29. Google Scholar.
The value of using qualitative methods within clinical trials is widely recognised. How qualitative research is integrated within trials units to achieve this is less clear. This paper describes the process through which qualitative research has been integrated within Cardiff University's Centre for Trials Research (CTR) in Wales, UK. We highlight facilitators of, and challenges to, integration.
We recommend that accreditation standards emphasize (1) data skills, (2) research design, (3) descriptive statistics, (4) critical analysis, (5) qualitative methods, and (6) both parameter estimation and significance testing; as well as (7) give precedence to foundational skills, (8) promote transferable skills, and (9) create space in ...
Study design and context. The present study is part of a larger research project investigating the long-term consequences of SPT on quality of life, working life, and healthcare contacts. This study had an inductive qualitative interview study design applying qualitative content analysis to analyse data [35,36,37]. This method searches for ...