Help Center Help Center
- Help Center
- Trial Software
- Product Updates
- Documentation
Solve linear assignment problem

Description
M = matchpairs( Cost , costUnmatched ) solves the linear assignment problem for the rows and columns of the matrix Cost . Each row is assigned to a column in such a way that the total cost is minimized. costUnmatched specifies the cost per row of not assigning each row, and also the cost per column of not having a row assigned to each column.
[ M , uR , uC ] = matchpairs( Cost , costUnmatched ) additionally returns indices for unmatched rows in uR and indices for unmatched columns in uC .
[ ___ ] = matchpairs( Cost , costUnmatched , goal ) specifies the goal of the optimization using any of the output argument combinations in previous syntaxes. goal can be 'min' or 'max' to produce matches that either minimize or maximize the total cost.
collapse all
Assign Flights with Minimal Cost
Assign salespeople to flights such that the total cost of transportation is minimized.
A company has four salespeople who need to travel to key cities around the country. The company must book their flights, and wants to spend as little money as possible. These salespeople are based in different parts of the country, so the cost for them to fly to each city varies.
This table shows the cost for each salesperson to fly to each key city.
Dallas Chicago New York City St. Louis Fred $ 6 0 0 $ 6 7 0 $ 9 6 0 $ 5 6 0 Beth $ 9 0 0 $ 2 8 0 $ 9 7 0 $ 5 4 0 Sue $ 3 1 0 $ 3 5 0 $ 9 5 0 $ 8 2 0 Greg $ 3 2 5 $ 2 9 0 $ 6 0 0 $ 5 4 0
Each city represents a sales opportunity. If a city is missed, then the company loses out on an average revenue gain of $2,000.
Create a cost matrix to represent the cost of each salesperson flying to each city.
Use matchpairs to assign the salespeople to the cities with minimal cost. Specify the cost of unassignment as 1000, since the cost of unassignment is counted twice if a row and a column remain unmatched.
matchpairs calculates the least expensive way to get a salesperson to each city.
Dallas Chicago New York City St. Louis Fred $ 6 0 0 $ 6 7 0 $ 9 6 0 $ 560 Beth $ 9 0 0 $ 280 $ 9 7 0 $ 5 4 0 Sue $ 310 $ 3 5 0 $ 9 5 0 $ 8 2 0 Greg $ 3 2 5 $ 2 9 0 $ 600 $ 5 4 0
Unequal Numbers of Rows and Columns
Match rows to columns when you have many more columns than rows in the cost matrix.
Create a 3-by-8 cost matrix. Since you have only three rows, matchpairs can produce at most three matches with the eight columns.
Use matchpairs to match the rows and columns of the cost matrix. To get the maximum number of matches, use a large cost of unassignment (relative to the magnitude of the entries in the cost matrix). Specify three outputs to return the indices of unmatched rows and columns.
Five of the columns in C are not matched with any rows.
Assign Taxis to Maximize Profit
Assign taxis to routes such that the profit is maximized.
A taxi company has several ride requests from across the city. The company wants to dispatch its limited number of taxis in a way that makes the most money.
This table shows the estimated taxi fare for each of five ride requests. Only three of the five ride requests can be filled.
Ride 1 Ride 2 Ride 3 Ride 4 Ride 5 Cab A $ 5 . 7 0 $ 6 . 3 0 $ 3 . 1 0 $ 4 . 8 0 $ 3 . 5 0 Cab B $ 5 . 8 0 $ 6 . 4 0 $ 3 . 3 0 $ 4 . 7 0 $ 3 . 2 0 Cab C $ 5 . 7 0 $ 6 . 3 0 $ 3 . 2 0 $ 4 . 9 0 $ 3 . 4 0
Create a profits matrix to represent the profits of each taxi ride.
Use matchpairs to match the taxis to the most profitable rides. Specify three outputs to return any unmatched rows and columns, and the 'max' option to maximize the profits. Specify the cost of unassignment as zero, since the company makes no money from unfilled taxis or ride requests.
matchpairs calculates the most profitable rides to fill. The solution leaves ride requests 3 and 5 unfilled.
Calculate the total profits for the calculated solution. Since costUnmatched is zero, you only need to add together the profits from each match.
Track Point Positions over Time
Use matchpairs to track the movement of several points by minimizing the total changes in distance.
Plot a grid of points at time t = 0 in green. At time t = 1 , some of the points move a small amount in a random direction.
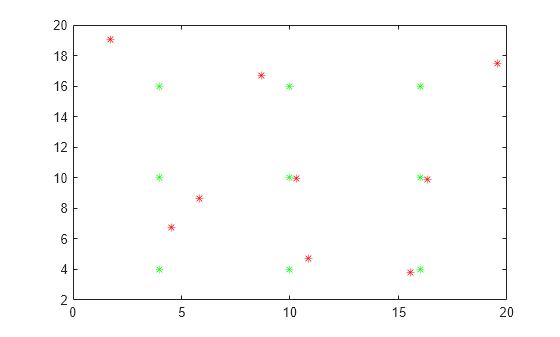
Use matchpairs to match the points at t = 0 with the points at t = 1 . To do this, first calculate a cost matrix where C(i,j) is the Euclidean distance from point i to point j .
Next, use matchpairs to match the rows and columns in the cost matrix. Specify the cost of unassignment as 1. With such a low cost of unassignment relative to the entries in the cost matrix, it is likely matchpairs will leave some points unmatched.
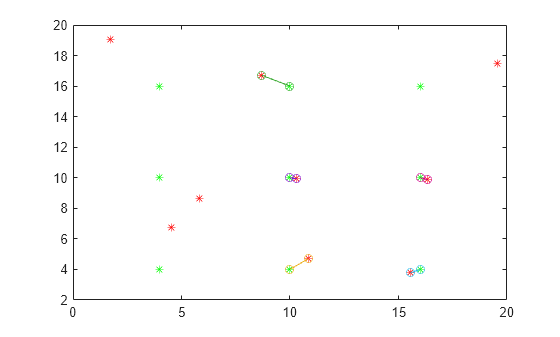
The values M(:,2) correspond to the original points ( x 0 , y 0 ) , while the values M(:,1) correspond to the moved points ( x 1 , y 1 ) .
Plot the matched pairs of points. The points that moved farther than 2*costUnmatched away from the original point remain unmatched.
Input Arguments
Cost — cost matrix matrix.
Cost matrix. Each entry Cost(i,j) specifies the cost of assigning row i to column j .
Data Types: single | double
costUnmatched — Cost of not matching scalar
Cost of not matching, specified as a scalar. matchpairs compares the value of 2*costUnmatched to the entries in Cost to determine whether it is more beneficial for a row or column to remain unmatched. Use this parameter to make matches more or less likely in the algorithm. For more information, see linear assignment problem .
Example: M = matchpairs(C,10) specifies a cost of 10 for not matching a row or column of C .
goal — Optimization goal 'min' (default) | 'max'
Optimization goal, specified as either 'min' or 'max' . The optimization goal specifies whether the total cost should be minimized or maximized.
Example: M = matchpairs(Cost,costUnmatched,'max') specifies that the rows and columns of Cost should be matched together to maximize the total cost.
Output Arguments
M — matches matrix.
Matches, returned as a matrix. M is a p -by- 2 matrix, where M(i,1) and M(i,2) are the row and column indices of a matched pair in the cost matrix. The rows of M are sorted with the second column in ascending order.
Each row and column can be matched a single time only, so each M(i,1) value and each M(i,2) value is unique.
M contains p matches, and p is less than or equal to the maximum number of matches min(size(Cost)) .
The cost of the matches in M is sum([Cost(M(1,1),M(1,2)), Cost(M(2,1),M(2,2)), ..., Cost(M(p,1),M(p,2))]) .
uR — Unassigned rows column vector
Unassigned rows, returned as a column vector of indices. The entries in uR indicate which rows in Cost are unassigned. Each entry in uR and uC contributes to the total cost of the solution according to costUnassigned .
uC — Unassigned columns column vector
Unassigned columns, returned as a column vector of indices. The entries in uC indicate which columns in Cost are unassigned. Each entry in uR and uC contributes to the total cost of the solution according to costUnassigned .
Linear Assignment Problem
The linear assignment problem is a way of assigning rows to columns such that each row is assigned to a column and the total cost of the assignments is minimized (or maximized). The cost of assigning each row to each column is captured in a cost matrix . The entry Cost(i,j) is the cost of assigning row i to column j .
The cost of unassignment assigns a cost to any row or column that is not matched. This practice allows for minimum-cost solutions that do not assign all rows or columns. If a row and column are not matched, this increases the total cost by 2*costUnmatched .
The total cost of a solution M is the sum of the cost of all matched pairs added to the cost of all unmatched pairs:
T C = ∑ i = 1 p Cost ( M ( i , 1 ) , M ( i , 2 ) ) + costUnmatched ⋅ ( m + n − 2 p )
In code the total cost is
Cost is an m -by- n matrix.
M is a p -by- 2 matrix, where M(i,1) and M(i,2) are the row and column of a matched pair.
(m+n-2*p) is the total number of unmatched rows and columns.
[1] Duff, I.S. and J. Koster. "On Algorithms For Permuting Large Entries to the Diagonal of a Sparse Matrix." SIAM J. Matrix Anal. & Appl. 22(4), 2001. pp 973–996.
Extended Capabilities
C/c++ code generation generate c and c++ code using matlab® coder™..
Usage notes and limitations:
Code generation does not support sparse matrix inputs for this function.
Version History
Introduced in R2019a
equilibrate | sprank | dmperm
MATLAB Command
You clicked a link that corresponds to this MATLAB command:
Run the command by entering it in the MATLAB Command Window. Web browsers do not support MATLAB commands.
Select a Web Site
Choose a web site to get translated content where available and see local events and offers. Based on your location, we recommend that you select: .
- Switzerland (English)
- Switzerland (Deutsch)
- Switzerland (Français)
- 中国 (English)
You can also select a web site from the following list:
How to Get Best Site Performance
Select the China site (in Chinese or English) for best site performance. Other MathWorks country sites are not optimized for visits from your location.
- América Latina (Español)
- Canada (English)
- United States (English)
- Belgium (English)
- Denmark (English)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- España (Español)
- Finland (English)
- France (Français)
- Ireland (English)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Luxembourg (English)
- Netherlands (English)
- Norway (English)
- Österreich (Deutsch)
- Portugal (English)
- Sweden (English)
- United Kingdom (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- New Zealand (English)
Contact your local office

Matlab Programming for Numerical Computation
Note: This exam date is subjected to change based on seat availability. You can check final exam date on your hall ticket.
Page Visits
Course layout.
The course will be covered in eight modules. Various aspects of MATLAB programming for numerical computation will be covered in these modules, with each module dedicated to on equivalent numerical topic. Each module will be covered in one week, with 2–2.5 hours lectures per week. There will be self-study problems at the end of several of these lectures. Assignments will also be posted periodically.
Module 1: Introduction to MATLAB Programming
Module 2: Approximations and Errors
Module 3: Numerical Differentiation and Integration
Module 4: Linear Equations
Module 5: Nonlinear Equations
Module 6: Regression and Interpolation
Module 7: Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) – Part 1
Module 8: Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE) – Practical aspects
Books and references
Instructor bio.

Prof. Niket Kaisare
Prof. Niket Kaisare is a Professor of Chemical Engineering in IIT-Madras. He works in the area of modeling, design and control for energy applications. He has over ten years of research/teaching experience in academia, and three-year experience in Industrial R&D. He uses computational software, including MATLAB, FORTRAN, Aspen and FLUENT extensively in his research and teaching. Faculty web-page: http://www.che.iitm.ac.in/~nkaisare/
Course certificate
- The course is free to enroll and learn from. But if you want a certificate, you have to register and write the proctored exam conducted by us in person at any of the designated exam centres.
- The exam is optional for a fee of Rs. 1000/- (Rupees one thousand only).
- Date and Time of Exams: 29th March 2020 , Morning session 9am to 12 noon; Afternoon Session 2pm to 5pm.
- Registration url: Announcements will be made when the registration form is open for registrations.
- The online registration form has to be filled and the certification exam fee needs to be paid. More details will be made available when the exam registration form is published. If there are any changes, it will be mentioned then.
- Please check the form for more details on the cities where the exams will be held, the conditions you agree to when you fill the form etc.
CRITERIA TO GET A CERTIFICATE:
- Average assignment score = 25% of average of best 6 assignments out of the total 8 assignments
- Exam score = 75% of the proctored certification exam score out of 100
- Final score = Average assignment score + Exam score
ELIGIBILITY FOR CERTIFICATE
- You will be eligible for certificate only if average assignment score >=10/25 AND the exam score >= 30/75
- If one of the two criteria is not met, you will not get the certificate even if the Final score >= 40/100.
- Certificate will have your name, photograph and the score in the final exam with the breakup.It will have the logos of NPTEL and IIT Madras. It will be e-verifiable at nptel.ac.in/noc .
- Only the e-certificate will be made available. Hard copies will not be dispatched.

DOWNLOAD APP

SWAYAM SUPPORT
Please choose the SWAYAM National Coordinator for support. * :
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

New Approach to Solve Assignment Problem using MATLAB

Assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem, in which the objective is to minimized total cost by assigning ‘m’ jobs to ‘n’ machines. By using MATLAB coding and some modification in ROA method, optimal solution can be trace for assignment problem within seconds. MATLAB coding result has given for various orders of illustrations.
Related Papers
International Journal of Latest Technology in Engineering, Management & Applied Science -IJLTEMAS (www.ijltemas.in)
It is observed that one of the reasons for voltage instability is voltage collapse. Generally the concept of reactive power management is used to mitigate voltage collapse. But in this work the fallowing novel concept is used. The mathematical derivations begin from the usage of the conventional voltage collapse indicators(VCPI) Interlinks are used in the power system to distribute real powers locally (Inter bus power transfer) to mitigate voltage collapse. Optimal assignment of Distributed generation capacities are found out at different buses to mitigate voltage collapse. A mathematical model is derived and this model helps to design a valid algorithm to take care of voltage collapse problems. The Implementation of the algorithm is done through a MATLAB program which is shown in the Appendix. But minimum reactive power is to be maintained in the system. Quadratic Programming is applied in the fields of Control and Communications [13], Optimizing the civil structural design[14],nonlinear programming applications are presented that have arisen in different industries, namely food and insurance[15], Economics portfolio selection, monopolists' profit maximization, inequality constrained least-squares estimation, spatial equilibrium analysis, goal programming with quadratic preferences, and optimal decision rules [16] , But in this work Quadratic Programming is applied to find a way to mitigate voltage collapse in a power system.
Maria Rojas
descripcion principios basicos de algebra lineal
In this paper, new alternative methods for simplex method, Big M method and dual simplex method are introduced. These methods are easy to solve linear programming problem. These are powerful methods. It reduces number of iterations and save valuable time.
IJESRT Journal
In the area of Linear Programming Problem (LPP), modeling of Transportation Problem (TP) is fundamental in solving most real life problems as far optimization is concerned. MATLAB is used for treating programming of LPP, a condition referred to as M-File that can result from codes. The Paper discusses to study TP that would calculate the use of MATLAB codes using a mathematical modeling. The model develops the transportation solution for the North West Corner Rule, Least Cost Method, Vogel's Approximation Method, and Modi method for the TP. It is clear that a lot of effort has been involved in by many researchers in inquire about of appropriate solution methods to such problem. Furthermore, analytical approach and MATLAB coding are the methods used by most researchers in the application of these efficient proposed techniques. In this paper, an equivalent MATLAB coding was written that would support in the computation of such problems with easiness especially when the problem at LPP and TP. For each model, we use a combination of analytical method and MATLAB coding to study the easiest way that would be efficient while find the solution of different problems. MATLAB is the powerful computational tool in operation research. The MATLAB coding method is better than analytical method for solving TP. This model gives us good result in Transportation problem.
archana pandey
Assignment problems arise in different situation where we have to find an optimal way to assign n-objects to mother objects in an injective fashion. The assignment problems are a well studied topic in combinatorial optimization. These problems find numerous application in production planning, telecommunication VLSI design, economic etc. The assignment problems is a special case of Transportation problem. Depending on the objective we want to optimize, we obtain the typical assignment problems. Assignment problem is an important subject discussed in real physical world we endeavor in this paper to introduce a new approach to assignment problem namely, matrix ones assignment method or MOA-method for solving wide range of problem. An example using matrix ones assignment methods and the existing Hungarian method have been solved and compared it graphically. Also some of the variations and some special cases in assignment problem and its applications have been discussed in the paper.
RSIS International
In this paper simulating annealing technique is used to minimize the number of solutions from orthogonal projections. Convexity is prior information about the object geometry in the discrete tomography. This information may be useful for reconstruction of binary matrix or binary image from their projections. Boundary point switching is used to find approximate solution. This technique gives better result as compare to general switching.
Asiel Mena Jimenez
The Internist
Jack Salmon
The Astrophysical Journal
David Knauth
AWOSIYAN DARE
RELATED PAPERS
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery
mariantonietta piscitelli
Revista Portuguesa de Pedagogia
Armanda Matos
Amutheezan Sivagnanam
Annals of Geophysics
Mohammad Ali sharifi
Journal of Geographical Sciences
Mingxi Shen
Diego Vaz Bevilaqua
Applied Physics A
Ayoub EL BARAKA
SIKLUS: Jurnal Teknik Sipil
muhammad yasin
Antonio Machado
Water Resources Research
Liliana Jaramillo
The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation
História da Educação
Alejo Levoratti
Priscilla Thindwa
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences
Academy of Strategic Management Journal
Leena Van Deventer
Vicente Matellán Olivera
留学生文凭证书办理须知 定做康卡迪亚大学毕业证书成绩单
Reinhard Pienitz
NSCC毕业证书 北西雅图社区学院学位证
Journal of Structural Chemistry
Ephraim Eliav
Journal of International Union for Preihhistoric and Protohistoric Sciences
Alessandra R G Giumlia-Mair
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Data Structures
- Linked List
- Binary Tree
- Binary Search Tree
- Segment Tree
- Disjoint Set Union
- Fenwick Tree
- Red-Black Tree
- Advanced Data Structures
Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- Hungarian Algorithm for Assignment Problem | Set 2 (Implementation)
- Introduction to Exact Cover Problem and Algorithm X
- Greedy Approximate Algorithm for Set Cover Problem
- Job Assignment Problem using Branch And Bound
- Implementation of Exhaustive Search Algorithm for Set Packing
- Channel Assignment Problem
- Chocolate Distribution Problem | Set 2
- Transportation Problem | Set 1 (Introduction)
- OLA Interview Experience | Set 11 ( For Internship)
- Top 20 Greedy Algorithms Interview Questions
- Job Sequencing Problem - Loss Minimization
- Prim's Algorithm (Simple Implementation for Adjacency Matrix Representation)
- Data Structures and Algorithms | Set 21
- Adobe Interview Experience | Set 55 (On-Campus Full Time for MTS profile)
- Amazon Interview Experience | Set 211 (On-Campus for Internship)
- OYO Rooms Interview Experience | Set 3 (For SDE-II, Gurgaon)
- C# Program for Dijkstra's shortest path algorithm | Greedy Algo-7
- Algorithms | Dynamic Programming | Question 7
- Amazon Interview | Set 46 (On-campus for Internship)
- For each row of the matrix, find the smallest element and subtract it from every element in its row.
- Do the same (as step 1) for all columns.
- Cover all zeros in the matrix using minimum number of horizontal and vertical lines.
- Test for Optimality: If the minimum number of covering lines is n, an optimal assignment is possible and we are finished. Else if lines are lesser than n, we haven’t found the optimal assignment, and must proceed to step 5.
- Determine the smallest entry not covered by any line. Subtract this entry from each uncovered row, and then add it to each covered column. Return to step 3.
Try it before moving to see the solution
Explanation for above simple example:
An example that doesn’t lead to optimal value in first attempt: In the above example, the first check for optimality did give us solution. What if we the number covering lines is less than n.
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3).
Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional arrays of size n to store the labels, matches, and auxiliary information needed for the algorithm.
In the next post, we will be discussing implementation of the above algorithm. The implementation requires more steps as we need to find minimum number of lines to cover all 0’s using a program. References: http://www.math.harvard.edu/archive/20_spring_05/handouts/assignment_overheads.pdf https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQDZNHwuuOY
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Mathematical
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.

Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
assignment-problem
Here are 92 public repositories matching this topic..., root-11 / graph-theory.
A simple graph library
- Updated Apr 29, 2024
mayorx / hungarian-algorithm
(Kuhn-Munkres) numpy implementation, rectangular matrix is supported (|X| <= |Y|). 100x100000 in 0.153 s.
- Updated Dec 8, 2022
HalemoGPA / Learn-Js
Elzero Web School Js Course Assignments Solutions
- Updated Feb 20, 2023
Gnimuc / Hungarian.jl
The Hungarian(Kuhn-Munkres) algorithm for Julia
- Updated Jan 29, 2023
aalmi / HungarianAlgorithm
A Java implementation of the Kuhn–Munkres assignment algorithm (Hungarian Algorithm)
- Updated Aug 10, 2019
HalemoGPA / Learn-CSS
Elzero Web School CSS Course Assignments Solutions
- Updated Aug 5, 2022
sharathadavanne / hungarian-net
Deep-learning-based implementation of the popular Hungarian algorithm that helps solve the assignment problem.
- Updated Aug 31, 2023
alieldeba / Elzero-Cpp-Assignments
All C++ Solutions Of Elzero Web School Channel Assignments and elzero.org Website Assignments
- Updated Sep 6, 2023
jbytecode / OperationsResearchModels.jl
A Julia package for operations research subjects
- Updated May 10, 2024
jundsp / Fast-Partial-Tracking
Fast partial tracking of audio with real-time capability through linear programming. Hungarian algorithm provides optimal spectral peak-to-peak matching in polynomial time.
- Updated Mar 6, 2021
YaleDHLab / pointgrid
Transform a 2D point distribution to a hex grid to avoid overplotting in data visualizations
- Updated Jun 30, 2021
phoemur / hungarian_algorithm
An implementation of the Hungarian Algorithm in C++
- Updated Dec 11, 2018
Gluttton / munkres-cpp
Generic implementation of Kuhn-Munkres (Hungarian) Algorithm in C++
- Updated Oct 14, 2023
oddg / hungarian-algorithm
A Go implementation of the Hungarian algorithm
- Updated Aug 9, 2017
HalemoGPA / Learn-HTML
Elzero Web School HTML Course
- Updated Sep 24, 2023
dutta-alankar / PH-354-2019-IISc-Assignment-Problems
Solutions to the complete set of assignment problems which I did while crediting Computational Physics course by Prof. Manish Jain at IISc, Physical Sciences department on 2019
- Updated May 30, 2021
Ibrahim5aad / kuhn-munkres-algorithm
A python program to solve assignment problem by the Kuhn–Munkres algorithm (The Hungarian Method).
- Updated Oct 22, 2021
EvanOman / AuctionAlgorithmScala
Scala Implementation of Bertsekas' Auction Algorithm
- Updated Jun 24, 2016
i10416 / munkres
Munkres(Hangarian) Algorithm Implimentation for Scala
- Updated Jun 4, 2023
Improve this page
Add a description, image, and links to the assignment-problem topic page so that developers can more easily learn about it.
Curate this topic
Add this topic to your repo
To associate your repository with the assignment-problem topic, visit your repo's landing page and select "manage topics."
Browse Course Material
Course info, instructors.
- Prof. Daniel Frey
- Prof. Gilbert Strang
Departments
- Mechanical Engineering
As Taught In
- Applied Mathematics
- Differential Equations
- Linear Algebra
Learning Resource Types
Engineering math: differential equations and linear algebra, assignments.
Note to OCW Users: MIT OpenCourseWare does not provide student access or discounts for MATLAB ® software . It can be purchased from The MathWorks ® . For more information about MATLAB Pricing and Licensing , contact The MathWorks directly.

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare
Help | Advanced Search
Computer Science > Robotics
Title: multi-auv kinematic task assignment based on self-organizing map neural network and dubins path generator.
Abstract: To deal with the task assignment problem of multi-AUV systems under kinematic constraints, which means steering capability constraints for underactuated AUVs or other vehicles likely, an improved task assignment algorithm is proposed combining the Dubins Path algorithm with improved SOM neural network algorithm. At first, the aimed tasks are assigned to the AUVs by improved SOM neural network method based on workload balance and neighborhood function. When there exists kinematic constraints or obstacles which may cause failure of trajectory planning, task re-assignment will be implemented by change the weights of SOM neurals, until the AUVs can have paths to reach all the targets. Then, the Dubins paths are generated in several limited cases. AUV's yaw angle is limited, which result in new assignments to the targets. Computation flow is designed so that the algorithm in MATLAB and Python can realizes the path planning to multiple targets. Finally, simulation results prove that the proposed algorithm can effectively accomplish the task assignment task for multi-AUV system.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The linear assignment problem is a way of assigning rows to columns such that each row is assigned to a column and the total cost of the assignments is minimized (or maximized). The cost of assigning each row to each column is captured in a cost matrix.The entry Cost(i,j) is the cost of assigning row i to column j.. The cost of unassignment assigns a cost to any row or column that is not matched.
Debugging with MATLAB Conway Game of Life Warm-up Conway Game of Life Implementation Library Exercises Homework More Projects ... assignment Problem Sets. theaters Lecture Videos. menu_book Online Textbook. assignment_turned_in Programming Assignments with Examples. Download Course.
Keywords: Assignment problem, MATLAB coding, ROA method. MSC Code: 90B80 INTRODUCTION Assignment Problem (AP) is completely degenerated form of a Transportation Problem. It appears in some decision-making situations. Such as assign tasks to machines, workers to jobs etc. AP refers to another special class of Linear Programming Problem in ...
Hungarian algorithm steps for minimization problem. Step 1: For each row, subtract the minimum number in that row from all numbers in that row. Step 2: For each column, subtract the minimum number in that column from all numbers in that column. Step 3: Draw the minimum number of lines to cover all zeroes.
K.GHADLE, Y. MULEY New approach to solve assignment problems using MATLAB, International Journal of Latest Technology in Engineering, 10 (2015), 36-39.
6.057 Introduction to MATLAB, Homework 1. Resource Type: Assignments. pdf. 1 MB 6.057 Introduction to MATLAB, Homework 1 Download File DOWNLOAD. Course Info ... assignment Programming Assignments. notes Lecture Notes. Download Course. Over 2,500 courses & materials
The course will be covered in eight modules. Various aspects of MATLAB programming for numerical computation will be covered in these modules, with each module dedicated to on equivalent numerical topic. Each module will be covered in one week, with 2-2.5 hours lectures per week. There will be self-study problems at the end of several of ...
Homework 3: Problem Solving (PDF - 1.4MB) This homework is designed to give you practice writing functions to solve problems. The problems in this homework are very common and you will surely encounter similar ones in your research or future classes. As before, the names of helpful functions are provided in bold where needed.
Assignment problem is a special case of transportation problem, in which the objective is to minimized total cost by assigning 'm' jobs to 'n' machines. By using MATLAB coding and some modification in ROA method, optimal solution can be trace for
Time complexity : O(n^3), where n is the number of workers and jobs. This is because the algorithm implements the Hungarian algorithm, which is known to have a time complexity of O(n^3). Space complexity : O(n^2), where n is the number of workers and jobs.This is because the algorithm uses a 2D cost matrix of size n x n to store the costs of assigning each worker to a job, and additional ...
MATLAB, which is faster and reliable. Assignment Problem with MATLAB has great practical and theoretical importance. The programming in MATLAB will save lot of time from complex and iterative calculations. It is also REFERENCES [1] Dimitri. P. Bertsekas., A New Algorithm for the Assignment Problem, Mathematical Programming, 21 (1981), 152-171.
A MATLAB App to solve Assignment Problem using RNN. assignment-problem operations-research matlab-gui Updated Dec 28, 2019; MATLAB; jundsp / Fast-Partial-Tracking Star 18. Code Issues Pull requests Fast partial tracking of audio with real-time capability through linear programming. Hungarian algorithm provides optimal spectral peak-to-peak ...
Debugging with MATLAB Conway Game of Life Warm-up Conway Game of Life Implementation Library Exercises Homework More Projects ... assignment Problem Sets. theaters Lecture Videos. menu_book Online Textbook. assignment_turned_in Programming Assignments with Examples. Download Course.
Assignment 6 (due 11/22) Problem set; As with assignment 5, use previous code (although there is not much MATLAB here) Assignment 7 (due 12/06) Problem set; Associated m-files; Assignment 8 (due 12/14) Problem set; Associated m-files; Downloading Assignments . All code provided in Assignments above will be bundled into one zipped file.
The syntax c{:} transforms a cell array in a list, and a list is a comma separated values, like in function arguments. Meaning that you can use the c{:} syntax as argument to other functions than deal. To see that, try the following: > z = plus(1,2) z = 3. > c = {1,2}; > z = plus(c{:}); z = 3.
Add this topic to your repo. To associate your repository with the assignment-problem topic, visit your repo's landing page and select "manage topics." GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
MATLAB Script for Problem 9 (M) Homework 2 (PDF) Homework 3 (PDF) Homework 4 (PDF) ... assignment Problem Sets. assignment_turned_in Programming Assignments with Examples. Download Course. Over 2,500 courses & materials Freely sharing knowledge with learners and educators around the world.
Matlab Grader: As previously announced, a new version of Matlab Grader LTI was installed on February 24, 2024. Instructors should pair their Canvas assignments to MATLAB and Simulink Online Courses LTI 1.3. The existing integration, MATLAB Coding Problem (deprecated), has been removed.
To deal with the task assignment problem of multi-AUV systems under kinematic constraints, which means steering capability constraints for underactuated AUVs or other vehicles likely, an improved task assignment algorithm is proposed combining the Dubins Path algorithm with improved SOM neural network algorithm. At first, the aimed tasks are assigned to the AUVs by improved SOM neural network ...