Networking | Cloud | DevOps | IaC

IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server is an important element to networking in the real world. User location cannot be predicted as they may be at and out of a desk and up and about should they need to do so. Tying them to a local VLAN may only be helpful if they are bound to desks in those locations, although the most ideal outcome, it is not the most practical.
It is only wise to incorporate IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server in areas where you expect different teams to come to. Meeting rooms could for a moment have the accounting group or the development group meeting there and based on the intelligent and dynamic vlan assignmnet with 802.1x authentication, users port-access are defined their appropriate vlans for their respective access to resources on the network.
How to Provision 802.1 X Authentication Step By Step With Dynamic VLAN Assignment With Windows Radius Server For 802.1x Clients.
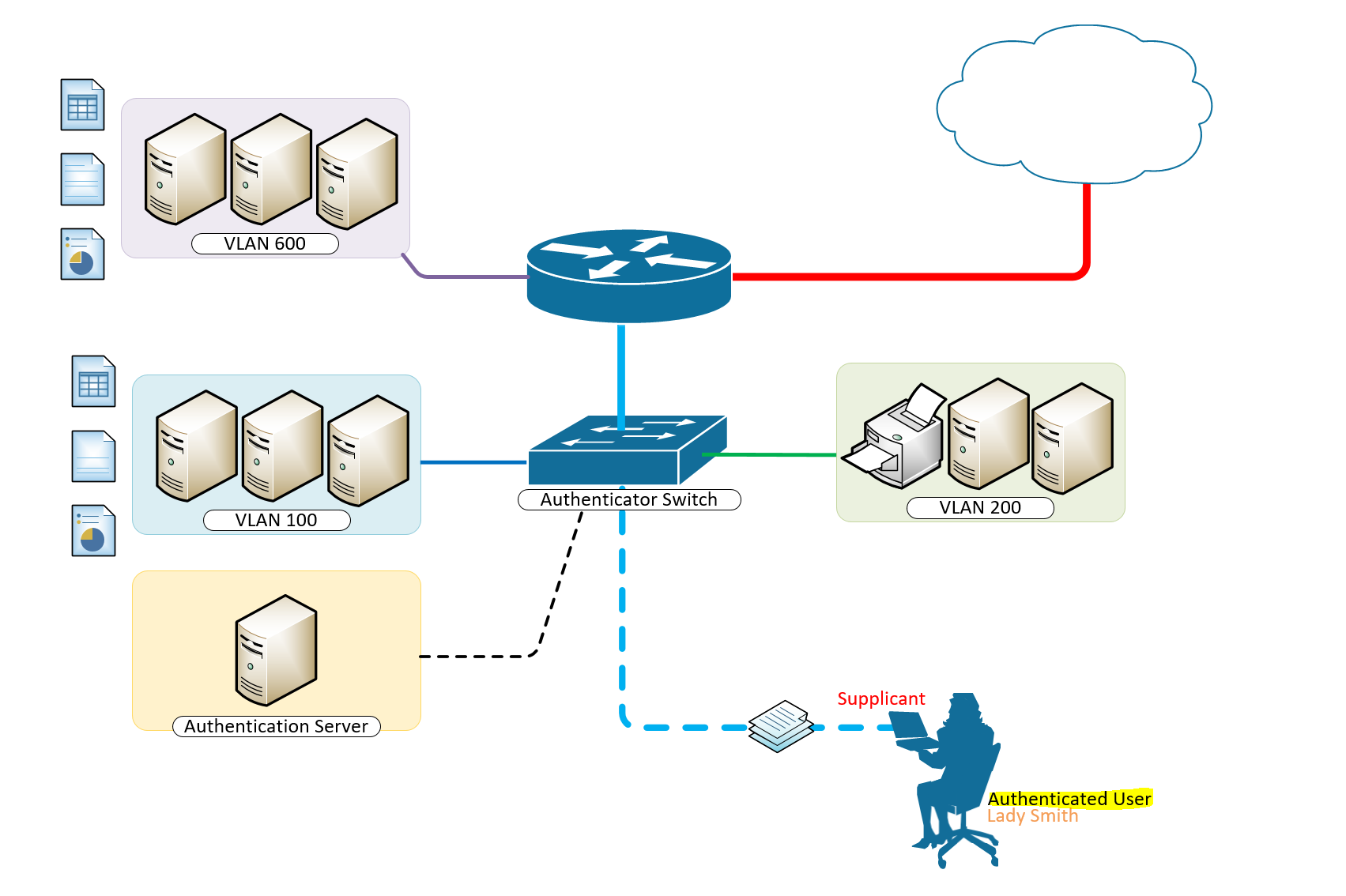
A typical configuration for a system under IEEE 802.1x Authentication control is shown in the following figure.
In this scenario, “Lady Smith” wishes to use services offered by servers on the LAN behind the switch. There are multiple VLANs with resources available based on user vlan membership. Her laptop computer is connected to a port on the Aruba 2920 Edge Switch that has 802.1x port authentication control enabled.
The laptop computer must therefore act in a supplicant role. Message exchanges take place between the supplicant and the authenticator which is the Aruba 2920 Switch, and the authenticator passes the supplicant’s credentials which is her (Windows Active Directory User Account Credentials) to the authentication server for verification. The NPS Server which is the authentication server then informs the authenticator whether or not the authentication attempt succeeded, at which point “Lady Smith” is either granted or denied access to the LAN behind the switch.
Setup Structure for IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
- Supplicant: Laptop running Microsoft Windows 10 or Windows 7
- Authenticator: HP Aruba 2920 Edge Switch
- Authentication Server: Microsoft NPS (Network Policy Server) running on Windows Server 2012 R2.
- User Database : Active Directory
For Windows Infrastructure
Create NPS Server – Add Role on Windows Server 2012 R2
- Create DHCP Scopes for VLANS
Create RADIUS Client on NAC using Network Policy Server
- Create Network Policies
- Configure a Network Policy for VLANs
- Start Wired Auto-Config Service
- Enable Network Authentication
Create the DHCP Scopes for VLAN100 and VLAN200 Groups
- Development Group Scope – VLAN 100
SVI: ip address 172.16.80.254 255.255.255.0 Scope Subnet: 172.16.80.1/24
- Accounting Group Scope – VLAN 200
SVI:ip address 172.16.70.254 255.255.255.0 Scope Subnet: 172.16.70.0/24
Secret Key: secret12
Add Edge Switch Management IP as the RADIUS Client
The Shared Secret Key: secret12 will be used in the Switch Configuration.
Create Network Policy Settings for Accounting Group for VLAN 200
Configuration Example
Here’s an example of how you might consider when configuring Microsoft NPS Server to assign users to a VLAN based on their user group, using NPS for the authentication and authorization of users. This configuration has worked flawlessly on the HP Aruba 2920 Switch. The key to getting this to work is the use of a RADIUS element called: ‘Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID’. This is a RADIUS attribute that may be passed back to the authenticator (i.e. the Aruba 2920 Switch) by the authentication server (i.e. Microsoft NPS Server) when a successful authentication has been achieved. There are a few other elements which need to accompany it, but this is the key element, as it specifies the VLAN number that the user should be assigned to.
The other elements that need to be returned by the NPS Server are as follows:
- Tunnel-PVT-Group-ID: 200
- Service-Type: Framed
- Tunnel-Type: VLAN
- Tunnel-Medium-Type: 802
For Client Infrastructure
On the Supplicant, Windows 7 or 10 configure the following steps on the Ethernet Adapter to enable IEEE 802.1X Authentication
For Network Infrastructure
Connect Server Infrastructure to VLAN 400
Create VLAN for Accounting Group
Create VLAN for Development Group
Create AAA Configuration on Switch for Radius Authentication
Download the Switch Configuration:
Test the IEEE 802.1X Authentication and Dynamic VLAN Assignment with NPS Radius Server
Verify Port-Access with the following user groups – VLAN 100 and VLAN 200
Think of what other clever things you can do from the information below;
Breakdown of Commands for RADIUS Authentication
Verification Commands
Thanks for reading. Please share your thoughts in the comment box below;
Published in Configuring , Design , Installing and Configuring , Networking , Security and Switching
- 802.1 x authentication step by step aruba
- 802.1 x authentication step by step cisco
- 802.1 x wireless authentication step by step
- 802.1x authentication process
- 802.1x authentication windows 10
- 802.1x authentication windows server 2012
- 802.1x certificate authentication
- assignment wlc
- cisco dot1x
- cisco ise dynamic vlan
- cisco ise dynamic vlan assignment wlc
- cisco wireless radius attributes
- configuration example
- dynamic vlan assignment cisco 2960 dynamic vlan configuration in packet tracer
- dynamic vlan assignment with windows radius server
- dynamic vlan cisco
- dynamic vlan ruckus
- meraki dynamic vlan assignment
- nps mac authentication wired
- nps policy for mac-based authentication
- radius multiple vlans
- vlan radius server
- vlan steering
- vmps server
Network Guys
Share your knowledge!
How to use 802.1x/mac-auth and dynamic VLAN assignment
Hello guys! Today I want to show you how to secure your edge-switches with 802.1x and mac-authentication fallback in combination with HPE comware-based switches. The 802.1x protocol is used for network access control. For devices like printers, cameras, etc. we will use mac-authentication as a fallback. We will also use dynamic VLAN assignment for the connected ports.
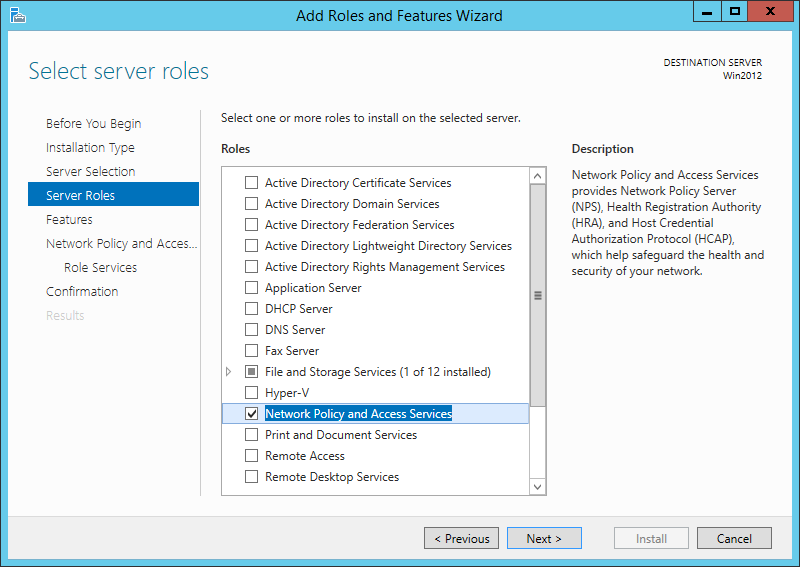
Our radius server will be Microsoft NPS. You can activate this role on the Windows server:
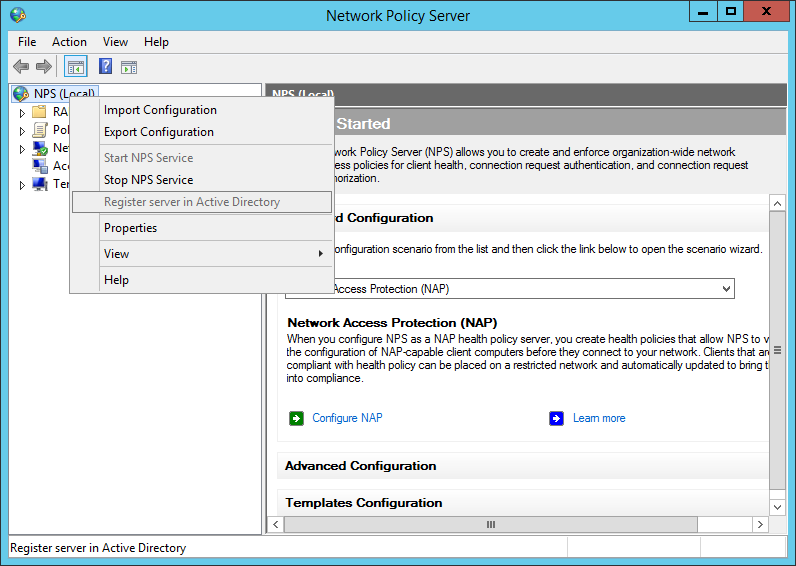
After the installation, open the NPS console and register the radius server in your Active Directory:
add your switches or your management network as a radius-client:
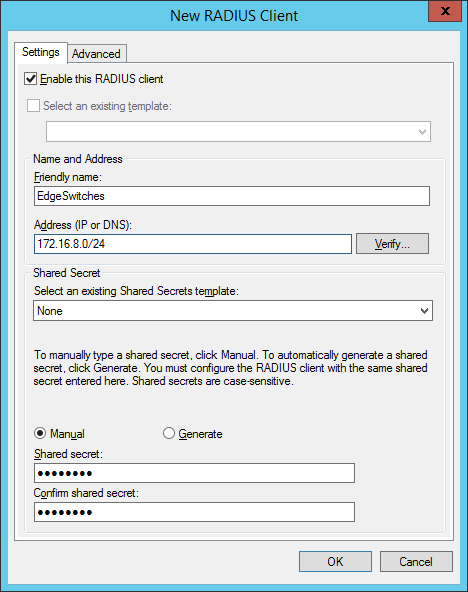
the shared secret will be used in the switch configuration. In created two groups within my test environment:
- “ VLAN2-802.1x ” containing computer accounts
- “ VLAN3-MAC-Auth ” containing user accounts (username+password = mac-address of the device)
So we will now configure two network policies for our network access control:
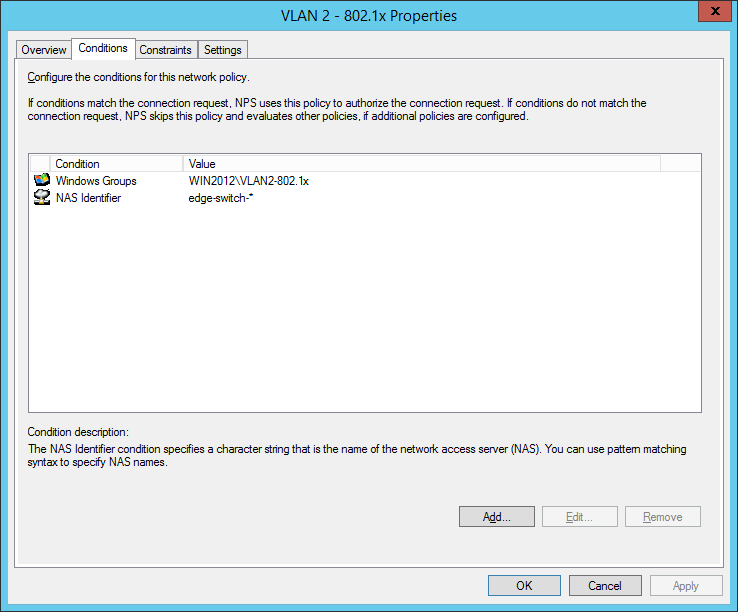
I also configured a NAS Identifier so no other device can use the radius server. The clients will use their computer certificate so you will need a running internal certification authority. Choose PEAP only as the authentication method:
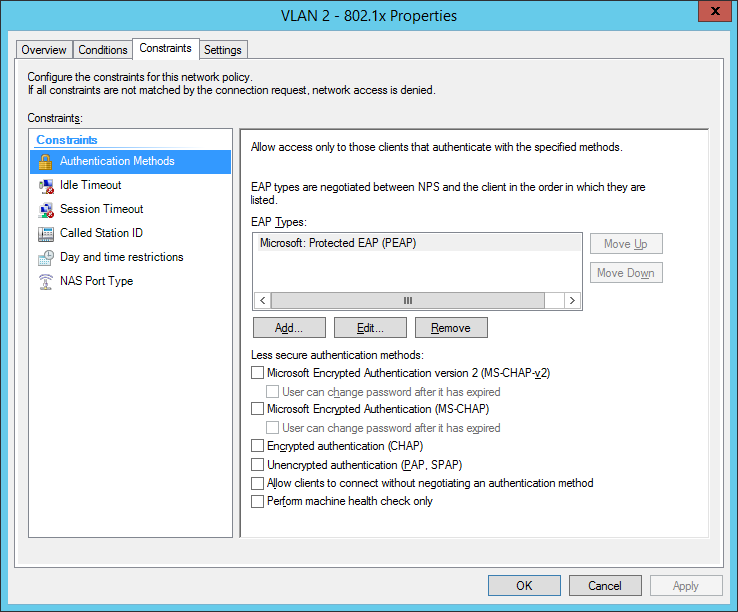
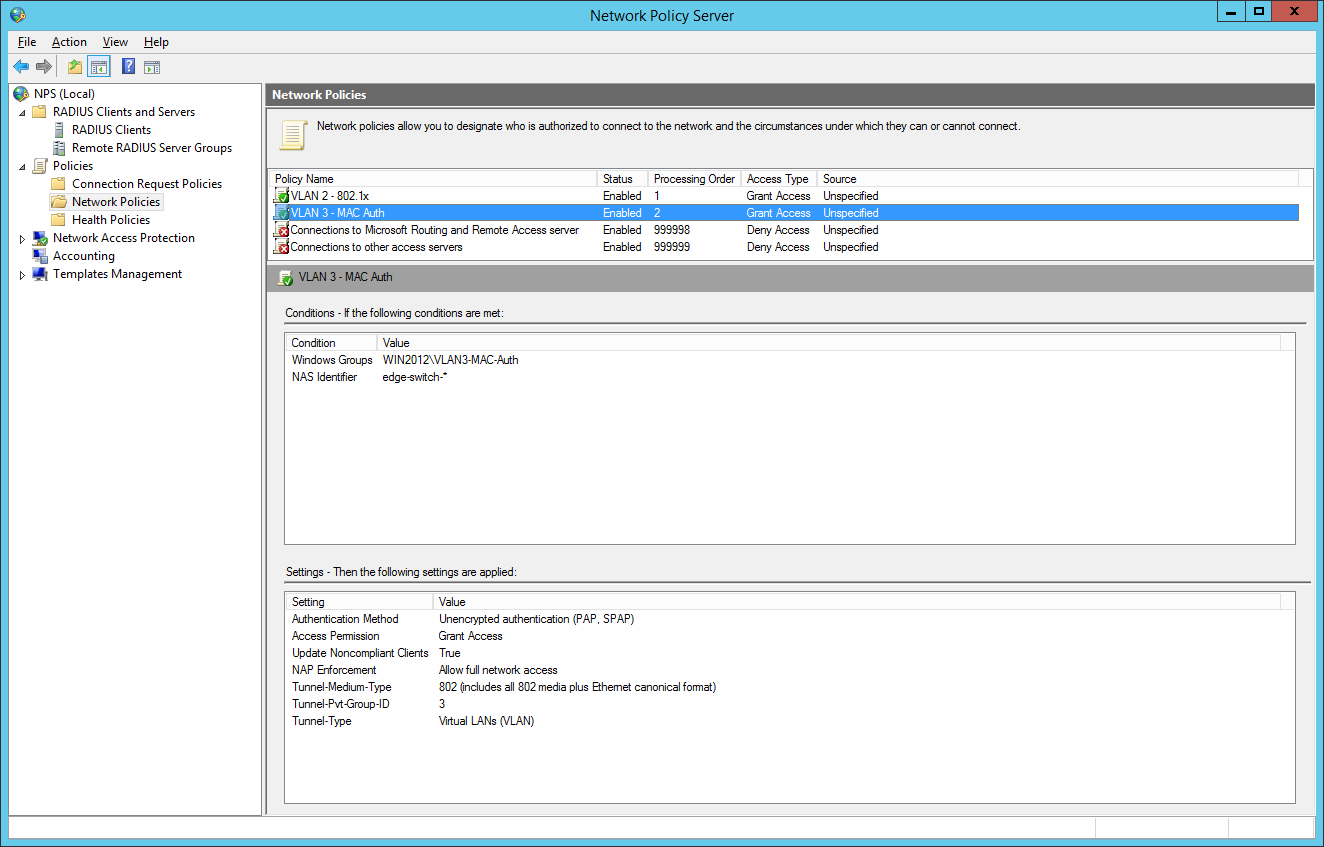
the next step is for our dynamic VLAN assignment. Dot1x devices are bound to VLAN 2:
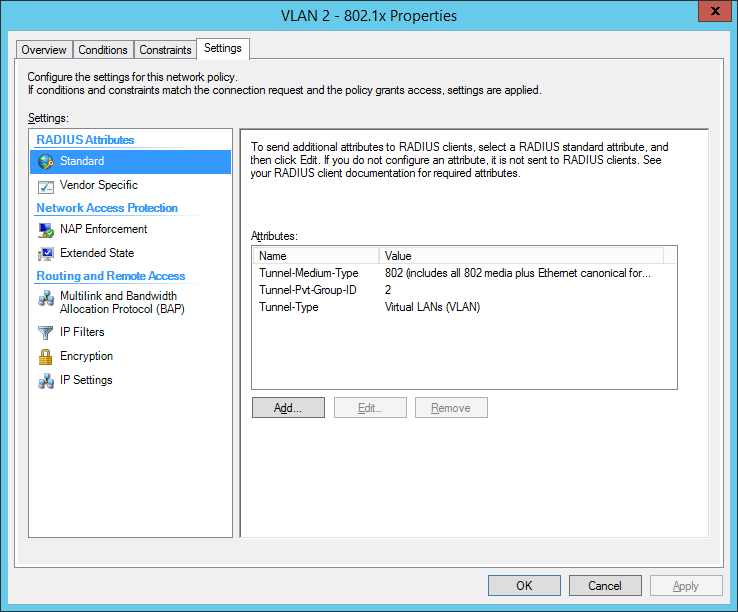
the final dot1x configuration in the NPS:
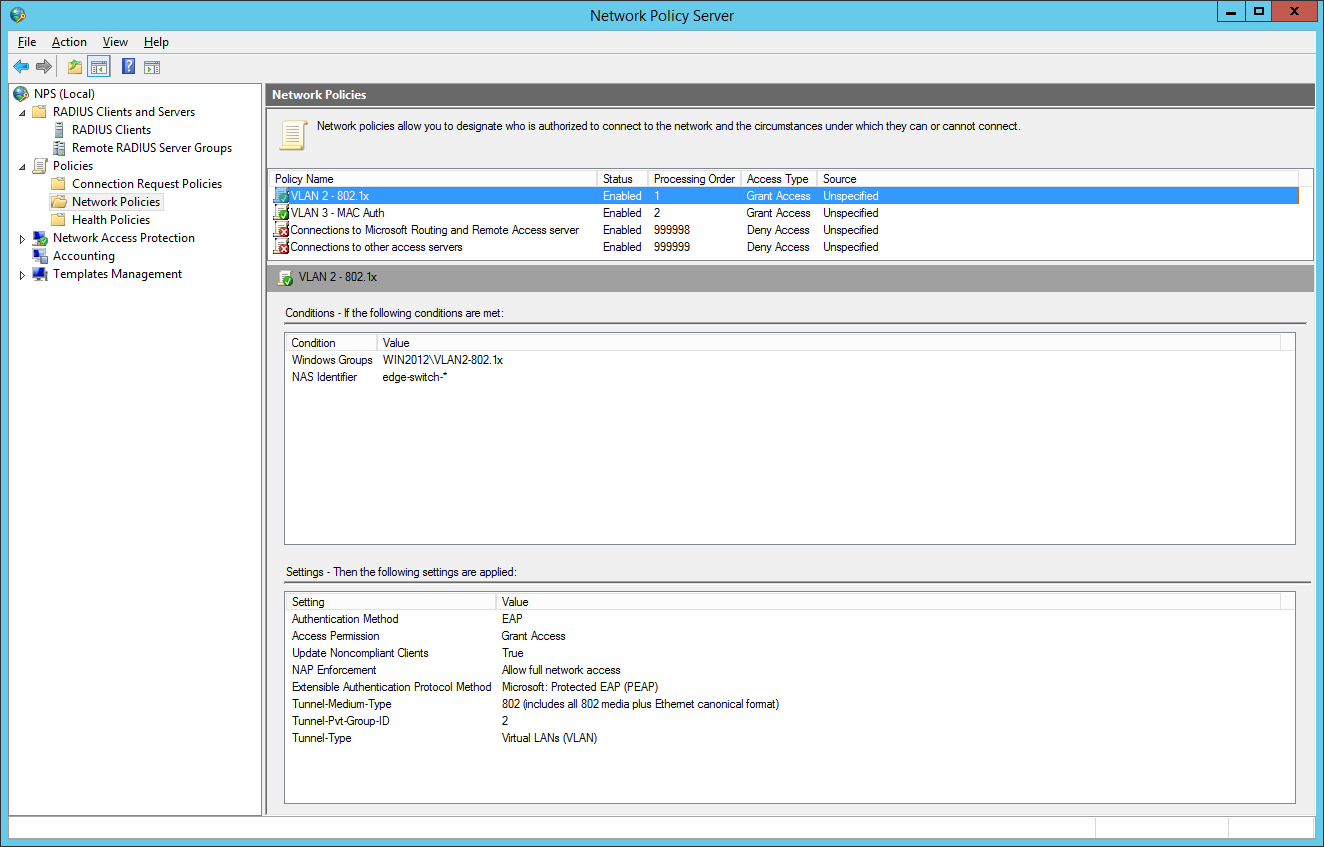
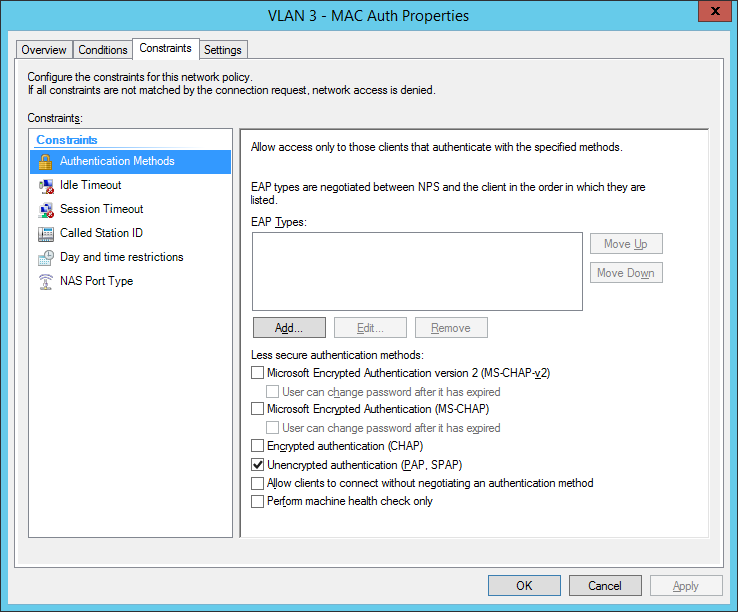
the second network policy is for the mac-based authentication:
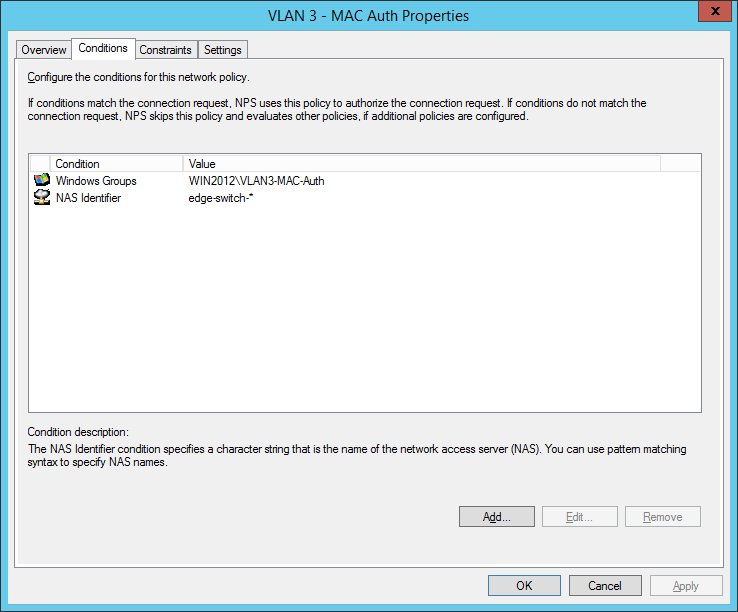
Comware switches are sending MAC-Auth-requests via PAP (maybe you know how to change it to CHAP):
final MAC auth profile:
for now we have built up our authentication server. Now let’s go to the switch configuration. You have global configuration parameters and parameters for each interface. The best way is to use interface-range command to be safe at your configuration. Users who cant authenticate, will be forced to VLAN 999 (quarantine VLAN with no gateway). Here are the global parameters with explanations inline:
now we will configure the interfaces: Added 2 entries
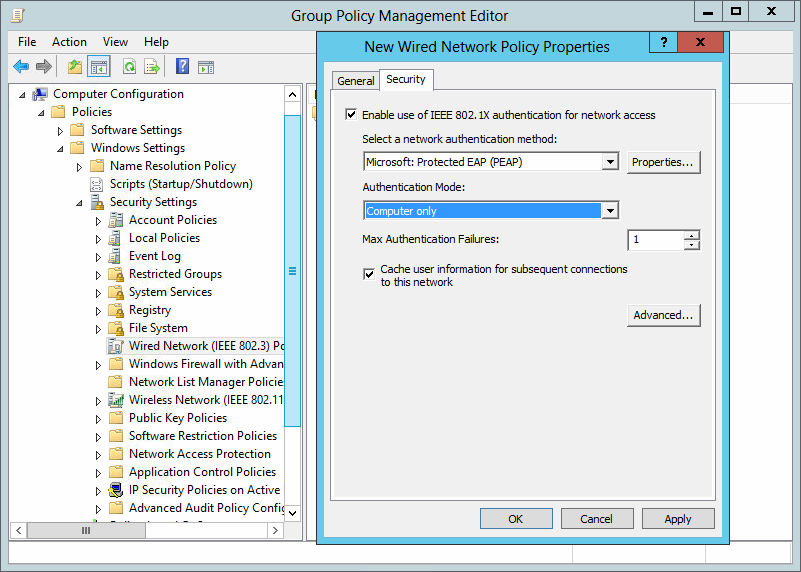
the last part is to configure all windows clients to send 802.1x auth data to the cable network. I’ve done this via a global group policy. You can find the settings under Computer Configuration / Policies / Windows Settings / Security Settings / Wired Network (IEEE 802.3) Policies:
So how does a working 802.1x-auth looks like?
%Jan 3 01:59:59:531 2013 edge-switch-01 DOT1X/6/DOT1X_LOGIN_SUCC: -IfName=GigabitEthernet1/0/10-MACAddr=0023-2415-42a3-AccessVLANID=1- AuthorizationVLANID=2 -Username= host/PC123.mycompany.local ; User passed 802.1X authentication and came online.
Successful Mac-Authentication of a printer:
%Jan 3 01:31:28:782 2013 de-pad-l19-edg01 MACA/6/MACA_LOGIN_SUCC: -IfName=GigabitEthernet1/0/9-MACAddr=0017-c82d-e9bf-AccessVLANID=1- AuthorizationVLANID=3 -Username= 0017c82de9bf -UsernameFormat=MAC address; User passed MAC authentication and came online.
I tried to draw a flow chart which shows the authentication process, I hope it’s ok for you :)
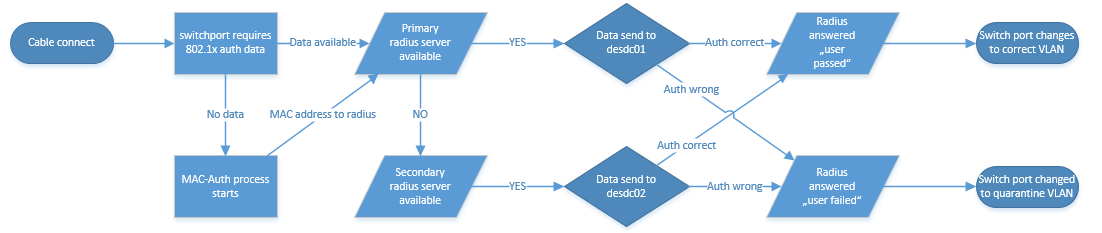
Do you have questions? Feel free to write them into the comments and I will try to answer.
Have a nice and sunny day!
/edit: If you can’t see success and failure events, follow this instruction: NPS / Radius Server is not logging
/edit 2018-05-14: I corrected the global and interface configuration, we had problems with the old configuration
12 Responses
Thanks for this, I need to setup dynamic VLAN assignment in the near future but for Juniper equipment.
This at least gives me a good starting point, thanks for the write up.
Many thanks for the perfect tutorial on How to use 802.1x/Mac-Auth and dynamic VLAN assignment. Many of us can take help from it. Really nice.
Nice write-up. This was a great starting point for configuring the base for dynamic polices. Thanks!
hi Mike, how ‘s about hybrid port with voice-vlan? does it work?
thanks Tung Duong
we had several problems with this config, currently we are investigating hyprid ports with “port security” command. I will update this post if we have prooved this version.
Can you tell me why I would do this over conventional static VLANs? What are the benefits radius dynamic VLANs?
we have customers which want to divide the network for clients, printers and “special devices”. So you have different group/radius-policies to directly place the devices in the right VLAN. Dynamic VLAN is only a bonus feature which you can use. Of course, you can use only the 802.1x and Mac authentication for security purpose.
I’m on the desktop side of things, so apologies if I use any incorrect terminology here.
Our Infrastructure team are looking at introducing 8021x in our schools. They have a test setup where all 8021x devices pick up a data centre VLAN regardless of which building they’re in – eg 10.100.50.
Each building WIRED has its own unique IP – SchoolA=10.120, SchoolB = 10.130 and so on.
I’ve asked if the 8021x setup can be where 8021x devices in SchoolA will get 10.120.50; SchoolB will get 10.130.50
This would allow us to easily determine which building LaptopA actually is, in the same way as we can with our wired desktops. It also saves on SCCM boundary issues causing applications/updates to be pulled over the WAN rather than the LAN.
It’s been suggested that this may not be possible. Could someone confirm this?
Thanks in advance.
Hello! This is of course possible!
My idea (with examples):
SchoolA=10.120 (Location: Chicago) SchoolB=10.130 (Location: Dallas)
So at Chicago you will have VLAN 333, every device is getting an IP address with 10.120.x.x. At Dallas every device in VLAN 333 is getting an IP address with 10.130.x.x. So the VLAN ID “333” is the same at every school but the DHCP scope and default gateway has it’s own address. So the device is getting the VLAN 333 at every location but another IP address. It’s very simple.
It’s not working if all schools are connected via Layer2 so VLAN333 can’t be a “standalone VLAN” at each geographical location.
Ask me any questions, I will try to help you.
- Pingback: 802.1x, MAC-Authentication and VLAN assignment at ProCurve/aruba Switches – Network Guy
- Pingback: Port Auth, Dynamic VLAN and Radius | samuelnotes
- Pingback: HPE Comware problem with mac authentication and printer - Network Guy
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Click on the button to load the content from jetpack.wordpress.com.
Load content
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Certificates

Post Categories
Post archives, recent posts.
- Sophos UTM 9.712-13 HA update problem 14. November 2022
- Sophos UTM 9.712-12 update released 24. August 2022
- Aruba OS Switch automatic vlan assignment for aruba APs 5. May 2022
- Sophos UTM 9.711-5 update released 22. April 2022
- Sophos UTM 9.710-1 update released 20. March 2022
Recent Comments
- Sophos Ssl Vpn Client Anmeldung - Login and Portal on Auto-Logon with Sophos SSL VPN Client (OpenVPN)
- Russell on Install Sophos UTM from USB Stick
- arno on Problems with incoming mails
- GigaTech IT on Installing Realtek Driver on ESXi 6.7
- Sophos User Portal Login Ssl Vpn - Online Login on Auto-Logon with Sophos SSL VPN Client (OpenVPN)
Franky’s Web Website from my friend Frank. News and Tricks about Microsoft products, primarly Exchange Server
Copyright by networkguy.de
Imprint · Privacy Policy
The Cisco Learning Network

gilarcejr_1127 asked a question.
Our dot1x is used for dyamic VLAN assignement and it works using this config:
switchport access vlan A
switchport mode access
switchport nonegotiate
authentication event fail action authorize vlan A
authentication event no-response action authorize vlan A
authentication host-mode multi-host
authentication open
authentication port-control auto
authentication violation restrict
dot1x pae authenticator
dot1x timeout quiet-period 1
dot1x timeout tx-period 6
dot1x max-reauth-req 10
spanning-tree portfast
However, we noticed that it first goes to VLAN A then goes to the VLAN B. This was an issue with on a client. So i was trying to create a setup that doesn't pass through the VLAN A but passes through VLAN 1 which is unrouted. This is my config:
It does work but only if the username is already cached in the windows PC. If I login using the same username in a new PC, it doesnt. What am I missing???
Please help.
Thanks in advance!
- CCIE Routing and Switching

I don't see your configuration for dynamic vlan assignment.
yes you have configured a fail vlan and an no-response vlan but this has nothing do to with dynamic vlan assignment.
What do you really want ? An alternative VLAN if the authentication fails because of lost connection to the server or the supplicant isn't an dot1x supplicant?
Furhter question why do you use host-mode multi-host?
kind regards,
gilarcejr_1127
The end goal is to have dynamic VLAN assignment. Whichever user logs in they should be given their respective VLANs from the Radius server.
The Windows PC are all dot1x capable. The reason there is multi host is that the PC is cascaded to an Avaya phone.
This actually made me wonder because I thought that the earlier config was for dynamic VLAN assignment. Is there another way of configuring dynamic VLAN assignment using dot1x?
Appreciate the responce
can't you use the voice vlan for the avaya phone?
(I don't know them - only the cisco and siemens phones and both are capable for voice vlan)
In my opinion it is a security issue to use host-mode multi-host but if there isn't another way then use it.
Here is a link to the guidelines for dot1x dynamic vlan assignment but there a whole of bunch other ways to implement it.
Perhaps with a VMPS old-school stuff
how do you authenticate your clients EAP-TLS or what else?
I'm just starting to learn the in depth details of dot1x...
Is it possible to dynamically assign also the voice VLAN? Also I'm also not aware on how to make an Avaya phone a supplicant so I thought of just putting it in the same VLAN as the PC.
Can you repost the link?
Here it is : 802.1X Authentication Services Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3850 Switches) - IEEE 802.1X VLAN…
That isn't an easy topic?
Try your best and I will lend your a little bit of my time.
from where are you?
your are welcome
Related Questions
Trending articles.
- Cisco Packet Tracer: Software de Simulación para Redes
- 200-301 CCNA Study Materials
- Packet Tracer Labs
- CCIE/CCDE: Book your Lab/Practical Exam
- Continuing Education Credits Automation
If you encounter a technical issue on the site, please open a support case .
Communities: Chinese | Japanese | Korean
Cisco.com © Copyright 2024 Cisco, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement Terms & Conditions Cookie Policy Trademarks

- Contact Sales

MS Switch Access Policies (802.1X)
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
Cisco Meraki MS switches offer the ability to configure access policies, which require connecting devices to authenticate against a RADIUS server before they are granted network access. These access policies are typically applied to ports on access-layer switches to prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network.
This article outlines options available for access policies, how to configure access policies in the Meraki dashboard, and the configuration requirements for RADIUS servers.
Making changes to an existing access policy can cause minor traffic disruption on all ports configured for that policy.
Each network can have a maximum of 8 access policies configured.
For troubleshooting guidance, please follow RADIUS Issue Resolution Guide .
Organization-wide RADIUS servers
Org-wide RADIUS servers are currently in Early Access Preview. Please refer to the Organization Settings document here for more information on how to define and use RADIUS server configurations at the organization level.
The Org-Wide RADIUS servers feature provides the ability to define one or many RADIUS servers once and then re-use the configuration across the organization for access policies.
Configuration
- After Org-Wide RADIUS Servers are configured at the organization level, navigate to the target access policy under Switching > Configure > Access policies
- Scroll to Radius Servers, and then in the box that says 'Select RADIUS', check the box beside the desired RADIUS server and save the changes
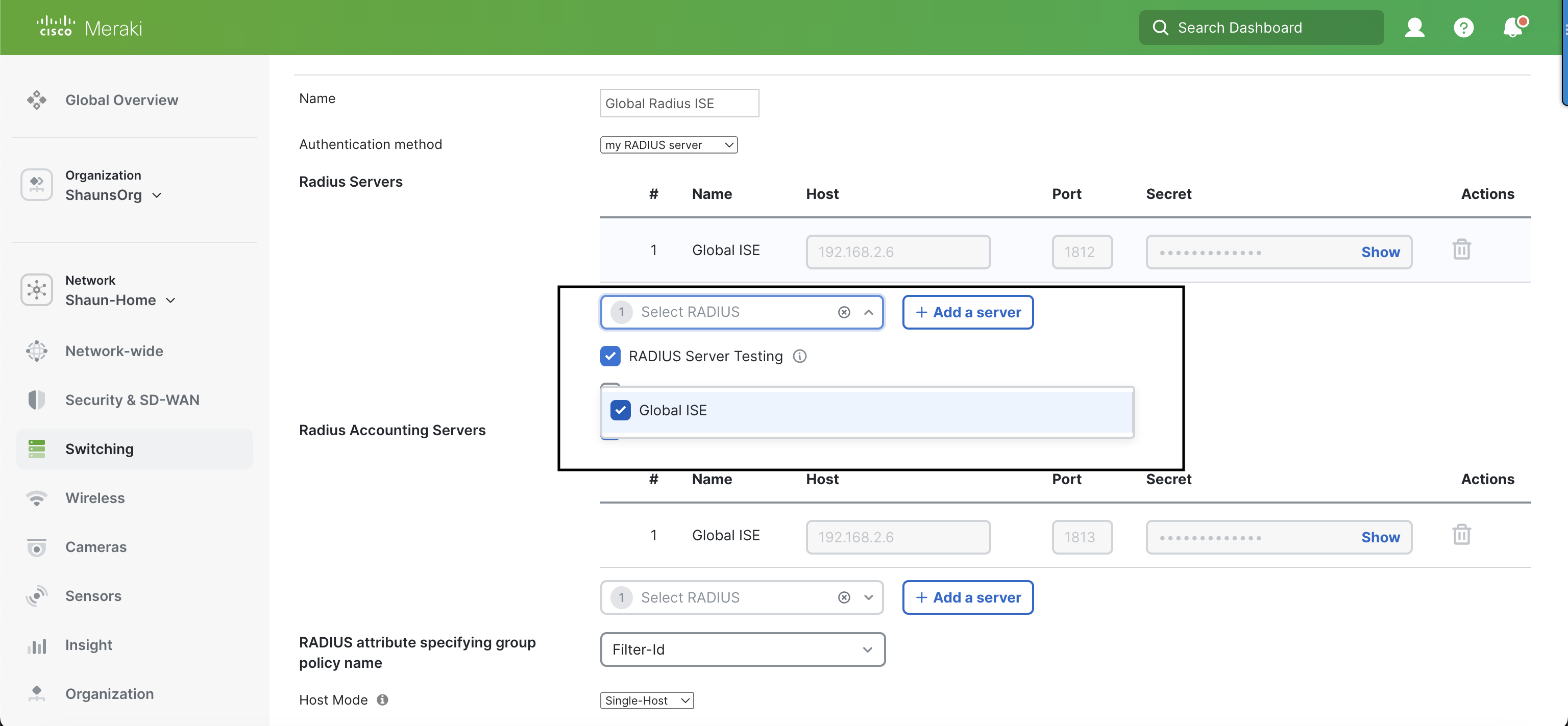
A maximum of 3 RADIUS servers defined in each access policy still applies when using Org-Wide Radius Servers
Support for all host modes is available from firmware version MS 10.12.
There are four authentication host modes to choose from:
- Single-Host (Default) With single-host authentication, a connected device will attempt authentication and if it fails to authenticate, the client will be denied access. This mode is recommended for switch ports with only one client attached. If multiple devices are connected to the same switch port (for example a device connected via a hub or daisy-chained off of a VoIP phone), only one client will be allowed network access upon successful authentication. All subsequent authentication requests from other clients will be ignored and they will not be granted access as a result.
Multi-Domain With multi-domain authentication, one device can be authenticated on each of the data and voice VLANs; if a second device is detected on one of the VLANs, the device will not be granted access. In this mode, Hybrid Authentication is used and Voice VLAN authentication is required. This mode is recommended for switch ports connected to a phone with a device behind the phone. Authentication is independent on each VLAN and will not affect the forwarding state of each other. To ensure proper authentication, a Voice VLAN must be specified on the switchport. Failure to specify this value will result in client devices being unable to pass traffic properly after authentication. Cisco Meraki switches require the following attribute pairs within the Access-Accept frame to put devices on the voice VLAN:
Cisco- AVPair device-traffic-class=voice
- Multi-Host With multi-host, a single successful authentication will put the port into a forwarding state. All subsequent authentication attempts are ignored. This is recommended in deployments where the authenticated device acts as a point of access to the network, for example, hubs and access points.
Note: The MS390 and C9300-Ms supports multi-auth multi-VLAN and will allow for multiple data domain sessions behind the same switch port to have different VLAN IDs assigned without blocking access.
Note: VLAN Profiles feature simplifies VLAN management across multiple sites by enabling dynamic assignment of VLANs based on descriptive names rather than numerical IDs. This facilitates easier management across multiple sites with varying VLAN configuration reducing the need for multiple RADIUS policies. Click here for additional information.

RADIUS Caching for MS390 and C9300-M
RADIUS caching allows for endpoints connecting to the switch to authenticate against a RADIUS server, and for the switch to cache the authorization result for that session. If the connection to the RADIUS server is severed, the switch will use the cached entry to reauthorize the endpoint. The switch will cache the authorization result for a default of 24 hours. This is user-configurable in the access policy.
Configuration:
Switching->Access Policies-> select your access policy
Navigate to RADIUS caching enabled and change status to enabled
(Optional) Navigate to RADIUS cache timeout and enter new value in hours
Default is 24hrs or One Day
Max Value is 720hrs
NOTE: For 802.1X sessions, a cached authorization will not send an EAPOL-Success message to the endpoint, but will re-authorize the session with the cached result. For windows machines, be sure to enable fallback to unauthorized access in the supplicant configuration for RADIUS Caching to work properly with windows machines.
Access Policy Types
There are three options available for an access policy in Dashboard:
- 802.1X (Default) When an 802.1X access policy is enabled on a switch port , a client that connects to that switch port will be prompted to provide their domain credentials. If the RADIUS server accepts these credentials as valid, their device will be granted access to the network and get an IP configuration. If no authentication is attempted, they will be put on a "guest" VLAN, if one is defined . 802.1X access policies are commonly used in enterprise environments, since they can authenticate against the existing domain userbase .
- MAC Authentication Bypass ( MAB ) When a MAB access policy is enabled on a switch port , the client's MAC address is authenticated against a RADIUS server without needing to prompt the user. If the server accepts the MAC as valid credentials for the network, the device will be allowed access. MAB access policies are useful for a more seamless user experience, restricting the network to specific devices without needing to prompt the user.
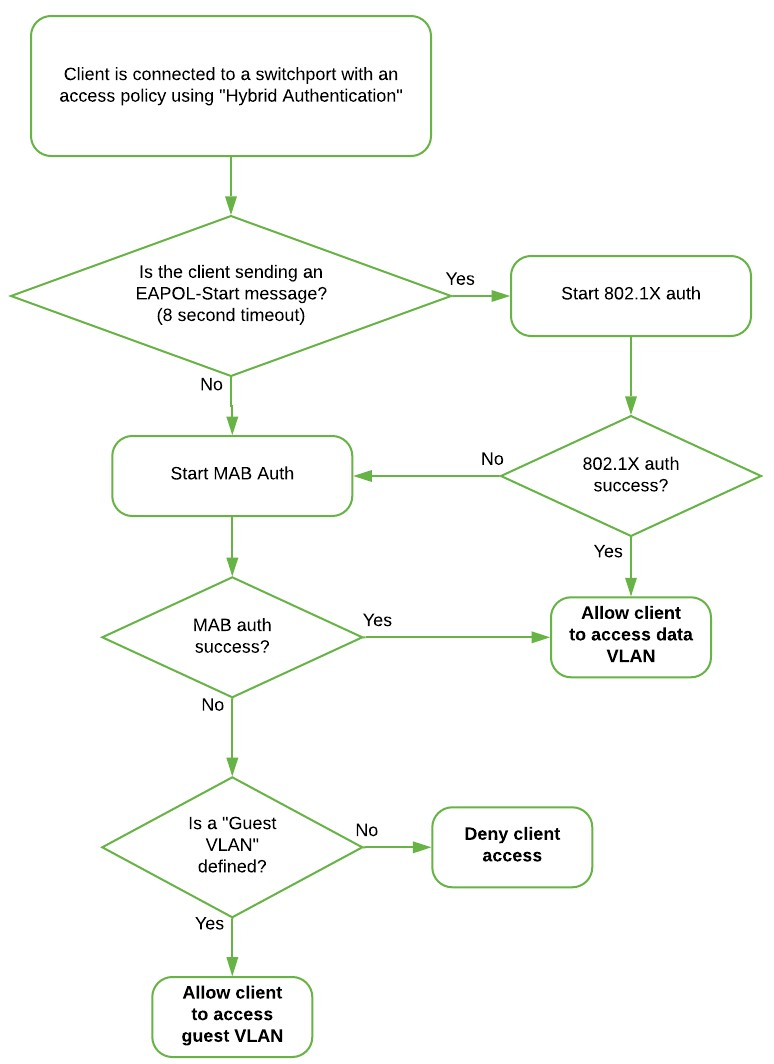
- Increase Access Speed When a policy is set to increase access speed, the 802.1X and MAB access-request will be send in parallel, which can allow for MAB devices with no supplicant to gain access to the network without waiting for the 802.1X process to time-out. The 802.1X response for the same device will always override the MAB result received. For devices with a supplicant, it is advised to either configure the supplicant, or disable the supplicant to use MAB when the MAB result is the desired authentication mechanism.
Warning: Cisco Identity Services Engine does not officially support increase access speed behaviors and can cause outcomes that are not desirable including higher Policy Services Node and Monitoring node load, as well as potentially undesirable authentication/authorization behaviors.
Change of Authorization (CoA)
Meraki MS and Catalyst 9300-M switches support CoA for RADIUS reauthentication and disconnection as well as port bouncing. For more information, please see the following KB article .
URL Redirect Walled Garden (Supported on MS210/225/250/350/355/390**/410/420/425 and C9300-M) By default, URL redirect is enabled with CoA. This can be used to redirect clients to a webpage for authentication. Before authentication, http traffic is allowed but the switch redirects it to the redirect-url. The walled garden can be used to limit access to the web server only. This feature will only be enabled if one or more supported switches are in the network. Configurations on this feature will be ignored by unsupported switches.
For URL redirect on the MS390 and C9300-Ms, there needs to be a walled-garden ACL name sent with the access-accept message from the RADIUS server. The first access-policy in the list will require an ACL name of Walled-Garden-00 and each subsequent access-policy will increment by 1. e.g. Access Policy 2 will be Walled-Garden-01. The Walled Garden ACL on the MS390 and C9300-Ms will allow DHCP, DNS, and IP access to the walled garden IP addresses.
NOTE: UDP/1700 is the default port used by all MS for CoA
**NOTE: MS390s and C9300-Ms support RADIUS URL-Redirect as of MS 15
Other RADIUS Features
- RADIUS Accounting RADIUS Accounting can be enabled to send start, interim-update (default interval of 20 minutes) and stop messages to a configured RADIUS accounting server for tracking connected clients. Meraki’s implementation follows the IETF’s RFC 2869 standard. As of MS 10.19, device sensor functionality for enhanced device profiling has been added by including CDP/LLDP information the RADIUS Accounting message (MS120/125/130/130R/220/225/250/320/350/355/410/425/450). As of 14.19+ the MS390 and C9300-Ms also supports device sensor with enhanced attributes across LLDP, CDP, mDNS, and DHCP for profiling.
- RADIUS Testing Meraki switches will periodically send Access-Request messages to these RADIUS servers using identity 'meraki_8021x_test' to ensure that the RADIUS servers are reachable. If unreachable, the switch would transition into an alerting status to indicate a failure. Actual server failover is based on the client authentication requests. Failed client authentications will have the switch failover to the next available configured server.
This feature must be enabled to track RADIUS server reachability. If not enabled, clients will continue to be put on the Guest or Critical Auth VLANs even after connectivity between the MS and RADIUS server has been restored.
RADIUS test messages are sent every 5 minutes.
MS390s and C9300-Ms support multi-vlan assignment, when using Multi-Auth as the host mode . This means that multiple client devices connected in the Data domain on the same port can be mapped to different VLANs through RADIUS assignment. This functionality is currently supported only on the MS390 and C9300-Ms switches.
Support for Dynamic VLAN Assignment for the Voice VLAN / domain was introduced in firmware version MS 15.
- Tunnel-Medium-Type: Choose 802 (Includes all 802 media plus Ethernet canonical format) for the Attribute value Commonly used for 802.1X.
- Tunnel-Private-Group-ID: Choose String and enter the VLAN desired (ex. "500") . This string will specify the VLAN ID 500 .
- Tunnel-Type: Choose Attribute value Commonly used for 802.1X and select Virtual LANs (VLANs)
- 802.1X Control Direction (Wake-on-LAN support) 802.1X Control Direction is set by default to "both" directions. In this mode, the switch port doesn't allow ingress or egress traffic through the switch port until after the port is authorized via 802.1X or MAB authentication. Control Direction can also be set to "inbound-only", in which case the switch port doesn't allow ingress traffic, but will allow limited egress traffic from the network through the switch port to reach the connected device. This is often used to allow Wake-on-LAN magic packets to wake a sleeping host on the connected port, at which point the host can attempt a normal 802.1X or MAB authentication to authorize the switch port for full ingress and egress traffic.
This feature is available in public preview/beta in dashboard as of Aug 2022 beginning in MS 15 for classic switches. The toggle will only appear on networks running MS 15 or later. Support is not available on MS390 switches as of MS 15, but is anticipated to be added in an upcoming release.
RADIUS Monitoring must be enabled to track RADIUS server reachability. If not enabled, clients will continue to be put on the Guest or Critical Auth VLANs even after connectivity between the MS and RADIUS server has been restored.
Client devices may fail RADIUS authentication because they do not comply with the network's security requirements. The failed authentication VLAN provides such clients with limited access to the network for remediation purposes.
Failed Authentication VLAN is only supported in the Single Host, Multi Host and Multi Domain modes. Access policies using Multi Auth mode are not supported on MS Classic Switches, only Cloud Managed Catalyst .
Re-authentication Interval When the Re-authentication Interval (time in seconds) is specified, the switch will periodically attempt authentication for clients connected to switch ports with access policies. Apart from providing for a better security policy by periodically validating client authentication in a network, the re-authentication timer also enables the recovery of clients placed in the Failed Authentication VLAN because of incomplete provisioning of credentials. Re-authentication will not occur if no re-authentication interval has been configured, or if a reauthentication-interval has been configured but the switch has lost connectivity to all of the RADIUS servers listed under the access policy.
Suspend Re-authentication when RADIUS servers are unreachable Periodic re-authentication of clients can be an issue when RADIUS servers are unreachable. The Suspend Re-authentication when RADIUS servers are unreachable allows users to choose whether the re-authentication should occur or not when none of the RADIUS servers are reachable. By default, re-authetication gets suspended when RADIUS servers are not reachable.
'Suspend re-authentication when RADIUS servers are unreachable,' is not a configurable option on the MS390 and C9300-M series switches . An MS390 and C9300-M switch will automatically ignore this configuration, and will always suspend client re-authentication, if it loses connectivity with the RADIUS server.
Critical Auth entication VLAN The critical authentication VLAN can be used to provide network connectivity to client devices connecting on switch ports controlled by an access policy when all of the RADIUS servers for that policy are unreachable or fail to respond to the authentication request on time. When the RADIUS servers are not reachable from the switch, authentication requests for clients attempting to connect to the network will fail, resulting in clients being denied access. Critical authentication VLAN ensures that these clients are still able to access the business-critical resources by placing them in a separate VLAN. This also allows network administrators to better control the network access available to clients when their identities cannot be established using RADIUS.
The critical data and critical voice VLANs should not be the same.
RADIUS Monitoring must be enabled to track RADIUS server reachability. If not enabled, clients will continue to be put on the Guest or Critical Auth VLANs even after connectivity between the MS and RADIUS server has been restored.
Configuring Critical Authentication VLAN or Failed Authentication VLAN under an access policy may affect its existing Guest VLAN behavior. Please consult the Interoperability and backward compatibility section of this document for details.
An "802.1X Canned EAP Success" event will be triggered if the authentication process places a client's VLAN on the critical, guest, or failed authentication VLAN. This alert is different from the "802.1X EAP Success" event where authentication is successful and planned connectivity is provided.
Critical Authentication VLAN is only supported in the Single Host, Multi Host and Multi Domain modes. Access policies using Multi Auth mode are not supported on MS Classic Switches, only Cloud Managed Catalyst .
Suspend port bounce When connectivity between the switch and any of the RADIUS servers is restored, the switch will attempt to authenticate the clients which it had placed in the Critical Authentication VLAN. The switch does this by bouncing (turning off and on) the switch ports on which these clients are connected. If required, this port-bounce action can be disabled by enabling the Suspend port bounce option. When port-bounce is suspended, the clients will be retained in the Critical Authentication VLAN until a re-authentication for these clients is manually triggered.
Interoperability and backward-compatibility in VLAN assignments
If Critical and/or Failed Authentication VLANs are specified in an Access Policy, the Guest VLAN functionality gets modified to ensure backward-compatibility and inter-op between the configured VLANs. Please refer to the Interoperability and backward-compatibility table below for more details on this.
The following matrix shows the remediation VLAN, if any, that client devices would be placed in for the different combinations of the remediation VLAN configuration options and the RADIUS authentication result.
1 When using hybrid authentication without increase access speed (concurrent-auth), a client failing both 802.1X and MAB authentication will also be placed in the Guest VLAN. Please refer to the Access Policy Types section of the MS Switch Access Policies documentation for details.
MS 14 is the minium firmware version required for the following configuration options.
- Failed Authentication VLAN
- Re-authentication Interval,
- Suspend Re-authentication when RADIUS servers are unreachable
- Critical Authentication VLANs
- Suspend port bounce
When using CWA - Central Web Authentication with Cisco ISE , please uncheck Increase Access Speed as this will result in CWA failing.
RADIUS Attributes
When an access policy is configured with a RADIUS server, authentication is performed using PAP. The following attributes are present in the Access-Request messages sent from MS switch to the RADIUS server.
- NAS-IP-Address
- Calling-Station-Id: Contains the MAC address of the end user machine (supplicant) (all caps, octets separated by hyphens, example: "AA-BB-CC-DD-EE-FF").
- Called-Station-Id: Contains the MAC address of the Meraki MS switch (all caps, octets separated by hyphens).
Note: MS390 and C9300-M has an exception, it will send MACID of the switch port in the Called-Station-Id AVP.
- NAS-Port-Type
- EAP-Message
- Message-Authenticator
Note: Please refer to RFC 2865 and RFC 3579 for details on these attributes, additional notes for certain attributes are included below.
Creating an Access Policy on Dashboard
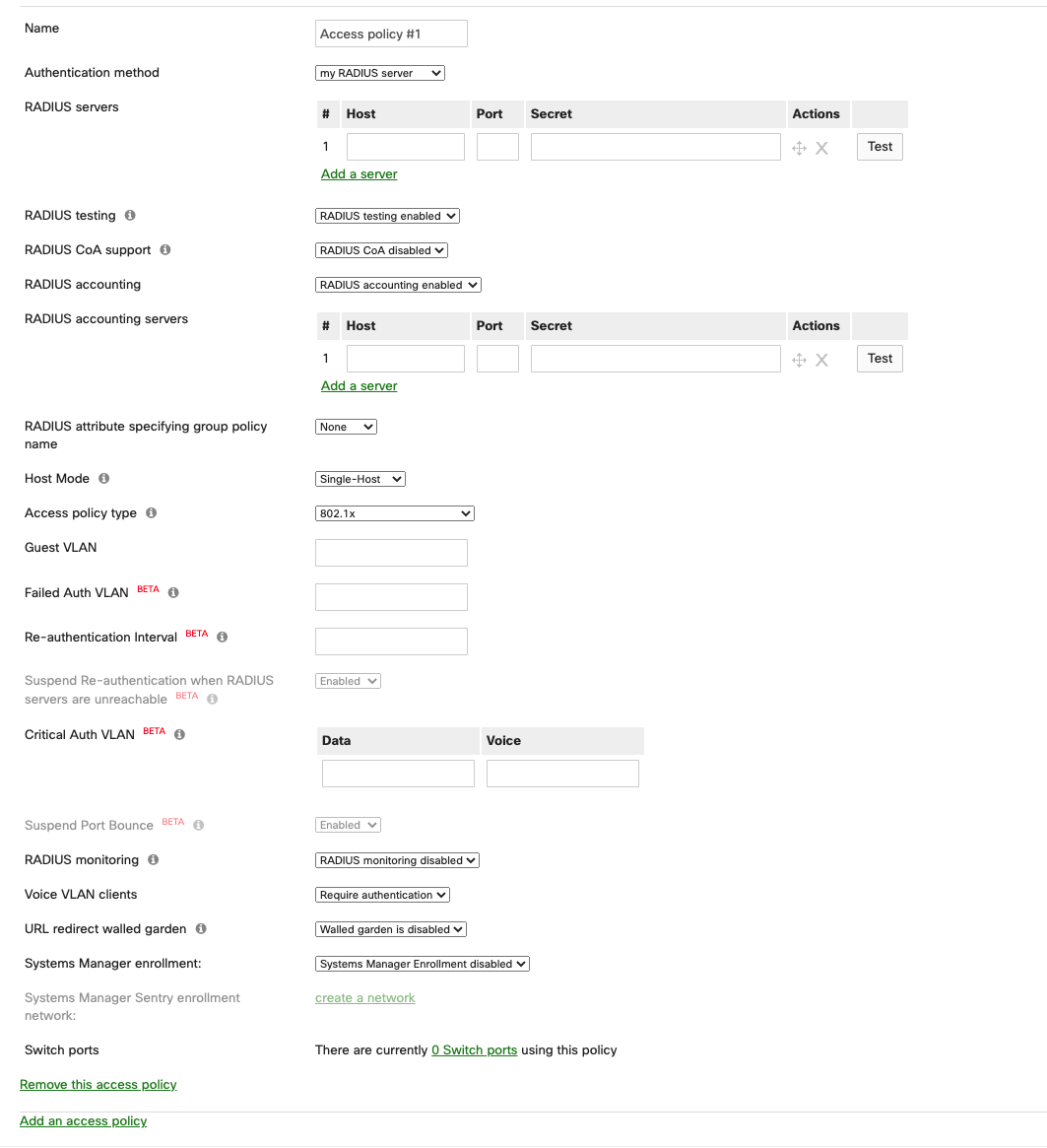
Creating an access policy using a custom radius server.
- On the dashboard navigate to Switching > Configure > Access policies.
- Click on the link Add an access policy in the main window then click the link to Add a server.
- Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server, the port (default is 1812), and the secret created earlier.
- Select the required options, as described above.
- Click Save changes.
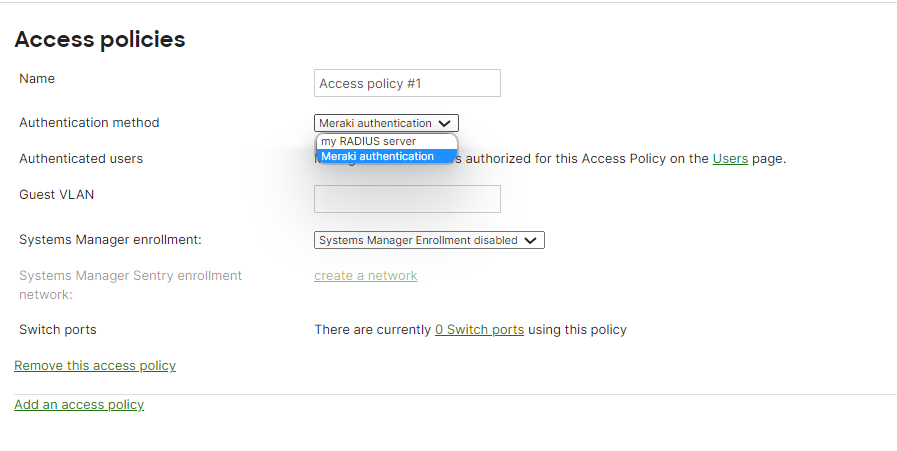
Creating an Access Policy Using Meraki Authentication
- Under Authentication method select Meraki Authentication.
- Select a Guest VLAN and whether to allow System Manager enrollment.
Apply Access Policy to Switch Ports
- Navigate to Switching > Monitor > Switch ports.
- Select the switch port(s) you would like to apply the access policy to and press the Edit button.
- Convert the switch port type from trunk to access . Note: you can only apply an Access Policy to an access port.
- From the Access Policy drop-down box, select the Access Policy you created and press the Update ports button.
Unmanaged Switches Between MS and Client for RADIUS Authentication
When using PEAP EAP-MSCHAPv2 on an MS switch port, if an unmanaged switch is between the end user machine (supplicant) and the RADIUS client (MS) the authentication will fail. The reasoning is explained below:
- The destination of the eapol (RADIUS exchange) frame is a special multicast address that 802.1D-compliant bridges do not forward.
- This destination is labeled as "nearest" in Wireshark which means that the frame should only be forwarded to the next layer 2 device.
- If the unmanaged switch is added into the topology between the client and the MS, the next layer 2 device is the unmanaged switch and because the multi-cast nearest address is not meant to traverse multiple switches, the unmanaged switch drops the packets. This prevents the client from being authorized.
There is a work-around to this but special considerations must be taken before implementing them:
- This is not due to a fault in the MS but is the way that eapol is designed.
- It is possible to circumvent this by using MAC based RADIUS authentication . If one machine authenticates via MAC based RADIUS through the MS on an unmanaged switch, the machine that has authenticated will be granted access. It is a workaround but it is less secure and requires more configuration on the NPS and DC.
Configuring 802.1X VLAN Assignment and MAB
1. Overview
2. Example for VLAN Assignment
3. Example for MAB
802.1X authentication is a network access control method which safeguards network security . If the client passes the RADIUS server authentication then the client can access the LAN. Otherwise, the client cannot access the LAN.
VLAN Assignment and MAB are two important features of 802.1X authentication, and act as safety controls.
VLAN Assignment
VLAN Assignment allows the RADIUS server to send the VLAN configuration to the port dynamically. VLAN Assignment is used together with 802.1X authentication. After the port is authenticated, the RADIUS server assigns the VLAN based on the username of the client connecting to the port. The username-to-VLAN mappings must already be stored in the RADIUS server database.
The figure below shows the typical topology of VLAN Assignment. VLAN Assignment is port-based. With VLAN Assignment enabled, the RADIUS server will send the VLAN configuration when the port is authenticated. VLAN IDs are assigned based on switch ports.
If the assigned VLAN is nonexistent on the switch, the switch will create the related VLAN automatically, add the authenticated port to the VLAN and change the PVID based on the assigned VLAN.
If the assigned VLAN exists on the switch, the switch will directly add the authenticated port to the related VLAN and change the PVID instead of creating a new VLAN .
If no VLAN is supplied by the RADIUS server or if 802.1X authentication is disabled, the port will be still in its original VLAN.

MAB (MAC Authentication Bypass) uses the MAC address of a device to determine whether the client can get access to the network. After checking the MAC addresses of the clients that you want to access the network, add these MAC addresses into the database of the RADIUS server. With MAB enabled on th port, the switch will learn the MAC address of the device automatically and send the authentication server a RADIUS access request frame with the client’s MAC address as the username and password. If the authorization succeeds, the RADIUS server grants the client access to the network. Thus devices can be authenticated without any client software installed. And MAB can be used to authenticate devices without 802.1X capability like IP phones.
MAB interacts with the other features:
802.1X authentication— MAB takes effect only if 802.1X authentication is enabled on the port.
VLAN Assignment— MAB can be used on a port with VLAN Assignment enabled. That is, if a client has an authorized MAC address identity, the switch assigns the client to a specific VLAN if VLAN Assignment is configured on the corresponding port.
2 Example for VLAN Assignment
2.1 Network Requirements
To enhance network security, a company requires that the employees can access the network normally only when their computers pass the authentication successfully. At the same time, to reduce the workload of the configuration, it is required that the ten authenticated computers can be automatically assigned to the VLANs of their departments. The network topology is shown as below.

2.2 Configuration Scheme
802.1X Authentication is commonly used in solving authentication and security problems for LAN ports. VLAN Assignment can assign multiple clients to different VLANs depending on their authentication information. Thus configure 802.1X Authentication and VLAN Assignment to meet the requirement.
The configuration is briefly summarized in the following outlines:
1) Build a RADIUS Server.
2) Configure 802.1X and VLAN Assignment on the switch.
3) Start the authentication on 802.1X client software.
2.3 RADIUS Server Introduction
A RADIUS server receives user authentication requests, authenticates the user, and then returns authentication results to the authenticator (the switch).
This guide takes FreeRADIUS.net as an example to build a RADIUS server. FreeRADIUS.net installation file can be downloaded from http://freeradius.net/index.html . Run the file and follow the wizard to install the FreeRADIUS.net on a local computer.
After installing FreeRADIUS.net on the computer, some configurations files should be modified to satisfy the 802.1X authentication requirements:
Modify the clients.conf to add RADIUS client (the switch) information.
Modify the users.conf to add user authentication information.
2.4 Configuration
Configuration Guidelines:
VLAN Assignment takes effect only when the control type is Port Based . Set the control type as Port Based on the ports connected to clients .
802.1X authentication and Port Security cannot be enabled at the same time. Before enabling 802.1X authentication, make sure that Port Security is disabled.
Keep 802.1X authentication disabled on ports connected to the authentication server, the internet and the management computer, which ensures the traffic will not be blocked for the switch.
Demonstrated with T2600G-28TS acting as the authenticator, FreeRADIUS.net acting as the RADIUS server and TP-Link 802.1X Client Software, the following sections provide configuration procedures. The configuration procedures on the switch will be given in two ways: using the GUI and using the CLI.
2.4.1 Build a RADIUS Server
For the network administrator, the first thing is to build a RADIUS server, and put the user information for employees into the RADIUS server. The network administrator can set different username and password for each employee or set a public username and password shared by all the employees in the same department. The setting of the username and password depends on the actual demands.

To avoid the format error of the adding code, use Notepad++ to edit configuration files.
One client section means a RADIUS client. You can choose one of the client sections and edit the following attributes. Or you can add a new client section to meet your requirements.
The clients.conf can be modified in three aspects:
The IP address of network segment of the authenticator (T2600G-28TS). After the installation is completed, the default configuration file contains the commonly used network segment. Thus you can keep it as default in most cases.
The secret which is the shared key between the RADIUS server and the switch. The RADIUS server and the switch use the key string to encrypt passwords and exchange responses.
The shortname which is used as an alias for the fully qualified domain name, or the IP address. A value can be filled in optionally for the shortname.
According to the network topology, add the following code and save the file.

The user information can be modified in four aspects:
User-name and User-Password , which is the authentication information of the clients . You can replace rfc3580 with the username which you want and replace demo with the new password. Or you can ignore the default user information and add new user information which has identical format in the next line.
Tunnel-Type , which indicates the tunneling protocol to be used. To configure VLAN Assignment, specify this value as VLAN.
Tunnel-Medium-Type , which indicates the transport medium to use when creating a tunnel for tunneling protocols. To configure VLAN Assignment, specify this value as IEEE-802.
Tunnel-Private-Group-Id , which indicates the group ID for a particular tunneled session, that is the assigned VLAN ID.
According to the network topology, add the following codes and save the file.

4) Click Restart FreeRaDIUS.net Service to restart FreeRaDIUS.net.
2.4.2 Configure VLAN Assignment on the Switch
Using the GUI
1) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > Global Config to load the following page. In the Global Config section, enable AAA function and click Apply .
2) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > Dot1x List to load the following page. In the Authentication Dot1x Method List section, select an existing RADIUS server group for authentication from the Pri1 drop-down list and click Apply .

3) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > RADIUS Config to load the following page. Enter the IP address of the RADIUS server and the shared key which is pre-defined in the Radius Clients.conf.

4) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Global Config to load the following page. In the Global Config section, enable 802.1X and VLAN Assignment globally and click Apply .

5) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Port Config to load the following page. Select the port 1/0/3-13 which you want to deploy 802.1X VLAN Assignment and set the status for port1/0/3-13 as Enable . Set the control type as Port Based for port1/0/3-13. Set the status for port 1/0/1 and port 1/0/2 as Disable so that the RADIUS server and the internet will not be blocked for the switch.

Using the CLI
1) Enable AAA globally and configure the RADIUS parameters.
T2600G-28TS#configure
T2600G-28TS(config)#aaa enable
T2600G-28TS(config)#aaa authentication dot1x default radius
T2600G-28TS(config)#radius -server host 192.168.0.253 auth-port 1812 key 123456
2) Globally enable 802.1X authentication and set the authentication protocol. Enable VLAN Assignment.
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1x system-auth-control
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1x auth-method eap
T2600G-28TS(config)#dot1x vlan-assignment
3) Disable 802.1X authentication on port 1/0/1and port 1/0/2. Enable 802.1X authentication on port 1/0/3, set the mode as Auto, and set the control type as Port-Based.
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/1-2
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#no dot1x
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#exit
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface range gigabitEthernet 1/0/3-13
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#dot1x
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#dot1x port-method port-based
T2600G-28TS(config-if-range)#dot1x port-control auto
4) Verify the configurations.
Verify the global configurations of 802.1X authentication:
T2600G-28TS#show dot1x global
802.1X State: Enabled
Authentication Method: EAP
Handshake State: Enabled
Guest VLAN State: Disabled
Guest VLAN ID: N/A
802.1X Accounting State: Disabled
802.1X VLAN Assignment State: Enabled
Quiet-period State: Disabled
Quiet-period Timer: 10 sec.
Max Retry-times For RADIUS Packet: 3
Supplicant Timeout: 3 sec.
Verify the configurations of 802.1X authentication on the port:
T2600G-28TS#show dot1x interface
Port State MAB State GuestVLAN PortControl PortMethod Authorized LAG
---- ------ ------------ ------------ -------------- -------------- ------------- -----
Gi1/0/1 disabled disabled disabled auto mac-based authorized N/A
Gi1/0/2 disabled disabled disabled auto mac-based authorized N/A
Gi1/0/3 enabled disabled disabled auto port-based unauthorized N/A
Gi1/0/4 enabled disabled disabled auto port-based unauthorized N/A
Verify the configurations of RADIUS:
T2600G-28TS#show aaa global
AAA global status: Enable
Module Login List Enable List
Console default default
Telnet default default
Ssh default default
Http default default
T2600G-28TS#show aaa authentication dot1x
Methodlist pri1 pri2 pri3 pri4
default radius -- -- --
T2600G-28TS#show aaa group radius
192.168.0.253
2.4.3 Set Up Authentication on 802.1X Client Software
Before the employee can access the internet, the employee should input the authentication information on the 802.1X Client Software. The authentication information is the username and password which is set by the network administrator in the RADIUS server.

2) Enter the username and password. In this example, enter “tplink” as the username and “admin1” as the password , which is set in the RADIUS server, then click Connect .

Then the 802.1X client software will automatically register to the RADIUS server and get the authority to the internet from the RADIUS server.

When passing the authentication, the following screen will appear.

2.5 Verify the Configuration Result
After all the configurations are completed, you can follow the steps below to verify whether 802.1X VLAN Assignment works. Taking port 3 for a example, you can check the switch by using GUI and CLI.
1) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Port Config to check whether the port 1/0/3 passes the 802.1X authentication successfully. After passing the 802.1X authentication successfully, the Authorized state will change from Unauthorized to Authorized .

2) Choose the menu VLAN > 802.1Q VLAN > Global Config to check whether the port 1/0/3 is assigned to the corresponding VLAN.

1) Verify the 802.1X authorization states on the port:
---- ----- ---------- --------- ------------- ------------- ------------- -----
Gi1/0/3 enabled disabled disabled auto port-based authorized N/A
2) Verify the VLAN information:
T2600G-28TS#show vlan
VLAN Name Status Ports
----- -------------------- --------- ----------------------------------------
1 System-VLAN active Gi1/0/1, Gi1/0/2, Gi1/0/4, Gi1/0/5,
Gi1/0/6, Gi1/0/7, Gi1/0/8, Gi1/0/9,
Gi1/0/10, Gi1/0/11, Gi1/0/12, Gi1/0/13,
Gi1/0/14, Gi1/0/15, Gi1/0/16, Gi1/0/17,
Gi1/0/18, Gi1/0/19, Gi1/0/20, Gi1/0/21,
Gi1/0/22, Gi1/0/23, Gi1/0/24, Gi1/0/25,
Gi1/0/26, Gi1/0/27, Gi1/0/28
5 N/A active Gi1/0/3
Primary Secondary Type Ports
------- --------- ------------------ ----------------------------------------
The port has been assigned to the related VLAN. That means 802.1X VLAN Assignment works.
3 Example for MAB
3.1 Network Requirements
The network administrator wants to restrict the authority of a device to access the network resources. The device should be authenticated before getting access to the internet. For convenience, it is better that the authentication process can be performed automatically. The network topology is shown as below.

3.2 Configuration Scheme
MAB uses the MAC address of a device to determine whether the device can get access to the network. Thus MAB can be used to authenticate devices without 802.1X Client Software.
The configuration is briefly summarized in two steps:
2) Configure MAB on TP-Link switch.
3.3 Configuration
MAB uses the MAC address of the client as the username and password. Please check the MAC addresses of the clients that you want to access the network in advance.
MAB takes effect only when 802.1X Authentication is enabled. Enable 802.1X Authentication on the ports connected to clients.
MAB takes effect only when Guest VLAN is disabled. Ensure that Guest VLAN is disabled when configuring MAB.
Keep 802.1X authentication disabled on ports connected to the authentication server, the internet and the management computer, which ensures they will not be blocked from accessing the switch.
Demonstrated with T2600G-28TS acting as the authenticator, FreeRADIUS.net acting as the RADIUS server, the following sections provide configuration procedures. The configuration procedures on the switch will be given in two ways: using the GUI and using the CLI.
3.3.1 Build a RADIUS Server
1) Go to http://freeradius.net/index.html to download the FreeRADIUS.net and follow the wizard to install it.

To avoid the format errors when adding code, use Notepad++ to edit configuration files.
One client section means a RADIUS client. You can choose one of the section clients and edit the following attributes. Or you can add a new client section to meet your requirements. The Clients.conf should be modified in three aspects:
The shortname which is used as an alias for the fully qualified domain name, or the IP address of the RADIUS client. A value can be filled in optionally for the short name.

MAB uses the MAC address as the username and password. You can replace rfc3580 and demo with the allowed MAC address. Or you can ignore the default user information and add the MAC address in the next line.
Add the following codes and save the file:

5) Click Restart FreeRaDIUS.net Service to restart FreeRaDIUS.net.
3.3.2 Configure MAB on the Switch
1) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > Global Config , enable AAA function on the switch and click Apply .
2) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > Dot1x List, select an existing RADIUS server group for authentication from the Pri1 drop-down list and click Apply .
3) Choose the menu Network Security > AAA > RADIUS Config , and enter 192.168.0.253 which is the IP address of the RADIUS server. Enter the shared key between the RADIUS server and the switch. The RADIUS server and the switch use the key string to encrypt passwords and exchange responses.

4) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Global Config , enable 802.1X globally and click Apply .

5) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Port Config to load the following page. Select port 1/0/3 and set the status as Enable and set Control Type as Port Based . Enable MAB for port 1/0/3. Set the status for port 1/0/1 and port 1/0/2 as Disable so that the RADIUS server and the internet will not be blocked for the switch.

1) Enable AAA globally.
2) Globally enable 802.1X authentication and set the authentication protocol.
3) Disable 802.1X authentication on port 1/0/1and port 1/10/2. Enable 802.1X authentication and MAB on port 1/0/3, set the mode as Auto, and set the control type as Port Based.
T2600G-28TS(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 1/0/3
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#dot1x
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#dot1x port-method port-based
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#dot1x port-control auto
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#dot1x mab
T2600G-28TS(config-if)#exit
802.1X VLAN Assignment State: Disabled
---- ----- --------- ----------- -------------- ----------- ------------- -----
Gi1/0/3 enabled enabled disabled auto port-based unauthorized N/A
3.4 Verify the Configuration Result
After all configurations are completed, you can follow the steps below to test whether MAB works.
1) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Port Config to check whether the port 1/0/3 has passed the authentication successfully.

The port authentication state changes from Unauthorized to Authorized , that is, the port has passed the authentication.
2) Open a web browser and browse a website to check whether the PC can get access to the internet.
---- ------- ------------ ------------ ------------ --------------- ------------ -----
Gi1/0/3 enabled enabled disabled auto port-based authorized N/A
2) Open a web browser and browse a website and to check whether the PC can get access to the internet.

Help us improve your experience.
Let us know what you think.
Do you have time for a two-minute survey?
ON THIS PAGE
Hierarchy level, description, required privilege level, release information.
Configure IEEE 802.1X authentication for Port-Based Network Access Control. 802.1X authentication is supported on interfaces that are members of private VLANs (PVLANs).
802.1X is disabled.
The remaining statements are explained separately. Search for a statement in CLI Explorer or click a linked statement in the Syntax section for details.
routing—To view this statement in the configuration. routing-control—To add this statement to the configuration.
Statement introduced in Junos OS Release 9.0.
ssl-certificate-path introduced in Junos OS Release 19.4.
ip-mac-session-binding introduced in Junos OS Release 20.2
Related Documentation
- Example: Setting Up 802.1X for Single-Supplicant or Multiple-Supplicant Configurations on an EX Series Switch
- Example: Setting Up 802.1X in Conference Rooms to Provide Internet Access to Corporate Visitors on an EX Series Switch
- Example: Setting Up VoIP with 802.1X and LLDP-MED on an EX Series Switch
- Example: Configuring Static MAC Bypass of 802.1X and MAC RADIUS Authentication on an EX Series Switch
- Example: Configuring MAC RADIUS Authentication on an EX Series Switch
- Configuring RADIUS Server Fail Fallback (CLI Procedure)
[EX/SBR/QFX] Dot1x configuration for EX-Series switches that authenticate via the Steel Belt Radius server
This article provides the dot1x configuration for EX-switches with supplicant multiple, in which a phone and a PC are connected to the switch that authenticates via the SBR server.
Supplicant multipe is used, as there are two supplicants (phone and PC) are connected on the ge-0/0/0 port. Requirements :
- Junos 9.0 or later on the EX switch.
- PC that has the Odyssey client or equivalent installed on it.
set protocols dot1x authenticator authentication-profile-name test set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/0.0 supplicant multiple set protocols dot1x authenticator interface ge-0/0/0.0 mac-radius set protocols access radius-server 30.30.30.2 port 1812 set protocols access radius-server 30.30.30.2 secret "$ABC123" set protocols access profile test authentication-order radius set protocols access profile test radius authentication-server 30.30.30.2 set protocols system authentication-order radius set protocols interfaces ge-0/0/0 unit 0 family ethernet-switching set protocols ethernet-switching-options voip vlan voice
- Name : The name that is used for authentication on the PC.
- Password : The password which we would be using to authenticate.
- Tunnel-Medium-Type : It is always 802 .
- Tunnel-Private-Group-ID : Name of the VLAN, in which the PC should fall.
- Tunnel-Type : It is always VLAN.
- Name : MAC Address of the phone.
- Password : MAC Address of the phone.
- Tunnel-Private-Group-ID : Name of the VLAN, in which the phone should fall.
- Tunnel-Type : It is Always VLAN.
- EAP Methods : All of the methods have to be selected under Authentication Policies . Note :Configuration of the settings on the phone is Configuring any settings on the Phone is not necessary as it does not do EAP and authenticates through MAC.
- Under the Configuration Profile , create a profile:
user@switch# run show dot1x interface detail ge-0/0/0.0 Role: Authenticator Administrative state: Auto Supplicant mode: Multiple Number of retries: 3 Quiet period: 60 seconds Transmit period: 30 seconds Mac Radius: Enabled Mac Radius Restrict: Disabled Reauthentication: Enabled Configured Reauthentication interval: 3600 seconds Supplicant timeout: 30 seconds Server timeout: 30 seconds Maximum EAPOL requests: 2 Guest VLAN member: Number of connected supplicants: 2 Supplicant: 0096E1128A6, 00:09:6E:11:28:A6 > Phone Operational state: Authenticated Backend Authentication state: Idle Authentcation method: Mac Radius Authenticated VLAN: voice Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds Reauthentication due in 33 seconds Supplicant: TEST1, 00:E0:4C:4D:11:88 > PC Operational state: Authenticated Backend Authentication state: Idle Authentcation method: Radius Authenticated VLAN: data Session Reauth interval: 60 seconds Reauthentication due in 33 seconds
AFFECTED PRODUCT SERIES / FEATURES
People also viewed.
dot1x guest-vlan-delay
Use dot1x guest-vlan-delay to enable 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay on a port.
Use undo dot1x guest-vlan-delay to disable the specified 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay on a port.
dot1x guest-vlan-delay { eapol | new-mac }
undo dot1x guest-vlan-delay [ eapol | new-mac ]
802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay is disabled on a port.
Layer 2 Ethernet interface view
Predefined user roles
network-admin
eapol : Specifies EAPOL-triggered 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay. This keyword takes effect if 802.1X authentication is triggered by EAPOL-Start packets.
new-mac : Specifies new MAC-triggered 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay. This keyword takes effect if 802.1X authentication is triggered by packets from unknown MAC addresses.
Usage guidelines
This command enables the device to delay assigning an 802.1X-enabled port to the 802.1X guest VLAN when 802.1X authentication is triggered on the port.
To use this feature, the 802.1X-enabled port must perform MAC-based access control.
When 802.1X authentication is triggered on a port, the device performs the following operations:
Sends a unicast EAP-Request/Identity packet to the MAC address that triggers the authentication.
Retransmits the packet if no response has been received within the username request timeout interval set by using the dot1x timer tx-period command.
Assigns the port the 802.1X guest VLAN after the maximum number of request attempts set by using the dot1x retry command is reached.
If you use the undo command without any keyword, the command disables both EAPOL-triggered and new MAC-triggered 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay on a port.
# Enable EAPOL-triggered 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay on .
Related commands
display dot1x
dot1x guest-vlan
dot1x retry
dot1x timer tx-period
© Copyright 2017 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP

COMMENTS
How to Provision 802.1 X Authentication Step By Step With Dynamic VLAN Assignment With Windows Radius Server For 802.1x Clients. A typical configuration for a system under IEEE 802.1x Authentication control is shown in the following figure.
802.1x Authentication with VLAN Assignment. The switch supports 802.1x authentication with VLAN assignment. After successful 802.1x authentication of a port, the RADIUS server sends the VLAN assignment to configure the switch port.
IEEE 802.1X VLAN Assignment. PDF - Complete Book (12.23 MB) PDF - This Chapter (1.12 MB) ... Device# show dot1x all Sysauthcontrol Enabled Dot1x Protocol Version 2 Dot1x Info for GigabitEthernet 1/0/1 ----- PAE = AUTHENTICATOR PortControl = AUTO ControlDirection = Both HostMode = MULTI_HOST ReAuthentication = ...
If the RADIUS server specifies a VLAN for an authenticated supplicant connected to an 802.1X authenticator port, this VLAN assignment overrides any Authorized-Client VLAN assignment configured on the authenticator port. This is because both VLANs are untagged, and the switch allows only one untagged VLAN membership per-port.
the next step is for our dynamic VLAN assignment. Dot1x devices are bound to VLAN 2: the final dot1x configuration in the NPS: the second network policy is for the mac-based authentication: Comware switches are sending MAC-Auth-requests via PAP (maybe you know how to change it to CHAP): final MAC auth profile:
The IEEE 802.1X VLAN Assignment feature is automatically enabled when IEEE 802.1X authentication is configured for an access port, which allows the RADIUS server to send a VLAN assignment to the device port. This assignment configures the device port so that network access can be limited for certain users.
Figure 13 802.1X authentication with dynamic VLAN assignment. RADIUS configuration. Create a user profile on the RADIUS server and configure the attributes in the following table. ... authentication critical-vlan 601 auth-default-vlan 2 restricted-vlan 100 auth-fail-action restricted-vlan re-authentication dot1x enable dot1x enable ethe 1/1/11 ...
The above example will not work if the VLAN assignment method is port based. The output of the show dot1x interface detail command, in conjunction with the MAC-based VLAN assignment, might vary from vendor to vendor; and for Juniper the above illustrated example is the expected behavior. Modification History 2022-12-29: Reviewed for accuracy ...
DOT1X Dynamic VLAN assignment. Hi Team, Our dot1x is used for dyamic VLAN assignement and it works using this config: int fa0/12. switchport access vlan A. switchport mode access. switchport nonegotiate. authentication event fail action authorize vlan A. authentication event no-response action authorize vlan A.
802.1X authentication of the port, the RADIUS server sends the VLAN assignment to the switch. The VLAN can be a "standard" VLAN or a private VLAN. On platforms that support Private VLANs, you can isolate hosts by assigning ports into PVLANs. When configured on the switch and the RADIUS server, 802.1X with VLAN assignment has these ...
It may be necessary to perform dynamic VLAN assignment on a per computer or per user basis. This can be done on your wired network via 802.1X authentication (RADIUS). MS390s and C9300-Ms support multi-vlan assignment, when using Multi-Auth as the host mode. This means that multiple client devices connected in the Data domain on the same port ...
In the Global Config section, enable 802.1X and VLAN Assignment globally and click Apply. 5) Choose the menu Network Security > 802.1X > Port Config to load the following page. Select the port 1/0/3-13 which you want to deploy 802.1X VLAN Assignment and set the status for port1/0/3-13 as Enable.
This article provides a method of configuring Dynamic VLAN assignment on the EX Switch/SRX with standard Windows XP2 client and Steel Belted RADIUS (SBR). The EX Switch/SRX acts as authenticator in 802.1X environment. The end user, also known as supplicant, uses Windows XP SP2, and the Authentication Server is SBR. ... Dot1x interface details ...
Cisco IOS software enables standards-based network access control at the access layer by using the 802.1X protocol to secure the physical ports where end users connect. This document focuses on deployment considerations specific to 802.1X, and includes the following sections: • IEEE 802.1X Overview.
Statement introduced in Junos OS Release 9.0. ssl-certificate-path introduced in Junos OS Release 19.4. ip-mac-session-binding introduced in Junos OS Release 20.2. Configure IEEE 802.1X authentication for Port-Based Network Access Control. 802.1X authentication is supported on interfaces that are members of private VLANs (PVLANs).
This article provides the dot1x configuration for EX-switches with supplicant multiple, in which a phone and a PC are connected to the switch that authenticates via the SBR server. ... Configuring Dynamic VLAN assignment on the EX Switch/SRX with standard Windows XP2 client and Steel Belted RADIUS (SBR) [ScreenOS] Steps to troubleshoot 802.1 x ...
In order to accomplish dynamic VLAN assignment with WLCs based on ISE to AD group mapping, these steps must be performed: ISE to AD integration and configuration of authentication and authorization policies for users on ISE. WLC configuration in order to support dot1x authentication and AAA override for SSID 'office_hq'.
Assigns the port the 802.1X guest VLAN after the maximum number of request attempts set by using the dot1x retry command is reached. If you use the undo command without any keyword, the command disables both EAPOL-triggered and new MAC-triggered 802.1X guest VLAN assignment delay on a port.
The IEEE 802.1X VLAN Assignment feature is automatically enabled when IEEE 802.1X authentication is configured for an access port, which allows the RADIUS server to send a VLAN assignment to the device port. This assignment configures the device port so that network access can be limited for certain users. Finding Feature Information, page 1.