- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)
A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master’s program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you through the main stages of proposal writing.
Disclosure: This post may contain affiliate links, which means I may earn a small commission if you make a purchase using the links below at no additional cost to you . I only recommend products or services that I truly believe can benefit my audience. As always, my opinions are my own.
1. Find a topic for your research proposal
2. develop your research idea, 3. conduct a literature review for your research proposal, 4. define a research gap and research question, 5. establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal, 6. specify an empirical focus for your research proposal, 7. emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal, 8. develop a methodology in your research proposal, 9. illustrate your research timeline in your research proposal.
Finding a topic for your research is a crucial first step. This decision should not be treated lightly.
Writing a master’s thesis takes a minimum of several weeks. In the case of PhD dissertations, it takes years. That is a long time! You don’t want to be stuck with a topic that you don’t care about.
How to find a research topic? Start broadly: Which courses did you enjoy? What issues discussed during seminars or lectures did you like? What inspired you during your education? And which readings did you appreciate?
Take a blank piece of paper. Write down everything that comes to your mind. It will help you to reflect on your interests.
Then, think more strategically. Maybe you have a rough idea of where you would like to work after graduation. Maybe a specific sector. Or even a particular company. If so, you could strategically alight your thesis topic with an issue that matters to your dream employer. Or even ask for a thesis internship.
Once you pinpoint your general topic of interest, you need to develop your idea.
Your idea should be simultaneously original, make a scientific contribution, prepare you for the (academic) job market, and be academically sound.
Freaking out yet?! Take a deep breath.
First, keep in mind that your idea should be very focused. Master and PhD students are often too ambitious. Your time is limited. So you need to be pragmatic. It is better to make a valuable contribution to a very specific question than to aim high and fail to meet your objectives.
Second, writing a research proposal is not a linear process. Start slowly by reading literature about your topic of interest. You have an interest. You read. You rethink your idea. You look for a theoretical framework. You go back to your idea and refine it. It is a process.
Remember that a good research proposal is not written in a day.
And third, don’t forget: a good proposal aims to establish a convincing framework that will guide your future research. Not to provide all the answers already. You need to show that you have a feasible idea.

If you are looking to elevate your writing and editing skills, I highly recommend enrolling in the course “ Good with Words: Writing and Editing Specialization “, which is a 4 course series offered by the University of Michigan. This comprehensive program is conveniently available as an online course on Coursera, allowing you to learn at your own pace. Plus, upon successful completion, you’ll have the opportunity to earn a valuable certificate to showcase your newfound expertise!
Academic publications (journal articles and books) are the foundation of any research. Thus, academic literature is a good place to start. Especially when you still feel kind of lost regarding a focused research topic.
Type keywords reflecting your interests, or your preliminary research idea, into an academic search engine. It can be your university’s library, Google Scholar , Web of Science , or Scopus . etcetera.
Look at what has been published in the last 5 years, not before. You don’t want to be outdated.
Download interesting-sounding articles and read them. Repeat but be cautious: You will never be able to read EVERYTHING. So set yourself a limit, in hours, days or number of articles (20 articles, for instance).
Now, write down your findings. What is known about your topic of interest? What do scholars focus on? Start early by writing down your findings and impressions.
Once you read academic publications on your topic of interest, ask yourself questions such as:
- Is there one specific aspect of your topic of interest that is neglected in the existing literature?
- What do scholars write about the existing gaps on the topic? What are their suggestions for future research?
- Is there anything that YOU believe warrants more attention?
- Do scholars maybe analyze a phenomenon only in a specific type of setting?
Asking yourself these questions helps you to formulate your research question. In your research question, be as specific as possible.
And keep in mind that you need to research something that already exists. You cannot research how something develops 20 years into the future.

A theoretical framework is different from a literature review. You need to establish a framework of theories as a lens to look at your research topic, and answer your research question.
A theory is a general principle to explain certain phenomena. No need to reinvent the wheel here.
It is not only accepted but often encouraged to make use of existing theories. Or maybe you can combine two different theories to establish your framework.
It also helps to go back to the literature. Which theories did the authors of your favourite publications use?
There are only very few master’s and PhD theses that are entirely theoretical. Most theses, similar to most academic journal publications, have an empirical section.
You need to think about your empirical focus. Where can you find answers to your research question in real life? This could be, for instance, an experiment, a case study, or repeated observations of certain interactions.
Maybe your empirical investigation will have geographic boundaries (like focusing on one city, or one country). Or maybe it focuses on one group of people (such as the elderly, CEOs, doctors, you name it).
It is also possible to start the whole research proposal idea with empirical observation. Maybe you’ve come across something in your environment that you would like to investigate further.
Pinpoint what fascinates you about your observation. Write down keywords reflecting your interest. And then conduct a literature review to understand how others have approached this topic academically.
Both master’s and PhD students are expected to make a scientific contribution. A concrete gap or shortcoming in the existing literature on your topic is the easiest way to justify the scientific relevance of your proposed research.
Societal relevance is increasingly important in academia, too.
Do the grandparent test: Explain what you want to do to your grandparents (or any other person for that matter). Explain why it matters. Do your grandparents understand what you say? If so, well done. If not, try again.
Always remember. There is no need for fancy jargon. The best proposals are the ones that use clear, straightforward language.
The methodology is a system of methods that you will use to implement your research. A methodology explains how you plan to answer your research question.
A methodology involves for example methods of data collection. For example, interviews and questionnaires to gather ‘raw’ data.
Methods of data analysis are used to make sense of this data. This can be done, for instance, by coding, discourse analysis, mapping or statistical analysis.
Don’t underestimate the value of a good timeline. Inevitably throughout your thesis process, you will feel lost at some point. A good timeline will bring you back on track.
Make sure to include a timeline in your research proposal. If possible, not only describe your timeline but add a visual illustration, for instance in the form of a Gantt chart.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox.
Subscribe and receive Master Academia's quarterly newsletter.
PhD thesis types: Monograph and collection of articles
Ten reasons not to pursue an academic career, related articles.

How to address data privacy and confidentiality concerns of AI in research

How to properly use AI in academic research

The best online courses for PhD researchers in 2024

Why and how to conduct a systematic literature review

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
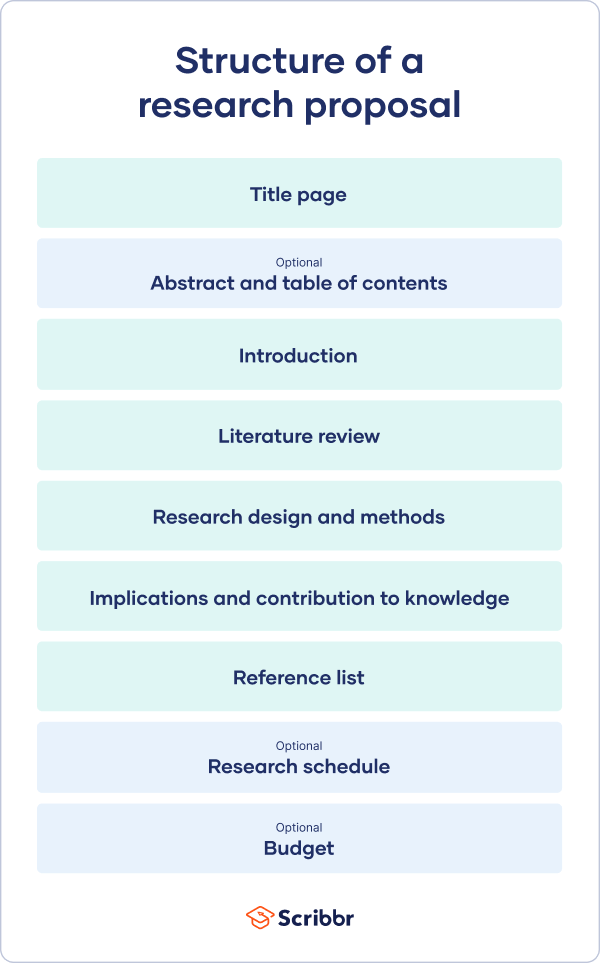
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
🎙️ PODCAST: Writing A Research Proposal
4 Time-Saving Tips To Fast-Track Your Proposal
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) and Ethar Al-Saraf (Phd) | March 2024
Crafting a well-thought-out research proposal is essential for gaining approval and setting a clear path for your research endeavours. In this episode of the Grad Coach Podcast, we explore four cheat codes that can help you fast-track your research proposal development process.

Episode Summary
————————————-
1: Define the What, Why, and How Before You Start
Before delving into the writing process, it is essential to pin down the what, why, and how of your research proposal. Clearly articulating the topic, rationale, and methodology before jumping into writing can provide a solid foundation for your proposal. Understanding the boundaries and parameters of your research topic is crucial for setting the stage for a successful research project.
2: Align Your Golden Thread
Ensuring that your research aim, research questions, and research objectives are perfectly aligned creates a golden thread that ties your entire proposal together. This alignment is vital for maintaining coherence and logic throughout your research project. By focusing on the interconnection between these key elements, you can establish a strong foundation for your research proposal.
3: Create a Solid Outline Before You Start Writing
Drawing up a clear outline before starting the writing process can streamline your proposal development. An outline serves as a roadmap, guiding the structure and content of your proposal. By outlining the key sections and components of your proposal, you can ensure that your ideas flow cohesively and logically, making it easier to develop a comprehensive and well-organized document.
4: Emphasise Significance and Viability
Highlighting the significance and viability of your proposed research is critical for gaining approval and demonstrating the feasibility of your project. By clearly articulating the meaningful contribution your research will make to the field and ensuring that your proposed methods are practical and attainable, you can strengthen your proposal’s credibility and persuasiveness.
In conclusion, crafting a successful research proposal requires careful planning, thoughtful consideration, and strategic execution. By following these four cheat codes, you can enhance the quality and effectiveness of your research proposal, setting the stage for a successful research project. Remember, a well-crafted proposal not only conveys your research ideas but also showcases your expertise and commitment to advancing knowledge in your field.
Need a helping hand?
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Recommended pages
- Undergraduate open days
- Postgraduate open days
- Accommodation
- Information for teachers
- Maps and directions
- Sport and fitness
Top tips for writing your research proposal
- Allow plenty of time to write your proposal and do not rush.
- Bear in mind that the individuals reviewing your application will often have to read a large number of proposals. Well-presented and clearly written proposals are more likely to stick in the reviewer’s mind.
- Research proposals do not have to be set in stone, as research often evolves as work progresses. Think of your proposal as a preliminary outline rather than a definitive summary of the final product.
- Make sure that you acknowledge the authors of all publications you reference in your proposal, to avoid any risk of plagiarism . You should paraphrase or use quotation marks where appropriate.
- Make sure that your research ideas and questions are very clearly stated. Your questions are as important as your results at this stage of the research.
- Make sure that the scope of your research is reasonable and realistic. Proposals are assessed not only on intellectual ambition and significance, but also the likelihood of completion.
- Make sure that your passion for the research topic shines through. Your proposal should be approached as a piece of persuasive writing – you want to establish the attention of your reader and convince them of your project’s significance.
- Make sure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent.
- Make sure that your proposal does not contain any errors. Proofread and edit your work a number of times before you submit it.
What is originality?
There are many ways in which you can demonstrate originality in your proposal. You could study something that has genuinely never been studied before, but we are not all lucky enough to be able to do this. As a result, you should think of other ways to make your proposal stand out as original.
- Identify problems, such as inconsistencies or gaps, in existing analysis.
- A fresh, critical discussion of texts, works and/or ideas that have been neglected by scholarship.
- Bring together disciplines and areas of work that have not been brought together before.
- Compare a topic in one country/language/business model/legal system/etc. with the same topic in another (a 'comparative study').
- Analyse an issue from a new perspective, or apply work from another discipline to your own, in order to create new knowledge, learning or practice (e.g. by bringing a theoretical approach to a problem that has not been applied before, at length).
- A study of the impact of a particular set of conditions, piece of legislation, series of events, government, etc.

How to Write a Successful Research Proposal
A research proposal is essentially a plan for work in order to test a hypothesis or set of hypotheses in order to answer a research question. One of the most important things to bear in mind when drafting a proposal is the fact that authors are required to tailor it to suit the audience. If the document being written is a PhD research proposal, it is imperative that authors follow the guidelines laid out by the university or faculty for this type of document. A PhD research proposal, as an example, will be read by experts in the field. This means that authors will be expected to use jargon specific to their area. If the research proposal forms part of a grant application , authors would have to write it so that reviewers who might not be as familiar with their specialty can easily understand the research problem and why the project should receive funding. A typical research proposal will generally include a title, summary of the aims and expected outcomes, literature review , research methodology, proposed timeline, and references. The characteristics of a good research title all generally focus on catching the reader’s attention. Again, word limits, formatting, and what is considered essential content will depend on the institution or faculty requirements and should be strictly adhered to.
Writing An Effective Research Proposal
Since the details of what should be in the research proposal will be governed by the institution, the rest of this article will focus on general hints to write a high-quality research proposal.
- Although introduction is the first major section, it is not mandatory that it has to be written first. Authors may find it easier to start writing the research methodology since methods have usually been standardized. Once this is on paper, it will help authors feel accomplished and will no longer be intimidated by a blank page.
- An effective research title should be easily understood by someone who is not a specialist in the field. It should be seen as more of a marketing tool than a demonstration of scientific knowledge. Authors should read the title aloud. Authors should consider if the title is easily understood and if the significance of what they are trying to accomplish clear. The purpose of the title is to pique the interest of the reader; which is why it needs to be concise and easily understood while communicating why this research needs to be done.
- Authors should ensure that the purpose of the research is apparent from the beginning of the document how the study could improve or change lives. If the research is not applied, this will be harder to justify but authors can cite examples of blue skies research that has led to technologies that are in use today. It is fairly well accepted by the research community that both fundamental and applied research projects are necessary. It is critical that anyone who reads the document agrees that the research question needs to be answered.
- Demonstrate competence. Even if we all agree that the PhD research proposal must be executed, the proposal will not be successful without some key elements. One of these elements is demonstrating that the infrastructure is in place to support the execution of the experiments. The team that will be conducting the work is also a critical component of this success. Authors should include evidence of their track record where possible to inspire confidence that they are the person for the job. Where authors lack competence, they may include collaborators with the necessary skills to help answer the research question.
- Authors should never underestimate how getting others to review their proposal can improve it. Often the suggestions will help clarify the document or they may suggest a new angle that has been missed out. Once authors have incorporated any suggestions that were found useful, it would be a good idea to ask a new person to review it before submission. Doing suggested corrections at this stage generally, means there will be fewer problems with the study identified by reviewers.
- Authors must remember that the proposal is not the final thesis. Reviewers expect proposals to change as the study commences. The results obtained may require authors to change direction or add new sections and that is acceptable. The most important thing is that authors continue to use the scientific method to find answers to their stated research question.
Key Points to Remember
These are just some guidelines on writing a research proposal. Writing a successful PhD research proposal means remembering to write for a specific audience and adhering to the format prescribed by the institution. There are a few characteristics of a good research title but the main thing authors need to remember is that the point of the title is to hold the reader’s attention and pique their interest in the rest of the research proposal. Authors should never submit the proposal without having someone else review it and should always feel free to work on whatever section they need to – there is no rule that says it has to be written in its presentation order.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Career Corner
- PhDs & Postdocs
How to Write a Data Management Plan During Grant Application
This article is also available in: Russian, Portuguese, Turkish, and Spanish

7 Tips to Draft a Compelling Budget for Grant Proposal
While financial support is crucial for conducting research, acquiring funds for your research is a…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Mastering the Art of Creating Successful Grant Proposals
Types of research funding Types of research funders Planning for a research proposal Writing a…

Overcoming Challenges in Academic Writing
Importance of good English writing skills Application of English grammar Writing an impactful grant proposal…

Cómo redactar una subvención de un millón de dólares
Elegir entre subvenciones y becas de investigación Identificación de los organismos de financiación Selección de…
Learning the Art of Crafting Effective Research Grant Proposals
Navigating the Grant Development Process
What You Should Know Before Writing a Research Grant Proposal

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Main navigation
- Graduate Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Dean's Welcome
- Graduate Education Statistics
- Registration and degree progress
- Writing research proposals
- Comprehensive Exams
- Policies and Guidelines
- Joint PhD/Cotutelles
- Supporting Graduate student well-being
- Graduate Research Trainee
Ten tips for writing your research proposal
1. follow the instructions.
Read and conform to all instructions found on the council website. Make sure that your proposal fits the criteria of the competition.
2. Break down your proposal into point form before writing your first draft.
Based on the total length of the proposal, decide whether you will have headings/subheadings and what they will be (e.g., Introduction, Background Material, Methodology, and so on). These headings can be selected based on the advice given in the specific award instructions. For each section, lay out in point form what you will discuss.
3. Know your audience.
- Describe your research proposal in non-technical terms. Use clear, plain language and avoid jargon.
- Make sure your proposal is free of typographic and grammatical errors.
- Remember that, at every level, adjudication committees are multi-disciplinary and will include researchers in fields other than your own.
- Therefore, follow the KIS principle – K eep I t S imple! Reviewers like it that way.
4. Make an impact in the first few sentences.
Reviewers are very busy people. You must grab their attention and excite them about your project from the very beginning. Make it easy for them to understand (and thus fund) your proposal. Show how your research is innovative and valuable. Remember, too, to show your enthusiasm for your project—enthusiasm is contagious!
Organize your proposal so that it is tight, well-integrated, and makes a point, focused on a central question (e.g., “I am looking at this to show...”). Depending on the discipline, a tight proposal is often best achieved by having a clear hypothesis or research objective and by structuring the research proposal in terms of an important problem to be solved or fascinating question to be answered. Make sure to include the ways in which you intend to approach the solution.
5. Have a clear title.
It is important that the title of your project is understandable to the general public, reflects the goal of the study, and attracts interest.
6. Emphasize multidisciplinary aspects of the proposal, if applicable.
7. show that your research is feasible..
Demonstrate that you are competent to conduct the research and have chosen the best research or scholarly environment in which to achieve your goals.
8. Clearly indicate how your research or scholarship will make a “contribution to knowledge” or address an important question in your field.
9. get the proposal reviewed and commented on by others..
Get feedback and edit. Then edit some more. And get more feedback. The more diverse opinion and criticism you receive on your proposal the better suited it will be for a multi-disciplinary audience.
10. Remember that nothing is set in stone.
Your research proposal is not a binding document; it is a proposal . It is well understood by all concerned that the research you end up pursuing may be different from that in your proposal. Instead of treating your proposal as a final, binding document, think of it as a flexible way to plan an exciting (but feasible) project that you would like to pursue.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License . Graduate and Postdoctoral Studies, McGill University .
Department and University Information
Graduate and postdoctoral studies.
How to Make a Research Proposal: Template, Sample, & Tips
A research proposal is a document that aims to show the significance and value of a particular project . It is common to have to write research proposals to acquire funding for various research projects. But that’s not all. Perhaps the most important function of a research proposal is that it will give you direction when you begin your research project.
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
This article by Custom Writing team describes best writing strategies and contains an excellent research proposal sample, a template, and useful info that will help you master your proposal.
- 🤔 How to Start?
- ❗ Typical Mistakes
🔗 References
🤔 research proposal: how to start.
Any research proposal starts from choosing a topic . This step seems simple, but this is not the case. It is crucial to take the time to choose a topic that is worth learning and excites you. Just imagine: your research is something that you’ll have to do for a long time. Will you be enthusiastic about your work in a year or two? This, of course, cannot be fully predicted. Still, it’s important that the topic captivates you at least now.
When starting to work on your research proposal , think of the following questions.
Be sure to write down the answers to these questions, and then you will be well on your way to writing a spectacular proposal. At this point, you should also spend time reading through your reference material and making notes from all your different sources .
If you need additional guidance, then check out this video that demonstrates how to write a research proposal.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
📃 Research Proposal Template
The structure of a research proposal differs depending on the requirements to it. However, the following parts should be included into a typical proposal.

In the next section, you’ll find a research proposal example that contains all of these components. Note that in the “References” section of this sample research proposal, APA style is used. You should follow the citation style recommended by your supervisor.
📑 Research Proposal Sample
Below is a research proposal example that is made in accordance with the template above. After the sample, you’ll find several comments on it.
The Effects of Teachers’ Non-verbal Responses on Students’ Outcomes
What makes this a good research proposal example? Here are five reasons:
- It includes only specific and relevant information.
- It discusses only the most critical aspects of the proposed investigation.
- It provides arguments for the use of certain methods.
- It is well-structured.
- It uses simple and direct language.
After reading and analyzing this research proposal sample, you have a much better understanding of how to write your own one. You will also find excellent research proposal examples on the website of the University of Queensland. And you can learn about the importance of a research proposal from our article .
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 15% off your first order!
If you have any questions on how to make a research proposal in MLA or APA formats, feel free to use our guides .
❗ Research Proposal Mistakes to Avoid
There are a number of common pitfalls you need to avoid when writing a research proposal. In order to avoid them, take a look at this list of mistakes and the correct approach for each:
Mistakes in Understanding
Grammatical mistakes.
- Research Proposal Guide For Hdr Candidates
- Example Student Research Proposals
- How To Write A Good Postgraduate Research Proposal
- Guidelines on writing a research proposal
- Examples of Research proposals
- How to write your research proposal
- Top tips for writing your research proposal
- Ten tips for writing your research proposal
- How to write a great research proposal
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Are you tired of getting average grades for your term papers? Well, that’s good that you’re here! It may be true that some excellent writing and time-management skills can help you create an impressive piece, but it’s not necessary. Most of the assignments have similar outlines, whether it’s a term...

Congratulations! A dissertation is your last step before getting your doctoral degree. But, no matter how great the excitement is, the frustration and panic might be overwhelming. And it’s understandable as there is a lot of pressure on you right now. The good news is that there is nothing to...

Most of the times, there is the same research paper format for different types of research. This makes it easy to learn the correct research essay format, no matter what you are writing.
![tips in writing research proposal Ultimate Report Writing Tips for Students: Best Ideas [Free]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/business-desk-with-keyboard-report-graph-284x153.jpg)
At some point, whether in school or university, you will be required to do report writing. Generally, reports are used to communicate information, which was compiled as a result of studies and analysis. For instance, academic reports are to discuss the findings of studies or surveys. The tips on report...

You are already required to write a bibliography. Why would you waste your time and effort on additional details and create an annotated one? Don’t worry. We have an excellent answer! Annotated bibliography would include such details as a brief overview of the content, usefulness, and some analysis of every...

A case study analysis is a typical assignment in business management courses. The task aims to show high school and college students how to analyze a current situation, determine what problems exist, and develop the best possible strategy to achieve the desired outcome. Many students feel anxious about writing case...

If you are a student, you might need to learn how to write a literature review at some point. But don’t think it’s the same as the book review or other types of academic writing you had to do in high school! A literature review is a close examination of...

So, have you been recently assigned a research project? Or, even worse, is it already due soon? The following research paper hacks will help you do it in record time. In the article, you’ll see ten things you can do to conduct a study and compose a piece like a...

Eating a delicacy, watching a good movie, and proving a point to an audience are the three things that make life seem better. Today, you’ll deal with the last one. You’re about to become a professional at public speaking and attention grabbing. Here, you can learn how to write a...
![tips in writing research proposal Library Research Paper: Example & Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/library-with-books-284x122.jpeg)
What is a library research paper? It’s nothing more than an academic writing project that summarizes the information on a specific topic taken from primary and secondary sources. There are numerous library research examples you can find online. But to complete this assignment, you should simply follow these essential steps:...
![tips in writing research proposal Research Analysis Paper: How to Analyze a Research Article [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/opened-book-library-table-284x153.jpg)
Do you need to write a research analysis paper but have no idea how to do that? Then you’re in the right place. While completing this type of assignment, your key aim is to critically analyze a research article. An article from a serious scientific journal would be a good...

You might be wondering about how to write a conclusion paragraph for a research paper. It may seem like your readers should understand your main arguments by the end, so there is no need for it. However, there are several aspects that prove the importance of a conclusion section in...
Thank you so much! Even I’m just a junior high student I still need to do an research so thanks to your help
My name is Mmoni in South Africa. Ooh wow what a resource pack wish could have accessed this classical tool last year. Great work of great minds . Thank you
Excellent! This is what I needed. Thank you.
I agree that starting your research paper or project proposal is one of the most challenging pieces of the process. I’ve found that if you can determine your general topic, you can articulate “what” it is that makes it of interest to you, and potentially others. From that point, you can create an interesting working title and build out an outline for your research, which will include your problem statement, purpose statement, and thesis statement. If you check out “Practical Research, first steps” in Udemy, you’ll find a course that walks you through this process step by step in less time than it would take to read a textbook on the topic! Thanks for this excellent information!
Oh, my goodness, Julia. You have no idea how much you helped me with my research proposal. The examples and things to look out for are greatly appreciated. You rock.
Definitely believe the idea that you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the web the easiest thing to be aware of. I definitely get annoyed while people consider worries that they just don’t know anything about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having a side effect, and people can take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks|
Great post I hope you continue to post great articles about stress. I am looking for home anxiety remedies. Do you know of anywhere to get some unbiased reviews of these? Again, thank you for this useful post.

Hey! Thanks for the feedback! Unfortunately, I’m not aware of where to find objective reviews, but I can tell you what helps me: a warm bath and a cup of green tea. Here are my remedies 🙂 Hope you will find needed resources and good luck on writing essays! If you need help, you can always contact us.

- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Struggling to Align Your Social Science Proposal’s Arguments and Concepts with Post-research Dissertation Writing?
Qualitative social science research—which includes ethnographic fieldwork, oral histories, interviews, focus groups, audio-visual recordings, and archival work—can significantly shift and reshape your research topic and, by extension, the writing of your dissertation. Many students who conduct qualitative research write their dissertation proposal months before they begin their research. When they return from research—or the ‘field’—and begin to write their dissertation chapters, they find that many of their original ideas concerning what is important and interesting about their topic has changed as a result of their research, reading and analysis. With their pre-research argument or hypothesis now subject to evolving evidence, students who engage in qualitative research find that they have to invest significant time in revising their main argument to align with research conducted during fieldwork. Instead of dedicating time to planning and writing out sections with pre-developed and well thought out arguments, students now have to focus on navigating evidence that requires new conceptualizations and sense-making.
Clearly, what we’re describing here isn’t one problem so much as a constellation of many problems that result from the tension between pre-fieldwork plans and post-fieldwork dissertation writing. In this entry, we offer a revision strategy that helps address a particularly common challenge for people engaged in social science research: how to revise your pre-research concepts and interpretative frameworks in light of evidence gathered during fieldwork.
As you begin the writing phase of your dissertation after completing your fieldwork research, you might realize that the key concepts that initially guided your interpretive framework no longer suffice. For example, your dissertation proposal might have been centered around the concepts of ‘nation’, ‘nation-state’ and ‘nationalism.’ But as you begin sifting through your qualitative research, you might discover that your data aligns better with concepts like ‘race’, ‘ethnicity’, and ‘homelands’. It might become evident to you that these new concepts don’t easily align with your original argument, in which case you’ll need to develop new arguments and claims derived from your research findings.
Instead of jumping straight into drafting chapters, you may find yourself first having to adopt new concepts and frameworks that lead you to approach your material differently. You may even find yourself torn and confused between pre-research arguments and concepts, and new findings that emerge from your qualitative research. This problem underscores the nature of qualitative social science research, where the work of revision often begins before the actual drafting of the dissertation. It begins with revising the qualitative interpretative frameworks when coding and analyzing data such as interviews and fieldnotes. At various points, the evidence emerging from your research may prompt a reassessment of concepts and interpretative frameworks that were initially employed, causing a shift towards concepts that are better suited to reflect the research findings.
Try the following exercise to resolve this tension between concepts formulated during the pre-research phase, and the moment of writing your dissertation during the post-research phase.
Step 1: Draw a table with three columns. Name the columns, “pre-research”, “research” and “post-research.” List concepts and/or interpretive frameworks identified from your pre-research proposal in the first column: for example, ‘ nation ’, ‘ nation-state’ and ‘ nationalism’ .
Step 2: Select one concept and trace it through the evidence and material you gathered during fieldwork. At this stage you are reading, analyzing, and coding your interviews, to see if this this concept resonates with your qualitative data. Ask yourself (1) whether this concept continues to be applicable to your project and (2) if there is enough data and evidence to justify the continued use of this concept.
Step 3: Based on your analysis of your interviews, you may determine that the original concept through which you framed your research is no longer quite right. If you think that concept is no longer right, cross it out in the first column. Now, list other concepts that might provide richer insights for your project in the second column. Consider each of these concepts against your field research. When one resonates especially well with your research, add that concept to your post-research column.
Step 4: Move on to your next ‘pre-research’ concept and repeat the steps mentioned above.
Need help with the Commons?
Email us at [email protected] so we can respond to your questions and requests. Please email from your CUNY email address if possible. Or visit our help site for more information:

- Terms of Service
- Accessibility
- Creative Commons (CC) license unless otherwise noted

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.
- Trending Blogs
- Geeksforgeeks NEWS
- Geeksforgeeks Blogs
- Tips & Tricks
- Website & Apps
- ChatGPT Blogs
- ChatGPT News
- ChatGPT Tutorial
- How to Search for a Word in Google Docs
- How To Share a PPT In Google Docs
- How To Add Stars In Google Docs
- How to Insert Word Art in Google Docs
- How to Use Find and Replace in Google Docs
- How To Link a Video To Google Docs
- How to Move a Table in Google Docs
- How to Remove Page Breaks in Google Docs
- How to Work Offline in Google Docs
- How to Open a Pdf in Google Docs
- How to Make A Resume on Google Docs
- How to Add a Page in Google Docs
- How To Use Google Docs To Write Blogs
- How to Make a Timeline in Google Docs
- How To Type Other Languages In Google Docs
- How to Use Add-Ons in Google Docs 2023
- How to add Page Numbers in Google Docs
- How to Insert a Vertical Line in Google Docs
- How to Insert Shapes in Google Docs
How to Write a Research Proposal in Google Docs
Ever wonder “ why ” something happens or “ how ” to fix a problem that keeps popping up? Maybe you have a wild “what if” idea. Those are awesome questions that can lead to amazing discoveries! A research proposal is your key to unlocking those answers and making a real difference.
Think of it like this: You’re a detective on a case. Google Docs is your super cool notepad to plan your investigation. This guide will show you how to use it, step-by-step, to write a killer research proposal.
Here’s what you’ll learn:
- How to grab people’s attention with a super interesting intro (think detective laying out the clues!)
- What to write in each part of your proposal (no need for fancy research jargon here!)
- How to use Google Docs’ awesome features to keep yourself organized and work with others (sharing is caring!).
So, put on your detective hat, open Google Docs, and let’s turn your question into a mind-blowing research proposal!
Table of Content
What is a Research Proposal?
Ph.d. research proposals, free research proposal templates by google docs, tips for a strong research proposal, faqs – writing a research proposal in google docs.
A research proposal is a blueprint for a research project . Writing a research proposal involves outlining your objectives , methodology, and expected outcomes . A research proposal includes Research Questions, background and significance, Literature review, methodology, Timeline, budget, and Expected outcomes. The purpose of making a research proposal is to convince others of the importance of the project. By using Google Docs , you can easily make any research proposal while collaborating with others.
- Your proposal should contain at least the following elements in the list of Ph.D. Research Proposal,
- A provisional title for the Proposal.
- A key question, hypothesis, or broad topic for further investigation.
- An outline of the key aims of the research proposal.
- A brief outline of key literature in the area.
Google Docs is a platform where it provides a variety of free templates in many fields. Anybody can check and edit the templates according to their need. Here are some of the free templates provided below for your reference where you can edit accordingly and make your research proposal differently.
Research Proposal Free Template 1

To Download this template Click here
Research Proposal Free Template 2

To Download this template Click Here
Research Proposal Free Template 3

Writing a research proposal in Google Docs is an easy process. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Sign in to Google Docs
Go to Google Docs and sign in to your Google account. If you don’t have one, you’ll need to create one.
.webp)
Step 2: Create a New Document
Click on the “+” (New) button to create a new document. You can choose a blank document or use a template if available.
.webp)
Step 3: Set Up Your Document
Set up your document according to the guidelines provided by your institution or the requirements of your research proposal. This includes formatting your title page, adding headings, and adjusting margins.

Step 4: Structure Your Proposal
Use headings (e.g., Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology) to organize your proposal into sections. You can easily add headings by selecting the text and choosing a heading style from the toolbar.

Step 5: Write Your Proposal
Start writing your proposal under each section heading. Google Docs provides a familiar word processing environment with basic formatting tools like bold, italic, and bullet points.

Step 6: Collaborate with Others
If you’re working with collaborators or seeking feedback, you can easily share your document with others. Click on the “Share” button in the top right corner, enter the email addresses of the people you want to share with and choose their permission level (e.g., edit, comment, view).

Step 7: Review and Edit
Once you’ve completed your proposal, review it carefully for any errors or inconsistencies. You can use the spelling and grammar check tools to help you proofread your document.

Step 8: Finalize Your Proposal
Make any final adjustments and ensure that your proposal meets all the requirements. Double-check formatting, headings, and citations before submitting.

Step 9: Save and Share
Google Docs automatically saves your work as you go, but it’s a good idea to save a final copy to your Google Drive or download it as a PDF or Word document. Share the final version with your advisor or colleagues as needed.
By following these steps, you can effectively write a research proposal using Google Docs and take advantage of its collaboration features and convenience.
- Put a precise objective and research question that your proposal aims to address.
- Ensure your proposal addresses a significant problem or gap in knowledge within your field.
- Conduct a Literature Review of existing research to provide context and support for your proposal.
- Outline the methods and techniques clearly that you’ll use to conduct your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and contributions of your research.
- Provide a realistic timeline for completing your project work.
- Clearly outline the budget needed for your research.
Writing a research proposal in Google Docs offers many benefits for researchers. The platform’s collaborative features enable teamwork, allowing multiple contributors to edit and provide feedback in real time. Google Docs’ auto-save function ensures that your work is constantly backed up, reducing the risk of data loss. By learning Google Docs’ features, researchers can turn up the proposal writing process and enhance their productivity. Therefore, utilizing Google Docs for making research proposals is an efficient and effective approach, motivating researchers to collaborate, create, and communicate their ideas easily.
Does Google Docs have a proposal template?
Yes, Google Docs offers many proposal templates. Open Google Docs, click on the Template Gallery, and search for “proposal” and you’ll get to see many of them. Then, select a template that suits your needs and customize it for your research proposal.
How do I write a research proposal for Google?
Use Google Docs to create a new document, structure it with sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, Results, Conclusion, and References, and collaborate with others by sharing the document.
What is the format of writing a research proposal?
The format of writing a research proposal typically includes, Title Page Abstract Introduction Literature Review Methodology Results and Discussion Conclusion References
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Google Docs
- Google Docs Tips
- Google docs
- Google Workspace
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
7 Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Seeking funding is a right of passage for many small business owners. While there are endless private and government-backed loans to choose from, if you’re looking to evade strict repayment terms and steep interest rates, it could be worth considering government business grants.
Government business grants are financial awards issued by federal, state, or local authorities. There are thousands of grants up for grabs through government website portals, but since this type of financing is designed to support the public, their eligibility criteria tend to be quite specific.
If you’re interested in pursuing this type of finance, we round up some government grants small businesses can apply for in May, including their specialisms, funding limits, and deadlines. We also offer some advice for writing your application, to make sure your proposal is as competitive as possible.
In this guide:
Government Small Business Grants to Apply For in May 2024
Tips for perfecting your government grant application.
Get the latest tech news, straight to your inbox
Don't miss out on the top business tech news with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel
By signing up to receive our newsletter, you agree to our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time.
There are thousands of government funds to apply for. If you want to cut through the noise, take a look at some of the most popular options below:
- Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) program
- Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting program
- 8(a) Business Development Program
- HUBZone Program
- Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)

1. Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program
- For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research
- Funding limit: Over $2 million
- Deadline: September 5, January 5, and April 5
The Small Business Innovation Research program was designed by the Small Business Administration to encourage US businesses to engage in Federal research and development. The competitive program is open to select small businesses and specifically encourages participation from women and socially or economically disadvantaged persons.
To be eligible for the SBIR program, your business must be for profit, be over 50% owned by permanent residents of the US, and have fewer than 500 employees. To apply for the grant, you need to register your business with SBIR, if you haven’t already, submit a proposal before one of the program’s tri-annual deadlines, and then respond to feedback and refine your concept if necessary.
Learn more about the SBIR grant, and how to apply here .
2. Small Business Technology Transfer (STTR) programs
- For: Small businesses that have paired up with a research institution
Like the SBIR, the Small Business Technology Transfer program is a government program focused on developing innovative solutions to pressing problems across the US. This type of funding aims to facilitate cooperative research and development efforts research between small business concerns and non-profit US research institutions, with the potential for commercialization of innovative technological solutions.
However, unlike the SBIR, this program requires the small business applicant to be teamed up with a non-profit research institution already, which typically takes the form of a university or Federal Laboratory. The STTR program is also focused on the transfer of technology from the research institution, rather than just the research alone.
Aside from being paired with a research institution, STTR’s eligibility criteria are nearly identical to SBIR’s.
Learn more about the STTR grant, and how to apply here .
3. Women-Owned Small Business (WOSB) Federal Contracting Program
- For: Women-owned businesses
- Funding limit: $4 million for service contracts and $6.5 million for manufacturing contracts
- Deadline: Rolling
The Women-Owned Small Business Federal Contracting Program was designed to build a level playing field for female business owners. The contracts are designated for specific industries where female-owned businesses are underrepresented. You can see which industries are eligible for the grant program here .
To be eligible for this program, you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by US women, and have an economically disadvantaged woman manage the day-to-day operations and make long-term decisions.
Learn more about WOSB, and how to apply here.
4. 8(a) Business Development Program
- For: Socially and economically disadvantaged business owners
- Funding limit: $7 million for acquisitions assigned manufacturing NAICS codes and $4.5 million for all other acquisitions
The 8(a) program is a nine-year program created by the SBA to financially support firms owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals. It’s designed to span nine years and helps eligible businesses access new business paths from government contracting.
Since the creation of the program in 1970, it has helped disadvantaged businesses gain access to billions of dollars in funding. To be eligible for the government grant, you must run a small business, be at least 51% owned and controlled by US citizens who are socially and economically disadvantaged, have a personal net worth of under $805 thousand, and demonstrate good character.
Learn more about the 8(a) business development program, and how to apply here .
5. HUBZone Program
- For: Small businesses in historically under-utilized business zones
- Funding limit: $3.5 million for products and services, and $5.5 million per contract for manufacturing
The HUBZone program is a SBA initiative designed to promote economic development and job growth in historically underutilized business zones (HUBZones). The program does so by offering financial grants to business owners operating within these communities.
To be eligible for this business grant you need to run a small business, have the business be at least 51% owned and controlled by a Community Development Corporation, an agricultural cooperative, an Alaska Native corporation, a Native Hawaiian organization, or an Indian tribe, have its main office located in a HUBZone, and have at least 35% of it employees living in the HUBZone for at least 45 days before applying.
Learn more about the HUBZone program, and how to apply here .
6. Small State Business Credit Initiative (SSBCI)
- For: Small businesses run by socially and economically disadvantaged individuals
- Funding limit: $20 million
The Small State Business Credit Initiative is a federal program designed to support entrepreneurship across the US. The grant program is provided by the US Department of the Treasury and was expanded by President Biden’s American Rescue Plan Act in 2021, providing an extra $10 billion in funding to eligible businesses.
In addition to providing capital support to small businesses, SSBCI can also provide technical assistance to eligible businesses through its Technical Assistance (TA) Grant Program. The SSBCI is available to businesses owner-occupied small businesses with 500 employees or less, and is specifically tailored to small businesses owned and controlled by socially and economically disadvantaged (SEDI) owners and very small businesses with less than 10 employees.
Learn more about the SSBCI program, and apply here .
7. U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA)
- For: Small businesses run by minorities
- Funding limit: Up to $350,000 for the first 10 months
The U.S. Department of Commerce Minority Business Development Agency (MBDA) is a Federal grants program designed to promote the growth of minority-owned businesses. The ultimate aim of the program is to provide minority business enterprises (MBEs) with access to funds, contracts, and market opportunities both in the US and globally.
To be eligible for MBDA assistance, a business must be owned or controlled by one or more socially or economically disadvantaged persons. The majority of business owners must also identify as racial minorities.
To apply for an MBDA business grant, you need to register your business with SAM.gov and Grants.gov if you haven’t already, align your proposal with the stated requirements, and submit your application before the deadline.
Learn more about the grant, and how to apply here .
Government grants offer a golden opportunity to businesses looking to grow or recover their business. However, due to the competitive nature of the financing, you need to ensure your grant proposal is polished and stands out from the crowd.
We understand that writing a grant application might seem like a daunting process, especially if you’re a first-timer. So, to give your proposal the best chance possible of succeeding, take heed of these pointers below.
- Give yourself enough time – You don’t want to be writing a grant application against the clock. Writing a proposal can take much longer than you expect, so to account for unexpected hold-ups we recommend giving yourself at least 45 days to complete your written application.
- Follow the instructions carefully – Don’t go off-piste when writing your application. Make sure you include all the information requested by the agency, and present it in the correct format.
- Be as concise and clear as possible – Ensure your application is written in clear, simple language, and use as many candid examples as possible to paint a clear image for your reader. If you use any graphs or imagery, make sure you label them clearly as well.
- Keep the audience in mind – The likelihood is that the reviewer won’t already be familiar with your business. To make sure you won’t gloss over necessary information write the proposal for an audience that’s hearing about your business for the first time.
- Develop a proofreading strategy – You don’t want to hamper your application’s success with silly mistakes like typos or grammatical errors. So, to ensure your proposal looks polished carefully proofread the application or outsource the service to a professional.
Stay informed on the top business tech stories with Tech.co's weekly highlights reel.
We're sorry this article didn't help you today – we welcome feedback, so if there's any way you feel we could improve our content, please email us at [email protected]
Written by:

11 Small Business Grants and Loans to Apply For in 2024
Getting a financial boost could be easier than you think,...

Company Offering $10K for a 30 Day Phone Detox, Apply Now
If you think you've got what it takes to do a one-month...

9 Innovative Startups To Watch Out For in 2024
Discover the startups that have triumphed over adversity in...

Claude 2.1: Anthropic’s ChatGPT Rival Gets New Killer Feature
As OpenAI hits the headlines for all the wrong reasons,...

COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Overview: 5 Proposal Writing Essentials. Understand your university's requirements and restrictions. Have a clearly articulated research problem. Clearly communicate the feasibility of your research. Pay very close attention to ethics policies. Focus on writing critically and concisely. 1. Understand the rules of the game.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Top Tips For Writing Your Research Proposal. Take time to write a good proposal. Well-presented and written proposals are more likely to stick in the reviewer's mind. Allow for flexibility as research proposals do not have to be set in stone. Avoid plagiarism. You should acknowledge the authors of all publications you reference.
Conduct a literature review for your research proposal. 4. Define a research gap and research question. 5. Establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal. 6. Specify an empirical focus for your research proposal. 7. Emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal.
Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Writing a research proposal in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
By focusing on the interconnection between these key elements, you can establish a strong foundation for your research proposal. 3: Create a Solid Outline Before You Start Writing. Drawing up a clear outline before starting the writing process can streamline your proposal development. An outline serves as a roadmap, guiding the structure and ...
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
Hannah Skaggs. Hannah, a writer and editor since 2017, specializes in clear and concise academic and business writing. She has mentored countless scholars and companies in writing authoritative and engaging content. Write a research proposal with purpose and accuracy. Learn about the objective, parts, and key elements of a research proposal in ...
Make sure that your passion for the research topic shines through. Your proposal should be approached as a piece of persuasive writing - you want to establish the attention of your reader and convince them of your project's significance. Make sure that your writing is clear, concise, and coherent. Make sure that your proposal does not ...
1. Write with your reviewers in mind. - Make sure your argument is easy to follow and clear. - Do not waste the time of your reviewers; get right to the point. - Include only essential information. - Write in a clear, engaging style. 2. Formulate clear research questions early in your proposal. - What do you want to know?
A typical research proposal will generally include a title, summary of the aims and expected outcomes, literature review, research methodology, proposed timeline, and references. The characteristics of a good research title all generally focus on catching the reader's attention. Again, word limits, formatting, and what is considered essential ...
external funder, the rules about writing a good research proposal are the same. You want to stand out from the crowd and have the best chance of being selected. This guide highlights the "Golden Rules" and provides tips on how to write a good research application. Prospective research students may find it useful when asked to provide
Ten tips for writing your research proposal. 1. Follow the instructions! Read and conform to all instructions found on the council website. Make sure that your proposal fits the criteria of the competition. 2. Break down your proposal into point form before writing your first draft. Based on the total length of the proposal, decide whether you ...
Include all contact details, not just an email address, along with an address in case an organization wants to send you mail. You may also want to add a table of contents, a chapter outline of your thesis, and your signature at the bottom of the document. There's also another important point worth noting. A common mistake that people make ...
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. ... Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; 'be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for ...
Discuss the definitions and/or categories you plan to use in your research. Discuss the research methods you will use and outline who will be the participants in your study. Discuss the results you expect to get from your investigation. Provide a list of the literature you used to write your proposal.
As you begin the writing phase of your dissertation after completing your fieldwork research, you might realize that the key concepts that initially guided your interpretive framework no longer suffice. For example, your dissertation proposal might have been centered around the concepts of 'nation', 'nation-state' and 'nationalism.'
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
A research proposal is a blueprint for a research project. Writing a research proposal involves outlining your objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. A research proposal includes Research Questions, background and significance, Literature review, methodology, Timeline, budget, and Expected outcomes.
1. Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program. For: Small businesses interested in carrying out innovation research Funding limit: Over $2 million Deadline: September 5, January 5, and ...