Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Writing Essays in Art History

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Art History Analysis – Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis
Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis.
A formal analysis is just what it sounds like – you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design elements – composition, color, line, texture, scale, contrast, etc. Questions to consider in a formal analysis is how do all these elements come together to create this work of art? Think of formal analysis in relation to literature – authors give descriptions of characters or places through the written word. How does an artist convey this same information?
Organize your information and focus on each feature before moving onto the text – it is not ideal to discuss color and jump from line to then in the conclusion discuss color again. First summarize the overall appearance of the work of art – is this a painting? Does the artist use only dark colors? Why heavy brushstrokes? etc and then discuss details of the object – this specific animal is gray, the sky is missing a moon, etc. Again, it is best to be organized and focused in your writing – if you discuss the animals and then the individuals and go back to the animals you run the risk of making your writing unorganized and hard to read. It is also ideal to discuss the focal of the piece – what is in the center? What stands out the most in the piece or takes up most of the composition?
A stylistic approach can be described as an indicator of unique characteristics that analyzes and uses the formal elements (2-D: Line, color, value, shape and 3-D all of those and mass).The point of style is to see all the commonalities in a person’s works, such as the use of paint and brush strokes in Van Gogh’s work. Style can distinguish an artist’s work from others and within their own timeline, geographical regions, etc.
Methods & Theories To Consider:
Expressionism
Instructuralism
Postmodernism
Social Art History
Biographical Approach
Poststructuralism
Museum Studies
Visual Cultural Studies
Stylistic Analysis Example:
The following is a brief stylistic analysis of two Greek statues, an example of how style has changed because of the “essence of the age.” Over the years, sculptures of women started off as being plain and fully clothed with no distinct features, to the beautiful Venus/Aphrodite figures most people recognize today. In the mid-seventh century to the early fifth, life-sized standing marble statues of young women, often elaborately dress in gaily painted garments were created known as korai. The earliest korai is a Naxian women to Artemis. The statue wears a tight-fitted, belted peplos, giving the body a very plain look. The earliest korai wore the simpler Dorian peplos, which was a heavy woolen garment. From about 530, most wear a thinner, more elaborate, and brightly painted Ionic linen and himation. A largely contrasting Greek statue to the korai is the Venus de Milo. The Venus from head to toe is six feet seven inches tall. Her hips suggest that she has had several children. Though her body shows to be heavy, she still seems to almost be weightless. Viewing the Venus de Milo, she changes from side to side. From her right side she seems almost like a pillar and her leg bears most of the weight. She seems be firmly planted into the earth, and since she is looking at the left, her big features such as her waist define her. The Venus de Milo had a band around her right bicep. She had earrings that were brutally stolen, ripping her ears away. Venus was noted for loving necklaces, so it is very possibly she would have had one. It is also possible she had a tiara and bracelets. Venus was normally defined as “golden,” so her hair would have been painted. Two statues in the same region, have throughout history, changed in their style.
Compare and Contrast Essay
Most introductory art history classes will ask students to write a compare and contrast essay about two pieces – examples include comparing and contrasting a medieval to a renaissance painting. It is always best to start with smaller comparisons between the two works of art such as the medium of the piece. Then the comparison can include attention to detail so use of color, subject matter, or iconography. Do the same for contrasting the two pieces – start small. After the foundation is set move on to the analysis and what these comparisons or contrasting material mean – ‘what is the bigger picture here?’ Consider why one artist would wish to show the same subject matter in a different way, how, when, etc are all questions to ask in the compare and contrast essay. If during an exam it would be best to quickly outline the points to make before tackling writing the essay.
Compare and Contrast Example:
Stele of Hammurabi from Susa (modern Shush, Iran), ca. 1792 – 1750 BCE, Basalt, height of stele approx. 7’ height of relief 28’
Stele, relief sculpture, Art as propaganda – Hammurabi shows that his law code is approved by the gods, depiction of land in background, Hammurabi on the same place of importance as the god, etc.
Top of this stele shows the relief image of Hammurabi receiving the law code from Shamash, god of justice, Code of Babylonian social law, only two figures shown, different area and time period, etc.
Stele of Naram-sin , Sippar Found at Susa c. 2220 - 2184 bce. Limestone, height 6'6"
Stele, relief sculpture, Example of propaganda because the ruler (like the Stele of Hammurabi) shows his power through divine authority, Naramsin is the main character due to his large size, depiction of land in background, etc.
Akkadian art, made of limestone, the stele commemorates a victory of Naramsin, multiple figures are shown specifically soldiers, different area and time period, etc.
Iconography
Regardless of what essay approach you take in class it is absolutely necessary to understand how to analyze the iconography of a work of art and to incorporate into your paper. Iconography is defined as subject matter, what the image means. For example, why do things such as a small dog in a painting in early Northern Renaissance paintings represent sexuality? Additionally, how can an individual perhaps identify these motifs that keep coming up?
The following is a list of symbols and their meaning in Marriage a la Mode by William Hogarth (1743) that is a series of six paintings that show the story of marriage in Hogarth’s eyes.
- Man has pockets turned out symbolizing he has lost money and was recently in a fight by the state of his clothes.
- Lap dog shows loyalty but sniffs at woman’s hat in the husband’s pocket showing sexual exploits.
- Black dot on husband’s neck believed to be symbol of syphilis.
- Mantel full of ugly Chinese porcelain statues symbolizing that the couple has no class.
- Butler had to go pay bills, you can tell this by the distasteful look on his face and that his pockets are stuffed with bills and papers.
- Card game just finished up, women has directions to game under foot, shows her easily cheating nature.
- Paintings of saints line a wall of the background room, isolated from the living, shows the couple’s complete disregard to faith and religion.
- The dangers of sexual excess are underscored in the Hograth by placing Cupid among ruins, foreshadowing the inevitable ruin of the marriage.
- Eventually the series (other five paintings) shows that the woman has an affair, the men duel and die, the woman hangs herself and the father takes her ring off her finger symbolizing the one thing he could salvage from the marriage.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
AP®︎/College Art History
Course: ap®︎/college art history > unit 1.
- What is art history and where is it going?
Introduction to art historical analysis
- How to do visual (formal) analysis in art history
- Art historical analysis (painting), a basic introduction using Goya's Third of May, 1808
- A brief history of representing the body in Western painting
- A brief history of representing of the body in Western sculpture
Art as physical object
Conservation, art as visual experience, visual (formal) analysis, art as cultural artifact, subject matter / iconography, function of art, thinking critically, want to join the conversation.
- Upvote Button navigates to signup page
- Downvote Button navigates to signup page
- Flag Button navigates to signup page

An introduction to art history
Art history "is a way to see what people thought, felt, believed, did, and imagined, by looking at the material things – buildings, paintings, gardens, sculptures, images, cities, objects – and the worlds that they made." (Griselda Pollock)
videos + essays
We're adding new content all the time!

Mudras in Buddhist art
Mudras are a set of hand gestures and finger positions that serve as symbols in Buddhist art.

Art history and world art history
“Art history is relevant” is not how the discipline of art history is typically framed in popular discourse.

Ever wondered…why study art of the past?
The reason people study the art of the past are varied - but all agree, it can tell us a lot about our own world.

Ever wondered… why people become art historians?
Studying art history isn't a conventional path to success — so why do people do it?

Art and empathy
Empathy is a term we hear a lot, but what does it mean and how does it work?

What is art history and where is it going?
Methods change, the canon expands, and we write history anew. Long focused on the West, the field is going global.

A brief history of the representation of the body in Western sculpture
Sculptors have had different goals at different times. Two recur: naturalism and abstraction.

A brief history of the representation of the body in Western painting
Respond to contemporary culture, or reclaim the past? Each artist decides how to approach the human form.
Your donations help make art history free and accessible to everyone!
The Courtauld is an internationally renowned centre for the teaching and research of art history and a major public gallery
Be part of an international community of influential art enthusiasts, thought leaders and change makers
Current students
Information and resources for students currently studying at The Courtauld
Stay in touch
Quick links, suggested searches, what is art history.
Art history – the study of art from across the world, and from the ancient to the present day – covers virtually every aspect of human history and experience. This is because it looks at works of art not just as objects, but as a way of understanding the world, and the societies in which they were created.
What were the conscious and unconscious choices that led to an artwork’s form and subject matter? What does its content – how people are represented, how religion is shown – tell you about the society in which it was created, and its history? How was it received when it was first put on display, and how has this changed?
By asking these questions, art historians gain a fascinating insight into how people throughout time and across the world lived, thought, felt and understood everything around them. Developing understanding of these challenges helps us make sense of the relationship between people, art and the forces that shape the world we live in today – and provides us with the critical skills to understand the visual world around us.
Why study Art History?
It combines the rigour of a history degree with the visual skills required to interpret works of art. It will help you develop critical skills, to think about art and history from a variety of perspectives, and to present your ideas succinctly and persuasively. These are all key skills that will help you to stand out in today’s job market. You will learn to analyse the role art plays in shaping society. Art History will introduce you to world-famous works of art, as well as others that are less well known but equally as fascinating to examine and study. You will get to explore new areas of Art History, and artworks from a variety of time periods, from all around the world, delivered in a range of different forms. If you enjoy reading history, studying literature or languages, looking at art, and are fascinated by the relationship between people, art, and the forces that have shaped the world we live in, then Art History is the subject for you.
"What is art history" - we asked our academics:
Dr Guido Rebecchini, Reader in Sixteenth-Century Southern European Art:
Artworks from the past communicate with us across centuries in a language that is much more mysterious and nuanced than one might first assume. Interrogating them and looking closely at what they represent, as well as at their materials and techniques, enables us to make contact with ideas, rituals, beliefs and practices wholly different from our own. Art historians therefore explore the gulf between the appearance of artworks – as we might see them today in museums, galleries and historical buildings – and the complex ideas behind their production.
It is important to remember that artworks produced in the Middle Ages and the Early Modern Period, in both the East and the West, were not intended to be displayed in museums. Instead, such artworks communicated with their audiences in spaces where rituals and practices that helped to form familial, civic and religious identities, such as palaces, churches and squares. Works of art were often made to mark marriages, births, deaths, and they reflected hopes and ambitions; in fact, they were often thought to have real agency in the world. Artworks were considered to possess holy powers, brought in procession, or stood in for absent people.
Ultimately, as art historians, we look closely and carefully, patiently and inquisitively, and ask questions incessantly. To do so, we analyse, compare and connect a wide range of difference sources and pieces of evidence; primarily the artworks themselves, but also documents, literature and many other traces of the past. By doing so, we locate works of art in the ecosystem in which they were conceived, which helps us to better understand how artworks of the past have shaped the world we live in. For these reasons, art history is a truly interdisciplinary: it demands that we take the vantage point of others, like the anthropologist does; that we see things in historical perspective, as the historian does; and that we consider how ideas related religion, family, gender, race, and politics are implicated in the art of the past. In conclusion, art history is an inquiry into human culture pursued mainly – but not only – by critically looking at the extraordinary images that past generations have left behind.
You might also like

Why does art history matter?
- Art Degrees
- Galleries & Exhibits
- Request More Info
Art History Resources
- Guidelines for Analysis of Art
- Formal Analysis Paper Examples
Guidelines for Writing Art History Research Papers
- Oral Report Guidelines
- Annual Arkansas College Art History Symposium
Writing a paper for an art history course is similar to the analytical, research-based papers that you may have written in English literature courses or history courses. Although art historical research and writing does include the analysis of written documents, there are distinctive differences between art history writing and other disciplines because the primary documents are works of art. A key reference guide for researching and analyzing works of art and for writing art history papers is the 10th edition (or later) of Sylvan Barnet’s work, A Short Guide to Writing about Art . Barnet directs students through the steps of thinking about a research topic, collecting information, and then writing and documenting a paper.
A website with helpful tips for writing art history papers is posted by the University of North Carolina.
Wesleyan University Writing Center has a useful guide for finding online writing resources.
The following are basic guidelines that you must use when documenting research papers for any art history class at UA Little Rock. Solid, thoughtful research and correct documentation of the sources used in this research (i.e., footnotes/endnotes, bibliography, and illustrations**) are essential. Additionally, these guidelines remind students about plagiarism, a serious academic offense.
Paper Format
Research papers should be in a 12-point font, double-spaced. Ample margins should be left for the instructor’s comments. All margins should be one inch to allow for comments. Number all pages. The cover sheet for the paper should include the following information: title of paper, your name, course title and number, course instructor, and date paper is submitted. A simple presentation of a paper is sufficient. Staple the pages together at the upper left or put them in a simple three-ring folder or binder. Do not put individual pages in plastic sleeves.
Documentation of Resources
The Chicago Manual of Style (CMS), as described in the most recent edition of Sylvan Barnet’s A Short Guide to Writing about Art is the department standard. Although you may have used MLA style for English papers or other disciplines, the Chicago Style is required for all students taking art history courses at UA Little Rock. There are significant differences between MLA style and Chicago Style. A “Quick Guide” for the Chicago Manual of Style footnote and bibliography format is found http://www.chicagomanualofstyle.org/tools_citationguide.html. The footnote examples are numbered and the bibliography example is last. Please note that the place of publication and the publisher are enclosed in parentheses in the footnote, but they are not in parentheses in the bibliography. Examples of CMS for some types of note and bibliography references are given below in this Guideline. Arabic numbers are used for footnotes. Some word processing programs may have Roman numerals as a choice, but the standard is Arabic numbers. The use of super script numbers, as given in examples below, is the standard in UA Little Rock art history papers.
The chapter “Manuscript Form” in the Barnet book (10th edition or later) provides models for the correct forms for footnotes/endnotes and the bibliography. For example, the note form for the FIRST REFERENCE to a book with a single author is:
1 Bruce Cole, Italian Art 1250-1550 (New York: New York University Press, 1971), 134.
But the BIBLIOGRAPHIC FORM for that same book is:
Cole, Bruce. Italian Art 1250-1550. New York: New York University Press. 1971.
The FIRST REFERENCE to a journal article (in a periodical that is paginated by volume) with a single author in a footnote is:
2 Anne H. Van Buren, “Madame Cézanne’s Fashions and the Dates of Her Portraits,” Art Quarterly 29 (1966): 199.
The FIRST REFERENCE to a journal article (in a periodical that is paginated by volume) with a single author in the BIBLIOGRAPHY is:
Van Buren, Anne H. “Madame Cézanne’s Fashions and the Dates of Her Portraits.” Art Quarterly 29 (1966): 185-204.
If you reference an article that you found through an electronic database such as JSTOR, you do not include the url for JSTOR or the date accessed in either the footnote or the bibliography. This is because the article is one that was originally printed in a hard-copy journal; what you located through JSTOR is simply a copy of printed pages. Your citation follows the same format for an article in a bound volume that you may have pulled from the library shelves. If, however, you use an article that originally was in an electronic format and is available only on-line, then follow the “non-print” forms listed below.
B. Non-Print
Citations for Internet sources such as online journals or scholarly web sites should follow the form described in Barnet’s chapter, “Writing a Research Paper.” For example, the footnote or endnote reference given by Barnet for a web site is:
3 Nigel Strudwick, Egyptology Resources , with the assistance of The Isaac Newton Institute for Mathematical Sciences, Cambridge University, 1994, revised 16 June 2008, http://www.newton.ac.uk/egypt/ , 24 July 2008.
If you use microform or microfilm resources, consult the most recent edition of Kate Turabian, A Manual of Term Paper, Theses and Dissertations. A copy of Turabian is available at the reference desk in the main library.
C. Visual Documentation (Illustrations)
Art history papers require visual documentation such as photographs, photocopies, or scanned images of the art works you discuss. In the chapter “Manuscript Form” in A Short Guide to Writing about Art, Barnet explains how to identify illustrations or “figures” in the text of your paper and how to caption the visual material. Each photograph, photocopy, or scanned image should appear on a single sheet of paper unless two images and their captions will fit on a single sheet of paper with one inch margins on all sides. Note also that the title of a work of art is always italicized. Within the text, the reference to the illustration is enclosed in parentheses and placed at the end of the sentence. A period for the sentence comes after the parenthetical reference to the illustration. For UA Little Rcok art history papers, illustrations are placed at the end of the paper, not within the text. Illustration are not supplied as a Powerpoint presentation or as separate .jpgs submitted in an electronic format.
Edvard Munch’s painting The Scream, dated 1893, represents a highly personal, expressive response to an experience the artist had while walking one evening (Figure 1).
The caption that accompanies the illustration at the end of the paper would read:
Figure 1. Edvard Munch, The Scream, 1893. Tempera and casein on cardboard, 36 x 29″ (91.3 x 73.7 cm). Nasjonalgalleriet, Oslo, Norway.
Plagiarism is a form of thievery and is illegal. According to Webster’s New World Dictionary, to plagiarize is to “take and pass off as one’s own the ideas, writings, etc. of another.” Barnet has some useful guidelines for acknowledging sources in his chapter “Manuscript Form;” review them so that you will not be mguilty of theft. Another useful website regarding plagiarism is provided by Cornell University, http://plagiarism.arts.cornell.edu/tutorial/index.cfm
Plagiarism is a serious offense, and students should understand that checking papers for plagiarized content is easy to do with Internet resources. Plagiarism will be reported as academic dishonesty to the Dean of Students; see Section VI of the Student Handbook which cites plagiarism as a specific violation. Take care that you fully and accurately acknowledge the source of another author, whether you are quoting the material verbatim or paraphrasing. Borrowing the idea of another author by merely changing some or even all of your source’s words does not allow you to claim the ideas as your own. You must credit both direct quotes and your paraphrases. Again, Barnet’s chapter “Manuscript Form” sets out clear guidelines for avoiding plagiarism.
VISIT OUR GALLERIES SEE UPCOMING EXHIBITS
- School of Art and Design
- Windgate Center of Art + Design, Room 202 2801 S University Avenue Little Rock , AR 72204
- Phone: 501-916-3182 Fax: 501-683-7022 (fax)
- More contact information
Connect With Us
UA Little Rock is an accredited member of the National Association of Schools of Art and Design.
The Writing Place
Resources – how to write an art history paper, introduction to the topic.
There are many different types of assignments you might be asked to do in an art history class. The most common are a formal analysis and a stylistic analysis. Stylistic analyses often involve offering a comparison between two different works. One of the challenges of art history writing is that it requires a vocabulary to describe what you see when you look at a painting, drawing, sculpture or other media. This checklist is designed to explore questions that will help you write these types of art history papers.
Features of An Art History Analysis Paper
Features of a formal analysis paper.
This type of paper involves looking at compositional elements of an object such as color, line, medium, scale, and texture. The goal of this kind of assignment it to demonstrate how these elements work together to produce the whole art object. When writing a formal analysis, ask yourself:
- What is the first element of the work that the audience’s eye captures?
- What materials were used to create the object?
- What colors and textures did the artist employ?
- How do these function together to give the object its overall aesthetic look?
Tips on Formal Analysis
- Describe the piece as if your audience has not seen it.
- Be detailed.
- The primary focus should be on description rather than interpretation.
Features of a Stylistic / Comparative Analysis
Similar to a formal analysis, a stylistic analysis asks you to discuss a work in relation to its stylistic period (Impressionism, Fauvism, High Renaissance, etc.). These papers often involve a comparative element (such as comparing a statue from Early Antiquity to Late Antiquity). When writing a stylistic analysis, ask yourself:
- How does this work fit the style of its historical period? How does it depart from the typical style?
- What is the social and historical context of the work? When was it completed?
- Who was the artist? Who commissioned it? What does it depict?
- How is this work different from other works of the same subject matter?
- How have the conventions (formal elements) for this type of work changed over time?
Tips for Stylistic and Comparative Analysis
- In a comparison, make a list of similarities and differences between the two works. Try to establish what changes in the art world may account for the differences.
- Integrate discussions of formal elements into your stylistic analysis.
- This type of paper can involve more interpretation than a basic formal analysis.
- Focus on context and larger trends in art history.
A Quick Practice Exercise...
Practice - what is wrong with these sentences.
The key to writing a good art history paper involves relating the formal elements of a piece to its historical context. Can you spot the errors in these sentences? What would make the sentences better?
- “Courbet’s The Stone Breakers is a good painting because he uses texture.”
- “Duchamp’s work is in the Dada style while Dali’s is Surrealist.”
- “Pope Julius II commissioned the work.”
- “Gauguin uses color to draw in the viewer’s eye.”
Answers for Practice Sentences
- Better: “Courbet’s The Stone Breakers is a radical painting because the artist used a palette knife to create a rough texture on the surface.”
- Better: “The use of everyday objects in Duchamp’s work reflects the Dada style while Dali’s incorporation of absurd images into his work demonstrates a Surrealist style.”
- Better: “In 1505, Pope Julius II commissioned the sculpture for his tomb.”
- Better: “The first element a viewer notices is the bold blue of the sky in Gauguin’s painting.”
Adapted by Ann Bruton, with the help of Isaac Alpert, From:
The Writing Center at UNC Handouts ( http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/art-history/ )
The Writing Center at Hamilton College ( http://www.hamilton.edu/writing/writing-resources/writing-an-art-history-paper )
Click here to return to the “Writing Place Resources” main page.
Art History Writing Guide
I. Introduction II. Writing Assignments III. Discipline-Specific Strategies IV. Keep in Mind V. Appendix
Introduction
At the heart of every art history paper is a close visual analysis of at least one work of art. In art history you are building an argument about something visual. Depending on the assignment, this analysis may be the basis for an assignment or incorporated into a paper as support to contextualize an argument. To guide students in how to write an art history paper, the Art History Department suggests that you begin with a visual observation that leads to the development of an interpretive thesis/argument. The writing uses visual observations as evidence to support an argument about the art that is being analyzed.
Writing Assignments
You will be expected to write several different kinds of art history papers. They include:
- Close Visual Analysis Essays
- Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays
- Research Papers
Close Visual Analysis pieces are the most commonly written papers in an introductory art history course. You will have to look at a work of art and analyze it in its entirety. The analysis and discussion should provide a clearly articulated interpretation of the object. Your argument for this paper should be backed up with careful description and analysis of the visual evidence that led you to your conclusion.
Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays combines formal analysis with close textual analysis.
Research papers range from theoretic studies to critical histories. Based on library research, students are asked to synthesize analyses of the scholarship in relation to the work upon which it is based.
Discipline-Specific Strategies
As with all writing assignment, a close visual analysis is a process. The work you do before you actually start writing can be just as important as what you consider when writing up your analysis.
Conducting the analysis :
- Ask questions as you are studying the artwork. Consider, for example, how does each element of the artwork contribute to the work's overall meaning. How do you know? How do elements relate to each other? What effect is produced by their juxtaposition
- Use the criteria provided by your professor to complete your analysis. This criteria may include forms, space, composition, line, color, light, texture, physical characteristics, and expressive content.
Writing the analysis:
- Develop a strong interpretive thesis about what you think is the overall effect or meaning of the image.
- Ground your argument in direct and specific references to the work of art itself.
- Describe the image in specific terms and with the criteria that you used for the analysis. For example, a stray diagonal from the upper left corner leads the eye to...
- Create an introduction that sets the stage for your paper by briefly describing the image you are analyzing and by stating your thesis.
- Explain how the elements work together to create an overall effect. Try not to just list the elements, but rather explain how they lead to or support your analysis.
- Contextualize the image within a historical and cultural framework only when required for an assignment. Some assignments actually prefer that you do not do this. Remember not to rely on secondary sources for formal analysis. The goal is to see what in the image led to your analysis; therefore, you will not need secondary sources in this analysis. Be certain to show how each detail supports your argument.
- Include only the elements needed to explain and support your analysis. You do not need to include everything you saw since this excess information may detract from your main argument.
Keep in Mind
- An art history paper has an argument that needs to be supported with elements from the image being analyzed.
- Avoid making grand claims. For example, saying "The artist wanted..." is different from "The warm palette evokes..." The first phrasing necessitates proof of the artist's intent, as opposed to the effect of the image.
- Make sure that your paper isn't just description. You should choose details that illustrate your central ideas and further the purpose of your paper.
If you find you are still having trouble writing your art history paper, please speak to your professor, and feel free to make an appointment at the Writing Center. For further reading, see Sylvan Barnet's A Short Guide to Writing about Art , 5th edition.
Additional Site Navigation
Social media links, additional navigation links.
- Alumni Resources & Events
- Athletics & Wellness
- Campus Calendar
- Parent & Family Resources
Helpful Information
Dining hall hours, next trains to philadelphia, next trico shuttles.
Swarthmore Traditions
How to Plan Your Classes

The Swarthmore Bucket List

Search the website
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Emotions
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music and Media
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Oncology
- Medical Toxicology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business Ethics
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous
- Next chapter >

1 (page 1) p. 1 What is art history?
- Published: January 2020
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
‘What is art history?’ discusses the term art history and draws distinctions between it and art appreciation and art criticism. It also considers the range of artefacts included in the discipline and how these have changed over time. The work of art is our primary evidence, and it is our interaction between this evidence and methods of enquiry that forms art history. Art appreciation and criticism are also linked to connoisseurship. Although art is a visual subject, we learn about it through reading and we convey our ideas about it mostly in writing. The social and cultural issues articulated by art history are examined through an analysis of four very different works of art.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.

Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Visiting Sleeping Beauties: Reawakening Fashion?
You must join the virtual exhibition queue when you arrive. If capacity has been reached for the day, the queue will close early.
- All Periods
- All Regions
- Departments / Collections

Gold, Griffins, and Greeks: Scythian Art and Cultural Interactions in the Black Sea

Ottoman Wedding Dresses, East to West

The Feathered Serpent Pyramid and Ciudadela of Teotihuacan (ca. 150–250 CE)

Teotihuacan (ca. 100 BCE–800 CE)

Stone Masks and Figurines from Northwest Argentina (500 BCE–650 CE)
All essays (1057), abraham and david roentgen, abstract expressionism, the achaemenid persian empire (550–330 b.c.), adélaïde labille-guiard (1749–1803), the aesthetic of the sketch in nineteenth-century france, african christianity in ethiopia, african christianity in kongo, african influences in modern art, african lost-wax casting, african rock art, african rock art of the central zone, african rock art of the northern zone, african rock art of the southern zone, african rock art: game pass, african rock art: tassili-n-ajjer (8000 b.c.–), african rock art: the coldstream stone, africans in ancient greek art, afro-portuguese ivories, the age of iron in west africa, the age of saint louis (1226–1270), the age of süleyman “the magnificent” (r. 1520–1566), the akkadian period (ca. 2350–2150 b.c.), albrecht dürer (1471–1528), alexander jackson davis (1803–1892), alfred stieglitz (1864–1946) and american photography, alfred stieglitz (1864–1946) and his circle, alice cordelia morse (1863–1961), allegories of the four continents, the amarna letters, america comes of age: 1876–1900, american bronze casting, american federal-era period rooms, american furniture, 1620–1730: the seventeenth-century and william and mary styles, american furniture, 1730–1790: queen anne and chippendale styles, american georgian interiors (mid-eighteenth-century period rooms), american impressionism, american ingenuity: sportswear, 1930s–1970s, american needlework in the eighteenth century, american neoclassical sculptors abroad, american portrait miniatures of the eighteenth century, american portrait miniatures of the nineteenth century, american quilts and coverlets, american relief sculpture, american revival styles, 1840–76, american rococo, american scenes of everyday life, 1840–1910, american sculpture at the world’s columbian exposition, chicago, 1893, american silver vessels for wine, beer, and punch, american women sculptors, americans in paris, 1860–1900, amulets and talismans from the islamic world, anatomy in the renaissance, ancient american jade, ancient egyptian amulets, ancient greek bronze vessels, ancient greek colonization and trade and their influence on greek art, ancient greek dress, ancient maya painted ceramics, ancient maya sculpture, ancient near eastern openwork bronzes, andean textiles, animals in ancient near eastern art, animals in medieval art, ann lowe (ca. 1898–1981), annibale carracci (1560–1609), anselm kiefer (born 1945), antelopes and queens: bambara sculpture from the western sudan: a groundbreaking exhibition at the museum of primitive art, new york, 1960, antique engraved gems and renaissance collectors, antoine watteau (1684–1721), antonello da messina (ca. 1430–1479), the antonine dynasty (138–193), antonio canova (1757–1822), apollo 11 (ca. 25,500–23,500 b.c.) and wonderwerk (ca. 8000 b.c.) cave stones, architectural models from the ancient americas, architecture in ancient greece, architecture in renaissance italy, architecture, furniture, and silver from colonial dutch america, archtop guitars and mandolins, arms and armor in medieval europe, arms and armor in renaissance europe, arms and armor—common misconceptions and frequently asked questions, art and craft in archaic sparta, art and death in medieval byzantium, art and death in the middle ages, art and identity in the british north american colonies, 1700–1776, art and love in the italian renaissance, art and nationalism in twentieth-century turkey, art and photography: 1990s to the present, art and photography: the 1980s, art and society of the new republic, 1776–1800, art and the fulani/fulbe people, art for the christian liturgy in the middle ages, art nouveau, the art of classical greece (ca. 480–323 b.c.), the art of ivory and gold in northern europe around 1000 a.d., the art of the abbasid period (750–1258), the art of the almoravid and almohad periods (ca. 1062–1269), art of the asante kingdom, the art of the ayyubid period (ca. 1171–1260), the art of the book in the ilkhanid period, the art of the book in the middle ages, art of the edo period (1615–1868), the art of the fatimid period (909–1171), art of the first cities in the third millennium b.c., art of the hellenistic age and the hellenistic tradition, the art of the ilkhanid period (1256–1353), art of the korean renaissance, 1400–1600, the art of the mamluk period (1250–1517), the art of the mughals after 1600, the art of the mughals before 1600, the art of the nasrid period (1232–1492), the art of the ottomans after 1600, the art of the ottomans before 1600, art of the pleasure quarters and the ukiyo-e style, art of the roman provinces, 1–500 a.d., the art of the safavids before 1600, the art of the seljuq period in anatolia (1081–1307), the art of the seljuqs of iran (ca. 1040–1157), art of the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries in naples, art of the sufis, the art of the timurid period (ca. 1370–1507), the art of the umayyad period (661–750), the art of the umayyad period in spain (711–1031), art, architecture, and the city in the reign of amenhotep iv / akhenaten (ca. 1353–1336 b.c.), the art, form, and function of gilt bronze in the french interior, arthur dove (1880–1946), an artisan’s tomb in new kingdom egypt, artistic interaction among cultures in medieval iberia, artists of the saqqakhana movement, the arts and crafts movement in america, the arts of iran, 1600–1800, arts of power associations in west africa, the arts of the book in the islamic world, 1600–1800, arts of the greater himalayas: kashmir, tibet, and nepal, arts of the mission schools in mexico, arts of the san people in nomansland, arts of the spanish americas, 1550–1850, asante royal funerary arts, asante textile arts, the ashcan school, asher brown durand (1796–1886), assyria, 1365–609 b.c., the assyrian sculpture court, astronomy and astrology in the medieval islamic world, asuka and nara periods (538–794), athenian vase painting: black- and red-figure techniques, athletics in ancient greece, augustan rule (27 b.c.–14 a.d.), the augustan villa at boscotrecase, auguste renoir (1841–1919), auguste rodin (1840–1917), augustus saint-gaudens (1848–1907), aztec stone sculpture, the bamana ségou state, barbarians and romans, the barbizon school: french painters of nature, baroque rome, baseball cards in the jefferson r. burdick collection, bashford dean and the development of helmets and body armor during world war i, baths and bathing culture in the middle east: the hammam, the bauhaus, 1919–1933, benin chronology, bessie potter vonnoh (1872–1955), birds of the andes, birth and family in the italian renaissance, the birth and infancy of christ in italian painting, the birth of islam, blackwater draw (ca. 9500–3000 b.c.), blackwork: a new technique in the field of ornament prints (ca. 1585–1635), blown glass from islamic lands, board games from ancient egypt and the near east, body/landscape: photography and the reconfiguration of the sculptural object, the book of hours: a medieval bestseller, boscoreale: frescoes from the villa of p. fannius synistor, botanical imagery in european painting, bronze sculpture in the renaissance, bronze statuettes of the american west, 1850–1915, buddhism and buddhist art, building stories: contextualizing architecture at the cloisters, burgundian netherlands: court life and patronage, burgundian netherlands: private life, byzantine art under islam, the byzantine city of amorium, byzantine ivories, the byzantine state under justinian i (justinian the great), byzantium (ca. 330–1453), calligraphy in islamic art, cameo appearances, candace wheeler (1827–1923), capac hucha as an inca assemblage, caravaggio (michelangelo merisi) (1571–1610) and his followers, carolingian art, carpets from the islamic world, 1600–1800, cave sculpture from the karawari, ceramic technology in the seljuq period: stonepaste in syria and iran in the eleventh century, ceramic technology in the seljuq period: stonepaste in syria and iran in the twelfth and early thirteenth centuries, ceramics in the french renaissance, cerro sechín, cerro sechín: stone sculpture, the cesnola collection at the metropolitan museum of art, charles eames (1907–1978) and ray eames (1913–1988), charles frederick worth (1825–1895) and the house of worth, charles james (1906–1978), charles sheeler (1883–1965), chauvet cave (ca. 30,000 b.c.), childe hassam (1859–1935), chinese buddhist sculpture, chinese calligraphy, chinese cloisonné, chinese gardens and collectors’ rocks, chinese handscrolls, chinese hardstone carvings, chinese painting, the chiton, peplos, and himation in modern dress, the chopine, christian dior (1905–1957), christopher dresser (1834–1904), classical antiquity in the middle ages, classical art and modern dress, classical cyprus (ca. 480–ca. 310 b.c.), classicism in modern dress, claude lorrain (1604/5–1682), claude monet (1840–1926), coffee, tea, and chocolate in early colonial america, collecting for the kunstkammer, colonial kero cups, colossal temples of the roman near east, commedia dell’arte, company painting in nineteenth-century india, conceptual art and photography, constantinople after 1261, contemporary deconstructions of classical dress, contexts for the display of statues in classical antiquity, cosmic buddhas in the himalayas, costume in the metropolitan museum of art, the countess da castiglione, courtly art of the ilkhanids, courtship and betrothal in the italian renaissance, cristobal balenciaga (1895–1972), the croome court tapestry room, worcestershire, the crucifixion and passion of christ in italian painting, the crusades (1095–1291), the cult of the virgin mary in the middle ages, cut and engraved glass from islamic lands, cyprus—island of copper, daguerre (1787–1851) and the invention of photography, the daguerreian age in france: 1839–55, the daguerreian era and early american photography on paper, 1839–60, the damascus room, daniel chester french (1850–1931), daoism and daoist art, david octavius hill (1802–1870) and robert adamson (1821–1848), death, burial, and the afterlife in ancient greece, the decoration of arms and armor, the decoration of european armor, the decoration of tibetan arms and armor, design reform, design, 1900–1925, design, 1925–50, design, 1950–75, design, 1975–2000, the development of the recorder, direct versus indirect casting of small bronzes in the italian renaissance, divination and senufo sculpture in west africa, domenichino (1581–1641), domestic art in renaissance italy, donatello (ca. 1386–1466), drawing in the middle ages, dress rehearsal: the origins of the costume institute, dressing for the cocktail hour, dualism in andean art, duncan phyfe (1770–1854) and charles-honoré lannuier (1779–1819), dutch and flemish artists in rome, 1500–1600, eagles after the american revolution, early cycladic art and culture, early documentary photography, early dynastic sculpture, 2900–2350 b.c., early excavations in assyria, early histories of photography in west africa (1860–1910), early maori wood carvings, early modernists and indian traditions, early netherlandish painting, early photographers of the american west: 1860s–70s, early qur’ans (8th–early 13th century), east and west: chinese export porcelain, east asian cultural exchange in tiger and dragon paintings, easter island, eastern religions in the roman world, ebla in the third millennium b.c., edgar degas (1834–1917): bronze sculpture, edgar degas (1834–1917): painting and drawing, edo-period japanese porcelain, édouard baldus (1813–1889), édouard manet (1832–1883), edward hopper (1882–1967), edward j. steichen (1879–1973): the photo-secession years, edward lycett (1833–1910), egypt in the late period (ca. 664–332 b.c.), egypt in the middle kingdom (ca. 2030–1650 b.c.), egypt in the new kingdom (ca. 1550–1070 b.c.), egypt in the old kingdom (ca. 2649–2130 b.c.), egypt in the ptolemaic period, egypt in the third intermediate period (ca. 1070–664 b.c.), egyptian faience: technology and production, egyptian modern art, egyptian red gold, egyptian revival, egyptian tombs: life along the nile, eighteenth-century european dress, the eighteenth-century pastel portrait, eighteenth-century silhouette and support, eighteenth-century women painters in france, el greco (1541–1614), élisabeth louise vigée le brun (1755–1842), elizabethan england, elsa schiaparelli (1890–1973), empire style, 1800–1815, the empires of the western sudan, the empires of the western sudan: ghana empire, the empires of the western sudan: mali empire, the empires of the western sudan: songhai empire, enameled and gilded glass from islamic lands, english embroidery of the late tudor and stuart eras, english ornament prints and furniture books in eighteenth-century america, english silver, 1600–1800, ernest hemingway (1899–1961) and art, ernst emil herzfeld (1879–1948) in persepolis, ernst emil herzfeld (1879–1948) in samarra, etching in eighteenth-century france: artists and amateurs, the etching revival in nineteenth-century france, ethiopia’s enduring cultural heritage, ethiopian healing scrolls, etruscan art, etruscan language and inscriptions, eugène atget (1857–1927), europe and the age of exploration, europe and the islamic world, 1600–1800, european clocks in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, european exploration of the pacific, 1600–1800, european revivalism, european tapestry production and patronage, 1400–1600, european tapestry production and patronage, 1600–1800, exchange of art and ideas: the benin, owo, and ijebu kingdoms, exoticism in the decorative arts, extravagant monstrosities: gold- and silversmith designs in the auricular style, eynan/ain mallaha (12,500–10,000 b.c.), fabricating sixteenth-century netherlandish boxwood miniatures, the face in medieval sculpture, famous makers of arms and armors and european centers of production, fashion in european armor, fashion in european armor, 1000–1300, fashion in european armor, 1300–1400, fashion in european armor, 1400–1500, fashion in european armor, 1500–1600, fashion in european armor, 1600–1700, fashion in safavid iran, fatimid jewelry, fell’s cave (9000–8000 b.c.), fernand léger (1881–1955), feudalism and knights in medieval europe, figural representation in islamic art, filippino lippi (ca. 1457–1504), fire gilding of arms and armor, the five wares of south italian vase painting, the flavian dynasty (69–96 a.d.), flemish harpsichords and virginals, flood stories, folios from the great mongol shahnama (book of kings), folios from the jami‘ al-tavarikh (compendium of chronicles), fontainebleau, food and drink in european painting, 1400–1800, foundations of aksumite civilization and its christian legacy (1st–8th century), fra angelico (ca. 1395–1455), francisco de goya (1746–1828) and the spanish enlightenment, françois boucher (1703–1770), frank lloyd wright (1867–1959), frans hals (1582/83–1666), frederic edwin church (1826–1900), frederic remington (1861–1909), frederick william macmonnies (1863–1937), the french academy in rome, french art deco, french art pottery, french decorative arts during the reign of louis xiv (1654–1715), french faience, french furniture in the eighteenth century: case furniture, french furniture in the eighteenth century: seat furniture, french porcelain in the eighteenth century, french silver in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, frescoes and wall painting in late byzantine art, from geometric to informal gardens in the eighteenth century, from italy to france: gardens in the court of louis xiv and after, from model to monument: american public sculpture, 1865–1915, the fulani/fulbe people, the function of armor in medieval and renaissance europe, funerary vases in southern italy and sicily, furnishings during the reign of louis xiv (1654–1715), gabrielle “coco” chanel (1883–1971) and the house of chanel, gardens in the french renaissance, gardens of western europe, 1600–1800, genre painting in northern europe, geometric abstraction, geometric and archaic cyprus, geometric art in ancient greece, geometric patterns in islamic art, george inness (1825–1894), george washington: man, myth, monument, georges seurat (1859–1891) and neo-impressionism, georgia o’keeffe (1887–1986), gerard david (born about 1455, died 1523), german and austrian porcelain in the eighteenth century, the ghent altarpiece, gian lorenzo bernini (1598–1680), gilbert stuart (1755–1828), giovanni battista piranesi (1720–1778), giovanni battista tiepolo (1696–1770), gladiators: types and training, glass from islamic lands, glass ornaments in late antiquity and early islam (ca. 500–1000), glass with mold-blown decoration from islamic lands, the gods and goddesses of canaan, gold in ancient egypt, gold in asante courtly arts, gold in the ancient americas, gold of the indies, the golden age of french furniture in the eighteenth century, the golden harpsichord of michele todini (1616–1690), golden treasures: the royal tombs of silla, goryeo celadon, the grand tour, the graphic art of max klinger, great plains indians musical instruments, great serpent mound, great zimbabwe (11th–15th century), the greater ottoman empire, 1600–1800, greek art in the archaic period, greek gods and religious practices, greek hydriai (water jars) and their artistic decoration, the greek key and divine attributes in modern dress, greek terracotta figurines with articulated limbs, gustave courbet (1819–1877), gustave le gray (1820–1884), hagia sophia, 532–37, the halaf period (6500–5500 b.c.), han dynasty (206 b.c.–220 a.d.), hanae mori (1926–2022), hans talhoffer’s fight book, a sixteenth-century manuscript about the art of fighting, harry burton (1879–1940): the pharaoh’s photographer, hasanlu in the iron age, haute couture, heian period (794–1185), hellenistic and roman cyprus, hellenistic jewelry, hendrick goltzius (1558–1617), henri cartier-bresson (1908–2004), henri de toulouse-lautrec (1864–1901), henri matisse (1869–1954), henry kirke brown (1814–1886), john quincy adams ward (1830–1910), and realism in american sculpture, heroes in italian mythological prints, hinduism and hindu art, hippopotami in ancient egypt, hiram powers (1805–1873), the hittites, the holy roman empire and the habsburgs, 1400–1600, hopewell (1–400 a.d.), horse armor in europe, hot-worked glass from islamic lands, the house of jeanne hallée (1870–1924), the housemistress in new kingdom egypt: hatnefer, how medieval and renaissance tapestries were made, the hudson river school, hungarian silver, icons and iconoclasm in byzantium, the idea and invention of the villa, ife (from ca. 6th century), ife pre-pavement and pavement era (800–1000 a.d.), ife terracottas (1000–1400 a.d.), igbo-ukwu (ca. 9th century), images of antiquity in limoges enamels in the french renaissance, impressionism: art and modernity, in pursuit of white: porcelain in the joseon dynasty, 1392–1910, indian knoll (3000–2000 b.c.), indian textiles: trade and production, indigenous arts of the caribbean, industrialization and conflict in america: 1840–1875, the industrialization of french photography after 1860, inland niger delta, intellectual pursuits of the hellenistic age, intentional alterations of early netherlandish painting, interior design in england, 1600–1800, interiors imagined: folding screens, garments, and clothing stands, international pictorialism, internationalism in the tang dynasty (618–907), introduction to prehistoric art, 20,000–8000 b.c., the isin-larsa and old babylonian periods (2004–1595 b.c.), islamic arms and armor, islamic art and culture: the venetian perspective, islamic art of the deccan, islamic carpets in european paintings, italian painting of the later middle ages, italian porcelain in the eighteenth century, italian renaissance frames, ivory and boxwood carvings, 1450–1800, ivory carving in the gothic era, thirteenth–fifteenth centuries, jacopo dal ponte, called bassano (ca. 1510–1592), jade in costa rica, jade in mesoamerica, jain manuscript painting, jain sculpture, james cox (ca. 1723–1800): goldsmith and entrepreneur, james mcneill whistler (1834–1903), james mcneill whistler (1834–1903) as etcher, jan gossart (ca. 1478–1532) and his circle, jan van eyck (ca. 1390–1441), the japanese blade: technology and manufacture, japanese illustrated handscrolls, japanese incense, the japanese tea ceremony, japanese weddings in the edo period (1615–1868), japanese writing boxes, jasper johns (born 1930), jean antoine houdon (1741–1828), jean honoré fragonard (1732–1806), jean-baptiste carpeaux (1827–1875), jean-baptiste greuze (1725–1805), jewish art in late antiquity and early byzantium, jews and the arts in medieval europe, jews and the decorative arts in early modern italy, jiahu (ca. 7000–5700 b.c.), joachim tielke (1641–1719), joan miró (1893–1983), johannes vermeer (1632–1675), johannes vermeer (1632–1675) and the milkmaid, john constable (1776–1837), john frederick kensett (1816–1872), john singer sargent (1856–1925), john singleton copley (1738–1815), john townsend (1733–1809), jōmon culture (ca. 10,500–ca. 300 b.c.), joseon buncheong ware: between celadon and porcelain, joseph mallord william turner (1775–1851), juan de flandes (active by 1496, died 1519), julia margaret cameron (1815–1879), the julio-claudian dynasty (27 b.c.–68 a.d.), kamakura and nanbokucho periods (1185–1392), the kano school of painting, kingdoms of madagascar: malagasy funerary arts, kingdoms of madagascar: malagasy textile arts, kingdoms of madagascar: maroserana and merina, kingdoms of the savanna: the kuba kingdom, kingdoms of the savanna: the luba and lunda empires, kings and queens of egypt, kings of brightness in japanese esoteric buddhist art, the kirtlington park room, oxfordshire, the kithara in ancient greece, kodak and the rise of amateur photography, kofun period (ca. 300–710), kongo ivories, korean buddhist sculpture (5th–9th century), korean munbangdo paintings, kushan empire (ca. second century b.c.–third century a.d.), la venta: sacred architecture, la venta: stone sculpture, the labors of herakles, lacquerware of east asia, landscape painting in chinese art, landscape painting in the netherlands, the lansdowne dining room, london, lapita pottery (ca. 1500–500 b.c.), lascaux (ca. 15,000 b.c.), late eighteenth-century american drawings, late medieval german sculpture, late medieval german sculpture: images for the cult and for private devotion, late medieval german sculpture: materials and techniques, late medieval german sculpture: polychromy and monochromy, the later ottomans and the impact of europe, le colis de trianon-versailles and paris openings, the legacy of genghis khan, the legacy of jacques louis david (1748–1825), leonardo da vinci (1452–1519), letterforms and writing in contemporary art, life of jesus of nazareth, life of the buddha, list of rulers of ancient egypt and nubia, list of rulers of ancient sudan, list of rulers of byzantium, list of rulers of china, list of rulers of europe, list of rulers of japan, list of rulers of korea, list of rulers of mesopotamia, list of rulers of south asia, list of rulers of the ancient greek world, list of rulers of the islamic world, list of rulers of the parthian empire, list of rulers of the roman empire, list of rulers of the sasanian empire, lithography in the nineteenth century, longevity in chinese art, louis comfort tiffany (1848–1933), louis-rémy robert (1810–1882), lovers in italian mythological prints, the lure of montmartre, 1880–1900, luxury arts of rome, lydenburg heads (ca. 500 a.d.), lydia and phrygia, made in india, found in egypt: red sea textile trade in the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries, made in italy: italian fashion from 1950 to now, the magic of signs and patterns in north african art, maiolica in the renaissance, mal’ta (ca. 20,000 b.c.), mangarevan sculpture, the manila galleon trade (1565–1815), mannerism: bronzino (1503–1572) and his contemporaries, the mantiq al-tair (language of the birds) of 1487, manuscript illumination in italy, 1400–1600, manuscript illumination in northern europe, mapungubwe (ca. 1050–1270), marcel duchamp (1887–1968), maria monaci gallenga (1880–1944), mary stevenson cassatt (1844–1926), the master of monte oliveto (active about 1305–35), the materials and techniques of american quilts and coverlets, the materials and techniques of english embroidery of the late tudor and stuart eras, mauryan empire (ca. 323–185 b.c.), medicine in classical antiquity, medicine in the middle ages, medieval aquamanilia, medieval european sculpture for buildings, medusa in ancient greek art, mendicant orders in the medieval world, the mesoamerican ballgame, mesopotamian creation myths, mesopotamian deities, mesopotamian magic in the first millennium b.c., the metropolitan museum’s excavations at nishapur, the metropolitan museum’s excavations at ctesiphon, the metropolitan museum’s excavations at qasr-i abu nasr, michiel sweerts and biblical subjects in dutch art, the middle babylonian / kassite period (ca. 1595–1155 b.c.) in mesopotamia, military music in american and european traditions, ming dynasty (1368–1644), minoan crete, mission héliographique, 1851, miyake, kawakubo, and yamamoto: japanese fashion in the twentieth century, moche decorated ceramics, moche portrait vessels, modern and contemporary art in iran, modern art in india, modern art in west and east pakistan, modern art in west asia: colonial to post-colonial, modern materials: plastics, modern storytellers: romare bearden, jacob lawrence, faith ringgold, momoyama period (1573–1615), monasticism in western medieval europe, the mon-dvaravati tradition of early north-central thailand, the mongolian tent in the ilkhanid period, monte albán, monte albán: sacred architecture, monte albán: stone sculpture, monumental architecture of the aksumite empire, the monumental stelae of aksum (3rd–4th century), mosaic glass from islamic lands, mountain and water: korean landscape painting, 1400–1800, muromachi period (1392–1573), music and art of china, music in ancient greece, music in the ancient andes, music in the renaissance, musical instruments of oceania, musical instruments of the indian subcontinent, musical terms for the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, mycenaean civilization, mystery cults in the greek and roman world, nabataean kingdom and petra, the nabis and decorative painting, nadar (1820–1910), the nahal mishmar treasure, nature in chinese culture, the nature of islamic art, the neoclassical temple, neoclassicism, neolithic period in china, nepalese painting, nepalese sculpture, netsuke: from fashion fobs to coveted collectibles, new caledonia, the new documentary tradition in photography, new ireland, new vision photography, a new visual language transmitted across asia, the new york dutch room, nicolas poussin (1594–1665), nineteenth-century american drawings, nineteenth-century american folk art, nineteenth-century american jewelry, nineteenth-century american silver, nineteenth-century classical music, nineteenth-century court arts in india, nineteenth-century english silver, nineteenth-century european textile production, nineteenth-century french realism, nineteenth-century iran: art and the advent of modernity, nineteenth-century iran: continuity and revivalism, nineteenth-century silhouette and support, nok terracottas (500 b.c.–200 a.d.), northern italian renaissance painting, northern mannerism in the early sixteenth century, northern song dynasty (960–1127), northwest coast indians musical instruments, the nude in baroque and later art, the nude in the middle ages and the renaissance, the nude in western art and its beginnings in antiquity, nudity and classical themes in byzantine art, nuptial furnishings in the italian renaissance, the old assyrian period (ca. 2000–1600 b.c.), orientalism in nineteenth-century art, orientalism: visions of the east in western dress, the origins of writing, ottonian art, pablo picasso (1881–1973), pachmari hills (ca. 9000–3000 b.c.), painted funerary monuments from hellenistic alexandria, painting formats in east asian art, painting in italian choir books, 1300–1500, painting in oil in the low countries and its spread to southern europe, painting the life of christ in medieval and renaissance italy, paintings of love and marriage in the italian renaissance, paolo veronese (1528–1588), the papacy and the vatican palace, the papacy during the renaissance, papyrus in ancient egypt, papyrus-making in egypt, the parthian empire (247 b.c.–224 a.d.), pastoral charms in the french renaissance, patronage at the early valois courts (1328–1461), patronage at the later valois courts (1461–1589), patronage of jean de berry (1340–1416), paul cézanne (1839–1906), paul gauguin (1848–1903), paul klee (1879–1940), paul poiret (1879–1944), paul revere, jr. (1734–1818), paul strand (1890–1976), period of the northern and southern dynasties (386–581), peter paul rubens (1577–1640) and anthony van dyck (1599–1641): paintings, peter paul rubens (1577–1640) and anthony van dyck (1599–1641): works on paper, petrus christus (active by 1444, died 1475/76), the phoenicians (1500–300 b.c.), photographers in egypt, photography and surrealism, photography and the civil war, 1861–65, photography at the bauhaus, photography in düsseldorf, photography in europe, 1945–60, photography in postwar america, 1945-60, photography in the expanded field: painting, performance, and the neo-avant-garde, photojournalism and the picture press in germany, phrygia, gordion, and king midas in the late eighth century b.c., the piano: the pianofortes of bartolomeo cristofori (1655–1731), the piano: viennese instruments, pictorialism in america, the pictures generation, pierre bonnard (1867–1947): the late interiors, pierre didot the elder (1761–1853), pieter bruegel the elder (ca. 1525–1569), pilgrimage in medieval europe, poetic allusions in the rajput and pahari painting of india, poets in italian mythological prints, poets, lovers, and heroes in italian mythological prints, polychrome sculpture in spanish america, polychromy of roman marble sculpture, popular religion: magical uses of imagery in byzantine art, portrait painting in england, 1600–1800, portraits of african leadership, portraits of african leadership: living rulers, portraits of african leadership: memorials, portraits of african leadership: royal ancestors, portraiture in renaissance and baroque europe, the portuguese in africa, 1415–1600, post-impressionism, postmodernism: recent developments in art in india, postmodernism: recent developments in art in pakistan and bangladesh, post-revolutionary america: 1800–1840, the postwar print renaissance in america, poverty point (2000–1000 b.c.), the praenestine cistae, prague during the rule of rudolf ii (1583–1612), prague, 1347–1437, pre-angkor traditions: the mekong delta and peninsular thailand, precisionism, prehistoric cypriot art and culture, prehistoric stone sculpture from new guinea, the pre-raphaelites, presidents of the united states of america, the print in the nineteenth century, the printed image in the west: aquatint, the printed image in the west: drypoint, the printed image in the west: engraving, the printed image in the west: etching, the printed image in the west: history and techniques, the printed image in the west: mezzotint, the printed image in the west: woodcut, printmaking in mexico, 1900–1950, private devotion in medieval christianity, profane love and erotic art in the italian renaissance, the pyramid complex of senwosret iii, dahshur, the pyramid complex of senwosret iii, dahshur: private tombs to the north, the pyramid complex of senwosret iii, dahshur: queens and princesses, the pyramid complex of senwosret iii, dahshur: temples, qin dynasty (221–206 b.c.), the qing dynasty (1644–1911): courtiers, officials, and professional artists, the qing dynasty (1644–1911): loyalists and individualists, the qing dynasty (1644–1911): painting, the qing dynasty (1644–1911): the traditionalists, the rag-dung, rare coins from nishapur, recognizing the gods, the rediscovery of classical antiquity, the reformation, relics and reliquaries in medieval christianity, religion and culture in north america, 1600–1700, the religious arts under the ilkhanids, the religious relationship between byzantium and the west, rembrandt (1606–1669): paintings, rembrandt van rijn (1606–1669): prints, renaissance drawings: material and function, renaissance keyboards, renaissance organs, renaissance velvet textiles, renaissance violins, retrospective styles in greek and roman sculpture, rinpa painting style, the rise of macedon and the conquests of alexander the great, the rise of modernity in south asia, the rise of paper photography in 1850s france, the rise of paper photography in italy, 1839–55, the rock-hewn churches of lalibela, roger fenton (1819–1869), the roman banquet, roman cameo glass, roman copies of greek statues, roman egypt, the roman empire (27 b.c.–393 a.d.), roman games: playing with animals, roman glass, roman gold-band glass, roman housing, roman inscriptions, roman luxury glass, roman mold-blown glass, roman mosaic and network glass, roman painting, roman portrait sculpture: republican through constantinian, roman portrait sculpture: the stylistic cycle, the roman republic, roman sarcophagi, roman stuccowork, romanesque art, romanticism, saint petersburg, saints and other sacred byzantine figures, saints in medieval christian art, the salon and the royal academy in the nineteenth century, san ethnography, sanford robinson gifford (1823–1880), the sasanian empire (224–651 a.d.), scenes of everyday life in ancient greece, scholar-officials of china, school of paris, seasonal imagery in japanese art, the seleucid empire (323–64 b.c.), senufo arts and poro initiation in northern côte d’ivoire, senufo sculpture from west africa: an influential exhibition at the museum of primitive art, new york, 1963, seventeenth-century european watches, the severan dynasty (193–235 a.d.), sèvres porcelain in the nineteenth century, shah ‘abbas and the arts of isfahan, the shah jahan album, the shahnama of shah tahmasp, shaker furniture, shakespeare and art, 1709–1922, shakespeare portrayed, shang and zhou dynasties: the bronze age of china, shoes in the costume institute, shōguns and art, shunga dynasty (ca. second–first century b.c.), sienese painting, silk textiles from safavid iran, 1501–1722, silks from ottoman turkey, silver in ancient egypt, sixteenth-century painting in emilia-romagna, sixteenth-century painting in lombardy, sixteenth-century painting in venice and the veneto, the solomon islands, south asian art and culture, southern italian vase painting, southern song dynasty (1127–1279), the spanish guitar, spiritual power in the arts of the toba batak, stained (luster-painted) glass from islamic lands, stained glass in medieval europe, still-life painting in northern europe, 1600–1800, still-life painting in southern europe, 1600–1800, the structure of photographic metaphors, students of benjamin west (1738–1820), the symposium in ancient greece, takht-i sulaiman and tilework in the ilkhanid period, talavera de puebla, tanagra figurines, tang dynasty (618–907), the technique of bronze statuary in ancient greece, techniques of decoration on arms and armor, telling time in ancient egypt, tenochtitlan, tenochtitlan: templo mayor, teotihuacan: mural painting, teotihuacan: pyramids of the sun and the moon, textile production in europe: embroidery, 1600–1800, textile production in europe: lace, 1600–1800, textile production in europe: printed, 1600–1800, textile production in europe: silk, 1600–1800, theater and amphitheater in the roman world, theater in ancient greece, theseus, hero of athens, thomas chippendale’s gentleman and cabinet-maker’s director, thomas cole (1801–1848), thomas eakins (1844–1916): painting, thomas eakins (1844–1916): photography, 1880s–90s, thomas hart benton’s america today mural, thomas sully (1783–1872) and queen victoria, tibetan arms and armor, tibetan buddhist art, tikal: sacred architecture, tikal: stone sculpture, time of day on painted athenian vases, tiraz: inscribed textiles from the early islamic period, titian (ca. 1485/90–1576), the tomb of wah, trade and commercial activity in the byzantine and early islamic middle east, trade and the spread of islam in africa, trade between arabia and the empires of rome and asia, trade between the romans and the empires of asia, trade relations among european and african nations, trade routes between europe and asia during antiquity, traditional chinese painting in the twentieth century, the transatlantic slave trade, the transformation of landscape painting in france, the trans-saharan gold trade (7th–14th century), turkmen jewelry, turquoise in ancient egypt, tutankhamun’s funeral, tutsi basketry, twentieth-century silhouette and support, the ubaid period (5500–4000 b.c.), ubirr (ca. 40,000–present), umberto boccioni (1882–1916), unfinished works in european art, ca. 1500–1900, ur: the royal graves, ur: the ziggurat, uruk: the first city, valdivia figurines, vegetal patterns in islamic art, velázquez (1599–1660), venetian color and florentine design, venice and the islamic world, 828–1797, venice and the islamic world: commercial exchange, diplomacy, and religious difference, venice in the eighteenth century, venice’s principal muslim trading partners: the mamluks, the ottomans, and the safavids, the vibrant role of mingqi in early chinese burials, the vikings (780–1100), vincent van gogh (1853–1890), vincent van gogh (1853–1890): the drawings, violin makers: nicolò amati (1596–1684) and antonio stradivari (1644–1737), visual culture of the atlantic world, vivienne westwood (born 1941) and the postmodern legacy of punk style, wadi kubbaniya (ca. 17,000–15,000 b.c.), walker evans (1903–1975), wang hui (1632–1717), warfare in ancient greece, watercolor painting in britain, 1750–1850, ways of recording african history, weddings in the italian renaissance, west asia: ancient legends, modern idioms, west asia: between tradition and modernity, west asia: postmodernism, the diaspora, and women artists, william blake (1757–1827), william henry fox talbot (1800–1877) and the invention of photography, william merritt chase (1849–1916), winslow homer (1836–1910), wisteria dining room, paris, women artists in nineteenth-century france, women china decorators, women in classical greece, women leaders in african history, 17th–19th century, women leaders in african history: ana nzinga, queen of ndongo, women leaders in african history: dona beatriz, kongo prophet, women leaders in african history: idia, first queen mother of benin, woodblock prints in the ukiyo-e style, woodcut book illustration in renaissance italy: florence in the 1490s, woodcut book illustration in renaissance italy: the first illustrated books, woodcut book illustration in renaissance italy: venice in the 1490s, woodcut book illustration in renaissance italy: venice in the sixteenth century, wordplay in twentieth-century prints, work and leisure: eighteenth-century genre painting in korea, x-ray style in arnhem land rock art, yamato-e painting, yangban: the cultural life of the joseon literati, yayoi culture (ca. 300 b.c.–300 a.d.), the year one, years leading to the iranian revolution, 1960–79, yuan dynasty (1271–1368), zen buddhism, 0 && essaysctrl.themev == 'departments / collections' && essaysctrl.deptv == null">, departments / collections '">.
The Value of Art Why should we care about art?
One of the first questions raised when talking about art is simple—why should we care? Art in the contemporary era is easy to dismiss as a selfish pastime for people who have too much time on their hands. Creating art doesn't cure disease, build roads, or feed the poor. So to understand the value of art, let’s look at how art has been valued through history and consider how it is valuable today.
The value of creating
At its most basic level, the act of creating is rewarding in itself. Children draw for the joy of it before they can speak, and creating pictures, sculptures and writing is both a valuable means of communicating ideas and simply fun. Creating is instinctive in humans, for the pleasure of exercising creativity. While applied creativity is valueable in a work context, free-form creativity leads to new ideas.
Material value
Through the ages, art has often been created from valuable materials. Gold , ivory and gemstones adorn medieval crowns , and even the paints used by renaissance artists were made from rare materials like lapis lazuli , ground into pigment. These objects have creative value for their beauty and craftsmanship, but they are also intrinsically valuable because of the materials they contain.
Historical value
Artwork is a record of cultural history. Many ancient cultures are entirely lost to time except for the artworks they created, a legacy that helps us understand our human past. Even recent work can help us understand the lives and times of its creators, like the artwork of African-American artists during the Harlem Renaissance . Artwork is inextricably tied to the time and cultural context it was created in, a relationship called zeitgeist , making art a window into history.
Religious value
For religions around the world, artwork is often used to illustrate their beliefs. Depicting gods and goddesses, from Shiva to the Madonna , make the concepts of faith real to the faithful. Artwork has been believed to contain the spirits of gods or ancestors, or may be used to imbue architecture with an aura of awe and worship like the Badshahi Mosque .
Patriotic value
Art has long been a source of national pride, both as an example of the skill and dedication of a country’s artisans and as expressions of national accomplishments and history, like the Arc de Triomphe , a heroic monument honoring the soldiers who died in the Napoleonic Wars. The patriotic value of art slides into propaganda as well, used to sway the populace towards a political agenda.
Symbolic value
Art is uniquely suited to communicating ideas. Whether it’s writing or painting or sculpture, artwork can distill complex concepts into symbols that can be understood, even sometimes across language barriers and cultures. When art achieves symbolic value it can become a rallying point for a movement, like J. Howard Miller’s 1942 illustration of Rosie the Riveter, which has become an icon of feminism and women’s economic impact across the western world.
Societal value
And here’s where the rubber meets the road: when we look at our world today, we see a seemingly insurmountable wave of fear, bigotry, and hatred expressed by groups of people against anyone who is different from them. While issues of racial and gender bias, homophobia and religious intolerance run deep, and have many complex sources, much of the problem lies with a lack of empathy. When you look at another person and don't see them as human, that’s the beginning of fear, violence and war. Art is communication. And in the contemporary world, it’s often a deeply personal communication. When you create art, you share your worldview, your history, your culture and yourself with the world. Art is a window, however small, into the human struggles and stories of all people. So go see art, find art from other cultures, other religions, other orientations and perspectives. If we learn about each other, maybe we can finally see that we're all in this together. Art is a uniquely human expression of creativity. It helps us understand our past, people who are different from us, and ultimately, ourselves.
Reed Enger, "The Value of Art, Why should we care about art?," in Obelisk Art History , Published June 24, 2017; last modified November 08, 2022, http://www.arthistoryproject.com/essays/the-value-of-art/.
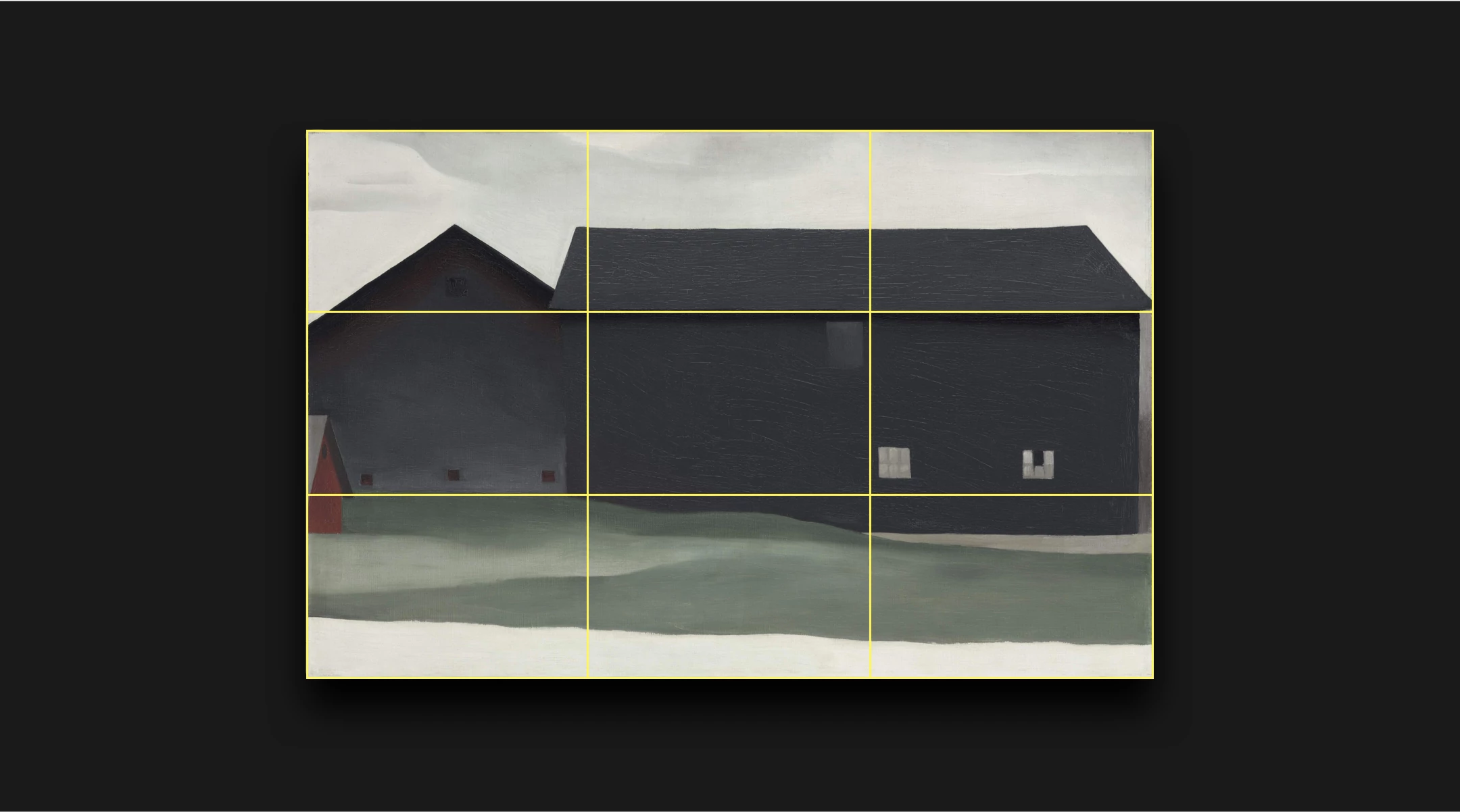

Basic Composition Techniques
A few easy tips

Is there such a thing as Bad Art?
Yes, but it's complicated

Art History Methodologies
Eight ways to understand art
By continuing to browse Obelisk you agree to our Cookie Policy
DEPARTMENT OF ART HISTORY
Why study art history.
Art history provides an excellent opportunity to develop the essential skills and talents that lie at the core of a good liberal arts education, including informed and critical reading, writing, and speaking. To these, it adds a particular attention to critical looking, building core skills in analyzing how the visual and physical qualities of buildings, images and objects can be used to communicate. In art history, we study the art and architecture of cultures around the world and across the millennia. We take a variety of approaches to our objects, but focus on understanding their aesthetic and historical significance as well as their social relevance. We ask how people make meaning in visual terms and, in turn, how we read and understand a world that is largely presented to us as visual information. Since Chicago is fortunate enough to boast a large number of world-famous museum collections and some of the world’s most extraordinary architecture, many of our classes emphasize on-site study and field trips.
With its broad historical, cultural, geographic, and methodological range, art history satisfies the expectations of burgeoning specialists while it also offers an excellent formation for those who intend to specialize in other areas. While many of our majors go on to careers in museums, galleries, arts reporting or academe, many others have successfully brought the skills honed in art history classrooms to the worlds of business, law, medicine and international relations.

Site Content
Essays on art and science.
Eric R. Kandel
Columbia University Press

Pub Date: March 2024
ISBN: 9780231212564
Format: Hardcover
List Price: $26.95 £22.00
Shipping Options
Purchasing options are not available in this country.
ISBN: 9780231559454
Format: E-book
List Price: $25.99 £22.00
- EPUB via the Columbia UP App
- PDF via the Columbia UP App
Anything Eric R. Kandel says about neuroscience or the relationship between art and neuroscience is noteworthy. He is not only brilliant at explaining difficult and complex scientific ideas and data in simple language but also well-informed about—and sympathetic to—twentieth-century art, and avails himself of an impressive range of art-historical literature. Nancy Princenthal, author of Unspeakable Acts: Women, Art, and Sexual Violence in the 1970s, and Joseph E. LeDoux, Henry And Lucy Moses Professor of Science, New York University
A lively, erudite inquiry into the experience of art. Kirkus Reviews
Eric R. Kandel’s ‘Essays on Art and Science’ is a fascinating, thought-provoking read that beautifully articulates the complex interplay between our brain’s inner workings and our emotional responses to art. It’s a testament to Kandel’s expertise and ability to make science approachable and relevant to our everyday experiences with art. This book is a must-read for anyone interested in the profound ways in which art and science intersect to define our perception of the world. Mental Health Affairs
- Read an excerpt in Book Post
- Read an excerpt "The Creative Brain" from as published in The Transmitter
About the Author
- Neuroscience and Biopsychology
- Neuropsychology
- Fine Arts and Art History
- Icon Link Plus Icon
Datebook: The Art World’s Summer Happenings to Add to Your Calendar
By Art in America
Art in America

The Art of Dying: Writings, 2019–2022 by Peter Schjeldahl

Few who read Peter Schjeldahl’s essay “The Art of Dying” when it was published in the New Yorker in late 2019 will ever forget its gimlet-eyed stare-down with death, but even more stirring was the fact that the fabled art critic managed to keep writing for nearly three years more. This book starts with the namesake masterpiece and collects all the rest of his words for the magazine until the end. On sale May 14
“Hilary Heron: A Retrospective” at the Irish Museum of Modern Art

In her 1949 sculpture Flight into Egypt , the Irish modernist Hilary Heron represented an episode from the book of Matthew as a highly abstracted form riding a barely visible horse on the march. The sculpture was, for her, a way of bringing the past into the present, and was intended to encompass the existentialist themes broached by others around her, including a distant relative, the playwright Samuel Beckett. The first Heron retrospective in decades will be mounted in Dublin, the city where she was born. May 24–Nov. 3
“Mickalene Thomas: All About Love” at the The Broad

In mixed-media paintings, installations, photographs, and more, Mickalene Thomas has foregrounded strong Black women in states of searching and selfassuredness. This survey—opening at the Broad in Los Angeles before moving on to the Barnes Foundation in Philadelphia and the Hayward Gallery in London— features 80 works made over the past 20 years, all assembled under an exhibition title borrowed from feminist writer bell hooks. May 25–Sept. 29
“In the House of the Trembling Eye: an exhibition staged by Allison Katz” at the Aspen Art Museum

At the 2022 Venice Biennale, Allison Katz exhibited a painting of two roosters dropping feed into a vessel; its style recalled that of mosaics found throughout Italy. Katz will return to ancient subject matter with this museum-filling show in Colorado rooted in her research into Pompeii, the Roman city famously buried in ash when Mount Vesuvius erupted. The rising Canadian painter has teased borrowing fresco fragments and other centuries-old objects for this exhibition, the details of which have been kept under wraps. May 29–Sept. 29
“Cindy Sherman at Cycladic: Early Works” at the Museum of Cycladic Art

Though not nearly as old as the works most commonly shown at this Athens institution, the formative offerings of photographer Cindy Sherman still mark the beginning of an era of sorts. More than 100 works from the 1970s and ’80s will feature in what’s being touted as Sherman’s first Athenian museum show, including photos from her epochal early series “Untitled Film Stills,” “Rear Screen Projections,” “Centerfolds,” and “Color Studies,” which helped expand the purview of self-portraiture in new narrative ways. May 30–Nov. 4
Arooj Aftab, Night Reign

On the rise as a singersongwriter of otherworldly talent, Arooj Aftab was born in Saudi Arabia to Pakistani expatriates who returned to their homeland in the ’90s. Since she moved to the United States to go to the Berklee College of Music, she has collaborated with musicians who have coursed in and around the art scene, including adventurous jazz pianist Vijay Iyer, poet/ singer Moor Mother, and DJ/composer Jace Clayton, among others. This gorgeous new album stands to expand her audience even further. On sale May 31
“Georgia O’Keeffe: ‘My New Yorks’” at the Art Institute of Chicago

With a wide-ranging array of themed shows—from a regrettable consideration of her sartorial style at the Brooklyn Museum in 2017 to a striking survey of her works on paper at MoMA last year—Georgia O’Keeffe has not lacked for attention of late. The most recent addition to her exhibition annals takes inspiration from the artist’s visions of New York City starting with her move into a Manhattan skyscraper in 1924. It will also include other paintings, drawings, and pastels from the ’20s and ’30s, all with a mind to expand conceptions of O’Keeffe, who is still most closely aligned with her flower paintings. June 2–Sept. 22
Zanele Muholi at Tate Modern

More than 260 photographs will feature in this comprehensive survey of the self-described “visual activist” who serves as a sharp-eyed chronicler of life in South Africa. Zanele Muholi often photographs LGBTQIA+ people, but the artist is most famous for self-portraits in which they project real power from their eyes, staring down their viewers and inviting them in at the same time. June 6–Jan. 26
Parade by Rachel Cusk

Writer Rachel Cusk is an art world favorite for her lucid meditations on artists and their work: her 2019 essay on painter Celia Paul’s tumultuous relationship with Lucian Freud, for example, tackled gendered power imbalances with her usual directness. In this new novel, she delves into the lives of artists in a much more abstract manner. Her focus is G, a male artist whose prismatic life involves instances of violence, both metaphorical and not. On sale June 18
“Toyin Ojih Odutola: Ilé Oriaku” at Kunsthalle Basel

The striking figurative works of Nigerian-born Toyin Ojih Odutola have become extraordinarily familiar without losing any of their power and poise. For her first solo institutional show in Switzerland, the artist—who favors materials including charcoal, pastel, and pencil—is showing all new works under a title that translates as “House of Abundance.” June 7–Sept. 1
“David Medalla: In Conversation with the Cosmos” at the Hammer Museum

How does one curate an institutional survey for an artist whose work resists being shown in museums? That is a question that guides this Los Angeles show for David Medalla, a Filipino artist whose most memorable work, A Stitch in Time ( 1968), began with his offering romantic partners handkerchiefs on which they could sew whatever they liked. Several decades before the rise of relational aesthetics in the ’90s, Medalla produced art whose essence was conversation and interpersonal exchange. The challenge for the Hammer will be whether those artworks still come alive, even when exhibited as mere objects. June 9–Sept. 15
Shara Hughes at Galerie Eva Presenhuber

One of the highlights of Zurich Art Weekend—just a one-hour train ride from the buzz of Art Basel, which opens a few days later—will be the next gallery show for the ascendant New York–based painter Shara Hughes, whose abstracted landscapes blaze with color. For her fifth solo show with Eva Presenhuber, the artist will fill the gallery’s Waldmannstrasse location with new large-scale paintings of trees, with a mind toward creating a forest of sorts. June 7–July 20

The fairest of all the art fairs will host 287 galleries from 40 countries this year, with 22 new enterprises joining the ranks. It will also be the first edition fully under the direction of Maike Cruse, whom former Art Basel Miami Beach director Noah Horowitz hired after assuming his role as the fair’s chief executive in 2022. Also of note: this year’s Parcours section, which adopts Basel itself as a canvas and exhibition space, will be organized by Stefanie Hessler, director of New York’s Swiss Institute. June 13–16
“The Deep West Assembly: Cauleen Smith” at the Astrup Fearnley Museum

“The Wanda Coleman Songbook,” Cauleen Smith’s recent show at 52 Walker gallery in New York, was a tender tribute to the Los Angeles poet that contained very few of her words spoken aloud. Instead, Smith alluded to Coleman’s writings through commissioned music and an expansive video installation filled with images of LA freeways. That work, like many other films by Smith, reflected on the multitude of ways that Black history is all around us. This show in Oslo will include a new film installation commissioned for the occasion, plus screenings of other films in her oeuvre. June 14–Sept. 15
“Poke in the Eye: Art of the West Coast Counterculture” at the Seattle Art Museum

While the New York avant-garde was a spirited community in the 1960s and ’70s, the scene on the West Coast was at least as restless—and often in wilder and weirder ways. The description of this show refers to “senselessness, absurdity, and fun,” as cited from writing around the antiestablishment Funk art movement in the Bay Area, and it promises works drawn from up and down the coast. June 21–Sept. 2
“Ho Tzu Nyen: Time and the Tiger” at the CCS Bard Hessel Museum of Art

Between 2012 and 2017, Ho Tzu Nyen created five videos about tigers that take up aspects of Southeast Asian history, mulling the painful legacy of colonialism in the region through a mix of fact and fiction. The powerful stories about loss told through these videos—British colonizers nearly hunted Malayan tigers out of existence—have made Ho one of Singapore’s most celebrated artists. Now, this midcareer survey at Bard College in Upstate New York allows US audiences to see why. June 22–Dec. 1
Dancing on My Own: Essays on Art, Collectivity, and Joy by Simon Wu

Taking his title from an anthem of steely defiance by the Swedish pop star Robyn, Simon Wu offers writings on art (from the mind of a critic, curator, and Art in America contributor) and such other topics as “the complicated sensation of the Telfar bag” and “clutter in his mother’s suburban garage and its meaning for himself and his family.” On sale June 25
“Gauguin’s World: Tōna Iho, Tōna Ao” at the National Gallery of Australia

As Paul Gauguin’s legacy continues to be reevaluated and revised, this show in the Australian capital of Canberra draws on some 140 of the artist’s best-known works, and promises new readings of them by way of contemporary perspectives. Noting that “in today’s context, Gauguin’s interactions in Polynesia in the later part of the 19th Century would not be accepted,” the show—curated by former Louvre Museum and Musée d’Orsay director Henri Loyrette—will delve beneath the surface of his paintings, viewing his art against the backdrop of colonialism. (The show travels to the Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, later in 2024.) June 29–Oct. 7
“I.M. Pei: Life Is Architecture” at M+

Billed as the first major retrospective for one of the 20th century’s most famous architects, this show in Hong Kong will feature drawings, sketches, videos, models, photographs, and documentation related to I.M. Pei’s many high-profile projects around the world. It will also include newly commissioned photographs of his buildings by seven “new generation” photographers, and models of built and unbuilt projects made in collaboration with local architecture schools. Opens June 29
“Samia Halaby: Eye Witness” at the MSU Broad Art Museum

This exhibition became an unexpected cause célèbre earlier this year when Indiana University, whose museum was meant to debut it, abruptly canceled the show, fueling speculation about what role Samia Halaby’s Palestinian nationality played in the decision. Now, the show at least has the benefit of opening at the artist’s alma mater, Michigan State University, during the Venice Biennale, where her lush abstractions are also currently on display. Expect the surge in interest in the 87-year-old painter, whose art has explicitly addressed forms of Palestinian resistance, to garner attention for this modest survey. June 29–Dec. 15
Rencontres d’Arles

Those making a summertime pilgrimage to Arles, the French city most closely associated with Vincent van Gogh, to toast Impressionism’s 150th anniversary will want to extend their stay for this photography festival, widely regarded as one of the best of its kind worldwide. The show offers many notable photography surveys, both well-known and not. See them all here, in one place, before they travel the globe. July 1–Sept. 29
Tokyo Gendai

During the inaugural edition of this fair last year, cofounder Magnus Renfrew called it “the beginning of a new chapter for the art scene in Japan.” The fair will now have a chance to bear that out in its second go-round, with sales generated by its mix of international blue-chip galleries and Tokyo-based enterprises likely acting as a litmus test for the Japanese art world’s strength. July 5–7
“Teresita Fernández/Robert Smithson” at SITE Santa Fe

This artist-driven exhibition curated by Teresita Fernández and Holt/Smithson Foundation director Lisa Le Feuvre will focus on two intergenerational artists’ “shared desire to recontextualize the complexities of art addressing the land.” Fernández and the late Robert Smithson—who helped define Land art in the 1960s and ’70s—will each be represented by some 30 works, and there’s good reason to think those works will take on new resonance in relation to each other. July 5–Oct. 28
“Martha Diamond: Deep Time” at the Colby College Museum of Art

Opening in Maine before making its way to the Aldrich Contemporary Art Museum in Connecticut this fall, this Martha Diamond survey covers five decades of a career devoted to painting pitched in the fertile middle of a lot of different movements. Diamond rendered her native New York City in forms that are both concrete and abstract, and enough of both to make the notion of choosing one or the other a fool’s errand. Diamond died this past December at the age of 79, and her first major monograph accompanies the show. July 13–Oct. 13
“Walter Price: Pearl Lines” at the Walker Art Center

American painter Walter Price creates large canvases that verge on inscrutability. They feature Black figures that fade in and out of focus, traversing vague landscapes that melt into abstraction. The sense of mystery these works convey extends even to Price’s shows themselves—he has titled nearly all his solo outings “Pearl Lines,” suggesting they are all related in ways that are not immediately obvious. This biggest of the artist’s surveys to date—in Minneapolis, and also called “Pearl Lines”—may enable viewers to crack Price’s code. Aug. 8–Dec. 8
A Complicated Passion: The Life and Work of Agnès Varda by Carrie Rickey

Five years on from her death, photographer and filmmaker Agnès Varda is inscribed in both film and art history, with the Criterion Collection releasing her entire filmography, and museums in France and Spain staging shows of her installations. Varda mania has fully arrived—and stands to continue with this new biography from Carrie Rickey, a former film critic for the Philadelphia Inquirer, who shows how the French New Wave filmmaker’s life inspired her deceptively light meditations on the passage of time, women’s rights, and more. On sale Aug. 13
“Leonilson: Now and Opportunity” at the Museu de Arte de São Paulo

Leonilson had a habit of associating Portuguese words with the wrong gender, a small act of rule-breaking that was mirrored by purposeful infractions in his art, which explicitly addressed his HIV diagnosis at a time when doing so was still taboo. Although he died at 36, the Brazilian artist left behind a formidable store of paintings, embroidered works, and installations that addressed fragile bodies and marginalization. His final years form the basis of this 150-work show, which is being staged amid a yearlong series of exhibitions about queerness at MASP. Aug. 23–Nov. 17
A Shipping Magnate’s New Orleans Penthouse Hits the Market for $17.5 Million
Exclusive: padma lakshmi and bare necessities cook up lingerie and swimwear collection, best apple deals for may 2024, cristiano ronaldo, binance sell nfts despite legal challenges, the best yoga mats for any practice, according to instructors.
ARTnews is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Art Media, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
A Documentary History of Art, Volume 1
- Elizabeth Gilmore Holt
Before you purchase audiobooks and ebooks
Please note that audiobooks and ebooks purchased from this site must be accessed on the Princeton University Press app. After you make your purchase, you will receive an email with instructions on how to download the app. Learn more about audio and ebooks .
Support your local independent bookstore.
- United States
- United Kingdom
Art & Architecture
A Documentary History of Art, Volume 1: The Middle Ages and the Renaissance
An illuminating one-volume compendium of primary documents on the art of medieval and Renaissance Europe

- Request Exam Copy
- Download Cover
This unique collection brings together notebooks, letters, treatises, and contracts dealing with the art of the Middle Ages and Renaissance, providing extraordinary insights into the personalities and conditions of the times and revealing the stylistic and philosophical concerns that evolved during these intensively creative eras. These documents, many of them available here in English for the first time, range from Raoul Glaber’s famous 1003 treatise on the synthesis of old and new art forms to Durand’s essay on Christian symbolism in art and the writings of Leonardo and Dürer on anatomy, perspective, and the recreation of reality. They trace how a medieval conception of life that was inspired, oriented, and dominated by the church evolved gradually into the great reawakening of the Renaissance in which humankind itself assumed primary importance in Western art.
Stay connected for new books and special offers. Subscribe to receive a welcome discount for your next order.
50% off sitewide with code FIFTY | May 7 – 31 | Some exclusions apply. See our FAQ .
- ebook & Audiobook Cart
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Morgan Spurlock, Documentarian Known for ‘Super Size Me,’ Dies at 53
His 2004 film followed Mr. Spurlock as he ate nothing but McDonald’s for a month. It was nominated for an Oscar, but it later came in for criticism.

By Clay Risen and Remy Tumin
Morgan Spurlock, a documentary filmmaker who gained fame with his Oscar-nominated 2004 film “ Super Size Me ,” which followed him as he ate nothing but McDonald’s for 30 days — but later stepped back from the public eye after admitting to sexual misconduct — died on Thursday in New York City. He was 53.
His brother Craig Spurlock said the cause was complications of cancer.
A self-described attention hound with a keen eye for the absurd, Mr. Spurlock was a playwright and television producer when he rocketed to global attention with “Super Size Me,” an early entry into the genre of gonzo participatory filmmaking that borrowed heavily from the confrontational style of Michael Moore and the up-close-and-personal influences of reality TV, which was then just emerging as a genre.
The film’s approach was straightforward: Mr. Spurlock would eat nothing but McDonald’s food for a month, and if a server at the restaurant offered to “supersize” the meal — that is, to give him the largest portion available for each item — he would accept.
The movie then follows Mr. Spurlock and his ever-patient girlfriend through his 30-day odyssey, splicing in interviews with health experts and visits to his increasingly disturbed physician. At the end of the month, he was 25 pounds heavier, depressed, puffy-faced and experiencing liver dysfunction.
The film, which debuted at the Sundance Film Festival, grossed over $22 million, made Mr. Spurlock a household name, earned him an Academy Award nomination for best documentary and helped spur a sweeping backlash against the fast-food industry — though only temporarily ; today, McDonald’s has 42,000 locations worldwide, its stock is near an all-time high, and 36 percent of Americans eat fast food on any given day.
“His movie,” the critic A.O. Scott wrote in The New York Times , “goes down easy and takes a while to digest, but its message is certainly worth the loss of your appetite.”
The film became a touchstone in American culture. By making himself a part of the story, Mr. Spurlock could be considered a forerunner of TikTok influencers and citizen-journalist YouTubers.
And even after the backlash against fast food subsided, “Super Size Me” remained a staple in high school health classes and a reference point for taking personal responsibility for one’s own diet.
But the film also came in for subsequent criticism. Some people pointed out that Mr. Spurlock refused to release the daily logs tracking his food intake. Health researchers were unable to replicate his results in controlled studies.
And in 2017, he admitted that he had not been sober for more than a week at a time in 30 years — meaning that, in addition to his “McDonald’s only” diet, he was drinking, a fact that he concealed from his doctors and the audience, and that most likely skewed his results.
The admission came in a statement in which he also revealed multiple incidents of sexual misconduct, including an encounter in college that he described as rape, as well as repeated infidelity and the sexual harassment of an assistant at his production company, Warrior Poets.
The statement, which Mr. Spurlock posted on Twitter in 2017, came as he was gearing up for the release of a sequel to the film, “ Super Size Me 2: Holy Chicken! ” on YouTube Red.
He stepped down from his production company, and YouTube dropped the film; it was instead released in 2019 by Samuel Goldwyn Films.
Morgan Valentine Spurlock was born on Nov. 7, 1970, in Parkersburg, W.Va., and grew up in Beckley, W.Va. His father, Ben, owned and operated an auto-repair shop, and his mother, Phyllis (Valentine) Spurlock, was a junior high school and high school guidance counselor.
He later said he grew up as a fan of 1970s and ’80s British comedies like “Monty Python’s Flying Circus” and “Blackadder.”
“I was doing funny walks round the house at 6 or 7,” he told The Independent in 2012 .
He studied film at New York University and received a bachelor’s degree in fine arts in 1993, then began his career as a production assistant on film projects around New York City, beginning with Luc Besson’s “Léon: The Professional” (1994).
He also began writing plays, including “The Phoenix,” which won an award at the 1999 New York International Fringe Festival.
Mr. Spurlock’s first foray onto the screen was a proto-reality show called “I Bet You Will,” which was also one of the first web-only programs. In five-minute segments, he would dare people to do something gross, or humiliating, or both — eating a “worm burrito,” for example — in exchange for a wad of cash.
The show drew millions of viewers, as well as the interest of MTV, which bought the program a few months after it debuted.
During a Thanksgiving visit to his parents in 2002, Mr. Spurlock saw a TV news story about two women who had sued McDonald’s, claiming that the chain had misled them about the nutritional value of its hamburgers, fries and sodas and caused them to gain significant weight.
“A spokesman for McDonald’s came on and said, you can’t link their obesity to our food — our food is healthy, it’s nutritious,” he told The New York Times in 2004 . “I thought, ‘If it’s so good for me, I should be able to eat it every day, right?’”
And thus, “Super Size Me” was born.
Mr. Spurlock took to fame eagerly, and, with his wide smile and handlebar mustache, was hard to miss. He became an unofficial spokesman for the wellness movement, hobnobbed with celebrity chefs — and scrambled to find a new project.
He did not want to lose the momentum generated by “Super Size Me,” nor did he want to go down in history only as the guy who ate a lot of Big Macs.
“I’ll be that guy till I die,” he told The Independent.
A follow-up film, “Where in the World Is Osama Bin Laden?” (2008), was not nearly as well received. Critics assailed him for making light of an international terrorist and for oversimplifying complicated global politics. More bricks were thrown when it emerged that he had put himself at significant personal risk while in Pakistan while his wife was at home with their newborn son.
Eventually, he did get somewhat past the shadow of “Super Size Me”: He teamed up with the actors Jason Bateman and Will Arnett to explore the male grooming industry in “Mansome” (2012) and followed the band One Direction around, resulting in the film “One Direction: This Is Us” (2013).
He produced films by other documentarians, including “The Other F Word” (2011), directed by Andrea Blaugrund Nevins, about punk rockers who became fathers, and “A Brony Tale” (2014), directed by Brent Hodge, about the subculture known as Bronies — adults, mostly men, who love the animated series “My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic.”
And he continued to make projects that leaned on the participatory style of “Super Size Me.” He created and starred in a series called “30 Days” for FX, in which a person, often Mr. Spurlock himself, would spend about a month embedded in a community much different from his own. One episode saw him spend 25 days in a Virginia jail.
Mr. Spurlock was married three times, to Priscilla Sommer, Alexandra Jamieson and Sara Bernstein; all three marriages ended in divorce. Along with his brother Craig, he is survived by another brother, Barry; his parents; and his sons, Laken and Kallen.
His decision to discuss his sexual past, which came at the height of the #Metoo movement, was met with a mix of praise and criticism. Though many people lauded him for coming forward, critics suggested that he was trying to get ahead of a story that was going to emerge anyway.
All agreed, though, that the decision came with consequences: “Career death,” The Washington Post declared it in 2022 , noting that the once-ubiquitous Mr. Spurlock had largely disappeared.
Clay Risen is a Times reporter on the Obituaries desk. More about Clay Risen
Remy Tumin is a reporter for The Times covering breaking news and other topics. More about Remy Tumin

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Art History Analysis - Formal Analysis and Stylistic Analysis. Typically in an art history class the main essay students will need to write for a final paper or for an exam is a formal or stylistic analysis. A formal analysis is just what it sounds like - you need to analyze the form of the artwork. This includes the individual design ...
In art history, however, you will be asked to gather your evidence from close observations of objects or images. Beyond painting, photography, and sculpture, you may be asked to write about posters, illustrations, coins, and other materials. Even though art historians study a wide range of materials, there are a few prevalent assignments that ...
The word "art" is derived from the Latin ars, which originally meant "skill" or "craft.". These meanings are still primary in other English words derived from ars, such as "artifact" (a thing made by human skill) and "artisan" (a person skilled at making things). The meanings of "art" and "artist," however, are not ...
Art versus artifact. The word "art" is derived from the Latin ars, which originally meant "skill" or "craft.". These meanings are still primary in other English words derived from ars, such as "artifact" (a thing made by human skill) and "artisan" (a person skilled at making things). The meanings of "art" and "artist ...
ART HISTORY: GUIDE TO ESSAY WRITING . The aim of formal essay writing is to engage your critical reading and writing skills to craft an articulate and polished essay. It provides an opportunity to consider a topic in depth, combining the synthesis of source materials with your own conclusions based on those materials.
Art History What this handout is about This handout discusses several common types of art history assignments, and talks about various strategies and resources that will help you write your art history papers. What is art history? Many students do not get a chance to study art history until they take a college course, so art
One of the most basic types of contextual analysis is the interpretation of subject matter. Much art is representational (i.e., it creates a likeness of something), and naturally we want to understand what is shown and why. Art historians call the subject matter of images iconography. Iconographic analysis is the interpretation of its meaning.
Guide for Writing in Art History. Art history courses cultivate critically analyze images, objects, and architectural spaces as well as academic discourse, scholarship, and historical sources. Art history is a humanistic discipline that brings together research to explore historical contexts while engaging in ways of looking at, describing, and ...
Art history essays play a pivotal role in art history studies, serving as a key medium through which students engage with and contribute to the field. These essays provide a platform for critical analysis, contextual understanding, and the exploration of artistic movements and themes. This article delves into the significance of art history ...
An introduction to art history. Art history "is a way to see what people thought, felt, believed, did, and imagined, by looking at the material things - buildings, paintings, gardens, sculptures, images, cities, objects - and the worlds that they made." (Griselda Pollock)
What is art history? Art history - the study of art from across the world, and from the ancient to the present day - covers virtually every aspect of human history and experience. This is because it looks at works of art not just as objects, but as a way of understanding the world, and the societies in which they were created.
The following are basic guidelines that you must use when documenting research papers for any art history class at UA Little Rock. Solid, thoughtful research and correct documentation of the sources used in this research (i.e., footnotes/endnotes, bibliography, and illustrations**) are essential. Additionally, these guidelines remind students ...
Generally, art history papers do not ask you to make a value judgment about the quality of a work, so there is no reason the writer should call the painting "good." Furthermore, the writer does not specify what the texture of the painting is like. All paintings have texture, so the write must describe more carefully.
Writing Assignments. You will be expected to write several different kinds of art history papers. They include: Close Visual Analysis Essays. Close Visual Analysis in dialogue with scholarly essays. Research Papers. Close Visual Analysispieces are the most commonly written papers in an introductory art history course.
The work of art is our primary evidence, and it is our interaction between this evidence and methods of enquiry that forms art history. Art appreciation and criticism are also linked to connoisseurship. Although art is a visual subject, we learn about it through reading and we convey our ideas about it mostly in writing.
Writing about art is basically a process of interpretation, and a common assignment in beginning as well as advanced art history courses is to write a response or analytical essay pertaining to a specific work, either a painting or sculpture. This usually suggests that you begin your essay with a straightforward description of the work followed ...
Art of the Pleasure Quarters and the Ukiyo-e Style; Art of the Roman Provinces, 1-500 A.D. The Art of the Safavids before 1600; The Art of the Seljuq Period in Anatolia (1081-1307) The Art of the Seljuqs of Iran (ca. 1040-1157) Art of the Seventeenth and Eighteenth Centuries in Naples; Art of the Sufis; The Art of the Timurid Period (ca ...
First, some examples. We'll begin with the pragmatic. In 1957, the architect Frank Lloyd Wright wrote: "Art is a discovery and development of elementary principles of nature into beautiful forms suitable for human use.". Another practical definition comes to us from Charles Eames: "Art resides in the quality of doing; process is not ...
Historical value. Artwork is a record of cultural history. Many ancient cultures are entirely lost to time except for the artworks they created, a legacy that helps us understand our human past. Even recent work can help us understand the lives and times of its creators, like the artwork of African-American artists during the Harlem Renaissance.
The history of art focuses on objects made by humans for any number of spiritual, narrative, philosophical, symbolic, conceptual, documentary, decorative, and even functional and other purposes, but with a primary emphasis on its aesthetic visual form. Visual art can be classified in diverse ways, such as separating fine arts from applied arts; inclusively focusing on human creativity; or ...
Venus de Milo, at the Louvre. Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today, art history examines broader aspects of visual culture, including the various visual and conceptual outcomes related to ...
Art history provides an excellent opportunity to develop the essential skills and talents that lie at the core of a good liberal arts education, including informed and critical reading, writing, and speaking. To these, it adds a particular attention to critical looking, building core skills in analyzing how the visual and physical qualities of ...
Art History and Anthropology: Modern Encounters, 1870-1970 2023 ... The Art of Remembering: Essays on African American Art and History 2024 The Art of Resistance: Painting by Candlelight in Mao's China 2017 The Art of Sculpture 1956 The Art of Solidarity: Visual and Performative Politics in Cold War Latin America ...
Essays on Art and Science. When we view a work of art, we often experience an emotional response, but the causes of our reactions are complex. Our knowledge of why we respond to art as we do is rooted in science—in psychology and biology. Eric R. Kandel traces the origins of this understanding to early twentieth-century Vienna, which gave ...
Writer Rachel Cusk is an art world favorite for her lucid meditations on artists and their work: her 2019 essay on painter Celia Paul's tumultuous relationship with Lucian Freud, for example ...
A Documentary History of Art, Volume 1: The Middle Ages and the Renaissance. ... range from Raoul Glaber's famous 1003 treatise on the synthesis of old and new art forms to Durand's essay on Christian symbolism in art and the writings of Leonardo and Dürer on anatomy, perspective, and the recreation of reality. ...
By Clay Risen and Remy Tumin. May 24, 2024. Morgan Spurlock, a documentary filmmaker who gained fame with his Oscar-nominated 2004 film " Super Size Me ," which followed him as he ate nothing ...