- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business

Growing Your Profits: Crafting a Comprehensive Cassava Farming Business Plan That Guarantees Success
Table of contents, what is cassava farming, why start a cassava farming business, benefits of cassava farming business, cassava farming business plan, conducting a market analysis for the cassava farming business, developing a production plan for the cassava farming, cassava farming financial plan , marketing and sales plan for cassava business, post-harvesting management operations in the cassava farming business, processing and value addition in cassava farming, risk management plan in the cassava farming business.
Cassava farming is a Profitable business venture that offers great profit potential, especially in tropical regions where it is widely grown. However, to ensure success and profitability, it is crucial to have a comprehensive business plan that covers all aspects of cassava farming, from seed to marketing and processing.

According to Food and Agriculture Organization, it is the third most important source of food with calories for human consumption in the tropics, with an estimated global production of over 280 million tons annually. With the right planning, cassava farming can provide farmers with a sustainable source of profits and promote food security in local communities.
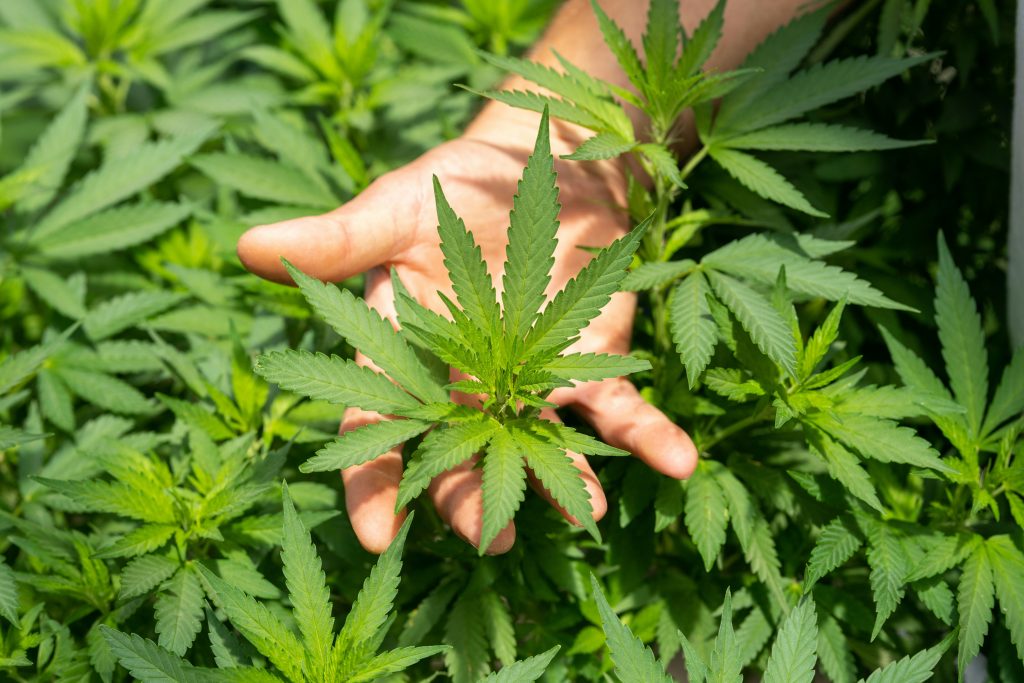
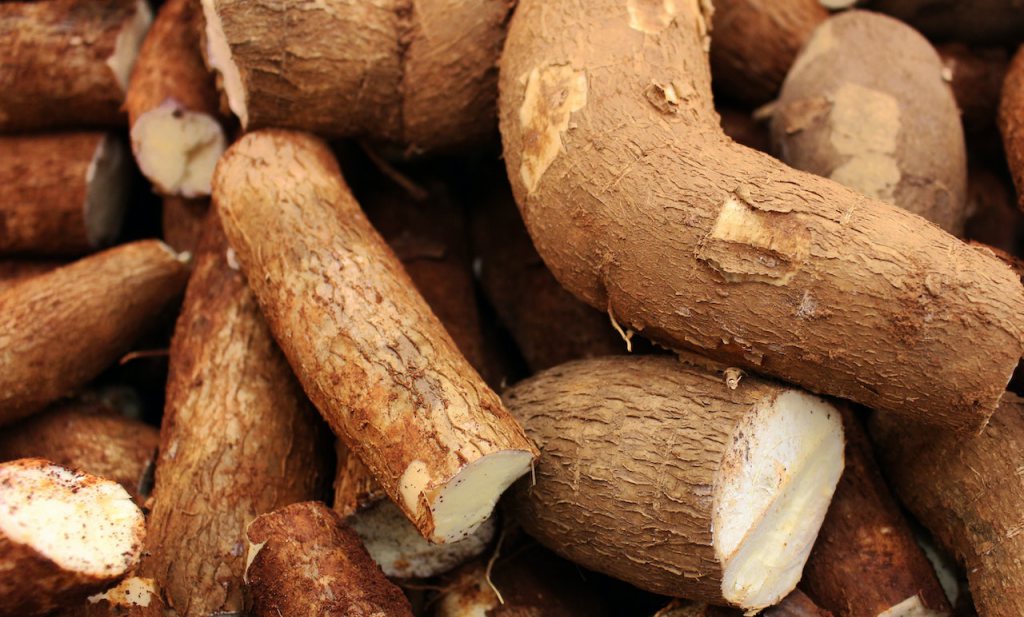
Cassava farming is the practice of cultivating the cassava plant, which is a tropical crop that is widely grown in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Cassava (Manihot esculenta) is a Euphorbiaceae plant. Perennial woody shrub with a strong and woody stem. Carbohydrate-rich roots are edible. The bush grows to 9 feet tall and has 30-centimeter tubers. Some reach a meter. Tapioca is processed cassava roots. Patients in India eat tapioca pearls.
Cassava is an important source of calories for millions of people in developing countries. It produces various food products, including flour, starch, and alcohol. It is a hardy and heat-tolerant crop that can overcome drought and other harsh environmental conditions, making it an ideal crop for farmers in tropical regions. Cassava farming can have both positive and negative environmental impacts. Poorly managed cassava farming can lead to soil degradation, deforestation, and biodiversity loss.
In case you missed it: Rice Cultivation in Greenhouse: A Profitable Business Plan for Sustainable Farming

- High demand: Cassava is a staple crop in many regions of the world, and demand for items made from it, including flour and starch, is rising.
- Low production costs: Because cassava is a hardy and tolerant crop that needs minimal upkeep and can tolerate drought and other extreme environmental conditions, it is comparatively cheap to grow.
- Profitability: Depending on the demand of the market, cassava farming can be a successful business. Potential profits can range from 30 to 60%.
- Employment: Cassava cultivation can provide local populations with employment possibilities, reducing poverty and enhancing the standard of living.
- Sustainable agriculture: When properly managed cassava cultivation is properly managed, it can support sustainable agricultural practices and help protect the environment.
- Food security: Cassava is an important source of calories for millions of people in developing countries, and it is a key crop for ensuring food security.
- Income generation: Cassava farming can provide a sustainable source of income for farmers, especially in rural areas where alternative income opportunities may be limited.
- Drought tolerance: Cassava is a hardy-tolerant crop that can withstand drought and other adverse climatic conditions, making it profitable for farmers in tropical regions.
- Versatility: Cassava can be processed into a wide range of food products, including flour, starch, and alcohol, providing multiple income streams for farmers.
- Environmental benefits: Properly managed cassava farming can help to restore degraded lands, prevent soil erosion, and promote biodiversity.
- Employment opportunities: Cassava processing can create employment opportunities in rural regions, particularly for women and youth.
- Economic development: Cassava processing can contribute to local economic development by creating value-added products and generating export revenues.
A cassava farming business plan should include a detailed analysis of the production process, cost of production, marketing and sales strategies, financial projections, and a risk management plan. Identify the target market and develop a value-added product plan to increase revenue.
In case you missed it: Buzzing Towards Success: Creating a Comprehensive Beekeeping Business Plan

Access to affordable and reliable farming inputs, such as fertilizers and improved seed varieties, should also be considered. The plan should also include strategies to mitigate post-harvest losses through proper storage, processing, and value addition. Adequate funding and financial management are critical for business growth and sustainability.
- Market size: It is crucial to calculate the potential size of the local and international markets for cassava and its related products. The yearly global cassava production is about 280 million tons, as reported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
- Demand and supply: The unique features of the cassava market’s demand and supply are necessary for understanding the market and building an effective approach. Cassava agricultural inputs, such as land, water, and fertilizer, must be evaluated, as must the present and projected demand for cassava and its products.
- Competition: Threats and opportunities can be gleaned from examining the firm’s rivals in the cassava market. The current production and pricing tactics and the market share of cassava farmers and processors must be evaluated.
- Market trends: Keeping up-to-date with market trends in cassava farming and processing can help to identify new opportunities and potential challenges for the business.
- Value addition: Assessing the potential value-added products produced from cassava can help increase business revenue and profitability.
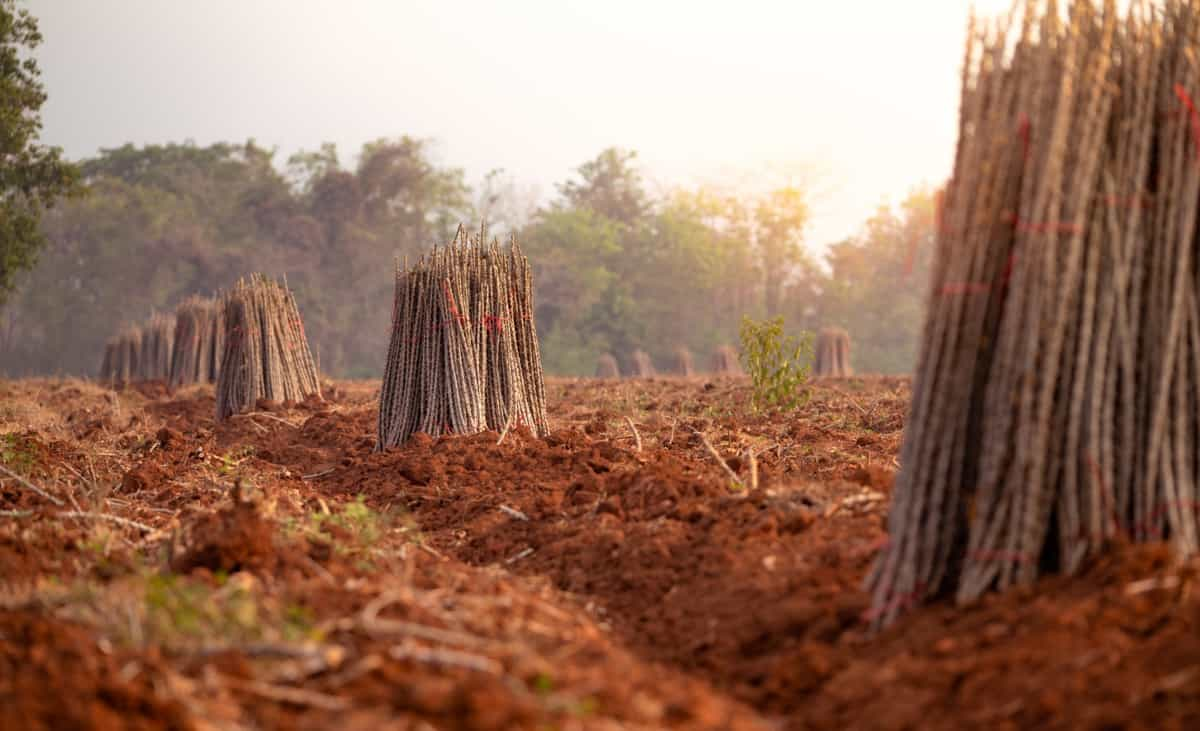
- Select the right variety: Choose a suitable variety for your soil type and climate. Many cassava varieties have varying growth rates and disease resistance, so select the one that best suits your needs. Choosing the right variety is crucial to yielding according to your needs. There are many varieties available, which vary from country to country.
- Prepare the soil: Clear the land of weeds and debris and ensure the soil is well-drained. The red laterite soil is most suitable for farming. Sandy loam soil is also beneficial. Use organic fertilizers to enrich the soil and improve the yield. Tapioca grows in soil pH ranges of 4.5 to 8.0. Cassava prefers temperatures between 25 and 29 °C (77 and 84 °F), but it can survive in temperatures ranging from 12 to 40 °C (54 to 104 °F).
In case you missed it: How to Craft a Successful Vertical Farming Business Plan

- Planting: Cassava is propagated by planting stem cuttings of around 15 cm in length before the wet season begins. Plant cassava stems in rows or mounds, ensuring they are not too deep in the soil. Cassava requires regular watering, especially during the first few weeks of planting. Planting seedlings from the nursery to the main field requires loose, moist soil. Loosen the dirt around the crop. Plant stem cuttings 5cm deep. Deeper planting may cause swelling and low yield.
- Drip irrigation is the most used sort of irrigation method for watering plants. Flooding the field is not recommended since tapioca cannot withstand large amounts of water. Drip also guarantees that water is only distributed at the plant’s base, near its roots.
- Weed management: Weeds can compete with cassava for nutrients, water, and sunlight. Regularly weeding the farm to keep the soil healthy and promote growth is important.
- Pest and disease control: Tapioca plants are susceptible to common diseases such as anthracnose, cassava mosaic disease, and bud necrosis. Insect pests such as nematodes, grasshoppers, cassava scales, and witches’ broom can also harm tapioca crops. Disease-free stakes, resistant varieties, and proper pest management can help control these issues. Mealybugs and other pests and diseases, such as cassava mosaic disease, can harm cassava. Regular inspection and treatment can help prevent damage and yield loss.
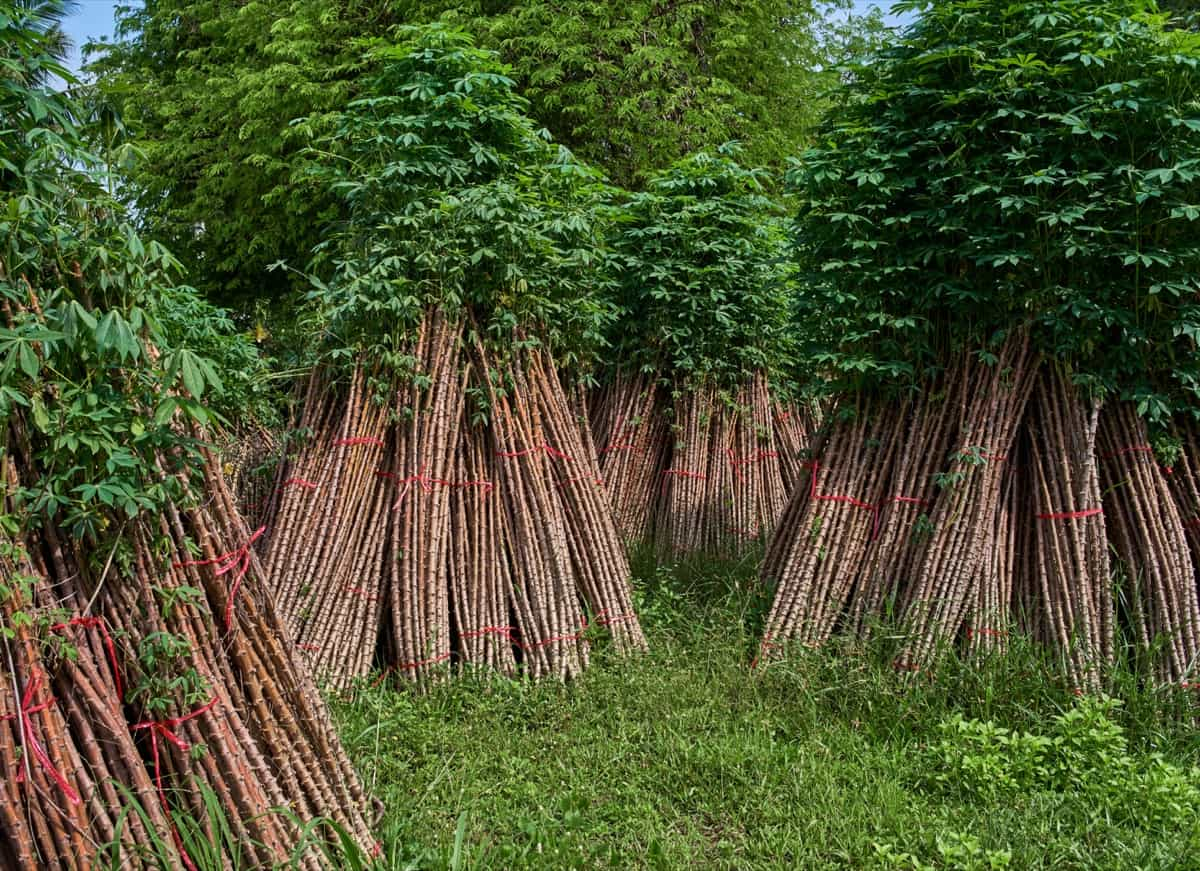
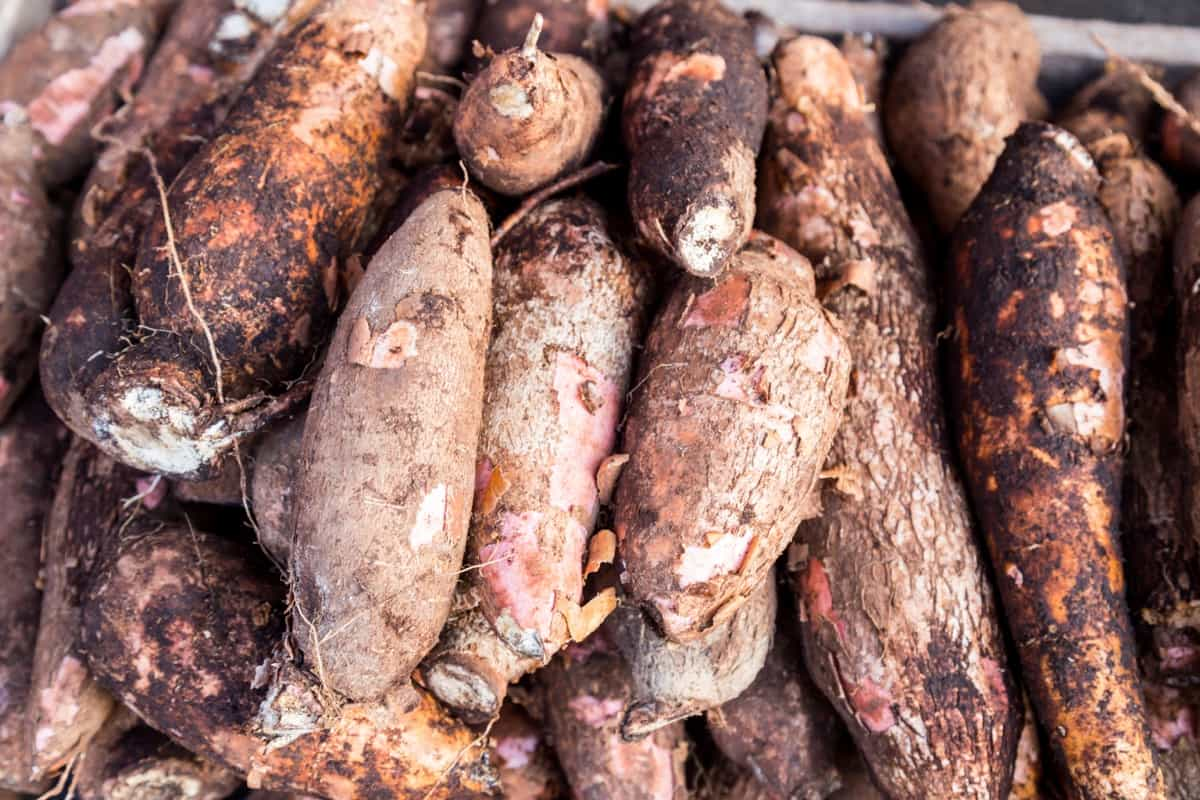
- Harvesting: Harvest mature cassava roots between 8-12 months after planting. Use a machete or hoe to cut the stem of the cassava plant and remove the tubers from the ground. The average yield of cassava is 10-15 tonnes per acre.
- Processing: After harvesting, process the cassava roots into various products such as garri, fufu, tapioca, starch, and flour. Use appropriate processing methods to ensure quality and safety.
- These production plans allow you to grow cassava successfully, maximize yield, continuously improve your farming techniques, and stay updated on modern farming technologies to increase productivity and profitability.
In case you missed it: How to Start Profitable Pygmy Goat Farming: Business Plan and Requirements
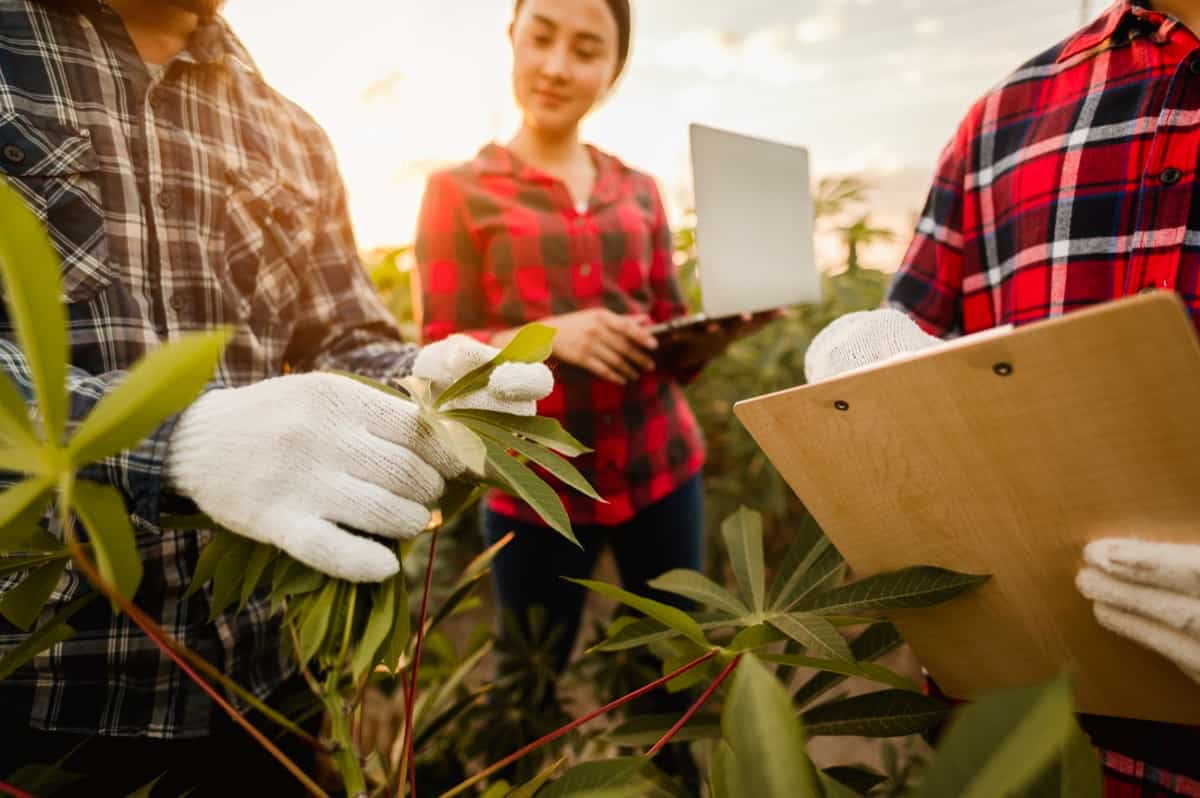

- Cost of production: The cost of producing one hectare of cassava can vary depending on factors such as land preparation, planting, fertilization, pest control, and harvesting. The average cost ranges from $1,200 to $1,500 per hectare.
- Expected yield: The average cassava yield per hectare is around 20 to 30 tons, depending on the farming practices and variety.
- Market price: The market price of cassava varies based on location and demand. The price ranges from $0.25 to $0.50 per pound in the United States.
- Revenues: Based on the yield and market price, a one-hectare farm could generate revenues of $10,000 to $15,000.
- Profit: After deducting the cost of production from the revenues, the profit per hectare could range from $8,500 to $13,500.
- Return on investment (ROI): The ROI for a cassava farming business can vary depending on the initial investment and other factors. However, with an average profit of $5,000–10,000 per hectare, a 100-hectare farm could generate $1 million annually.
- Determine the specific market segment to focus on, such as food processing industries, animal feed manufacturers, or households.
- Create a distinct brand that distinguishes your cassava goods from competitors.
- Establish a distribution network: Create channels to ensure products are available to customers.
- Use technology to improve brand visibility and reach new customers, such as social media, e-commerce platforms, and digital marketing tools.
- Set moderate prices that entice customers while also maintaining a profit.
- Develop relationships: cultivate positive ties with suppliers, customers, and industry stakeholders.
- Participate in exhibits and trade shows to market your business and network with potential consumers.
After harvesting, cassava is susceptible to post-harvest physiological deterioration (PPD) due to the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). This results in a blackened and unpalatable tuber, limiting its shelf life and export potential. However, overexpressing a cyanide-insensitive alternative oxidase can increase shelf life by up to three weeks by suppressing ROS. Breeding cassava varieties more tolerant to PPD has also been explored.
In 2020, Nigeria was the world’s largest cassava producer, with 60 million tonnes produced. Cassava is a drought-tolerant crop that can grow well in marginal soils and poor pH levels, making it suitable for certain parts of Africa and South America. Cassava can be processed into various products, such as cassava starch, flour, and bread, and can be preserved using fungicides, plastic wrapping, wax coating, or freezing.
- Cassava can be processed into value-added products such as flour, starch, chips, and ethanol.
- Cassava flour is used as a substitute for wheat flour in many gluten-free products, while cassava starch is used to produce food and non-food products.
- Cassava chips are used for animal feed and industrial purposes such as ethanol production.
- Ethanol can be produced from cassava by fermentation and distillation and can be used as a biofuel or source of industrial alcohol.
- Processing cassava involves peeling, washing, grating, and pressing the roots to extract the starch, which is dried and packaged.
- Value-addition activities in cassava farming can increase the crop’s profitability and improve farmers’ livelihoods.
- Cassava value chains are important for creating market linkages and improving the competitiveness of cassava-based products.
- Several countries have established cassava processing zones to promote value addition and create employment opportunities.
In case you missed it: Key Rules to Start Totapari Goat Farming from Scratch: Requirements and Business Plan

Some common risks in cassava farming include weather fluctuations, pests and diseases, market volatility, and price fluctuations. Farmers should consider implementing risk management strategies such as crop diversification, pest and disease control measures, market analysis and price forecasting, and crop insurance to mitigate these risks.
Additionally, farmers can invest in research and development to improve crop yields and disease resistance. It is also essential to maintain good relationships with suppliers, buyers, and other stakeholders in the cassava value chain to ensure a stable market for the produce.
A comprehensive cassava farming business plan is essential for success in the cassava industry. With a clear understanding of market demand, production costs, marketing strategies, and risk management, farmers can maximize their profits and ensure the long-term viability of their businesses. By focusing on these key components, farmers can grow their profits and succeed in the competitive world of cassava farming.
Ultimate Guide to Natural Vegetable Farming
Natural farming for sustainable livestock management, dairy farm technology in india: the future of dairy husbandry, comprehensive guide to organic farming in villages, modern sheep farming technology: the future of sheep husbandry, goat farming technology: the future of goat husbandry.
- How to Build a Low-budget Goat Shed: Cheap Ideas and Tips
Goat Farming Training Programs in India: A Beginner’s Guide
Types of pesticides used in agriculture: a beginner’s guide, economical aquaculture: a guide to low-budget fish farming, 15 common planting errors that can doom your fruit trees, how to make houseplants bushy: effective tips and ideas, innovative strategies for boosting coconut pollination and yield, pollination strategies for maximum pumpkin yield, the complete guide to chicken fattening: strategies for maximum growth.
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
This is a good guide to extension workers.
Very detailed and insightful. How can I engage your services?
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
How to Build a Low-budget Goat Shed: Cheap Ideas and...
Natural solutions for tulip problems: 100% effective remedies for leaf..., natural solutions for peony leaf and flower problems: 100% effective..., maximizing profits with avocado contract farming in india: a comprehensive..., natural solutions for hydrangea problems: 100% effective remedies for leaf..., borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.
- The Agriculture Dictionary
- Agriculture & Nature
- Business & Investment
- Farm Animals
- How To Start
- Innovation & Technology
- Pest Control
- Uncategorized
Cassava Farming: A Complete Guide
Cassava (Manihot esculenta), also known as tapioca or yuca, is a versatile and resilient crop that has been a staple food for millions of people around the world. Cassava farming can be a profitable and rewarding venture, but it requires careful planning, knowledge, and dedication.
This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to start and run a successful cassava farm, covering everything from land preparation and planting to harvesting and marketing strategies.

Table of content
Introduction, conducting research and feasibility study, land selection and preparation, cassava planting and cultivation.
- Nutrient Management and Irrigation
- Weed Control and Crop Maintenance
- Harvest and Post-Harvest Handling
Marketing and Sales Strategies
- Challenges in Cassava Farming and Troubleshooting
- The Bottom Line
Cassava, scientifically known as Manihot esculenta, is a tropical root crop that has been cultivated and consumed by various cultures for centuries. Its resilience, adaptability, and high nutritional value make it a staple food for millions of people around the world, particularly in Africa , Asia , and South America .
As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food security and sustainable agriculture practices increases. This presents an excellent opportunity for aspiring farmers to venture into cassava farming as a profitable and rewarding business.
The Importance of Cassava as a Crop
Cassava serves as a crucial source of carbohydrates, providing sustenance to millions in regions where other staple crops may not thrive due to challenging environmental conditions. Its drought-tolerance and ability to grow in poor soils have earned it the title of “the survival crop” in many tropical regions.
Additionally, cassava is gluten-free and contains essential nutrients such as calcium, potassium, and vitamins A and C, making it a valuable component of a balanced diet.
Beyond its role as a staple food, cassava has numerous industrial applications, including the production of starch, flour, ethanol, and animal feed. As the demand for alternative energy sources and biodegradable materials increases, the market for cassava-based products continues to expand.
Benefits of Starting a Cassava Farm
- Profitability: Cassava farming can be a profitable venture due to the high demand for the crop and its various by-products in local and international markets.
- Low Input Requirements: Cassava farming is relatively low-maintenance compared to other crops. It requires less water and fertilizers, making it a cost-effective option for farmers.
- Resilience: Cassava is well-adapted to diverse environmental conditions, including poor soil, drought, and heat, making it a dependable crop even in challenging climates.
- Market Demand: The growing global population and the need for sustainable food sources create a constant demand for cassava-based products.
- Diversification: Cassava farming offers multiple value chains, allowing farmers to explore different products and markets for increased income streams.
Understanding the Market Demand and Trends
Before starting a cassava farm, conducting thorough market research is essential. Analyzing the local, regional, and international demand for cassava and its derivatives will help farmers identify potential customers and market opportunities. Key considerations include:
- Local Consumption: Understanding the consumption patterns of cassava and its products in the local community will help determine the potential demand.
- Export Opportunities: Investigating the export potential of cassava products can open up lucrative markets and boost farm revenues.
- Value Addition: Identifying opportunities for value addition, such as cassava processing into chips, flour, or starch, can significantly increase profitability.
- Health and Dietary Trends: Awareness of health-conscious consumer preferences can help farmers tailor their products to meet specific dietary requirements.
- Government Policies and Support: Researching government policies and initiatives related to agriculture and cassava farming can provide valuable insights into available support and incentives.
- Identifying suitable cassava varieties
- Analyzing the local climate and soil conditions
- Assessing the market demand and competition
- Creating a business plan
- Understanding production cost and returns
- Risk assessment and mitigation
- Securing financing and investment
Identifying Suitable Cassava Varieties : The success of cassava farming largely depends on selecting appropriate cassava varieties that are well-suited to the local climate and market demands.
Different cassava varieties have varying characteristics, including yield, resistance to pests and diseases, and processing qualities. Farmers should consult with agricultural experts, extension services, or local research institutions to identify the best varieties for their specific farming conditions.
Analyzing the Local Climate and Soil Conditions : Cassava thrives in tropical and subtropical climates with temperatures between 25°C to 35°C (77°F to 95°F) and an annual rainfall of 1,000mm to 1,500mm (39 to 59 inches). It can also grow in areas with lower rainfall, provided there is access to irrigation.
Conducting a thorough analysis of the local climate and soil conditions is crucial for successful cultivation. Farmers should consider factors such as temperature, rainfall patterns, soil pH, and soil fertility. Soil testing can help determine the nutrient levels and identify any deficiencies, allowing for tailored fertilization plans.
Assessing the Market Demand and Competition : Understanding the market demand for cassava and its products is essential for making informed decisions about the scale of the farm and the products to focus on.
Farmers should assess the local demand for fresh cassava roots, as well as the demand for processed products like cassava flour, starch, and chips. Additionally, studying the competition can help identify gaps in the market and potential niches for the farm to fill.
Engaging with potential buyers and processors early on can provide valuable insights into their requirements and preferences.
Creating a Business Plan : A well-structured business plan is a roadmap for the cassava farm’s success. It should outline the farm’s objectives, financial projections, production targets, marketing strategies, and risk management plans.
The business plan should also include a detailed budget, covering all expenses from land preparation to post-harvest handling. A solid business plan will not only help secure financing but also serve as a guide for the farm’s development and growth.
Understanding Production Costs and Returns : Farmers need to calculate the production costs involved in cassava farming. This includes costs related to land preparation, planting materials, fertilizers, labor, irrigation, pest control, and equipment.
Understanding the production costs allows farmers to set appropriate pricing for their products and ensures profitability. Additionally, analyzing potential returns based on market prices and expected yields can help estimate the farm’s profitability and payback period.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation : Farming, like any business, comes with inherent risks. Weather fluctuations, pest and disease outbreaks, market price volatility, and logistical challenges can impact cassava farm operations.
Farmers should assess potential risks and develop strategies to mitigate them. Diversification, insurance, and good agricultural practices can help reduce the impact of adverse events on the farm’s productivity and profitability.
Securing Financing and Investment : Starting a cassava farm may require initial capital investment for land acquisition, infrastructure setup, and operational expenses. Farmers can explore various financing options, including bank loans, government grants, or private investors.
A comprehensive business plan will be instrumental in convincing potential investors or lenders of the farm’s viability and potential for success.
- Choosing the right location for the farm
- Testing soil fertility and pH levels
- Clearing and preparing the land for planting
- Implementing sustainable farming practices
- Establishing windbreaks and Agroforestry
Choosing the Right Location for the Farm : Selecting the appropriate location for a cassava farm is critical to its success. Ideally, the farm should be situated in a tropical or subtropical region with a consistent temperature range of 25°C to 35°C (77°F to 95°F).
Cassava requires well-distributed rainfall of 1,000mm to 1,500mm (39 to 59 inches) annually, but it can tolerate drier conditions if irrigation is available. Proper drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging, which can be detrimental to cassava roots.
Access to transportation and markets is also a crucial consideration for easy distribution of products.
Testing Soil Fertility and pH Levels : Before commencing cultivation, it is essential to assess the soil’s fertility and pH levels. Cassava thrives in well-drained, sandy loam soils with a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
Conducting a soil test will provide valuable information about nutrient levels and any necessary soil amendments. If the soil is deficient in certain nutrients, appropriate fertilizers or organic matter can be added to enhance soil fertility.
Clearing and Preparing the Land for Planting : Once the land is selected, the next step is to clear it of weeds, rocks, and other debris. Mechanized tools like tractors or bulldozers can be used for large-scale clearing, while manual labor can be employed for smaller areas.
After clearing, the land should be plowed or tilled to loosen the soil and prepare a suitable seedbed for planting. Farmers should take care to avoid soil compaction, as it can hinder root development.
Implementing Sustainable Farming Practices : In recent years, sustainable farming practices have gained prominence due to their environmental and economic benefits. Farmers are encouraged to adopt conservation tillage methods that reduce soil erosion and improve soil structure.
Additionally, employing organic and biological pest control methods can minimize the use of synthetic pesticides, promoting natural biodiversity.
Establishing Windbreaks and Agroforestry : In areas prone to strong winds, planting windbreaks around the farm can protect the cassava crop from damage. Windbreaks can consist of trees, shrubs, or even tall grasses strategically placed to block the wind’s force.
Agroforestry practices, which involve intercropping cassava with trees or other crops, can enhance ecosystem resilience and provide additional income streams.
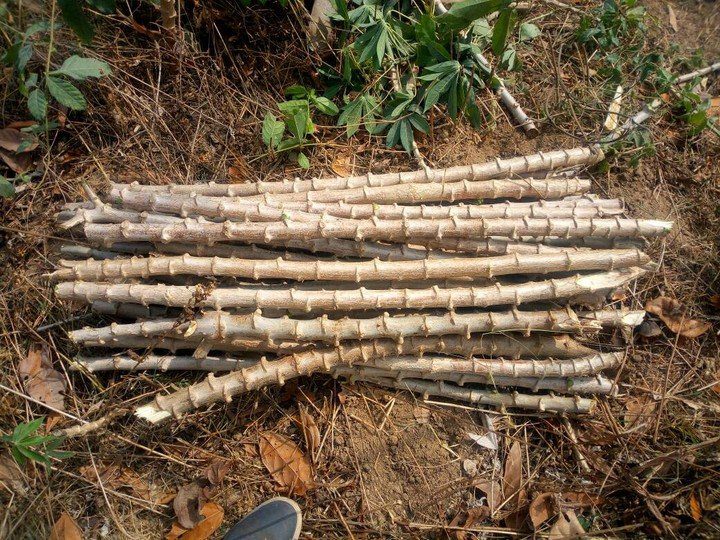

- Selecting high-quality planting materials
- Propagating cassava through stem cuttings
- Planting technique and spacing
- Managing pest and diseases
- Nutrient management and irrigation
Selecting High-Quality Planting Materials : The success of cassava farming starts with the selection of healthy and disease-free planting materials. Cassava is propagated using stem cuttings, which are obtained from mature, disease-free plants.
Farmers should choose stems that are at least 20-30 centimeters long, with several nodes. It is advisable to source planting materials from reputable suppliers or select healthy stems from existing cassava plants on the farm.
Propagating Cassava through Stem Cuttings : Cassava stems are planted directly into the soil for propagation. Before planting, the cuttings should be allowed to dry and form a protective callus on the cut ends.
Planting can be done manually by making holes or furrows in the soil and inserting the cuttings at an angle of about 45 degrees.
Planting Techniques and Spacing : The spacing and planting techniques can vary depending on the cassava variety and the farmer’s objectives. For commercial farming, a well-planned row planting method is commonly used.
Rows facilitate weed control, irrigation, and the application of fertilizers. Depending on the variety, the recommended spacing between plants is typically 1 meter by 1 meter or 1.5 meters by 1.5 meters.
Managing Pests and Diseases : Cassava is susceptible to various pests and diseases that can negatively impact yield and quality. Common pests include mealybugs, spider mites, and whiteflies, while diseases like cassava mosaic disease (CMD) and cassava bacterial blight (CBB) can be devastating.
Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) practices, such as using resistant varieties, promoting natural predators, and employing cultural controls, can effectively manage pest and disease pressures.
Nutrient management and Irrigation
- Understanding cassava’s nutrient requirements
- Applying organic and inorganic fertilizers
- Implementing efficient irrigation systems
- Water management and conservation practices
- Monitoring and adjusting nutrient and irrigation regimes
Understanding Cassava’s Nutrient Requirements: Cassava has specific nutrient needs at different stages of growth. During the early stages, the plant requires higher levels of nitrogen (N) for foliage development.
As it progresses to the later stages, the demand for phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) increases to support root development and overall plant health. Adequate nutrient management is crucial for achieving optimal yields and ensuring the crop’s resilience to pests and diseases.
Applying Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers: Farmers can choose between organic and inorganic fertilizers to meet the nutrient requirements of cassava. Organic fertilizers, such as compost, animal manure, or green manure, contribute to soil fertility and improve its structure.
Inorganic fertilizers, on the other hand, provide precise nutrient formulations and are readily available to the plants. It is advisable to conduct soil tests to determine the specific nutrient deficiencies and tailor the fertilizer application accordingly.
Implementing Efficient Irrigation Systems: Proper irrigation is vital for the successful cultivation of cassava, especially in areas with irregular rainfall patterns. The timing and amount of water provided are critical factors that affect cassava growth and root formation.
Drip irrigation is considered one of the most efficient methods for cassava farming, as it delivers water directly to the root zone, reducing wastage and water stress on the plant. Irrigation scheduling should consider the stage of growth, soil moisture levels, and prevailing weather conditions.
Water Management and Conservation Practices: To conserve water and maintain optimal soil moisture, farmers can adopt various water management practices. Mulching the soil with organic materials helps retain moisture, suppress weed growth, and regulate soil temperature.
Implementing rainwater harvesting systems can also supplement irrigation needs during dry periods, reducing dependency on groundwater or other external water sources.
Monitoring and Adjusting Nutrient and Irrigation Regimes: Regular monitoring of the crop’s health and growth is essential for timely adjustments in nutrient and irrigation management. Farmers should closely observe plant growth, leaf color, and overall health indicators.
Visual symptoms of nutrient deficiencies, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth, should be promptly addressed through appropriate nutrient supplementation. Additionally, soil moisture levels should be monitored, and irrigation schedules adjusted as needed to avoid water stress.
Weed Control and crop maintenance
- Identifying common weeds in cassava farms
- Implementing effective weed control methods
- Monitoring and managing crop health
- Pruning and supporting cassava plants
Identifying Common Weeds in Cassava Farms: Weeds compete with cassava plants for nutrients, sunlight, and water, negatively impacting yield and quality. Understanding the common weed species in the region is crucial for effective weed control.
Common weeds in cassava farms include grasses, broad-leaved plants, and sedges. Some of the most problematic weeds include elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum), spear grass (Imperata cylindrica), and pigweed (Amaranthus spp.).
Implementing Effective Weed Control Methods: Several weed control methods can be employed to keep weed populations in check:
- Hand Weeding: Manual removal of weeds by hand is a cost-effective and environmentally friendly method. It is labor-intensive, making it more suitable for small-scale farms.
- Mechanical Weeding: Mechanical tools, such as hoes or cultivators, can be used for larger farms. They help remove weeds from the soil surface and disrupt their growth.
- Mulching: Applying organic mulch, such as straw or crop residues, helps suppress weed growth and conserve soil moisture. It also improves soil fertility as the mulch decomposes.
- Herbicides: Selective herbicides can be used to control specific weed species without harming cassava plants. Careful application and adherence to safety guidelines are essential when using herbicides.
Monitoring and Managing Crop Health: Regular monitoring of the crop’s health is crucial for detecting and addressing any issues promptly. Farmers should regularly inspect the cassava plants for signs of pest infestations, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies.
Early detection allows for timely interventions and prevents problems from escalating. Farmers can seek advice from agricultural extension services or agronomists if they encounter any challenges with crop health.
Pruning and Supporting Cassava Plants: As cassava plants grow, they develop an extensive branching system with lower leaves that may come into contact with the soil. Pruning involves removing these lower leaves to improve airflow around the plant and reduce the risk of fungal infections.
Pruning also directs the plant’s energy towards root development, enhancing overall yields. Proper pruning should be done carefully to avoid injuring the main stem.
Harvest and post-harvest handling
- Determining the right time to harvest cassava
- Harvesting techniques and tools
- Cassava processing options for value addition
- Handling and transporting harvested cassava
- Ensuring post-harvest quality and storage
- Value addition and market opportunities
Determining the Right Time to Harvest Cassava: Harvesting cassava at the appropriate time is crucial for achieving optimal yield and quality. Cassava roots are ready for harvest when they reach maturity, typically between 8 to 12 months after planting, depending on the variety and local growing conditions.
Signs of maturity include the yellowing of lower leaves and the development of a thick bark on the tubers. Farmers should avoid leaving cassava in the ground for too long, as over-mature roots may become fibrous and less suitable for consumption or processing.
Harvesting Techniques and Tools: Cassava harvesting requires care and precision to avoid damaging the delicate roots. Farmers can use simple tools such as digging forks or cutlasses to loosen the soil around the roots before lifting them gently from the ground. It is essential to handle the roots with care to minimize bruising and damage.
Handling and Transporting Harvested Cassava: After harvesting, the cassava roots need to be transported quickly to minimize post-harvest losses. During transportation, the roots should be placed in baskets or crates to protect them from mechanical injury.
If the distance to the processing or storage facility is long, farmers can cover the roots with moist, clean sawdust or sand to maintain their freshness and prevent dehydration.
Cassava Processing Options for Value Addition: Cassava can be processed into various products to add value and increase profitability. Common processing options include:
- Cassava Flour: Cassava roots can be peeled, washed, grated, and then dried to produce cassava flour, which is used in various culinary applications.
- Cassava Starch: Starch is extracted from cassava roots, resulting in a valuable ingredient for food and industrial use.
- Cassava Chips: Sliced cassava roots are dried to produce chips, which can be consumed as snacks or used in animal feed.
- Cassava Paste and Garri: Cassava roots can be fermented and processed into a sticky paste or roasted to produce garri, a popular West African food product.
Ensuring Post-Harvest Quality and Storage: Proper post-harvest handling is critical to maintaining the quality and shelf life of cassava products. Farmers should take care to remove damaged or spoiled roots during sorting.
The roots should be cleaned and stored in a cool, dry place to prevent molding and spoilage. For processed cassava products, appropriate packaging is essential to protect them from moisture, pests, and contamination.
Value Addition and Market Opportunities: Processing cassava into value-added products offers additional income opportunities for farmers. By diversifying their products, farmers can tap into different market segments, both locally and internationally.
Understanding consumer preferences and market demands for various cassava products can guide farmers in choosing the most profitable processing options.
- Establishing market connections
- Branding and packaging cassava products
- Pricing strategies and market positioning
- Developing a distribution network
- Promoting cassava consumption
- Exploring export opportunities
- Building customer loyalty and feedback mechanism
Establishing Market Connections: Effective marketing begins with building strong market connections. Farmers should identify potential buyers, processors, or distributors for their cassava products. This can include local markets, supermarkets, food processing companies, and export opportunities.
Building relationships with buyers and understanding their requirements can help farmers tailor their products to meet market demands.
Branding and Packaging Cassava Products: Branding plays a significant role in product recognition and consumer loyalty. Developing a unique brand identity for cassava products can help differentiate them in the market.
Farmers should invest in attractive and informative packaging that highlights the product’s quality and benefits. Proper labeling with essential product information, certifications, and nutritional details can instill consumer confidence.
Pricing Strategies and Market Positioning: Determining the right pricing strategy is crucial for balancing profitability and competitiveness. Farmers should consider production costs, market demand, and competitors’ prices when setting their product prices.
Market positioning is also essential; farmers can choose to position their cassava products as premium, organic, or competitively priced, depending on their target market segment.
Developing a Distribution Network: Efficient distribution is essential to ensure that cassava products reach consumers promptly and in good condition. Farmers should establish an effective distribution network that covers both local and distant markets.
This may involve collaboration with wholesalers, retailers, or logistics companies to handle transportation and storage.
Promoting Cassava Consumption: Promoting cassava consumption and its nutritional benefits can expand market opportunities. Farmers can engage in educational campaigns and cooking demonstrations to raise awareness about cassava’s versatility and health benefits. Collaborating with nutritionists or local health organizations can add credibility to the promotional efforts.
Exploring Export Opportunities: For farmers with access to international markets, exporting cassava products can be a lucrative venture. However, exporting requires compliance with import regulations, quality standards, and certification requirements of the target countries. Engaging with export agencies and trade organizations can provide valuable insights and support for export ventures.
Building Customer Loyalty and Feedback Mechanisms: Customer satisfaction is key to building long-term relationships and securing repeat business. Farmers should actively seek feedback from customers to understand their preferences and expectations. Incorporating customer feedback into product improvement and quality enhancement efforts can lead to enhanced customer loyalty.
Challenges in cassava farming and troubleshooting
1. Pest and Disease Management
- Challenge: Cassava is vulnerable to various pests and diseases, such as cassava mosaic disease (CMD), cassava bacterial blight (CBB), and mealybugs.
- Troubleshooting: Farmers should implement integrated pest management (IPM) practices, use disease-resistant varieties, practice crop rotation, and apply appropriate pesticides when necessary. Early detection and prompt action are critical to preventing severe infestations.
2. Drought and Water Management:
- Challenge: Cassava requires sufficient water, but drought and irregular rainfall can pose a challenge in some regions.
- Troubleshooting: Implementing efficient irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting, mulching, and water conservation practices can help mitigate the effects of water scarcity.
3. Poor Soil Fertility:
- Challenge: Nutrient-deficient soils can result in stunted growth and reduced yields.
- Troubleshooting: Farmers should conduct soil tests to identify nutrient deficiencies and apply appropriate fertilizers or organic matter to improve soil fertility.
4. Weeds and Weed Control:
- Challenge: Weeds compete with cassava for resources and can reduce crop productivity.
- Troubleshooting: Employing manual or mechanical weeding, mulching, and using herbicides selectively can effectively control weeds.
5. Post-Harvest Losses:
- Challenge: Improper post-harvest handling can lead to spoilage and reduced product quality.
- Troubleshooting: Farmers should ensure prompt harvesting, proper cleaning, sorting, and appropriate storage conditions to minimize post-harvest losses.
6. Market Access and Price Fluctuations:
- Challenge: Accessing reliable markets and dealing with price fluctuations can impact profitability.
- Troubleshooting: Establishing long-term contracts with buyers, diversifying market channels, and value addition through processing can provide stability and better control over prices.
7. Lack of Financial Resources:
- Challenge: Starting and maintaining a cassava farm can require significant initial investment and ongoing financial resources.
- Troubleshooting: Farmers can explore financing options, government grants, or partnerships with investors to secure the necessary capital. Creating a well-structured business plan can also attract financial support.
8. Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events:
- Challenge: Climate change can result in unpredictable weather patterns and extreme events, impacting cassava growth and yields.
- Troubleshooting: Implementing climate-resilient farming practices, such as crop diversification, improving water management, and using drought-resistant varieties, can enhance the farm’s resilience.
9. Lack of Technical Knowledge and Training:
- Challenge: Inexperienced farmers may face difficulties in managing various aspects of cassava farming effectively.
- Troubleshooting: Participating in agricultural training programs, workshops, and seeking guidance from experienced farmers or agricultural extension services can enhance technical knowledge and skills.
10. Transportation and Infrastructure Challenges:
- Challenge: Limited transportation and inadequate infrastructure can hinder the timely delivery of cassava products to markets.
- Troubleshooting: Farmers can collaborate with local transportation providers or invest in their transportation facilities to improve logistics.
The bottom line
Cassava farming offers great potential for profitability and food security, but it requires careful planning and diligent execution. From conducting research and selecting suitable varieties to implementing effective pest management and marketing strategies, this comprehensive guide covers essential steps to establish and run a successful cassava farm.
By addressing challenges, staying informed on market trends, and adopting sustainable practices, farmers can ensure the longevity and prosperity of their cassava farming endeavors. With dedication and adaptability, cassava farming can contribute to both economic growth and sustainable agriculture practices.
Read also: Cashew nuts
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Related News

Fiber Crops Examples

BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE On ROOTS AND TUBERS (Cassava Production) Location OYO STATE, NIGERIA

Related Papers
Martin Chiona
Cassava has advantages over many other crops in that it tolerates very poor acid soils and still gives reasonable yields, is drought-tolerant, and has no fixed harvest date giving great flexibility to farming systems. However, present cassava yields of about 10 metric tons (t)/ha are far below the known potential of 50 t/ha or more. The reasons for this are poor agronomic practices (especially weed control), use of varieties of low yield potential, and losses due to diseases and pests. Yields can be improved with little extra input by (1) using correct agronomic practices, such as the optimum spacing, adequate weed control, and good quality planting material; (2) using varieties of known high yield potential; and (3) planting disease-free cuttings and resistant varieties. The future yield potential of cassava was estimated to be close to 90 ton/ha per year under ideal conditions. Resume Le manioc presente par rapport a de nombreuses autres cultures les avantages suivants: ii tolere ...
West African Journal of Applied Ecology
Emmanuel Kwesi Otoo
Agricultural Systems
malachy O Akoroda
Agro-Science
Yemi Olojede
Field Crops Research
Mabrouk El-Sharkawy , Javier Molina
Ifeanyi Ojiako
Crop Protection
Friday Ekeleme
Hemant Nitturkar
Rohanie Maharaj
A study was conducted in split-plot design to determine the effect of singleand double-row plantings on the yield of four sweet potato cultivars (local names: „Manager‟s Pudding‟, „Caroline Lee‟, „CBS 49‟ and „CBS 32‟) commonly planted on the estates of the Barbados Agricultural Management Company Ltd. Cuttings were established on raised beds 5.5 ft apart. Single-rows consisted of cuttings placed on the centre of the beds with a spacing of 1 ft intra-row. For the double-rows, cuttings were established on both sides of the bed with 1.5 ft between rows and 1 ft intra-row. Shortly after establishment, the sweet potato was sprayed with Fusilade® (Fluazifop-pbutyl) using the recommended rate for the control of grass weeds. Mono-ammonium Phosphate was manually placed 6 inches away from all cuttings, after they were well established, at a rate of 100 lb per acre. Yield data showed that double-row planting of „Caroline Lee‟, „CBS 49‟, „Manager‟s Pudding‟ and „CBS 32‟ resulted in 21.3%, 31.4...
RELATED PAPERS
Experimental Agriculture
Jules Pretty
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences
Naresh Mehta
International Letters of Natural Sciences
Mallikarjuna Rao Talluri
Naomi Schapiro
Arthur Nadú Rangel
Redox Biology
Shuchen Xin
Murilo Pinto
Mert Bolat , Rahmi Bolat
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Mark Krystal
tyghfg hjgfdfd
European Journal of Internal Medicine
Carlos Cafri
Shiv Bhatta
Robert L. Byer
Terra Latinoamericana
Marco Antonio Inzunza Ibarra
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health
Rivka Tuval-Mashiach
Neil Foster
Regional Formation and Development Studies
Vilma Atkociuniene
Transactions of the American Mathematical Society
Riccardo Biagioli
Scripta Scientifica Medica
M. Novakova
Michael Epis
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- All comments
Cassava: The Power Crop for Africa’s Food Future
- Share this article:

- 0 Population growth in Africa (3): six misconceptions about solutions 21 feb 2024
- 0 Five misconceptions about population growth in Africa (2) 9 feb 2024
- 0 Don’t Doubt: Intensify African Agriculture (2) 8 mrt 2023
- 2 Intensification of African agriculture serves food security, nature, climate and people (1) 8 feb 2023
- 0 Manual Harvesting, Infrastructural Deficits, Others Aiding Africa’s 100m MT Food Losses 16 okt 2021
- 0 Bridging the inequality gap in agriculture 25 jun 2021
- 0 Food Safety: Being responsible and responding to our ability 11 jun 2021
- 4 Africa is in between two era’s, like the West 9 jun 2021
- 0 Cooperatives: Achieving Financial Inclusion for Smallholder Farmers 4 jun 2021
- 19 ‘Africa needs to develop both its agriculture and food processing industry’ 15 aug 2020
The cassava processing market is being driven significantly by the extended applications in the end-use industries. The increasing use in the food industry and a corresponding rising demand from the feed industry drive the demand for processed cassava further and stimulate the market growth
Log in to comment and rate other comments. No account yet? Register now !
- Monday, May 27, 2024

© 2023 - Businessday NG. All Rights Reserved.

Standard Cassava Processing Business Plan with 3 Years Financial Analysis
We have developed a comprehensive and standardised cassava processing business plan, encompassing a range of products such as garri, flour, starch, and more. The purpose of this plan is to assist entrepreneurs in securing funds from investors, applying for bank loans, or accessing grants.
The cassava processing industry has witnessed significant growth and holds immense potential in Nigeria. As of the latest data, Nigeria stands as the largest cassava producer globally, surpassing Brazil by one-third and exceeding the production capacities of Thailand and Indonesia by almost double. Presently, Nigeria produces approximately 42 million metric tonnes (MT) of cassava annually, a figure projected to grow significantly by the year 2025 as government empowers more farmers.
Despite being the leading cassava producer, Nigeria’s involvement in the international cassava trade remains limited due to its focus on the domestic food market. The country predominantly utilises subsistence production methods, which are insufficient to meet industrial-level demands.
Recognising the need for commercial cassava production and processing both locally and internationally, recent and past governments have introduced policies to encourage and support this sector.
The Government Initiative on Cassava, aimed to highlight the potential of cassava as a foreign exchange earner for Nigeria. Additionally, it sought to develop the cassava production system to meet national demand sustainably. One of the primary objectives of this initiative was to generate more than US$7 billion in value-added cassava exports by the year 2025.
The vision for cassava encompassed rural industrial development, increasing incomes for producers, processors, and traders, and contributing to food security by shifting cassava from a primarily subsistence food to an industrial crop used in the production of ethanol, starch, pellets, and high-quality cassava flour for export.
To achieve this ambitious goal, Nigeria must adopt a demand-driven approach to promote, develop, and diversify its cassava-based industries.
By utilising our standardised business plan, entrepreneurs in the cassava processing sector can save valuable time, money, and energy. It serves as a strategic roadmap, enabling them to attract investors, secure bank loans, and access grants while leveraging Nigeria’s status as a global cassava production leader and harnessing the potential of the local and international markets.
If you are interested in starting or growing your cassava business and need a cassava business plan, we have one for you.
The cassava processing business plan comes with a 3-year financial analysis.
The complete cassava processing business plan is in Word Doc format, and the financial analysis is in Excel so that you can edit it to suit your taste.
The cassava processing business plan is fully updated with current research on how to start a cassava processing business, get the attention of the market, retain it, and make huge profits.
The cassava processing business plan also has an in-depth analysis of cassava processing equipment.
3-year automated financial model in MS Excel with complete industry research for this cassava business plan
To get this standard CASSAVA PROCESSING business plan for only N10,000
Let me give you an idea of what you should expect from the business plan:
1) Table of Contents
2) Executive Summary: The summary includes an introduction, product and service descriptions, marketing and sales, among others
3) Company Overview : This includes
- Mission Statement
- History and Current Status
- Markets and Products
- Keys to success
- Cost summary
4) Product description : All our products are described including other unique features.
5) Industry and Market Analysis
- Introduction
- Industry analysis
- Market analysis
- Customer analysis
- Competitor analysis
- SWOT Analysis
6) Marketing Strategy
- Target Market Strategy
- Product/Service Strategy
- Pricing Strategy
- Distribution Strategy
- Advertising and Promotion Strategy
- Sales Strategy
- Marketing and sales Forecasts
7) Operations
- Operations Strategy
- Scope of Operations
- Operating Expenses
8) Development
- Development Strategy
- Development Timeline
- Development Expenses
9) Management
- Company Organization
- Management Team
- Administrative Expenses
10) Summary of Financials
- Financial Assumptions
- Financial Forecasts
- Projected Cash Flow
- Income statement
iii. Balance sheet
- Profit and loss
- Profit Margin, chart etc
- Financial Risks
11) Appendices
Support for Product/Service Description (e.g., diagrams, pictures, etc.)
Support for Marketing and Sales Plan
Support for Development Plan
Support for Operations Plan
Resumes of Management Team
Financial Statements
- Income Statement [3 years]
- Balance Sheets [3 years]
- Cash Flow Statements [3 years]
- Ratio Analysis [3 years]
- Other supporting financial statements
What is the cost of the cassava processing Business Plan?
Well if I say N30,000 it is worth it but I won’t give you that amount and not even N20,000.
What about N15,000 ? I won’t still give you that amount. But for a LIMITED TIME I will allow you to pay N10,000
To access this standard cassava processing business plan, pay N10,000 into any of the accounts below:
You can pay into any of the following accounts:
Account Name: Etimate Global Services Account Number: 1150007557 Bank: Skye Bank or
Account Name: Utibe Etim Account Number: 0007852498 Bank: GTB or Account Name: Utibe Etim Account Number: 2012483183 Bank: UBA
AFTER PAYMENT: Please text or email your name, phone number, payment details, and your email address to 07031542324 or [email protected] and your cassava processing business plan will be sent to you
OTHER STANDARD CASSAVA BUSINESS PLANS
- Cassava Farming Business Plan With 3 Years Financial Analysis (N10,000) – Order Now
- Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan With 3 Years Financial Analysis (N10,000) – Order Now
- Ethanol Business Plan With 3 Years Financial Projections (N10,000) – Order Now
We have developed over 120 business plans and you can click the the link below to check them out.
CLICK HERE TO CHECK THE FULL LIST OF ALL THE BUSINESS PLANS WE HAVE HERE
WHAT CUSTOMERS ARE SAYING

I want to say a big thank you for the business plan you sent. The plan is rich and detailed and professionally developed as explained on your web page. In fact the plan worth more than price. I have gone through the financial template and I have made some changes to suit my needs and would present it to my banker next. Am I going to present it together with the financial template or should I only present the business plan?
I have gone through the financial template and I have made some changes to suit my needs and would present it to my banker next. Am I going to present it together with the financial template or should I only present the business plan?
Can I also send it for you to help me review the financial before I submit?
Mrs. Esther Enudi

07031542324
utibeman(@)gmail.com
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Share this:
About the author.
3 thoughts on “Standard Cassava Processing Business Plan with 3 Years Financial Analysis”
HI can i get this biz plan for 5000
Am highly interested in cassava processing business plan. Can you please assist me to have it if I pay 5000 Naira?
This is very educative, lucrative and interesting
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Business Documents & Templates
- Management & Strategy
Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan

Executive Summary
Agro Business Cassava Company is an agro-based company that focuses on cultivating improved varieties of cassava and also processing the cassava various products like cassava flake and starch. Agro Cassava Company is based in Imo State and has acquired 20 Hectaces of land for the farm land and also the processing plant.
As a company based in Owerri, Imo State and we have identified our target customers within Imo State and the neighbouring state and will grow into a business with outstanding sales by year three.
The processing plant will not only process our own harvested cassava, but we will be getting cassava from local farmers and process them to different products.
Nigeria is the highest cassava producer in the world, producing a third more than Brazil and almost double the production capacity of Thailand and Indonesia. Nigeria currently produces about 38 million metric tonnes (MT) per annum; a figure expected to double by 2020. Although the world leader in cassava production, Nigeria is not an active participant in cassava trade in the international markets because most of her cassava is targeted at the domestic food market. Her production methods are primarily subsistence in nature and therefore unable to support industrial level demands.
Global Demand for Nigerian Cassava Products, the world looks up to Nigeria for her cassava needs because we are the largest producers in the world. Unfortunately, we cannot help them because we consume over 38.7 million tons of our output as food and also our cassava products are more expensive than those of other countries. There is too much pressure on our cassava because it is used as food, raw materials and for export.
Currently, Agro Business has a main focus, which is to grow healthy and improved varieties of cassava. After harvesting, the cassava are further processed into its end product (flour and starch). Agro Business’s cassavas are grown in the best conditions to ensure that our cassava are disease-free and are or high quality. In other to ensure that our product stands out from our competitors, we employ the best farming technique and equipment to ensure quality cassavas that is fortified with vitamin A. Agro Business Company’s cassava are of the best varieties, the following varieties are recommended for their high yield and processing quality: TMS 30572, NR 8082, NR8083, TMS 4(2) 1425, TMS 81/00110, TMS 92/0326. Other varieties will also be added with time.
Table of Contents
1. Executive Summary
1.1 Objectives
1.2 Mission
1.3 Keys to Success
2. Company Summary
2.1 Company Ownership
2.2 Location and Facilities
2.3 Startup Summary
2.3.1 Required Funds
3. Product Description
3.1 Future Products
4. Market Analysis Summary
4.1 Market Segmentation
4.2 Target Market Segment Analysis
4.3 Industry Analysis
4.4 Challenges Facing the Cassava Flour Industry
4.5 SWOT Analysis
4.6 External Environmental Analysis
4.7 Competition and Buying Patterns
4.7.1 Main Competitors
4.8 Sales Strategy
4.8.1 Sales Forecast
5. Production Summary
5.1 Suppliers
5.2 Receiving
5.3 Storage
5.4 By-products
5.5 Production Process
6. Strategy and Implementation Summary
6.1 Competitive Edge
6.2 Marketing Strategy
6.3 Web Plan Summary
6.4 Website Marketing Strategy
6.5 Development Requirements
7. Management Summary
7.1 Organisational Structure
7.2 Management Team
7.3 Personnel Plan
Table: Salaries and Wages
8. Financial Plan
8.1 Important Assumptions
8.2 Break-even Analysis
Table: Break-even Analysis
8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
Table: Profit and Loss 3 years summary
Table: Profit and Loss first year
Table: Profit and Loss second year
Table: Profit and Loss third year
8.4 Projected Cashflow
Chart: Cashflow
Table: Cashflow year two
Table: Cashflow year three
8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
Table: Balance Sheet year one
Table: Balance Sheet year two
Table: Balance Sheet year three
Table: Fixed Operating Expenses
8.6 Long term Plan
Frequently Asked Questions About Cassava Farming
Is Cassava Farming Profitable?
Cassava farming can be very profitable if done right. Nigeria especially, is a big producer of cassava, in fact the biggest in the world, according to the Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations, 2023.
How to Write a Business Plan for Cassava Farming
First, carry out your feasibility research and identify your target market. Determine the resources you will need - labour, capital, land etc). Establish a business structure (if you don’t have one). Create a financial plan/budget. These have all been done in this Cassava Farming Business Plan. You can download and adapt to your own specific needs.
What is the Best Time to Plant Cassava?
Cassava can be normally planted at the beginning of the rainy season in Nigeria (April/May). This can extend to September/October.
Challenges of Cassava Farming
Some of the challenges you encounter in cassava farming include; long maturation cycle, cassava bacterial blight, cyanogenic levels, etc
What are the Different Stages in Cassava Farming?
Selection of site/land
Clearing and soil preparation
Picking the cassava variety to plant
Planting Cassava stems
Weed control
Fertilisation and manure management
Management of pest and disease
Resources, A. (2024). Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan. Afribary . Retrieved from https://afribary.com/templates/cassava-farming-and-processing-business-plan
Resources, Africana "Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan" Afribary . Afribary, 21 Mar. 2024, https://afribary.com/templates/cassava-farming-and-processing-business-plan. Accessed 27 May. 2024.
Resources, Africana . "Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan". Afribary , Afribary, 21 Mar. 2024. Web. 27 May. 2024. .
Resources, Africana . "Cassava Farming and Processing Business Plan" Afribary (2024). Accessed May 27, 2024. https://afribary.com/templates/cassava-farming-and-processing-business-plan
Document Details
Related works, catering business plan, piggery farming business plan, cosmetics business plan, hotel business plan, fashion (clothing) business plan, travel agency business plan, fuel station business plan, transport business plan, salon and spa business plan, day care business plan.
Privacy Policy | Refund Policy | Terms | Copyright | © 2024, Afribary Limited. All rights reserved.
Payment Method
Pay with card/bank/ussd/mobile money.
We accept several ATM, debit, credit cards. We also process bank transfer, direct bank debit, mobile money and USSD payments. Click "Pay Now" below to pay online and access works immediately.

Cassava Processing Plant Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business Plans » Agriculture Sector » Agro Processing
Are you about starting a cassava processing plant? If YES, here’s a complete sample cassava processing plant business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE .
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a cassava processing plant. We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample cassava processing plant marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for cassava processing plants. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
If you live in the united states, you might not know the value of going into the cassava processing business. This is because it is not a popular business in the US. But do you know that processed cassava is a major raw material cum ingredient in the production of alcoholic beverages?
As a matter of fact, cassava can be processed into biofuel, animal feed, laundry starch and for medicinal use. The good part is that cassava can be cultivated in the United States of America.
Cassava processing business is known to be a profitable business and over the years, it has evolved from small scale to a global industry in most countries where it is carried out. If you are considering starting a cassava processing business, the good news is that you can’t get it wrong.
This is because cassava can be processed into various forms for consumption by humans and livestock. It is important to state that starting a cassava processing business comes with its own fair share of challenges, but that does not rule out the fact that it is indeed a profitable business venture.
An aspiring entrepreneur can either choose to start a cassava processing business on a small scale or on a large scale depending on their financial status.
So, if you have decided to go into the cassava processing business, then you should ensure that you carry out thorough feasibility studies and market survey. Business plan is yet another very important business document that you should not take for granted when launching your own cassava processing business.
Below is a sample cassava processing business plan template that can help you to successfully write your own with little or no difficulty.
A Sample Cassava Processing Plant Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
Businesses in the cassava farming cum processing industry primarily grow different species of cassavas and process them for different purpose. As a matter of fact, worldwide, 800 million people depend on processed cassava as their primary food staple especially in Sub – Sahara Africa, South America and some parts of Asia.
Cassava is known to be the third-largest source of food carbohydrates in the tropics, after rice and maize. Cassava is indeed a major staple food in Africa, providing a basic food for over five million people. It is one of the most drought-tolerant crops, capable of growing on marginal soils. Nigeria is the world’s largest producer of cassava, while Thailand is the largest exporter of dried cassava.
Cassava is extensively cultivated as an annual crop in tropical and subtropical regions for its edible starchy tuberous root, a major source of carbohydrates. Although it is often called yuca in Spanish and in the United States, it is important to state that it differs from yucca, an unrelated fruit-bearing shrub in the family Asparagaceae.
The Cassava Farming cum Cassava Processing Industry is indeed a very large industry and pretty much thriving in countries such as Nigeria, Thailand, Brazil, Indonesia and Republic of the Congo et al. In 2014, global production of cassava root was 268 million tones, with Nigeria as the world’s largest producer of nearly 55 million tones or 21 percent of the world total.
According to the American Cancer Society, cassava is ineffective as an anti-cancer agent: “there is no convincing scientific evidence that cassava or tapioca is effective in preventing or treating cancer”.
As a matter of fact, with the recent advancement in technology, farmers can now comfortably grow crops such as cassava in a country where such crops can hardly survive and in places where there are few farm land.
One thing is certain when it comes to cassava processing business, if you are able to conduct your market research and feasibility studies before choosing a location for your cassava processing plant, you are more likely not going to struggle to grow the business.
2. Executive Summary
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a world class and registered cassava processing company that will be based in the outskirts of Dallas, Texas – United States.
We have done our detailed market research and feasibility studies and we were able to secure a suitable facility to build our processing plant. Our cassava processing plant is a going to be standard one hence will be involved in commercial cassava cultivation, laundry starch and animal feed production.
We will produce laundry starch, animal feeds and other products and ensure that they flood the market both in the United States and in other countries of the world; we want to compete with the best in the industry. We have also hired some key employees who are currently undergoing training so as to be able to fit into the ideal picture of the 21 st century cassava processing plant workforce that we want to build.
We are in the cassava processing business because we want to leverage on the vast opportunities available in the processing industry, to contribute our quota in growing the U.S. economy, in national food production, raw materials production for industries, to export our products from the United States to other countries and over and above to make profit.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is well positioned to become one of the leading cassava processing companies in the United States of America, which is why we have been able to source for the best hands and processing machinery to run the business with.
We have put process and strategies in place that will help us employ best practices when it comes to cassava processing as required by the regulating bodies in the United States of America.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a family business that is owned by Mr. Ola Williams and his immediate family members. The business will be fully and single handedly financed by Ola Williams and his immediate family members.
Before starting Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. Ola Williams has worked with some of the leading food processing and laundry starch production plants in the United States of America; he has a degree (B.Sc.) in Agriculture Science from A & M University Texas.
3. Our Products and Services
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a world class cassava processing company that is committed to producing processed and well – packaged cassava products for both the United States’ market and the global market. We are in this line of business to make profits, and we will ensure that we do all that is allowed by the law of the United States of America to achieve our business goals and objectives.
These are the products we will produce;
- Production of cassava flakes
- Production of tapioca
- Production of laundry starch
- Production of animal feeds
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our Vision is to become one of the leading laundry starch and animal feed production brand not just in the United States of America but also on the global stage.
- Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a world class cassava production company that is in business to produce laundry starch and animal feeds et al for both the United States market and the international market. We want our well – packaged laundry starch and animal feeds to flood every nooks and crannies of the United States and other countries of the world.
Our Business Structure
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a cassava processing company that intends starting small in Dallas – Texas, but hope to grow big in order to compete favorably with leading cassava processing companies both in the United States and on a global stage.
We are aware of the importance of building a solid business structure that can support the picture of the kind of world class business we want to own. This is why we are committed to only hire the best hands in and around Texas.
At Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. we will ensure that we hire people that are qualified, hardworking, dedicated, customer centric and are ready to work to help us build a prosperous business that will benefit all our stakeholders.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our senior management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of five years or more as agreed by the management of the farm. In view of the above, Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. have decided to hire qualified and competent hands to occupy the following positions;
- Chief Operating Officer
- Administrator / Accountant
- Laundry Starch and Animal Feeds Production Plant Manager
- Sales and Marketing Executive
- Field Employees
- Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Operating Officer:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results; developing incentives; developing a climate for offering information and opinions; providing educational opportunities.
- Creates and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
Administrator/Accountant
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the organization
- Serves as internal auditor for the organization
Laundry Starch and Animal Feed Production Manager/Supervisor
- Responsible for managing the laundry starch and animal feed production plant
- Supervises other workers within the department
- Works closely with the CEO to achieve the organizations’ goals and objectives
Sales and Marketing Officer
- Recognizes and reaches out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of relevant projects.
- Writes winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with company policy
- Responsible for handling business research, marker surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops executes and evaluates new plans for expanding increase sales
- Documents all customer contact and information
- Represents the company in strategic meetings
- Aids the increase sales and growth for the organization
Field Workers/Contract Staff
- Responsible for preparing the cassava that are to be processed
- Responsible for operating the cassava processing machine
- Backs up in loading and unloading raw materials and finished goods
- Carries out task in line with the stated job description
- Handles any other duties as assigned by the line manager
Client Service Executive/Front Desk Officer
- Welcomes guests and clients to the farm by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Ensures that all contacts with clients (e-mail, walk-In center, SMS or phone) provides the client with a personalized customer service experience of the highest level
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s products and services
- Manages administrative duties assigned by the manager in an effective and timely manner
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s products, promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
- Receives parcels / documents for Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.
- Distribute mails in Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.
6. SWOT Analysis
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. does not intend to launch out with trial and error hence the need to conduct a proper SWOT analysis. We know that if we get it right from the onset, we would have succeeded in creating the foundation that will help us build a standard cassava processing plant that will favorably compete with leading cassava processing plants in the United States of America and in the rest part of the world.
We are quite aware that there are several large, medium and small scale cassava processing companies all over Dallas – Texas and even in the same location where we intend locating ours, which is why we are following the due process of establishing a business.
We know that if a proper SWOT analysis is conducted for our business, we will be able to position our business to maximize our strength, leverage on the opportunities that will be available to us, mitigate our risks and be welled equipped to confront our threats.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. employed the services of an expert HR and Business Analyst with bias in the food processing industry to help us conduct a thorough SWOT analysis and to help us create a Business model that will help us achieve our business goals and objectives.
Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.;
Our strength as a cassava processing company is the fact that we have healthy relationships with loads of major players (both suppliers and buyers of cassava and processed cassava products) within and outside of the United States.
We have some of the latest commercial cassava processing equipment that will help us process and package cassava products in commercial quantities with less stress. Aside from our relationship (network) and equipment, we can confidently boast that we have some the most experienced hands in Dallas – Texas under our payroll.
Our weakness could be that we are a new cassava processing company in the United States, and perhaps the fact that cassava processing plant is not a popular venture in the US. We are aware of this and from our projection will overcome this weakness with time and turn it to a major advantage for the business which is why we are into laundry starch and animal feed production.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities that are available to us cannot be quantified; we know that there are loads of individuals who consume both organic and non – organic processed cassava in different forms both in the United States of America and other parts of the world.
We will ensure that we maximize the opportunities available to us. We will ensure that we create business structure and framework that will enable us go into biofuel production and the production of other alcoholic beverages from our cassava processing plant.
Some of the threats and challenges that we are likely going to face when we start our own cassava processing plant are global economic downturn that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters (drought, epidemics), unfavorable government policies and the arrival of a competitor within same location.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
One of the common trends in the cassava processing line of business is that most players in the industry are no longer concentrating only on processing cassava into various products but also running a standard commercial cassava farm.
So also, it is difficult to find a cassava processing plant engage in the processing of just a product; they are usually in the production of several products that can be gotten from cassava. Beside cassava can be consumed by both human and livestock hence it is ideal to process, package and ship laundry starch, animal feed, alcoholic beverages and biofuel et al to other countries of the world with ease.
8. Our Target Market
It is a known fact that the consumers of processed cassava and also those who benefit from the business value chain are all encompassing.
Almost every household make use or products from cassava or consumes cassava in different processed forms. In essence, a cassava processing company should be able to sell its products to as many people as possible including laundries, alcoholic beverage production companies, laundry starch production companies, livestock farmers and other production companies that make use of cassava byproducts.
We will ensure that we position our business to attract consumers of processed cassava products not just in the United States of America alone but also in other parts of the world which is why we will be exporting our products to other countries of the world.
Our Competitive Advantage
The truth is that it is easier to find entrepreneurs flocking towards an industry that is known to generate consistent income which is why there are a growing number of food processing companies in the United States of America and of course in most parts of the world.
As a matter of fact, entrepreneurs are encouraged by the government to embrace food production. This is so because part of the success of any nation is her ability to cultivate her own food and also export foods to other nations of the world.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is fully aware that there are competitions when it comes to selling processed cassava products all over the globe, which is why we decided to carry out thorough research so as to know how to take advantage of the available market in the United States and in other parts of the world.
We have done our homework and we have been able to highlight some factors that will give us competitive advantage in the marketplace; some of the factors are effective and reliable cassava processing processes that can help us sell our produce at competitive prices, good network and excellent relationship management.
Another competitive advantage that we are bringing to the industry is the fact that we have designed our business to operate an all-round standard cassava processing plant alongside our cassava farm. With this, we will be able to take advantage of all the available opportunities within the industry.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is in the cassava processing line of business for the purpose of maximizing profits hence we have decided to explore all the available opportunities within the industry to achieve our corporate goals and objectives.
Below are the sources we intend exploring to generate income for Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.
- Production and sale of cassava flakes and tapioca
- Production and sale of laundry starch and animal feeds.
- Production and sale of animal feeds
- Production and sale of biofuel
10. Sales Forecast
We conducted a thorough market survey and feasibility studies and we were able to discover that the sales generated by a cassava processing plant depends on the size of the plant and the products they are producing.
We have perfected our sales and marketing strategies and we are set to hit the ground running and we are quite optimistic that we will meet or even surpass our set sales target of generating enough income and build the business from survival to sustainability.
We have been able to critically examine the cassava processing business and we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast.
- First Fiscal Year: $200,000
- Second Fiscal Year-: $400,000
- Third Fiscal Year-: $750,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown that can impact negatively on household spending, bad weather cum natural disasters, and unfavorable government policies. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are quite aware that the reason why some cassava processing companies hardly make good profits is their inability to get steady supply of raw materials for their plant. In view of that, we decided to set up a standard commercial cassava farm to help us maximize profits.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited base on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall goal of the organization. We want to build a standard and world – class cassava processing company that will leverage on word of mouth advertisement from satisfied clients.
Over and above, we have perfected our sale and marketing strategies first by networking with agriculture merchants and companies that rely on retail processed cassava products. In summary, Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. will adopt the following strategies in marketing our processed cassava products;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to stake holders in the retail industry, households, laundromat, textile companies, livestock farms and production companies that rely on supply of processed cassava products.
- Advertise our business in related magazines and websites
- List our business on yellow pages ads
- Attend related food processing expos, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Engage in direct marketing
- Encourage the use of Word of mouth marketing (referrals)
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
Any business that wants to grow beyond the corner of the street or the city they are operating from must be ready and willing to utilize every available means to advertise and promote the business. We intend growing our business which is why we have perfected plans to build our brand via every available means.
We know that it is important to create strategies that will help us boost our brand awareness and to create a corporate identity for our cassava processing business. Below are the platforms we will leverage on to boost our cassava processing company – brand and to promote and advertise our business;
- Place adverts on both print (newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community based events
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our processed cassava products
- Install our billboards in strategic locations all around Dallas – Texas
- Engage in roadshows from time to time in targeted neighborhoods
- Distribute our fliers and handbills in target areas
- Contact laundries, livestock farms and production companies that rely on supply of processed cassava as raw materials, agriculture produce merchants and residence in our target areas by calling them up and informing them of our business
- List our company in local directories
- Advertise our company in our official website and employ strategies that will help us pull traffic to the site.
- Ensure that all our staff members wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles and trucks are well branded with our company logo
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Some of the factors that will help you sell your processed cassava products at the right price that will guarantee that you make profits is dependent on your strategy while some of the factors are beyond your control.
For example, if the climatic condition is unfavorable and if there are natural disasters in the location where you have your cassava farm, then it will directly affect the harvest of cassava and ultimately the prices of your processed cassava products.
We are quite aware that one of the easiest means of penetrating the market and acquiring loads of customers for all our processed cassava products is to sell them at competitive prices hence we will do all we can to ensure that the prices of our products are going to be what other cassava processing companies would look towards beating.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via Point of Sale Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via mobile money transfer
- Payment via bank draft
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our clients make payment without any stress on their part. Our bank account numbers will be made available on our website and promotional materials.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
When it comes to calculating the cost of starting a cassava processing plant with commercial cassava farms, there are some key factors that should serve as a guide. Factor such as the capacity of cassava processing plant you want to own, the product you want to produce and the size of the commercial cassava farm.
Besides, in setting up any business, the amount or cost will depend on the approach and scale you want to undertake. If you intend to start a world – class cassava processing plant, then you would need a good amount of capital as you would need to ensure that your employees are well taken care of, and that your production plant is conducive enough for workers to be creative and productive.
This means that the start-up can either be low or high depending on your goals, vision and aspirations for your business.
The tools and equipment that will be used are nearly the same cost everywhere, and any difference in prices would be minimal and can be overlooked. As for the detailed cost analysis for starting a cassava processing company; it might differ in other countries due to the value of their money.
Below are some of the basic areas we will spend our startup capital in setting up our cassava processing company;
- The total fee for incorporating the business in United States of America – $750
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $9,400
- The amount needed to acquire/lease a facility – $50,000
- The amount required for constructing a standard cassava processing plant – $150,000
- The cost for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines et al – $20,000
- The amount required for purchase of the first set of cassava supply et al – $50,000
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $40,000
- The cost of launching an official website – $600
- The amount required for payment of workers for a period of 3 months – $100,000
- Additional Expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,000
Going by the report from detailed research and feasibility studies conducted, we will need an average of $350,000 to start a standard cassava processing plant with commercial cassava farm.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.
No matter how fantastic your business idea might be, if you don’t have the required money to finance the business, the business might not become a reality. Finance is a very important factor when it comes to starting a standard cassava processing plan with commercial cassava farm. No doubt raising startup capital for a business might not come cheap, but it is a task that an entrepreneur must go through.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is a family business that will be owned and managed by Ola Williams and his immediate family members. They are the sole financier of the firm, but may likely welcome other partners later which is why they decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital for the business to just three major sources.
These are the areas where we intend sourcing for fund for Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co.;
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings and sale of his stocks
- Generate part of the startup capital from friends and other extended family members
- Generate a larger chunk of the startup capital from the bank (loan facility).
N.B: We have been able to generate about $100,000 ( Personal savings $80,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000 ) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $250,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of the employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business, then it won’t be too long before the business close shop.
One of our major goals of starting Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without the need for injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running. We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to sell our processed and packaged laundry starch and animal feeds, biofuel and other processed cassava products a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are well prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Ola Williams® Cassava Processing Co. will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our organization’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and re – training of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts various banks in the United States: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of all forms of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Leasing of facility in Dallas – Texas and construct processing plant: Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Startup Capital Generation: Completed
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging Marketing/Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed work tools, machines and equipment: Completed
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Farm land Treatment, Health and Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with key players in the industry (agriculture farm produce merchants, production companies that rely on supply of processed cassava products and transporter/haulage companies et al): Completed
Related Posts:
- Coconut Oil Production Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Rice Processing Mill Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Soybean Oil Production Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Garri Processing Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Wheat Flour Mill Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Start Your Business
- Grow Your Business
- Business Ideas
- Business Plan Writing

How To Start A Lucrative Cassava Farming Business In Nigeria And Africa: The Complete Guide
Cassava farming is one of the major agricultural practices in Nigeria, as the crop is a staple food for millions of people in the country. Cassava is a tropical crop that is well-suited to the climate and soil conditions in Nigeria, and it is grown in all parts of the country. Nigeria is one of the largest cassava producers in the world, with an estimated production of over 54 million metric tons in 2020.
The importance of cassava farming in Nigeria cannot be overemphasized, as the crop is not only a major source of food but also a source of income for millions of farmers and other stakeholders along the value chain. Cassava is a versatile crop that can be processed into various products such as garri, fufu, starch, flour, and animal feed, among others. The crop is also a major source of raw material for the production of ethanol and other industrial products.
In recent years, the Nigerian government has made efforts to promote cassava farming as a means of diversifying the economy and reducing the country’s dependence on oil. The government has also initiated policies and programs aimed at increasing cassava production and improving the quality of the crop. Additionally, the poultry industry in Nigeria has provided a market for cassava products such as cassava peel meal and cassava chips, which are used as feed for poultry.
Despite the numerous benefits of cassava farming in Nigeria, the sector is faced with several challenges, including inadequate funding, low yields, and lack of access to modern farming technologies. However, with the right support from the government and other stakeholders, cassava farming in Nigeria has the potential to contribute significantly to the country’s economy and improve the livelihoods of millions of people.
If you’re looking for an agricultural business that would ensure you always almost sell out all your harvests, cassava farming is one great farming business to start.
See Also: How To Start A Lucrative Poultry Farming Business In Nigeria: The Complete Guide
What Is Cassava?
Cassava, scientifically known as Manihot esculenta, is a starchy root vegetable that is widely grown and consumed in Nigeria and Africa. It is an important staple crop that is used in many traditional dishes and also serves as a source of income for many small-scale farmers.
What Is Cassava Farming In Nigeria and Africa About?
Cassava farming is the cultivation of cassava plants for food, feed, and industrial uses. Cassava is an important crop in Nigeria and many other countries in the tropical regions of the world. It is a starchy root vegetable that is rich in carbohydrates and a good source of dietary fiber, minerals, and vitamins. Cassava farming has become a major agricultural enterprise in Nigeria due to the numerous benefits and business opportunities it offers. The crop is used for various purposes such as food, animal feed, alcohol production, starch production, and biofuel production. Cassava farming is an important source of livelihood for millions of farmers in Nigeria, and it has the potential to contribute significantly to the country’s economic growth and development.
Benefits of Cassava Farming In Nigeria and Africa
Cassava farming is an important economic activity in Nigeria and across Africa, providing a range of benefits to farmers, consumers, and the wider economy. Here are 10 benefits of cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa:
- Food security: Cassava is a staple food crop in many African countries and is a reliable source of food for millions of people.
- Income generation: Cassava farming is an important source of income for smallholder farmers, providing employment and income opportunities for rural communities.
- Drought resistance: Cassava is drought-resistant and can grow in marginal environments, making it an important crop for food security in regions with unpredictable rainfall.
- Soil fertility: Cassava farming can improve soil fertility, as the crop has a deep root system that can break up compacted soils and increase soil organic matter.
- Climate resilience: Cassava is an important crop for climate resilience, as it can tolerate a wide range of temperatures and is resistant to pests and diseases.
- Nutritional value: Cassava is a rich source of carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, and is an important food source for vulnerable populations.
- Industrial applications: Cassava can be processed into a range of industrial products, including starch, ethanol, and animal feed, providing additional income streams for farmers.
- Export opportunities: Cassava products are in high demand in international markets, providing export opportunities for farmers and processors.
- Gender empowerment: Cassava farming can provide opportunities for women and girls to participate in agriculture and generate income.
- Reduced poverty: Cassava farming can help reduce poverty and improve livelihoods, particularly in rural communities where other economic opportunities may be limited.
See Also: How To Start A Lucrative Tomato Farming Business In Nigeria (Comprehensive Guide + eBook)
Health Benefits of Cassava
Cassava is a starchy root vegetable that is widely cultivated and consumed in Nigeria and Africa. Here are 15 health benefits of cassava:
- Good source of energy: Cassava is a rich source of carbohydrates, which makes it an excellent source of energy for the body.
- Helps in digestion: Cassava is rich in dietary fiber, which helps in promoting healthy digestion and prevents constipation.
- Lowers cholesterol levels: Cassava contains compounds that help in reducing bad cholesterol levels in the body, thus reducing the risk of heart disease.
- Good for the immune system: Cassava is rich in vitamin C, which helps in boosting the immune system and protecting the body against infections.
- Improves brain function: Cassava contains vitamin B6, which helps in improving brain function and reducing the risk of cognitive decline.
- Rich in minerals: Cassava is rich in minerals like calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are essential for maintaining healthy bones, muscles, and nerve function.
- Helps in weight management: Cassava is low in calories and fat, making it an excellent food for those trying to manage their weight.
- Reduces inflammation: Cassava contains compounds that have anti-inflammatory properties, which help in reducing inflammation in the body.
- Good for the skin: Cassava is rich in vitamin C, which helps in promoting healthy skin and reducing the risk of skin damage.
- Helps in treating diarrhea: Cassava contains compounds that have anti-diarrheal properties, making it an effective treatment for diarrhea.
- Rich in antioxidants: Cassava is rich in antioxidants, which help in reducing oxidative stress and preventing cell damage.
- Promotes healthy blood circulation: Cassava contains compounds that help in improving blood circulation, which is essential for maintaining good health.
- Good for the eyes: Cassava is rich in vitamin A, which helps in promoting healthy eyes and reducing the risk of eye diseases.
- Good for the heart: Cassava contains compounds that help in reducing the risk of heart disease by lowering blood pressure and improving blood flow.
- Helps in treating arthritis: Cassava contains compounds that have anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective treatment for arthritis.
See Also: 50+ Lucrative Farming & Agricultural Business Ideas In Nigeria And Africa
Business Opportunities In Cassava Farming In Nigeria and Africa
Sure, here are 10 business opportunities of cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa:
- Cassava Processing: There is a high demand for processed cassava products such as flour, starch, and chips, which are used in various industries, including food, textile, and paper. This presents a significant opportunity for cassava farmers to venture into cassava processing.
- Animal Feed Production: Cassava is an important ingredient in animal feed production, particularly for poultry, pigs, and fish. Cassava farmers can earn additional income by selling cassava peels and other by-products to animal feed manufacturers.
- Biofuel Production: Cassava is a rich source of starch, which can be converted into biofuel. This presents a significant business opportunity for cassava farmers to supply raw materials to biofuel producers.
- Ethanol Production: The demand for ethanol as a fuel additive is increasing, and cassava is a viable source of ethanol production. Cassava farmers can supply ethanol producers with the raw material.
- Textile Production: Cassava fibers can be processed into textiles, presenting an opportunity for cassava farmers to enter the textile industry.
- Cassava Flour Production: Cassava flour is an alternative to wheat flour and is used in various food products. Cassava farmers can process their cassava tubers into flour for sale.
- Alcohol Production: Cassava can be fermented to produce alcoholic beverages such as beer and wine. Cassava farmers can venture into alcohol production as a value-added business.
- Medicine Production: Cassava has medicinal properties and is used in the production of various drugs. Cassava farmers can supply cassava roots to pharmaceutical companies.
- Cassava Chips Production: Cassava chips are a popular snack and can be processed and packaged for sale. Cassava farmers can add value to their cassava harvest by producing and selling chips.
- Export: The demand for cassava products is high in other African countries and beyond, presenting a great opportunity for cassava farmers to export their products and earn foreign exchange.
These are just a few examples of the business opportunities available in cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa. With the right resources and expertise, cassava farming can be a profitable business venture.
See Also: How To Start A Profitable Fish Farming Business In Nigeria
− Export Business −
Make Your First $25,000 Exporting Products From Nigeria WITHOUT SPENDING YOUR OWN MONEY!
Our in-depth online export course is specifically designed to help you build a successful export business from scratch IN 90 DAYS WITHOUT LOSING MONEY FROM YOUR INVESTMENTS OR SPENDING YOUR OWN MONEY! And in the process, show you how to MAKE YOUR FIRST $25,000 from the export business within the first 3 months of finishing the course.
Click Here To Learn More >>
Facts about cassava farming in nigeria and africa.
here are 20 facts about cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa:
- Cassava is one of the most important food crops in Nigeria and Africa, providing food and income for millions of people.
- Nigeria is the world’s largest producer of cassava, accounting for about 20% of global production.
- Cassava is a drought-tolerant crop that can grow in a wide range of soils and climatic conditions, making it an important crop for smallholder farmers in Africa.
- Cassava can be processed into a variety of products, including flour, starch, and ethanol.
- Cassava is a rich source of carbohydrates, fiber, and essential vitamins and minerals, making it an important part of a balanced diet.
- Cassava is also an important feed crop for livestock, particularly for poultry and pigs.
- Cassava farming is an important source of income for smallholder farmers, particularly women, who make up a significant portion of cassava farmers in Africa.
- The processing and marketing of cassava products also provides employment opportunities for people along the value chain.
- The cassava value chain in Nigeria and Africa is often characterized by low productivity and limited access to markets, posing challenges for smallholder farmers.
- There are ongoing efforts to improve the productivity and profitability of cassava farming in Africa through research and development of new varieties and technologies.
- Cassava farming has a low environmental impact, as it requires less water and fertilizer than other crops and can help to improve soil quality.
- The leaves of the cassava plant are also edible and can be used to make nutritious vegetable dishes.
- Cassava is an important food security crop, particularly during times of drought and other climate shocks.
- In addition to food and income, cassava farming can also provide social benefits, such as community building and cultural preservation.
- The global market for cassava products is growing, particularly for ethanol, which is used as a biofuel.
- Cassava is a versatile crop that can be grown in a variety of systems, including intercropping and agroforestry.
- The use of improved cassava varieties and good agricultural practices can help to increase yields and improve the quality of cassava products.
- Cassava farming can contribute to sustainable development in Africa, particularly through its potential to support smallholder livelihoods and food security.
- Cassava is also an important crop for nutrition-sensitive agriculture, as it can help to address malnutrition and other health challenges.
- There are ongoing efforts to promote the development of cassava value chains in Africa, including through policy and investment support.
See Also: The Comprehensive Guide To Real Estate Investment
Types Of Cassava Farming In Nigeria and Africa
Cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa can be broadly classified into two types: subsistence and commercial farming.
Subsistence cassava farming is practiced by small-scale farmers who cultivate cassava mainly for household consumption or for sale at the local markets. The farms are generally small in size, with low input and output, and mostly rain-fed. Farmers use traditional and manual methods for planting, harvesting and processing cassava.
Commercial cassava farming, on the other hand, involves large-scale cultivation of cassava for sale to the industrial market. The farms are often mechanized, with high input and output. Commercial cassava farming also involves the use of improved and hybrid cassava varieties, as well as modern agricultural practices such as irrigation, fertilizer application, and pest and disease management. The crops are sold to processing companies for the production of various products such as garri, flour, starch, and animal feed.
Apart from these two types, there are also other forms of cassava farming such as intercropping, where cassava is grown alongside other crops, and organic cassava farming, where no synthetic chemicals are used in the cultivation process.
Types Of Cassavas In Nigeria and Africa
There are various types of cassava grown in Nigeria and Africa. Some of the common types of cassava include:
- TMS 30572: This is a high-yielding cassava variety that is resistant to pests and diseases. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TME 419: This variety is known for its high yield, good taste, and fast maturity. It is mostly grown in Nigeria, Uganda, and other East African countries.
- TMS 98/0581: This is a variety of cassava that is resistant to pests and diseases. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 98/0505: This is a variety of cassava that is high-yielding and has good nutritional value. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 4(2) 1425: This is a variety of cassava that is resistant to pests and diseases. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 30555: This is a variety of cassava that is high-yielding and has good nutritional value. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 92/0326: This is a variety of cassava that is resistant to pests and diseases. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 92/0057: This is a variety of cassava that is high-yielding and has good nutritional value. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 96/1414: This is a variety of cassava that is resistant to pests and diseases. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
- TMS 92/0067: This is a variety of cassava that is high-yielding and has good nutritional value. It is mostly grown in Nigeria and other West African countries.
See Also: How To Start An E-Commerce Business In Nigeria: The Comprehensive Cost
The Planting & Harvesting Seasons For Cassava In Nigeria and Africa
The planting and harvest seasons for cassava in Nigeria and Africa vary depending on the region and climate. Generally, cassava is planted in Nigeria and Africa in the rainy season, which typically starts in March and ends in October. The best planting time for cassava is in the early rainy season when the soil is moist enough to support germination and growth.
The harvest season for cassava usually starts six to twelve months after planting, depending on the variety and climate. In Nigeria and Africa, cassava is typically harvested from October to December, during the dry season, when the tubers are fully matured and ready for processing. Cassava can be harvested by hand or using machines such as harvesters and diggers. After harvest, the cassava roots are processed into various products such as garri, fufu, and starch.
How To Start Cassava Farming In Nigeria: Step-By-Step Guide
here’s a guide on how to start cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa:
- Conduct research and feasibility study: Before venturing into cassava farming, it is important to research and study the crop to understand its demands, market value, and potential profit margins. Identify the best planting season and varieties suitable for the soil type in your area.
- Acquire a farmland: Once you have conducted your research, secure a farmland suitable for cassava farming. The soil must be well-drained and not waterlogged.
- Prepare the land: Clear the land and make ridges or mounds for planting. You can use machines or employ manual labor.
- Get quality cassava stems: Buy high-quality stems from reliable sources. Avoid stems that have been affected by pests or diseases.
- Planting: Cut the stems into pieces and plant them in the ridges, ensuring they are not too deep in the soil. Plant during the rainy season and ensure the soil is moist.
- Maintain the farm: Weed the farm regularly and apply fertilizer as required. Also, ensure the farm is well-drained and watered when necessary.
- Harvesting: Harvest cassava between 8-12 months of planting. Ensure you harvest only mature cassava as immature ones may not have reached their potential yield.
- Processing: After harvesting, you can process the cassava into various products such as garri, fufu, tapioca, starch, and flour.
- Marketing: Market your cassava products to various buyers, including local markets, processing companies, and exporters.
- Continuously improve: Continuously look for ways to improve the farm’s productivity and profitability. Attend seminars and workshops on modern farming techniques and technologies.
By following these steps, you can start a successful cassava farming business in Nigeria and Africa.
See Also: How To Write The Perfect Business Plan In Nigeria and Africa That Will Get Funded: The Complete Guide
How To Process & Package Cassava In Nigeria or Africa
The following are the step-by-step guide on how to process and package cassava in Nigeria and Africa:
- Harvesting: Cassava is ready for harvest 9-12 months after planting, depending on the variety. To harvest, the farmer uses a machete or hoe to cut the stem of the cassava plant, leaving the tubers in the ground.
- Washing and peeling: After harvesting, the cassava tubers are washed to remove dirt and other impurities. The tubers are then peeled with a sharp knife or cassava peeling machine to remove the outer brown layer.
- Grating: The peeled cassava is grated with a grater or a cassava processing machine. This process is important to break down the cassava into smaller pieces for easier processing.
- Pressing: The grated cassava is placed in a hydraulic press or a manual press to remove excess water. This process is important to reduce the water content in the cassava, making it easier to process and package.
- Drying: The pressed cassava is spread on a flat surface to dry under the sun or in a drying machine. This process helps to reduce the moisture content of the cassava, making it suitable for processing into different products.
- Milling: The dried cassava is milled into flour using a milling machine. The flour can be used to make different cassava-based products like garri, fufu, and tapioca.
- Packaging: The cassava flour is packaged in airtight bags or containers to preserve its freshness and prevent contamination.
- Storage and distribution: The packaged cassava flour is stored in a cool and dry place to prevent spoilage. The cassava flour can be distributed to different markets and sold to consumers.
See Also: How To Start A Lucrative Palm Oil Production Business In Nigeria And Africa: The Complete Guide
Types Of Equipment & Tools Used In The Cassava Farming Business In Nigeria or Africa
- Cassava peeling machine: This machine is used to remove the outer brown skin of the cassava before further processing. It is designed to save time and labor while improving the quality of the finished product.
- Cassava washing machine: This machine is used to wash and clean the peeled cassava before further processing. It helps to remove dirt, sand, and other impurities from the cassava.
- Cassava grating machine: This machine is used to grate the cassava into smaller pieces or mash. It can also be used for the production of garri, fufu, and other cassava-based products.
- Cassava dewatering machine: This machine is used to remove excess water from the grated cassava. It is a crucial step in the production of cassava flour and starch.
- Cassava flour milling machine: This machine is used to mill the dried cassava chips into flour. It can also be used for the production of garri.
- Cassava starch extraction machine: This machine is used to extract starch from the cassava pulp. It involves a process of washing, crushing, and sieving the cassava pulp to separate the starch from the fibers.
- Cassava flour sifting machine: This machine is used to sieve the cassava flour to remove lumps and impurities.
- Cassava packing machine: This machine is used to package the finished cassava flour or other cassava-based products. It can be manual or automatic, depending on the scale of production.
See Also: How To Start A Business In Nigeria and Africa: The Complete Guide
Target Market For The Cassava Farming Business In Nigeria or Africa
- Food Industry: Cassava products such as garri, fufu, and tapioca are staple foods in many parts of Nigeria and Africa. These products have a ready market in urban and rural areas, where they are consumed as a substitute for rice, yam, and other starchy foods. Cassava flour and starch are also used as ingredients in the production of various food products, such as bread, biscuits, and noodles.
- Livestock Feed Industry: Cassava leaves and peels are a good source of animal feed, especially for pigs and poultry. Cassava meal, a by-product of cassava processing, is also used as a feed ingredient for livestock. The demand for cassava-based animal feed is expected to increase as the livestock industry in Nigeria and Africa continues to grow.
- Industrial Applications: Cassava starch is used in various industrial applications, such as paper, textile, and pharmaceutical industries. The demand for cassava starch is expected to grow as these industries expand in Nigeria and Africa.
- Export Market: Cassava products such as garri, fufu, and tapioca have a significant demand in the international market, especially in the Caribbean, South America, and Asia. Nigeria is one of the leading exporters of cassava products in the world, and there is a growing opportunity for other African countries to tap into this market.
See Also: How To Start A Lucrative Import/Export Business In Nigeria and Africa: The Complete Guide
How To Sell or Market Cassava Products In Nigeria or Africa
Here are 10 ways to sell or market cassava products in Nigeria and Africa:
- Local markets: Sell your cassava products, such as garri, fufu, and tapioca, at local markets in your area. This is an effective way to reach your target customers who prefer fresh, locally produced food.
- Online marketplaces: You can also sell your cassava products on online marketplaces like Jumia, Konga, and Amazon. This allows you to reach customers beyond your local area and grow your customer base.
- Supermarkets and grocery stores: Partner with supermarkets and grocery stores to stock your cassava products on their shelves. This will give your products more visibility and make them accessible to a wider range of customers.
- Export: Exporting cassava products is a lucrative business opportunity, particularly to countries like China and Europe, where there is high demand for cassava products. You can sell your cassava products through export companies or directly to international buyers.
- Food processing companies: Partner with food processing companies that use cassava as an ingredient in their products. This can provide a steady market for your cassava and ensure that your products are used in higher-value products.
- Direct to consumer delivery: Offer direct to consumer delivery of your cassava products. Customers can place orders on your website or social media pages, and you can deliver the products to their doorstep.
- Restaurants and food vendors: Partner with restaurants and food vendors to supply them with your cassava products. This can provide a steady market and increase the visibility of your products.
- Catering services: Partner with catering services to supply them with your cassava products for events and parties. This can provide a consistent stream of revenue for your business.
- Cooperative societies: Join cooperative societies to access a wider market for your cassava products. These societies can provide a platform for networking, learning, and marketing your products to a wider audience.
- Advertise on social media: Use social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram to advertise your cassava products. Social media is a powerful tool for reaching a wider audience and generating leads for your business.
Challenges Of Cassava Farming In Nigeria and Africa
Cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa is an important agricultural activity that provides income and sustenance for many smallholder farmers. However, like any other agricultural enterprise, cassava farming comes with its own set of challenges. Here are 15 challenges that cassava farmers in Nigeria and Africa may face:
- Pest and disease management: Cassava is susceptible to pests and diseases, which can significantly reduce yields.
- Lack of access to quality seeds: Quality seeds are crucial for a successful cassava farm, but many farmers may not have access to them.
- Climate change: Changes in rainfall patterns, temperature, and extreme weather events can negatively impact cassava production.
- Limited access to credit: Many smallholder farmers may not have access to credit to purchase inputs or invest in their farms.
- Poor soil quality: Cassava requires well-draining, fertile soil to grow properly, but many farmers may not have access to such soils.
- High labor costs: Cassava farming requires significant labor input, which can be costly for farmers.
- Limited access to markets: Cassava farmers may face difficulty accessing markets to sell their products.
- High transportation costs: The cost of transporting cassava products to markets can be prohibitive for smallholder farmers.
- Lack of processing facilities: Many smallholder farmers may not have access to processing facilities to add value to their cassava products.
- Limited knowledge and technical know-how: Many smallholder farmers may not have the technical know-how required for successful cassava farming.
- Inadequate storage facilities: Cassava roots can deteriorate quickly if not stored properly, but many farmers may not have access to adequate storage facilities.
- Poor road infrastructure: Poor road infrastructure can make it difficult for farmers to transport their products to markets.
- Competition with other crops: Farmers may face competition with other crops for land, resources, and market access.
- Land tenure issues: Land tenure issues can make it difficult for farmers to secure land for cassava farming.
- Inadequate government support: Government policies and support for cassava farming may be insufficient, limiting the potential for the sector to grow and develop.
Overall, while cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa has significant potential, there are many challenges that farmers may face. Addressing these challenges requires a multifaceted approach that includes improving access to inputs and credit, enhancing technical know-how, improving infrastructure, and increasing government support for the sector.
See Also: How To Start A Lucrative Onion Farming Business (Complete Guide)
To Sum It Up
In conclusion, cassava farming presents a significant opportunity for farmers and entrepreneurs in Nigeria and Africa as a whole. With the numerous benefits, business opportunities, and market demand, cassava farming can be a profitable venture.
The versatility of cassava, as both a food and industrial crop, makes it a valuable asset that can contribute to food security and economic development in the region. However, the challenges, such as disease and pests, lack of access to finance and market, and low mechanization, need to be addressed to achieve the full potential of cassava farming.
With the right resources, knowledge, and skills, anyone can start cassava farming, from small-scale subsistence farmers to large-scale commercial farms. It is essential to follow the best practices for planting, harvesting, processing, and marketing to maximize yields and profits.
Overall, cassava farming in Nigeria and Africa holds tremendous potential to contribute to the growth and development of the agriculture sector, increase income for farmers and entrepreneurs, and improve food security and nutrition in the region.
Professional Business Plan Writing Service Writing a bank and investor ready professional CASSAVA farming business plan can be challenging. If you need a professional and affordable business plan service, STARTUPTIPSDAILY’S MBA STANDARD PROFESSIONAL BUSINESS PLAN WRITING SERVICE is perfect for your business. All you have to do is request an understanding of your proposed business model, and you’d have a professional MBA standard business plan ready for you in anywhere from 5 to 14 days. YOU CAN CLICK HERE TO GET STARTED WITH USING STARTUPTIPSDAILY’S PROFESSIONAL BUSINESS PLAN WRITING SERVICE TO CREATE THE PERFECT BUSINESS PLAN THAT’D GET ACCEPTED ANYWHERE.
What are your thoughts on how to start cassava farming in Nigeria, Africa, or any other part of the world? Let me know by leaving a comment below.
Image Source: Pixabay
Latest articles
How To Increase Your Profits With TradingView
How To Start A Lucrative Export of Limestone From Nigeria and Africa To International Buyers: The Complete Guide
How To Start A Lucrative Export of Calcium Carbonate From Nigeria and Africa To International Buyers: The Complete Guide
How To Start A Lucrative Calcium Carbonate Production and Supply Business In Nigeria and Africa: The Complete Guide
Related articles
174 Comments
Hi Thanks for sharing your knowledge,it’s very informative and helpful. I wanted to know if the figures and data are recent inorder for me to complete my cassava business plan. I want to own my own cassava processing plant but in a small scare, do you know how much this will cost me?
Hi Charles,
The figures will differ based on your region and inflation.
You should make price enquiries in your location to be fully certain that your costing is well written for your business plan.
Thank you for asking.
I found your topic informative and make me want to learn this business. i want to venture into cassava business be it processing or cultivation from the the beginning but I dont have any experience whatsoever on it which now bring me to my real questions;
1 . How can one source for Cassava 2 . What to budget for buying 3 . How to do the processing 4 . What to produce 5 . How to Market the product 6 . Are there any organization to join when venturing into this
Please kindly enlighten us on these highlighted questions and also add your own if I have missed out anything .
Best Regards
Hi Adeniyi,
A cassava farming e-book would soon be available on the blog.
Do lookout for it.
Hi May i get a copy of cassava farming ebook through my email address. Thanks
When the eBook is available, everyone that reads this article would know about it.
I by name zubairu Mohammed I want to for cassava business an I have a land but I don’t have the farmashal sapot
Hi Zubairu,
Have you tried reaching out to the Bank of Agriculture?
Thank you for the comment.
Hi, thank u for those pieces of information. I’m writing a business proposal for cassava cultivation. I would like your assistance on the steps to consider.
Hi Vitalis,
Please send an email to [email protected] and I’d be happy to help.
email address [email protected]
I have 2 acres of land rented and I want to plant on it. What kind of crops can I plant now? Is it advisable to plant cassava now?
Any crop is right if you have a large ready market for it.
First try to get buyers. If they bulge both in large numbers and desperacy, you can know the right crop you should venture into.
Fermentation Tank: NGN 220,000 Hydraulic Press: NGN 280,000 Hammer Mill: NGN 700,000 The above is for wat… wat end product of cassava will it give?
A cassava farming book answering all your questions would soon be available on the blog.
For now, you can do a google search on each to understand them.
good morning sir, pls how can i get your phone no. i need to talk to you on a farm proposal i need. thanks
Hi Johnson,
Please send an email to [email protected]
Hello Stan please I’d like to know if you have a personal experience in cassava farming and if yes where do you have your farm, what is your hectrage like, and what variety of cassava did you plant? Joseph Odama from the international institute of tropical agriculture (IITA) Ibadan. Telephone+2348060181862. Thanks.
We do farm consulting and so, work with different farmers to enlighten people through the blog.
You can also reach me via [email protected]
Thank you for asking still.
Hello Mr. Stan, I have about 20 hectares of land and I wish to cultivate cassava in it. Please i need help and assistance. How many tonnes of cassava can be harvested in a hectare on land and how much is a tonne?
Roughly about 25 to 30 tonnes of cassava can be cultivated on one hectare of land.
Thank you for your response. Pls how much is a tonne of cassava in the market? Can you please inbox me your contact number for your one n one assistance.
It depends.
A Metric Tonne of cassava chips is 25,000 Naira.
A Metric Tonne of cassava flour is 135,000 Naira.
A Metric Tonne of cassava starch is 648,000 Naira.
These prices would have changed because of the inflation.
But you get the idea.
Thank you very much. Please if it’s okay with you, can you be my consultant regarding this venture. Just let me know your mind, thank you.
You can always ask me any questions.
Just send an email to [email protected] and I’ll try my best to always reply.
wow! these prices are good. please i would love to know which market these sale prices are quoted from. Nigerian market? or European or American market. God bless you for these info
These are last year’s prices.
We’d update as soon as we can.
U are Gof sent especially for people like me I really appreciate the good work more grease to ur elbow.pls can u help with an example of well articulated business plan/proposal for a Grant I am applying for
Thank you for the commendation, Ahotu.
Please send an email to [email protected] regarding the business plan.
Do have a great time.
Thank you for sharing, I find it very handy especially at this time that I am thinking of venturing into the Agribusiness world
Thank you for the commendation Bosun.
Thanks for all these information
Thank you for the commendation Olu.
pls, i need to know how buy cassava tuber from farmers in nigeria because i want to venture into agriculture tell me the details the address, email, the price and any other information i need to know thanks.God bless u
To get the real time costs, I’d advice you visit a market or several cassava farms.
The variations in their prices will give you the best idea.
Do leave a comment on your findings.
Hello Mr Stan, please what is a tonne I don’t understand also I have four plot of land 400 by 400 please what quantity of cassava someone can get from it . Thanks Olukayode David
The answer is quite tardy because, it depends on how many can be grown all year round.
I’d advise you visit an existing cassava farm to get a comprehensive answer on that.
But pending then, anyone who runs an active cassava farm could leave the answer as a comment.
Then again, thank you for asking.
This is a wonderful lesson sir. Plz sir during saling how can I sale the product so that I can get my profi or i my saling the cassava direct from the farm or i will have to process it before? Thank you.
Hi If I invest on cassava farm on an area of 1 hectares what will be my return on investment?
Hi Okechukwu,
We’d have to do a more updated market research to cover that.
We’re also working on a cassava farming eBook that will cover that.
[…] Source: Stan Edom […]
Thank you for the information because information is power.i would like to ask you sir, i like to venture into agric. business but am little bit confused whether to go into pigry or cassava? your advice
Only venture into what you have a sound knowledge of and have seen another succeed at.
This should guide you to make a great decision.
Thank you for the comment Yinka.
Is the ebook on casava farming available yet?
The eBook is in the works.
When it’s done, I’ll do well to let everyone know.
Well done. Great write up
Thank you for the commendation Kehinde.
Have a great time!
good post…keep it up its actually help in my research on cassava farming
I’m glad it helped your research AK.
This write up is xtremely informative and poverty alleviating indeed.Recent market survey tells about the skyrocketing price of the white yam flour popularly call (Elubo Lafun). Well done keep it up @ more grease to ur elbow.Riches lies in filthiness @ only the sensitive @ wise can discover it.Let’s go back to our known african profession
Thank you for the commendation Marcus.
Have a wonderful time!
Pls how can I get a high yield variety cassava stems to buy in Benin City, Edo state.
You can get cassava stems from Ososa and Odogbolu axis in Ogun state.
I’m not too familiar with the Edo state axis, but you can find three businesses in Edo state that can sell you cassava stems here >>> http://www.vconnect.com/edo/list-of-cassava-stem-vendors-search_p670
Overtime, more people will leave valuable comments here that can answer more of your questions and others.
This write up is highly educative and informative I really appreciate the effort of the write May God Almighty continue to be with u My question is that can u assist to give a rough estimate on the cost of farming cassava on 10acres of land. thanks for your anticipated response.
Hi Adenusi,
Thank you for the kind words.
Concerning your question:
It depends on if the farmland has been cleared for cultivation or not.
If trees are present and you’re currently purchasing the cassava stem cuttings, engaging labour, carrying out irrigation, clearing the land, and more, you could spend about 500,000 Naira ($1063).
If trees are absent, you could spend about 300,000 Naira ($638).
10acres, for clearing the land by tractor budget around 605,000,for bedding, it’s around 80,000, for buying the cassava stem 50,000 and some other additional cost, I just started my own 10acre
Please Fakorede, I need to have a discussion with you. Please leave a text on my mobile 08135387614 and I will call in return.
Dear Fakorede, can we talk on whatsapp or through email? 08066705231 or [email protected] . Thanks as i await your response
please fakorede i need your phone number for guides on this business. Here is mine 08033242780
Thank you for the information
You’re welcome Abasiama.
Hello Stanley. Weldone for the good work. Pls, I am interested in the cassava farming. I met a professional farmer who told me that to get 1acre of land, clearing and cultivating on lease is #60k and havesting is #150k i.e during havesting time 1acre of land of cassava can only give #150k but I was wondering how can I acre of land give 150k where 1 pickup motor is #120k in ogun state. Pls. How much can I make in one acre of cassava land. Thx.
The reality is the fertility of the soil will determine what value of cassava you’d harvest and the cost of clearing and harvesting is dependent on your negotiating power.
Also, generating 150,000 Naira ($500) for an acre now (2016/2017) is a far cry. It is most likely 100,000 Naira worth of cassava max, except if the land is very fertile, and so, can produce larger and better cassava yields.
This is one reason people buy acres of land to cultivate cassava crops.
hello Mr Stan pls are u saying #60,000 can cultivate 1acre of cassava farmland with due considerations to cost of herbicides, pesticides and fertilizer and other farm inputs. my second question is that I was told by a consultant that from a very good fertile land we should be able to get 25-30 tonnes pls is it true with respect to your answer above (#100,000) that you said is realistic
Hi Bankole,
All you stated are valid.
Bankole meant to say that the consultant said 25-30 tonnes of cassava can be obtained from 1acre of land. But you earlier said that, that is attainable on 1 hectare land.
Could you please give some clarity. I am extremely glad to find myself here. Good bless you Stan
The factors surrounding the crop’s growth determines what is possible and what is not.
I sincerely appreciate your effort Stan …more grease to your elbow… please kindly inform me when the ebook on cassava processing is available
Thank you for the kind words Taofik.
I’ll do well to let everyone know once the eBook is available.
More grease to your elbows Mr. Stanley M interested for the ebook
Thank you for the commendation Tobias.
When the eBook is available, I’ll do well to let everyone know.
Without a bankable biz proposal,collateral and connection,can there be any loan from the said bank?Is there any loan,at all? Great job u’re doing here!Waitn 4 d e-book!
The truth is, it’s better you go through a business plan competition like AYEEN. They shortlist business plans and help facilitate funding for them through the Bank of Industry (BOI). Last year, they helped about 500 businesses.
The eBook is currently in the works. When it’s available, I’ll do well to let everyone know.
pls Mr Stan, how much do you think a bundle of cassava cost now?
I’m not quite sure about now due to the exchange rate.
pls help me out, some one said to buy cassava stem for an acre will cost like 60k, pls aw true is that? and how many heaps can be made for cassava cultivation on an acre ? pls how much averagely (profit) can be gotten from an acre?
The profit from an acre is largely dependent on your cost of labour and your cassava yield. The yield is determined by the fertility level of the land and if you’re using high yield cassava stem cuttings or not. The truth is after 12 months, you may not make up to 100,000 Naira in profits if you’re not using high yield cassava stem cuttings. The larger the scale at which you execute your cassava farm, the more profitable you can be.
Also, you can’t completely determine how many stem cuttings will work for an acre because the farmland measurements are different per state. The best way to know for sure in your own state is to buy and plant.
Concerning heaps per acre, the tubers don’t grow in proportion to each other. some are usually far bigger than others, resulting in different numbers on every harvest.
very interesting motivating
Thank you for the comment Elias.
Great information on agriculture poroject. My question is how many strands of cassava plant will an Acre of land contain.
That’s a very broad question and no one really has an answer to that.
Great work and thanks for sharing. I have just acquired 65 acres of land and prefer to plant cassava, maize and soya beans mainly. The farm is in Ido local government of Oyo State. Please where can we source high quality seeds and cassava cuttings we need. Also what is the quantity we need for the space. Regards
You can get seeds from some locations in Ogun State.
Also, we’re starting up an affordable agric supply chain service for small businesses soon.
It will be available sometime in May or early July.
We’ll do well to announce once it is.
Hello kunle, am currently within ido local government and privileged to have an access to land for farming right now, however I believe I can help or assist on reputable places of where to get high quality cassava stem cuttings and maize seeds as well, the maize seeds have planted has been good from the result am seeing even by planting 1 seed, 2 seeds, 3 seeds and 4 seeds per hole, have seen a 98% germination rate so far. As for the cassava stems, it depends on the specie you want which is also dependent on the market you are targeting. if you have further questions you can let me know and you can also contact me for more information Through my email [email protected]
Thank you Oluwafemi, Sorry, I have been out of town for some time but will contact you shortly.
Kunle Owoseje
Hi stan, Trust you are doing good.could you please send e book on cassava plantation to my email.
Hi Benjamin,
When the eBook is available, we’ll do well to let everyone know.
I need a business plan to follow as a guide in writing mine …please help
Hi Oladele,
Thanks for this post. Pls do cassave grow anywhere? Or still depends on land nutrients.
Hi Micheal,
The growth of every kind of farm product is highly dependent on the soil type and atmospheric conditions.
Hi, I have always desired to go into Agriculture however, I am still comtemplating on the particular product to cultivate, the quantity of land to purchase, the cost implication and the location for the farm. I need a guide for the different options of crops with the inherent pros and cons to enable me make a good choice. I will very much love to chat and talk with you on this if you will be available.
You can reach me via email at [email protected] or via phone at the phone number listed on the contact us page.
Pls, can u test land soil ?
Can testing soil reduce chemical and fertilizer one needed?
The answer to all your questions is a yes.
Hi Stan, Great job you’ve done with this write up. May God enrich your life and enlarge your coast as you have done for several people with this info.
Thank you for the kind words Segun.
I wish you the same.
Tanks so much Stan.I’ve learnt alot from this post. I just need a little clarification,u said 25-30tonnes can be gotten 4rm an hectare of land and each tonne cost about 25,000naira. If that is the case how come u said ones profit in an hectare of land may not be up to 100,000naira,when 25,000×30tonnes should be giving about 750000.please clarify me on this. tt
The price per ton varies. And 25,000 is for cassava chips, not tubers, which would be harvested.
Once you factor in all the direct costs and expenses, you’re left with little.
So it’s advisable to go large scale or use high-yield stem cuttings, so you can try to meet the 25 to 30 tons harvest potential.
Thanks for sharing this information. But i wish to ask if after i harvest the cassava can i still use the harvested stem as seed? and again, is a plot equivalent to an acre?
Hi Chinedu,
1). The cassava stems can be planted.
2). An acre is roughly about 6 plots of land.
Sir i also wish to ask how a cassava stem can be stored.
One way you can store your cassava stems is by burying them after harvest, so they don’t dry up. They can also be stored in trenches under the shades of mostly plantains, amongst several other methods like roguing.
And againg I already have about an hectre of land availale in Ukwa East, Abia State, and from your land specs, i believe the land qualifies to be used as a cassava farm, because Ukwa East lga is known to have a flatbed landscape. Sir, pardon me to ask if it is necessary to wait till April before i can plant my cassava if i want to use irrigation farming method. I plan to use artificial water instead of waiting for the rain, don’t know if it is possible?
I really love what you guys are doing, a big thanks to you all. In the future when are investment yield i would really want to have you guys as my consultant.
An irrigation system is expensive for small farmers and will eat into your profits.
To confirm if the land is fertile, please contact the local agricultural association in your state.
They should be able to help you out better.
Hello, I can say this for sure, what you’ve got on your site is revolutionary and enough to change anybody’s life. Just stumbled on your site and have been going through your articles and honestly at about 12:17am, I can’t hide my excitement cos I found just what I’ve been looking for. I will love to have your thought on Cassava processing in huge commercial scale, if it’s profitable as standalone venture. Picking a start with the thought of the financial implications and other requirements has left me somewhat stuck if not overwhelmed. I will really appreciate a perspective for direction. Thanks.
Hi Gabriel,
Before considering the profitable scale, you need to consider your ability to build a strong supply chain network.
I’d also advise you carry out a feasibility study before you begin.
Hello Stan… This is such a wonderful piece and I am about to start up my own cassava farm. I just acquired 10acres of land in Ogun state. I don’t have any experience in Farming and I have a budget of 500k for the 10 acres which is to cover all labour cost as well as planting. This is a fertile land cos there are lots of cassava farms around. My fear is how to control pest and rodents and how much do I stand to gain on 10acres. Thank you
Hi Oludayo,
Your yield is relative to the type of stem cuttings planted and your farming practice.
I’d advice you hire professionals to manage your farm at its inception, for you.
without Agriculture what can we do for the life of our country,we thank God for the gitf of Agriculture in Nigeria.
Thank you for the comment, Joseph.
there is land but no money to start a good farm. am asking how do I start
You could try to raise money from family and friends first.
Thanks for your good work. I have a 3acres plantain Farm. I just registered the Agric business and need to write a business plan as agro hub to other farmers on organic crops and animals. Thanks ahead
Hi Adedeji,
help me with the business plan you wrote
Hi thanks for the information, can I use half plot of land for commercial farming of cassava?
You’d achieve next to nothing with a half plot.
The minimum you should consider using is a hectare.
Hello Stan, You are such a gift…. Can u advise on Inter-cropping maize and castor…and also which do u think is more profitable,maize or cassava farming please.I will also like to chat u on whatsapp pls….08137575773
The profitability of any business lies in the strength of the entrepreneur’s supply chain.
I hope you do understand.
You can reach me on the phone number listed on the contact us page.
Hello Mr Stan, Thank you for educating us about this great opportunity, and also for your prompt articulated responses to questions asked. May God continue to bless you.
Thank you for the kind words, Ikenna.
May God bless you too.
thanks, please how much does it cost to proccess 4tonne of cassava into gari using mechanical method (i.e cassava proccessing plant)
Hi Arinola,
I may not be able to give that answer, but I’d advise you do a market research to get a current figure.
Hi Stan. I can only say thank you very much for all you are doing for Nigerians who are interested in agriculture. May God bless you abundantly and the Holy Book says that “He adds no pain to His blessings.” Please I want to know which is more profitable between cassava farming and yam farming giving that all conditions are right? thank you very much in advance for your response.
My take is Cassava farming.
Ultimately, the strength of your supply chain network determines the returns on your investments.
Good job Stan.
Thank you for the commendation, Adeola.
Good day Mr Stan.
I am Adeola. I have gone through your responses to peoples’ question and thanks for the selfless contribution.
I plan venturing into garri processing using my cassava farming as source of raw materials.
I need a business plan on both cassava farming and garri processing. Am interested in what tonage of garri can the machine process per day and what tonage of cassava required. This will inform me of how many acres of land do i need to plan for in order not to run out of raw materials throughout the year.
I also need your ebook on cassava farming. I need to know the best time to plant my cassava.
Thank u for your early response.
I believe I’ve sent you an email, Adeola.
Good Afternoon Mr. Stan, pls is the e-book ready. Am thinking of going into cassava farming and I believe that the book will help me. [email protected]
The eBook will be live on the blog in two weeks.
Do be on the look out for it.
Hi, Please can you send me a comprehensive business plan for cassava farming and garri processing on a large scale in order to develop my Own.
This is really awesome and inspiring. I have been doing a lot of research lately on which of the crops to start farming. I buy the idea of this cassava farming and I will be glad if I can have access to the Ebook on Cassava farming. Thanks for the good work and empowerment of startups.
The book will be available soon.
I am James Mwape, a Zambian. I want to venture into cassava production and processing. I have been encouraged by the way Nigerians handle cassava. My main interest at the moment is in finished products which can be sold by simple businesses. I asking you to give me information on some of these products. I would appreciate if you can provide me with any information you think can be useful. Thanks in anticipation.
There’s a wide array of processed products like ethanol, flour, garri, and much more that you can get from Cassava.
A google search would be a great way to start.
How can one identify the cassava possessing the qualities you mentioned above in your discussion on SELECTING THE BEST CASSAVA VARIETY TO PLANT?
I’d advise you reach out to Cassava Growers on how to get high yield cassava stem cuttings.
Lovely post, I hope the ebook is out Mr Stan
Soon, Taiwo.
Stan, you’re doing a great job here. Keep it up
Thank you for the commendation, Charles.
Do have a great time!
GOOD JOB, pls what period of the year can one cultivate cassava and yam and how many month will it take to be harvest.
Hi Abdulwahab,
The best time is around April/May.
I’ll need the ebook too, Gmail: [email protected] .
Thanks in anticipation
Good morning Stan,
I am pleased to send you this mail. Hope you and yours are doing great.
My brother has a 53 acre yet to be cultivated land in Oyo state, he wants to go into planting and cropping of cassava, maize and cashew.
What suggestions do you have for him and is it possible to get a robust business plan to drive them?
Warm regards.
Hi Abidemi,
I’d advise he works with consultants to help him setup the farm.
Hello Abidemi, getting a competent consultant or a professional is the best solution on cultivating the 53 acres, However I can be of great impact either as a consultant, professional or any other. I have a cassava farm of my own, and I also belong to a cooperative whereby we are cultivating cassava and maize on 450 acres next planting season. However, so many people lose money in farming due to lack of technical know-how which I can provide like selecting and getting a viable specie of cassava through stakeholders in IITA. conditions to be met for bumper harvest etc. You can contact me Via my email: [email protected] for my services.
Akinwa Oluwafemi, weldone. Please do you have the idea of how much is required to set up a garri processing company? And all to set up a cassava farm?
Good morning stan, you are doing a great job here, I really do appreciate your effort! please I want to start cassava farming on an acre of land in ogun state basically for garri processing, I am deeply interested on how not to run out of raw material after the 1st harvest so production can continue all year round! and please do you have any idea of how I can get a locally fabricated peelers, washers,graters, de-watering system or big hydraulics system, all equipment needed to set up a small scale garri processing factory with less labour? my e mail is [email protected]
Hi Dehinde,
The best place to fabricate anything now is in Nnewi, Anambra state.
Good day Stan, great piece… I’m planning to go into cassava production. However your cost breakdown analysis was about 2 years ago. Please can you send an updated one if it’s not too inconvenient.
Hi Ferdinand,
We can prepare you a business plan with updated financials.
Do let me know if you’re interested in the service by sending an email to [email protected]
Hi Stan, I have approximately 8 hectares of Cassava farm which will be fully matured by May. I want to sell to industries using Cassava starch/syrup for production. I have no contact for that now. Can you link me?
please i need a prepared business plan with updated financials for the next five years.
Hi it’s me iskaba iskelebete iskoloboto when are we getting our cassava ebook
You are really doing a great job. thanks for the info shared. Please I would love to invest in one acre of cassava farm. I am a corporate guy, but I am really interested in farming but dont have the time. Can you give me a profitability analysis of investing in one acre of cassava farm.
Is the eBook on cassava farming out?
Good work.Please,send me a business plan on Cassava farming on three acres land.
Please send an email to [email protected] .
Mr Stanley, thank you so much for the great work you’ve been doing here. I found it educative and informative which allow me to take bold step. Thank you ones again.
Mr Stanley, I appreciate your good deeds, this platform is educative and informative. I just stubby into this blog through Google search, I have one acre of land want to cultivate plaintain and cassava on it; please I wish to know if I can start this month. Thank you so much for the great work.
Please I need a comprehensive business plan for cassava farming and gaari production on a large scale. [email protected]
am very grateful for these information on cassava farming, more grease to your elbow. pls i want to know if one can cultivate cassava twice in a year. secondly i want to no if there are companies in enugu or environs that needs cassava tubers? thirdly, how much to lease an hectare of land? thanks
Please i have a very fertile farm land of 5000 plots for lease/sale in umuosi, Ndoki, Oyigbo, Rivers state. Note free light is available here too. contact me on whatsapp +2348181624843
I really enjoy reading this, I stumble into it while googling on the most lucrative things to plant. I’m thinking of investing in farming even though I have no idea on it, what I have in mind is to grow any of these things: cassava, maize or plaintain. I want to lease about two to three acres of land because I don’t know how expensive buying the land may be. Please I need advise on how to go about these things as I know next to nothing on them. Thank you.
Thank you sir, i have see your response toward people requests, pls i need a business plan on cassava farming for 5 years
Comments are closed.
Popular articles
How To Start A Lucrative Dry Kpomo (Cow Skin) Production Business In Nigeria and Africa: The Complete Guide + Business Plan
How To Start A Lucrative Foodstuff Supply Business in Nigeria and Africa: The Complete Guide
How To Start A Lucrative Potato Farming Business In Nigeria Or Africa: The Complete Guide
50+ Lucrative Farming and Agricultural Business Ideas In Nigeria And Africa
Recent Articles
Subscribe to get the latest news, offers and special announcements.
© Copyright 2023 - Startup Tips Daily Media
Sustainable Cassava: A Case Study of Global Sustainability
- First Online: 22 May 2024
Cite this chapter

- Shrikaant Kulkarni 4 , 5
Part of the book series: World Sustainability Series ((WSUSE))
Cassava (Manihot esculenta), a staple crop is very vital in ensuring food security in tropical countries. Cassava cultivation has its own agricultural and environmental impacts like destruction of habitat and degradation of soil if its cultivation, production, and recovery are not managed well. Therefore, agricultural and environmental implications may arise and need to be taken care of before recommending cassava farming as the “best agricultural practice”. What is proposed is systematic and scientific research on practices employed in cassava cultivation and its impact on recovery efficiency, quality, profitability, conservation of natural resources, sustenance of natural habitats and biodiversity, bio-systems, and ecosystems, apart from other agricultural and environmental fallouts. This study will help map and further our knowledge about the multi-functionality and sustainability of cassava farming practices. This chapter discusses the good farming practices that are responsible for producing cassava with better yield as well as the impact of cassava farming on agriculture and the environment at large. The discussion will also shed light on the factors influencing production efficiency and the reasons for production inefficiency. It will also dwell upon some policy recommendations to improve cassava cultivation, production, and recovery scenarios.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Adem Esmail B, Geneletti D (2018) Multi-criteria decision analysis for nature conservation: a review of 20 years of applications. Methods Ecol Evol 9:42–53
Article Google Scholar
Agwu EA, Anyaeche CL (2007) Adoption of improved cassava varieties in six rural communities in Anambra state, Nigeria. Afr J Biotechnol 6(2):89–98
Google Scholar
Allem AC (2002) The origins and taxonomy of cassava. In: Hillocks RJ, Thresh JM, Bellotti AC (eds) Cassava: biology, production and utilization. CABI Publishing, pp 1–16
Anshebo T, Tofu A, Tsegaye E, Tadesse T, Kifle A, Dange Y (2004) New cassava varieties for the tropical semi-arid climate of Ethiopia. Proceedings of the 9th international society for tropical root crops-Africa branch (ISTRC-AB) symposium
Antle JM (2008) Climate change and agriculture: economic impacts. Choices—Mag Food, Farm, Resour Issues 23(1):9–11
Atser G, Dixon A, Ekeleme F, Chikoye D, Dashiell K, Ayankanmi T (2017) The ABC of weed management in cassava production in Nigeria: a training manual. International institute of tropical agriculture (IITA)
Ayinde OE, Ajewole OO, Ogunlade I, Adewumi MO (2010) Empirical analysis of agricultural production and climate change: a case study of Nigeria. J Sustain Dev Afr 12(6):275–283
Biruk S (2013) The assessment of root crops contribution to household food security: the case of Soddo Zuria district, SNNPR
Burns A, Gleadow R, Cliff J, Zacarias A, Cavagnaro T (2010) Cassava: the drought, war and famine crop in a changing world. Sustainability 2:3572–3607
CSA (2018) Ethiopians’ demography and agricultural products estimates, Ethiopia
Dada AD (2016) Taking local industry to global market: the case for Nigerian cassava processing companies. Eur J Manag Bus Econ 7:80–92
Dicks L, Haddaway N, Hernández-Morcillo M, Mattsson B, Randall N, Failler P (2017) Knowledge synthesis for environmental decisions: an evaluation of existing methods, and guidance for their selection, use and development: a report from the EKLIPSE project
Doré T, Makowski D, Malézieux E, Munier-Jolain N, Tchamitchian M, Tittonell P (2011) Facing up to the paradigm of ecological intensification in agronomy: revisiting methods, concepts and knowledge. Eur J Agron 34:197–210
El-Sharkawy M (2012) Stress-tolerant cassava: the role of integrative ecophysiology-breeding research in crop improvement. Open J Soil Sci 2:162. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojss.2012.22022
Enete AA (2013) Challenges of agricultural adaptation to climate change: the case of cassava post-harvest in Southeast Nigeria. Int J Clim Change Strat Mgt 5(4):455–470
Ewubare DB, Ologhadien ST (2019) Impact of agricultural financing on cassava production in Nigeria. Int J Econ Financ Manag 4:50–57
Ezekiel AA, Olawuyi SO, Ganiyu MO, Ojedokun IK, Adeyemo SS (2012) Effects of climate change on cassava productivity in Ilesa-east local government area, Osun state, Nigeria. Br J Arts Soc Sci 10(2):153–162
FAO statistics (2020a)
FAO statistics (2020b)
FAO (2018) FAOSTAT database. http://www.fao.org/faostat/
Fermont AM (2009) Cassava and soil fertility in intensifying smallholder farming systems of East Africa. Wageningen University, Wageningen, Netherlands
Fermont AM, van Asten PJA, Tittonell P, van Wijk MT, Giller KE (2009) Closing the cassava yield gap: an analysis from smallholder farms in East Africa. Field Crops Res 112:24–36
Food and Agriculture Data (2019)
Graffham A, Naziri D, Sergeant A, Sanni L, Abayomi L, Siwoku B (2019) Market opportunities for cassava in Nigeria. Gates Open Res 3:924. https://doi.org/10.21955/gatesopenres.1115809
Hassan R, Nhemachena C (2008) Determinants of African farmers’ strategies for adapting to climate change: multinomial choice analysis. Afri J Agric Res Econ 2(1):83–104
Henri-Ukoha A (2020) Assessment of the viability of climate adaptation strategies of cassava based farmers in southern Nigeria. J Agric Food Sci 18(1):105–117
Hillocks RJ, Thresh JM, Bellotti AC (eds) (2002) Cassava biology, production and utilization. CABI Publishing
Howeler R, Aye TM (2014) Sustainable management of cassava in Asia: from research to practice. International center for tropical agriculture (CIAT)
Howeler R, Lutaladio N, Thomas G (2013) Save and grow: cassava. A guide to sustainable production intensification
Ikuemonisan ES, Mafimisebi TE, Ajibefun I, Adenegan K (2020) Cassava production in Nigeria: trends, instability and decomposition analysis (1970–2018). Heliyon 6(10):2–4
Inegbedion HE, Inegbedion EE, Obadiaru ED, Asaleye AJ, Ayeni A, Aremu C (2020) Cassava attractiveness in Nigeria: a policy improvement approach. J Agribus Dev Emerg Econ 10:157–175. https://doi.org/10.1108/JADEE-05-2019-0068
IPCC (2013) Climate change 2013: the physical science basis. contribution of working group I to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. In: Stocker TF, Qin D, Plattner GK, Tignor M, Allen SK, Boschung J, Nauels A, Xia Y, Bex V, Midgley PM (eds) Cambridge University Press
IPCC (2014) Summary for policymakers, climate change: impacts, adaptation, and vulnerability. Part A: global and sectoral aspects. Contribution of working group II to the fifth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. Cambridge University Press
James KL, Randall NP, Haddaway NR (2016) A methodology for systematic mapping in environmental sciences. Environ Evid 5:7
Jarvis A, Ramirez-Villegas J, Campo BVH, Navarro-Racines C (2012) Is cassava the answer to African climate change adaptation? Trop Plant Biol 5:9–29
Kebede A, Teshome B, Wondimu A, Belay A, Wodajo B, Lakew A (2012) Detoxification and consumption of cassava based foods in South West Ethiopia. Pak J Nutr 11:237. https://doi.org/10.3923/pjn.2012.237.242
Article CAS Google Scholar
Kintché K, Hauser S, Mahungu NM, Ndonda A, Lukombo S, Nhamo N et al (2017) Cassava yield loss in farmer fields was mainly caused by low soil fertility and suboptimal management practices in two provinces of the democratic Republic of Congo. Eur J Agron 89:107–123
Kormawa P, Akoroda M (2003) Cassava supply chain arrangement for industrial utilization in Nigeria. IITA
Laekemariam F (2016) Soil nutrient status of smallholder cassava farms in southern Ethiopia. J Biol Agric Healthc 6:12–18
Legesse ZL (2018) Determinant factors and their coping strategies of cassava production of farm households: the case of Amaro district in Southern Nations, nationalities and peoples regional state of Ethiopia. Int J Innov Res Educ Sci 5:2349–5219
Lenka S, Lenka NK (2014) Conservative tillage for climate change mitigation-the reality. Clim Change Environ Sustain 2(1):1–9
Louhichi K, Temursho U, Colen L, Paloma SG (2019) Upscaling the productivity performance of the agricultural commercialization cluster initiative in Ethiopia
Matemilola S (2017) The challenges of food security in Nigeria. Open Access Libr J 4(12):1–22. https://doi.org/10.4236/oalib.1104185
Mathende J (2006) An analysis of the production of cassava as a food security option for Zimbabwe. University of Pretoria, Pretoria, South Africa
McQuate GT (2011) Assessment of attractiveness of cassava as a roosting plant for the melon fly Bactrocera cucurbitae, and the oriental fruit fly, B. dorsalis. J Insect Sci 11:30. https://doi.org/10.1673/031.011.0130
Morris ML, Binswanger-Mikhize HP, Byerlee D (2009) Awakening Africa’s sleeping giant: prospects for commercial agriculture in the Guinea Savannah zone and beyond. The World Bank
Mulualem T, Dagne Y (2015) Farmer’s appraisal, manifestation and scaling up of improved cassava technologies in moisture stressed areas of southern Ethiopia. J Genet Environ Resour 3:100–105
Mulualem T, WeldeMichael G, Benti T, Walle T (2013) Genetic diversity of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) genotypes in Ethiopia. Greener J Agric Sci 3:636–642. https://doi.org/10.15580/GJAS.2013.3.061013658
Mustefa B, Ayele A, Tilahun M, Parabathina RK (2017) Studies on economic efficiency of coffee production in Ilu Abbabor Zone, Oromia region, Ethiopia. J Agric Econ Rural Dev 3:293–306
Nassar NM (2007) Wild and indigenous cassava, Manihot esculenta Crantz diversity: an untapped genetic resource. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:1523–1530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-006-9144-y
Nwaiwu IU, Ohajianya DO, Orebiyi JS et al (2014) Climate change trend and appropriate mitigation and adaptation strategies in Southeast Nigeria. Glob J Biol Agric Health Sci 3(1):120–125
Nwokoro SO, Orheruata AM, Ordiah PM (2002) Replacement of maize with cassava sievates in cockerel starter diets: effect on performance and carcass characteristics. Trop Anim Health Prod 34(2):163–167
Obayelu AE, Olarewaju TO, Oyelami NL (2014) Effect of rural infrastructure on profitability and productivity of cassava-based farms in Odogbolu local government area, Ogun state, Nigeria. J Agric Sci Belgrade 59(2):187–200
Ogunniyi LT, Ajao AO, Olapade-Ogunwole F, Ganiyu MO (2012) Resource-use efficiency of cassava production in Atakunmosa local government area of Osun state. Prime J Soc Sci 1:27–30
Ogunpaimo OR, Dipeolu AO, Ogunpaimo OJ, Akinbode SO (2011) Determinants of choice of climate change adaptation options among cassava farmers, in southwest Nigeria. FUTO J Ser 6(1):25–39
Owoeye RS (2020) Factors influencing cassava farmers’ choices of climate adaptation strategies in rainforest agro-ecological zone of southwest, Nigeria. Int J Environ Agric Res 6(3):4–9
Parmar A, Fikre A, Sturm B, Hensel O (2018) Post-harvest management and associated food losses and by-products of cassava in southern Ethiopia. Food Sec 10:419–435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-018-0774-7
Poole N (2010) Zambia cassava sector policy—recommendations in support of strategy implementation
Pretty J, Toulmin C, Williams S (2011) Sustainable intensification in African agriculture. Int J Agric Sustain 9:5–24
Ravindranath NH, Sathaye JA (2002) Climate change and developing countries (1st edn). Kluwer Academic Publishers. https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-47980-X
Reynolds TW, Waddington SR, Anderson CL, Chew A, True Z, Cullen A (2015) Environmental impacts and constraints associated with the production of major food crops in Sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia. Food Secur 7:795–822
Sarka S (2017) Factors affecting farmers’ market participation decision and amount of cassava supplied to the market in Wolaita Zone, Snnpr, Ethiopia. J Econ Sustain Dev 8:7
Shackelford GE, Steward PR, German RN, Sait SM, Benton TG (2015) Conservation planning in agricultural landscapes: hotspots of conflict between agriculture and nature. Divers Distrib 21:357–367
Sutherland WJ, Wordley CFR (2018) A fresh approach to evidence synthesis. Nature 558:364
Tadesse B, Tilahun Y, Bekele T, Mekonen G (2021) Assessment of challenges of crop production and marketing in Bench-Sheko, Kaffa, Sheka, and West-Omo zones of Southwest Ethiopia. Heliyon 7:e07319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07319
Tenge JDG, Hella JP (2004) Social and economic factors affecting the adoption of soil and water conservation in West Usambara highlands, Tanzania. Land Degrad Dev 15(2):99–114
Ugwuoke BC, Attamah CO (2019) Linkages between the agricultural development programme and the local government agricultural development in Southeast, Nigeria. J Agric Ext 23(1):130–137
UN (2017) World population prospects: the 2017 revision, key findings and advance tables
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Faculty of Business, Victorian Institute of Technology, Melbourne, Australia
Shrikaant Kulkarni
Centre for Research Impact and Outcome, Chitkara University, Chandigarh, India
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shrikaant Kulkarni .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Engineering Sciences, Padm. Dr. V. B. Kolte College of Engineering, Pune, Maharashtra, India
Department of Chemistry, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
A. K. Haghi
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2024 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Kulkarni, S. (2024). Sustainable Cassava: A Case Study of Global Sustainability. In: Kulkarni, S., Haghi, A.K. (eds) Global Sustainability. World Sustainability Series. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57456-6_10
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-57456-6_10
Published : 22 May 2024
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-57455-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-57456-6
eBook Packages : Earth and Environmental Science Earth and Environmental Science (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Henan Doing Mechanical Equipment Co.,Ltd
Establish the cassava processing plant , include casssava starch processing plant , cassava flour plant and garri processing plant

+8613526615783

- Garri processing plant
- Cassava machinery
Business plan for cassava starch processing plant
1.Introduction of cassava starch and its processing:
For the made of business plan for cassava starch processing plant, firstly, it's essential to introduce the cassava starch processing condations for now. With the cassava starch used in all kinds of production advantages appeared, cassava starch cost quantity increased a lot, and more and more people all over the world turned their eye in the cassava starch. Cassava with highstarch content, about 24%, is a good material to produce starch, about 4 ton cassava can produce 1 ton starch, with high ecnomic benefit. Now, the cassava planting area like Nigeria, Ghana, Thailand, South Africa as the cassava starch main production area, and China, America, EU, etc. as the main importing countries for cassava starch, especially in recently two years, the cassava starch price increase continuously, the cassava starch processing plant has been a good project . So to make a business plan for cassava starch processing plant is very important.
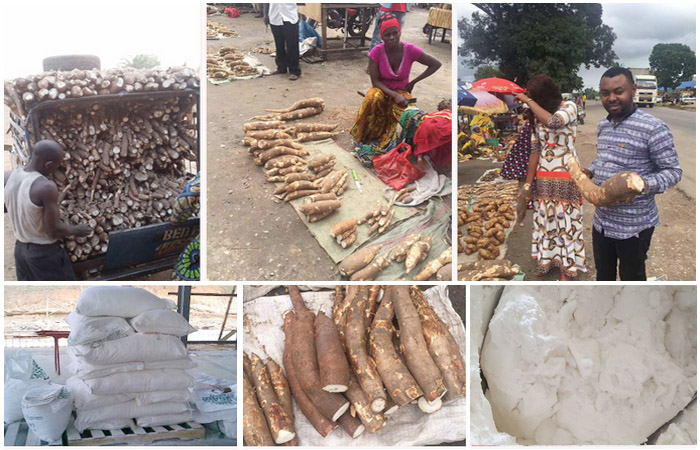

Cassava and cassava starch
2.Analysis of investment and revenue in the business plan for cassava starch processing plant:
Use the capacity 1 ton cassava starch for example, and the actually cost and the cassava starch price in order to the local condation shall prevail.
(1) The cassava starch sales price: $560, Each ton cassava starch net profit about $105.
(2) Counter as the 50ton cassava starch capacity per day, the net profit is $5,250. Annual profit about $1,575,000(300 working days each year).
Cassava can be plant and harvest almost whole year, so the cassava starch processing is continuous, the revenue also continuously, so the cassava starch processing plant ecnomic benefit is very high.
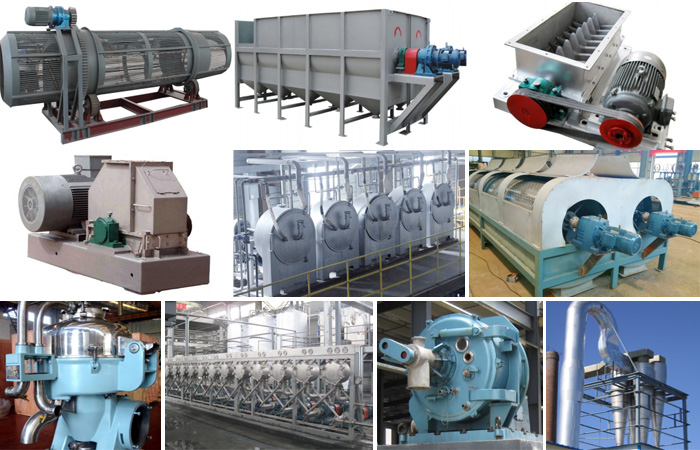

Main machinery for cassava starch processing
3. Cassava starch processing technology and main machinery :
The technology process:
Fresh cassava→Cassava cleaning→Cassava crushing→Starch slurry seperating→Desanding→Protein remove→Dewater→Drying
Main machinery:
Dry sieve & paddle washer→Cutting machine & rasper→Centrifuge sieve→Desander→Hydrocyclone & disc seperator→Vacuum filter→Airflow dryer
The machinery select is the most important section in the business plan for cassava starch processing plant, after all, a good technology and high quality machinery directly decided the final cassava starch quality. If you use the cassava chips as the raw material to produce cassava starch, you need equipped with the cassava chips soak pool, and no need the cleaning section and cutting machine. But it's essential to tell you that the fresh cassava with higher starch content than cassava chips.

Doing Company
4.The features and advantages of Doing Company cassava starch processing plant:
(1) Outstanding cassava starch production technology, starch extraction rate can reach to 95%, under same finalstarch capacity, saving the raw material cost.
(2) We concentrated on cassava starch production machinery design and manufacturer, it makes us more professional.We also learn about the cassava cultivation and processing current situation in Ghana and other areas, can give you best and suitable advice. This also show our strength to made for you the business plan for cassava starch processing plant.
(3) Our cassava starch production special desian with manual principle, compared with others, more advanced with high ecnomic benefit, high availability and high working efficiency.
(4) Automatic and continuously working, fully sealing process prevent the starch attached air, guarantee the starch no pollution and pure white.
(5) Doing Comapny cassava starch production in machinery has passed EU CE Certification, and through the third party(BV, TUV) detection. Don't worry about the quality and service life.

Welcome to DOING
To sum up, we can make a perfect business plan for cassava starch processing plant for you. Doing Company cassava starch processing plant equipped with a fully automatic control system, with short production time cost, cassavafrom cleaning to the finished starch product only need 10-15 minutes, effectively avoid the materials exposed to the air for a long time and oxidative browning and dust and microbial the secondary pollution, improve the productionefficiency and quality of cassava starch. Our airflow dryer can keep the original flavor of the starch. So if you have any problems about the business plan for cassava starch processing plant, contact us freely, and then you can discuss withour engineer.
PREV: Doing Company cultural activity for new employee
NEXT: DOING cassava processing machines technology upgrading
Doing Company cultural activity for new employee
DOING cassava processing machines technology upgrading
Leave a message
Tel/Whatsapp
0086 135 2661 5783
0086 371 5677 1822
elina881130
No.133 Yaozhai Road, Jinshui District, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China

Tel/Whatsapp:

How to Write a Cassava Starch Business Production Plan
Cassava starch is a popular ingredient used in many food and industrial products, such as noodles, paper, and pharmaceuticals. The increasing demand for cassava starch presents an opportunity for entrepreneurs to start a cassava starch business. However, to start a successful cassava starch business, one must have a clear and comprehensive business production plan.
A business plan is a document that outlines the objectives, strategies, and actions that a business will take to achieve its goals. In this article, we will discuss how to write a cassava starch business production plan. But before we dive in, let’s take a brief look at what a business plan is.
Table of Contents
What Is A Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that outlines the goals and strategies of a business. It’s like a roadmap that helps entrepreneurs to identify the steps they need to take to start and run a successful business. A business plan covers everything from the products or services the business will offer, to the target market, marketing strategies, financial projections, and more.
Think of it like a recipe for your favourite dish. Just as a recipe outlines the ingredients and steps necessary to create a delicious meal, a business plan outlines the steps necessary to create a successful business. Without a recipe, you might end up with a dish that doesn’t taste quite right. Similarly, without a business plan, you might end up with a business that doesn’t succeed.
A well-crafted business plan can help entrepreneurs to identify potential challenges and opportunities, develop a marketing strategy that resonates with their target audience, and secure funding from investors or lenders. It’s an essential tool for anyone looking to start or grow a business, and it’s a key component of success.
Step By Step Guide On How To Write A Cassava Starch Business Production Plan
Before writing a business production plan, it is crucial to research the cassava starch production industry. This research will provide insight into the market demand, competitors, and production process. Some of the essential things to consider during the research phase include:
- Market demand: Conduct market research to understand the current and future demand for cassava starch in the target market. Identify the current and potential customers and their needs.
- Competitors: Identify existing cassava starch producers in the market, their strengths and weaknesses, and the strategies they use to reach their target market.
- Production process: Understand the cassava starch production process, the raw materials required, and the equipment needed.
Executive Summary
The executive summary is the first section of the business production plan. It provides a brief overview of the business, including the goals and objectives. The executive summary should be concise and engaging, capturing the reader’s attention and encouraging them to read further. This section should include:
- The business name and location
- The business goals and objectives
- The target market and the products or services offered
- The management team and their experience
- The amount of funding required
Company Description
In the company description section, provide more details about the business, including its history, mission, vision, and values. This section should answer questions such as:
- Why are you starting a cassava starch production business?
- What are your long-term goals for the business?
- What values do you want the business to represent?
- What is your vision for the business?
Product and Services
This section should describe the cassava starch products and services offered by the business. Explain how the cassava starch is produced, its uses, and its unique selling points. This section should also discuss any plans to diversify the product line in the future.
Market Analysis:
The market analysis section should provide an in-depth analysis of the cassava starch market. It should include information about the target market, competition, and trends. Some of the key things to consider when conducting a market analysis include:
- Market size and growth potential.
- Target customer demographics and their needs.
- Competitors and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Industry trends and market forecasts.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
In this section, outline the marketing and sales strategies that will be used to reach and persuade customers to purchase the cassava starch. Some of the key things to consider include:
- Promotion: What promotional strategies will be used to create awareness and interest in the cassava starch? Will you use digital marketing, trade shows, or other methods?
- Pricing: What will be the pricing strategy for the cassava starch? Will it be competitive or premium pricing?
- Distribution: How will the cassava starch be distributed? Will it be sold directly to customers or through distributors?
Operation Plan
The operations plan should describe how the cassava starch will be produced, packaged, and distributed. It should include detailed information about the location, equipment, and raw materials required. Some of the key things to consider when developing an operations plan include:
- Location: Where will the cassava starch production plant be located? Is the location easily accessible, and are there any regulatory requirements that need to be considered?
- Equipment: What equipment will be needed to produce the cassava starch? What is the cost of the equipment, and where will it be sourced?
- Raw materials: What are the raw materials needed to produce the cassava starch, and where will they be sourced? Is there a reliable supplier, and what are the costs?
- Packaging and distribution: How will the cassava starch be packaged, and what are the costs? What distribution channels will be used to get the product to the target market?
Management and Organization
In this section, describe the management team and the organizational structure of the business. It should include information about the skills and experience of the management team and their roles in the business. It should also include details about any advisors or consultants that will be used.
Financial Plan:
The financial plan should include the projected income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. It should also include information about the startup costs, funding sources, and break-even analysis. Some of the key things to consider when developing a financial plan include:
- Startup costs: What are the costs associated with starting the cassava starch production business, including equipment, raw materials, and marketing?
- Funding sources: How will the business be funded? Will it be through personal savings, loans, grants or investments?
- Revenue projections: What are the projected revenues for the business? What are the costs associated with production, packaging, and distribution?
- Break-even analysis: What is the break-even point for the business, and how long will it take to reach it?
It is essential to remember that the business production plan is a living document that should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in the market, industry, and business operations. With a solid business production plan in place, entrepreneurs can confidently pursue their dreams of starting and growing a successful cassava starch business.
Final Thoughts on Cassava Starch Business Production Plan
Writing a business production plan for a cassava starch business requires careful research, planning, and execution. By following the steps outlined in this article, entrepreneurs can develop a comprehensive and effective business production plan that will guide them towards success in the cassava starch production industry.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- Premium News
- Biden Economy
- EV Deep Dive
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds
- Top Mutual Funds
- Highest Open Interest
- Highest Implied Volatility
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Charts
- Currency Converter
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Mutual Funds
- Credit cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Personal Loans
- Student Loans
- Car Insurance
- Morning Brief
- Market Domination
- Market Domination Overtime
- Asking for a Trend
- Opening Bid
- Stocks in Translation
- Lead This Way
- Good Buy or Goodbye?
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
- Newsletters
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Cassava sciences, inc. (sava)'s technical outlook is bright after key golden cross.
After reaching an important support level, Cassava Sciences, Inc. (SAVA) could be a good stock pick from a technical perspective. SAVA recently experienced a "golden cross" event, which saw its 50-day simple moving average breaking out above its 200-day simple moving average.
A golden cross is a technical chart pattern that can signify a potential bullish breakout. It's formed from a crossover involving a security's short-term moving average breaking above a longer-term moving average, with the most common moving averages being the 50-day and the 200-day, since bigger time periods tend to form stronger breakouts.
There are three stages to a golden cross. First, there must be a downtrend in a stock's price that eventually bottoms out. Then, the stock's shorter moving average crosses over its longer moving average, triggering a positive trend reversal. The third stage is when a stock continues the upward momentum to higher prices.
A golden cross contrasts with a death cross, another widely-followed chart pattern that suggests bearish momentum could be on the horizon.
Over the past four weeks, SAVA has gained 6.7%. The company currently sits at a #3 (Hold) on the Zacks Rank, also indicating that the stock could be poised for a breakout.
The bullish case only gets stronger once investors take into account SAVA's positive earnings outlook for the current quarter. There have been 1 upwards revisions compared to none lower over the past 60 days, and the Zacks Consensus Estimate has moved up as well.
Investors should think about putting SAVA on their watchlist given the ultra-important technical indicator and positive move in earnings estimates.
Want the latest recommendations from Zacks Investment Research? Today, you can download 7 Best Stocks for the Next 30 Days. Click to get this free report
Cassava Sciences, Inc. (SAVA) : Free Stock Analysis Report
To read this article on Zacks.com click here.
Zacks Investment Research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
cassava peels in the first year of production. 150 tones is equivalent to 150,000kg. And the Dried And the Dried High Quality Cassava Peel (DHQCP) will be bagged in 50kg rubber bag.
If YES, here's a complete sample cassava farming business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE. ... Brazil, Indonesia and Republic of the Congo et al. In 2014, global production of cassava root was 268 million tones, with Nigeria as the world's largest producer of nearly 55 million tones or 21 percent of the world total.
Low production costs: Because cassava is a hardy and tolerant crop that needs minimal upkeep and can tolerate drought and other extreme environmental conditions, it is comparatively cheap to grow. Profitability: Depending on the demand of the market, cassava farming can be a successful business. Potential profits can range from 30 to 60%.
A solid business plan will not only help secure financing but also serve as a guide for the farm's development and growth. Understanding Production Costs and Returns: Farmers need to calculate the production costs involved in cassava farming. This includes costs related to land preparation, planting materials, fertilizers, labor, irrigation ...
Get your complete copy of the Business plan through this link. It will take only a second. https://selar.co/odl4. Cameroon is one of the main cassava-consuming countries. The national production was estimated at 3.5 million tons in 2018 with an average yield of 14 tons/ha. The cassava sector is important and requires special attention given the ...
cassava production. This publication is therefore, produced to highlight the possible areas of cassava production that will enhance on-farm productivity. It is expected to be a training guide for farmers, extension workers, government agencies, NGOs, researchers, students, and all partners in the cassava production industry.
BUSINESS PLAN TEMPLATE On ROOTS AND TUBERS (Cassava Production) Location OYO STATE, NIGERIA 16th May, 2019 TABLE OF CONTENT Introduction 1 Business Profile 2 List of Tables Table 1 Labour Input Table 2 Recommended Input Table 3 Farm Tools & Equipments Table 4 Production Output Table 5 Distribution & Sales Output Table 6 Summary Of Business Plan Cost Estimates INTRODUCTION Cassava farming is ...
Hence, it is regarded as one of the most important tropical root crops in Africa. In 2018, the total annual production of cassava in Africa was 169 million tonnes. West Africa was the main production area with a total production of 93 million tonnes, which represents 55% of the production of cassava in Africa and 33.5% of the world production.
This guide reviews basic aspects applied to the varieties of cassava, the production methods, the market, the uses and the commercialization. This includes starch production techniques and its ...
n Enhance agricultural business management capacities of 300 entrepreneurs n Cassava productivity will be enhanced to double the current yields - from 10 tonnes to at least 20 tonnes per hectare - through the creation of demand for quality cassava products n Robust cassava value chains and market linkages and Expected results from CAMAP
Producing Gari from Cassava: An illustrated guide for smallholder cassava processors 2 his pictorial guide focuses on building the capacity of smallholder farmers and food processors to produce gari as a business he guide illustrates the euipment and sills needed to produce good uality gari y following this guide, smallholder
The production process of ethanol from cassava involves peeling and washing of cassava, milling/grating, pressure cooking, fermentation and distillation. A tone of cassava will produce a minimum of 200 litres of ethanol. To establish this project, implementation procedures are: feasibility studies preparation, finance sourcing, procurement of ...
The cassava processing business plan comes with a 3-year financial analysis. The complete cassava processing business plan is in Word Doc format, and the financial analysis is in Excel so that you can edit it to suit your taste. The cassava processing business plan is fully updated with current research on how to start a cassava processing ...
Originating in LAC, cassava has a traditional standing that challenges production and technology adoption. In 2018, LAC produced about 10% of world's cassava production In industrialised and productive regions of Brazil yields of 30-35 t/ha are usual. In other areas, average yields are 10-15 t/ha. Outside of Brazil and Paraguay, there has been
Executive Summary. Agro Business Cassava Company is an agro-based company that focuses on cultivating improved varieties of cassava and also processing the cassava various products like cassava flake and starch. Agro Cassava Company is based in Imo State and has acquired 20 Hectaces of land for the farm land and also the processing plant.
Title: Cassava.cdr Author: pc Created Date: 4/1/2021 6:07:14 AM
BUDGET FOR CASSAVA PRODUCTION BUSINESS PLAN S/N ITEM QTY/NAIRA QTY COST. 1. Renting of land 10,000 1 20,000 2. Cutlass 1000 2 2,000 3. Cassava stem 300 60 bundles 18,000 4. Hand weeder 500 2 1000 5. Land clearing 20,000 6. Packing and burning 10,000 7. Weeding 10,000 Two times 20,000 8.
The amount needed to acquire/lease a facility - $50,000. The amount required for constructing a standard cassava processing plant - $150,000. The cost for acquiring the required working tools and equipment/machines et al - $20,000. The amount required for purchase of the first set of cassava supply et al - $50,000.
Cassava farmers can venture into alcohol production as a value-added business. Medicine Production: Cassava has medicinal properties and is used in the production of various drugs. Cassava farmers can supply cassava roots to pharmaceutical companies. Cassava Chips Production: Cassava chips are a popular snack and can be processed and packaged ...
Cassava is a woody perennial plant belonging to the spurge family (Euphorbiaceae) (Hillocks et al. 2002).The origin of Cassava lies in South America (Allem 2002), although it is grown throughout sub- and tropical regions.Cassava is looked upon as a crop that is resistant to drought, war, and famine since it is cultivable under adverse conditions (e.g., unfertile soils) in tune with the ...
cassava as a viable foreign exchange earner for Nigeria, and also development of the cassava production system in order to sustain the national demand. The challenge however, is how Nigeria can earn US$5 billion from value added cassava exports by the year 2007. The vision for cassava is that it will spur rural industrial development, helping
Cassava and cassava starch. 2.Analysis of investment and revenue in the business plan for cassava starch processing plant: Use the capacity 1 ton cassava starch for example, and the actually cost and the cassava starch price in order to the local condation shall prevail. (1) The cassava starch sales price: $560, Each ton cassava starch net ...
Writing a business production plan for a cassava starch business requires careful research, planning, and execution. By following the steps outlined in this article, entrepreneurs can develop a comprehensive and effective business production plan that will guide them towards success in the cassava starch production industry. Spread the love. to ...
'It addresses immediate hunger but also yields long-term benefits. Our association has thirty members now. The extra income allows us to diversify our crops. We are planning to plant cassava and onions.' Emmanuel Atiku. Image: George Ocen/Cordaid. The Business Support Facilitators (BSFs) are pivotal in the project.
-President tells Bonasika outreach Farmers here reaped more than 20 million pounds of cassava in 2024. This disclosure was made by President Irfaan Ali
The roadmap action plan requires many relevant researches and developments as supporting database. ... (TTSA, 2010). The expected production capacity of PLA in Thailand was estimated from the availability of cassava production studied by the NIA (Suppasri and Sermcheep, 2010). By transforming cassava starch to glucose, ... a Learneo, Inc. business
Comprising 52 dedicated members (out of which 86% are women) hailing from diverse surrounding communities, the cooperative was founded in 2005 and registered as a corporate entity, being incorporated under the Cooperative Development Agency (CDA) in Liberia. It manages a sprawling 65-hectare farmland, nurturing the growth of rice, cassava, and ...
SAVAW. After reaching an important support level, Cassava Sciences, Inc. (SAVA) could be a good stock pick from a technical perspective. SAVA recently experienced a "golden cross" event, which saw ...
The Minister of Agriculture Dr. J. Alexander Nuetah has told the farmers in Gbadin and the citizens of Nimba that the Government of Liberia, through the Ministry of Agriculture, will bring Gbadin back to its prewar status in terms of rice production. He said the Ministry of Agriculture will build dams to supply the entire farmland in Gbadin to ...
Murat Sartas is a scientist, developer, and advisor specializing in innovation, scaling… · Experience: Global National Agricultural Systems Consortium · Education: MIT Sloan School of Management · Location: Kigali City · 500+ connections on LinkedIn. View Murat SARTAS (Ph.D.)'s profile on LinkedIn, a professional community of 1 billion members.