Cultural Identity Essay
27 August, 2020
12 minutes read
Author: Elizabeth Brown
No matter where you study, composing essays of any type and complexity is a critical component in any studying program. Most likely, you have already been assigned the task to write a cultural identity essay, which is an essay that has to do a lot with your personality and cultural background. In essence, writing a cultural identity essay is fundamental for providing the reader with an understanding of who you are and which outlook you have. This may include the topics of religion, traditions, ethnicity, race, and so on. So, what shall you do to compose a winning cultural identity essay?


Cultural Identity Paper: Definitions, Goals & Topics

Before starting off with a cultural identity essay, it is fundamental to uncover what is particular about this type of paper. First and foremost, it will be rather logical to begin with giving a general and straightforward definition of a cultural identity essay. In essence, cultural identity essay implies outlining the role of the culture in defining your outlook, shaping your personality, points of view regarding a multitude of matters, and forming your qualities and beliefs. Given a simpler definition, a cultural identity essay requires you to write about how culture has influenced your personality and yourself in general. So in this kind of essay you as a narrator need to give an understanding of who you are, which strengths you have, and what your solid life position is.
Yet, the goal of a cultural identity essay is not strictly limited to describing who you are and merely outlining your biography. Instead, this type of essay pursues specific objectives, achieving which is a perfect indicator of how high-quality your essay is. Initially, the primary goal implies outlining your cultural focus and why it makes you peculiar. For instance, if you are a french adolescent living in Canada, you may describe what is so special about it: traditions of the community, beliefs, opinions, approaches. Basically, you may talk about the principles of the society as well as its beliefs that made you become the person you are today.
So far, cultural identity is a rather broad topic, so you will likely have a multitude of fascinating ideas for your paper. For instance, some of the most attention-grabbing topics for a personal cultural identity essay are:
- Memorable traditions of your community
- A cultural event that has influenced your personality
- Influential people in your community
- Locations and places that tell a lot about your culture and identity
Cultural Identity Essay Structure
As you might have already guessed, composing an essay on cultural identity might turn out to be fascinating but somewhat challenging. Even though the spectrum of topics is rather broad, the question of how to create the most appropriate and appealing structure remains open.
Like any other kind of an academic essay, a cultural identity essay must compose of three parts: introduction, body, and concluding remarks. Let’s take a more detailed look at each of the components:
Introduction
Starting to write an essay is most likely one of the most time-consuming and mind-challenging procedures. Therefore, you can postpone writing your introduction and approach it right after you finish body paragraphs. Nevertheless, you should think of a suitable topic as well as come up with an explicit thesis. At the beginning of the introduction section, give some hints regarding the matter you are going to discuss. You have to mention your thesis statement after you have briefly guided the reader through the topic. You can also think of indicating some vital information about yourself, which is, of course, relevant to the topic you selected.
Your main body should reveal your ideas and arguments. Most likely, it will consist of 3-5 paragraphs that are more or less equal in size. What you have to keep in mind to compose a sound ‘my cultural identity essay’ is the argumentation. In particular, always remember to reveal an argument and back it up with evidence in each body paragraph. And, of course, try to stick to the topic and make sure that you answer the overall question that you stated in your topic. Besides, always keep your thesis statement in mind: make sure that none of its components is left without your attention and argumentation.
Conclusion
Finally, after you are all finished with body paragraphs and introduction, briefly summarize all the points in your final remarks section. Paraphrase what you have already revealed in the main body, and make sure you logically lead the reader to the overall argument. Indicate your cultural identity once again and draw a bottom line regarding how your culture has influenced your personality.
Best Tips For Writing Cultural Identity Essay
Writing a ‘cultural identity essay about myself’ might be somewhat challenging at first. However, you will no longer struggle if you take a couple of plain tips into consideration. Following the tips below will give you some sound and reasonable cultural identity essay ideas as well as make the writing process much more pleasant:
- Start off by creating an outline. The reason why most students struggle with creating a cultural identity essay lies behind a weak structure. The best way to organize your ideas and let them flow logically is to come up with a helpful outline. Having a reference to build on is incredibly useful, and it allows your essay to look polished.
- Remember to write about yourself. The task of a cultural identity essay implies not focusing on your culture per se, but to talk about how it shaped your personality. So, switch your focus to describing who you are and what your attitudes and positions are.
- Think of the most fundamental cultural aspects. Needless to say, you first need to come up with a couple of ideas to be based upon in your paper. So, brainstorm all the possible ideas and try to decide which of them deserve the most attention. In essence, try to determine which of the aspects affected your personality the most.
- Edit and proofread before submitting your paper. Of course, the content and the coherence of your essay’s structure play a crucial role. But the grammatical correctness matters a lot too. Even if you are a native speaker, you may still make accidental errors in the text. To avoid the situation when unintentional mistakes spoil the impression from your essay, always double check your cultural identity essay.
A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]

- TUTORING & TEST PREP
- TALK TO AN ADVISOR
Alternative Pathways to a Career in Computer Science
Recent posts, subscribe here, more expert advice, let's get existential: how to write a college essay about identity.

When you’re a teenager, you’re probably too busy to sit down and think about your own identity. No one exactly assigns you “introspection time” as homework (though, if you’re my student, this has very likely happened). So when you start working on your college essays, it might be the first time you truly start thinking about how you can express who you are in a way that will help a group of strangers understand something about you. Let’s be honest—it feels like a lot of pressure to sum up your identity in 250 words or less. But we’re here to help.
There are many different types of application essays you’ll need to write, as my colleague Annie so perfectly laid out here . But we’re going to talk about one type in particular: the essays about identity and diversity. These are powerful college essays that give admissions officers an opportunity to glimpse into your daily life and understand your unique experiences. For some students, though, these essays can be daunting to think about and write.
Ever wonder why colleges are asking these questions? Well, the simple answer is that they want to get to know you more. Aside from your academic interests, your activities, and your accomplishments in the classroom, there really isn’t that much space to talk about things like your ethnic background, religion, gender identity, or local community. And these are things colleges want to know about you, too!
How Do You Write a Good Identity and Diversity Essay?
Before you start writing, let’s define a few terms you might run into while drafting your college essays about identity and diversity.
Who are you? I know what you’re thinking—it’s way too early in the morning to get this existential. I hear you. But let’s break this down. Identity is made up of many qualities: personality, culture, ethnic or racial background, sexual orientation, gender, physical ability, and linguistic background, among others. Maybe you identify really strongly with the religion on Mom’s side of the family, but not Dad’s. Maybe you speak a language not typical of folks from your culture. Maybe you have recently come into your gender identity and finally feel like yourself. Why is that identity important to the way you define who you are? Think of it like this: If you’ve met someone new, and your goal is to help them get to know you in the shortest amount of time possible, how would you be able to accomplish this? What’s your tagline? That’s how you’ll want to tackle this type of college essay.
Diversity
One individual person can’t be diverse. But when a college is referring to diversity, they’re usually looking to their student body and asking how you, as an individual with your own identity, can add to their diversity. What experiences have you had in your life that might help you make the student body more diverse? Have you dealt with dyslexia and come to terms with how best to learn, keeping your abilities in mind? If so, how can you contribute to other students who might learn differently? Did you grow up as the oldest of 10 siblings and have to take care of them on a daily basis? What kind of responsibilities did you have and how did that influence you? These don’t need to be visible qualities. The goal of the diversity college essay is to understand how these identifying factors can help you contribute to a school in a way they haven’t seen before.
Let’s define community. You may associate it with the city or neighborhood you live in. But a community doesn’t have to be geographical. It doesn’t even have to be formal. Community can come from that sense of connection you have with like-minded people. It can be built with people you’ve shared experiences with. So, when we think of community in this sense, we could be thinking about the community that exists within your apartment complex. We could be thinking about the youth group at your mosque. We could be thinking about your little group of artists within your science and tech magnet school. Think about what communities you are a part of, and be prepared to talk about your place within them.
You might think that these questions are only being asked by small liberal arts schools—but that’s not true. Bigger schools and colleges also want to get to know all of the thousands of students they’re bringing to campus as part of their class.
.png?width=600&height=200&name=Blog%20CTAs%20(8).png)
Big Name Colleges that Care About Diversity
To give you a glimpse of the variety, here are a few examples of college essays where these identity and diversity may come into play:
University of Michigan
“Everyone belongs to many different communities and/or groups defined by (among other things) shared geography, religion, ethnicity, income, cuisine, interest, race, ideology, or intellectual heritage. Choose one of the communities to which you belong, and describe that community and your place within it.”
University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill
“Expand on an aspect of your identity (for example, your religion, culture, race, sexual or gender identity, affinity group, etc.). How has this aspect of your identity shaped your life experiences thus far?”
Pomona College
“Tell us about an experience when you dealt with disagreement or conflict around different perspectives within a community.”
Sarah Lawrence College
“Sarah Lawrence College's community places strong value in inclusion and diversity. In 250-500 words, tell us about what you value in a community and how your perspective, lived experiences, or beliefs might contribute to your College community.”
Remember what these colleges are trying to understand: who you are and what has influenced you to become the person you are today (identity), where you come from (community), and how you might be able to add to the diversity of their college campus. Once you really get to the core and understand the intent of these types of college essays, you’ll absolutely be able to write in an earnest and genuine way. We say this frequently at Collegewise, but it’s worth repeating here, especially when it comes to essays about identity and diversity. Just be yourself.
About Us: With more than twenty years of experience, Collegewise counselors and tutors are at the forefront of the ever-evolving admissions landscape. Our work has always centered on you: the student. And just like we’ve always done, we look for ways for you to be your best self - whether it’s in the classroom, in your applications or in the right-fit college environment. Our range of tools include counseling , test prep , academic tutoring , and essay management, all with the support of our proprietary platform , leading to a 4x higher than average admissions rates.
Recommended Articles

College applications without essays: do they exist?

5 College Essay Examples & What to Avoid

How to Write a College Transfer Essay
Subscribe to email updates.
- Tutoring & Test Prep
- Our Counselors
© 2024 Collegewise. All Rights Reserved. Privacy


How to Write an Essay about Your Identity

If you’re looking for a simple way to write an essay about your identity, then you’ve found the perfect tutorial!
Writing an essay about your identity can be a great way to highlight who you are as a person and explore your values, experiences, and characteristics. So, in this tutorial, I will show you how to write such an essay in five simple steps effectively. We’ll also work on a sample essay so you can see how to put these steps into practice.
Let’s get started!
Step 1. Plan the word count for your essay’s paragraphs.
Doing this first step is important if you want to make things simpler for you while writing an essay. You’ll get to know exactly how many words each paragraph will have, which makes the process quicker.
Note that essays have three parts you must include:
- The introductory paragraph
- Three body paragraphs
- The concluding paragraph
For example, suppose you need a 300-word paragraph. How would you distribute 300 words across five paragraphs? Here’s a simple way to do that:

That’s all you need for your essay — short introductory and concluding paragraphs and three concise body paragraphs.
Step 2. Select your main idea and supporting points.
You need to come up with a central idea that will give you a frame of reference for the rest of your essay. To do this, you can first consider what your identity is. Then, determine what shapes this identity.
For example, are you an artist? Maybe you’re imaginative and creative! Do you have a unique perspective on things? Do you like expressing yourself visually?
Or maybe, you’re a doctor? Do you have extensive knowledge and expertise in the field of medicine? Do you possess strong problem-solving and critical-thinking skills?
Whatever they are, you will use them as your basis — your essay’s thesis .
For our sample essay, we can use this as our main idea: “My identity as an educator has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and my inborn creativity.”
Next, we will use the Power of Three to divide this main idea into three supporting points.

The Power of Three is a three-part structure that helps you produce your body paragraphs.
Let’s see how it works for our sample essay. In this case, we will use three things that could shape someone’s identity as an educator:
- My faith is an integral part of my identity.
- Parenthood has had a significant impact on my identity.
- Creativity has been a part of my identity for as long as I can remember.
Now we have what we need to start writing our essay. Let’s go to the next step!
Step 3. Write the introductory paragraph.
To write an introductory paragraph , you can follow the diagram below:

First, you need an introduction — an opening sentence that briefly sets the essay’s context. Next, you will include your thesis and three supporting points.
Here’s an example:
Introductory Paragraph
“Different factors, including beliefs, experiences, and innate qualities, shape our identities. For me, my identity as an educator has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and my inborn creativity. My faith guides my values and principles in teaching. My experiences as a parent have also helped me develop empathy and understanding toward my students. And my inborn creativity allows me to come up with innovative ways to present lessons, engage my students, and foster a positive learning environment.”
As you can tell, the introductory paragraph proceeds from general to specific , starting from the introduction, followed by the thesis and three supporting points.
Step 4. Write the body paragraphs.
Our essay will contain three body paragraphs that expound our supporting points. Here’s how to structure a body paragraph in any essay:

Body paragraphs start with a topic sentence that briefly summarizes the entire paragraph. Next, you will explain and illustrate your point using example/s .
Paragraph 1
“My faith is an integral part of my identity. My faith guides me in creating a safe and positive learning environment for my students. I strive to make my classroom a safe space where my students feel welcomed and valued. I model kindness and compassion, which I hope inspires and encourages my students to treat each other with the same level of respect and understanding.”
Note that the topic sentence gives context to the entire body paragraph. The following sentences explain the supporting point, and the rest illustrates it with an example.
Paragraph 2
“Parenthood has had a significant impact on my identity as an educator. It has taught me to approach teaching with compassion and empathy. As a parent, I learned that everyone has unique needs and struggles that require understanding and, if possible, a personalized approach to teaching. I apply this principle in my classroom by taking the time to get to know my students and understand their personal learning styles and circumstances. I schedule one-on-one meetings with students and offer them encouragement and resources to help those struggling to catch up.”
Paragraph 3
“Creativity has always been a part of my identity, especially as an educator. It is essential in creating engaging learning experiences for my students. I constantly look for fun and innovative ways to present lessons that will help them foster a love for learning. I incorporate hands-on activities and projects in my lessons to challenge my students creatively and critically about the material. For example, when I taught animal classification last academic year, I organized a field trip to a local zoo where the students observed and learned firsthand about the animals and ecosystems they were studying.”
Like paragraph 1, body paragraphs 2 and 3 follow the exact same structure outlined in the diagram above. It proceeds from the topic sentence to the explanation and example.
Excellent! Now we’re ready for the final step.
Step 5. Write the concluding paragraph.
The most time-proven way to write a concluding paragraph for any essay is to simply paraphrase all the points you’ve already mentioned in the introductory paragraph. Don’t copy and paste it! Instead, you can check your introductory paragraph and write the concluding paragraph based on it.
Let’s try this method to write the concluding paragraph in our sample essay:
“A combination of our beliefs, experiences, and characteristics shape our identities. As an educator, my identity has been shaped by my faith, parenthood, and creativity. My faith guides me in modeling important values in my classroom. Parenthood has taught me to approach teaching with empathy. And my creativity enables me to present material in innovative and engaging ways, which helps foster a love for learning in my students.”
We only restated the points in the introductory paragraph but used different words. Doing so makes writing the concluding paragraph pretty quick and simple.
And now we’re done! I hope you find this tutorial helpful.
Now it’s time for you to write your essay about your identity!
Tutor Phil is an e-learning professional who helps adult learners finish their degrees by teaching them academic writing skills.
Recent Posts
How to Write a 300 Word Essay - Simple Tutorial
https://youtu.be/qXST2gJbkhw If you need to write a 300-word essay, you’ve come to the right place. I’m Tutor Phil, and in this tutorial I’ll guide you through the process step by...
Essay Writing for Beginners: 6-Step Guide with Examples
https://youtu.be/w6yanrc1a_g If you need to write an essay, whether for a college course or to pass a writing test, this guide will take you through the process step-by-step. Even if you have...

Photo by Trent Parke/Magnum
You are a network
You cannot be reduced to a body, a mind or a particular social role. an emerging theory of selfhood gets this complexity.
by Kathleen Wallace + BIO
Who am I? We all ask ourselves this question, and many like it. Is my identity determined by my DNA or am I product of how I’m raised? Can I change, and if so, how much? Is my identity just one thing, or can I have more than one? Since its beginning, philosophy has grappled with these questions, which are important to how we make choices and how we interact with the world around us. Socrates thought that self-understanding was essential to knowing how to live, and how to live well with oneself and with others. Self-determination depends on self-knowledge, on knowledge of others and of the world around you. Even forms of government are grounded in how we understand ourselves and human nature. So the question ‘Who am I?’ has far-reaching implications.
Many philosophers, at least in the West, have sought to identify the invariable or essential conditions of being a self. A widely taken approach is what’s known as a psychological continuity view of the self, where the self is a consciousness with self-awareness and personal memories. Sometimes these approaches frame the self as a combination of mind and body, as René Descartes did, or as primarily or solely consciousness. John Locke’s prince/pauper thought experiment, wherein a prince’s consciousness and all his memories are transferred into the body of a cobbler, is an illustration of the idea that personhood goes with consciousness. Philosophers have devised numerous subsequent thought experiments – involving personality transfers, split brains and teleporters – to explore the psychological approach. Contemporary philosophers in the ‘animalist’ camp are critical of the psychological approach, and argue that selves are essentially human biological organisms. ( Aristotle might also be closer to this approach than to the purely psychological.) Both psychological and animalist approaches are ‘container’ frameworks, positing the body as a container of psychological functions or the bounded location of bodily functions.
All these approaches reflect philosophers’ concern to focus on what the distinguishing or definitional characteristic of a self is, the thing that will pick out a self and nothing else, and that will identify selves as selves, regardless of their particular differences. On the psychological view, a self is a personal consciousness. On the animalist view, a self is a human organism or animal. This has tended to lead to a somewhat one-dimensional and simplified view of what a self is, leaving out social, cultural and interpersonal traits that are also distinctive of selves and are often what people would regard as central to their self-identity. Just as selves have different personal memories and self-awareness, they can have different social and interpersonal relations, cultural backgrounds and personalities. The latter are variable in their specificity, but are just as important to being a self as biology, memory and self-awareness.
Recognising the influence of these factors, some philosophers have pushed against such reductive approaches and argued for a framework that recognises the complexity and multidimensionality of persons. The network self view emerges from this trend. It began in the later 20th century and has continued in the 21st, when philosophers started to move toward a broader understanding of selves. Some philosophers propose narrative and anthropological views of selves. Communitarian and feminist philosophers argue for relational views that recognise the social embeddedness, relatedness and intersectionality of selves. According to relational views, social relations and identities are fundamental to understanding who persons are.
Social identities are traits of selves in virtue of membership in communities (local, professional, ethnic, religious, political), or in virtue of social categories (such as race, gender, class, political affiliation) or interpersonal relations (such as being a spouse, sibling, parent, friend, neighbour). These views imply that it’s not only embodiment and not only memory or consciousness of social relations but the relations themselves that also matter to who the self is. What philosophers call ‘4E views’ of cognition – for embodied, embedded, enactive and extended cognition – are also a move in the direction of a more relational, less ‘container’, view of the self. Relational views signal a paradigm shift from a reductive approach to one that seeks to recognise the complexity of the self. The network self view further develops this line of thought and says that the self is relational through and through, consisting not only of social but also physical, genetic, psychological, emotional and biological relations that together form a network self. The self also changes over time, acquiring and losing traits in virtue of new social locations and relations, even as it continues as that one self.
H ow do you self-identify? You probably have many aspects to yourself and would resist being reduced to or stereotyped as any one of them. But you might still identify yourself in terms of your heritage, ethnicity, race, religion: identities that are often prominent in identity politics. You might identify yourself in terms of other social and personal relationships and characteristics – ‘I’m Mary’s sister.’ ‘I’m a music-lover.’ ‘I’m Emily’s thesis advisor.’ ‘I’m a Chicagoan.’ Or you might identify personality characteristics: ‘I’m an extrovert’; or commitments: ‘I care about the environment.’ ‘I’m honest.’ You might identify yourself comparatively: ‘I’m the tallest person in my family’; or in terms of one’s political beliefs or affiliations: ‘I’m an independent’; or temporally: ‘I’m the person who lived down the hall from you in college,’ or ‘I’m getting married next year.’ Some of these are more important than others, some are fleeting. The point is that who you are is more complex than any one of your identities. Thinking of the self as a network is a way to conceptualise this complexity and fluidity.
Let’s take a concrete example. Consider Lindsey: she is spouse, mother, novelist, English speaker, Irish Catholic, feminist, professor of philosophy, automobile driver, psychobiological organism, introverted, fearful of heights, left-handed, carrier of Huntington’s disease (HD), resident of New York City. This is not an exhaustive set, just a selection of traits or identities. Traits are related to one another to form a network of traits. Lindsey is an inclusive network, a plurality of traits related to one another. The overall character – the integrity – of a self is constituted by the unique interrelatedness of its particular relational traits, psychobiological, social, political, cultural, linguistic and physical.
Figure 1 below is based on an approach to modelling ecological networks; the nodes represent traits, and the lines are relations between traits (without specifying the kind of relation).
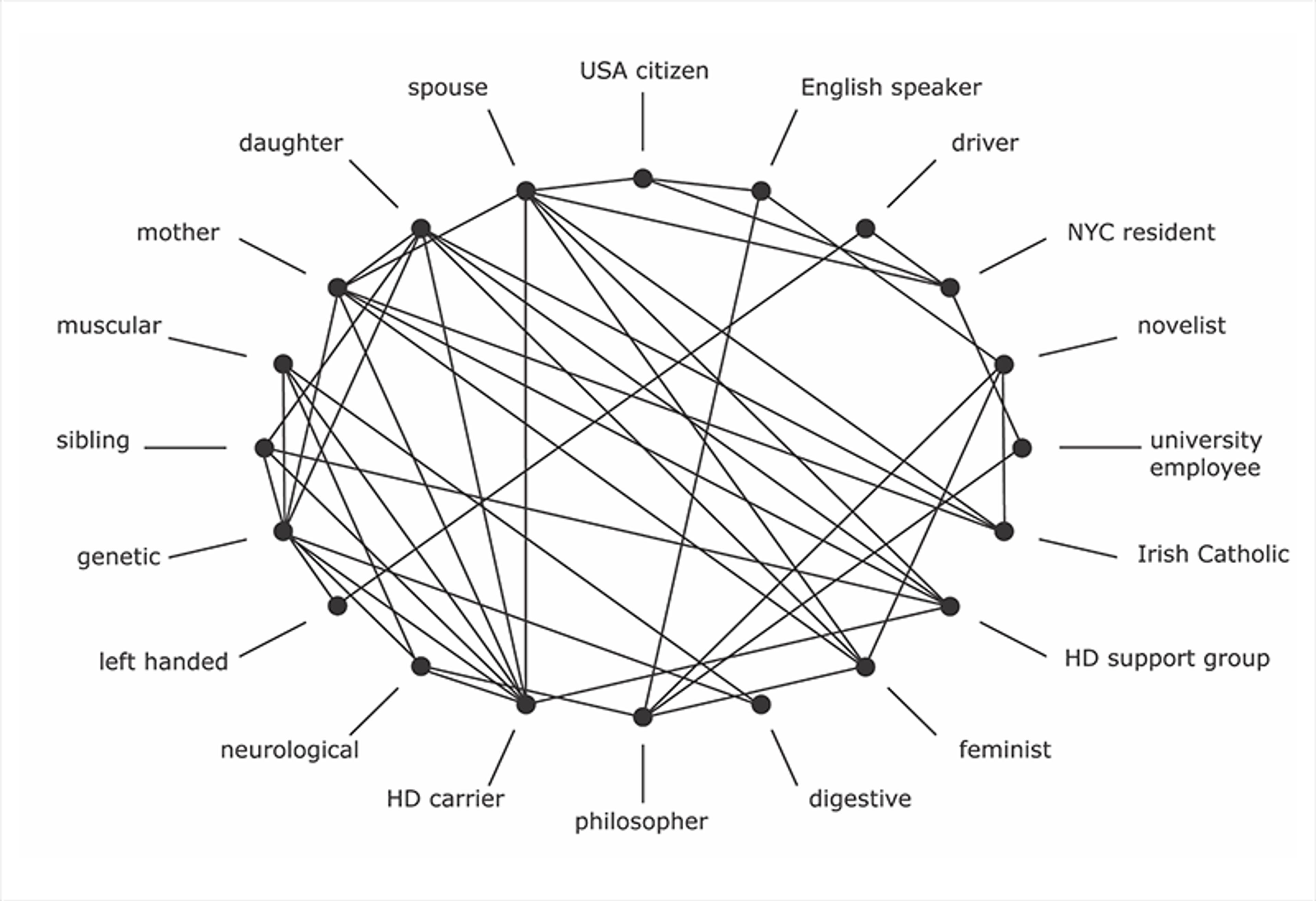
We notice right away the complex interrelatedness among Lindsey’s traits. We can also see that some traits seem to be clustered, that is, related more to some traits than to others. Just as a body is a highly complex, organised network of organismic and molecular systems, the self is a highly organised network. Traits of the self can organise into clusters or hubs, such as a body cluster, a family cluster, a social cluster. There might be other clusters, but keeping it to a few is sufficient to illustrate the idea. A second approximation, Figure 2 below, captures the clustering idea.
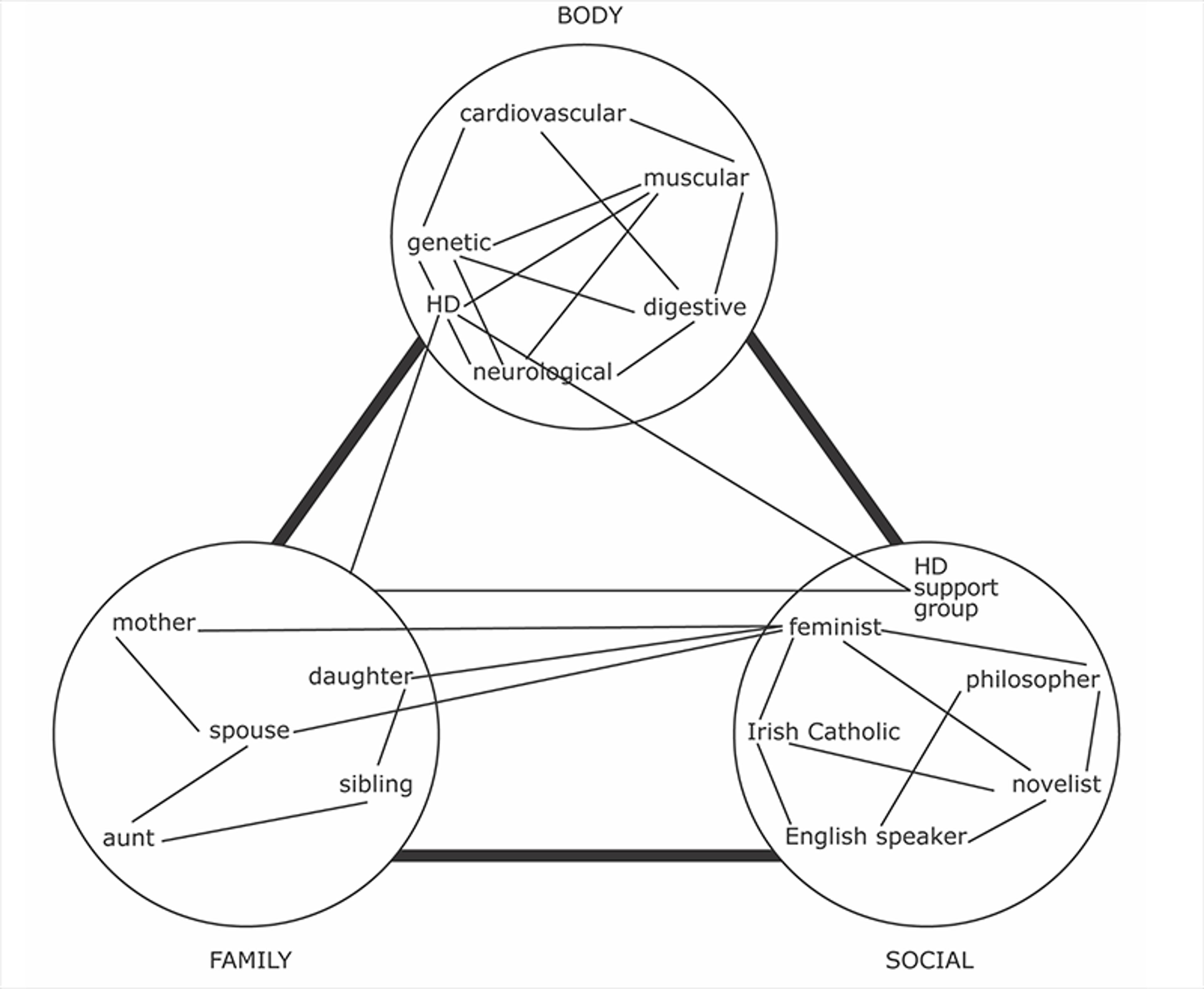
Figures 1 and 2 (both from my book , The Network Self ) are simplifications of the bodily, personal and social relations that make up the self. Traits can be closely clustered, but they also cross over and intersect with traits in other hubs or clusters. For instance, a genetic trait – ‘Huntington’s disease carrier’ (HD in figures 1 and 2) – is related to biological, family and social traits. If the carrier status is known, there are also psychological and social relations to other carriers and to familial and medical communities. Clusters or sub-networks are not isolated, or self-enclosed hubs, and might regroup as the self develops.
Sometimes her experience might be fractured, as when others take one of her identities as defining all of her
Some traits might be more dominant than others. Being a spouse might be strongly relevant to who Lindsey is, whereas being an aunt weakly relevant. Some traits might be more salient in some contexts than others. In Lindsey’s neighbourhood, being a parent might be more salient than being a philosopher, whereas at the university being a philosopher is more prominent.
Lindsey can have a holistic experience of her multifaceted, interconnected network identity. Sometimes, though, her experience might be fractured, as when others take one of her identities as defining all of her. Suppose that, in an employment context, she isn’t promoted, earns a lower salary or isn’t considered for a job because of her gender. Discrimination is when an identity – race, gender, ethnicity – becomes the way in which someone is identified by others, and therefore might experience herself as reduced or objectified. It is the inappropriate, arbitrary or unfair salience of a trait in a context.
Lindsey might feel conflict or tension between her identities. She might not want to be reduced to or stereotyped by any one identity. She might feel the need to dissimulate, suppress or conceal some identity, as well as associated feelings and beliefs. She might feel that some of these are not essential to who she really is. But even if some are less important than others, and some are strongly relevant to who she is and identifies as, they’re all still interconnected ways in which Lindsey is.
F igures 1 and 2 above represent the network self, Lindsey, at a cross-section of time, say at early to mid-adulthood. What about the changeableness and fluidity of the self? What about other stages of Lindsey’s life? Lindsey-at-age-five is not a spouse or a mother, and future stages of Lindsey might include different traits and relations too: she might divorce or change careers or undergo a gender identity transformation. The network self is also a process .
It might seem strange at first to think of yourself as a process. You might think that processes are just a series of events, and your self feels more substantial than that. Maybe you think of yourself as an entity that’s distinct from relations, that change is something that happens to an unchangeable core that is you. You’d be in good company if you do. There’s a long history in philosophy going back to Aristotle arguing for a distinction between a substance and its properties, between substance and relations, and between entities and events.
However, the idea that the self is a network and a process is more plausible than you might think. Paradigmatic substances, such as the body, are systems of networks that are in constant process even when we don’t see that at a macro level: cells are replaced, hair and nails grow, food is digested, cellular and molecular processes are ongoing as long as the body is alive. Consciousness or the stream of awareness itself is in constant flux. Psychological dispositions or attitudes might be subject to variation in expression and occurrence. They’re not fixed and invariable, even when they’re somewhat settled aspects of a self. Social traits evolve. For example, Lindsey-as-daughter develops and changes. Lindsey-as-mother is not only related to her current traits, but also to her own past, in how she experienced being a daughter. Many past experiences and relations have shaped how she is now. New beliefs and attitudes might be acquired and old ones revised. There’s constancy, too, as traits don’t all change at the same pace and maybe some don’t change at all. But the temporal spread, so to speak, of the self means that how a self as a whole is at any time is a cumulative upshot of what it’s been and how it’s projecting itself forward.
Anchoring and transformation, sameness and change: the cumulative network is both-and , not either-or
Rather than an underlying, unchanging substance that acquires and loses properties, we’re making a paradigm shift to seeing the self as a process, as a cumulative network with a changeable integrity. A cumulative network has structure and organisation, as many natural processes do, whether we think of biological developments, physical processes or social processes. Think of this constancy and structure as stages of the self overlapping with, or mapping on to, one another. For Lindsey, being a sibling overlaps from Lindsey-at-six to the death of the sibling; being a spouse overlaps from Lindsey-at-30 to the end of the marriage. Moreover, even if her sibling dies, or her marriage crumbles, sibling and spouse would still be traits of Lindsey’s history – a history that belongs to her and shapes the structure of the cumulative network.
If the self is its history, does that mean it can’t really change much? What about someone who wants to be liberated from her past, or from her present circumstances? Someone who emigrates or flees family and friends to start a new life or undergoes a radical transformation doesn’t cease to have been who they were. Indeed, experiences of conversion or transformation are of that self, the one who is converting, transforming, emigrating. Similarly, imagine the experience of regret or renunciation. You did something that you now regret, that you would never do again, that you feel was an expression of yourself when you were very different from who you are now. Still, regret makes sense only if you’re the person who in the past acted in some way. When you regret, renounce and apologise, you acknowledge your changed self as continuous with and owning your own past as the author of the act. Anchoring and transformation, continuity and liberation, sameness and change: the cumulative network is both-and , not either-or .
Transformation can happen to a self or it can be chosen. It can be positive or negative. It can be liberating or diminishing. Take a chosen transformation. Lindsey undergoes a gender transformation, and becomes Paul. Paul doesn’t cease to have been Lindsey, the self who experienced a mismatch between assigned gender and his own sense of self-identification, even though Paul might prefer his history as Lindsey to be a nonpublic dimension of himself. The cumulative network now known as Paul still retains many traits – biological, genetic, familial, social, psychological – of its prior configuration as Lindsey, and is shaped by the history of having been Lindsey. Or consider the immigrant. She doesn’t cease to be the self whose history includes having been a resident and citizen of another country.
T he network self is changeable but continuous as it maps on to a new phase of the self. Some traits become relevant in new ways. Some might cease to be relevant in the present while remaining part of the self’s history. There’s no prescribed path for the self. The self is a cumulative network because its history persists, even if there are many aspects of its history that a self disavows going forward or even if the way in which its history is relevant changes. Recognising that the self is a cumulative network allows us to account for why radical transformation is of a self and not, literally, a different self.
Now imagine a transformation that’s not chosen but that happens to someone: for example, to a parent with Alzheimer’s disease. They are still parent, citizen, spouse, former professor. They are still their history; they are still that person undergoing debilitating change. The same is true of the person who experiences dramatic physical change, someone such as the actor Christopher Reeve who had quadriplegia after an accident, or the physicist Stephen Hawking whose capacities were severely compromised by ALS (motor neuron disease). Each was still parent, citizen, spouse, actor/scientist and former athlete. The parent with dementia experiences loss of memory, and of psychological and cognitive capacities, a diminishment in a subset of her network. The person with quadriplegia or ALS experiences loss of motor capacities, a bodily diminishment. Each undoubtedly leads to alteration in social traits and depends on extensive support from others to sustain themselves as selves.
Sometimes people say that the person with dementia who doesn’t know themselves or others anymore isn’t really the same person that they were, or maybe isn’t even a person at all. This reflects an appeal to the psychological view – that persons are essentially consciousness. But seeing the self as a network takes a different view. The integrity of the self is broader than personal memory and consciousness. A diminished self might still have many of its traits, however that self’s history might be constituted in particular.
Plato, long before Freud, recognised that self-knowledge is a hard-won and provisional achievement
The poignant account ‘Still Gloria’ (2017) by the Canadian bioethicist Françoise Baylis of her mother’s Alzheimer’s reflects this perspective. When visiting her mother, Baylis helps to sustain the integrity of Gloria’s self even when Gloria can no longer do that for herself. But she’s still herself. Does that mean that self-knowledge isn’t important? Of course not. Gloria’s diminished capacities are a contraction of her self, and might be a version of what happens in some degree for an ageing self who experiences a weakening of capacities. And there’s a lesson here for any self: none of us is completely transparent to ourselves. This isn’t a new idea; even Plato, long before Freud, recognised that there were unconscious desires, and that self-knowledge is a hard-won and provisional achievement. The process of self-questioning and self-discovery is ongoing through life because we don’t have fixed and immutable identities: our identity is multiple, complex and fluid.
This means that others don’t know us perfectly either. When people try to fix someone’s identity as one particular characteristic, it can lead to misunderstanding, stereotyping, discrimination. Our currently polarised rhetoric seems to do just that – to lock people into narrow categories: ‘white’, ‘Black’, ‘Christian’, ‘Muslim’, ‘conservative’, ‘progressive’. But selves are much more complex and rich. Seeing ourselves as a network is a fertile way to understand our complexity. Perhaps it could even help break the rigid and reductive stereotyping that dominates current cultural and political discourse, and cultivate more productive communication. We might not understand ourselves or others perfectly, but we often have overlapping identities and perspectives. Rather than seeing our multiple identities as separating us from one another, we should see them as bases for communication and understanding, even if partial. Lindsey is a white woman philosopher. Her identity as a philosopher is shared with other philosophers (men, women, white, not white). At the same time, she might share an identity as a woman philosopher with other women philosophers whose experiences as philosophers have been shaped by being women. Sometimes communication is more difficult than others, as when some identities are ideologically rejected, or seem so different that communication can’t get off the ground. But the multiple identities of the network self provide a basis for the possibility of common ground.
How else might the network self contribute to practical, living concerns? One of the most important contributors to our sense of wellbeing is the sense of being in control of our own lives, of being self-directing. You might worry that the multiplicity of the network self means that it’s determined by other factors and can’t be self -determining. The thought might be that freedom and self-determination start with a clean slate, with a self that has no characteristics, social relations, preferences or capabilities that would predetermine it. But such a self would lack resources for giving itself direction. Such a being would be buffeted by external forces rather than realising its own potentialities and making its own choices. That would be randomness, not self-determination. In contrast, rather than limiting the self, the network view sees the multiple identities as resources for a self that’s actively setting its own direction and making choices for itself. Lindsey might prioritise career over parenthood for a period of time, she might commit to finishing her novel, setting philosophical work aside. Nothing prevents a network self from freely choosing a direction or forging new ones. Self-determination expresses the self. It’s rooted in self-understanding.
The network self view envisions an enriched self and multiple possibilities for self-determination, rather than prescribing a particular way that selves ought to be. That doesn’t mean that a self doesn’t have responsibilities to and for others. Some responsibilities might be inherited, though many are chosen. That’s part of the fabric of living with others. Selves are not only ‘networked’, that is, in social networks, but are themselves networks. By embracing the complexity and fluidity of selves, we come to a better understanding of who we are and how to live well with ourselves and with one another.
To read more about the self, visit Psyche , a digital magazine from Aeon that illuminates the human condition through psychology, philosophical understanding and the arts.
Quantum theory
Quantum dialectics
When quantum mechanics posed a threat to the Marxist doctrine of materialism, communist physicists sought to reconcile the two
Jim Baggott

Nations and empires
A United States of Europe
A free and unified Europe was first imagined by Italian radicals in the 19th century. Could we yet see their dream made real?
Fernanda Gallo

Stories and literature
On Jewish revenge
What might a people, subjected to unspeakable historical suffering, think about the ethics of vengeance once in power?
Shachar Pinsker

Building embryos
For 3,000 years, humans have struggled to understand the embryo. Now there is a revolution underway
John Wallingford

Design and fashion
Sitting on the art
Given its intimacy with the body and deep play on form and function, furniture is a ripely ambiguous artform of its own
Emma Crichton Miller

Learning to be happier
In order to help improve my students’ mental health, I offered a course on the science of happiness. It worked – but why?
Language and Identity Essay
Introduction.
- Language and Gender
- Language and Racial Identity
- Language and Social Status
Works Cited
Language serves as a vital means of expression, facilitating communication and interaction. It’s not merely a tool for conveying thoughts but is intrinsically linked with an individual’s identity. The question arises: How is language profoundly intertwined with identity?
Individuals, each with their unique characteristics, employ language to express their distinctions or commonalities. In particular, language can be a unifying force for people belonging to a specific social group, highlighting the bond between language and identity from the beginning.
An individual’s identity is not fixed; it varies depending on the situation, purpose, and context. When people find themselves in new environments, they often reshape their identities to adapt. This adaptability underscores the need to explore how environmental changes can redefine the link between language and identity.
Language can also indicate a person’s social status, race, nationality, or gender. Typically, members of a specific group share a common language, reinforcing their unity. This shared linguistic experience solidifies group identity and fosters a sense of belonging through shared experiences and ease of communication.
In this language and identity essay, we explore the dynamic interplay between these two concepts, exploring how they mutually influence and define each other.
Language and Identity: Gender
The intersection of language and gender identity reveals distinct patterns. Across various cultures, gender-based variations in speech are prevalent. Historically, linguistic differences have been observed in how women and men communicate. These differences often stem from the divergent social statuses of men and women, significantly influencing their manner of speaking. Power dynamics and societal roles of subordination between genders typically manifest in their vocabulary choices.
In many societies, there is an expectation for women to use more refined and polite language compared to men. Such cultural norms frequently discourage women from using profanity or obscene language. In these contexts, women often occupy a subordinate position, with their social liberties being more restricted than men’s. This disparity can increase insecurity, uncertainty, and a lack of confidence among women (Talbot 35). Consequently, the use of language within a society can indicate the level of social freedom and gender equality. The linguistic choices of men and women are integral to the discourse on language and identity. Those are not merely reflections of individual preferences but norms deeply embedded in societal structures and expectations. Gendered language norms, as explored in educational settings, not only shape communication styles but also reinforce gender stereotypes and roles, perpetuating inequality. Thus, studying language about gender identity, a key component in teacher education programs, provides critical insights into the broader societal dynamics and power relations that govern gender interactions.
Language and Identity: Race
The intricate relationship between language and racial or ethnic identity is undeniable. An individual’s history shapes their language, leading to those with similar racial backgrounds often using similar languages for communication. One’s mother tongue, acquired at birth, is a fundamental aspect of racial identity, providing a crucial sense of belonging, especially in early life.
In many households, a specific language is used for family communication. This habitual use of a language fosters an association with affection and intimacy, setting it apart from the language used in public settings. For example, Hispanic families living in America often identify Spanish as a critical component of their racial identity.
Consequently, while they might use English in public spaces, they prefer Spanish for intimate conversations with friends and family. Spanish allows for expressing emotions and thoughts in ways that might be more challenging in English (Talbot 173). Speaking a particular language can create a bond among its speakers, delineating an ‘us versus them’ dynamic with those who do not say it.
However, this practice can also lead to social isolation for minorities who speak a different language than the majority. They may struggle to relate to those who do not speak their native language or express themselves in the dominant public language. Even in monolingual societies, people often resort to a distinct language or dialect within their close social circles, aiding in more apparent emotional expression.
The narrative “Aria” by Richard Rodriguez illustrates the role of language as a marker of racial identity. Rodriguez recounts how Spanish, the sole language spoken at home, influenced his upbringing in California, where English was the norm. This use of Spanish fostered a warm, familial environment.
This language choice created a comfortable and inviting atmosphere at home, but it also labeled English speakers as “flos gringos” – the others (Rodriguez 134). While Spanish strengthened familial bonds and provided a sense of identity, it simultaneously isolated the family socially, limiting their interactions to Spanish-speaking relatives.
The exclusive use of Spanish at home adversely affected Rodriguez and his siblings’ educational progress. A shift occurred when nuns from their school intervened, prompting the family to start using English at home. This change markedly improved their social interactions. However, over time, Rodriguez lost proficiency in Spanish, leading his relatives to call him “pocho derogatorily” – a term for someone who has lost their identity (Rodriguez 137). To his relatives, speaking Spanish was a crucial element of their identity. “Aria” underscores the significance of language in racial identity. Despite assimilating into American society, Rodriguez experienced a nostalgic connection to his heritage whenever he heard Spanish spoken, indicating its enduring link to his racial identity.
Language and Identity: Social Status
The social status of individuals often manifests in their speech patterns. Educational attainment significantly influences language proficiency, as those from higher social classes typically access better education. This access equips them with the skills to use language effectively in communication.
People from various social backgrounds tend to exhibit distinct dialects. These dialectic variations reflect their diverse social experiences. Grammatical differences are not the only distinguishing factors; phonological and phonetic variations are also prevalent, leading to distinct accents among different social statuses. Therefore, the linguistic divide between social classes acts as both a consequence and a reinforcer of social stratification, mirroring the complexities of societal hierarchies. This phenomenon underscores the intricate relationship between language use and social identity, where speech patterns become markers of social positioning and mobility.
During the nineteenth century, slavery was a prevalent institution in America. Slaves were relegated to the lowest social echelon. Slave owners were intent on preserving this hierarchy, deeming it improper for slaves to acquire literacy skills. The ability to read and write was seen as a potential elevation of the slaves’ intellectual status, which could threaten the established order. Thus, the enforced illiteracy of slaves perpetuated their subjugation and created a linguistic divide between them and their masters (Jones and Christensen 45). In modern times, every society exhibits some form of social stratification. This concept refers to the structured ranking of social classes within a societal hierarchy. Their relative social distances influence the linguistic impact between social groups. Language changes in a higher social class might have little to no effect on the language used by lower social classes. Conversely, social groups closely aligned in status may share similar linguistic traits.
Language is integral in facilitating effective communication between two parties. However, its efficiency largely depends on both parties’ language understanding. As such, language can be a tool for enhancing or impeding communication. Individuals need to understand the nuances of words within the specific language used.
Misinterpretation of language can lead to incorrect perceptions of the message being conveyed. This issue often arises because some words may have varied meanings depending on the context. Therefore, the speaker must assess the listener’s ability to comprehend the information, which should be a central consideration in the communication process (Tan 142). This ensures that the intended message is accurately understood.
Language has two main functions. It helps communicate and gives a group of people a sense of identity and pride. People usually identify themselves with a specific language. Various groups use jargon that is only comprehensible to people within the group.
Language may show the social status, gender, and race of an individual. People who belong to different social statuses usually use other languages. In addition, different genders use different language vocabularies. A study on the language vocabulary of different genders may help determine a society’s social freedom. Language is a source of racial identity. People usually use a specific language when communicating with people from their race. The use of this language creates racial identity.
Jones, Malinda E., and Ann E. Christensen. “Learning to Read.” Constructing Strong Foundations of Early Literacy . Routledge, 2022. 33-46.
Talbot, Mary, ed. Language and Power in The Modern World . Edinburgh University Press, 2019.
Rodriguez, Richard. “Aria.” The Blair Reader: Exploring Issues and Ideas . Ed. Laurie G. Kirszner and Stephen R. Mandell. Ontario: Pearson Education Canada, 2007, pp. 133-139.
Tan, Amy “Mother Tongue.” The Blair Reader: Exploring Issues and Ideas . Ed. Laurie G. Kirszner and Stephen R. Mandell. Ontario: Pearson Education Canada, 2007, pp. 140-144.
- Opinion About the Course and the Author Richard Rodriguez
- Embarking on Research by Rau, Gao and Wu (2006) and by Rodriguez, Ooms and Montanez (2008)
- The Achievement of Desire
- Sarah Baartman Discussion
- Sarah Baartman: A Victim of Discrimination
- Evidence of Racism in the American Schools
- Analysis on Religion, Racism and Family Conflicts
- Race, Inclusion, Exclusion, and Segregation
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, December 11). Language and Identity Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/
"Language and Identity Essay." IvyPanda , 11 Dec. 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Language and Identity Essay'. 11 December.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Language and Identity Essay." December 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
1. IvyPanda . "Language and Identity Essay." December 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Language and Identity Essay." December 11, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/relationship-between-language-and-identity/.
Essays about Culture and Identity: 9 Examples And Prompts
Writing essays about culture and identity will help you explore your understanding of it. Here are examples that will give you inspiration for your next essay.
Culture can refer to customs, traditions, beliefs, lifestyles, laws, artistic expressions, and other elements that cultivate the collective identity. Different cultures are established across nations, regions, communities, and social groups. They are passed on from generation to generation while others evolve or are abolished to give way to modern beliefs and systems.
While our cultural identity begins at home, it changes as we involve ourselves with other groups (friends, educational institutions, social media communities, political groups, etc.) Culture is a very relatable subject as every person is part of a culture or at least can identify with one. Because it spans broad coverage, there are several interesting cultural subjects to write about.
Our culture and identity are dynamic. This is why you may find it challenging to write about it. To spark your inspiration, check out our picks of the best culture essays.
1. Sweetness and Light by Matthew Arnolds
2. how auto-tune revolutionized the sound of popular music by simon reynolds, 3. how immigration changes language by john mcwhorter, 4. the comfort zone: growing up with charlie brown by jonathan franzen, 5. culture and identity definition by sandra graham, 6. how culture and surroundings influence identity by jeanette lucas, 7. how the food we eat reflects our culture and identity by sophia stephens, 8. identity and culture: my identity, culture, and identity by april casas, 9. how america hinders the cultural identity of their own citizens by seth luna, 1. answer the question, “who am i”, 2. causes of culture shock, 3. your thoughts on dystopia and utopia, 4. gender inequality from a global perspective, 5. the most interesting things you learned from other cultures, 6. the relationship between cultural identity and clothes, 7. describe your culture, 8. what is the importance of honoring your roots , 9. how can a person adapt to a new culture, 10. what artistic works best express your country’s culture, 11. how has social media influenced human interaction, 12. how do you protect the cultures of indigenous peoples, 13. are k-pop and k-drama sensations effectively promoting korea’s culture , 14. what is the importance of cultural diversity.
“… [A]nd when every man may say what he likes, our aspirations ought to be satisfied. But the aspirations of culture, which is the study of perfection, are not satisfied, unless what men say, when they may say what they like, is worth saying,—has good in it, and more good than bad.”
Arnolds compels a re-examination of values at a time when England is leading global industrialization and beginning to believe that greatness is founded on material progress.
The author elaborates why culture, the strive for a standard of perfection, is not merely driven by scientific passions and, more so, by materialistic affluence. As he esteems religion as “that voice of the deepest human experience” to harmonize men in establishing that ideal society, Arnolds stresses that culture is the effort to “make reason and the will of God prevail” while humanizing gained knowledge to be society’s source of “sweetness and light.”
“Few innovations in sound production have been simultaneously so reviled and so revolutionary. Epoch-defining or epoch-defacing, Auto-Tune is indisputably the sound of the 21st century so far.”
Reynolds shows how Auto-Tune has shaped a pop music genre that has cut across cultures. The article maps out the music landscape Auto-Tune created and examines its impact on the culture of song productions and the modern taste for music. While the author debunks accusations that Auto-Tune destroyed the “natural” process of creating music, he also points out that the technology earned its reverence with big thanks to society’s current custom of using technology to hide blemishes and other imperfections.
Looking for more? Check out these essays about culture shock .
“… [T]he heavy immigration that countries like Italy are experiencing will almost certainly birth new kinds of Italian that are rich with slang, somewhat less elaborate than the standard, and… widely considered signs of linguistic deterioration, heralding a future where the “original” standard language no longer exists.”
American linguist McWhorter pacifies fears over the death of “standard” languages amid the wave of immigration to Europe. On the contrary, language is a vital expression of a culture, and for some, preserving is tantamount to upholding a cultural standard.
However, instead of seeing the rise of new “multiethnolects” such as the Black English in America and Kiezdeutsch in Germany as threats to language and culture, McWhorter sees them as a new way to communicate and better understand the social groups that forayed these new languages.
“I wonder why “cartoonish” remains such a pejorative. It took me half my life to achieve seeing my parents as cartoons. And to become more perfectly a cartoon myself: what a victory that would be.”
This essay begins with a huge fight between Franzen’s brother and father to show how the cultural generation gap sweeping the 60s has hit closer to home. This generation gap, where young adults were rejecting the elders’ old ways in pursuit of a new and better culture, will also be the reason why his family ends up drifting apart. Throughout the essay, Franzen treads this difficult phase in his youth while narrating fondly how Peanuts, a pop culture icon at the time, was his source of escape.
“…Culture is… your background… and Identity is formed where you belong to… Leopold Sedar Senghor and Shirley Geok-Lin Lim both talks about how culture and identity can impact… society…”
In this essay, Graham uses “To New York” by Senghor and “Learning To Love America” by Lim as two pieces of literature that effectively describe the role of culture and identity to traveling individuals.
The author refers to Sengho’s reminder that people can adapt but must not forget their culture even if they go to a different place or country. On the other hand, Lim discusses immigrants’ struggle to have double identities.
“Culture is something that surrounds all of us and progress to shape our lives every day… Identity is illustrated as the state of mind in which someone or something distinguishes their own character traits that lead to determining who they really are, what they represent.”
Lucas is keen on giving examples of how his culture and surroundings influence an individual’s identity. She refers to Kothari’s “If you are what you eat, then what am I?” which discusses Kothari’s search for her identity depending on what food she eats. Food defines a person’s culture and identity, so Kothari believes that eating food from different countries will change his identity.
Lucas also refers to “Down These Mean Streets” by Piri Thomas, which argues how different cultural and environmental factors affect us. Because of what we encounter, there is a possibility that we will become someone who we are not.
“What we grow is who we are. What we buy is who we are. What we eat is who we are.”
Stephens’ essay teaches its readers that the food we grow and eat defines us as a person. She explains that growing a crop and harvesting it takes a lot of effort, dedication, and patience, which mirrors our identity.
Another metaphor she used is planting rice: it takes skills and knowledge to make it grow. Cooking rice is more accessible than cultivating it – you can quickly cook rice by boiling it in water. This reflects people rich in culture and tradition but who lives simpler life.
“Every single one has their own unique identity and culture. Culture plays a big role in shaping your identity. Culture is what made me the person I am today and determines who or what I choose to associate myself with.”
Casas starts her piece by questioning who she is. In trying to learn and define who she is, she writes down and describes herself and her personality throughout the essay. Finally, she concludes that her culture is a big part of her identity, and she must understand it to understand herself.
“When it comes to these stereotypes we place on each other, a lot of the time, we succumb to the stereotypes given to us. And our cultural identity is shaped by these expectations and labels others give us. That is why negative stereotypes sometimes become true for a whole group or community.”
In this essay, Luna talks about how negative stereotyping in the United States led to moral distortion. For example, Americans are assumed to be ignorant of other countries’ cultures, making it difficult to understand other people’s cultures and lifestyles.
She believes that stereotyping can significantly affect an individual or group’s identity. She suggests Americans should improve their intellectual competence by being sensitive to other people’s cultures.
14 Prompts on Essays about Culture and Identity
You can discuss many things on the subject of culture and identity. To give you a starting point, here are some prompts to help you write an exciting essay about culture.
If you are interested in learning more, check out our essay writing tips and our round-up of the best essay checkers .
Understanding your personality is vital since continuous interaction with others can affect your personality. Write about your culture and identity; what is your personality? How do you define yourself? Everyone is unique, so by writing an essay about who you are, you’ll be able to understand why you act a certain way and connect with readers who have the same values.
Here’s a guide on writing a descriptive essay to effectively relay your experience to your readers.
Sometimes, people need to get out of their comfort zone and interact with other individuals with different cultures, beliefs, or traditions. This is to broaden one’s perspective about the world. Aside from discussing what you’ve learned in that journey, you can also focus on the bits that shocked you.
You can talk about a tradition or value that you found so bizarre because it differs from your culture. Then add how you processed it and finally adapted to it.

Dystopia and Utopia are both imagined worlds. Dystopia is a world where people live in the worst or most unfavorable conditions, while Utopia is the opposite.
You can write an essay about what you think a Dystopian or Utopian world may look like, how these societies will affect their citizens, etc. Then, consider what personality citizens of each world may have to depend on the two worlds’ cultures.
Today, more and more people are fighting for others to accept or at least respect the LGBTQ+ community. However, countries, territories, and religions still question their rights.
In your essay, you can talk about why these institutions react the way they do and how culture dictates someone’s identity in the wrong way. Before creating your own, feel free to read other essays and articles to learn more about the global gender inequality issue.
The world has diverse cultures, traditions, and values. When you travel to a new place, learning and writing about your firsthand experiences with unique cultures and rituals will always be an interesting read.
In this prompt, you’ll research other cultures and how they shaped their group’s identity. Then, write about the most exciting aspects you’ve learned, why you found them fascinating, and how they differ from your culture.
Those proud of their culture will wear clothes inspired by them. Some wear the same clothes even if they aren’t from the same culture. The debate over cultural appropriation and culture appreciation is still a hot topic.
In this essay, you may start with the traditions of your community or observances your family celebrates and gathers for. Then, elaborate on their origins and describe how your community or family is preserving these practices.
Learning about your roots, ancestors, and family cultures can help strengthen your understanding of your identity and foster respect for other cultures. Explore this topic and offer examples of what others have learned. Has the journey always been a positive experience? Delve into this question for an engaging and interesting essay.
When a person moves country, it can be challenging to adapt to a new culture. If there are new people at work or school, you can interview them and ask how they are coping with their new environment. How different is this from what they have been used to, and what unique traditions do they find interesting?
Focus on an art piece that is a source of pride and identity to your country’s culture, much like the Tinikling of the Philippines or the Matryoshka dolls of Russia. Explore its origins and evolution up to its current manifestation and highlight efforts that are striving to protect and promote these artistic works.
The older generation did not have computers in their teen years. Ask about how they dated in their younger years and how they made friends. Contrast how the younger generation is building their social networks today. Write what culture of socialization works better for you and explain why.
Take in-depth navigation of existing policies that protect indigenous peoples. Are they sufficient to serve these communities needs, and are they being implemented effectively? There is also the challenge of balancing the protection of these traditions against the need to protect the environment, as some indigenous practices add to the carbon footprint. How is your government dealing with this challenge?
A large population is now riding the Hallyu or the Korean pop culture, with many falling in love with the artists and Korea’s food, language, and traditional events. Research how certain Korean films, TV series, or music have effectively attracted fans to experience Korea’s culture. Write about what countries can learn from Korea in promoting their own cultures.
Environments that embrace cultural diversity are productive and innovative. To start your essay, assess how diverse your workplace or school is. Then, write your personal experiences where working with co-workers or classmates from different cultures led to new and innovative ideas and projects. Combine this with the personal experiences of your boss or the principal to see how your environment benefits from hosting a melting pot of cultures.
If you aim for your article to effectively change readers’ perspectives and align with your opinion, read our guide to achieving persuasive writing .

Aisling is an Irish journalist and content creator with a BA in Journalism & New Media. She has bylines in OK! Magazine, Metro, The Inquistr, and the Irish Examiner. She loves to read horror and YA. Find Aisling on LinkedIn .
View all posts
So much is at stake in writing a conclusion. This is, after all, your last chance to persuade your readers to your point of view, to impress yourself upon them as a writer and thinker. And the impression you create in your conclusion will shape the impression that stays with your readers after they've finished the essay.
The end of an essay should therefore convey a sense of completeness and closure as well as a sense of the lingering possibilities of the topic, its larger meaning, its implications: the final paragraph should close the discussion without closing it off.
To establish a sense of closure, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude by linking the last paragraph to the first, perhaps by reiterating a word or phrase you used at the beginning.
- Conclude with a sentence composed mainly of one-syllable words. Simple language can help create an effect of understated drama.
- Conclude with a sentence that's compound or parallel in structure; such sentences can establish a sense of balance or order that may feel just right at the end of a complex discussion.
To close the discussion without closing it off, you might do one or more of the following:
- Conclude with a quotation from or reference to a primary or secondary source, one that amplifies your main point or puts it in a different perspective. A quotation from, say, the novel or poem you're writing about can add texture and specificity to your discussion; a critic or scholar can help confirm or complicate your final point. For example, you might conclude an essay on the idea of home in James Joyce's short story collection, Dubliners , with information about Joyce's own complex feelings towards Dublin, his home. Or you might end with a biographer's statement about Joyce's attitude toward Dublin, which could illuminate his characters' responses to the city. Just be cautious, especially about using secondary material: make sure that you get the last word.
- Conclude by setting your discussion into a different, perhaps larger, context. For example, you might end an essay on nineteenth-century muckraking journalism by linking it to a current news magazine program like 60 Minutes .
- Conclude by redefining one of the key terms of your argument. For example, an essay on Marx's treatment of the conflict between wage labor and capital might begin with Marx's claim that the "capitalist economy is . . . a gigantic enterprise of dehumanization "; the essay might end by suggesting that Marxist analysis is itself dehumanizing because it construes everything in economic -- rather than moral or ethical-- terms.
- Conclude by considering the implications of your argument (or analysis or discussion). What does your argument imply, or involve, or suggest? For example, an essay on the novel Ambiguous Adventure , by the Senegalese writer Cheikh Hamidou Kane, might open with the idea that the protagonist's development suggests Kane's belief in the need to integrate Western materialism and Sufi spirituality in modern Senegal. The conclusion might make the new but related point that the novel on the whole suggests that such an integration is (or isn't) possible.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay:
- Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas.
- Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up." These phrases can be useful--even welcome--in oral presentations. But readers can see, by the tell-tale compression of the pages, when an essay is about to end. You'll irritate your audience if you belabor the obvious.
- Resist the urge to apologize. If you've immersed yourself in your subject, you now know a good deal more about it than you can possibly include in a five- or ten- or 20-page essay. As a result, by the time you've finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you've produced. (And if you haven't immersed yourself in your subject, you may be feeling even more doubtful about your essay as you approach the conclusion.) Repress those doubts. Don't undercut your authority by saying things like, "this is just one approach to the subject; there may be other, better approaches. . ."
Copyright 1998, Pat Bellanca, for the Writing Center at Harvard University
Calculate for all schools
Your chance of acceptance, your chancing factors, extracurriculars, essays about personal identity.
Hi all! I'm thinking about writing an essay that focuses on my personal identity. What are some ways to make this type of essay engaging and interesting to colleges? Any examples I should check out for inspiration? Thanks in advance!
Hello! Writing an essay that focuses on your personal identity can be a powerful way to showcase your unique experiences, interests, and perspectives. To make this type of essay engaging and interesting to colleges, consider the following tips:
1. Be authentic and vulnerable: Share your true feelings, thoughts, and struggles as they pertain to your identity. By being open about your experiences, you create a deep connection with the reader.
2. Focus on a specific aspect: Instead of trying to cover every detail of your identity, choose one or two key facets that define you. Delving into particular experiences and emotions will allow you to demonstrate depth and create a more compelling narrative.
3. Use descriptive language and vivid imagery: Paint a picture for the reader by using descriptive words and vivid imagery. This will help them visualize and connect with your story on a deeper level.
4. Show rather than tell: Instead of simply stating your thoughts and feelings about your identity, use anecdotes and examples to illustrate your point. By showing the reader your experiences, you'll create a more compelling and engaging essay.
5. Incorporate growth and development: Demonstrate how your understanding of your identity has evolved over time, and how it has shaped you as a person. This could include personal challenges you've faced, accomplishments, or newfound insights.
6. Reflect on the impact: Discuss how your identity has influenced your decisions, interests, and relationships. This reflection will help demonstrate the importance of your identity and its role in your life.
For examples and inspiration, you can browse through essays shared by students who were admitted to top colleges. Just be mindful not to copy their ideas or writing styles. Instead, use these examples to inspire your own unique angle in exploring your personal identity.
Best of luck with your essay and application process!
Most Popular
10 days ago
Inspiration vs Plagiarism
How to write a synthesis essay.
11 days ago
How to Cite a Bill
How to write a 5 paragraph essay, openai prepares to launch web search feature for chatgpt, rivaling google and perplexity, what is your identity essay sample, example.

Identity, in itself, is difficult to define—let alone ourselves as a persona. It seems that identity is what we and others say we are. In this case, identity is flexible and fluid. It can change at a moment’s notice, as who we are is a story we and others tell ourselves. Identity is not a solid, carved-into-stone statement. Moment to moment, our identities are shaping and reshaping themselves.
Yet, if I was to try to define my identity concretely within a worldly view, I would say I am primarily a person focused on creativity and spirituality. Every day, I write poetry, play percussion, and sing. I regularly submit my poetry to journals, and perform in concerts as a percussionist. I enjoy singing sometimes in concerts, but mostly I sing for my own enjoyment at home and while on walks. In terms of spirituality, I meditate each morning and night, and listen to spiritual music during the day. I also enjoy pondering about spiritual philosophies from Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, and many other religions and traditions. I try to remain in a meditative state throughout the day.
I can get more mundane and say that I am a 33-year-old Caucasian male, American, who was born in Seattle, Washington, and currently live there. I have a wife, no children, and a pug. I work as a content coordinator and editor. My favorite food is either Mexican cuisine or Italian cuisine. I am both an introvert and extrovert. I took an IQ test and got a near-genius score. I have had five surgeries. I have won awards for my writing. I like to occasionally play chess, and was crazy about this game in high school. My personality is a mix of bubbliness and introspectiveness. There is so much to list off, but I do not know how interesting it would be for readers to trudge through.
Examining my identity, I realized that yes, I am this surface identity that anyone can fill out in a personality test. However, underneath this layer of identity, I believe there is a more universal identity. Through meditation, I have experienced moments and spans of time when all my thoughts, physical sensations, and emotions were so far away from being perceived directly that I felt detached from them. The discovery that my identity could simply be consciousness was startling. In addition to being surprised, I realized that this state is available for all of us—that pure consciousness could be our universal identity.
What does that mean for identity itself? Well, I believe we might fooling ourselves that we are, say, a 33-year-old Caucasian male from Seattle who writes poetry every day and loves taking walks with his pug. This is only a superficial layer of identity that is constantly adapting and changing according to the environment, circumstances, and happenings. The universal identity of pure consciousness is always the same, and can be said to be the most secure form of identity. Also, if we view people as pure consciousness, then it is difficult to have prejudice or ill will for them. This body and all of its components are only a container for this pure consciousness. Do not ask me how and why this pure consciousness is there, though. I do not have enough knowledge to answer this question properly.
This is one example of a reflective essay. As you may have noticed, it’s a concise but comprehensive analysis of the chosen topic. If it’s your first time writing something like this, don’t be afraid to ask for help from the best assignment writers . It’s not an easy task and searching for guidance is a natural thing to be doing.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Identity Essay Examples & Samples
Balancing personal health details with privacy considerations. essay sample and references.

Nov 20 2023
Diary of Anne Frank summary

Oct 07 2023
Shaped by Two Cultures, Bound by One Identity Personal Statement Example
Remember Me
Is English your native language ? Yes No
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
- Search Menu
Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
Conclusion: The Identity of Identity
- Published: February 2019
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
The word ‘identity’ suggests immutability, self-sameness, and permanency, while in fact it does what other words also do: it changes its meaning, now so rapidly that it is hard to keep track. ‘Conclusion: the identity of identity’ concludes that, on the individual level, identities have become a matter of negotiating and, as the need to do so arises, renegotiating your place, your purpose, and your presentation in everyday life. On the collective level, identities are fuzzy sets rather than clearly delineated groups. Yet, the assertion of, search for, and preoccupation with, identity keeps growing and invading ever more spheres of life. There are no indications that the identity wave is flattening.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
17 Essay Conclusion Examples (Copy and Paste)

Essay conclusions are not just extra filler. They are important because they tie together your arguments, then give you the chance to forcefully drive your point home.
I created the 5 Cs conclusion method to help you write essay conclusions:

I’ve previously produced the video below on how to write a conclusion that goes over the above image.
The video follows the 5 C’s method ( you can read about it in this post ), which doesn’t perfectly match each of the below copy-and-paste conclusion examples, but the principles are similar, and can help you to write your own strong conclusion:
💡 New! Try this AI Prompt to Generate a Sample 5Cs Conclusion This is my essay: [INSERT ESSAY WITHOUT THE CONCLUSION]. I want you to write a conclusion for this essay. In the first sentence of the conclusion, return to a statement I made in the introduction. In the second sentence, reiterate the thesis statement I have used. In the third sentence, clarify how my final position is relevant to the Essay Question, which is [ESSAY QUESTION]. In the fourth sentence, explain who should be interested in my findings. In the fifth sentence, end by noting in one final, engaging sentence why this topic is of such importance.
Remember: The prompt can help you generate samples but you can’t submit AI text for assessment. Make sure you write your conclusion in your own words.
Essay Conclusion Examples
Below is a range of copy-and-paste essay conclusions with gaps for you to fill-in your topic and key arguments. Browse through for one you like (there are 17 for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays). Once you’ve found one you like, copy it and add-in the key points to make it your own.
1. Argumentative Essay Conclusions
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of _____________. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as ____________, it remains clear that the benefits/merits of _____________ far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support _____________. In the coming years, _____________ will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for _____________.
Version 1 Filled-In
The arguments presented in this essay demonstrate the significant importance of fighting climate change. While there are some strong counterarguments, such as the claim that it is too late to stop catastrophic change, it remains clear that the merits of taking drastic action far outweigh the potential downsides. The evidence presented throughout the essay strongly support the claim that we can at least mitigate the worst effects. In the coming years, intergovernmental worldwide agreements will be increasingly important. Therefore, continual advocacy for the position presented in this essay will be necessary, especially due to its significant implications for humankind.

As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding _____________ is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that _____________, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that _____________. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that _____________ not only leads to ____________, but it may also be a necessity for _____________. Moving forward, _____________ should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for _____________. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate _____________ more effectively into society.
Version 2 Filled-In
As this essay has shown, it is clear that the debate surrounding climate change is multifaceted and highly complex. While there are strong arguments opposing the position that we should fight climate change, there remains overwhelming evidence to support the claim that action can mitigate the worst effects. A careful analysis of the empirical evidence suggests that strong action not only leads to better economic outcomes in the long term, but it may also be a necessity for preventing climate-related deaths. Moving forward, carbon emission mitigation should be a priority for all stakeholders involved, as it promises a better future for all. The focus should now shift towards how best to integrate smart climate policies more effectively into society.
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that _____________ holds the potential to significantly alter/improve _____________. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for _____________. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that _____________ presents the most effective solution/approach to _____________. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of _____________ for developing a better _____________. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including _____________.
Version 3 Filled-In
Based upon the preponderance of evidence, it is evident that addressing climate change holds the potential to significantly improve the future of society. The counterarguments, while noteworthy, fail to diminish the compelling case for immediate climate action. Following an examination of both sides of the argument, it has become clear that widespread and urgent social action presents the most effective solution to this pressing problem. Consequently, it is imperative that society acknowledge the value of taking immediate action for developing a better environment for future generations. Failing to address this topic could lead to negative outcomes, including more extreme climate events and greater economic externalities.
See Also: Examples of Counterarguments
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for _____________. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that _____________. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that _____________ is the most sufficient option for _____________. The implications of embracing _____________ do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more _____________. Therefore, the solution of _____________ should be actively pursued by _____________.
Version 4 Filled-In
On the balance of evidence, there is an overwhelming case for immediate tax-based action to mitigate the effects of climate change. While the counterarguments offer valid points that are worth examining, they do not outweigh or overcome the argument that action is urgently necessary. An evaluation of both perspectives on this topic concludes that taking societal-wide action is the most sufficient option for achieving the best results. The implications of embracing a society-wide approach like a carbon tax do not only have immediate benefits, but they also pave the way for a more healthy future. Therefore, the solution of a carbon tax or equivalent policy should be actively pursued by governments.
2. Expository Essay Conclusions
Overall, it is evident that _____________ plays a crucial role in _____________. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of _____________ on _____________. By understanding the key facts about _____________, practitioners/society are better equipped to navigate _____________. Moving forward, further exploration of _____________ will yield additional insights and information about _____________. As such, _____________ should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on _____________.
Overall, it is evident that social media plays a crucial role in harming teenagers’ mental health. The analysis presented in this essay demonstrates the clear impact of social media on young people. By understanding the key facts about the ways social media cause young people to experience body dysmorphia, teachers and parents are better equipped to help young people navigate online spaces. Moving forward, further exploration of the ways social media cause harm will yield additional insights and information about how it can be more sufficiently regulated. As such, the effects of social media on youth should remain a focal point for further discussions and studies on youth mental health.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of _____________. Through a careful examination of _____________, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on _____________. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that _____________. As research continues to emerge, the importance of _____________ will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of _____________ is not merely desirable, but imperative for _____________.
To conclude, this essay has explored the multi-faceted aspects of globalization. Through a careful examination of globalization, this essay has illuminated its significant influence on the economy, cultures, and society. This understanding allows society to appreciate the idea that globalization has both positive and negative effects. As research continues to emerge, the importance of studying globalization will only continue to grow. Therefore, an understanding of globalization’s effects is not merely desirable, but imperative for judging whether it is good or bad.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that _____________ serves a pivotal role in _____________. By delving into the intricacies of _____________, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in _____________. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on _____________. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of _____________ can only deepen and expand.
Reflecting on the discussion, it is clear that mass media serves a pivotal role in shaping public opinion. By delving into the intricacies of mass media, we have gained valuable insights into its impact and significance. This knowledge will undoubtedly serve as a guiding principle in shaping the media landscape. Moving forward, it is paramount to remain open to further explorations and studies on how mass media impacts society. In this way, our understanding and appreciation of mass media’s impacts can only deepen and expand.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of _____________ in the context of _____________. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect _____________ has on _____________. The knowledge gained from exploring _____________ will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in _____________. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding _____________ will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of _____________ to better navigate and influence _____________.
In conclusion, this essay has shed light on the importance of bedside manner in the context of nursing. The evidence and analysis provided underscore the profound effect compassionate bedside manner has on patient outcome. The knowledge gained from exploring nurses’ bedside manner will undoubtedly contribute to more informed and effective decisions in nursing practice. As we continue to progress, the significance of understanding nurses’ bedside manner will remain paramount. Hence, we should strive to deepen our knowledge of this topic to better navigate and influence patient outcomes.
See More: How to Write an Expository Essay
3. Compare and Contrast Essay Conclusion
While both _____________ and _____________ have similarities such as _____________, they also have some very important differences in areas like _____________. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of _____________ and _____________ has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on _____________. For example, as highlighted in the essay, ____________. Despite their differences, both _____________ and _____________ have value in different situations.
While both macrosociology and microsociology have similarities such as their foci on how society is structured, they also have some very important differences in areas like their differing approaches to research methodologies. Through this comparative analysis, a broader understanding of macrosociology and microsociology has been attained. The choice between the two will largely depend on the researcher’s perspective on how society works. For example, as highlighted in the essay, microsociology is much more concerned with individuals’ experiences while macrosociology is more concerned with social structures. Despite their differences, both macrosociology and microsociology have value in different situations.
It is clear that _____________ and _____________, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in _____________. On the other hand, their contrasts in _____________ shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to _____________. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to _____________.
It is clear that behaviorism and consructivism, while seeming to be different, have shared characteristics in their foci on knowledge acquisition over time. On the other hand, their contrasts in ideas about the role of experience in learning shed light on their unique features. The analysis provides a more nuanced comprehension of these subjects. In choosing between the two, consideration should be given to which approach works best in which situation. Despite their disparities, it’s crucial to acknowledge the importance of both when it comes to student education.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that _____________ and _____________ share similarities such as _____________, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in _____________. The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as _____________. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both _____________ and _____________ play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to _____________.
Reflecting on the points discussed, it’s evident that red and orange share similarities such as the fact they are both ‘hot colors’, while also demonstrating unique differences, particularly in their social meaning (red meaning danger and orange warmth). The preference for one over the other would typically depend on factors such as personal taste. Yet, regardless of their distinctions, both red and orange play integral roles in their respective areas, significantly contributing to color theory.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of _____________ and _____________ have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as _____________ give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, _____________ will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both _____________ and _____________ hold significant value within the context of _____________, and each contributes to _____________ in its own unique way.
Ultimately, the comparison and contrast of driving and flying have revealed intriguing similarities and notable differences. Differences such as their differing speed to destination give deeper insights into their unique and shared qualities. When it comes to choosing between them, urgency to arrive at the destination will likely be a deciding factor. Despite these differences, it is important to remember that both driving and flying hold significant value within the context of air transit, and each contributes to facilitating movement in its own unique way.
See Here for More Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
4. Critical Essay Conclusion
In conclusion, the analysis of _____________ has unveiled critical aspects related to _____________. While there are strengths in _____________, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on _____________, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of _____________ should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
In conclusion, the analysis of flow theory has unveiled critical aspects related to motivation and focus. While there are strengths in achieving a flow state, its limitations are equally telling. This critique provides a more informed perspective on how humans achieve motivation, revealing that there is much more beneath the surface. Moving forward, the understanding of flow theory of motivation should evolve, considering both its merits and flaws.
To conclude, this critical examination of _____________ sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While _____________ presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of _____________. Therefore, future engagements with _____________ should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
To conclude, this critical examination of postmodern art sheds light on its multi-dimensional nature. While postmodernism presents notable advantages, it is not without its drawbacks. This in-depth critique offers a comprehensive understanding of how it has contributed to the arts over the past 50 years. Therefore, future engagements with postmodern art should involve a balanced consideration of its strengths and weaknesses.
Upon reflection, the critique of _____________ uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as ________, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of _____________, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of _____________ should be taken into account when considering ____________.
Upon reflection, the critique of marxism uncovers profound insights into its underlying intricacies. Despite its positive aspects such as its ability to critique exploitation of labor, it’s impossible to overlook its shortcomings. This analysis provides a nuanced understanding of marxism’s harmful effects when used as an economic theory, highlighting the necessity for a balanced approach in future interactions. Indeed, both the strengths and weaknesses of marxism should be taken into account when considering the use of its ideas in real life.
Ultimately, this critique of _____________ offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of _____________ such as __________ are significant, yet its limitations such as _________ are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of _____________ but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around _____________ continue to embrace this balanced approach.
Ultimately, this critique of artificial intelligence offers a detailed look into its advantages and disadvantages. The strengths of artificial intelligence, such as its ability to improve productivity are significant, yet its limitations such as the possibility of mass job losses are not insignificant. This balanced analysis not only offers a deeper understanding of artificial intelligence but also underscores the importance of critical evaluation. Hence, it’s crucial that future discussions around the regulation of artificial intelligence continue to embrace this balanced approach.
This article promised 17 essay conclusions, and this one you are reading now is the twenty-first. This last conclusion demonstrates that the very best essay conclusions are written uniquely, from scratch, in order to perfectly cater the conclusion to the topic. A good conclusion will tie together all the key points you made in your essay and forcefully drive home the importance or relevance of your argument, thesis statement, or simply your topic so the reader is left with one strong final point to ponder.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives
This essay about Adolf Hitler’s racial identity examines his pseudoscientific belief in Aryan superiority, despite his own non-Aryan appearance. It discusses the impact of his racial ideologies on Nazi policies, leading to the Holocaust. Recent genetic studies on Hitler’s ancestry are considered, highlighting the complexity of human genetics and the flaws in Hitler’s racial theories. The essay underscores the dangers of pseudoscience in shaping destructive ideologies.
How it works
Adolf Hitler’s racial identity, both from historical and genetic perspectives, has been a subject of intense scrutiny and speculation. As the leader of Nazi Germany, Hitler’s racial ideologies had catastrophic consequences, leading to the genocide of six million Jews and millions of others deemed racially or politically undesirable. Understanding Hitler’s racial identity requires examining his own beliefs and the limited genetic information available today.
Hitler’s racial views were rooted in a pseudoscientific belief in the superiority of the “Aryan” race.
He saw this race as the purest branch of the human family, characterized by features such as blonde hair, blue eyes, and fair skin. According to Hitler, the Aryans were the creators of all that was good in human history. Conversely, he deemed other races, particularly Jews and Slavs, as inferior and a threat to Aryan purity. This belief system formed the basis of his genocidal policies and the broader Nazi ideology of racial hierarchy.
Ironically, Hitler’s own appearance did not conform to his ideal Aryan prototype. He had dark hair and was of average height, with physical features that did not stand out as distinctly Aryan. This discrepancy has led to various speculations and conspiracies about his true racial origins. Some have suggested that Hitler might have had Jewish or Slavic ancestry, theories often fueled more by his vehement anti-Semitism and the self-hatred it might imply rather than by any concrete evidence.
Recent genetic studies, though limited, have provided some intriguing insights. A notable investigation into Hitler’s ancestry was conducted by journalist Jean-Paul Mulders and historian Marc Vermeeren, who collected DNA samples from Hitler’s known relatives. The study revealed that Hitler’s lineage included the haplogroup E1b1b1, which is relatively rare in Western Europe and more common in North Africa and among Ashkenazi Jews. This finding does not conclusively determine that Hitler had Jewish ancestry, as the haplogroup is also found among non-Jewish populations in Southern Europe and North Africa. However, it does highlight the complexity and diversity of human genetics, which often contradict simplistic racial categorizations.
These genetic revelations are fascinating, but they must be approached with caution. Genetic markers alone cannot define one’s identity or heritage in the simplistic and deterministic way that Hitler and his followers believed. Furthermore, the interpretation of genetic data is complex and can be easily misrepresented or misunderstood, especially when filtered through the lens of contemporary racial ideologies.
From a historical perspective, Hitler’s racial identity is less about his own ancestry and more about the catastrophic impact of his racial theories. His obsession with racial purity and eugenics led to policies that sought to “cleanse” Germany and its occupied territories of those deemed racially inferior. The Nuremberg Laws of 1935, which prohibited marriage and sexual relations between Jews and non-Jews, were a direct manifestation of his racial ideology. The concept of “racial hygiene” permeated Nazi policy, leading to forced sterilizations, euthanasia programs, and ultimately, the Holocaust.
Hitler’s racial views were heavily influenced by the racial theories popular in early 20th-century Europe. The ideas of Arthur de Gobineau, Houston Stewart Chamberlain, and other racial theorists provided a pseudo-intellectual framework for his beliefs. These theories posited a hierarchy of races, with the Aryan race at the top and Jews, Africans, and others at the bottom. Hitler’s own experiences and prejudices shaped how he interpreted and implemented these ideas. His time in Vienna, a city with a significant Jewish population and a hotbed of anti-Semitic politics, likely played a crucial role in solidifying his racial views.
The concept of race itself is now understood to be a social construct rather than a scientifically valid biological category. Modern genetics has shown that the genetic differences between human populations are minimal and do not align with traditional racial classifications. This scientific understanding starkly contrasts with the racial pseudoscience that underpinned Nazi ideology. Hitler’s racial identity, then, is a reminder of the dangers of conflating cultural and political ideologies with scientific facts.
In conclusion, Adolf Hitler’s racial identity is a complex subject that intertwines his personal beliefs, the pseudoscientific theories of his time, and the modern understanding of genetics. While some genetic studies suggest that Hitler may have had a more diverse ancestry than he would have acknowledged, these findings are ultimately less significant than the historical impact of his racial ideologies. Hitler’s obsession with racial purity led to some of the most horrific atrocities in human history, underscoring the peril of allowing pseudoscience and bigotry to dictate policy. Understanding this context is crucial in preventing the repetition of such destructive ideologies in the future.

Cite this page
The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives. (2024, May 21). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/
"The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives." PapersOwl.com , 21 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/ [Accessed: 24 May. 2024]
"The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives." PapersOwl.com, May 21, 2024. Accessed May 24, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/
"The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives," PapersOwl.com , 21-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/. [Accessed: 24-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Racial Identity of Adolf Hitler: Historical and Genetic Perspectives . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-racial-identity-of-adolf-hitler-historical-and-genetic-perspectives/ [Accessed: 24-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Letter of Recommendation
What I’ve Learned From My Students’ College Essays
The genre is often maligned for being formulaic and melodramatic, but it’s more important than you think.

By Nell Freudenberger
Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn’t supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they’re afraid that packaging the genuine trauma they’ve experienced is the only way to secure their future. The college counselor at the Brooklyn high school where I’m a writing tutor advises against trauma porn. “Keep it brief , ” she says, “and show how you rose above it.”
I started volunteering in New York City schools in my 20s, before I had kids of my own. At the time, I liked hanging out with teenagers, whom I sometimes had more interesting conversations with than I did my peers. Often I worked with students who spoke English as a second language or who used slang in their writing, and at first I was hung up on grammar. Should I correct any deviation from “standard English” to appeal to some Wizard of Oz behind the curtains of a college admissions office? Or should I encourage students to write the way they speak, in pursuit of an authentic voice, that most elusive of literary qualities?
In fact, I was missing the point. One of many lessons the students have taught me is to let the story dictate the voice of the essay. A few years ago, I worked with a boy who claimed to have nothing to write about. His life had been ordinary, he said; nothing had happened to him. I asked if he wanted to try writing about a family member, his favorite school subject, a summer job? He glanced at his phone, his posture and expression suggesting that he’d rather be anywhere but in front of a computer with me. “Hobbies?” I suggested, without much hope. He gave me a shy glance. “I like to box,” he said.
I’ve had this experience with reluctant writers again and again — when a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously. Of course the primary goal of a college essay is to help its author get an education that leads to a career. Changes in testing policies and financial aid have made applying to college more confusing than ever, but essays have remained basically the same. I would argue that they’re much more than an onerous task or rote exercise, and that unlike standardized tests they are infinitely variable and sometimes beautiful. College essays also provide an opportunity to learn precision, clarity and the process of working toward the truth through multiple revisions.
When a topic clicks with a student, an essay can unfurl spontaneously.
Even if writing doesn’t end up being fundamental to their future professions, students learn to choose language carefully and to be suspicious of the first words that come to mind. Especially now, as college students shoulder so much of the country’s ethical responsibility for war with their protest movement, essay writing teaches prospective students an increasingly urgent lesson: that choosing their own words over ready-made phrases is the only reliable way to ensure they’re thinking for themselves.
Teenagers are ideal writers for several reasons. They’re usually free of preconceptions about writing, and they tend not to use self-consciously ‘‘literary’’ language. They’re allergic to hypocrisy and are generally unfiltered: They overshare, ask personal questions and call you out for microaggressions as well as less egregious (but still mortifying) verbal errors, such as referring to weed as ‘‘pot.’’ Most important, they have yet to put down their best stories in a finished form.
I can imagine an essay taking a risk and distinguishing itself formally — a poem or a one-act play — but most kids use a more straightforward model: a hook followed by a narrative built around “small moments” that lead to a concluding lesson or aspiration for the future. I never get tired of working with students on these essays because each one is different, and the short, rigid form sometimes makes an emotional story even more powerful. Before I read Javier Zamora’s wrenching “Solito,” I worked with a student who had been transported by a coyote into the U.S. and was reunited with his mother in the parking lot of a big-box store. I don’t remember whether this essay focused on specific skills or coping mechanisms that he gained from his ordeal. I remember only the bliss of the parent-and-child reunion in that uninspiring setting. If I were making a case to an admissions officer, I would suggest that simply being able to convey that experience demonstrates the kind of resilience that any college should admire.
The essays that have stayed with me over the years don’t follow a pattern. There are some narratives on very predictable topics — living up to the expectations of immigrant parents, or suffering from depression in 2020 — that are moving because of the attention with which the student describes the experience. One girl determined to become an engineer while watching her father build furniture from scraps after work; a boy, grieving for his mother during lockdown, began taking pictures of the sky.
If, as Lorrie Moore said, “a short story is a love affair; a novel is a marriage,” what is a college essay? Every once in a while I sit down next to a student and start reading, and I have to suppress my excitement, because there on the Google Doc in front of me is a real writer’s voice. One of the first students I ever worked with wrote about falling in love with another girl in dance class, the absolute magic of watching her move and the terror in the conflict between her feelings and the instruction of her religious middle school. She made me think that college essays are less like love than limerence: one-sided, obsessive, idiosyncratic but profound, the first draft of the most personal story their writers will ever tell.
Nell Freudenberger’s novel “The Limits” was published by Knopf last month. She volunteers through the PEN America Writers in the Schools program.
The Federalist Papers
Appearing in New York newspapers as the New York Ratification Convention met in Poughkeepsie, John Jay, Alexander Hamilton and James Madison wrote as Publius and addressed the citizens of New York through the Federalist Papers. These essays subsequently circulated and were reprinted throughout the states as the Ratification process unfolded in other states. Initially appearing as individual items in several New York newspapers, all eighty-five essays were eventually combined and published as The Federalist . Click here to view a chronology of the Printing and Reprintings of The Federalist .
Considerable debate has surrounded these essays since their publication. Many suggest they represent the best exposition of the Constitution to date. Their conceptual design would affirm this view. Others contend that they were mere propaganda to allay fears of the opposition to the Constitution. Regardless, they are often included in the canon of the world’s great political writings. A complete introduction exploring the purpose, authorship, circulation, and reactions to The Federalist can be found here.
General Introduction
- No. 1 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 27 October 1787
Concerning Dangers from Foreign Force and Influence
- No. 2 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 31 October 1787
- No. 3 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 3 November 1787
- No. 4 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 7 November 1787
- No. 5 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 10 November 1787
Concerning Dangers from Dissensions Between the States
- No. 6 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 14 November 1787
- No. 7 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 17 November 1787
- No. 8 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 20 November 1787
- No. 9 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 21 November 1787
The Union as a Safeguard Against Domestic Faction and Insurrection
- No. 10 (Madison) New York Daily Advertiser , 22 November 1787
The Utility of the Union in Respect to Commercial Relations and a Navy
- No. 11 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 24 November 1787
The Utility of the Union in Respect to Revenue
- No. 12 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 27 November 1787
Advantage of the Union in Respect to Economy in Government
- No. 13 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 28 November 1787
Objections to the Proposed Constitution from Extent of Territory Answered
- No. 14 (Madison) New York Packet , 30 November 1787
The Insufficiency of the Present Confederation to Preserve the Union
- No. 15 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 1 December 1787
- No. 16 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 4 December 1787
- No. 17 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 5 December 1787
- No. 18 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Packet , 7 December 1787
- No. 19 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 8 December 1787
- No. 20 (Madison with Hamilton) New York Packet , 11 December 1787
- No. 21 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 12 December 1787
- No. 22 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 14 December 1787
The Necessity of Energetic Government to Preserve of the Union
- No. 23 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 18 December 1787
Powers Necessary to the Common Defense Further Considered
- No. 24 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 19 December 1787
- No. 25 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 21 December 1787
Restraining the Legislative Authority in Regard to the Common Defense
- No. 26 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 22 December 1787
- No. 27 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 25 December 1787
- No. 28 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 26 December 1787
Concerning the Militia
- No. 29 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 9 January 1788
Concerning the General Power of Taxation
- No. 30 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 28 December 1787
- No. 31 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 1 January 1788
- Nos. 32–33 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 2 January 1788
- No. 34 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 4 January 1788
- No. 35 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 5 January 1788
- No. 36 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 8 January 1788
The Difficulties of the Convention in Devising a Proper Form of Government
- No. 37 (Madison) New York Daily Advertiser , 11 January 1788
- No. 38 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 12 January 1788
The Conformity of the Plan to Republican Principles
- No. 39 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 16 January 1788
The Powers of the Convention to Form a Mixed Government Examined
- No. 40 (Madison) New York Packet , 18 January 1788
General View of the Powers Conferred by the Constitution
- No. 41 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 19 January 1788
- No. 42 (Madison) New York Packet , 22 January 1788
- No. 43 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 23 January 1788
Restrictions on the Authority of the Several States
- No. 44 (Madison) New York Packet , 25 January 1788
Alleged Danger from the Powers of the Union to the State Governments
- No. 45 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 26 January 1788
Influence of the State and Federal Governments Compared
- No. 46 (Madison) New York Packet , 29 January 1788
Structure of the New Government and the Distribution of Powers
- No. 47 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 30 January 1788
Departments Should Not Be So Far Separated
- No. 48 (Madison) New York Packet , 1 February 1788
Guarding Against the Encroachments of Any One Department of Government
- No. 49 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 2 February 1788
Periodic Appeals to the People Considered
- No. 50 (Madison) New York Packet , 5 February 1788
Structure of Government Must Furnish Proper Checks and Balances
- No. 51 (Madison) New York Independent Journal , 6 February 1788
The House of Representatives
- No. 52 (Madison?) New York Packet , 8 February 1788
- No. 53 (Madison or Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 9 February 1788
The Apportionment of Members Among the States
- No. 54 (Madison) New York Packet , 12 February 1788
The Total Number of the House of Representatives
- No. 55 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 13 February 1788
- No. 56 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 16 February 1788
The Alleged Tendency of the Plan to Elevate the Few at the Expense of the Many
- No. 57 (Madison?) New York Packet , 19 February 1788
Objection That the Numbers Will Not Be Augmented as Population Increases
- No. 58 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 20 February 1788
Concerning the Power of Congress to Regulate the Election of Members
- No. 59 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 22 February 1788
- No. 60 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 23 February 1788
- No. 61 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 26 February 1788
- No. 62 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 27 February 1788
- No. 63 (Madison?) New York Independent Journal , 1 March 1788
- No. 64 (Jay) New York Independent Journal , 5 March 1788
- No. 65 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 7 March 1788
Objections to the Power of the Senate to Set as a Court for Impeachments
- No. 66 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 8 March 1788
The Executive Department
- No. 67 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 11 March 1788
The Mode of Electing the President
- No. 68 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 12 March 1788
The Real Character of the Executive
- No. 69 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 14 March 1788
The Executive Department Further Considered
- No. 70 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 15 March 1788
The Duration in Office of the Executive
- No. 71 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 18 March 1788
Re-Eligibility of the Executive Considered
- No. 72 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 19 March 1788
Provision for The Support of the Executive, and the Veto Power
- No. 73 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 21 March 1788
The Command of the Military and Naval Forces, and the Pardoning Power
- No. 74 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 25 March 1788
The Treaty Making Power of the Executive
- No. 75 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 26 March 1788
The Appointing Power of the Executive
- No. 76 (Hamilton) New York Packet , 1 April 1788
Appointing Power and Other Powers of the Executive Considered
- No. 77 (Hamilton) New York Independent Journal , 2 April 1788
The Judiciary Department
- No. 78 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
- No. 79 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Powers of the Judiciary
- No. 80 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued, and the Distribution of the Judicial Authority
- No. 81 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued
- No. 82 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
The Judiciary Continued in Relation to Trial by Jury
- No. 83 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Miscellaneous Objections to the Constitution Considered
- No. 84 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Concluding Remarks
- No. 85 (Hamilton) Book Edition, Volume II, 28 May 1788
Jump to navigation
Forgotten Spaces: Ecocriticism Social Justice, and the U.S. South (Collection of Essays)
The U.S. South is often a forgotten space within ecocritical discussions, yet it provides fruitful ground for thinking about environmental issues. In 2019, in the first edited collection of essays on the topic, Zachary Vernon notes that focusing attention on this bioregion might help “provide a way out of the limitations of thinking too locally or too globally,” and it might inspire a group of stakeholders to come to the table as well (7). One problem with ecocritical approaches is the long history of representing the U.S. South as an “internal other in the national imagination: colonized, subordinate, primitive, developmentally arrested, or even regressive” (Watson 254). Another issue is that both the environmental humanities and Southern studies have frequently been white spaces. This proposed anthology convenes a conversation about the U.S. South and environmental issues with an eye towards social justice. We seek theoretically-sophisticated essays attentive to intersections between race, class, gender, and sexuality within the U.S. South to round out our proposed collection. Interdisciplinary environmental research from a variety of frameworks and disciplines is welcome, including literature, film, art, history, popular culture, public memory, sociology, political science, and geography.
Questions to consider:
- Why does the U.S. South seem like a forgotten space within ecocritical discussions?
- How do we reach across entrenched divides and academic silos to engage in cross-disciplinary engagement with ecocritical concerns about the South?
- What entanglements might we find between race, environment, gender, sexuality, class, and social justice?
- How have artists, writers, activists, and cultural workers of color engaged with representing the environment, and what might their creative labor contribute to wider discussions beyond the academy?
- How are rural and urban environments represented in the U.S. South? How are they represented from outside?
- What constitutes the commons in the South? Was there ever really a Southern commons?
- How are public parks, museums, and recreation areas curated in the South, and what might we learn about entanglements between race and the environment through attending to these spaces?
- What is the history of traveling southward or leaving the South? What kinds of cultural constructions represent the region as a place to return to or escape from?
- How might we interrogate Donna Haraway’s phrase “the plantationocene” to consider the vexed history of work, nature, and captivity in Southern spaces?
- How might we consider Settler colonialism, genocide, and Indian Removal within an ecocritical framework? How has a legacy of Settler colonialist violence in the South impacted the environment?
- Can indigenous practices, beliefs, and cultural production be mobilized towards a Southern ecocriticism?
- What are the many varieties of experience within different souths?
Other possible topics:
- Climate change and its impact on southern spaces. Southern climate diaspora.
- Hurricanes, floods, tornados. Natural disasters and social justice.
- Disaster capitalism and southern spaces.
- Sacrifice zones. Industrial pollution.
- Carceral, military, and/or institutional Southern spaces.
- Queer ecology and queer ecological souths.
- Global approaches to environment and the U.S. South.
- Animals and animality in southern cultural productions. Domestic/wild/wilding.
- Southern megacities and the built environment in the U.S. South.
- Race and nature in the South.
- White supremacy and public spaces.
We seek MLA-formatted essays from 4,000-7,000 words. Please submit abstracts of 250-500 words by July 15, 2024. Notification of acceptance will be made by Aug. 1, 2024. And final essays will be due October 15, 2024. We will be submitting the proposal, table of contents, and sample essays to academic presses by Aug. 1, 2024.
Send abstracts and questions to: Katie Simon, Georgia College and State University, [email protected] and Catherine Bowlin, Elon University, [email protected]
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Race and Ethnicity — Cultural Identity
Essays on Cultural Identity
What makes a good cultural identity essay topics.
When it comes to writing a cultural identity essay, choosing the right topic is crucial. A good essay topic should be thought-provoking, unique, and relevant to today's society. It should also allow for in-depth exploration and analysis. In this section, we will discuss What Makes a Good cultural identity essay topic and provide recommendations on how to brainstorm and choose an essay topic.
When brainstorming essay topics, it's important to consider your own interests and experiences. Reflect on your own cultural background and think about topics that resonate with you personally. Additionally, consider current events and societal issues that are relevant to cultural identity. This can help you choose a topic that is both timely and impactful.
Another important factor to consider when choosing a cultural identity essay topic is the level of complexity and depth it offers. A good essay topic should allow for meaningful exploration and analysis, rather than just surface-level discussion. Look for topics that are multi-dimensional and can be approached from various angles.
In addition, consider the potential impact of the topic. A good cultural identity essay topic should have significance and relevance beyond just the individual writer. It should be able to engage readers and provoke thoughtful discussion.
Overall, a good cultural identity essay topic should be personal, relevant, complex, and impactful. It should allow for in-depth exploration and analysis, and resonate with both the writer and the reader.
Best Cultural Identity Essay Topics
- The impact of globalization on cultural identity
- The role of language in shaping cultural identity
- Cultural appropriation in the fashion industry
- The influence of social media on cultural identity
- The interplay between religion and cultural identity
- The portrayal of cultural identity in literature and film
- The significance of traditional food in cultural identity
- The impact of immigration on cultural identity
- The evolution of cultural identity in the digital age
- The intersection of gender and cultural identity
- The role of education in shaping cultural identity
- The representation of cultural identity in art and music
- The impact of colonialism on cultural identity
- The influence of technology on cultural identity
- The role of family in shaping cultural identity
- The impact of cultural identity on mental health
- The relationship between cultural identity and national identity
- The significance of cultural festivals in shaping identity
- The impact of cultural identity on social justice movements
- The portrayal of cultural identity in the media
Cultural Identity essay topics Prompts
- Imagine a world where cultural identity is completely fluid and constantly changing. How would this impact society and individual experiences?
- Write about a time when you felt a strong connection to your cultural identity. What was the experience like, and how did it shape your sense of self?
- Consider the role of language in shaping cultural identity. How does language influence the way we perceive ourselves and others?
- Explore the concept of cultural hybridity and its impact on individual and collective identity.
- Reflect on the ways in which cultural identity can be both a source of pride and a source of conflict. How can individuals navigate these complexities in today's world?
Choosing a cultural identity essay topic is an important step in the writing process. By considering your own experiences, the complexity of the topic, and its potential impact, you can choose a topic that is both engaging and meaningful. With the recommendations and list of topics provided in this article, you are well-equipped to begin your exploration of cultural identity through writing.
Peru Culture Vs American Culture
The navajo creation story, made-to-order essay as fast as you need it.
Each essay is customized to cater to your unique preferences
+ experts online
Summary of "Mericans" by Sandra Cisneros
I am proud of my cultural identity, the importance of cultural identity and socialization in education, cultural identity and the importance of preserving culture, let us write you an essay from scratch.
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Cultural Identity of an Indonesian Immigrant
I am proud to be mexican, my cultural identity: who i am, cultural identity in city of clowns by daniel alarcón, get a personalized essay in under 3 hours.
Expert-written essays crafted with your exact needs in mind
The Impact of Globalization to Cultural Identity
A topic of cultural identity in gene yang’s american born chinese, the theme of sruggling with cultural identity: the inheritance of loss by karen desi, the connection of food and identity, unique culture of nicaragua, egypt, mexico, and united states: understanding cultural similarities and differences, analyzing cultural systems through a sociologist perspective, benefits of cross-culture awareness, understanding the significance of personal identity, the role of student life in the identity formation, a shared national identity of britain in the period 1830-1951, puerto rican identity in the united states, the culture of canada, the national and cultural identity in children's films toy story 3 and spirited away, experiencing different cultures: my personal experience, living in the czech republic, the role of cultural norm in formulating a person’s identity, african music as a part of social and cultural context, complexities of cultural identity in frozen river, relation of cultural industries and cultural heritage.
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct culture.
There are three pieces that make up a person's cultural identity, these are cultural knowledge, category label, and social connections.
1. Schwartz, S. J., Zamboanga, B. L., & Weisskirch, R. S. (2008). Broadening the study of the self: Integrating the study of personal identity and cultural identity. Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 2(2), 635-651. (https://compass.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/j.1751-9004.2008.00077.x) 2. Hall, S. (1989). Cultural identity and cinematic representation. Framework: The Journal of Cinema and Media, (36), 68-81. (https://www.jstor.org/stable/44111666) 3. Bhugra, D. (2004). Migration, distress and cultural identity. British medical bulletin, 69(1), 129-141. (https://academic.oup.com/bmb/article/69/1/129/523340) 4. Jo Hatch, M., & Schultz, M. (1997). Relations between organizational culture, identity and image. European Journal of marketing, 31(5/6), 356-365. (https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/eb060636/full/html) 5. Lucy, S. (2007). Ethnic and cultural identities. In Archaeology of Identity (pp. 96-119). Routledge. (https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780203087572-10/ethnic-cultural-identities-sam-lucy) 6. Karst, K. L. (1985). Paths to belonging: The constitution and cultural identity. NCL Rev., 64, 303. (https://heinonline.org/HOL/LandingPage?handle=hein.journals/nclr64&div=21&id=&page=) 7. Otcu, B. (2010). Heritage language maintenance and cultural identity formation: The case of a Turkish Saturday school in New York City. Heritage Language Journal, 7(2), 273-298. (https://brill.com/view/journals/hlj/7/2/article-p273_6.xml) 8. Schachter, E. P. (2005). Context and identity formation: A theoretical analysis and a case study. Journal of Adolescent Research, 20(3), 375-395. (https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/0743558405275172) 9. Hall, S., & Ghazoul, F. (2012). Cultural identity and diaspora. Alif: Journal of Comparative Poetics, (32), 257-258. (https://go.gale.com/ps/i.do?id=GALE%7CA302403835&sid=googleScholar&v=2.1&it=r&linkaccess=abs&issn=11108673&p=AONE&sw=w&userGroupName=anon%7E81809ec)
Relevant topics
- American Identity
- Mexican American
- Intercultural Communication
- Physical Appearance
- Indigenous People
- African American
- Media Analysis
- Effects of Social Media
- Sex, Gender and Sexuality
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Bibliography
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
What does John Green's book of essays say about the Indy 500? About the Indianapolis nod

Author John Green is no stranger to Indianapolis and the Indy 500, which is Sunday at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
Green has many works in his back pocket, including several with nods to Indianapolis. It seems fitting to revisit some of the mentions as we wait for drivers to start their engines.
The IndyStar has several guides to get fans ready for the Greatest Spectacle in Racing including a printable starting lineup , how to tune in to the race from outside the racetrack and what people can bring to the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
What to know about John Green and the Indy 500:
What does John Green's book of essays say about the Indy 500?
In " The Anthropocene Reviewed ," Green writes essays reviewing different topics from Halley's Comet to Diet Dr Pepper and even the Indianapolis 500, the IndyStar previously reported.
Need a break? Play the USA TODAY Daily Crossword Puzzle.
He wrote the Indy 500 review during the pandemic.
“I wanted to write about my experience of suddenly being unable to go to the race, and how it felt to go through all the same rituals that I always go through on that Sunday, and to bike to the race as I always do and to arrive at an empty Speedway, with the gates locked shut."
"It can be hard at times because we have to get used to a new normal to be able to reflect on how much has been lost in the last year and a half," he said. "And obviously the loss of fans at the speedway wasn't one of the big losses, but it was a loss. One loss among billions. For me, it was a way to feel that."
But people don't have to feel that loss again as they can attend the race on Sunday.
The book, which was released in 2021, is his first work of nonfiction and is inspired by his podcast of the same name where he also published monthly reviews.
'The Anthropocene Reviewed': John Green's new nonfiction book finds wonder in Diet Dr Pepper, Indianapolis 500
What John Green books mention Indianapolis?
"The Fault in Our Stars" and "Turtles All the Way Down" are both situated in Indianapolis.
In the latter, there are many references to the city, including:
- White River
- Pogue's Run
- Michigan Road mansion
- Applebee’s at 86th and Ditch
- IU Health North Hospital
- The Indianapolis Star
- The Indianapolis Prize
- Juan Solomon Park
Others are reading: John Green’s ‘Turtles’ at home in Indianapolis
Is John Green from Indianapolis?
Not originally.
In his webpage , Green states that he grew up in Orlando. He moved to Indianapolis in 2007 when his wife got a job at the Indianapolis Museum of Art, the IndyStar previously reported.
John Green on TikTok: Author still can't stop talking about how great Indianapolis is
How to watch 'Turtles All the Way Down'
The movie adaptation is now available streaming on Max .
When is the 2024 Indy 500?
This year's Indy 500 race is on Sunday at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway.
David Lindquist, Rachel Fradette and Ethan May contributed to this article.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Сultural Identity Essay Examples. First and foremost, a cultural identity essay is the one where you share your vision of the world and personality. Below is an example that you might consider when writing your next cultural identity essay. I was born in Italy to a German family. My mother comes from the capital of Germany - Berlin, while my ...
Identity is made up of many qualities: personality, culture, ethnic or racial background, sexual orientation, gender, physical ability, and linguistic background, among others. Maybe you identify really strongly with the religion on Mom's side of the family, but not Dad's. Maybe you speak a language not typical of folks from your culture.
2 pages / 1129 words. Introduction From the age of pre-school into adolescence and even adulthood an individual's identity along with their self-conception are ever-changing and advancing, alternating and developing. Founded of cognitive ability, a feeling of individuality greatly hinges on numerous life encounters.
At highly competitive schools, supplemental diversity essays require students to address how they will enhance the student body with a unique perspective, identity, or background. In the Common Application and applications for several other colleges, some main essay prompts ask about how your background, identity, or experience has affected you.
He argues that, the identity of a soul alone in an embryo of man is one and same that is the identity of it in a fully grown up man. Personal Identity & Self-Reflection. In the reflection, Ivan examined his past life and the values that he had lived by in all of his life. Ship of Theseus and Personal Identity.
Conclusion. In conclusion, self-analysis is a fundamental aspect of personal development. By reflecting on my personal background and experiences, strengths and weaknesses, ... The Impact of the Five Core Social Motives on Social Change Identity Essay. As human beings, our social behavior and interactions are often guided by a set of ...
That's all you need for your essay — short introductory and concluding paragraphs and three concise body paragraphs. Step 2. Select your main idea and supporting points. You need to come up with a central idea that will give you a frame of reference for the rest of your essay.
Step 1: Return to your thesis. To begin your conclusion, signal that the essay is coming to an end by returning to your overall argument. Don't just repeat your thesis statement —instead, try to rephrase your argument in a way that shows how it has been developed since the introduction. Example: Returning to the thesis.
Identity is an essential and complex characteristic of human beings - it describes who we are as individuals. There are multiple essay topics about identity being considered: cultural (including national, linguistic), intellectual, emotional, etc. Identity is defined by worldviews, beliefs, understandings, character or intellectual traits, manners, habits, preferences and dislikes,...
Just as a body is a highly complex, organised network of organismic and molecular systems, the self is a highly organised network. Traits of the self can organise into clusters or hubs, such as a body cluster, a family cluster, a social cluster. There might be other clusters, but keeping it to a few is sufficient to illustrate the idea.
When exploring your future in an essay, be sure to explore who you are as a person and why your future goals make sense based on your character traits and passions. This self-reflection will make for a powerful essay. 3. Who I Want to Be. Not all who I am essays need to be about who you currently are.
Essay 1: Sharing an identity or background through a montage. Essay 2: Overcoming a challenge, a sports injury narrative. Essay 3: Showing the influence of an important person or thing. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about college application essays.
Highlight the "so what". At the beginning of your paper, you explain to your readers what's at stake—why they should care about the argument you're making. In your conclusion, you can bring readers back to those stakes by reminding them why your argument is important in the first place. You can also draft a few sentences that put ...
The intricate relationship between language and racial or ethnic identity is undeniable. An individual's history shapes their language, leading to those with similar racial backgrounds often using similar languages for communication. One's mother tongue, acquired at birth, is a fundamental aspect of racial identity, providing a crucial ...
Cooking rice is more accessible than cultivating it - you can quickly cook rice by boiling it in water. This reflects people rich in culture and tradition but who lives simpler life. 8. Identity And Culture: My Identity, Culture, And Identity by April Casas. "Every single one has their own unique identity and culture.
Finally, some advice on how not to end an essay: Don't simply summarize your essay. A brief summary of your argument may be useful, especially if your essay is long--more than ten pages or so. But shorter essays tend not to require a restatement of your main ideas. Avoid phrases like "in conclusion," "to conclude," "in summary," and "to sum up ...
Hello! Writing an essay that focuses on your personal identity can be a powerful way to showcase your unique experiences, interests, and perspectives. To make this type of essay engaging and interesting to colleges, consider the following tips: 1. Be authentic and vulnerable: Share your true feelings, thoughts, and struggles as they pertain to your identity.
Essay Sample, Example. Identity, in itself, is difficult to define—let alone ourselves as a persona. It seems that identity is what we and others say we are. In this case, identity is flexible and fluid. It can change at a moment's notice, as who we are is a story we and others tell ourselves. Identity is not a solid, carved-into-stone ...
The word 'identity' suggests immutability, self-sameness, and permanency, while in fact it does what other words also do: it changes its meaning, now so rapidly that it is hard to keep track. 'Conclusion: the identity of identity' concludes that, on the individual level, identities have become a matter of negotiating and, as the need to ...
Personal identity is a complex topic because many things can influence who you are and what makes you different from anyone else. In conclusion I believe that my soul, my ability to make memories, my consciousness, and the different stages in my life makeup my personal identity. This essay was reviewed by. Dr. Oliver Johnson.
Essay Conclusion Examples. Below is a range of copy-and-paste essay conclusions with gaps for you to fill-in your topic and key arguments. Browse through for one you like (there are 17 for argumentative, expository, compare and contrast, and critical essays). Once you've found one you like, copy it and add-in the key points to make it your own.
Hitler's racial identity, then, is a reminder of the dangers of conflating cultural and political ideologies with scientific facts. In conclusion, Adolf Hitler's racial identity is a complex subject that intertwines his personal beliefs, the pseudoscientific theories of his time, and the modern understanding of genetics.
A new analysis of selective colleges' applications found that many added essay prompts centered around identity and diversity after the Supreme Court's affirmative action decision. When the U.S. Supreme Court struck down affirmative action in two lawsuits against Harvard University and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill last ...
May 14, 2024. Most high school seniors approach the college essay with dread. Either their upbringing hasn't supplied them with several hundred words of adversity, or worse, they're afraid ...
Prompt 2: Overcoming challenges. Prompt 3: Questioning a belief or idea. Prompt 4: Appreciating an influential person. Prompt 5: Transformative event. Prompt 6: Interest or hobby that inspires learning. Prompt 7: Free topic. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about college application essays.
The Federalist Papers. Appearing in New York newspapers as the New York Ratification Convention met in Poughkeepsie, John Jay, Alexander Hamilton and James Madison wrote as Publius and addressed the citizens of New York through the Federalist Papers. These essays subsequently circulated and were reprinted throughout the states as the ...
We seek MLA-formatted essays from 4,000-7,000 words. Please submit abstracts of 250-500 words by July 15, 2024. Notification of acceptance will be made by Aug. 1, 2024. And final essays will be due October 15, 2024. We will be submitting the proposal, table of contents, and sample essays to academic presses by Aug. 1, 2024.
In addition, consider the potential impact of the topic. A good cultural identity essay topic should have significance and relevance beyond just the individual writer. It should be able to engage readers and provoke thoughtful discussion. Overall, a good cultural identity essay topic should be personal, relevant, complex, and impactful.
In 2023, Antigona, by José Watanabe: A bilingual edition with critical essays, was awarded the Translation Prize of the American Society for Theater Research, and Dr. Perez Diaz also won the 2024 Bolchazy Pedagogy Book Award, awarded by CAMWS. We are so proud of you, Dr. Pérez Díaz!
Play the USA TODAY Daily Crossword Puzzle. He wrote the Indy 500 review during the pandemic. "I wanted to write about my experience of suddenly being unable to go to the race, and how it felt to ...