How to Write Limitations of the Study (with examples)
This blog emphasizes the importance of recognizing and effectively writing about limitations in research. It discusses the types of limitations, their significance, and provides guidelines for writing about them, highlighting their role in advancing scholarly research.
Updated on August 24, 2023

No matter how well thought out, every research endeavor encounters challenges. There is simply no way to predict all possible variances throughout the process.
These uncharted boundaries and abrupt constraints are known as limitations in research . Identifying and acknowledging limitations is crucial for conducting rigorous studies. Limitations provide context and shed light on gaps in the prevailing inquiry and literature.
This article explores the importance of recognizing limitations and discusses how to write them effectively. By interpreting limitations in research and considering prevalent examples, we aim to reframe the perception from shameful mistakes to respectable revelations.

What are limitations in research?
In the clearest terms, research limitations are the practical or theoretical shortcomings of a study that are often outside of the researcher’s control . While these weaknesses limit the generalizability of a study’s conclusions, they also present a foundation for future research.
Sometimes limitations arise from tangible circumstances like time and funding constraints, or equipment and participant availability. Other times the rationale is more obscure and buried within the research design. Common types of limitations and their ramifications include:
- Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study.
- Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data.
- Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data.
- Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of the findings.
- Ethical: limits the access, consent, or confidentiality of the data.
Regardless of how, when, or why they arise, limitations are a natural part of the research process and should never be ignored . Like all other aspects, they are vital in their own purpose.
Why is identifying limitations important?
Whether to seek acceptance or avoid struggle, humans often instinctively hide flaws and mistakes. Merging this thought process into research by attempting to hide limitations, however, is a bad idea. It has the potential to negate the validity of outcomes and damage the reputation of scholars.
By identifying and addressing limitations throughout a project, researchers strengthen their arguments and curtail the chance of peer censure based on overlooked mistakes. Pointing out these flaws shows an understanding of variable limits and a scrupulous research process.
Showing awareness of and taking responsibility for a project’s boundaries and challenges validates the integrity and transparency of a researcher. It further demonstrates the researchers understand the applicable literature and have thoroughly evaluated their chosen research methods.
Presenting limitations also benefits the readers by providing context for research findings. It guides them to interpret the project’s conclusions only within the scope of very specific conditions. By allowing for an appropriate generalization of the findings that is accurately confined by research boundaries and is not too broad, limitations boost a study’s credibility .
Limitations are true assets to the research process. They highlight opportunities for future research. When researchers identify the limitations of their particular approach to a study question, they enable precise transferability and improve chances for reproducibility.
Simply stating a project’s limitations is not adequate for spurring further research, though. To spark the interest of other researchers, these acknowledgements must come with thorough explanations regarding how the limitations affected the current study and how they can potentially be overcome with amended methods.
How to write limitations
Typically, the information about a study’s limitations is situated either at the beginning of the discussion section to provide context for readers or at the conclusion of the discussion section to acknowledge the need for further research. However, it varies depending upon the target journal or publication guidelines.
Don’t hide your limitations
It is also important to not bury a limitation in the body of the paper unless it has a unique connection to a topic in that section. If so, it needs to be reiterated with the other limitations or at the conclusion of the discussion section. Wherever it is included in the manuscript, ensure that the limitations section is prominently positioned and clearly introduced.
While maintaining transparency by disclosing limitations means taking a comprehensive approach, it is not necessary to discuss everything that could have potentially gone wrong during the research study. If there is no commitment to investigation in the introduction, it is unnecessary to consider the issue a limitation to the research. Wholly consider the term ‘limitations’ and ask, “Did it significantly change or limit the possible outcomes?” Then, qualify the occurrence as either a limitation to include in the current manuscript or as an idea to note for other projects.
Writing limitations
Once the limitations are concretely identified and it is decided where they will be included in the paper, researchers are ready for the writing task. Including only what is pertinent, keeping explanations detailed but concise, and employing the following guidelines is key for crafting valuable limitations:
1) Identify and describe the limitations : Clearly introduce the limitation by classifying its form and specifying its origin. For example:
- An unintentional bias encountered during data collection
- An intentional use of unplanned post-hoc data analysis
2) Explain the implications : Describe how the limitation potentially influences the study’s findings and how the validity and generalizability are subsequently impacted. Provide examples and evidence to support claims of the limitations’ effects without making excuses or exaggerating their impact. Overall, be transparent and objective in presenting the limitations, without undermining the significance of the research.
3) Provide alternative approaches for future studies : Offer specific suggestions for potential improvements or avenues for further investigation. Demonstrate a proactive approach by encouraging future research that addresses the identified gaps and, therefore, expands the knowledge base.
Whether presenting limitations as an individual section within the manuscript or as a subtopic in the discussion area, authors should use clear headings and straightforward language to facilitate readability. There is no need to complicate limitations with jargon, computations, or complex datasets.
Examples of common limitations
Limitations are generally grouped into two categories , methodology and research process .
Methodology limitations
Methodology may include limitations due to:
- Sample size
- Lack of available or reliable data
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic
- Measure used to collect the data
- Self-reported data

The researcher is addressing how the large sample size requires a reassessment of the measures used to collect and analyze the data.
Research process limitations
Limitations during the research process may arise from:
- Access to information
- Longitudinal effects
- Cultural and other biases
- Language fluency
- Time constraints

The author is pointing out that the model’s estimates are based on potentially biased observational studies.
Final thoughts
Successfully proving theories and touting great achievements are only two very narrow goals of scholarly research. The true passion and greatest efforts of researchers comes more in the form of confronting assumptions and exploring the obscure.
In many ways, recognizing and sharing the limitations of a research study both allows for and encourages this type of discovery that continuously pushes research forward. By using limitations to provide a transparent account of the project's boundaries and to contextualize the findings, researchers pave the way for even more robust and impactful research in the future.
Charla Viera, MS
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Limitations in Research – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Limitations in Research
Limitations in research refer to the factors that may affect the results, conclusions , and generalizability of a study. These limitations can arise from various sources, such as the design of the study, the sampling methods used, the measurement tools employed, and the limitations of the data analysis techniques.
Types of Limitations in Research
Types of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Sample Size Limitations
This refers to the size of the group of people or subjects that are being studied. If the sample size is too small, then the results may not be representative of the population being studied. This can lead to a lack of generalizability of the results.
Time Limitations
Time limitations can be a constraint on the research process . This could mean that the study is unable to be conducted for a long enough period of time to observe the long-term effects of an intervention, or to collect enough data to draw accurate conclusions.
Selection Bias
This refers to a type of bias that can occur when the selection of participants in a study is not random. This can lead to a biased sample that is not representative of the population being studied.
Confounding Variables
Confounding variables are factors that can influence the outcome of a study, but are not being measured or controlled for. These can lead to inaccurate conclusions or a lack of clarity in the results.
Measurement Error
This refers to inaccuracies in the measurement of variables, such as using a faulty instrument or scale. This can lead to inaccurate results or a lack of validity in the study.
Ethical Limitations
Ethical limitations refer to the ethical constraints placed on research studies. For example, certain studies may not be allowed to be conducted due to ethical concerns, such as studies that involve harm to participants.
Examples of Limitations in Research
Some Examples of Limitations in Research are as follows:
Research Title: “The Effectiveness of Machine Learning Algorithms in Predicting Customer Behavior”
Limitations:
- The study only considered a limited number of machine learning algorithms and did not explore the effectiveness of other algorithms.
- The study used a specific dataset, which may not be representative of all customer behaviors or demographics.
- The study did not consider the potential ethical implications of using machine learning algorithms in predicting customer behavior.
Research Title: “The Impact of Online Learning on Student Performance in Computer Science Courses”
- The study was conducted during the COVID-19 pandemic, which may have affected the results due to the unique circumstances of remote learning.
- The study only included students from a single university, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other institutions.
- The study did not consider the impact of individual differences, such as prior knowledge or motivation, on student performance in online learning environments.
Research Title: “The Effect of Gamification on User Engagement in Mobile Health Applications”
- The study only tested a specific gamification strategy and did not explore the effectiveness of other gamification techniques.
- The study relied on self-reported measures of user engagement, which may be subject to social desirability bias or measurement errors.
- The study only included a specific demographic group (e.g., young adults) and may not be generalizable to other populations with different preferences or needs.
How to Write Limitations in Research
When writing about the limitations of a research study, it is important to be honest and clear about the potential weaknesses of your work. Here are some tips for writing about limitations in research:
- Identify the limitations: Start by identifying the potential limitations of your research. These may include sample size, selection bias, measurement error, or other issues that could affect the validity and reliability of your findings.
- Be honest and objective: When describing the limitations of your research, be honest and objective. Do not try to minimize or downplay the limitations, but also do not exaggerate them. Be clear and concise in your description of the limitations.
- Provide context: It is important to provide context for the limitations of your research. For example, if your sample size was small, explain why this was the case and how it may have affected your results. Providing context can help readers understand the limitations in a broader context.
- Discuss implications : Discuss the implications of the limitations for your research findings. For example, if there was a selection bias in your sample, explain how this may have affected the generalizability of your findings. This can help readers understand the limitations in terms of their impact on the overall validity of your research.
- Provide suggestions for future research : Finally, provide suggestions for future research that can address the limitations of your study. This can help readers understand how your research fits into the broader field and can provide a roadmap for future studies.
Purpose of Limitations in Research
There are several purposes of limitations in research. Here are some of the most important ones:
- To acknowledge the boundaries of the study : Limitations help to define the scope of the research project and set realistic expectations for the findings. They can help to clarify what the study is not intended to address.
- To identify potential sources of bias: Limitations can help researchers identify potential sources of bias in their research design, data collection, or analysis. This can help to improve the validity and reliability of the findings.
- To provide opportunities for future research: Limitations can highlight areas for future research and suggest avenues for further exploration. This can help to advance knowledge in a particular field.
- To demonstrate transparency and accountability: By acknowledging the limitations of their research, researchers can demonstrate transparency and accountability to their readers, peers, and funders. This can help to build trust and credibility in the research community.
- To encourage critical thinking: Limitations can encourage readers to critically evaluate the study’s findings and consider alternative explanations or interpretations. This can help to promote a more nuanced and sophisticated understanding of the topic under investigation.
When to Write Limitations in Research
Limitations should be included in research when they help to provide a more complete understanding of the study’s results and implications. A limitation is any factor that could potentially impact the accuracy, reliability, or generalizability of the study’s findings.
It is important to identify and discuss limitations in research because doing so helps to ensure that the results are interpreted appropriately and that any conclusions drawn are supported by the available evidence. Limitations can also suggest areas for future research, highlight potential biases or confounding factors that may have affected the results, and provide context for the study’s findings.
Generally, limitations should be discussed in the conclusion section of a research paper or thesis, although they may also be mentioned in other sections, such as the introduction or methods. The specific limitations that are discussed will depend on the nature of the study, the research question being investigated, and the data that was collected.
Examples of limitations that might be discussed in research include sample size limitations, data collection methods, the validity and reliability of measures used, and potential biases or confounding factors that could have affected the results. It is important to note that limitations should not be used as a justification for poor research design or methodology, but rather as a way to enhance the understanding and interpretation of the study’s findings.
Importance of Limitations in Research
Here are some reasons why limitations are important in research:
- Enhances the credibility of research: Limitations highlight the potential weaknesses and threats to validity, which helps readers to understand the scope and boundaries of the study. This improves the credibility of research by acknowledging its limitations and providing a clear picture of what can and cannot be concluded from the study.
- Facilitates replication: By highlighting the limitations, researchers can provide detailed information about the study’s methodology, data collection, and analysis. This information helps other researchers to replicate the study and test the validity of the findings, which enhances the reliability of research.
- Guides future research : Limitations provide insights into areas for future research by identifying gaps or areas that require further investigation. This can help researchers to design more comprehensive and effective studies that build on existing knowledge.
- Provides a balanced view: Limitations help to provide a balanced view of the research by highlighting both strengths and weaknesses. This ensures that readers have a clear understanding of the study’s limitations and can make informed decisions about the generalizability and applicability of the findings.
Advantages of Limitations in Research
Here are some potential advantages of limitations in research:
- Focus : Limitations can help researchers focus their study on a specific area or population, which can make the research more relevant and useful.
- Realism : Limitations can make a study more realistic by reflecting the practical constraints and challenges of conducting research in the real world.
- Innovation : Limitations can spur researchers to be more innovative and creative in their research design and methodology, as they search for ways to work around the limitations.
- Rigor : Limitations can actually increase the rigor and credibility of a study, as researchers are forced to carefully consider the potential sources of bias and error, and address them to the best of their abilities.
- Generalizability : Limitations can actually improve the generalizability of a study by ensuring that it is not overly focused on a specific sample or situation, and that the results can be applied more broadly.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Limitations of the Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the interpretation of the findings from your research. Study limitations are the constraints placed on the ability to generalize from the results, to further describe applications to practice, and/or related to the utility of findings that are the result of the ways in which you initially chose to design the study or the method used to establish internal and external validity or the result of unanticipated challenges that emerged during the study.
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Theofanidis, Dimitrios and Antigoni Fountouki. "Limitations and Delimitations in the Research Process." Perioperative Nursing 7 (September-December 2018): 155-163. .
Importance of...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better that you identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and have your grade lowered because you appeared to have ignored them or didn't realize they existed.
Keep in mind that acknowledgment of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research. If you do connect your study's limitations to suggestions for further research, be sure to explain the ways in which these unanswered questions may become more focused because of your study.
Acknowledgment of a study's limitations also provides you with opportunities to demonstrate that you have thought critically about the research problem, understood the relevant literature published about it, and correctly assessed the methods chosen for studying the problem. A key objective of the research process is not only discovering new knowledge but also to confront assumptions and explore what we don't know.
Claiming limitations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations . Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the results and conclusions. Limitations require a critical, overall appraisal and interpretation of their impact. You should answer the question: do these problems with errors, methods, validity, etc. eventually matter and, if so, to what extent?
Price, James H. and Judy Murnan. “Research Limitations and the Necessity of Reporting Them.” American Journal of Health Education 35 (2004): 66-67; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com.
Descriptions of Possible Limitations
All studies have limitations . However, it is important that you restrict your discussion to limitations related to the research problem under investigation. For example, if a meta-analysis of existing literature is not a stated purpose of your research, it should not be discussed as a limitation. Do not apologize for not addressing issues that you did not promise to investigate in the introduction of your paper.
Here are examples of limitations related to methodology and the research process you may need to describe and discuss how they possibly impacted your results. Note that descriptions of limitations should be stated in the past tense because they were discovered after you completed your research.
Possible Methodological Limitations
- Sample size -- the number of the units of analysis you use in your study is dictated by the type of research problem you are investigating. Note that, if your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to find significant relationships from the data, as statistical tests normally require a larger sample size to ensure a representative distribution of the population and to be considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred. Note that sample size is generally less relevant in qualitative research if explained in the context of the research problem.
- Lack of available and/or reliable data -- a lack of data or of reliable data will likely require you to limit the scope of your analysis, the size of your sample, or it can be a significant obstacle in finding a trend and a meaningful relationship. You need to not only describe these limitations but provide cogent reasons why you believe data is missing or is unreliable. However, don’t just throw up your hands in frustration; use this as an opportunity to describe a need for future research based on designing a different method for gathering data.
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic -- citing prior research studies forms the basis of your literature review and helps lay a foundation for understanding the research problem you are investigating. Depending on the currency or scope of your research topic, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic. Before assuming this to be true, though, consult with a librarian! In cases when a librarian has confirmed that there is little or no prior research, you may be required to develop an entirely new research typology [for example, using an exploratory rather than an explanatory research design ]. Note again that discovering a limitation can serve as an important opportunity to identify new gaps in the literature and to describe the need for further research.
- Measure used to collect the data -- sometimes it is the case that, after completing your interpretation of the findings, you discover that the way in which you gathered data inhibited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results. For example, you regret not including a specific question in a survey that, in retrospect, could have helped address a particular issue that emerged later in the study. Acknowledge the deficiency by stating a need for future researchers to revise the specific method for gathering data.
- Self-reported data -- whether you are relying on pre-existing data or you are conducting a qualitative research study and gathering the data yourself, self-reported data is limited by the fact that it rarely can be independently verified. In other words, you have to the accuracy of what people say, whether in interviews, focus groups, or on questionnaires, at face value. However, self-reported data can contain several potential sources of bias that you should be alert to and note as limitations. These biases become apparent if they are incongruent with data from other sources. These are: (1) selective memory [remembering or not remembering experiences or events that occurred at some point in the past]; (2) telescoping [recalling events that occurred at one time as if they occurred at another time]; (3) attribution [the act of attributing positive events and outcomes to one's own agency, but attributing negative events and outcomes to external forces]; and, (4) exaggeration [the act of representing outcomes or embellishing events as more significant than is actually suggested from other data].
Possible Limitations of the Researcher
- Access -- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, data, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or limited in some way, the reasons for this needs to be described. Also, include an explanation why being denied or limited access did not prevent you from following through on your study.
- Longitudinal effects -- unlike your professor, who can literally devote years [even a lifetime] to studying a single topic, the time available to investigate a research problem and to measure change or stability over time is constrained by the due date of your assignment. Be sure to choose a research problem that does not require an excessive amount of time to complete the literature review, apply the methodology, and gather and interpret the results. If you're unsure whether you can complete your research within the confines of the assignment's due date, talk to your professor.
- Cultural and other type of bias -- we all have biases, whether we are conscience of them or not. Bias is when a person, place, event, or thing is viewed or shown in a consistently inaccurate way. Bias is usually negative, though one can have a positive bias as well, especially if that bias reflects your reliance on research that only support your hypothesis. When proof-reading your paper, be especially critical in reviewing how you have stated a problem, selected the data to be studied, what may have been omitted, the manner in which you have ordered events, people, or places, how you have chosen to represent a person, place, or thing, to name a phenomenon, or to use possible words with a positive or negative connotation. NOTE : If you detect bias in prior research, it must be acknowledged and you should explain what measures were taken to avoid perpetuating that bias. For example, if a previous study only used boys to examine how music education supports effective math skills, describe how your research expands the study to include girls.
- Fluency in a language -- if your research focuses , for example, on measuring the perceived value of after-school tutoring among Mexican-American ESL [English as a Second Language] students and you are not fluent in Spanish, you are limited in being able to read and interpret Spanish language research studies on the topic or to speak with these students in their primary language. This deficiency should be acknowledged.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Senunyeme, Emmanuel K. Business Research Methods. Powerpoint Presentation. Regent University of Science and Technology; ter Riet, Gerben et al. “All That Glitters Isn't Gold: A Survey on Acknowledgment of Limitations in Biomedical Studies.” PLOS One 8 (November 2013): 1-6.
Structure and Writing Style
Information about the limitations of your study are generally placed either at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so the reader knows and understands the limitations before reading the rest of your analysis of the findings, or, the limitations are outlined at the conclusion of the discussion section as an acknowledgement of the need for further study. Statements about a study's limitations should not be buried in the body [middle] of the discussion section unless a limitation is specific to something covered in that part of the paper. If this is the case, though, the limitation should be reiterated at the conclusion of the section.
If you determine that your study is seriously flawed due to important limitations , such as, an inability to acquire critical data, consider reframing it as an exploratory study intended to lay the groundwork for a more complete research study in the future. Be sure, though, to specifically explain the ways that these flaws can be successfully overcome in a new study.
But, do not use this as an excuse for not developing a thorough research paper! Review the tab in this guide for developing a research topic . If serious limitations exist, it generally indicates a likelihood that your research problem is too narrowly defined or that the issue or event under study is too recent and, thus, very little research has been written about it. If serious limitations do emerge, consult with your professor about possible ways to overcome them or how to revise your study.
When discussing the limitations of your research, be sure to:
- Describe each limitation in detailed but concise terms;
- Explain why each limitation exists;
- Provide the reasons why each limitation could not be overcome using the method(s) chosen to acquire or gather the data [cite to other studies that had similar problems when possible];
- Assess the impact of each limitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of your study; and,
- If appropriate, describe how these limitations could point to the need for further research.
Remember that the method you chose may be the source of a significant limitation that has emerged during your interpretation of the results [for example, you didn't interview a group of people that you later wish you had]. If this is the case, don't panic. Acknowledge it, and explain how applying a different or more robust methodology might address the research problem more effectively in a future study. A underlying goal of scholarly research is not only to show what works, but to demonstrate what doesn't work or what needs further clarification.
Aguinis, Hermam and Jeffrey R. Edwards. “Methodological Wishes for the Next Decade and How to Make Wishes Come True.” Journal of Management Studies 51 (January 2014): 143-174; Brutus, Stéphane et al. "Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations." Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. "Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature." Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh. Writing the Empirical Social Science Research Paper: A Guide for the Perplexed. January 24, 2012. Academia.edu; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation. Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Writing Tip
Don't Inflate the Importance of Your Findings!
After all the hard work and long hours devoted to writing your research paper, it is easy to get carried away with attributing unwarranted importance to what you’ve done. We all want our academic work to be viewed as excellent and worthy of a good grade, but it is important that you understand and openly acknowledge the limitations of your study. Inflating the importance of your study's findings could be perceived by your readers as an attempt hide its flaws or encourage a biased interpretation of the results. A small measure of humility goes a long way!
Another Writing Tip
Negative Results are Not a Limitation!
Negative evidence refers to findings that unexpectedly challenge rather than support your hypothesis. If you didn't get the results you anticipated, it may mean your hypothesis was incorrect and needs to be reformulated. Or, perhaps you have stumbled onto something unexpected that warrants further study. Moreover, the absence of an effect may be very telling in many situations, particularly in experimental research designs. In any case, your results may very well be of importance to others even though they did not support your hypothesis. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that results contrary to what you expected is a limitation to your study. If you carried out the research well, they are simply your results and only require additional interpretation.
Lewis, George H. and Jonathan F. Lewis. “The Dog in the Night-Time: Negative Evidence in Social Research.” The British Journal of Sociology 31 (December 1980): 544-558.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Sample Size Limitations in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes are typically smaller in qualitative research because, as the study goes on, acquiring more data does not necessarily lead to more information. This is because one occurrence of a piece of data, or a code, is all that is necessary to ensure that it becomes part of the analysis framework. However, it remains true that sample sizes that are too small cannot adequately support claims of having achieved valid conclusions and sample sizes that are too large do not permit the deep, naturalistic, and inductive analysis that defines qualitative inquiry. Determining adequate sample size in qualitative research is ultimately a matter of judgment and experience in evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be applied and the particular research method and purposeful sampling strategy employed. If the sample size is found to be a limitation, it may reflect your judgment about the methodological technique chosen [e.g., single life history study versus focus group interviews] rather than the number of respondents used.
Boddy, Clive Roland. "Sample Size for Qualitative Research." Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal 19 (2016): 426-432; Huberman, A. Michael and Matthew B. Miles. "Data Management and Analysis Methods." In Handbook of Qualitative Research . Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 428-444; Blaikie, Norman. "Confounding Issues Related to Determining Sample Size in Qualitative Research." International Journal of Social Research Methodology 21 (2018): 635-641; Oppong, Steward Harrison. "The Problem of Sampling in qualitative Research." Asian Journal of Management Sciences and Education 2 (2013): 202-210.
- << Previous: 8. The Discussion
- Next: 9. The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: May 18, 2024 11:38 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How to present limitations in research
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Limitations don’t invalidate or diminish your results, but it’s best to acknowledge them. This will enable you to address any questions your study failed to answer because of them.
In this guide, learn how to recognize, present, and overcome limitations in research.
- What is a research limitation?
Research limitations are weaknesses in your research design or execution that may have impacted outcomes and conclusions. Uncovering limitations doesn’t necessarily indicate poor research design—it just means you encountered challenges you couldn’t have anticipated that limited your research efforts.
Does basic research have limitations?
Basic research aims to provide more information about your research topic. It requires the same standard research methodology and data collection efforts as any other research type, and it can also have limitations.
- Common research limitations
Researchers encounter common limitations when embarking on a study. Limitations can occur in relation to the methods you apply or the research process you design. They could also be connected to you as the researcher.
Methodology limitations
Not having access to data or reliable information can impact the methods used to facilitate your research. A lack of data or reliability may limit the parameters of your study area and the extent of your exploration.
Your sample size may also be affected because you won’t have any direction on how big or small it should be and who or what you should include. Having too few participants won’t adequately represent the population or groups of people needed to draw meaningful conclusions.
Research process limitations
The study’s design can impose constraints on the process. For example, as you’re conducting the research, issues may arise that don’t conform to the data collection methodology you developed. You may not realize until well into the process that you should have incorporated more specific questions or comprehensive experiments to generate the data you need to have confidence in your results.
Constraints on resources can also have an impact. Being limited on participants or participation incentives may limit your sample sizes. Insufficient tools, equipment, and materials to conduct a thorough study may also be a factor.
Common researcher limitations
Here are some of the common researcher limitations you may encounter:
Time: some research areas require multi-year longitudinal approaches, but you might not be able to dedicate that much time. Imagine you want to measure how much memory a person loses as they age. This may involve conducting multiple tests on a sample of participants over 20–30 years, which may be impossible.
Bias: researchers can consciously or unconsciously apply bias to their research. Biases can contribute to relying on research sources and methodologies that will only support your beliefs about the research you’re embarking on. You might also omit relevant issues or participants from the scope of your study because of your biases.
Limited access to data : you may need to pay to access specific databases or journals that would be helpful to your research process. You might also need to gain information from certain people or organizations but have limited access to them. These cases require readjusting your process and explaining why your findings are still reliable.
- Why is it important to identify limitations?
Identifying limitations adds credibility to research and provides a deeper understanding of how you arrived at your conclusions.
Constraints may have prevented you from collecting specific data or information you hoped would prove or disprove your hypothesis or provide a more comprehensive understanding of your research topic.
However, identifying the limitations contributing to your conclusions can inspire further research efforts that help gather more substantial information and data.
- Where to put limitations in a research paper
A research paper is broken up into different sections that appear in the following order:
Introduction
Methodology
The discussion portion of your paper explores your findings and puts them in the context of the overall research. Either place research limitations at the beginning of the discussion section before the analysis of your findings or at the end of the section to indicate that further research needs to be pursued.
What not to include in the limitations section
Evidence that doesn’t support your hypothesis is not a limitation, so you shouldn’t include it in the limitation section. Don’t just list limitations and their degree of severity without further explanation.
- How to present limitations
You’ll want to present the limitations of your study in a way that doesn’t diminish the validity of your research and leave the reader wondering if your results and conclusions have been compromised.
Include only the limitations that directly relate to and impact how you addressed your research questions. Following a specific format enables the reader to develop an understanding of the weaknesses within the context of your findings without doubting the quality and integrity of your research.
Identify the limitations specific to your study
You don’t have to identify every possible limitation that might have occurred during your research process. Only identify those that may have influenced the quality of your findings and your ability to answer your research question.
Explain study limitations in detail
This explanation should be the most significant portion of your limitation section.
Link each limitation with an interpretation and appraisal of their impact on the study. You’ll have to evaluate and explain whether the error, method, or validity issues influenced the study’s outcome and how.
Propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives
In this section, suggest how researchers can avoid the pitfalls you experienced during your research process.
If an issue with methodology was a limitation, propose alternate methods that may help with a smoother and more conclusive research project. Discuss the pros and cons of your alternate recommendation.
Describe steps taken to minimize each limitation
You probably took steps to try to address or mitigate limitations when you noticed them throughout the course of your research project. Describe these steps in the limitation section.
- Limitation example
“Approaches like stem cell transplantation and vaccination in AD [Alzheimer’s disease] work on a cellular or molecular level in the laboratory. However, translation into clinical settings will remain a challenge for the next decade.”
The authors are saying that even though these methods showed promise in helping people with memory loss when conducted in the lab (in other words, using animal studies), more studies are needed. These may be controlled clinical trials, for example.
However, the short life span of stem cells outside the lab and the vaccination’s severe inflammatory side effects are limitations. Researchers won’t be able to conduct clinical trials until these issues are overcome.
- How to overcome limitations in research
You’ve already started on the road to overcoming limitations in research by acknowledging that they exist. However, you need to ensure readers don’t mistake weaknesses for errors within your research design.
To do this, you’ll need to justify and explain your rationale for the methods, research design, and analysis tools you chose and how you noticed they may have presented limitations.
Your readers need to know that even when limitations presented themselves, you followed best practices and the ethical standards of your field. You didn’t violate any rules and regulations during your research process.
You’ll also want to reinforce the validity of your conclusions and results with multiple sources, methods, and perspectives. This prevents readers from assuming your findings were derived from a single or biased source.
- Learning and improving starts with limitations in research
Dealing with limitations with transparency and integrity helps identify areas for future improvements and developments. It’s a learning process, providing valuable insights into how you can improve methodologies, expand sample sizes, or explore alternate approaches to further support the validity of your findings.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
What are the limitations in research and how to write them?
Learn about the potential limitations in research and how to appropriately address them in order to deliver honest and ethical research.
It is fairly uncommon for researchers to stumble into the term research limitations when working on their research paper. Limitations in research can arise owing to constraints on design, methods, materials, and so on, and these aspects, unfortunately, may have an influence on your subject’s findings.
In this Mind The Graph’s article, we’ll discuss some recommendations for writing limitations in research , provide examples of various common types of limitations, and suggest how to properly present this information.
What are the limitations in research?
The limitations in research are the constraints in design, methods or even researchers’ limitations that affect and influence the interpretation of your research’s ultimate findings. These are limitations on the generalization and usability of findings that emerge from the design of the research and/or the method employed to ensure validity both internally and externally.
Researchers are usually cautious to acknowledge the limitations of their research in their publications for fear of undermining the research’s scientific validity. No research is faultless or covers every possible angle. As a result, addressing the constraints of your research exhibits honesty and integrity .
Why should include limitations of research in my paper?
Though limitations tackle potential flaws in research, commenting on them at the conclusion of your paper, by demonstrating that you are aware of these limitations and explaining how they impact the conclusions that may be taken from the research, improves your research by disclosing any issues before other researchers or reviewers do .
Additionally, emphasizing research constraints implies that you have thoroughly investigated the ramifications of research shortcomings and have a thorough understanding of your research problem.
Limits exist in any research; being honest about them and explaining them would impress researchers and reviewers more than disregarding them.
Remember that acknowledging a research’s shortcomings offers a chance to provide ideas for future research, but be careful to describe how your study may help to concentrate on these outstanding problems.
Possible limitations examples
Here are some limitations connected to methodology and the research procedure that you may need to explain and discuss in connection to your findings.
Methodological limitations
Sample size.
The number of units of analysis used in your study is determined by the sort of research issue being investigated. It is important to note that if your sample is too small, finding significant connections in the data will be challenging, as statistical tests typically require a larger sample size to ensure a fair representation and this can be limiting.
Lack of available or reliable data
A lack of data or trustworthy data will almost certainly necessitate limiting the scope of your research or the size of your sample, or it can be a substantial impediment to identifying a pattern and a relevant connection.
Lack of prior research on the subject
Citing previous research papers forms the basis of your literature review and aids in comprehending the research subject you are researching. Yet there may be little if any, past research on your issue.
The measure used to collect data
After finishing your analysis of the findings, you realize that the method you used to collect data limited your capacity to undertake a comprehensive evaluation of the findings. Recognize the flaw by mentioning that future researchers should change the specific approach for data collection.
Issues with research samples and selection
Sampling inaccuracies arise when a probability sampling method is employed to choose a sample, but that sample does not accurately represent the overall population or the relevant group. As a result, your study suffers from “sampling bias” or “selection bias.”
Limitations of the research
When your research requires polling certain persons or a specific group, you may have encountered the issue of limited access to these interviewees. Because of the limited access, you may need to reorganize or rearrange your research. In this scenario, explain why access is restricted and ensure that your findings are still trustworthy and valid despite the constraint.
Time constraints
Practical difficulties may limit the amount of time available to explore a research issue and monitor changes as they occur. If time restrictions have any detrimental influence on your research, recognize this impact by expressing the necessity for a future investigation.
Due to their cultural origins or opinions on observed events, researchers may carry biased opinions, which can influence the credibility of a research. Furthermore, researchers may exhibit biases toward data and conclusions that only support their hypotheses or arguments.
The structure of the limitations section
The limitations of your research are usually stated at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so that the reader is aware of and comprehends the limitations prior to actually reading the rest of your findings, or they are stated at the end of the discussion section as an acknowledgment of the need for further research.
The ideal way is to divide your limitations section into three steps:
1. Identify the research constraints;
2. Describe in great detail how they affect your research;
3. Mention the opportunity for future investigations and give possibilities.
By following this method while addressing the constraints of your research, you will be able to effectively highlight your research’s shortcomings without jeopardizing the quality and integrity of your research.
Present your research or paper in an innovative way
If you want your readers to be engaged and participate in your research, try Mind The Graph tool to add visual assets to your content. Infographics may improve comprehension and are easy to read, just as the Mind The Graph tool is simple to use and offers a variety of templates from which you can select the one that best suits your information.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Unlock Your Creativity
Create infographics, presentations and other scientifically-accurate designs without hassle — absolutely free for 7 days!
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags

Research Limitations: A Comprehensive Guide
Embarking on a research journey is an exciting endeavor, but every study has its boundaries and constraints. Understanding and transparently acknowledging these limitations is a crucial aspect of scholarly work. In this guide, we'll explore the concept of research limitations, why they matter, and how to effectively address and navigate them in your academic endeavors.
1. Defining Research Limitations:
- Definition: Research limitations are the constraints or shortcomings that affect the scope, applicability, and generalizability of a study.
- Inherent in Research: Every research project, regardless of its scale or significance, possesses limitations.
2. Types of Research Limitations:
- Methodological Limitations: Constraints related to the research design, data collection methods, or analytical techniques.
- Sampling Limitations: Issues associated with the representativeness or size of the study sample.
- Contextual Limitations: Restrictions stemming from the specific time, place, or cultural context of the study.
- Resource Limitations: Constraints related to time, budget, or access to necessary resources.
3. Why Acknowledge Limitations?
- Transparency: Acknowledging limitations demonstrates transparency and honesty in your research.
- Robustness of Findings: Recognizing limitations adds nuance to your findings, making them more robust.
- Future Research Directions: Addressing limitations provides a foundation for future researchers to build upon.
4. Identifying Research Limitations:
- Reflect on Methodology: Consider the strengths and weaknesses of your research design, data collection methods, and analysis.
- Examine Sample Characteristics: Evaluate the representativeness and size of your study sample.
- Consider External Factors: Assess external factors that may impact the generalizability of your findings.
5. How to Address Limitations:
- In the Methodology Section: Clearly articulate limitations in the methodology section of your research paper.
- Offer Solutions: If possible, propose ways to mitigate or address identified limitations.
- Future Research Suggestions: Use limitations as a springboard to suggest areas for future research.
6. Common Phrases to Express Limitations:
- "This study is not without limitations."
- "One limitation of our research is..."
- "It is important to acknowledge the constraints of this study, including..."
7. Examples of Addressing Limitations:
- Example 1 (Methodological): "While our survey provided valuable insights, the reliance on self-reported data introduces the possibility of response bias."
- Example 2 (Sampling): "The small sample size of our study limits the generalizability of our findings to a broader population."
- Example 3 (Resource): "Due to budget constraints, our research was limited to a single geographical location, potentially impacting the external validity."
8. Balancing Strengths and Limitations:
- Emphasize Contributions: Highlight the contributions and strengths of your research alongside the limitations.
- Maintain a Positive Tone: Discuss limitations objectively without undermining the significance of your study.
9. Feedback and Peer Review:
- Seek Feedback: Share your research with peers or mentors to gain valuable insights.
- Peer Review: Embrace the feedback received during the peer-review process to enhance the robustness of your work.
10. Continuous Reflection:
- Throughout the Research Process: Continuously reflect on potential limitations during the entire research process.
- Adjust as Needed: Be willing to adjust your approach as you encounter unforeseen challenges.
Conclusion:
Understanding and effectively addressing research limitations is a hallmark of rigorous and responsible scholarship. By openly acknowledging these constraints, you not only enhance the credibility of your work but also contribute to the broader academic discourse. Embrace the nuances of your research journey, navigate its limitations thoughtfully, and pave the way for future investigations.
Related Guides
- What is Plagiarism? : Types, Examples and How to Avoid it
- Research Methods : A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Write an Essay Outline: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Mastering the Art of Writing a Research Introduction
- How to Write the Abstract of Your Research Paper?
- How to Write a Research Question?

Writing Limitations of Research Study — 4 Reasons Why It Is Important!
It is not unusual for researchers to come across the term limitations of research during their academic paper writing. More often this is interpreted as something terrible. However, when it comes to research study, limitations can help structure the research study better. Therefore, do not underestimate significance of limitations of research study.
Allow us to take you through the context of how to evaluate the limits of your research and conclude an impactful relevance to your results.
Table of Contents
What Are the Limitations of a Research Study?
Every research has its limit and these limitations arise due to restrictions in methodology or research design. This could impact your entire research or the research paper you wish to publish. Unfortunately, most researchers choose not to discuss their limitations of research fearing it will affect the value of their article in the eyes of readers.
However, it is very important to discuss your study limitations and show it to your target audience (other researchers, journal editors, peer reviewers etc.). It is very important that you provide an explanation of how your research limitations may affect the conclusions and opinions drawn from your research. Moreover, when as an author you state the limitations of research, it shows that you have investigated all the weaknesses of your study and have a deep understanding of the subject. Being honest could impress your readers and mark your study as a sincere effort in research.

Why and Where Should You Include the Research Limitations?
The main goal of your research is to address your research objectives. Conduct experiments, get results and explain those results, and finally justify your research question . It is best to mention the limitations of research in the discussion paragraph of your research article.
At the very beginning of this paragraph, immediately after highlighting the strengths of the research methodology, you should write down your limitations. You can discuss specific points from your research limitations as suggestions for further research in the conclusion of your thesis.
1. Common Limitations of the Researchers
Limitations that are related to the researcher must be mentioned. This will help you gain transparency with your readers. Furthermore, you could provide suggestions on decreasing these limitations in you and your future studies.
2. Limited Access to Information
Your work may involve some institutions and individuals in research, and sometimes you may have problems accessing these institutions. Therefore, you need to redesign and rewrite your work. You must explain your readers the reason for limited access.
3. Limited Time
All researchers are bound by their deadlines when it comes to completing their studies. Sometimes, time constraints can affect your research negatively. However, the best practice is to acknowledge it and mention a requirement for future study to solve the research problem in a better way.
4. Conflict over Biased Views and Personal Issues
Biased views can affect the research. In fact, researchers end up choosing only those results and data that support their main argument, keeping aside the other loose ends of the research.
Types of Limitations of Research
Before beginning your research study, know that there are certain limitations to what you are testing or possible research results. There are different types that researchers may encounter, and they all have unique characteristics, such as:
1. Research Design Limitations
Certain restrictions on your research or available procedures may affect your final results or research outputs. You may have formulated research goals and objectives too broadly. However, this can help you understand how you can narrow down the formulation of research goals and objectives, thereby increasing the focus of your study.
2. Impact Limitations
Even if your research has excellent statistics and a strong design, it can suffer from the influence of the following factors:
- Presence of increasing findings as researched
- Being population specific
- A strong regional focus.
3. Data or statistical limitations
In some cases, it is impossible to collect sufficient data for research or very difficult to get access to the data. This could lead to incomplete conclusion to your study. Moreover, this insufficiency in data could be the outcome of your study design. The unclear, shabby research outline could produce more problems in interpreting your findings.
How to Correctly Structure Your Research Limitations?
There are strict guidelines for narrowing down research questions, wherein you could justify and explain potential weaknesses of your academic paper. You could go through these basic steps to get a well-structured clarity of research limitations:
- Declare that you wish to identify your limitations of research and explain their importance,
- Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices.
- Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future.
In this section, your readers will see that you are aware of the potential weaknesses in your business, understand them and offer effective solutions, and it will positively strengthen your article as you clarify all limitations of research to your target audience.
Know that you cannot be perfect and there is no individual without flaws. You could use the limitations of research as a great opportunity to take on a new challenge and improve the future of research. In a typical academic paper, research limitations may relate to:
1. Formulating your goals and objectives
If you formulate goals and objectives too broadly, your work will have some shortcomings. In this case, specify effective methods or ways to narrow down the formula of goals and aim to increase your level of study focus.
2. Application of your data collection methods in research
If you do not have experience in primary data collection, there is a risk that there will be flaws in the implementation of your methods. It is necessary to accept this, and learn and educate yourself to understand data collection methods.
3. Sample sizes
This depends on the nature of problem you choose. Sample size is of a greater importance in quantitative studies as opposed to qualitative ones. If your sample size is too small, statistical tests cannot identify significant relationships or connections within a given data set.
You could point out that other researchers should base the same study on a larger sample size to get more accurate results.
4. The absence of previous studies in the field you have chosen
Writing a literature review is an important step in any scientific study because it helps researchers determine the scope of current work in the chosen field. It is a major foundation for any researcher who must use them to achieve a set of specific goals or objectives.
However, if you are focused on the most current and evolving research problem or a very narrow research problem, there may be very little prior research on your topic. For example, if you chose to explore the role of Bitcoin as the currency of the future, you may not find tons of scientific papers addressing the research problem as Bitcoins are only a new phenomenon.
It is important that you learn to identify research limitations examples at each step. Whatever field you choose, feel free to add the shortcoming of your work. This is mainly because you do not have many years of experience writing scientific papers or completing complex work. Therefore, the depth and scope of your discussions may be compromised at different levels compared to academics with a lot of expertise. Include specific points from limitations of research. Use them as suggestions for the future.
Have you ever faced a challenge of writing the limitations of research study in your paper? How did you overcome it? What ways did you follow? Were they beneficial? Let us know in the comments below!
Frequently Asked Questions
Setting limitations in our study helps to clarify the outcomes drawn from our research and enhance understanding of the subject. Moreover, it shows that the author has investigated all the weaknesses in the study.
Scope is the range and limitations of a research project which are set to define the boundaries of a project. Limitations are the impacts on the overall study due to the constraints on the research design.
Limitation in research is an impact of a constraint on the research design in the overall study. They are the flaws or weaknesses in the study, which may influence the outcome of the research.
1. Limitations in research can be written as follows: Formulate your goals and objectives 2. Analyze the chosen data collection method and the sample sizes 3. Identify your limitations of research and explain their importance 4. Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices 5. Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future
Excellent article ,,,it has helped me big
This is very helpful information. It has given me an insight on how to go about my study limitations.
Good comments and helpful
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Diversity and Inclusion
- Trending Now
The Silent Struggle: Confronting gender bias in science funding
In the 1990s, Dr. Katalin Kariko’s pioneering mRNA research seemed destined for obscurity, doomed by…

- Promoting Research
Plain Language Summary — Communicating your research to bridge the academic-lay gap
Science can be complex, but does that mean it should not be accessible to the…

Addressing Barriers in Academia: Navigating unconscious biases in the Ph.D. journey
In the journey of academia, a Ph.D. marks a transitional phase, like that of a…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical inference
Research population and sample serve as the cornerstones of any scientific inquiry. They hold the…

- Manuscript Preparation
- Publishing Research
Research Problem Statement — Find out how to write an impactful one!
What Is a Research Problem Statement? A research problem statement is a clear, concise, and…
How to Develop a Good Research Question? — Types & Examples
5 Effective Ways to Avoid Ghostwriting for Busy Researchers
Top 5 Key Differences Between Methods and Methodology

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?

Organizing Academic Research Papers: Limitations of the Study
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The limitations of the study are those characteristics of design or methodology that impacted or influenced the application or interpretation of the results of your study. They are the constraints on generalizability and utility of findings that are the result of the ways in which you chose to design the study and/or the method used to establish internal and external validity.
Importance of...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study’s limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and be graded down because you appear to have ignored them.
Keep in mind that acknowledgement of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research. If you do connect your study's limitations to suggestions for further research, be sure to explain the ways in which these unanswered questions may become more focused because of your study.
Acknowledgement of a study's limitations also provides you with an opportunity to demonstrate to your professor that you have thought critically about the research problem, understood the relevant literature published about it, and correctly assessed the methods chosen for studying the problem. A key objective of the research process is not only discovering new knowledge but also to confront assumptions and explore what we don't know.
Claiming limitiations is a subjective process because you must evaluate the impact of those limitations . Don't just list key weaknesses and the magnitude of a study's limitations. To do so diminishes the validity of your research because it leaves the reader wondering whether, or in what ways, limitation(s) in your study may have impacted the findings and conclusions. Limitations require a critical, overall appraisal and interpretation of their impact. You should answer the question: do these problems with errors, methods, validity, etc. eventually matter and, if so, to what extent?
Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation . Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com.
Descriptions of Possible Limitations
All studies have limitations . However, it is important that you restrict your discussion to limitations related to the research problem under investigation. For example, if a meta-analysis of existing literature is not a stated purpose of your research, it should not be discussed as a limitation. Do not apologize for not addressing issues that you did not promise to investigate in your paper.
Here are examples of limitations you may need to describe and to discuss how they possibly impacted your findings. Descriptions of limitations should be stated in the past tense.
Possible Methodological Limitations
- Sample size -- the number of the units of analysis you use in your study is dictated by the type of research problem you are investigating. Note that, if your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to find significant relationships from the data, as statistical tests normally require a larger sample size to ensure a representative distribution of the population and to be considered representative of groups of people to whom results will be generalized or transferred.
- Lack of available and/or reliable data -- a lack of data or of reliable data will likely require you to limit the scope of your analysis, the size of your sample, or it can be a significant obstacle in finding a trend and a meaningful relationship. You need to not only describe these limitations but to offer reasons why you believe data is missing or is unreliable. However, don’t just throw up your hands in frustration; use this as an opportunity to describe the need for future research.
- Lack of prior research studies on the topic -- citing prior research studies forms the basis of your literature review and helps lay a foundation for understanding the research problem you are investigating. Depending on the currency or scope of your research topic, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic. Before assuming this to be true, consult with a librarian! In cases when a librarian has confirmed that there is a lack of prior research, you may be required to develop an entirely new research typology [for example, using an exploratory rather than an explanatory research design]. Note that this limitation can serve as an important opportunity to describe the need for further research.
- Measure used to collect the data -- sometimes it is the case that, after completing your interpretation of the findings, you discover that the way in which you gathered data inhibited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results. For example, you regret not including a specific question in a survey that, in retrospect, could have helped address a particular issue that emerged later in the study. Acknowledge the deficiency by stating a need in future research to revise the specific method for gathering data.
- Self-reported data -- whether you are relying on pre-existing self-reported data or you are conducting a qualitative research study and gathering the data yourself, self-reported data is limited by the fact that it rarely can be independently verified. In other words, you have to take what people say, whether in interviews, focus groups, or on questionnaires, at face value. However, self-reported data contain several potential sources of bias that should be noted as limitations: (1) selective memory (remembering or not remembering experiences or events that occurred at some point in the past); (2) telescoping [recalling events that occurred at one time as if they occurred at another time]; (3) attribution [the act of attributing positive events and outcomes to one's own agency but attributing negative events and outcomes to external forces]; and, (4) exaggeration [the act of representing outcomes or embellishing events as more significant than is actually suggested from other data].
Possible Limitations of the Researcher
- Access -- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or otherwise limited, the reasons for this need to be described.
- Longitudinal effects -- unlike your professor, who can literally devote years [even a lifetime] to studying a single research problem, the time available to investigate a research problem and to measure change or stability within a sample is constrained by the due date of your assignment. Be sure to choose a topic that does not require an excessive amount of time to complete the literature review, apply the methodology, and gather and interpret the results. If you're unsure, talk to your professor.
- Cultural and other type of bias -- we all have biases, whether we are conscience of them or not. Bias is when a person, place, or thing is viewed or shown in a consistently inaccurate way. It is usually negative, though one can have a positive bias as well. When proof-reading your paper, be especially critical in reviewing how you have stated a problem, selected the data to be studied, what may have been omitted, the manner in which you have ordered events, people, or places and how you have chosen to represent a person, place, or thing, to name a phenomenon, or to use possible words with a positive or negative connotation. Note that if you detect bias in prior research, it must be acknowledged and you should explain what measures were taken to avoid perpetuating bias.
- Fluency in a language -- if your research focuses on measuring the perceived value of after-school tutoring among Mexican-American ESL [English as a Second Language] students, for example, and you are not fluent in Spanish, you are limited in being able to read and interpret Spanish language research studies on the topic. This deficiency should be acknowledged.
Brutus, Stéphane et al. Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations. Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Senunyeme, Emmanuel K. Business Research Methods . Powerpoint Presentation. Regent University of Science and Technology.
Structure and Writing Style
Information about the limitations of your study are generally placed either at the beginning of the discussion section of your paper so the reader knows and understands the limitations before reading the rest of your analysis of the findings, or, the limitations are outlined at the conclusion of the discussion section as an acknowledgement of the need for further study. Statements about a study's limitations should not be buried in the body [middle] of the discussion section unless a limitation is specific to something covered in that part of the paper. If this is the case, though, the limitation should be reiterated at the conclusion of the section.
If you determine that your study is seriously flawed due to important limitations , such as, an inability to acquire critical data, consider reframing it as a pilot study intended to lay the groundwork for a more complete research study in the future. Be sure, though, to specifically explain the ways that these flaws can be successfully overcome in later studies.
But, do not use this as an excuse for not developing a thorough research paper! Review the tab in this guide for developing a research topic . If serious limitations exist, it generally indicates a likelihood that your research problem is too narrowly defined or that the issue or event under study is too recent and, thus, very little research has been written about it. If serious limitations do emerge, consult with your professor about possible ways to overcome them or how to reframe your study.
When discussing the limitations of your research, be sure to:
- Describe each limitation in detailed but concise terms;
- Explain why each limitation exists;
- Provide the reasons why each limitation could not be overcome using the method(s) chosen to gather the data [cite to other studies that had similar problems when possible];
- Assess the impact of each limitation in relation to the overall findings and conclusions of your study; and,
- If appropriate, describe how these limitations could point to the need for further research.
Remember that the method you chose may be the source of a significant limitation that has emerged during your interpretation of the results [for example, you didn't ask a particular question in a survey that you later wish you had]. If this is the case, don't panic. Acknowledge it, and explain how applying a different or more robust methodology might address the research problem more effectively in any future study. A underlying goal of scholarly research is not only to prove what works, but to demonstrate what doesn't work or what needs further clarification.
Brutus, Stéphane et al. Self-Reported Limitations and Future Directions in Scholarly Reports: Analysis and Recommendations. Journal of Management 39 (January 2013): 48-75; Ioannidis, John P.A. Limitations are not Properly Acknowledged in the Scientific Literature. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 60 (2007): 324-329; Pasek, Josh. Writing the Empirical Social Science Research Paper: A Guide for the Perplexed . January 24, 2012. Academia.edu; Structure: How to Structure the Research Limitations Section of Your Dissertation . Dissertations and Theses: An Online Textbook. Laerd.com; What Is an Academic Paper? Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Writing Tip
Don't Inflate the Importance of Your Findings! After all the hard work and long hours devoted to writing your research paper, it is easy to get carried away with attributing unwarranted importance to what you’ve done. We all want our academic work to be viewed as excellent and worthy of a good grade, but it is important that you understand and openly acknowledge the limitiations of your study. Inflating of the importance of your study's findings in an attempt hide its flaws is a big turn off to your readers. A measure of humility goes a long way!
Another Writing Tip
Negative Results are Not a Limitation!
Negative evidence refers to findings that unexpectedly challenge rather than support your hypothesis. If you didn't get the results you anticipated, it may mean your hypothesis was incorrect and needs to be reformulated, or, perhaps you have stumbled onto something unexpected that warrants further study. Moreover, the absence of an effect may be very telling in many situations, particularly in experimental research designs. In any case, your results may be of importance to others even though they did not support your hypothesis. Do not fall into the trap of thinking that results contrary to what you expected is a limitation to your study. If you carried out the research well, they are simply your results and only require additional interpretation.
Yet Another Writing Tip
A Note about Sample Size Limitations in Qualitative Research
Sample sizes are typically smaller in qualitative research because, as the study goes on, acquiring more data does not necessarily lead to more information. This is because one occurrence of a piece of data, or a code, is all that is necessary to ensure that it becomes part of the analysis framework. However, it remains true that sample sizes that are too small cannot adequately support claims of having achieved valid conclusions and sample sizes that are too large do not permit the deep, naturalistic, and inductive analysis that defines qualitative inquiry. Determining adequate sample size in qualitative research is ultimately a matter of judgment and experience in evaluating the quality of the information collected against the uses to which it will be applied and the particular research method and purposeful sampling strategy employed. If the sample size is found to be a limitation, it may reflect your judgement about the methodological technique chosen [e.g., single life history study versus focus group interviews] rather than the number of respondents used.
Huberman, A. Michael and Matthew B. Miles. Data Management and Analysis Methods. In Handbook of Qualitative Research. Norman K. Denzin and Yvonna S. Lincoln, eds. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 1994), pp. 428-444.
- << Previous: 8. The Discussion
- Next: 9. The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
21 Research Limitations Examples
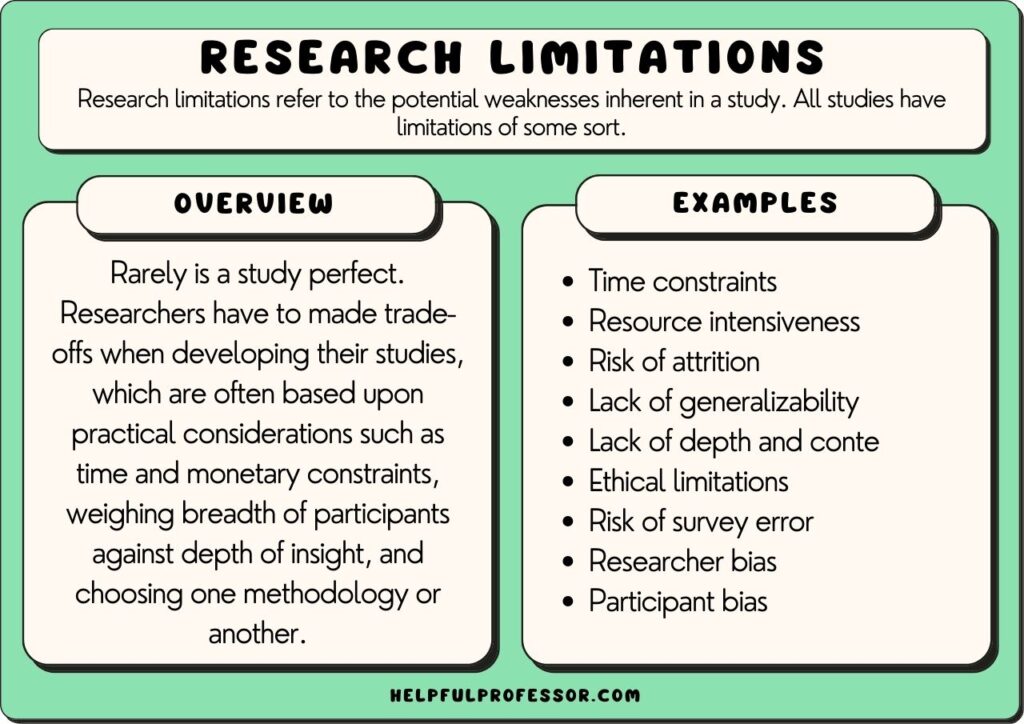
Research limitations refer to the potential weaknesses inherent in a study. All studies have limitations of some sort, meaning declaring limitations doesn’t necessarily need to be a bad thing, so long as your declaration of limitations is well thought-out and explained.
Rarely is a study perfect. Researchers have to make trade-offs when developing their studies, which are often based upon practical considerations such as time and monetary constraints, weighing the breadth of participants against the depth of insight, and choosing one methodology or another.
In research, studies can have limitations such as limited scope, researcher subjectivity, and lack of available research tools.
Acknowledging the limitations of your study should be seen as a strength. It demonstrates your willingness for transparency, humility, and submission to the scientific method and can bolster the integrity of the study. It can also inform future research direction.
Typically, scholars will explore the limitations of their study in either their methodology section, their conclusion section, or both.
Research Limitations Examples
Qualitative and quantitative research offer different perspectives and methods in exploring phenomena, each with its own strengths and limitations. So, I’ve split the limitations examples sections into qualitative and quantitative below.
Qualitative Research Limitations
Qualitative research seeks to understand phenomena in-depth and in context. It focuses on the ‘why’ and ‘how’ questions.
It’s often used to explore new or complex issues, and it provides rich, detailed insights into participants’ experiences, behaviors, and attitudes. However, these strengths also create certain limitations, as explained below.
1. Subjectivity
Qualitative research often requires the researcher to interpret subjective data. One researcher may examine a text and identify different themes or concepts as more dominant than others.
Close qualitative readings of texts are necessarily subjective – and while this may be a limitation, qualitative researchers argue this is the best way to deeply understand everything in context.
Suggested Solution and Response: To minimize subjectivity bias, you could consider cross-checking your own readings of themes and data against other scholars’ readings and interpretations. This may involve giving the raw data to a supervisor or colleague and asking them to code the data separately, then coming together to compare and contrast results.
2. Researcher Bias
The concept of researcher bias is related to, but slightly different from, subjectivity.
Researcher bias refers to the perspectives and opinions you bring with you when doing your research.
For example, a researcher who is explicitly of a certain philosophical or political persuasion may bring that persuasion to bear when interpreting data.
In many scholarly traditions, we will attempt to minimize researcher bias through the utilization of clear procedures that are set out in advance or through the use of statistical analysis tools.
However, in other traditions, such as in postmodern feminist research , declaration of bias is expected, and acknowledgment of bias is seen as a positive because, in those traditions, it is believed that bias cannot be eliminated from research, so instead, it is a matter of integrity to present it upfront.
Suggested Solution and Response: Acknowledge the potential for researcher bias and, depending on your theoretical framework , accept this, or identify procedures you have taken to seek a closer approximation to objectivity in your coding and analysis.
3. Generalizability
If you’re struggling to find a limitation to discuss in your own qualitative research study, then this one is for you: all qualitative research, of all persuasions and perspectives, cannot be generalized.
This is a core feature that sets qualitative data and quantitative data apart.
The point of qualitative data is to select case studies and similarly small corpora and dig deep through in-depth analysis and thick description of data.
Often, this will also mean that you have a non-randomized sample size.
While this is a positive – you’re going to get some really deep, contextualized, interesting insights – it also means that the findings may not be generalizable to a larger population that may not be representative of the small group of people in your study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that take a quantitative approach to the question.
4. The Hawthorne Effect
The Hawthorne effect refers to the phenomenon where research participants change their ‘observed behavior’ when they’re aware that they are being observed.
This effect was first identified by Elton Mayo who conducted studies of the effects of various factors ton workers’ productivity. He noticed that no matter what he did – turning up the lights, turning down the lights, etc. – there was an increase in worker outputs compared to prior to the study taking place.
Mayo realized that the mere act of observing the workers made them work harder – his observation was what was changing behavior.
So, if you’re looking for a potential limitation to name for your observational research study , highlight the possible impact of the Hawthorne effect (and how you could reduce your footprint or visibility in order to decrease its likelihood).
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight ways you have attempted to reduce your footprint while in the field, and guarantee anonymity to your research participants.
5. Replicability
Quantitative research has a great benefit in that the studies are replicable – a researcher can get a similar sample size, duplicate the variables, and re-test a study. But you can’t do that in qualitative research.
Qualitative research relies heavily on context – a specific case study or specific variables that make a certain instance worthy of analysis. As a result, it’s often difficult to re-enter the same setting with the same variables and repeat the study.
Furthermore, the individual researcher’s interpretation is more influential in qualitative research, meaning even if a new researcher enters an environment and makes observations, their observations may be different because subjectivity comes into play much more. This doesn’t make the research bad necessarily (great insights can be made in qualitative research), but it certainly does demonstrate a weakness of qualitative research.
6. Limited Scope
“Limited scope” is perhaps one of the most common limitations listed by researchers – and while this is often a catch-all way of saying, “well, I’m not studying that in this study”, it’s also a valid point.
No study can explore everything related to a topic. At some point, we have to make decisions about what’s included in the study and what is excluded from the study.
So, you could say that a limitation of your study is that it doesn’t look at an extra variable or concept that’s certainly worthy of study but will have to be explored in your next project because this project has a clearly and narrowly defined goal.
Suggested Solution and Response: Be clear about what’s in and out of the study when writing your research question.
7. Time Constraints
This is also a catch-all claim you can make about your research project: that you would have included more people in the study, looked at more variables, and so on. But you’ve got to submit this thing by the end of next semester! You’ve got time constraints.
And time constraints are a recognized reality in all research.
But this means you’ll need to explain how time has limited your decisions. As with “limited scope”, this may mean that you had to study a smaller group of subjects, limit the amount of time you spent in the field, and so forth.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will build on your current work, possibly as a PhD project.
8. Resource Intensiveness
Qualitative research can be expensive due to the cost of transcription, the involvement of trained researchers, and potential travel for interviews or observations.
So, resource intensiveness is similar to the time constraints concept. If you don’t have the funds, you have to make decisions about which tools to use, which statistical software to employ, and how many research assistants you can dedicate to the study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will gain more funding on the back of this ‘ exploratory study ‘.
9. Coding Difficulties
Data analysis in qualitative research often involves coding, which can be subjective and complex, especially when dealing with ambiguous or contradicting data.
After naming this as a limitation in your research, it’s important to explain how you’ve attempted to address this. Some ways to ‘limit the limitation’ include:
- Triangulation: Have 2 other researchers code the data as well and cross-check your results with theirs to identify outliers that may need to be re-examined, debated with the other researchers, or removed altogether.
- Procedure: Use a clear coding procedure to demonstrate reliability in your coding process. I personally use the thematic network analysis method outlined in this academic article by Attride-Stirling (2001).
Suggested Solution and Response: Triangulate your coding findings with colleagues, and follow a thematic network analysis procedure.

10. Risk of Non-Responsiveness
There is always a risk in research that research participants will be unwilling or uncomfortable sharing their genuine thoughts and feelings in the study.
This is particularly true when you’re conducting research on sensitive topics, politicized topics, or topics where the participant is expressing vulnerability .
This is similar to the Hawthorne effect (aka participant bias), where participants change their behaviors in your presence; but it goes a step further, where participants actively hide their true thoughts and feelings from you.
Suggested Solution and Response: One way to manage this is to try to include a wider group of people with the expectation that there will be non-responsiveness from some participants.
11. Risk of Attrition
Attrition refers to the process of losing research participants throughout the study.
This occurs most commonly in longitudinal studies , where a researcher must return to conduct their analysis over spaced periods of time, often over a period of years.
Things happen to people over time – they move overseas, their life experiences change, they get sick, change their minds, and even die. The more time that passes, the greater the risk of attrition.
Suggested Solution and Response: One way to manage this is to try to include a wider group of people with the expectation that there will be attrition over time.
12. Difficulty in Maintaining Confidentiality and Anonymity
Given the detailed nature of qualitative data , ensuring participant anonymity can be challenging.
If you have a sensitive topic in a specific case study, even anonymizing research participants sometimes isn’t enough. People might be able to induce who you’re talking about.
Sometimes, this will mean you have to exclude some interesting data that you collected from your final report. Confidentiality and anonymity come before your findings in research ethics – and this is a necessary limiting factor.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight the efforts you have taken to anonymize data, and accept that confidentiality and accountability place extremely important constraints on academic research.
13. Difficulty in Finding Research Participants
A study that looks at a very specific phenomenon or even a specific set of cases within a phenomenon means that the pool of potential research participants can be very low.
Compile on top of this the fact that many people you approach may choose not to participate, and you could end up with a very small corpus of subjects to explore. This may limit your ability to make complete findings, even in a quantitative sense.
You may need to therefore limit your research question and objectives to something more realistic.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight that this is going to limit the study’s generalizability significantly.
14. Ethical Limitations
Ethical limitations refer to the things you cannot do based on ethical concerns identified either by yourself or your institution’s ethics review board.
This might include threats to the physical or psychological well-being of your research subjects, the potential of releasing data that could harm a person’s reputation, and so on.
Furthermore, even if your study follows all expected standards of ethics, you still, as an ethical researcher, need to allow a research participant to pull out at any point in time, after which you cannot use their data, which demonstrates an overlap between ethical constraints and participant attrition.
Suggested Solution and Response: Highlight that these ethical limitations are inevitable but important to sustain the integrity of the research.
For more on Qualitative Research, Explore my Qualitative Research Guide
Quantitative Research Limitations
Quantitative research focuses on quantifiable data and statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s often used to test hypotheses, assess relationships and causality, and generalize findings across larger populations.
Quantitative research is widely respected for its ability to provide reliable, measurable, and generalizable data (if done well!). Its structured methodology has strengths over qualitative research, such as the fact it allows for replication of the study, which underpins the validity of the research.
However, this approach is not without it limitations, explained below.
1. Over-Simplification
Quantitative research is powerful because it allows you to measure and analyze data in a systematic and standardized way. However, one of its limitations is that it can sometimes simplify complex phenomena or situations.
In other words, it might miss the subtleties or nuances of the research subject.
For example, if you’re studying why people choose a particular diet, a quantitative study might identify factors like age, income, or health status. But it might miss other aspects, such as cultural influences or personal beliefs, that can also significantly impact dietary choices.
When writing about this limitation, you can say that your quantitative approach, while providing precise measurements and comparisons, may not capture the full complexity of your subjects of study.
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest a follow-up case study using the same research participants in order to gain additional context and depth.
2. Lack of Context
Another potential issue with quantitative research is that it often focuses on numbers and statistics at the expense of context or qualitative information.
Let’s say you’re studying the effect of classroom size on student performance. You might find that students in smaller classes generally perform better. However, this doesn’t take into account other variables, like teaching style , student motivation, or family support.
When describing this limitation, you might say, “Although our research provides important insights into the relationship between class size and student performance, it does not incorporate the impact of other potentially influential variables. Future research could benefit from a mixed-methods approach that combines quantitative analysis with qualitative insights.”
3. Applicability to Real-World Settings
Oftentimes, experimental research takes place in controlled environments to limit the influence of outside factors.
This control is great for isolation and understanding the specific phenomenon but can limit the applicability or “external validity” of the research to real-world settings.
For example, if you conduct a lab experiment to see how sleep deprivation impacts cognitive performance, the sterile, controlled lab environment might not reflect real-world conditions where people are dealing with multiple stressors.
Therefore, when explaining the limitations of your quantitative study in your methodology section, you could state:
“While our findings provide valuable information about [topic], the controlled conditions of the experiment may not accurately represent real-world scenarios where extraneous variables will exist. As such, the direct applicability of our results to broader contexts may be limited.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will engage in real-world observational research, such as ethnographic research.
4. Limited Flexibility
Once a quantitative study is underway, it can be challenging to make changes to it. This is because, unlike in grounded research, you’re putting in place your study in advance, and you can’t make changes part-way through.
Your study design, data collection methods, and analysis techniques need to be decided upon before you start collecting data.
For example, if you are conducting a survey on the impact of social media on teenage mental health, and halfway through, you realize that you should have included a question about their screen time, it’s generally too late to add it.
When discussing this limitation, you could write something like, “The structured nature of our quantitative approach allows for consistent data collection and analysis but also limits our flexibility to adapt and modify the research process in response to emerging insights and ideas.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use mixed-methods or qualitative research methods to gain additional depth of insight.
5. Risk of Survey Error
Surveys are a common tool in quantitative research, but they carry risks of error.
There can be measurement errors (if a question is misunderstood), coverage errors (if some groups aren’t adequately represented), non-response errors (if certain people don’t respond), and sampling errors (if your sample isn’t representative of the population).
For instance, if you’re surveying college students about their study habits , but only daytime students respond because you conduct the survey during the day, your results will be skewed.
In discussing this limitation, you might say, “Despite our best efforts to develop a comprehensive survey, there remains a risk of survey error, including measurement, coverage, non-response, and sampling errors. These could potentially impact the reliability and generalizability of our findings.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use other survey tools to compare and contrast results.
6. Limited Ability to Probe Answers
With quantitative research, you typically can’t ask follow-up questions or delve deeper into participants’ responses like you could in a qualitative interview.
For instance, imagine you are surveying 500 students about study habits in a questionnaire. A respondent might indicate that they study for two hours each night. You might want to follow up by asking them to elaborate on what those study sessions involve or how effective they feel their habits are.
However, quantitative research generally disallows this in the way a qualitative semi-structured interview could.
When discussing this limitation, you might write, “Given the structured nature of our survey, our ability to probe deeper into individual responses is limited. This means we may not fully understand the context or reasoning behind the responses, potentially limiting the depth of our findings.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that engage in mixed-method or qualitative methodologies to address the issue from another angle.
7. Reliance on Instruments for Data Collection
In quantitative research, the collection of data heavily relies on instruments like questionnaires, surveys, or machines.
The limitation here is that the data you get is only as good as the instrument you’re using. If the instrument isn’t designed or calibrated well, your data can be flawed.
For instance, if you’re using a questionnaire to study customer satisfaction and the questions are vague, confusing, or biased, the responses may not accurately reflect the customers’ true feelings.
When discussing this limitation, you could say, “Our study depends on the use of questionnaires for data collection. Although we have put significant effort into designing and testing the instrument, it’s possible that inaccuracies or misunderstandings could potentially affect the validity of the data collected.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will use different instruments but examine the same variables to triangulate results.
8. Time and Resource Constraints (Specific to Quantitative Research)
Quantitative research can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially when dealing with large samples.
It often involves systematic sampling, rigorous design, and sometimes complex statistical analysis.
If resources and time are limited, it can restrict the scale of your research, the techniques you can employ, or the extent of your data analysis.
For example, you may want to conduct a nationwide survey on public opinion about a certain policy. However, due to limited resources, you might only be able to survey people in one city.
When writing about this limitation, you could say, “Given the scope of our research and the resources available, we are limited to conducting our survey within one city, which may not fully represent the nationwide public opinion. Hence, the generalizability of the results may be limited.”
Suggested Solution and Response: Suggest future studies that will have more funding or longer timeframes.
How to Discuss Your Research Limitations
1. in your research proposal and methodology section.
In the research proposal, which will become the methodology section of your dissertation, I would recommend taking the four following steps, in order:
- Be Explicit about your Scope – If you limit the scope of your study in your research question, aims, and objectives, then you can set yourself up well later in the methodology to say that certain questions are “outside the scope of the study.” For example, you may identify the fact that the study doesn’t address a certain variable, but you can follow up by stating that the research question is specifically focused on the variable that you are examining, so this limitation would need to be looked at in future studies.
- Acknowledge the Limitation – Acknowledging the limitations of your study demonstrates reflexivity and humility and can make your research more reliable and valid. It also pre-empts questions the people grading your paper may have, so instead of them down-grading you for your limitations; they will congratulate you on explaining the limitations and how you have addressed them!
- Explain your Decisions – You may have chosen your approach (despite its limitations) for a very specific reason. This might be because your approach remains, on balance, the best one to answer your research question. Or, it might be because of time and monetary constraints that are outside of your control.
- Highlight the Strengths of your Approach – Conclude your limitations section by strongly demonstrating that, despite limitations, you’ve worked hard to minimize the effects of the limitations and that you have chosen your specific approach and methodology because it’s also got some terrific strengths. Name the strengths.
Overall, you’ll want to acknowledge your own limitations but also explain that the limitations don’t detract from the value of your study as it stands.
2. In the Conclusion Section or Chapter
In the conclusion of your study, it is generally expected that you return to a discussion of the study’s limitations. Here, I recommend the following steps:
- Acknowledge issues faced – After completing your study, you will be increasingly aware of issues you may have faced that, if you re-did the study, you may have addressed earlier in order to avoid those issues. Acknowledge these issues as limitations, and frame them as recommendations for subsequent studies.
- Suggest further research – Scholarly research aims to fill gaps in the current literature and knowledge. Having established your expertise through your study, suggest lines of inquiry for future researchers. You could state that your study had certain limitations, and “future studies” can address those limitations.
- Suggest a mixed methods approach – Qualitative and quantitative research each have pros and cons. So, note those ‘cons’ of your approach, then say the next study should approach the topic using the opposite methodology or could approach it using a mixed-methods approach that could achieve the benefits of quantitative studies with the nuanced insights of associated qualitative insights as part of an in-study case-study.
Overall, be clear about both your limitations and how those limitations can inform future studies.
In sum, each type of research method has its own strengths and limitations. Qualitative research excels in exploring depth, context, and complexity, while quantitative research excels in examining breadth, generalizability, and quantifiable measures. Despite their individual limitations, each method contributes unique and valuable insights, and researchers often use them together to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon being studied.
Attride-Stirling, J. (2001). Thematic networks: an analytic tool for qualitative research. Qualitative research , 1 (3), 385-405. ( Source )
Atkinson, P., Delamont, S., Cernat, A., Sakshaug, J., & Williams, R. A. (2021). SAGE research methods foundations . London: Sage Publications.
Clark, T., Foster, L., Bryman, A., & Sloan, L. (2021). Bryman’s social research methods . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Köhler, T., Smith, A., & Bhakoo, V. (2022). Templates in qualitative research methods: Origins, limitations, and new directions. Organizational Research Methods , 25 (2), 183-210. ( Source )
Lenger, A. (2019). The rejection of qualitative research methods in economics. Journal of Economic Issues , 53 (4), 946-965. ( Source )
Taherdoost, H. (2022). What are different research approaches? Comprehensive review of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method research, their applications, types, and limitations. Journal of Management Science & Engineering Research , 5 (1), 53-63. ( Source )
Walliman, N. (2021). Research methods: The basics . New York: Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
APA Citation Generator
MLA Citation Generator
Chicago Citation Generator
Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Present the Limitations of the Study Examples
What are the limitations of a study?
The limitations of a study are the elements of methodology or study design that impact the interpretation of your research results. The limitations essentially detail any flaws or shortcomings in your study. Study limitations can exist due to constraints on research design, methodology, materials, etc., and these factors may impact the findings of your study. However, researchers are often reluctant to discuss the limitations of their study in their papers, feeling that bringing up limitations may undermine its research value in the eyes of readers and reviewers.
In spite of the impact it might have (and perhaps because of it) you should clearly acknowledge any limitations in your research paper in order to show readers—whether journal editors, other researchers, or the general public—that you are aware of these limitations and to explain how they affect the conclusions that can be drawn from the research.
In this article, we provide some guidelines for writing about research limitations, show examples of some frequently seen study limitations, and recommend techniques for presenting this information. And after you have finished drafting and have received manuscript editing for your work, you still might want to follow this up with academic editing before submitting your work to your target journal.
Why do I need to include limitations of research in my paper?
Although limitations address the potential weaknesses of a study, writing about them toward the end of your paper actually strengthens your study by identifying any problems before other researchers or reviewers find them.
Furthermore, pointing out study limitations shows that you’ve considered the impact of research weakness thoroughly and have an in-depth understanding of your research topic. Since all studies face limitations, being honest and detailing these limitations will impress researchers and reviewers more than ignoring them.

Where should I put the limitations of the study in my paper?
Some limitations might be evident to researchers before the start of the study, while others might become clear while you are conducting the research. Whether these limitations are anticipated or not, and whether they are due to research design or to methodology, they should be clearly identified and discussed in the discussion section —the final section of your paper. Most journals now require you to include a discussion of potential limitations of your work, and many journals now ask you to place this “limitations section” at the very end of your article.
Some journals ask you to also discuss the strengths of your work in this section, and some allow you to freely choose where to include that information in your discussion section—make sure to always check the author instructions of your target journal before you finalize a manuscript and submit it for peer review .
Limitations of the Study Examples
There are several reasons why limitations of research might exist. The two main categories of limitations are those that result from the methodology and those that result from issues with the researcher(s).
Common Methodological Limitations of Studies
Limitations of research due to methodological problems can be addressed by clearly and directly identifying the potential problem and suggesting ways in which this could have been addressed—and SHOULD be addressed in future studies. The following are some major potential methodological issues that can impact the conclusions researchers can draw from the research.
Issues with research samples and selection
Sampling errors occur when a probability sampling method is used to select a sample, but that sample does not reflect the general population or appropriate population concerned. This results in limitations of your study known as “sample bias” or “selection bias.”
For example, if you conducted a survey to obtain your research results, your samples (participants) were asked to respond to the survey questions. However, you might have had limited ability to gain access to the appropriate type or geographic scope of participants. In this case, the people who responded to your survey questions may not truly be a random sample.
Insufficient sample size for statistical measurements
When conducting a study, it is important to have a sufficient sample size in order to draw valid conclusions. The larger the sample, the more precise your results will be. If your sample size is too small, it will be difficult to identify significant relationships in the data.
Normally, statistical tests require a larger sample size to ensure that the sample is considered representative of a population and that the statistical result can be generalized to a larger population. It is a good idea to understand how to choose an appropriate sample size before you conduct your research by using scientific calculation tools—in fact, many journals now require such estimation to be included in every manuscript that is sent out for review.
Lack of previous research studies on the topic
Citing and referencing prior research studies constitutes the basis of the literature review for your thesis or study, and these prior studies provide the theoretical foundations for the research question you are investigating. However, depending on the scope of your research topic, prior research studies that are relevant to your thesis might be limited.
When there is very little or no prior research on a specific topic, you may need to develop an entirely new research typology. In this case, discovering a limitation can be considered an important opportunity to identify literature gaps and to present the need for further development in the area of study.
Methods/instruments/techniques used to collect the data
After you complete your analysis of the research findings (in the discussion section), you might realize that the manner in which you have collected the data or the ways in which you have measured variables has limited your ability to conduct a thorough analysis of the results.
For example, you might realize that you should have addressed your survey questions from another viable perspective, or that you were not able to include an important question in the survey. In these cases, you should acknowledge the deficiency or deficiencies by stating a need for future researchers to revise their specific methods for collecting data that includes these missing elements.
Common Limitations of the Researcher(s)
Study limitations that arise from situations relating to the researcher or researchers (whether the direct fault of the individuals or not) should also be addressed and dealt with, and remedies to decrease these limitations—both hypothetically in your study, and practically in future studies—should be proposed.
Limited access to data
If your research involved surveying certain people or organizations, you might have faced the problem of having limited access to these respondents. Due to this limited access, you might need to redesign or restructure your research in a different way. In this case, explain the reasons for limited access and be sure that your finding is still reliable and valid despite this limitation.
Time constraints
Just as students have deadlines to turn in their class papers, academic researchers might also have to meet deadlines for submitting a manuscript to a journal or face other time constraints related to their research (e.g., participants are only available during a certain period; funding runs out; collaborators move to a new institution). The time available to study a research problem and to measure change over time might be constrained by such practical issues. If time constraints negatively impacted your study in any way, acknowledge this impact by mentioning a need for a future study (e.g., a longitudinal study) to answer this research problem.
Conflicts arising from cultural bias and other personal issues
Researchers might hold biased views due to their cultural backgrounds or perspectives of certain phenomena, and this can affect a study’s legitimacy. Also, it is possible that researchers will have biases toward data and results that only support their hypotheses or arguments. In order to avoid these problems, the author(s) of a study should examine whether the way the research problem was stated and the data-gathering process was carried out appropriately.
Steps for Organizing Your Study Limitations Section
When you discuss the limitations of your study, don’t simply list and describe your limitations—explain how these limitations have influenced your research findings. There might be multiple limitations in your study, but you only need to point out and explain those that directly relate to and impact how you address your research questions.
We suggest that you divide your limitations section into three steps: (1) identify the study limitations; (2) explain how they impact your study in detail; and (3) propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives. By following this sequence when discussing your study’s limitations, you will be able to clearly demonstrate your study’s weakness without undermining the quality and integrity of your research.
Step 1. Identify the limitation(s) of the study
- This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations.
The first step is to identify the particular limitation(s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don’t need to write a long review of all possible study limitations. A 200-500 word critique is an appropriate length for a research limitations section. In the beginning of this section, identify what limitations your study has faced and how important these limitations are.
You only need to identify limitations that had the greatest potential impact on: (1) the quality of your findings, and (2) your ability to answer your research question.

Step 2. Explain these study limitations in detail
- This part should comprise around 60-70% of your discussion of limitations.
After identifying your research limitations, it’s time to explain the nature of the limitations and how they potentially impacted your study. For example, when you conduct quantitative research, a lack of probability sampling is an important issue that you should mention. On the other hand, when you conduct qualitative research, the inability to generalize the research findings could be an issue that deserves mention.
Explain the role these limitations played on the results and implications of the research and justify the choice you made in using this “limiting” methodology or other action in your research. Also, make sure that these limitations didn’t undermine the quality of your dissertation .
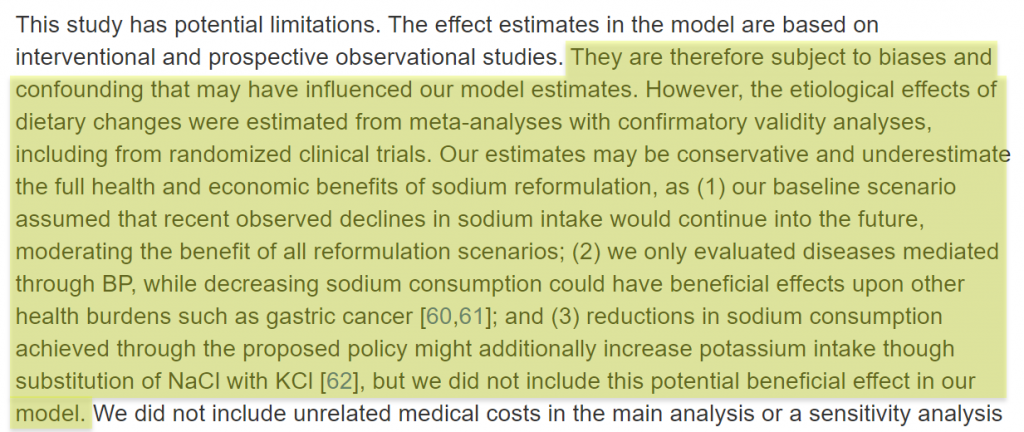
Step 3. Propose a direction for future studies and present alternatives (optional)
- This part should comprise around 10-20% of your discussion of limitations.
After acknowledging the limitations of the research, you need to discuss some possible ways to overcome these limitations in future studies. One way to do this is to present alternative methodologies and ways to avoid issues with, or “fill in the gaps of” the limitations of this study you have presented. Discuss both the pros and cons of these alternatives and clearly explain why researchers should choose these approaches.
Make sure you are current on approaches used by prior studies and the impacts they have had on their findings. Cite review articles or scientific bodies that have recommended these approaches and why. This might be evidence in support of the approach you chose, or it might be the reason you consider your choices to be included as limitations. This process can act as a justification for your approach and a defense of your decision to take it while acknowledging the feasibility of other approaches.
P hrases and Tips for Introducing Your Study Limitations in the Discussion Section
The following phrases are frequently used to introduce the limitations of the study:
- “There may be some possible limitations in this study.”
- “The findings of this study have to be seen in light of some limitations.”
- “The first is the…The second limitation concerns the…”
- “The empirical results reported herein should be considered in the light of some limitations.”
- “This research, however, is subject to several limitations.”
- “The primary limitation to the generalization of these results is…”
- “Nonetheless, these results must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.”
- “As with the majority of studies, the design of the current study is subject to limitations.”
- “There are two major limitations in this study that could be addressed in future research. First, the study focused on …. Second ….”
For more articles on research writing and the journal submissions and publication process, visit Wordvice’s Academic Resources page.
And be sure to receive professional English editing and proofreading services , including paper editing services , for your journal manuscript before submitting it to journal editors.
Wordvice Resources
Proofreading & Editing Guide
Writing the Results Section for a Research Paper
How to Write a Literature Review
Research Writing Tips: How to Draft a Powerful Discussion Section
How to Captivate Journal Readers with a Strong Introduction
Tips That Will Make Your Abstract a Success!
APA In-Text Citation Guide for Research Writing
Additional Resources
- Diving Deeper into Limitations and Delimitations (PhD student)
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Limitations of the Study (USC Library)
- Research Limitations (Research Methodology)
- How to Present Limitations and Alternatives (UMASS)
Article References
Pearson-Stuttard, J., Kypridemos, C., Collins, B., Mozaffarian, D., Huang, Y., Bandosz, P.,…Micha, R. (2018). Estimating the health and economic effects of the proposed US Food and Drug Administration voluntary sodium reformulation: Microsimulation cost-effectiveness analysis. PLOS. https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1002551
Xu, W.L, Pedersen, N.L., Keller, L., Kalpouzos, G., Wang, H.X., Graff, C,. Fratiglioni, L. (2015). HHEX_23 AA Genotype Exacerbates Effect of Diabetes on Dementia and Alzheimer Disease: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. PLOS. Retrieved from https://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1001853

Research Limitations
It is for sure that your research will have some limitations and it is normal. However, it is critically important for you to be striving to minimize the range of scope of limitations throughout the research process. Also, you need to provide the acknowledgement of your research limitations in conclusions chapter honestly.
It is always better to identify and acknowledge shortcomings of your work, rather than to leave them pointed out to your by your dissertation assessor. While discussing your research limitations, don’t just provide the list and description of shortcomings of your work. It is also important for you to explain how these limitations have impacted your research findings.
Your research may have multiple limitations, but you need to discuss only those limitations that directly relate to your research problems. For example, if conducting a meta-analysis of the secondary data has not been stated as your research objective, no need to mention it as your research limitation.
Research limitations in a typical dissertation may relate to the following points:
1. Formulation of research aims and objectives . You might have formulated research aims and objectives too broadly. You can specify in which ways the formulation of research aims and objectives could be narrowed so that the level of focus of the study could be increased.
2. Implementation of data collection method . Because you do not have an extensive experience in primary data collection (otherwise you would not be reading this book), there is a great chance that the nature of implementation of data collection method is flawed.
3. Sample size. Sample size depends on the nature of the research problem. If sample size is too small, statistical tests would not be able to identify significant relationships within data set. You can state that basing your study in larger sample size could have generated more accurate results. The importance of sample size is greater in quantitative studies compared to qualitative studies.
4. Lack of previous studies in the research area . Literature review is an important part of any research, because it helps to identify the scope of works that have been done so far in research area. Literature review findings are used as the foundation for the researcher to be built upon to achieve her research objectives.
However, there may be little, if any, prior research on your topic if you have focused on the most contemporary and evolving research problem or too narrow research problem. For example, if you have chosen to explore the role of Bitcoins as the future currency, you may not be able to find tons of scholarly paper addressing the research problem, because Bitcoins are only a recent phenomenon.
5. Scope of discussions . You can include this point as a limitation of your research regardless of the choice of the research area. Because (most likely) you don’t have many years of experience of conducing researches and producing academic papers of such a large size individually, the scope and depth of discussions in your paper is compromised in many levels compared to the works of experienced scholars.
You can discuss certain points from your research limitations as the suggestion for further research at conclusions chapter of your dissertation.
My e-book, The Ultimate Guide to Writing a Dissertation in Business Studies: a step by step assistance offers practical assistance to complete a dissertation with minimum or no stress. The e-book covers all stages of writing a dissertation starting from the selection to the research area to submitting the completed version of the work within the deadline. John Dudovskiy

Research Limitations & Delimitations
What they are and how they’re different (with examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: David Phair (PhD) | September 2022
If you’re new to the world of research, you’ve probably heard the terms “ research limitations ” and “ research delimitations ” being thrown around, often quite loosely. In this post, we’ll unpack what both of these mean, how they’re similar and how they’re different – so that you can write up these sections the right way.
Overview: Limitations vs Delimitations
- Are they the same?
- What are research limitations
- What are research delimitations
- Limitations vs delimitations
First things first…
Let’s start with the most important takeaway point of this post – research limitations and research delimitations are not the same – but they are related to each other (we’ll unpack that a little later). So, if you hear someone using these two words interchangeably, be sure to share this post with them!
Research Limitations
Research limitations are, at the simplest level, the weaknesses of the study , based on factors that are often outside of your control as the researcher. These factors could include things like time , access to funding, equipment , data or participants . For example, if you weren’t able to access a random sample of participants for your study and had to adopt a convenience sampling strategy instead, that would impact the generalizability of your findings and therefore reflect a limitation of your study.
Research limitations can also emerge from the research design itself . For example, if you were undertaking a correlational study, you wouldn’t be able to infer causality (since correlation doesn’t mean certain causation). Similarly, if you utilised online surveys to collect data from your participants, you naturally wouldn’t be able to get the same degree of rich data that you would from in-person interviews .
Simply put, research limitations reflect the shortcomings of a study , based on practical (or theoretical) constraints that the researcher faced. These shortcomings limit what you can conclude from a study, but at the same time, present a foundation for future research . Importantly, all research has limitations , so there’s no need to hide anything here – as long as you discuss how the limitations might affect your findings, it’s all good.
Research Delimitations
Alright, now that we’ve unpacked the limitations, let’s move on to the delimitations .
Research delimitations are similar to limitations in that they also “ limit ” the study, but their focus is entirely different. Specifically, the delimitations of a study refer to the scope of the research aims and research questions . In other words, delimitations reflect the choices you, as the researcher, intentionally make in terms of what you will and won’t try to achieve with your study. In other words, what your research aims and research questions will and won’t include.
As we’ve spoken about many times before, it’s important to have a tight, narrow focus for your research, so that you can dive deeply into your topic, apply your energy to one specific area and develop meaningful insights. If you have an overly broad scope or unfocused topic, your research will often pull in multiple, even opposing directions, and you’ll just land up with a muddy mess of findings .
So, the delimitations section is where you’ll clearly state what your research aims and research questions will focus on – and just as importantly, what they will exclude . For example, you might investigate a widespread phenomenon, but choose to focus your study on a specific age group, ethnicity or gender. Similarly, your study may focus exclusively on one country, city or even organization. As long as the scope is well justified (in other words, it represents a novel, valuable research topic), this is perfectly acceptable – in fact, it’s essential. Remember, focus is your friend.
Need a helping hand?
Conclusion: Limitations vs Delimitations
Ok, so let’s recap.
Research limitations and research delimitations are related in that they both refer to “limits” within a study. But, they are distinctly different. Limitations reflect the shortcomings of your study, based on practical or theoretical constraints that you faced.
Contrasted to that, delimitations reflect the choices that you made in terms of the focus and scope of your research aims and research questions. If you want to learn more about research aims and questions, you can check out this video post , where we unpack those concepts in detail.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

18 Comments
Good clarification of ideas on how a researcher ought to do during Process of choice
Thank you so much for this very simple but explicit explanation on limitation and delimitation. It has so helped me to develop my masters proposal. hope to recieve more from your site as time progresses
Thank you for this explanation – very clear.
Thanks for the explanation, really got it well.
This website is really helpful for my masters proposal
Thank you very much for helping to explain these two terms
I spent almost the whole day trying to figure out the differences
when I came across your notes everything became very clear
thanks for the clearly outlined explanation on the two terms, limitation and delimitation.
Very helpful Many thanks 🙏
Excellent it resolved my conflict .
I would like you to assist me please. If in my Research, I interviewed some participants and I submitted Questionnaires to other participants to answered to the questions, in the same organization, Is this a Qualitative methodology , a Quantitative Methodology or is it a Mixture Methodology I have used in my research? Please help me
How do I cite this article in APA format
Really so great ,finally have understood it’s difference now
Getting more clear regarding Limitations and Delimitation and concepts
I really appreciate your apt and precise explanation of the two concepts namely ; Limitations and Delimitations.
This is a good sources of research information for learners.
thank you for this, very helpful to researchers
Very good explained
Great and clear explanation, after a long confusion period on the two words, i can now explain to someone with ease.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Training videos | Faqs

Limitations in Research – A Simplified Guide with Examples
Limitations are flaws and shortcomings of your study. It is very important that you discuss the limitations of your study in the discussion section of your research paper. In this blog, we provide tips for presenting study limitations in your paper along with some real-world examples.
1. Should I Report the Limitations of My Work?

Most studies will have some form of limitation. So be honest and don’t hide your limitations. You have to tell your readers how your limitations might influence the outcomes and conclusions of your research. In reality, your readers and reviewers will be impressed with your paper if you are upfront about your limitations.
2. Examples
Let’s look at some examples. We have selected a variety of examples from different research topics.
2.1. Limitations Example 1
Following example is from a Medical research paper.
✔ The authors talk about the limitations and emphasis the importance of reconfirming the findings in a much larger study Study design and small sample size are important limitations. This could have led to an overestimation of the effect. Future research should reconfirm these findings by conducting larger-scale studies. _ Limitation s _ How it might affect the results? _ How to fix the limitation?
The authors are saying that the main limitations of the study are the small sample size and weak study design. Then they explain how this might have affected their results. They are saying that it is possible that they are overestimating the actual effect they are measuring. Then finally they are telling the readers that more studies with larger sample sizes should be conducted to reconfirm the findings.
As you can see, the authors are clearly explaining three things here: (1) What is the limitation? (2) How it might affect the study outcomes? and (3) What should be done to address the limitation?
2.2. Limitations Example 2
Following example is from an Engineering research paper.
✔ The authors are acknowledging the limitations and warning readers against generalizing the research findings However, some study limitations should be acknowledged. The experiments do not fully consider the problems that can appear in real situations. Hence, caution should be taken with generalizing the findings and applying them to real-life situations. _ Acknowledging limitations _ Explaining the limitation _ How it might affect the results?
The authors acknowledge that their study has some limitations. Then they explain what the limitations are. They are saying that their experiments do not consider all problems that might occur in real-life situations. Then they explain how this might affect their research outcomes. They are saying that readers should be careful when generalizing the results to practical real-world situations, because there is a possibility that the methods might fail.
2.3. Limitations Example 3
It is important to remember not to end your paper with limitations. Finish your paper on a positive note by telling your readers about the benefits of your research and possible future directions. In the following example, right after listing the limitations, the authors proceed to talk about the positive aspects of the work.
✔ The authors finish their paper on a positive note by talking about the benefits of their work and possible future work With this limited study, it is not known whether this finding can be applied to all clinical scenarios. Notwithstanding these limitations, this study has proven that Ultrasound can potentially serve as a more efficient alternative to X-rays in diagnosis. Future directions include studying the effects of different ultrasound pulsing schemes on pain relief. Another interesting direction would be to consider applications in nonhuman primates. _ Limitations _ Benefits of the work _ Possible future directions
The authors are saying that their experiments were somewhat limited and are not sure if their findings apply to the wider clinical practice. Then the authors highlight the benefits of their research. The authors say that their study has proven that ultrasound can be used instead of X-rays for diagnosis of certain types of diseases. Then they are explaining how future research can extend this work further. The authors are suggesting that it will be interesting to explore if ultrasound can be used for the treatment of chronic pain. And they are also suggesting that future studies can explore treating certain types of animal diseases with ultrasound. This is a very good example of how to finish the discussion section of your paper on a positive note.
Limitations are a vital component of the discussion section of your research paper. Remember, every study has limitations. There is no such thing as a perfect study. One of the major mistakes beginner writers make is hiding the limitations in the paper. Don’t do this, reviewers will reject your paper. Explain clearly how your limitations might have impacted your results, and provide ideas to mitigate them in the future. For further reading, please refer to our blogs on handling negative results and advanced tactics to address study limitations.
If you have any questions, please drop a comment below, and we will answer as soon as possible. We also recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , academic writing phrases and research paper examples which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
Similar Posts

How to Handle Negative Results in your Research Paper?
In this blog, we will see how to effectively communicate negative and unexpected findings in your paper with detailed examples.

How to Make Your Study Limitations Sound Positive?
In this blog, we will look at some clever techniques to present the study limitations without reducing the impact of your work.

Writing a Questionnaire Survey Research Paper – Example & Format
In this blog, we will explain how to write a survey questionnaire paper and discuss all the important points to consider while writing the research paper.

Research Methodology – 5 Beginner Writing Mistakes to Avoid
In this blog, we will look at five common mistakes to avoid while writing the methodology section of your research paper.

Materials and Methods Examples and Writing Tips
In this blog, we will go through many materials and methods examples and understand how to write a clear and concise method section for your research paper.

How to Create a Research Paper Outline?
In this blog we will see how to create a research paper outline and start writing your research paper.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 10 Share Facebook
- 1 Share Twitter
- 0 Share LinkedIn
- 0 Share Email

- Event Website Publish a modern and mobile friendly event website.
- Registration & Payments Collect registrations & online payments for your event.
- Abstract Management Collect and manage all your abstract submissions.
- Peer Reviews Easily distribute and manage your peer reviews.
- Conference Program Effortlessly build & publish your event program.
- Virtual Poster Sessions Host engaging virtual poster sessions.
- Customer Success Stories
- Wall of Love ❤️
8 Challenges Faced by Researchers (and Tips to Help)

Published on 18 Jan 2023
Being a researcher is a rewarding career for many reasons: You get to explore new ideas, work with cutting-edge technology, learn about the world, and have important discussions with like-minded individuals.
But, research doesn’t come without its challenges.
Luckily, challenges get easier to overcome when you don’t feel alone in facing them. So, we’ve put together a list of the top 8 challenges that researchers face and some tips to help.

1. Choosing your research topic
Starting a new research project and narrowing your focus to a single topic is one of the first challenges you’ll learn to face as an early-career researcher . And, it’s also one of the most important ones.
Your topic for each new research project is the foundation on which all your other work rests, so it’s vital that you take your time in tackling this challenge. A well-thought-out topic can also help you avoid some of the challenges that we’ll discuss later in this article.
TIP: Stay flexible and consider all the angles
Obviously, you’re going to want to research something that’s compelling enough to hold your interest. But, picking a good topic requires much more than just deciding what you’re most excited about.
Start by identifying a few gaps in your research niche along with different angles you could take on each. You don’t have to change the world with your work, but you do want to pinpoint places where you can make a difference (i.e. adding something new to the body of knowledge that exists).
Evaluate each topic for how realistically you can achieve it. What resources do you have available? Are you short on money? Will it be hard to find people (participants or team members)? Are you on a time limit? Take all these factors into consideration to choose a topic that will be manageable for you.
Your final research topic will likely look a lot different from the one you had in your head when you first started out. Stay flexible as you discover potential barriers and develop new angles that you can take to overcome them.
2. Finding research funding
Another common challenge that researchers face is finding the money they need to get the research done. Sometimes this comes alongside the shock of how much the required materials, tools, and assistance will cost. Research is more expensive than most people imagine.
In addition, there are many researchers competing for the same grants and funding. So, the competition can be fierce, especially for early-career researchers and researchers in developing countries .
If you can’t pull together enough funding, you may have to make compromises that limit how effectively and efficiently you can complete your research. Depending on the project requirements, it’s possible you’ll have to postpone your research until enough money is secured.
TIP: Think outside your social and geographical boxes
It’s easy to get discouraged while on the hunt for funding. So, remind yourself that there will always be more opportunities. Start by reaching out to your network. Request letters of support to help you apply for the grants that you’ve identified.
Don’t be afraid to branch out. Search for sources online and apply for funding available from potential international research partners. Just because your own country doesn’t have the funding doesn’t mean there isn’t someone, somewhere else that will pay you to complete your research.
3. Convincing others of the value of your research
Your research may be important. But, few people will take your word for it without a little convincing. For projects that take a long time to execute or require significant resources, you’ll have to do even more convincing. Unfortunately, the best methods for estimating and demonstrating the impact of research aren’t always clear.
Even after you’ve completed your project, you’ll likely be asked to demonstrate the impact of your research to your funders/stakeholders. This is an important step for solidifying your reputation and that of your research institution.
TIP: Reflect on your research purpose
Set aside some reflection time throughout the development and execution of your research. Use this time to put your purpose under a microscope. Remind yourself why you began this project, what good has come from it already, and what more can be achieved. Reflection exercises help you maintain confidence in your goal. They also ensure that you always have something relevant to say when someone asks: “So, why should I care?”
In addition, it never hurts to improve your scientific storytelling skills . Getting people to care about concepts that they don’t fully understand is a difficult task. Storytelling can help you convince varied audiences of the value of your research.
4. Overcoming imposter syndrome
Researchers have to expose themselves and their work to criticism. While others are criticizing the value of your work, it can be hard to maintain a high level of confidence in yourself. And when your work takes a turn you didn’t expect, feelings of self-doubt can easily creep in.
If you start doubting your own skills and accomplishments, or feel that you’re not as capable as others, you might be experiencing imposter syndrome . It’s a problem that people in all professions face and, in severe cases, it can cause someone to feel like a fraud in spite of all they’ve accomplished.
TIP: Remind yourself of your research (and personal) success
If you’re experiencing feelings of self-doubt, boost your confidence by reviewing past research projects and reminding yourself of your achievements. Lining up the facts in front of you can help with overcoming feelings of inadequacy. If you don’t have a large research record, think about other personal or academic achievements that you’re proud of.
Seek help from others, whether that’s constructive feedback on your work or advice from a mental health professional. And, consider trying something completely new as a hobby outside of your research. Trying new things can shake you out of your usual thought patterns and, most importantly, it gives you permission to be okay with being “bad” at something.
5. Building a good research team (or finding collaborators)
Research is rarely done alone. Chances are you’re going to need a research team to support you (or collaborators in the same field of research to connect with).
If you’ve never built a research team before, you may struggle to know where to start. You may not even be sure what kind of people you work well with.
If you’re looking for research collaborators , you’ll quickly realize that your biggest competitors are often your best potential partners. The research community is a complicated environment and the “publish or perish” mentality doesn’t always foster natural cooperation.
TIP: Use all available resources and expand your network
Think about the resources closely available to you. If you’re early in your career, look for mentoring schemes at your institution or apply for funding to attend academic conferences . If you already have a significant network, think about potential collaborators you can reach out to within it.
When you’ve exhausted the closest available options, create more collaboration opportunities and be intentional in growing your network. In particular, consider looking for team members and connections who bring a perspective that challenges your usual way of thinking.
6. Recruiting research participants (or collecting samples)
Managing participant recruitment and sample collection is a difficult part of many research projects. It’s often the biggest hurdle between the question you have and the data you need to answer it.
Low email open rates, lack of support from institutions, and restrictive regulations are all frustrating for researchers in search of willing (and relevant) research participants. These recruitment issues can become even more prominent when your research focuses on socially-sensitive or politically-charged topics.
TIP: Don’t be afraid to ask (but be sure to come prepared)
Using research tools that help you recruit and collect data from participants is a given. But, these tools won’t help if you’re afraid or unprepared to ask for help.
Prepare a good argument for why people should participate in your research. Learn to sell your story and come up with potential incentives if needed. Finally, have all your forms and information ready if people ask for it.
Then, reach out to your network (or list of potential participants). The worst that can happen is that some will say “No.” And, when they do, don’t let that stop you. Get back up, dust yourself off, and try again. Perseverance is key.
7. Staying self-motivated and managing your time
When you’re managing a research project, it can seem like there’s never enough hours in the day. There’s an ongoing battle between considering all perspectives to keep your research balanced and taking a deep enough dive to make sure your research has an impact. It’s likely that you’ll have commitments outside of your research project as well. So, you’ll be fighting to maintain a good balance between other work, administrative, and personal tasks.
As your research project drags on, you may also start hitting a motivational wall. When you’re the person in charge of maintaining deadlines, the temptation to procrastinate on tasks you don’t enjoy can throw timelines off track.
TIP: Plan and put accountability systems in place
There’s plenty of advice out there to help you with motivation. In particular, if you take the proper care when planning your research project , you’ll be setting yourself up for success. Choosing a topic that is interesting and engaging is key in helping you fight motivational burnout later in the process.
If your topic is engaging but you’re still struggling with time management, try some of these tips:
- Map your project in a visual calendar: If you haven’t already done this, sit down and input deadlines/tasks into a digital or physical calendar to help you break down your research project into more manageable chunks. It lifts some of the mental burden of remembering tasks and gives you a handy tool to see if you’re on track.
- Set up a reward system: Whether it’s going out for a nice meal, binging your favorite TV show, or going on a fun day trip, think of rewards that are meaningful to you and tie them to specific project milestones. Follow through and give yourself those well-deserved breaks when you accomplish the associated milestones.
- Find accountability buddies: Share your research goals with someone you trust and ask them to follow up with you. Knowing that someone other than yourself expects an update every few weeks can be extremely motivating.
8. Ensuring your research doesn’t sit and collect dust
Unfortunately, there are times when research that took a long time and a lot of effort is never used. Sometimes, this is because the expectations of the researcher and the funders didn’t line up. But more often, it’s because of a lack of effective effort to communicate the research results to stakeholders who can leverage it.
In the context of knowledge management, there is also a large body of partially completed research and data sets that are effectively “lost” to the larger community. When you’re incentivized to move on to your next research project quickly, you might deprioritize tasks like making your old research and unused data sets easily accessible to those who are looking for it (including your future self).
Even fully completed research is facing a knowledge management crisis. As mentioned in this study on researcher challenges by ExLibris:
“Advances in technology have changed the demands for transparency in sharing research… Most scholars (almost 60%) are now obligated to make their raw research datasets openly available with their published work. However, over a quarter of them (26%) find it difficult to do so in the context of current research data management solutions.”
TIP: Wrap up your research with the future in mind
When the end is in sight and you’re excited to move onto a new research topic, think about the impact that you want your research to have. If you don’t take the time to communicate your findings effectively or make your insights easily available, all the hard work you did could end up having a minimal real-world effect.
On a similar note, knowledge management benefits your future self. All of those notes and data that you didn’t publish? Where and how will you store them in case you want to access them later? Organize this information while it’s still fresh in your mind. Otherwise, you could find yourself staring at notes years later that seem like they were written in a foreign language. Even worse: bad organization could prevent you from even finding your old notes/data at all.
Research challenges: Expecting the unexpected
Being a researcher is full of unpredictable challenges. Careful preparation and planning can help with some of the common ones that come up. But, there will always be issues that catch you completely off guard.
While it would be great to be able to “expect the unexpected,” the most effective strategy for managing challenges is to simply keep an open mind. Recognize early on that your research is never going to go exactly the way you anticipate (and embrace that as part of the fun of being a researcher).
Maintain a curious enthusiasm about your research question and your research process. It will help you think outside of the box when unexpected challenges inevitably arise.
5 Best Event Registration Platforms for Your Next Conference
By having one software to organize registrations and submissions, a pediatric health center runs aro...
5 Essential Conference Apps for Your Event
In today’s digital age, the success of any conference hinges not just on the content and speakers bu...

Cultural Relativity and Acceptance of Embryonic Stem Cell Research
Article sidebar.

Main Article Content
There is a debate about the ethical implications of using human embryos in stem cell research, which can be influenced by cultural, moral, and social values. This paper argues for an adaptable framework to accommodate diverse cultural and religious perspectives. By using an adaptive ethics model, research protections can reflect various populations and foster growth in stem cell research possibilities.
INTRODUCTION
Stem cell research combines biology, medicine, and technology, promising to alter health care and the understanding of human development. Yet, ethical contention exists because of individuals’ perceptions of using human embryos based on their various cultural, moral, and social values. While these disagreements concerning policy, use, and general acceptance have prompted the development of an international ethics policy, such a uniform approach can overlook the nuanced ethical landscapes between cultures. With diverse viewpoints in public health, a single global policy, especially one reflecting Western ethics or the ethics prevalent in high-income countries, is impractical. This paper argues for a culturally sensitive, adaptable framework for the use of embryonic stem cells. Stem cell policy should accommodate varying ethical viewpoints and promote an effective global dialogue. With an extension of an ethics model that can adapt to various cultures, we recommend localized guidelines that reflect the moral views of the people those guidelines serve.
Stem cells, characterized by their unique ability to differentiate into various cell types, enable the repair or replacement of damaged tissues. Two primary types of stem cells are somatic stem cells (adult stem cells) and embryonic stem cells. Adult stem cells exist in developed tissues and maintain the body’s repair processes. [1] Embryonic stem cells (ESC) are remarkably pluripotent or versatile, making them valuable in research. [2] However, the use of ESCs has sparked ethics debates. Considering the potential of embryonic stem cells, research guidelines are essential. The International Society for Stem Cell Research (ISSCR) provides international stem cell research guidelines. They call for “public conversations touching on the scientific significance as well as the societal and ethical issues raised by ESC research.” [3] The ISSCR also publishes updates about culturing human embryos 14 days post fertilization, suggesting local policies and regulations should continue to evolve as ESC research develops. [4] Like the ISSCR, which calls for local law and policy to adapt to developing stem cell research given cultural acceptance, this paper highlights the importance of local social factors such as religion and culture.
I. Global Cultural Perspective of Embryonic Stem Cells
Views on ESCs vary throughout the world. Some countries readily embrace stem cell research and therapies, while others have stricter regulations due to ethical concerns surrounding embryonic stem cells and when an embryo becomes entitled to moral consideration. The philosophical issue of when the “someone” begins to be a human after fertilization, in the morally relevant sense, [5] impacts when an embryo becomes not just worthy of protection but morally entitled to it. The process of creating embryonic stem cell lines involves the destruction of the embryos for research. [6] Consequently, global engagement in ESC research depends on social-cultural acceptability.
a. US and Rights-Based Cultures
In the United States, attitudes toward stem cell therapies are diverse. The ethics and social approaches, which value individualism, [7] trigger debates regarding the destruction of human embryos, creating a complex regulatory environment. For example, the 1996 Dickey-Wicker Amendment prohibited federal funding for the creation of embryos for research and the destruction of embryos for “more than allowed for research on fetuses in utero.” [8] Following suit, in 2001, the Bush Administration heavily restricted stem cell lines for research. However, the Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005 was proposed to help develop ESC research but was ultimately vetoed. [9] Under the Obama administration, in 2009, an executive order lifted restrictions allowing for more development in this field. [10] The flux of research capacity and funding parallels the different cultural perceptions of human dignity of the embryo and how it is socially presented within the country’s research culture. [11]
b. Ubuntu and Collective Cultures
African bioethics differs from Western individualism because of the different traditions and values. African traditions, as described by individuals from South Africa and supported by some studies in other African countries, including Ghana and Kenya, follow the African moral philosophies of Ubuntu or Botho and Ukama , which “advocates for a form of wholeness that comes through one’s relationship and connectedness with other people in the society,” [12] making autonomy a socially collective concept. In this context, for the community to act autonomously, individuals would come together to decide what is best for the collective. Thus, stem cell research would require examining the value of the research to society as a whole and the use of the embryos as a collective societal resource. If society views the source as part of the collective whole, and opposes using stem cells, compromising the cultural values to pursue research may cause social detachment and stunt research growth. [13] Based on local culture and moral philosophy, the permissibility of stem cell research depends on how embryo, stem cell, and cell line therapies relate to the community as a whole . Ubuntu is the expression of humanness, with the person’s identity drawn from the “’I am because we are’” value. [14] The decision in a collectivistic culture becomes one born of cultural context, and individual decisions give deference to others in the society.
Consent differs in cultures where thought and moral philosophy are based on a collective paradigm. So, applying Western bioethical concepts is unrealistic. For one, Africa is a diverse continent with many countries with different belief systems, access to health care, and reliance on traditional or Western medicines. Where traditional medicine is the primary treatment, the “’restrictive focus on biomedically-related bioethics’” [is] problematic in African contexts because it neglects bioethical issues raised by traditional systems.” [15] No single approach applies in all areas or contexts. Rather than evaluating the permissibility of ESC research according to Western concepts such as the four principles approach, different ethics approaches should prevail.
Another consideration is the socio-economic standing of countries. In parts of South Africa, researchers have not focused heavily on contributing to the stem cell discourse, either because it is not considered health care or a health science priority or because resources are unavailable. [16] Each country’s priorities differ given different social, political, and economic factors. In South Africa, for instance, areas such as maternal mortality, non-communicable diseases, telemedicine, and the strength of health systems need improvement and require more focus. [17] Stem cell research could benefit the population, but it also could divert resources from basic medical care. Researchers in South Africa adhere to the National Health Act and Medicines Control Act in South Africa and international guidelines; however, the Act is not strictly enforced, and there is no clear legislation for research conduct or ethical guidelines. [18]
Some parts of Africa condemn stem cell research. For example, 98.2 percent of the Tunisian population is Muslim. [19] Tunisia does not permit stem cell research because of moral conflict with a Fatwa. Religion heavily saturates the regulation and direction of research. [20] Stem cell use became permissible for reproductive purposes only recently, with tight restrictions preventing cells from being used in any research other than procedures concerning ART/IVF. Their use is conditioned on consent, and available only to married couples. [21] The community's receptiveness to stem cell research depends on including communitarian African ethics.
c. Asia
Some Asian countries also have a collective model of ethics and decision making. [22] In China, the ethics model promotes a sincere respect for life or human dignity, [23] based on protective medicine. This model, influenced by Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), [24] recognizes Qi as the vital energy delivered via the meridians of the body; it connects illness to body systems, the body’s entire constitution, and the universe for a holistic bond of nature, health, and quality of life. [25] Following a protective ethics model, and traditional customs of wholeness, investment in stem cell research is heavily desired for its applications in regenerative therapies, disease modeling, and protective medicines. In a survey of medical students and healthcare practitioners, 30.8 percent considered stem cell research morally unacceptable while 63.5 percent accepted medical research using human embryonic stem cells. Of these individuals, 89.9 percent supported increased funding for stem cell research. [26] The scientific community might not reflect the overall population. From 1997 to 2019, China spent a total of $576 million (USD) on stem cell research at 8,050 stem cell programs, increased published presence from 0.6 percent to 14.01 percent of total global stem cell publications as of 2014, and made significant strides in cell-based therapies for various medical conditions. [27] However, while China has made substantial investments in stem cell research and achieved notable progress in clinical applications, concerns linger regarding ethical oversight and transparency. [28] For example, the China Biosecurity Law, promoted by the National Health Commission and China Hospital Association, attempted to mitigate risks by introducing an institutional review board (IRB) in the regulatory bodies. 5800 IRBs registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry since 2021. [29] However, issues still need to be addressed in implementing effective IRB review and approval procedures.
The substantial government funding and focus on scientific advancement have sometimes overshadowed considerations of regional cultures, ethnic minorities, and individual perspectives, particularly evident during the one-child policy era. As government policy adapts to promote public stability, such as the change from the one-child to the two-child policy, [30] research ethics should also adapt to ensure respect for the values of its represented peoples.
Japan is also relatively supportive of stem cell research and therapies. Japan has a more transparent regulatory framework, allowing for faster approval of regenerative medicine products, which has led to several advanced clinical trials and therapies. [31] South Korea is also actively engaged in stem cell research and has a history of breakthroughs in cloning and embryonic stem cells. [32] However, the field is controversial, and there are issues of scientific integrity. For example, the Korean FDA fast-tracked products for approval, [33] and in another instance, the oocyte source was unclear and possibly violated ethical standards. [34] Trust is important in research, as it builds collaborative foundations between colleagues, trial participant comfort, open-mindedness for complicated and sensitive discussions, and supports regulatory procedures for stakeholders. There is a need to respect the culture’s interest, engagement, and for research and clinical trials to be transparent and have ethical oversight to promote global research discourse and trust.
d. Middle East
Countries in the Middle East have varying degrees of acceptance of or restrictions to policies related to using embryonic stem cells due to cultural and religious influences. Saudi Arabia has made significant contributions to stem cell research, and conducts research based on international guidelines for ethical conduct and under strict adherence to guidelines in accordance with Islamic principles. Specifically, the Saudi government and people require ESC research to adhere to Sharia law. In addition to umbilical and placental stem cells, [35] Saudi Arabia permits the use of embryonic stem cells as long as they come from miscarriages, therapeutic abortions permissible by Sharia law, or are left over from in vitro fertilization and donated to research. [36] Laws and ethical guidelines for stem cell research allow the development of research institutions such as the King Abdullah International Medical Research Center, which has a cord blood bank and a stem cell registry with nearly 10,000 donors. [37] Such volume and acceptance are due to the ethical ‘permissibility’ of the donor sources, which do not conflict with religious pillars. However, some researchers err on the side of caution, choosing not to use embryos or fetal tissue as they feel it is unethical to do so. [38]
Jordan has a positive research ethics culture. [39] However, there is a significant issue of lack of trust in researchers, with 45.23 percent (38.66 percent agreeing and 6.57 percent strongly agreeing) of Jordanians holding a low level of trust in researchers, compared to 81.34 percent of Jordanians agreeing that they feel safe to participate in a research trial. [40] Safety testifies to the feeling of confidence that adequate measures are in place to protect participants from harm, whereas trust in researchers could represent the confidence in researchers to act in the participants’ best interests, adhere to ethical guidelines, provide accurate information, and respect participants’ rights and dignity. One method to improve trust would be to address communication issues relevant to ESC. Legislation surrounding stem cell research has adopted specific language, especially concerning clarification “between ‘stem cells’ and ‘embryonic stem cells’” in translation. [41] Furthermore, legislation “mandates the creation of a national committee… laying out specific regulations for stem-cell banking in accordance with international standards.” [42] This broad regulation opens the door for future global engagement and maintains transparency. However, these regulations may also constrain the influence of research direction, pace, and accessibility of research outcomes.
e. Europe
In the European Union (EU), ethics is also principle-based, but the principles of autonomy, dignity, integrity, and vulnerability are interconnected. [43] As such, the opportunity for cohesion and concessions between individuals’ thoughts and ideals allows for a more adaptable ethics model due to the flexible principles that relate to the human experience The EU has put forth a framework in its Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being allowing member states to take different approaches. Each European state applies these principles to its specific conventions, leading to or reflecting different acceptance levels of stem cell research. [44]
For example, in Germany, Lebenzusammenhang , or the coherence of life, references integrity in the unity of human culture. Namely, the personal sphere “should not be subject to external intervention.” [45] Stem cell interventions could affect this concept of bodily completeness, leading to heavy restrictions. Under the Grundgesetz, human dignity and the right to life with physical integrity are paramount. [46] The Embryo Protection Act of 1991 made producing cell lines illegal. Cell lines can be imported if approved by the Central Ethics Commission for Stem Cell Research only if they were derived before May 2007. [47] Stem cell research respects the integrity of life for the embryo with heavy specifications and intense oversight. This is vastly different in Finland, where the regulatory bodies find research more permissible in IVF excess, but only up to 14 days after fertilization. [48] Spain’s approach differs still, with a comprehensive regulatory framework. [49] Thus, research regulation can be culture-specific due to variations in applied principles. Diverse cultures call for various approaches to ethical permissibility. [50] Only an adaptive-deliberative model can address the cultural constructions of self and achieve positive, culturally sensitive stem cell research practices. [51]
II. Religious Perspectives on ESC
Embryonic stem cell sources are the main consideration within religious contexts. While individuals may not regard their own religious texts as authoritative or factual, religion can shape their foundations or perspectives.
The Qur'an states:
“And indeed We created man from a quintessence of clay. Then We placed within him a small quantity of nutfa (sperm to fertilize) in a safe place. Then We have fashioned the nutfa into an ‘alaqa (clinging clot or cell cluster), then We developed the ‘alaqa into mudgha (a lump of flesh), and We made mudgha into bones, and clothed the bones with flesh, then We brought it into being as a new creation. So Blessed is Allah, the Best of Creators.” [52]
Many scholars of Islam estimate the time of soul installment, marked by the angel breathing in the soul to bring the individual into creation, as 120 days from conception. [53] Personhood begins at this point, and the value of life would prohibit research or experimentation that could harm the individual. If the fetus is more than 120 days old, the time ensoulment is interpreted to occur according to Islamic law, abortion is no longer permissible. [54] There are a few opposing opinions about early embryos in Islamic traditions. According to some Islamic theologians, there is no ensoulment of the early embryo, which is the source of stem cells for ESC research. [55]
In Buddhism, the stance on stem cell research is not settled. The main tenets, the prohibition against harming or destroying others (ahimsa) and the pursuit of knowledge (prajña) and compassion (karuna), leave Buddhist scholars and communities divided. [56] Some scholars argue stem cell research is in accordance with the Buddhist tenet of seeking knowledge and ending human suffering. Others feel it violates the principle of not harming others. Finding the balance between these two points relies on the karmic burden of Buddhist morality. In trying to prevent ahimsa towards the embryo, Buddhist scholars suggest that to comply with Buddhist tenets, research cannot be done as the embryo has personhood at the moment of conception and would reincarnate immediately, harming the individual's ability to build their karmic burden. [57] On the other hand, the Bodhisattvas, those considered to be on the path to enlightenment or Nirvana, have given organs and flesh to others to help alleviate grieving and to benefit all. [58] Acceptance varies on applied beliefs and interpretations.
Catholicism does not support embryonic stem cell research, as it entails creation or destruction of human embryos. This destruction conflicts with the belief in the sanctity of life. For example, in the Old Testament, Genesis describes humanity as being created in God’s image and multiplying on the Earth, referencing the sacred rights to human conception and the purpose of development and life. In the Ten Commandments, the tenet that one should not kill has numerous interpretations where killing could mean murder or shedding of the sanctity of life, demonstrating the high value of human personhood. In other books, the theological conception of when life begins is interpreted as in utero, [59] highlighting the inviolability of life and its formation in vivo to make a religious point for accepting such research as relatively limited, if at all. [60] The Vatican has released ethical directives to help apply a theological basis to modern-day conflicts. The Magisterium of the Church states that “unless there is a moral certainty of not causing harm,” experimentation on fetuses, fertilized cells, stem cells, or embryos constitutes a crime. [61] Such procedures would not respect the human person who exists at these stages, according to Catholicism. Damages to the embryo are considered gravely immoral and illicit. [62] Although the Catholic Church officially opposes abortion, surveys demonstrate that many Catholic people hold pro-choice views, whether due to the context of conception, stage of pregnancy, threat to the mother’s life, or for other reasons, demonstrating that practicing members can also accept some but not all tenets. [63]
Some major Jewish denominations, such as the Reform, Conservative, and Reconstructionist movements, are open to supporting ESC use or research as long as it is for saving a life. [64] Within Judaism, the Talmud, or study, gives personhood to the child at birth and emphasizes that life does not begin at conception: [65]
“If she is found pregnant, until the fortieth day it is mere fluid,” [66]
Whereas most religions prioritize the status of human embryos, the Halakah (Jewish religious law) states that to save one life, most other religious laws can be ignored because it is in pursuit of preservation. [67] Stem cell research is accepted due to application of these religious laws.
We recognize that all religions contain subsets and sects. The variety of environmental and cultural differences within religious groups requires further analysis to respect the flexibility of religious thoughts and practices. We make no presumptions that all cultures require notions of autonomy or morality as under the common morality theory , which asserts a set of universal moral norms that all individuals share provides moral reasoning and guides ethical decisions. [68] We only wish to show that the interaction with morality varies between cultures and countries.
III. A Flexible Ethical Approach
The plurality of different moral approaches described above demonstrates that there can be no universally acceptable uniform law for ESC on a global scale. Instead of developing one standard, flexible ethical applications must be continued. We recommend local guidelines that incorporate important cultural and ethical priorities.
While the Declaration of Helsinki is more relevant to people in clinical trials receiving ESC products, in keeping with the tradition of protections for research subjects, consent of the donor is an ethical requirement for ESC donation in many jurisdictions including the US, Canada, and Europe. [69] The Declaration of Helsinki provides a reference point for regulatory standards and could potentially be used as a universal baseline for obtaining consent prior to gamete or embryo donation.
For instance, in Columbia University’s egg donor program for stem cell research, donors followed standard screening protocols and “underwent counseling sessions that included information as to the purpose of oocyte donation for research, what the oocytes would be used for, the risks and benefits of donation, and process of oocyte stimulation” to ensure transparency for consent. [70] The program helped advance stem cell research and provided clear and safe research methods with paid participants. Though paid participation or covering costs of incidental expenses may not be socially acceptable in every culture or context, [71] and creating embryos for ESC research is illegal in many jurisdictions, Columbia’s program was effective because of the clear and honest communications with donors, IRBs, and related stakeholders. This example demonstrates that cultural acceptance of scientific research and of the idea that an egg or embryo does not have personhood is likely behind societal acceptance of donating eggs for ESC research. As noted, many countries do not permit the creation of embryos for research.
Proper communication and education regarding the process and purpose of stem cell research may bolster comprehension and garner more acceptance. “Given the sensitive subject material, a complete consent process can support voluntary participation through trust, understanding, and ethical norms from the cultures and morals participants value. This can be hard for researchers entering countries of different socioeconomic stability, with different languages and different societal values. [72]
An adequate moral foundation in medical ethics is derived from the cultural and religious basis that informs knowledge and actions. [73] Understanding local cultural and religious values and their impact on research could help researchers develop humility and promote inclusion.
IV. Concerns
Some may argue that if researchers all adhere to one ethics standard, protection will be satisfied across all borders, and the global public will trust researchers. However, defining what needs to be protected and how to define such research standards is very specific to the people to which standards are applied. We suggest that applying one uniform guide cannot accurately protect each individual because we all possess our own perceptions and interpretations of social values. [74] Therefore, the issue of not adjusting to the moral pluralism between peoples in applying one standard of ethics can be resolved by building out ethics models that can be adapted to different cultures and religions.
Other concerns include medical tourism, which may promote health inequities. [75] Some countries may develop and approve products derived from ESC research before others, compromising research ethics or drug approval processes. There are also concerns about the sale of unauthorized stem cell treatments, for example, those without FDA approval in the United States. Countries with robust research infrastructures may be tempted to attract medical tourists, and some customers will have false hopes based on aggressive publicity of unproven treatments. [76]
For example, in China, stem cell clinics can market to foreign clients who are not protected under the regulatory regimes. Companies employ a marketing strategy of “ethically friendly” therapies. Specifically, in the case of Beike, China’s leading stem cell tourism company and sprouting network, ethical oversight of administrators or health bureaus at one site has “the unintended consequence of shifting questionable activities to another node in Beike's diffuse network.” [77] In contrast, Jordan is aware of stem cell research’s potential abuse and its own status as a “health-care hub.” Jordan’s expanded regulations include preserving the interests of individuals in clinical trials and banning private companies from ESC research to preserve transparency and the integrity of research practices. [78]
The social priorities of the community are also a concern. The ISSCR explicitly states that guidelines “should be periodically revised to accommodate scientific advances, new challenges, and evolving social priorities.” [79] The adaptable ethics model extends this consideration further by addressing whether research is warranted given the varying degrees of socioeconomic conditions, political stability, and healthcare accessibilities and limitations. An ethical approach would require discussion about resource allocation and appropriate distribution of funds. [80]
While some religions emphasize the sanctity of life from conception, which may lead to public opposition to ESC research, others encourage ESC research due to its potential for healing and alleviating human pain. Many countries have special regulations that balance local views on embryonic personhood, the benefits of research as individual or societal goods, and the protection of human research subjects. To foster understanding and constructive dialogue, global policy frameworks should prioritize the protection of universal human rights, transparency, and informed consent. In addition to these foundational global policies, we recommend tailoring local guidelines to reflect the diverse cultural and religious perspectives of the populations they govern. Ethics models should be adapted to local populations to effectively establish research protections, growth, and possibilities of stem cell research.
For example, in countries with strong beliefs in the moral sanctity of embryos or heavy religious restrictions, an adaptive model can allow for discussion instead of immediate rejection. In countries with limited individual rights and voice in science policy, an adaptive model ensures cultural, moral, and religious views are taken into consideration, thereby building social inclusion. While this ethical consideration by the government may not give a complete voice to every individual, it will help balance policies and maintain the diverse perspectives of those it affects. Embracing an adaptive ethics model of ESC research promotes open-minded dialogue and respect for the importance of human belief and tradition. By actively engaging with cultural and religious values, researchers can better handle disagreements and promote ethical research practices that benefit each society.
This brief exploration of the religious and cultural differences that impact ESC research reveals the nuances of relative ethics and highlights a need for local policymakers to apply a more intense adaptive model.
[1] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[2] Poliwoda, S., Noor, N., Downs, E., Schaaf, A., Cantwell, A., Ganti, L., Kaye, A. D., Mosel, L. I., Carroll, C. B., Viswanath, O., & Urits, I. (2022). Stem cells: a comprehensive review of origins and emerging clinical roles in medical practice. Orthopedic reviews , 14 (3), 37498. https://doi.org/10.52965/001c.37498
[3] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk ; Kimmelman, J., Hyun, I., Benvenisty, N. et al. Policy: Global standards for stem-cell research. Nature 533 , 311–313 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/533311a
[4] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2023). Laboratory-based human embryonic stem cell research, embryo research, and related research activities . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/blog-post-title-one-ed2td-6fcdk
[5] Concerning the moral philosophies of stem cell research, our paper does not posit a personal moral stance nor delve into the “when” of human life begins. To read further about the philosophical debate, consider the following sources:
Sandel M. J. (2004). Embryo ethics--the moral logic of stem-cell research. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 207–209. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048145 ; George, R. P., & Lee, P. (2020, September 26). Acorns and Embryos . The New Atlantis. https://www.thenewatlantis.com/publications/acorns-and-embryos ; Sagan, A., & Singer, P. (2007). The moral status of stem cells. Metaphilosophy , 38 (2/3), 264–284. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24439776 ; McHugh P. R. (2004). Zygote and "clonote"--the ethical use of embryonic stem cells. The New England journal of medicine , 351 (3), 209–211. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMp048147 ; Kurjak, A., & Tripalo, A. (2004). The facts and doubts about beginning of the human life and personality. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences , 4 (1), 5–14. https://doi.org/10.17305/bjbms.2004.3453
[6] Vazin, T., & Freed, W. J. (2010). Human embryonic stem cells: derivation, culture, and differentiation: a review. Restorative neurology and neuroscience , 28 (4), 589–603. https://doi.org/10.3233/RNN-2010-0543
[7] Socially, at its core, the Western approach to ethics is widely principle-based, autonomy being one of the key factors to ensure a fundamental respect for persons within research. For information regarding autonomy in research, see: Department of Health, Education, and Welfare, & National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research (1978). The Belmont Report. Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research.; For a more in-depth review of autonomy within the US, see: Beauchamp, T. L., & Childress, J. F. (1994). Principles of Biomedical Ethics . Oxford University Press.
[8] Sherley v. Sebelius , 644 F.3d 388 (D.C. Cir. 2011), citing 45 C.F.R. 46.204(b) and [42 U.S.C. § 289g(b)]. https://www.cadc.uscourts.gov/internet/opinions.nsf/6c690438a9b43dd685257a64004ebf99/$file/11-5241-1391178.pdf
[9] Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act of 2005, H. R. 810, 109 th Cong. (2001). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/109/hr810/text ; Bush, G. W. (2006, July 19). Message to the House of Representatives . National Archives and Records Administration. https://georgewbush-whitehouse.archives.gov/news/releases/2006/07/20060719-5.html
[10] National Archives and Records Administration. (2009, March 9). Executive order 13505 -- removing barriers to responsible scientific research involving human stem cells . National Archives and Records Administration. https://obamawhitehouse.archives.gov/the-press-office/removing-barriers-responsible-scientific-research-involving-human-stem-cells
[11] Hurlbut, W. B. (2006). Science, Religion, and the Politics of Stem Cells. Social Research , 73 (3), 819–834. http://www.jstor.org/stable/40971854
[12] Akpa-Inyang, Francis & Chima, Sylvester. (2021). South African traditional values and beliefs regarding informed consent and limitations of the principle of respect for autonomy in African communities: a cross-cultural qualitative study. BMC Medical Ethics . 22. 10.1186/s12910-021-00678-4.
[13] Source for further reading: Tangwa G. B. (2007). Moral status of embryonic stem cells: perspective of an African villager. Bioethics , 21(8), 449–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8519.2007.00582.x , see also Mnisi, F. M. (2020). An African analysis based on ethics of Ubuntu - are human embryonic stem cell patents morally justifiable? African Insight , 49 (4).
[14] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics , 22 (2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[15] Jecker, N. S., & Atuire, C. (2021). Bioethics in Africa: A contextually enlightened analysis of three cases. Developing World Bioethics, 22(2), 112–122. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12324
[16] Jackson, C.S., Pepper, M.S. Opportunities and barriers to establishing a cell therapy programme in South Africa. Stem Cell Res Ther 4 , 54 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt204 ; Pew Research Center. (2014, May 1). Public health a major priority in African nations . Pew Research Center’s Global Attitudes Project. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2014/05/01/public-health-a-major-priority-in-african-nations/
[17] Department of Health Republic of South Africa. (2021). Health Research Priorities (revised) for South Africa 2021-2024 . National Health Research Strategy. https://www.health.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2022/05/National-Health-Research-Priorities-2021-2024.pdf
[18] Oosthuizen, H. (2013). Legal and Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research in South Africa. In: Beran, R. (eds) Legal and Forensic Medicine. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-32338-6_80 , see also: Gaobotse G (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[19] United States Bureau of Citizenship and Immigration Services. (1998). Tunisia: Information on the status of Christian conversions in Tunisia . UNHCR Web Archive. https://webarchive.archive.unhcr.org/20230522142618/https://www.refworld.org/docid/3df0be9a2.html
[20] Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[21] Kooli, C. Review of assisted reproduction techniques, laws, and regulations in Muslim countries. Middle East Fertil Soc J 24 , 8 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43043-019-0011-0 ; Gaobotse, G. (2018) Stem Cell Research in Africa: Legislation and Challenges. J Regen Med 7:1. doi: 10.4172/2325-9620.1000142
[22] Pang M. C. (1999). Protective truthfulness: the Chinese way of safeguarding patients in informed treatment decisions. Journal of medical ethics , 25(3), 247–253. https://doi.org/10.1136/jme.25.3.247
[23] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[24] Wang, Y., Xue, Y., & Guo, H. D. (2022). Intervention effects of traditional Chinese medicine on stem cell therapy of myocardial infarction. Frontiers in pharmacology , 13 , 1013740. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.1013740
[25] Li, X.-T., & Zhao, J. (2012). Chapter 4: An Approach to the Nature of Qi in TCM- Qi and Bioenergy. In Recent Advances in Theories and Practice of Chinese Medicine (p. 79). InTech.
[26] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[27] Luo, D., Xu, Z., Wang, Z., & Ran, W. (2021). China's Stem Cell Research and Knowledge Levels of Medical Practitioners and Students. Stem cells international , 2021 , 6667743. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6667743
[28] Zhang, J. Y. (2017). Lost in translation? accountability and governance of Clinical Stem Cell Research in China. Regenerative Medicine , 12 (6), 647–656. https://doi.org/10.2217/rme-2017-0035
[29] Wang, L., Wang, F., & Zhang, W. (2021). Bioethics in China’s biosecurity law: Forms, effects, and unsettled issues. Journal of law and the biosciences , 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1093/jlb/lsab019 https://academic.oup.com/jlb/article/8/1/lsab019/6299199
[30] Chen, H., Wei, T., Wang, H. et al. Association of China’s two-child policy with changes in number of births and birth defects rate, 2008–2017. BMC Public Health 22 , 434 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12839-0
[31] Azuma, K. Regulatory Landscape of Regenerative Medicine in Japan. Curr Stem Cell Rep 1 , 118–128 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40778-015-0012-6
[32] Harris, R. (2005, May 19). Researchers Report Advance in Stem Cell Production . NPR. https://www.npr.org/2005/05/19/4658967/researchers-report-advance-in-stem-cell-production
[33] Park, S. (2012). South Korea steps up stem-cell work. Nature . https://doi.org/10.1038/nature.2012.10565
[34] Resnik, D. B., Shamoo, A. E., & Krimsky, S. (2006). Fraudulent human embryonic stem cell research in South Korea: lessons learned. Accountability in research , 13 (1), 101–109. https://doi.org/10.1080/08989620600634193 .
[35] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[36] Association for the Advancement of Blood and Biotherapies. https://www.aabb.org/regulatory-and-advocacy/regulatory-affairs/regulatory-for-cellular-therapies/international-competent-authorities/saudi-arabia
[37] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21 (1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
[38] Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: Interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics , 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6
Culturally, autonomy practices follow a relational autonomy approach based on a paternalistic deontological health care model. The adherence to strict international research policies and religious pillars within the regulatory environment is a great foundation for research ethics. However, there is a need to develop locally targeted ethics approaches for research (as called for in Alahmad, G., Aljohani, S., & Najjar, M. F. (2020). Ethical challenges regarding the use of stem cells: interviews with researchers from Saudi Arabia. BMC medical ethics, 21(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12910-020-00482-6), this decision-making approach may help advise a research decision model. For more on the clinical cultural autonomy approaches, see: Alabdullah, Y. Y., Alzaid, E., Alsaad, S., Alamri, T., Alolayan, S. W., Bah, S., & Aljoudi, A. S. (2022). Autonomy and paternalism in Shared decision‐making in a Saudi Arabian tertiary hospital: A cross‐sectional study. Developing World Bioethics , 23 (3), 260–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/dewb.12355 ; Bukhari, A. A. (2017). Universal Principles of Bioethics and Patient Rights in Saudi Arabia (Doctoral dissertation, Duquesne University). https://dsc.duq.edu/etd/124; Ladha, S., Nakshawani, S. A., Alzaidy, A., & Tarab, B. (2023, October 26). Islam and Bioethics: What We All Need to Know . Columbia University School of Professional Studies. https://sps.columbia.edu/events/islam-and-bioethics-what-we-all-need-know
[39] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[40] Ababneh, M. A., Al-Azzam, S. I., Alzoubi, K., Rababa’h, A., & Al Demour, S. (2021). Understanding and attitudes of the Jordanian public about clinical research ethics. Research Ethics , 17 (2), 228-241. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016120966779
[41] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[42] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[43] The EU’s definition of autonomy relates to the capacity for creating ideas, moral insight, decisions, and actions without constraint, personal responsibility, and informed consent. However, the EU views autonomy as not completely able to protect individuals and depends on other principles, such as dignity, which “expresses the intrinsic worth and fundamental equality of all human beings.” Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[44] Council of Europe. Convention for the protection of Human Rights and Dignity of the Human Being with regard to the Application of Biology and Medicine: Convention on Human Rights and Biomedicine (ETS No. 164) https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list?module=treaty-detail&treatynum=164 (forbidding the creation of embryos for research purposes only, and suggests embryos in vitro have protections.); Also see Drabiak-Syed B. K. (2013). New President, New Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research Policy: Comparative International Perspectives and Embryonic Stem Cell Research Laws in France. Biotechnology Law Report , 32 (6), 349–356. https://doi.org/10.1089/blr.2013.9865
[45] Rendtorff, J.D., Kemp, P. (2019). Four Ethical Principles in European Bioethics and Biolaw: Autonomy, Dignity, Integrity and Vulnerability. In: Valdés, E., Lecaros, J. (eds) Biolaw and Policy in the Twenty-First Century. International Library of Ethics, Law, and the New Medicine, vol 78. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-05903-3_3
[46] Tomuschat, C., Currie, D. P., Kommers, D. P., & Kerr, R. (Trans.). (1949, May 23). Basic law for the Federal Republic of Germany. https://www.btg-bestellservice.de/pdf/80201000.pdf
[47] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Germany . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-germany
[48] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Finland . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-finland
[49] Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Spain . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-spain
[50] Some sources to consider regarding ethics models or regulatory oversights of other cultures not covered:
Kara MA. Applicability of the principle of respect for autonomy: the perspective of Turkey. J Med Ethics. 2007 Nov;33(11):627-30. doi: 10.1136/jme.2006.017400. PMID: 17971462; PMCID: PMC2598110.
Ugarte, O. N., & Acioly, M. A. (2014). The principle of autonomy in Brazil: one needs to discuss it ... Revista do Colegio Brasileiro de Cirurgioes , 41 (5), 374–377. https://doi.org/10.1590/0100-69912014005013
Bharadwaj, A., & Glasner, P. E. (2012). Local cells, global science: The rise of embryonic stem cell research in India . Routledge.
For further research on specific European countries regarding ethical and regulatory framework, we recommend this database: Regulation of Stem Cell Research in Europe . Eurostemcell. (2017, April 26). https://www.eurostemcell.org/regulation-stem-cell-research-europe
[51] Klitzman, R. (2006). Complications of culture in obtaining informed consent. The American Journal of Bioethics, 6(1), 20–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/15265160500394671 see also: Ekmekci, P. E., & Arda, B. (2017). Interculturalism and Informed Consent: Respecting Cultural Differences without Breaching Human Rights. Cultura (Iasi, Romania) , 14 (2), 159–172.; For why trust is important in research, see also: Gray, B., Hilder, J., Macdonald, L., Tester, R., Dowell, A., & Stubbe, M. (2017). Are research ethics guidelines culturally competent? Research Ethics , 13 (1), 23-41. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016116650235
[52] The Qur'an (M. Khattab, Trans.). (1965). Al-Mu’minun, 23: 12-14. https://quran.com/23
[53] Lenfest, Y. (2017, December 8). Islam and the beginning of human life . Bill of Health. https://blog.petrieflom.law.harvard.edu/2017/12/08/islam-and-the-beginning-of-human-life/
[54] Aksoy, S. (2005). Making regulations and drawing up legislation in Islamic countries under conditions of uncertainty, with special reference to embryonic stem cell research. Journal of Medical Ethics , 31: 399-403.; see also: Mahmoud, Azza. "Islamic Bioethics: National Regulations and Guidelines of Human Stem Cell Research in the Muslim World." Master's thesis, Chapman University, 2022. https://doi.org/10.36837/ chapman.000386
[55] Rashid, R. (2022). When does Ensoulment occur in the Human Foetus. Journal of the British Islamic Medical Association , 12 (4). ISSN 2634 8071. https://www.jbima.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/2-Ethics-3_-Ensoulment_Rafaqat.pdf.
[56] Sivaraman, M. & Noor, S. (2017). Ethics of embryonic stem cell research according to Buddhist, Hindu, Catholic, and Islamic religions: perspective from Malaysia. Asian Biomedicine,8(1) 43-52. https://doi.org/10.5372/1905-7415.0801.260
[57] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[58] Lecso, P. A. (1991). The Bodhisattva Ideal and Organ Transplantation. Journal of Religion and Health , 30 (1), 35–41. http://www.jstor.org/stable/27510629 ; Bodhisattva, S. (n.d.). The Key of Becoming a Bodhisattva . A Guide to the Bodhisattva Way of Life. http://www.buddhism.org/Sutras/2/BodhisattvaWay.htm
[59] There is no explicit religious reference to when life begins or how to conduct research that interacts with the concept of life. However, these are relevant verses pertaining to how the fetus is viewed. (( King James Bible . (1999). Oxford University Press. (original work published 1769))
Jerimiah 1: 5 “Before I formed thee in the belly I knew thee; and before thou camest forth out of the womb I sanctified thee…”
In prophet Jerimiah’s insight, God set him apart as a person known before childbirth, a theme carried within the Psalm of David.
Psalm 139: 13-14 “…Thou hast covered me in my mother's womb. I will praise thee; for I am fearfully and wonderfully made…”
These verses demonstrate David’s respect for God as an entity that would know of all man’s thoughts and doings even before birth.
[60] It should be noted that abortion is not supported as well.
[61] The Vatican. (1987, February 22). Instruction on Respect for Human Life in Its Origin and on the Dignity of Procreation Replies to Certain Questions of the Day . Congregation For the Doctrine of the Faith. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/congregations/cfaith/documents/rc_con_cfaith_doc_19870222_respect-for-human-life_en.html
[62] The Vatican. (2000, August 25). Declaration On the Production and the Scientific and Therapeutic Use of Human Embryonic Stem Cells . Pontifical Academy for Life. https://www.vatican.va/roman_curia/pontifical_academies/acdlife/documents/rc_pa_acdlife_doc_20000824_cellule-staminali_en.html ; Ohara, N. (2003). Ethical Consideration of Experimentation Using Living Human Embryos: The Catholic Church’s Position on Human Embryonic Stem Cell Research and Human Cloning. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology . Retrieved from https://article.imrpress.com/journal/CEOG/30/2-3/pii/2003018/77-81.pdf.
[63] Smith, G. A. (2022, May 23). Like Americans overall, Catholics vary in their abortion views, with regular mass attenders most opposed . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/05/23/like-americans-overall-catholics-vary-in-their-abortion-views-with-regular-mass-attenders-most-opposed/
[64] Rosner, F., & Reichman, E. (2002). Embryonic stem cell research in Jewish law. Journal of halacha and contemporary society , (43), 49–68.; Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[65] Schenker J. G. (2008). The beginning of human life: status of embryo. Perspectives in Halakha (Jewish Religious Law). Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 25 (6), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-008-9221-6
[66] Ruttenberg, D. (2020, May 5). The Torah of Abortion Justice (annotated source sheet) . Sefaria. https://www.sefaria.org/sheets/234926.7?lang=bi&with=all&lang2=en
[67] Jafari, M., Elahi, F., Ozyurt, S. & Wrigley, T. (2007). 4. Religious Perspectives on Embryonic Stem Cell Research. In K. Monroe, R. Miller & J. Tobis (Ed.), Fundamentals of the Stem Cell Debate: The Scientific, Religious, Ethical, and Political Issues (pp. 79-94). Berkeley: University of California Press. https://escholarship.org/content/qt9rj0k7s3/qt9rj0k7s3_noSplash_f9aca2e02c3777c7fb76ea768ba458f0.pdf https://doi.org/10.1525/9780520940994-005
[68] Gert, B. (2007). Common morality: Deciding what to do . Oxford Univ. Press.
[69] World Medical Association (2013). World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA , 310(20), 2191–2194. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2013.281053 Declaration of Helsinki – WMA – The World Medical Association .; see also: National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research . U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html
[70] Zakarin Safier, L., Gumer, A., Kline, M., Egli, D., & Sauer, M. V. (2018). Compensating human subjects providing oocytes for stem cell research: 9-year experience and outcomes. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics , 35 (7), 1219–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1171-z https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6063839/ see also: Riordan, N. H., & Paz Rodríguez, J. (2021). Addressing concerns regarding associated costs, transparency, and integrity of research in recent stem cell trial. Stem Cells Translational Medicine , 10 (12), 1715–1716. https://doi.org/10.1002/sctm.21-0234
[71] Klitzman, R., & Sauer, M. V. (2009). Payment of egg donors in stem cell research in the USA. Reproductive biomedicine online , 18 (5), 603–608. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60002-8
[72] Krosin, M. T., Klitzman, R., Levin, B., Cheng, J., & Ranney, M. L. (2006). Problems in comprehension of informed consent in rural and peri-urban Mali, West Africa. Clinical trials (London, England) , 3 (3), 306–313. https://doi.org/10.1191/1740774506cn150oa
[73] Veatch, Robert M. Hippocratic, Religious, and Secular Medical Ethics: The Points of Conflict . Georgetown University Press, 2012.
[74] Msoroka, M. S., & Amundsen, D. (2018). One size fits not quite all: Universal research ethics with diversity. Research Ethics , 14 (3), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747016117739939
[75] Pirzada, N. (2022). The Expansion of Turkey’s Medical Tourism Industry. Voices in Bioethics , 8 . https://doi.org/10.52214/vib.v8i.9894
[76] Stem Cell Tourism: False Hope for Real Money . Harvard Stem Cell Institute (HSCI). (2023). https://hsci.harvard.edu/stem-cell-tourism , See also: Bissassar, M. (2017). Transnational Stem Cell Tourism: An ethical analysis. Voices in Bioethics , 3 . https://doi.org/10.7916/vib.v3i.6027
[77] Song, P. (2011) The proliferation of stem cell therapies in post-Mao China: problematizing ethical regulation, New Genetics and Society , 30:2, 141-153, DOI: 10.1080/14636778.2011.574375
[78] Dajani, R. (2014). Jordan’s stem-cell law can guide the Middle East. Nature 510, 189. https://doi.org/10.1038/510189a
[79] International Society for Stem Cell Research. (2024). Standards in stem cell research . International Society for Stem Cell Research. https://www.isscr.org/guidelines/5-standards-in-stem-cell-research
[80] Benjamin, R. (2013). People’s science bodies and rights on the Stem Cell Frontier . Stanford University Press.
Mifrah Hayath
SM Candidate Harvard Medical School, MS Biotechnology Johns Hopkins University
Olivia Bowers
MS Bioethics Columbia University (Disclosure: affiliated with Voices in Bioethics)
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License .
Supervisors’ emotion regulation in research supervision: navigating dilemmas in an accountability-based context
- Open access
- Published: 18 May 2024
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Jiying Han 1 ,
- Lei Jin 1 &
- Hongbiao Yin ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5424-587X 2
Given the complexity and high demands of research supervision and the intricate emotional experiences of supervisors, there is a need to explore how they regulate their emotions, particularly across various disciplinary backgrounds. The current study explored the emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors during the process of supervising graduate students. Based on data collected through semi-structured interviews, observations, and documentation from six research supervisors in different institutions in China, seven emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors were identified and further categorized into two groups, that is, antecedent-focused (prevention, intervention, reinterpretation, reconcentration, and detachment) and response-focused (suppression and expression) emotion regulation strategies. The findings shed light on the dilemmas faced by supervisors and the paradox aroused from the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision within an accountability-based managerial context. The implications for supervisors’ emotion regulation in authentic supervisory situations are discussed, and insights for universities’ policy-making are offered.
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Introduction
Since the 1990s, educational research has undergone an “affective turn” as a result of the critique of the long-standing Cartesian dualism between emotionality and rationality (Zembylas, 2021 ). Over the following three decades, the dynamic and complex nature of teacher emotion has been explored from various perspectives and approaches (Agudo, 2018 ). Since emotion can significantly impact various stages of the teaching process, either facilitating or hindering it (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ), opportunities for emotion regulation can be identified in educational contexts at any time (Taxer & Gross, 2018 ). In higher education, although emotion regulation has been proven significant to teacher development and well-being (Xie, 2021 ), the majority of research has been conducted within the context of classroom instruction (Tao et al., 2022 ), leaving that of research supervision in graduate education unexplored.
In graduate education, emotion plays an important role in the supervisory process and relationship building which involves a series of emotional interactions essential for both supervisors and graduate students. The existing research has demonstrated an increasing need for supervisors to develop emotion regulation skills to cope with the challenges and provide emotional support in research supervision (Wollast et al., 2023 ). On the one hand, supervisors need to employ emotion regulation strategies in the challenging supervisory contexts, as accountability-based policies and the blurring of personal and academic relationships between supervisors and graduate students may trigger complex emotional experiences such as anxiety and worry for supervisors (Xu, 2021 ). On the other hand, the provision of support from supervisors is strongly linked to the emotional well-being and research success of graduate students (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ). Specifically, supervisors’ emotion regulation plays a crucial role in providing emotional support to graduate students, which in turn has a positive impact on graduate students’ well-being and their belief about their further academic pursuits (Han & Xu, 2023 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ).
Of the limited research on emotion in graduate education, much has been conducted to investigate the influence of graduate students’ emotion regulation on their mental health and academic engagement (Saleem et al., 2022 ). However, there is a paucity of studies which have researched supervisors’ emotions and emotion regulation during the supervisory process. With the aim of unpacking how research supervisors employ emotion regulation strategies in real supervisory scenarios to effectively fulfill their roles, and to gain insights into the nature of research supervision, this qualitative study explores the emotion regulation strategies used by supervisors in the process of research supervision.
Literature review
Teacher emotion and emotion regulation.
Emotion, once considered inferior to cognition, has gained increasing attention in the social sciences, including in educational research (Han & Xu, 2023 ). The current recognition of the intricate interplay between emotion and cognition in teaching and learning highlights the importance of emphasizing teacher emotion in both teacher development and teacher well-being (Chen & Cheng, 2022 ). Emotion is complex and difficult to define (Chen & Cheng, 2022 ), and the connotation of emotion has shifted from an intrapersonal perspective to a relational one, emphasizing interactions between individuals and their environment during emotion generation (Campos et al., 2011 ).
Under the relational view of emotion, individuals can achieve social goals in most jobs involving interpersonal interactions through emotion regulation (Brotheridge & Grandey, 2002 ). Emotion regulation refers to “the processes by which individuals influence which emotions they have, when they have them, and how they experienced and expressed their emotions” (Gross, 1998 , p. 275). In the educational field, a growing interest of research in emotion regulation has emerged since the 1990s (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ; Zembylas, 2021 ), as teaching has been viewed as “an emotional practice” (Hargreaves, 1998 , p. 835). Due to the importance of emotion in teachers’ professional lives, it is crucial for teachers to regulate their emotions to achieve improved teaching and learning outcomes. Specifically, enhancing positive emotions can foster better teacher-student relationships, promote creativity in teaching, and strengthen students’ learning motivation; inappropriately managed negative emotions can have adverse effects on these aspects (Hargreaves, 1998 ). Although teachers’ emotion regulation has been widely examined (e.g., Taxer & Frenzel, 2015 ; Yin, 2015 , 2016a , 2016b ; Yin et al., 2018 ) most studies, influenced by the concept of emotional labor, have mainly focused on two types of emotion regulation strategies: deep acting (the act of internalizing a desired emotion, matching expressed emotion with felt emotion) and surface acting (the act of altering emotional expression without regulating inner feelings) (Grandey, 2000 ; Hochschild, 1983 ). Comparatively, Gross’s ( 1998 ) process model of emotion regulation provides a more nuanced framework to examine teachers’ employment of a wider range of emotion regulation strategies. According to Gross ( 1998 , 2015 ), emotion regulation could be achieved through two main approaches: the antecedent-focused and response-focused approach. The former entails strategies that seek to avoid or regulate emotions by modifying the factors triggering emotion generation, which include situation selection, situation modification, attention deployment, and cognitive changes. The latter modifies an individual’s expressions and responses after the emotions have fully manifested, directly influencing physiological, experiential, or behavioral responses.
In recent years, the predominant focus of studies, guided by Gross’s ( 1998 ) process model, has been on investigating the motivations, strategies, and outcomes of teachers’ intrapersonal emotion regulation (e.g., Taxer & Gross, 2018 ; To & Yin, 2021 ; Xu, 2021 ). Teachers’ motivations for emotional regulation stem from their diverse teaching goals, including managing the impressions that various parties have of them, adapting to intensive educational reforms for survival, and enhancing students’ concentration levels (Hosotani, 2011 ; Xu, 2021 ). As for emotion regulation strategies, the existing literature has mainly been conducted under Gross’s ( 2015 ) model, and revealed a series of antecedent-focused (e.g., situation selection, attention deployment, and cognitive change) and response-focused strategies (e.g., suppression, relaxation, and avoidance) to cope with the ambivalent demands and enormous workload faced by teachers. Remarkably, certain strategies that reflect the unique nature of teachers’ work, such as genuine expression (Yin, 2015 ; Yin, 2016a , 2016b ) and interpersonal strategies (To & Yin, 2021 ), have been identified. Regarding outcomes of emotion regulation, genuine expression of emotion and cognitive appraisal strategies were found helpful to improve the effectiveness of classroom teaching and to maintain a balance between teachers’ professional and personal dimensions of their identities (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ). In contrast, suppressing, pretending, and restraining emotions may cause emotional dissonance and less received social support (Yin, 2015 ).
Emotion regulation and research supervision
In graduate education, supervisors’ emotional experiences are triggered by the complexity and high demands of research supervision (Han & Xu, 2023 ). The conflicting roles of taking responsibility for both supporter and supervisor simultaneously, the contradiction between supervisors’ high expectations of students’ learning autonomy and graduate students’ unsatisfactory performance, and the blurred boundaries between supervisory relationship and friendship (Han & Xu, 2023 ; Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ) are major challenges encountered by research supervisors. These challenges lead to various emotional experiences on the part of supervisors, including positive emotions, such as joy and love (Halse & Malfroy, 2010 ), and more prevalent negative emotions, such as anger, and disappointment (Sambrook et al., 2008 ). Given the diverse range of emotions that emerge during the supervision process, it is necessary for supervisors to employ various emotion regulation strategies to accomplish effective research supervision.
According to literature, emotion regulation is strongly associated with research supervision in three areas. First, effective research supervision requires a constructive and supportive supervisory relationship, which is facilitated by supervisors’ emotion regulation. As poorly managed supervision relationships contribute to low academic completion rates, supervisors are required to establish a respectful and caring relationship with their students (Halse & Malfroy, 2010 ). However, creating and maintaining such relationships can be challenging. Specifically, during the interactions with graduate students, supervisors are expected to offer emotional supports, including encouragement, motivation, and recognition based on students’ individual needs while ensuring that any critical feedback is delivered constructively (Lee, 2008 ). However, excessive emotional engagement or close relationships with students may hinder their ability to provide constructive criticism (Lee, 2008 ). As such, supervisors must strike a balance between offering emotional support and providing constructive feedback, thereby developing a successful educational partnership with their students.
Second, the emotional support provided by supervisors plays a positive role in facilitating graduate students’ research productivity and emotional well-being (Han & Wang, 2024 ; Wollast et al., 2023 ). In terms of research success, supervisors who encourage critical thinking and support constructive controversies tend to produce higher achievement and retention rates than those who adopt a directive and authoritarian approach (Johnson, 2001 ). Furthermore, emotional support from supervisors has been linked to higher levels of research self-efficacy and emotional well-being among graduate students (Diekman et al., 2011 ). Specifically, structure and autonomy support strongly influence graduate students’ feelings and expectations about their future academic success. Thus, in academic settings, supervisors should adopt effective emotion regulation strategies, offering constructive feedback, close guidance, and attentiveness to maintain graduate students’ motivation and mental well-being.
Third, effective emotion regulation is also critical for the well-being of research supervisors themselves. When faced with repeated frustrating events such as a lack of student progress and demanding requirements in accountability-based supervisory contexts, supervisors may experience feelings of exhaustion, particularly when they perceive their supportive efforts as being ineffective (Xu, 2021 ). Failing to regulate these negative emotions with effective strategies can lead to the accumulation and intensification of undesirable feelings, resulting in detrimental effects on supervisors’ well-being and job satisfaction, which may ultimately lead to their emotional burnout and disengagement (To & Yin, 2021 ).
So far, the very limited research on research supervisors’ emotion regulation in medical and scientific disciplines found that although supervisors use instructional strategy modification (e.g., directly pointing out students’ writing deficiencies), cognitive change (e.g., reappraising the relationship between students’ underachievement and their supervision), and response regulation (e.g., lowering their voice to calm themselves) to deal with negative emotions (Han & Xu, 2023 ), they still have difficulties in stepping out of negative emotions (Sambrook et al., 2008 ). Meanwhile, supervisors from different disciplines may use different emotion regulation strategies due to disciplinary differences in occupational challenges, societal expectations, and specific work environments (Veniger & Kočar, 2018 ). Therefore, it is necessary for researchers to investigate the emotion regulation of supervisors with different disciplinary backgrounds.
Based on the literature, underpinned by Gross’s ( 2015 ) process model, the present qualitative multi-case study aims to investigate the emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors from different disciplinary backgrounds. Specifically, the study seeks to answer this core research question: What strategies do research supervisors use to regulate their emotions during the supervision process?
As the in-depth understanding of supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies relies on the narratives of their journey of research supervision, we used narrative inquiry to explore supervisors’ lived experiences in supervising graduate students. Narrative inquiry emphasizes the co-construction of specific experiences by the researcher and participants (Friedensen et al., 2024 ; Riessman, 2008 ), which allows us to co-construct the meaning of emotion regulation with participants through qualitative data including interviews, observations, and documents.
Research context: Emphasizing the accountability of research supervision
The Chinese research supervision system has its roots in the nineteenth century, evolving alongside the development of graduate education (Xie & Zhu, 2008 ). Within this system, research supervisors play a crucial role in research-based master’s and doctoral education. In 1961, a supervisor accountability system was formalized, placing the responsibility on supervisors for overseeing students in research projects, journal publications, and dissertation completion. Under the guidance of supervisors, students engage in specialized courses, master the latest advancements in a specific field, and conduct research (Peng, 2015 ).
In recent years, with the rapid growth of graduate education in China, both supervisors and graduate students have expressed concerns about the quality of research supervision (Xu & Liu, 2023 ). Thus, national policies have been introduced to stipulate supervisors’ responsibilities and enhance the overall supervision quality, with a particular emphasis on the accountability of research supervisors. In 2020, the Accountability Measures for Educational Supervision, released by China’s Ministry of Education ( 2020 ), outlined a code of conduct for supervisors, emphasizing that supervisors bear the primary responsibility for cultivating postgraduate students. Specifically, supervisors are held accountable for various aspects of graduate students’ academic progress, including the quality of dissertations, academic conduct, and the appropriate utilization of research funds. Failure to fulfill these responsibilities may result in serious consequences, such as disqualification from supervising students or the revocation of teaching credentials.
Participants
To explore a wide range of emotional experiences and emotion regulation strategies that arise when supervising students at various stages of their academic journey, participants were purposively selected based on the following three criteria: (1) doctoral supervisors with the qualifications to oversee research-based master’s students and PhD candidates were considered, which allows us to gain insights into their emotions in supervising students at different academic stages; (2) supervisors with a minimum of 5 years of supervision were selected, as their long-term experience would provide a comprehensive understanding of the depth and evolution of emotion regulation strategies; (3) supervisors of both hard and soft disciplines were involved, as disciplinary features may significantly shape supervisors’ styles, potentially leading to their diverse emotions and emotion regulation strategies. Finally, six doctoral supervisors from four universities in China agreed to participate in the study voluntarily and were informed of the research purpose and ethical principles before the study. Table 1 provides a summary of the demographic information for all participants.
Data collection
The positionality statement is essential as the authors’ roles may influence the data collection process. Specifically, two authors are doctoral supervisors with rich experience in research supervision, and one author is a doctoral student. Participants for this study were recruited from the authors’ colleagues or recommendations from friends. In the spirit of self-reflexivity, we acknowledge our positions in research supervision and recognize that our relationships with participants may impact our collection and interpretations of the data. However, the authors had attempted to minimize the possible influence through continuous reflection, crosscheck, and discussions during the data analysis and interpretation.
To produce convincing qualitative accounts, collecting data from multiple sources including semi-structured interviews, observations, and documentation was employed in the current study from November 2022 to April 2023.
The primary source of data was individual interviews with each participant. To gather participants’ narratives of critical events in their research supervision, an interview protocol was designed according to our research purpose, but the interview questions were sufficiently flexible to enable the interviewer to adapt the content according to the specific interview situation. The interviews lasted between 120 and 150 min, during which the participants were asked to describe critical events in their research supervision, their emotional experiences, and whether and how they regulated their emotions. Follow-up questions were asked to gain a more profound understanding of their emotion regulation strategies when they provided surprising and ambiguous responses. Sample interview questions included “What emotions do you typically experience as a research supervisor?” and “Do you regulate your emotions induced by research supervision? If so, how?” All interview questions were presented in Chinese, the participants’ first language, and were audio-recorded and transcribed verbatim.
Observation was used to complement the data obtained from interviews. Before the observation, all supervisors and their students were informed about the research purpose and ethical principles. Then non-participant observation during their group and individual meetings proceeded only with their voluntary participation. Supervisors’ supervisory methods, activities, meeting atmosphere, and emotions of meeting members were recorded to supplement and validate the data collected through the interview. A short follow-up interview was then conducted with supervisors, focusing on their reflections on emotional events that occurred during the observed group and individual meetings.
Documentation was also used as a supplementary method. With the consent of the participants and their students, supervisors’ annotations and feedback on graduate students’ manuscripts, unofficial posts about supervision on social media (e.g., WeChat moments sharing), and chat logs between supervisors and students were collected to obtain additional information about the participants’ emotional experiences and supervisory practices. Table 2 presents the interview durations, the total minutes recorded during observations, the length of follow-up interviews, and the specific number and types of documents reviewed by both supervisors and students.
Data analysis
The analysis involved a three-level coding process (Yin, 2016a , 2016b ). First, interview transcripts were repeatedly read to label data excerpts that addressed the research questions. Initial codes were based on participants’ original perspectives and then iteratively refined and combined. Second, the coding system was organized according to Gross’s ( 2015 ) process model of emotional regulation, which distinguishes between antecedent-focused and response-focused strategies. Meanwhile, the study also remained open to other emotion regulation strategies that were evident in the empirical data. Third, the coding system was distilled to capture the nature of the identified strategies, resulting in three types of emotion regulation strategies. During the analysis process, the data were classified and organized using the NVivo software.
To strengthen the credibility of the data analysis, the interview transcripts were carefully examined multiple times to ensure that the data were accurately reflected in the coding scheme. Moreover, the coding scheme was collaboratively developed by the authors, and any discrepancies in classification were thoroughly deliberated to achieve mutual agreement. The final coding system, along with sub-categories and patterns, is presented in Table 3 .
In sum, seven emotion regulation strategies in research supervision emerged from the empirical data, which can be grouped into two categories, namely, antecedent-focused strategies and response-focused strategies.
Antecedent-focused strategies
Supervisors used antecedent-focused strategies to regulate the external situation and their internal cognition before the emotions were generated.
Prevention involves the prediction and avoidance of situations that may lead to undesirable emotional experiences during supervision prior to the generation of emotions. Prevention strategies were frequently utilized in the graduate student recruitment process and early stages of supervision, as a means of avoiding undesirable situations. On the former occasion, supervisors identified multiple recruitment indicators, such as research experiences and GPA, to avoid supervisory situations that may lead to negative emotions. This is commonly related to their former supervisory experience: “It was frustrating to supervise a student who was not invested in her work, so I have to implement a rigorous recruitment process to prioritize candidates who are truly interested in research, rather than rashly recruiting students” (P1-interview).
Supervisors remain vigilant once a supervisory relationship was established, as they are required by accountability-based policies to be responsible for students’ research performance and safety. Many supervisors stressed the significance of “establishing rules and regulations” (P4-interview) in the early stages of supervision to avoid infuriation and disappointment with students’ academic misconduct. Therefore, establishing an academic code of conduct is an effective prevention strategy for supervisors: “I’m frustrated by academic misconduct among students, as discovering data falsification in student-published articles holds me accountable, risking serious consequences for my academic career. So I frequently emphasize the need for high academic honesty and integrity standards” (P2-interview, observation).
Another concern that worried supervisors, especially those of science and technology, is student safety: “Whenever I hear about a laboratory explosion that causes student injuries, it makes me very nervous” (P3-interview, documentation). It is crucial for the institutions and supervisors to establish comprehensive laboratory safety rules and educate students on safety protocols before conducting experiments: “I told my graduate students: Failure to obey laboratory rules and lack of safety awareness can lead to immediate accidents that not only affect yourself but also pose a risk to other students” (P3-interview).
Intervention
Intervention is the most commonly employed strategy by supervisors to enhance the effectiveness of their supervision once a supervisory relationship is established. They employed various intervention strategies to improve students’ academic attitude and develop their academic ability.
Specifically, supervisors improved their students’ engagement and altered procrastination either by scaffolding their research or enforcing discipline and prohibitions. On the one hand, our participants acknowledged the importance of instructional scaffolding in the supervisory process.
We need to cultivate students’ interest so that they can actively engage in research. For instance, I often demonstrate interesting phenomena between the English and Chinese languages to generate my students’ curiosity. Then I am delighted to see their willingness to immerse themselves in linguistic research. (P5-interview)
On the other hand, some supervisors emphasized the enforcement of discipline in supervision. One supervisor expressed disappointment and dissatisfaction with the lackadaisical research atmosphere within the entire research group. In response, she implemented strict discipline and prohibitions to restrict students from engaging in activities unrelated to research in the office (P2-observation).
Finding a student watching a movie in the office angered me as it may disturb other students trying to focus on their studies. So, activities like watching movies and listening to music are not allowed in our office. By rigorously enforcing these rules, our research group was able to collaborate more effectively and ultimately achieve satisfactory results. (P2-interview)
Furthermore, intervention strategies were also used to enhance graduate students’ academic competency. Modifying supervisory activities was considered as a useful method. One supervisor shared: “We used to read literature in our group meeting together, but it was not effective. I felt frustrated and decided to change our meeting activities this semester.” As a result, the supervisor organized students to provide feedback on each other’s manuscripts in weekly group meetings, because “it was very effective in improving their writing abilities” (P1-interview, observation).
Interestingly, some supervisors opted to micromanage students’ research processes when they were disappointed with their research performance
At first, I encouraged students to independently identify research topics, but I later realized with disappointment that it was challenging for them to identify gaps in the existing literature. To make things more efficient, I started assigning research projects directly to help them complete their dissertation and meet the graduation requirements. (P5-interview)
Reinterpretation
Reinterpretation refers to the process of cognitively reappraising a supervisory situation from different perspectives to change its emotional impact. Supervising a graduate student who lacks interest in research was described as a “prolonged and painful undertaking” (P4-interview). However, one supervisor noted that: “Dwelling on negative emotions can be unproductive as it does not necessarily solve problems. Despite the challenging experience, I have gained valuable insights and will be better equipped to handle such situation” (P4-interview).
In addition to explaining the meaning of the situations from supervisors’ viewpoints, they reconsidered the events from graduate students’ perspectives to rationalize their unsatisfactory performance and procrastination. For example, supervisors understood students’ time arrangements when they procrastinated: “I used to become annoyed when students failed to submit assignments punctually… Now I know that students need a balance between work and rest. They need adequate time for rest” (P5-interview).
On occasion, supervisors reappraised the connection between students’ misbehaviors and the effort they invested from the perspective of the teacher-student relationship.
I felt angry when things happened, but I wouldn’t let that emotion affect my life. I see myself as a supervisor to students, not a parent, so I don’t hold high expectations for them. If students choose not to follow my guidance, it’s not my concern anymore. (P6-interview)
Reconcentration
Reconcentration is the strategy by which supervisors focus on another aspect of supervision or divert attention away from supervision with the intent of changing emotional consequences. Specifically, during the supervisory process, supervisors prepared themselves to be optimistic by reminding themselves of their students’ strengths: “I was anxious about a student who always made slow progress in research. But when I later realized that his incremental results were consistently good, indicating that he was very meticulous, I felt much better” (P2-interview, observation).
Apart from diverting attention during supervision in working environments, the participants highlighted the importance of balancing personal and professional life to manage negative emotions that may arise during supervision.
After giving birth, I realized that caring for a child demands a considerable amount of time and energy. Then I redirected my attention from supervising students to my family. Thankfully, my family provides a supportive environment, and the pleasant moments shared with my family members helped me overcome negative emotions associated with work. (P4-interview)
Detachment refers to the act of separating from or terminating the supervisory relationship to disengage from negative emotions. This strategy was often employed when intervention, reinterpretation, and reconcentration strategies were ineffective. When supervisors found that various proactive measures failed to resolve the challenges in research supervision, they experienced enduring feelings of helplessness, confusion, and distress. One supervisor expressed deep frustration, stating, “I’ve exhausted all efforts—careful communication with her and her parents, and providing my support during her experiments. Yet, she continued to resist making progress with her experiments and dissertation. I felt lost in supervising this student” (P4-interview). As a result, they have to release themselves from the emotionally harmful supervisory relationships.
Some supervisors chose to disengage, meaning they no longer actively push the student: “Continuing to push a student who refused to participate in research despite all my efforts would only increase my frustration. I have decided to let him go and will no longer push him” (P5-interview).
In some extreme cases that evoke negative emotions, supervisors even terminated the supervisory relationship.
Supervising this student was a painful experience as his inaction negatively affected the entire research team. Other students started following his behavior and avoided conducting experiments. It made me feel suffocated. I had to terminate my supervision to avoid any further negative impact on the team and myself… I felt relieved after he left. (P3-interview)
Response-focused strategies
Response-focused emotion regulation involves the use of strategies after an emotion has already been generated.
Suppression
Suppression involves consciously attempting to inhibit behavioral and verbal emotional responses. Although supervisors experienced negative moods during research supervision, some refrained from expressing these emotions to students. Certain supervisors believed that criticism hinders problem-solving. One participant explained, “While interacting with students, I found some are genuinely fearful of supervisor authority. In such cases, venting emotions on students only heightens their fear, makes them hesitant to express themselves or their confusion in research, and ultimately hinders their progress” (P1-interview). In addition, some supervisors believed that expressing anger or disappointment toward students could harm their self-efficacy in research. One supervisor stated, “Obtaining a master’s degree is a challenging journey, especially for novice researchers. Confidence is crucial for their success. As a supervisor, I refrain from expressing negative emotions as it can hurt students’ feelings and even damage their confidence” (P3-interview).
As mentioned by the supervisors above, expressing anger and disappointment to graduate students may not resolve issues but damage their self-efficacy. In challenging situations where negative emotions were hard to suppress, supervisors opted to temporarily suspend supervision activities or introduce new tasks to regain composure: “Sometimes revising students’ manuscripts can be a painful task. To avoid the risk of expressing negative emotions to them, I often temporarily suspend the revision. Sometimes I take a walk until I feel calmer and more collected” (P1-interview).
In supervision, expressing emotion is another effective strategy for regulating supervisors’ emotions. Although supervisors were aware that expressing negative emotions may sometimes negatively affect students’ feelings, the importance of their own emotional well-being was emphasized, as “expressing feelings helped me recover from negative moods faster” (P6-interview). However, supervisors had different expressive styles when interacting with their students.
Some supervisors expressed their anger and dissatisfaction to their students directly, through behavioral or verbal emotional responses. A supervisor recounted an incident, “During a phone call with her, I lost my temper because of her terrible attitude, and ended up throwing my phone” (P4-interview).
Interestingly, given that “graduate students are all adults” (P6-interview), some supervisors expressed their emotions more tactfully, taking care not to lose their temper and cause distress to their students. One supervisor “felt angry with a student’s poor writing.” However, instead of scolding the student directly, he made a joke during a one-to-one meeting, saying “It’s not that you wrote poorly. It’s that I am not clever enough to comprehend your writing.” The student laughed, and then the supervision was conducted in a relaxed atmosphere. The supervisor explained: “I do not hide my emotions but prefer to avoid losing my temper and instead use humor to guide my students better” (P5-interview, observation).
This study contributes to the existing literature on emotion regulation by providing detailed insights into how emotion regulation strategies were utilized by research supervisors. It also sheds light on the dilemmas supervisors encounter and the paradox between the context-dependent nature of research supervision and the accountability-based managerial context.
Supervisors’ dilemmas in research supervision
Our study demonstrated supervisors’ capacity to proactively employ diverse emotion regulation strategies when coping with difficulties in research supervision. It also revealed some paradoxical phenomena within the supervisors’ utilization of these emotion regulation strategies, highlighting the dilemmas they encountered in the context of research supervision.
In general, supervisors in our study demonstrated a higher tendency to employ antecedent-focused strategies for emotion regulation rather than response-focused strategies, which can alleviate their emotional burnout and enhance their well-being. Specifically, participants utilized intervention strategies as antecedent-focused strategies to improve the effectiveness of research supervision, rather than seeking consolation to alleviate generated emotions. Previous research has indicated that antecedent-focused strategies were associated with increased life satisfaction (Feinberg et al., 2012 ). By intervening in the emotion generation process at an early stage, these strategies can potentially alter the emotional trajectory, contributing to improved well-being among supervisors (Gross & John, 2003 ).
While supervisors displayed a strong inclination to utilize diverse strategies to enhance the effectiveness of their supervision, our findings unveiled two paradoxical phenomena in their emotion regulation strategies, indicating the dilemmas that supervisors faced in authentic supervisory situations. First, in antecedent-focused strategies aimed at modifying situations that may trigger negative emotions, numerous interventions and detachments highlighted the conflicts supervisors encountered as they strived to balance adequate assistance and excessive interference. Specifically, while participants in our study “inspired students through scaffolding” or “encouraged students’ autonomous learning,” they also “micromanaged students’ research process” or “enforced discipline” to enhance supervision efficiency. This pedagogical paradox concerning the choice between intervening and non-intervening approaches has generated ongoing debate in existing research (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). Both approaches have the potential to evoke negative emotional experiences for supervisors and graduate students. Research found that a highly intervening approach has negative implications for both supervisors and graduate students (Lee, 2020 ). Students who have encountered autonomy-exploitative behavior from their supervisors, such as being restricted to specific research topics and methodologies, have reported experiencing negative emotions (Cheng & Leung, 2022 ). For supervisors, the burden of an intervening approach, the dissonance between supervisors’ expectations and students’ actual research progress, as well as students deviating from conventional practices (Han & Xu, 2023 ), all contribute to feelings of frustration, sadness, and exhaustion. Nevertheless, non-intervening approaches do not always fulfill the expectations of both parties either. Supervisors who encouraged graduate students’ autonomous action acknowledged the value of promoting their independent thinking, which has been identified as a significant predictor of students’ research self-efficacy (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ). However, students who initially expected their supervisors to play a leadership role felt dissatisfied and disappointed when supervisors were reluctant to offer explicit guidance (Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). This misunderstanding of supervisors’ intentions can ultimately generate negative effects on supervisors’ emotional experiences (Xu, 2021 ).
Another evident paradoxical phenomenon arises in the response-focused strategies employed after emotions have already been triggered. Although supervisors opted to suppress their negative emotional expression to safeguard the confidence and self-esteem of mature learners, there were instances when they outpoured their disappointment and anger to students, aiming to swiftly step out of their negative moods. The act of expressing and suppressing emotions highlights the dilemma of cultivating a mutually beneficial relationship that promotes emotional well-being for both supervisors and students. On the one hand, the existing literature emphasizes the importance of supervisors being sensitive to students’ emotional experiences (Bastalich, 2017 ). The inherent power imbalance in supervisor-student relationships may create a sense of student dependency on their supervisors (Friedensen et al., 2024 ; Janssen & Vuuren, 2021 ). Excessive criticism from supervisors can potentially lead to feelings of loss, and alienation throughout students’ academic journey, which highlights supervisors’ responsibility to manage their emotional criticism in supervisory interactions (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). On the other hand, although pursuing a research degree is a challenging journey for graduate students, it is important to acknowledge the vulnerability of research supervisors and their need for support (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). Power dynamics within supervisory relationships, particularly when students challenge or disregard supervisors’ advice, can lead to repression and disengagement for supervisors if negative emotions are not effectively regulated (Xu, 2021 ). Thus, recognizing supervisors’ needs and allowing for emotional expressions are also essential in developing a relationship that is mutually beneficial and conducive to the well-being of both parties (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ).
The conflicts between research supervision and institutional policies
The dilemmas present in supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies inherently illustrate the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision. However, as modern higher education institutions move toward implementing accountability-based policies that aim to standardize and quantify research supervision (Jedemark & Londos, 2021 ), conflicts between the nature of supervision and these institutional policies not only place an emotional burden on supervisors, but also endanger the quality of graduate education.
The dilemmas observed in supervisors’ emotion regulation strategies highlight the divergent understandings between supervisors and graduate students regarding their respective responsibilities and the boundaries of the supervisor-student relationship. This divergence is influenced by context-dependent factors in research supervision, including the beliefs, motivations, and initiatives of the individuals involved (Denis et al., 2018 ). Due to the difficulty in achieving a perfect agreement on these context-dependent factors, it becomes challenging to establish a standard for what constitutes an ideal beneficial research supervision (Bøgelund, 2015 ). In authentic supervisory situations, the relationships between supervisors and graduate students can range from formal and distant to informal and intimate in both academic and social interactions (Parker-Jenkins, 2018 ). Therefore, research supervision is a highly context-dependent and non-standardized practice that relies on the capabilities of supervisors and students, which are shaped by their individual experiences and personalities.
This nature of research supervision underscores the significance of avoiding standardization and a “one size fits all” approach. However, as higher education institutions move toward a corporate managerial mode, research supervision is increasingly perceived as a service provided within a provider-consumer framework, and the fundamental aspects of research supervision are being reshaped to align with a culture of performance measurement, control, and accountability (Taylor et al., 2018 ). In modern academia, universities and institutions have established specific guidelines and protocols for research supervision, which require supervisors to follow diligently and take accountability in the supervision process (Figueira et al., 2018 ).
The presence of extensive external scrutiny or accountability ignored the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision, leading to adverse effects on both supervisors and graduate students. On the one hand, supervisors face significant pressure within an accountability-based context. They are expected to serve as facilitators of structured knowledge transmission, which is enforced through the demanding requirements and time-consuming tasks associated with supervisory practices (Halse, 2011 ). However, the distinctive characteristics of various disciplines and the interdependent relationship between the supervisory context and graduate students’ learning process are neglected (Liang et al., 2021 ). Such a narrow focus on knowledge transmission may pose potential threats to supervisors’ autonomy and academic freedom, generating their feelings of self-questioning, helplessness, and demotivation (Halse, 2011 ). Supervisors in our study reported many examples of emotion regulation strategies utilized to cope with performative and accountability pressures in their workplace. Specifically, the responsibility to ensure timely doctoral completions, prioritize students’ safety, and maintain accountability for those experiencing delays or violating research codes evoked feelings of nervousness, pressure, and insecurity among supervisors.
On the other hand, interventionist supervision within accountability-driven supervisory contexts is perceived as detrimental to students’ academic innovation (Bastalich, 2017 ). The prevailing environment of heightened performativity and accountability alters supervisors’ attitudes toward academic risk-taking, thereby influencing their supervisory practices (Figueira et al., 2018 ). For example, participants in our study utilized prevention and intervention strategies to mitigate potential negative occurrences. This included adopting a directive approach to supervise students’ work and dissuading them from undertaking risky or time-consuming methods to ensure timely completion. However, such micromanagement may stifle innovation, thereby inhibiting doctoral students’ development as independent researchers (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ). Providing pre-packaged research projects or excessive support may hinder students’ acquisition of essential knowledge, skills, and expertise required for their future pursuits, potentially obstructing their progress toward independent thinking (Gruzdev et al., 2020 ).
The conflicts between the prevailing shift from autonomy to accountability in higher education and the context-dependent and non-standardized nature of research supervision highlight the necessity for practice-informed evaluations for research supervision. This finding resonates with previous studies on policy-making in graduate education (Taylor et al., 2018 ), which emphasized the challenges of establishing evidence-based institutional policies to capture the intricate realities of supervision in practice.
Limitations
This study contributes to the understanding of research supervisors’ work by examining their emotion regulation strategies in authentic supervisory situations. However, certain limitations should be addressed for future research. First, the small sample size is a significant limitation, as only six supervisors participated. Future studies may increase the sample size and enhance diversity within the sample. Second, as our study only involved perspectives from research supervisors, future studies may consider incorporating the perceptions of both supervisors and graduate students and analyzing the level of convergence and divergence between the obtained results to enhance the validity of data collection.
Implications for practice
Despite being situated in China’s supervisory accountability system, our study holds broader implications in the global context. As the shift toward corporatized management models in higher education worldwide reshapes research supervision to align with performance measurement and accountability culture (Jedemark & Londos, 2021 ), our results offer implications for research supervision and policy-making beyond the Chinese context.
First, for research supervisors and graduate students, the intricate and dynamic nature of research supervision revealed in our study makes it challenging to offer direct recommendations for optimal emotion regulation strategies. Instead, supervisors are encouraged to adaptively employ a range of emotion regulation strategies in different supervisory situations to enhance their emotional well-being. Additionally, recognizing the context-dependent nature of research supervision, both research supervisors and graduate students are urged to take into account factors such as each other’s beliefs, motivations, and initiatives in their research and daily interactions.
Second, in light of the discrepancy between the current standardized accountability measures in higher education and the context-dependent nature of research supervision, it is imperative for universities and institutions to develop practice-based policies that are tailored to supervisors’ and students’ academic development, avoiding generic and assumed approaches. To effectively address the distinctive requirements of research supervision, policy-makers are strongly encouraged to implement multi-dimensional, discipline-oriented evaluation systems for supervisors in the future.
Data Availability
Data from this study cannot be shared publicly because participants may still be identifiable despite efforts to anonymise the data. Therefore, data will only be made available for researchers who meet criteria for access to confidential data.
Agudo, J. D. M. (Ed.). (2018). Emotions in second language teaching: Theory, research and teacher education . Springer.
Google Scholar
Bastalich, W. (2017). Content and context in knowledge production: A critical review of doctoral supervision literature. Studies in Higher Education, 42 (7), 1145–1157.
Article Google Scholar
Bøgelund, P. (2015). How supervisors perceive PhD supervision-and how they practice it. International Journal of Doctoral Studies, 10 , 39–55.
Brotheridge, C. M., & Grandey, A. A. (2002). Emotional labor and burnout: Comparing two perspectives of “people work.” Journal of Vocational Behavior, 60 (1), 17–39.
Campos, J. J., Walle, E. A., Dahl, A., & Main, A. (2011). Reconceptualizing emotion regulation. Emotion Review, 3 (1), 26–35.
Chen, J., & Cheng, T. (2022). Review of research on teacher emotion during 1985–2019: A descriptive quantitative analysis of knowledge production trends. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 37 (2), 417–438.
Cheng, M. W. T., & Leung, M. L. (2022). “I’m not the only victim...” Student perceptions of exploitative supervision relation in doctoral degree. Higher Education, 84 (3), 523–540.
Denis, C., Colet, N. R., & Lison, C. (2018). Doctoral supervision in North America: Perception and challenges of supervisor and supervisee. Higher Education Studies, 9 (1), 30–39.
Diekman, A. B., Clark, E. K., Johnston, A. M., Brown, E. R., & Steinberg, M. (2011). Malleability in communal goals and beliefs influences attraction to stem careers: Evidence for a goal congruity perspective. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 101 (5), 902–918.
Feinberg, M., Willer, R., Antonenko, O., & John, O. P. (2012). Liberating reason from the passions: Overriding intuitionist moral judgments through emotion reappraisal. Psychological Science, 23 (7), 788–795.
Figueira, C., Theodorakopoulos, N., & Caselli, G. (2018). Unveiling faculty conceptions of academic risk taking: A phenomenographic study. Studies in Higher Education, 43 (8), 1307–1320.
Friedensen, R. E., Bettencourt, G. M., & Bartlett, M. L. (2024). Power-conscious ecosystems: Understanding how power dynamics in US doctoral advising shape students’ experiences. Higher Education, 87 (1), 149–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-023-00998-x
Grandey, A. A. (2000). Emotional regulation in the workplace: A new way to conceptualize emotional labor. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 (1), 95–110.
Gross, J. J. (1998). The emerging field of emotion regulation: An integrative review. Review of General Psychology, 2 , 271–299.
Gross, J. J. (2015). Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry, 26 (1), 1–26.
Gross, J. J., & John, O. P. (2003). Individual differences in two emotion regulation processes: Implications for affect, relationships, and well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 85 (2), 348.
Gruzdev, I., Terentev, E., & Dzhafarova, Z. (2020). Superhero or hands-off supervisor? An empirical categorization of PhD supervision styles and student satisfaction in Russian universities. Higher Education, 79 (5), 773–789.
Gu, J., Levin, J. S., & Luo, Y. (2018). Reproducing “academic successors” or cultivating “versatile experts”: Influences of doctoral training on career expectations of Chinese PhD students. Higher Education, 76 (3), 427–447.
Halse, C. (2011). ‘Becoming a supervisor’: The impact of doctoral supervision on supervisors’ learning. Studies in Higher Education, 36 (5), 557–570.
Halse, C., & Malfroy, J. (2010). Retheorizing doctoral supervision as professional work. Studies in Higher Education, 35 (1), 79–92.
Han, Y., & Xu, Y. (2023). Emotional support from the perspective of extrinsic emotion regulation: Insights of computer science. Teaching in Higher Education, 28 (7), 1725–1743.
Han, J., & Wang, T. (2024). Exploring graduate students’ research characteristics, emotional exhaustion, mastery approach, and research career commitment: insights from the JD-R theory. Studies in Higher Education, 1–15.
Hargreaves, A. (1998). The emotional practice of teaching. Teaching and Teacher Education, 14 (8), 835–854.
Hochschild, A. R. (1983). The managed heart: Commercialization of human feeling . University of California Press.
Hosotani, R. (2011). Emotional experience, expression, and regulation of high-quality Japanese elementary school teachers. Teaching and Teacher Education, 27 (6), 1039–1048.
Janssen, S., & Vuuren, M. (2021). Sensemaking in supervisor-doctoral student relationships: Revealing schemas on the fulfillment of basic psychological needs. Studies in Higher Education, 46 (12), 2738–2750.
Jedemark, M., & Londos, M. (2021). Four different assessment practices: How university teachers handle the field of tension between professional responsibility and professional accountability. Higher Education, 81 (6), 1293–1309.
Johnson, J. W. (2001). The relative importance of task and contextual performance dimensions to supervisor judgments of overall performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 86 (5), 984–996.
Lee, A. (2008). How are doctoral students supervised? Concepts of doctoral research supervision. Studies in Higher Education, 33 (3), 267–281.
Lee, A. (2020). Successful research supervision: Advising students doing research (2nd ed.). Routledge.
Liang, W., Liu, S., & Zhao, C. (2021). Impact of student-supervisor relationship on postgraduate students’ subjective well-being: A study based on longitudinal data in China. Higher Education, 82 (2), 273–305.
Ministry of Education, PRC. (2020). The accountability measures for educational supervision [yanjiusheng zhidao xingwei zhunze]. http://www.moe.gov.cn/srcsite/A22/s7065/202011/t20201111_499442.html . Accessed 17 May 2024.
Parker-Jenkins, M. (2018). Mind the gap: Developing the roles, expectations and boundaries in the doctoral supervisor–supervisee relationship. Studies in Higher Education, 43 (1), 57–71.
Peng, H. (2015). Assessing the quality of research supervision in mainland Chinese higher education. Quality in Higher Education, 21 (1), 89–100.
Riessman, C. K. (2008). Narrative methods for the human sciences . Sage.
Saleem, M. S., Isha, A. S., Awan, M. I., Yusop, Y. B., & Naji, G. M. (2022). Fostering academic engagement in post-graduate students: Assessing the role of positive emotions, positive psychology, and stress. Frontiers in Psychology, 13 , 920395.
Sambrook, S., Stewart, J., & Roberts, C. (2008). Doctoral supervision... A view from above, below and the middle! Journal of Further and Higher Education, 32 (1), 71–84.
Tao, Y., Liu, X., Hou, W., Niu, H., Wang, S., Ma, Z., & Zhang, L. (2022). The mediating role of emotion regulation strategies in the relationship between big five personality traits and anxiety and depression among Chinese firefighters. Frontiers in Public Health, 10 , 901686.
Taxer, J. L., & Frenzel, A. C. (2015). Facets of teachers’ emotional lives: A quantitative investigation of teachers’ genuine, faked, and hidden emotions. Teaching and Teacher Education, 49 , 78–88.
Taxer, J. L., & Gross, J. J. (2018). Emotion regulation in teachers: The “why” and “how”. Teaching and Teacher Education, 74 , 180–189.
Taylor, S., Kiley, M., & Humphrey, R. (2018). A handbook for doctoral supervisors (2nd ed.). Routledge.
To, K. H., & Yin, H. (2021). Being the weather gauge of mood: Demystifying the emotion regulation of kindergarten principals. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 30 (4), 315–325.
Veniger, K. A., & Kočar, S. (2018). The impact of academic discipline on university teaching and pedagogical training courses. Croatian Journal of Education, 20 (4), 1261–1298.
Wollast, R., Aelenei, C., Chevalère, J., Van der Linden, N., Galand, B., Azzi, A., Frenay, M., & Klein, O. (2023). Facing the dropout crisis among PhD candidates: The role of supervisor support in emotional well-being and intended doctoral persistence among men and women. Studies in Higher Education, 48 (6), 813–828.
Xie, A. B., & Zhu, Y. (2008). Retrospect and prospect of Chinese degree and graduate education development in the past three decades. Degree and Graduate Education, 11 , 19–29.
Xie, F. (2021). A study on Chinese EFL teachers’ work engagement: The predictability power of emotion regulation and teacher resilience. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 735969.
Xu, Y. (2021). Unpacking the emotional dimension of doctoral supervision: Supervisors’ emotions and emotion regulation strategies. Frontiers in Psychology, 12 , 651859.
Xu, Y., & Liu, J. A. (2023). Exploring and understanding perceived relationships between doctoral students and their supervisors in China. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 10 (1), 1–10.
Yin, H. (2015). The effect of teachers’ emotional labour on teaching satisfaction: Moderation of emotional intelligence. Teachers and Teaching, 21 (7), 789–810.
Yin, H. (2016a). Knife-like mouth and tofu-like heart: Emotion regulation by Chinese teachers in classroom teaching. Social Psychology of Education, 19 (1), 1–22.
Yin, H., Huang, S., & Lv, L. (2018). A multilevel analysis of job characteristics, emotion regulation and teacher well-being: A job demands-resources model. Frontiers in Psychology, 9 , 2395.
Yin, R. K. (2016b). Qualitative research from start to finish (2nd ed.). Guilford Press.
Zembylas, M. (2021). The affective turn in educational theory. Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Education. https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.1272 . Accessed 17 May 2024.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants who made this publication possible.
This work was supported by the Project of Outstanding Young and Middle-aged Scholars of Shandong University, Shandong University Program of Graduate Education and Reform (grant number XYJG2023037) and the General Research Fund of Hong Kong SAR (grant number CUHK 14608922).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Foreign Languages and Literature, Shandong University, Jinan, 250100, Shandong, China
Jiying Han & Lei Jin
Department of Curriculum and Instruction, Faculty of Education, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shatin, N.T., Hong Kong, SAR, China
Hongbiao Yin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Jiying Han: writing—original draft preparation, writing—reviewing and editing; Lei Jin: writing—original draft preparation, formal analysis; Hongbiao Yin: conceptualization, validation, writing—reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hongbiao Yin .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Han, J., Jin, L. & Yin, H. Supervisors’ emotion regulation in research supervision: navigating dilemmas in an accountability-based context. High Educ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-024-01241-x
Download citation
Accepted : 13 May 2024
Published : 18 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10734-024-01241-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Emotion regulation
- Research supervision
- Accountability
- Graduate education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Med Ethics Hist Med
Ethical challenges of researchers in qualitative studies: the necessity to develop a specific guideline
Mahnaz sanjari.
1 Nursing PhD Candidate, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Fatemeh Bahramnezhad
Fatemeh khoshnava fomani, mahnaz shoghi.
2 Assistant Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Mohammad Ali Cheraghi
3 Associate Professor, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran.
Considering the nature of qualitative studies, the interaction between researchers and participants can be ethically challenging for the former, as they are personally involved in different stages of the study. Therefore, formulation of specific ethical guidelines in this respect seems to be essential. The present paper aimed to discuss the necessity to develop explicit guidelines for conducting qualitative studies with regard to the researchers’ role. For this purpose, a literature review was carried out in domestic and international databases by related keywords.
Health care providers who carry out qualitative research have an immense responsibility. As there is no statistical analysis in qualitative studies, the researcher has to both evaluate what he or she observes and to interpret it. Providing researchers with the necessary skills and applying stringent supervision can lead to better extraction of reliable information from qualitative studies. This article presents a debate in order to illustrate how researchers could cover the ethical challenges of qualitative studies and provide applicable and trustworthy outcomes.
Researchers face ethical challenges in all stages of the study, from designing to reporting. These include anonymity, confidentiality, informed consent, researchers’ potential impact on the participants and vice versa. It seems of paramount importance that health care providers, educators and clinicians be well informed of all the different aspects of their roles when acting as qualitative researchers. Hence, these adroit roles need to be well defined, and the use of practical guidelines and protocols in all stages of qualitative studies should be encouraged.
Introduction
In the recent millennium, the constant trend of change in the demands of the community as well as transforming the trend of knowledge production has highlighted the necessity for researchers to adopt a more comprehensive approach. Increasingly, many academic disciplines are utilizing qualitative research (QR) as the qualitative method investigating the why and how of the process of a developed concept ( 1 , 2 ). Qualitative research is sometimes defined as interpretive research, and as interpretations can be incorrect or biased, the findings may be controversial ( 3 ). However, qualitative research is not only useful as the first stage of quantitative research, but can also play a key role in ‘validating’ it or in providing a different viewpoint on the same social phenomena ( 4 ).
Qualitative studies tend to use methods that result in text production rather than numerical outputs. Given that the researcher is considered to be the research instrument, and the plan of inquiry needs to be developed and altered as the study progresses, a qualitative researcher cannot depend upon traditional approaches to address certain concerns such as bias and credibility. Therefore, learning from a series of mistakes is often considered an integral part of qualitative research ( 5 , 6 ).
In this study, a literature review was carried out in international electronic databases including PubMed, Web of Sciences, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL), Scopus, Ebsco, EMBASE and Science Direct without any time limitation, using the search terms “qualitative research”, “researchers’ role”, “ethical challenges” and “ethical guidelines”. These keywords were also searched on national electronic databases including Scientific Information Database (SID), Iran Medex and Medical Articles Library (Medlib) using the same strategy.
Authors of the present article endeavor to shine a light on the ethical issues affecting researchers and propose strategies to face the ethical challenges of qualitative studies, so as to provide applicable and trustworthy outcomes. This could be the basis for the formulation of specific ethical guidelines in this regard.
An overview on qualitative research in health care
Up to the 1970s, qualitative research was solely employed by anthropologists and sociologists. During the 1970s and 1980s, however, it was favored by various disciplines and experts of different branches of science and humanity such as health care, psychology , nursing, management, political science , education, and communication studies ( 2 , 7 ).
Qualitative research has been conducted in the field of nursing in order to identify, describe and explain related concepts, experiences and phenomena and to develop the nursing knowledge. Nursing professionals simultaneously introduced qualitative research to their peers. Since 1970, qualitative research has been performed to achieve the concepts of patient care and other main perceptions in the nursing profession. Qualitative studies provide nurses with sensitivity to the lived experiences of individuals from different nursing care aspects ( 4 , 8 ).
Role of researchers in qualitative studies
In the case of nurses who perform qualitative research, ethical issues are raised when the nurse-patient relationship in the research area leads to some degree of therapeutic communication for the participants ( 9 ). Thus, nurse researchers must be aware of the impact of the questioning on the participants, and in order to decrease such harmful effects on human subjects, the “reflexive approach” is recommended ( 10 ).
In qualitative studies researchers are often required to clarify their role in the research process ( 11 ). In the QR procedure the researcher is involved in all stages of the study from defining a concept to design, interview, transcription, analysis, verification and reporting the concepts and themes. Therefore, whenever instruments are involved in qualitative research, a human being will be an integral part of the process ( 12 ).
It is argued that humans have increasingly become the “instrument of choice” for naturalistic research due to certain characteristics: they are highly responsive to environmental stimuli, have the ability to interact with the situation, pull together different pieces of information at multiple levels simultaneously, and perceive situations holistically; moreover, they are able to process findings the instant they become available, can present immediate feedback, and feel unusual responses. Nevertheless, researchers need to improve the abilities that make them appropriate human instruments and consequently, their interpersonal skills are of major importance in natural settings and study processes ( Table 1 ) ( 13 , 14 ).
Researcher’s role in qualitative methods at a glance
Ethical challenges in qualitative studies:
The researcher-participant relationship.
The relationship and intimacy that is established between the researchers and participants in qualitative studies can raise a range of different ethical concerns, and qualitative researchers face dilemmas such as respect for privacy, establishment of honest and open interactions, and avoiding misrepresentations ( 19 ). Ethically challenging situations may emerge if researchers have to deal with contradicting issues and choose between different methodological strategies in conflict arises. In such cases, disagreements among different components such as participants, researchers, researchers’ discipline, the funding body and the society may be inevitable ( 20 , 21 ). Some important ethical concerns that should be taken into account while carrying out qualitative research are: anonymity, confidentiality and informed consent ( 22 ).
According to Richards and Schwartz’ findings ( 22 ), the term ‘confidentiality’ conveys different meanings for health care practitioners and researchers. For health care practitioners, confidentiality means that no personal information is to be revealed except in certain situations. For researchers, however, the duty of confidentiality is less clear and involves elaboration of the form of outcome that might be expected from the study ( 22 , 23 ).
The researcher must endeavor to minimize the possibility of intrusion into the autonomy of study participants by all means. When highly sensitive issues are concerned, children and other vulnerable individuals should have access to an advocate who is present during initial phases of the study, and ideally, during data gathering sessions. It is sometimes even necessary that the researcher clarify in writing which persons can have access to the initial data and how the data might be used ( 24 , 25 ).
Informed consent has been recognized as an integral part of ethics in research carried out in different fields. For qualitative researchers, it is of the utmost importance to specify in advance which data will be collected and how they are to be used ( 26 ). The principle of informed consent stresses the researcher’s responsibility to completely inform participants of different aspects of the research in comprehensible language. Clarifications need to include the following issues: the nature of the study, the participants’ potential role, the identity of the researcher and the financing body, the objective of the research, and how the results will be published and used ( 27 ).
Informed consent naturally requires ongoing negotiation of the terms of agreement as the study progresses ( 26 ). Many people consider it necessary to participate in research that their peers, community and/or society may benefit from. Therefore, qualitative health researchers need to clarify that the research they carry out will benefit science and can contribute to the improvement of health policy ( 5 ).
Research design
The qualitative method is utilized to explain, clarify and elaborate the meanings of different aspects of the human life experience. Therefore, researchers can interpret people’s experiences because they are involved in human activities. The principle of ‘no harm’ to participants ought to be considered by researchers, who should be aware of the potential harms that might be inflicted upon study subjects. Obviously, sometimes a conflict between the right to know (defended on the basis of benefits to the society) and the right of privacy (advocated based on the rights of the individual) may happen ( 27 , 28 ).
There are several effective strategies to protect personal information, for instance secure data storage methods, removal of identifier components, biographical details amendments and pseudonyms (applicable to names of individuals, places and organizations) ( 27 ). Researchers have the responsibility of protecting all participants in a study from potentially harmful consequences that might affect them as a result of their participation. It is getting increasingly common for research ethics committees to seek documented proof of consent in a written, signed, and ideally, witnessed form. Researchers can only do their best to protect their respondent’s identity and hold the information strictly confidential as there would be no guarantee for it otherwise ( 29 ). Furthermore, in investigations of sensitive topics where written consent puts the informants at risk, audio recorded oral consent would be more appropriate ( 30 ).
Development of personal relationships with participants may be inevitable while collecting certain data. Therefore, researchers should seriously consider the potential impact they may have on the participants and vice versa, and details of such interactions should be clearly mentioned in research proposals ( 23 ). Overall, the role of the researcher as (a) stranger, (b) visitor, (c) initiator, (d) insider-expert or other should be well defined and explained ( 3 ). As Brenner quoted Kvale state that, preparing an ethical protocol can cover issues in a qualitative research project from planning through reporting ( 30 ).
Data gathering and data analysis
In qualitative research, data are collected with a focus on multifaceted interviews and narratives to produce a description of the experiences. The researchers, therefore, play the role of a mediator between the experiences of the respondents and the community of concerned people ( 28 , 31 ). The post-interview comment sheet could assist the researcher to note the feelings of informants, as well as interpretations and comments that occurred during the interview ( 32 ).
Data collection needs to be as overt as possible, and findings should be recorded. Although there is no guarantee of absolute confidentiality, openly recording field notes assists participants to decide what they wish to have on the record. In health care research, the problem may be even more exaggerated as the researcher is sometimes the health provider as well ( 33 ).
In comparison with other research methods, ethnography has singular characteristics. When a researcher aims to study the culture of certain people, living amongst them is inevitable. This method of collecting data is a subject of debate from an ethical point of view. Long presence of the researcher amongst people of a particular culture necessitates informed consent. Participants should always be aware of the information that has been obtained and is being recorded, and consent to it. Sometimes this cannot be achieved easily and conflicts may happen, as in studies of cultural and ethnic characteristics ( 18 ).
The physical presence of the researchers within the culture requires them to be responsible for their role and potential consequences on the field. For instance, when criminals or a group of war veterans suffering from a disease are the subject of a study, the risks involved in living amongst them should be considered. Ethnographers must be vigilant about any distractions stemming from close interactions that can be potentially harmful to participants in the long run ( 33 , 34 ). Researchers can benefit from supervision sessions directed at learning, mentoring and skill development, all of which can foster their ability to carry out research without risking their health. Adequate professional supervision (which may be outside of the university) can be of service to researchers in dealing with the potential stress associated with the study ( 35 – 37 ).
In order to gain explicit data, ethnographers need to know the role of instrument details. There are eleven steps defined in ethnography which are meant to assist researchers. These steps include participant observation, ethnographic record, descriptive observation, taxonomic analysis, selected observation, componential analysis, discovering the cultural theme, cultural inventory, and finally writing ethnography ( 38 , 39 ).
Researchers should always be aware of the precise reason for involvement in a study in order to prevent undesirable personal issues. The probability of exposure to vicarious trauma as a result of the interviews needs to be evaluated. Interviewers should be properly scheduled to provide the researcher with sufficient recovery time and reduce the risk of emotional exhaustion, while allowing ample time for analysis of the objective and emotional aspects of the research. It is also necessary for the researcher to be familiar with signs of extreme fatigue and be prepared to take necessary measures before too much harm is done ( 40 – 42 ).
In qualitative studies, researchers have a great responsibility and play many different roles. It is argued that qualitative research that deals with sensitive topics in depth can pose emotional and other risks to both participants and researchers. Clear protocols for dealing with distress should be in place so that both parties involved in research can use them if necessary. It is not usually easy to predict what topics are likely to lead to distress, and researchers should therefore receive sufficient training in predicting traumatic situations.
Preventive measures for researchers who carry out sensitive qualitative studies should include official arrangements for a peer support program consisting of a list of researchers who are involved, or a constellation of researcher support activities aiming at improving psychological fitness in the form of a professional confidence building module. Other such measures include offering adequate supervision to provide opportunities for self-development and self-care, and facilitating the process of self-reflection and self-monitoring.
Strategies for emotional distancing need to be considered and adopted if the research topic or participants have the potential to be emotionally challenging. An appropriate planning should be in place before the commencement of the fieldwork, and it must be perfectly clear how the study should be conducted and what level of relationship development is necessary. Measures must also be taken so that levels of self-disclosure, objective displays of emotion during the interviews, and strategies to end the relationships are well defined and communicated.
One of the most prominent tasks of qualitative researchers is to minimize the flaws in observation and endeavor to gain truthful knowledge. Therefore, it is necessary for researchers to continuously update their investigation skills in terms of methodology and find novel techniques to better carry out studies in the field of health and sociology.
As explained before, qualitative research is carried out in natural settings, which requires researchers to work in close collaboration with other members of the team and under direct supervision to discuss and resolve issues as they arise. Therefore, development of practical strategies and communicating them to researchers can be of great benefit and assist them in conducting more perceptive qualitative studies. It is noteworthy that such research should be directed towards making a difference in people’s lives, improving care delivery in different settings and at all levels, and providing a framework for health sciences without any ethical disturbances.
As a result of the extensive body of research in the field of medical sciences, patients comprise a large proportion of the public who are frequently subjects of studies. Research Ethics Committees are formed to provide independent advice to participants, researchers, funders/sponsors and healthcare organizations on the extent to which research proposals comply with universally endorsed ethical standards.
In the history of social and medical science, there have been a few research studies that seriously injured people, and many more in which their welfare was not sufficiently protected. Nations and research associations have taken steps to prevent hurtful and intrusive research. To return to the matter of privacy, the researcher should not rely solely on the informant to identify possible intrusion, but needs to work at anticipating it in advance. Confidentiality does not necessarily preclude intrusion, as anonymity by itself is not enough to protect a person’s privacy or prevent disclosure of personal issues. Investigators should refrain from soliciting private information that is not closely related to the research question.
Considering the aforementioned challenges, it is recommended to conduct further research in order to provide meticulous and explicit ethical protocols, guidelines and codes with respect to qualitative studies.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to offer special thanks to Dr. Ali Tootee for his assistance in the language editing of this article.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Common types of limitations and their ramifications include: Theoretical: limits the scope, depth, or applicability of a study. Methodological: limits the quality, quantity, or diversity of the data. Empirical: limits the representativeness, validity, or reliability of the data. Analytical: limits the accuracy, completeness, or significance of ...
Limitation #2: Time & Money. Almost every researcher will face time and budget constraints at some point. Naturally, these limitations can affect the depth and breadth of your research - but they don't need to be a death sentence. Effective planning is crucial to managing both the temporal and financial aspects of your study.
Identify the limitations: Start by identifying the potential limitations of your research. These may include sample size, selection bias, measurement error, or other issues that could affect the validity and reliability of your findings. Be honest and objective: When describing the limitations of your research, be honest and objective.
Possible Limitations of the Researcher. Access-- if your study depends on having access to people, organizations, data, or documents and, for whatever reason, access is denied or limited in some way, the reasons for this needs to be described.Also, include an explanation why being denied or limited access did not prevent you from following through on your study.
Here's an example of a limitation explained in a research paper about the different options and emerging solutions for delaying memory decline. These statements appeared in the first two sentences of the discussion section: "Approaches like stem cell transplantation and vaccination in AD [Alzheimer's disease] work on a cellular or molecular level in the laboratory.
Writing the limitations of the research papers is often assumed to require lots of effort. However, identifying the limitations of the study can help structure the research better. Therefore, do not underestimate the importance of research study limitations. 3. Opportunity to make suggestions for further research.
The ideal way is to divide your limitations section into three steps: 1. Identify the research constraints; 2. Describe in great detail how they affect your research; 3. Mention the opportunity for future investigations and give possibilities. By following this method while addressing the constraints of your research, you will be able to ...
1. Defining Research Limitations: Definition: Research limitations are the constraints or shortcomings that affect the scope, applicability, and generalizability of a study. Inherent in Research: Every research project, regardless of its scale or significance, possesses limitations. 2. Types of Research Limitations: Methodological Limitations ...
build reviewers' trust in you and your research, discussing every drawback, no matter how small, can give the impression that the study is irreparably flawed. For each limitation you identify, provide a sentence that refutes the limitation or that provides information to counterbalance or otherwise minimize the limitation's perceived impact.
3. Identify your limitations of research and explain their importance. 4. Provide the necessary depth, explain their nature, and justify your study choices. 5. Write how you are suggesting that it is possible to overcome them in the future. Limitations can help structure the research study better.
Conducting research from planning to publication can be a very rewarding process. However, multiple preventable setbacks can occur within each stage of research. While these inefficiencies are an inevitable part of the research process, understanding common pitfalls can limit those hindrances. Many issues can present themselves throughout the research process. It has been said about academics ...
Always acknowledge a study's limitations. It is far better for you to identify and acknowledge your study's limitations than to have them pointed out by your professor and be graded down because you appear to have ignored them. Keep in mind that acknowledgement of a study's limitations is an opportunity to make suggestions for further research.
6. Limited Scope. "Limited scope" is perhaps one of the most common limitations listed by researchers - and while this is often a catch-all way of saying, "well, I'm not studying that in this study", it's also a valid point. No study can explore everything related to a topic.
Limitations put medical research articles at risk. The accumulation of limitations (variables having additional limitation components) are gaps and flaws diluting the probability of validity. There is currently no assessment method for evaluating the effect(s) of limitations on research outcomes other than awareness that there is an effect.
Take your time with the planning process. "It's worth consulting other researchers, doing a pilot study to test it, before you go out spending the time, money, and energy to do the big study," Crawford says. "Because once you begin the study, you can't stop.". Challenge: Assembling a Research Team.
Abstract. Study limitations represent weaknesses within a research design that may influence outcomes and conclusions of the research. Researchers have an obligation to the academic community to present complete and honest limitations of a presented study. Too often, authors use generic descriptions to describe study limitations.
Step 1. Identify the limitation (s) of the study. This part should comprise around 10%-20% of your discussion of study limitations. The first step is to identify the particular limitation (s) that affected your study. There are many possible limitations of research that can affect your study, but you don't need to write a long review of all ...
Research Limitations. It is for sure that your research will have some limitations and it is normal. However, it is critically important for you to be striving to minimize the range of scope of limitations throughout the research process. Also, you need to provide the acknowledgement of your research limitations in conclusions chapter honestly.
Research limitations and research delimitations are related in that they both refer to "limits" within a study. But, they are distinctly different. Limitations reflect the shortcomings of your study, based on practical or theoretical constraints that you faced. Contrasted to that, delimitations reflect the choices that you made in terms of ...
2.2. Limitations Example 2. Following example is from an Engineering research paper. The authors are acknowledging the limitations and warning readers against generalizing the research findings. However, some study limitations should be acknowledged. The experiments do not fully consider the problems that can appear in real situations.
Limitations generally fall into some common categories, and in a sense we can make a checklist for authors here. Price and Murnan ( 2004) gave an excellent and detailed summary of possible research limitations in their editorial for the American Journal of Health Education. They discussed limitations affecting internal and external validity ...
2. Finding research funding. Another common challenge that researchers face is finding the money they need to get the research done. Sometimes this comes alongside the shock of how much the required materials, tools, and assistance will cost. Research is more expensive than most people imagine.
Voices in Bioethics is currently seeking submissions on philosophical and practical topics, both current and timeless. Papers addressing access to healthcare, the bioethical implications of recent Supreme Court rulings, environmental ethics, data privacy, cybersecurity, law and bioethics, economics and bioethics, reproductive ethics, research ethics, and pediatric bioethics are sought.
Given the complexity and high demands of research supervision and the intricate emotional experiences of supervisors, there is a need to explore how they regulate their emotions, particularly across various disciplinary backgrounds. The current study explored the emotion regulation strategies employed by research supervisors during the process of supervising graduate students. Based on data ...
Up to the 1970s, qualitative research was solely employed by anthropologists and sociologists. During the 1970s and 1980s, however, it was favored by various disciplines and experts of different branches of science and humanity such as health care, psychology, nursing, management, political science, education, and communication studies (2, 7).
Researchers in the Department of Communication at the University of Arkansas are conducting a research study aimed at understanding the narratives of college students during the COVID-19 pandemic. As part of our exploration, we're eager to hear from seniors of 2024! ... Your insights will contribute to a deeper understanding of the challenges ...
Government schemes in agriculture are essential for fostering sectoral development, providing financial support, and implementing strategic initiatives to enhance the overall well-being and productivity of farmers. The current research was conducted during the fiscal year 2021-22, involving the collection of data from a sample of 480 farmers in the state of Rajasthan. The purpose of the study ...
The Chinese economy is transitioning from high-speed development to high-quality development, and water environmental governance is a key factor promoting economic transformation. Due to low returns and high investment in China's water environmental governance, the PPP (public-private-partnership) model is often adopted. However, the PPP model has historically faced challenges adapting to ...