- Departments and Units
- Majors and Minors
- LSA Course Guide
- LSA Gateway

Search: {{$root.lsaSearchQuery.q}}, Page {{$root.page}}
- Accessibility
- Undergraduates
- Instructors
- Alums & Friends

- ★ Writing Support
- Minor in Writing
- First-Year Writing Requirement
- Transfer Students
- Writing Guides
- Peer Writing Consultant Program
- Upper-Level Writing Requirement
- Writing Prizes
- International Students
- ★ The Writing Workshop
- Dissertation ECoach
- Fellows Seminar
- Dissertation Writing Groups
- Rackham / Sweetland Workshops
- Dissertation Writing Institute
- Guides to Teaching Writing
- Teaching Support and Services
- Support for FYWR Courses
- Support for ULWR Courses
- Writing Prize Nominating
- Alums Gallery
- Commencement
- Giving Opportunities
- How Do I Write an Intro, Conclusion, & Body Paragraph?
- How Do I Make Sure I Understand an Assignment?
- How Do I Decide What I Should Argue?
- How Can I Create Stronger Analysis?
- How Do I Effectively Integrate Textual Evidence?
- How Do I Write a Great Title?
- What Exactly is an Abstract?
- How Do I Present Findings From My Experiment in a Report?
- What is a Run-on Sentence & How Do I Fix It?
- How Do I Check the Structure of My Argument?
- How Do I Incorporate Quotes?
- How Can I Create a More Successful Powerpoint?
- How Can I Create a Strong Thesis?
- How Can I Write More Descriptively?
- How Do I Incorporate a Counterargument?
- How Do I Check My Citations?
See the bottom of the main Writing Guides page for licensing information.
Traditional Academic Essays In Three Parts
Part i: the introduction.
An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you’re writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things:
- Gets the reader’s attention. You can get a reader’s attention by telling a story, providing a statistic, pointing out something strange or interesting, providing and discussing an interesting quote, etc. Be interesting and find some original angle via which to engage others in your topic.
- Provides a specific and debatable thesis statement. The thesis statement is usually just one sentence long, but it might be longer—even a whole paragraph—if the essay you’re writing is long. A good thesis statement makes a debatable point, meaning a point someone might disagree with and argue against. It also serves as a roadmap for what you argue in your paper.
Part II: The Body Paragraphs
Body paragraphs help you prove your thesis and move you along a compelling trajectory from your introduction to your conclusion. If your thesis is a simple one, you might not need a lot of body paragraphs to prove it. If it’s more complicated, you’ll need more body paragraphs. An easy way to remember the parts of a body paragraph is to think of them as the MEAT of your essay:
Main Idea. The part of a topic sentence that states the main idea of the body paragraph. All of the sentences in the paragraph connect to it. Keep in mind that main ideas are…
- like labels. They appear in the first sentence of the paragraph and tell your reader what’s inside the paragraph.
- arguable. They’re not statements of fact; they’re debatable points that you prove with evidence.
- focused. Make a specific point in each paragraph and then prove that point.
Evidence. The parts of a paragraph that prove the main idea. You might include different types of evidence in different sentences. Keep in mind that different disciplines have different ideas about what counts as evidence and they adhere to different citation styles. Examples of evidence include…
- quotations and/or paraphrases from sources.
- facts , e.g. statistics or findings from studies you’ve conducted.
- narratives and/or descriptions , e.g. of your own experiences.
Analysis. The parts of a paragraph that explain the evidence. Make sure you tie the evidence you provide back to the paragraph’s main idea. In other words, discuss the evidence.
Transition. The part of a paragraph that helps you move fluidly from the last paragraph. Transitions appear in topic sentences along with main ideas, and they look both backward and forward in order to help you connect your ideas for your reader. Don’t end paragraphs with transitions; start with them.
Keep in mind that MEAT does not occur in that order. The “ T ransition” and the “ M ain Idea” often combine to form the first sentence—the topic sentence—and then paragraphs contain multiple sentences of evidence and analysis. For example, a paragraph might look like this: TM. E. E. A. E. E. A. A.
Part III: The Conclusion
A conclusion is the last paragraph of your essay, or, if you’re writing a really long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to conclude. A conclusion typically does one of two things—or, of course, it can do both:
- Summarizes the argument. Some instructors expect you not to say anything new in your conclusion. They just want you to restate your main points. Especially if you’ve made a long and complicated argument, it’s useful to restate your main points for your reader by the time you’ve gotten to your conclusion. If you opt to do so, keep in mind that you should use different language than you used in your introduction and your body paragraphs. The introduction and conclusion shouldn’t be the same.
- For example, your argument might be significant to studies of a certain time period .
- Alternately, it might be significant to a certain geographical region .
- Alternately still, it might influence how your readers think about the future . You might even opt to speculate about the future and/or call your readers to action in your conclusion.
Handout by Dr. Liliana Naydan. Do not reproduce without permission.

- Information For
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Faculty and Staff
- Alumni and Friends
- More about LSA
- How Do I Apply?
- LSA Magazine
- Student Resources
- Academic Advising
- Global Studies
- LSA Opportunity Hub
- Social Media
- Update Contact Info
- Privacy Statement
- Report Feedback

How to Write a Research Paper: Parts of the Paper
- Choosing Your Topic
- Citation & Style Guides This link opens in a new window
- Critical Thinking
- Evaluating Information
- Parts of the Paper
- Writing Tips from UNC-Chapel Hill
- Librarian Contact
Parts of the Research Paper Papers should have a beginning, a middle, and an end. Your introductory paragraph should grab the reader's attention, state your main idea, and indicate how you will support it. The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas.
1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses. Use keywords that help explain your paper's topic to the reader. Try to avoid abbreviations and jargon. Think about keywords that people would use to search for your paper and include them in your title.
2. The Abstract The abstract is used by readers to get a quick overview of your paper. Typically, they are about 200 words in length (120 words minimum to 250 words maximum). The abstract should introduce the topic and thesis, and should provide a general statement about what you have found in your research. The abstract allows you to mention each major aspect of your topic and helps readers decide whether they want to read the rest of the paper. Because it is a summary of the entire research paper, it is often written last.
3. The Introduction The introduction should be designed to attract the reader's attention and explain the focus of the research. You will introduce your overview of the topic, your main points of information, and why this subject is important. You can introduce the current understanding and background information about the topic. Toward the end of the introduction, you add your thesis statement, and explain how you will provide information to support your research questions. This provides the purpose and focus for the rest of the paper.
4. Thesis Statement Most papers will have a thesis statement or main idea and supporting facts/ideas/arguments. State your main idea (something of interest or something to be proven or argued for or against) as your thesis statement, and then provide your supporting facts and arguments. A thesis statement is a declarative sentence that asserts the position a paper will be taking. It also points toward the paper's development. This statement should be both specific and arguable. Generally, the thesis statement will be placed at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. The remainder of your paper will support this thesis.
Students often learn to write a thesis as a first step in the writing process, but often, after research, a writer's viewpoint may change. Therefore a thesis statement may be one of the final steps in writing.
Examples of Thesis Statements from Purdue OWL
5. The Literature Review The purpose of the literature review is to describe past important research and how it specifically relates to the research thesis. It should be a synthesis of the previous literature and the new idea being researched. The review should examine the major theories related to the topic to date and their contributors. It should include all relevant findings from credible sources, such as academic books and peer-reviewed journal articles. You will want to:
- Explain how the literature helps the researcher understand the topic.
- Try to show connections and any disparities between the literature.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research.
- Reveal any gaps that exist in the literature.
More about writing a literature review. . .
6. The Discussion The purpose of the discussion is to interpret and describe what you have learned from your research. Make the reader understand why your topic is important. The discussion should always demonstrate what you have learned from your readings (and viewings) and how that learning has made the topic evolve, especially from the short description of main points in the introduction.Explain any new understanding or insights you have had after reading your articles and/or books. Paragraphs should use transitioning sentences to develop how one paragraph idea leads to the next. The discussion will always connect to the introduction, your thesis statement, and the literature you reviewed, but it does not simply repeat or rearrange the introduction. You want to:
- Demonstrate critical thinking, not just reporting back facts that you gathered.
- If possible, tell how the topic has evolved over the past and give it's implications for the future.
- Fully explain your main ideas with supporting information.
- Explain why your thesis is correct giving arguments to counter points.
7. The Conclusion A concluding paragraph is a brief summary of your main ideas and restates the paper's main thesis, giving the reader the sense that the stated goal of the paper has been accomplished. What have you learned by doing this research that you didn't know before? What conclusions have you drawn? You may also want to suggest further areas of study, improvement of research possibilities, etc. to demonstrate your critical thinking regarding your research.
- << Previous: Evaluating Information
- Next: Research >>
- Last Updated: Feb 13, 2024 8:35 AM
- URL: https://libguides.ucc.edu/research_paper
Research Paper
How to write a body of a research paper.

The main part of your research paper is called “the body.” To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.
The first sentence of your second paragraph should continue the transition from the end of your introduction to present your first topic.Often too, your first sentence will be your “topic sentence,” the sentence that presents the topic, point, or argument that will be presented in the paragraph. The body of the paragraph should contain evidence, in the form of a discussion using quotations and examples, that supports or “proves” the topic. The final sentence of the paragraph should provide a transition to the third paragraph of the paper where the second topic will be presented.
- The third and fourth paragraphs follow the same format as the second:
- Transition or topic sentence.
- Topic sentence (if not included in the first sentence).
- Supporting sentences including a discussion, quotations, or examples that support the topic sentence.
- Concluding sentence that transitions to the next paragraph.
The topic of each paragraph will be supported by the evidence you itemized in your outline. However, just as smooth transitions are required to connect your paragraphs, the sentences you write to present your evidence should possess transition words that connect ideas, focus attention on relevant information, and continue your discussion in a smooth and fluid manner.
You presented the main idea of your paper in the thesis statement. In the body, every single paragraph must support that main idea. If any paragraph in your paper does not, in some way, back up the main idea expressed in your thesis statement, it is not relevant, which means it doesn’t have a purpose and shouldn’t be there.
Each paragraph also has a main idea of its own. That main idea is stated in a topic sentence, either at the beginning or somewhere else in the paragraph. Just as every paragraph in your paper supports your thesis statement, every sentence in each paragraph supports the main idea of that paragraph by providing facts or examples that back up that main idea. If a sentence does not support the main idea of the paragraph, it is not relevant and should be left out.
A paper that makes claims or states ideas without backing them up with facts or clarifying them with examples won’t mean much to readers. Make sure you provide enough supporting details for all your ideas. And remember that a paragraph can’t contain just one sentence. A paragraph needs at least two or more sentences to be complete. If a paragraph has only one or two sentences, you probably haven’t provided enough support for your main idea. Or, if you have trouble finding the main idea, maybe you don’t have one. In that case, you can make the sentences part of another paragraph or leave them out.
Logical order
Arrange the paragraphs in the body of your paper in an order that makes sense, so that each main idea follows logically from the previous one. Likewise, arrange the sentences in each paragraph in a logical order.
If you carefully organized your notes and made your outline, your ideas will fall into place naturally as you write your draft. The main ideas, which are building blocks of each section or each paragraph in your paper, come from the Roman-numeral headings in your outline. The supporting details under each of those main ideas come from the capital-letter headings. In a shorter paper, the capital-letter headings may become sentences that include supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline. In a longer paper, the capital letter headings may become paragraphs of their own, which contain sentences with the supporting details, which come from the Arabic numerals in your outline.
Transition Words and Phrases
In addition to keeping your ideas in logical order, transitions are another way to guide readers from one idea to another. Transition words and phrases are important when you are suggesting or pointing out similarities between ideas, themes, opinions, or a set of facts. As with any perfect phrase, transition words within paragraphs should not be used gratuitously. Their meaning must conform to what you are trying to point out, as shown in the examples below:
- “Accordingly” or “in accordance with” indicates agreement. For example :Thomas Edison’s experiments with electricity accordingly followed the theories of Benjamin Franklin, J. B. Priestly, and other pioneers of the previous century.
- “Analogous” or “analogously” contrasts different things or ideas that perform similar functions or make similar expressions. For example: A computer hard drive is analogous to a filing cabinet. Each stores important documents and data.
- “By comparison” or “comparatively”points out differences between things that otherwise are similar. For example: Roses require an alkaline soil. Azaleas, by comparison, prefer an acidic soil.
- “Corresponds to” or “correspondingly” indicates agreement or conformity. For example: The U.S. Constitution corresponds to England’s Magna Carta in so far as both established a framework for a parliamentary system.
- “Equals,”“equal to,” or “equally” indicates the same degree or quality. For example:Vitamin C is equally as important as minerals in a well-balanced diet.
- “Equivalent” or “equivalently” indicates two ideas or things of approximately the same importance, size, or volume. For example:The notions of individual liberty and the right to a fair and speedy trial hold equivalent importance in the American legal system.
- “Common” or “in common with” indicates similar traits or qualities. For example: Darwin did not argue that humans were descended from the apes. Instead, he maintained that they shared a common ancestor.
- “In the same way,”“in the same manner,”“in the same vein,” or “likewise,” connects comparable traits, ideas, patterns, or activities. For example: John Roebling’s suspension bridges in Brooklyn and Cincinnati were built in the same manner, with strong cables to support a metallic roadway. Example 2: Despite its delicate appearance, John Roebling’s Brooklyn Bridge was built as a suspension bridge supported by strong cables. Example 3: Cincinnati’s Suspension Bridge, which Roebling also designed, was likewise supported by cables.
- “Kindred” indicates that two ideas or things are related by quality or character. For example: Artists Vincent Van Gogh and Paul Gauguin are considered kindred spirits in the Impressionist Movement. “Like” or “as” are used to create a simile that builds reader understanding by comparing two dissimilar things. (Never use “like” as slang, as in: John Roebling was like a bridge designer.) For examples: Her eyes shone like the sun. Her eyes were as bright as the sun.
- “Parallel” describes events, things, or ideas that occurred at the same time or that follow similar logic or patterns of behavior. For example:The original Ocktoberfests were held to occur in parallel with the autumn harvest.
- “Obviously” emphasizes a point that should be clear from the discussion. For example: Obviously, raccoons and other wildlife will attempt to find food and shelter in suburban areas as their woodland habitats disappear.
- “Similar” and “similarly” are used to make like comparisons. For example: Horses and ponies have similar physical characteristics although, as working farm animals, each was bred to perform different functions.
- “There is little debate” or “there is consensus” can be used to point out agreement. For example:There is little debate that the polar ice caps are melting.The question is whether global warming results from natural or human-made causes.
Other phrases that can be used to make transitions or connect ideas within paragraphs include:

- Use “alternately” or “alternatively” to suggest a different option.
- Use “antithesis” to indicate a direct opposite.
- Use “contradict” to indicate disagreement.
- Use “on the contrary” or “conversely” to indicate that something is different from what it seems.
- Use “dissimilar” to point out differences between two things.
- Use “diverse” to discuss differences among many things or people.
- Use “distinct” or “distinctly” to point out unique qualities.
- Use “inversely” to indicate an opposite idea.
- Use “it is debatable,” “there is debate,” or “there is disagreement” to suggest that there is more than one opinion about a subject.
- Use “rather” or “rather than” to point out an exception.
- Use “unique” or “uniquely” to indicate qualities that can be found nowhere else.
- Use “unlike” to indicate dissimilarities.
- Use “various” to indicate more than one kind.
Writing Topic Sentences
Remember, a sentence should express a complete thought, one thought per sentence—no more, no less. The longer and more convoluted your sentences become, the more likely you are to muddle the meaning, become repetitive, and bog yourself down in issues of grammar and construction. In your first draft, it is generally a good idea to keep those sentences relatively short and to the point. That way your ideas will be clearly stated.You will be able to clearly see the content that you have put down—what is there and what is missing—and add or subtract material as it is needed. The sentences will probably seem choppy and even simplistic.The purpose of a first draft is to ensure that you have recorded all the content you will need to make a convincing argument. You will work on smoothing and perfecting the language in subsequent drafts.
Adding Evidence
Transitioning from your topic sentence to the evidence that supports it can be problematic. It requires a transition, much like the transitions needed to move from one paragraph to the next. Choose phrases that connect the evidence directly to your topic sentence.
Phrases for Supporting Topic Sentences
- Consider this: (give an example or state evidence).
- If (identify one condition or event) then (identify the condition or event that will follow).
- It should go without saying that (point out an obvious condition).
- Note that (provide an example or observation).
- Take a look at (identify a condition; follow with an explanation of why you think it is important to the discussion).
- The authors had (identify their idea) in mind when they wrote “(use a quotation from their text that illustrates the idea).”
- The point is that (summarize the conclusion your reader should draw from your research).
- This becomes evident when (name the author) says that (paraphrase a quote from the author’s writing).
- We see this in the following example: (provide an example of your own).
- (The author’s name) offers the example of (summarize an example given by the author).
If an idea is controversial, you may need to add extra evidence to your paragraphs to persuade your reader. You may also find that a logical argument, one based solely on your evidence, is not persuasive enough and that you need to appeal to the reader’s emotions. Look for ways to incorporate your research without detracting from your argument.
Writing Transition Sentences
It is often difficult to write transitions that carry a reader clearly and logically on to the next paragraph (and the next topic) in an essay. Because you are moving from one topic to another, it is easy to simply stop one and start another. Great research papers, however, include good transitions that link the ideas in an interesting discussion so that readers can move smoothly and easily through your presentation. Close each of your paragraphs with an interesting transition sentence that introduces the topic coming up in the next paragraph.
Transition sentences should show a relationship between the two topics.Your transition will perform one of the following functions to introduce the new idea:
- Indicate that you will be expanding on information in a different way in the upcoming paragraph.
- Indicate that a comparison, contrast, or a cause-and-effect relationship between the topics will be discussed.
- Indicate that an example will be presented in the next paragraph.
- Indicate that a conclusion is coming up.
Transitions make a paper flow smoothly by showing readers how ideas and facts follow one another to point logically to a conclusion. They show relationships among the ideas, help the reader to understand, and, in a persuasive paper, lead the reader to the writer’s conclusion.
Each paragraph should end with a transition sentence to conclude the discussion of the topic in the paragraph and gently introduce the reader to the topic that will be raised in the next paragraph. However, transitions also occur within paragraphs—from sentence to sentence—to add evidence, provide examples, or introduce a quotation.
The type of paper you are writing and the kinds of topics you are introducing will determine what type of transitional phrase you should use. Some useful phrases for transitions appear below. They are grouped according to the function they normally play in a paper. Transitions, however, are not simply phrases that are dropped into sentences. They are constructed to highlight meaning. Choose transitions that are appropriate to your topic and what you want the reader to do. Edit them to be sure they fit properly within the sentence to enhance the reader’s understanding.
Transition Phrases for Comparisons:
- We also see
- In addition to
- Notice that
- Beside that,
- In comparison,
- Once again,
- Identically,
- For example,
- Comparatively, it can be seen that
- We see this when
- This corresponds to
- In other words,
- At the same time,
- By the same token,
Transition Phrases for Contrast:
- By contrast,
- On the contrary,
- Nevertheless,
- An exception to this would be …
- Alongside that,we find …
- On one hand … on the other hand …
- [New information] presents an opposite view …
- Conversely, it could be argued …
- Other than that,we find that …
- We get an entirely different impression from …
- One point of differentiation is …
- Further investigation shows …
- An exception can be found in the fact that …
Transition Phrases to Show a Process:
- At the top we have … Near the bottom we have …
- Here we have … There we have …
- Continuing on,
- We progress to …
- Close up … In the distance …
- With this in mind,
- Moving in sequence,
- Proceeding sequentially,
- Moving to the next step,
- First, Second,Third,…
- Examining the activities in sequence,
- Sequentially,
- As a result,
- The end result is …
- To illustrate …
- Subsequently,
- One consequence of …
- If … then …
- It follows that …
- This is chiefly due to …
- The next step …
- Later we find …
Phrases to Introduce Examples:
- For instance,
- Particularly,
- In particular,
- This includes,
- Specifically,
- To illustrate,
- One illustration is
- One example is
- This is illustrated by
- This can be seen when
- This is especially seen in
- This is chiefly seen when
Transition Phrases for Presenting Evidence:
- Another point worthy of consideration is
- At the center of the issue is the notion that
- Before moving on, it should be pointed out that
- Another important point is
- Another idea worth considering is
- Consequently,
- Especially,
- Even more important,
- Getting beyond the obvious,
- In spite of all this,
- It follows that
- It is clear that
- More importantly,
- Most importantly,
See the examples of effective transitions for more.
Draft Your Conclusion
Every good paper ends with a strong concluding paragraph. To write a good conclusion, sum up the main points in your paper. To write an even better conclusion, include a sentence or two that helps the reader answer the question, “So what?” or “Why does all this matter?” If you choose to include one or more “So What?” sentences, remember that you still need to support any point you make with facts or examples. Remember, too, that this is not the place to introduce new ideas from “out of the blue.” Make sure that everything you write in your conclusion refers to what you’ve already written in the body of your paper.
Read more on How to Write a Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- How to write a research paper
Last updated
11 January 2024
Reviewed by
With proper planning, knowledge, and framework, completing a research paper can be a fulfilling and exciting experience.
Though it might initially sound slightly intimidating, this guide will help you embrace the challenge.
By documenting your findings, you can inspire others and make a difference in your field. Here's how you can make your research paper unique and comprehensive.
- What is a research paper?
Research papers allow you to demonstrate your knowledge and understanding of a particular topic. These papers are usually lengthier and more detailed than typical essays, requiring deeper insight into the chosen topic.
To write a research paper, you must first choose a topic that interests you and is relevant to the field of study. Once you’ve selected your topic, gathering as many relevant resources as possible, including books, scholarly articles, credible websites, and other academic materials, is essential. You must then read and analyze these sources, summarizing their key points and identifying gaps in the current research.
You can formulate your ideas and opinions once you thoroughly understand the existing research. To get there might involve conducting original research, gathering data, or analyzing existing data sets. It could also involve presenting an original argument or interpretation of the existing research.
Writing a successful research paper involves presenting your findings clearly and engagingly, which might involve using charts, graphs, or other visual aids to present your data and using concise language to explain your findings. You must also ensure your paper adheres to relevant academic formatting guidelines, including proper citations and references.
Overall, writing a research paper requires a significant amount of time, effort, and attention to detail. However, it is also an enriching experience that allows you to delve deeply into a subject that interests you and contribute to the existing body of knowledge in your chosen field.
- How long should a research paper be?
Research papers are deep dives into a topic. Therefore, they tend to be longer pieces of work than essays or opinion pieces.
However, a suitable length depends on the complexity of the topic and your level of expertise. For instance, are you a first-year college student or an experienced professional?
Also, remember that the best research papers provide valuable information for the benefit of others. Therefore, the quality of information matters most, not necessarily the length. Being concise is valuable.
Following these best practice steps will help keep your process simple and productive:
1. Gaining a deep understanding of any expectations
Before diving into your intended topic or beginning the research phase, take some time to orient yourself. Suppose there’s a specific topic assigned to you. In that case, it’s essential to deeply understand the question and organize your planning and approach in response. Pay attention to the key requirements and ensure you align your writing accordingly.
This preparation step entails
Deeply understanding the task or assignment
Being clear about the expected format and length
Familiarizing yourself with the citation and referencing requirements
Understanding any defined limits for your research contribution
Where applicable, speaking to your professor or research supervisor for further clarification
2. Choose your research topic
Select a research topic that aligns with both your interests and available resources. Ideally, focus on a field where you possess significant experience and analytical skills. In crafting your research paper, it's crucial to go beyond summarizing existing data and contribute fresh insights to the chosen area.
Consider narrowing your focus to a specific aspect of the topic. For example, if exploring the link between technology and mental health, delve into how social media use during the pandemic impacts the well-being of college students. Conducting interviews and surveys with students could provide firsthand data and unique perspectives, adding substantial value to the existing knowledge.
When finalizing your topic, adhere to legal and ethical norms in the relevant area (this ensures the integrity of your research, protects participants' rights, upholds intellectual property standards, and ensures transparency and accountability). Following these principles not only maintains the credibility of your work but also builds trust within your academic or professional community.
For instance, in writing about medical research, consider legal and ethical norms , including patient confidentiality laws and informed consent requirements. Similarly, if analyzing user data on social media platforms, be mindful of data privacy regulations, ensuring compliance with laws governing personal information collection and use. Aligning with legal and ethical standards not only avoids potential issues but also underscores the responsible conduct of your research.
3. Gather preliminary research
Once you’ve landed on your topic, it’s time to explore it further. You’ll want to discover more about available resources and existing research relevant to your assignment at this stage.
This exploratory phase is vital as you may discover issues with your original idea or realize you have insufficient resources to explore the topic effectively. This key bit of groundwork allows you to redirect your research topic in a different, more feasible, or more relevant direction if necessary.
Spending ample time at this stage ensures you gather everything you need, learn as much as you can about the topic, and discover gaps where the topic has yet to be sufficiently covered, offering an opportunity to research it further.
4. Define your research question
To produce a well-structured and focused paper, it is imperative to formulate a clear and precise research question that will guide your work. Your research question must be informed by the existing literature and tailored to the scope and objectives of your project. By refining your focus, you can produce a thoughtful and engaging paper that effectively communicates your ideas to your readers.
5. Write a thesis statement
A thesis statement is a one-to-two-sentence summary of your research paper's main argument or direction. It serves as an overall guide to summarize the overall intent of the research paper for you and anyone wanting to know more about the research.
A strong thesis statement is:
Concise and clear: Explain your case in simple sentences (avoid covering multiple ideas). It might help to think of this section as an elevator pitch.
Specific: Ensure that there is no ambiguity in your statement and that your summary covers the points argued in the paper.
Debatable: A thesis statement puts forward a specific argument––it is not merely a statement but a debatable point that can be analyzed and discussed.
Here are three thesis statement examples from different disciplines:
Psychology thesis example: "We're studying adults aged 25-40 to see if taking short breaks for mindfulness can help with stress. Our goal is to find practical ways to manage anxiety better."
Environmental science thesis example: "This research paper looks into how having more city parks might make the air cleaner and keep people healthier. I want to find out if more green spaces means breathing fewer carcinogens in big cities."
UX research thesis example: "This study focuses on improving mobile banking for older adults using ethnographic research, eye-tracking analysis, and interactive prototyping. We investigate the usefulness of eye-tracking analysis with older individuals, aiming to spark debate and offer fresh perspectives on UX design and digital inclusivity for the aging population."
6. Conduct in-depth research
A research paper doesn’t just include research that you’ve uncovered from other papers and studies but your fresh insights, too. You will seek to become an expert on your topic––understanding the nuances in the current leading theories. You will analyze existing research and add your thinking and discoveries. It's crucial to conduct well-designed research that is rigorous, robust, and based on reliable sources. Suppose a research paper lacks evidence or is biased. In that case, it won't benefit the academic community or the general public. Therefore, examining the topic thoroughly and furthering its understanding through high-quality research is essential. That usually means conducting new research. Depending on the area under investigation, you may conduct surveys, interviews, diary studies , or observational research to uncover new insights or bolster current claims.
7. Determine supporting evidence
Not every piece of research you’ve discovered will be relevant to your research paper. It’s important to categorize the most meaningful evidence to include alongside your discoveries. It's important to include evidence that doesn't support your claims to avoid exclusion bias and ensure a fair research paper.
8. Write a research paper outline
Before diving in and writing the whole paper, start with an outline. It will help you to see if more research is needed, and it will provide a framework by which to write a more compelling paper. Your supervisor may even request an outline to approve before beginning to write the first draft of the full paper. An outline will include your topic, thesis statement, key headings, short summaries of the research, and your arguments.
9. Write your first draft
Once you feel confident about your outline and sources, it’s time to write your first draft. While penning a long piece of content can be intimidating, if you’ve laid the groundwork, you will have a structure to help you move steadily through each section. To keep up motivation and inspiration, it’s often best to keep the pace quick. Stopping for long periods can interrupt your flow and make jumping back in harder than writing when things are fresh in your mind.
10. Cite your sources correctly
It's always a good practice to give credit where it's due, and the same goes for citing any works that have influenced your paper. Building your arguments on credible references adds value and authenticity to your research. In the formatting guidelines section, you’ll find an overview of different citation styles (MLA, CMOS, or APA), which will help you meet any publishing or academic requirements and strengthen your paper's credibility. It is essential to follow the guidelines provided by your school or the publication you are submitting to ensure the accuracy and relevance of your citations.
11. Ensure your work is original
It is crucial to ensure the originality of your paper, as plagiarism can lead to serious consequences. To avoid plagiarism, you should use proper paraphrasing and quoting techniques. Paraphrasing is rewriting a text in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. Quoting involves directly citing the source. Giving credit to the original author or source is essential whenever you borrow their ideas or words. You can also use plagiarism detection tools such as Scribbr or Grammarly to check the originality of your paper. These tools compare your draft writing to a vast database of online sources. If you find any accidental plagiarism, you should correct it immediately by rephrasing or citing the source.
12. Revise, edit, and proofread
One of the essential qualities of excellent writers is their ability to understand the importance of editing and proofreading. Even though it's tempting to call it a day once you've finished your writing, editing your work can significantly improve its quality. It's natural to overlook the weaker areas when you've just finished writing a paper. Therefore, it's best to take a break of a day or two, or even up to a week, to refresh your mind. This way, you can return to your work with a new perspective. After some breathing room, you can spot any inconsistencies, spelling and grammar errors, typos, or missing citations and correct them.
- The best research paper format
The format of your research paper should align with the requirements set forth by your college, school, or target publication.
There is no one “best” format, per se. Depending on the stated requirements, you may need to include the following elements:
Title page: The title page of a research paper typically includes the title, author's name, and institutional affiliation and may include additional information such as a course name or instructor's name.
Table of contents: Include a table of contents to make it easy for readers to find specific sections of your paper.
Abstract: The abstract is a summary of the purpose of the paper.
Methods : In this section, describe the research methods used. This may include collecting data , conducting interviews, or doing field research .
Results: Summarize the conclusions you drew from your research in this section.
Discussion: In this section, discuss the implications of your research . Be sure to mention any significant limitations to your approach and suggest areas for further research.
Tables, charts, and illustrations: Use tables, charts, and illustrations to help convey your research findings and make them easier to understand.
Works cited or reference page: Include a works cited or reference page to give credit to the sources that you used to conduct your research.
Bibliography: Provide a list of all the sources you consulted while conducting your research.
Dedication and acknowledgments : Optionally, you may include a dedication and acknowledgments section to thank individuals who helped you with your research.
- General style and formatting guidelines
Formatting your research paper means you can submit it to your college, journal, or other publications in compliance with their criteria.
Research papers tend to follow the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), or Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS) guidelines.
Here’s how each style guide is typically used:
Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS):
CMOS is a versatile style guide used for various types of writing. It's known for its flexibility and use in the humanities. CMOS provides guidelines for citations, formatting, and overall writing style. It allows for both footnotes and in-text citations, giving writers options based on their preferences or publication requirements.
American Psychological Association (APA):
APA is common in the social sciences. It’s hailed for its clarity and emphasis on precision. It has specific rules for citing sources, creating references, and formatting papers. APA style uses in-text citations with an accompanying reference list. It's designed to convey information efficiently and is widely used in academic and scientific writing.
Modern Language Association (MLA):
MLA is widely used in the humanities, especially literature and language studies. It emphasizes the author-page format for in-text citations and provides guidelines for creating a "Works Cited" page. MLA is known for its focus on the author's name and the literary works cited. It’s frequently used in disciplines that prioritize literary analysis and critical thinking.
To confirm you're using the latest style guide, check the official website or publisher's site for updates, consult academic resources, and verify the guide's publication date. Online platforms and educational resources may also provide summaries and alerts about any revisions or additions to the style guide.
Citing sources
When working on your research paper, it's important to cite the sources you used properly. Your citation style will guide you through this process. Generally, there are three parts to citing sources in your research paper:
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation.
Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
In-text citations include the author's surname and the date of the citation.
Footnotes appear at the bottom of each page of your research paper. They may also be summarized within a reference list at the end of the paper.
A reference list includes all of the research used within the paper at the end of the document. It should include the author, date, paper title, and publisher listed in the order that aligns with your citation style.
10 research paper writing tips:
Following some best practices is essential to writing a research paper that contributes to your field of study and creates a positive impact.
These tactics will help you structure your argument effectively and ensure your work benefits others:
Clear and precise language: Ensure your language is unambiguous. Use academic language appropriately, but keep it simple. Also, provide clear takeaways for your audience.
Effective idea separation: Organize the vast amount of information and sources in your paper with paragraphs and titles. Create easily digestible sections for your readers to navigate through.
Compelling intro: Craft an engaging introduction that captures your reader's interest. Hook your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
Thorough revision and editing: Take the time to review and edit your paper comprehensively. Use tools like Grammarly to detect and correct small, overlooked errors.
Thesis precision: Develop a clear and concise thesis statement that guides your paper. Ensure that your thesis aligns with your research's overall purpose and contribution.
Logical flow of ideas: Maintain a logical progression throughout the paper. Use transitions effectively to connect different sections and maintain coherence.
Critical evaluation of sources: Evaluate and critically assess the relevance and reliability of your sources. Ensure that your research is based on credible and up-to-date information.
Thematic consistency: Maintain a consistent theme throughout the paper. Ensure that all sections contribute cohesively to the overall argument.
Relevant supporting evidence: Provide concise and relevant evidence to support your arguments. Avoid unnecessary details that may distract from the main points.
Embrace counterarguments: Acknowledge and address opposing views to strengthen your position. Show that you have considered alternative arguments in your field.
7 research tips
If you want your paper to not only be well-written but also contribute to the progress of human knowledge, consider these tips to take your paper to the next level:
Selecting the appropriate topic: The topic you select should align with your area of expertise, comply with the requirements of your project, and have sufficient resources for a comprehensive investigation.
Use academic databases: Academic databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and JSTOR offer a wealth of research papers that can help you discover everything you need to know about your chosen topic.
Critically evaluate sources: It is important not to accept research findings at face value. Instead, it is crucial to critically analyze the information to avoid jumping to conclusions or overlooking important details. A well-written research paper requires a critical analysis with thorough reasoning to support claims.
Diversify your sources: Expand your research horizons by exploring a variety of sources beyond the standard databases. Utilize books, conference proceedings, and interviews to gather diverse perspectives and enrich your understanding of the topic.
Take detailed notes: Detailed note-taking is crucial during research and can help you form the outline and body of your paper.
Stay up on trends: Keep abreast of the latest developments in your field by regularly checking for recent publications. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant journals, and attend conferences to stay informed about emerging trends and advancements.
Engage in peer review: Seek feedback from peers or mentors to ensure the rigor and validity of your research . Peer review helps identify potential weaknesses in your methodology and strengthens the overall credibility of your findings.
- The real-world impact of research papers
Writing a research paper is more than an academic or business exercise. The experience provides an opportunity to explore a subject in-depth, broaden one's understanding, and arrive at meaningful conclusions. With careful planning, dedication, and hard work, writing a research paper can be a fulfilling and enriching experience contributing to advancing knowledge.
How do I publish my research paper?
Many academics wish to publish their research papers. While challenging, your paper might get traction if it covers new and well-written information. To publish your research paper, find a target publication, thoroughly read their guidelines, format your paper accordingly, and send it to them per their instructions. You may need to include a cover letter, too. After submission, your paper may be peer-reviewed by experts to assess its legitimacy, quality, originality, and methodology. Following review, you will be informed by the publication whether they have accepted or rejected your paper.
What is a good opening sentence for a research paper?
Beginning your research paper with a compelling introduction can ensure readers are interested in going further. A relevant quote, a compelling statistic, or a bold argument can start the paper and hook your reader. Remember, though, that the most important aspect of a research paper is the quality of the information––not necessarily your ability to storytell, so ensure anything you write aligns with your goals.
Research paper vs. a research proposal—what’s the difference?
While some may confuse research papers and proposals, they are different documents.
A research proposal comes before a research paper. It is a detailed document that outlines an intended area of exploration. It includes the research topic, methodology, timeline, sources, and potential conclusions. Research proposals are often required when seeking approval to conduct research.
A research paper is a summary of research findings. A research paper follows a structured format to present those findings and construct an argument or conclusion.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
- 10 research paper
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Body Paragraphs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Body paragraphs: Moving from general to specific information
Your paper should be organized in a manner that moves from general to specific information. Every time you begin a new subject, think of an inverted pyramid - The broadest range of information sits at the top, and as the paragraph or paper progresses, the author becomes more and more focused on the argument ending with specific, detailed evidence supporting a claim. Lastly, the author explains how and why the information she has just provided connects to and supports her thesis (a brief wrap-up or warrant).

Moving from General to Specific Information
The four elements of a good paragraph (TTEB)
A good paragraph should contain at least the following four elements: T ransition, T opic sentence, specific E vidence and analysis, and a B rief wrap-up sentence (also known as a warrant ) –TTEB!
- A T ransition sentence leading in from a previous paragraph to assure smooth reading. This acts as a hand-off from one idea to the next.
- A T opic sentence that tells the reader what you will be discussing in the paragraph.
- Specific E vidence and analysis that supports one of your claims and that provides a deeper level of detail than your topic sentence.
- A B rief wrap-up sentence that tells the reader how and why this information supports the paper’s thesis. The brief wrap-up is also known as the warrant. The warrant is important to your argument because it connects your reasoning and support to your thesis, and it shows that the information in the paragraph is related to your thesis and helps defend it.
Supporting evidence (induction and deduction)
Induction is the type of reasoning that moves from specific facts to a general conclusion. When you use induction in your paper, you will state your thesis (which is actually the conclusion you have come to after looking at all the facts) and then support your thesis with the facts. The following is an example of induction taken from Dorothy U. Seyler’s Understanding Argument :
There is the dead body of Smith. Smith was shot in his bedroom between the hours of 11:00 p.m. and 2:00 a.m., according to the coroner. Smith was shot with a .32 caliber pistol. The pistol left in the bedroom contains Jones’s fingerprints. Jones was seen, by a neighbor, entering the Smith home at around 11:00 p.m. the night of Smith’s death. A coworker heard Smith and Jones arguing in Smith’s office the morning of the day Smith died.
Conclusion: Jones killed Smith.
Here, then, is the example in bullet form:
- Conclusion: Jones killed Smith
- Support: Smith was shot by Jones’ gun, Jones was seen entering the scene of the crime, Jones and Smith argued earlier in the day Smith died.
- Assumption: The facts are representative, not isolated incidents, and thus reveal a trend, justifying the conclusion drawn.
When you use deduction in an argument, you begin with general premises and move to a specific conclusion. There is a precise pattern you must use when you reason deductively. This pattern is called syllogistic reasoning (the syllogism). Syllogistic reasoning (deduction) is organized in three steps:
- Major premise
- Minor premise
In order for the syllogism (deduction) to work, you must accept that the relationship of the two premises lead, logically, to the conclusion. Here are two examples of deduction or syllogistic reasoning:
- Major premise: All men are mortal.
- Minor premise: Socrates is a man.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
- Major premise: People who perform with courage and clear purpose in a crisis are great leaders.
- Minor premise: Lincoln was a person who performed with courage and a clear purpose in a crisis.
- Conclusion: Lincoln was a great leader.
So in order for deduction to work in the example involving Socrates, you must agree that (1) all men are mortal (they all die); and (2) Socrates is a man. If you disagree with either of these premises, the conclusion is invalid. The example using Socrates isn’t so difficult to validate. But when you move into more murky water (when you use terms such as courage , clear purpose , and great ), the connections get tenuous.
For example, some historians might argue that Lincoln didn’t really shine until a few years into the Civil War, after many Union losses to Southern leaders such as Robert E. Lee.
The following is a clear example of deduction gone awry:
- Major premise: All dogs make good pets.
- Minor premise: Doogle is a dog.
- Conclusion: Doogle will make a good pet.
If you don’t agree that all dogs make good pets, then the conclusion that Doogle will make a good pet is invalid.
When a premise in a syllogism is missing, the syllogism becomes an enthymeme. Enthymemes can be very effective in argument, but they can also be unethical and lead to invalid conclusions. Authors often use enthymemes to persuade audiences. The following is an example of an enthymeme:
If you have a plasma TV, you are not poor.
The first part of the enthymeme (If you have a plasma TV) is the stated premise. The second part of the statement (you are not poor) is the conclusion. Therefore, the unstated premise is “Only rich people have plasma TVs.” The enthymeme above leads us to an invalid conclusion (people who own plasma TVs are not poor) because there are plenty of people who own plasma TVs who are poor. Let’s look at this enthymeme in a syllogistic structure:
- Major premise: People who own plasma TVs are rich (unstated above).
- Minor premise: You own a plasma TV.
- Conclusion: You are not poor.
To help you understand how induction and deduction can work together to form a solid argument, you may want to look at the United States Declaration of Independence. The first section of the Declaration contains a series of syllogisms, while the middle section is an inductive list of examples. The final section brings the first and second sections together in a compelling conclusion.
How to Write a Research Paper

If you already have a headache trying to understand what research paper is all about, we have created an ultimate guide for you on how to write a research paper. You will find all the answers to your questions regarding structure, planning, doing investigation, finding the topic that appeals to you. Plus, you will find out the secret to an excellent paper. Are you at the edge of your seat? Let us start with the basics then.
- What is a Research Paper
- Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
- Report Papers and Thesis Papers
- How to Start a Research Paper
- How to Choose a Topic for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Plan
- How to Do Research
- How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Rough Draft
- How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Body of a Research Paper
- How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Revise and Edit a Research Paper
- How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper
- What Makes a Good Research Paper
Research Paper Writing Services
What is a research paper.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
You probably know the saying ‘the devil is not as black as he is painted’. This particular saying is absolutely true when it comes to writing a research paper. Your feet are cold even with the thought of this assignment. You have heard terrifying stories from older students. You have never done this before, so certainly you are scared. What is a research paper? How should I start? What are all these requirements about?
Luckily, you have a friend in need. That is our writing service. First and foremost, let us clarify the definition. A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides information about a particular topic that you’ve researched . In other words, you choose a topic: about historical events, the work of some artist, some social issues etc. Then you collect data on the given topic and analyze it. Finally, you put your analysis on paper. See, it is not as scary as it seems. If you are still having doubts, whether you can handle it yourself, we are here to help you. Our team of writers can help you choose the topic, or give you advice on how to plan your work, or how to start, or craft a paper for you. Just contact us 24/7 and see everything yourself.
5 Reasons for Writing a Research Paper
Why should I spend my time writing some academic paper? What is the use of it? Is not some practical knowledge more important? The list of questions is endless when it comes to a research paper. That is why we have outlined 5 main reasons why writing a research paper is a good thing.
- You will learn how to organize your time
If you want to write a research paper, you will have to learn how to manage your time. This type of assignment cannot be done overnight. It requires careful planning and you will need to learn how to do it. Later, you will be able to use these time-managing skills in your personal life, so why not developing them?
- You will discover your writing skills
You cannot know something before you try it. This rule relates to writing as well. You cannot claim that you cannot write until you try it yourself. It will be really difficult at the beginning, but then the words will come to your head themselves.
- You will improve your analytical skills
Writing a research paper is all about investigation and analysis. You will need to collect data, examine and classify it. These skills are needed in modern life more than anything else is.
- You will gain confidence
Once you do your own research, it gives you the feeling of confidence in yourself. The reason is simple human brain likes solving puzzles and your assignment is just another puzzle to be solved.
- You will learn how to persuade the reader
When you write your paper, you should always remember that you are writing it for someone to read. Moreover, you want this someone to believe in your ideas. For this reason, you will have to learn different convincing methods and techniques. You will learn how to make your writing persuasive. In turns, you will be able to use these methods in real life.
What is the Difference between Report and Thesis Papers?
A common question is ‘what is the difference between a report paper and a thesis paper?’ The difference lies in the aim of these two assignments. While the former aims at presenting the information, the latter aims at providing your opinion on the matter. In other words, in a report paper you have to summarize your findings. In a thesis paper, you choose some issue and defend your point of view by persuading the reader. It is that simple.
A thesis paper is a more common assignment than a report paper. This task will help a professor to evaluate your analytical skills and skills to present your ideas logically. These skills are more important than just the ability to collect and summarize data.
How to Write a Research Paper Step by Step
Research comes from the French word rechercher , meaning “to seek out.” Writing a research paper requires you to seek out information about a subject, take a stand on it, and back it up with the opinions, ideas, and views of others. What results is a printed paper variously known as a term paper or library paper, usually between five and fifteen pages long—most instructors specify a minimum length—in which you present your views and findings on the chosen subject.

It is not a secret that the majority of students hate writing a research paper. The reason is simple it steals your time and energy. Not to mention, constant anxiety that you will not be able to meet the deadline or that you will forget about some academic requirement.
We will not lie to you; a research paper is a difficult assignment. You will have to spend a lot of time. You will need to read, to analyze, and to search for the material. You will probably be stuck sometimes. However, if you organize your work smart, you will gain something that is worth all the effort – knowledge, experience, and high grades.
The reason why many students fail writing a research paper is that nobody explained them how to start and how to plan their work. Luckily, you have found our writing service and we are ready to shed the light on this dark matter.
We have created a step by step guide for you on how to write a research paper. We will dwell upon the structure, the writing tips, the writing strategies as well as academic requirements. Read this whole article and you will see that you can handle writing this assignment and our team of writers is here to assist you.
How to Start a Research Paper?

It all starts with the assignment. Your professor gives you the task. It may be either some general issue or specific topic to write about. Your assignment is your first guide to success. If you understand what you need to do according to the assignment, you are on the road to high results. Do not be scared to clarify your task if you need to. There is nothing wrong in asking a question if you want to do something right. You can ask your professor or you can ask our writers who know a thing or two in academic writing.
It is essential to understand the assignment. A good beginning makes a good ending, so start smart.
Learn how to start a research paper .
Choosing a Topic for a Research Paper

We have already mentioned that it is not enough to do great research. You need to persuade the reader that you have made some great research. What convinces better that an eye-catching topic? That is why it is important to understand how to choose a topic for a research paper.
First, you need to delimit the general idea to a more specific one. Secondly, you need to find what makes this topic interesting for you and for the academia. Finally, you need to refine you topic. Remember, it is not something you will do in one day. You can be reshaping your topic throughout your whole writing process. Still, reshaping not changing it completely. That is why keep in your head one main idea: your topic should be precise and compelling .
Learn how to choose a topic for a research paper .
How to Write a Proposal for a Research Paper?

If you do not know what a proposal is, let us explain it to you. A proposal should answer three main questions:
- What is the main aim of your investigation?
- Why is your investigation important?
- How are you going to achieve the results?
In other words, proposal should show why your topic is interesting and how you are going to prove it. As to writing requirements, they may differ. That is why make sure you find out all the details at your department. You can ask your departmental administrator or find information online at department’s site. It is crucial to follow all the administrative requirements, as it will influence your grade.
Learn how to write a proposal for a research paper .
How to Write a Research Plan?

The next step is writing a plan. You have already decided on the main issues, you have chosen the bibliography, and you have clarified the methods. Here comes the planning. If you want to avoid writer’s block, you have to structure you work. Discuss your strategies and ideas with your instructor. Think thoroughly why you need to present some data and ideas first and others second. Remember that there are basic structure elements that your research paper should include:
- Thesis Statement
- Introduction
- Bibliography
You should keep in mind this skeleton when planning your work. This will keep your mind sharp and your ideas will flow logically.
Learn how to write a research plan .
How to Do Research?

Your research will include three stages: collecting data, reading and analyzing it, and writing itself.
First, you need to collect all the material that you will need for you investigation: films, documents, surveys, interviews, and others. Secondly, you will have to read and analyze. This step is tricky, as you need to do this part smart. It is not enough just to read, as you cannot keep in mind all the information. It is essential that you make notes and write down your ideas while analyzing some data. When you get down to the stage number three, writing itself, you will already have the main ideas written on your notes. Plus, remember to jot down the reference details. You will then appreciate this trick when you will have to write the bibliography.
If you do your research this way, it will be much easier for you to write the paper. You will already have blocks of your ideas written down and you will just need to add some material and refine your paper.
Learn how to do research .
How to Write an Outline for a Research Paper?

To make your paper well organized you need to write an outline. Your outline will serve as your guiding star through the writing process. With a great outline you will not get sidetracked, because you will have a structured plan to follow. Both you and the reader will benefit from your outline. You present your ideas logically and you make your writing coherent according to your plan. As a result, this outline guides the reader through your paper and the reader enjoys the way you demonstrate your ideas.
Learn how to write an outline for a research paper . See research paper outline examples .
How to Write a Thesis Statement for a Research Paper?

Briefly, the thesis is the main argument of your research paper. It should be precise, convincing and logical. Your thesis statement should include your point of view supported by evidence or logic. Still, remember it should be precise. You should not beat around the bush, or provide all the possible evidence you have found. It is usually a single sentence that shows your argument. In on sentence you should make a claim, explain why it significant and convince the reader that your point of view is important.
Learn how to write a thesis statement for a research paper . See research paper thesis statement examples .
Should I Write a Rough Draft for a Research Paper?

Do you know any writer who put their ideas on paper, then never edited them and just published? Probably, no writer did so. Writing a research paper is no exception. It is impossible to cope with this assignment without writing a rough draft.
Your draft will help you understand what you need to polish to make your paper perfect. All the requirements, academic standards make it difficult to do everything flawlessly at the first attempt. Make sure you know all the formatting requirements: margins, words quantity, reference requirements, formatting styles etc.
Learn how to write a rough draft for a research paper .
How to Write an Introduction for a Research Paper?

Let us make it more vivid for you. We have narrowed down the tips on writing an introduction to the three main ones:
- Include your thesis in your introduction
Remember to include the thesis statement in your introduction. Usually, it goes at the end of the first paragraph.
- Present the main ideas of the body
You should tell the main topics you are going to discuss in the main body. For this reason, before writing this part of introduction, make sure you know what is your main body is going to be about. It should include your main ideas.
- Polish your thesis and introduction
When you finish the main body of your paper, come back to the thesis statement and introduction. Restate something if needed. Just make it perfect; because introduction is like the trailer to your paper, it should make the reader want to read the whole piece.
Learn how to write an introduction for a research paper . See research paper introduction examples .
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper?

A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument.
It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic. Stay focused and do not be sidetracked. You have your outline, so follow it.
Here are the main tips to keep in head when writing a body of a research paper:
- Let the ideas flow logically
- Include only relevant information
- Provide the evidence
- Structure the paragraphs
- Make the coherent transition from one paragraph to another
See? When it is all structured, it is not as scary as it seemed at the beginning. Still, if you have doubts, you can always ask our writers for help.
Learn how to write a body of a research paper . See research paper transition examples .
How to Write a Conclusion for a Research Paper?

Writing a good conclusion is important as writing any other part of the paper. Remember that conclusion is not a summary of what you have mentioned before. A good conclusion should include your last strong statement.
If you have written everything according to the plan, the reader already knows why your investigation is important. The reader has already seen the evidence. The only thing left is a strong concluding thought that will organize all your findings.
Never include any new information in conclusion. You need to conclude, not to start a new discussion.
Learn how to write a conclusion for a research paper .
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper?

An abstract is a brief summary of your paper, usually 100-200 words. You should provide the main gist of your paper in this short summary. An abstract can be informative, descriptive or proposal. Depending on the type of abstract, you need to write, the requirements will differ.
To write an informative abstract you have to provide the summary of the whole paper. Informative summary. In other words, you need to tell about the main points of your work, the methods used, the results and the conclusion of your research.
To write a descriptive abstract you will not have to provide any summery. You should write a short teaser of your paper. That is to say, you need to write an overview of your paper. The aim of a descriptive abstract is to interest the reader.
Finally, to write a proposal abstract you will need to write the basic summary as for the informative abstract. However, the difference is the following: you aim at persuading someone to let you write on the topic. That is why, a proposal abstract should present your topic as the one worth investigating.
Learn how to write an abstract for a research paper .
Should I Revise and Edit a Research Paper?

Revising and editing your paper is essential if you want to get high grades. Let us help you revise your paper smart:
- Check your paper for spelling and grammar mistakes
- Sharpen the vocabulary
- Make sure there are no slang words in your paper
- Examine your paper in terms of structure
- Compare your topic, thesis statement to the whole piece
- Check your paper for plagiarism
If you need assistance with proofreading and editing your paper, you can turn to the professional editors at our service. They will help you polish your paper to perfection.
Learn how to revise and edit a research paper .
How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper?

First, let us make it clear that bibliography and works cited are two different things. Works cited are those that you cited in your paper. Bibliography should include all the materials you used to do your research. Still, remember that bibliography requirements differ depending on the formatting style of your paper. For this reason, make sure you ask you professor all the requirements you need to meet to avoid any misunderstanding.
Learn how to write a bibliography for a research paper .
The Key Secret to a Good Research Paper
Now when you know all the stages of writing a research paper, you are ready to find the key to a good research paper:
- Choose the topic that really interests you
- Make the topic interesting for you even if it is not at the beginning
- Follow the step by step guide and do not get sidetracked
- Be persistent and believe in yourself
- Really do research and write your paper from scratch
- Learn the convincing writing techniques and use them
- Follow the requirements of your assignment
- Ask for help if needed from real professionals
Feeling more confident about your paper now? We are sure you do. Still, if you need help, you can always rely on us 24/7.
We hope we have made writing a research paper much easier for you. We realize that it requires lots of time and energy. We believe when you say that you cannot handle it anymore. For this reason, we have been helping students like you for years. Our professional team of writers is ready to tackle any challenge.
All our authors are experienced writers crafting excellent academic papers. We help students meet the deadline and get the top grades they want. You can see everything yourself. All you need to do is to place your order online and we will contact you. Writing a research paper with us is truly easy, so why do not you check it yourself?
Additional Resources for Research Paper Writing:
- Anthropology Research
- Career Research
- Communication Research
- Criminal Justice Research
- Health Research
- Political Science Research
- Psychology Research
- Sociology Research
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you’re on board with our cookie policy

- A Research Guide
- Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Body Paragraph Structure
Introduction.
- Referrences
- Ways to start paragraph
- Step by step guide
- Research paragraph examples

Learning the basics of a paragraph structure
- Title (cover page).
- Introduction.
- Literature review.
- Research methodology.
- Data analysis.
- Conclusion.
- Reference page.
5 winning ways to start a body paragraph
- Topic Sentence : it should provide a clear focus and introduce the specific aspect you will discuss. For example, “One key factor influencing climate change is…”.
- Opening Statement: grab your readers’ attention with a thought-provoking or surprising statement related to your topic. For instance, “The alarming increase in global temperatures has reached a critical point, demanding immediate action.”
- Quotation: find a relevant quote from a reputable source. It won’t only add credibility to your research but will also engage the reader right from the start.
- Anecdote or example: start your academic paragraph with a funny story or a real-world example that illustrates the significance of your research topic.
- Background information : provide a brief background or context for the topic you are about to discuss. For example, “In recent years, the prevalence of cyber-attacks has skyrocketed, posing a severe threat to individuals, organizations, and even national security.”
A step-by-step guide to starting a concise body paragraph
Step 1: introduce the main point or argument., step 2: provide evidence or examples., step 3: explain and analyze., step 4: connect to the main argument., step 5: review and revise., flawless body paragraph example: how does it look.
- Topic Sentence: Rising global temperatures have significant implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.
- Evidence/Example 1: According to a study by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), global average temperatures have increased by 1.1 degrees Celsius since pre-industrial times (IPCC, 2021). This temperature rise has led to melting polar ice caps and glaciers, rising sea levels, and coastal erosion (Smith et al., 2019).
- Explanation/Analysis 1: The significant increase in global temperatures has caused observable changes in the Earth’s physical environment. The melting of polar ice caps not only contributes to the rise in sea levels but also disrupts marine ecosystems.
- Evidence/Example 2: In addition to the loss of coastal habitats, higher temperatures have also resulted in shifts in the geographical distribution of species. Research by Parmesan and Yohe (2019) indicates that many plant and animal species have altered their ranges and migration patterns in response to changing climate conditions.
- Explanation/Analysis 2: The observed shifts in species distribution highlight the vulnerability of ecosystems to climate change. As temperature zone modification, species that cannot adapt or migrate to suitable habitats may face reduced reproductive success and increased risk of extinction.
- Connect to the main argument: These examples demonstrate that the rising global temperatures associated with climate change have profound implications for ecosystems and biodiversity.

The bottom line

- Writing a Research Paper
- Research Paper Title
- Research Paper Sources
- Research Paper Problem Statement
- Research Paper Thesis Statement
- Hypothesis for a Research Paper
- Research Question
- Research Paper Outline
- Research Paper Summary
- Research Paper Prospectus
- Research Paper Proposal
- Research Paper Format
- Research Paper Styles
- AMA Style Research Paper
- MLA Style Research Paper
- Chicago Style Research Paper
- APA Style Research Paper
- Research Paper Structure
- Research Paper Cover Page
- Research Paper Abstract
- Research Paper Introduction
- Research Paper Body Paragraph
- Research Paper Literature Review
- Research Paper Background
- Research Paper Methods Section
- Research Paper Results Section
- Research Paper Discussion Section
- Research Paper Conclusion
- Research Paper Appendix
- Research Paper Bibliography
- APA Reference Page
- Annotated Bibliography
- Bibliography vs Works Cited vs References Page
- Research Paper Types
- What is Qualitative Research

Receive paper in 3 Hours!
- Choose the number of pages.
- Select your deadline.
- Complete your order.
Number of Pages
550 words (double spaced)
Deadline: 10 days left
By clicking "Log In", you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We'll occasionally send you account related and promo emails.
Sign Up for your FREE account

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
13.1 Formatting a Research Paper
Learning objectives.
- Identify the major components of a research paper written using American Psychological Association (APA) style.
- Apply general APA style and formatting conventions in a research paper.
In this chapter, you will learn how to use APA style , the documentation and formatting style followed by the American Psychological Association, as well as MLA style , from the Modern Language Association. There are a few major formatting styles used in academic texts, including AMA, Chicago, and Turabian:
- AMA (American Medical Association) for medicine, health, and biological sciences
- APA (American Psychological Association) for education, psychology, and the social sciences
- Chicago—a common style used in everyday publications like magazines, newspapers, and books
- MLA (Modern Language Association) for English, literature, arts, and humanities
- Turabian—another common style designed for its universal application across all subjects and disciplines
While all the formatting and citation styles have their own use and applications, in this chapter we focus our attention on the two styles you are most likely to use in your academic studies: APA and MLA.
If you find that the rules of proper source documentation are difficult to keep straight, you are not alone. Writing a good research paper is, in and of itself, a major intellectual challenge. Having to follow detailed citation and formatting guidelines as well may seem like just one more task to add to an already-too-long list of requirements.
Following these guidelines, however, serves several important purposes. First, it signals to your readers that your paper should be taken seriously as a student’s contribution to a given academic or professional field; it is the literary equivalent of wearing a tailored suit to a job interview. Second, it shows that you respect other people’s work enough to give them proper credit for it. Finally, it helps your reader find additional materials if he or she wishes to learn more about your topic.
Furthermore, producing a letter-perfect APA-style paper need not be burdensome. Yes, it requires careful attention to detail. However, you can simplify the process if you keep these broad guidelines in mind:
- Work ahead whenever you can. Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” includes tips for keeping track of your sources early in the research process, which will save time later on.
- Get it right the first time. Apply APA guidelines as you write, so you will not have much to correct during the editing stage. Again, putting in a little extra time early on can save time later.
- Use the resources available to you. In addition to the guidelines provided in this chapter, you may wish to consult the APA website at http://www.apa.org or the Purdue University Online Writing lab at http://owl.english.purdue.edu , which regularly updates its online style guidelines.
General Formatting Guidelines
This chapter provides detailed guidelines for using the citation and formatting conventions developed by the American Psychological Association, or APA. Writers in disciplines as diverse as astrophysics, biology, psychology, and education follow APA style. The major components of a paper written in APA style are listed in the following box.
These are the major components of an APA-style paper:
Body, which includes the following:
- Headings and, if necessary, subheadings to organize the content
- In-text citations of research sources
- References page
All these components must be saved in one document, not as separate documents.
The title page of your paper includes the following information:
- Title of the paper
- Author’s name
- Name of the institution with which the author is affiliated
- Header at the top of the page with the paper title (in capital letters) and the page number (If the title is lengthy, you may use a shortened form of it in the header.)
List the first three elements in the order given in the previous list, centered about one third of the way down from the top of the page. Use the headers and footers tool of your word-processing program to add the header, with the title text at the left and the page number in the upper-right corner. Your title page should look like the following example.

The next page of your paper provides an abstract , or brief summary of your findings. An abstract does not need to be provided in every paper, but an abstract should be used in papers that include a hypothesis. A good abstract is concise—about one hundred fifty to two hundred fifty words—and is written in an objective, impersonal style. Your writing voice will not be as apparent here as in the body of your paper. When writing the abstract, take a just-the-facts approach, and summarize your research question and your findings in a few sentences.
In Chapter 12 “Writing a Research Paper” , you read a paper written by a student named Jorge, who researched the effectiveness of low-carbohydrate diets. Read Jorge’s abstract. Note how it sums up the major ideas in his paper without going into excessive detail.

Write an abstract summarizing your paper. Briefly introduce the topic, state your findings, and sum up what conclusions you can draw from your research. Use the word count feature of your word-processing program to make sure your abstract does not exceed one hundred fifty words.
Depending on your field of study, you may sometimes write research papers that present extensive primary research, such as your own experiment or survey. In your abstract, summarize your research question and your findings, and briefly indicate how your study relates to prior research in the field.
Margins, Pagination, and Headings
APA style requirements also address specific formatting concerns, such as margins, pagination, and heading styles, within the body of the paper. Review the following APA guidelines.
Use these general guidelines to format the paper:
- Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch.
- Use double-spaced text throughout your paper.
- Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point).
- Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section. Page numbers appear flush right within your header.
- Section headings and subsection headings within the body of your paper use different types of formatting depending on the level of information you are presenting. Additional details from Jorge’s paper are provided.

Begin formatting the final draft of your paper according to APA guidelines. You may work with an existing document or set up a new document if you choose. Include the following:
- Your title page
- The abstract you created in Note 13.8 “Exercise 1”
- Correct headers and page numbers for your title page and abstract
APA style uses section headings to organize information, making it easy for the reader to follow the writer’s train of thought and to know immediately what major topics are covered. Depending on the length and complexity of the paper, its major sections may also be divided into subsections, sub-subsections, and so on. These smaller sections, in turn, use different heading styles to indicate different levels of information. In essence, you are using headings to create a hierarchy of information.
The following heading styles used in APA formatting are listed in order of greatest to least importance:
- Section headings use centered, boldface type. Headings use title case, with important words in the heading capitalized.
- Subsection headings use left-aligned, boldface type. Headings use title case.
- The third level uses left-aligned, indented, boldface type. Headings use a capital letter only for the first word, and they end in a period.
- The fourth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are boldfaced and italicized.
- The fifth level follows the same style used for the previous level, but the headings are italicized and not boldfaced.
Visually, the hierarchy of information is organized as indicated in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” .
Table 13.1 Section Headings
A college research paper may not use all the heading levels shown in Table 13.1 “Section Headings” , but you are likely to encounter them in academic journal articles that use APA style. For a brief paper, you may find that level 1 headings suffice. Longer or more complex papers may need level 2 headings or other lower-level headings to organize information clearly. Use your outline to craft your major section headings and determine whether any subtopics are substantial enough to require additional levels of headings.
Working with the document you developed in Note 13.11 “Exercise 2” , begin setting up the heading structure of the final draft of your research paper according to APA guidelines. Include your title and at least two to three major section headings, and follow the formatting guidelines provided above. If your major sections should be broken into subsections, add those headings as well. Use your outline to help you.
Because Jorge used only level 1 headings, his Exercise 3 would look like the following:
Citation Guidelines
In-text citations.
Throughout the body of your paper, include a citation whenever you quote or paraphrase material from your research sources. As you learned in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , the purpose of citations is twofold: to give credit to others for their ideas and to allow your reader to follow up and learn more about the topic if desired. Your in-text citations provide basic information about your source; each source you cite will have a longer entry in the references section that provides more detailed information.
In-text citations must provide the name of the author or authors and the year the source was published. (When a given source does not list an individual author, you may provide the source title or the name of the organization that published the material instead.) When directly quoting a source, it is also required that you include the page number where the quote appears in your citation.
This information may be included within the sentence or in a parenthetical reference at the end of the sentence, as in these examples.
Epstein (2010) points out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Here, the writer names the source author when introducing the quote and provides the publication date in parentheses after the author’s name. The page number appears in parentheses after the closing quotation marks and before the period that ends the sentence.
Addiction researchers caution that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (Epstein, 2010, p. 137).
Here, the writer provides a parenthetical citation at the end of the sentence that includes the author’s name, the year of publication, and the page number separated by commas. Again, the parenthetical citation is placed after the closing quotation marks and before the period at the end of the sentence.
As noted in the book Junk Food, Junk Science (Epstein, 2010, p. 137), “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive.”
Here, the writer chose to mention the source title in the sentence (an optional piece of information to include) and followed the title with a parenthetical citation. Note that the parenthetical citation is placed before the comma that signals the end of the introductory phrase.
David Epstein’s book Junk Food, Junk Science (2010) pointed out that “junk food cannot be considered addictive in the same way that we think of psychoactive drugs as addictive” (p. 137).
Another variation is to introduce the author and the source title in your sentence and include the publication date and page number in parentheses within the sentence or at the end of the sentence. As long as you have included the essential information, you can choose the option that works best for that particular sentence and source.
Citing a book with a single author is usually a straightforward task. Of course, your research may require that you cite many other types of sources, such as books or articles with more than one author or sources with no individual author listed. You may also need to cite sources available in both print and online and nonprint sources, such as websites and personal interviews. Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.2 “Citing and Referencing Techniques” and Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provide extensive guidelines for citing a variety of source types.
Writing at Work
APA is just one of several different styles with its own guidelines for documentation, formatting, and language usage. Depending on your field of interest, you may be exposed to additional styles, such as the following:
- MLA style. Determined by the Modern Languages Association and used for papers in literature, languages, and other disciplines in the humanities.
- Chicago style. Outlined in the Chicago Manual of Style and sometimes used for papers in the humanities and the sciences; many professional organizations use this style for publications as well.
- Associated Press (AP) style. Used by professional journalists.
References List
The brief citations included in the body of your paper correspond to the more detailed citations provided at the end of the paper in the references section. In-text citations provide basic information—the author’s name, the publication date, and the page number if necessary—while the references section provides more extensive bibliographical information. Again, this information allows your reader to follow up on the sources you cited and do additional reading about the topic if desired.
The specific format of entries in the list of references varies slightly for different source types, but the entries generally include the following information:
- The name(s) of the author(s) or institution that wrote the source
- The year of publication and, where applicable, the exact date of publication
- The full title of the source
- For books, the city of publication
- For articles or essays, the name of the periodical or book in which the article or essay appears
- For magazine and journal articles, the volume number, issue number, and pages where the article appears
- For sources on the web, the URL where the source is located
The references page is double spaced and lists entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name. If an entry continues for more than one line, the second line and each subsequent line are indented five spaces. Review the following example. ( Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” , Section 13.3 “Creating a References Section” provides extensive guidelines for formatting reference entries for different types of sources.)

In APA style, book and article titles are formatted in sentence case, not title case. Sentence case means that only the first word is capitalized, along with any proper nouns.
Key Takeaways
- Following proper citation and formatting guidelines helps writers ensure that their work will be taken seriously, give proper credit to other authors for their work, and provide valuable information to readers.
- Working ahead and taking care to cite sources correctly the first time are ways writers can save time during the editing stage of writing a research paper.
- APA papers usually include an abstract that concisely summarizes the paper.
- APA papers use a specific headings structure to provide a clear hierarchy of information.
- In APA papers, in-text citations usually include the name(s) of the author(s) and the year of publication.
- In-text citations correspond to entries in the references section, which provide detailed bibliographical information about a source.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- Research guides
Writing an Educational Research Paper
Research paper sections, customary parts of an education research paper.
There is no one right style or manner for writing an education paper. Content aside, the writing style and presentation of papers in different educational fields vary greatly. Nevertheless, certain parts are common to most papers, for example:
Title/Cover Page
Contains the paper's title, the author's name, address, phone number, e-mail, and the day's date.
Not every education paper requires an abstract. However, for longer, more complex papers abstracts are particularly useful. Often only 100 to 300 words, the abstract generally provides a broad overview and is never more than a page. It describes the essence, the main theme of the paper. It includes the research question posed, its significance, the methodology, and the main results or findings. Footnotes or cited works are never listed in an abstract. Remember to take great care in composing the abstract. It's the first part of the paper the instructor reads. It must impress with a strong content, good style, and general aesthetic appeal. Never write it hastily or carelessly.
Introduction and Statement of the Problem
A good introduction states the main research problem and thesis argument. What precisely are you studying and why is it important? How original is it? Will it fill a gap in other studies? Never provide a lengthy justification for your topic before it has been explicitly stated.
Limitations of Study
Indicate as soon as possible what you intend to do, and what you are not going to attempt. You may limit the scope of your paper by any number of factors, for example, time, personnel, gender, age, geographic location, nationality, and so on.
Methodology
Discuss your research methodology. Did you employ qualitative or quantitative research methods? Did you administer a questionnaire or interview people? Any field research conducted? How did you collect data? Did you utilize other libraries or archives? And so on.
Literature Review
The research process uncovers what other writers have written about your topic. Your education paper should include a discussion or review of what is known about the subject and how that knowledge was acquired. Once you provide the general and specific context of the existing knowledge, then you yourself can build on others' research. The guide Writing a Literature Review will be helpful here.
Main Body of Paper/Argument
This is generally the longest part of the paper. It's where the author supports the thesis and builds the argument. It contains most of the citations and analysis. This section should focus on a rational development of the thesis with clear reasoning and solid argumentation at all points. A clear focus, avoiding meaningless digressions, provides the essential unity that characterizes a strong education paper.
After spending a great deal of time and energy introducing and arguing the points in the main body of the paper, the conclusion brings everything together and underscores what it all means. A stimulating and informative conclusion leaves the reader informed and well-satisfied. A conclusion that makes sense, when read independently from the rest of the paper, will win praise.
Works Cited/Bibliography
See the Citation guide .
Education research papers often contain one or more appendices. An appendix contains material that is appropriate for enlarging the reader's understanding, but that does not fit very well into the main body of the paper. Such material might include tables, charts, summaries, questionnaires, interview questions, lengthy statistics, maps, pictures, photographs, lists of terms, glossaries, survey instruments, letters, copies of historical documents, and many other types of supplementary material. A paper may have several appendices. They are usually placed after the main body of the paper but before the bibliography or works cited section. They are usually designated by such headings as Appendix A, Appendix B, and so on.
- << Previous: Choosing a Topic
- Next: Find Books >>
- Last Updated: Dec 5, 2023 2:26 PM
- Subjects: Education
- Tags: education , education_paper , education_research_paper
How to Write a Research Paper
#scribendiinc
The research paper writing process
In the first article of this two part series, we discussed how to research a term paper . In this article, we will discuss how to write a term or research paper.
Write your thesis statement
After you have spent some time finding your sources and absorbing the information, you should then be able to come up with a thesis statement that tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter. This statement is a road map for the research paper, telling the reader what to expect. It usually consists of a single sentence somewhere in your first paragraph and makes a claim that others might later dispute!
For optimal organization, take the time to write an outline that indicates the main aspects to be discussed. This includes deciding on the order of your sub-topics and which key points you will use as evidence to support your position.
Keep the body of your research paper in good shape
The body is the largest part of a research paper; in it you collect and arrange evidence that will persuade the reader of your argument. It should, therefore, have a logical organization. If the paper is long, it is a good idea to partition the body into sections using headings and sub-headings. This includes using parenthetical citations when referencing another author's work in the body of your text.
Sometimes the beginning isn't the best place to start...
Write the introduction and conclusion of your research paper last in order to ensure accuracy. The introduction is the key to letting your readers know where you are headed and what you hope to accomplish. Remember that while the organization of your research paper may be clear to you, it may not necessarily be clear to your readers. Therefore, the introduction should acquaint them with the journey ahead, making it easier for them to understand what follows and helping to improve their evaluation of your work. Tell your readers in concise terms what the subject of the paper is, what it is that you hope to find out, and how you will go about doing so.
Encapsulating your findings in the conclusion is not the only place in the research paper where you make your voice heard. Your analysis should appear throughout. A common ESL mistake is reciting facts in the body of their essay and then waiting until the conclusion to say what they mean. Good research papers bring data, events, and other material together, interpreting the facts throughout. The conclusion should summarize what you have said in the body and should stress the evidence that supports your analysis.
Don't forget your references
Once your research paper is finished, compile your reference list. This is an alphabetical listing of all the sources you referenced in the body of your paper. If you made notes about your sources, this task should be straightforward. Be sure to follow whatever style guide your professor or school recommends. We have an example APA Reference page and an example MLA Works Cited for your reference.
Edit your research paper to ensure clarity
Once you have the pieces of your research paper in place, it's time to polish, polish, polish! Double-check everything. Ensure you have correctly cited your sources, checked your spelling and grammar, and re-read your paper several times, checking for sense, logical structure, and organization. Readers will judge your paper not only on the quality of research, but also on the quality of the writing.
Ta da! You've done it—your research paper is complete! Just think about what you've learned: not just about your subject, but about the whole investigative process.
Image source: Patrik Goethe/Stocksnap.io
Perfect Your Paper Prior to Submission
Hire an expert academic editor , or get a free sample.
Have You Read?
"The Complete Beginner's Guide to Academic Writing"
Related Posts

Essay Writing: Traffic Signals for the Reader

How to Research a Term Paper

How to Write a Great Thesis Statement
Upload your file(s) so we can calculate your word count, or enter your word count manually.
We will also recommend a service based on the file(s) you upload.
English is not my first language. I need English editing and proofreading so that I sound like a native speaker.
I need to have my journal article, dissertation, or term paper edited and proofread, or I need help with an admissions essay or proposal.
I have a novel, manuscript, play, or ebook. I need editing, copy editing, proofreading, a critique of my work, or a query package.
I need editing and proofreading for my white papers, reports, manuals, press releases, marketing materials, and other business documents.
I need to have my essay, project, assignment, or term paper edited and proofread.
I want to sound professional and to get hired. I have a resume, letter, email, or personal document that I need to have edited and proofread.
Prices include your personal % discount.
Prices include % sales tax ( ).

- Program Finder
- Admissions Services
- Course Directory
- Academic Calendar
- Hybrid Campus
- Lecture Series
- Convocation
- Strategy and Development
- Implementation and Impact
- Integrity and Oversight
- In the School
- In the Field
- In Baltimore
- Resources for Practitioners
- Articles & News Releases
- In The News
- Statements & Announcements
- At a Glance
- Student Life
- Strategic Priorities
- Inclusion, Diversity, Anti-Racism, and Equity (IDARE)
- What is Public Health?
research@BSPH
The School’s research endeavors aim to improve the public’s health in the U.S. and throughout the world.
- Funding Opportunities and Support
- Faculty Innovation Award Winners
Conducting Research That Addresses Public Health Issues Worldwide
Systematic and rigorous inquiry allows us to discover the fundamental mechanisms and causes of disease and disparities. At our Office of Research ( research@BSPH), we translate that knowledge to develop, evaluate, and disseminate treatment and prevention strategies and inform public health practice. Research along this entire spectrum represents a fundamental mission of the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
From laboratories at Baltimore’s Wolfe Street building, to Bangladesh maternity wards in densely packed neighborhoods, to field studies in rural Botswana, Bloomberg School faculty lead research that directly addresses the most critical public health issues worldwide. Research spans from molecules to societies and relies on methodologies as diverse as bench science and epidemiology. That research is translated into impact, from discovering ways to eliminate malaria, increase healthy behavior, reduce the toll of chronic disease, improve the health of mothers and infants, or change the biology of aging.
120+ countries
engaged in research activity by BSPH faculty and teams.
of all federal grants and contracts awarded to schools of public health are awarded to BSPH.
citations on publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
publications where BSPH was listed in the authors' affiliation in 2019-2023.
Departments
Our 10 departments offer faculty and students the flexibility to focus on a variety of public health disciplines
Centers and Institutes Directory
Our 80+ Centers and Institutes provide a unique combination of breadth and depth, and rich opportunities for collaboration
Institutional Review Board (IRB)
The Institutional Review Board (IRB) oversees two IRBs registered with the U.S. Office of Human Research Protections, IRB X and IRB FC, which meet weekly to review human subjects research applications for Bloomberg School faculty and students
Generosity helps our community think outside the traditional boundaries of public health, working across disciplines and industries, to translate research into innovative health interventions and practices
Introducing the research@BSPH Ecosystem
The research@BSPH ecosystem aims to foster an interdependent sense of community among faculty researchers, their research teams, administration, and staff that leverages knowledge and develops shared responses to challenges. The ultimate goal is to work collectively to reduce administrative and bureaucratic barriers related to conducting experiments, recruiting participants, analyzing data, hiring staff, and more, so that faculty can focus on their core academic pursuits.

Research at the Bloomberg School is a team sport.
In order to provide extensive guidance, infrastructure, and support in pursuit of its research mission, research@BSPH employs three core areas: strategy and development, implementation and impact, and integrity and oversight. Our exceptional research teams comprised of faculty, postdoctoral fellows, students, and committed staff are united in our collaborative, collegial, and entrepreneurial approach to problem solving. T he Bloomberg School ensures that our research is accomplished according to the highest ethical standards and complies with all regulatory requirements. In addition to our institutional review board (IRB) which provides oversight for human subjects research, basic science studies employee techniques to ensure the reproducibility of research.
Research@BSPH in the News
Four bloomberg school faculty elected to national academy of medicine.
Considered one of the highest honors in the fields of health and medicine, NAM membership recognizes outstanding professional achievements and commitment to service.
The Maryland Maternal Health Innovation Program Grant Renewed with Johns Hopkins
Lerner center for public health advocacy announces inaugural sommer klag advocacy impact award winners.
Bloomberg School faculty Nadia Akseer and Cass Crifasi selected winners at Advocacy Impact Awards Pitch Competition

Impact of the use of cannabis as a medicine in pregnancy, on the unborn child: a systematic review and meta-analysis protocol
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Introduction: The use of cannabis for medicinal purposes is on the rise. As more people place their trust in the safety of prescribed alternative plant-based medicine and find it easily accessible, there is a growing concern that pregnant women may be increasingly using cannabis for medicinal purposes to manage their pregnancy symptoms and other health conditions. The aim of this review is to investigate the use of cannabis for medicinal purposes during pregnancy, describe the characteristics of the demographic population, and to measure the impact on the unborn child and up to twelve months postpartum. Methods and analyses: Research on pregnant women who use cannabis for medicinal purposes only and infants up to one year after birth who experienced in utero exposure to cannabis for medicinal purposes will be included in this review. Reviews, randomised controlled trials, case control, cross-sectional and cohort studies, that have been peer reviewed and published between 1996 and April 2024 as a primary research paper that investigates prenatal use of cannabis for medicinal purposes on foetal, perinatal, and neonatal outcomes, will be selected for review. Excluding cover editorials, letters, commentaries, protocols, conference papers and book chapters. Effects of illicit drugs use, alcohol misuse and nicotine exposure on neonate outcome will be controlled by excluding studies reporting on the concomitant use of such substances with cannabis for medicinal purposes during pregnancy. All titles and abstracts will be reviewed independently and in duplicate by at least two researchers. Records will be excluded based on title and abstract screening as well as publication type. Where initial disagreement exists between reviewers regarding the inclusion of a study, team members will review disputed articles status until consensus is gained. Selected studies will then be assessed by at least two independent researchers for risk bias assessment using validated tools. Data will be extracted and analysed following a systematic review and meta-analysis methodology. The statistical analysis will combine three or more outcomes that are reported in a consistent manner. The systematic review and meta-analysis will follow the PRISMA guidelines to facilitate transparent reporting [1].
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Funding Statement
This study did not receive any funding.
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
The study will use ONLY openly available human data from studies published in biomedical and scientific journals.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
All data produced in the present work are contained in the manuscript.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (323)
- Allergy and Immunology (627)
- Anesthesia (163)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2367)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (288)
- Dermatology (206)
- Emergency Medicine (379)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (834)
- Epidemiology (11765)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (702)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3729)
- Geriatric Medicine (348)
- Health Economics (632)
- Health Informatics (2392)
- Health Policy (929)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (896)
- Hematology (340)
- HIV/AIDS (780)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13302)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (767)
- Medical Education (365)
- Medical Ethics (104)
- Nephrology (398)
- Neurology (3493)
- Nursing (198)
- Nutrition (523)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (673)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (661)
- Oncology (1819)
- Ophthalmology (535)
- Orthopedics (218)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (232)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (446)
- Pediatrics (1032)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (420)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3172)
- Public and Global Health (6135)
- Radiology and Imaging (1278)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (745)
- Respiratory Medicine (825)
- Rheumatology (379)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (372)
- Sports Medicine (322)
- Surgery (400)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (145)
Help | Advanced Search
Electrical Engineering and Systems Science > Signal Processing
Title: full-wave em simulation analysis of human body blockage by dense 2d antenna arrays.
Abstract: Recently, proposals of human-sensing-based services for cellular and local area networks have brought indoor localization to the attention of several research groups. In response to these stimuli, various Device-Free Localization (DFL) techniques, also known as Passive Localization methods, have emerged by exploiting ambient signals to locate and track individuals that do not carry any electronic device. This study delves into human passive indoor localization through full-wave electromagnetic simulations. For the scope, we exploit simulations from the commercial tool FEKO software that employs the Method of Moments (MoM). In particular, we collect and analyze the electric field values in a scenario constituted by a dense 2D/3D deployment of receivers in the presence of an anthropomorphic mobile target. The paper describes in detail the collected dataset and provides a first analysis based on a statistical approach. Possible use cases are also investigated through examples in the context of passive localization, sensing, and imaging.
Submission history
Access paper:.
- HTML (experimental)
- Other Formats
References & Citations
- Google Scholar
- Semantic Scholar
BibTeX formatted citation
Bibliographic and Citation Tools
Code, data and media associated with this article, recommenders and search tools.
- Institution
arXivLabs: experimental projects with community collaborators
arXivLabs is a framework that allows collaborators to develop and share new arXiv features directly on our website.
Both individuals and organizations that work with arXivLabs have embraced and accepted our values of openness, community, excellence, and user data privacy. arXiv is committed to these values and only works with partners that adhere to them.
Have an idea for a project that will add value for arXiv's community? Learn more about arXivLabs .
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Antioxidants (Basel)

Antioxidants in Hops: Bioavailability, Health Effects and Perspectives for New Products
Corina-aurelia zugravu.
1 Department of Hygiene and Ecology, “Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 050463 Bucharest, Romania; [email protected] or
Roxana-Elena Bohiltea
2 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, “Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy Bucharest, 020021 Bucharest, Romania; [email protected] or
Teodor Salmen
3 Department of Diabetes, Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases, “Prof. Dr. N.C.Paulescu” National Institute of Diabetes, 030167 Bucharest, Romania
Elena Pogurschi
4 Faculty of Animal Productions Engineering and Management, University of Agronomic Sciences and Veterinary Medicine of Bucharest, 57 Marasti Blvd, 011464 Bucharest, Romania; [email protected] or
Marina Ruxandra Otelea
5 Clinical Department 5, “Carol Davila” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, 050463 Bucharest, Romania; [email protected] or
Hop plant ( Humulus lupulus L.) has been used by humans for ages, presumably first as a herbal remedy, then in the manufacturing of different products, from which beer is the most largely consumed. Female hops cones have different useful chemical compounds, an important class being antioxidants, mainly polyphenols. This narrative review describes the main antioxidants in hops, their bioavailability and biological effects, and the results obtained by now in the primary and secondary prevention of several non-communicable diseases, such as the metabolic syndrome related diseases and oncology. This article presents in vitro and in vivo data in order to better understand what was accomplished in terms of knowledge and practice, and what needs to be clarified by additional studies, mainly regarding xantohumol and its derivates, as well as regarding the bitter acids of hops. The multiple protective effects found by different studies are hindered up to now by the low bioavailability of some of the main antioxidants in hops. However, there are new promising products with important health effects and perspectives of use as food supplements, in a market where consumers increasingly search for products originating directly from plants.
1. Introduction
Hops Humulus Lupulus Linnaeus is a plant known and cultivated by humans for a very long time. Early evidence links its origin to ancient China, later found in most temperate areas of the world [ 1 ]. Though today we associate hops with beer production, and this was true for centuries, its initial use has been different. Hops were often used as medicinal plants in the popular pharmacopoeia, designed to relieve the symptoms of a large number of health problems [ 2 ]. It has been attributed anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, as well as diuretic, digestive, sedative, progestogenic properties, even being considered a cure for insomnia. For this wide range of health benefits, it was regarded as a life prolonging plant [ 3 ].
The main component of the hops used today is the cone, the female inflorescence of the plant, but other areas of the hops plant also prove to be useful (the leaves, stems or rhizome). There are several bioactive molecules that underlie the sanogenetic effects of the plant [ 1 , 4 , 5 ]. For example, in the cone glands, the primary metabolites are the bitter resins and the aromatics. The secondary substances belong to three categories of substances: resins, oils and polyphenols (4–14% dried weight) [ 6 , 7 ] ( Figure 1 ).

Antioxidants in hops.
There are two types of bitter resins: alpha acids (mainly humulone) and beta acids (mainly lupulone). As for polyphenols, they can be classified into: flavonols (quercitin and kaempherol), flavon-3-oils (the main ones being catechin, epicatechin, proanthocyanidins), phenolic carboxylic acids (ferulic acid) and, in lesser quantities, prenyl flavonoids such as xanthohumol (0.1–1% on dry weight) [ 8 , 9 ] and isoxanthohumol. Their very small quantities do not necessary preclude a biological effect. For example, isoxanthohumol is transformed in the intestine into prenylnaringenin, a phytoestrogen uptaken by the intestinal cell. Depending on the individual microbiota, it was estimated that one third of the population could produce high enough levels to reach the threshold for a biological effect [ 10 ].
The bioactive components of hops are still under research, due to their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects. Their primary or secondary prevention properties regarding some chronic, degenerative diseases with great prevalence in the contemporary world gave them a special importance. Most studies focus on the action of prenylflavonoids (xanthohumol and its derivatives), which were considered, until recently, the only substances of pharmaceutical importance in hops [ 11 ].
2. Bioavailability of the Active Substances
As for all foods, bioavailability is crucial when evaluating the practical consequences of hops components. Studies show that the bioavailability is rather low [ 12 , 13 ], and ways for increasing it were developed. One alternative is prenylation, which increases the biological activity of dietary flavonoids by enhancing their affinity for estrogen receptors, facilitate the interaction with cellular membranes and proteins. As a consequence, they tend to remain for longer time in certain target cells and have greater antioxidant effect [ 14 ]. The bioavailability is increased in the presence of the prenyl group, which decreases the polarity of flavonoids. Degradation of xanthohumol in the intestine is also influenced by the prenyl group. The presence of this group slows down the degradation of xanthohumol [ 14 , 15 ].
The bioavailability of prenylflavonoids is not only influenced by the presence or absence of functional groups. The human microbiota, as stated above, greatly influences the resulting metabolites ( Figure 2 ), which may be of pharmaceutical importance as well. Numerous studies have been performed to identify them, and less to assess their bioavailability.

Transformation of xantohumol in the digestive system.
Depending on the predominant microorganisms in microbiota, the metabolic products may be different, with an activity similar or different to that of the initial substances [ 16 ].
Xanthohumol, the main substance studied among the many components of hops, has a low bioavailability to oral administration, which limits its sanogenetic effects [ 13 ]. Nookandeh et al. showed that more than 80% of the products of the intestinal degradation of the orally administered xanthohumol to laboratory animals was excreted in feces [ 17 ]. Similar results were found by Avula et al. who concluded that most of the administered xanthohumol is excreted in feces in the 24 hours after administration. Studies conducted on Caco-2 cells showed that xanthohumol accumulates in the cytosol, binds to the cellular proteins [ 18 ] and even has the ability to insert inside the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, which makes a rapid transmembrane transfer very difficult [ 19 , 20 , 21 ].
Novak et al. investigated the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of pure xantohumiol or a hops extract, comparing the oral with the iv routes in rats. There were no differences due to sex, but the oral absorption was very low compared with the iv route. The probability of a hepato-entero-hepatic recirculation of the compounds was also postulated, based on the peaks of plasma levels after ingestion [ 22 ].
A blinded randomized study with different doses of xanthohumol given orally showed similarities with the animal experiments. This study highlighted that plasma xanthohumol significantly increases only after more than 60 mg. Two peaks in plasma xanthohumol (as observed in animal experiments), 1 h and 4 h after administration, were observed; the half time was around 20 h [ 23 ].
Low bioavailability was noted also for Iso-α-acids (IAA) and the reduced derivates, dihydro-iso-α-acids (DHIAA) and tetrahydro-iso-α-acids (THIAA). However, reduced metabolites had a higher bioavailability [ 24 ].
Cattoor et al. also carried out an analysis of the absorption of bitter acids from hops through Caco-2 monolayers. Membrane permeability was higher for alpha than for beta acids. Consequently, oral administration of beta acids had a low absorption, probably limited by the active transporters of P-gp and MRP-2 efflux and by phase II metabolism [ 25 ].
As low bioavailability is common to many plant bioactive substances, new forms of administration and new additives are being tested to improve or address this issue in the near future.
3. Biological Effects
The bioactive components of hops are still in the researchers’ objective, for their role in primary or secondary prevention of some chronic, degenerative diseases with great prevalence in the contemporary world, in which oxidative mechanisms play an important role. An antioxidant is a substance that delays or prevents the oxidation of a substrate, thus reducing the oxidative stress. As reactive oxygen species (ROS) are produced during the normal metabolism, a good balance between oxidative and anti-oxidant mechanisms is necessary. Generally, the antioxidants are divided in enzymatic (e.g., superoxide dismutase, glutathione reductase, catalase, peroxidase, etc.) and nonenzymatic (e.g., glutathione, vitamins).
The oxidative stress is enhanced in many pathological circumstances. Activation of the inflammatory cells during defense against microorganisms [ 26 ], cells with low supply in oxygen in chronic or acute ischemia, excess NO formation as in autoimmune diseases [ 27 ] or allergies [ 28 ], are circumstances of excess oxidative compounds production.
The type of hops, the extraction method of the antioxidant substances and the assays used to assess the antioxidant power (the radical scavenging ability or the ability to inhibit lipid oxidation under accelerated conditions) are some of determinants of the variability in the results when evaluating hops antioxidative efficacy [ 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 ].
However, these data should be interpreted with caution, and cannot be fully extrapolated to real life, as many of the substances in hops act synergistically and combine their antioxidant effects, with the anti-inflammatory or antiproliferative ones.
Most studies focused on the action of prenylflavonoids (xanthohumol and its derivatives) which were considered, until recently, the only substances of pharmaceutical importance [ 11 ]. More recently, studies on the action of bitter acids (humulone and lupulone) utilized as brewing additives have also given interesting results [ 11 ].
In this review, we will focus on two pathological conditions associated with oxidative stress in which a possible role of the hops compounds have been investigated: cancer and metabolic syndrome.
4. Hops Antioxidants and Cancer
Hops substances and cancer have been extensively researched during time and from the multitude of components, xanthohumol was frequently under scrutiny.
The substance was discovered in 1957 [ 33 ], its properties being brought to light only in the recent decades [ 34 ]. After ingestion, xanthohumol undergoes transformations, sometimes resulting in substances with a higher antioxidant power and a wider spectrum of action. It was noticed that xanthohumol is transformed by a non-enzymatic mechanism in isoxanthohumol and enzymatically, in 8 and 6-prenylnaringenin and in desmethylxanthohumol [ 35 , 36 ].
The positive action of xanthohumol in neoplasms was shown for tumors with various localizations, from lung or digestive system (colon, pancreas), to endocrine (thyroid) or genito-urinary (cervical, ovarian), head and neck, skin, malignant melanoma or leukemia [ 37 , 38 ].
The ways in which xanthohumol acts were the subject of a large number of studies are summarized by Jiang et al. in a 2018 article [ 37 ].
The action of xanthohumol is probably achieved by the inhibitory action on two signaling pathways with an essential role in maintaining the appearance of malignancy and in achieving metastases: Akt and NF-κB. Xanthohumol induces apoptosis of cancer cells by stimulating pro-apoptotic proteins (Bax, PARP, AIF- caspase-3, -8, -9) and by inhibiting proliferation, achieved by inhibiting Notch1, mTOR, STAT3. Xanthohumol also acts on the migration and invasion of neoplastic cells, probably by inhibiting FAK and MMP-2 expression [ 37 ]. Moreover, xanthohumol seems to act synergistically with the usual chemotherapeutic treatments, which is certainly a positive factor because it could theoretically allow for a decrease in the doses administered. Jiang et al. note that xanthohumol influences various proteins that bear upon proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis or resistance to many chemotherapeutics in cancer patients, without the exact mechanisms being known at this time.
Girisa et al. conclude that hops have an important anticancer potential, acting by modifying both signaling pathways (Akt, AMPK, ERK, IGFBP2, NF-κB, and STAT3), and by modulating proteins (Notch1, caspases, MMPs, Bcl-2, cyclin D1), oxidative stress markers, miRNAs and tumor suppressor proteins [ 39 ].
A very interesting aspect is related to the antioxidant action of xanthohumol. It is known that in the etiology of neoplasms, from cell proliferation to local invasion and metastases, oxidative stress is involved, on the regulation of which many oncological treatments are based. It is just that the accumulation of free radicals is not only a cause, but also a factor that determines the sensitivity to treatment [ 40 ], many chemotherapeutic agents acting precisely to stimulate the formation of free radicals in neoplastic cells [ 41 ]. In this context, it was shown that, although it has a high antioxidant power, xanthohumol also induces an important production of free radicals in various neoplastic cell lines, causing their apoptosis [ 42 , 43 , 44 ] ( Figure 3 ).

The oxidative stress: a common mechanism of action of xantohumol and chemotherapeutics on cancer cells.
Wei et al. concluded that xanthohumol also causes an imbalance between intracellular antioxidants, such as SOD, and the production of free radicals, which potentiates xanthohumol’s apoptotic and antimetastatic, antiproliferative action. High levels of free radicals, which are easily reached by depressing cellular antioxidant systems, reduce NF-κB activity, leading to cell death [ 45 ].
Xanthohumol stimulated the anticancer actions of high ROS by the NF-κB signaling pathway. Future studies should show the extent to which classical neoplastic treatments could benefit from the associated administration of xanthohumol products in clinical practice.
An important activity of xanthohumol is related to metastasis formation. After xanthohumol proved to be effective in pulmonary adenocarcinoma, Sławińska-Brych et al. also confirmed its effectiveness in inhibiting metastatic processes. The mechanisms involved in the antiinvasive action appear to be the inhibition of the ERK/MAPK pathway and the suppression of FAK and PI3/AKT signaling [ 46 ].
Other mechanisms seem to be common to xanthohumol, iso-xanthohumol and 8-prenylnaringenin, as antioxidant and anticancer agents. They refer to the action on Aldose reductase (AKR1B1) and a counterpart, AKR1B10. Both substances are overexpressed in neoplasms with various localizations, from lung and prostate, to breast. This makes them potential treatment targets. Seliger et al. showed that xanthohumol, iso-xanthohumol and 8-prenylnaringenin substantially and indiscriminately inhibit B1 and B10 [ 47 ].
Recently, new studies reveal the action of xanthohumol in neoplasms with localizations that had not been previously followed. One of these is the stomach. Gastric cancer is a form of cancer with a high incidence and a very poor prognosis. Wei et al.’s 2018 study confirms that xanthohumol has a deleterious effect on gastric cancer cells, but not on healthy gastric cells. Xanthohumol inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis and reduces cancer cell metastases, most likely by free radical overproduction [ 44 ].
An interesting subject could be the effects of xanthohumol in colorectal cancer, from the perspective of the previously mentioned reduced bioavailability, which leaves most of the ingested substance in contact with the terminal areas of the digestive system. Scagliarini et al. show that xanthohumol, applied on cancer cell cultures, can activate cell cycle disruptions, even in non-toxic concentrations, by reducing cyclins A and B and concomitantly increasing cyclin E [ 48 ]. Apoptosis was found in some of the most resistant cell lines 48 h after the debut of treatment with xanthohimol, and their sensitization to the action of usual chemotherapeutics was also noticed. Xanthumol activated p53 and p21, which recommends the substance as a pre-treatment of chemotherapy, not only to increase its effectiveness, but also to reduce the therapeutical dose and, consequently, the side effects. Taking into account the conclusions of Ambroz’s study [ 49 ], which reports antagonistic effects on concomitant administration of xanthohumol/chemotherapy, it was concluded that administration should be staged, in order to avoid decreasing the efficacy of the chemotherapeutics. It should be noted that other studies confirmed the cytotoxic action of other prenylflavonoids in hops on colonic proliferative cells, but xanthohumol had the most active contribution [ 50 ].
Harish et al. [ 12 ] summarized the mechanisms in which xanthohumol exerts its antineoplastic action in vitro, as follows: induction or inhibition of apoptosis, modulator of oncogenic signaling pathways, the free radical formation, and the ERK1/2, NF-κB, and Akt signals. The major courses of action differ after the location of the cancer. For example, in breast cancer it acts by decreasing the expression of Notch1, survivin and Ki-67, and by potentiating the expression of capsase 3, simultaneously inhibiting STAT3 and MDR 1. Another neoplastic localization in which xanthohumol was effective is the prostate, where it induced apoptosis via TNF-Related Apoptosis Inducing Ligand as well as by depolarizing mitochondria by activating procaspases 3, 8 and 9. One has to take into consideration difficulty of in vivo assessments, especially due to the reduced bioavailability of oral administration.
Recently, minor components of the antioxidant profile of hops were highlighted and investigated, having synergistic effects and being sometimes more active than xanthohumol. One of the minor natural compounds is xanthohumol C, which inhibits mammary neoplastic cell lines more intensely than xanthohumol or xanthumol-enriched hops extract. The mechanism of action of xanthohumol C appears to be different from that of xanthohumol; it seems to be involved in endoplasmic reticulum stress and in altering the adhesion of cells to each other [ 51 ]. Xanthohumol C is a chalcone with various types of action, including cytotoxic [ 52 ] and antioxidant [ 7 , 53 ] manifested in the context of neoplasms. Xanthohumol C was described by Stevens et al. [ 54 ] and due to difficulties in obtaining pure substances and, consequently, to the interference of other minor compounds, they noticed a lower antiproliferative action in certain neoplastic cell lines (breast, colon, prostate) than the one of xanthohumol [ 52 ].
Other hops substances were studied in relation to neoplasms, especially the bitter acids. Humulon shows anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects on skin cancer [ 55 ]. Lupulon activates apoptotic pathways including apoptotic TRAIL-receptors, in human cancer colon cells and in the equivalent metastatic cells, even in TRAIL resistant cancer cells [ 56 , 57 ]. Both substances show promising effects for cancer prophylaxis and treatment.
5. Hops and the Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors for diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases in the presence of central obesity. The criteria for diagnosis metabolic syndrome are the expression of the impairment of lipid and glucose metabolism, insulin resistance and the endothelial dysfunction. All these pathological findings have in common excessive ROS formation. In the following lines, we will present data on how the compounds of hops could influence the components of the metabolic syndrome.
5.1. Obesity
As mentioned above, central obesity (clinically assessed by the abdominal circumference) is a key element of the metabolic syndrome. Obesity induces systemic oxidative stress through superoxide generation, enhanced oxidative phosphorylation, reduced activity of anti-oxidant enzymes, hyperleptinemia, and activation of the polyol and hexosamine pathways [ 58 ]. In this respect, reduction in body adipose tissue would contribute to the homeostasis of the oxidative status.
In animal experiments, xanthohumol was able to reduce body weight, lipid absorption and plasma glucose [ 59 , 60 ]. Metabolomic studies showed that xanthohumol induces a catabolic status [ 61 ]. In this experiment, the effect of xanthohumol was dose dependent; while in low doses the uncoupled effect was the main consequence, at higher levels xanthohumol inhibited the mitochondrial respiration in white and brown preadipocytes and in the muscle cells. The energy depletion activates energy production mechanism other than the mitochondrial ATP, such as the creatine kinase system, lactate production from pyruvate, glycolysis and the degradation of the macronutrient complexes, finally leading to the anti-obesity effects.
Another interesting study showed that xanthohumol and tetrahydroxanthohumol suppress diet-induced accumulation of lipid in liver, in the subcutaneous and in the mesenteric adipose tissue in mice [ 62 ]. This effect was partially due to an increase in energy expenditure. The study also revealed the affinity of xanthohumol and tetrahydroxanthohumol to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), with an inhibitory effect of the metabolic pathways induced by this transcription factor. Another positive effect on body weight of the PPARγ inhibition is the suppression of the adipocyte’s differentiation. Referring to the oxidative status, PPARγ is generally considered a modulator with preponderant antioxidative role; PPARγ initiates the transcription of the catalase, manganese superoxide-dismutase and inhibits of the pro-oxidative inducible NO-synthetase and cyclooxygenase-2 [ 63 ]. Whether the antioxidative effect of body mass reduction induced by hops compounds will prevail or not on their inhibitory effect of PPARγ remains to be established by future research.
Xanthohumol prevents lipid oxidation in liver, as shown in an experiment with carbon tetrachloride in rats [ 64 ]. The non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a clinical entity linked to the metabolic syndrome, also involves the lipid oxidation among other pathogenic mechanisms and the inhibition of this process induced by xanthohumol might be of benefit. In fact, the xanthohumol has been investigated for the possible prevention of lipid and bile acids accumulation in liver [ 65 ]. It has been shown that xanthohumol ameliorates HFD-induced hepatic injury and the dysfunctional lipid and bile acid metabolism.
5.2. High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol (HDL-c)
HDL-c reduction is an indirect marker of the reverse transport of cholesterol for hepatic processing and biliary excretion. Though, if HDL-c is low, cholesterol accumulates in peripheral tissues (e.g., vascular, pancreas, muscle) contributing to atherogenesis, impaired insulin secretion and insulin resistance. Besides the cholesterol transport, HDL-c also has a significant antioxidative activity on low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c) and also on the cellular membranes of erythrocytes and astrocytes [ 66 ]. The metabolic syndrome implies not only a diminished quantity of HDL-c, but also a reduction in the antioxidant capacity of this lipoprotein [ 67 ]. HDL-c directly protects LDL-c from oxidation induced by ROS and by removing oxidized lipids from LDL-c; therefore, the amount of oxidized LDL-c, the major initiator of the inflammatory process in atherosclerosis, is reduced [ 66 ].
Isohumulone is able to raise the HDL-c in plasma and reduces the atherogenic index in a dose–dependent manner, at least in experimental models [ 68 ]. The mechanism seems to be mediated by the activation of the PPARα, which has a significant role in increasing the transfer of cholesterol from VLDL/IDL to the HDL-c through increasing the hepatic expression of the phospholipid transfer protein [ 69 ].
Even if the antioxidant activity of HDL-c on the oxidized LDL-c has not been directly assessed, the inhibition of this oxidative process was demonstrated, as prenyl flavonoids extracted from hops were able to suppress, in vitro, the oxidation of low-density lipoproteins induced by peroxynitrite [ 70 ].
5.3. Triglycerides (TG)
TG metabolism is impaired in metabolic syndrome. The visceral adiposity increases the release of free fatty acids in the portal system and the production of TG in hepatocytes. In insulin resistance status, the hepatic TG synthesis is promoted and the high plasma levels decreases the clearance of the VLDL [ 71 ]. The TG-rich lipoproteins release in the peripheral endothelium neutral and oxidized free fatty acids that propagate the local inflammation and damage of the vascular wall [ 72 ]. In experimental studies, xanthohumol lowered the plasma TG even in rats fed with a high fat diet [ 60 ]. The mechanisms revealed by this study were the reduction in hepatic fatty acid synthesis and the enhanced excretion of TG through feces, probably by a decline in lipid absorption. They also confirmed previous experimental data about the reduction of the SREBP1c expression in hepatic cells [ 73 ], a nuclear receptor which controls the fatty acid and TG synthesis in the liver [ 74 ]. Similar effects were obtained with another isomerized hops extract, in which the most active compound was isohumulones [ 75 ]. The mechanism was related to the diminution in lipid absorption, secondary to the inhibition of the pancreatic lipase [ 76 ]. The effect of beer and/or the beer compounds on the pancreatic exocrine secretion is still debatable and very much depends on the methods used to estimate in vitro the level and the content of the secretion. Some authors suggested that the stimulatory effect of the non-alcoholic components of beer (e.g., for the pancreatic amylase production) are neutralized by the direct inhibitory effect of circulating ethanol [ 77 ].
Activation of PPARα, as previously mentioned, lowers the hepatic TG stores and the suppression of TG secretion from hepatocytes [ 78 ], but these effects depend on the genetic polymorphisms of the PPARα gene and on the epigenetic modifications related to the interaction with the environmental factors [ 79 ]. To the best of our knowledge, the epigenetic modifications induced by hops compounds on the PPARα gene expression have not been studied yet.
Taken together, these data assemble in a positive effect on the lipid metabolism related to the different compounds of hops. The translation of these experiments to preventive measures needs definitely more research. In a prospective cohort of more than 8000 persons, beer consumption was associated with metabolic risk, but there was a large variation according to the level of consumption. In the multivariate analysis, the OR for moderate consumption (<1–2 drinks/week was 1.07 (CI = 0.75–1.52) compared to the non-drinkers, but for heavy drinkers (≥7 drinks/week) the OR increased significantly 1.56 (CI = 0.94–2.62). In what concerns the lipid profile, heavy drinkers had higher TG, but lower risk for low HDL-c in plasma. Unfortunately, the authors did not report if there is any point in which there is no negative influence on TG and the positive effect on HDL-c is still present.
5.4. Glycaemia
Impaired fasting glycemia or impaired glucose tolerance define prediabetes, a condition frequently associated with the metabolic syndrome. In a randomized trial, a 4-week treatment with isohumolone in prediabetic patients significantly reduced the fasting glucose and the HbA1C as compared to placebo [ 80 ].
Intermittent high glucose environment stimulates superoxide production and enhances endothelial cell apoptosis to an even greater extent than exposure to a constant high glucose level [ 81 , 82 ].
Hops compounds reduce the oxidative status related to hyperglycemia in a direct or indirect mode. For example, xanthohumol seems to have a direct effect on the systemic and local (endothelial, renal, liver) oxidative status, as noticed with beer supplemented with xanthohumol administered to diabetic rats. In this experiment, xanthohumol increased the activity of glutathione reductase, which, in turn, increases the ratio of reduced/oxidized glutathione. Xanthohumol also normalized the level of H 2 O 2 , reduced the 3-Nitrotyrosine and the carbonylation of proteins [ 83 ], showing an interference with many antioxidative mechanisms. Indirect effects refer to the capacity of different hops compounds to reduce glycemia. For example, in mice fed on a high fat diet, tetrahydroxanthohumol significantly improved the glucose clearance, reducing the time and peak of hyperglycemia [ 62 ]. In another experiment, xanthohumol was able to reduce glycemia in a dose dependent manner, but this effect was noticed only in male rats [ 59 ]. Data about the mechanisms by which xanthohumo decreases glycemia continue to emerge. Reduction in the hepatic glucose output is a possible mechanism. Xanthohumol acts as a ligand for the farnesoid X receptor (FXR), a nuclear receptor that regulates genes involved in gluconeogenesis [ 73 ]. Another mechanism is the reduction in carbohydrates absorption. Indeed, inhibition of the amylase [ 76 ] and α-glucosidase [ 84 ] reduces the absorption and promotes the excretion of carbohydrates in feces. Regarding other components of hops, isohumulones seem to have a positive effect in correcting hyperglycemia [ 80 ].
6. Safety and Prospects
Scientists try to develop new products based on hops that capitalize on its proven sanogenetic effects. They take into account the studies regarding the antioxidant effects of hops’ components, correlated with the consumer’s desire to have products of natural origin. Moreover, in addition to hops fruits, the use of hops leaves with a high antioxidants content is also considered [ 85 ]. Of course, most of the new products benefit not only from the antioxidant effect, but also from other positive actions of the existing substances in hops, with convergent effects. Thus, the antioxidant effect is often combined with anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and antifungal effects.
An important discussion refers to the possible excess of antioxidants in diets, especially related to influencing neoplasms [ 86 , 87 ]. Of course, the bioavailability of many antioxidants is quite low when administered through food. Today, however, there are supplements that ensure increased bioavailability and which can be used in much larger quantities than anticipated, leading to the entry of high levels of antioxidants into metabolism. Thus, their safety can be questioned. As for the ingredients of hops, they have been evaluated in relation to consumers’ safety and it was concluded that the extracts and bitter acids are safe when used short term and in adequate quantities, such as 300 mg/day for extracts, for a period of 3 months and 35 mg/day for bitter acids, for the same duration [ 88 ]. The safety of xanthohumol was studied in vitro and in vivo (on rats) in the context of its use as an antineoplastic agent. It was noticed that the substance selectively targets cancer cells, not raising major problems with short-term administration in high doses [ 89 , 90 , 91 ].
Another aspect to consider is the possible interference of hops substances in drugs metabolism. Prenylflavonoids interfere with the activity and expression of phase II enzymes in Caco2 cells, modulating the expression and activity of glutathione S-transferase and catechol-O-methyltransferase and inhibiting sulfotransferase. The expression of uridine diphosphate (UDP)-glucuronosyl transferase 1A6 mRNA was potentiated and that of glutathione S-transferase 1A1/2 was inhibited [ 50 ].
These elements must be taken into account when prescribing hops supplements with concomitant medicinal products.
As with other phytotherapeutic products, the best way is to eat foods or supplements in physiological doses [ 92 ], and from this point of view, hops is considered a useful plant when designing functional products. Overcoming problems of bioavailability is still a challenge.
When developing a hops-based product, the first element to consider is the use of hops with a maximum content of antioxidants. The quantitative and qualitative level of antioxidants varies depending on different factors. Thus, there are different varieties of hops with different levels of antioxidants [ 5 ]. The timing of harvesting hops is also an important factor [ 93 ]. Subsequently, the processing of hops, from drying to heat treatment, also changes the level of antioxidants. For example, there are studies that show that their level is higher in fresh hops, although drying does not induce major losses [ 94 ]. The implementation of some biotechnologies for the modification of hops is taken into consideration, resulting in high levels of xanthohumol and/or 8 prenilnaringenin. These types of hops can be utilized for the production of beer, but also of some supplements [ 8 ].
Finally, if antioxidants are separated from hops for use in supplements or fortified foods, the extraction methods can play an important role in the level and types of antioxidants obtained [ 4 , 5 ].
The utilization of hops and its components in functional foods is not, to date, supported by any health claim under relevant European legislation. There is not, at least so far, an accepted claim, and the only evaluated and rejected one refers to a supplement that used the phytoestrogen activity of prenylnaringenin [ 95 ].
However, there is a potential to see products with health claims and not only in the category of supplements, but also in food (e.g., beer) as studies in the field will provide new and conclusive data [ 96 , 97 ].
Some of the perspectives for hops-based products are presented in Figure 4 .

Perspectives for hops based products.
To date, the use of infusions or extracts of hops in food has been investigated, as antioxidants that increases the stability of some essential components (proteins, fats) and some important organoleptic elements (color). In fact, in beer, hops have a preservative action due to the antioxidant capacity [ 98 ]. Villalobos-Delgado et al. [ 99 ] confirmed preservative effects, especially of hops in powdered form, when applied to raw or prepared meat products, refrigerated or frozen. During storage at low temperatures, the action of oxidases in meat continues, albeit at a slower rate. Even at this level, the blocking effect of hops is noticed. The use of the antioxidant action of hops in preserving foods, thus prolonging their shelf life, has a lot of potential, especially for meat products, where it increases not only their freshness, but also their functional properties [ 100 , 101 , 102 ].
However, taste alteration can be a barrier. In this sense, in order to avoid the bitter taste often associated with the addition of hops, new products are developed. An example is the development of lecithin-based nanoliposomes in which lupulone and xanthohumol aresimultaneosly encapsulated, with an antioxidant power that was preserved. The capsules can be used in various foods [ 103 ].
Other foods in which hops extracts were added are bakery products. Along with the antifungal action, hops extract and adjacent lactic acid bacteria were used in leavens to produce bread. The consequence was an increase in the concentration of polyphenols in bread and a rise in its antioxidant activity [ 104 ].
The antioxidants in hops were also used in the production of protective food films. Emulsion films based on different biopolymers were manufactured with the addition of alcoholic hops extract in different concentrations, resulting in films with a higher antioxidant capacity and therefore with a higher degree of protection against food spoilage [ 105 ].
Beyond such uses, hops and its components can be used in the production of functional beverages, to offer them, along with enhanced organoleptic qualities, the advantage of a significant intake of antioxidants. This trend is all the more positive, as evaluations regarding the aromatic preferences of consumers reveal the presence of hops among the first 12 favorite flavors [ 106 ].
The most promising field is ultimately the development of beer-like beverages, the staple where hops have been used for centuries.
An example of such a product is Aliophen R, an unfermented beverage based on malt and hops and possessing a polyphenol load similar to that of beers on the market. Experimental studies show that the product has an effective antioxidant and chemopreventive action, all the more important, as it can be consumed in larger quantities than beer because it does not contain alcohol [ 107 ].
Hops extract can be added to various fruit juices. In the study by Mashkour et al., hops extract was added to cherry juice, where it significantly increased the antioxidant capacity of the mixture and the sensory evaluation score [ 108 ].
New types of beer, enriched in polyphenols, from collateral products resulting in the beer industry (pellets enriched in lupulin) are also tested [ 109 ]. The result are beers that have a level of antioxidant power, up to 21.5% higher than regular beer. In these types of beer, special attention must be paid to collateral organoleptic changes, which may or may not be agreed by consumers.
The use for the enrichment of some very aromatic types of hops can fulfill both objectives: of obtaining a functional type of beer, with increased antioxidant power, and that of producing an attractive product for the consumer [ 110 ].
Beyond modified or enriched products, beer itself can be manufactured by processes that increase the level of antioxidants in the final product. Various attempts have been made in this regard [ 5 ] and the most promising seems to be a new method, based on hydrodynamic cavitation process, which allows a higher level of xanthohumol, desmethylxanthohumol and 6-prenylnaringenin to be maintained. This process was used before with other positive results, but it is also effective in obtaining beers with a higher level of antioxidants [ 111 ].
7. Conclusions
In conclusion, hops are a repository of bioactive substances, of promising perspectives in the prophylaxis and treatment of chronic diseases of great prevalence in the modern world. So far investigated only in vitro and in vivo on experimental animals, these substances are awaiting confirmation in clinical trials.
Along with the development of new functional products, which will provide concentrated and precise quantities of hops’ ingredients, the industry is expected to develop forms with increased bioavailability, which will solve the current problems raised by the poor absorption following the oral administration of some important antioxidants from hops.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.-A.Z. and M.R.O.; methodology, R.-E.B.; software, E.P.; validation, E.P., M.R.O. and C.-A.Z.; formal analysis, T.S.; investigation, T.S.; resources, C.-A.Z.; data curation, T.S.; writing—original draft preparation, C.-A.Z.; writing—review and editing, T.S.; visualization, R.-E.B.; supervision, C.-A.Z.; project administration, C.-A.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
The publication fee for this article was financed by the Center of Studies for Beer, Health and Nutrition.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- Alzheimer's disease & dementia
- Arthritis & Rheumatism
- Attention deficit disorders
- Autism spectrum disorders
- Biomedical technology
- Diseases, Conditions, Syndromes
- Endocrinology & Metabolism
- Gastroenterology
- Gerontology & Geriatrics
- Health informatics
- Inflammatory disorders
- Medical economics
- Medical research
- Medications
- Neuroscience
- Obstetrics & gynaecology
- Oncology & Cancer
- Ophthalmology
- Overweight & Obesity
- Parkinson's & Movement disorders
- Psychology & Psychiatry
- Radiology & Imaging
- Sleep disorders
- Sports medicine & Kinesiology
- Vaccination
- Breast cancer
- Cardiovascular disease
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- Colon cancer
- Coronary artery disease
- Heart attack
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Kidney disease
- Lung cancer
- Multiple sclerosis
- Myocardial infarction
- Ovarian cancer
- Post traumatic stress disorder
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Schizophrenia
- Skin cancer
- Type 2 diabetes
- Full List »
share this!
May 9, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
Study: Deep learning-based whole-body PSMA PET/CT attenuation correction utilizing Pix-2-Pix GAN
by Impact Journals LLC
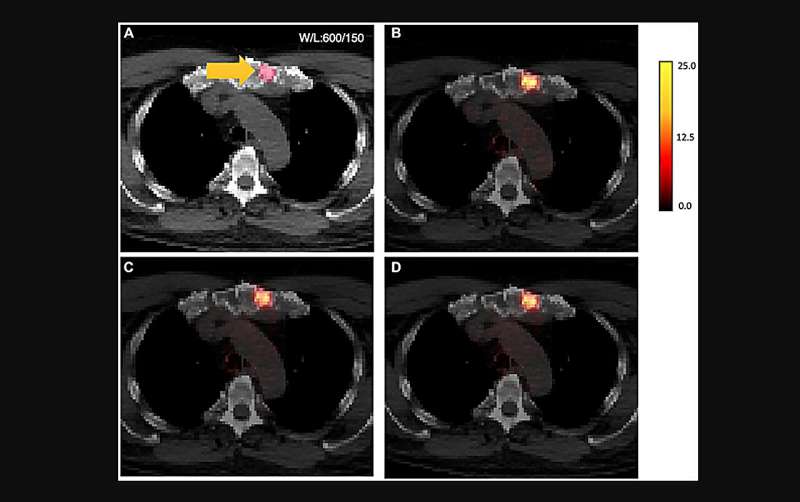
A new research paper was published in Oncotarget , titled "Deep learning-based whole-body PSMA PET/CT attenuation correction utilizing Pix-2-Pix GAN."
Radiation dosage limits the sequential PET/CT studies oncology patients can undergo during their treatment follow-up course.
In this new study, researchers from the National Institutes of Health's National Cancer Institute proposed an artificial intelligence (AI) tool to produce attenuation-corrected PET (AC-PET) images from non-attenuation-corrected PET (NAC-PET) images to reduce need for low-dose CT scans.
"AI-generated PET images have clinical potential for reducing the need for CT scans for attenuation correction while preserving quantitative markers and image quality in prostate cancer patients," write the researchers.
A deep learning algorithm based on 2D Pix-2-Pix generative adversarial network (GAN) architecture was developed from paired AC-PET and NAC-PET images. 18F-DCFPyL PSMA (prostate-specific membrane antigen) PET-CT studies from 302 prostate cancer patients split into training, validation, and testing cohorts (n = 183, 60, 59, respectively). Models were trained with two normalization strategies: Standard Uptake Value (SUV)-based and SUV-Nyul-based.
Scan-level performance was evaluated by normalized mean square error (NMSE), mean absolute error (MAE), structural similarity index (SSIM), and peak signal-to-noise ratio (PSNR). Lesion-level analysis was performed in regions-of-interest prospectively from nuclear medicine physicians. SUV metrics were evaluated using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC), repeatability coefficient (RC), and linear mixed-effects modeling.
Median NMSE, MAE, SSIM, and PSNR were 13.26%, 3.59%, 0.891, and 26.82, respectively, in the independent test cohort. ICC for SUVmax and SUVmean were 0.88 and 0.89, which indicated a high correlation between original and AI-generated quantitative imaging markers. Lesion location, density (Hounsfield units), and lesion uptake were all shown to impact relative error in generated SUV metrics (all p < 0.05).
"The Pix-2-Pix GAN model for generating AC-PET demonstrates SUV metrics that highly correlate with original images. AI-generated PET images show clinical potential for reducing the need for CT scans for attenuation correction while preserving quantitative markers and image quality," state the authors.
Explore further
Feedback to editors

Climate change is likely to aggravate brain conditions, study finds
8 hours ago

Researchers develop innovative platform for modeling human muscle diseases in worms
10 hours ago
Pre- and post-surgical immunotherapy improves outcomes for patients with operable lung cancer, Phase III study finds
Study finds reduced risk of breast cancer following bariatric surgery in women with hyperinsulinemia

Treatment-resistant depression linked to body mass index: Study
Chiropractic associated with lower likelihood of tramadol prescription in adults with sciatica
Study finds two genes of the germline are essential for the development of brain tumors in Drosophila
Study reveals immunotherapy's potential in boosting immune systems of older individuals
Alzheimer's disease processes without symptoms. How is that possible?
Breaking bad blood: How rogue neutrophils help lung cancer spread
11 hours ago
Related Stories
Double contrast learning helps to remove ring artifacts in computed tomography image
Oct 25, 2023
New SPECT/CT technique shows impressive biomarker identification, offers increased access for prostate cancer patients
Apr 16, 2024
PSMA PET/CT clearly differentiates prostate cancer from benign tissue
Feb 5, 2018

Enhancing PET image quality with deep learning
Sep 27, 2023
Artificial intelligence shown to more rapidly and objectively determine calcium scores than physicians
Sep 15, 2022
Bone scans overstage prostate cancer at initial staging compared with PSMA PET: Study
Nov 9, 2023
Recommended for you

This time, it's personal: Enhancing patient response to cancer immunotherapy
Tumor tissue on a chip: New possibilities for cell therapies and personalized medicine
14 hours ago

Researchers determine the mutations that protect mice from B-cell cancers
17 hours ago
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Medical Xpress in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter

May. 13, 2024
Rice study reveals insights into protein evolution.

Rice University’s Peter Wolynes and his research team have unveiled a breakthrough in understanding how specific genetic sequences, known as pseudogenes, evolve. Their paper was published May 13 by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Journal.
Led by Wolynes, the D.R. Bullard-Welch Foundation Professor of Science, professor of chemistry, biosciences and physics and astronomy and co-director of the Center for Theoretical Biological Physics (CTBP), the team focused on deciphering the complex energy landscapes of de-evolved, putative protein sequences corresponding to pseudogenes.

Pseudogenes are segments of DNA that once encoded proteins but have since lost their ability to do so due to sequence degradation — a phenomenon referred to as devolution. Here, devolution represents an unconstrained evolutionary process that occurs without the usual evolutionary pressures that regulate functional protein-coding sequences.
Despite their inactive state, pseudogenes offer a window into the evolutionary journey of proteins.
“Our paper explains that proteins can de-evolve,” Wolynes said. “A DNA sequence can, by mutations or other means, lose the signal that tells it to code for a protein. The DNA continues to mutate but does not have to lead to a sequence that can fold.”
The researchers studied junk DNA in a genome that has de-evolved. Their research revealed that a mutation accumulation in pseudogene sequences typically disrupts the native network of stabilizing interactions, making it challenging for these sequences, if they were to be translated, to fold into functional proteins.
However, the researchers observed instances where certain mutations unexpectedly stabilized the folding of pseudogenes at the cost of altering their previous biological functions.
They identified specific pseudogenes, such as cyclophilin A, profilin-1 and small ubiquitin-like modifier 2 protein, where stabilizing mutations occurred in regions crucial for binding to other molecules and other functions, suggesting a complex balance between protein stability and biological activity.
Moreover, the study highlights the dynamic nature of protein evolution as some previously pseudogenized genes may regain their protein-coding function over time despite undergoing multiple mutations.
Using sophisticated computational models, the researchers interpreted the interplay between physical folding landscapes and the evolutionary landscapes of pseudogenes. Their findings provide evidence that the funnellike character of folding landscapes comes from evolution.
“Proteins can de-evolve and have their ability to fold compromised over time due to mutations or other means,” Wolynes said. “Our study offers the first direct evidence that evolution is shaping the folding of proteins.”
Along with Wolynes, the research team includes lead author and applied physics graduate student Hana Jaafari ; CTBP postdoctoral associate Carlos Bueno ; University of Texas at Dallas graduate student Jonathan Martin; Faruck Morcos, associate professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at UT-Dallas; and CTBP biophysics researcher Nicholas P. Schafer.
The implications of this research extend beyond theoretical biology with potential applications in protein engineering, Jaafari said.
“It would be interesting to see if someone at a lab could confirm our results to see what happens to the pseudogenes that were more physically stable,” Jaafari said. “We have an idea based on our analysis, but it’d be compelling to get some experimental validation.”

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The body of a research paper is the main part that supports your thesis statement and argument. It should be organized in a logical order, with relevant information, facts and examples, and transitions. Learn how to write topic sentences, paragraphs, and transitions with examples and tips.
The body is always divided into paragraphs. You can work through the body in three main stages: Create an outline of what you want to say and in what order. Write a first draft to get your main ideas down on paper. Write a second draft to clarify your arguments and make sure everything fits together. This article gives you some practical tips ...
Part I: The Introduction. An introduction is usually the first paragraph of your academic essay. If you're writing a long essay, you might need 2 or 3 paragraphs to introduce your topic to your reader. A good introduction does 2 things: Gets the reader's attention. You can get a reader's attention by telling a story, providing a statistic ...
The body of the paper should expand on what you have stated in the introduction. Finally, the conclusion restates the paper's thesis and should explain what you have learned, giving a wrap up of your main ideas. 1. The Title The title should be specific and indicate the theme of the research and what ideas it addresses.
The main part of your research paper is called "the body.". To write this important part of your paper, include only relevant information, or information that gets to the point. Organize your ideas in a logical order—one that makes sense—and provide enough details—facts and examples—to support the points you want to make.
A research paper is a piece of academic writing that provides analysis, interpretation, and argument based on in-depth independent research. About us; ... To contribute to the body of knowledge: Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies ...
Academic papers are like hourglasses. The paper opens at its widest point; the introduction makes broad connections to the reader's interests, hoping they will be persuaded to follow along, then gradually narrows to a tight, focused, thesis statement. The argument stays relatively narrow and focused on the thesis throughout the body, or the middle
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
First, provide a brief citation in the body of your essay. This is also known as a parenthetical or in-text citation. Second, include a full citation in the Reference list at the end of your paper. Different types of citations include in-text citations, footnotes, and reference lists.
This resource outlines the generally accepted structure for introductions, body paragraphs, and conclusions in an academic argument paper. Keep in mind that this resource contains guidelines and not strict rules about organization. Your structure needs to be flexible enough to meet the requirements of your purpose and audience.
How to Write a Body of a Research Paper? A body is the main part of your research paper. In this part, you will include all the needed evidence; you will provide the examples and support your argument. It is important to structure your paragraphs thoroughly. That is to say, topic sentence and the evidence supporting the topic.
A primary research paper involves writing body paragraphs to effectively communicate the study's purpose, methods, results, and conclusions. While there may be some variations depending on the discipline and journal guidelines, the following paragraph structure is commonly used: Introduction. The body of research paper sets the stage.
An effective research paper focuses on the writer's ideas. The introduction and conclusion present and revisit the writer's thesis. The body of the paper develops the thesis and related points with information from research. Ideas and information taken from outside sources must be cited in the body of the paper and in the references section.
Set the top, bottom, and side margins of your paper at 1 inch. Use double-spaced text throughout your paper. Use a standard font, such as Times New Roman or Arial, in a legible size (10- to 12-point). Use continuous pagination throughout the paper, including the title page and the references section.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
It describes the essence, the main theme of the paper. It includes the research question posed, its significance, the methodology, and the main results or findings. Footnotes or cited works are never listed in an abstract. Remember to take great care in composing the abstract. It's the first part of the paper the instructor reads.
The body is the largest part of a research paper; in it you collect and arrange evidence that will persuade the reader of your argument. It should, therefore, have a logical organization. If the paper is long, it is a good idea to partition the body into sections using headings and sub-headings. This includes using parenthetical citations when ...
The aim of this paper was to carry out a narrative review of the existing literature on key protective and risk factors that are being related to higher positive BI and lower negative BI (i.e., sense of embodiment, self-compassion, and body shame). ... Thus, there is a large body of research on the psychopathological symptoms associated with BI ...
The impact of stress on body function: A review. Any intrinsic or extrinsic stimulus that evokes a biological response is known as stress. The compensatory responses to these stresses are known as stress responses. Based on the type, timing and severity of the applied stimulus, stress can exert various actions on the body ranging from ...
In order to provide extensive guidance, infrastructure, and support in pursuit of its research mission, research@BSPH employs three core areas: strategy and development, implementation and impact, and integrity and oversight. Our exceptional research teams comprised of faculty, postdoctoral fellows, students, and committed staff are united in our collaborative, collegial, and entrepreneurial ...
Learn how to format a research paper in different style guides: APA, MLA, and Chicago. Find free Microsoft Word templates for each format and get tips on citations, headings, page layout, and more.
Yes The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below: The study will use ONLY openly available human data from studies published in biomedical and scientific journals. ... that have been peer reviewed and published between 1996 and April 2024 as a primary research paper that ...
Recently, proposals of human-sensing-based services for cellular and local area networks have brought indoor localization to the attention of several research groups. In response to these stimuli, various Device-Free Localization (DFL) techniques, also known as Passive Localization methods, have emerged by exploiting ambient signals to locate and track individuals that do not carry any ...
Hop plant (Humulus lupulus L.) has been used by humans for ages, presumably first as a herbal remedy, then in the manufacturing of different products, from which beer is the most largely consumed.Female hops cones have different useful chemical compounds, an important class being antioxidants, mainly polyphenols. This narrative review describes the main antioxidants in hops, their ...
A research paper outline is a useful tool to aid in the writing process, providing a structure to follow with all information to be included in the paper clearly organized. A quality outline can make writing your research paper more efficient by helping to: Organize your thoughts; Understand the flow of information and how ideas are related
A new research paper was published in Oncotarget, titled "Deep learning-based whole-body PSMA PET/CT attenuation correction utilizing Pix-2-Pix GAN." Radiation dosage limits the sequential PET/CT ...
Rice University's Peter Wolynes and his research team have unveiled a breakthrough in understanding how specific genetic sequences, known as pseudogenes, evolve. Their paper was published May 13 by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America Journal.. Led by Wolynes, the D.R. Bullard-Welch Foundation Professor of Science, professor of chemistry ...