- Crafting an Effective Partner Business Plan: Essential Elements for Success
Share this article
Print/Download PDF

By Harrison Barnes
Rate this article
909 Reviews Average: 5 out of 5

Discuss Partners on Top Law Schools
- ideas on how to network with judge's son who is partner?
- Networking/taking a partner at a firm out to lunch?
- NYC Study Partners- for those truly motivated
- 165+/Retake Study Partner?
- Arizona Study Partner

Partner Business Plans: Key Elements
- The Crucial Role of Business Plans in Law Firm Partner Success
- Maximize Portables in Your Business Plan in Order to Maximize Interest in You
The Importance of a Great Business Plan
Professional Goals For Partner Status
Making an evaluation of your existing practice, describing your vision as a partner, creating a strategy for growth.
- A partner's fit culturally
- The viability of a partner's practice for the long-term
- A partner's record of excellent client service to long-term clients and producing business
- A partner's history of consistently increasing collections
- A partner's practice fit in connection with the firm's strategic plan for expansion
- Whether a partner's practice area is one that is targeted for growth
- Whether the partner brings portable business and/or specific expertise needed in a particular practice area
- The opportunities the partner would bring for business development and significant cross-selling were the partner to join the firm
- Whether the partner's historical information is reflective of consistent productivity
- Whether the partner's client base fits within the firm's client structure
- Any potential conflicts that would preclude the firm from hiring the partner
- A partner's current compensation and compensation expectation
- A partner's potential contribution to the firm's bottom line/profitability
- A partner's fit within the firm's current attorney roster
- A partner's reason for leaving his or her current firm (voluntary/mutual arrangement) and whether the partner would be a problem
- Creative: Serve as a marketing piece on the partner and enable the firm to assess the partner's business potential. It should also provide an outlet to the partner to step out of the resume format and chart his or her previous performance and future prospects for business in a creative format.
- Illustrative: Illustrate to a firm that the partner is thinking about his or her practice as a business and set forth his or her plan for the future.
- Persuasive: Persuade the firm to hire the partner.
- Historical: Chart a historical record of the partner's history of creating business opportunities and his or her ability to develop and foster client relationships over an extended period of time.
- Demonstrative: Demonstrate a partner's business-development skills, initiative, and ability to contribute not only to his or her own success but also to the success of his or her colleagues through cross-selling efforts. It should also demonstrate ways a partner can contribute to a firm's financial bottom line, enhance its practice-group development, and ultimately bring added value to the team.
- Prophetic: Prophesy what the partner believes he or she will be able to accomplish in his or her practice and for the firm in the short and long term.
- Preparatory: Prepare the partner for the interviewing process.
Introduction
- Provide a narrative including professional history, practice overview, and a description of areas of expertise. This section may highlight briefly particular areas of expertise that the firm does not currently have.
- Describe the partner's role historically as a business developer.
- Briefly touch upon why the partner believes he or she would be a good fit for a particular firm.
Market Research/Analysis
- Give analysis of local need for services in partner's practice area.
- Describe local competition/other law firms with similar practices.
- Give overview of need in local market for partners with his or her expertise.
- Describe why partner believes firm provides the best platform in the marketplace for his or her particular practice area.
Current Client Base
- Describe current portable clients (use generic or specific).
- Describe key industries serviced.
- Discuss other partners' clients partner is servicing.
Additional Contacts to Develop
- Discuss contacts not yet tapped.
- Given market analysis, project possible targets in local, regional, national, or international markets.
- Discuss possible expansion of business from current client base.
Cross-Selling Opportunities
- Describe cross-selling opportunities with current clients.
- Describe cross-selling opportunities with known key clients of prospective firm.
- Discuss other practice areas at current firm to which partner is delegating work.
- Discuss services your clients are requesting that you cannot currently service at your firm and could otherwise capture at the new firm .
Other Business-Development Sources
- Describe additional business contacts you are pursuing or plan to pursue
- Speeches, publications
- Community organizations
- Bar associations
- Internal marketing initiatives
- Client seminars/newsletters
Long-Term Strategy Goals and Targets
- Set targets for expansion of practice in terms of collections, attorneys, and clients/industries.
- Consider possibility of local to regional to national growth patterns.
- Consider growth in other key competencies which may be affected by partner's long-term success.
- Discuss long-term strategies in connection with firm's overall strategic plan and practice-group development plans.
Historical Collections, Billing Rates, and Billable Hours
- If a partner with a lower billing rate structure, chart the anticipated rate increases by portable client or anticipated timeline for rate increases to current clients. Discuss any alternative billing arrangements you currently have in place with clients.
- Include three-year client collections history by client (as originating attorney and as billing attorney on other attorneys' matters). Include projection for current fiscal year.
- Include three-year billing rate history.
- Include three-year historical compensation history (including bonus information).
- Include three-year billable hour history.
- Note pending projects contributing to future collections.
- Include a summary of anticipated collection projections for the next three to five years.
- Business-development budget
- Time commitments from partners in other practice areas for cross-selling purposes
- Key staff needed (secretary, paralegals, etc.)
- Foreign-language skill requirements
- Travel expenses
- Marketing materials, presentations, etc.
Creative Conclusion
- Recap key points in plan, added value partner brings, and reasons he or she would be a good fit.
- Emphasize flexibility of plan and eagerness and willingness to discuss and modify in accordance with firm's plans and objectives.
- See 30 Ways to Generate Business as an Attorney for more information.
Want to continue reading?
Become a free bcg attorney search subscriber..
Once you become a subscriber you will have unlimited access to all of BCG’s articles.
There is absolutely no cost!
Harrison Barnes does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for attorneys and law students each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can attend anonymously and ask questions about your career, this article, or any other legal career-related topics. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
Harrison also does a weekly free webinar with live Q&A for law firms, companies, and others who hire attorneys each Wednesday at 10:00 am PST. You can sign up for the weekly webinar here: Register on Zoom
You can browse a list of past webinars here: Webinar Replays
You can also listen to Harrison Barnes Podcasts here: Attorney Career Advice Podcasts
You can also read Harrison Barnes' articles and books here: Harrison's Perspectives
Harrison Barnes is the legal profession's mentor and may be the only person in your legal career who will tell you why you are not reaching your full potential and what you really need to do to grow as an attorney--regardless of how much it hurts. If you prefer truth to stagnation, growth to comfort, and actionable ideas instead of fluffy concepts, you and Harrison will get along just fine. If, however, you want to stay where you are, talk about your past successes, and feel comfortable, Harrison is not for you.
Truly great mentors are like parents, doctors, therapists, spiritual figures, and others because in order to help you they need to expose you to pain and expose your weaknesses. But suppose you act on the advice and pain created by a mentor. In that case, you will become better: a better attorney, better employees, a better boss, know where you are going, and appreciate where you have been--you will hopefully also become a happier and better person. As you learn from Harrison, he hopes he will become your mentor.
To read more career and life advice articles visit Harrison's personal blog.
Article Categories
- Legal Recruiter ➝
- Attorney Career Advice ➝
- Advice for Partners ➝
- Business Plans
Do you want a better legal career?
Hi, I'm Harrison Barnes. I'm serious about improving Lawyers' legal careers. My only question is, will it be yours?

About Harrison Barnes
Harrison is the founder of BCG Attorney Search and several companies in the legal employment space that collectively gets thousands of attorneys jobs each year. Harrison is widely considered the most successful recruiter in the United States and personally places multiple attorneys most weeks. His articles on legal search and placement are read by attorneys, law students and others millions of times per year.
Find Similar Articles:
- strategic Partnerships
- risk Analysis
- regulatory Compliance
- professional Development
- Partner Business Plans
- legal Advice
- law Firm Planning
- governance Strategies
- goal Setting
- financial Management
- crisis Management
- corporate Structure
- contract Negotiation
- conflict Resolution
- business Law
Active Interview Jobs
Featured jobs.
Location: Indiana - Fort Wayne
Location: New York - New York City
Most Viewed Jobs
Location: Louisiana - Baton Rouge
Location: California - Laguna Hills
Upload Your Resume
Upload your resume to receive matching jobs at top law firms in your inbox.
Additional Resources
- Harrison's Perspectives
- Specific Practice Areas
- The Winning Mindset
BCG Reviews
I honestly do not think that I would have found the firm that I ultimately accepted a job offer with had it not been for.... Read more >
Thomas Wilmoth
Elon University, Class Of 210
My favorite thing about BCG Attorney Search was the attention to detail. They had very quick reaction times whenever I n.... Read more >
Columbia University Law School, Class Of 2014
Sarah handled everything and cared about and was interested in what we were interested in, and wanted to support us and .... Read more >
Colby Davis
UCLA School of Law, Class Of 2015
I worked with my legal placement professional and she was wonderful. She was my favorite thing about working with BCG.
Sarah Warren Smith
University of Richmond School of Law, Class Of 2011
I appreciated how I felt my legal placement professional was really personable and friendly. She wanted to get in touch .... Read more >
Taeva Shefler
New York University School of Law, Class Of 2013
As a new attorney with less than a year of experience, I was skeptical that BCG could help me. I thought one needed an e.... Read more >
New York University Law School, Class Of 2014
Popular Articles by Harrison Barnes
- What is Bar Reciprocity and Which States Allow You to Waive Into the Bar?
- What Do Law Firm Titles Mean: Of Counsel, Non-Equity Partner, Equity Partner Explained
- Top 6 Things Attorneys and Law Students Need to Remove from Their Resumes ASAP
- Why Going In-house Is Often the Worst Decision a Good Attorney Can Ever Make
- Top 9 Ways For Any Attorney To Generate a Huge Book of Business
Helpful Links
- The BCG Attorney Search Guide to Basic Law Firm Economics and the Billable Hour: What Every Attorney Needs to Understand to Get Ahead
- Quick Reference Guide to Practice Areas
- Refer BCG Attorney Search to a Friend
- BCG Attorney Search Core Values
- Recent BCG Attorney Search Placements
- What Makes a World Class Legal Recruiter
- What Makes BCG Attorney Search The Greatest Recruiting Firm in the World
- Top 10 Characteristics of Superstar Associates Who Make Partner
- Off-the-Record Interview Tips From Law Firm Interviewers
- Relocating Overseas
- Writing Samples: Top-12 Frequently Asked Questions
- The 'Dark Side' of Going In-house
- "Waive" Goodbye To Taking Another Bar Exam: Typical Requirements and Tips to Effectively Manage the Waive-in Process
- Changing Your Practice Area
- Moving Your Career to Another City
- A Comprehensive Guide to Working with a Legal Recruiter
- A Comprehensive Guide to Bar Reciprocity: What States Have Reciprocity for Lawyers and Allow You to Waive into The Bar
Related Articles

A Career Guide for Law Firm Partners
Practice Management

Marketing Your Law Firm Through Practice Groups
Related Video
- What is a Counsel and How does it Compare to a Partner�
Related Podcast
- How Any Attorney Can Get a $100+ Million Book of Business, Become a Partner in a Major Law Firm, or Start a Successful Business and Retire Whenever They Want�
When you use BCG Attorney Search you will get an unfair advantage because you will use the best legal placement company in the world for finding permanent law firm positions.
Don't miss out!
Submit Your Resume for Review
Register for Unlimited Access to BCG
Sign-up to receive the latest articles and alerts
Already a subscriber? Sign in here.
Business Plan for Partnership Firm
A business plan for partnership firm is recommended for anyone entering into a business partnership. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Updated November 2, 2020:
A business plan for a partnership firm is recommended for anyone entering into a business partnership. A business partnership is two or more people working together to run a business. Each person takes on equal risks and rewards that come from the business. A proper business plan is ideal for handling current and future business decisions.
Steps For Planning a Business Partnership
- Write a mission statement to clearly state the direction and goals the business plans to take. By writing a mission statement, the partners agree to the company's direction now and in the future.
- Develop a reimbursement plan for the costs and investments incurred during startup. The amount of money provided for the startup is not always equal. Therefore, it is beneficial to make a plan that takes this into account with repayment and returns on investment. Avoiding arguments over the value of the startup amount versus levels of sweat equity will be removed with a reimbursement plan.
- Create a method to resolve partner disputes. If an odd number of members are part of the partnership, you can choose to vote democratically. In the case of two partners, the partners may split areas of the business having the final say. For example, one person can make final decisions on marketing and sales planning, while the other person makes final decisions on financial planning.
- Appoint an outside panel of advisors, or ombudsman , to resolve any internal disputes. Trusted experts should always be used to avoid ruining the partner relationship.
- Divide all the responsibilities of the partners related to labor and management and assign the amount of compensation they will receive. The compensation is not always equal based on the workload the partner takes on.
- Request that outside experts review the partnership agreement for any legal or accounting mistakes. The experts may be able to point out unknown problems that exist in the agreement. This review should take place before the partnership begins business operations.
Partnership Deed
A partnership deed and partnership agreement are the same, but the partnership deed is in writing . A partnership agreement can exist solely through verbal communications or actions. A partnership deed is recommended for businesses as it clearly defines the terms of the partnership.
The partnership deed helps prove the agreed-upon terms if there are any conflicts. Without a deed, the rules to settle disputes will fall to the state laws where the partnership exists. This creates another issue where one partner may file suit to benefit from the existing laws. Legal action can be avoided with a partnership deed that lists all details of the business that the partners agreed to when they began the business.
Partner Business Plans
When legal firms are looking to add a new partner, a well-written business plan that shows the new partners' intent to grow the business will make them stand out from the rest of the applicants. The business plan should exceed the expectations of the firm.
The key elements of the business plan are:
- Create an introduction that details your professional history, areas of expertise, and why you are the right fit for the firm.
- Provide market research and analysis of the needs of the local area, what competition exists, and why the firm offers the best way to reach this marketplace.
- Describe your current client base, prospective clients, and untapped areas you'd like to reach.
- Include any cross-selling opportunities that exist with current and prospective clients.
- Share ways you can develop business sources including publications, speeches, client seminars, newsletters, and similar.
- Explain your long-term strategy to meet the goals and targets that will benefit the firm.
- Show a history of collections, billing rates, and billable hours and projections for the current year, three-years, and five-years.
- Time the partners must invest.
- Key staff will be needed (paralegals, secretaries, etc.)
- Travel expenses.
- Marketing materials,
- Presentations.
- Foreign language skill requirements.
End with a conclusion that is creative recaps the important points in the plan, what value will be added to the firm, and why you are the best fit for the firm.
If you need help with a business plan for a partnership firm, you can post your legal need on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Limited Partnership Rules: Everything You Need To Know
- Purpose of Partnership: Everything You Need To Know
- Authority of Partners in Partnership: What You Need to Know
- Partnership Agreement Between Company and Individual
- Limited Company Partnership Agreement
- How to Make a Partnership Agreement Legally Binding?
- Contract for Business Partners
- Disadvantages of Partnership
- General Partnership
- Partnership and Company
Need more referrals from your network?
Download our free Referralology ebook with over 50 tips on how to grow your client portfolio by referral and turn your networking into a referral generating machine.

Pop-up Form

How to create your partner business plan in 5 easy steps

One of the partner business plan tools we use with our small firm clients is the STAGe model. This is widely used to create 3-year or 12-month business plans for them. The good news is that it is versatile enough to help you create your 3-year partner business plan or 12-month partner business plan or vision for your practice. In this article ,I explain how to use the tool, plus you can download a template to create your 3-year partner business plan or 12-month partner business plan for your own practice.
What does the tool enable you to do?
The STAGe Tool is a one-page vision summarising your practice’s expected performance over the next 3 years or 12 months. It gives you a simple visual way to explain how your practice will develop in the future. In other words, it acts as a very simple, but highly effective tool to help you create your partner business plan – a key component of your business case for partner.
The tool consists of 5 circles that correspond to now, year 1, year 2, year (or the timescales of your choice.), or Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4. The circles are dissected by axes which represent the performance measures that best illustrate how your practice will develop. Each performance measure is broken down into what it will be at each year. This article assumes you are creating a 3-year partner business plan. However, you can also use the same template to create a 12-month partner business plan.
Click here to download your free PDF of the STAGe model to help you rapidly put together your partner Business plan.
Here is a completed STAGe tool:
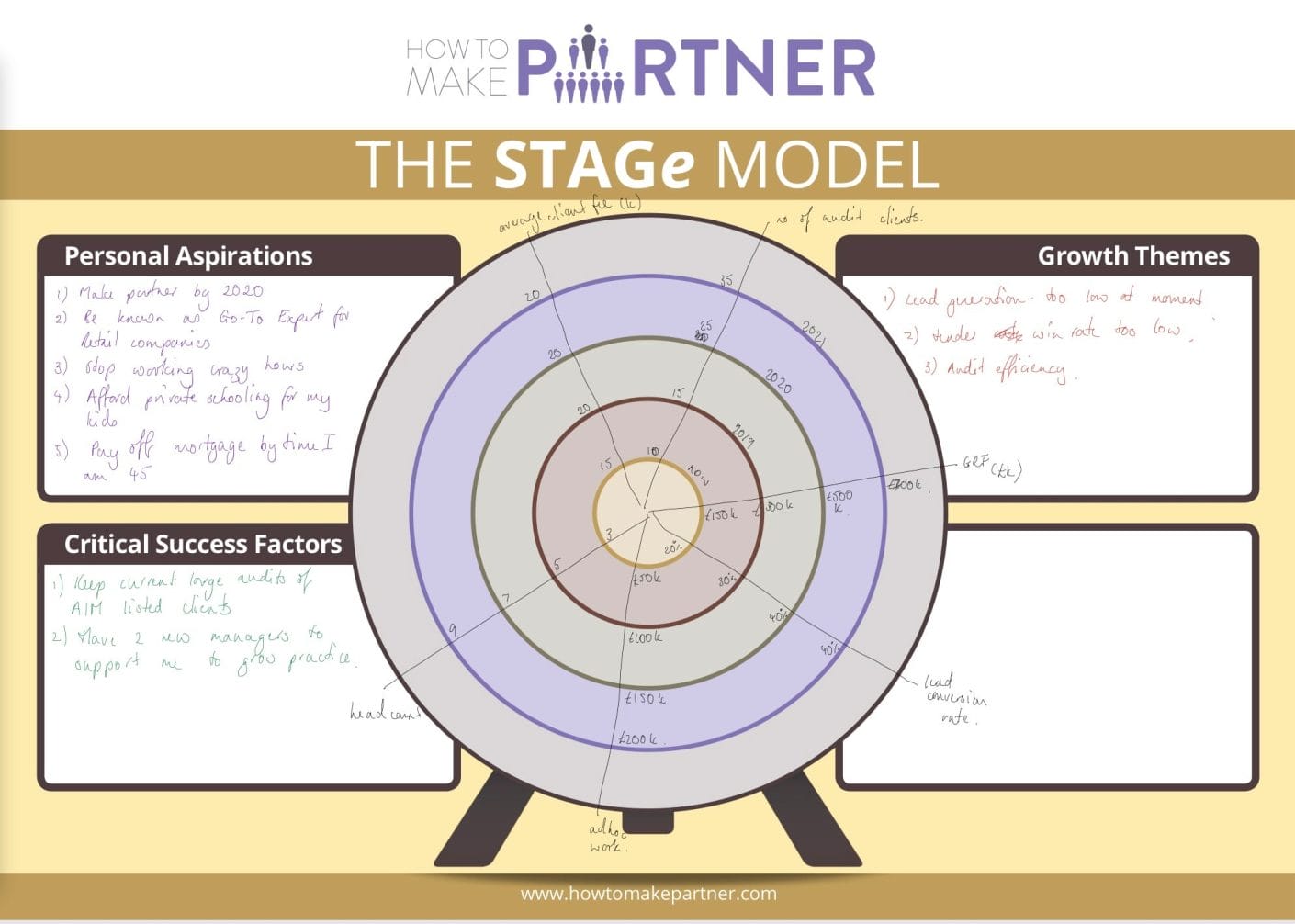
Stage 1: Envision the future
Take a moment to think about where you want your practice to be in 3 years if you are successful at the partnership vote. (Or 12 months if you are being asked to create a 12-month partner business plan) You may find it useful to do this exercise away from your desk and distractions.
You may like to consider the following areas:
- Average spend?
- Services offered?
- Key accounts won? Or were panels appointed too?
- Revenue and/or GRF?
- Key metrics which are important for your firm, e.g. WIP, Lockup, utilisation?
- Contribution to the firm?
- Structure of your team/practice?
- Development required?
Business Development
- No. of leads required a month?
- Referrers needed?
- Sectors/markets/Niche to target?
Read: What needs to go in the 12-month marketing plan for your business case for partner
Stage 2: Identify the really important metrics or things for your practice

In stage 2, you identify what are the really important things for you and your practice. Those things that if you focus on them you will achieve your 3-year. These then become the axes on your STAGe diagram. Ideally, you will identify 8-12 measures of performance to accurately show how you will grow your practice in the next three years.
One of the most sought-after courses in our Progress to Partner Academy i s called “ How to Build a Cast-Iron Business Case for Partner” .It’s a must-have in your arsenal of tools and guidance to help with your career progression. There is also a section in Progress to Partner Academy on the Partnership Admissions process with guides and recordings to help you find your way through the system. Check it out!
Stage 3: Identify your year 3 performance measures
Now take the STAGe template and label your performance measures and name the years on the concentric circles. For each performance, measure the axis and add what you are currently achieving. You now want to define your year 3 performance measures. By defining year 3 first you can then work backward towards your 12-month targets.
It can be very helpful to start the year 3 discussions by considering the fundamental financial measures for your practice such as revenue, GRF, turnover, profit, or contribution. This is because they are normally easier to complete, and it often sets the agenda for the rest of the performance measures.
Stage 4: Identify year 1 and 2 performance measures
Once you have completed your year 3 performance measures you then want to work along each of the performance measures axes to complete year 1 and year 2 goals. You may like to use questions such as:
“If I am to achieve this level of performance in year 3, what level should I achieve in year 2?”
Then…
“If I am to achieve this level of performance in year 2, what do I need to achieve in year 1? Is this too big a stretch from where I am now?”
At the end of this stage, you should have a fully completed diagram with each performance measure having a number or statement for each year on the diagram.
Stage 5: Critically review your partner business plan

Now you have completed the partner business plan, it is time to critically review it. That means:
- Are the targets really feasible? Do the numbers stack up and relate to each other?
- Is it stretching enough? Or could you easily achieve more?
- Have you missed anything? Is anything really obvious? Any blind spots?
If you haven’t already click here to download your free PDF of the STAGe model to help you rapidly put together your partner Business plan.
Once you have completed your partner business plan, it’s time to get feedback on it, plus identify the projects or activities which are critical to achieving your year 1 targets.
For more guidance on how to progress your career in your firm why not sign up to my weekly newsletter here and you’ll find out what you need to be working on in your career development (and how to make the time for your career development) to progress your career in your firm.
Or Check out our How to Build a Cast-Iron Business Case for Partner self study course . ✔️ What makes a good Business Case for Partner ✔️ 5 things you need to consider so the partners take notice of you ✔️ What needs to go into your 12-month business development plan
Related Post

5 ways growing your online presence NOW can help you sign up the right clients later
With so many people working remotely right now, there has never been a more important time to have an online presence. Think about it, everyone is at home and searching online, so if you don’t have a presence, how will your prospects find you? We have always stressed how vitally important your online footprint is…
CONTINUE READING > >

How to deal with a tough work colleague
Read this article for over 6 tips to successfully deal with tough colleagues.
Serving Aspiring Partners the World Over
London UK, New York US, Melbourne Australia, Amsterdam Holland, Delhi India, Toronto Canada, Dublin Ireland, Berlin Germany, Singapore, Mexico City.

How To Make Partner is a trading name of Excedia Group Ltd.
Registered address and mailing address: Unit A, Angel Business Centre, 1 Luton Road, Toddington, Dunstable, Bedfordshire, England, LU5 6DE
Free Resources
I need help with.
About Us | Courses | Our Coaches | Testimonials | GDPR Policy | Privacy Statement
Partner Business Plans in 2024: Why are They so Important?

Introduction
Business plans serve as a foundational framework that aligns the operational strategy of your partner firms with the overarching goals and expectations of your company. Tailored for each partner, these business plans outline specific sales, marketing, and training objectives that are designed to be in perfect sync with your organization's aspirations. These plans are indispensable tools for effectively overseeing your network, enabling you to evaluate and measure performance continually and, as needed, take strategic actions to bolster your partners on their path to success.
By collaboratively constructing business plans in conjunction with each partner, you foster a sense of cohesion within your indirect sales ecosystem. This shared roadmap ensures that all partners are working in synergy, collectively pursuing the identified actions necessary for accomplishing mutual success, further strengthening the strategic alignment between your firm and its partner network.
Develop Partner Bussiness Plan: Two Key Steps to Consider
1. know your partners well.
A thorough understanding of your partner network is a fundamental prerequisite for the successful development of partner business planning. Within your indirect sales ecosystem, business providers, integrators, value-added resellers (VARs), IT service companies, and resellers each operate within distinct logic and economic models. Acquiring deep insights into the nuances of each partner type is crucial for crafting business plans that align with both your partner's strategic objectives and your company's overarching goals.
Isabelle Castellanet, the founder of IXC, a firm specializing in Partners and Growth, emphasizes the importance of recognizing the diverse expectations and requirements of partners based on their typology. She notes, "Depending on the typology of its network, it is important to see that the partners do not expect the same information. A wholesaler, for example, does not require the same information and tools as a VAR, an integrator, or even a third-party publisher who prescribes or resells for you."
Recognizing these key elements in partner business planning ensures that your efforts are tailored to cater to the specific needs and expectations of each partner category, ultimately fostering a more productive and mutually beneficial collaboration.
2. Have a Well-Defined Global Business Objective
Creating a robust business plan in collaboration with your partner necessitates a well-defined and quantifiable overarching business objective. This objective must be crystal clear and expressed in measurable terms. For instance, it could be aimed at achieving specific milestones, such as:
- Capturing more than 20% of the market share in France for your product;
- Reaching an annual turnover target of "X" amount or;
- Expanding your operations to attain 5% of the turnover in a new country.
This overarching business objective serves as the cornerstone upon which you will construct the business plans tailored for each of your partners. The core concept is to apportion individual objectives to your partners that harmonize with your global strategy. Consequently, each partner's unique business plan becomes an instrumental component contributing to the fulfillment of your company's overarching business objective. This strategic alignment ensures that the combined efforts of your partner network work in unison to advance your business toward its ultimate goals.
.png)
Establishing a Partner Business Plan: The Objectives
Setting objectives within your partner's business plan is essential, engaging, and decisive for the success of the partnership. Aligned with the main objective of your business, these objectives, whether quantitative or qualitative, must be measurable and, therefore, quantified.
Set Quantitative Targets
Based on a careful analysis of historical sales performance, specific criteria such as outcomes, geographical location, and seniority within the partner network, distinct objectives will be strategically allocated to each partner. These objectives encompass a variety of key areas that guide their contributions to the partnership:
- Business Objectives on Sales Volume and Turnover: Partners will be tasked with well-defined business goals related to sales volume and revenue generation. These objectives may be tailored to the partner's track record, the market potential in their location, and their historical sales figures. This approach ensures that targets are realistic and achievable, motivating partners to excel in their specific market segments.
- Marketing Objectives through Event and Webinar Organization: In addition to sales targets, partners will also be entrusted with marketing objectives, which often involve organizing events and webinars. These events serve as crucial touchpoints for engaging potential customers and driving brand awareness. The specific objectives may vary depending on the partner's strengths and past performance, encouraging them to leverage their marketing expertise to enhance the partnership's overall success.
By customizing these objectives based on partner history and characteristics, the partnership becomes more adaptable and efficient, with each partner playing a unique role in contributing to the collective success of the collaboration. This tailored approach maximizes the potential for growth and achievement within the network.
Set Qualitative Objectives
Incorporating qualitative objectives into your business plan imparts a heightened level of professionalism to your partner network. This is especially pivotal when embarking on new indirect sales partnerships. Training sessions play a central role in this process, serving as a crucial avenue for partners to equip their sales teams with comprehensive knowledge about your brand. These sessions not only elevate your partners' understanding of your products but also empower them to embrace and disseminate your vision over the short, medium, and long-term horizons. This alignment ensures that they are seamlessly integrated into your strategic framework. As an illustrative example, you may set a target, such as achieving a certification for a specific number of "X" sales, within your business plan.
To ensure the optimal monitoring of your business plan and to gauge the progress of your partners, it is imperative to implement KPIs. These quantifiable benchmarks enable you to assess the attainment of objectives, offering valuable insights into areas where potential refinements or additional support may be necessary. By embracing KPIs, you introduce a structured, data-driven approach that ensures the partnership remains on a well-tracked trajectory toward realizing the objectives outlined in your business plan.
Have Regular Monitoring
In pursuit of ongoing refinement and shared operational efficiency, it's essential that these objectives are periodically defined and subject to regular monitoring. Constructing a business plan without a system for ongoing objective assessment is a critical oversight, as it can become too late to take corrective action should your partner deviate from their established objectives. To ensure the long-term success of your collaborative efforts, it's highly advisable to assess and potentially adjust objectives on a monthly basis, accounting for variances such as weaker performance in a specific month, such as August.
KPIs play a pivotal role in facilitating the monitoring and analysis of your partners, allowing you to identify both their strengths and areas that may require improvement. With a monthly review and a systematic reporting mechanism, you gain the capability to:
- Set Realistic Objectives : By closely aligning objectives with the current conditions on the ground, you ensure that they remain practical and attainable in the context of evolving market dynamics.
- Monitor Implementation and Achievement : Regular tracking using KPIs enables you to gauge how well partners are executing planned actions and progressing towards the predefined objectives, offering insights into areas that might need attention.
- Provide Support : Armed with this detailed data, you are better equipped to initiate timely and targeted actions that can help partners overcome challenges and, in turn, assist them in reaching their objectives. This proactive approach ensures that your partnership remains adaptive and robust, fostering sustained success in a dynamic business landscape.
The Essential Tool to Build a Business Plan and Manage it
In the endeavor to establish a comprehensive business plan and ensure its effective management with full transparency into your partner's activities, a PRM, or Partner Relationship Management system, emerges as the quintessential tool. Going beyond the capabilities of conventional management software, a PRM empowers you to systematically structure your indirect sales processes and engage with your partner ecosystem in real time, irrespective of the hour or location.
When crafting business plans for your partners within a proficient PRM platform, you can expect to benefit in several key ways:
- Tailored Business Plans : A robust PRM system should facilitate the seamless definition of unique business plans for each partner, accommodating their specific objectives, strengths, and market dynamics. This tailored approach ensures that each partner's plan is finely tuned to optimize success.
- Real-Time Progress Tracking : The PRM offers the invaluable advantage of real-time progress tracking for the objectives set within these business plans. It allows you to stay updated on your partner's performance, offering insights into their achievements and areas that might require attention or support.
- KPI Integration : Effective PRM systems seamlessly integrate KPIs into the platform, providing you with a set of critical metrics that pinpoint what is vital for the success of your partner's business plan. These KPIs offer the ability to focus on the most significant aspects of your partnership, enabling data-driven decision-making and strategic adjustments as needed.
By leveraging a PRM , your business can optimize its partnership management, ensuring that business plans are not only efficiently established but also actively tracked and adjusted as necessary, fostering the mutual success of both your company and your partner network.
Build your partnership program and strengthen partner engagement.
Looking for inspiration to never stop learning.

Partner Program Tiers: The Set Up Process A-Z

The Top 9 Skills to Look For in a Partnership Manager
Your right to know, why are partner business plans important, what elements should be included in a partner business plan, how do you write a business plan for a partner, what are the 3 types of partners in a business set up, what is an example of a strategic partnership plan, still have questions.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Types
How To Build a Winning Business Partnership
Darrell Zahorsky is an expert in search engine optimization (SEO) and marketing. He has worked for companies and clients such as Blackberry, ADP, and Subway.
Have the Same Vision
- Define Roles
Choose the Right Structure
Anticipate disputes, spell out financial responsibilities.
- Plan for How to Get Out
Hold Partner Meetings
Revisit the agreement as you grow, the partnership agreement, frequently asked questions. (faqs).
Dan Dalton / Getty Images
Partnerships are a simple way for two or more people to own a business together. There are several types of partnerships that differ in terms of who is liable for debts and lawsuits. You may want to form a partnership to test a business idea before committing to a more formal business structure.
There are quite a few issues you should address with your prospective partner before forming a partnership. Attend to these issues before you start, and you have a better chance of a successful venture.
Key Takeaways
- A partnership is a business structure that involve two or more people who are in business together.
- A successful partnership starts with partners who have the same vision for the business.
- As you create your partnership you should define roles, spell out financial contributions and pay, decide what happens when you have disputes, and discuss what happens when one or all parties want to end the partnership.
- Continue to revisit your partnership agreement as your business grows.
For a partnership to be successful, all parties involved should agree on the same strategic direction for the company. If one partner wants to build a well-known national chain of retail outlets and the other partner only cares about earning a decent living, the business is destined to fail. Set a clear, agreed-upon course for the business that meets the needs of both partners.
Define Business Roles and Responsibilities
A winning business partnership capitalizes on the strengths and skills of each partner. Divide business roles according to each individual's strengths. For example, if one partner is strong in marketing, operations, and finance and the other partner excels in sales, human resources and leadership then split tasks accordingly.
Binding agreement authority is the ability to enter into contracts with other entities. You might consider deciding if any partner has this authority, and in what scope. You and your business partner could split this authority based on the responsibilities you each take on.
If your partner is responsible for procurement, they could enter a contract with a supplier without needing to confer with you. By agreeing who can make these kinds of decisions, you mitigate the risk of conflicts down the road.
The structure you choose for your business will dictate how you and your partner pay taxes for the business. Limited liability companies and general partnerships have different liabilities and tax responsibilities.
Avoid the 50-50 Split
It may seem logical and fair to equally split decision making. However, this kind of split can impair decisions. Instead of a stalemate when you can't come to a compromise, consider developing a way to overcome differences.
If this is not possible, then consider using an outside source to weigh in on big-ticket disagreements. You may not want this source to have final decision ability, but see if they will analyze the situation and give you their opinion for a course of action. If needed, get more than one opinion.
There will be disagreements between partners. Not many pairs of people can agree 100% of the time. You should consider how you are going to handle disputes between each other, with employees, suppliers, customers or any other stakeholders.
One way to deal with this is to include a mandatory arbitration clause in your partnership agreement and the contracts you make with other entities. Arbitration is the use of an outside party to determine the outcome of disagreements and disputes.
Arbitration is a legally recognized method of dispute resolution. Binding arbitration means that all parties involved agree to abide by the decision of the arbitrator.
You should decide with your partner how much each of you is going to contribute to setting up your business or partnership. If you are both already operating, the costs may not be as high as if you both needed to start out.
Everyone has their own limit for tolerating risk. Financial risk can be more stressful than physical risk because it affects much more than your own safety. You should discuss with your partner how much financial risk you both can tolerate, and set limits.
An example of risk could be the method that you choose to finance your business. There is generally more risk involved with debt financing than with equity financing (using loans to finance instead of issuing shares, venture capitalists, etc.).
You may not have much of a choice at first how you finance your business, but be sure all parties understand the risks, and how much each person is responsible for.
The type of business you put together will also dictate the risk that you assume. Creating a limited liability company keeps owners from personal responsibility for the debts of a failed business.
When you create your partnership, you should discuss the expectations for pay.
Most businesses do not generate profit within the first year or even the second year . The number one reason new businesses fail is that they don't have enough cash to pay the business' and owner's bills. Ensure you and your business partner know how you are going to make ends meet.
Generally, in a partnership, the assets belong to the business unless specified in the partnership agreement. Partners will then own a percentage of the value of the company property based on the agreement. This is usually only a concern for businesses when they are closing out, and owners are working through who gets what.
Plan for Buy-Outs, Dissolutions, and Exits
Partnerships dissolve for many reasons. One partner may decide the partnership is no longer beneficial. You should include buy-out terms in case one partner wants to leave.
You might consider adding a dissolution clause to the partnership agreement. If the partnership is not working out, it would be beneficial to have pre-agreed terms for splitting things up.
An exit strategy is a plan if both partners should want out. This is can be accomplished by selling the company, or by selling all the inventory, assets, and interests a business has.
A strong business partnership is built on open communication. Meet on a regular basis so you can share grievances, review roles, provide constructive criticism, and discuss future plans for the growth or direction of your business.
Your business may grow over time as you and your partner work together. You may want to readdress your partnership agreement as your business grows. You may need to add more partners, include senior employees, and include expansion agreements.
You could include this in your initial agreement, but it might be better to wait until you are in a position to consider growth and expansion.
It is simple to set up a partnership because there are no legal documents to file. A written agreement, signed by all partners, is a legal document recognized by law.
Partnerships are often an oral agreement between two or more parties. Oral agreements can present problems in case of disagreements, even though they are legally binding. Instead, avoid potential problems by drawing up a partnership agreement.
Your partnership agreement should include the following (at a minimum):
- Amount of equity invested by each partner
- The type of business
- How profits and loss will be shared
- Decision-making policies
- Partners' pay and other compensation such as bonuses
- Distribution of assets upon dissolution of the business
- Provisions for changes to the partnership or provisions for dissolving the partnership
- Parameters of a dispute settlement clause
- Settlement of the business in case of death or incapacitation
- Restrictions regarding authority and expenditures
- Expected length of the partnership
It's always worth considering a business partnership structure when you find someone who complements your skill set and you know will add value to your company. These partnerships can be enjoyable and lucrative if the right foundation is cemented in the beginning.
What kinds of business partnerships are there?
There are three types of partnerships. A general partnership (GP) involves partners who all have liability for debts and lawsuits. In a limited partnership (LP), one or more general partners manage the business and have liability, while other partners don't participate in the operations and don't have liability. Finally, in a limited liability partnership (LLP), all partners have limited liability.
What's the difference between a partnership and an LLC?
A limited liability company (LLC) with two or more members (owners) is treated as a partnership for income tax purposes. The main difference between an LLC and a partnership is that in an LLC, members don't hold personal liability for the company. In many partnerships, only limited partners are protected from personal liability for the company.
Small Business Administration. " Choose a Business Structure ."
Cornell Law School Legal Information Institute. " Alternative Dispute Resolution ."
Small Business Administration Office of Advocacy. " Small Business Facts ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Limited Liability Company (LLC) ."
- Analysis & Opinion
- Buyer's Guides
- Market Presence Indices
- Compensation Reports
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Advertiser Series
- Publisher Series
- Agency Series
- Partner Marketing Series
- Investor & Advisor Series
- Leadership Series
- Career Management Series
Subscribe to Our Newsletter .
How To Build A Partnership Business Plan
This is editorial content made possible by

Partnerships have been an integral part of many go-to-market strategies for decades. For some brands, they drive an enormous share of total sales. For others, they drive next to nothing. What separates successful programs from unsuccessful ones is often the focus emanating from a strong business plan. As with any other go-to-market approach, partnership requires analysis and planning to achieve maximum potential.
A partnership business plan can help companies understand the channel's potential and the investments necessary to achieve those results. It also identifies the business partnership priorities that the team should focus on for maximum business impact. It’s different from a standard business plan in that you are not providing a rationale for an entire business but instead creating a roadmap for this critical business channel.
Setting appropriate expectations is even more critical than for other channels because of misconceptions many business leaders have about partnership. Many companies pursue partnership because they believe it will be a low/no-cost approach to driving sales. Somehow, goes this flawed thinking, the business partner will do most or all of the work of promoting the brand, and we can sit back and reap the benefits.
Certainly, one great rationale for the channel is strong ROI, but partnerships require resources and focus to succeed. A business plan can help clarify the business potential of the marketing strategy and the people, systems, and processes needed to achieve those results. This eGuide outlines the essentials for a strong partnership business plan and provides tips on how to deliver it. It provides insight as to what resources are needed to reach goals.
It is important to first set up the costs of setting up a program and the basic formula for customer acquisition.
The basic costs of a partner marketing program are:
Fixed costs:
- Software to recruit, track and pay partners. This can also be a variable costs since some platforms charge a percentage of sale. But, most have a component that is a flat fee.
- Service/headcount to recruit and manage partners. This can be an agency, an in house team or managed service from your tech platform. Sometimes agencies will work on a commission basis, but mostly this will be a relatively stable annual cost. Regardless, be aware that unlike programmatic, search or social, partnership marketing is still relationship driven and requires humans to connect. This takes time and it is facilitated by people who have relationships.
Variable costs:
- Commissions paid to partners for a sale.
- Any additional media costs including placement fees.
Note: be sure to build in a ramp up time for your partner program. Unlike search or social you can't just "turn on" a partner program. You need time to recruit partners and activate these partners. There is a lot of blocking and tackling involved and you should not expect to see results overnight. The rule of thumb is six months until full activation, but that varies by industry.
Customer Acquisition Cost
Ultimately, the success of failure of a new marketing channel will be its ability to acquire customers at an equal or lower cost than other channels. Start by identifying your overall CAC so that you can determine if your partnership financial and operating plans will be effective.
The basic formula is: {Fixed costs (like software, service, people) + (variable costs *volume)} / customers = CAC
Why Business Plans are Important
As partnership and affiliate play an increasingly important role in the total go-to-market for a brand, companies expect their leaders to offer a strong business case for additional investment. A solid partnership business plan will:
- Help the company understand the business potential for partnerships
- Enable business owners to understand and predict costs and benefits for proper resource and revenue planning
- Provide straightforward ways to track progress toward achieving channel goals
- Identify potential risks to achieving the goals and how to mitigate them
- Establish a clear timeline of when a company can expect to achieve goals
- Provide a complete picture so that the company can make an informed business decision on whether and how to invest in the partnerships channel
Beyond these tangible benefits, there is also the advantage of presenting and interpreting the opportunity in a context accessible to leaders within and beyond marketing.
Critical Components
Here’s a summary of critical elements for a partnership business plan and why they are important:
Executive Summary: This brief synopsis should highlight the key findings in the plan, from projected revenue and costs to the various advantages and risks of pursuing this line of business. Writing this part of your plan last is best after fully developing the other elements.
Scope and Description: This section of the plan provides a high-level outline of the types of partnerships you recommend pursuing - not channel by channel but rather in the context of what characteristics must be present in a potential partnership to warrant pursuit. We’ll provide a list of thought-starter questions to help you keep this high level and strategic rather than too specific and tactical.
Competitive Analysis: This section outlines how your key competitors leverage performance partnerships to build their businesses. Understanding competitive partnership activity contributes valuable learnings to your decisions about which partnerships to pursue.
Recommended Partnership Types: This section will enable you to list the types of partnerships you believe warrant pursuit, in priority order. The number of available partnership types is constantly expanding, so it makes sense to prioritize partnerships based on your revenue, profit, and brand equity goals. You should also consider what signals are available to ensure that potential partners are likely to consider working with you.
Operating Plan: Here is where you will outline the people, software, budget, and other resources required. You should also outline why your team is qualified and likely to succeed in building out the channel.
Financial Plan: Outline the costs and revenue expectations according to the approaches and timelines in use by your company. The level of granularity here really depends on how your company plans go-to-market initiatives and reports on performance.
Headwinds and Tailwinds: This section outlines the uncertainties that may help or hinder your ability to hit your targets.
Let’s consider each of these sections individually.
Executive Summary
Smart business opportunities can always be explained in a relatively small amount of words or “space.” Many companies require the rationale for an entire multi-million dollar business to be summarized in a single page. You can try to hit that target or give yourself two pages. But not more than that. Your ability to outline a business succinctly helps senior executives quickly understand why they should prioritize your initiative and demonstrates your ability to focus on what’s most important. Ask yourself:
- How can I explain performance partnerships, the potential range of available opportunities, and why partnership represents an advantageous channel for business development?
- What do senior executives need to know to understand the business potential of the partnerships channel?
- What arguments and data are essential to evaluate this channel properly?
- What topline data should I include to demonstrate the business value of pursuing the channel?
Providing hard numbers in your summary is critical if you are to gain buy-in from your leadership team. They must weigh any financial investment decision against the potential business value of other initiatives competing for resources. Make it easy for leaders to understand the enormous revenue and profit from partnerships. Use this channel's massive ROI and ROAS to telegraph why your recommendation warrants commitment.
It can be tempting to try to write this section first. Don’t yield to that desire. By building out your other plan sections first, you will have ready access to the information for the executive summary.
Scope and Description
This critical section explains the range of partners and types of partnerships you recommend pursuing. Having articulated guard rails will help your team focus on the best opportunities and help prevent “swoop and poop” requests from outside leaders and teams.
Start by declaring your commitment to PERFORMANCE or OUTCOMES-BASED partnerships, and define this category clearly. From there, outline other criteria that will help guide your decisions on whether to pursue and accept specific partners and programs. Consider:
- What sort of scale should a partner offer to warrant your time and attention?
- What brand considerations should be taken into account?
- What targeting considerations should be “musts”?
- Are you willing to pursue temporary partners, or do you want to focus only on evergreen relationships, and why?
Competitive Analysis
Competitive analysis can be an invaluable aid in guiding partnership decisions. Including competitive analysis in your plan serves several purposes:
- It helps establish the channel as a viable option for your business
- It provides insight into the potential scale and most significant opportunity sectors
- It can help you determine appropriate offers so you can build your sales and profit models
- It provides urgency to senior management (FOMO)
Competitive information is an aid to judgment, not a predictor of your results. It helps establish a baseline from which you can develop plans to surpass competitive program performance.
Here are a series of questions to help you gather as much relevant data as possible quickly:
- What sorts of offers are my competitors making in their affiliate programs? You can also get great insights into how your competitors manage programs on knoji.com. Most programs also have affiliate intake pages on their sites that can be found in site footers or with Google.
- What can you learn about the business structure of your competitors? Use LinkedIn employee searches as a starting point here.
- Visit the top cashback and coupon sites to see if your competitors are active there.
- Use an SEO tool like SemRush, Moz, or Ahrefs to search for competitor backlinks.
- Monitor their websites and social media to look for signs of partnerships and offer programs.
- Subscribe to their marketing automation email programs (assuming your domain isn’t blocked. It usually won’t be.)
- Is there evidence that they use influencers to deliver brand messages and drive direct sales? What are the terms under which they work with influencers? Often it is easy to find insights on your influencer platform tool or by doing Google searches for program pages.
- Large partners can sometimes share publicly available info to help you structure successful programs.
- Searching for “Brand Trademark + Deals” can often uncover search partners and other partners active in a brand’s programs.
- Searching LinkedIn for partnership-related titles can give you a sense of the size and focus of a brand program.
- Search the offer “malls” of credit card reward programs to see if your competitors have offers available there. Note that card-linked offers are generally confined to retailer brands, so that can simplify your search.
These and other strategies can help you understand the partnerships competitors are pursuing and the specifics of their commission offers.
Recommended Partnership Types
Explain the specific classes of partnership that you want to pursue. Some categories to consider include:
- Traditional Affiliates (e.g., RMN, GSG)
- Mainstream Publishers (e.g., Conde Nast)
- Blogger Influencers (e.g., Pioneer Woman)
- Social Influencers (e.g., Paul’s Hardware)
- Fintech Partners (e.g., Venmo)
- Card-Linked Offers (e.g., Cardlytics/CC Reward Programs)
- BNPLs (e.g., Klarna)
- Conversion Optimization Partners (e.g., RevLifter)
- Travel Rewards Programs (e.g., United Mileage Plus)
- Clubs and Associations (e.g., AARP Rewards)
- Employee Benefits and Rewards Programs (e.g., Bucketlist)
- Brand-to-Brand Partnerships (e.g., brands in related categories)
This is by no means an exhaustive list but does include many of the most popular partnership categories for consideration.
The right partners for your business depend on your brand, price point, buying cycle, compensation rate, and other factors unique to your category and market position. Further, your brand values and brand equity also play critical roles. For example, some brands are entirely opposed to offering discounts publicly, which might rule out certain traditional affiliates. Other brands might be a great fit for travel rewards programs. Still others might be ideal for influencer programs because many opinion leaders write about your category.
Naturally, some of these channels are more developed than others. Some market sizing data is available for the most developed categories like traditional affiliates. Others will have a dearth of information. But even in those categories that are less developed, you can put pen to paper to make some estimates of potential sales from a channel.
Creating an Operating Plan
Any business needs resources to enable its establishment and growth. A partnership business is no different. An operating plan outlines the people, investment, and other resources necessary to facilitate success.
When creating a partnership operating plan, it’s valuable to start your thinking with “hats, not heads.” Define the roles and associated responsibilities needed before thinking about the individuals who fill them. While extraordinary individuals have tremendous value in a business plan, starting with hats instead of heads ensures that the needs of the business dictate the organization, not the wants of specific individuals.
For a company to deliver scalable and repeatable results, you need to create an organization and operating principles that are not dependent on specific “superstar” individuals. Investors say that one of the most common mistakes businesses make is building an organization and planning dependent on "superhuman" individuals. Remember that your star players can power more success for a business plan - they are not the essence of that plan. If you struggle with this recommendation, consider this: would you base your entire partnership program on an individual partner?
From there, you need to think about the financial investment you need. Take the time to think through your needs. Many people rush through this stage and later find themselves strapped when forgotten expense types emerge. At the same time, recognize that a business plan is also an expression of the potential value that can be driven through the channel. “Sandbagging” may price you out of consideration. Similarly, delivering too rosy a picture can help you skate through the early stages only to be called on the carpet later when your projections prove inaccurate.
The operating plan development process should be one in which you choose what to do first and what can wait. Think through what the company wants from you. Do you need to be profitable by month three or year three? You want the aggressiveness of your recommendation to align with company goals and investment style.
You cannot do everything at once, or you will do everything poorly. Prioritize the opportunities and layout why you have chosen those priorities. Consider the law of threes. Accept that few organizations can do more than three big things simultaneously. “Big” is a subjective measure, and bigness varies based on that organization's size and core competencies. Still, this concept helps guide people to a reasonable number of priorities for a period. Some would suggest that even three is too many. But surely we can all agree that more than three is a bad idea. Finally, it is often helpful to deliver multiple operating plans for different revenue projections/trajectories. Offer a low, medium, and high investment scenario to match the low, medium, and high revenue and profit projections you define in the next step.
After developing your “hats, not heads” plan, it’s perfectly valid to summarize the outstanding qualifications of those team members you have on hand to meet the business needs. Do so in the context of how they enhance your hat-defined org. That helps give your management team greater confidence in the wisdom of funding the initiative.
Creating a Financial Plan
The operating plan is a critical input for your financial plan. The financial plan is a projection of the revenue and profit from the channel. While, as you develop it, you will likely return to other elements of the business plan to adjust assumptions and figures, having baseline or ballpark figures for those elements of your program is crucial as you start to define the potential value of the business to your company.
There are many templates for building a financial plan available online. They are generally similar and often available without cost. They will require some adaptation to “fit” a partnership initiative, but they provide a good foundation.
Additionally, check with your CFO or company financial team to see if they have a model they believe in. This serves several purposes:
- It aligns your effort to a format they are familiar with
- It ensures that it is easy to understand your recommendations and compare your plan to other potential company investments
- It demonstrates that you wish to partner with the financial team, which will be critical for your success.
If your financial team has a financial planning and analysis (“FP&A”) person, find out if you can ask for their help building your models. This will help you immeasurably and ensures that one of the critical evaluator/influencers is on your side later. Treat your company's financial team as a potential investor because that's what they are.
Identifying Headwinds and Tailwinds
It’s valuable to consider what macro changes could positively or negatively impact your success. Think both inside and outside the box in this area. Competitors, economic forces, and regulatory changes are three important considerations here, but there are likely others. Ask yourself:
- What does an unsuccessful versus successful partnership look like?
- What might affect customer receptivity to my products, services, and offers?
- What might affect the willingness of the best partners to work with me?
- What could positively or negatively affect the commission or payments I have to make per desired outcome?
- What partnership agreement requirements could have a material impact on our success or liability?
- What might limit the availability of data essential for measurement and optimization?
Once you have arrayed these potential challenges, you may be able to think of ways to reduce your exposure. Start by thinking about how intellectual property, speed to market, partnership exclusivity agreements, or other tools could help mitigate these threats. But whether or not you can think of ways to protect yourself from these risks, having identified these potential issues helps the business fully understand the opportunity you bring to them.
No sensible business leader will expect the partnership channel to be risk-free, but they will want to understand the scale and likelihood of the dangers. If your company cannot tolerate the potential problems associated with one or more of these key risk areas, better to know now than when it happens, and you have to explain the situation to the management team.
Conclusions
A partnership business plan's format, breadth, and depth should align with how your company expects such recommendations to be made. In general, it’s valuable to have an executive summary presentation and a more in-depth document available, along with detailed spreadsheets that chronicle your establishment and growth expectations.
For some, doing all this work may feel like a waste of time. After all, aren’t the benefits of a robust business plan obvious? But the plan not only helps your company understand and assess the opportunity. It also ensures that you have thought through the way forward and can make more of the right decisions on days 1, 91, 366, etc. Planning is good. Prioritization is good.
Having a plan also helps an organization understand what they approve and what will be necessary to achieve a strong partnership revenue stream. As discussed earlier, many companies enter into partnership thinking it is a low effort, low-cost means of driving rapid growth. By setting appropriate expectations and outlining the tremendous revenue and profit potential, you set yourself up for maximum success.
You may also like...
B2b affiliate marketing: analytics guide.
Data analytics plays a pivotal role in B2B affiliate marketing by providing ...
Partnerstack Makes Aggressive Move Where Others Have Only Gestured.
Summary: B2B affiliate network PartnerStack received $29M in a series B funding ...
Brands and Agencies: Master the Commerce Content Ecosystem (Part 1)
Commerce content is propelling growth in our industry. To maximize the opportunity, ...
Martech Record Glossary: OPM
OPM: Outsourced Program Management An OPM is agency that handles the ...
Exclusive Content Under One Roof .
Join our community of performance marketing professionals to unlock Martech Record member only content.

Copy short link
How to Create a Partnership Proposal [With Free Template]
When embarking on a business partnership, expect challenges. Partners have different personalities, working styles, daily schedules, and initial investments. You need to juggle working together (possibly for the first time) while addressing market needs and differentiating yourself from competitors.
A partnership proposal can help make those challenges a little less daunting by clarifying the details of your collaboration before you even launch your business. It can get everyone on the same page, reducing the risks of detrimental disagreements later on.
But drafting such a proposal is no small task.
To help you on your journey, we’ve got step-by-step instructions and a helpful partnership proposal template .

What’s in this guide :
Why you need a business partnership proposal
How to create a proposal for a business partnership, partnership proposal template & software.
Research shows that 70% of business partnerships fail—and (here’s the good news) a clear agreement is one of the best ways to improve your odds of success.
Oftentimes, partners will equally share the burden of losses and the gift of gains. But your share should reflect what you put into the business, both in terms of time and money. So if one partner will be giving more, they should also get more out of it. By accurately calculating equity, salaries, and profit draws in advance, you can be sure that each partner is getting their fair share according to their initial investment and ongoing role in the company.
A partnership proposal with clear terms can help settle any financial or legal matters that may arise later. But on a more positive note, it will also improve the quality of your collaboration. When all the terms are laid on the table up front (and no one is guessing or assuming), communication between partners will begin with a much stronger foundation—paving the way for a more profitable relationship.
Creating a proposal for your business partnership is complicated, but fortunately, you don’t have to go it alone. Follow these simple steps to cover all of your bases.
Step 1. Research what your proposal should include
The first step is to research what you need to include in your proposal, such as the share of profit and loss, the managing duties of each partner, and what should happen in the event of the death of a partner. This is a critical legal document so you need to get it right..
You don’t have to get it perfect the first time, as the terms will likely require negotiation. But covering all of the necessary information will demonstrate your attention to detail and ensure that the preceding negotiations are thorough.
Make sure to research requirements that are unique to your partnership type , which usually falls into one of these 3 categories:
General partnership - Shared day-to-day operations and liability for debts and owners.
Limited partnership - One or more partner doesn’t participate in day-to-day operations and is not liable for debts or lawsuits (but receives profits). This is typically used for inactive investors.
Limited liability partnership - Liability protection is extended to all partners so that no one is responsible for the actions of another partner. This is typically used for professionals operating out of shared office space, such as accountants, financial advisors, or plastic surgeons.
Because the taxation structure will affect the way that earnings are distributed and reported, you should also research details specific for your province or state of incorporation as well as your entity type (limited liability corporation, c-corp, etc.).
Brainstorm more information to include based on your unique business and what each partner brings to the table. For instance, if one partner is joining the partnership with a large social media following of ideal customers, you might want to outline how that social media account is expected to be used and what content will not be permitted on that account once the partnership begins.
If you use a partnership proposal template, you’ll save a lot of time on both research and writing. Preview our template here.

Make sure to consult with a business lawyer to get their take on the necessary terms.
Step 2. Outline your proposal
Now that you have your checklist for what to include in your proposal, it’s time to start organizing all of that information into a cohesive outline. A proposal template will save you time here. Start off with the template and then include additional terms that matter to your business.
We suggest this outline for your partnership proposal:
Name and Business - Basic business details like business name and address.
Term - When the agreement begins.
Capital - How partnership capital will be maintained.
Profit and Loss - How profits and losses will be shared and credited.
Salaries and Drawings - How salaries and profit draws will be managed.
Interest - Whether or not initial investments will receive guaranteed interest payments.
Management Duties and Restrictions - How management duties will be split, and what tasks can’t be undertaken without agreement from all partners.
Banking - What chequing account(s) will be used.
Books - How bookkeeping will be managed.
Voluntary Termination - How the partnership can be voluntarily dissolved, and how assets will be distributed if this occurs.
Death - What will happen in the event of the death of a partner.
Arbitration - Basic statement on arbitration for the agreement and the legal association that will be used.
You might be wondering if you need to add a cover letter to your outline. If you don’t need to convince anyone to join the founding team, you probably don’t need a cover letter. But if you’re trying to win over a partner, then check out this guide to writing a cover letter and add your letter to the very beginning of your proposal.
Step 3. Write the proposal sections
Time to write.
A partnership proposal has a very different style than most other business proposals , which are typically sent to prospective clients in order to win deals. For those proposals, you’re trying to sell . But with a partnership proposal, you’re trying to clarify . The prospective partner needs to know what they’re signing off on in order to give you a yes. What’s expected of them? What percentage of equity will they receive?
Because the goal is different, the writing style should be different too. Write using clear, simple, and legally accurate language for the majority of the proposal. By keeping the language of the proposal straightforward , you’ll eliminate any confusion and potential for disagreements later.
Take this text from our partnership agreement template as an example of the writing style you should aim for:
A separate capital account shall be maintained for each partner. Neither partner shall withdraw any part of his/her capital account. Upon the demand of either partner, the capital accounts of the partners shall be maintained at all times in the proportions in which the partners share in the profits and losses of the partnership.
If you need to create content to convince on-the-fence partners, you can do so with your cover letter, business plan, or presentation slides that will go along with the proposal. You might cover the addressable market, your competitive advantage, pricing model, etc.
Step 4. Add e-signatures
The next step is to add e-signatures to your proposal. This will turn the proposal into a binding agreement, so that once signed by all partners, the partnership can begin with clear terms.
You should add the e-signatures to the final page of the proposal.

Make sure that the e-signature software you use is legally binding .
Step 5. Review, sign, and send it
And lastly, it’s time to make sure your proposal is perfect. Review all of the terms and make sure you’ve covered everything in your checklist.
If you can afford it, have a business lawyer review your agreement before you sign and send it. This should be cheaper than having them draft an agreement from scratch (and can save you a lot of money and stress in the long run).
When you’re ready, sign the proposal yourself and then send it for signature to your partners.
You should not open up any bank accounts, file articles of incorporation, take out loans, or conduct any other activity with financial implications until the proposal is signed by all partners. If you do, a partner could later argue that they’re not liable. Instead, use the time before the proposal is signed to work on your business plan and research your addressable market.
Proposify makes it easy to create beautiful proposals for both internal and external use. We offer 75 unique proposal templates that show you exactly what to include and help you draft your proposals quickly.
You can also design your own proposal templates, save content snippets, and track stats on proposal views and closed deals.

How to Write a Business Proposal [Steps, Tips, & Templates]
September 30, 2022

Ready to make every deal a closed deal?
Get started with a free Proposify 14-day trial. No credit card required. Just more closed deals.
- AI Transformation
- Application Development
- Audience Engagement
- Channel Management
- Content Development
- Data Analytics
- Growth Initiatives
- Program Operations
- Strategic Planning
- Marketing Management
- Sales Management
- Operations Management
- Product Management
- Resource Center
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Community & Culture
- Contact Sales
- Contact Hiring

The Essential Guide to Partner Planning
Build your partner planning framework.
A business plan for partnership encompasses how both parties will not only meet short-term objectives, but also put long-term growth strategies into place that drive partnership sustainability.
A channel partner business plan, specifically, is a roadmap for aligning goals, defining actions, and allocating resources between your organization and its partners. The plan should outline specific outcomes and commitments from both parties, fostering mutual accountability and clarity in partnership objectives.
Partner planning aims to have the right quantity of products in the right places at the right times to satisfy customer demand in an efficient, cost-effective manner. While the concept seems elementary on the surface, the complexity arises once you dig deeper. A channel leader must review their partner business plan to ensure the strategy aligns with the company’s desired business outcomes.
Through years of experience and a rigorous approach, our team of channel experts at Spur Reply have identified five essential steps to guide partner planning.
Step #1: Understand the present strengths and weaknesses of current efforts
Step #2: know your growth levers, step #3 define the required ecosystem need, step #4 evaluate partner performance, step #5 create partner-level action plans.
Developing an understanding and maintaining a line of sight into the strengths and weaknesses of your channel strategy is integral to driving revenue acceleration through the partner channel. It is essential to review, analyze, and benchmark your teams’ and programs’ performance regularly and can be done using a model that examines 18 points of execution across six primary areas:
- Are you set up to reach your strategic objectives? Capacity planning: Do your existing partners deliver enough sales velocity to hit your targets? Joint business planning : Are you ensuring your partners are aligned to the right goals? Partner scoring : Do you know who the right partners are?
- Have you created a model that will continually grow your base? Partner business proposition : Is everyone aligned on the compelling reason you beat the competition? Partner onboarding : Are you maximizing partner activations throughout your recruitment efforts? Partner recruitment : Do you understand and act on the profile of your best possible candidates?
- How good are your partners at selling your goods and services? Campaign development : Do you know which partners are effective marketers of your solutions? Go-to-market playbook : How aligned are your partners and field sellers to deliver unified joint sales? Partner enablement : Are you arming your partners with the tools that help them with customers?
- Are your costs-to-serve too high for you and your partners? Channel incentives : Is your contra-revenue program driving value? Deal registration : Does your program incentivize sales behavior or simply transfer margin? Partner investment framework : Are you getting sufficient return on your other investments?
- Do your programs keep partners loyal? Cloud revenues structure : Have you made the same shift to the cloud as you expect from partners? IP development : Do partners see you supporting their future IP development? Partner program : Does your program deliver enough value to partners?
- Do you execute most effectively and efficiently? Partner co-selling model : Are you partner managers what’s expected? Performance dashboard : Do you hold all stakeholders accountable to the same metrics? Pipeline management : How central is managing a specific partner pipeline for your partner field sales?
Use these questions as a guide to review the performance of your channel programs. You should be able to classify the health of your channel processes as one of the following:
- Unstructured (few formal processes in place)
- Ad Hoc (processes defined as guidelines with limited adherence)
- Advanced (multiple scenario-based processes in place)
- Robust (automated processes adjust based on defined parameters)
- Structured (formal process with disciplined adherence)
Formally benchmarking your programs and processes will then allow you to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of your channel programs.

Another critical element of partner planning is the ability to diagnose channel performance against a vendor’s strategic product focus and growth model. Spur Reply has developed the Growth Profile TM Strategic Model to help map product priorities to sales and partner performance in a quantifiable manner. The model is composed of 4 quadrants to classify which products are in each stage of the growth cycle:
Incubate - Break into new markets and technology by concentrating on research and development efforts with a new or existing channel or direct resources.
Optimize – Maintain sales with programmatic reductions by redirecting resources from low-performing elements to higher-performing elements to increase efficiency and effectiveness.
Perform – Maximize sales and current revenue flow with existing partners and direct sales resources.
Transform – Strengthen to scale or achieve performance leadership by recruiting new partners or adding additional direct sales resources.
Having a clear understanding of your growth profile is essential, as it quickly helps you determine the right strategic balance to recruit, grow, develop, or prune your direct and partner sales base.
Managing your partnership community to ensure it contains the right mix of partners is vital to sound channel management. Partner managers need to have both a full understanding of the company’s partner community and how to optimize the community’s performance — using five simple levers.
- Contribution : What is the sales velocity of each partner? Sales velocity refers to how quickly the company converts leads to sales and the value of each of those closed deals over a set period. Almost everyone measures sales velocity, and you likely have data to calculate the rate for each partner.
- Consumption : How effective is the partner at driving customer adoption and usage? If contribution represents revenue, then consumption is the increase in the average customer’s lifetime value through affiliation with the product or service.
- Coverage : What markets does the partner cover? Your ecosystem capacity is influenced by the mix of partner types and the number of partners in each segment, as well as partner attributes such as customer served, business models, and solutions offered.
- Capability : How aligned with strategic products is the partner? Capability is a combination of the partner’s knowledge and its effectiveness at bringing it to bear with targeted customers. Every revenue dollar is not equal when it comes to building a growth engine, and a partner’s capability is critical.
- Commitment : How steady and certain are the partner’s results? Most partners work with multiple vendors, so loyalty is a crucial determinant of channel revenue. A partner’s commitment will affect how it contributes to your growth curve.
Planning should inform channel management activities such as data-driven models for recruitment and development, balancing engagements based on strategy and performance requirements, and testing partner business propositions across segments.
In the evolving channel space, leaders have limited resources to influence partners and meet business objectives, and a standard partner scoring system can boost partner value and returns. Partner scoring can reveal the strengths and weaknesses of each partner, revealing opportunities for potential incentives, management, and scaling strategies.
We believe that partner scoring should be more than a forecasting tool. The framework can help increase sales, improve ROI, and re-direct partner behaviors to high-value actions. Spur Reply uses a three-step approach for calculating a Partner Evaluated Revenue Capacity (PERC) score, considering both current performance and potential for growth.
- Use the 5Cs to rank each partner. The 5Cs are Contribution, Consumption, Capability, Coverage, Commitment. For each, set weights based on your channel strategy and intricacies of your partner ecosystem.
- Rate each partner into peer-levels using a simple five-star rating. Partners that score well in the 5Cs are 5-star partners and the scale should adjust down from there.
- Calculate a final PERC score across the star grouping of partners in order to assess whether a partner is performing above, at, or below average for similarly sized partners.
The PERC score allows you to create an action plan for partners and even extend the model to get more value. You can evolve from the core model and customize your PERC score, create better dashboards, compare like partners, simplify research, and strengthen capacity planning.
The final element of effective channel planning is partner business planning, which improves your ability to set goals, manage commitments, and drive partner performance against benchmarks.
We recommend you track partners and build out your channel management strategy in five key areas:
Business Model – The design of a partner’s business
Industry Importance – The partner’s focus area
Product Focus – The products the partner highlights and emphasizes
Program Membership – Partner program membership and status
Vendor Alignment – The vendors your partner is working with
By developing a firm understanding of these five aspects and leveraging data-driven insights to adjust strategies accordingly, companies can optimize their channel management strategy and accelerate revenue.
While each element of an effective channel plan is individually important, none are successful in silos. The elements of a high functioning channel plan are interrelated as they inform and influence one another.
Set the right goals
When contemplating a successful partner channel, the more partners the better, right? The more partners you have re-selling, the more revenue you and your company will enjoy.
Why more doesn’t always equal better
When it comes to your partner strategy, more is not necessarily better. At a certain point, the right kind of partner becomes more critical to the success of your channel than the quantity of partners.

Spur Reply recently worked on a project at a large software independent software vendor (ISV) that develops ERP and CRM solutions. The company wanted to adjust and refine its channel strategy, which was large, and through data analysis, it was clear that some trimming was necessary for two reasons: an unbalanced partner community and too many partners overall.
Creating balance in your partnership community
The right mix of large and small partners is an essential for a well-balanced channel program. Too many times, a customer would be best served by the right partner, but with a channel that is oversaturated with them, the perfect match doesn’t happen. Capacity planning and economic modeling can help you look beyond just the sticker price on a partner relationship.
Efficiently supporting your partners
Every partner, regardless of size, quality, or ambition, needs support. Whether it’s incident response, training, or marketing, partners management requires budget, and partners not driving revenue can easily eat up your support allocations. Plus, if your channel is oversaturated, you can end up with too many partners chasing a limited number of customers. Avoid having so many partners that it limits your return.
Benchmark your channel efforts against your direct sales
Both direct and indirect sales are essential elements of your go-to-market effort. Channel leaders must never forget the most important reason for an indirect sales motion is scale. You have partners because they help you win customers, drive sales, and enter markets where you wouldn’t otherwise have the presence or meet the cost structure.
In an age where new products are hitting the marketplace at an unprecedented rate, companies are tasked with the challenge of developing strategies to find the right partners to sell the right products at the right time. You can optimize channel revenue and profitability with a robust understanding of the stage of your product in the growth cycle.
However, before you can develop a channel strategy based on your product growth profile, you’ll need to understand the elements of the growth cycle and how each one influences channel decision making.
What is Product Growth Mapping?
Spur Reply has developed a proven system for product growth mapping called the Growth Profile Strategic Model. The model is built upon the idea that products fall into one of four quadrants: Incubate, Optimize, Perform, and Transform. The model helps you map your product priorities to your sales and partner performance in a quantifiable manner and optimize profitability for each product.
The axes of the graph you’ll create are labeled “Percentage of Total Revenue” (Y-Axis) and “Percentage Growth” (X-Axis). The elements of the graph and their descriptions are displayed on the grid in the following order:
Incubate – Break into new markets and technology by focusing on research and development efforts with a new or existing channel or direct resources (bottom left quadrant).
Optimize – Maintain sales with programmatic reductions by redirecting resources from low-performing elements to higher-performing elements to increase efficiency and effectiveness (bottom left quadrant).
Perform – Maximize sales and current revenue flow with existing partners and direct sales resources (top left quadrant).
Transform – Strengthen to scale or achieve performance leadership by recruiting new partners or adding additional direct sales resources (top right quadrant).
Thresholds to determine when products move from one quadrant to another are set based on company size, product offerings in the market, and the amount of revenue each product drives. A company with one great product bringing in most of the revenue may set their percentage of revenue threshold at 5% so that it will include more than one product. On the contrary, a company with several extensive offerings may set their threshold for this axis at 10% or 15%.
For this example, let’s say for a company the percentage of revenue threshold is 10%, and the percentage growth threshold is 5%. A product in the incubate phase is growing at a steady rate but does not yet make up more than 10% of the company’s total revenue. Products in the transform quadrant are those that drive more than 10 percent of the company’s revenue and are experiencing growth higher than the threshold of 5%. Performing products are typically great products already at scale, accounting for greater than 10 percent of total revenue, but the growth has plateaued and is below the 5% threshold. Products in the optimize quadrant are being phased out because they are not growing enough and make up less than 10% of revenue.
Now that you have a good grasp of the model, we can look at how this influences the channel strategy for each product.
Why is Product Growth Mapping important?
Having a clear understanding of your growth profile is essential. It quickly helps you determine how to recruit, grow, develop, or prune your direct and partner sales base and invest in each product in the most efficient manner.
An important piece of context is that growing sales through partners means you need to use one or more of these strategies:
Convince current partners selling a different product begin selling a new product
Leverage current partners sell more of that same product
Recruit entirely new partners who have never worked with you begin selling a new product
Every partner growth strategy uses these three significant engines, so keep them in mind as you choose partners to sell your products.
How Product Growth Mapping affects partner choice
Within each quadrant — and the corresponding growth cycle phase — there are typical partners that sell products in each.
Starting in the incubate stage, the chances of recruiting new partners to sell relatively new products is slim to none. You don’t know them, they don’t know you, and chances are they aren’t overly familiar with the product. Instead, you will likely leverage partners you have worked with before and who you have an existing relationship. These partners often have a low-risk profile and have experience selling innovative products in an unproven marketplace.
In the transform quadrant, we see a completely different story. Now we rely on all three partner growth engines to sell a product. Current partners start to sell more of what they traditionally sold. Other partners are willing and excited sell a new product, and new companies from an entirely different space or an adjacent space view this as an attractive opportunity and jump in to sell the new product.
In the perform stage the product has reached maturation, and very few new partners are coming on because the market is already developed. The only exception is if the partner is a laggard in the marketplace, and this is the strategy they have adopted for this product. The focus here is to keep current partners selling, if possible, to stave off a deceleration of sales.
Once a product reaches the optimize quadrant, the strategy is to figure out how to pull back investment and roll partners off that product.
Also, channel managers need an investment model for each phase of the growth cycle. Most funds dedicated to product marketing should be focused on products in the incubate stage, even though they are bringing in little or no revenue as they ramp up. This money can be spent incenting partners or developing a joint venture to decrease the risk of selling a new, unproven product.
As you move through the model to transform and perform, you spend less money in each stage to fuel product growth because the products mature and gain traction in the market. As the product reaches the optimize quadrant, you want to invest as little as possible to keep the product afloat and devote resources toward the end of life milestones and rolling partners off that product. Having a consistent mathematical model that drives the investment strategy for the growth cycle is equally as important as having a sound partner engagement strategy in place.
Common mistakes to avoid
When developing investment and partner engagement strategies for different stages of the growth model, we often see two significant mistakes: selling a product before it’s ready to move from perform to optimize stage and developing an investment model based on the traditional cost-of-sale model.
The first mistake is incenting partners to sell a new product before a product is ready to move from the perform stage to the optimize stage. We often see new products cannibalize old ones, and sales of the old product are cut short because partners begin to focus all of their attention selling a new and exciting product. A vendor must be careful with their launch and incentive strategies to avoid this partner behavior.
The second major mistake we see is companies developing an investment model based on a traditional cost-of-sale model. Companies will spend their product marketing budget in the wrong quadrant, most often the perform quadrant, because it drives the most revenue. Instead, devote this budget towards a product in the incubate quadrant — even though the current revenue is low.
With technology changing so rapidly today, having a great product simply isn’t enough. You also need go-to-market efficiency and data-driven tools for managing partners and channel sales. Whether you are doing annual business planning or trying to determine your best partner strategy, knowing your growth profile is essential. You can quickly and efficiently assess which products are in the growth cycle and determine the right strategic balance to recruit, grow, develop, or prune your direct and partner sales base.
Roll it out to partners
Every business wants to accelerate its revenue, yet it’s a tough goal to reliably accomplish. Combining product advantage with go-to-market efficacy is the key to consistently achieving revenue acceleration.
You have a great product or solution but, in a market saturated with competition, you need an effective go-to-market and business plans to meet your goals.
How do you make planning valuable for both you and your partners?
The best partner business plans are mutually beneficial, helping both you and your partners to grow faster than your organic growth paths. Fostering channel partner growth requires expanding your partner base as well as nurturing existing partnerships to unlock their full potential. You must consistently identify opportunities for partner expansion into new markets, verticals, or customer segments. By implementing targeted growth initiatives into your partner business plans, such as joint marketing campaigns, co-selling programs, or incentive strategies, you can catalyze partner-driven revenue growth and strengthen your market position.
To make sure the plans will deliver accelerated results, you’ll need to take a critical look at six areas of your business and answer the following questions:
- Partner Selection : Which partners will help me grow faster?
- Capacity Planning : Can I grow better through existing or new partners?
- Performance Measures : How can I confidently measure partner performance?
- Incentive Impact : Are my incentives rewarding or reflecting partner behavior?
- PAM/CDM Productivity : How can I drive more revenue, and higher partner satisfaction, with my field resources?
- Program Effectiveness : Do my programs make a difference with the right level of return?
Now that you have identified the necessary elements, it’s time to structure those them into a practical, adjustable plan. At Spur Reply, planning is a four-step process: assess, learn, plan, document.
Assess > Learn > Plan > Document
First, you need to set your goals and select your growth partners. It will require you to assess and analyze your partners’ growth profile. Specifically, you need to look at the difference between their organic growth and your desired growth for them. How can you get your partner’s growth up to a level that will reach or surpass your revenue goals?
Once you have your goals and growth partners set, you need to understand performance drivers and growth areas. Leverage the work you have already done for capacity planning and partner scoring to learn what you need from partners.
After you determine your most valuable partners, you can finally set up your plan . In this step, you will define business outcomes and partner commitment. A good business plan sets the right expectations by covering off on what the partner and vendor commit to across several components:
Partner Commitments
- Outcomes – What are the business results you both seek?
- Actions – What are the specific steps the partner will take to accomplish the desired outcomes?
- Pro Tip – We recommend not micromanaging the partner. Agree to business outcomes, allow partners to deviate as needed, and hold them accountable to their results and agreement.
Vendor Commitments
- Resources – Which staff, programs, and other tools will you provide to the partner?
- Investments – What incentives are you willing to offer partners with the right performance?
- Pro Tip – We recommend paying MDF slightly before partner actions to help drive capability and efficiency.
Now that you have your plan, you’ll need to document it and both of your commitments correctly, which involves sharing the plan and driving performance accountability. By sharing the business plan in this way allows all stakeholders to review the plans (the partner, the partner’s account manager, and whoever has corporate responsibility for outcomes).
As you go through the planning and documentation process, leverage the opportunity to make sure you understand your partners.
First, use your partner business plan to develop profiles for your partners by collecting information that allows you to benchmark future performance. Then, make sure you have set up a timeframe with performance milestones, specific outcomes, and investments based on rewarding performance against commitments and completion criteria.
With your partner planning process set up and documented, make sure to track your performance against the 5Cs in your Quarterly Business Reviews (QBRs). Whether under, at, or exceeding goals, determine if you need to adjust the plan, reset the goals, or reallocate the investments.
Fueling effective partner sales execution
Effective partner sales execution ultimately hinges on successful partner planning. Effective selling requires you to translate strategic plans into tangible actions, leverage sales enablement tools, and provide ongoing support to partners throughout the sales cycle. As a channel leader, it’s critical to prioritize continuous monitoring and optimization of partner sales activities, identifying areas for improvement and implementing corrective measures as needed. Additionally, regular performance reviews and feedback loops allow you to assess your channel partner growth strategies and make informed adjustments that will better maximize revenue generation.
No matter how developed your channel partner ecosystem, creating robust partner business plans will improve the go-to-market efficacy and revenue acceleration of your product.

Richard Flynn
Related articles.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 10 Partnership Plan Templates with Examples and Samples

DivyanshuKumar Rai
When partners enter a business at the outset, they are motivated and excited to embark on this exciting new adventure together. Initially, they agree on almost everything. These new entrepreneurs think they will be in business together for the rest of their lives or until they sell the company for untold millions of dollars.
They believe that nothing can or will go wrong. They are so sure of each other that they never bother to get a written partnership plan. What could possibly go wrong in this scenario? The short answer is, "A LOT!"
The reality is that, despite dreams of longevity and unwavering trust, business owners' desires and expectations change over time. A written partnership plan can manage these expectations and give each partner confidence in the business's future. A written plan can serve as a safeguard that protects both the business venture and the investment of each partner.
Now, you might be thinking, “How to get an effective partnership plan in place?” The quick answer: Partnership Plan Templates .
Every business requires a partnership plan. Small businesses seek out partnerships more to achieve their goals and objectives. Building a strategic partnership is more complicated than creating a partnership document, but it is the first step toward action. SlideTeam’s partnership plan templates maneuver your ship to the shore.
Let’s explore these!
Template 1: Vendor Strategic Partnership Engagement Plan
Get this Strategic Partnership Plan PPT Template and deliver an impactful presentation to your audience. Its layout is divided into four sections, each describing a critical aspect: Plan, Analyze, Identify, and Act. There’s a specified section for review to ensure you have that extra cushion to make amendments, wherever necessary. Get this template now.
Download this template

Template 2: Strategic Partnerships Event Planning Service Company Profile PPT Template
This PowerPoint Template works wonders when you want to explain the role of strategic partnerships within an organization. It has ample space to highlight points you want to deliver in your presentation. You can use its standard layout to emphasize key details, including partner location, services they monitor, objectives, and more. Download it now.

Template 3: Internal Communication Plan For Partnership Firm
The importance of proper communication in the successful accomplishment of business objectives can’t be overstated. With SlideTeam’s handpicked internal communication plan template, you can enjoy the convenience of an uninterrupted flow of information across departments in your company. This plan layout describes:
- Reasons for communication
- Communication activity
- Communication channel
- Individual responsible
Download now.

Template 4: Marketing Campaign Initiated by Partnership Timeline
Build a weekly timeline for your marketing campaign using this fantastic PPT Template. Till the campaign goes live, you can include and track KPIs to ensure your effort is successful. Here, there are some predefined parameters that you can use: Target mapping exercises, Prepare brands and categories, Assign partner roles, risk register update, Negotiation and recruitment, and Activation and management. Download it now.
Template 5: Global Partnership Management for Planning and Communication
Global partnership management is a painstaking task that can be made easy with our exemplary template. It has a unique framework that explains key insights encompassing the five stages, namely: Prepare, Share Knowledge, Plan, Execute, and Achieve Results. Being 100% editable, you can tweak the design and include points in this template to serve your purpose. Download it now.
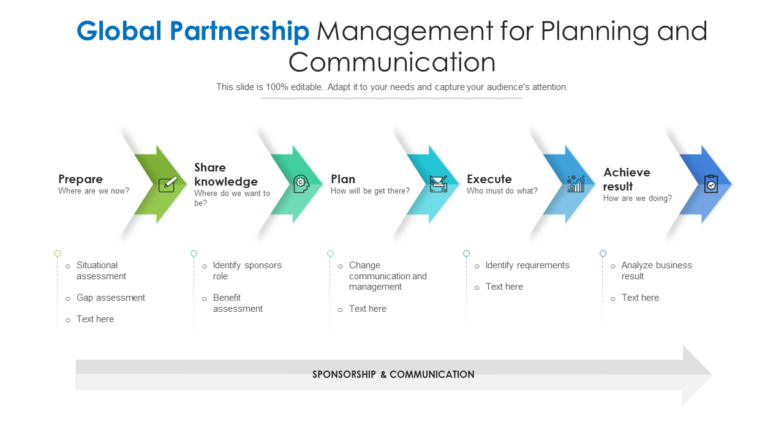
Template 6: Six Months Teamwork Partnership Strategy Roadmap
Teamwork is the key to success! We know you would have heard this phrase at least a million times, but it doesn’t take away even a slight bit of truth. Build a six-month teamwork partnership framework using our exceptional PowerPoint Template. It highlights the team member and phases spread across a month-wise timeline. The phases include:
- Develop partnership strategy
- How the partnership will operate
- Ensure stakeholder support
- Resource allocation
- Review the partnership development process
Template 7: Five-yearly Teamwork Partnership Strategy Roadmap
With a similar design to the previous template, this template accelerates the process of building a five-year teamwork partnership strategy roadmap. It has some predefined phases which you can change to suit your business requirements. You can present it to higher management to get their approval on the partnership roadmap you are long working on. Get it now.
Template 8: Planned Partnership Strategy PPT Template
If you need a pre-built framework for drafting a planned partnership strategy, this is the perfect piece for you. Its layout is designed into five stages that you can use to explain critical insights that underline your strategy. You can also use it to highlight KPIs as well. Get it now.
Template 9: Strategic Partnership Showing Teamwork
‘Strategic partnership’ is a complex subject that commands resources to spark clarity in your audience. Lucky for you, SlideTeam has prepared this template that touches every essential parameter that encompasses it. This template highlights the points of collaboration, teamwork, strategy, plan, performance, and success. It is a roadmap with checkpoints you need to surpass to foster better partnerships within your organization. Download it now.
Template 10: Partnership Action Plan PPT Presentation
A partnership action plan boiled down into three stages! Hard to believe, isn’t it? SlideTeam presents a PPT Template that displays a layout that does just that. It has three levels: Action, Planning, and Partnership. The idea behind these stages is, you have to define relevant actions to ensure your organizational plans aren’t affected. Doing so will ensure there’s a more inclusive partnership forging in your company across departments. Get it now.

Partnerships are critical to the success of any business. Merchants and traders have used the principles of strategic partnership to conduct their businesses since the genesis of trade and commerce; the trend continues today.
A partnership can take many forms, from business owners working together to invest in a project to firms sharing technical knowledge and ideas. Whatever a company does, finding the right partnership plan template that benefits both parties is critical. (And that’s why SlideTeam has put together this list of top 10 partnership plan templates!)
FAQs on Partnership Plan
What is a partnership plan.
A partnership plan is a way two or more parties in a business agree on conducting the venture together. Each party takes different functions to perform, helping the business run more efficiently. This plan is documented in the form of an agreement. This document lays down the ground rules on how the partners will handle business responsibilities, ownership and investments, profits and losses, and company management.
While "partners" usually refers to two people, there is no limit to how many partners can form a business partnership in this context.
How do you create a partnership plan?
When forming a business partnership, it is critical to draft a partnership plan contract that outlines all of the terms and conditions of the professional relationship. Your business partnership plan should include a list of all partners and should address the following issues:
- Name of the partnership
- Partnership goals
- Partnership duration
- Contribution amounts of each partner (cash, property, services, future contributions)
- Each partner ownership interest (assets)
- Management roles and terms of authority of each partner
- Accounting obligations
- Distribution of profits and losses between the partners
- Salaries, work hours, sick leaves, and vacation times of each partner
- Permissions and restrictions on any outside business activity
- Buyout options of partners
- Process for adding new partners or removing original partners
- Terms and conditions of termination of the partnership
What are the stages of partnership?
Here are the five stages of partnership:
Stage I. The Singles Stage (Non-Partnering)
Stage II. The Searching Stage (Pre-Partnering)
Stage III. The Courtship Stage (Active Partnering)
Stage IV. The Bonding Stage (Consolidated Partnering)
Stage V. The Commitment Stage (Going to Scale)
What are the 5 principles of partnership?
There are five basic tenets that work together to form a framework for establishing a solid foundation for effective business relationships.
- Shared knowledge
- Agreed Goals
- Balance of return
While some of these are easier to quantify than others, each has a significant impact on the partnership's strength.
Related posts:
- How to Design the Perfect Service Launch Presentation [Custom Launch Deck Included]
- Quarterly Business Review Presentation: All the Essential Slides You Need in Your Deck
- [Updated 2023] How to Design The Perfect Product Launch Presentation [Best Templates Included]
- 99% of the Pitches Fail! Find Out What Makes Any Startup a Success
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Partnership Agreement Templates for Harmonious Synchronization

Top 10 Strategic Partnership Proposal Templates To Form Successful Alliances (Free PDF Attached)
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

Step-by-Step Guide to Writing a Simple Business Plan
By Joe Weller | October 11, 2021
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
A business plan is the cornerstone of any successful company, regardless of size or industry. This step-by-step guide provides information on writing a business plan for organizations at any stage, complete with free templates and expert advice.
Included on this page, you’ll find a step-by-step guide to writing a business plan and a chart to identify which type of business plan you should write . Plus, find information on how a business plan can help grow a business and expert tips on writing one .
What Is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a document that communicates a company’s goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered.
A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals. That said, a typical business plan will include the following benchmarks:
- Product goals and deadlines for each month
- Monthly financials for the first two years
- Profit and loss statements for the first three to five years
- Balance sheet projections for the first three to five years
Startups, entrepreneurs, and small businesses all create business plans to use as a guide as their new company progresses. Larger organizations may also create (and update) a business plan to keep high-level goals, financials, and timelines in check.
While you certainly need to have a formalized outline of your business’s goals and finances, creating a business plan can also help you determine a company’s viability, its profitability (including when it will first turn a profit), and how much money you will need from investors. In turn, a business plan has functional value as well: Not only does outlining goals help keep you accountable on a timeline, it can also attract investors in and of itself and, therefore, act as an effective strategy for growth.
For more information, visit our comprehensive guide to writing a strategic plan or download free strategic plan templates . This page focuses on for-profit business plans, but you can read our article with nonprofit business plan templates .
Business Plan Steps
The specific information in your business plan will vary, depending on the needs and goals of your venture, but a typical plan includes the following ordered elements:
- Executive summary
- Description of business
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Description of organizational management
- Description of product or services
- Marketing plan
- Sales strategy
- Funding details (or request for funding)
- Financial projections
If your plan is particularly long or complicated, consider adding a table of contents or an appendix for reference. For an in-depth description of each step listed above, read “ How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step ” below.
Broadly speaking, your audience includes anyone with a vested interest in your organization. They can include potential and existing investors, as well as customers, internal team members, suppliers, and vendors.
Do I Need a Simple or Detailed Plan?
Your business’s stage and intended audience dictates the level of detail your plan needs. Corporations require a thorough business plan — up to 100 pages. Small businesses or startups should have a concise plan focusing on financials and strategy.
How to Choose the Right Plan for Your Business
In order to identify which type of business plan you need to create, ask: “What do we want the plan to do?” Identify function first, and form will follow.
Use the chart below as a guide for what type of business plan to create:
Is the Order of Your Business Plan Important?
There is no set order for a business plan, with the exception of the executive summary, which should always come first. Beyond that, simply ensure that you organize the plan in a way that makes sense and flows naturally.
The Difference Between Traditional and Lean Business Plans
A traditional business plan follows the standard structure — because these plans encourage detail, they tend to require more work upfront and can run dozens of pages. A Lean business plan is less common and focuses on summarizing critical points for each section. These plans take much less work and typically run one page in length.
In general, you should use a traditional model for a legacy company, a large company, or any business that does not adhere to Lean (or another Agile method ). Use Lean if you expect the company to pivot quickly or if you already employ a Lean strategy with other business operations. Additionally, a Lean business plan can suffice if the document is for internal use only. Stick to a traditional version for investors, as they may be more sensitive to sudden changes or a high degree of built-in flexibility in the plan.
How to Write a Business Plan Step by Step
Writing a strong business plan requires research and attention to detail for each section. Below, you’ll find a 10-step guide to researching and defining each element in the plan.
Step 1: Executive Summary
The executive summary will always be the first section of your business plan. The goal is to answer the following questions:
- What is the vision and mission of the company?
- What are the company’s short- and long-term goals?
See our roundup of executive summary examples and templates for samples. Read our executive summary guide to learn more about writing one.
Step 2: Description of Business
The goal of this section is to define the realm, scope, and intent of your venture. To do so, answer the following questions as clearly and concisely as possible:
- What business are we in?
- What does our business do?
Step 3: Market Analysis
In this section, provide evidence that you have surveyed and understand the current marketplace, and that your product or service satisfies a niche in the market. To do so, answer these questions:
- Who is our customer?
- What does that customer value?
Step 4: Competitive Analysis
In many cases, a business plan proposes not a brand-new (or even market-disrupting) venture, but a more competitive version — whether via features, pricing, integrations, etc. — than what is currently available. In this section, answer the following questions to show that your product or service stands to outpace competitors:
- Who is the competition?
- What do they do best?
- What is our unique value proposition?
Step 5: Description of Organizational Management
In this section, write an overview of the team members and other key personnel who are integral to success. List roles and responsibilities, and if possible, note the hierarchy or team structure.
Step 6: Description of Products or Services
In this section, clearly define your product or service, as well as all the effort and resources that go into producing it. The strength of your product largely defines the success of your business, so it’s imperative that you take time to test and refine the product before launching into marketing, sales, or funding details.
Questions to answer in this section are as follows:
- What is the product or service?
- How do we produce it, and what resources are necessary for production?
Step 7: Marketing Plan
In this section, define the marketing strategy for your product or service. This doesn’t need to be as fleshed out as a full marketing plan , but it should answer basic questions, such as the following:
- Who is the target market (if different from existing customer base)?
- What channels will you use to reach your target market?
- What resources does your marketing strategy require, and do you have access to them?
- If possible, do you have a rough estimate of timeline and budget?
- How will you measure success?
Step 8: Sales Plan
Write an overview of the sales strategy, including the priorities of each cycle, steps to achieve these goals, and metrics for success. For the purposes of a business plan, this section does not need to be a comprehensive, in-depth sales plan , but can simply outline the high-level objectives and strategies of your sales efforts.
Start by answering the following questions:
- What is the sales strategy?
- What are the tools and tactics you will use to achieve your goals?
- What are the potential obstacles, and how will you overcome them?
- What is the timeline for sales and turning a profit?
- What are the metrics of success?
Step 9: Funding Details (or Request for Funding)
This section is one of the most critical parts of your business plan, particularly if you are sharing it with investors. You do not need to provide a full financial plan, but you should be able to answer the following questions:
- How much capital do you currently have? How much capital do you need?
- How will you grow the team (onboarding, team structure, training and development)?
- What are your physical needs and constraints (space, equipment, etc.)?
Step 10: Financial Projections
Apart from the fundraising analysis, investors like to see thought-out financial projections for the future. As discussed earlier, depending on the scope and stage of your business, this could be anywhere from one to five years.
While these projections won’t be exact — and will need to be somewhat flexible — you should be able to gauge the following:
- How and when will the company first generate a profit?
- How will the company maintain profit thereafter?
Business Plan Template

Download Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Smartsheet
This basic business plan template has space for all the traditional elements: an executive summary, product or service details, target audience, marketing and sales strategies, etc. In the finances sections, input your baseline numbers, and the template will automatically calculate projections for sales forecasting, financial statements, and more.
For templates tailored to more specific needs, visit this business plan template roundup or download a fill-in-the-blank business plan template to make things easy.
If you are looking for a particular template by file type, visit our pages dedicated exclusively to Microsoft Excel , Microsoft Word , and Adobe PDF business plan templates.
How to Write a Simple Business Plan
A simple business plan is a streamlined, lightweight version of the large, traditional model. As opposed to a one-page business plan , which communicates high-level information for quick overviews (such as a stakeholder presentation), a simple business plan can exceed one page.
Below are the steps for creating a generic simple business plan, which are reflected in the template below .
- Write the Executive Summary This section is the same as in the traditional business plan — simply offer an overview of what’s in the business plan, the prospect or core offering, and the short- and long-term goals of the company.
- Add a Company Overview Document the larger company mission and vision.
- Provide the Problem and Solution In straightforward terms, define the problem you are attempting to solve with your product or service and how your company will attempt to do it. Think of this section as the gap in the market you are attempting to close.
- Identify the Target Market Who is your company (and its products or services) attempting to reach? If possible, briefly define your buyer personas .
- Write About the Competition In this section, demonstrate your knowledge of the market by listing the current competitors and outlining your competitive advantage.
- Describe Your Product or Service Offerings Get down to brass tacks and define your product or service. What exactly are you selling?
- Outline Your Marketing Tactics Without getting into too much detail, describe your planned marketing initiatives.
- Add a Timeline and the Metrics You Will Use to Measure Success Offer a rough timeline, including milestones and key performance indicators (KPIs) that you will use to measure your progress.
- Include Your Financial Forecasts Write an overview of your financial plan that demonstrates you have done your research and adequate modeling. You can also list key assumptions that go into this forecasting.
- Identify Your Financing Needs This section is where you will make your funding request. Based on everything in the business plan, list your proposed sources of funding, as well as how you will use it.
Simple Business Plan Template

Download Simple Business Plan Template
Microsoft Excel | Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF | Smartsheet
Use this simple business plan template to outline each aspect of your organization, including information about financing and opportunities to seek out further funding. This template is completely customizable to fit the needs of any business, whether it’s a startup or large company.
Read our article offering free simple business plan templates or free 30-60-90-day business plan templates to find more tailored options. You can also explore our collection of one page business templates .
How to Write a Business Plan for a Lean Startup
A Lean startup business plan is a more Agile approach to a traditional version. The plan focuses more on activities, processes, and relationships (and maintains flexibility in all aspects), rather than on concrete deliverables and timelines.
While there is some overlap between a traditional and a Lean business plan, you can write a Lean plan by following the steps below:
- Add Your Value Proposition Take a streamlined approach to describing your product or service. What is the unique value your startup aims to deliver to customers? Make sure the team is aligned on the core offering and that you can state it in clear, simple language.
- List Your Key Partners List any other businesses you will work with to realize your vision, including external vendors, suppliers, and partners. This section demonstrates that you have thoughtfully considered the resources you can provide internally, identified areas for external assistance, and conducted research to find alternatives.
- Note the Key Activities Describe the key activities of your business, including sourcing, production, marketing, distribution channels, and customer relationships.
- Include Your Key Resources List the critical resources — including personnel, equipment, space, and intellectual property — that will enable you to deliver your unique value.
- Identify Your Customer Relationships and Channels In this section, document how you will reach and build relationships with customers. Provide a high-level map of the customer experience from start to finish, including the spaces in which you will interact with the customer (online, retail, etc.).
- Detail Your Marketing Channels Describe the marketing methods and communication platforms you will use to identify and nurture your relationships with customers. These could be email, advertising, social media, etc.
- Explain the Cost Structure This section is especially necessary in the early stages of a business. Will you prioritize maximizing value or keeping costs low? List the foundational startup costs and how you will move toward profit over time.
- Share Your Revenue Streams Over time, how will the company make money? Include both the direct product or service purchase, as well as secondary sources of revenue, such as subscriptions, selling advertising space, fundraising, etc.
Lean Business Plan Template for Startups

Download Lean Business Plan Template for Startups
Microsoft Word | Adobe PDF
Startup leaders can use this Lean business plan template to relay the most critical information from a traditional plan. You’ll find all the sections listed above, including spaces for industry and product overviews, cost structure and sources of revenue, and key metrics, and a timeline. The template is completely customizable, so you can edit it to suit the objectives of your Lean startups.
See our wide variety of startup business plan templates for more options.
How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
A business plan for a loan, often called a loan proposal , includes many of the same aspects of a traditional business plan, as well as additional financial documents, such as a credit history, a loan request, and a loan repayment plan.
In addition, you may be asked to include personal and business financial statements, a form of collateral, and equity investment information.
Download free financial templates to support your business plan.
Tips for Writing a Business Plan
Outside of including all the key details in your business plan, you have several options to elevate the document for the highest chance of winning funding and other resources. Follow these tips from experts:.
- Keep It Simple: Avner Brodsky , the Co-Founder and CEO of Lezgo Limited, an online marketing company, uses the acronym KISS (keep it short and simple) as a variation on this idea. “The business plan is not a college thesis,” he says. “Just focus on providing the essential information.”
- Do Adequate Research: Michael Dean, the Co-Founder of Pool Research , encourages business leaders to “invest time in research, both internal and external (market, finance, legal etc.). Avoid being overly ambitious or presumptive. Instead, keep everything objective, balanced, and accurate.” Your plan needs to stand on its own, and you must have the data to back up any claims or forecasting you make. As Brodsky explains, “Your business needs to be grounded on the realities of the market in your chosen location. Get the most recent data from authoritative sources so that the figures are vetted by experts and are reliable.”
- Set Clear Goals: Make sure your plan includes clear, time-based goals. “Short-term goals are key to momentum growth and are especially important to identify for new businesses,” advises Dean.
- Know (and Address) Your Weaknesses: “This awareness sets you up to overcome your weak points much quicker than waiting for them to arise,” shares Dean. Brodsky recommends performing a full SWOT analysis to identify your weaknesses, too. “Your business will fare better with self-knowledge, which will help you better define the mission of your business, as well as the strategies you will choose to achieve your objectives,” he adds.
- Seek Peer or Mentor Review: “Ask for feedback on your drafts and for areas to improve,” advises Brodsky. “When your mind is filled with dreams for your business, sometimes it is an outsider who can tell you what you’re missing and will save your business from being a product of whimsy.”
Outside of these more practical tips, the language you use is also important and may make or break your business plan.
Shaun Heng, VP of Operations at Coin Market Cap , gives the following advice on the writing, “Your business plan is your sales pitch to an investor. And as with any sales pitch, you need to strike the right tone and hit a few emotional chords. This is a little tricky in a business plan, because you also need to be formal and matter-of-fact. But you can still impress by weaving in descriptive language and saying things in a more elegant way.
“A great way to do this is by expanding your vocabulary, avoiding word repetition, and using business language. Instead of saying that something ‘will bring in as many customers as possible,’ try saying ‘will garner the largest possible market segment.’ Elevate your writing with precise descriptive words and you'll impress even the busiest investor.”
Additionally, Dean recommends that you “stay consistent and concise by keeping your tone and style steady throughout, and your language clear and precise. Include only what is 100 percent necessary.”
Resources for Writing a Business Plan
While a template provides a great outline of what to include in a business plan, a live document or more robust program can provide additional functionality, visibility, and real-time updates. The U.S. Small Business Association also curates resources for writing a business plan.
Additionally, you can use business plan software to house data, attach documentation, and share information with stakeholders. Popular options include LivePlan, Enloop, BizPlanner, PlanGuru, and iPlanner.
How a Business Plan Helps to Grow Your Business
A business plan — both the exercise of creating one and the document — can grow your business by helping you to refine your product, target audience, sales plan, identify opportunities, secure funding, and build new partnerships.
Outside of these immediate returns, writing a business plan is a useful exercise in that it forces you to research the market, which prompts you to forge your unique value proposition and identify ways to beat the competition. Doing so will also help you build (and keep you accountable to) attainable financial and product milestones. And down the line, it will serve as a welcome guide as hurdles inevitably arise.
Streamline Your Business Planning Activities with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.

with Garrison & Sisson
Business Plans for Lateral Partners – Good vs. Great
Most effective business plans, if not done correctly, are relatively useless. Why? Because many partners end up borrowing a template from a friend at another firm, and they just fill in the sections.
There is not that much thought about why certain information is included, and how it fits with the LPQ and the overall business case for joining the new firm. Effective business plans often read like a rehash of a partner’s website biography and contain duplicative information that will be included in other documents as part of the due diligence process.
But effective business plans don’t have to be superfluous, and here are recommendations.
There are three main questions partners have regarding effective business plans:
- “Should I have a effective business plan?”
- “If so, when should it be presented to the firm?”
- “What should the business plan include?”
Main Purpose of Business Plan
Before I answer the above three questions about effective business plans and it’s important to explain that the purpose of a effective business plan is to show your future vision for your practice at a particular firm.
Effective Business plans are used in conjunction with a Lateral Partner Questionnaire (LPQ), which is a detailed questionnaire that focuses on various aspects of your practice and includes questions about the historical, current, and projected financial aspects and economics of your practice. Taken together, these provide firms with the most comprehensive 360 degree view of your practice and how it will potentially fit in to the new firm.
In short : The LPQ looks at your past and present practice, and also encompasses projections for the future. Business plans supplement the LPQ by putting more “meat on the bones” about your current practice, where you want to go, and how you plan to get there. The business plan is also, at times, a stand-alone document that can be used at the new firm to present to the executive/hiring committee to explain why you should be hired.
Now let’s address each of the above three questions.
- “Should I have a business plan?” Answer: it depends.
If you have an immediately portable practice that is at least self-sustaining (meaning you can keep yourself busy with your own work), or the new firm has enough work to keep you busy based on your unique skillset, a business plan may not be needed. The information that you include in the LPQ will likely be sufficient.
If it’s unclear as to whether you may have enough business to keep yourself busy, a business plan is important to help explain your vision and plan for your practice. It’s a piece of the puzzle that helps the new firm answer, “What’s the likelihood this partner will be successful at our firm?”
- “When should it be presented to a firm?”
Do not present a business plan before you are interviewing (the exception is if you are coming from the government).
The business plan must be tailored to each specific firm you are considering, and you will learn important information during the interview process that you will use to help build your case as to why you and your practice is a good fit for the new firm. A big mistake is presenting a generic business plan. I remember attending a seminar a few years ago on lateral partner business plans, and the speakers (hiring partners at law firms) basically said, “We don’t like generic business plans and think they are sort of useless. If we actually want a business plan, it should be focused on our firm specifically.”
Your business plan ideally connects these dots: (1) what the firm wants to accomplish, (2) what you want to accomplish, and (3) how coming together could help you both accomplish these mutual goals. You are (obviously) unable to connect the dots if you have a generic business plan that is presented at the outset. As a result, presenting it after a round or two of discussions will enable you to connect the dots much better.
- “What information should it contain?”
The level of detail included in your business plan will depend upon your particular circumstances, where you are in the process, and what you wish to highlight. Below are the most relevant sections that can be presented. Think of this as a general lateral partner business plan template, which should be modified and tailored based on your specific situation.
DETAILS TO INCLUDE IN THE BUSINESS PLAN
- Practice Description . Briefly describe nature of your practice, including areas of expertise or specialization; ideal to provide breakdowns (e.g., example 30% M&A, 25% private equity, etc.).
- Practice Development to Date : What you have done to develop your practice to date. Although the LPQ will cover your business development track record, it doesn’t hurt to reiterate your main clients, origination track record over the past few years, and your billing rate.
- Highlights/Accomplishments : Any highlights about your practice (e.g., particular high-profile deals or cases) and/or industry recognition.
- Firm Citizenship: Leadership roles, etc.
- Key Strengths : What are your unique strengths as a partner? Where do you see yourself adding the most value to a new firm/practice?
- Future Goals : Where you want your practice to be in the next 3-5 years. For example, do you want to expand your practice area or enhance a particular industry focus? Are there additional clients you want to pursue, but you are limited at your current firm due to conflicts, rates, or geography?
- Industry Trends : What industries do you focus on? What is happening in your particular industries that could create more opportunity at the new firm? What are the untapped opportunities and how are you positioned to capitalize on them?
- Limitations or Challenges with Current Firm (this is optional, depending on the particular circumstances of your situation) : Why are your future goals difficult to accomplish at your current firm? Note: the challenges can also be “softer” factors such as the manner in which client credit is shared is not consistent with the type of culture in which you enjoy practicing, etc. Be careful, however, not to come across as venting your frustrations. The more this is focused on business and limitations to your practice, the better.
- Your understanding of the new firm’s goals/strategic needs as it pertains to your practice (based on your discussions).
- How your background/experience could fit into the firm’s goals/strategic needs.
- How the new firm could help you (1) more easily accomplish your goals and/or (2) reduce some of the challenges with your current firm. In short, how could both sides come together in a way that meets everyone’s needs.
- Your Network of Contacts : Include a list or chart of people you would plan to continue receiving business from, and who would you expect to approach to develop new business. The ideal format for the headers is the name, company, title, and the nature of your relationship, including how long your have represented the client (if they are a current client). This can include the new firm’s clients to the extent it has been discussed already. If you do mention the new firm’s clients, be sure to take a collaborative tone that includes pitching together as a group and not as a lone wolf. Note : Some partners are understandably reluctant to “share their rolodex” too early in the process. If you are uncomfortable, it’s ok to hold off on providing too much detail regarding your network if it’s still early in the process and you are unsure if the firm is a fit. If the firm presses you for information on your network and future prospects, you can equalize the process by asking the firm to share information on their main clients/contacts as well, so it’s more of a “mutual brainstorming.”
- Specific Business Development/External-Facing Activities : Many business plans have generic sections such as “Writing: I plan to write articles” or “Speaking: I plan to speak at industry conferences to help get my and the firm’s name out there.” There is nothing wrong with this, but it often comes across as very generic. To make more of an impact, provide specific examples of what you have done to date, and what you plan to continue doing. For example, are you on the Board of any high-profile publications or do you often participate at certain industry conferences?
The business plan is not a one-size-fits all approach, but the above provides more clarity on the key issues these documents involve and how to best approach this part of the lateral hiring process.
Subscribe for Updates
Your information will be kept confidential.

Author: Dan Binstock
Dan co-owns Garrison & Sisson, where he focuses on lateral partner and practice group placements. He has consistently been recognized as one of the Top 100 Global Legal Strategists and Consultants by LawDragon, and authored "The Attorney's Guide to Using (or Not Using) Legal Recruiters." Dan is the Immediate Past President of the National Association of Legal Search Consultants (NALSC), where he also served as Chair of the Ethics Committee. Visit here to learn more about Dan, or contact him confidentially with any questions at (202) 559-0492 or [email protected].
Home / The Guide / Entering the Market / Business Plans for Lateral Partners – Good vs. Great
Related Articles
The waiting period and lateral partner interviews.

Navigating Lateral Partner Ethical Considerations – Interview with Tina Solis (Nixon Peabody)
The lateral partner questionnaire (lpq), search lateral partners.com, table of contents.
How to Find a Business Partner
Briana Morgaine
12 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
Entrepreneurs have a reputation for trying to do it all singlehandedly.
In the early days of starting your business, you may feel like you’re wearing several hats—too many, in fact.
For this reason, you might consider working with a business partner. Not only does having a business partner distribute some of the work, it gives you someone to bounce ideas off of, the benefit of an additional skill set, and a colleague who feels as passionately about your business idea as you do.
But, how can you find and cultivate a business partner relationship like that?
I asked several entrepreneurs their advice on how to find a business partner; they shared with me where they found their business partners, and what advice they would give to entrepreneurs hoping to start a business partnership.
While you might be fortunate enough to meet your future business partner in line for coffee one morning, not everyone finds themselves in such serendipitous situations.
Sometimes, you have to do some legwork, and go out of your way to seek out a great business partner. Here are several places to find the perfect partner for your business.
- Tap into your co-worker pool, both past and present
Choosing a business partner from your co-workers, either those you currently work with or from a previous job, can be a great way to find someone to start your business with. Not only is it convenient, but choosing a business partner that you have already worked with can give you a huge advantage over picking a partner you haven’t worked with yet.
Why? You already know how your potential partner does business. You know if they are hardworking, reliable, and honest—or if they’re the type to waltz into work every morning 20 minutes late, or spend all day complaining about their hangover. Choosing a business partner from your current or previous coworkers means you’ll probably already have an idea of how well the two of you work together as well, which can save you heartache down the road.
- Go into business with a friend (even though some experts will advise against it)
This one seems easy, but partnering up with friends is one of the most common ways to find a business partner. We saw it with David Daneshgar of BloomNation, and countless other businesses have been started because friends decided to team up and work together.
“Our best friends are usually the best business partners,” says Viola Ng, co-founder and marketing manager for Pointshogger.
Though she recommends partnering with a friend, Viola points out that the friend you choose to partner with doesn’t have to be your platonic other half. “We aren’t the BFFs who have the same interests or the same education background […] in fact we are almost at the opposite spectrum: He’s the lawyer/finance guy, and I am the marketing/design girl.”
Partnering up with friends has its inherent potential drawbacks: It is possible that if the business venture goes south, you may lose out on the friendship. But, if you have clear communication, choose someone with a personality and skill set that compliments your own, and make sure you are both on the same page, many of these concerns can be avoided. We’ll cover that more later when we discuss the things to consider before choosing your partner.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Take advantage of networking—either online or through in-person events
Jillian Darlington, founder of the MomCo app, met her business partner on HeraHub, an online networking community that offers coworking space for women. “At the time, I was a member of Hera Hub [and] it is through that network that I found Beth Bryan. She had recently been laid off from her corporate job and was doing consulting work for some local companies and entrepreneurs,” says Jillian.
“We immediately clicked and were the perfect team because our skills complemented each other. After three weeks of working together, Beth approached me about investing and becoming a permanent part of MomCo. That is when she became my co-founder and we have been two moms on a mission ever since.”
If you are a member of any online networking groups, this may be a great place find your business partner. If you do not currently belong to any groups, consider joining one; there is a networking group for virtually every occupation under the sun.
A professional association is a good place to start, as well as a simple Google search for networking in your industry, which will likely reveal plenty of options.
Not only that, networking groups in general are a great place to find potential business partners, and there are likely to be some in your city that meet in person. Most cities will have at least one general networking Meetup group, and larger cities may have industry specific groups as well.
- Consider partnering up with a sibling or other family member
Going into business with siblings is similar to going into business with friends—only if the business-end of the relationship takes a dive, you can’t as easily dissolve the relationship (this could be a positive or a negative, depending on how you look at it).
“People often express surprise that my brother and I own a business together and can work alongside each other every day,” says Danielle Kunkle of Boomer Benefits. “I always share with them that I started this agency with two other partners, only to quickly find out that no one else worked as hard as I did, so I was giving away two thirds of every commission to people who weren’t pulling their weight.”
As a solution, Danielle went into business with her brother. “It was my mom who suggested inviting my brother to join me, and it was ingenious because we were raised by the same parents to have the same work ethic, and he and I have both been entrepreneurs since childhood.”
- Attend a business course or industry-related training, and keep an eye out for partners
If you are seeking to further your knowledge about your industry, learn how to run a business, and generally better yourself as an entrepreneur, you may be attending or have considered some type of business course. While these have the obvious benefit of improving your skill and understanding of your field, why not use the opportunity to look for a potential business partner?
“I found my business partner in an business development course I was taking, and we literally just ‘clicked,’” says Shannon Conheady, CEO and co-founder of RepairQuote. Since the two met through an entrepreneurship class, Shannon knew that they were equally committed. “We both had a decent idea that the other was interested and committed to launching a venture,” he says.
Your local community college or extension school affiliated with a larger university is likely to have business development courses, which can have the dual benefit of teaching you valuable skills while also expanding your network, placing you in contact with other like-minded entrepreneurs.
- Here are 5 things to consider:
Now that we’ve gone over a few of the places you can look to find a business partner, there are several things to consider before you commit.
How do you know if your partner is “the one”? Here are five considerations that will make your decision to work together that much easier.
1. Find someone with a complimentary personality–just like you would in a romantic relationship
If you’ve noticed that advice on picking a partner sounds an awful lot like relationship advice, you’re right; finding a business partner is a lot like finding a romantic partner. “You need different personalities, but also have to be able to completely get along,” says Jim Belosic, CEO of ShortStack. “It’s sort of like a marriage.”
He adds: “If I married a woman like myself, we’d be completely reckless and the house would never be clean. My wife balances that side of me and it’s the same thing with my business partner.”
Why does this balance matter in business? For the same reasons it matters in a romantic relationship—complimentary personalities help balance each other. “[My business partner] balances some of the risks that I want to take with logic but at the same time I balance some of his ideas that may be too tech-y for our users,” says Jim. “He works well by himself and my personality allows us to manage a team, so collectively we make a great team.”
2. Choose a partner you can trust
“A good partner is basically about finding someone you can trust—and that is not always easy,” says Matthew Reischer, founder of Legal Marketing Inc. “My current partner is my brother, and it truly is the easiest partnership I have ever been involved with as there is much less acrimony, disputes or conflicts that often seemed to be the case with my prior partners.”
This is one area where having a past history isn’t a negative; siblings, family members, and friends are often the people we trust the most. As trust is such an integral part of the business relationship, friends and family can make excellent business partners for this reason.
If your business partner is someone you have more recently met and perhaps share less history with, be sure to determine as soon as possible if they are trustworthy. It sounds obvious, but if you have any reservations about the trustworthiness of your potential partner, don’t ignore them—it may save you trouble in the long run.
3. Make sure to define the parameters of your, uhh, “relationship”
Remember how I said finding a business partner is a lot like finding a romantic partner? Well, it is—but there’s one important aspect that the two relationships should not have in common.
Viola suggests having an honest conversation with your potential partner about the status of the relationship and any potential romantic involvement, especially if the partner is a friend or someone you share history with.
“If you’ve always had a thing for your best friend but you never told them, now is the time to discuss,” she says. “Any surprises in that route of relationship matters can be lethal to the business.” Remember what happened between the co-founders (and ex-romantic partners) Whitney Wolfe and Justin Mateen of Tinder?
Viola made sure to have this discussion with her friend and business partner Matthew, so as not to run into any situation that could potentially hurt their business. “Once things get awkward, it will be very difficult to stay professional at that point without letting personal emotions come into play,” she says. “The friendship can suffer and so will the business. A startup takes long hours and hard work to make it successful, so you and your business partner/best friend will have to spend a lot of time together.”
4. Pick a partner who is hungry to succeed
You want a partner who is as passionate about the business as you are, so seek out individuals who share your commitment and your drive. “Look for someone who is involved with their craft outside of regular business hours,” says Shannon. “If you are looking for a good developer, attend local meetups within the coding community.”
Why does this matter? “Because if they are spending their own free time to attend these meetups, they are passionate about what they do, and it will reflect in their work,” he says.
“Your potential partner should be as hungry to succeed as you are,” says Jim.
He adds that this drive for success will also help establish equality in the relationship. “If one person has all the money and the other has all the expertise, there can be bitterness. If you’re both struggling and you both put everything you have on the table, you’re going to work equally as hard to be successful. You’re both going to get the same rewards and go through the same triumphs.”
5. Consider a partner in a different field
While it might be tempting to look for partners who know your industry as well as you do, a business partner doesn’t need to have your same same skill set, training, and experience. In fact, it’s a good idea to look for a partner who brings a different viewpoint and work history to the table.
Partnering with someone who has a different background and skill set can help both you and your business partner, as you may be able to leverage your differing strengths and weaknesses.
“Know your strengths and weaknesses so you can choose a business partner to fill in where you fall short,” suggests Viola. “It works even better with someone who is different from you so that you can get a perspective of things you never think of.”
Not only will this lend your business fresh perspective, it can also eliminate squabbles. “If you and your partner both have expertise in public relations, you’re always going to be arguing over who is right and who is wrong,” says Jim. “I’m a marketing guy and my co-founder is a developer, so I don’t question his stuff and he doesn’t question my stuff, mainly because we don’t really know what the other person does. It works out great that way.”
- Take time to find the right business partner
Having a business partner can help lead a business to greatness, but don’t feel the pressure to rush into anything.
Worse than not having someone to partner with would be choosing a business partner with different goals, a work style that doesn’t mesh with your own, or a personality that clashes with yours.
Jillian sums it up nicely:
“To other entrepreneurs, I would recommend that they find someone that has as much passion as they do in their business.
Being an entrepreneur is hard, there are long days, and it can be lonely at times. Having a great co-founder will help them get through these hard times.
It will only work if both people have passion for the business and truly believe in what they are doing.”
Bri Morgaine is a seasoned content marketing leader with a decade of experience in copy editing, social media operations, and content strategy— having honed her skills at industry giants like Palo Alto Software and Andreessen Horowitz.

Table of Contents
- Take advantage of networking—either online or through in-person events
Related Articles

14 Min. Read
How to Form a Corporation

3 Min. Read
How to Plan for Changes in Partnership Ownership with a Buy-Sell Agreement

7 Min. Read
How Limited Liability Companies (LLCs) Are Taxed

5 Min. Read
How Many Business Partners Should You Have? Maybe Zero
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Find a Business Partner Online

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
There's no doubt that starting a small business can be a time-consuming and demanding process—especially if you're doing it all on your own. For this—among other reasons—you may decide to work with a partner to start your business.
Finding the right business partner, however, is essential. After all, this individual will be the person you trust to help you manage your finances, make important decisions, and run your day-to-day business operations. So, whether you haven't had luck finding a partner through more traditional channels or you're simply looking to streamline your search process, you might be wondering: Should you start a business with someone you met online?
In short, the answer is yes—as long as you approach the process carefully—and we're here to help. In this guide, we'll explain how to find a business partner online with tips from experienced entrepreneurs, as well as review the best websites to use to start your search.

How to find a business partner online in 9 steps
When you're trying to find a business partner online, you can follow these nine steps to get started:
1. Solidify your business idea.
Before you bring a co-founder on board, you’ll need to ensure that you have a clear, developed small business idea.
If you're still working out details and are hoping to meet a partner who can help draft a business plan, you'll need to make this clear and upfront in your search. Wherever you are in the development process, put your most updated plan in writing so you can present a snapshot to serious partner candidates.
How much do you need?
with Fundera by NerdWallet
We’ll start with a brief questionnaire to better understand the unique needs of your business.
Once we uncover your personalized matches, our team will consult you on the process moving forward.
2. Define what you're looking for in a business partner.
The kind of partner you’re looking for largely depends on the kind of business owner you are, in addition to your anticipated business needs. For instance, a seasoned business owner might seek a technical expert to take charge of product development for their new company; a first-time entrepreneur may have the expertise to start a business but need a partner with management and operational experience.
This being said, you should take stock of both your strengths and your shortcomings as a future small business owner. You should seek a partner whose experience, skills, and general demeanor complements the first and bolsters the second. You might even write out a "business partner job description" to help you vet candidates as you continue through the process.
3. Update your online presence.
Now that you have a better sense of your business idea and what you're looking for in your business partner, you'll want to make sure that any potential business partner candidates have the opportunity to learn more about you.
And what’s the first thing you do when someone sends you a friend request on Facebook, connects with you on LinkedIn, or follows you on Twitter? You probably Google them. You can expect that any prospective partner candidates you reach out to online will do the same to you.
For that reason, you want to make sure that you’re discoverable by search and that the results are work-appropriate and up to date. As a test, you can try searching your name in private browsing (incognito) mode.
If you’re difficult to find via search, you might consider creating a personal website—it’s a great way to put yourself out there and post content under your name. And even if your social media profiles are personal, they might be the highest-ranking results for you, so you'll want to consider linking to your business or website while you’re searching for a business partner.
All of this being said, it's important to remember that you don’t need to use every networking or social media platform available. But you should have a page on the professional platforms, like LinkedIn or AngelList, so people can message you directly (and verify your identity).
4. Leverage your existing online network.
After you've updated your website and social media profiles, you might start your actual search for a business partner by leveraging your existing online network.
Ask fellow entrepreneurs in your LinkedIn, Facebook, or email network about how they found their business partners— that might give you some ideas about reaching out to people you already know or utilizing the resources you have access to. As an example, college or university alumni networks often include professional outlets, events, and even mentoring programs—and in many cases, these include Facebook groups, LinkedIn pages, and job listings on college or university websites.
Similarly, you might find that simply reaching out to entrepreneurs that you already know by email to let them know that you're looking for a business partner can result in a variety of referrals. You'll never know who you can reach or find by simple "word of mouth"—even if it's through the power of email.
5. Search online startup, co-founder, and business communities.
In addition to utilizing your existing network, there are a variety of online communities designed specifically for entrepreneurs looking to find a business partner online.
Although this would normally seem like a strange comparison, in this case, just like online dating, there are different types of sites depending on how you'd prefer to find and meet your business partner.
For example, there are network matchmaking-style websites, like CoFoundersLab, that allow you to create a free or premium account—and based on your profile, use AI algorithms to suggest the best matches for co-founders, partners, and team members.
Then, there are much more informal websites that can be used to find a business partner such as the active /r/cofounder subreddit, where entrepreneurs who are looking for co-founders or business partners post about their business, who they're looking for, and where interested candidates can contact them for more information.
Of course, if you’re initially hesitant to have extended discussions online with potential business partners, you can start by using virtual forums that connect you to in-person meetings. Meetup.com, for example, has an entire category devoted to "career and business" and can direct you to online or in-person gatherings of like-minded professionals in your area.
To this point, when you're learning how to find a business partner online, one important thing to keep in mind is how distance could potentially impact the logistics of your business partnership.
For instance, Richard Shaw started LogbookLoan with a business partner he met through the /r/entrepreneur subreddit, and although the relationship was positive, there were some drawbacks of working with a remote co-founder. He said: It was more the distance that meant the partnership didn't work; my morning was my partner’s evening, and it was hard to schedule Skype calls or get answers to emails the same day. This caused the business to slow down. We both realized it wasn't working and parted ways amicably.
6. Vet potential candidates.
The next step in learning how to find a business partner online? Vetting your potential candidates.
Once you've identified one or a few individuals that you think might make a good fit for your business partner, you'll want to find out as much as you can about them—just as you would with an employee before hiring them. This helps ensure that, first of all, the person is in fact who they say they are—and, second, provides some background information about their career and experience.
So, to vet potential candidates, you'll want to:
Ask to see their resume.
Search for them online—including a basic Google search, as well as on social media and networking platforms. If you're having trouble finding them online, you'll likely want to find some other way to verify their identity. There are a variety of reliable HR background check websites that might be worth considering.
Review their previous work—either from their LinkedIn, personal or business website, or portfolio. You might also ask for a reference from a previous client or business partner that you can speak to.
To this last point, Cristian Rennella, CEO and founder of elMejorTrato, told us that the most important thing to know about a partner is the quality of their work. Having started companies with both old friends and new partners he met online, he said if someone has the right track record—and can prove their work—it really doesn't matter how you initially came into contact.
7. Set up interviews.
After you've verified the identity of your candidates and found one or a few that you feel comfortable moving forward with, you'll want to move to the "interview" stage.
Contact the individual and set up a time for a conversation. Before you pitch someone on the business you want to start, however, you should look beyond their resume and try to figure out what excites them professionally.
Remember, as much as you are interviewing a candidate, you’re also trying to recruit them. In your first meeting, whether it’s in person or over the phone, don’t forget to market yourself as a great business partner, too.
And of course, when you're having this conversation, don’t underestimate the importance of aligning on more than objective business goals. You'll want to keep in mind your core personal and business values as well—if you and your business partner don’t value the same things, it's much more likely you'll face conflicts down the line.
8. Conduct a trial period.
Once you’ve found a prospective co-founder you’re excited about, verified their identity, shared your business plan, and ideally met in person or over a video call, you might be tempted to launch full-force into your partnership.
Unfortunately, when you're learning how to find a business partner online, or in-person for that matter, you won't want to rush into things. Instead, you'll want to start by conducting a trial period—a trial period can be informative for both you and your potential partner and help you both determine if the partnership is a good fit before taking on the risks of starting a business together.
As an example, Dave Hermansen, a veteran ecommerce entrepreneur, recommends starting incrementally with a potential business partner by hiring them for a project at an existing business:
"Practically all of my solid partnerships have started with getting to know the other person by hiring them first to do different things for our already existing companies. Later, after I can see how well we really mesh, I have been able to offer partnerships in either existing or new business ventures with the person."
9. Draft a partnership agreement.
After the trial period, you'll hopefully decide that you've found the right business partner. In this case, you'll want to take the proper steps to make the partnership official—provided your new co-founder is willing to accept the position.
You should draft a partnership or founders agreement that outlines the structure of your business, as well as the arrangement between the two of you as partners. This agreement should address issues such as:
Business idea and goals
Salary and compensation
Roles and responsibilities
Equity breakdown
Intellectual property
How disputes are settled
Exit strategies
To ensure that the document covers all of your basis and is legally binding, consider working with a business attorney to help you through the process.
Best websites for finding a business partner online
Now that you have a better sense of exactly how to find a business partner online, let's review a few more of the websites you can use during the search process:
CoFoundersLab: Mentioned above, this matchmaking-style website allows you to create a profile and find a business partner, co-founder, or team member based on their AI algorithm.
Founder2be: With Founder2be, you can create a profile and browse their network of other entrepreneurs looking for co-founders, designers, marketers, developers, and more.
Cofoundme: Using Cofoundme , you can register your profile and get matched with potential partners. You also can publish business ideas, browse startups, and create job postings.
FoundersNation: Set up like a classic dating site, FoundersNation allows you to create a free profile and browse co-founders in your area with specific skills to find the right partner for your business.
StartHawk: StartHawk is a platform specifically created to matching entrepreneurs looking for their business partners. With StartHawk, you can use a variety of filters to narrow your co-founder search and use their internal messaging system to communicate with potential candidates.
IdeasVoice: IdeasVoice is a global collaboration site that allows aspiring entrepreneurs to share and workshop business ideas, discuss projects, and even find business partners. You can sign up for a free account, or opt for IdeaVoice premium services for advanced search, profile promotion, among other benefits.
AngelList: Although you may be familiar with AngelList as a job search site, many entrepreneurs also use this platform to post positions for co-founders and business partners—especially in the tech industry.
Reddit: As we mentioned above, many small business owners have actually found success using subreddits dedicated to finding business partners or co-founders, such as the /r/entrepreneur subreddit or the /r/cofounder subreddit.
LinkedIn: As you might expect, LinkedIn is designed for business networking—and although it might take some more time and effort—it is definitely a worthwhile resource to use when searching for a business partner online.
Meetup: Even though Meetup.com may be a less direct way of finding a business partner online, it can certainly be helpful when you're just starting your search. Plus, they have groups and topics specifically devoted to business partnerships and networking.

Start Your Dream Business
The bottom line
It's important to remember that you'll want to take the necessary precautions when looking for a business partner online—do the proper research, verify candidates' identities, and follow general internet best practices.
Overall, like most aspects of starting a business, finding your co-founder might involve some trial and error. In this case, you can try to embrace that opportunity, keep an open mind, and talk to multiple candidates before making a decision. After all, the top priority in finding the right person is your compatibility as business partners.
This article originally appeared on JustBusiness, a subsidiary of NerdWallet.
On a similar note...

Lateral Partner Integration Requires Business Development Plan

When a lateral is hired into a new firm, following the tone set during the recruiting process is essential. The firm needs to ensure the lateral is set up for success on day one. Openness, honesty, and transparency are key.
A 12-month marketing and business development plan should be created as a roadmap for integrating new lateral hires and partnering them with a business development liaison. The assigned liaison should host regular check-in calls and serve as the lateral’s initial point of contact for all client development activities.
Setting the Stage
An introductory call between the lateral and their assigned BD liaison should take place prior to their start date or within the first two weeks. This should be the first in a series of integration meetings that take place during the lateral’s first year.
The goal of the meeting is to help the lateral understand the resources of the firm, services the marketing and BD department provides (i.e., requests for proposals, pitches, collateral, conference/speaking engagement prep, awards & rankings, bio updates, etc.) and to answer firm questions that may not have been addressed during the recruiting process.
The lateral and liaison should discuss any immediate client needs/opportunities, expectations, what support the lateral needs, and alert clients about the move.
The lateral should walk away from the meeting feeling confident, comfortable, and with a clear path forward.
Read more: Lateral Partner Recruiting Must Focus on Honesty and Clear Data
Introduction and Implementation
The BD liaison must also obtain a fulsome knowledge of the lateral’s practice, portable book of business, client targets, and preferred marketing styles. They should ascertain the partner’s strengths and weaknesses, as well as business goals and objectives.
The liaison needs to know why the lateral was hired—their niche expertise, specific client needs, and regional presence—to help identify cross-sell opportunities, make appropriate introductions to targeted attorneys within the firm, and plug the lateral into pre-existing client and industry teams. Prioritization should be placed on client-facing activities and the lawyer’s strengths.
The new partner’s BD liaison should have the same information as the legal recruiting team, which includes the lateral’s resume, partner questionnaire, offer letter, and revenue goals. Armed with these resources, the business development liaison is positioned as a part of the firm’s long time revenue strategy for the lateral partner, versus as a document producer.
Positioning the BD liaison as a key to the lateral’s success at the onset will encourage the partner to engage them in a meaningful way with strategy, innovation, and revenue generating activities for a sustaining practice. This allows the partner to focus on delivering quality legal services, while the BD liaison can focus on collaboratively growing their book of business.
Having a thoughtful, written integration plan is imperative. A written process ensures not only accountability, but gives each lateral the same onboarding experience regardless of which practice group or industry team they sit in.
During each meeting, the liaison should probe the lateral on topics such as satisfaction with the firm, sense of being valued, client growth opportunities, bandwidth and utilization, and cross-selling successes or frustrations. Regular status updates should be provided to firm leadership and other stakeholders. If the lateral flags an issue or perceived roadblock, the liaison should dig deeper to understand the root cause, and work with leadership to course correct.
It’s critical that firms not overpromise and underdeliver. For example, a lateral may have been hired to inherit a portfolio that fell through, or perhaps market fluctuations prohibited the opening of a new office that the lateral was intended to join. It’s important to keep the lateral’s business development liaison informed of these developments so they can monitor follow-though, manage expectations, and help pivot if necessary.
The firm should be clear about their commitments. Conversely, expectations for new partners’ client development and relationship building activities, for example, should also be addressed directly.
The most successful laterals are engaged and actively participate in regular integration calls. Holding 90-day reviews that include members of the recruiting team and practice group or department leaders can provide an opportunity for the partner to be heard as well as to receive direct feedback.
Integration Process
Avoid letting new lateral partners fall between the cracks, especially if they’re rainmakers or inexperienced business developers, by having a continuity plan that includes the written integration process. The BD liaisons shouldn’t work in silos.
Find a collaboration tool that works for the team’s communication style and commit to using it. Keep detailed records and have a plan of continued support should the assigned BD liaison leave the firm, or if there is significant recent or impending change happening within the firm, such as a merger or acquisition.
Recruiting and integration don’t cease when a merger is on the horizon, and the potential for new laterals to get lost in transition during a major change increases. Firms must adapt their recruiting and integration strategies not only to speak to the newly merged firm’s emerging cultural differentiators but also to how laterals will be supported in a fluid environment.
This article does not necessarily reflect the opinion of Bloomberg Industry Group, Inc., the publisher of Bloomberg Law and Bloomberg Tax, or its owners.
Author Information
Brian J. Carrozza is director of client development at Goulston & Storrs.
Courtney C. Hudson is business development manager at Baker, Donelson, Bearman, Caldwell & Berkowitz.
Megan K. Senese is co-founder and principal at stage, a women-owned business development and legal marketing firm.
Write for Us: Author Guidelines
To contact the editors responsible for this story: Jada Chin at [email protected] ; Jessie Kokrda Kamens at [email protected]
Learn more about Bloomberg Law or Log In to keep reading:
Learn about bloomberg law.
AI-powered legal analytics, workflow tools and premium legal & business news.
Already a subscriber?
Log in to keep reading or access research tools.
Yakima Basin Integrated Plan
The Yakima Basin Integrated Plan (YBIP) is a collaboration of state, federal, tribal, business, and community organizations committed to addressing water, fishery, habitat and climate variability challenges to ensure a robust Yakima River Basin within its built and natural systems. Building a future for water, wildlife, and working lands. https://yakimabasinintegratedplan.org/
- South Fork Tieton Bridge Fish Passage Improvement
Related Stories

Partner Category
We often partner with non-governmental conservation organizations on conservation projects, whether it's to conserve identified species such as the monarch butterfly or to advise on land acquisition for conservation so that it has the greatest benefit for species.
We work with other federal agencies to help them meet their legal responsibilities as well as their mission.
Those who experience the outdoors and wildlife first-hand become its greatest conservationists. We partner with these groups to foster their love of wildlife and conservation.
Here we partner with a wider variety of other organizations on projects to meet shared conservation goals.
Our hands-on stewardship and public engagement is often done in conjunction with state and provincial agencies.
We partner with federally recognized Tribes, Alaska Native organizations, Alaska Native corporations and the Native Hawaiian community to manage or influence important habitats for wildlife.
Other Partners
Here are just a few of our National Partners. You can view the full list of FWS partners, along with the regions and areas of focus our work together entails.

Partnership Services
Through our partnerships we are able to expand our capabilities through the inclusion of services in areas such as:
- Grant opportunities
- Sponsorship of grants
- Cooperative Agreements
To find out more about how our partner provides services view our partner services below.

Learn about our priorities, statutory authority and functions.
You are exiting the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service website
You are being directed to
We do not guarantee that the websites we link to comply with Section 508 (Accessibility Requirements) of the Rehabilitation Act. Links also do not constitute endorsement, recommendation, or favoring by the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service.
What fintech can teach us about secure supply chains

In today’s digital world, supply chain security is now a leading priority for businesses within every industry. Yet, a global survey found the average number of supply chain breaches that negatively impacted organizations increased by 26% from 2022 to 2023 1 .
In this article, Matthew West and Bryan Taaffe of DHL’s Global Financial and Professional Services unit unveil the ways fintech security has evolved to act as a blueprint for secure and reliable supply chains, and the specific best practices that can be carried across to other industries.
A new era of fintechs
Any breaches in the supply chain software used for managing logistics can have catastrophic and wide-ranging consequences. Safeguarding the flow of goods and sensitive data, whilst upholding safety and quality standards, relies on a range of processes, from data encryption to track and trace logistics. For businesses with global operations, navigating the intricacies of international trade regulations adds a further layer of complexity. Amidst this, there are many lessons the fintech industry can teach us about secure supply chains.
Research by McKinsey 2 shows that revenues in the fintech industry are expected to grow almost three times faster than those in the traditional banking sector between 2023 and 2028. At DHL Express, we’ve witnessed a new generation of banks and financial services emerge in recent years – many as entirely digital enterprises. These fintechs are typically quick at decision-making and fast to scale as they bring new and innovative services to an audience hungry for elevated online experiences.
Yet with the growth of these “digital disruptors”, new challenges and risks arise. Our role as a secure logistics provider is to guide them through all aspects of fintech security, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and maintaining their trust with customers and partners.

Much of this starts with what we are best known for: speed. The faster a valuable item such as a credit card moves from A to B, the less risk there is that it’ll be intercepted by a fraudulent party. Our express service also benefits the fintech company; after all, the sooner a customer receives their card, the sooner they’ll start spending. This too applies to payment technology such as point-of-sale terminals for retailers, which is why the question for any business deliberating over express shipping should be, “What would we lose in revenue for each additional day our goods are in transit?”
This speed is combined with advanced track and trace logistics. DHL has less of a dependency on third parties than any of our main competitors; everything stays within our network which provides end-to-end visibility along the supply chain. When one of our fintech customers sends, for example, a payment card with DHL Express, they’ll benefit from a system that scans that item on average 28 times on its journey. The customer then receives real-time notifications about their shipment’s progress for reassurance.
We also have a Denied Party screening program in place – a crucial step that we’ve found fintechs sometimes overlook. Our software will scan the contact and address information on a shipment and run it against the applicable Denied Party lists of individuals and entities – i.e. those that applicable law prohibits or restricts the provision of economic resources to, or the engagement in transactions with, due to their involvement in illegal activities. The system’s advanced algorithm determines the risk, and where necessary, the shipment is halted whilst we seek further identification from the receiving entity to ensure they’re a safe party*.

Final-mile security
The last mile of our service is really the point at which secure e-commerce fulfilment is married with delivering our fintech customers’ end users an exceptional experience. This begins with ensuring accurate address data; our extensive database allows us to validate addresses so that sensitive documents and parcels are always delivered to the right address. Then there’s our On Demand Delivery service. This gives customers the flexibility and convenience of choosing exactly when and where their deliveries are made, with full tracking for peace of mind. The sender can also implement a “Direct Signature Required” stipulation for extra security.
The future of supply chain resilience
Whilst the finance sector has embraced digitalization, the fast, secure movement of sensitive documents and items remains essential to its day-to-day operations. In the early days of DHL, the founders delivered important documents for their banking clients personally, accompanying them on flights to ensure their safe delivery, whilst simultaneously launching the international express industry. Now, as the fintech sector has developed to adopt computers, IoT devices and AI software, DHL will continue to invest in cutting-edge security processes to negate supply chain risks.

“The term ‘resilience’ is the business buzzword of this decade, but a key cornerstone of resilience is security. Customers entrust us with high value goods – from technology products to luxury fashion labels, lifesaving medical devices to vaccines – we handle hundreds of thousands of shipments daily. Our relentless focus on security and regular training helps build business resilience for us, and our customers’ supply chains.”
Ken Lee, CEO for Asia Pacific, DHL Express
Building a secure ecosystem: key security practices for your business’s supply chain
Leverage track and trace logistics.
Having full visibility of goods as they move through your supply chain will reduce incidences of loss or theft. Track and trace technology automates this process, scanning the goods at crucial checkpoints right up to the moment they’re delivered to the intended recipient.
Prioritize secure data encryption
For online businesses, data encryption is a necessary step to prevent sensitive financial and customer data from being stolen. In simple terms, the process “scrambles” data into a code that can only be unlocked with a unique digital key. For SMEs, Google Chrome’s encrypting service is a good service to consider. Digital signatures and multi-factor authentication are further ways to protect data.
Create an incident response plan
Preparing for a worst-case scenario is important. Setting out an easy-to-implement response plan for the event of a data breach will help your business minimize reputational damage and revenue losses.
Adhere to global regulations
For businesses involved in cross-border transactions, complying with international trade regulations is crucial. Beyond customs and border rules, this also includes things like environmental initiatives, labor laws, and safety standards. Understanding and complying with these mitigates the risks of legal action and reputational damage, whilst safeguarding against theft, data breaches and unauthorized access.
Choose a trusted logistics partner
DHL Express has received 400 TAPA (Transported Asset Protection Association) certifications worldwide – one of the most rigorous logistics and supply chain security certifications. The independently audited authentication is widely respected as the leading security standard in this sector and focuses on the way in which high-value goods are handled, warehoused and transported. DHL Express is the global industry leader in terms of number of TAPA certified facilities, and our experts are ready to help your business implement the highest standards of supply chain security.
1 – Supply Chain Brain, December 2023
2 – McKinsey, October 2023
* DHL’s Denied Party screening is part of its internal Export Control and Sanctions Compliance Program which ensures DHL fulfils its legal obligations as a logistics service provider. DHL’s screening is not meant to replace the exporter/customer’s due diligence obligations to ensure compliance with the applicable sanctions and export control law.
Similar Stories

Citi executive in charge of implementing bank's restructuring departs
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Lananh Nguyen in New York and Manya Saini in Bengaluru; Editing by Krishna Chandra Eluri
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

Brazilian pulp and paper company Suzano has been in talks with its advisers about sweetening its $15 billion acquisition offer for International Paper , people familiar with the matter said on Monday.

Business Chevron

Samsung Electronics picks veteran executive to tackle 'chip crisis' amid AI boom
Samsung Electronics has replaced the chief of its semiconductor division to help the group overcome a "chip crisis", amid a booming market for AI chips where analyst say the world's biggest memory chipmaker lags peers.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Partner business plans are important for any company seeking to maximize its success. They can help to create a vision and direction for an organization, define key objectives, and develop strategies to achieve those objectives. The key elements of a successful partner business plan include: 1. Vision and Strategy: A clear vision and strategy ...
A partner business plan is a document that summarizes annual or quarterly goals for a partnership. Often, these plans touch on: Training and certification. Marketing efforts. Co-selling strategy. Revenue targets. Customer expansion and retention.
A business plan is a list of goals that are defined for a specific time period, and that will be tracked to measure the performance of the partner. This differs from the partnership agreement, which is the contract you sign at the beginning of the relationship to define legal boundaries. Business plans provide a roadmap for you and your partner.
Steps For Planning a Business Partnership. Write a mission statement to clearly state the direction and goals the business plans to take. By writing a mission statement, the partners agree to the company's direction now and in the future. Develop a reimbursement plan for the costs and investments incurred during startup.
One of the partner business plan tools we use with our small firm clients is the STAGe model. This is widely used to create 3-year or 12-month business plans for them. The good news is that it is versatile enough to help you create your 3-year partner business plan or 12-month partner business plan or vision for your practice.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Develop Partner Bussiness Plan: Two Key Steps to Consider. 1. Know Your Partners Well. A thorough understanding of your partner network is a fundamental prerequisite for the successful development of partner business planning. Within your indirect sales ecosystem, business providers, integrators, value-added resellers (VARs), IT service ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
A winning business partnership capitalizes on the strengths and skills of each partner. Divide business roles according to each individual's strengths. For example, if one partner is strong in marketing, operations, and finance and the other partner excels in sales, human resources and leadership then split tasks accordingly.
A solid partnership business plan will: Help the company understand the business potential for partnerships. Enable business owners to understand and predict costs and benefits for proper resource and revenue planning. Provide straightforward ways to track progress toward achieving channel goals.
If you need to create content to convince on-the-fence partners, you can do so with your cover letter, business plan, or presentation slides that will go along with the proposal. You might cover the addressable market, your competitive advantage, pricing model, etc. Step 4. Add e-signatures. The next step is to add e-signatures to your proposal.
A channel partner business plan, specifically, is a roadmap for aligning goals, defining actions, and allocating resources between your organization and its partners. The plan should outline specific outcomes and commitments from both parties, fostering mutual accountability and clarity in partnership objectives.
Keep Your Partnership Proposal On-Brand. Consistent branding is a crucial aspect of running a business. So, keep every page of your partnership proposal consistent with your brand identity.. Consider your brand colors, brand fonts, logo and other branding elements. If you haven't defined your brand identity yet, choose design elements that match your brand personality.
1. Draft a co-owner agreement. You should put in place a co-owner agreement to make it clear how decisions will be made, how profits will be split, and what happens if someone leaves the company ...
The quick answer: Partnership Plan Templates. Every business requires a partnership plan. Small businesses seek out partnerships more to achieve their goals and objectives. Building a strategic partnership is more complicated than creating a partnership document, but it is the first step toward action. SlideTeam's partnership plan templates ...
A successful small business partnership is akin to a good marriage. Both require not just short-term mutual interest but long-term compatibility. You need compatible values and vision, compatible financial resources and expectations, and compatible goals.
A business plan is a document that communicates a company's goals and ambitions, along with the timeline, finances, and methods needed to achieve them. Additionally, it may include a mission statement and details about the specific products or services offered. A business plan can highlight varying time periods, depending on the stage of your company and its goals.
4. Determine how many cases you need to meet that revenue goal. If you are only handling two or three cases per month, the number you came up with above might look outrageous. It's not. For example, let's use the 2023 median pay of $126,930 a year in annual revenue as our goal, with a flat fee of $3,000 per client.
Effective Business plans are used in conjunction with a Lateral Partner Questionnaire (LPQ), which is a detailed questionnaire that focuses on various aspects of your practice and includes questions about the historical, current, and projected financial aspects and economics of your practice. Taken together, these provide firms with the most ...
5. Consider a partner in a different field. While it might be tempting to look for partners who know your industry as well as you do, a business partner doesn't need to have your same same skill set, training, and experience. In fact, it's a good idea to look for a partner who brings a different viewpoint and work history to the table.
A business plan is a document that helps small business owners determine the viability of their business idea. Combining market research and financial analysis, a professional business plan helps startup CEOs and potential investors determine if the company can compete in the target market. Typically, a good business plan consists of the following:
When you're trying to find a business partner online, you can follow these nine steps to get started: 1. Solidify your business idea. Before you bring a co-founder on board, you'll need to ...
Legal experts explain the keys to lateral partner integration. Firms need to develop a business development plan, liaison. When a lateral is hired into a new firm, following the tone set during the recruiting process is essential. The firm needs to ensure the lateral is set up for success on day one. Openness, honesty, and transparency are key.
Yakima Basin Integrated Plan. The Yakima Basin Integrated Plan (YBIP) is a collaboration of state, federal, tribal, business, and community organizations committed to addressing water, fishery, habitat and climate variability challenges to ensure a robust Yakima River Basin within its built and natural systems.
Shares of streaming giant Netflix Inc (NASDAQ:NFLX) hit new 52-week highs Monday, which comes as the company recently shared an update on its ad-supported plan. An analyst praises the company's ...
Our role as a secure logistics provider is to guide them through all aspects of fintech security, ensuring the protection of sensitive data and maintaining their trust with customers and partners. Much of this starts with what we are best known for: speed. The faster a valuable item such as a credit card moves from A to B, the less risk there ...
The Metropolitan Airports Commission (MAC) board approved the long-term plan for Minneapolis-St. Paul International Airport (MSP) today. The MSP Airport 2040 Long-Term Plan outlines potential ...
Separately, EyeCare Partners earlier this month named Joel Day as executive vice president of finance, adding that he will take the company's CFO post effective June 1. He most recently has been ...
Citigroup's (C.N) Titi Cole, a top executive in charge of implementing its sweeping restructuring plan, is leaving the bank, an internal memo seen by Reuters showed on Tuesday. Cole, as the head ...