

The Role of Visual Communication in Marketing and Advertising

Students Trained & Placed
Sq.Ft.of training area
Worldwide Alumni Network
Kitchen Training Facility
UP to Scholarships
Placement Assistance
International & National Internships only at 5-star Properties
One to One Corporate Mentorship
An Entrepreneurial Culture at the Campus
Dignified with Rankings
Amongst india's most promising hotel management institute by higher education review 2022.

Ranked Top Hotel Management Institute awarded by Times Education Icon 2022

Quality Education, Outstanding Administration & Leading Infrastructure by Educational Excellence Awards & Conference 2021

Outstanding Performance in Virtual Knowledge Delivery During Pandemic by Educational Excellence Awards & Conference 2021
Visual communication refers to using visuals such as images, videos, and graphics to convey information and ideas. In the world of marketing and advertising, visual communication plays a crucial role in capturing the attention of potential customers and conveying brand messages effectively. In fact, research shows that people are more likely to remember information presented through visuals than through text alone.
This blog post will delve into the role of visual communication in marketing and advertising. We will explore the different types of visuals used in marketing and advertising, the key elements of effective visual communication design, and emerging trends and technologies in visual communication. By the end of this blog, you will know the importance of visual communication in marketing and advertising and how to use it effectively in your campaigns.
Importance of Visual Communication in Marketing
Visuals are effective in communicating messages because they have the ability to capture attention and convey emotions and complex ideas in a simple and concise way. They can evoke emotions, stimulate the senses, and make a lasting impression on the viewer.
In marketing and advertising, visuals are used to communicate brand messages, showcase products and services, and connect with consumers on an emotional level. For example, a company may use an image of a happy family enjoying a product to convey a sense of happiness and well-being associated with their brand. Similarly, a fashion brand may use images of models wearing their clothing to convey a sense of style and sophistication.
Visuals can also help increase brand awareness and recognition by creating a strong visual identity for a brand. Through consistent use of visual elements such as colours, logos, and imagery, a brand can establish a unique identity that differentiates it from other competitors and helps it stand out in the minds of consumers.
Overall, the importance of visual communication in marketing and advertising cannot be overstated. By leveraging the power of visuals, brands can effectively communicate their messages, connect with consumers on an emotional level, and create a strong visual identity that helps them get recognition in a crowded marketplace.
Types of Visual Communication in Marketing and Advertising
Visual communication in marketing and advertising can take many forms, including images, videos, infographics, and animations. Each type of visual communication has its own advantages and disadvantages, and brands must carefully consider which type of visual will best communicate their message to their target audience.
Images are one of the most common forms of visual communication in marketing and advertising. They can quickly capture attention, convey emotions, and showcase products or services. However, images may be less effective at communicating complex information or data.
Videos are another popular form of visual communication, and they have become increasingly important in recent years with the rise of now with the rise of platforms such as YouTube and TikTok. Videos can be used to tell a story, showcase products or services, and provide a behind-the-scenes look at a brand. However, videos require more resources to produce than images and may not be as effective at capturing attention in a fast-scrolling digital environment.
Infographics can effectively communicate complex information and data in a clear and concise way. They can be used to showcase statistics, compare products or services, and explain processes or concepts. However, infographics can be challenging to design and may not be as engaging as other types of visuals.
Animations are a type of visual communication that can effectively capture attention and convey complex information or concepts. They can help in telling a story, showcase products or services, and provide a unique and engaging visual experience. However, animations require more resources to produce than images or infographics.
Successful marketing and advertising campaigns often use different types of visual communication to communicate their message to their target audience effectively. For example, a fashion brand may use images to showcase their clothing, videos to provide a behind-the-scenes look at their design process, and infographics to compare their products to those of competitors. Using various visual communication tools, brands can create a comprehensive and engaging marketing and advertising campaign that resonates with their target audience.
Key Elements of Effective Visual Communication Design
Colour: Colour is an essential element of visual communication design , and it can evoke emotions and create a sense of brand identity. Choosing the right colour scheme is crucial to creating effective visuals conveying the desired message.
Typography: Typography refers to the text's style, arrangement, and appearance. The right typography can enhance a message's visual impact and help create a cohesive brand identity.
Layout: The layout of a visual is crucial so that the message is communicated effectively. An effective layout must be visually appealing, easy to navigate, and strategically designed to draw attention to the most important information.
Composition: Composition refers to how different elements are arranged within the visual. An effective composition can make the message stand out and help create a sense of balance and harmony in the overall design.
The Future of Visual Communication in Marketing and Advertising
The future of visual communication in marketing and advertising is exciting and rapidly evolving. As technology advances and consumers demand more immersive and interactive experiences, new trends are emerging in visual communication. Here, we will discuss some of these emerging trends and technologies and explore how they may shape the future of marketing and advertising.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) are two emerging technologies transforming how we experience visual content. AR allows users to overlay digital information onto the physical world, while VR creates a fully immersive digital environment. Both technologies offer unique opportunities for marketers to create engaging and interactive content that resonates with consumers. For example, a retail store could use AR to allow customers to try on clothes virtually, while a travel company could use VR to transport customers to exotic destinations.
Interactive content is another popular trend in marketing and advertising. Interactive content refers to any type of content that requires active participation from the user, such as quizzes, polls, and games. This type of content can be highly engaging and memorable and help build a stronger connection between the brand and the consumer.
Finally, personalised visual content is becoming increasingly important in marketing and advertising. Advances in data analytics and artificial intelligence are allowing marketers to tailor visual content to individual consumers based on their preferences and behaviours. This personalised approach can help increase engagement and conversion rates, as consumers are more likely to respond positively to relevant content tailored to their needs.
Visual communication plays a crucial role in marketing and advertising. It allows brands to effectively communicate their message, convey emotions, and increase brand awareness and recognition. Through the use of various types of visuals, such as images, videos, infographics, and animations, brands can create successful marketing campaigns that resonate with their audience.
Amongst India's most promising Hotel Management Institute by Higher Education Review 2021

Alumni Talks
Hitesh Singh | OUR ALUMNI OUR HONOUR | BAIHTM | ITM Institute of Hotel Management
Visit Our Campus

ITM Institute of Hotel Management - Andheri (Mumbai)

ITM Institute of Hotel Management - Nerul (Navi Mumbai)
Enquire Now
Recent posts.
- 7 Highest Paying Fashion Jobs With Salaries
- Interior Design Courses After 12th - Complete guide
- Essential Fashion Designer Skills in 2024
- Designing Courses After 12th - Complete Guide
- How does a Bachelor of Design course help a student's career?
- 6 Reasons to Learn Fashion Designing 2024
- How Do Fashion Designers Use Geometry?
- Which Subjects Are Taught In Fashion Designing Courses
- How to Become a Fashion Designer after 12th?
- How to become an interior designer in 2024?
Who We Are And What Can We do?
Programs offered.

Bachelor of Science Honours in Digital Film Making and VFX
Location: navi mumbai,

Bachelor of Design in UX Design
Location: mumbai,

IDM Bachelor of Science Honours in Game Design and Development

Bachelor of Design in Interior Design

Bachelor of Science Honours in Animation & VFX

Bachelor of Design in Animation and VFX

Bachelor of Design in Visual Communication

Bachelor of Design in Fashion Design
Download brochure.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design 15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation & why is it important?
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

4. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
5. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
6. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
8. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

9. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo . But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s tools enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Ultimately, creating a memorable visual presentation isn’t just about throwing together pretty slides. It’s about mastering the art of making your message stick, captivating your audience and leaving a mark.
Lucky for you, Venngage simplifies the process of creating great presentations, empowering you to concentrate on delivering a compelling message. Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

The Power of Visual Communication in Marketing
January 30, 2023 / Blog
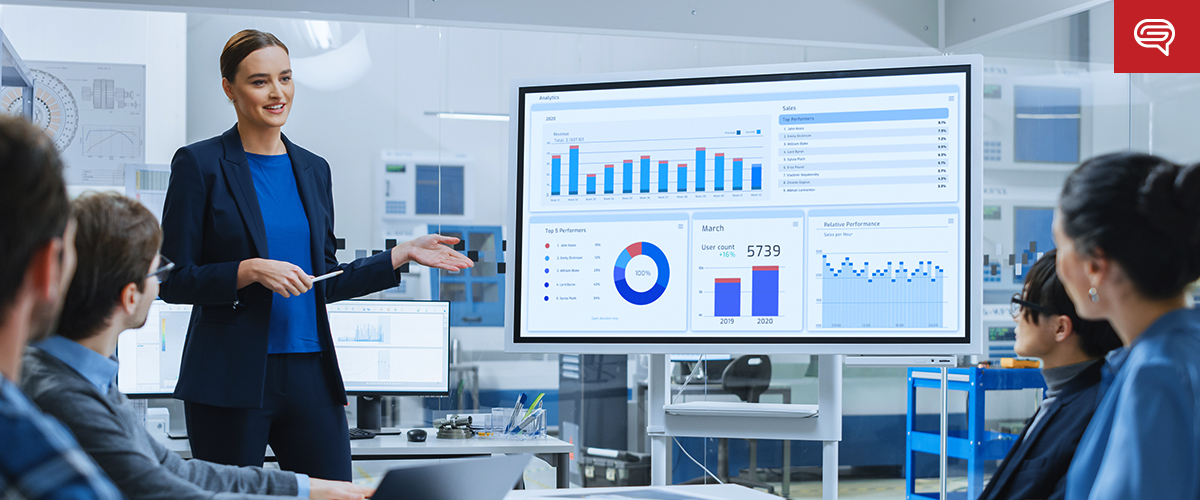

Visual communication in marketing leverages the power of visual elements such as images, graphics, videos, and interactive content to effectively convey a message or story. It is a strategy that aims to grab attention, strengthen brand recognition, and enhance communication with the target audience.
Need a Presentation Designed? Click Here To View Our Amazing Portfolio
Over the years, visual communication has become a tool businesses use to stand out from the competition, increase conversions and sales, and achieve cost-effective marketing solutions. As technology continues to advance and the digital landscape evolves, the importance of visual communication in marketing will only continue to grow.
The benefits of visual communication in marketing
Visual communication in marketing is a powerful tool that can provide numerous benefits. From increased engagement and retention to improved brand recognition and recall, the use of visual elements in marketing can enhance the effectiveness of a business’s marketing efforts.
Increased engagement and retention
Visual elements, such as images, videos, and infographics, can boost the shareability and memorability of content on social media, leading to increased engagement and retention among the audience. This can result in greater brand awareness and loyalty.
Improved brand recognition and recall
A consistent visual identity, created using visual elements like logos, colors, and imagery, can make it easier for consumers to identify and remember a brand, resulting in improved brand recognition and recall. By implementing a consistent visual style throughout all marketing materials, businesses can establish a strong and memorable brand identity that will remain ingrained in the minds of consumers.

More effective storytelling and message delivery
By utilizing visual elements like images , videos, and interactive content, businesses can create a more captivating and immersive story. This can be especially beneficial for storytelling, allowing businesses to establish a stronger emotional connection with their audience, and convey their message more effectively.
Increased conversions and sales
Visual communication can be pivotal in the customer decision-making process. By displaying products or services through visual elements such as images and videos, businesses can make them more alluring and engaging, thereby increasing the chances of purchase and resulting in more conversions and sales.
Cost-effective marketing solution
Visual communication enables businesses to craft an engaging and memorable experience for their audience without incurring high marketing expenses. This approach proves to be a cost-effective solution, particularly for small businesses and startups, to connect with their target market and establish a strong brand identity.
Stand out from the competition
In the current digital landscape, competition is intense. Utilizing visual communication can assist businesses in distinguishing themselves by providing an engaging and unforgettable experience for their target audience. By utilizing visual elements such as images, videos, and interactive content, businesses can create a distinct brand identity that will set them apart from their competitors.

Hiring a presentation design agency
A presentation design agency can create visually appealing and effective marketing materials that grab the audience’s attention and effectively convey the message. Professional design is essential for the success of visual communication in marketing, as it can make marketing more impactful, memorable, and effective.
Here are the benefits of hiring a presentation design agency:
Professional design and expertise
Presentation design agencies can create eye-catching and effective visual communication materials that grab the audience’s attention and effectively convey messages. They have the expertise and experience to tailor designs to the specific needs of your business and audience.
Wide range of services
A presentation design agency can provide a wide range of services, including custom designs for marketing materials, brochures, infographics, videos, and interactive content. They can help establish a consistent visual identity across all materials, leading to improved brand recognition and recall.

Tailored solutions
A presentation design agency can collaborate with your business to understand your brand, audience, and goals, and create customized solutions that fit your specific needs. This can help establish a unique and distinctive visual identity that differentiates your business from competitors.
Visual communication in marketing is a proven strategy that can captivate an audience, convey messages effectively, and create a lasting impact. By enlisting the services of a presentation design agency, businesses can ensure that their visual communication is polished, professional, and impactful, leading to successful marketing campaigns and a competitive edge in the market.
Popular Posts

Common Challenges in Tailoring Presentations—and Solutions

Dos and Don’ts of Pre-Seed Pitch Deck Creation

How to Write a Teaser Pitch Deck that Captivates

Tips for a Persuasive How It Works Slide

What Not to Do When Presenting Funding History

Why Raising Funds Without a Pitch Deck Can Backfire

Home » Uncategorized » Seven Reasons Visuals Are So Effective in Advertising
The Yale Ledger is a student-led magazine showcasing content from around the Yale community.
If you are affiliated with the Yale student community and have an article you want to share, please email Layla Winston .
If you notice any spam or inappropriate content, please contact us so we can remove it.
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- November 2023
- October 2023
- September 2023
- August 2023
- February 2023
- January 2023
- December 2022
- November 2022
- October 2022
- September 2022
- August 2022
- February 2022
- January 2022
- December 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021

Seven Reasons Visuals Are So Effective in Advertising
Using visual elements and graphics has been a powerful part of marketing for many years. By creating an ad that is colorful, well-designed, and attractive, marketers are more likely to catch the attention of their potential customers as well as remain in their memory. Marketing teams and researchers spend a lot of time learning about the best ways to reach, influence, and impact their audience and have become highly successful. Researchers have found that one of the ways marketers can be most effective is by employing visual elements in their advertising. Visual marketing is highly effective for several reasons:
Visuals Grab Consumers’ Attention
Visuals can catch the attention of your audience quickly. In today’s world of advertising and information overload, catching and holding the attention of your audience and helping your ad stand out are among the essential elements of effective marketing. Creating attractive, simple, eye-catching visuals can help your advertising efforts stand out and be noticed. Using a social media or video marketing agency can help you to capture the attention of consumers, become a recognizable brand, and appeal to your target audience.
Graphic Elements Are Easy to Understand
Visual elements in advertising have the power to convey complex ideas or messages in a simple and concise manner. A well-designed visual, such as an infographic, can communicate a lot of information at a glance, making it easier for the audience to understand and remember the message being conveyed. Creating well-made visuals that bring a strong impact and deliver a message that people can quickly understand is key to utilizing visuals effectively.
Creating helpful value-add infographics that your customers can actually use, learn from, or benefit from is a powerful way to grow your audience. Consumers who agree with or appreciate the information in your graphics are likely to share it on their social media, and they are also likely to have friends who are similar to them. This is why using visuals will help organically promote your business, as well as help your audience feel heard and understood.
Visuals Can Have an Emotional Impact
Visuals can be a good way to create an emotional impact in your advertising. Emotions play a significant role in decision-making, and visual marketing can effectively influence the audience’s perception and feelings toward a brand or product. By creating emotional impacts in your audience, you can inspire them to make a decision today about your product, especially when coupled with a sincere and clear call to action.
There are many ways to add emotion and feeling to your visual elements and many different scientific principles that can help you do this effectively. By using colors, images, graphics, and design elements, visual marketing can tap into the viewer’s emotions, whether it’s joy, excitement, curiosity, or empathy.
Create Increased Engagement by Using Graphics
You can also use visual elements in your marketing to help generate higher engagement rates. People are more likely to share and comment on visual, engaging, and humorous posts on social media. In addition, visuals help catch consumers’ attention as they are flipping through magazines, watching television, or scrolling social media. By creating more engagement and catching the attention of more viewers, visual advertising helps spread your message, build a stronger connection with your audience, and foster brand loyalty.
In order to benefit from the increased engagement and connection that visuals can bring, be prepared to stay on top of your social media accounts. Make sure that you or your marketing team are regularly engaging with clients on social media by answering questions, responding to comments, and staying on top of customer concerns and complaints. This helps to close the engagement loop that your visuals create and keeps your customers feeling heard and connected.
Utilize Visuals for Information Retention
Visual components, graphics, and photographs have been shown to enhance information retention and recall. Studies have found that people remember information better when it is presented visually compared to text alone. Visuals can help create mental associations and triggers which can aid in memory recall, making both the message and your brand more memorable and impactful. This is one reason that brands work so hard to promote their logo and style. Remember to add your logo and name to all your visuals, and make sure that you have a cohesive style in your marketing. This can help your brand stay forefront in your audience’s memories.
Foster Cross-Cultural Appeal With Visuals
Visuals such as graphics, cartoons, and photographs have a universal language that transcends cultural and language barriers. They can communicate ideas and concepts without relying heavily on text, making them more accessible to a global audience. This is particularly advantageous in today’s interconnected world where brands aim to reach diverse markets. If you are trying to appeal to a cross-cultural or multilingual audience, use visuals to help create a cohesive and consistent style. No matter what language your advertisements are written in or what specific culture they are targeting, they should have some form of cohesion with your larger advertising campaign as a whole. This can help your brand become recognizable across many platforms and situations.
Logos and Color Can Help Create Your Brand Image
You can create a powerful, recognizable brand image by utilizing visual elements. Color, graphics, logos, and style can all be used to form a cohesive marketing strategy. By using visuals in a consistent, well-planned way, marketers can capitalize on brand recognition to help build momentum in their advertising. Visual elements are so powerful that many well-known brands no longer add their names to their television, online, or graphic advertising efforts, relying instead on their well-known logos, brand style, and colors to get their message and brand across.
Visual-based marketing works so well because it leverages the way the human brain naturally works. The human brain’s natural inclination towards visual stimuli helps advertisers effectively communicate messages over cultural and language barriers, helps to create a strong brand image, facilitates emotional decision-making, and creates powerful memories. Incorporating visual elements into marketing strategies can significantly enhance the effectiveness and impact of communication efforts.
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Powered by WordPress / Academica WordPress Theme by WPZOOM
Best Digital Marketing Blog
4 tips for creating a memorable visual presentation, digital marketing | jun 22, 2023.
Sensory marketing explores the five senses to connect the audience to the brand with the objective of conversion. Therefore, a visual presentation needs to be very well thought out by the responsible designer during its development and construction.
In this area, presentations are constant. However, they are not always designed to be attractive and efficient. An error that can delay project/budget approval and even jeopardize closing with a client.
The purpose of this post is to talk about the importance of visual presentations for the marketing sector and bring the top 4 tips on how to create an impactful visual presentation to surprise the public!
Why Is Visual Presentation So Important in Marketing?
There are several ways to dialogue with the consumer and marketing has the challenge of attracting and stimulating lead action. In order to convey a positive and effective message in this communication, it is necessary to be strategic and use conversion mechanisms.
In visual presentation using background Powerpoint templates is essential, especially in digital marketing, judging by the behavior of people, who pay more attention to graphic elements. In the online environment, dynamism and interactivity prevail, demanding creativity from marketing professionals and agencies.

How to Impact the Audience With Good Presentations?
In a layout of colors, images, and texts, the visual presentation must facilitate the understanding of the audience. There are 4 tips that can help you develop amazing presentations with high conversion power!
Let’s go through the top 4 tips for creating a memorable visual presentation in 2023:
- Build slides based on the consumer journey
Knowing the audience profile, their needs, and their pains is essential to plan marketing strategies. In this context, it is necessary to understand what stage they are in to build a presentation based on their buying journey.
The slides have a sequence that needs to be respected so that the audience can follow the speaker’s reasoning. A speech different from what is seen on the screen, in addition to compromising credibility, can confuse the audience’s understanding.
- Use legible and compatible fonts
When creating a visual presentation , be empathetic and put yourself in the audience’s shoes, imagining how they would like to consume the content. The fonts must be easy to read, and contextualize in a visual identity compatible with the reality of the addressed public.
The font size, design, and color influence the audience’s desire to stay tuned in the presentation. Small letters, shaded and full of effects, can get tired very quickly and ruin the chances of conversion.
- Use colors according to the customer’s visual identity
In the same way, the colors must be designed to facilitate assimilation without exaggeration and extravagance. The use of videos and examples of graphic pieces of the project can help to give more depth to the idea.
The Psychology of Colors can help in this sense as it brings a study with the meaning and stimulus of colors. In this way, this harmonic combination of tones can create an immediate attunement and familiarity with the audience.
- Use numbers and data creatively
Data is important but if used incorrectly it can become dull and have a reverse effect. Numbers and statistics help confirm a performance or result and can be used in a visual presentation as long as you are creative.
For example, if the objective is to talk about sales success, use percentages instead of values. If the idea is to show the evolution of preference for a product, an objective graph can better present this result.

Conclusion:
With a good background presentation, you can create impactful visual presentations for the marketing industry. Marketing’s job is to sell and for that, it needs to make potential customers prefer the brand to any other on the market.
The visual presentation must provoke enough emotion for the lead to make one more decision and move forward, going against the brand’s products.
Digital Marketing
Amy harrison.

Top Digital Marketing Agencies in Egypt in 2020

7 Resources for Surviving Your Business and Rebuilding It From the Ground Up
Related article.

Digital Advertising
The future of content creation: how ai video editing tools are transforming digital marketing.

From Keywords to Conversions: The SEM Optimization Process

25+ Best Digital Marketing Campaigns in the US in 2019

Consumer Behavior
10 useful social media management strategies in times of crisis: covid-19 outbreak 2020.
- Digital Events
- Job Opportunities
- Latest Updates
- For Agencies
- Search Agencies
- Agency Membership
- Why Join DMC?
- Advertise With Us
- Write for Us
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe for our newsletter!
COPYRIGHTS DIGITAL MARKETING COMMUNITY 2019

The Importance of Visual Communication: Definition, Examples, & Benefits
Visual communication is a powerful and versatile way to convey ideas, information, and possibly emotions. This article aims to discuss the importance of visual communication, providing an overview of its various definitions, examples of its use, and the associated benefits.
It offers a comprehensive analysis of a range of topics, from visual literacy and storyboarding to using infographics to display data. In addition, this article covers how to best utilize visuals to enhance messages and create effective campaigns.
So, step into the world of visual communication and explore how it can help make any presentation, report, or project more successful.
What is Visual Communication?
Visual communication is the art of using visuals to express ideas and information. From text, diagrams, illustrations, photographs, and videos to graphic design – there are many different types of visuals that can be used in visual communication. When visual images are combined together, they create a powerful presentation that can effectively communicate any message.
Graphic design is one of the six main categories within visual communication; it uses visuals to create layouts and designs. Advertising also falls into this category as it uses visuals to promote products or services. Photography and illustration capture moments or tell stories visually appealing, while web design and video production use visuals for interactive experiences users can engage with.
The four main types of visual communication are typography, graphics, layout, and motion. Typography involves creating typefaces, while graphics include illustrations, images, and logos. Layout arranges these elements on a page or screen, while motion adds animation for a dynamic experience. All these components work together to form an effective message that resonates with viewers!
Finally, the part of the brain responsible for processing all this visual information is called the visual cortex – an incredibly powerful area capable of quickly making sense of what we see!
Why Is Visual Communication Important?
Visual communication is a powerful tool for people to express their ideas and concepts in an efficient, effective way. Through visuals and visual mediums such as data visualizations, presentations, and graphic design, complex topics can be presented in a more understandable format. Visual communication is used in advertising, public relations, and design – you name it – to help people comprehend information quickly and accurately.
Visuals are the bridge that traditional word-focused communication fails to build. By using body language and adding images into the message mix, one can communicate ideas with greater impact than words alone. Visuals have the power to inspire change and reach large audiences without language barriers getting in the way.
The purpose of visual communication is clear: understand complex info, create compelling presentations, and advertise products or services effectively. But if done wrong? Misunderstandings and confusion will follow suit! That’s why it’s important to consider both pros & cons before implementing visuals into your marketing strategy. A 2019 study showed that attention spans are decreasing at an alarming rate – making visuals even more essential for capturing viewers’ attention spans today!
It Increases Engagement
Visual communication can be a powerful tool for reaching potential customers. It’s an effective way to make your brand more memorable, as iconic ads can become widely known and remembered. To engage viewers, incorporate high-quality images and videos into content, tailor visuals to the audience, and use visuals to capture their interest. Visual communication also has the power to inspire change or evoke emotion through symbols and visual metaphors. Plus, it helps build trust with customers by creating a positive first impression that encourages action.
It Enhances Learning and Retention
Visual communication strategy can be used to connect strategy with the VAK theory, which states that people learn through visual, auditory, and kinesthetic methods. By incorporating strong visual communication strategies, one can cater to the needs of visual learners and create a positive learning environment. Visuals also allow viewers to pay attention to, think about, and understand a message; they are also more memorable than text content alone, making the end product more memorable.
Incorporating visuals into communication can also help to increase understanding of the process, reduce confusion, and motivate employees. When presenting complex information, visuals can bridge the gap between concepts and words, making the content more engaging and aiding in comprehension. The visual cortex, the part of the brain responsible for processing visual information, is also an important aspect of visual communication, as it can help people to retain information.
It Helps Create Connections
Visual communication can be a powerful tool for influencing and persuading people’s opinions. By creating connections and using visuals to clarify a message, one can create meaningful content that leaves an impression. But inconsistencies in visuals can lead to confusion or alienation of customers.
This form of visual communication helps us build relationships with people from all over the world – especially in this digital age where visuals are more important than ever before. They provide a clear way to share ideas and thoughts while also evoking emotions and answering the question, “why should I care?”.
Organizational systems help avoid any potential confusion or conflict by providing everyone involved with a reference point. Visuals can also present process documents quickly, so teams understand new organizational processes easily. And visual storytelling makes messages stick longer, making them more memorable for viewers.
How to Use Visual Communication Effectively
Visual communication is a powerful tool for any organization, helping to engage viewers and create lasting impressions. It involves conveying messages or ideas using visual elements such as photos, videos, graphs, typography, charts, maps, and illustrations.
When it comes to visual communication strategies, there are many options – from selecting elements to create meaning for the audience to incorporating visuals that add depth and context. Common tools used by graphic designers include charts, graphs, and diagrams.
To make effective use of visual communication, you can employ symbols to convey meaning; utilize color to communicate visually and evoke emotion; incorporate visuals into marketing materials; craft a message that educates, motivates, and engages with design principles; all while making sure your message is memorable!
Read our blog posts about
What is Mass Communication? How to Communicate with a Large Audience What Is Corporate Communication: The Basics Why is Intercultural Communication Important
Visual and Kinesthetic Imagery
Visual and kinesthetic imagery is like a bridge between complex ideas and technical information, helping people to process changes cross over into understanding. It can evoke emotions, add details that text alone cannot convey, and provide a reference point for further exploration.
In education, visuals such as process diagrams such as mind maps allow students to better understand and organize complex information. Pie charts, bar graphs, and other data visualizations also help illustrate points in an engaging way. For organizations, visuals can make unclear expectations clearer while keeping everyone on the same page. Visual storytelling is a powerful tool for communicating complex info in an appealing manner.
Data Storytelling
Data storytelling is a way to use visuals to communicate information, ideas, and processes in an interesting manner. Visuals can be used to show risk, handle large amounts of data, and emphasize comparisons. When creating visual content, it’s important to consider the target audience and choose visuals that are relevant to them – images, diagrams, charts, videos, etc. Incorporating visuals into emails or presentations makes the message more engaging and memorable.
Coherence is also essential when it comes to data storytelling – making sure all visuals tell one story together so they provide a clear, unified message. Data storytelling is invaluable for organizations in this digital age as it helps engage customers in new ways; healthcare providers can use visuals to explain complex info, while businesses on social media can differentiate from competitors with visual communication.
To make effective visual communication possible, there are some basics you should know about: understand what works best for your target audience, be aware of different ways you could improve visual imagery, and utilize tools available at your disposal. With these tips, you’ll create visuals that will engage people’s attention and motivate them!
Benefits of Visual Communication
Visual communication is a powerful tool for businesses and organizations to communicate effectively and engage their target audiences. By incorporating visual elements such as data visualization, visual storytelling, and content marketing into communication strategies, companies can create an unforgettable experience for customers while promoting products or services.
The advantages of visual communication are plentiful – from creating a more understandable representation of information that surpasses language barriers to forming a concrete connection with the viewer. It also helps build brand recognition by crafting a professional image for businesses.
Using visuals in business has many benefits, including increased connection among team members and audiences, improved engagement, heightened brand awareness, and more memorable content. Visuals can quickly convey complex ideas which viewers can easily process and remember; they also make dry information easier to digest by adding context to it. Data visualization is essential in effective visual communication since it allows businesses to analyze large amounts of data sets, recognize relationships between them, and spot trends. Additionally, dynamic visuals keep users informed on the latest news, thus keeping them engaged with the company’s message.
In conclusion, utilizing the benefits of visual communication is key in helping businesses communicate effectively with their targeted audiences while increasing sales and building brand awareness at the same time. It improves reception and retention of information, making processes simpler to understand and reducing confusion or mistakes along the way; plus, it brings up $1 200 per year productivity per employee who consumes content as part of their job role! Nonprofits, too, benefit from this type of visual communication tool as it updates stakeholders on campaigns or research results swiftly yet efficiently!

Visual communication is an essential tool allowing us to express the most complex of ideas effectively and engage with our audiences quickly and in an innovative way. It serves as an efficient way to break language barriers, offers an intriguing method for storytelling, aids comprehension of topics, and lets businesses reach larger customer bases through their visual presentation.
In terms of the implementation of visual aid, there are a few tactics to be aware of when it comes to effective visual communication. Visuals such as video and imagery can be used to increase engagement and understanding, while data storytelling can help create meaningful connections across cultures. With the potential benefits offered by visual media, businesses have the opportunity to spark change, deepen customer engagement, and improve learning retention.
All this makes visual communication an important tool for modern meeting demands and driving growth in any organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is visual communication, and why is it important.
Visual communication is the transmission of ideas and information via visual elements such as text, images, graphics, and other components communicating information. It is an important tool for businesses to convey information, promote their products or services, and create meaningful connections with their audience.
Visual aids to communication can be seen in typography, logos, website design, videos, photographs, illustrations, and other visuals.
What is the benefit of visual communication?
The benefit of visual communication is that it helps to get messages across quickly and effectively; communicating visually engages an audience better than words alone and can be used to reinforce written or spoken health messages.
Visuals are also more flexible and attention-grabbing, making complex concepts easier to comprehend.
What is the importance of visual communications 10 points?
Visual communication is essential for meaningful, effective communication as it enables us to convey ideas quickly and effectively. It connects with people emotionally, helps clarify complex concepts, and assists in making persuasive arguments.
Visuals can increase retention of the conveyed message and evoke an emotional response from the viewer. Aug 18, 2021
Why is visual communication an important skill?
Visual communication is a powerful tool for conveying information to an audience quickly and effectively. It allows us to better understand complex concepts and information, draw conclusions, solve problems, and convey messages with clarity.
Visuals play an important role in how we interact with the world around us and can bring greater depth and understanding to communication.
What is meant by visual communication?
Visual communication is the process of conveying messages or ideas through visuals, such as images, videos, diagrams, graphs, and illustrations. Visual communication can be used to communicate ideas more effectively than using words alone and can have a powerful impact on an audience.
Leave a Comment Cancel
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Email Address:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Advertising Functions and Strategies
Advertising: pay to play.

Advertising is any paid form of communication from an identified sponsor or source that draws attention to ideas, goods, services or the sponsor itself. Most advertising is directed toward groups rather than individuals, and advertising is usually delivered through media such as television, radio, newspapers and, increasingly, the Internet. Ads are often measured in impressions (the number of times a consumer is exposed to an advertisement).
Advertising is a very old form of promotion with roots that go back even to ancient times. In recent decades, the practices of advertising have changed enormously as new technology and media have allowed consumers to bypass traditional advertising venues. From the invention of the remote control, which allows people to ignore advertising on TV without leaving the couch, to recording devices that let people watch TV programs but skip the ads, conventional advertising is on the wane. Across the board, television viewership has fragmented, and ratings have fallen.
Print media are also in decline, with fewer people subscribing to newspapers and other print media and more people favoring digital sources for news and entertainment. Newspaper advertising revenue has declined steadily since 2000. [1] Advertising revenue in television is also soft, and it is split across a growing number of broadcast and cable networks. Clearly companies need to move beyond traditional advertising channels to reach consumers. Digital media outlets have happily stepped in to fill this gap. Despite this changing landscape, for many companies advertising remains at the forefront of how they deliver the proper message to customers and prospective customers.
The Purpose of Advertising
Advertising has three primary objectives: to inform, to persuade, and to remind.
- Informative Advertising creates awareness of brands, products, services, and ideas. It announces new products and programs and can educate people about the attributes and benefits of new or established products.
- Persuasive Advertising tries to convince customers that a company’s services or products are the best, and it works to alter perceptions and enhance the image of a company or product. Its goal is to influence consumers to take action and switch brands, try a new product, or remain loyal to a current brand.
- Reminder Advertising reminds people about the need for a product or service, or the features and benefits it will provide when they purchase promptly.

When people think of advertising, often product-focused advertisements are top of mind—i.e., ads that promote an organization’s goods or services. Institutional advertising goes beyond products to promote organizations, issues, places, events, and political figures. Public service announcements (PSAs) are a category of institutional advertising focused on social-welfare issues such as drunk driving, drug use, and practicing a healthy lifestyle. Usually PSAs are sponsored by nonprofit organizations and government agencies with a vested interest in the causes they promote.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Advertising
As a method of marketing communication, advertising has both advantages and disadvantages. In terms of advantages, advertising creates a sense of credibility or legitimacy when an organization invests in presenting itself and its products in a public forum. Ads can convey a sense of quality and permanence, the idea that a company isn’t some fly-by-night venture. Advertising allows marketers to repeat a message at intervals selected strategically. Repetition makes it more likely that the target audience will see and recall a message, which improves awareness-building results. Advertising can generate drama and human interest by featuring people and situations that are exciting or engaging. It can introduce emotions, images, and symbols that stimulate desire, and it can show how a product or brand compares favorably to competitors. Finally, advertising is an excellent vehicle for brand building, as it can create rational and emotional connections with a company or offering that translate into goodwill. As advertising becomes more sophisticated with digital media, it is a powerful tool for tracking consumer behaviors, interests, and preferences, allowing advertisers to better tailor content and offers to individual consumers. Through the power of digital media, memorable or entertaining advertising can be shared between friends and go viral—and viewer impressions skyrocket.
The primary disadvantage of advertising is cost. Marketers question whether this communication method is really cost-effective at reaching large groups. Of course, costs vary depending on the medium, with television ads being very expensive to produce and place. In contrast, print and digital ads tend to be much less expensive. Along with cost is the question of how many people an advertisement actually reaches. Ads are easily tuned out in today’s crowded media marketplace. Even ads that initially grab attention can grow stale over time. While digital ads are clickable and interactive, traditional advertising media are not. In the bricks-and-mortar world, it is difficult for marketers to measure the success of advertising and link it directly to changes in consumer perceptions or behavior. Because advertising is a one-way medium, there is usually little direct opportunity for consumer feedback and interaction, particularly from consumers who often feel overwhelmed by competing market messages.
Developing Effective Ads: The Creative Strategy
Effective advertising starts with the same foundational components as any other IMC campaign: identifying the target audience and the objectives for the campaign. When advertising is part of a broader IMC effort, it is important to consider the strategic role advertising will play relative to other marketing communication tools. With clarity around the target audience, campaign strategy, and budget, the next step is to develop the creative strategy for developing compelling advertising. The creative strategy has two primary components: the message and the appeal .
The message comes from the messaging framework discussed earlier in this module: what message elements should the advertising convey to consumers? What should the key message be? What is the call to action? How should the brand promise be manifested in the ad? How will it position and differentiate the offering? With advertising, it’s important to remember that the ad can communicate the message not only with words but also potentially with images, sound, tone, and style.

Marketers also need to consider existing public perceptions and other advertising and messages the company has placed in the market. Has the prior marketing activity resonated well with target audiences? Should the next round of advertising reinforce what went before, or is it time for a fresh new message, look, or tone?
Along with message, the creative strategy also identifies the appeal , or how the advertising will attract attention and influence a person’s perceptions or behavior. Advertising appeals can take many forms, but they tend to fall into one of two categories: informational appeal and emotional appeal.
The informational appeal offers facts and information to help the target audience make a purchasing decision. It tries to generate attention using rational arguments and evidence to convince consumers to select a product, service, or brand. For example:
- More or better product or service features: Ajax “Stronger Than Dirt”
- Cost savings: Walmart “Always Low Prices”
- Quality: John Deere “Nothing runs like a Deere”
- Customer service: Holiday Inn “Pleasing people the world over”
- New, improved: Verizon “Can you hear me now? Good.”
The following Black+Decker commercial relies on an informational appeal to promote its product. (Note: There is no speech in this video; only instrumental music.)
https://youtube.com/watch?v=w6tqDoJQokM
Text alternative for “Black and Decker 20V MAX” (opens in new window).
The emotional appeal targets consumers’ emotional wants and needs rather than rational logic and facts. It plays on conscious or subconscious desires, beliefs, fears, and insecurities to persuade consumers and influence their behavior. The emotional appeal is linked to the features and benefits provided by the product, but it creates a connection with consumers at an emotional level rather than a rational level. Most marketers agree that emotional appeals are more powerful and differentiating than informational appeals. However, they must be executed well to seem authentic and credible to the the target audience. A poorly executed emotional appeal can come across as trite or manipulative. Examples of emotional appeals include:
- Self-esteem: L’Oreal “Because I’m worth it”
- Happiness: Coca-Cola “Open happiness”
- Anxiety and fear: World Health Organization “Smoking Kills”
- Achievement: Nike “Just Do It”
- Attitude: Apple “Think Different”
- Freedom: Southwest “You are now free to move about the country”
- Peace of Mind: Allstate “Are you in good hands?”
- Popularity: NBC “Must-see TV”
- Germophobia: Chlorox “For life’s bleachable moments, there’s Chlorox”
The following Heinz Ketchup commercial offers a humorous example of an ad based entirely on an emotional appeal:
Developing the Media Plan
The media plan is a document that outlines the strategy and approach for an advertising campaign, or for the advertising component in an IMC campaign. The media plan is developed simultaneously with the creative strategy. A standard media plan consists of four stages: (a) stating media objectives; (b) evaluating media; (c) selecting and implementing media choices; and (d) determining the media budget.
Media objectives are normally stated in terms of three dimensions:
- Reach: number of different persons or households exposed to a particular media vehicle or media schedule at least once during a specified time period.
- Frequency: the number of times within a given time period that a consumer is exposed to a message.
- Continuity: the timing of media assertions (e.g. 10 per cent in September, 20 per cent in October, 20 per cent in November, 40 per cent in December and 10 per cent the rest of the year).
The process of evaluating media involves considering each type of advertising available to a marketer, and the inherent strengths and weaknesses associated with each medium. The table below outlines key strengths and weaknesses of major types of advertising media. Television advertising is a powerful and highly visible medium, but it is expensive to produce and buy air time. Radio is quite flexible and inexpensive, but listenership is lower and it typically delivers fewer impressions and a less-targeted audience. Most newspapers and magazines have passed their advertising heydays and today struggle against declining subscriptions and readership. Yet they can be an excellent and cost-effective investment for reaching some audiences. Display ads offer a lot of flexibility and creative options, from wrapping buses in advertising to creating massive and elaborate 3-D billboards. Yet their reach is limited to their immediate geography. Online advertising such as banner ads, search engine ads, paid listings, pay-per-click links and similar techniques offers a wide selection of opportunities for marketers to attract and engage with target audiences online. Yet the internet is a very crowded place, and it is difficult for any individual company to stand out in the crowd.
The evaluation process requires research to assess options for reaching their target audience with each medium, and how well a particular message fits the audience in that medium. Many advertisers rely heavily on the research findings provided by the medium, by their own experience, and by subjective appraisal to determine the best media for a given campaign.
To illustrate, if a company is targeting young-to-middle-aged professional women to sell beauty products, the person or team responsible for the media plan should evaluate what options each type of media offers for reaching this audience. How reliably can television, radio, newspapers or magazines deliver this audience? Media organizations maintain carefully-researched information about the size, demographics and other characteristics of their viewership or readership.
Cable and broadcast TV networks know which shows are hits with this target demographic and therefore which advertising spots to sell to a company targeting professional women. Likewise newspapers know which sections attract the eyeballs of female audiences, and magazines publishers understand very well the market niches their publications fit. Online advertising becomes a particularly powerful tool for targeted advertising because of the information it captures and tracks about site visitors: who views and clicks on ads, where they visit and what they search for.
Not only does digital advertising provide the opportunity to advertise on sites that cater to a target audience of professional women, but it can identify which of these women are searching for beauty products, and it can help a company target these individuals more intensely and provide opportunities for follow-up interaction.The following video further explains how digital advertising targets and tracks individuals based on their expressed interests and behaviors.
You can view the transcript for “Behavioral Targeting” here (opens in new window) .
Selection and Implementation
The media planner must make decisions about the media mix and timing, both of which are restricted by the available budget. The media-mix decision involves choosing the best combination of advertising media to achieve the goals of the campaign. This is a difficult task, and it usually requires evaluating each medium quantitatively and qualitatively to select a mix that optimizes reach and budget. Unfortunately, there are few valid rules of thumb to guide this process, in part because it is difficult to compare audiences across different types of advertising media. For example, Nielsen ratings measure audiences based on TV viewer reports of the programs watched, while outdoor (billboard) audience-exposure estimates are based on counts of the number of automobiles that pass particular outdoor poster locations. The “timing of media” refers to the actual placement of advertisements during the time periods that are most appropriate, given the selected media objectives. It includes not only the scheduling of advertisements, but also the size and position of the advertisement.
There are three common patterns for advertising scheduling:
- Continuous advertising runs ads steadily at a given level indefinitely. This schedule works well products and services that are consumed on a steady basis throughout the year, and the purpose of advertising is to nudge consumers, remind them and keep a brand or product top-of-mind.
- Flighting involves heavy spurts of advertising, followed by periods with no advertising. This type of schedule makes sense for products or services that are seasonal in nature, like tax services, as well as one-time or occasional events.
- Pulsing mixes continuous scheduling with flighting, to create a constant drum-beat of ads, with periods of greater intensity. This approach matches products and services for which there is year-round appeal, but there may be some seasonality or periods of greater demand or intensity. Hotels and airlines, for example, might increase their advertising presence during the holiday season.
When considering advertising as a marketing communication method, companies need to balance the cost of advertising–both of producing the advertising pieces and buying placement—against the total budget for the IMC program. The selection and scheduling of media have a huge impact on budget: advertising that targets a mass audience is generally more expensive than advertising that targets a local or niche audience. It is important for marketers to consider the contribution advertising will make to the whole. Although advertising is generally one of the more expensive parts of the promotion mix, it may be a worthwhile investment if it contributes substantially to the reach and effectiveness of the whole program. Alternatively, some marketers spend very little on advertising because they find other methods are more productive and cost-effective for reaching their target segments.
Anatomy of an Advertisement
Advertisements use several common elements to deliver the message. The visual is the picture, image, or situation portrayed in the advertisement. The visual also considers the emotions, style, or look-and-feel to be conveyed: should the ad appear tender, businesslike, fresh, or supercool? All of these considerations can be conveyed by the visual, without using any words.
The headline is generally what the viewer reads first—i.e., the words in the largest typeface. The headline serves as a hook for the appeal: it should grab attention, pique interest, and cause the viewer to keep reading or paying attention. In a radio or television ad, the headline equivalent might be the voice-over of a narrator delivering the primary message, or it might be a visual headline, similar to a print ad.
In print ads, a subhead is a smaller headline that continues the idea introduced in the headline or provides more information. It usually appears below the headline and in a smaller typeface.
The body copy provides supporting information. Generally it appears in a standard, readable font. The call to action may be part of the body copy, or it may appear elsewhere in a larger typeface or color treatment to draw attention to itself.
A variety of brand elements may also appear in an advertisement. These include the name of the advertiser or brand being advertised, the logo, a tagline, hashtag, Web site link, or other standard “branded” elements that convey brand identity. These elements are an important way of establishing continuity with other marketing communications used in the IMC campaign or developed by the company. For example, print ads for an IMC campaign might contain a campaign-specific tagline that also appears in television ads, Website content, and social media posts associated with the campaign.
Ad Testing and Measurement

When organizations are poised to make a large investment in any type of advertising, it is wise to conduct marketing research to test the advertisements with target audiences before spending lots of money on ads and messages that may not hit the mark. Ad testing may preview messages and preliminary ad concepts with members of a target segment to see which ones resonate best and get insight about how to fine-tune messages or other aspects of the ad to make them more effective. Organizations may conduct additional testing with near-final advertising pieces to do more fine-tuning of the messages and visuals before going public.
To gauge the impact of advertising, organizations may conduct pre-tests and post-tests of their target audience to measure whether advertising has its intended effect. A pre-test assesses consumer attitudes, perceptions, and behavior before the advertising campaign. A post-test measures the same things afterward to determine how the ads have influenced the target audience, if at all.
Companies may also measure sales before, during, and after advertising campaigns run in the geographies or targets where the advertising appeared. This provides information about the return on investment for the campaign, which is how much the advertising increased sales relative to how much money it cost to execute. Ideally advertising generates more revenue and, ultimately profits, than it costs to mount the advertising campaign.
- Weissman, J. (2014, April 28). The decline of newspapers hits a stunning milestone. Slate. http://www.slate.com/blogs/moneybox/2014/04/28/decline_of_newspapers_hits_a_milestone_print_revenue_is_lowest_since_1950.html ↵
Advertising Functions and Strategies Copyright © by Enyonam Osei-Hwere and Patrick Osei-Hwere is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
<strong data-cart-timer="" role="text"></strong>
Flickr user BRICK 101, Creative Commons
- Visual Arts
- English & Literature
Media Awareness I: The Basics of Advertising How are consumers influenced by media marketing?
In this 6-8 lesson, students will examine the influence of advertising from past and present-day products. Students apply design principles to illustrate a product with background and foreground. This is the first lesson designed to accompany the media awareness unit.
Get Printable Version Copy to Google Drive
Lesson Content
- Preparation
- Instruction
Learning Objectives
Students will:
- Analyze print, video, and audio advertisements.
- Evaluate the influence that advertising exerts on people through the media.
- Interpret the purpose of advertising and what the term “target audience” means.
- Discuss interpretations and inferences from product or service advertisements.
- Use principles of art and design to create an advertisement of their own.
- Demonstrate an illustration with background and foreground.
Standards Alignment
National Core Arts Standards National Core Arts Standards
VA:Cr2.1.6a Demonstrate openness in trying new ideas, materials, methods, and approaches in making works of art and design.
VA:Cr2.1.7a Demonstrate persistence in developing skills with various materials, methods, and approaches in creating works of art or design.
VA:Cr2.1.8a Demonstrate willingness to experiment, innovate, and take risks to pursue ideas, forms, and meanings that emerge in the process of artmaking or designing
VA:Cr3.1.6a Reflect on whether personal artwork conveys the intended meaning and revise accordingly
VA:Cr3.1.7a Reflect on and explain important information about personal artwork in an artist statement or another format.
VA:Cr3.1.8a Apply relevant criteria to examine, reflect on, and plan revisions for a work of art or design in progress.
VA:Re.7.2.6a Analyze ways that visual components and cultural associations suggested by images influence ideas, emotions, and actions.
VA:Re.7.2.7a Analyze multiple ways that images influence specific audiences.
VA:Re.7.2.8a Compare and contrast contexts and media in which viewers encounter images that influence ideas, emotions, and actions.
VA:Re8.1.6a Interpret art by distinguishing between relevant and non-relevant contextual information and analyzing subject matter, characteristics of form and structure, and use of media to identify ideas and mood conveyed.
VA:Re8.1.7a Interpret art by analyzing artmaking approaches, the characteristics of form and structure, relevant contextual information, subject matter, and use of media to identify ideas and mood conveyed.
VA:Re8.1.8a Interpret art by analyzing how the interaction of subject matter, characteristics of form and structure, use of media, artmaking approaches, and relevant contextual information contributes to understanding messages or ideas and mood conveyed.
MA:Re7.1.6a Identify, describe, and analyze how message and meaning are created by components in media artworks.
MA:Re7.1.7a Describe, compare, and analyze the qualities of and relationships between the components in media artworks.
MA:Re7.1.8a Compare, contrast, and analyze the qualities of and relationships between the components and style in media artworks.
MA:Re8.1.6 Analyze the intent of a variety of media artworks, using given criteria.
MA:Re8.1.7 Analyze the intent and meaning of a variety of media artworks, using self developed criteria.
MA:Re8.1.8 Analyze the intent and meanings of a variety of media artworks, focusing on intentions, forms, and various contexts.
MA:Cn11.1.6a Research and show how media artworks and ideas relate to personal life, and social, community, and cultural situations, such as personal identity, history, and entertainment.
MA:Cn11.1.7a Research and demonstrate how media artworks and ideas relate to various situations, purposes and values, such as community, vocations, and social media.
MA:Cn11.1.8a Demonstrate and explain how media artworks and ideas relate to various contexts, purposes, and values, such as democracy, environment, and connecting people and places.
Common Core State Standards Common Core State Standards
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 6 topics, texts, and issues, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.1.A Come to discussions prepared, having read or studied required material; explicitly draw on that preparation by referring to evidence on the topic, text, or issue to probe and reflect on ideas under discussion.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.1.B Follow rules for collegial discussions, set specific goals and deadlines, and define individual roles as needed.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.1.C Pose and respond to specific questions with elaboration and detail by making comments that contribute to the topic, text, or issue under discussion.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.1.D Review the key ideas expressed and demonstrate understanding of multiple perspectives through reflection and paraphrasing.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.6.2 Interpret information presented in diverse media and formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) and explain how it contributes to a topic, text, or issue under study.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 7 topics, texts, and issues, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1.A Come to discussions prepared, having read or researched material under study; explicitly draw on that preparation by referring to evidence on the topic, text, or issue to probe and reflect on ideas under discussion.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1.B Follow rules for collegial discussions, track progress toward specific goals and deadlines, and define individual roles as needed.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1.C Pose questions that elicit elaboration and respond to others' questions and comments with relevant observations and ideas that bring the discussion back on topic as needed.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.1.D Acknowledge new information expressed by others and, when warranted, modify their own views.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.7.2 Analyze the main ideas and supporting details presented in diverse media and formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) and explain how the ideas clarify a topic, text, or issue under study.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.1 Engage effectively in a range of collaborative discussions (one-on-one, in groups, and teacher-led) with diverse partners on grade 8 topics, texts, and issues, building on others' ideas and expressing their own clearly.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.1.A Come to discussions prepared, having read or researched material under study; explicitly draw on that preparation by referring to evidence on the topic, text, or issue to probe and reflect on ideas under discussion.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.1.B Follow rules for collegial discussions and decision-making, track progress toward specific goals and deadlines, and define individual roles as needed.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.1.C Pose questions that connect the ideas of several speakers and respond to others' questions and comments with relevant evidence, observations, and ideas.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.1.D Acknowledge new information expressed by others, and, when warranted, qualify or justify their own views in light of the evidence presented.
ELA-LITERACY.SL.8.2 Analyze the purpose of information presented in diverse media and formats (e.g., visually, quantitatively, orally) and evaluate the motives (e.g., social, commercial, political) behind its presentation.
Recommended Student Materials
Editable Documents : Before sharing these resources with students, you must first save them to your Google account by opening them, and selecting “Make a copy” from the File menu. Check out Sharing Tips or Instructional Benefits when implementing Google Docs and Google Slides with students.
- Common Advertising Strategies
- Slide: Product Advertisements
- Product Discussion Questions
- Elements and Principles of Art
- Slide: Illustration Examples
- Criteria for Success: Product Illustration
Teacher Background
Teachers should use age-appropriate advertisements and products. Bring a collection of sample products for students to observe. Visit Advertising 101: Tips to Get you Started and review Common Advertising Strategies before teaching the lesson. Preview the other two lessons in the unit, Media Awareness II: Key Concepts in Advertising and Media Awareness III: Helping a Product Cross the Finish Line .
Student Prerequisites
Students should have a basic understanding of advertising and their favorite products.
Accessibility Notes
Provide preferential seating and captions for visual presentations. Give students the option to create an audio advertisement as opposed to a visual one.
- Display a few children’s products (games, cereals, toys, devices, DVDs, etc.) around the classroom. Ask students to “turn and talk” and answer the following question: What is one of your favorite products and why?
- Initiate a class discussion in which each student shares what they like/dislike about their product.
- Have all students brainstorm different categories of kid-oriented products. Create a “t-chart” with a running list of these products on one side, then write down the reasons for valuing each item on the other.
- Introduce students to the three-part lesson on advertising. Ask students, who have heard of the term “advertising?” How is advertising related to the product we listed on the “t-chart?”
- Distribute or display the resource, Common Advertising Strategies . Review the basics of advertising and marketing and inform the students that they will be using their knowledge to create an advertisement for their favorite kid-oriented product.
- Show the students examples of print and video ads from the Slide: Product Advertisements . Be mindful of any students that may need one type of advertisement over the other. See “Accessibility Accommodations” for modifications.
- Begin a discussion about advertisements. Ask: Would you want to buy this product? If so, what about the advertisement caught your attention? Who is the target audience for the advertisement? How do you know? Based on the Common Advertising Strategies resource, which marketing techniques do the advertisements use?
- Ask students to bring a favorite product from home. This can include food, a toy, or any product they enjoy.
- Have students divide into pairs or small groups and temporarily exchange with one another their product and the associated advertisement. This discussion will promote an enhanced understanding of advertising and the effect it can have on the audience. If for any reason the student does not have a product, allow them to choose a product from the teacher’s collection or one on the web.
- Display the Product Discussion Questions and encourage students to elaborate on their product.
- Allow students approximately 5 – 10 minutes to discuss their products. Then, ask each group to summarize their discussion points.
Reflect
- Distribute the Elements and Principles of Art resource to students and review the Criteria for Success: Product Illustration . Explain to students that the class will only focus on a few of the elements and principles for the next activity (students will draw his/her item from observation).
- Model the concept of using overlapping lines to create the illusion of foreground/background space in the picture plane. Show students the Slide: Illustration Examples to analyze the foreground/background space illusion technique. Also, do a quick sketch to illustrate the process in detail. The background will then be drawn in to show where the item is usually kept at home (shelf, drawer, etc.).
- Explain to students that this drawing will become an advertisement for their product.
- Distribute 18” x 12” newsprint paper and pencils and have students begin their drawings. Allow sufficient time for students to complete the assignment. Offer additional modeling and feedback for students who need support. Encourage them to collaborate with their classmates for constructive feedback.
- Assess students’ knowledge with a written response. Have students compare the various choices made in the placement of the object on the page and the principle of balance.
- Collect drawings, as students will use these drawings as a springboard during the next lesson.
- Ask students to bring in an example of an advertisement for a product to discuss during the next lesson.
- Using their notes from the discussion on kid-oriented products, students will expand upon their knowledge by researching various advertisements for the products they listed (games, CDs, interactive toys, etc.). Using a double-sided journal entry, each student will choose one type of product and then record the characteristics of the product’s advertisement. The ads can be television, radio, internet, or print ads. During the next lesson, have students report their findings.
- Have students review Digital Marketing strategies and infographic advertisements by visiting age-appropriate websites. Then have them create their own digital add or infographic using Animaker , Smore , or a graphic design tool like Google Drawings . This activity helps students to compare and contrast various websites and how they use marketing to attract consumers.
Advertisements

Radio Ad: Rocky Mountain Rides
Tonya Abari
JoDee Scissors
November 15, 2021
Related Resources
Lesson media awareness ii: key concepts in advertising.
In this 6-8 lesson, students will continue the exploration of advertising and media awareness. Students will examine the purpose, target audience, and value of advertisements. Students will then create original, hand-drawn advertisements. This is the second lesson designed to accompany the media awareness unit.

Lesson Media Awareness III: Crossing the Finish Line
In this 6-8 lesson, students will develop and market a new children’s product. They will apply advertising design strategies to market their product. This is the third lesson designed to accompany the media awareness unit.

Article Raising “Art Smart” Students in the 21st Century
So, what are 21st century skills exactly? Why do they matter to “art smart” parents and how do we help our kids?
- Life Skills

Collection Media Arts
Audio, video, animation, photography, and technology. From Depression-era images that captured the attention of a nation, to student-produced videos on local artists, to how to make your own blood and guts special effects, explore the ever-changing world of media arts.

Kennedy Center Education Digital Learning
Eric Friedman Director, Digital Learning
Kenny Neal Manager, Digital Education Resources
Tiffany A. Bryant Manager, Operations and Audience Engagement
Joanna McKee Program Coordinator, Digital Learning
JoDee Scissors Content Specialist, Digital Learning
Connect with us!
Generous support for educational programs at the Kennedy Center is provided by the U.S. Department of Education. The content of these programs may have been developed under a grant from the U.S. Department of Education but does not necessarily represent the policy of the U.S. Department of Education. You should not assume endorsement by the federal government.
Gifts and grants to educational programs at the Kennedy Center are provided by A. James & Alice B. Clark Foundation; Annenberg Foundation; the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation; Bank of America; Bender Foundation, Inc.; Carter and Melissa Cafritz Trust; Carnegie Corporation of New York; DC Commission on the Arts and Humanities; Estée Lauder; Exelon; Flocabulary; Harman Family Foundation; The Hearst Foundations; the Herb Alpert Foundation; the Howard and Geraldine Polinger Family Foundation; William R. Kenan, Jr. Charitable Trust; the Kimsey Endowment; The King-White Family Foundation and Dr. J. Douglas White; Laird Norton Family Foundation; Little Kids Rock; Lois and Richard England Family Foundation; Dr. Gary Mather and Ms. Christina Co Mather; Dr. Gerald and Paula McNichols Foundation; The Morningstar Foundation;
The Morris and Gwendolyn Cafritz Foundation; Music Theatre International; Myra and Leura Younker Endowment Fund; the National Endowment for the Arts; Newman’s Own Foundation; Nordstrom; Park Foundation, Inc.; Paul M. Angell Family Foundation; The Irene Pollin Audience Development and Community Engagement Initiatives; Prince Charitable Trusts; Soundtrap; The Harold and Mimi Steinberg Charitable Trust; Rosemary Kennedy Education Fund; The Embassy of the United Arab Emirates; UnitedHealth Group; The Victory Foundation; The Volgenau Foundation; Volkswagen Group of America; Dennis & Phyllis Washington; and Wells Fargo. Additional support is provided by the National Committee for the Performing Arts.
Social perspectives and language used to describe diverse cultures, identities, experiences, and historical context or significance may have changed since this resource was produced. Kennedy Center Education is committed to reviewing and updating our content to address these changes. If you have specific feedback, recommendations, or concerns, please contact us at [email protected] .
By using this site, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms & Conditions which describe our use of cookies.
Reserve Tickets
Review cart.
You have 0 items in your cart.
Your cart is empty.
Keep Exploring Proceed to Cart & Checkout
Donate Today
Support the performing arts with your donation.
To join or renew as a Member, please visit our Membership page .
To make a donation in memory of someone, please visit our Memorial Donation page .
- Custom Other


Guiding Principles of the Advertising
1. Legal 1.1 Advertisers have primary responsibility for ensuring that their products and advertisements are legal.
1.2 Advertisements should comply with the law and should not incite anyone to break it.
1.3 Advertisers must not state or imply that a product can legally be sold if it cannot.
1.4 Advertisements should not contain anything which might lead or lend support to criminal, illegal or reckless activities, nor should they appear to condone such activities.
1.5 Advertisers must ensure advertisements are placed on legitimate platforms which are in compliance with the law.
2. Truthful Presentation 2.1 All descriptions, claims and comparisons which relate to matters of objectively ascertainable fact should be capable of substantiation, and advertisers and advertising agencies are required to hold such substantiation ready for scrutiny without delay to the Advertising Standards Malaysia.
3. Social Responsibility 3.1 Advertisements should not without justifiable reason play on fear exploit misfortune or suffering.
3.2 Advertisements should not exploit consumers who are superstitious.
3.3 Advertisements should not contain anything which might lead or lend support to acts of violence or anti-social behaviour, nor should they appear to condone such acts.
3.4 Advertisements should respect human dignity and should not incite or condone any form of discrimination, including that based upon ethnic or national origin, religion, gender, age, disability or sexual orientation.
3.5 Advertisements should not disparage or cause unfair comparison.
4. Honesty 4.1 Advertisements should not be framed so as to abuse the trust of the consumer or exploit his lack of experience or knowledge.
5. Decency 5.1 Advertisements should not contain statements or visual presentations offensive to the standards of decency prevailing among those who are likely to be exposed to them.
TYPES OF ADVERTISEMENTS 1. Claims 1.1 Advertisements should not contain any statements or visual presentation which directly or by implication, omission, ambiguity, or exaggerated claim, that is likely to mislead the consumer about the product advertised, the advertiser, or about any other product or advertiser, in particular with regard to:
(i) Characteristics such as nature, composition, method and date of manufacture, fitness for purpose, range of use, quantity, and commercial or geographical origin.
(ii) Value or total price actually to be paid.
(iii) Other terms of purchase, such as hire purchase and credit sale.
(iv) Conditions of delivery, exchange, return, repair and maintenance
(v) The terms of any guarantee.
(vi) Copyright and industrial property rights such as patents, trademarks, designs and models, and trade names.
(vii) Official or other recognition of approval, awards or medals, prizes or diplomas.
(viii) Scientific, statistical, or other research data quoted in advertisements should be neither misleading nor irrelevant.
1.2 It is seldom possible to substantiate general claims by an advertiser that his product is of superlative quality (best, finest) in a manner which is universally acceptable. Such claims, however, are permissible under this Code, provided that their inclusion in an advertisement does not create a false impression concerning any quality possessed by the product which is capable of assessment in the light of generally accepted standards of judgment.
1.3 Obvious hyperbole, which is intended to attract attention or to amuse, is permissible provided that it is not likely to be taken as a positive claim to superior or superlative status.
1.4 Where a substantial division of informed opinion exists or may reasonably be expected to exist, as to the acceptability of any evidence which is required to substantiate a claim in an advertisement, it should neither state nor imply that the claim is universally true or that it enjoys universal support, nor that it represents anything other than the advertiser’s opinion or of such other authorities as may be named.
1.5 Advertisements should not misuse research results or quotations from technical and scientific literature. Statistics should not be presented so as to imply that they have greater validity than is the case. Scientific terms should not be misused, and scientific jargon and irrelevances should not be used to make claims appear to have scientific basis they do not possess.
1.6 Where advertisement claims are expressly stated to be based on, or supported by, independent research or assessment, the source and the date of this should be indicated. Where this is not possible, for whatever reason, such claims to independent support should not be made. Where a claim relating to research or testing is based on the advertiser’s own work or work done at his request, it should be clear form the text of the advertisement that such is the basis of the claim.
2. Value of Goods 2.1 So far as is relevant, the following provisions apply to claims as to the value of service or facilities offered by way of advertisement as well as to the value of goods.
2.2 Consumers should not be led to overestimate the value of goods whether by exaggeration or through unrealistic comparisons with other goods or prices.
2.3 Advertisers should be ready to substantiate any claim made as to the value in cash terms of goods offered at a lower price or given free; and any saving to the consumer claimed to result from the offer of goods at a price lower than their actual value.
2.4 Substantiation should be by reference to the actual price(s) of identical goods, or goods of a directly comparable kind and quality, which are generally available.
2.5 Where a comparison is made between the respective cash values or prices of goods which are not identical, the advertiser should clearly indicate that this is the case. 2.6 Reference to recommended retail prices will not be accepted as substantiation for
value of saving claims in the absence of information of the kind required in 4.3.4 as to the price at which the goods are currently on general sale.
2.7 In calculating a notional retail value of goods which is exclusive to him, or for which no direct standard of comparison exists, the advertiser should add to the cost of the goods to him a reasonable mark-up only, bearing in mind the widespread availability of many goods at substantial discounts. He should also make clear that the advertised goods are available from him only and that consequently the value claimed is his own assessment and does not relate to the actual cost of similar goods.
3. Use of the Word “Free” 3.1 Products should not be described as “free” where there is any cost to the consumer, aside from, the actual cost of any delivery, freight or postage. Where such costs are payable by the consumer, then this must be clearly stated in the advertisement. 3.2 Where a claim is made that the purchase of one product includes another product to be provided “free”, the advertiser should be able to show that he will not be able immediately and directly to recover the cost of supplying the “free” product whether in whole or in part.
3.3 In particular, an advertisement in these circumstances should not make an attempt to recover the cost to the advertiser of the product by such methods as the imposition of packing and handling charges; inflating the true cost of delivery, freight or postage; an increase in the usual price of the product with which the “free” product is offered; a reduction in its quality, or quantity.
3.4 A trial may be described as ‘’free’ although the consumer is expected to pay the cost of returning the goods, provided that the advertisement makes this clear.
4. “Up to…” and “from…” claims 4.1 Claims, whether as to prices or performance, which use formulae such as ‘up to X km per litre’ or ‘prices from as low RMX.XX’ are not acceptable where there is a likelihood of the consumer being misled as to the availability or as to the applicability of the benefits offered. Such claims should not be used:
(i) When the price or other advantage claimed bears no relation to the general level of prices or benefits, and in particular where it does not apply to the goods or services actually advertised or to more than an insignificant proportion of them.
(ii) When the claims apply to spoilt or imperfect goods, or to goods or services, which are in some respect less complete, or subject to greater limitations than the
bulk of those not on offer.
5. Direct Supply 5.1 Claims that goods are available ‘direct from the manufacturer’ and the like are not acceptable where the advertiser cannot substantiate the implication that the consumer will benefit, usually in cash terms, from the elimination of one stage or more than in the normal process of distribution.
6. Wholesale 6.1 No advertisement should state or imply that goods offered for retail are being offered at wholesale prices unless the advertiser can prove that the prices in question are not higher than those which are currently sold to the retail trade.
6.2 For the purpose of this ruling, a wholesaler is defined as a merchant who purchases stocks for supply to retailers and other classes of trade buyers.
7. Comparisons 7.1 Advertisements containing comparisons with other advertisers, or other products are permissible in the interest of vigorous competition and public information, provided they comply with the terms of the Code.
7.2 The subject matter of a comparison should not be chosen in such a way as to confer an artificial advantage upon the advertiser or so as to suggest that a better bargain is offered than is truly the case.
7.3 Points of comparison should be based on facts which can be substantiated and should not be unfairly selected. In particular: (i) The basis of comparison should be the same for all the products being compared and should be clearly stated in the advertisement so that it can be seen that like is being compared with like.
(ii) Where items are listed and compared with those of competitors’ products, the list should be complete or else the advertisement should make clear that the items are only a selection.
8. Disparagement and Denigration 8.1 Advertisements should not attack or discredit other products, advertisers or advertisements directly or by implication.
8.2 An advertisement should not contain derogatory remarks or innuendoes about any person or organisation. It must not criticise, directly or by inference, the Government of any country.
8.3 Advertisements should not contain any statement that either expressly or by implication disparage any profession, products, service or advertiser in an unfair or misleading way.
9. Exploitation of Name or Goodwill 9.1 Advertisements should not make unjustifiable use of the name or any initials of any firm, company or institution.
9.2 Advertisements should not take unfair advantage of the goodwill attached to the trade name or symbol of another firm or its products, or the goodwill acquired by its advertising campaign.
9.3 Attention is drawn to the provision governing the use of the Malaysian Arms and Flag, and the National Anthem. Details may be obtained from the offices of the Prime Minister or the Ministry of Arts, Culture and Heritage.
10. Imitation 10.1 Advertisements should not be so similar in general layout, copy, slogans, visual presentation, music or sound effects to other advertisements as to be likely to mislead or confuse.
10.2 Particular care should be taken in the packaging and labelling of goods to avoid causing confusion with competing products.
11. Testimonials 11.1 Advertisements should not contain or refer to any testimonial or endorsement unless it is genuine and related to the personal experience over a reasonable period of time of the person giving it. Testimonials or endorsements which are obsolete or otherwise no longer applicable, (e.g. where there has been a significant change in formulation of the product concerned) should not be used.
11.2 Testimonials per se should not contain any statement or implication contravening the provisions of this Code and should not be used in a manner likely to mislead. 11.3 Testimonials should not make any claim to efficacy which cannot justifiably be attributed to the use of the product. Any specific or measurable results claimed should be fairly presented. Where ‘before’ and ‘after’ claims are made, they should be expressed and illustrated in such a way as to permit a fair comparison to be made.
11.4 Where any testimonial contains an expression which conflicts with this Code, the advertiser may amend the testimonial so as to remove the source of conflict,
provided that, in so doing, he does not distort the sense of original views expressed by the person giving the testimonial.
11.5 Testimonials from persons resident outside Malaysia are not acceptable unless an indication of their address and country of residence is given in the advertisement.
11.6 Particular care should be taken to ensure that advertisements based upon fictitious characters are not framed so as to give the impression that real people are involved; in particular they should not contain ‘testimonials’ or ‘endorsements’ which may give such an impression. Where an illustration of a person is used in conjunction with a testimonial implying personal endorsement of the product, that person should be the person giving the testimonial.
11.7 Advertisers and their agencies should hold ready copies of any testimonials used in advertising for inspection by the Advertising Standards Malaysia. Such copies should be signed and dated by the persons providing the testimonials, and should confirm what is said in any advertisement. When an advertisement containing a testimonial is submitted for the first time for publication, a copy of the testimonial statement should accompany the advertisement, for the publisher’s retention.
11.8 Where a testimonial is given by a person with professional qualifications, care should be taken that in indicating those qualifications the advertiser does not cause the person giving the testimonial to transgress any regulations of the professional institution(s) to which he belongs.
12. Protection of Privacy and Exploitation of the Individual 12.1 Advertisements should not, except in circumstances noted in 10.2 portray or refer to by whatever means, any living person, unless their express prior permission has been obtained. This requirement applies to all persons, including public figures and foreign nationals. Advertisers should also take care not to offend the religious or other susceptibilities of those connected in any way with deceased persons depicted or referred to in any advertisement.
12.2 This ruling does not apply to:- (i) The use of crowd background shots in which individuals are recognizable, provided that neither the portrayal, nor the context in which they appear, is defamatory, offensive or humiliating. However, an advertiser should withdraw any such advertisements if a reasonable objection is received from a person depicted;
(ii) Advertisements for books, films, radio or television programmes, press
features and the like in which there appear portrayals or references to individuals who form part of their subject matter;
(iii) To police or other official notices; and
(iv) The rare occasions when in the opinion of ASA the reference and portrayal in question is not inconsistent with the subject’s right to a reasonable degree of privacy, and does not constitute an unjustifiable commercial exploitation of his fame or reputation.
13. Safety 13.1 Advertisements should not, without justifiable reason, show or refer to dangerous practices or manifest a disregard for safety. Special care should be taken in advertisements directed towards or depicting children or young people.
14. Guarantees 14.1 Advertisements should not contain any reference to a ‘guarantee’ or ‘warranty’ which takes away or diminishes any rights which would otherwise be enjoyed by consumers; purport so to do; or may be understood by the consumer as so doing.
14.2 Where an advertisement expressly offers, in whatever form, a guarantee or warranty as to the quality, life, composition, origin, duration, etc. of any product, the full terms of that guarantee should be available in printed form for the consumer to inspect and, normally, to retain before he makes the purchase.
14.3 Even if there is a money back undertaking, (for which see 13 below) words like ‘guarantee’, ‘guaranteed’, should not be used merely to emphasise that a factual description is true, e.g. ‘guaranteed pure orange juice;’ ‘ guaranteed to contain 20% protein.’ Nor should the words be used merely for descriptive purpose. E.g. guaranteed goodness; guaranteed satisfaction. Otherwise the term is validly used in cases where a material, remedial action is offered in addition to that already required by law or accepted trade practice, or where it is clearly used colloquially, not importing any obligation. e.g. guaranteed to brighten the dullest room.
14.4 Phrases such as ‘satisfaction guaranteed’, ‘unconditionally guaranteed’ and the like which are not specific as to terms, duration and limitation on availability, may be used only where a full refund will be given, at the option of the purchaser, throughout the reasonably anticipated life of the product, against any defect or damage arising as a result of the fault of the manufacturer or retailer.
15. Money-Back Undertakings 15.1 Neither guarantee or warranty, nor any word derived from either should be used in an advertisement to describe or refer to an undertaking, the substance of which is merely to refund the price of a product within a brief trial period to dissatisfied purchasers. Where such an undertaking is given in an advertisement the time within which claims must be made by the consumer should be clearly stated and should make due allowance for the time taken for delivery and return of the product.
16. Stridency 16.1 No advertisements should use disturbing or irritating sound effects where sound is incorporated.
17. Sensitivities 17.1 No advertisement should make any irrelevant references to any name, incident, concept or religious significance.
17.2 No advertisement should contain statements or suggestions which may offend the religious, political, sentimental or racial susceptibilities of any community.
17.3 No attempt should be made to exploit any abnormal national or international events or conditions.
18. Subliminal Advertising 18.1 No advertisements may include any technical device which, by using images of very brief duration or by any other means, exploits the possibilities of conveying a message to, or otherwise influencing the minds of members of an audience without their being aware, or fully aware, of what has been done.
19. Outdoor 19.1 Posters or billboards (except those under the auspices of government or other recognized bodies) are prohibited, if such posters and billboards:
(i) depict murder, scenes of terror, horror or acts of violence;
(ii) are calculated to demoralize, or could be held to extenuate crime or incite its commission;
(iii) depict or refer to indecency, obscenity, nudity or striptease;
(iv) are likely, through wording, design or possible defacement, to offend the travelling public.
20. Identification of Advertisements 20.1 Advertisements should be clearly distinguishable as such, whatever their form and whatever the medium used. When an advertisement appears in a medium which contains news, editorial or programme matter it should be so designed, produced and presented that it will be readily recognized as an advertisement.
20.2 There is an obligation on all concerned with the preparation and/or publication of an advertisement to ensure that anyone who looks at the advertisement is able to see, without looking at it closely, that it is an advertisement and not an editorial matter.
20.3 In the case of a single advertisement, the following guidelines should apply: (i) If the advertisement occupies less than half a page, it should be boxed- in completely; if half-page or more, it should be separated from any adjacent matter by a distinct border.
(ii) By-lines of staff journalists should not be used. It is, however, permissible to publish by-lines of experts and well-known public figures.
(iii) Particular care should be taken wherever the size and style of type in the advertisement is the same as, or closely resembles, that of the editorial matter.
20.4 Where paid-for space is in the style of an editorial, whether paid for by the same or different advertisers, particular care is needed to ensure that no part can be mistaken for editorial matter. The word ADVERTISEMENT should stand alone, at the head of the advertisement in such size and weight and type as to be easily seen.
20.5 As a general rule, where an advertisement or series of advertisements paid for by the same organization or by organizations under the same control extends over more than one page, the word ADVERTISEMENT should be printed at the head of each page in such a way that a reader cannot fail to see it. Similarly where a supplement is paid for wholly by an advertiser or advertisers, it should normally be headed in bold letters with the words ADVERTISING FEATURE, and carry the word(s) ADVERTISEMENT or ADVERTISING FEATURE at the head of each page.
20.6 No guidance can cover every case. It may not be enough merely to follow to the letter what is said above. It may also be necessary to re- look at each advertisement to ensure it is clearly distinguishable from the editorial content of the publication.
21. Switch Selling 21.1 Direct sale advertising is that placed by an advertiser with the intention that the products or services advertised, or some other products or services, should be sold or provided at the home of any person responding to the advertisement.
21.2 Direct sale advertisements are not acceptable without adequate assurances from the advertiser and his advertising agency that the products advertised will be available at the price stated in the advertisement within a reasonable time to be specified by the advertiser from stock sufficient to meet potential demand; and that sales representatives when calling upon persons responding to the advertisement will demonstrate and make available for sale the products advertised.
21.3 It will be taken as prima facie evidence of misleading and unacceptable bait advertising for the purpose of switch selling if an advertiser’s salesman seriously disparages or belittles the cheaper article advertised or indicate unreasonable delays in obtaining delivery or otherwise places difficulties in the way of its purchase.20. Unsolicited Home Visits
21.1 Where it is the intention of an advertiser to send a representative to call on respondents to his advertisement such fact must be apparent from the advertisement or from any particulars subsequently supplied; and the respondent must be given an adequate opportunity to refuse any such call.
22. Inertia Selling 22.1 If it is established that an advertiser is using his advertisements as a means to supply unsolicited goods, for which payment is later, demanded, his advertisement should no longer be accepted.
23. Non-Availability of Advertised Products 23.1 Advertisements should not be submitted for publication unless the advertiser has reasonable grounds to believe that he can supply any demand likely to be created by his advertising.
23.2 In particular, no attempt should be made to use the advertising of unavailable or non-existent products as a means of assessing likely public demand, should such a product be offered in the future.
23.3 Where it becomes clear that an advertised product is notavailable,(in circumstances where the public are not likely to assume from advertising its ready availability) immediate action should be taken to ensure that future advertisements for the product are promptly amended or withdrawn.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Facilitate a sense of responsiveness, trust and demand. Semiotics. Semiotics, or the study of symbols and signs, is a common technique used in advertising. Popular brands and companies use unique ...
In marketing and advertising, visuals are used to communicate brand messages, showcase products and services, and connect with consumers on an emotional level. For example, a company may use an image of a happy family enjoying a product to convey a sense of happiness and well-being associated with their brand. Similarly, a fashion brand may use ...
May 22, 2020. Visual communication is a way to communicate ideas graphically in ways that are efficient and help to convey more meaning. It's a critical element of any content marketing strategy. This is because visuals can help to evoke emotions in your audience, provide stronger examples for your message and so much more.
There are two main visual paths: the "z-shaped" path and the "f-shaped" path. The z-shaped path means our eyes move across the content in a zigzag, going back and forth on the diagonal. The f-shaped path is similar to how we would read a block of text, back and forth in straight lines. Be intentional in the visual path you want to use.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls. To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It's like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable. 8.
Visual engagement is necessary for successful brand marketing. It helps customers remember you. Visual engagement involves creating opportunities for people to interact with your brand's visual content through social media. This article reflects on the importance of visual engagement and how it can change your brand game. Written By.
January 30, 2023 / Blog. Visual communication in marketing leverages the power of visual elements such as images, graphics, videos, and interactive content to effectively convey a message or story. It is a strategy that aims to grab attention, strengthen brand recognition, and enhance communication with the target audience.
Visual elements in advertising have the power to convey complex ideas or messages in a simple and concise manner. A well-designed visual, such as an infographic, can communicate a lot of information at a glance, making it easier for the audience to understand and remember the message being conveyed. Creating well-made visuals that bring a ...
Sensory marketing explores the five senses to connect the audience to the brand with the objective of conversion. Therefore, a visual presentation needs to be very well thought out by the responsible designer during its development and construction. In this area, presentations are constant.
When visual images are combined together, they create a powerful presentation that can effectively communicate any message. Graphic design is one of the six main categories within visual communication; it uses visuals to create layouts and designs. Advertising also falls into this category as it uses visuals to promote products or services.
Here are some simple tips our agency follows when using images and videos to promote our clients' brands: • Use high-quality visuals. • Tell a story with your visuals. • Be consistent with ...
The Purpose of Advertising. Advertising has three primary objectives: to inform, to persuade, and to remind. Informative Advertising creates awareness of brands, products, services, and ideas. It announces new products and programs and can educate people about the attributes and benefits of new or established products.
To our knowledge, this is the first article that provides an image-based strategy for SMIs to overcome the negative effects of ad recognition. It extends persuasion knowledge theory by showing that advertisers can leverage consumers' recognition of persuasion attempts to their advantage by adjusting the visual presentation of commercial elements.
It has been responsible for many classic adverts and advertising icons. The Verbal and the Visual 203 includes the quotation in English togeth er with the author's name.
Several factors seem to hold back scholarship in advertising creativity: (1) contrasting empirical results on its effects in terms of ad and brand outcomes (e.g., Lee and Mason 1999; Smith, Chen, and Yang 2008; Till and Baack 2005), (2) disagreements over what creativity is and how it should be assessed (e.g., Modig and Dahlen 2019; Smith, Chen, and Yang 2008), (3) limited understanding of ...
Analyze print, video, and audio advertisements. Evaluate the influence that advertising exerts on people through the media. Interpret the purpose of advertising and what the term "target audience" means. Discuss interpretations and inferences from product or service advertisements. Use principles of art and design to create an advertisement ...
Click the card to flip 👆. 1. grab attention. visuals are better at getting/keeping attention. 2. stick in memory. visuals persist in mind because people remember messages as visual fragments/key images. 3. cement belief. seeing is believing. 4. tell interesting stories.
Guiding Principles of the Advertising. 1. Legal. 1.1 Advertisers have primary responsibility for ensuring that their products and advertisements are legal. 1.2 Advertisements should comply with the law and should not incite anyone to break it. 1.3 Advertisers must not state or imply that a product can legally be sold if it cannot.
Responsible for the nonverbal aspect of the message, the design, which determines the visual look and intuitive feel of the ad. Creative Director (typically a former copywriter or art director), who is ultimately responsible for the creative product--the form the final ad takes. Creatives. The people who work in the creative department.
Visual Merchandising - Retail also is responsible for designing visual vehicles to introduce new products and initiative to retailers and creating visual product presentations for in-store promotions and special events that build market share and maximize sales and profit per square foot of retail selling space.
ADV CH 8. The term "creatives" refers to the. -final presentation of an advertising and marketing campaign to the client. -people who work in the creative department. -most important elements of the marketing mix. -roles played by all of the people within an advertising agency. -stages of integration between the visual and nonvisual elements of ...
B) the creative director. The term "creatives" refers to the A) people who work in the creative department. B) most important elements of the marketing mix. C) roles played by all of the people within an advertising agency. D) stages of integration between the visual and nonvisual elements of an ad.
A. people who work in the creative department. B. most important elements of the marketing mix. C. roles played by all of the people within an advertising agency. D. stages of integration between the visual and nonvisual elements of an ad. E. final presentation of an advertising and marketing campaign to the client.