
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

8.3 Social Class in the United States
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish objective and subjective measures of social class.
- Outline the functionalist view of the American class structure.
- Outline the conflict view of the American class structure.
- Discuss whether the United States has much vertical social mobility.
There is a surprising amount of disagreement among sociologists on the number of social classes in the United States and even on how to measure social class membership. We first look at the measurement issue and then discuss the number and types of classes sociologists have delineated.
Measuring Social Class
We can measure social class either objectively or subjectively . If we choose the objective method, we classify people according to one or more criteria, such as their occupation, education, and/or income. The researcher is the one who decides which social class people are in based on where they stand in regard to these variables. If we choose the subjective method, we ask people what class they think they are in. For example, the General Social Survey asks, “If you were asked to use one of four names for your social class, which would you say you belong in: the lower class, the working class, the middle class, or the upper class?” Figure 8.3 “Subjective Social Class Membership” depicts responses to this question. The trouble with such a subjective measure is that some people say they are in a social class that differs from what objective criteria might indicate they are in. This problem leads most sociologists to favor objective measures of social class when they study stratification in American society.
Figure 8.3 Subjective Social Class Membership
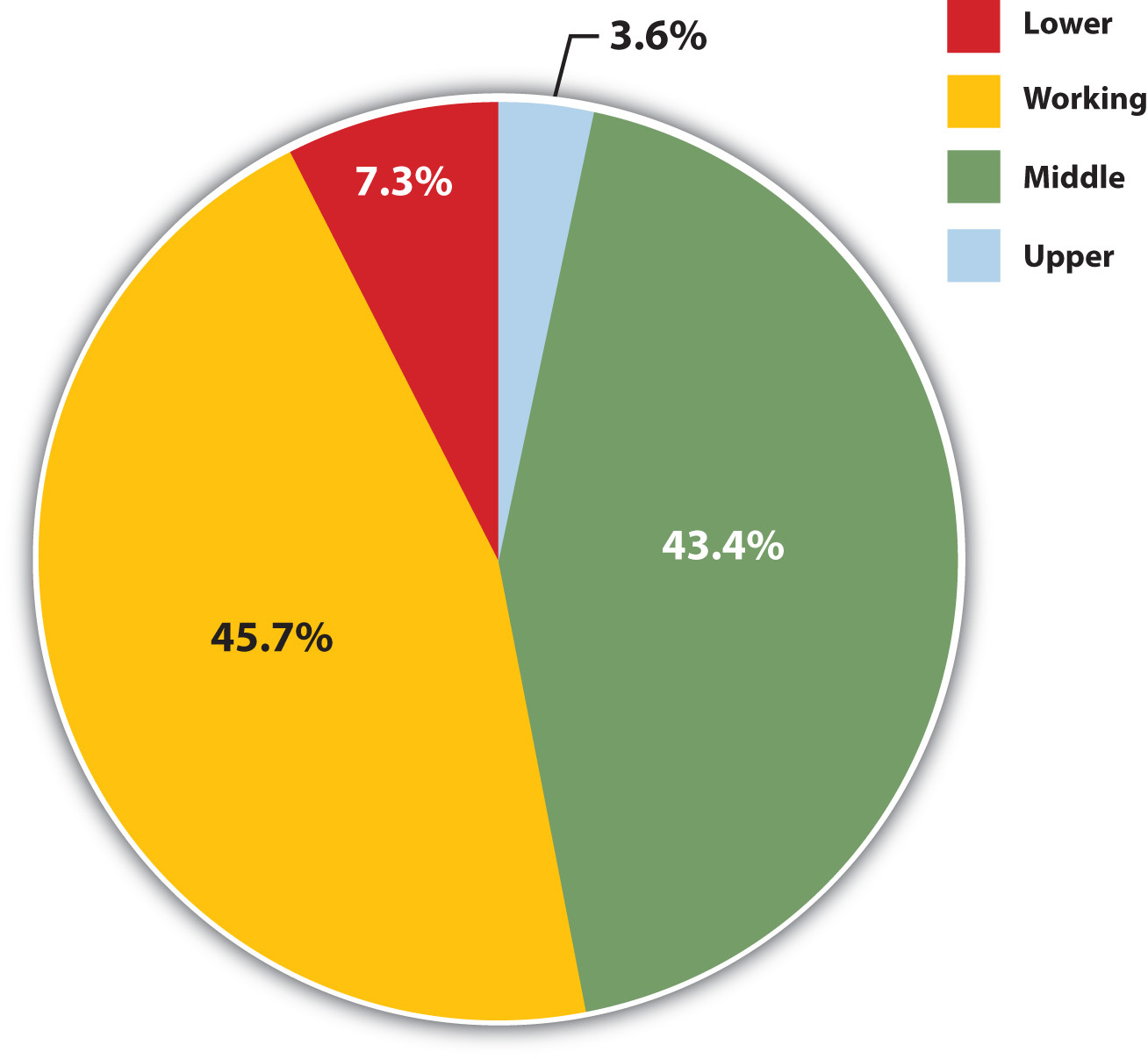
Source: Data from General Social Survey, 2008.
Yet even here there is disagreement between functionalist theorists and conflict theorists on which objective measures to use. Functionalist sociologists rely on measures of socioeconomic status (SES) , such as education, income, and occupation, to determine someone’s social class. Sometimes one of these three variables is used by itself to measure social class, and sometimes two or all three of the variables are combined (in ways that need not concern us) to measure social class. When occupation is used, sociologists often rely on standard measures of occupational prestige. Since the late 1940s, national surveys have asked Americans to rate the prestige of dozens of occupations, and their ratings are averaged together to yield prestige scores for the occupations (Hodge, Siegel, & Rossi, 1964). Over the years these scores have been relatively stable. Here are some average prestige scores for various occupations: physician, 86; college professor, 74; elementary school teacher, 64; letter carrier, 47; garbage collector, 28; and janitor, 22.
Despite SES’s usefulness, conflict sociologists prefer different, though still objective, measures of social class that take into account ownership of the means of production and other dynamics of the workplace. These measures are closer to what Marx meant by the concept of class throughout his work, and they take into account the many types of occupations and workplace structures that he could not have envisioned when he was writing during the 19th century.
For example, corporations have many upper-level managers who do not own the means of production but still determine the activities of workers under them. They thus do not fit neatly into either of Marx’s two major classes, the bourgeoisie or the proletariat. Recognizing these problems, conflict sociologists delineate social class on the basis of several factors, including the ownership of the means of production, the degree of autonomy workers enjoy in their jobs, and whether they supervise other workers or are supervised themselves (Wright, 2000).
The American Class Structure
As should be evident, it is not easy to determine how many social classes exist in the United States. Over the decades, sociologists have outlined as many as six or seven social classes based on such things as, once again, education, occupation, and income, but also on lifestyle, the schools people’s children attend, a family’s reputation in the community, how “old” or “new” people’s wealth is, and so forth (Coleman & Rainwater, 1978; Warner & Lunt, 1941). For the sake of clarity, we will limit ourselves to the four social classes included in Figure 8.3 “Subjective Social Class Membership” : the upper class, the middle class, the working class, and the lower class. Although subcategories exist within some of these broad categories, they still capture the most important differences in the American class structure (Gilbert, 2011). The annual income categories listed for each class are admittedly somewhat arbitrary but are based on the percentage of households above or below a specific income level.
The Upper Class
Depending on how it is defined, the upper class consists of about 4% of the U.S. population and includes households with annual incomes (2009 data) of more than $200,000 (DeNavas-Walt, Proctor, & Smith, 2010). Some scholars would raise the ante further by limiting the upper class to households with incomes of at least $500,000 or so, which in turn reduces this class to about 1% of the population, with an average wealth (income, stocks and bonds, and real estate) of several million dollars. However it is defined, the upper class has much wealth, power, and influence (Kerbo, 2009).

The upper class in the United States consists of about 4% of all households and possesses much wealth, power, and influence.
Steven Martin – Highland Park Mansion – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Members of the upper-upper class have “old” money that has been in their families for generations; some boast of their ancestors coming over on the Mayflower . They belong to exclusive clubs and live in exclusive neighborhoods; have their names in the Social Register ; send their children to expensive private schools; serve on the boards of museums, corporations, and major charities; and exert much influence on the political process and other areas of life from behind the scenes. Members of the lower-upper class have “new” money acquired through hard work, lucky investments, and/or athletic prowess. In many ways their lives are similar to those of their old-money counterparts, but they do not enjoy the prestige that old money brings. Bill Gates, the founder of Microsoft and the richest person in the United States in 2009, would be considered a member of the lower-upper class because his money is too “new.” Because he does not have a long-standing pedigree, upper-upper class members might even be tempted to disparage his immense wealth, at least in private.
The Middle Class
Many of us like to think of ourselves in the middle class, as Figure 8.3 “Subjective Social Class Membership” showed, and many of us are. The middle class includes the 46% of all households whose annual incomes range from $50,000 to $199,999. As this very broad range suggests, the middle class includes people with many different levels of education and income and many different types of jobs. It is thus helpful to distinguish the upper-middle class from the lower-middle class on the upper and lower ends of this income bracket, respectively. The upper-middle class has household incomes from about $150,000 to $199,000, amounting to about 4.4% of all households. People in the upper-middle class typically have college and, very often, graduate or professional degrees; live in the suburbs or in fairly expensive urban areas; and are bankers, lawyers, engineers, corporate managers, and financial advisers, among other occupations.

The upper-middle class in the United States consists of about 4.4% of all households, with incomes ranging from $150,000 to $199,000.
Alyson Hurt – Back Porch – CC BY-NC 2.0.
The lower-middle class has household incomes from about $50,000 to $74,999, amounting to about 18% of all families. People in this income bracket typically work in white-collar jobs as nurses, teachers, and the like. Many have college degrees, usually from the less prestigious colleges, but many also have 2-year degrees or only a high school degree. They live somewhat comfortable lives but can hardly afford to go on expensive vacations or buy expensive cars and can send their children to expensive colleges only if they receive significant financial aid.
The Working Class

The working class in the United States consists of about 25% of all households, whose members work in blue-collar jobs and less skilled clerical positions.
Lisa Risager – Ebeltoft – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Working-class households have annual incomes between about $25,000 and $49,999 and constitute about 25% of all U.S. households. They generally work in blue-collar jobs such as factory work, construction, restaurant serving, and less skilled clerical positions. People in the working class typically do not have 4-year college degrees, and some do not have high school degrees. Although most are not living in official poverty, their financial situation is very uncomfortable. A single large medical bill or expensive car repair would be almost impossible to pay without going into considerable debt. Working-class families are far less likely than their wealthier counterparts to own their own homes or to send their children to college. Many of them live at risk for unemployment as their companies downsize by laying off workers even in good times, and hundreds of thousands began to be laid off when the U.S. recession began in 2008.
The Lower Class
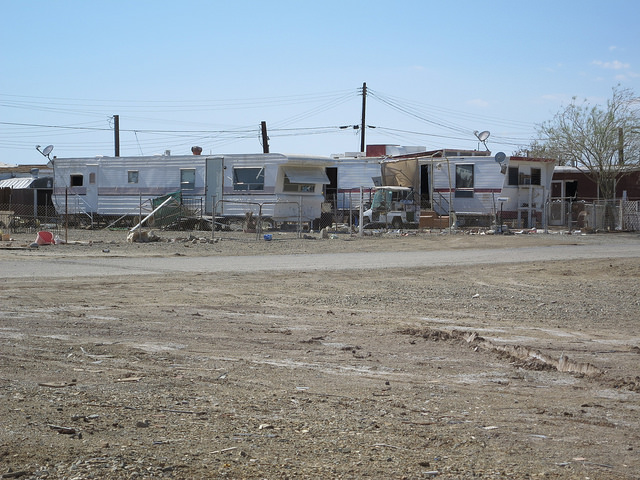

The lower class or poor in the United States constitute about 25% of all households. Many poor individuals lack high school degrees and are unemployed or employed only part time.
Chris Hunkeler – Trailer Homes – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Although lower class is a common term, many observers prefer a less negative-sounding term like the poor, which is the term used here. The poor have household incomes under $25,000 and constitute about 25% of all U.S. households. Many of the poor lack high school degrees, and many are unemployed or employed only part time in semiskilled or unskilled jobs. When they do work, they work as janitors, house cleaners, migrant laborers, and shoe shiners. They tend to rent apartments rather than own their own homes, lack medical insurance, and have inadequate diets. We will discuss the poor further when we focus later in this chapter on inequality and poverty in the United States.
Social Mobility
Regardless of how we measure and define social class, what are our chances of moving up or down within the American class structure? As we saw earlier, the degree of vertical social mobility is a key distinguishing feature of systems of stratification. Class systems such as in the United States are thought to be open, meaning that social mobility is relatively high. It is important, then, to determine how much social mobility exists in the United States.
Here we need to distinguish between two types of vertical social mobility. Intergenerational mobility refers to mobility from one generation to the next within the same family. If children from poor parents end up in high-paying jobs, the children have experienced upward intergenerational mobility. Conversely, if children of college professors end up hauling trash for a living, these children have experienced downward intergenerational mobility. Intragenerational mobility refers to mobility within a person’s own lifetime. If you start out as an administrative assistant in a large corporation and end up as an upper-level manager, you have experienced upward intragenerational mobility. But if you start out from business school as an upper-level manager and get laid off 10 years later because of corporate downsizing, you have experienced downward intragenerational mobility.
Sociologists have conducted a good deal of research on vertical mobility, much of it involving the movement of males up or down the occupational prestige ladder compared to their fathers, with the earliest studies beginning in the 1960s (Blau & Duncan, 1967; Featherman & Hauser, 1978). For better or worse, the focus on males occurred because the initial research occurred when many women were still homemakers and also because women back then were excluded from many studies in the social and biological sciences. The early research on males found that about half of sons end up in higher-prestige jobs than their fathers had but that the difference between the sons’ jobs and their fathers’ was relatively small. For example, a child of a janitor may end up running a hardware store but is very unlikely to end up as a corporate executive. To reach that lofty position, it helps greatly to have parents in jobs much more prestigious than a janitor’s. Contemporary research also finds much less mobility among African Americans and Latinos than among non-Latino whites with the same education and family backgrounds, suggesting an important negative impact of racial and ethnic discrimination (see Chapter 7 “Deviance, Crime, and Social Control” ).
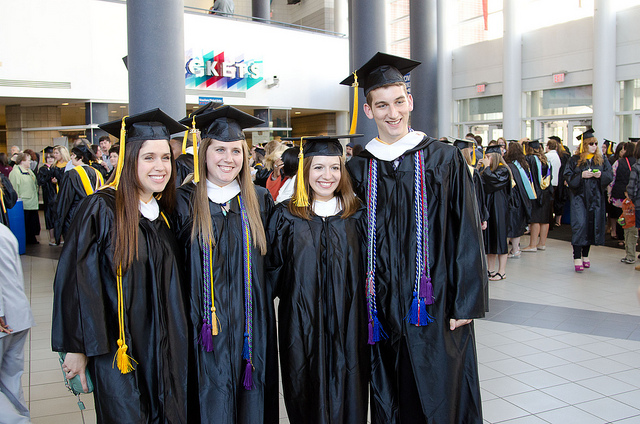

A college education is a key step toward achieving upward social mobility. However, the payoff of education is often higher for men than for women and for whites than for people of color.
Nazareth College – Commencement 2013 – CC BY 2.0.
A key vehicle for upward mobility is formal education. Regardless of the socioeconomic status of our parents, we are much more likely to end up in a high-paying job if we attain a college degree or, increasingly, a graduate or professional degree. Figure 8.4 “Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007” vividly shows the difference that education makes for Americans’ median annual incomes. Notice, however, that for a given level of education, men’s incomes are greater than women’s. Figure 8.4 “Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007” thus suggests that the payoff of education is higher for men than for women, and many studies support this conclusion (Green & Ferber, 2008). The reasons for this gender difference are complex and will be discussed further in Chapter 11 “Gender and Gender Inequality” . To the extent vertical social mobility exists in the United States, then, it is higher for men than for women and higher for whites than for people of color.
Figure 8.4 Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007
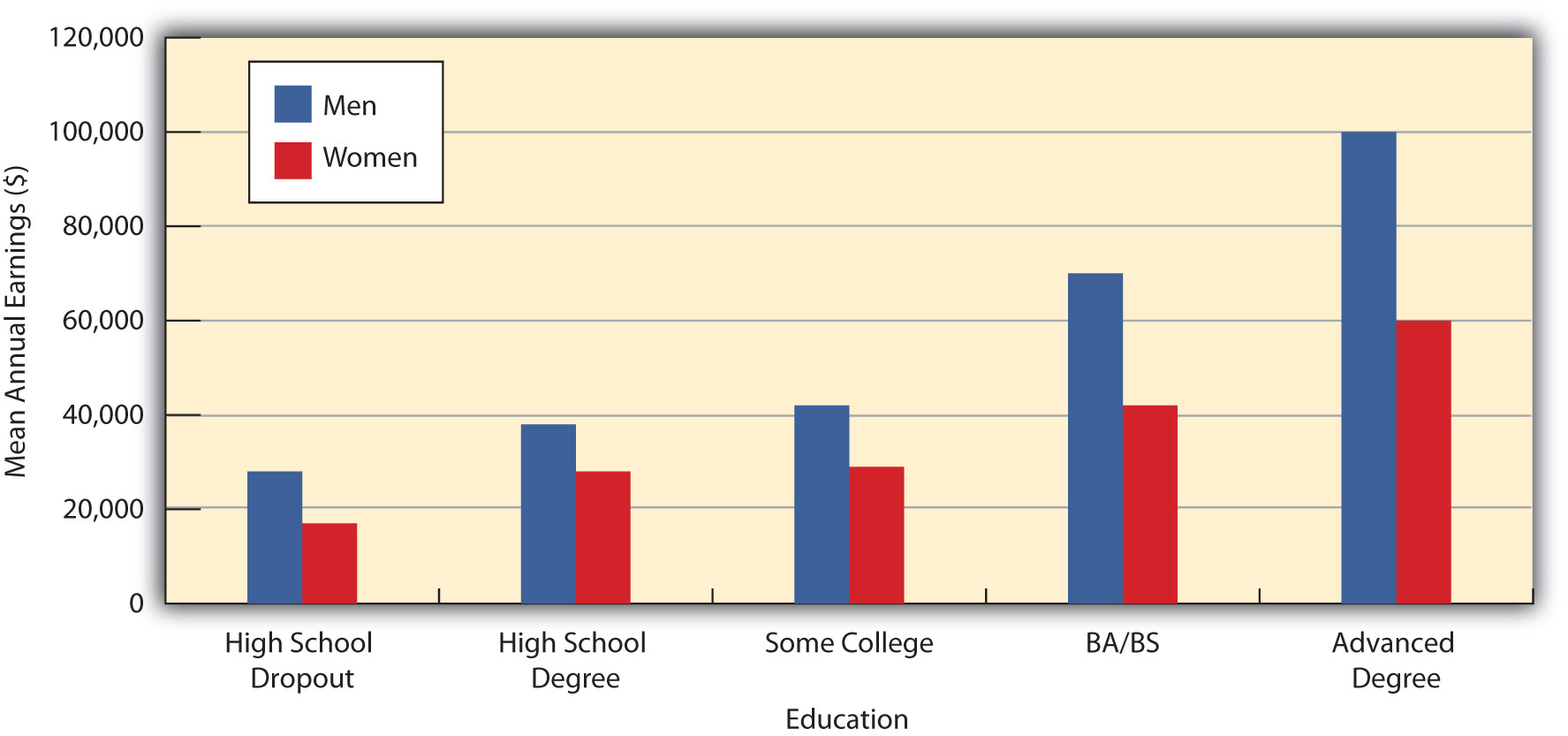
Source: Data from U.S. Census Bureau. (2010). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2010 . Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab .
Certainly the United States has upward social mobility, even when we take into account gender and racial discrimination. Whether we conclude the United States has a lot of vertical mobility or just a little is the key question, and the answer to this question depends on how the data are interpreted. People can and do move up the socioeconomic ladder, but their movement is fairly limited. Hardly anyone starts at the bottom of the ladder and ends up at the top. As we see later in this chapter, recent trends in the U.S. economy have made it more difficult to move up the ladder and have even worsened the status of some people.
One way of understanding the issue of U.S. mobility is to see how much parents’ education affects the education their children attain. Figure 8.5 “Parents’ Education and Percentage of Respondents Who Have a College Degree” compares how General Social Survey respondents with parents of different educational backgrounds fare in attaining a college (bachelor’s) degree. For the sake of clarity, the figure includes only those respondents whose parents had the same level of education as each other: they either both dropped out of high school, both were high school graduates, or both were college graduates.
Figure 8.5 Parents’ Education and Percentage of Respondents Who Have a College Degree
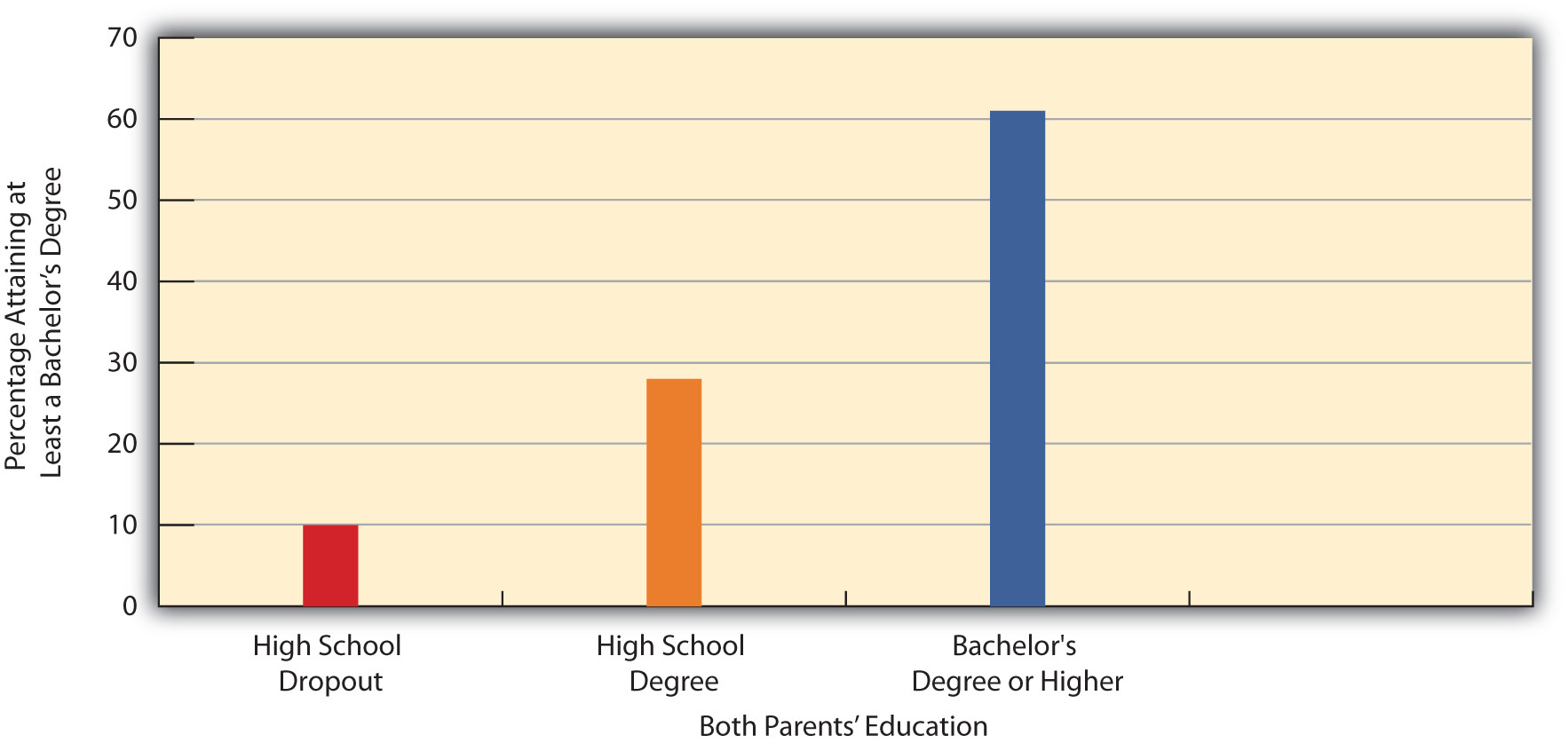
As Figure 8.5 “Parents’ Education and Percentage of Respondents Who Have a College Degree” indicates, we are much more likely to get a college degree if our parents had college degrees themselves. The two bars for respondents whose parents were high school graduates or dropouts, respectively, do represent upward mobility, because the respondents are graduating from college even though their parents did not. But the three bars taken together also show that our chances of going to college depend heavily on our parents’ education (and presumably their income and other aspects of our family backgrounds). The American Dream does exist, but it is much more likely to remain only a dream unless we come from advantaged backgrounds. In fact, there is less vertical mobility in the United States than in other Western democracies. As a recent analysis summarized the evidence, “There is considerably more mobility in most of the other developed economies of Europe and Scandinavia than in the United States” (Mishel, Bernstein, & Shierholz, 2009, p. 108).
Key Takeaways
- Several ways of measuring social class exist. Functionalist and conflict sociologists disagree on which objective criteria to use in measuring social class. Subjective measures of social class, which rely on people rating their own social class, may lack some validity.
- Sociologists disagree on the number of social classes in the United States, but a common view is that the United States has four classes: upper, middle, working, and lower. Further variations exist within the upper and middle classes.
- The United States has some vertical social mobility, but not as much as several nations in Western Europe.
For Your Review
- Which way of measuring social class do you prefer, objective or subjective? Explain your answer.
- Which objective measurement of social class do you prefer, functionalist or conflict? Explain your answer.
Blau, P. M., & Duncan, O. D. (1967). The American occupational structure . New York, NY: Wiley.
Coleman, R. P., & Rainwater, L. (1978). Social standing in America . New York, NY: Basic Books.
DeNavas-Walt, C., Proctor, B. D., & Smith, J. C. (2010). Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2009 (Current Population Report P60-238). Washington, DC: U.S. Census Bureau.
Featherman, D. L., & Hauser, R. M. (1978). Opportunity and change . New York, NY: Academic Press.
Gilbert, D. (2011). The American class structure in an age of growing inequality (8th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press.
Green, C. A., & Ferber, M. A. (2008). The long-term impact of labor market interruptions: How crucial is timing? Review of Social Economy, 66 , 351–379.
Hodge, R. W., Siegel, P., & Rossi, P. (1964). Occupational prestige in the United States, 1925–63. American Journal of Sociology, 70 , 286–302.
Kerbo, H. R. (2009). Social stratification and inequality . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Mishel, L., Bernstein, J., & Shierholz, H. (2009). The state of working America 2008/2009 . Ithaca, NY: ILR Press [An imprint of Cornell University Press].
Warner, W. L., & Lunt, P. S. (1941). The social life of a modern community . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Wright, E. O. (2000). Class counts: Comparative studies in class analysis . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Sociology Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essay Examples >
- Essays Topics >
- Essay on Sociology
Social Classes Essay Example
Type of paper: Essay
Topic: Sociology , Social Class , Countries , Wealth , Theory , Society , Money , Education
Words: 1700
Published: 02/11/2020
ORDER PAPER LIKE THIS
Introduction
Social class is an age old concept referring to a group of people with similar status, power, influence and wealth. Social class refers to the social stratification of the society based on social, economic and educational status. However, the definition of class is not uniform across the countries and societies. There exist different theories of social class division and its impact on us. The word 'class' derives from the Latin word “classis”. During census people were categorized into different “classis” based on their wealth in ancient Rome. Wealth is still the biggest factor in determining class strata. This essay will highlight different theories of social class and different social factors that differentiate social classes, subsequently touching upon the probable social challenges encountered by someone while moving from one social ladder to another.
Social Class: Theories
Social class models are based on economics, sociology and psychology. Historically the most popular model is the common stratum model that divides society into three simple hierarchy of upper class, middle class and lower or working class. According to this theory, society is divided into different classes based on mainly two factors, economic and social. Apart from the common stratum model, there exists a Marxian class theory proposed by Karl Marx. Marx believed that class is a combination of subjective and objective factors. Objectively, a class shares a common relationship in terms of output. Subjectively, members of a class believe that they share some common interests. This class perception is not only a common feeling of shared interest of one’s own class but it also indicates how the society should be. As per the class theory of Marx, two classes - bourgeoisie and proletariat constitute the major two strata of the social class. Bourgeoisies are the wealthy section of a society controlling power through money. Proletariats are laborers who depend on bourgeoisies to earn money by selling labor. Marx explained in his theory about how ultimately bourgeoisies would be eliminated from the society and all would turn equal. Marx envisions a classless society in which there will be no class, no state and no need for money and everything will be shared and the society will run based on needs and not based on profits. Max Weber was a 19th century German philosopher and sociologist who presented another class theory. Weber’s theory is known as ‘Three component theory of stratification’. According to Weber, society is not stratified on the basis of economic status alone; it is also dependent on status and power. In Weber’s definition class or economic position definitely creates social strata but it is not the only factor. Status is another factor creating divide in the society. For Example, poets or saints may not be rich but they enjoy very high status or social class in the society. Power is another factor dividing society into different classes. For example, a person working in FBI may not be affluent monetary wise but he has immense power giving him a higher status in the society.
Modern Day Class Strata
In modern day world, social class stratification is based on the common three stratum model. This model divides the society into three strata - the upper class, middle class and lower class. Upper class is composed of people who are born wealthy or who are wealthy through inheritance or both. In most of the countries the upper class is determined by wealth. For example, in underdeveloped countries and developing countries like India, China, Kenya, Egypt and others a financially wealthy person always belongs to the upper class. The same is applicable in most of the developed countries as well. However, in some countries only people born into high society or aristocratic bloodlines are deemed as members of the upper class. Those who have amassed wealth through business or commercial activity are viewed as nouveau riche (New Charter University). This is particularly apparent in Britain where the concept of royal family and royal blood decides the upper or royal class. The third kinds of people considered to be upper class are politicians. In most of the countries, politicians are vested with huge power which gives them a social status one notch above the rest. Middle Class is the most dynamic among all class definitions. The definition of this class category changes with changing society and changing time. The common definition is that middle class are those people working on behalf of the owners to control and manage the laborers and they also work in highly skilled areas. Middle class definition of US is very broad and includes people who in many other societies will be considered lower class. The middle class concept in developed societies is broadening as more and more labor intensive work is now being outsourced to developing countries with only high end works being retained in developed countries. Middle class population is educated and highly skilled and in most of the cases earns enough money to live a decent life with secure future. Depending on the annual income bracket ranging from $50,000 to $199,999, American middle class is segmented into upper and lower middle class with upper middle class potentially earning between the range of $150,000 to $199,000 and lower middle class earning within the range of $50,000 to $74,999 (New Charter University). Upper middle class people are usually graduates with professional degrees practicing professions like law, banking, corporate sector, finance, engineering and other occupations. Lower middle class people are also highly educated involved in white-collar professions of teaching, nursing and the like. Lower class also known as the working class are the people working in blue-collar low paying jobs in factories, construction sites, restaurants and clerical positions. They have little or no economic security as they always live in the fear of losing their jobs. They don't have adequate technological expertise like the middle class to work in better paying jobs.
Changing Social Class: Challenges
All of us are born into some social strata of the society and cultural setting. Based on the class we receive education, healthcare, community and religious influences. This brings in some common behavioral pattern inside us knowingly or unknowingly. Most of us are born and die in the same social class (AAAS). People born in lower class have every possibility that they will also die poor. People born in the upper or middle classes are most likely to die as same. Only an individual or a group of individuals can move up the social ladder through massive individual or social initiative. As we have seen in the previous section that the main difference between a lower class person and an upper class person is the special skill and knowledge. This can be achieved through better education. Lower class people cannot move into the middle class strata of the society because for better education often money is required which they do not have. This barrier can be minimized by making education more affordable to lower class. We have seen more people moving into middle class where the basic education is same for all and is affordable by all. The US is one of the great examples of a society which has decreased its lower class by making basic education available to all. Moving into upper class from middle class is not that easy. The main difference between a upper class and middle class person is money. The main three things determining the upper class are wealth, high born and power. Middle class people cannot be high born and hence in order to acquire the status of upper class they have to either attain power or money. Power can be achieved by getting into positions of importance like Member of Parliament or minister of local, state or central government. Money can be achieved by getting into business ventures. On the other hand, getting down to the bottom of the social ladder seems to be an easier process. Upper class people who are born amidst wealth and power may lose all of it if they maintain an extravagant lifestyle and make injudicious investments.
Social class is an old concept that determines the social stratification existing in a society on the basis of economic position, social status and educational qualification. There are different theories of social class like common stratum model, Marxian class theory and Weber's three component theory of stratification. In today's world social class stratification relies on the common three stratum model which divides society into three distinct sections - upper class, middle class and lower class. Usually, based on the social setting and the availability of resources for learning skill and education, people born into each specific class die the same as they were born into. But since the difference between a middle class and lower class is the difference in education and skill, if education can be made affordable to all then chances of lower class people going one notch up the social ladder to middle class position are higher, but the same is not true for people aspiring to reach the upper class position because then they have to earn enough money and power to earn high status. Compared to difficulty in social climb, it is lot easier for one to climb down the social strata. A rich person can turn poor if he does no work and wastes money making bad investments.
Works Cited
Marx's Theory of Social Class and Class Structure, 28 Sept. 1999. Web. 14 July 2013 <http://uregina.ca/~gingrich/s28f99.htm> Shortell, Prof. Timothy. Weber's Theory of Social Class, Department of Sociology, Brooklyn College, Web. 14 July 2013 <http://www.brooklynsoc.org/courses/43.1/weber.html> Social Class in the United States, New Charter University, Web. 14 July 2013 <https://new.edu/resources/social-class-in-the-united-states> Social Class, Social Change, and Poverty, AAAS. Web. 14 July 2013 <http://sciencenetlinks.com/lessons/social-class-social-change-and-poverty/> Lareau, Annette and Conley, Dalton. Social Class: How Does It Work?, Russell Sage Foundation (August 2008). Print. Argyle, Michael. The Psychology of Social Class, Routledge: 1 edition (January 27, 1994). Print. Weber's View of Stratification, Boundless. Web. 14 July 2013 <https://www.boundless.com/sociology/understanding-global-stratification-and-inequality/sociological-theories-and-global-inequality/weber-s-view-of-stratification/>

Cite this page
Share with friends using:
Removal Request

Finished papers: 2837
This paper is created by writer with
ID 285254961
If you want your paper to be:
Well-researched, fact-checked, and accurate
Original, fresh, based on current data
Eloquently written and immaculately formatted
275 words = 1 page double-spaced

Get your papers done by pros!
Other Pages
Approach essays, legal drinking age essays, different styles essays, obese essays, scarce resources essays, war ii essays, the play essays, harsh essays, psychosocial essays, effective leadership essays, music theory essays, essay on after school delinquency prevention program, free research paper on follow up compliance with pre arranged primary care providers post emergency room, health care essay sample, cyber bullying essay, republican and liberal democratic positions essay sample, low back pain cost of illness essay sample, code of ethics for physical therapists without the use of drugs essay, report on internal briefing paper, research paper on procedures in the physical sciences, powers of congress essay, sample essay on receiving feedback, culturally responsive teachers in todays diverse classroom essay samples, example of objectives report, literary analysis assignment essay example, good chinese immigration to the united states of america research paper example, free report about comparison between social identity and realistic conflict theories, hand washing and bacteria report sample, example of the andrea yates case essay, free literature review on differential effects of egfr ligands on endocytic, external analysis of hd motorcycle manufacturer case study sample, good example of mathematics paper report, example of interactive advertisin campaign course work, essay on e business, free art architecture research paper example, art in the middle east research papers example, invasion of privacy case studies, public debt case studies, fatality case studies, timeliness case studies, cruise ship case studies, incapacity case studies, tracheostomy case studies.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Social Class in the United States
Learning objectives.
- Distinguish objective and subjective measures of social class.
- Discuss whether the United States has much vertical social mobility.
Most sociologists define social class as a grouping based on similar social factors like wealth, income, education, and occupation. These factors affect how much power and prestige a person has. Social stratification reflects an unequal distribution of resources. In most cases, having more money means having more power or more opportunities. There is a surprising amount of disagreement among sociologists on the number of social classes in the United States and even on how to measure social class membership. We first look at the measurement issue and then discuss the number and types of classes sociologists have delineated.
Measuring Social Class
We can measure social class either objectively or subjectively . If we choose the objective method, we classify people according to one or more criteria, such as their occupation, education, and/or income. The researcher is the one who decides which social class people are in based on where they stand in regard to these variables. If we choose the subjective method, we ask people what class they think they are in. For example, the General Social Survey asks, “If you were asked to use one of four names for your social class, which would you say you belong in: the lower class, the working class, the middle class, or the upper class?” Figure 8.3 “Subjective Social Class Membership” depicts responses to this question. The trouble with such a subjective measure is that some people say they are in a social class that differs from what objective criteria might indicate they are in. This problem leads most sociologists to favor objective measures of social class when they study stratification in American society.
Figure 8.3 Subjective Social Class Membership
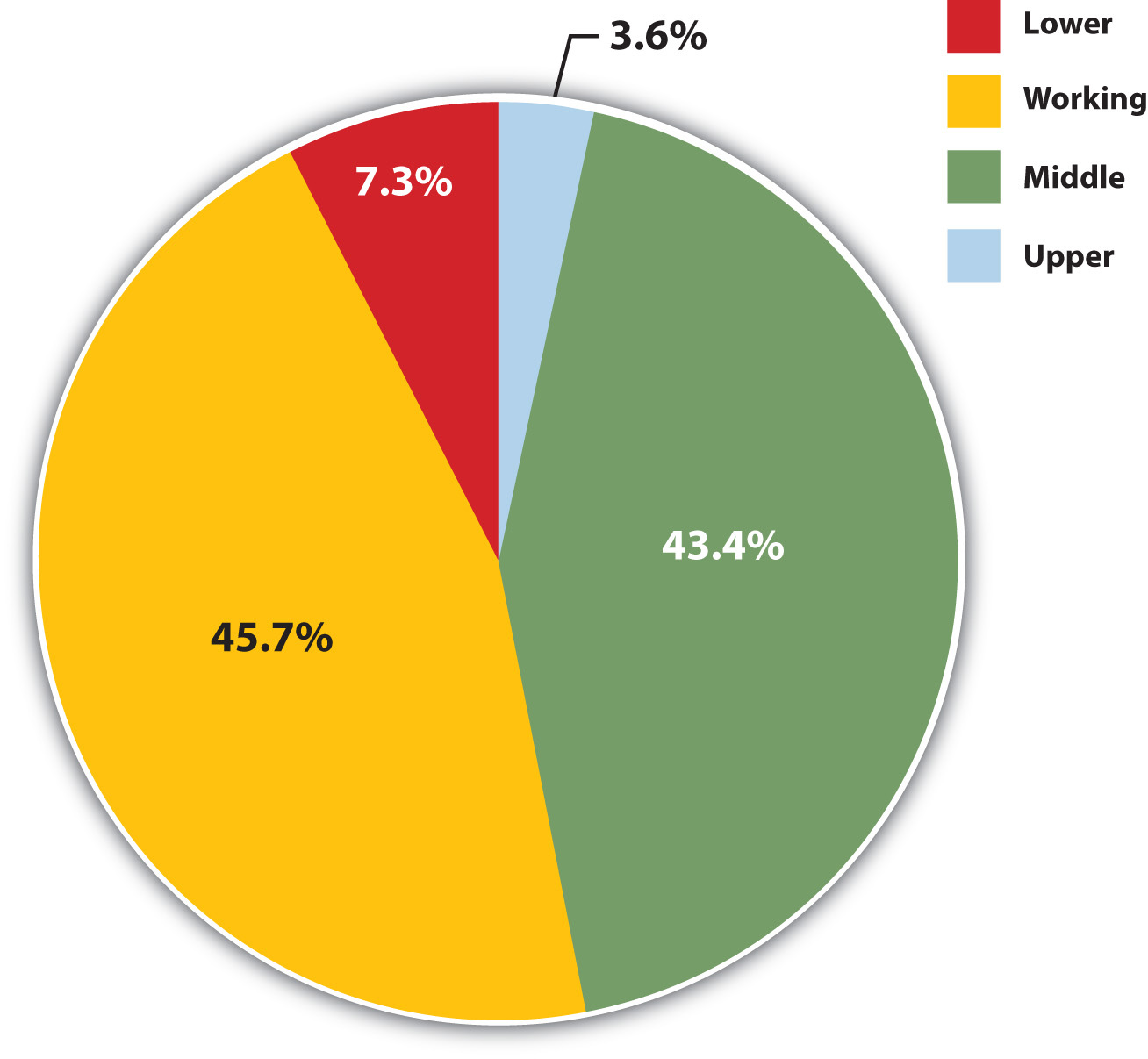
Source: Data from General Social Survey, 2008.
Yet even here there is disagreement between functionalist theorists and conflict theorists on which objective measures to use. Functionalist sociologists rely on measures of socioeconomic status (SES) , such as education, income, and occupation, to determine someone’s social class. Sometimes one of these three variables is used by itself to measure social class, and sometimes two or all three of the variables are combined (in ways that need not concern us) to measure social class. When occupation is used, sociologists often rely on standard measures of occupational prestige. Since the late 1940s, national surveys have asked Americans to rate the prestige of dozens of occupations, and their ratings are averaged together to yield prestige scores for the occupations (Hodge, Siegel, & Rossi, 1964). Over the years these scores have been relatively stable. Here are some average prestige scores for various occupations: physician, 86; college professor, 74; elementary school teacher, 64; letter carrier, 47; garbage collector, 28; and janitor, 22.
Despite SES’s usefulness, conflict sociologists prefer different, though still objective, measures of social class that take into account ownership of the means of production and other dynamics of the workplace. These measures are closer to what Marx meant by the concept of class throughout his work, and they take into account the many types of occupations and workplace structures that he could not have envisioned when he was writing during the 19th century.
For example, corporations have many upper-level managers who do not own the means of production but still determine the activities of workers under them. They thus do not fit neatly into either of Marx’s two major classes, the bourgeoisie or the proletariat. Recognizing these problems, conflict sociologists delineate social class on the basis of several factors, including the ownership of the means of production, the degree of autonomy workers enjoy in their jobs, and whether they supervise other workers or are supervised themselves (Wright, 2000).
The American Class Structure
As should be evident, it is not easy to determine how many social classes exist in the United States. Over the decades, sociologists have outlined as many as six or seven social classes based on such things as, once again, education, occupation, and income, but also on lifestyle, the schools people’s children attend, a family’s reputation in the community, how “old” or “new” people’s wealth is, and so forth (Coleman & Rainwater, 1978; Warner & Lunt, 1941). For the sake of clarity, we will limit ourselves to the four social classes included in Figure 8.3 “Subjective Social Class Membership” : the upper class, the middle class, the working class, and the lower class. Although subcategories exist within some of these broad categories, they still capture the most important differences in the American class structure (Gilbert, 2011). The annual income categories listed for each class are admittedly somewhat arbitrary but are based on the percentage of households above or below a specific income level.
The Upper Class
The upper class is considered the top, and only the powerful elite get to see the view from there. In the United States, people with extreme wealth make up 1 percent of the population, and they own one-third of the country’s wealth (Beeghley 2008).
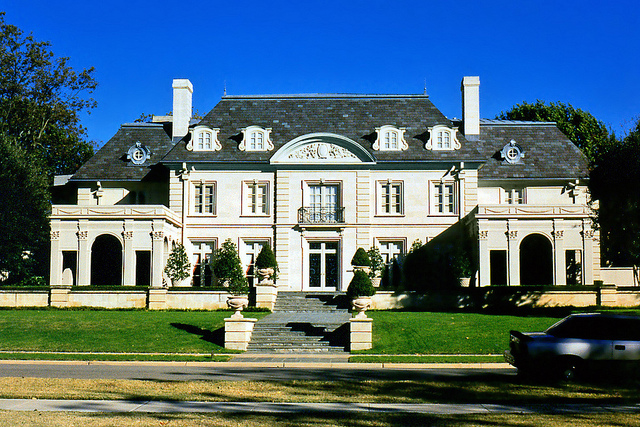

The upper class in the United States consists of about 1% of all households and possesses much wealth, power, and influence.
Steven Martin – Highland Park Mansion – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Money provides not just access to material goods, but also access to a lot of power. As corporate leaders, members of the upper class make decisions that affect the job status of millions of people. As media owners, they influence the collective identity of the nation. They run the major network television stations, radio broadcasts, newspapers, magazines, publishing houses, and sports franchises. As board members of the most influential colleges and universities, they influence cultural attitudes and values. As philanthropists, they establish foundations to support social causes they believe in. As campaign contributors, they sway politicians and fund campaigns, sometimes to protect their own economic interests.
U.S. society has historically distinguished between “old money” (inherited wealth passed from one generation to the next) and “new money” (wealth you have earned and built yourself). While both types may have equal net worth, they have traditionally held different social standings. People of old money, firmly situated in the upper class for generations, have held high prestige. Their families have socialized them to know the customs, norms, and expectations that come with wealth. Often, the very wealthy don’t work for wages. Some study business or become lawyers in order to manage the family fortune. Others, such as Paris Hilton and Kim Kardashian, capitalize on being a rich socialite and transform that into celebrity status, flaunting a wealthy lifestyle.
However, new-money members of the upper class are not oriented to the customs and mores of the elite. They haven’t gone to the most exclusive schools. They have not established old-money social ties. People with new money might flaunt their wealth, buying sports cars and mansions, but they might still exhibit behaviors attributed to the middle and lower classes.
The Middle Class
Many people consider themselves middle class, but there are differing ideas about what that means. People with annual incomes of $150,000 call themselves middle class, as do people who annually earn $30,000. That helps explain why, in the United States, the middle class is broken into upper and lower subcategories. Upper-middle-class people tend to hold bachelor’s and postgraduate degrees. They’ve studied subjects such as business, management, law, or medicine. Lower-middle-class members hold bachelor’s degrees from four-year colleges or associate’s degrees from two-year community or technical colleges.
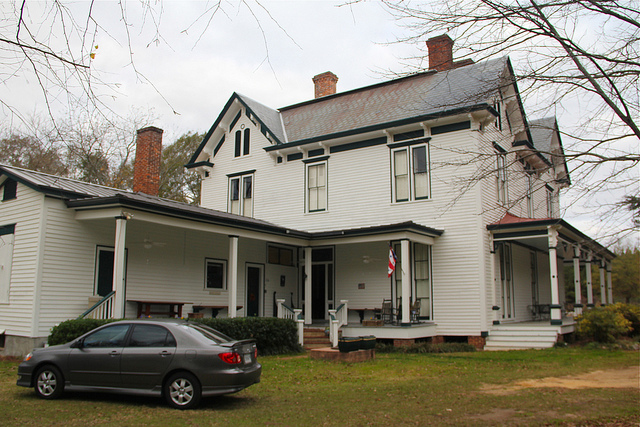

The upper-middle class in the United States consists of about 4.4% of all households, with incomes ranging from $150,000 to $199,000.
Alyson Hurt – Back Porch – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Comfort is a key concept to the middle class. Middle-class people work hard and live fairly comfortable lives. Upper-middle-class people tend to pursue careers that earn comfortable incomes. They provide their families with large homes and nice cars. They may go skiing or boating on vacation. Their children receive high-quality education and healthcare (Gilbert 2010).
In the lower middle class, people hold jobs supervised by members of the upper middle class. They fill technical, lower-level management or administrative support positions. Compared to lower-class work, lower-middle-class jobs carry more prestige and come with slightly higher paychecks. With these incomes, people can afford a decent, mainstream lifestyle, but they struggle to maintain it. They generally don’t have enough income to build significant savings. In addition, their grip on class status is more precarious than in the upper tiers of the class system. When budgets are tight, lower-middle-class people are often the ones to lose their jobs.
The Working Class
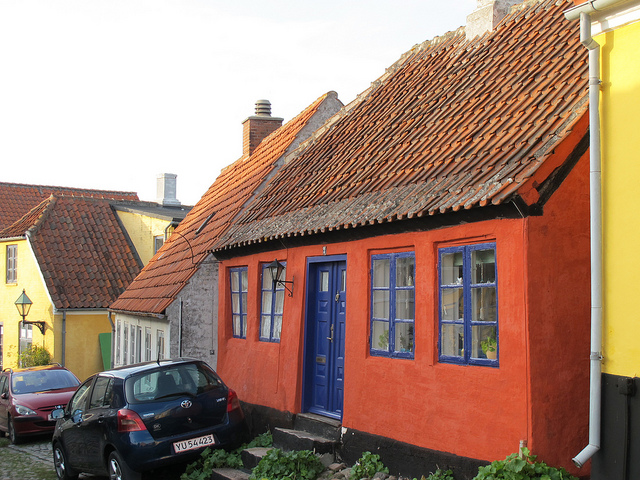

The working class in the United States consists of about 25% of all households, whose members work in blue-collar jobs and less skilled clerical positions.
Lisa Risager – Ebeltoft – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Working-class households generally work in blue-collar jobs such as factory work, construction, restaurant serving, and less skilled clerical positions. People in the working class typically do not have 4-year college degrees, and some do not have high school degrees. Although most are not living in official poverty, their financial situation is very uncomfortable. A single large medical bill or expensive car repair would be almost impossible to pay without going into considerable debt. Working-class families are far less likely than their wealthier counterparts to own their own homes or to send their children to college. Many of them live at risk for unemployment as their companies downsize by laying off workers even in good times, and hundreds of thousands began to be laid off when the U.S. recession began in 2008.
The Lower Class
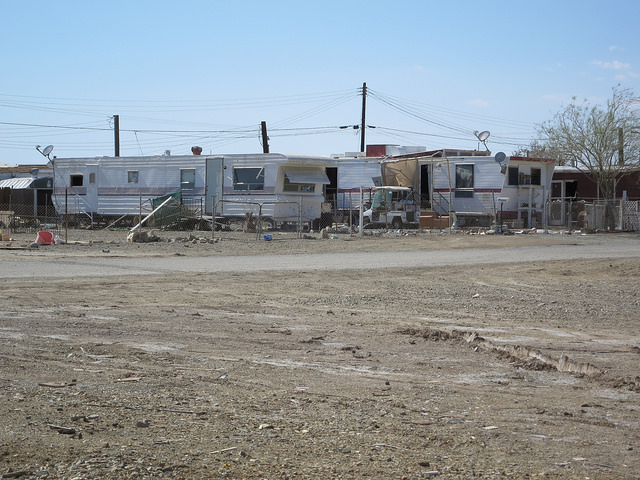

The lower class or poor in the United States constitute about 25% of all households. Many poor individuals lack high school degrees and are unemployed or employed only part time.
Chris Hunkeler – Trailer Homes – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Although lower class is a common term, many observers prefer a less-negative sounding term like the poor, which is used here. Just like the middle and upper classes, the lower class can be divided into subsets: the working class, the working poor, and the underclass. Compared to the lower middle class, lower-class people have less of an educational background and earn smaller incomes. They work jobs that require little prior skill or experience and often do routine tasks under close supervision.
The working poor have unskilled, low-paying employment. However, their jobs rarely offer benefits such as healthcare or retirement planning, and their positions are often seasonal or temporary. They work as sharecroppers, migrant farm workers, house cleaners, and day laborers. Some are high school dropouts. Some are illiterate, unable to read job ads.
How can people work full-time and still be poor? Even working full-time, millions of the working poor earn incomes too meager to support a family. Minimum wage varies from state to state, but in many states it is approaching $8.00 per hour (Department of Labor 2014). At that rate, working 40 hours a week earns $320. That comes to $16,640 a year, before tax and deductions. Even for a single person, the pay is low. A married couple with children will have a hard time covering expenses.
The underclass is the United States’ lowest tier. Members of the underclass live mainly in inner cities. Many are unemployed or underemployed. Those who do hold jobs typically perform menial tasks for little pay. Some of the underclass are homeless. For many, welfare systems provide a much-needed support through food assistance, medical care, housing, and the like.
We will discuss the poor further when we focus later in this chapter on inequality and poverty in the United States.
Social Mobility
Social mobility refers to the ability to change positions within a social stratification system. When people improve or diminish their economic status in a way that affects social class, they experience social mobility.
Individuals can experience upward or downward social mobility for a variety of reasons. Upward mobility refers to an increase—or upward shift—in social class. In the United States, people applaud the rags-to-riches achievements of celebrities like Oprah Winfrey or LeBron James. But the truth is that relative to the overall population, the number of people who rise from poverty to wealth is very small. Still, upward mobility is not only about becoming rich and famous. In the United States, people who earn a college degree, get a job promotion, or marry someone with a good income may move up socially. In contrast, downward mobility indicates a lowering of one’s social class. Some people move downward because of business setbacks, unemployment, or illness. Dropping out of school, losing a job, or getting a divorce may result in a loss of income or status and, therefore, downward social mobility.

Nazareth College – Commencement 2013 – CC BY 2.0.
A key vehicle for upward mobility is formal education. Regardless of the socioeconomic status of our parents, we are much more likely to end up in a high-paying job if we attain a college degree or, increasingly, a graduate or professional degree. Figure 8.4 “Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007” vividly shows the difference that education makes for Americans’ median annual incomes. Notice, however, that for a given level of education, men’s incomes are greater than women’s. Figure 8.4 “Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007” thus suggests that the payoff of education is higher for men than for women, and many studies support this conclusion (Green & Ferber, 2008). The reasons for this gender difference are complex and will be discussed further in Chapter 11 “Gender and Gender Inequality” . To the extent vertical social mobility exists in the United States, then, it is higher for men than for women and higher for whites than for people of color.
Figure 8.4 Education and Median Earnings of Year-Round, Full-Time Workers, 2007
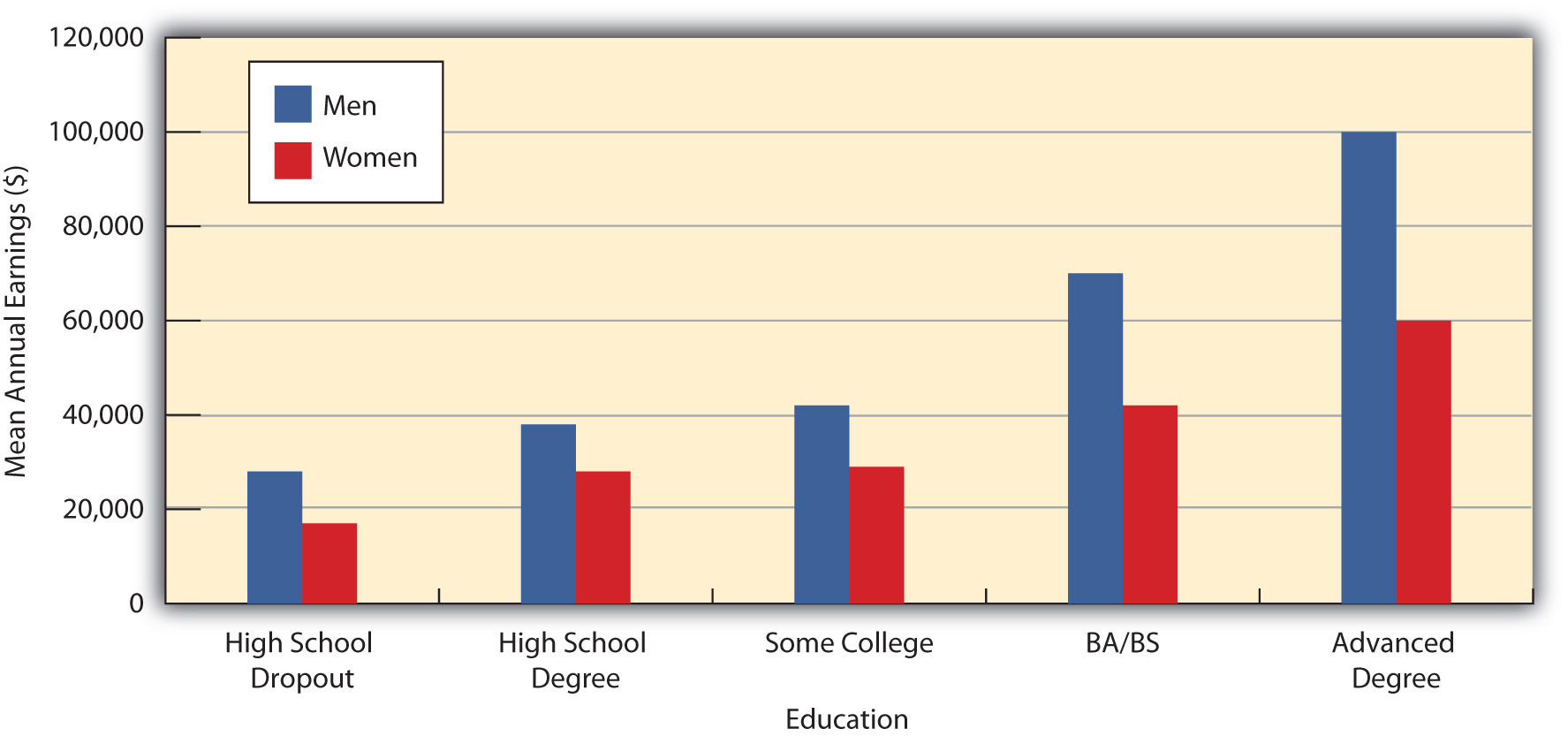
Source: Data from U.S. Census Bureau. (2010). Statistical abstract of the United States: 2010 . Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office. Retrieved from http://www.census.gov/compendia/statab .
It is not uncommon for different generations of a family to belong to varying social classes. This is known as intergenerational mobility . For example, an upper-class executive may have parents who belonged to the middle class. In turn, those parents may have been raised in the lower class. Patterns of intergenerational mobility can reflect long-term societal changes.
Similarly, intragenerational mobility refers to changes in a person’s social mobility over the course of his or her lifetime. For example, the wealth and prestige experienced by one person may be quite different from that of his or her siblings.
Structural mobility happens when societal changes enable a whole group of people to move up or down the social class ladder. Structural mobility is attributable to changes in society as a whole, not individual changes. In the first half of the twentieth century, industrialization expanded the U.S. economy, raising the standard of living and leading to upward structural mobility. In today’s work economy, the recent recession and the outsourcing of jobs overseas have contributed to high unemployment rates. Many people have experienced economic setbacks, creating a wave of downward structural mobility.
When analyzing the trends and movements in social mobility, sociologists consider all modes of mobility. Scholars recognize that mobility is not as common or easy to achieve as many people think. In fact, some consider social mobility a myth. The American Dream does exist, but it is much more likely to remain only a dream unless we come from advantaged backgrounds. In fact, there is less vertical mobility in the United States than in other Western democracies. As a recent analysis summarized the evidence, “There is considerably more mobility in most of the other developed economies of Europe and Scandinavia than in the United States” (Mishel, Bernstein, & Shierholz, 2009, p. 108).
Key Takeaways
- Several ways of measuring social class exist. Functionalist and conflict sociologists disagree on which objective criteria to use in measuring social class. Subjective measures of social class, which rely on people rating their own social class, may lack some validity.
- Sociologists disagree on the number of social classes in the United States, but a common view is that the United States has four classes: upper, middle, working, and lower. Further variations exist within the upper and middle classes.
- The United States has some vertical social mobility, but not as much as several nations in Western Europe.
Beeghley, Leonard. 2008. The Structure of Social Stratification in the United States . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Coleman, R. P., & Rainwater, L. (1978). Social standing in America . New York, NY: Basic Books.
Gilbert, D. (2011). The American class structure in an age of growing inequality (8th ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge Press.
Green, C. A., & Ferber, M. A. (2008). The long-term impact of labor market interruptions: How crucial is timing? Review of Social Economy, 66 , 351–379.
Hodge, R. W., Siegel, P., & Rossi, P. (1964). Occupational prestige in the United States, 1925–63. American Journal of Sociology, 70 , 286–302.
Mishel, L., Bernstein, J., & Shierholz, H. (2009). The state of working America 2008/2009 . Ithaca, NY: ILR Press [An imprint of Cornell University Press].
Warner, W. L., & Lunt, P. S. (1941). The social life of a modern community . New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
Wright, E. O. (2000). Class counts: Comparative studies in class analysis . New York, NY: Cambridge University Press.
Introduction to Sociology: Understanding and Changing the Social World Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
What Is Social Class, and Why Does it Matter?
How Sociologists Define and Study the Concept
smartboy10 / Getty Images
- Key Concepts
- Major Sociologists
- News & Issues
- Research, Samples, and Statistics
- Recommended Reading
- Archaeology
- Ph.D., Sociology, University of California, Santa Barbara
- M.A., Sociology, University of California, Santa Barbara
- B.A., Sociology, Pomona College
Class, economic class, socio-economic class, social class. What's the difference? Each refers to how people are sorted into groups—specifically ranked hierarchies —in society. There are, in fact, important differences among them.
Economic Class
Economic class refers specifically to how one ranks relative to others in terms of income and wealth. Simply put, we are sorted into groups by how much money we have. These groups are commonly understood as lower (the poorest), middle, and upper class (the richest). When someone uses the word "class" to refer to how people are stratified in society, they are most often referring to this.
The model of economic class we use today is a derivation of German philosopher Karl Marx 's (1818–1883) definition of class, which was central to his theory of how society operates in a state of class conflict. In that state, an individual's power comes directly from one's economic class position relative to the means of production—one is either an owner of capitalist entities or a worker for one of the owners. Marx and fellow philosopher Friedrich Engels (1820–1895) presented this idea in " The Manifesto of the Communist Party ," and Marx expounded in much greater length in volume one of his work called "Capital."
Socio-Economic Class
Socio-economic class, also known as socioeconomic status and often abbreviated as SES, refers to how other factors, namely occupation and education, are combined with wealth and income to rank a person relative to others in society. This model is inspired by the theories of German sociologist Max Weber (1864–1920), who viewed the stratification of society as a result of the combined influences of economic class, social status (the level of a person's prestige or honor relative to others), and group power (what he called "party"). Weber defined "party" as the level of one's ability to get what they want, despite how others may fight them on it. Weber wrote about this in an essay titled "The distribution of power within the political community: Class, status, party," in his 1922 book "Economy and Society," published after his death.
Socio-economic class is a more complex formulation than economic class because it takes into account the social status attached to certain professions considered prestigious, like doctors and professors, for example, and to educational attainment as measured in academic degrees. It also takes into account the lack of prestige or even stigma that may be associated with other professions, like blue-collar jobs or the service sector, and the stigma often associated with not finishing high school. Sociologists typically create data models that draw on ways of measuring and ranking these different factors to arrive at a low, middle, or high SES for a given person.
Social Class
The term "social class" is often used interchangeably with SES, both by the general public and by sociologists alike. Very often when you hear it used, that is what it means. In a technical sense, however, social class is used to refer specifically to the characteristics that are less likely to change, or harder to change, than one's economic status, which is potentially changeable over time. In such a case, social class refers to the socio-cultural aspects of one's life, namely the traits, behaviors, knowledge, and lifestyle that one is socialized into by one's family. This is why class descriptors like "lower," "working," "upper," or "high" can have social as well as economic implications for how we understand the person described.
When someone uses "classy" as a descriptor, they are naming certain behaviors and lifestyle and framing them as superior to others. In this sense, social class is determined strongly by one's level of cultural capital , a concept developed by French sociologist Pierre Bourdieu (1930–2002) in his 1979 work "Distinction: A Social Critique of the Judgement of Taste." Bourdieu said that levels of class are determined by the attainment of a specific set of knowledge, behaviors, and skills that allow a person to navigate in society.
Why Does It Matter?
So why does class, however you want to name it or slice it, matter? It matters to sociologists because the fact that it exists reflects unequal access to rights, resources, and power in society—what we call social stratification . As such, it has a strong effect on the access an individual has to education, the quality of that education, and how high a level he or she can reach. It also affects who one knows socially, and the extent to which those people can provide advantageous economic and employment opportunities, political participation and power, and even health and life expectancy, among many other things.
Sources and Further Reading
- Cookson Jr., Peter W. and Caroline Hodges Persell. "Preparing for Power: America's Elite Boarding Schools." New York: Basic Books, 1985.
- Marx, Karl. " Capital: A Critique of Political Economy ." Trans. Moore, Samuel, Edward Aveling and Friedrich Engels. Marxists.org, 2015 (1867).
- Marx, Karl, and Friedrich Engels. " The Communist Manifesto ." Trans. Moore, Samuel and Friedrich Engels. Marxists.org, 2000 (1848).
- Weber, Max. "Economy and Society." ed. Roth, Guenther and Claus Wittich. Oakland: University of California Press, 2013 (1922).
- The Differences Between Socialism and Communism
- What Is Capitalism?
- What You Need to Know About Economic Inequality
- What Is Social Stratification, and Why Does It Matter?
- Understanding Karl Marx's Class Consciousness and False Consciousness
- The Sociology of Consumption
- Understanding Alienation and Social Alienation
- Introduction to Sociology
- Max Weber's Key Contributions to Sociology
- Understanding Conflict Theory
- What Is Cultural Capital? Do I Have It?
- Visualizing Social Stratification in the U.S.
- What is a Norm? Why Does it Matter?
- What Does Consumerism Mean?
- Definition of Scapegoat, Scapegoating, and Scapegoat Theory
- 15 Major Sociological Studies and Publications
112 Social Class Essay Topics
🏆 best essay topics on social class, 🔎 easy social class research paper topics, 🎓 most interesting social class research titles, 💡 simple social class essay ideas, ❓ social class research questions.
- Social Classes in 19th Century British Literature
- Joseph Kahl and Dennis Gilbert’s Model of Social Class
- Social Class and Sports Participation
- Social Class and Difference in Theatrical Comedies
- Lawyer’s Social Class Position in Weber’s Views
- Social Class and Socialization Relations
- Social Classes and Discrimination in “A Rose for Emily”
- Social Class and Discrimination Practices This paper examines the concept of social class and the influence of history on the formation of stereotypical perceptions and the emergence of discrimination experiences.
- Social Class in the Greed Poem by Philip Schultz Philip Schultz is one of the renowned poets who used his work to portray various issues that affect the stability of a given nation.
- The Importance of Social Class Showed in Two Novels Both play The Importance of Being Earnest by Oscar Wilde and Pygmalion by Bernard Shaw demonstrate the importance of social status in the Victorian era.
- The Importance of Social Classes Social class is an effective technique for allocating roles in society. A society establishes people’s social duties through role allocation.
- Social Class Experience at College The social class to which students belong does have a significant effect on the experience of the students at a college and the opportunities that are presented to them.
- Social Class Impact on Family Life Single-parent homes incline to have low social classes since they violate social morals. They tend to contribute to social and financial instability.
- Social Class, Life Chances and Goals Achievement This paper will describe the phenomenon of social classes and explore how class affiliation affects life chances and goals achievement.
- Social Stratification, Social Mobility, and Social Classes In sociology, social stratification refers to the classification of people within Society based on their education, wealth, income, power, and family background.
- Police Officers Treatment Towards Civilians Based on Social Class Several investigations proved the various policemen’s performances towards civilians of a different social class.
- Youth as a Social Class and Phenomenon Review The given selection of the articles has been chosen on the basis of two criteria: they deal with the youth and they explain different aspects and issues connected with media education
- Social Class in the United States How Dennis Gilbert and Joseph Kahl’s model of social class, identify family’s social class position on the social class ladder.
- Social Classes and Capitalism: Sociological Theories This article focuses on the ideas of capitalism based on social classes while describing the concepts of perspective, conflict, symbolic interaction, and functionalism.
- “Mothers on Display: Lunchboxes, Social Class and Moral Accountability” by Harman “Mothers on Display: Lunchboxes, Social Class and Moral Accountability” seeks to address parents’ moral accountability through everyday activities.
- Social Class Mobility in Our Times Some sociologists argue that sociology must be value-free and free of personal or emotional bias. Others say that ultimate objectivity is neither possible nor desirable.
- My Family’s Social Class and Mine Sociologists like Weber have implied that it is generally determined by similarity in income, influence, and rank.
- The Living Place and Social Class Connection This paper is written with the aim of studying the relationship between place and class, namely, whether moving to a larger city affects the standard of living.
- Social Class and Social Movements There are differences between income and wealth, and through these differences, one can understand the meaning of social class.
- Sociological Issues About Social Class and Poverty, Race and Ethnicity, Gender The aim of this paper is to describe different sociological issues in the USA, such as social class and poverty, race and ethnicity, gender, etc.
- Social Class, Race, and Health The paper explores the way social class and race differences may lead to inequalities when receiving healthcare.
- Social Class in America Social stratification in America has seen the rise of social classes. These classes have their basis on education, gender, race, income, and wealth.
- Wealth to Create Wealth: Social Class in America According to Nasseri, social class is the distinction between groups and individuals these distinctions are different from one society to another.
- Literacy in Different Social Class In their works, Collins, Scribner, Brandt, Burton, and Hamilton discuss point out that literacy categorically contributes to social class distinction.
- Social Classes in the Canadian Society Social inequality affects various aspects of human life such as property rights, education, healthcare, and quality shelter.
- Social Class, Education, Intelligence Correlation This paper highlights the differences and similarities of two articles to determine the attitudes towards a potential correlation between social class, education, and intelligence.
- Use of Social Programs by Social Class in Canada This paper analyzes the different social classes in Canada. It will research and analyze the historical background of social stratification, current state of affairs, theories and statistics.
- Absolutism: Social Class and Absolute Ruler
- How Social Class Can Change the Way People Handle Punishments?
- Cognition and Cultural Change in Social Class
- Race, Social Class, and Society’s Unequal Distribution According to Max Weber
- Agency and Communion From the Perspective of Self Versus Others: The Moderating Role of Social Class
- Gender Inequality and Social Class Differences in Society
- Language and Social Class in “The Adventures of Huckleberry Finn”
- Social Class and Language: The American Class System
- Race, Ethnicity, and Social Class in American Cities
- Racism, Discrimination, and Social Class Explored in “To Kill A Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- Social Class, Alcohol Business, and Crime During Prohibition in the 1920s
- How Social Class Affects the Educational Attainment of Boys and Girls?
- Money and Social Class in “Great Expectations” and “Pride and Prejudice”
- Social Class and Body Weight Among Chinese Urban Adults: The Role of the Middle Classes in the Nutrition Transition
- Race and Social Class: Education and Criminal Justice System
- Social Class: Maintaining Divisions Within Society
- Addressing Sexual Role and Social Class and Its Impact on Life
- How Poverty, Social Class, and Culture Influence the Way People Respond to Health and Illness
- American Comedy and Issues of Social Class in America
- How Social Class Affects a Person’s Development in Judith Guest’s “Juno” and Mary Shelley’s “Frankenstein”
- Emily Bronte and D.H Lawrence’s Exploration of Social Class
- How Social Class Shapes Adolescent Financial Socialization: Understanding Differences in the Transition to Adulthood
- Genealogy and Social Class: Prejudice in “Harry Potter”
- Does Your Social Class Determine Your Future?
- Social Class and Its Effect on Love: Wuthering Heights
- The Impact of Social Class on Inequalities in Educational Outcomes
- How Social Class Can Influence the Buying Behavioral Pattern of Consumers?
- Social Class In 16th Century England
- Feudalism: Social Class and National Government
- How Social Class and Crime Are Intertwined?
- Emma and Social Class in “The Canterbury Tales”
- Social Class and Public Health: Determining Your Health
- Links Between Young Children’s Behavior and Achievement: The Role of Social Class and Classroom Composition
- Jane Eyre: Feminism and Social Class
- Social Class Divide in the American Education System
- English Social Class Hierarchy in “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
- Sir Arthur Conan Doyle and Robert Louis Stevenson on Social Class
- Marx and Weber’s Views on Social Class and Inequality
- Economic Behavior, Social Class Income, and Consumer Behavior
- Social Class and Ethnic Inequalities in Education
- The Role of Interpersonal Justice Trajectories and Social Class in Perceived Legitimacy of Authority Figures
- Regency Era: Social Class and Money
- How Social Class and Power Can Affect the Lives of Different Individuals?
- Cultural Representations of Social Class
- Link Between Social Class and Health Inequalities
- Social Class and Higher Risk of Divorce
- Pygmalion: Social Class and Doolittle
- ‘New’ and ‘Old’ Social Risks: Life Cycle and Social Class Perspectives on Social Exclusion in Ireland
- Education and Social Class: Conflict Theory and Education
- Race and Social Class: An Asian Market
- What Kind of Society Is Divided Into Social Classes?
- Which Are the Different Kinds of Social Class?
- What Is the Impact of Social Classes on People and Society?
- What Roles Do Race and Social Class Continue to Play in the United States?
- Why Is Social Class Important?
- Are There Social Classes in Totalitarianism?
- Which Social Class Has Emerged in Russia Since 1985?
- What Is the Difference Between Marx’s and Weber’s Theories of Social Class?
- How Does Social Class Influence Parenting Styles?
- What Social Class Were Clergy in Victorian England?
- What Is the Difference Between Social Class and Social Stratification?
- Who Was Part of the Highest Social Class of New Spain?
- What Is the Five-Category Social Class Measure?
- How Did Karl Marx Define Social Class?
- How Do Social Class, Gender, and Sexuality Combine to Define a Person’s Roles in the Family?
- What Social Class Expanded as a Result of Industrialization?
- What Were the Three Social Classes of Ancient Rome?
- What Is Social Class Identity?
- Which Social Class Suffered the Most From Industrialization?
- How Does Social Class Affect Mental Health of a Working Class Person?
- How Did the Code of Hammurabi Reflect Different Social Classes?
- What Is Social Class Discrimination?
- What Health Effects Do Variations in Race, Ethnicity, and Social Class Have?
- How Is Social Class Portrayed in “Jane Eyre”?
- What Were the Main Social Classes in the Feudal System?
- What Do the Social Classes Owe Each Other?
- What Social Class Was the Emphasis of the Northern Renaissance?
- What Do Sociologists Use to Measure Social Class?
- Is Income a Key Factor in Determining a Person’s Social Class?
- How Was Social Class Determined in the Regency Era?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, October 26). 112 Social Class Essay Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/social-class-essay-topics/
"112 Social Class Essay Topics." StudyCorgi , 26 Oct. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/social-class-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '112 Social Class Essay Topics'. 26 October.
1. StudyCorgi . "112 Social Class Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/social-class-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "112 Social Class Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/social-class-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "112 Social Class Essay Topics." October 26, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/social-class-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Social Class were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 9, 2024 .
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Persistent Grip of Social Class on College Admissions
The SAT is falling out of favor, but a study looking at essays suggests “soft factors” have their own issues.
By Arvind Ashok
It’s hard to disentangle social class from the college admissions process. The University of California system says it’s trying, announcing recently that it’s dropping consideration of the SAT and ACT. (It was part of a settlement in a lawsuit alleging that the tests are biased along lines of race, wealth and disability.)
More than half of U.S. colleges have made the tests optional for fall of 2021 admissions, according to FairTest , a group opposed to college entrance testing.
Because those tests are receiving so much scrutiny, it’s easy to overlook the influence of socioeconomic background on other admissions yardsticks.
Take the college essay. It’s the most important “soft factor” and the fourth-most important overall factor — after grades, curriculum strength and standardized test scores — according to a 2019 survey of admissions employees.
But essays can be polished by a paid professional third party, or helped along by an upper-middle-class parent.
In another sign of the persistent pull of social class, a recent working paper from authors affiliated with the Student Narrative Lab at Stanford shows that essay content, when quantified through a computer program, is more highly correlated with household income than SAT scores are.
Researchers did not analyze whether these signs of status affect an essay’s quality, or speculate on whether they would make any difference in an evaluation by an admissions officer. But the research suggests that much of the socioeconomic information critics accuse the SAT of reflecting can also be found in essays.
The paper used software to classify essays written by nearly 60,000 applicants to the University of California system in 2016. The essays were quantified partly through syntax choices. The number of commas, total punctuation and longer words were correlated with higher household income, for example, although that doesn’t necessarily equate to better writing.
The content was also quantified by word choice patterns, which are associated with particular topics. Admissions officials might not look more favorably upon essays written on certain themes, but it’s still notable that there are significant differences in the topics associated with higher and lower household incomes.
The topics associated more with students from higher-income households tended to be “more thematically abstract: human nature, seeking answers and sensory experiences,” said AJ Alvero, an education Ph.D. candidate at Stanford and one of the authors of the paper.
Topics more associated with lower-household-income students “were about interpersonal relationships (e.g. multiple topics about family) and school issues like tutoring groups and time management.”
A prior study by the same authors found similar patterns in income difference. A co-author of the study, Sonia Giebel, a Ph.D. candidate in sociology of education at Stanford, stressed along with the other authors that the content they identified was not a marker of essay quality, but pointed to a broader theme: “Class patterns are likely to be present across all the elements used to make admissions decisions.”
Poorer students, beyond writing their reality, may also be more likely to write about “economic insecurity” and “abuse” because of trying to meet perceived expectations. Even without specific guidance from admissions offices, they might feel obligated to “ sell their pain .”
In contrast with much of the rest of the world, American admissions officers have a lot of discretion. Relying on elements like the essay gives them leeway to judge merit away from close scrutiny. The history of the so-called holistic approach — looking at the whole applicant and not just academic metrics — has not always been encouraging.
As Jerome Karabel wrote in his book “ The Chosen, ” relying on nonacademic characteristics had its origins in policies starting in the 1920s that aimed to limit the number of Jews admitted to elite universities. More recently, the discretion and opacity in admissions have been seen by some as harming high-scoring Asian students by penalizing them based on “character” or “fit.”
Despite this, the holistic approach seems here to stay. “I do think that it’s very possible that in this first full year of test-optional being widespread, there very well could be more emphasis in some applications on the soft factors, with the essay being one of them, along with recommendations and extracurriculars,” said Robin Miller, a consultant at the admissions counseling firm IvyWise who formerly worked in admissions at Georgetown and Vanderbilt.
Colleges may want to pursue egalitarian goals, but they have other aims, too. They need to meet tuition revenue targets, and some colleges face a more dire financial situation because of the pandemic.
Analysis of data on recruiting visits by colleges has shown that richer, whiter high schools tend to receive more visits. The persistence of legacy admissions at some elite colleges — many of which have more students from the top 1 percent of income than the bottom 40 percent — shows that though social mobility may be a goal, it can conflict with pleasing potential donors and attracting sufficient numbers of students who don’t need financial aid.
Shifting away from standardized tests closes down some avenues for class bias like test prep (even though research finds prep has only a modest effect on test scores), but leaves many others.
Standout extracurricular activities might be accessible only to the wealthy. Or they can even be faked entirely, as in the infamous Operation Varsity Blues scandal.
Colleges are caught between multiple goals: predicting the people most likely to succeed academically; maintaining their ranking ; identifying talent missed by conventional metrics; collecting adequate tuition income; enrolling a diverse class of students; encouraging and enabling social mobility; complying with legal constraints on affirmative action, among others.
Supporters of the SAT say it’s effective at predicting college academic performance. But if predictive validity were the main goal of admissions, you could argue for directly using higher socioeconomic class as a qualifier for admission because wealthier students tend to transition to college more easily. (Jesse Rothstein of the University of California, Berkeley, made that point last year in testimony against the use of the SAT.)
Nonacademic factors like an essay don’t offer an obvious numerical pecking order like a G.P.A. or SAT score. Reliance on soft factors can allow college admissions offices to pursue their goals but deflect questions about which of the goals they prioritize.
Admissions officials can say they consider every individual’s unique traits, but it appears these traits are mostly inseparable from socioeconomic indicators in applications. Colleges still have to make tough decisions in showing what they truly value, but it seems their decision-making will now be more obscured from the public.
Arvind Ashok is a recent graduate of the University of Texas at Austin, currently deferring enrollment to law school. You can follow him on Twitter at @arvind__ashok .
Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination
Need to write a social class inequality essay? Discrimination and injustice might take place everywhere: in the spheres of education, healthcare, and so on. Find here critical reviews of three articles on the topic. Get inspired to write your own story of social class and inequality!
Introduction
- The War Against the Poor
- Middle of the Class
- When Shelter Feels Like a Prison
Works Cited
There are several attitudes that the middle class and the rich have towards the poor. These attitudes stem from the belief that the world is a just place and people get what they deserve. If one works hard enough and perseveres he or she will be rich. However, the poor person is in that state because of poor decisions such as immorality, crime and alcoholism, lack of ambition and perseverance.
These negative attitudes have caused the middle class and the rich to distance themselves from the poor. The stereotyping of the poor is the genesis of class discrimination. The poor have been excluded as the rest of the nation goes on with their lives.
In this paper, I analyze three articles on social class and inequality to find out whether the authors’ views agree with mine on the negative attitudes towards the poor by the middle class and the rich and the way they have distanced themselves from the poor.
Social Inequality in The War Against the Poor
Herbert Hans, in his article the war against the poor instead of programs to end poverty is arguing that government officials are not addressing poverty but instead making life difficult for the poor. Welfare expenses have always been small however the budget is becoming more and more restrictive.
The poor are being accused of enjoying welfare instead of looking for a job and making sure they remain childless throughout their adolescence. The middle class and the rich feel they are working so hard and the poor are not. These poor people are lumped together with the criminals and accused of making the streets unsafe. The poor have become an excuse or scapegoat for the problems in society. Instead of admitting the decline in morality, the poor are accused of being the only ones with unmarried lovers. Once they get their life in order then they can receive welfare. They are being forced to live up to moral expectations that the working class and the rich speak but do not practice (Hans, 2007, pg 506).
Clearly class bigotry needs to be addressed. The poor have moral failings that are highly noticeable than the middle class but it does not mean it is at a higher proportion. The rich and middle class have access to counseling facilities to tell them their moral failings is as a result of prior abuse or disease.
The poor do not want to marry the fathers of their babies as they are jobless. There is actually scarcity of work; it is not true that the poor do not want to work. The government should address poverty through actively engaging in job creation initiatives and ensuring the actual crime of the poor does not fall below a certain percentage.
The War Against the Poor: Critical Review
The author’s views on class discrimination agree with my views. He concurs that judging the poor harshly for their moral failings and the ability to secure a job is wrong. The middle class and the rich also have moral failings and the middle class has also been experiencing unemployment as jobs are scarce.
Crime and mental illnesses should be viewed as some of the effects of poverty. It is not that the poor and mostly the Blacks have higher criminal tendencies. The middle class and the rich to stop discriminating against the poor and having someone to blame.
The author has also highlighted other concerns that I agree with. Hans says that the government, politicians and public are making life tougher for the poor. I agree with Hans that the focus should be on creation of jobs for the poor. If the country does not stop attacking the poor, the morale, quality of life and economic competitiveness will only go down.
Discrimination in Middle of the Class
The article Middle of the class published in the Economists is an argumentative piece of writing that questions the sustainability of the American Dream. America has always been defined as a country where anyone can become rich or wealthy if they just work hard. Shows like American Idol prove this.
The country has had presidents from humble backgrounds like Benjamin Franklin who was the 15 th child of a candle maker. However the equality of opportunity in America for all its citizens is rapidly diminishing.
The author gives the statistical figures on how the rich have become richer while the poor have become even poorer widening the income gap even more. Secondly social mobility has gone down. A lower and lower percentage of people are able to change the social class they are in through increase in earnings over a period of ten years.
There have also been changes in the economy with a shift towards technical skills requiring workers who have a university degree. This has caused a high increase of the income gap between college and high school graduates. It has become hard to climb the corporate ladder or change jobs if one does not have a university degree. The author suggests that the American society is becoming an educational stratified society
in other words a meritocracy. The rise in university education is also providing a hurdle for middle class families to attend elite universities. The representation of the rich in these elite universities has increased more than the representation of the poor. The mean income of the families that have enrolled their children in Harvard is $150,000(The Economist, 2007, pg 528).
During the period 2001-2004, States found themselves facing a budget squeeze. They responded by increasing the fees of state colleges where the middle class take their children to learn. This proves that the American system is enforcing more income inequalities through educational differences. The rich children are more likely to get a degree than a child from the bottom quarter income level.
There is also a worrying trend in the society that further aggravates class and educational stratification. The chances of an individual getting access to a good education, a good job and good prospects in life is determined by the family the person is born into.
College graduates tend to marry college graduates. Therefore in the graduates home the returns of the degree is double and their children benefit even more with opportunities to attend better schools.
There is therefore great trouble in being poor. If in the American society to be socially mobile you must have a great education, a job and married with children then the rich start off with higher advantages.
There needs to be policy changes where the method by which schools are financed is changed and giving more federal help to poorer colleges. This will only happen when the American politicians and the public recognize there is a problem.

Middle of the Class: Critical Review
The author, like Hans concurs with my argument that the poor are being judged too harshly in society. The reason the poor are not able to support themselves is not that they are lazy or lack ambition.
Rather there is a limitation on the equality of opportunity when it comes to the middle class and the poor in the corporate world. The country is being affected by globalization and technology changes; therefore the requirement of a degree is becoming mandatory.
If what it takes to succeed in the American corporate society is the attainment of a degree then the government should ensure that children from all social backgrounds have access to this type of education. Making education costs high does not help the poor and middle class at all.
It only goes to aggravate the existent inequalities between the rich and the poor. As the author has given statistics, in the last few years the rich have been becoming richer and the poor becoming poorer. The government needs to step in and address the situation.
Social Inequality in When Shelter Feels Like a Prison
The two articles narrated on the stereotypes held by society towards the poor while the article in the Economist discusses the widening gap between the rich and the poor. Both papers focus on the poor. The third article written by Charmion Brown tells of the author’s experiences growing up in a homeless shelter. The real life story further reinforces my argument on the distancing of the poor by society.
In light of her first hand experiences in the place she feels she can only compare it a prison. First of all, the place is cramped with four bunk beds fitted in each tiny room (Browne, 2007, pg 531).
There is absolutely no privacy. One has to take care of their things or they will be stolen. There is a queue for food for the homeless. The author learnt that if you do not make the line two hours before the kitchen is open, one would miss food. There are no curtains in the bathrooms yet the facility is being shared by more than one hundred people. The author felt like the place was a prison.
When Shelter Feels Like a Prison: Critical Review
The author’s experiences in the shelter confirm my views on the abandonment of the poor and homeless in the shelters. The author narrates how the social workers are rare and have no time for them. It is a prison. The government and public needs to stop abandoning the shelters. The living conditions needs to be improved. In my argument I had put forward the assumptions society has concerning the poor people.
They are not successful because they are lazy. The author cautions society and informs them that there were people from broken homes in the shelter due to drug abuse, AIDS and early pregnancy and not because they are lazy. The poor also lack knowledge on how to improve their lives.
The three articles have gone further to reinforce my argument on the existence of negative attitudes and stereotypes for the poor in society. Hans goes further to explain that it is because the poor have become a scapegoat to make other members in the society better. In my argument I had put forward the way society views the world in black and white. The hardworking succeed the poor are the lazy ones.
The article in the economist supports my argument and goes ahead to tell society that actually there is a limitation on equality of opportunity in the country. One may desire a job but he cannot get that job. In my argument I also said that the society distances itself from the poor. The article, When Shelter feels like a Prison clearly shows the abandonment of the poor by society.
Browne, Charmion. “When Shelter Feels Like a Prison” Writing in the Disciplines: A Reader for Writers . Ed. Mary Kennedy. 6 th Ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. 2007. Print.
Hans, Herbert. “The war against the poor instead of programs to end poverty” Writing in the Disciplines: A Reader for Writers . Ed. Mary Kennedy. 6 th Ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. 2007. Print.
The Economist. “The Middle Class” Writing in the Disciplines: A Reader for Writers . Ed. Mary Kennedy. 6 th Ed. New Jersey: Prentice Hall. 2007. Print.
- Comparison Between Confucius and Han Feizi
- Are Word Processing Programs Making Students Lazy?
- Asian Studies: The Han as a Confucian State
- Break up of a Relationship
- Causes of Divorce in America
- Five Viewpoints on Human Nature
- Pre Marriage Counseling: One Year Before Getting Married
- Gender and Media – Relation to Women
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, June 4). Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-class-and-inequality/
"Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination." IvyPanda , 4 June 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/social-class-and-inequality/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination'. 4 June.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination." June 4, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-class-and-inequality/.
1. IvyPanda . "Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination." June 4, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-class-and-inequality/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Essay on Social Class Inequality & Discrimination." June 4, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/social-class-and-inequality/.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Wiley Open Access Collection

The psychology of social class: How socioeconomic status impacts thought, feelings, and behaviour
Antony s. r. manstead.
1 Cardiff University, UK
Drawing on recent research on the psychology of social class, I argue that the material conditions in which people grow up and live have a lasting impact on their personal and social identities and that this influences both the way they think and feel about their social environment and key aspects of their social behaviour. Relative to middle‐class counterparts, lower/working‐class individuals are less likely to define themselves in terms of their socioeconomic status and are more likely to have interdependent self‐concepts; they are also more inclined to explain social events in situational terms, as a result of having a lower sense of personal control. Working‐class people score higher on measures of empathy and are more likely to help others in distress. The widely held view that working‐class individuals are more prejudiced towards immigrants and ethnic minorities is shown to be a function of economic threat, in that highly educated people also express prejudice towards these groups when the latter are described as highly educated and therefore pose an economic threat. The fact that middle‐class norms of independence prevail in universities and prestigious workplaces makes working‐class people less likely to apply for positions in such institutions, less likely to be selected and less likely to stay if selected. In other words, social class differences in identity, cognition, feelings, and behaviour make it less likely that working‐class individuals can benefit from educational and occupational opportunities to improve their material circumstances. This means that redistributive policies are needed to break the cycle of deprivation that limits opportunities and threatens social cohesion.
We are all middle class now. John Prescott, former Labour Deputy Prime Minister, 1997
Class is a Communist concept. It groups people as bundles and sets them against one another. Margaret Thatcher, former Conservative Prime Minister, 1992
One of the ironies of modern Western societies, with their emphasis on meritocratic values that promote the notion that people can achieve what they want if they have enough talent and are prepared to work hard, is that the divisions between social classes are becoming wider, not narrower. In the United Kingdom, for example, figures from the Equality Trust ( 2017 ) show that the top one‐fifth of households have 40% of national income, whereas the bottom one‐fifth have just 8%. These figures are based on 2012 data. Between 1938 and 1979, income inequality in the United Kingdom did reduce to some extent, but in subsequent decades, this process has reversed. Between 1979 and 2009/2010, the top 10% of the population increased its share of national income from 21% to 31%, whereas the share received by the bottom 10% fell from 4% to 1%. Wealth inequality is even starker than income inequality. Figures from the UK's Office for National Statistics (ONS, 2014 ) show that in the period 2012–2014, the wealthiest 10% of households in Great Britain owned 45% of household wealth, whereas the least wealthy 50% of households owned <9%. How can these very large divisions in material income and wealth be reconciled with the view that the class structure that used to prevail in the United Kingdom until at least the mid‐20th century is no longer relevant, because the traditional working class has ‘disappeared’, as asserted by John Prescott in one of the opening quotes, and reflected in the thesis of embourgeoisement analysed by Goldthorpe and Lockwood ( 1963 )? More pertinently for the present article, what implications do these changing patterns of wealth and income distribution have for class identity, social cognition, and social behaviour?
The first point to address concerns the supposed disappearance of the class system. As recent sociological research has conclusively shown, the class system in the United Kingdom is very much still in existence, albeit in a way that differs from the more traditional forms that were based primarily on occupation. In one of the more comprehensive recent studies, Savage et al . ( 2013 ) analysed the results of a large survey of social class in the United Kingdom, the BBC's 2011 Great British Class Survey, which involved 161,400 web respondents, along with the results of a nationally representative sample survey. Using latent class analysis, the authors identified seven classes, ranging from an ‘elite’, with an average annual household income of £89,000, to a ‘precariat’ with an average annual household income of £8,000. Among the many interesting results is the fact that the ‘traditional working‐class’ category formed only 14% of the population. This undoubtedly reflects the impact of de‐industrialization and is almost certainly the basis of the widely held view that the ‘old’ class system in the United Kingdom no longer applies. As Savage et al .'s research clearly shows, the old class system has been reconfigured as a result of economic and political developments, but it is patently true that the members of the different classes identified by these researchers inhabit worlds that rarely intersect, let alone overlap. The research by Savage et al . revealed that the differences between the social classes they identified extended beyond differences in financial circumstances. There were also marked differences in social and cultural capital, as indexed by size of social network and extent of engagement with different cultural activities, respectively. From a social psychological perspective, it seems likely that growing up and living under such different social and economic contexts would have a considerable impact on people's thoughts, feelings and behaviours. The central aim of this article was to examine the nature of this impact.
One interesting reflection of the complicated ways in which objective and subjective indicators of social class intersect can be found in an analysis of data from the British Social Attitudes survey (Evans & Mellon, 2016 ). Despite the fact that there has been a dramatic decline in traditional working‐class occupations, large numbers of UK citizens still describe themselves as being ‘working class’. Overall, around 60% of respondents define themselves as working class, and the proportion of people who do so has hardly changed during the past 33 years. One might reasonably ask whether and how much it matters that many people whose occupational status suggests that they are middle class describe themselves as working class. Evans and Mellon ( 2016 ) show quite persuasively that this self‐identification does matter. In all occupational classes other than managerial and professional, whether respondents identified themselves as working class or middle class made a substantial difference to their political attitudes, with those identifying as working class being less likely to be classed as right‐wing. No wonder Margaret Thatcher was keen to dispense with the concept of class, as evidenced by the quotation at the start of this paper. Moreover, self‐identification as working class was significantly associated with social attitudes in all occupational classes. For example, these respondents were more likely to have authoritarian attitudes and less likely to be in favour of immigration, a point I will return to later. It is clear from this research that subjective class identity is linked to quite marked differences in socio‐political attitudes.
A note on terminology
In what follows, I will refer to a set of concepts that are related but by no means interchangeable. As we have already seen, there is a distinction to be drawn between objective and subjective indicators of social class. In Marxist terms, class is defined objectively in terms of one's relationship to the means of production. You either have ownership of the means of production, in which case you belong to the bourgeoisie, or you sell your labour, in which case you belong to the proletariat, and there is a clear qualitative difference between the two classes. This worked well when most people could be classified either as owners or as workers. As we have seen, such an approach has become harder to sustain in an era when traditional occupations have been shrinking or have already disappeared, a sizeable middle‐class of managers and professionals has emerged, and class divisions are based on wealth and social and cultural capital.
An alternative approach is one that focuses on quantitative differences in socioeconomic status (SES), which is generally defined in terms of an individual's economic position and educational attainment, relative to others, as well as his or her occupation. As will be shown below, when people are asked about their identities, they think more readily in terms of SES than in terms of social class. This is probably because they have a reasonable sense of where they stand, relative to others, in terms of economic factors and educational attainment, and perhaps recognize that traditional boundaries between social classes have become less distinct. For these reasons, much of the social psychological literature on social class has focused on SES as indexed by income and educational attainment, and/or on subjective social class, rather than social class defined in terms of relationship to the means of production. For present purposes, the terms ‘working class’, which tends to be used more by European researchers, and ‘lower class’, which tends to be used by US researchers, are used interchangeably. Similarly, the terms ‘middle class’ and ‘upper class’ will be used interchangeably, despite the different connotations of the latter term in the United States and in Europe, where it tends to be reserved for members of the land‐owning aristocracy. A final point about terminology concerns ‘ideology’, which will here be used to refer to a set of beliefs, norms and values, examples being the meritocratic ideology that pervades most education systems and the (related) ideology of social mobility that is prominent in the United States.
Socioeconomic status and identity
Social psychological analyses of identity have traditionally not paid much attention to social class or SES as a component of identity. Instead, the focus has been on categories such as race, gender, sexual orientation, nationality and age. Easterbrook, Kuppens, and Manstead ( 2018 ) analysed data from two large, representative samples of British adults and showed that respondents placed high subjective importance on their identities that are indicative of SES. Indeed, they attached at least as much importance to their SES identities as they did to identities (such as ethnicity or gender) more commonly studied by self and identity researchers. Easterbrook and colleagues also showed that objective indicators of a person's SES were robust and powerful predictors of the importance they placed on different types of identities within their self‐concepts: Those with higher SES attached more importance to identities that are indicative of their SES position, but less importance on identities that are rooted in basic demographics or related to their sociocultural orientation (and vice versa).
To arrive at these conclusions, Easterbook and colleagues analysed data from two large British surveys: The Citizenship Survey (CS; Department for Communities and Local Government, 2012 ); and Understanding Society: The UK Household Longitudinal Study (USS; Buck & McFall, 2012 ). The CS is a (now discontinued) biannual survey of a regionally representative sample of around 10,000 adults in England and Wales, with an ethnic minority boost sample of around 5,000. The researchers analysed the most recent data, collected via interviews in 2010–2011. The USS is an annual longitudinal household panel survey that began in 2009. Easterbrook and colleagues analysed Wave 5 (2013–2014), the more recent of the two waves in which the majority of respondents answered questions relevant to class and other social identities.
Both the CS and the USS included a question about the extent to which respondents incorporated different identities into their sense of self. Respondents were asked how important these identities were ‘to your sense of who you are’. The CS included a broad range of identities, including profession, ethnic background, family, gender, age/life stage, income and education. The USS included a shorter list of identities, including profession, education, ethnic background, family, gender and age/life stage. When the responses to these questions were factor analysed, Easterbrook and colleagues found three factors that were common to the two datasets: SES‐based identities (e.g., income), basic‐demographic identities (e.g., age), and identities based on sociocultural orientation (e.g., ethnic background). In both datasets, the importance of each of these three identities was systematically related to objective indicators of the respondents’ SES: As the respondent's SES increased, the subjective importance of SES‐related identities increased, whereas the importance of basic‐demographic and (to a lesser extent) sociocultural identities decreased. Interestingly, these findings echo those of a qualitative, interview‐based study conducted with American college students: Aries and Seider ( 2007 ) found that affluent respondents were more likely than their less affluent counterparts to acknowledge the importance of social class in shaping their identities. As the researchers put it, ‘The affluent students were well aware of the educational benefits that had accrued from their economically privileged status and of the opportunities that they had to travel and pursue their interests. The lower‐income students were more likely to downplay class in their conception of their own identities than were the affluent students’ (p. 151).
Thus, despite SES receiving relatively scant attention from self and identity researchers, there is converging quantitative and qualitative evidence that SES plays an important role in structuring the self‐concept.
Contexts that shape self‐construal: Home, school, and work
Stephens, Markus, and Phillips ( 2014 ) have analysed the ways in which social class shapes the self‐concept through the ‘gateway contexts’ of home, school, and work. With a focus on the United States, but with broader implications, they argue that social class gives rise to culture‐specific selves and patterns of thinking, feeling, and acting. One type of self they label ‘hard interdependence.’ This, they argue, is characteristic of those who grow up in low‐income, working‐class environments. As the authors put it, ‘With higher levels of material constraints and fewer opportunities for influence, choice, and control, working‐class contexts tend to afford an understanding of the self and behavior as interdependent with others and the social context’ (p. 615). The ‘hard’ aspect of this self derives from the resilience that is needed to cope with adversity. The other type of self the authors identify is ‘expressive independence’, which is argued to be typical of those who grow up in affluent, middle‐class contexts. By comparison with working‐class people, those who grow up in middle‐class households ‘need to worry far less about making ends meet or overcoming persistent threats … Instead, middle‐class contexts enable people to act in ways that reflect and further reinforce the independent cultural ideal – expressing their personal preferences, influencing their social contexts, standing out from others, and developing and exploring their own interests’ (p. 615). Stephens and colleagues review a wide range of work on socialization that supports their argument that the contexts of home, school and workplace foster these different self‐conceptions. They also argue that middle‐class schools and workplaces use expressive independence as a standard for measuring success, and thereby create institutional barriers to upward social mobility.
The idea that schools are contexts in which social class inequalities are reinforced may initially seem puzzling, given that schools are supposed to be meritocratic environments in which achievement is shaped by ability and effort, rather than by any advantage conferred by class background. However, as Bourdieu and Passeron ( 1990 ) have argued, the school system reproduces social inequalities by promoting norms and values that are more familiar to children from middle‐class backgrounds. To the extent that this helps middle‐class children to outperform their working‐class peers, the ‘meritocratic’ belief that such performance differences are due to differences in ability and/or effort will serve to ‘explain’ and legitimate unequal performance. Consistent with this argument, Darnon, Wiederkehr, Dompnier, and Martinot ( 2018 ) primed the concept of merit in French fifth‐grade schoolchildren and found that this led to lower scores on language and mathematics tests – but that this only applied to low‐SES children. Moreover, the effect of the merit prime on test performance was mediated by the extent to which the children endorsed meritocratic beliefs. Here, then, is evidence that the ideology of meritocracy helps to reproduce social class differences in school settings.
Subjective social class
Stephens et al .’s ( 2014 ) conceptualization of culture‐specific selves that vary as a function of social class is compatible with the ‘subjective social rank’ argument advanced by Kraus, Piff, and Keltner ( 2011 ). The latter authors argue that the differences in material resources available to working‐ and middle‐class people create cultural identities that are based on subjective perceptions of social rank in relation to others. These perceptions are based on distinctive patterns of observable behaviour arising from differences in wealth, education, and occupation. ‘To the extent that these patterns of behavior are both observable and reliably associated with individual wealth, occupational prestige, and education, they become potential signals to others of a person's social class’ (Kraus et al ., 2011 , p. 246). Among the signals of social class is non‐verbal behaviour. Kraus and Keltner ( 2009 ) studied non‐verbal behaviour in pairs of people from different social class backgrounds and found that whereas upper‐class individuals were more disengaged non‐verbally, lower‐class individuals exhibited more socially engaged eye contact, head nods, and laughter. Furthermore, when naïve observers were shown 60‐s excerpts of these interactions, they used these disengaged versus engaged non‐verbal behavioural styles to make judgements of the educational and income backgrounds of the people they had seen with above‐chance accuracy. In other words, social class differences are reflected in social signals, and these signals can be used by individuals to assess their subjective social rank. By comparing their wealth, education, occupation, aesthetic tastes, and behaviour with those of others, individuals can determine where they stand in the social hierarchy, and this subjective social rank then shapes other aspects of their social behaviour. More recent research has confirmed these findings. Becker, Kraus, and Rheinschmidt‐Same ( 2017 ) found that people's social class could be judged with above‐chance accuracy from uploaded Facebook photographs, while Kraus, Park, and Tan ( 2017 ) found that when Americans were asked to judge a speaker's social class from just seven spoken words, the accuracy of their judgments was again above chance.
The fact that there are behavioural signals of social class also opens up the potential for others to hold prejudiced attitudes and to engage in discriminatory behaviour towards those from a lower social class, although Kraus et al . ( 2011 ) focus is on how the social comparison process affects the self‐perception of social rank, and how this in turn affects other aspects of social behaviour. These authors argue that subjective social rank ‘exerts broad influences on thought, emotion, and social behavior independently of the substance of objective social class’ (p. 248). The relation between objective and subjective social class is an interesting issue in its own right. Objective social class is generally operationalized in terms of wealth and income, educational attainment, and occupation. These are the three ‘gateway contexts’ identified by Stephens et al . ( 2014 ). As argued by them, these contexts have a powerful influence on individual cognition and behaviour who operate within them, but they do not fully determine how individuals developing and living in these contexts think, feel, and act. Likewise, there will be circumstances in which individuals who objectively are, say, middle‐class construe themselves as having low subjective social rank as a result of the context in which they live.
There is evidence from health psychology that measures of objective and subjective social class have independent effects on health outcomes, with subjective social class explaining variation in health outcomes over and above what can be accounted for in terms of objective social class (Adler, Epel, Castellazzo, & Ickovics, 2000 ; Cohen et al ., 2008 ). For example, in the prospective study by Cohen et al . ( 2008 ), 193 volunteers were exposed to a cold or influenza virus and monitored in quarantine for objective and subjective signs of illness. Higher subjective class was associated with less risk of becoming ill as a result of virus exposure, and this relation was independent of objective social class. Additional analyses suggested that the impact of subjective social class on likelihood of becoming ill was due in part to differences in sleep quantity and quality. The most plausible explanation for such findings is that low subjective social class is associated with greater stress. It may be that seeing oneself as being low in subjective class is itself a source of stress, or that it increases vulnerability to the effects of stress.
Below I organize the social psychological literature on social class in terms of the impact of class on three types of outcome: thought , encompassing social cognition and attitudes; emotion , with a focus on moral emotions and prosocial behaviour; and behaviour in high‐prestige educational and workplace settings. I will show that these impacts of social class are consistent with the view that the different construals of the self that are fostered by growing up in low versus high social class contexts have lasting psychological consequences.
Social cognition and attitudes
The ways in which these differences in self‐construal shape social cognition have been synthesized into a theoretical model by Kraus, Piff, Mendoza‐Denton, Rheinschmidt, and Keltner ( 2012 ). This model is shown in Figure 1 . They characterize the way lower‐class individuals think about the social environment as ‘contextualism’, meaning a psychological orientation that is motivated by the need to deal with external constraints and threats; and the way that upper‐class people think about the social environment as ‘solipsism’, meaning an orientation that is motivated by internal states such as emotion and by personal goals. One way in which these different orientations manifest themselves is in differences in responses to threat. The premise here is that lower‐class contexts are objectively characterized by greater levels of threat, as reflected in less security in employment, housing, personal safety, and health. These chronic threats foster the development of a ‘threat detection system’, with the result that people who grow up in such environments have a heightened vigilance to threat.

Model of the way in which middle‐ and working‐class contexts shape social cognition, as proposed by Kraus et al . ( 2012 ). From Kraus et al . ( 2012 ), published by the American Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
Another important difference between the contextualist lower‐class orientation and the solipsistic upper‐class one, according to Kraus et al . ( 2012 ), is in perceived control. Perceived control is closely related to other key psychological constructs, such as attributions. The evidence shows very clearly that those with lower subjective social class are also lower in their sense of personal control, and it also suggests that this reduced sense of control is related to a preference for situational (rather than dispositional) attributions for a range of social phenomena, including social inequality. The logic connecting social class to perceptions of control is straightforward: Those who grow up in middle‐ or upper‐class environments are likely to have more material and psychological resources available to them, and as a result have stronger beliefs about the extent to which they can shape their own social outcomes; by contrast, those who grow up in lower‐class environments are likely to have fewer resources available to them, and as a result have weaker beliefs about their ability to control their outcomes. There is good empirical support for these linkages. In a series of four studies, Kraus, Piff, and Keltner ( 2009 ) found that, by comparison with their higher subjective social class counterparts, lower subjective social class individuals (1) reported lower perceived control and (2) were more likely to explain various phenomena, ranging from income inequality to broader social outcomes like getting into medical school, contracting HIV, or being obese, as caused by external factors, ones that are beyond the control of the individual. Moreover, consistent with the authors’ reasoning, there was a significant indirect effect of subjective social class on the tendency to see phenomena as caused by external factors, via perceived control.
Another important social cognition measure in relation to social class is prejudice. There are two aspects of prejudice in this context. One is prejudice against people of a different class than one's own and especially attitudes towards those who are poor or unemployed; the other is the degree to which people's prejudiced attitudes about other social groups are associated with their own social class. Regarding attitudes to people who belong to a different social class, the UK evidence clearly shows that attitudes to poverty have changed over the last three decades, in that there is a rising trend for people to believe that those who live in need do so because of a lack of willpower, or because of laziness, accompanied by a corresponding decline in the belief that people live in need because of societal injustice (Clery, Lee, & Kunz, 2013 ). Interestingly, in their analysis of British Social Attitudes data over a period of 28 years, Clery et al . conclude that ‘there are no clear patterns of change in the views of different social classes, suggesting changing economic circumstances exert an impact on attitudes to poverty across society, not just among those most likely to be affected by them’ (p. 18). Given the changing attitudes to poverty, it is unsurprising to find that public attitudes to welfare spending and to redistributive taxation have also changed in a way that reflects less sympathy for those living in poverty. For example, attitudes to benefits for the unemployed have changed sharply in the United Kingdom since 1997, when a majority of respondents still believed that benefits were too low. By 2008, an overwhelming majority of respondents believed that these benefits were too high (Taylor‐Gooby, 2013 ). The way in which economic austerity has affected attitudes to these issues was the subject of qualitative research conducted by Valentine ( 2014 ). Interviews with 90 people in northern England, drawn from a range of social and ethnic backgrounds, showed that many respondents believed that unemployment is due to personal, rather than structural, failings, and that it is a ‘lifestyle choice’, leading interviewees to blame the unemployed for their lack of work and to have negative attitudes to welfare provision. Valentine ( 2014 , p. 2) observed that ‘a moralised sense of poverty as the result of individual choice, rather than structural disadvantage and inequality, was in evidence across the majority of respondents’, and that ‘Negative attitudes to welfare provision were identified across a variety of social positions and were not exclusively reserved to individuals from either working class or middle class backgrounds’.
Turning to the attitudes to broader social issues held by members of different social classes, there is a long tradition in social science of arguing that working‐class people are more prejudiced on a number of issues, especially with respect to ethnic minorities and immigrants (e.g., Lipset, 1959 ). Indeed, there is no shortage of evidence showing that working‐class white people do express more negative attitudes towards these groups. One explanation for this association is that working‐class people tend to be more authoritarian – a view that can be traced back to the early research on the authoritarian personality (Adorno, Frenkel‐Brunswik, Levinson, & Sanford, 1950 ). Recent research providing evidence in favour of this view is reported by Carvacho et al . ( 2013 ). Using a combination of cross‐sectional surveys and longitudinal studies conducted in Europe and Chile, these authors focused on the role of ideological attitudes, in the shape of right‐wing authoritarianism (RWA; Altemeyer, 1998 ) and social dominance orientation (SDO; Sidanius & Pratto, 1999 ), as mediators of the relation between social class and prejudice. To test their predictions, the researchers analysed four public opinion datasets: one based on eight representative samples in Germany; a second based on representative samples from four European countries (France, Germany, Great Britain, and the Netherlands); a third based on longitudinal research in Germany; and a fourth based on longitudinal research in Chile. Consistent with previous research, the researchers found that income and education, the two indices of social class that they used, predicted higher scores on a range of measures of prejudice, such that lower income and education were associated with greater prejudice – although education proved to be a more consistently significant predictor of prejudice than income did. RWA and SDO were negatively associated with income and education, such that higher scores on income and education predicted lower scores on RWA and SDO. Finally, there was also evidence consistent with the mediation hypothesis: The associations between income and education, on the one hand, and measures of prejudice, on the other, were often (but not always) mediated by SDO and (more consistently) RWA. Carvacho and colleagues concluded that ‘the working class seems to develop and reproduce an ideological configuration that is generally well suited for legitimating the social system’ (p. 283).
Indeed, a theme that emerges from research on social class and attitudes is that ideological factors have a powerful influence on attitudes. The neoliberal ideology that has dominated political discourse in most Western, industrialized societies in the past three decades has influenced attitudes to such an extent that even supporters of left‐of‐centre political parties, such as the Labour Party in the United Kingdom, regard poverty as arising from individual factors and tend to hold negative beliefs about the level of welfare benefits for the unemployed. Such attitudes are shared to a perhaps surprising extent by working‐class people (Clery et al ., 2013 ) and, as we have seen, the research by Carvacho et al . ( 2013 ) suggests that working‐class people endorse ideologies that endorse and preserve a social system that materially disadvantages them.
The notion that people who are disadvantaged by a social system are especially likely to support it is known as the ‘system justification hypothesis’, which holds that ‘people who suffer the most from a given state of affairs are paradoxically the least likely to question, challenge, reject, or change it’ (Jost, Pelham, Sheldon, & Sullivan, 2003 , p. 13). The rationale for this prediction derives in part from cognitive dissonance theory (Festinger, 1957 ), the idea being that it is psychologically inconsistent to experience oppression but not to protest against the system that causes it. One way to reduce the resulting dissonance is to support the system even more strongly, in the same way that those who have to go through an unpleasant initiation rite in order to join a group or organization become more strongly committed to it.
Two large‐scale studies of survey data (Brandt, 2013 ; Caricati, 2017 ) have cast considerable doubt on the validity of this hypothesis, showing that any tendency for people who are at the bottom of a social system to be more likely to support the system than are their advantaged counterparts is, at best, far from robust. Moreover, it has been argued that there is in any case a basic theoretical inconsistency between system justification theory and cognitive dissonance theory (Owuamalam, Rubin, & Spears, 2016 ). However, the fact that working‐class people may not be more supportive of the capitalist system than their middle‐ and upper‐class counterparts does not mean that they do not support the system. Thus, the importance of Carvacho et al .'s ( 2013 ) findings is not necessarily undermined by the results reported by Brandt ( 2013 ) and Caricati ( 2017 ). Being willing to legitimate the system is not the same thing as having a stronger tendency to do this than people who derive greater advantages from the system.
The finding that there is an association between social class and prejudice has also been explained in terms of economic threat. The idea here is that members of ethnic minorities and immigrants also tend to be low in social status and are therefore more likely to be competing with working‐class people than with middle‐class people for jobs, housing, and other services. A strong way to test the economic threat explanation would be to assess whether higher‐class people are prejudiced when confronted with immigrants who are highly educated and likely to be competing with them for access to employment and housing. Such a test was conducted by Kuppens, Spears, Manstead, and Tausch ( 2018 ). These researchers examined whether more highly educated participants would express negative attitudes towards highly educated immigrants, especially when threat to the respondents’ own jobs was made salient, either by drawing attention to the negative economic outlook or by subtly implying that the respondents’ own qualifications might be insufficient in the current job market. Consistent with the economic threat hypothesis, a series of experimental studies with student participants in different European countries showed that attitudes to immigrants were most negative when the immigrants also had a university education.
The same researchers also combined US census data with American National Election Study survey data to examine whether symbolic racism was higher in areas where there was a higher number of Blacks with a similar education to that of the White participants. In areas where Blacks were on average less educated, a higher number Blacks was associated with more symbolic racism among Whites who had less education, but in areas where Blacks were on average highly educated, a higher number of Blacks was associated with more symbolic racism on the part of highly educated White people. Again, these findings are consistent with the view that prejudice arises from economic threat.
Research reported by Jetten, Mols, Healy, and Spears ( 2017 ) is also relevant to this issue. These authors examined how economic instability affects low‐SES and high‐SES people. Unsurprisingly, they found that collective angst was higher among low‐SES participants. However, they also found that high‐SES participants expressed anxiety when they were presented with information suggesting that there was high economic instability, that is, that the ‘economic bubble’ might be about to burst. Moreover, they were more likely to oppose immigration when economic instability was said to be high, rather than low. These results reflect the fact that high‐SES people have a lot to lose in times of economic crisis, and that this ‘fear of falling’ is associated with opposition to immigration.
Together, these results provide good support for an explanation of the association between social class and prejudice in terms of differential threat to the group (see also Brandt & Henry, 2012 ; Brandt & Van Tongeren, 2017 ). Ethnic minorities and immigrants typically pose most threat to the economic well‐being of working‐class people who have low educational qualifications, and this provides the basis for the observation that working‐class people are more likely to be prejudiced. The fact that higher‐educated and high‐SES people express negative views towards ethnic minorities and immigrants when their economic well‐being is threatened shows that it is perceived threat to one's group's interests that underpins this prejudice. It is also worth noting that the perception of threat to a group's economic interests is likely to be greater during times of economic recession.
Emotion and prosocial behaviour
A strong theme emerging from research investigating the relation between social class and emotion is that lower‐class individuals score more highly on measures of empathy. The rationale for expecting such a link is that because lower‐class individuals are more inclined to explain events in terms of external factors, they should be more sensitive to the ways in which external events shape the emotions of others, and therefore better at judging other people's emotions. A complementary rationale is that the tendency for lower social class individuals to be more socially engaged and to have more interdependent social relationships should result in greater awareness of the emotions experienced by others. This reasoning was tested in three studies reported by Kraus, Côté, and Keltner ( 2010 ).
In the first of these studies, the authors examined the relation between educational attainment (a proxy for social class) and scores on the emotion recognition subscale of the Mayer‐Salovey‐Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (Mayer, Salovey, & Caruso, 2002 ). High‐school‐educated participants attained a higher score than did their college‐educated counterparts. In a second study, pairs of participants took part in a hypothetical job interview in which an experimenter asked each of them a set of standard questions. This interaction provided the basis for the measure of empathic accuracy, in that each participant was asked to rate both their own emotions and their partner's emotions during the interview. Subjective social class was again related to empathic accuracy, with lower‐class participants achieving a higher score. Moreover, lower‐class participants were more inclined to explain decisions they made in terms of situational rather than dispositional factors, and the relation between subjective social class and empathy was found to be mediated by this tendency to explain decisions in terms of situational factors. The researchers conducted a third study in which they manipulated subjective social class. This time they assessed empathic accuracy using the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test (Baron‐Cohen, Wheelwright, Hill, Raste, & Plumb, 2001 ). Participants who were temporarily induced to experience lower social class were better at recognizing emotions from the subtle cues available from the eye region of the face.
These findings are compatible with the view that lower social class individuals are more sensitive to contextual variation and more inclined to explain events in situational terms. However, some aspects of the results are quite surprising. For example, there seems to be no compelling reason to predict that greater sensitivity to contextual variation would be helpful in judging static facial expressions, which were the stimuli in Studies 1 and 3 of Kraus et al .'s ( 2010 ) research. Thus, the relation between social class and emotion recognition in these studies would seem to depend on the notion that the greater interdependence that is characteristic of lower‐class social environments fosters greater experience with, and therefore knowledge of, the relation between facial movement and subjective emotion, although it still seems surprising that a temporary induction of lower subjective social class, as used in Study 3, should elicit the same effect as extensive real‐life experience of inhabiting lower‐class environments.
If lower‐class individuals are more empathic than their higher‐class counterparts, and are therefore better at recognizing the distress or need of others, this is likely to influence their behaviour in settings where people are distressed and/or in need. This, indeed, is what the evidence suggests. In a series of four studies, Piff, Kraus, Côté, Cheng, and Keltner ( 2010 ) found a consistent tendency for higher‐class individuals to be less inclined to help others than were their lower‐class counterparts. In Study 1, participants low in subjective social class made larger allocations in a dictator game (a game where you are free to allocate as much or as little of a resource to another person as you want) played with an anonymous other than did participants high in subjective social class. In Study 2, subjective social class was manipulated by asking participants to compare themselves to people either at the very top or very bottom of the status hierarchy ladder, the idea being that subjective social class should be lower for those making upward comparisons and higher for those making downward comparisons. Prosocial behaviour was measured by asking participants to indicate the percentage of income that people should spend on a variety of goods and services, one of which was charitable donations. Participants who were induced to experience lower subjective social class indicated that a greater percentage of people's annual salary should be spent on charitable donations compared to participants who were induced to experience higher subjective social class. In Study 3, the researchers used a combination of educational attainment and household income to assess social class and used social value orientation (Van Lange, De Bruin, Otten, & Joireman, 1997 ) as a measure of egalitarian values. These two variables were used to predict behaviour in a trust game. Consistent with predictions, lower‐class participants showed greater trust in their anonymous partner than did their higher‐class counterparts, and this relation was mediated by egalitarian values. In their final study, the researchers manipulated compassion by asking participants in the compassion condition to view a 46‐s video about child poverty. Higher‐ and lower‐class participants were then given the chance to help someone in need. The researchers predicted that helping would only be moderated by compassion among higher‐class participants, on the grounds that lower‐class participants would already be disposed to help, and the results were consistent with this prediction. Overall, these four studies are consistent in showing that, relative to higher‐class people, lower‐class people are more generous, support charity to a greater extent, are more trusting towards a stranger, and more likely to help a person in distress.
The reliability of this finding has been called into question by Korndörfer, Egloff, and Schmukle ( 2015 ), who found contrary evidence in a series of studies. One way to resolve these apparently discrepant findings is to argue, as Kraus and Callaghan ( 2016 ) did, that the relation between social class and prosocial behaviour is moderated by a number of factors, including whether the context is a public or private one. To test this idea, Kraus and Callaghan ( 2016 ) conducted a series of studies in which they manipulated whether donations made to an anonymous other in a dictator game were made in a private or public context. In the private context, the donor remained anonymous. In the public context, the donor's name and city of residence were announced, along with the donation. Lower‐class participants were more generous in private than in public, whereas the reverse was true for higher‐class participants. Interestingly, higher‐class participants were more likely to expect to feel proud about acting prosocially, and this difference in anticipated pride mediated the effect of social class on the difference between public and private donations.
The fact that lower‐class people have been found to hold more egalitarian values and to be more likely to help regardless of compassion level suggests that it is the greater resources of higher‐class participants that makes them more selfish and therefore less likely to help others. This ‘selfishness’ account of the social class effect on prosocial behaviour is supported by another series of studies reported by Piff, Stancato, Côté, Mendoza‐Denton, and Keltner ( 2012 ), who found that, relative to lower‐class individuals, higher‐class people were more likely to show unethical decision‐making tendencies, to take valued goods from others, to lie in a negotiation, to cheat to increase their chances of winning a prize and to endorse unethical behaviour at work. There was also evidence that these unethical tendencies were partly accounted for by more favourable attitudes towards greed among higher‐class people. Later research shows that the relation between social class and unethical behaviour is moderated by whether the behaviour benefits the self or others. Dubois, Rucker, and Galinsky ( 2015 ) varied who benefited from unethical behaviour and showed that the previously reported tendency for higher‐class people to make more unethical decisions was only observed when the outcome was beneficial to the self. These findings are consistent with the view that the greater resources enjoyed by higher‐class individuals result in a stronger focus on the self and a reduced concern for the welfare of others.
Interestingly, this stronger self‐focus and lesser concern for others’ welfare on the part of higher‐class people are more evident in contexts characterized by high economic inequality. This was shown by Côté, House, and Willer ( 2015 ), who analysed results from a nationally representative US survey and showed that higher‐income respondents were only less generous in the offers they made to an anonymous other in a dictator game than their lower‐income counterparts in areas that were high in economic inequality, as reflected in the Gini coefficient. Indeed, in low inequality areas, there was evidence that higher‐income respondents were more generous than their lower‐income counterparts. To test the causality of this differential association between income and generosity in high and low inequality areas, the authors conducted an experiment in which participants were led to believe that their home state was characterized by high or low degree of economic inequality and then played a dictator game with an anonymous other. High‐income participants were less generous than their low‐income counterparts in the high inequality condition but not in the low inequality condition.
A possible issue with Côté et al . ( 2015 ) research in the current context is that it focuses on income rather than class. Although these variables are clearly connected, class is generally thought to be indexed by more than income. The research nevertheless suggests that economic inequality plays a key role in shaping the attitudes and behaviours of higher‐class individuals. There are at least three (not mutually exclusive) explanations for this influence of inequality. One is that inequality increases the sense of entitlement in higher‐class people, because they engage more often in downward social comparisons. Another is that higher‐class people may be more concerned about losing their privileged position in society if they perceive a large gap between the rich and the poor. A final explanation is that higher‐class people may be more highly motivated to justify their privileged position in society when the gap between rich and poor is a large one. Whichever of these explanations is correct – and they may all be to some extent – the fact that prosocial behaviour on the part of higher‐class individuals decreases under conditions of high economic inequality is important, given that the United States is one of the most economically unequal societies in the industrialized world. In unequal societies, then, it seems safe to conclude that on average, higher‐class individuals are less likely than their lower‐class counterparts to behave prosocially, especially where the prosocial behaviour is not public in nature.
Universities and workplaces
The selective nature of higher education (HE), involving economic and/or qualification requirements to gain entry, makes a university a high‐status context. Working‐class people seeking to attain university‐level qualifications are therefore faced with working in an environment in which they may feel out of place. Highly selective universities such as Oxford and Cambridge in the United Kingdom, or Harvard, Stanford, and Yale in the United States, are especially likely to appear to be high in status and therefore out of reach. Indeed, the proportion of working‐class students at Oxford and Cambridge is strikingly low. According to the UK's Higher Education Statistics Agency , the percentage of students at Oxford and Cambridge who were from routine/manual occupational backgrounds was 11.5 and 12.6, respectively, in the academic year 2008/9. This compares with an ONS figure of 37% of all people aged between 16 and 63 in the United Kingdom being classified with such backgrounds. The figures for Oxford and Cambridge are extreme, but they illustrate a more general phenomenon, both in the United Kingdom and internationally: students at elite, research‐led universities are more likely to come from middle‐ and upper‐class backgrounds than from working‐class backgrounds (Jerrim, 2013 ).
The reasons for the very low representation of working‐class students at these elite institutions are complex (Chowdry, Crawford, Dearden, Goodman, & Vignoles, 2013 ), but at least one factor is that many working‐class students do not consider applying because they do not see themselves as feeling at home there. They see a mismatch between the identity conferred by their social backgrounds and the identity they associate with being a student at an elite university. This is evident from ethnographic research. For example, Reay, Crozier, and Clayton ( 2010 ) interviewed students from working‐class backgrounds who were attending one of four HE institutions, including an elite university (named Southern in the report). A student at Southern said this about her mother's reaction to her attending this elite university: ‘I don't think my mother really approves of me going to Southern. It's not what her daughter should be doing so I don't really mention it when I go home. It's kind of uncomfortable to talk about it’ (p. 116). In a separate paper, Reay, Crozier, and Clayton ( 2009 ) focus on the nine students attending Southern, examining whether these students felt like ‘fish out of water’. Indeed, there was evidence of difficulty in adjusting to the new environment, both socially and academically. One student said, ‘I wasn't keen on Southern as a place and all my preconceptions were “Oh, it's full of posh boarding school types”. And it was all true … it was a bit of a culture shock’ (p. 1111), while another said, ‘If you were the best at your secondary school … you're certainly not going to be the best here’ (p. 1112). A similar picture emerges from research in Canada by Lehmann ( 2009 , 2013 ), who interviewed working‐class students attending a research‐intensive university, and found that the students experienced uncomfortable conflicts between their new identities as university students and the ties they had with family members and non‐student friends.
Such is the reputation of elite, research‐intensive universities that working‐class high‐school students are unlikely to imagine themselves attending such institutions, even if they are academically able. Perceptions of these universities as elitist are likely to deter such students from applying. Evidence of this deterrence comes from research conducted by Nieuwenhuis, Easterbrook, and Manstead ( 2018 ). They report two studies in which 16‐ to 18‐year‐old secondary school students in the United Kingdom were asked about the universities they intended to apply to. The studies were designed to test the theoretical model shown in Figure 2 , which was influenced by prior work on the role of identity compatibility conducted by Jetten, Iyer, Tsivrikos, and Young ( 2008 ). According to the model in Figure 2 , SES influences university choice partly through its impact on perceived identity compatibility and anticipated acceptance at low‐ and high‐status universities.

Theoretical model of the way in which the socioeconomic status ( SES ) influences application to high‐status universities as a result of social identity factors and academic achievement, as proposed by Nieuwenhuis et al . ( 2018 ).
In the first study conducted by Nieuwenhuis and colleagues, students who were 6 months away from making their university applications responded to questions about their perceptions of two universities, one a research‐intensive, selective university (SU), the other a less selective university (LSU). Both universities were located in the same geographical region, not far from the schools where the participants were recruited. In the second study, students who were 6 weeks away from making their university applications responded to similar questions, but this time about three universities in the region, two of which were the same as those in Study 1, while the third was a highly selective institution (HSU). The questions put to respondents measured their perceptions of identity compatibility (e.g., consistency between family background and decision to go to university) and anticipated acceptance (e.g., anticipated identification with students at the university in question). Measures of parental education and academic achievement in previous examinations were taken, as well as the three universities to which they would most like to apply, which were scored in accordance with a published national league table.
In both studies, it was found that relatively disadvantaged students (whose parents had low levels of educational attainment) scored lower on identity compatibility and that low scores on identity compatibility were associated with lower anticipated acceptance at the SU (Study 1) or at the HSU (Study 2). These anticipated acceptance scores, in turn, predicted the type of university to which participants wanted to apply, with those who anticipated feeling accepted at more selective universities being more likely to apply to higher status universities. All of these relations were significant while controlling for academic achievement. Together, the results of these studies show that perceptions of acceptance at different types of university are associated with HE choices independently of students’ academic ability. This helps to explain why highly able students from socially disadvantaged backgrounds are more likely to settle for less prestigious universities.
Alternatively, working‐class students may opt out of HE altogether. Hutchings and Archer ( 2001 ) interviewed young working‐class people who were not participating in HE and found that a key reason for their non‐participation was a perception that the kinds of HE institutions that were realistically available to them were second‐rate: ‘[O]ur respondents constructed two very different pictures of HE. One was of Oxbridge and campus universities, pleasant environments in which middle‐class students … can look forward to achieving prestigious degrees and careers. The second construction was of rather unattractive buildings in which “skint” working‐class students … have to work hard under considerable pressure, combining study with a job and having little time for social life. This second picture was the sort of HE that our respondents generally talked about as available to them, and they saw it as inferior to ‘real’ HE’ (p. 87).
Despite the deterrent effect of perceived identity incompatibility and lack of psychological fit, some working‐class students do gain entry to high‐status universities. Once there, they are confronted with the same issues of fit. Stephens, Fryberg, Markus, Johnson, and Covarrubias ( 2012 ) describe this as ‘cultural mismatch’, arguing that the interdependent norms that characterize the working‐class backgrounds of most first‐generation college students in the United States do not match the middle‐class independent norms that prevail in universities offering 4‐year degrees and that this mismatch leads to greater discomfort and poorer academic performance. Their cultural mismatch model is summarized in Figure 3 .

Model of cultural mismatch proposed by Stephens, Fryberg, Markus, et al . ( 2012 ). The mismatch is between first‐generation college students’ norms, which are more interdependent than those of continuing‐generation students, and the norms of independence that prevail in universities. From Stephens, Fryberg, Markus, et al . ( 2012 ), published by the American Psychological Association. Reprinted with permission.
To test this model, Stephens, Fryberg, Markus, et al . ( 2012 ) surveyed university administrators at the top 50 national universities and the top 25 liberal arts colleges. The majority of the 261 respondents were deans. They were asked to respond to items expressing interdependent (e.g., learn to work together with others) or independent (e.g., learn to express oneself) norms, selecting those that characterized their institution's culture or choosing statements reflecting what was more often emphasized by the institution. More than 70% of the respondents chose items reflecting a greater emphasis on independence than on interdependence. Similar results were found in a follow‐up study involving 50 administrators at second‐tier universities and liberal arts colleges, showing that this stronger focus on independence was not only true of elite institutions. Moreover, a longitudinal study of first‐generation students found that this focus on independence did not match the students’ interdependent motives for going to college, in that first‐generation students selected fewer independent motives (e.g., become an independent thinker) and twice as many interdependent motives (e.g., give back to the community), compared to their continuing‐generation counterparts, and that this greater focus on interdependent motives was associated with lower grades in the first 2 years of study, even after controlling for race and SAT scores.
As Stephens and her colleagues have shown elsewhere (e.g., Stephens, Brannon, Markus, & Nelson, 2015 ), there are steps that can be taken to reduce working‐class students’ perception that they do not fit with their university environment. These authors argue that ‘a key goal of interventions should be to fortify and to elaborate school‐relevant selves – the understanding that getting a college degree is central to “who I am”, “who I hope to become”, and “the future I envision for myself”’ (p. 3). Among the interventions that they advocate as ways of creating a more inclusive culture at university are: providing working‐class role models; diversifying the way in which university experience is represented, so that university culture also provides ways of achieving interdependent goals that may be more compatible with working‐class students’ values; and ensuring that working‐class students have a voice, for example, by providing forums in which they can express shared interests and concerns.
Although there is a less well‐developed line of work on the ways in which high‐status places of work affect the aspirations and behaviours of working‐class employees, there is good reason to assume that the effects and processes identified in research on universities as places to study generalize to prestigious employment organizations as places to work (Côté, 2011 ). To the extent that many workplaces are dominated by middle‐class values and practices, working‐class employees are likely to feel out of place (Ridgway & Fisk, 2012 ). This applies both to gaining entry to the workplace, by negotiating the application and selection process (Rivera, 2012 ), and (if successful) to the daily interactions between employees in the workplace. In the view of Stephens, Fryberg, and Markus ( 2012 ), many workplaces are characterized by cultures of expressive independence, where working‐class employees are less likely to feel at home. As Stephens et al . ( 2014 , p. 626) argue, ‘This mismatch between working‐class employees and their middle‐class colleagues and institutions could also reduce employees’ job security and satisfaction, continuing the cycle of disadvantage for working‐class employees.’
Towards an integrative model
The work reviewed here provides the basis for an integrative model of how social class affects thoughts, feelings, and behaviour. The model is shown in Figure 4 and builds on the work of others, especially that of Nicole Stephens and colleagues and that of Michael Kraus and colleagues. At the base of the model are differences in the material circumstances of working‐class and middle‐class people. These differences in income and wealth are associated with differences in social capital, in the form of friendship networks, and cultural capital, in the form of tacit knowledge about how systems work, that have a profound effect on the ways in which individuals who grow up in these different contexts construe themselves and their social environments. For example, if you have family members or friends who have university degrees and/or professional qualifications, you are more likely to entertain these as possible futures than if you do not have these networks; and if through these networks you have been exposed to libraries, museums, interviews, and so on, you are more likely to know how these cultural institutions work, less likely to be intimidated by them, and more likely to make use of them. In sum, a middle‐class upbringing is more likely to promote the perception that the environment is one full of challenges that can be met rather than threats that need to be avoided. These differences in self‐construal and models of interpersonal relations translate into differences in social emotions and behaviours that are noticeable to self and others, creating the opportunity for people to rank themselves and others, and for differences in norms and values to emerge. To the extent that high‐status institutions in society, such as elite universities and prestigious employers, are characterized by norms and values that are different from those that are familiar to working‐class people, the latter will feel uncomfortable in such institutions and will perform below their true potential.

Integrative model of how differences in material conditions generate social class differences and differences in social cognition, emotion, and behaviour.
Also depicted in Figure 4 is the way in which ideology moderates the relations between social class, on the one hand, and social cognition and social behaviour, on the other, and the ways in which economic inequality and threat moderate the relations between psychological dispositions and social behaviour. Although there is good evidence for many of the proposed relations depicted in the model, there is relatively little hard evidence concerning the moderating roles of ideology and economic inequality and threat. There is evidence that economic threat is associated with prejudice (e.g., Billiet, Meuleman, & De Witte, 2014 ), and that this also applies to higher‐educated people (e.g., Kuppens et al ., 2018 ). There is also evidence that high economic inequality increases the tendency for high‐income people to be less generous to others (Côté et al ., 2015 ), but these are influences that need further examination. Likewise, there is evidence of the moderating impact of ideology on the translation from social class to social cognition and behaviour (e.g., Wiederkehr, Bonnot, Krauth‐Gruber, & Darnon, 2015 ), but this, too, is an influence that merits additional investigation. A further point worth making is that much of the work on which this integrative model is based was conducted in the United States, which raises the question of the extent to which it is applicable to other contexts. There are some differences between the United States and other Western, industrialized countries that are relevant to the model. For example, the United States is more economically unequal than virtually every other industrialized country (Piketty & Saez, 2014 ). At the same time, the perceived degree of social mobility is greater in the United States than in other countries (Isaacs, 2008 ) – although the reality is that social mobility is lower in the United States (and indeed in the United Kingdom; see Social Mobility Commission, 2017 ) than in many other industrialized counties (Isaacs, 2008 ). These differences in economic inequality and ideology mean that the moderating roles played by these factors may vary from one country to another. For example, there is evidence that those in Europe who are poor or on the left of the political spectrum are more concerned with and unhappy about inequality than are their American counterparts, which may be related to different beliefs about social mobility (Alesina, Di Tella, & MacCulloch, 2004 ). Although there seems to be no good reason to question the generalizability of the other relations posited in the model, there is an obvious need to expand the research base on which the model is founded.
Prospects for social change
The cycle of disadvantage that starts with poor material conditions and ends with lower chances of entering and succeeding in the very contexts (universities and high‐status workplaces) that could increase social mobility is not going to be changed in the absence of substantial pressure for social change. It is therefore interesting that when people are asked about social inequality, they generally say that they are in favour of greater equality.
Norton and Ariely ( 2011 ) asked a nationally representative sample of more than 5,500 Americans to estimate the (then) current wealth distribution in the United States and also to express their preferences for how wealth should be distributed. The key findings from this research were (1) that respondents greatly underestimated the degree of wealth inequality in the United States, believing that the wealthiest 20% of the population owned 59% of the wealth, where the actual figure is 84% and (2) that their preferred distribution of wealth among citizens was closer to equality than even their own incorrect estimations of the distribution (e.g., they expressed a preference that the top 20% should own 32% of the nation's wealth). This also held for wealthy respondents and Republican voters – albeit to a lesser extent than their poorer and Democrat counterparts. Similar results for Australian respondents were reported by Norton, Neal, Govan, Ariely, and Holland ( 2014 ).
These studies have been criticized on the grounds that the ‘quintile’ methodology they use provides respondents with an anchor (20%) from which they adjust upwards or downwards. However, when Eriksson and Simpson ( 2012 ) used a different methodology, they found that although American respondents’ preferences for wealth distribution were more unequal than those found using the quintile methodology, they were still much more egalitarian than the actual distribution. Similar conclusions were reached in a study of American adolescents conducted by Flanagan and Kornbluh ( 2017 ), where participants expressed a strong preference for a much more egalitarian society than the degree of stratification they perceived to exist in the United States. It is also worth noting that similar findings have been reported in a study of preferences for income inequality (Kiatpongsan & Norton, 2014 ), where it was found that American respondents underestimated the actual difference in income between CEOs and unskilled workers (354:1), and that their preferences regarding this difference (7:1) were more egalitarian than were their estimates (30:1).
Given the evidence that citizens consistently express a preference for less wealth and income inequality than what currently prevails in many societies, it is worth considering why there is not greater support for redistributive policies. It is known that one factor that weakens support for such policies is a belief in social mobility. American participants have been found to overestimate the degree of social mobility in the United States (Davidai & Gilovich, 2015 ; Kraus & Tan, 2015 ), and Shariff, Wiwad, and Aknin ( 2016 ) have shown, using a combination of survey and experimental methods, that higher perceived mobility leads to greater acceptance of income inequality. These authors also showed that the effect of their manipulation of perceived income mobility on tolerance for inequality was mediated by two factors: the expectation that respondents’ children would be upwardly mobile; and perceptions of the degree to which someone's economic standing was the result of effort, rather than luck. This suggests that people's attitudes to income inequality – and therefore their support for steps to reduce it – are shaped by their perceptions that (1) higher incomes are possible to achieve, at least for their children, and (2) when these higher incomes are achieved, they are deserved. It follows that any intervention that reduces the tendency to overestimate income mobility should increase support for redistributive policies.
Another factor that helps to account for lack of support for redistribution is people's perceptions of their own social standing or rank. Brown‐Iannuzzi, Lundberg, Kay, and Payne ( 2015 ) have shown that subjective status is correlated with support for redistributive policies, and that experimentally altering subjective status leads to changes in such support. In both cases, lower subjective status was associated with stronger support for redistribution, even when actual resources and self‐interest were held constant. So one's perception of one's own relative social rank influences support for redistribution. This points to the importance of social comparisons and suggests that those who compare themselves with others who have a lower social standing are less likely to be supportive of redistribution.
Evidence that people's attitudes to inequality and to policies that would reduce it can be influenced by quite straightforward interventions comes from research reported by McCall, Burk, Laperrière, and Richeson ( 2017 ). In three studies, these researchers show that exposing American participants to information about the rising economic inequality, compared to control information, led to stronger perceptions that economic success is due to structural factors rather than individual effort. In the largest of the three studies, involving a representative sample of American adults, it was also found that information about rising inequality led to greater endorsement of policies that could be implemented by government and by business to reduce inequality. This research shows that, under the right conditions, even those living in a society that is traditionally opposed to government intervention would support government policies to reduce inequality.
Also relevant to the likelihood of people taking social action on this issue is how descriptions of inequality are framed. Bruckmüller, Reese, and Martiny ( 2017 ) have shown that relatively subtle variations in such framing, such as whether an advantaged group is described as having more or a disadvantaged group is described as having less, influence perceptions of the legitimacy of these differences; larger differences between groups were evaluated as less legitimate when the disadvantaged group was described as having less. Perceptions of the illegitimacy of inequality in group outcomes are likely to evoke group‐based anger, which in turn is known to be one of the predictors of collective action (Van Zomeren, Spears, Fischer, & Leach, 2004 ).
There is solid evidence that the material circumstances in which people develop and live their lives have a profound influence on the ways in which they construe themselves and their social environments. The resulting differences in the ways that working‐class and middle‐ and upper‐class people think and act serve to reinforce these influences of social class background, making it harder for working‐class individuals to benefit from the kinds of educational and employment opportunities that would increase social mobility and thereby improve their material circumstances. At a time when economic inequality is increasing in many countries, this lack of mobility puts a strain on social cohesion. Most people believe that economic inequality is undesirable and, when presented with the evidence of growing inequality, say that they would support government policies designed to reduce it. Given that the social class differences reviewed here have their origins in economic inequality, it follows that redistributive (or ‘predistributive’; Taylor‐Gooby, 2013 ) policies are urgently needed to create greater equality.
Acknowledgements
Thanks are due to Colin Foad, Matt Easterbrook, Russell Spears and John Drury for their helpful comments on a previous version of this paper.
- Adler, N. E. , Epel, E. S. , Castellazzo, G. , & Ickovics, J. R. (2000). Relationship of subjective and objective social status with psychological and physiological functioning: Preliminary data in healthy, White women . Health Psychology , 19 , 586–592. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.19.6.586 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Adorno, T. W. , Frenkel‐Brunswik, E. , Levinson, D. J. , & Sanford, R. N. (1950). The authoritarian personality . New York, NY: Harper & Row. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alesina, A. , Di Tella, R. , & MacCulloch, R. (2004). Inequality and happiness: Are Europeans and Americans different? Journal of Public Economics , 88 , 2009–2042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpubeco.2003.07.006 [ Google Scholar ]
- Altemeyer, R. A. (1998). The other “authoritarian personality” . Advances in Experimental Social Psychology , 30 , 47–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0065-2601(08)60382-2 [ Google Scholar ]
- Aries, E. , & Seider, M. (2007). The role of social class in the formation of identity: A study of public and elite private college students . Journal of Social Psychology , 147 , 137–157. https://doi.org/10.3200/socp.147.2.137-157 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Baron‐Cohen, S. , Wheelwright, S. , Hill, J. , Raste, Y. , & Plumb, I. (2001). The “Reading the mind in the eyes” test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high‐functioning autism . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines , 42 , 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00715 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker, J. C. , Kraus, M. W. , & Rheinschmidt‐Same, M. (2017). Cultural expressions of social class and their implications for group‐related beliefs and behaviors . Journal of Social Issues , 73 , 158–174. https://doi.org/10.1111/josi.12209 [ Google Scholar ]
- Billiet, J. , Meuleman, B. , & De Witte, H. (2014). The relationship between ethnic threat and economic insecurity in times of economic crisis: Analysis of European Social Survey data . Migration Studies , 2 , 135–161. https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnu023 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bourdieu, P. , & Passeron, J.‐C. (1990). Reproduction in education, society and culture (2nd ed.). London, UK: Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brandt, M. J. (2013). Do the disadvantaged legitimize the social system? A large‐scale test of the status‐legitimacy hypothesis . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 104 , 765–785. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031751 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brandt, M. J. , & Henry, P. J. (2012). Psychological defensiveness as a mechanism explaining the relationship between low socioeconomic status and religiosity . International Journal for the Psychology of Religion , 22 , 321–332. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508619.2011.646565 [ Google Scholar ]
- Brandt, M. J. , & Van Tongeren, D. R. (2017). People both high and low on religious fundamentalism are prejudiced toward dissimilar groups . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 112 ( 1 ), 76–97. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspp0000076 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown‐Iannuzzi, J. L. , Lundberg, K. B. , Kay, A. C. , & Payne, B. K. (2015). Subjective status shapes political preferences . Psychological Science , 26 , 15–26. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797614553947 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bruckmüller, S. , Reese, G. , & Martiny, S. E. (2017). Is higher inequality less legitimate? Depends on how you frame it! British Journal of Social Psychology , 56 , 766–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjso.12202 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Buck, N. , & McFall, S. (2012). Understanding society: Design overview . Longitudinal and Life Course Studies , 3 , 5–17. https://doi.org/10.14301/llcs.v3i1.159 [ Google Scholar ]
- Caricati, L. (2017). Testing the status‐legitimacy hypothesis: A multilevel modeling approach to the perception of legitimacy in income distribution in 36 nations . Journal of Social Psychology , 157 , 532–540. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224545.2016.1242472 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carvacho, H. , Zick, A. , Haye, A. , González, R. , Manzi, J. , Kocik, C. , & Bertl, M. (2013). On the relation between social class and prejudice: The roles of education, income, and ideological attitudes . European Journal of Social Psychology , 43 , 272–285. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.1961 [ Google Scholar ]
- Chowdry, H. , Crawford, C. , Dearden, L. , Goodman, A. , & Vignoles, A. (2013). Widening participation in higher education: Analysis using linked administrative data . Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series A , 176 , 431–457. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-985x.2012.01043.x [ Google Scholar ]
- Clery, E. , Lee, L. , & Kunz, S. (2013). Public attitudes to poverty and welfare, 1983–2011: Analysis using British attitudes data . London, UK: NatCen Social Research. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen, S. , Alper, C. M. , Doyle, W. J. , Adler, N. , Treanor, J. J. , & Turner, R. B. (2008). Objective and subjective socioeconomic status and susceptibility to the common cold . Health Psychology , 27 , 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.27.2.268 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Côté, S. (2011). How social class shapes thoughts and actions in organizations . Research in Organizational Behavior , 31 , 43–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riob.2011.09.004 [ Google Scholar ]
- Côté, S. , House, J. , & Willer, R. (2015). High economic inequality leads higher‐income individuals to be less generous . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 112 , 15838–15843. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511536112 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Darnon, C. , Wiederkehr, V. , Dompnier, B. , & Martinot, D. (2018). ‘Where there is a will, there is a way’: Belief in school meritocracy and the social‐class achievement gap . British Journal of Social Psychology , 57 , 250–262. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjso.12214 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidai, S. , & Gilovich, T. (2015). Building a more mobile America – One income quintile at a time . Perspectives on Psychological Science , 10 , 60–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691614562005 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Department for Communities and Local Government . (2012). Citizenship survey . Retrieved from http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20120919133219/http://www.communities.gov.uk/communities/research/citizenshipsurvey/
- Dubois, D. , Rucker, D. D. , & Galinsky, A. D. (2015). Social class, power, and selfishness: When and why upper and lower class individuals behave unethically . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 108 , 436–449. https://doi.org/10.1037/pspi0000008 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Easterbrook, M. , Kuppens, T. , & Manstead, A. S. R. (2018). Socioeconomic status and the structure of the self‐concept . Unpublished manuscript, University of Sussex. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Equality Trust . (2017). How has inequality changed? Retrieved from https://www.equalitytrust.org.uk/how-has-inequality-changed
- Eriksson, K. , & Simpson, B. (2012). What do Americans know about inequality? It depends on how you ask them . Judgment and Decision Making , 7 , 741–745. [ Google Scholar ]
- Evans, G. , & Mellon, J. (2016). Social class: Identity, awareness and political attitudes: Why are we still working class? British Social Attitudes , 33 , 1–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Festinger, L. (1957). A theory of cognitive dissonance . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flanagan, C. A. , & Kornbluh, M. (2017). How unequal is the United States? Adolescents’ images of social stratification . Child Development . Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12954 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Goldthorpe, J. H. , & Lockwood, D. (1963). Affluence and the British class structure . Sociological Review , 11 , 133–163. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-954x.1963.tb01230.x [ Google Scholar ]
- Higher Education Statistics Agency . Retrieved from https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis/students/overviews?keyword=All&year=13
- Hutchings, M. , & Archer, L. (2001). ‘Higher than Einstein’: Constructions of going to university among working‐class non‐participants . Research Papers in Education , 16 , 69–91. https://doi.org/10.1080/02671520010011879 [ Google Scholar ]
- Isaacs, J. B. (2008). International comparisons of social mobility . Washington, DC: Pew Charitable Trusts. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jerrim, J. (2013). Family background and access to high ‘status’ universities . London, UK: The Sutton Trust. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jetten, J. , Iyer, A. , Tsivrikos, D. , & Young, B. M. (2008). When is individual mobility costly? The role of economic and social identity factors . European Journal of Social Psychology , 38 , 866–879. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.471 [ Google Scholar ]
- Jetten, J. , Mols, F. , Healy, N. , & Spears, R. (2017). “Fear of falling”: Economic instability enhances collective angst among societies’ wealthy class . Journal of Social Issues , 73 , 61–79. https://doi.org/10.1111/josi.12204 [ Google Scholar ]
- Jost, J. T. , Pelham, B. W. , Sheldon, O. , & Sullivan, B. N. (2003). Social inequality and the reduction of ideological dissonance on behalf of the system: Evidence of enhanced system justification among the disadvantaged . European Journal of Social Psychology , 33 , 13–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejsp.127 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kiatpongsan, S. , & Norton, M. I. (2014). How much (more) should CEOs make? A universal desire for more equal pay . Perspectives on Psychological Science , 9 , 587–593. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691614549773 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Korndörfer, M. , Egloff, B. , & Schmukle, S. C. (2015). A large scale test of the effect of social class on prosocial behavior . PLoS One , 10 ( 7 ), e0133193 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0133193 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , & Callaghan, N. (2016). Social class and prosocial behavior: The moderating role of public versus private contexts . Social Psychological and Personality Science , 7 , 769–777. https://doi.org/10.1177/1948550616659120 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , Côté, S. , & Keltner, D. (2010). Social class, contextualism, and empathic accuracy . Psychological Science , 21 , 1716–1723. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956797610387613 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , & Keltner, D. (2009). Signs of socioeconomic status: A thin‐slicing approach . Psychological Science , 20 , 99–106. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9280.2008.02251.x [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , Park, J. W. , & Tan, J. J. X. (2017). Signs of social class: The experience of economic inequality in everyday life . Perspectives on Psychological Science , 12 , 422–435. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616673192 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , Piff, P. K. , & Keltner, D. (2009). Social class, the sense of control, and social explanation . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 97 , 992–1004. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0016357 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , Piff, P. K. , & Keltner, D. (2011). Social class as culture: The convergence of resources and rank in the social realm . Current Directions in Psychological Science , 20 , 246–250. https://doi.org/10.1177/0963721411414654 [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , Piff, P. K. , Mendoza‐Denton, R. , Rheinschmidt, M. L. , & Keltner, D. (2012). Social class, solipsism, and contextualism: How the rich are different from the poor . Psychological Review , 119 , 546–572. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028756 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kraus, M. W. , & Tan, J. J. (2015). Americans overestimate social class mobility . Journal of Experimental Social Psychology , 58 , 101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2015.01.005 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuppens, T. , Spears, R. , Manstead, A. S. R. , & Tausch, N. (2018). Education and lower prejudice towards immigrants and ethnic minorities: A question of increased enlightenment or reduced economic threat? Unpublished manuscript, University of Groningen. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lehmann, W. (2009). Becoming middle class: How working‐class university students draw and transgress moral class boundaries . Sociology , 43 , 631–647. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038509105412 [ Google Scholar ]
- Lehmann, W. (2013). Habitus transformation and hidden injuries: Successful working‐class university students . Sociology of Education , 87 ( 1 ), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038040713498777 [ Google Scholar ]
- Lipset, S. M. (1959). Democracy and working‐class authoritarianism . American Sociological Review , 24 , 482–501. https://doi.org/10.2307/2089536 [ Google Scholar ]
- Mayer, J. D. , Salovey, P. , & Caruso, D. R. (2002). Mayer‐Salovey‐Caruso Emotional Intelligence Test (MSCEIT) user's manual . Toronto, ON: Multi‐Health Systems. [ Google Scholar ]
- McCall, L. , Burk, D. , Laperrière, M. , & Richeson, J. A. (2017). Exposure to rising inequality shapes Americans’ opportunity beliefs and policy support . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 114 , 9593–9598. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1706253114 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nieuwenhuis, M. , Easterbrook, M. , & Manstead, A. S. R. (2018). Accounting for unequal access to higher education: The role of social identity factors . Unpublished manuscript, University of Sussex. [ Google Scholar ]
- Norton, M. I. , & Ariely, D. (2011). Building a better America – One wealth quintile at a time . Perspectives on Psychological Science , 6 , 9–12. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691610393524 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Norton, M. I. , Neal, D. T. , Govan, C. L. , Ariely, D. , & Holland, E. (2014). The not‐so‐common wealth of Australia: Evidence for a cross‐cultural desire for a more equal distribution of wealth . Analyses of Social Issues and Public Policy , 14 , 339–351. https://doi.org/10.1111/asap.12058 [ Google Scholar ]
- Office for National Statistics . (2014). Wealth in Great Britain Wave 4: 2012 to 2014 . Retrieved from https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/personalandhouseholdfinances/incomeandwealth/compendium/wealthingreatbritainwave4/2012to2014
- Owuamalam, C. K. , Rubin, M. , & Spears, R. (2016). The system justification conundrum: Re‐examining the cognitive dissonance basis for system justification . Frontiers in Psychology , 7 , 1889 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01889 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piff, P. K. , Kraus, M. W. , Côté, S. , Cheng, B. , & Keltner, D. (2010). Having less, giving more: The influence of social class on prosocial behavior . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 99 , 771–784. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0020092 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piff, P. K. , Stancato, D. , Côté, S. , Mendoza‐Denton, R. , & Keltner, D. (2012). Higher social class predicts increased unethical behavior . Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences , 109 , 4086–4091. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118373109 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Piketty, T. , & Saez, E. (2014). Inequality in the long run . Science , 344 , 838–843. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1251936 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reay, D. , Crozier, G. , & Clayton, J. (2009). ‘Strangers in paradise’? Working‐class students in elite universities Sociology , 43 , 1103–1121. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038509345700 [ Google Scholar ]
- Reay, D. , Crozier, G. , & Clayton, J. (2010). ‘Fitting in’ or ‘standing out’: Working‐class students in UK higher education . British Educational Research Journal , 36 ( 1 ), 107–124. https://doi.org/10.1080/01411920902878925 [ Google Scholar ]
- Ridgway, C. L. , & Fisk, S. R. (2012). Class rules, status dynamics, and “gateway” interactions In Fiske S. T. & Markus H. R. (Eds.), Facing social class: How societal rank influences interaction (pp. 131–151). New York, NY: Russell Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rivera, L. (2012). Hiring as cultural matching: The case of elite professional service firms . American Sociological Review , 77 , 999–1022. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003122412463213 [ Google Scholar ]
- Savage, M. , Devine, F. , Cunningham, N. , Taylor, M. , Li, Y. , Hjellbrekke, J. , … Miles, A. (2013). A new model of social class? Findings from the BBC's Great British class experiment . Sociology , 47 , 219–250. https://doi.org/10.1177/0038038513481128 [ Google Scholar ]
- Shariff, A. F. , Wiwad, D. , & Aknin, L. B. (2016). Income mobility breeds tolerance for income inequality: Cross‐national and experimental evidence . Psychological Science , 11 , 373–380. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691616635596 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sidanius, J. , & Pratto, F. (1999). Social dominance: An intergroup theory of social hierarchies and oppression . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781139175043 [ Google Scholar ]
- Social Mobility Commission . (2017). State of the nation 2017: Social mobility in Great Britain . London, UK: HM Stationery Office; Retrieved from https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/662744/State_of_the_Nation_2017_-_Social_Mobility_in_Great_Britain.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephens, N. M. , Brannon, T. N. , Markus, H. R. , & Nelson, J. E. (2015). Feeling at home in college: Fortifying school‐relevant selves to reduce social class disparities in higher education . Social Issues and Policy Review , 9 ( 1 ), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1111/sipr.12008 [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephens, N. M. , Fryberg, S. A. , & Markus, H. R. (2012). It's your choice: How the middle‐class model of independence disadvantages working class Americans In Fiske S. T. & Markus H. R. (Eds.), Facing social class: How societal rank influences interaction (pp. 87–106). New York, NY: Russell Sage. [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephens, N. M. , Fryberg, S. A. , Markus, H. R. , Johnson, C. , & Covarrubias, R. (2012). Unseen disadvantage: How American universities’ focus on independence undermines the academic performance of first‐generation college students . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 102 , 1178–1197. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0027143 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephens, N. M. , Markus, H. M. , & Phillips, L. T. (2014). Social class culture cycles: How three gateway contexts shape selves and fuel inequality . Annual Review of Psychology , 65 , 611–634. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010213-115143 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Taylor‐Gooby, P. (2013). Why do people stigmatise the poor at a time of rapidly increasing inequality, and what can be done about it? The Political Quarterly , 84 ( 1 ), 31–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-923x.2013.02435.x [ Google Scholar ]
- Valentine, G. (2014). Inequality and class prejudice in an age of austerity . Sheffield, UK: Sheffield Political Economy Research Institute; Retrieved from http://speri.dept.shef.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2014/10/Brief8-inequality-and-class-prejudice-in-an-age-of-austerity.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Lange, P. A. , De Bruin, E. , Otten, W. , & Joireman, J. A. (1997). Development of prosocial, individualistic, and competitive orientations: Theory and preliminary evidence . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 73 , 733 https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.73.4.733 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Van Zomeren, M. , Spears, R. , Fischer, A. H. , & Leach, C. W. (2004). Put your money where your mouth is! Explaining collective action tendencies through group‐based anger and group efficacy . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 87 , 649–664. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.87.5.649 [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiederkehr, V. , Bonnot, V. , Krauth‐Gruber, S. , & Darnon, C. (2015). Belief in school meritocracy as a system‐justifying tool for low status students . Frontiers in Psychology , 6 , 1053 https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01053 [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Your Article Library
Essay on social class (918 words).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Read this comprehensive essay on Social Class !
One of the important elements of social stratification is the ‘Class’. A social class is ‘a category or group of persons having a definite status in society which permanently determines their relations to other groups’. Social classes have been defined by various thinkers “in different manner. The notion of objectivity of class existence is the main contribution of Karl Marx. His emphasis is on the economic factors. Power, style of life and property determine the class status of individuals in the society.
Karl Marx defined the social classes by their relation to the means of production (ownership or non-ownership). In modern capitalist society there are two principal classes the capitalist and the proletariat.

Image Courtesy : borderzine.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/philip-levine-utep-honors-class.jpg
Max Weber, like Marx, is another German thinker who has seen the importance of economic factor in the classification of a society. He has defined class as a group of persons having the same ‘life chances’ or social opportunities, as determined typically by economic conditions. He agreed with the fundamental tenet of Marx that control over property is a basic fact in the determination of the life chances of an individual or a class.
That is to say, the members of a particular class will have more or less chance of getting good things of life – things such as a high standard of living, leisure etc. Thus, Weber’s definition of class is broadly similar to that of Marx. To the economic dimension Weber added two other dimensions, prestige and power. He saw these factors as separate but interacting bases of social hierarchy.
His notions are that property creates classes, prestige creates status groups and power creates parties. Like Marx, Weber recognized the important role of property in giving rise to status group. However, he gave it less importance than Marx did. Weber had given emphasis on life-style in deciding status group. Weber says that status groups are formed on the basis of prestige and honour. He admits that difference in property can constitute the basis for differences in honour or prestige.
Many modern sociologists regard status as the basic criterion of social class. “A social class” as defined by Maclver and Page, “is any portion of a community marked off from the rest by social status”. According to this view, classes arise wherever social differentiations in terms of language, locality, faction or specialization are associated with a status hierarchy. These differentiations may give rise to significant class phenomena only when they develop common sentiments.
These sentiments imply feeling of equality among the members of one’s own class, a feeling of inferiority in relation to these above in the social hierarchy and a feeling of superiority to those below. What is most important in making class distinction is the sense of status which is sustained by economic, political or ecclestical power and by the distinctive modes of life and cultural expression corresponding to them. In this sense the status separates one class from the other. Thus, classes are status marked and group conscious strata.
It follows that the division of society into classes on the basis of status is unavoidable. But the primary determinant of status is unquestionably economic. In a class-ridden society, a man possessing wealth has resources through which he can exercise both economic and political power. Weber’s approach is, sociologically, more agreeable because he referred to the conditions which led to the different types of classes in a society. Social class are defacto groups and their basis is mainly economic. But they are more than economic groups.
Nature of Social Class :
1. the system is ubiquitous:.
Class system is a universal phenomenon. It is prevalent in all modern and complex social systems.
2. Class is an Economic Group:
Social classes are determined by their relation to means of production. A social class also includes wealth, property, income etc.
3. Class is also a Status Group:
Class is also related to status dimension. Status groups are composed of persons having the same life style and in joining similar social honour. Thus, status consciousness separates the individuals both physically and psychologically.
4. An Achieved Pattern:
In class system status is achieved, not ascribed. Class is open and elastic and mobility is possible. A man can, by his effort and initiative, change his class and thereby rise in social status.
5. Feeling of Class-consciousness:
Feeling of class consciousness is experienced among the members of a particular class. The members feel a sense of equality within their own class and a sense of superiority or inferiority in relation to the members of lower or higher classes.
6. Prestige Dimension:
The persons of a particular class develop status consciousness and this is reflected through the status symbols of different class groups. The status symbols of the upper classes are considered prestigious, whereas the status symbols of the middle classes are considered less prestigious.
7. Relatively Stable Group:
A class is a stable group. It is not temporary like a crowd or mob. Although social mobility in the class system is possible, class cannot be interpreted as transitory. Under certain extraordinary situations such as revolutions, movements etc. the class is subject to rapid transformation.
8. Varieties of Life-styles:
A particular social class is marked off from the other classes by its life-styles. Life-style include the mode of living such as, the dress pattern, the type of house, the leisure time activities, the mode of consumption, the exposure to media and the mode of communication etc.
Related Articles:
- The Nature of Social Class
- Social Class in India: Class Typology and Class Consciousness
Social Class
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Essay On Social Issues
500 words essay on social issues.
Social Issues is an undesirable state which opposes society or a certain part of society. It refers to an unwanted situation that frequently results in problems and continues to harm society . Social issues can cause a lot of problems that can be beyond the control of just one person. Through an essay on social issues, we will learn why they are harmful and what types of social issues we face.

Drawbacks of Social Issues
Social issues have a lot of drawbacks that harms our society. They are situations that have an adverse and damaging result on our society. They arise when the public leaves nature or society from an ideal situation.
If you look closely, you will realize that almost all types of social issues have common origins. In the sense that they all are interconnected somehow. Meaning to say, if one solves the other one is also most likely to resolve.
Social issues have a massive lousy effect on our society and ultimately, it affects all of us. In order to solve some social issues, we need a common approach. No society is free from social issues, almost every one of them has some social issue or the other.
For instance, in India, you will find a lot of social issues which the country is facing. It ranges from the caste system to child labour and gender inequality to religious conflicts. Thus, we are going through a critical time where we all must come together to free our society from undesirable social evils.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Major Social Issues
There are a lot of social issues we are facing right now, some more prominent than the others. First of all, poverty is a worldwide issue. It gives birth to a lot of other social issues which we must try to get away with at the earliest.
Further, countries like India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan and more are facing the issue of the caste system since times unknown. It results in a lot of caste violence and inequality which takes the lives of many on a daily basis.
Moreover, child labour is another major social issue that damages the lives of young children. Similarly, illiteracy also ruins the lives of many by destroying their chances of a bright future.
In developing countries mostly, child marriage still exists and is responsible for ruining many lives. Similarly, dowry is a very serious and common social issue that almost all classes of people partake in.
Another prominent social issue is gender inequality which takes away many opportunities from deserving people. Domestic violence especially against women is a serious social issue we must all fight against.
Other social issues include starvation, child sex abuse, religious conflicts, child trafficking, terrorism , overpopulation, untouchability, communalism and many more. It is high time we end these social issues.
Conclusion of the Essay on Social Issues
A society can successfully end social issues if they become adamant. These social issues act as a barrier to the progress of society. Thus, we must all come together to fight against them and put them to an end for the greater good.
FAQ on Essay on Social Issues
Question 1: What is the meaning of social problem?
Answer 1: A social problem refers to any condition or behaviour which has a negative impact on a large number of people. It is normally recognized as a condition or behaviour that needs to be addressed.
Question 2: What are the effects of social issues?
Answer 2: Social issues affect our society adversely. Most importantly, it disturbs the harmony of society and gives rise to hostility and suspicion. Moreover, it creates large-scale social dissatisfaction, suffering and misery.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Hamlet — The Theme Of Social Class And Power In Shakespeare’s Hamlet
The Theme of Social Class and Power in Shakespeare’s Hamlet
- Categories: Hamlet William Shakespeare
About this sample

Words: 1209 |
Published: Feb 8, 2022
Words: 1209 | Pages: 2 | 7 min read
- Skinfill, M. (1996). Reconstructing Class in Faulkner's Late Novels: The Hamlet and the Discovery of Capital. Studies in American Fiction, 24(2), 151-169. (https://muse.jhu.edu/article/440423)
- Prior, L. T. (1969). Theme, Imagery, and Structure In" The Hamlet". The Mississippi Quarterly, 22(3), 237-256. (https://www.jstor.org/stable/26473806)
- Brotton, J. (2013). Ways of Seeing Hamlet. In Hamlet (pp. 161-176). Routledge. (https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9780203060520-10/ways-seeing-hamlet-jerry-brotton)
- Guagliardo, E. J. (2021). The Experience of Authority: Hamlet and the Political Aesthetics of Majesty. English Literary Renaissance, 51(3), 476-502. (https://www.journals.uchicago.edu/doi/abs/10.1086/715427)
- Haque, F. (2016). Revenge and Vengeance in Shakespeare’s Hamlet: A Study of Hamlet’s Pursuit and Procrastination Regarding Revenge. Journal Of Humanities And Social Science, 21(9), 55-59. (http://un.uobasrah.edu.iq/lectures/3541.pdf)

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
4 pages / 1814 words
2 pages / 700 words
1 pages / 422 words
4 pages / 1712 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Hamlet
The Bard of Avon has bestowed upon us a plethora of literary masterpieces that continue to captivate readers and transcend time. Among his many plays, "Hamlet" stands out as one of his most celebrated and enduring tragedies. [...]
William Shakespeare's play, Hamlet, is a timeless classic that explores various themes and motifs, including the theme of suicide. Throughout the play, the main character, Hamlet, is portrayed as contemplating self-destruction [...]
William Shakespeare's Hamlet is one of the most celebrated plays in literature, known for its complex characters, themes, and language. Written in the early 17th century, Hamlet has endured the test of time and continues to be [...]
The ultimate stage of revenge is delayed when Hamlet goes into exile following Polonius's murder. During his absence, Hamlet's lover, Ophelia, goes mad and tragically drowns (Shakespeare 17). However, Hamlet eventually returns [...]
Hamlet and Macbeth are two of William Shakespeare's most famous plays. Each share not only fame, however, but format: Both feature main characters with tragic flaws that become their demise. In the cases of Hamlet and Macbeth, [...]
Insanity is defined as doing something over and over again and expecting a different outcome. In Shakespeare's Hamlet, the young and not fully mature Hamlet might be thought of as insane. However, although he says and [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
A New Dawn: the Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor
This essay about the Wagner Act of 1935 explores its transformative impact on American labor relations. It outlines how the act, born from the economic turmoil of the Great Depression, empowered workers to organize and bargain collectively, thereby addressing longstanding inequalities in the workplace. By establishing the National Labor Relations Board and safeguarding workers’ rights to unionize, the Wagner Act paved the way for a more equitable society, shaping the trajectory of American labor and fostering the emergence of the middle class. Despite criticisms and subsequent amendments, the core principles of the Wagner Act remain central to ongoing discussions about workers’ rights and social justice in the United States.
How it works
In the tumultuous landscape of early 20th-century America, where the echoes of the Great Depression reverberated through every corner of society, the Wagner Act of 1935 emerged as a beacon of hope for the working class. Born from the crucible of economic hardship and social inequality, this landmark legislation, formally known as the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), heralded a new era in labor relations, forever altering the dynamics between employers and employees.
Against a backdrop of widespread poverty, unemployment, and exploitation, the Wagner Act represented a bold departure from the laissez-faire attitudes that had long dominated American labor policy.
Crafted in the crucible of the Great Depression, this legislation sought to redress the power imbalances that had plagued the nation’s workforce for decades. Led by the vision of Senator Robert F. Wagner of New York, the architects of the Wagner Act envisioned a future where workers would be empowered to assert their rights and demand fair treatment in the workplace.
Enacted on July 5, 1935, the Wagner Act was a watershed moment in American labor history, establishing the framework for collective bargaining and unionization that endures to this day. At its core was the creation of the National Labor Relations Board (NLRB), a federal agency tasked with enforcing labor laws and adjudicating disputes between employers and employees. Under the auspices of the NLRB, workers gained newfound protections against unfair labor practices and the freedom to organize without fear of reprisal.
Central to the Wagner Act was the recognition of workers’ rights to form and join labor unions, engage in collective bargaining, and advocate for their interests through concerted action. This groundbreaking provision marked a seismic shift in the balance of power between labor and management, empowering workers to negotiate for better wages, benefits, and working conditions. In the wake of the Wagner Act, union membership soared, as workers across the country embraced their newfound rights and sought to improve their lives through collective action.
The impact of the Wagner Act extended far beyond the realm of labor relations, shaping the broader trajectory of American society in profound ways. By elevating the status of workers and giving voice to the disenfranchised, the act laid the groundwork for the emergence of the American middle class and the prosperity that characterized much of the 20th century. Moreover, the principles enshrined in the Wagner Act served as a catalyst for social progress, inspiring subsequent generations to fight for justice, equality, and dignity in all aspects of life.
Despite its transformative impact, the Wagner Act was not without its critics. Business interests and conservative politicians decried the act as government overreach, arguing that it stifled economic growth and undermined the free market. In the years that followed, efforts were made to roll back some of the act’s provisions, culminating in the passage of the Taft-Hartley Act in 1947. Yet, despite these challenges, the core principles of the Wagner Act remained intact, serving as a bulwark against unchecked corporate power and a beacon of hope for workers around the country.
In conclusion, the Wagner Act of 1935 stands as a testament to the enduring power of collective action and the resilience of the human spirit in the face of adversity. By enshrining the rights of workers to organize and bargain collectively, the act laid the foundation for a more just and equitable society, where all individuals have the opportunity to thrive and succeed. As we reflect on the legacy of the Wagner Act, let us reaffirm our commitment to the values of solidarity, fairness, and social justice that it embodies, and continue the ongoing struggle for a better future for all.
Cite this page
A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor. (2024, May 28). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/
"A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor." PapersOwl.com , 28 May 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/ [Accessed: 30 May. 2024]
"A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor." PapersOwl.com, May 28, 2024. Accessed May 30, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/
"A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor," PapersOwl.com , 28-May-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/. [Accessed: 30-May-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). A New Dawn: The Impact of the Wagner Act on American Labor . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/a-new-dawn-the-impact-of-the-wagner-act-on-american-labor/ [Accessed: 30-May-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The American Class Structure. As should be evident, it is not easy to determine how many social classes exist in the United States. Over the decades, sociologists have outlined as many as six or seven social classes based on such things as, once again, education, occupation, and income, but also on lifestyle, the schools people's children attend, a family's reputation in the community, how ...
Social Classes in "Metropolis" Film by Fritz Lang. Some of the most important issues raised in Metropolis are the class division in the society, the gap between the rich and the poor, loyalty, brotherhood, and friendship, the tyranny and autocracy of politicians, the […] Social Class Status Differences. Social class is the status of the ...
Social class is an age old concept referring to a group of people with similar status, power, influence and wealth. Social class refers to the social stratification of the society based on social, economic and educational status. However, the definition of class is not uniform across the countries and societies.
Social class refers to a hierarchy of societal classes that categorizes individuals based on various factors. This essay provides an overview of social class, the factors influencing social class status differences, the consequences of social class status differences, social class mobility, and implications for society.
The American Class Structure. As should be evident, it is not easy to determine how many social classes exist in the United States. Over the decades, sociologists have outlined as many as six or seven social classes based on such things as, once again, education, occupation, and income, but also on lifestyle, the schools people's children attend, a family's reputation in the community, how ...
In such a case, social class refers to the socio-cultural aspects of one's life, namely the traits, behaviors, knowledge, and lifestyle that one is socialized into by one's family. This is why class descriptors like "lower," "working," "upper," or "high" can have social as well as economic implications for how we understand the person described.
Social class is the status of the society in which individuals are classified on basis of political, economic and cultural perspectives. Wealth, income and occupation are the major aspects of economic social classification. We will write a custom essay on your topic. Political social class is characterized by Status and power, while the ...
Essay about Social Class. Social class refers to the system of stratification of the different groups of people in a society. These different forms of classification are, in most instances, based on gender ethnicity and age. Social class makes everyone's lives extremely different. For example: How long one can expect to live.
Social Classes In Australia Essay. Evidence of social classes within societies can be seen throughout many different cultures and countries. The social classes can be broken up into four categories, the Upper or Elite class constituting approximately 1% of the population, the Middle class which accounts for around 60% of the population ...
3 pages / 1461 words. The idea of social class and socio-economic status being related to race/ethnicity can be demonstrated using several examples. This essay will discuss topics such as; the criminalisation of racial and ethnic groups and the discrimination of certain ethnic-minority groups, such as in housing.
Theories of social class were fully elaborated only in the 19th century as the modern social sciences, especially sociology, developed.Political philosophers such as Thomas Hobbes, John Locke, and Jean-Jacques Rousseau discussed the issues of social inequality and stratification, and French and English writers in the late 18th and early 19th centuries put forth the idea that the nonpolitical ...
The aim of this paper is to describe different sociological issues in the USA, such as social class and poverty, race and ethnicity, gender, etc. Social Class, Race, and Health. The paper explores the way social class and race differences may lead to inequalities when receiving healthcare. Social Class in America.
But essays can be polished by a paid professional third party, or helped along by an upper-middle-class parent. In another sign of the persistent pull of social class, a recent working paper from ...
The Inspector is used as a figure of morality; he is there to make the family realise that they have an easy life resting upon the hard and difficult work of the lower class. As JB Priestley was a socialist and a founder of the Socialist Commonwealth Party, he wanted to see the collapse of the class system. The Inspector tries to make the other ...
The Great Gatsby, by F. Scott Fitzgerald, is a story about the difficulty of changing one's future and repeating one's past. In the novel, the society that makes up New York's social classes are defined as the elites, who are the ones born into wealth, the newly rich, who've only recently gained wealth, and the working class, who are ...
PAGES 2 WORDS 617. Social Classes in America. The American dream is what many people hopes to attain in their lives. Many Americans, or even non-Americans who migrated to America, pursue a goal in life that they call the American Dream. Within this dream is an objective of being in the American workforce. Sad as it is in reality, however, this ...
Social class is a critical theme in the novel The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald as it focuses on life during the 1920s in the Roaring Twenties era.The author sets up the novel into distinct social classes - upper class, middle-class and lower class to Throughout the novel The Great Gatsby, the author F. Scott Fitzgerald makes a connection between the setting presented in the novel and ...
The stereotyping of the poor is the genesis of class discrimination. The poor have been excluded as the rest of the nation goes on with their lives. In this paper, I analyze three articles on social class and inequality to find out whether the authors' views agree with mine on the negative attitudes towards the poor by the middle class and ...
Written by S.E. Hinton and published in 1967, The Outsiders is a coming-of-age novel that explores the lives of two rival groups, the Greasers and the Socs, in 1960s Oklahoma. The novel delves into the struggles, conflicts, and relationships of the characters, and one of the central themes of the novel is the exploration of social class and identity. . Through the experiences of the characters ...
Below I organize the social psychological literature on social class in terms of the impact of class on three types of outcome: thought, encompassing social cognition and attitudes; emotion, with a focus on moral emotions and prosocial behaviour; and behaviour in high‐prestige educational and workplace settings. I will show that these impacts ...
ADVERTISEMENTS: Read this comprehensive essay on Social Class ! One of the important elements of social stratification is the 'Class'. A social class is 'a category or group of persons having a definite status in society which permanently determines their relations to other groups'. Social classes have been defined by various thinkers "in different manner. […]
500 Words Essay On Social Issues. Social Issues is an undesirable state which opposes society or a certain part of society. It refers to an unwanted situation that frequently results in problems and continues to harm society.Social issues can cause a lot of problems that can be beyond the control of just one person.
Get custom essay. William Shakespeare's Hamlet shows how individuals that have power and a higher social status often end up disrupting and tearing apart families, kingdoms and lives of others. The example of social class issues in Hamlet relates to many issues in today's age that people with power and high social status go through.
Essay Example: In the tumultuous landscape of early 20th-century America, where the echoes of the Great Depression reverberated through every corner of society, the Wagner Act of 1935 emerged as a beacon of hope for the working class. Born from the crucible of economic hardship and social inequality