
How To Structure Your Literature Review
3 options to help structure your chapter.
By: Amy Rommelspacher (PhD) | Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | November 2020 (Updated May 2023)
Writing the literature review chapter can seem pretty daunting when you’re piecing together your dissertation or thesis. As we’ve discussed before , a good literature review needs to achieve a few very important objectives – it should:
- Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic
- Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these
- Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one)
- Inform your own methodology and research design
To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure . Get the structure of your literature review chapter wrong and you’ll struggle to achieve these objectives. Don’t worry though – in this post, we’ll look at how to structure your literature review for maximum impact (and marks!).

But wait – is this the right time?
Deciding on the structure of your literature review should come towards the end of the literature review process – after you have collected and digested the literature, but before you start writing the chapter.
In other words, you need to first develop a rich understanding of the literature before you even attempt to map out a structure. There’s no use trying to develop a structure before you’ve fully wrapped your head around the existing research.
Equally importantly, you need to have a structure in place before you start writing , or your literature review will most likely end up a rambling, disjointed mess.
Importantly, don’t feel that once you’ve defined a structure you can’t iterate on it. It’s perfectly natural to adjust as you engage in the writing process. As we’ve discussed before , writing is a way of developing your thinking, so it’s quite common for your thinking to change – and therefore, for your chapter structure to change – as you write.
Need a helping hand?
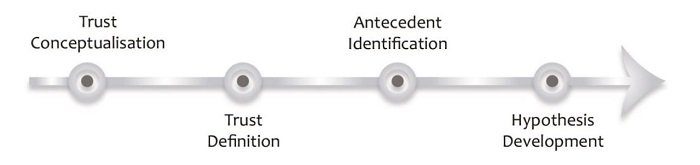
Like any other chapter in your thesis or dissertation, your literature review needs to have a clear, logical structure. At a minimum, it should have three essential components – an introduction , a body and a conclusion .
Let’s take a closer look at each of these.
1: The Introduction Section
Just like any good introduction, the introduction section of your literature review should introduce the purpose and layout (organisation) of the chapter. In other words, your introduction needs to give the reader a taste of what’s to come, and how you’re going to lay that out. Essentially, you should provide the reader with a high-level roadmap of your chapter to give them a taste of the journey that lies ahead.
Here’s an example of the layout visualised in a literature review introduction:
Your introduction should also outline your topic (including any tricky terminology or jargon) and provide an explanation of the scope of your literature review – in other words, what you will and won’t be covering (the delimitations ). This helps ringfence your review and achieve a clear focus . The clearer and narrower your focus, the deeper you can dive into the topic (which is typically where the magic lies).
Depending on the nature of your project, you could also present your stance or point of view at this stage. In other words, after grappling with the literature you’ll have an opinion about what the trends and concerns are in the field as well as what’s lacking. The introduction section can then present these ideas so that it is clear to examiners that you’re aware of how your research connects with existing knowledge .

2: The Body Section
The body of your literature review is the centre of your work. This is where you’ll present, analyse, evaluate and synthesise the existing research. In other words, this is where you’re going to earn (or lose) the most marks. Therefore, it’s important to carefully think about how you will organise your discussion to present it in a clear way.
The body of your literature review should do just as the description of this chapter suggests. It should “review” the literature – in other words, identify, analyse, and synthesise it. So, when thinking about structuring your literature review, you need to think about which structural approach will provide the best “review” for your specific type of research and objectives (we’ll get to this shortly).
There are (broadly speaking) three options for organising your literature review.

Option 1: Chronological (according to date)
Organising the literature chronologically is one of the simplest ways to structure your literature review. You start with what was published first and work your way through the literature until you reach the work published most recently. Pretty straightforward.
The benefit of this option is that it makes it easy to discuss the developments and debates in the field as they emerged over time. Organising your literature chronologically also allows you to highlight how specific articles or pieces of work might have changed the course of the field – in other words, which research has had the most impact . Therefore, this approach is very useful when your research is aimed at understanding how the topic has unfolded over time and is often used by scholars in the field of history. That said, this approach can be utilised by anyone that wants to explore change over time .

For example , if a student of politics is investigating how the understanding of democracy has evolved over time, they could use the chronological approach to provide a narrative that demonstrates how this understanding has changed through the ages.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself to help you structure your literature review chronologically.
- What is the earliest literature published relating to this topic?
- How has the field changed over time? Why?
- What are the most recent discoveries/theories?
In some ways, chronology plays a part whichever way you decide to structure your literature review, because you will always, to a certain extent, be analysing how the literature has developed. However, with the chronological approach, the emphasis is very firmly on how the discussion has evolved over time , as opposed to how all the literature links together (which we’ll discuss next ).
Option 2: Thematic (grouped by theme)
The thematic approach to structuring a literature review means organising your literature by theme or category – for example, by independent variables (i.e. factors that have an impact on a specific outcome).
As you’ve been collecting and synthesising literature , you’ll likely have started seeing some themes or patterns emerging. You can then use these themes or patterns as a structure for your body discussion. The thematic approach is the most common approach and is useful for structuring literature reviews in most fields.
For example, if you were researching which factors contributed towards people trusting an organisation, you might find themes such as consumers’ perceptions of an organisation’s competence, benevolence and integrity. Structuring your literature review thematically would mean structuring your literature review’s body section to discuss each of these themes, one section at a time.

Here are some questions to ask yourself when structuring your literature review by themes:
- Are there any patterns that have come to light in the literature?
- What are the central themes and categories used by the researchers?
- Do I have enough evidence of these themes?
PS – you can see an example of a thematically structured literature review in our literature review sample walkthrough video here.
Option 3: Methodological
The methodological option is a way of structuring your literature review by the research methodologies used . In other words, organising your discussion based on the angle from which each piece of research was approached – for example, qualitative , quantitative or mixed methodologies.
Structuring your literature review by methodology can be useful if you are drawing research from a variety of disciplines and are critiquing different methodologies. The point of this approach is to question how existing research has been conducted, as opposed to what the conclusions and/or findings the research were.

For example, a sociologist might centre their research around critiquing specific fieldwork practices. Their literature review will then be a summary of the fieldwork methodologies used by different studies.
Here are some questions you can ask yourself when structuring your literature review according to methodology:
- Which methodologies have been utilised in this field?
- Which methodology is the most popular (and why)?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the various methodologies?
- How can the existing methodologies inform my own methodology?
3: The Conclusion Section
Once you’ve completed the body section of your literature review using one of the structural approaches we discussed above, you’ll need to “wrap up” your literature review and pull all the pieces together to set the direction for the rest of your dissertation or thesis.
The conclusion is where you’ll present the key findings of your literature review. In this section, you should emphasise the research that is especially important to your research questions and highlight the gaps that exist in the literature. Based on this, you need to make it clear what you will add to the literature – in other words, justify your own research by showing how it will help fill one or more of the gaps you just identified.
Last but not least, if it’s your intention to develop a conceptual framework for your dissertation or thesis, the conclusion section is a good place to present this.

Example: Thematically Structured Review
In the video below, we unpack a literature review chapter so that you can see an example of a thematically structure review in practice.
Let’s Recap
In this article, we’ve discussed how to structure your literature review for maximum impact. Here’s a quick recap of what you need to keep in mind when deciding on your literature review structure:
- Just like other chapters, your literature review needs a clear introduction , body and conclusion .
- The introduction section should provide an overview of what you will discuss in your literature review.
- The body section of your literature review can be organised by chronology , theme or methodology . The right structural approach depends on what you’re trying to achieve with your research.
- The conclusion section should draw together the key findings of your literature review and link them to your research questions.
If you’re ready to get started, be sure to download our free literature review template to fast-track your chapter outline.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

27 Comments
Great work. This is exactly what I was looking for and helps a lot together with your previous post on literature review. One last thing is missing: a link to a great literature chapter of an journal article (maybe with comments of the different sections in this review chapter). Do you know any great literature review chapters?
I agree with you Marin… A great piece
I agree with Marin. This would be quite helpful if you annotate a nicely structured literature from previously published research articles.
Awesome article for my research.
I thank you immensely for this wonderful guide
It is indeed thought and supportive work for the futurist researcher and students
Very educative and good time to get guide. Thank you
Great work, very insightful. Thank you.
Thanks for this wonderful presentation. My question is that do I put all the variables into a single conceptual framework or each hypothesis will have it own conceptual framework?
Thank you very much, very helpful
This is very educative and precise . Thank you very much for dropping this kind of write up .
Pheeww, so damn helpful, thank you for this informative piece.
I’m doing a research project topic ; stool analysis for parasitic worm (enteric) worm, how do I structure it, thanks.
comprehensive explanation. Help us by pasting the URL of some good “literature review” for better understanding.
great piece. thanks for the awesome explanation. it is really worth sharing. I have a little question, if anyone can help me out, which of the options in the body of literature can be best fit if you are writing an architectural thesis that deals with design?
I am doing a research on nanofluids how can l structure it?
Beautifully clear.nThank you!
Lucid! Thankyou!
Brilliant work, well understood, many thanks
I like how this was so clear with simple language 😊😊 thank you so much 😊 for these information 😊
Insightful. I was struggling to come up with a sensible literature review but this has been really helpful. Thank you!
You have given thought-provoking information about the review of the literature.
Thank you. It has made my own research better and to impart your work to students I teach
I learnt a lot from this teaching. It’s a great piece.
I am doing research on EFL teacher motivation for his/her job. How Can I structure it? Is there any detailed template, additional to this?
You are so cool! I do not think I’ve read through something like this before. So nice to find somebody with some genuine thoughts on this issue. Seriously.. thank you for starting this up. This site is one thing that is required on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m asked to do conceptual, theoretical and empirical literature, and i just don’t know how to structure it
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Literature reviews
- Book a session
What is a literature review?
Finding your sources, structuring your review, critical writing, literature reviews, critiques and annotated bibliographies.
- Science and Health-based reviews This link opens in a new window
- Quick resources (5-10 mins)
- e-learning and books (30 mins+)
- SkillsCheck This link opens in a new window
- ⬅ Back to Skills Centre This link opens in a new window

Looking for sessions and tutorials on this topic? Find out more about our session types and how to register to book for sessions. You can view our full and up-to-date availability in UniHub Appointments and Events .
Not sure where to start developing your academic skills? Take the SkillsCheck for personalised recommendations on how to build your academic writing and study skills alongside your course.
Literature reviews take on many forms at university: you could be asked to write a literature review as a stand-alone document or as part of a dissertation or thesis. You may also be asked to write an annotated bibliography or a critical review - both of these assignments are closely related to literature reviews, and follow many of the same conventions.
A literature review is an extended piece of writing that should collate, link and evaluate key sources related to a chosen topic or research question. Rather than simply summarising the existing research on your chosen topic, you should aim to show which papers can be clustered around a similar theme or topic - they may have a shared methodology, or have been carried out in the same context. You will be looking for strengths and weaknesses in the research, questioning the relevance and significance of the results in relation to your topic, and looking for any gaps or under researched areas. Your writing should make these thoughts and evaluations clear to the reader, so that they have a good understanding and overview of the body of research you have chosen to investigate.
Here is a short video that explains a literature review from the perspective of the reader:
Salter, J. [Dr. Jodie Salter]. (2016, March 14). Writing the Literature Review: A Banquet Hall Analogy [Video file]. Retrieved from: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QE_Us8UjS6
Using Library Search
The more you read around your subject, the more familiar you will become with the current literature, and you will start to build a map of the sources you already have, and the information you are missing. A clear search strategy can help fill these gaps in your knowledge, and your themes or topics of interest can be used as key search terms when looking for further resources.
Top tips for searching the Library Gateway
- Use Boolean terms to help the search engine recognise which words should be treated as a phrase. For example, if you search “costume design” , the search engine will know to treat “costume design” as a phrase, not two separate words.
- You can then add AND and OR to add in additional terms and synonyms. For example, “costume design” AND “film” will only find articles or sources that include both of these terms together, helping you to narrow your search. To go wider, think about adding in synonyms using the OR function: “costume design” AND “film” or “cinema” or “movies”.
- You can also use an asterisk (*) to search for a word stem to help widen your search. For example, if you search teach*, this will find articles that include the word teach, teacher, teachers, teaching and so on.
- Decide at the start on what your inclusion and exclusion criteria will be. These might include limits on: - Date of publication - Language - Type/group of participants - Peer-reviewed journals - Keywords and synonyms - Type of study, ie. systematic review, case study etc.
Search strategies
Explore the following resources for more information on search strategy models:
- PICO (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome) - Used primarily in Health Sciences but offers a clear step-by-step approach to literature searching that could be adapted for use in other subjects.
- SPIDER - Developed from the PICK method, SPIDER searching is used mainly in qualitative research to identify a phenomenon or behaviour, rather than a specific intervention (more quantitative).
Finding the gap

You might have heard about finding the gap in your literature review - but what does this mean?
Looking for the gap in the literature means finding an aspect of your topic that hasn't been fully explored by researchers. This might be because you are researching a new technique or technology, or that your method or approach hasn't been used before in your field of study. You don't always need to find a gap, but it is a good way of demonstrating your literature searching skills and ability to compare a wide range of different sources. If you are able to find one, introduce the gap towards the end of the literature review, so that the reader can trace your path through the evidence first.
Literature review structure: A three-tier model
Imagine you are explaining your dissertation topic to a friend for the first time. Even for someone on the same degree course, they would need some context on the topic before you introduced more detail and complex examples.
A literature review follows the same ‘funnel’ narrative , moving from general themes to more specific detail:

- Appraisal grid A template for taking notes from reading that enables you to find clear links and similarities for discussion in your literature review.
- PEP tables A template for organising notes from your reading by themes, theories and perspectives.
Paragraph structure
Each paragraph of your literature review should bring together or synthesise two or more pieces of reading (these could be articles, book chapters, reports, videos, policy documents etc.)
Synthesis is the term we use in academic writing to describe the process of creating an opinion or argument based on a trend you find in the literature. If you are able to synthesis evidence, you are not only creating a robust argument (by avoiding relying too heavily on just one piece of writing) but you are also showing that you are a critical writer that can make conclusions based on a diverse range of evidence. Bingo!
As in other forms of academic writing, the paragraphs in your literature review should have four key sections:
Compare the following paragraphs against this four-part structure - which version is more critical?
Although both paragraphs use the TIED structure, we can see that the discussion in paragraph B is much more developed, and gives a specific suggestion about how future research could be conducted. We can also see that the evidence in paragraph B is clearly linked together , and that the conclusions or critical features of the papers are explained to the reader. Although drawing on the same evidence, paragraph A summarises and describes the research papers , rather than giving an evaluation or clear comparison of the different sources.
Focusing on the discussion sections (in bold), we can see that paragraph B is more critical , as it answers a key questions to keep in mind when writing critically: 'so what?' What conclusion or take home message do you want the reader to get from the evidence you have presented? ‘Therefore’, ‘Consequently’ and ‘As a result’ are all good terms to use here, as they prompt you to be clear and explicitly explain on interpretation of the source you have included.
Other types of literature review
Not all literature reviews form part of a dissertation. Use the tabs below for guidance on different assignment formats related to literature reviews:

- What are the emotional and behavioral impacts of therapy dogs for autistic children?
- How might aptitude be tested and measured in puppies selected for guide dog training?
- What are the key success factors for dogs as social media influencers on Instagram and Facebook?
Your initial reading will help you to identify trends or themes in the literature that might help to focus your search. You can then follow the standard structure for writing a literature review, using the funnel structure from this guide.
A critical review, or ‘critique’, involves breaking a journal article down into its key sections so that you can evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each part. Making notes on each of the following headings is a useful way to kickstart your analysis of any article:
- Research aim
- Research approach (ie. quantitative)
- Ethical issues
- Data collection method
- Data analysis method
- Generalisability/transferability
This list is not exhaustive and depending on your discipline, there may be other relevant categories to focus on in the article, such as theoretical models or implications for practice. The subheadings from the article will also provide an overview of the key sections to include in your review, and you may already have an idea from your wider reading of what sections often appear in articles in your field of study. Breaking down the article in this way allows you to focus your critique and evaluation, highlighting significant or relevant aspects of the article to the reader . Your assessment criteria will help you to identify which elements of the article to include in your critique: for example, if you needed to include a reflection on how the article links to your professional practice, it would make sense to include your thoughts on the articles key findings and transferability in your critique. For examples of sentence starters and academic language to use in your critical review, take a look at the following resources:
- Writing a critical review, UCL
- Academic Phrasebank, University of Manchester

An annotated bibliography combines a correctly formatted list of references (APA) with a short paragraph that gives:
- a short summary of the source, that picks out the key points of the article, such as context and setting, participants and conclusions;
- a brief evaluation of the strengths and weaknesses of the article;
- a sentence or two on the relevance of the source to your question or topic – what does it contribute to your knowledge of the subject, and in what ways might its relevance be limited?
Sources are not discussed together in the same paragraph, but the document itself will have a key theme or topic that ties the different sources together – almost like a module reading list: Brym, R., Godbout, M., Hoffbauer, A., Menard, G. & Huiquan Zhang, T. (2014) Social media in the 2011 Egyptian uprising. The British Journal of Sociology , 65 : 266-271. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-4446.12080 This article conducts a comparative analysis of quantitative data on social media usage and political engagement during the 2011 Egyptian uprising, using new bit.ly and Gallup survey results. The study generates a large amount of data on the key differences in social media usage between active demonstrators and sympathetic onlookers. Most significantly, the study explores the key drivers of participating in social unrest, such as a lack of confidence in the government, and how these are facilitated by social media. However, by only gathering quantitative data, the study is limited in its ability to provide an insight into how protestors narrate and explain their involvement in the protests in their own words. Overall, this article offers significant evidence to support a study of the importance of social media in contemporary political movements, and is particularly useful as one of few studies to focus on events outside of Europe and North America. Be sure to check your assessment criteria for tips on how you should evaluate your sources: for example, you might be asked to include specific methodology types or to link your sources to professional practice.
Two key principles apply to every literature review, whether it is part of a dissertation or an individual assignment:
1. A literature review is more than just a list of sources. The articles and evidence you include must be linked together around shared themes and characteristics, or highlight significant disagreements and contrast. Map your reading using keywords or themes that occur in multiple articles - these can be used as subheadings in your draft literature review.
2. While it is important to show that you are familiar with research in your field, you also need to show that you can evaluate and offer interpretations of the evidence you present to the reader. Remember to keep answering the 'so what?' question as you write.
- << Previous: Book a session
- Next: Science and Health-based reviews >>
- Last Updated: Apr 17, 2024 1:52 PM
- URL: https://libguides.shu.ac.uk/literaturereviews


Funnel Plot in a Systematic Review

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
Systematic reviews are considered the gold standard in evidence-based research. These intensive “studies of studies” involve taking a systematic approach to collect, assess, and synthesize relevant literature on a specific subject, including peer-reviewed journal articles, gray literature, and other sources, to answer a well-defined research question. Systematic reviews, like other reviews, can also be prone to bias. The bias types that are most evaluated in systematic reviews are selection bias, reporting bias, detection bias, and attrition bias. But this can be prevented through several checks before you start the review. For example, ensuring that the eligibility criteria in a systematic review is well defined when designing the systematic review protocol of a systematic review article , will reduce the risk of selection bias during study selection. An effective tool called a funnel plot is designed to examine the existence of a publication bias, among studies included in a systematic review, or the tendency of authors to only publish studies with significant results, other reporting biases, and small study effects.
What Is A Funnel Plot In Systematic Reviews?
A funnel plot is a simple scatter plot of the treatment effects estimated from individual studies against a measure of the study size. The x-axis (horizontal axis) shows the results of the study, expressed as an odds or risk ratio or a percent difference, while the y-axis (vertical axis) displays the sample size or an index of precision. Other measures could also be plotted, such as reciprocals, or variances.
The scale of the y-axis is reversed; studies with higher precision are placed at the top while studies with lower precision are placed at the bottom. At the bottom where the low precision studies are placed, the points that represent the mean value of effect in each study are widely spread. The spread of these points begins to reduce, as you move upwards in the y-axis. This effect creates a plot that resembles a pyramid or an inverted funnel.
What Is The Purpose Of Funnel Plots?
A funnel plot is designed to check for the existence of publication bias, other reporting biases, and systematic heterogeneity in a systematic review. These are biases caused by the absence of information from unpublished sources (missing studies), or selective outcome reporting of a study’s result (missing outcomes). For example, the study authors may omit information that they may feel does not agree with their findings. In the absence of publication bias, the funnel plot, as its name suggests, should create a symmetrical funnel-shaped distribution. Deviations from this, like an asymmetrical plot, may indicate that there is a bias.
That said, it’s important to note that publication bias is only one of the issues examined by funnel plots. These plots can also assess small study effects, or the tendency for smaller studies to show larger treatment effects.
How to Interpret a Funnel Plot?
Funnel plots, typically, are symmetrical or asymmetrical. Here’s how to interpret them:
Symmetrical Funnel Plot
A “well-behaved” data set, one where the precision of the estimated intervention effect increases as the size of the study increases will yield a symmetric inverted funnel shape. This signifies the unlikeliness of bias.
Asymmetrical Funnel Plot
An asymmetrical funnel plot can indicate the presence of a bias, suggesting a relationship between treatment effect estimate and study precision. With these deviant shapes, you can assume the possibility of publication bias, small-study effects, or study heterogeneity. Asymmetry can also be caused by the use of an inappropriate effect measure. Whatever the cause, an asymmetric funnel plot leads to doubts about the systematic review. In this case, an investigation must be done to get to the bottom of the possible cause and correct the mistake.
Systematic reviews are one of the most rigorous research processes. But they’re not without risks as they can be prone to biases. Researchers can use tools to prevent these challenges—a funnel plot is one way to do it as it’s designed to check for publication bias, other reporting biases, and small study effects. Another great way to ensure that your systematic review is accurate, objective, and comprehensive is to use a literature review software like DistillerSR, which helps you automate each stage of your review to securely produce evidence-based research faster, and more precisely. This gives you the time and energy to focus on evaluating other information to ensure that your protocol is free from any biases.
3 Reasons to Connect


Writing the Dissertation - Guides for Success: The Literature Review
- Writing the Dissertation Homepage
- Overview and Planning
- The Literature Review
- The Methodology
- The Results and Discussion
- The Conclusion
- The Abstract
- Getting Started
- Research Gap
- What to Avoid
Overview of writing the literature review
Conducting a literature review enables you to demonstrate your understanding and knowledge of the existing work within your field of research. Doing so allows you to identify any underdeveloped areas or unexplored issues within a specific debate, dialogue or field of study. This, in turn, helps you to clearly and persuasively demonstrate how your own research will address one or more of these gaps.
Disciplinary differences
Please note: this guide is not specific to any one discipline. The literature review can vary depending on the nature of the research and the expectations of the school or department. Please adapt the following advice to meet the demands of your dissertation and the expectations of your school or department. Consult your supervisor for further guidance; you can also check out Writing Across Subjects guide .
Guide contents
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common expectations for the literature review chapter, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows:
- Getting Started - Defines the literature review and presents a table to help you plan.
- Process - Explores choosing a topic, searching for sources and evaluating what you find.
- Structure - Presents key principles to consider in terms of structure, with examples to illustrate the concepts.
- Research gap - Clarifies what is meant by 'gap' and gives examples of common types of gaps.
- What to Avoid - Covers a few frequent mistakes you'll want to...avoid!
- FAQs - Answers to common questions about research gaps, literature availability and more.
- Checklist - Includes a summary of key points and a self-evaluation checklist.
Training and tools
- The Academic Skills team has recorded a Writing the Dissertation workshop series to help you with each section of a standard dissertation, including a video on writing the literature review .
- Check out the library's online Literature Review: Research Methods training.
- Our literature reviews summary guide provides links to further information and videos.
- The dissertation planner tool can help you think through the timeline for planning, research, drafting and editing.
- iSolutions offers training and a Word template to help you digitally format and structure your dissertation.

What is the literature review?
The literature review of a dissertation gives a clear, critical overview of a specific area of research. Our main Writing the Dissertation - Overview and Planning guide explains how you can refine your dissertation topic and begin your initial research; the next tab of this guide, 'Process', expands on those ideas. In summary, the process of conducting a literature review usually involves the following:
- Conducting a series of strategic searches to identify the key texts within that topic.
- Identifying the main argument in each source, the relevant themes and issues presented and how they relate to each other.
- Critically evaluating your chosen sources and determining their strengths, weaknesses, relevance and value to your research along with their overall contribution to the broader research field.
- Identifying any gaps or flaws in the literature which your research can address.
Literature review as both process and product
Writers should keep in mind that the phrase 'literature review' refers to two related, but distinct, things:
- 'Literature review' refers, first, to the active process of discovering and assessing relevant literature.
- 'Literature review' refers, second, to the written product that emerges from the above process.
This distinction is vital to note because every dissertation requires the writer to engage with and consider existing literature (i.e., to undertake the active process ). Research doesn't exist in a void, and it's crucial to consider how our work builds from or develops existing foundations of thought or discovery. Thus, even if your discipline doesn't require you to include a chapter titled 'Literature Review' in your submitted dissertation, you should expect to engage with the process of reviewing literature.
Why is it important to be aware of existing literature?
- You are expected to explain how your research fits in with other research in your field and, perhaps, within the wider academic community.
- You will be expected to contribute something new, or slightly different, so you need to know what has already been done.
- Assessing the existing literature on your topic helps you to identify any gaps or flaws within the research field. This, in turn, helps to stimulate new ideas, such as addressing any gaps in knowledge, or reinforcing an existing theory or argument through new and focused research.
Not all literature reviews are the same. For example, in many subject areas, you are expected to include the literature review as its own chapter in your dissertation. However, in other subjects, the dissertation structure doesn't include a dedicated literature review chapter; any literature the writer has reviewed is instead incorporated in other relevant sections such as the introduction, methodology or discussion.
For this reason, there are a number of questions you should discuss with your supervisor before starting your literature review. These questions are also great to discuss with peers in your degree programme. These are outlined in the table below (see the Word document for a copy you can save and edit):
- Dissertation literature review planning table
Literature review: the process
Conducting a literature review requires you to stay organised and bring a systematic approach to your thinking and reading. Scroll to continue reading, or click a link below to jump immediately to that section:
Choosing a topic
The first step of any research project is to select an interesting topic. From here, the research phase for your literature review helps to narrow down your focus to a particular strand of research and to a specific research question. This process of narrowing and refining your research topic is particularly important because it helps you to maintain your focus and manage your material without becoming overwhelmed by sources and ideas.
Try to choose something that hasn’t been researched to death. This way, you stand a better chance of making a novel contribution to the research field.
Conversely, you should avoid undertaking an area of research where little to no work has been done. There are two reasons for this:
- Firstly, there may be a good reason for the lack of research on a topic (e.g. is the research useful or worthwhile pursuing?).
- Secondly, some research projects, particularly practice-based ones involving primary research, can be too ambitious in terms of their scope and the availability of resources. Aim to contribute to a topic, not invent one!
Searching for sources
Researching and writing a literature review is partly about demonstrating your independent research skills. Your supervisor may have some tips relating to your discipline and research topic, but you should be proactive in finding a range of relevant sources. There are various ways of tracking down the literature relevant to your project, as outlined below.
Make use of Library Search
One thing you don’t want to do is simply type your topic into Google and see what comes up. Instead, use Library Search to search the Library’s catalogue of books, media and articles.
Online training for 'Using databases' and 'Finding information' can be found here . You can also use the Library's subject pages to discover databases and resources specific to your academic discipline.
Engage with others working in your area
As well as making use of library resources, it can be helpful to discuss your work with students or academics working in similar areas. Think about attending relevant conferences and/or workshops which can help to stimulate ideas and allows you to keep track of the most current trends in your research field.
Look at the literature your sources reference
Finding relevant literature can, at times, be a long and slightly frustrating experience. However, one good source can often make all the difference. When you find a good source that is both relevant and valuable to your research, look at the material it cites throughout and follow up any sources that are useful. Also check if your source has been cited in any more recent publications.

Think of the bibliography/references page of a good source as a series of breadcrumbs that you can follow to find even more great material.
Evaluating sources
It is very important to be selective when choosing the final sources to include in your literature review. Below are some of the key questions to ask yourself:
- If a source is tangentially interesting but hasn’t made any particular contribution to your topic, it probably shouldn’t be included in your literature review. You need to be able to demonstrate how it fits in with the other sources under consideration, and how it has helped shape the current state of the literature.
- There might be a wealth of material available on your chosen subject, but you need to make sure that the sources you use are appropriate for your assignment. The safest approach to take is to use only academic work from respected publishers. However, on occasions, you might need to deviate from traditional academic literature in order to find the information you need. In many cases, the problem is not so much the sources you use, but how you use them. Where relevant, information from newspapers, websites and even blogs are often acceptable, but you should be careful how you use that information. Do not necessarily take any information as factual. Instead be critical and interpret the material in the context of your research. Consider who the writer is and how this might influence the authority and reliability of the information presented. Consult your supervisor for more specific guidance relating to your research.
- The mere fact that something has been published does not automatically guarantee its quality, even if it comes from a reputable publisher. You will need to critique the content of the source. Has the author been thorough and consistent in their methodology? Do they present their thesis coherently? Most importantly, have they made a genuine contribution to the topic?
Keeping track of your sources
Once you have selected a source to use in your literature review, it is useful to make notes on all of its key features, including where it comes from, what it says, and what its main strengths and weaknesses are. This way you can easily re-familiarise yourself with a source without having to re-read it. Keeping an annotated bibliography is one way to do this.
Alternately, below is a table you can copy and fill out for each source (see the Word document to save an editable copy for yourself). Software such as EndNote also allows you to keep an electronic record of references and your comments on them.
- Source evaluation table
Writing your literature review
As we explored in the 'Getting Started' tab, the literature review is both a process you follow and (in most cases) a written chapter you produce. Thus, having engaged the review process, you now need to do the writing itself. Please continue reading, or click a heading below to jump immediately to that section.
Guiding principles
The structure of the final piece will depend on the discipline within which you are working as well as the nature of your particular research project. However, here are a few general pieces of advice for writing a successful literature review:
- Show the connections between your sources. Remember that your review should be more than merely a list of sources with brief descriptions under each one. You are constructing a narrative. Show clearly how each text has contributed to the current state of the literature, drawing connections between them.
- Engage critically with your sources. This means not simply describing what they say. You should be evaluating their content: do they make sound arguments? Are there any flaws in the methodology? Are there any relevant themes or issues they have failed to address? You can also compare their relative strengths and weaknesses.
- Signpost throughout to ensure your reader can follow your narrative. Keep relating the discussion back to your specific research topic.
- Make a clear argument. Keep in mind that this is a chance to present your take on a topic. Your literature review showcases your own informed interpretation of a specific area of research. If you have followed the advice given in this guide you will have been careful and selective in choosing your sources. You are in control of how you present them to your reader.
There are several different ways to structure the literature review chapter of your dissertation. Two of the most common strategies are thematic structure and chronological structure (the two of which can also be combined ). However you structure the literature review, this section of the dissertation normally culminates in identifying the research gap.
Thematic structure
Variations of this structure are followed in most literature reviews. In a thematic structure , you organise the literature into groupings by theme (i.e., subtopic or focus). You then arrange the groupings in the most logical order, starting with the broadest (or most general) and moving to the narrowest (or most specific).
The funnel or inverted pyramid
To plan a thematic structure structure, it helps to imagine your themes moving down a funnel or inverted pyramid from broad to narrow. Consider the example depicted below, which responds to this research question:
What role did the iron rivets play in the sinking of the Titanic?
The topic of maritime disasters is the broadest theme, so it sits at the broad top of the funnel. The writer can establish some context about maritime disasters, generally, before narrowing to the Titanic, specifically. Next, the writer can narrow the discussion of the Titanic to the ship's structural integrity, specifically. Finally, the writer can narrow the discussion of structural integrity to the iron rivets, specifically. And voila: there's the research gap!

The broad-to-narrow structure is intuitive for readers. Thus, it is crucial to consider how your themes 'nest inside' one another, from the broad to the narrow. Picturing your themes as nesting dolls is another way to envision this literature review structure, as you can see in the image below.

As with the funnel, remember that the first layer (or in this case, doll) is largest because it represents the broadest theme. In terms of word count and depth, the tinier dolls will warrant more attention because they are most closely related to the research gap or question(s).
The multi-funnel variation
The example above demonstrates a research project for which one major heading might suffice, in terms of outlining the literature review. However, the themes you identify for your dissertation might not relate to one another in such a linear fashion. If this is the case, you can adapt the funnel approach to match the number of major subheadings you will need.
In the three slides below, for example, a structure is depicted for a project that investigates this (fictional) dissertation research question: does gender influence the efficacy of teacher-led vs. family-led learning interventions for children with ADHD? Rather than nesting all the subtopics or themes in a direct line, the themes fall into three major headings.
The first major heading explores ADHD from clinical and diagnostic perspectives, narrowing ultimately to gender:
- 1.1 ADHD intro
- 1.2 ADHD definitions
- 1.3 ADHD diagnostic criteria
- 1.4 ADHD gender differences
The second major heading explores ADHD within the classroom environment, narrowing to intervention types:
- 2.1 ADHD in educational contexts
- 2.2 Learning interventions for ADHD
- 2.2.1 Teacher-led interventions
- 2.2.2 Family-led interventions
The final major heading articulates the research gap (gender differences in efficacy of teacher-led vs. family-led interventions for ADHD) by connecting the narrowest themes of the prior two sections.
Multi-funnel literature review structure by Academic Skills Service
To create a solid thematic structure in a literature review, the key is thinking carefully and critically about your groupings of literature and how they relate to one another. In some cases, your themes will fit in a single funnel. In other cases, it will make sense to group your broad-to-narrow themes under several major headings, and then arrange those major headings in the most logical order.
Chronological structure
Some literature reviews will follow a chronological structure . As the name suggests, a review structured chronologically will arrange sources according to their publication dates, from earliest to most recent.
This approach can work well when your priority is to demonstrate how the research field has evolved over time. For example, a chronological arrangement of articles about artificial intelligence (AI) would allow the writer to highlight how breakthroughs in AI have built upon one another in sequential order.
A chronological structure can also suit literature reviews that need to capture how perceptions or understandings have developed across a period of time (including to the present day). For example, if your dissertation involves the public perception of marijuana in the UK, it could make sense to arrange that discussion chronologically to demonstrate key turning points and changes of majority thought.
The chronological structure can work well in some situations, such as those described above. That being said, a purely chronological structure should be considered with caution. Organising sources according to date alone runs the risk of creating a fragmented reading experience. It can be more difficult in a chronological structure to properly synthesize the literature. For these reasons, the chronological approach is often blended into a thematic structure, as you will read more about, below.
Combined structures
The structures of literature reviews can vary drastically, and for any given dissertation there will be many valid ways to arrange the literature.
For example, many literature reviews will combine the thematic and chronological approaches in different ways. A writer might match their major headings to themes or subtopics, but then arrange literature chronologically within the major themes identified. Another writer might base their major headings on chronology, but then assign thematic subheadings to each of those major headings.
When considering your options, try to imagine your reader or audience. What 'flow' will allow them to best follow the discussion you are crafting? When you are reading articles, what structural approaches do you appreciate in terms of ease and clarity?
Identifying the gap
The bulk of your literature review will explore relevant points of development and scholarly thought in your research field: in other words, 'Here is what has been done so far, thus here is where the conversation now stands'. In that way, you position your project within a wider academic discussion.
Having established that context, the literature review generally culminates in an articulation of what remains to be done: the research gap your project addresses. See the next tab for further explanation and examples.
Demystifying the research gap
The term research gap is intimidating for many students, who might mistakenly believe that every single element of their research needs to be brand new and fully innovative. This isn't the case!
The gap in many projects will be rather niche or specific. You might be helping to update or re-test knowledge rather than starting from scratch. Perhaps you have repeated a study but changed one variable. Maybe you are considering a much discussed research question, but with a lesser used methodological approach.
To demonstrate the wide variety of gaps a project could address, consider the examples below. The categories used and examples included are by no means comprehensive, but they should be helpful if you are struggling to articulate the gap your literature review has identified.
***P lease note that the content of the example statements has been invented for the sake of demonstration. The example statements should not be taken as expressions of factual information.
Gaps related to population or geography
Many dissertation research questions involve the study of a specific population. Those populations can be defined by nationality, ethnicity, gender, sexuality, socioeconomic class, political beliefs, religion, health status, or other factors. Other research questions target a specific geography (e.g. a country, territory, city, or similar). Perhaps your broader research question has been pursued by many prior scholars, but few (or no) scholars have studied the question in relation to your focal population or locale: if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: As established above, the correlations between [ socioeconomic status ] and sustainable fashion purchases have been widely researched. However, few studies have investigated the potential relationship between [ sexual identity ] and attitudes toward sustainable fashion. Therefore...
- Example 2: Whilst the existing literature has established a clear link between [ political beliefs ] and perceptions of socialized healthcare, the influence of [ religious belief ] is less understood, particularly in regards to [ Religion ABC ].
- Example 3: Available evidence confirms that the widespread adoption of Technology XYZ in [ North America ] has improved manufacturing efficiency and reduced costs in the automotive sector. Using predictive AI models, the present research seeks to explore whether deployment of Technology XYZ could benefit the automotive sector of [ Europe ] in similar ways.
Gaps related to theoretical framework
The original contribution might involve examining something through a new lens. Theoretical framework refers, most simply, to the theory or theories a writer will use to make sense of and shape (i.e., frame ) their discussion. Perhaps your topic has been analysed in great detail through certain theoretical lenses, but you intend to frame your analysis using a theory that fewer scholars have applied to the topic: if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: Existing discussions of the ongoing revolution in Country XYZ frame the unrest in terms of [ theory A ] and [ theory B ]. The present research will instead analyse the situation using [ theory C ], allowing greater insight into...
- Example 2: In the first section of this literature review, I examined the [ postmodern ], [ Marxist ], and [ pragmatist ] analyses that dominate academic discussion of The World According to Garp. By revisiting this modern classic through the lens of [ queer theory ], I intend to...
Gaps related to methodological approach
The research gap might be defined by differences of methodology (see our Writing the Methodology guide for more). Perhaps your dissertation poses a central question that other scholars have researched, but they have applied different methods to find the answer(s): if so, that's a gap.
- Example 1: Previous studies have relied largely upon the [ qualitative analysis of interview transcripts ] to measure the marketing efficacy of body-positive advertising campaigns. It is problematic that little quantitative data underpins present findings in this area. Therefore, I will address this research gap by [ using algorithm XYZ to quantify and analyse social-media interactions ] to determine whether...
- Example 2: Via [ quantitative and mixed-methods studies ], previous literature has explored how demographic differences influence the probability of a successful match on Dating App XYZ. By instead [ conducting a content analysis of pre-match text interactions ] on Dating App XYZ, I will...
Scarcity as a gap
Absolutes such as never and always rarely apply in academia, but here is an exception: in academia, a single study or analysis is never enough. Thus, the gap you address needn't be a literal void in the discussion. The gap could instead have to do with replicability or depth/scope. In these cases, you are adding value and contributing to the academic process by testing emerging knowledge or expanding underdeveloped discussions.
- Example: Initial research points to the efficacy of Learning Strategy ABC in helping children with dyslexia build their reading confidence. However, as detailed earlier in this review, only four published studies have tested the intervention, and two of those studies were conducted in a laboratory. To expand our growing understanding of how Learning Strategy ABC functions in classroom environments, I will...
Elapsed time as a gap
Academia values up-to-date knowledge and findings, so another valid type of gap relates to elapsed time. Many factors that can influence or shape research findings are ever evolving: technology, popular culture, and political climates, to name just a few. Due to such changes, it's important for scholars in most fields to continually update findings. Perhaps your dissertation adds value by contributing to this process.
For example, imagine if a scholar today were to rely on a handbook of marketing principles published in 1998. As good as that research might have been in 1998, technology (namely, the internet) has advanced drastically since then. The handbook's discussion of online marketing strategies will be laughably outdated when compared to more recent literature.
- Example: A wide array of literature has explored the ways in which perceptions of gender influence professional recruitment practices in the UK. The bulk of said literature, however, was published prior to the #MeToo movement and resultant shifts in discourse around gender, power imbalances and professional advancement. Therefore...
What to avoid
This portion of the guide will cover some common missteps you should try to avoid in writing your literature review. Scroll to continue reading, or click a heading below to jump immediately to that section.
Writing up before you have read up
Trying to write your literature review before you have conducted adequate research is a recipe for panic and frustration. The literature review, more than any other chapter in your dissertation, depends upon your critical understanding of a range of relevant literature. If you have only dipped your toe into the pool of literature (rather than diving in!), you will naturally struggle to develop this section of the writing. Focus on developing your relevant bases of knowledge before you commit too much time to drafting.
Believing you need to read everything
As established above, a literature review does require a significant amount of reading. However, you aren't expected to review everything ever written about your topic. Instead, aim to develop a more strategic approach to your research. A strategic approach to research looks different from one project to the next, but here are some questions to help you prioritise:
- If your field values up-to-date research and discoveries, carefully consider the 'how' and 'what' before investing time reading older sources: how will the source function in your dissertation, and what will it add to your writing?
- Try to break your research question(s) down into component parts. Then, map out where your literature review will need to provide extensive detail and where it can instead present quicker background. Allocate your research time and effort accordingly.
Omitting dissenting views or findings
While reviewing the literature, you might discover authors who disagree with your central argument or whose own findings contradict your hypothesis. Don't omit those sources: embrace them! Remember, the literature review aims to explore the academic dialogue around your topic: disagreements or conflicting findings are often part of that dialogue, and including them in your writing will create a sense of rich, critical engagement. In fact, highlighting any disagreements amongst scholars is a great way to emphasise the relevance of, and need for, your own research.
Miscalculating the scope
As shown in the funnel structure (see 'Structure' tab for more), a literature review often starts broadly and then narrows the dialogue as it progresses, ultimately bringing the reader to the dissertation's specific research topic (e.g. the funnel's narrowest point).
Within that structure, it's common for writers to miscalculate the scope required. They might open the literature review far too broadly, dedicating disproportionate space to developing background information or general theory; alternately, they might rush into the narrowest part of the discussion, failing to develop any sense of surrounding context or background, first.
It takes trial and error to determine the appropriate scope for your literature review. To help with this...
- Imagine your literature review subtopics cascading down a stairwell, as in the illustration below.
- Place the broadest concepts on the highest steps, then narrow down to the most specific concepts on the lowest steps: the scope 'zooms in' as you move down the stairwell.
- Now, consider which step is the most logical starting place for your readers. Do they need to start all the way at the top, or should you 'zoom in'?

The illustration above shows a stairwell diagram of a dissertation that aims to analyse Stephen King's horror novel The Stand through the lens of a specific feminist literary theory.
- If the literature review began on one of the bottom two steps, this would feel rushed and inadequate. The writer needs to explore and define the relevant theoretical lens before they discuss how it has been applied by other scholars.
- If the literature review began on the very top step, this would feel comically broad in terms of scope: in this writing context, the reader doesn't require a detailed account of the entire history of feminism!
The third step, therefore, represents a promising starting point: not too narrow, not too broad.
The 'islands' structure
Above all else, a literature review needs to synthesize a range of sources in a logical fashion. In this context, to synthesize means to bring together, connect, weave, and/or relate. A common mistake writers make is failing to conduct such synthesis, and instead discussing each source in isolation. This leads to a disconnected structure, with each source treated like its own little 'island'. The island approach works for very few projects.
Some writers end up with this island structure because they confuse the nature of the literature review with the nature of an annotated bibliography . The latter is a tool you can use to analyse and keep track of individual sources, and most annotated bibliographies will indeed be arranged in a source-by-source structure. That's fine for pre-writing and notetaking, but to structure the literature review, you need to think about connections and overlaps between sources rather than considering them as stand-alone works.
If you are struggling to forge connections between your sources, break down the process into tiny steps:
- e.g. Air pollution from wood-burning stoves in homes.
- e.g. Bryant and Dao (2022) found that X% of small particle pollution in the United Kingdom can be attributed to the use of wood-burning stoves.
- e.g. A study by Williams (2023) reinforced those findings, indicating that small particle pollution has...
- e.g. However, Landers (2023) cautions that factor ABC and factor XYZ may contribute equally to poor air quality, suggesting that further research...
The above exercise is not meant to suggest that you can only write one sentence per source: you can write more than that, of course! The exercise is simply designed to help you start synthesizing the literature rather than giving each source the island treatment.
Q: I still don't get it - what's the point of a literature review?
A: Let's boil it down to three key points...
- The literature review provides a platform for you, as a scholar, to demonstrate your understanding of how your research area has evolved. By engaging with seminal texts or the most up-to-date findings in your field, you can situate your own research within the relevant academic context(s) or conversation(s).
- The literature review allows you to identify the research gap your project addresses: in other words, what you will add to discussions in your academic field.
- Finally, the literature review justifies the reason for your research. By exploring existing literature, you can highlight the relevance and purpose of your own research.
Q: What if I don't have a gap?
A: It's normal to struggle with identifying a research gap. This can be particularly true if you are working in a highly saturated research area, broadly speaking: for example, if you are studying the links between nutrition and diabetes, or if you are studying Shakespeare.

The 'What to Avoid' tab explained that miscalculating the scope is a common mistake in literature reviews. If you are struggling to identify your gap, scope might be the culprit, particularly if you are working in a saturated field. Remember that the gap is the narrowest part of the funnel, the smallest nesting doll, the lowest step: this means your contribution in that giant academic conversation will need to be quite 'zoomed in':
This is not a valid gap → Analysing Shakespeare's sonnets.
This might be a valid gap → Conducting an ecocritical analysis of the visual motifs of Shakespeare's final five procreation sonnets (e.g. sonnets number thirteen to seventeen).
In the above example, the revised attempt to articulate a gap 'zooms in' by identifying a particular theoretical lens (e.g. ecocriticism), a specific convention to analyse (e.g. use of visual motifs), and a narrower object (e.g. five sonnets rather than all 150+). The field of Shakespeare studies might be crowded, but there is nonetheless room to make an original contribution.
Conversely, it might be difficult to identify the gap if you are working not in a saturated field, but in a brand new or niche research area. How can you situate your work within a relevant academic conversation if it seems like the 'conversation' is just you talking to yourself?

In these cases, rather than 'zooming in', you might find it helpful to 'zoom out'. If your topic is niche, think creatively about who will be interested in your results. Who would benefit from understanding your findings? Who could potentially apply them or build upon them? Thinking of this in interdisciplinary terms is helpful for some projects.
Tip: Venn diagrams and mind maps are great ways to explore how your research connects to, and diverges from, the existing literature.
Q: How many references should I use in my literature review?
A: This question is risky to answer because the variations between individual projects and disciplines make it impossible to provide a universal answer. The fact is that one dissertation might have 50 more references than another, yet the two projects could be equally rigorous and successful in fulfilling their research aims.
With that warning in mind, let's consider a 'standard' dissertation of around 10K words. In that context, referencing 30 to 40 sources in your literature review tends to work well. Again, this is not a universally accurate rule, but a ballpark figure for you to contemplate. If the 30 to 40 estimate seems frighteningly high to you, do remember that many sources will be used sparingly rather than being mulled over at length. Consider this example:
In British GP practices, pharmaceutical treatment is most often prescribed for Health Condition XYZ ( Carlos, 2019; Jones, 2020 ; Li, 2022 ). Lifestyle modifications, such as physical exercise or meditation practices, have only recently...
When writing critically, it's important to validate findings across studies rather than trusting only one source. Therefore, this writer has cited three recent studies that agree about the claim being made. The writer will delve into other sources at more length, but here, it makes sense to cite the literature and move quickly along.
As you search the databases and start following the relevant trails of 'research bread crumbs', you will be surprised how quickly your reference list grows.
Q: What if there isn't enough relevant literature on my topic?
A: Think creatively about the literature you are using and engaging with. A good start is panning out to consider your topic more broadly: you might not identify articles that discuss your exact topic, but what can you discover if you shift your focus up one level?
Imagine, for example, that Norah is researching how artificial intelligence (AI) can be used to provide dance instruction. She discovers that no one has written about this topic. Rather than panicking, she breaks down her research question into its component parts to consider what research might exist.
- First, dance instruction: literature on how dance has traditionally been taught (i.e., not with AI) is still relevant because it will provide background and context. To appreciate the challenges or opportunities that transition to AI instruction might bring, we need to understand the status quo. Norah might also search for articles that analyse how other technological shifts have affected dance instruction: for example, how YouTube popularized at-home dance study, or how live video services like Zoom enabled real-time interaction between dance pupils and teachers despite physical distance.
- Next, artificial intelligence used for instruction: Norah can seek out research on, and examples of, the application of AI for instructive purposes. Even if those purposes don't involve dance, such literature can contribute to illustrating the broader context around Norah's project.
- Could it be relevant to discuss the technologies used to track an actor's real-life movements and convert them into the motions of a video game character? Perhaps there are parallels!
- Could it be relevant to explore research on applications of AI in creative writing and visual art? Could be relevant since dance is also a creative field!
In summary, don't panic if you can't find research on your exact question or topic. Think through the broader context and parallel ideas, and you will soon find what you need.
Q: What if my discipline doesn't require a literature review chapter?
A: This is a great question. Whilst many disciplines dictate that your dissertation should include a chapter called Literature Review , not all subjects follow this convention. Those subjects will still expect you to incorporate a range of external literature, but you will nest the sources under different headings.
For example, some disciplines dictate an introductory chapter that is longer than average, and you essentially nest a miniature literature review inside the introduction, itself. Although the writing is more condensed and falls under a subheading of the introduction, the techniques and principles of writing a literature review (for example, moving from the broad to the narrow) will still prove relevant.
Some disciplines include chapters with names like Background , History , Theoretical Framework , etc. The exact functions of such chapters differ, but they have this in common: reviewing literature. You can't provide a critical background or history without synthesizing external sources. To illustrate your theoretical framework, you need to synthesize a range of literature that defines the theory or theories you intend to use.
Therefore, as stated earlier in this guide, you should be prepared to review and synthesize a range of literature regardless of your discipline. You can tailor the purpose of that synthesis to the structure and demands of writing in your subject area.

Q: Does my literature review need to include every source I plan to use in my discussion chapter?
A: The short answer is 'no' - there are some situations in which it is okay to use a source in your discussion chapter that you didn't integrate into your literature review chapter.
Imagine, for example, that your study produced a surprising result: a finding that you didn't anticipate. To make sense of that result, you might need to conduct additional research. That new research will help you explain the unexpected result in your discussion chapter.
More often, however, your discussion will draw on, or return to, sources from your literature review. After all, the literature review is where you paint a detailed picture of the conversation surrounding your research topic. Thus, it makes sense for you to relate your own work to that conversation in the discussion.
The literature review provides you an opportunity to engage with a rich range of published work and, perhaps for the first time, critically consider how your own research fits within and responds to your academic community. This can be a very invigorating process!
At the same time, it's likely that you will be juggling more academic sources than you have ever used in a single writing project. Additionally, you will need to think strategically about the focus and scope of your work: figuring out the best structure for your literature review might require several rounds of re-drafting and significant edits.
If you are usually a 'dive in without a plan and just get drafting' kind of writer, be prepared to modify your approach if you start to feel overwhelmed. Mind mapping, organising your ideas on a marker board, or creating a bullet-pointed reverse outline can help if you start to feel lost.
Alternately, if you are usually a 'create a strict, detailed outline and stick to it at all costs' kind of writer, keep in mind that long-form writing often calls for writers to modify their plans for content and structure as their work progresses and evolves. It can help such writers to schedule periodic 'audits' of their outlines, with the aim being to assess what is still working and what else needs to be added, deleted or modified.
Here’s a final checklist for writing your literature review. Remember that not all of these points will be relevant for your literature review, so make sure you cover whatever’s appropriate for your dissertation. The asterisk (*) indicates any content that might not be relevant for your dissertation. You can save your own copy of the checklist to edit using the Word document, below.
- Literature review self-evaluation checklist

- << Previous: Overview and Planning
- Next: The Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/writing_the_dissertation

- Research Guides
Writing Literature Reviews
- Literature Review Overview
- Organizing Your Lit Review
- Tips for Writing Your Lit Review
Need Assistance?
Find your librarian, schedule a research appointment, today's hours : , what is a literature review.
A literature review ought to be a clear, concise synthesis of relevant information. A literature review should introduce the study it precedes and show how that study fits into topically related studies that already exist. Structurally, a literature review ought to be something like a funnel: start by addressing the topic broadly and gradually narrow as the review progresses.
from Literature Reviews by CU Writing Center
Why review the literature?
Reference to prior literature is a defining feature of academic and research writing. Why review the literature?
- To help you understand a research topic
- To establish the importance of a topic
- To help develop your own ideas
- To make sure you are not simply replicating research that others have already successfully completed
- To demonstrate knowledge and show how your current work is situated within, builds on, or departs from earlier publications
from Literature Review Basics from University of La Verne
Tips & Tricks
Before writing your own literature review, take a look at these resources which share helpful tips and tricks:
Lectures & Slides
- Literature Reviews | CU Writing Center
- Writing a Literature Review | CU Writing Center
- Revising a Literature Review | CU Writing Center
- Literature Reviews: How to Find and Do Them
- Literature Reviews: An Overview
How-To Guides
- Literature Reviews | Purdue OWL
- Literature Reviews | University of North Carolina
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature | University of Wisconsin
- Literature Review: The What, Why and How-to Guide | University of Connecticut
- Literature Reviews | Florida A & M
- Conduct a Literature Review | SUNY
- Literature Review Basics | University of LaVerne
Sample Literature Reviews
- Sample Literature Reviews | University of West Florida
- Sample APA Papers: Literature Review | Purdue OWL
- Next: Organizing Your Lit Review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2020 3:12 PM
- URL: https://libguides.cedarville.edu/c.php?g=969394

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
3 Planning Your Research: Reviewing the Literature and Developing Questions
ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS
- What is relevant literature? What are the best ways to find it?
- What are the best ways to organize your relevant literature?
- What are the intended outcomes of reviewing your relevant literature?
Nearly all research begins with a review of literature that is relevant to the topic of research, even if it is only a casual review. Reviewing the available literature on your topic is a vital step in the research process. The literature review process provides an anchor for your inquiry. O’Leary (2004, p. 66) states, the “production of new knowledge is fundamentally dependent on past knowledge” because “it is virtually impossible for researchers to add to a body of literature if they are not conversant with it.” By reviewing the literature in the initial stages of the inquiry process, researchers are better able to:
- Understand their topic;
- Develop and focus a topic;
- Provide a clear rationale for, or better situate, their topic;
- Fine-tune their research questions.
In terms of thinking about methodology and the actual research process, reviewing the literature can help researchers:
- Identify well-vetted data collection and analysis methods on their topic;
- Determine whether to replicate a previous study, or develop a completely new study;
- Add rigor and validity to the research by validating the topic, methods, and significance.
Lastly, reviewing the literature also helps the researcher make sense of their findings, in both their field of study and in their educational context, by:
- Assessing whether the findings correlate with findings from another study;
- Determining which of the findings are different than previous studies;
- Determining which of the findings are unique to the researcher’s educational context. [1]
As you may see, the literature review is the backbone, anchor, or foundation of your research study. Overall the review of literature helps you answer three important questions that are the result of the bullet points outlined above. The literature review helps you answer the following:
- What do we know about your topic?
- What do we not know about your topic?
- How does your research address the gap between what we know and what we don’t about your topic?
After reviewing the literature, if you are able to answer those three questions, you will have a very clear and well-rationalized justification for your inquiry. If you cannot answer those questions, then you should probably keep reviewing the literature by looking for related topics or synonyms of major concepts.
While an extensive review of the literature about your topic of study is expected, you should also be realistic as to what you are able to manage. For topics that have a lot of research literature available, make sure you establish parameters for your research, such as:
- Temporal (e.g., only articles in the last 5 or 10 years)
- Content Area (e.g., only in science and math classrooms)
- Age or grade (e.g., only middle school classrooms)
- Research Subject (e.g., girls only, teachers, struggling readers)
These categories provide only a few examples, but parameters like these can make your review of literature much more manageable and your study much more focused.
What Types of Literature Should You Consider in Your Review?
It is helpful to consider the characteristics, purposes, and outcomes of different types of literature. Below are four broad categories I identify within educational research literature. I want to emphasize that my categories are in no way definitive, and only represent my own understanding.
Policy-Based Literature
Policy-based literature includes official documents that outline education policy with which the practitioner needs to be familiar. For example, the Common Core Standards or Content Standards are often refenced in articles to situate the need for research in relation to the standards; if my topic was on place-based education with middle school social studies students, I might have to look at national social studies standards. There also may be initiatives launched by organizations or researchers that become accepted practice. The documents that launch these initiatives (e.g., reports, articles, speeches) would also be useful to review. An example would be the Report of the National Reading Panel: Teaching Children to Read report from the National Reading Panel. These documents may provide rationale, based on the theories and concepts they utilize, and they may provide new ways of thinking about your topic. Similarly, if your topic is based on the local context, recent newspaper articles could also provide policy-type insights. All of these policy-based insights will be useful in providing the landscape or background for your work.
Theoretical Literature
Once you have identified your theoretical perspective, it is also important to locate your research within the appropriate theoretical literature. Many of you may be engaged in highly practice-based or small-scale research and wonder if you need a theoretical basis in your literature review. Regardless of the extent of your project, theoretical literature will help with the rigor and validity of your study and will help identify any theoretical views that underlie your topic. For example, if your study focuses on the place-based education in enhancing social studies students’ learning, it is highly probable that you would cite Kolb’s (1984/2014) work on Experiential Learning. By using Kolb’s work, you situate your research theoretically in the area of experiential learning.
Applicable Literature
Applicable literature will account for the bulk of your literature review. The previous two types of literature provide indication as to where your research is rationalized professionally and situated theoretically. Applicable literature will mainly come from journals related to your specific field of study. If I was doing a study in a social studies classroom, I would look at the journals The Social Studies, Social Education, and Social Studies Research and Practice . Use Google Scholar or your university library databases to examine literature in your specific area. When using these search engines and databases, start as specific as possible with your topic and related concepts. Using the example of place-based learning from above, I would search for “place-based learning” and “social studies” and “middle school” and “historic sites”. If I did not find many articles with this first search, then I would remove “historic sites” and search again. Books or handbooks on research may also have some useful studies to support your literature review section.
Methodological Literature
When sharing or reporting your work, you will want to review and cite research methodology literature to justify the methods you chose. When reading other research articles, pay attention to the research methods used by researchers. It is especially important to find articles that use and cite action research methodology. This type of literature will provide further support of your data gathering and analysis methods. Again, your methods should fit within your theoretical and epistemological stances. In addition, you’ll want to review data collection methods and potentially borrow or adapt rubrics or surveys from other studies.
Sources of Relevant Literature
When searching for these four types of literature, there are two ways to think about possible sources:
- primary sources include government publications, policy documents, research papers, dissertations, conference presentations and institutional occasional papers with accounts of research;
- secondary sources use primary sources as references, such as papers written for professional conferences and journals, books written for practicing professionals and book reviews. This is often called “reference mining” as you look through the reference lists of other studies and then return to the primary source that was cited.
Secondary sources are often just as valuable as primary sources, or potentially more valuable. When beginning your search, secondary sources can provide links to a wealth of primary sources that the secondary source author has already vetted for you, and likely with similar intentions. This is especially true of research handbooks. You will come across both types of literature wherever you search, and they both provide a landscape for your topic and add value to your literature review.
Regardless of being a primary or secondary source, you want to make sure the literature you review is peer-reviewed. Peer-reviewed simply means that the article was reviewed by two to three scholars in the field before it was published. Books, or edited books, would have also gone through a peer-review process. We often recommend teachers to look at professional books from reputable publishing companies and professional organizations, such as ASCD, NCTE, NCTM, or NCSS. This is a way for scholars to objectively review each other’s work to maintain a high level of quality and ethics in the publication of research. Most databases have mostly peer-reviewed journals, and often provide a filter to sort out the non-peer-reviewed journals.
Using the Internet
The internet is a valuable research tool and is becoming increasingly efficient and reliable in providing peer-reviewed literature. Sites like Google Scholar are especially useful. Often, and depending on the topic, the downside of internet-based searches is that it will generate thousands or millions of sources. This can be overwhelming, especially for new researchers, and you will have to develop ways to narrow down the results.
Professional organization websites will also have resources or links to sources that have typically been vetted. With all internet sources, you should evaluate the information for credibility and authority.
Evaluating sources from the Internet
Evaluating internet sources is a whole field of study and research within itself, and an in-depth discussion would take away from the focus of this book. However, O’ Dochartaigh (2007) provides a chapter to help guide the internet source evaluation process. Here is a brief summary, based on O’ Dochartaigh’s book, to give you a general idea of the task of evaluating sources:
- Examine if the material belongs to an advocacy group. Many times, these sources are fine, however, they require extra examination for bias or funding interests.
- As mentioned above, many academic papers are published in refereed journals which are subject to peer-review. Papers found on academic or university websites are typically refereed in some manner; however, some papers are posted by academics on their personal sites and have not been reviewed by other academics. Papers published solely by academics or other experts require further scrutiny before citing.
- When you are reviewing newspaper and magazine articles from the internet be weary of potential conflicts of interest based on the political stance of that periodical.
Therefore, it is wise to consider the objectivity of any source you find on the internet before you accept the literature.
We always recommend that students consider a few questions in their evaluation of sources, which are similar to the formal questions outlined by O’ Dochartaigh (2007):
- Is it clear who is responsible for the document?
- Is there any information about the person or organization responsible for the page?
- Is there a copyright statement?
- Does it have other publications that reinforce its authority?
- Are the sources clearly listed so they can be verified?
- Is there an editorial involvement?
- Are the spelling and grammar correct?
- Are biases and affiliations clearly stated?
- Are there dates for when the document was last updated or revised?
Organizing your Literature
When you begin, here are some things to think about as your read the literature. Again, these are not definitive, but merely provided for guidance. These questions are especially focused on other action research literature:
Questions to Think about as You Examine the Literature
- What was the context of their research?
- Who was involved? Was it a collaborative project?
- Was the choice of using action research as a method justified? Are any models discussed?
- What ‘actions’ actually took place?
- How was data gathered?
- How was data analyzed?
- Were ethical considerations addressed? How?
- What were the conclusions? Were they justified using appropriate evidence?
- Was the report accessible? Useful?
- Is it possible to replicate the study?
Regardless of the amount of literature you review, your challenge will be to organize the literature in way that is manageable and easy to reference. It is important to keep a record of what you read and how it relates conceptually to your topic. Some researchers even use the questions above to organize their literature. It is easy to read and think about the content of an article by making brief notes, however, this is often not enough to initially begin to develop your study or write about your findings. I will state the obvious here: organizing your literature search efficiently from the start is vital!
No matter how you choose to record or document the articles you read (e.g., paper, computer, photo), I would suggest thinking about the format in terms of index cards. Index cards are a very practical and simple model because the space limits you to be precise in recording vital information about each article. I typically create a document on my computer, allow each article the space of an index card, and focus on recording the following information:
- Journal/Book Chapter Title
- Main Arguments/Key findings
- Pertinent Quote(s)
- Implications
- Connective Points (how does it relate to my work and/or other articles)
I find that these aspects provide the information I need to be refreshed on the article and to be able to use it upon review.
There are also a lot of computer applications that are very useful and efficient in managing your literature. For example, Mendeley © provides comprehensive support for reviewing literature, even allowing you to store the article itself and make comments or highlights in text. There are also many citation apps that are helpful if you continue this research agenda and use roughly the same literature for each project.
Using the Literature
Think ahead to when you have collected and read a good amount of literature on your topic. You are now ready to use the literature to think about your topic, your research question, and the methods you plan to use. It might be helpful to peek ahead to Chapter 7 where I discuss writing the literature review for a report to give you an idea of the end goal. The primary purpose of engaging in a literature review is to provide knowledge to construct a framework for understanding the landscape of your topic. I often suggest for students to think of it as constructing an argument for your research decisions, or as if you are telling a story of how we got to this point in researching your topic. Either way you are situating your research in what we know and don’t know about your topic.
Naturally we tend to think about, and potentially write about, the literature in relation to the article’s author (e.g. Clark and Porath (2016) found that…). However, more commonly today in educational research you will find that literature reviews are organized by themes. It can be a little more organic to think about literature in terms of themes because they emerge or become more defined as you read. Also thinking thematically allows the articles to naturally connect and build on each other, whereas thinking in terms of authors can fragment thinking about the topic. In terms of thinking thematically, here are some guidelines:
- Identify the significant themes that have emerged organically from the literature review. These themes would be concepts or ideas that you typed or wrote down in your note-taking or management system.
- Introduce the common concepts or ideas by themes, instead of by authors’ disjointed viewpoints. Paragraphs in a thematic literature review begin like: The research on teacher self-efficacy has identified several key factors that contribute to strong self-efficacy… .
- Lastly, once you have introduced each theme and explained it, then present evidence from your readings to demonstrate the parameters of the knowledge on the theme, including areas of agreement and disagreement among researchers. Using the evidence, explain what the evidence for the theme means to your topic and any of your own relational or critical commentary.
Another way to think about structuring a literature review is a funnel model. A funnel model goes from broad topic, to sub-topics, to link to the study being undertaken. You can think of a literature review as a broad argument using mini-arguments. To use the funnel model, list your topic and the related subtopics, then design questions to answer with the literature. For example if our topic was discussion-based online learning, we might ask the following questions before reading the literature:
- Why is discussion important in learning?
- How does discussion support the development of social, cognitive, and teacher presence in an online course?
- What does research say about the use of traditional discussion boards ?
- What does the research say about asynchronous, video-based discussion ?
- How have other researchers compared written and video responses?
- How does this literature review link to my study?
O’Leary (2004) provides an interesting representation and model of the purpose for the literature review in the research process, in Figure 3.1. We will leave this for you to think about before moving on to Chapter 4.
- We will talk about this aspect of literature reviews further in Chapters 6 and 7. ↵
Action Research Copyright © by J. Spencer Clark; Suzanne Porath; Julie Thiele; and Morgan Jobe is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Writers' Center
Eastern Washington University
Writing the Literature Review
The literature review, questions your literature review might address, tips for writing a literature review, tips for organizing your sources.
[ Back to resource home ]

[email protected] 509.359.2779
Cheney Campus JFK Library Learning Commons
Stay Connected!
inside.ewu.edu/writerscenter Instagram Facebook
- Occupational Therapy Sample
- Social Work Sample
- POOR Literature Review Sample This is how NOT to write a literature review.
What is a literature review?
When we hear the word "literature," we often think of great classic novels or poetry, but in this case "literature" refers to the body of work you consulted in order to make a conclusive recommendation about an issue. In other words, a literature review is a synthesis (more on synthesis below) of many articles and other published materials on a certain research topic. Depending on the field, the literature review might be a stand-alone piece or part of a larger research article.
Why write one?
By writing a literature review, you are entering into an academic conversation about an issue. You need to show that you understand what research has already been done in your field and how your own research fits into it.
1. What do we already know in the immediate area concerned?
2. What are the characteristics/traits of the key concepts or the main factors or variables?
3. What are the relationships between these key concepts, factors or variables?
4. What are the existing theories?
5. Where are the inconsistencies or other shortcomings in our knowledge and understanding?
6. What views need to be (further) tested?
7. What evidence is lacking, inconclusive, contradictory or too limited?
8. What research designs or methods seem unsatisfactory?
9. How does this research provide context for my own work?
Synthesis involves but goes beyond summary. Rather than simply summarizing sources (as an annotated bibliography does), synthesis also does the following:
- shows the relationships between sources (how are they similar or different, how do they build off one another, where are the gaps)
- shows how sources relate to your own work (provides the context for your research)
- sometimes evaluates the methods or conclusions of sources
Synthesis literally means to bring together, to combine separate elements to make a cohesive whole. Here are some analogies to help with the concept of synthesis:

Credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/pcapemax2007/8711542470

Architecture: Each main idea is an element of architecture: a shape, a material, a color. All of the elements come together to form a coherent look (synthesis).

Remember your purpose.
Keeping your own research question or goals in mind as you read will help you decide which sources to include in your review and which ones to briefly mention or leave out entirely.
Know and organize your sources.
Use a free citation manager to keep track of and categorize articles in library databases. Use different colors to highlight different "threads" or "notes" (main ideas) of your sources. Take lots of notes.
Look for threads patiently.
Be patient with yourself during this process. It will take time to read, reread, annotate, and start to see connections beween sources.
Use transition phrases that indicate synthesis.
Language is your key to showing connections between ideas on paper. Consider using transition phrases like the following, or borrow phrasing that you like from other articles. (It's not plagiarism to use common phrases.)
Organize your review like a funnel.
Start by addressing the larger context of the issue at hand. Gradually work to the more specific aspects you will be looking at. Finally, narrow into your own project and research.
Read plenty of sample literature reviews in your field.
Literature reviews vary in purpose and format from field to field, so use published literature review articles in your discipline as models. You can find a few annotated samples on this page.
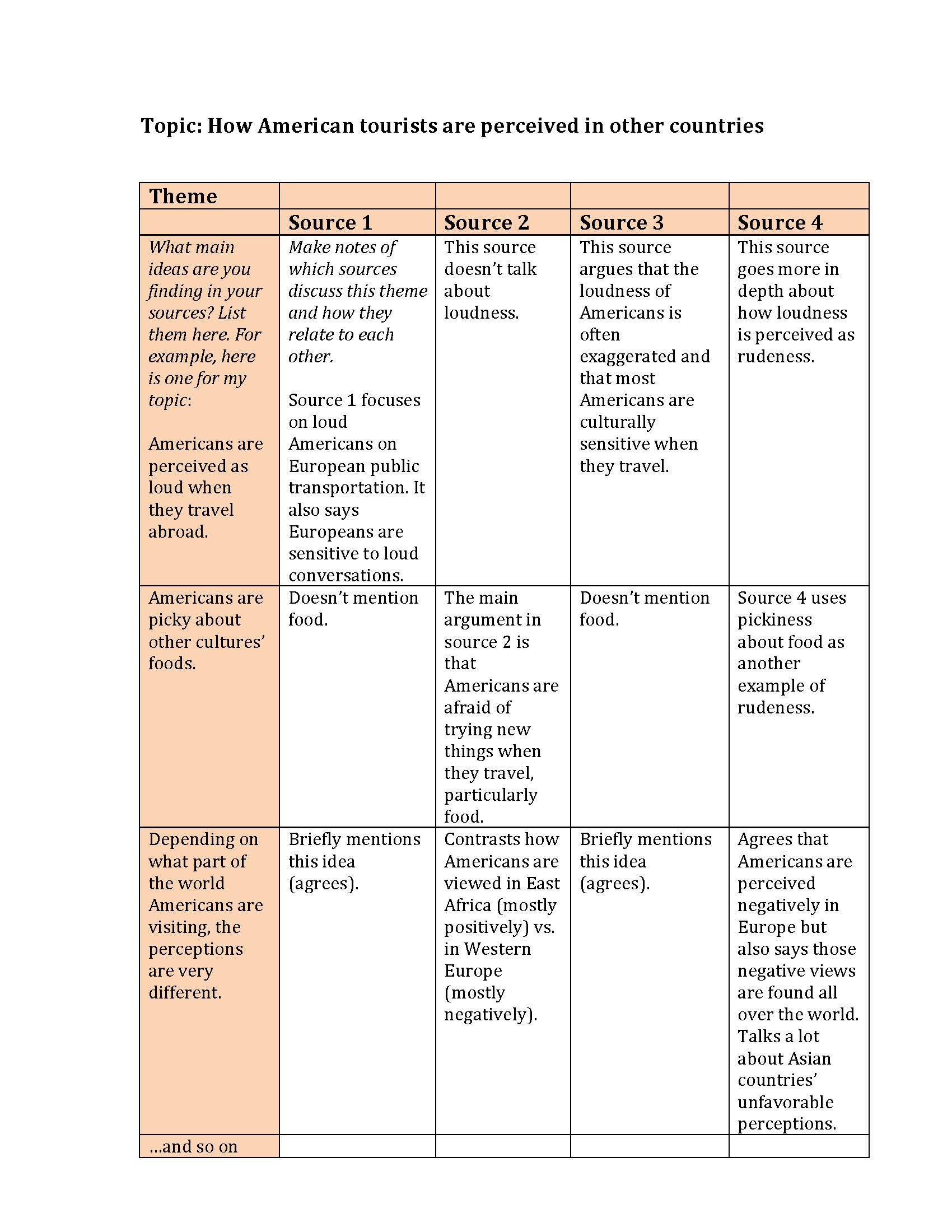
- Last Updated: Apr 25, 2024 2:50 PM
- URL: https://research.ewu.edu/writers_c_lit_review
Adopting a Funnel Strategy and Using Mind Mapping to Visualize the Research Design
- First Online: 25 May 2023
Cite this chapter

- Uche M. Mbanaso 4 ,
- Lucienne Abrahams 5 &
- Kennedy Chinedu Okafor 6
481 Accesses
This chapter explains the need to adopt a research strategy and illustrates the funnel strategy that enables the researcher to move from identifying the flaws, or defects or gaps that require attention to scoping the problem statement, finalizing the research proposal as a foundation for data collection and analysis and conducting the experiments or fieldwork, through to the point of analysis and thesis writing. It presents the funnel strategy as a roadmap that can be applied to completing the various phases of the research. The chapter demonstrates the application of mind mapping techniques (graphical representations of what to do and how to do it) to the identified research problem. It sets out a series of major activities as part of the mind mapping process. It presents a series of visuals, for example, artificial intelligence and robotics sub-topics.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
If you find that any of the following material is not downloadable at the listed url, please search on ResearchGate at https://www.researchgate.net/ or, alternatively, search on the full name of the article, book, or paper.
Bibliography
APA. (n.d.). APA style guide . https://apastyle.apa.org/
Carlsson, S. A. (2006). Design science research in information systems: A critical realist perspective. In ACIS 2006 Proceedings, Australia . https://aisel.aisnet.org/acis2006/40/
Crowe, M., & Sheppard, L. (2016). Mind mapping research methods. Quality & Quantity, 46 , 1493–1504. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-011-9463-8
Article Google Scholar
Ellis, T., & Levy, Y. (2009). Towards a guide for novice researchers on research methodology: Review and proposed methods. Issues in Informing Science and Information Technology, 6 , 323–337. https://doi.org/10.28945/1062
Ernest, P. (1996). Varieties of constructivism: A framework for comparison. In L. Steffe, P. Nesher, P. Cobb, G. Goldin, & B. Greer (Eds.), Theories of mathematical learning . Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203053126
Chapter Google Scholar
Hassani, H. (2017). Research methods in computer science: The challenges and issues . https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.04080.pdf
Hauberg, J. (2011). Research by design: A research strategy. Architecture & Education Journal, 5 . https://www.researchgate.net/publication/279466514_Research_by_design_a_research_strategy
Hevner, A., March, S., Park, J., & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS Quarterly, 28 (1), 75–105. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/201168946_Design_Science_in_Information_Systems_Research
Indulska, M., & Recker, J. (2010). Design science in IS research: A literature analysis. In S. Gregor & D. Hart (Eds.), Information systems foundations: The role of design science . ANU Press. https://doi.org/10.22459/isf.12.2010.13
MacIntyre, S., Dalkir, K., Paul, P., & Kitimbo, I. (2014). Utilizing evidence-based lessons learned for enhanced organizational innovation and change . Business Science Reference.
Google Scholar
McLaren, T., & Buijs, P. (2011). A design science approach for developing information systems research instruments. In H. Jain, A. Sinha & P. Vitharana (Eds.), Lecture notes in computer science: Vol. 6629. Service-oriented perspectives in design science research (pp. 1–10). Springer. http://www.rug.nl/staff/p.buijs/design_science_approach_for_developing_isr_instruments.pdf
Mosina, C. (2020). Understanding the diffusion of the Internet: Redesigning the global diffusion of the Internet framework . [Research report, Master of Arts in ICT Policy and Regulation]. LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand. http://wiredspace.wits.ac.za/handle/10539/30723
Oates, B. J. (2006). Researching information systems and computing . SAGE Publications. https://books.google.co.za/books/about/Researching_Information_Systems_and_Comp.html?id=ztrj8aph-4sC
Pajares, F. (2007). The elements of a proposal . Emory University. https://www.uky.edu/~eushe2/Pajares/proposal.html
Riggins, F. J., & Wamba, S. F. (2015). Research directions on the adoption, usage, and impact of the internet of things through the use of big data analytics. Proceedings of the 2015 48th Hawaii International Conference on Systems Science, USA , 1531–1540. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2015.186
Salhin, A., Kyiu, A., Taheri, B., Porter, C., Valantasis-Kanellos, N., & König, C. (2016). Quantitative data gathering methods and techniques. In A. Paterson, D. Leung, W. Jackson, R. MacIntosh, & K. D. O’Gorman (Eds.), Research methods for accounting and finance . Goodfellow Publishers. https://doi.org/10.23912/978-1-910158-88-3-3226
Software Testing Help. (2021, March 27). 10 best mind mapping software in 2021 . [website]. https://www.softwaretestinghelp.com/mind-map-software/
ThinkBuzan Ltd. (2010). Mind mapping: Scientific research and studies . [online]. https://www.slideshare.net/elsavonlicy/mind-mapping-evidence-report
Wilson, K., Copeland-Solas, E., & Guthrie-Dixon, N. (2016). A preliminary study on the use of mind mapping as a visual-learning strategy, in general education science classes for Arabic speakers in The United Arab Emirates. Journal of the Scholarship of Teaching and Learning, 16 (1), 31–52. https://doi.org/10.14434/josotl.v16i1.19181
Wolcott, P., Press, L., McHenry, W., Goodman, S., & Foster, W. (2001). A framework for assessing the global diffusion of the Internet. Journal of the Association for Information Systems, 2 . https://doi.org/10.17705/1jais.00018
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Cybersecurity Studies, Nasarawa State University, Keffi, Nigeria
Uche M. Mbanaso
LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
Lucienne Abrahams
Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Kennedy Chinedu Okafor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Mbanaso, U.M., Abrahams, L., Okafor, K.C. (2023). Adopting a Funnel Strategy and Using Mind Mapping to Visualize the Research Design. In: Research Techniques for Computer Science, Information Systems and Cybersecurity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_4
Published : 25 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-30030-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-30031-8
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Writing a Literature Review
When writing a research paper on a specific topic, you will often need to include an overview of any prior research that has been conducted on that topic. For example, if your research paper is describing an experiment on fear conditioning, then you will probably need to provide an overview of prior research on fear conditioning. That overview is typically known as a literature review.
Please note that a full-length literature review article may be suitable for fulfilling the requirements for the Psychology B.S. Degree Research Paper . For further details, please check with your faculty advisor.
Different Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews come in many forms. They can be part of a research paper, for example as part of the Introduction section. They can be one chapter of a doctoral dissertation. Literature reviews can also “stand alone” as separate articles by themselves. For instance, some journals such as Annual Review of Psychology , Psychological Bulletin , and others typically publish full-length review articles. Similarly, in courses at UCSD, you may be asked to write a research paper that is itself a literature review (such as, with an instructor’s permission, in fulfillment of the B.S. Degree Research Paper requirement). Alternatively, you may be expected to include a literature review as part of a larger research paper (such as part of an Honors Thesis).
Literature reviews can be written using a variety of different styles. These may differ in the way prior research is reviewed as well as the way in which the literature review is organized. Examples of stylistic variations in literature reviews include:
- Summarization of prior work vs. critical evaluation. In some cases, prior research is simply described and summarized; in other cases, the writer compares, contrasts, and may even critique prior research (for example, discusses their strengths and weaknesses).
- Chronological vs. categorical and other types of organization. In some cases, the literature review begins with the oldest research and advances until it concludes with the latest research. In other cases, research is discussed by category (such as in groupings of closely related studies) without regard for chronological order. In yet other cases, research is discussed in terms of opposing views (such as when different research studies or researchers disagree with one another).
Overall, all literature reviews, whether they are written as a part of a larger work or as separate articles unto themselves, have a common feature: they do not present new research; rather, they provide an overview of prior research on a specific topic .
How to Write a Literature Review
When writing a literature review, it can be helpful to rely on the following steps. Please note that these procedures are not necessarily only for writing a literature review that becomes part of a larger article; they can also be used for writing a full-length article that is itself a literature review (although such reviews are typically more detailed and exhaustive; for more information please refer to the Further Resources section of this page).
Steps for Writing a Literature Review
1. Identify and define the topic that you will be reviewing.
The topic, which is commonly a research question (or problem) of some kind, needs to be identified and defined as clearly as possible. You need to have an idea of what you will be reviewing in order to effectively search for references and to write a coherent summary of the research on it. At this stage it can be helpful to write down a description of the research question, area, or topic that you will be reviewing, as well as to identify any keywords that you will be using to search for relevant research.
2. Conduct a literature search.
Use a range of keywords to search databases such as PsycINFO and any others that may contain relevant articles. You should focus on peer-reviewed, scholarly articles. Published books may also be helpful, but keep in mind that peer-reviewed articles are widely considered to be the “gold standard” of scientific research. Read through titles and abstracts, select and obtain articles (that is, download, copy, or print them out), and save your searches as needed. For more information about this step, please see the Using Databases and Finding Scholarly References section of this website.
3. Read through the research that you have found and take notes.
Absorb as much information as you can. Read through the articles and books that you have found, and as you do, take notes. The notes should include anything that will be helpful in advancing your own thinking about the topic and in helping you write the literature review (such as key points, ideas, or even page numbers that index key information). Some references may turn out to be more helpful than others; you may notice patterns or striking contrasts between different sources ; and some sources may refer to yet other sources of potential interest. This is often the most time-consuming part of the review process. However, it is also where you get to learn about the topic in great detail. For more details about taking notes, please see the “Reading Sources and Taking Notes” section of the Finding Scholarly References page of this website.
4. Organize your notes and thoughts; create an outline.
At this stage, you are close to writing the review itself. However, it is often helpful to first reflect on all the reading that you have done. What patterns stand out? Do the different sources converge on a consensus? Or not? What unresolved questions still remain? You should look over your notes (it may also be helpful to reorganize them), and as you do, to think about how you will present this research in your literature review. Are you going to summarize or critically evaluate? Are you going to use a chronological or other type of organizational structure? It can also be helpful to create an outline of how your literature review will be structured.
5. Write the literature review itself and edit and revise as needed.
The final stage involves writing. When writing, keep in mind that literature reviews are generally characterized by a summary style in which prior research is described sufficiently to explain critical findings but does not include a high level of detail (if readers want to learn about all the specific details of a study, then they can look up the references that you cite and read the original articles themselves). However, the degree of emphasis that is given to individual studies may vary (more or less detail may be warranted depending on how critical or unique a given study was). After you have written a first draft, you should read it carefully and then edit and revise as needed. You may need to repeat this process more than once. It may be helpful to have another person read through your draft(s) and provide feedback.
6. Incorporate the literature review into your research paper draft.
After the literature review is complete, you should incorporate it into your research paper (if you are writing the review as one component of a larger paper). Depending on the stage at which your paper is at, this may involve merging your literature review into a partially complete Introduction section, writing the rest of the paper around the literature review, or other processes.
Further Tips for Writing a Literature Review
Full-length literature reviews
- Many full-length literature review articles use a three-part structure: Introduction (where the topic is identified and any trends or major problems in the literature are introduced), Body (where the studies that comprise the literature on that topic are discussed), and Discussion or Conclusion (where major patterns and points are discussed and the general state of what is known about the topic is summarized)
Literature reviews as part of a larger paper
- An “express method” of writing a literature review for a research paper is as follows: first, write a one paragraph description of each article that you read. Second, choose how you will order all the paragraphs and combine them in one document. Third, add transitions between the paragraphs, as well as an introductory and concluding paragraph. 1
- A literature review that is part of a larger research paper typically does not have to be exhaustive. Rather, it should contain most or all of the significant studies about a research topic but not tangential or loosely related ones. 2 Generally, literature reviews should be sufficient for the reader to understand the major issues and key findings about a research topic. You may however need to confer with your instructor or editor to determine how comprehensive you need to be.
Benefits of Literature Reviews
By summarizing prior research on a topic, literature reviews have multiple benefits. These include:
- Literature reviews help readers understand what is known about a topic without having to find and read through multiple sources.
- Literature reviews help “set the stage” for later reading about new research on a given topic (such as if they are placed in the Introduction of a larger research paper). In other words, they provide helpful background and context.
- Literature reviews can also help the writer learn about a given topic while in the process of preparing the review itself. In the act of research and writing the literature review, the writer gains expertise on the topic .
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
- UCSD Library Psychology Research Guide: Literature Reviews
External Resources
- Developing and Writing a Literature Review from N Carolina A&T State University
- Example of a Short Literature Review from York College CUNY
- How to Write a Review of Literature from UW-Madison
- Writing a Literature Review from UC Santa Cruz
- Pautasso, M. (2013). Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review. PLoS Computational Biology, 9 (7), e1003149. doi : 1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
1 Ashton, W. Writing a short literature review . [PDF]
2 carver, l. (2014). writing the research paper [workshop]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Research Paper Structure
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos
Literature Reviews
- "How To" Books
- Examples of Literature Reviews
- Collecting Resources for a Literature Review
- Organizing the Literature Review
- Writing the Literature Review
- Endnote This link opens in a new window
- Evaluating Websites
Organization
Organization of your Literature Review
What is the most effective way of presenting the information? What are the most important topics, subtopics, etc., that your review needs to include? What order should you present them?
Just like most academic papers, literature reviews must contain at least three basic elements: an introduction or background information section; the body of the review containing the discussion of sources; and, finally, a conclusion and/or recommendations section to end the paper.
Introduction: Gives a quick idea of the topic of the literature review, such as the central theme or organizational pattern.
Body: Contains your discussion of sources and is organized either chronologically, thematically, or methodologically (see below for more information on each).
Conclusions/Recommendations: Discuss what you have drawn from reviewing the literature so far. Where might the discussion proceed?
Once you have the basic categories in place, then you must consider how you will present the sources themselves within the body of your paper. Create an organizational method to focus this section even further.
To help you come up with an overall organizational framework for your review, consider the following scenario and then three typical ways of organizing the sources into a review:
You've decided to focus your literature review on materials dealing with sperm whales. This is because you've just finished reading Moby Dick, and you wonder if that whale's portrayal is really real. You start with some articles about the physiology of sperm whales in biology journals written in the 1980's. But these articles refer to some British biological studies performed on whales in the early 18th century. So you check those out. Then you look up a book written in 1968 with information on how sperm whales have been portrayed in other forms of art, such as in Alaskan poetry, in French painting, or on whale bone, as the whale hunters in the late 19th century used to do. This makes you wonder about American whaling methods during the time portrayed in Moby Dick, so you find some academic articles published in the last five years on how accurately Herman Melville portrayed the whaling scene in his novel.
Chronological
If your review follows the chronological method, you could write about the materials above according to when they were published. For instance, first you would talk about the British biological studies of the 18th century, then about Moby Dick, published in 1851, then the book on sperm whales in other art (1968), and finally the biology articles (1980s) and the recent articles on American whaling of the 19th century. But there is relatively no continuity among subjects here. And notice that even though the sources on sperm whales in other art and on American whaling are written recently, they are about other subjects/objects that were created much earlier. Thus, the review loses its chronological focus.
By publication
Order your sources chronologically by publication if the order demonstrates a more important trend. For instance, you could order a review of literature on biological studies of sperm whales if the progression revealed a change in dissection practices of the researchers who wrote and/or conducted the studies.
Another way to organize sources chronologically is to examine the sources under a trend, such as the history of whaling. Then your review would have subsections according to eras within this period. For instance, the review might examine whaling from pre-1600-1699, 1700-1799, and 1800-1899. Using this method, you would combine the recent studies on American whaling in the 19th century with Moby Dick itself in the 1800-1899 category, even though the authors wrote a century apart.
Thematic reviews of literature are organized around a topic or issue, rather than the progression of time. However, progression of time may still be an important factor in a thematic review. For instance, the sperm whale review could focus on the development of the harpoon for whale hunting. While the study focuses on one topic, harpoon technology, it will still be organized chronologically. The only difference here between a "chronological" and a "thematic" approach is what is emphasized the most: the development of the harpoon or the harpoon technology.
More authentic thematic reviews tend to break away from chronological order. For instance, a thematic review of material on sperm whales might examine how they are portrayed as "evil" in cultural documents. The subsections might include how they are personified, how their proportions are exaggerated, and their behaviors misunderstood. A review organized in this manner would shift between time periods within each section according to the point made.
Methodological
A methodological approach differs from the two above in that the focusing factor usually does not have to do with the content of the material. Instead, it focuses on the "methods" of the researcher or writer. For the sperm whale project, one methodological approach would be to look at cultural differences between the portrayal of whales in American, British, and French art work. Or the review might focus on the economic impact of whaling on a community. A methodological scope will influence either the types of documents in the review or the way in which these documents are discussed.
Once you've decided on the organizational method for the body of the review, the sections you need to include in the paper should be easy to figure out. They should arise out of your organizational strategy. In other words, a chronological review would have subsections for each vital time period. A thematic review would have subtopics based upon factors that relate to the theme or issue.
Sometimes, though, you might need to add additional sections that are necessary for your study, but do not fit in the organizational strategy of the body. What other sections you include in the body is up to you. Put in only what is necessary. Here are a few other sections you might want to consider:
Current Situation: Information necessary to understand the topic or focus of the literature review.
History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology.
Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information. For instance, you might explain that your review includes only peer-reviewed articles and journals.
Questions for Further Research: What questions about the field has the review sparked? How will you further your research as a result of the review?
- << Previous: Collecting Resources for a Literature Review
- Next: Writing the Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Nov 2, 2021 12:11 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.stonybrook.edu/literature-review
- Request a Class
- Hours & Locations
- Ask a Librarian
- Special Collections
- Library Faculty & Staff
Library Administration: 631.632.7100
- Stony Brook Home
- Campus Maps
- Web Accessibility Information
- Accessibility Barrier Report Form

Comments or Suggestions? | Library Webmaster

Except where otherwise noted, this work by SBU Libraries is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .
Literature reviews: Reviewing for research
- Reviewing for research
- Stand-alone review
- Scoping and planning
- Screening and appraising
- The process of reviewing
- Planning a search strategy
On this page:
“The researcher first addresses the current state of knowledge about the study question. Then, based on these findings, the researcher proposes a thesis defining an issue for further study” Lawrence A Machi, The Literature Review: Six Steps to Success
This page concentrates on undertaking a literature review as the first stage of a research-based dissertation or independent project. Such a review needs to both position your study within the wider literature and justify the research question that you are asking. This page is looking at a traditional literature review rather than a systematic review which has its own page in this guide.
What a literature review for a research project should do
Position your research within the wider body of literature on the topic.
Demonstrate an in-depth understanding of your topic area.
Identify who the major thinkers are.
Identify what research has already been done in that area.
Find gaps or new directions to help you formulate your own question.
Identify the main research methodologies in your area.
Identify the main areas of agreement or controversy.
Convince the reader that your research questions are significant , important and interesting.
Convince the reader that your research will make an original contribution.
What a literature review is, and isn't
- Critical analysis
- Evaluation of previous research on a topic
- Addressing a clearly articulated question (or questions)

- A descriptive list
- Summaries of books/articles
- Exhausted bibliography of everything written on the topic
- Your arguments and ideas

The structure of a literature review
Funnel structure.
The most common structure is one where you start your literature review looking at the bigger picture and then increasingly focus onto the specific aspects you are interested in. This is known as a funnel structure.

- As can be seen, the review starts by looking at a fair number of papers but not in great detail - these position your research within the wider literature to show how your topic fits in to the bigger picture.
- The review then moves to consider a number of papers (less than the previous part) in a bit more detail. These papers cover more narrow categories that are closer to your topic but not matched directly.
- The review should then focus on a few papers that are the most relevant to your work. You are likely to look at these in considerably more detail.
- You finish the review by confirming how the literature has led you to your specific question.
Jigsaw structure
Sometimes, if your topic area has clear sub-areas it can be more appropriate to use a jigsaw structure.

- Give a proportion of your review to each sub-area.
- Discuss the links between each of the sub-areas.
- Make sure your conclusion pulls these together and shows where your research will fit into this picture.
Chronological structure
This structure is not particularly common but can be useful for some reviews - specifically when you need to show how ideas have changed through time . For example, in medicine you could look at how treatments for a particular condition have progressed from early treatments to the present day.

- You will begin with the earliest papers, grouping them together by publication date. For example, papers from 1990-1999 then papers from 2000-2009, then 2010-2019, finishing with the very latest papers from 2020 onwards.
- You focus on how the research (ideas, theories or methods) has changed over the period and emphasise the key changes that happened.
- You finish by showing how this led you to choose the direction that your own research will take.
Top Tips Video
- << Previous: Home
- Next: Stand-alone review >>
- Last Updated: Apr 9, 2024 3:41 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/literaturereviews
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem
Conducting a Literature Review: Home
What is a literature review.
A literature review is a body of text that aims to review the critical points of current knowledge on a particular topic. Most often associated with science-oriented literature, such as a thesis, the literature review usually proceeds a research proposal, methodology and results section. Its ultimate goals is to bring the reader up to date with current literature on a topic and forms that basis for another goal, such as the justification for future research in the area. (retrieved from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Literature_review )
Print Resources
Many resources on research methodology include a chapter on literature review. Try these titles:
- SAGE Research Methods "SAGE Research Methods (SRM) is a research tool supported by a newly devised taxonomy that links content and methods terms. It provides the most comprehensive picture available today of research methods (quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods)across the social and behavioural sciences."
There are many resources available on the internet and in print to help you conduct a literature review. For graduate students working on a thesis, the most important resource is your graduate committee chair. Also, if you are an ILR student, don't forget to speak with one of Catherwood's reference librarians. They have subject matter expertise and can help you find research materials, as well as show you relevant databases and resources, including Zotero , an online bibliographic management system. Cornell students can also take advantage of the John S. Knight Institute for Writing in the Disciplines , which offers a walk-in tutoring Service.
Additional Resources for Writing Literature Reviews
- Library Research at Cornell by Michael Engle Last Updated Mar 22, 2024 6544 views this year
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting Writing Advice from the University of Toronto Health Sciences Writing Centre.
- Write a Literature Review Research guide from the University Library, UC Santa Cruz
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature From the Writing Center at University of Wisconsin - Madison.
Searching the Library Catalog
Conducting a guided keyword search from the Cornell University Library Catalog , using the terms "research methodology" or "qualitative research" will provide additional results, and adding the term "social sciences" to the search will help narrow the results. You can also use this list of the classification numbers for theses by department . We also offer a finding guide to dissertations and theses that you may find useful!
We also recommend you look through other theses - often your graduate chair will have copies.

- Last Updated: Feb 4, 2021 9:22 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/ilrlitreview
- Do Not Sell My Personal Info

- ⋅
How A Full-Funnel SEO & PR Strategy Can Drive Leads & Sales
Unlock the power of full-funnel SEO and PR integration. Learn how to influence audience behavior and achieve top search engine rankings.

Integrating digital PR & SEO with a full-funnel strategy both influences audience behavior and top-three rankings in search engines.
In my recent webinar with Search Engine Journal about how to earn links with digital PR , I didn’t have time to dive into the importance of the audience journey and a full-funnel strategy. This article is to remedy that.
Have you found that ranking in search engines is more difficult lately? Or maybe your link building isn’t driving the top 3 ranking it used to.
Google representatives have been actively discussing the decrease in the importance of links in Google’s algorithm.
What does this mean?
This doesn’t seem to mean links don’t work, but that links and brand mentions in the context of the audience’s journey are factors that help to break into the top 3 positions of Google – and, I believe, eventually, how you’ll make it into SGE or other high-visibility areas of search.
A full-funnel PR and SEO strategy is a method for building links and brand mentions in the context of the audience’s journey online, creating an off-page user experience.
Here’s a quick snapshot of the key takeaways you’ll find throughout this article:
- Audience Journey Insight: Your audience interacts with diverse content across platforms long before they search, influencing their perception and decision-making.
- Case Study: Lectric eBikes showcased how aligning content with the customer journey and securing authoritative links and mentions can significantly boost SEO performance, brand trust, and, ultimately, sales.
- Strategy Blueprint: This guide offers a structured approach for businesses to navigate digital marketing complexities efficiently, guiding the audience from awareness to conversion.
- Integration of Digital PR and SEO: Combining digital PR and SEO creates a cohesive journey that guides the audience from awareness to decision-making, influencing audience behavior and search engine rankings.
- Digital PR for SEO: Digital PR links and brand mentions are in the context of the audience journey and are needed to rank in the top three positions in search.
Off-Page Audience Experience With The Brand Matters
Google recommends being helpful to the audience and demonstrating Experience, Expertise, Authority, and trust ( E-E-A-T ) in a category to rank highly.
Your audiences are constantly looking for a solution that solves their problem or creates an opportunity, and for trusted sources to guide them through the decision-making process.
They may become aware of this problem or the solutions long before they even reach the search engines.
The chart below illustrates the sites that receive the most visits vs. those that send the most referral traffic.
This data indicates that search engines will drive the most traffic to sites, but any given audience spends a significant amount of time engaging on other platforms, digesting content about various topics.
Social and News sites get 20% and 12% of the shares of visits, respectively, while search engines drive over 70% of total traffic.
If the audience is using several touchpoints to learn about a given product or solution, wouldn’t Google use these to determine which company is a helpful source and what its E-E-A-T is for those topics?
I had my digital PR data team at PureLinq gather data for sites that ranked in Google for a seed set of cybersecurity keywords.
We then identified all of the keywords that those sites ranked in the top three positions. From that, we gathered data about the count of brand mentions and brand search volume for each domain.
The chart below shows the number of brand mentions (x-axis), U.S. search volume for brand keywords (y-axis), and the count of keywords in the top three (bubble size). Larger bubbles mean a higher count of keywords ranked in the top three.
This data set is only for cybersecurity brands.
As brand mentions increase, the bubbles grow in size, showing that a larger number of brand mentions correlates with a higher count in the top three rankings.
Brand mentions seem to influence ranking. I know there are a large number of confounding variables in this analysis. However, the idea that Google can use these measures to identify E-E-A-T is believable.
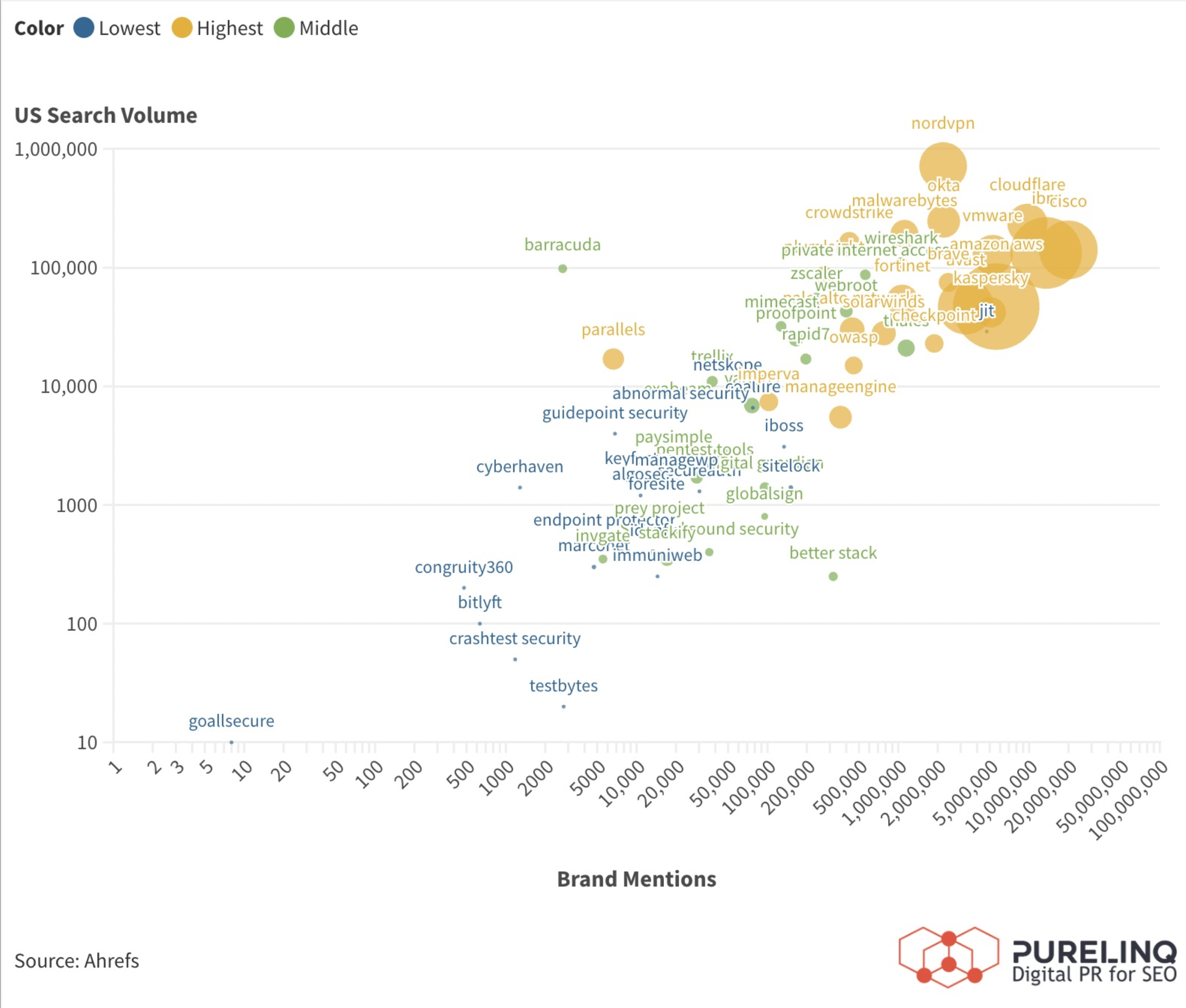
How does this play out in the real world? To understand more, I looked at Lectric eBike.
Case Study: Lectric eBike Full Funnel PR & SEO
This case study demonstrates the power of integrating digital PR with SEO to create a cohesive and effective full-funnel marketing strategy.
The key to success was the strategic alignment of content across all stages of the customer journey, ensuring that each piece contributed to building awareness, trust, and, finally, decision-making confidence.
By securing authoritative links and mentions, Lectric eBikes not only improved its SEO performance but also established itself as a trusted brand in the eyes of consumers and search engines alike.
The rise in organic visibility and brand searches directly contributed to the overall increase in website traffic and, ultimately, sales.
This case underscores the importance of a holistic approach to digital marketing, where PR and SEO work hand in hand to guide the customer journey from awareness to conversion.
Maximum Organic Visibility
At the time of this analysis, Lectric was ranked in position 1 for “ebike” and 3 for “ebikes.”
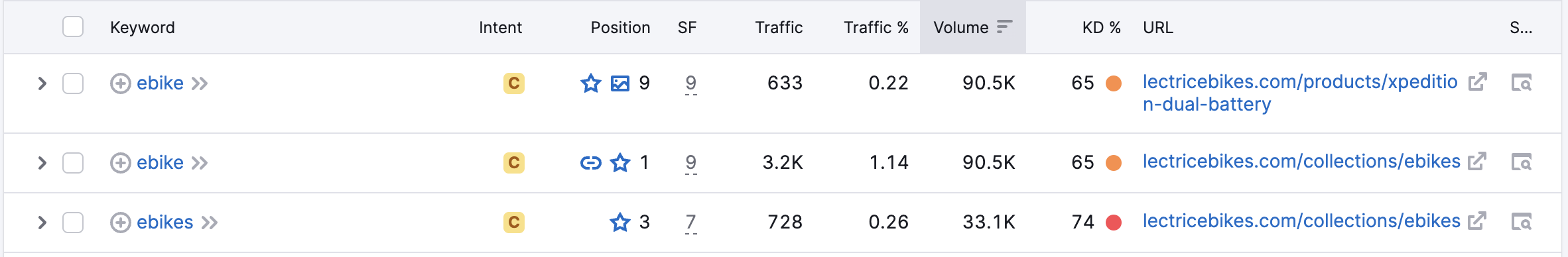
As a result of the non-brand and brand visibility, the website went from <40,000 estimated clicks per month to over 200,000 in just about 2 years – and it still seems to be growing.
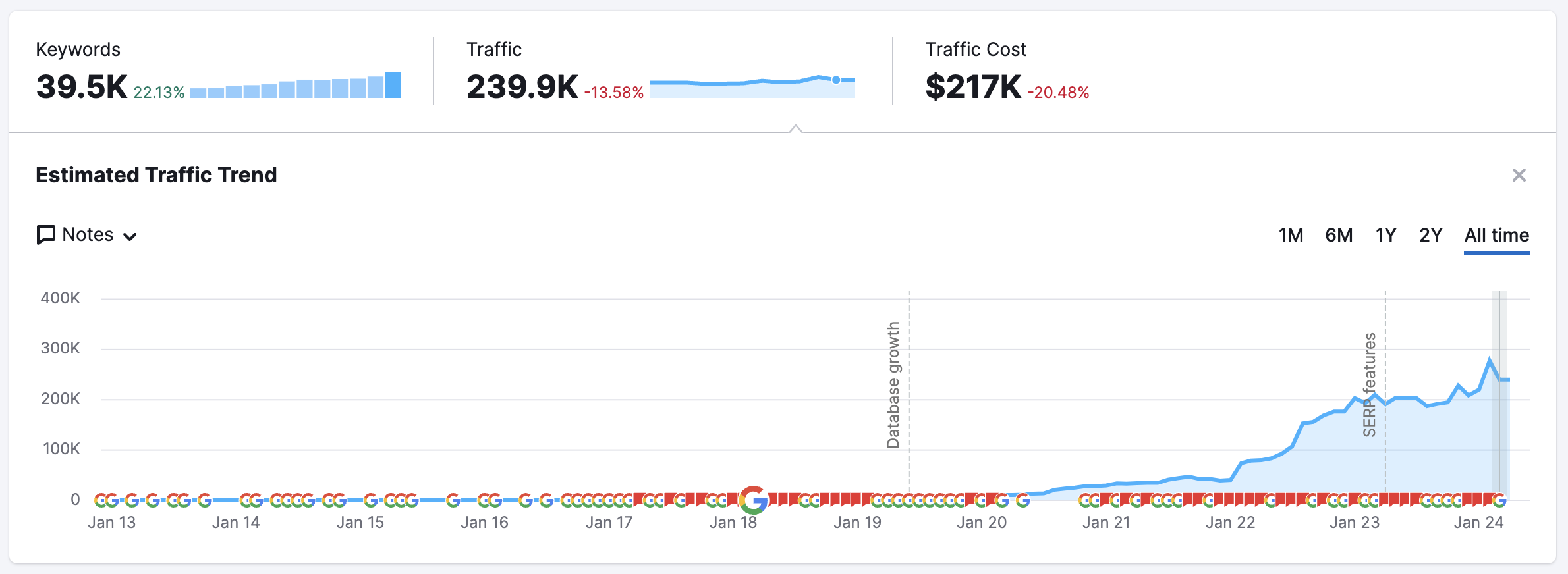
How They Did It
Lectric integrated digital PR and SEO together with a full-funnel PR & SEO strategy.
Late in 2022, Lectric began to secure more media links & brand mentions.
At first glance, you might think that the growth in backlinks was the major factor in the organic traffic growth.
The famous Ahrefs chart shows a strong correlation between the number of referring domains and organic traffic growth.
However, this chart causes much confusion since it doesn’t tell the full story.
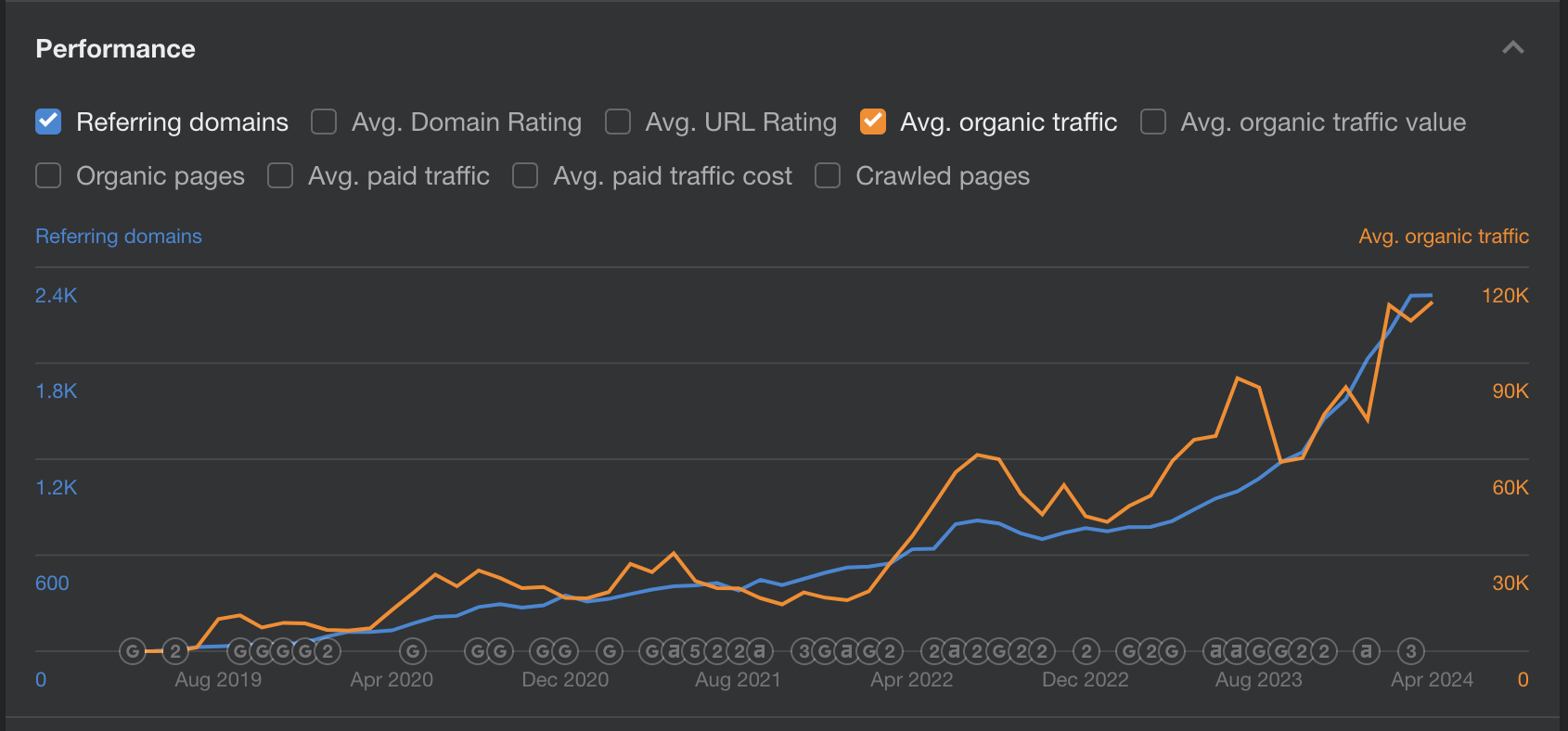
Note : Semrush and Ahrefs have very different traffic estimates lately. However, any traffic estimate will be inherently inaccurate. They estimate these based on position, average monthly search volume, and estimated clickthrough rate (CTR) using Google’s keyword planner data. They all calculate CTR differently.
A little more digging with Ahref’s content explorer and BuzzSumo shows that the site saw growth in brand mentions starting in mid-2022, around the same time the organic traffic began to grow.
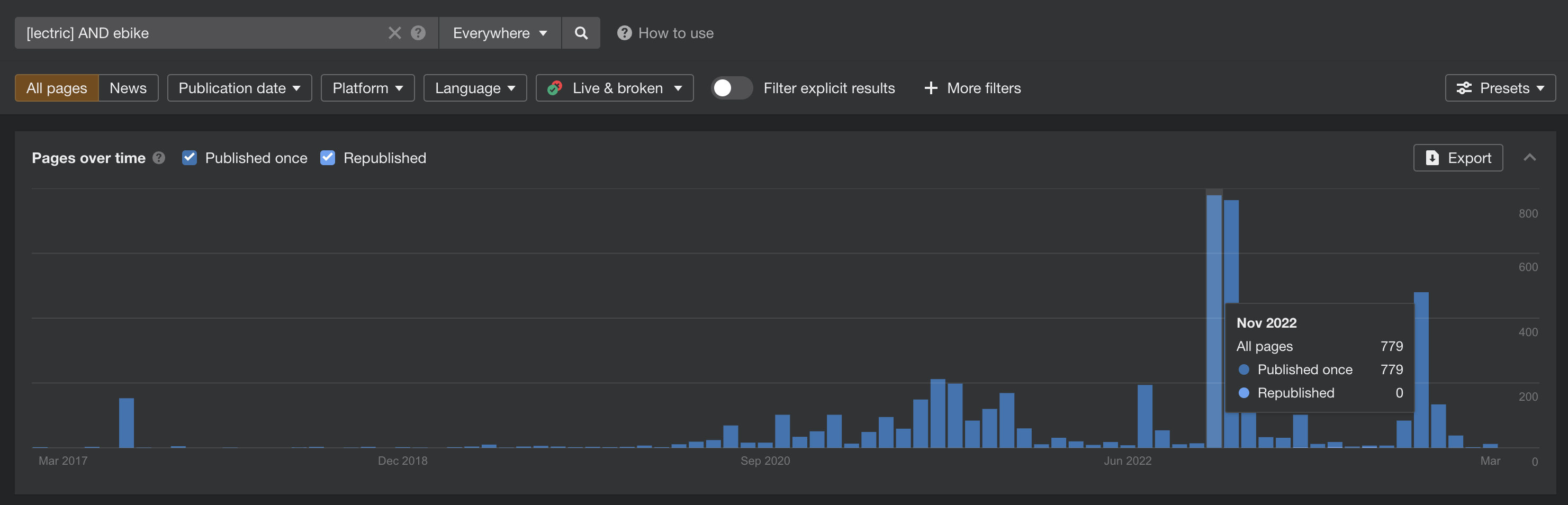
Lectric gained much of the organic traffic improvement by focusing on creating content for each stage of the audience journey.
The brand generated links and brand mentions based on the audience’s needs and wants, driving brand search volume.
Lectric eBikes secured media coverage on environmental and technology news platforms and podcasts. This effort placed the brand in front of a broad audience, emphasizing its commitment to eco-friendliness and innovation.
Placements gained during this stage aimed to educate the audience on the environmental benefits of e-bikes, leveraging unique data and expert commentary to secure media coverage.
- Consumers are drawn to sustainable transportation, seeing e-bikes as a way to align with environmental values. ( Rv Lifestyle )
- The unique, self-funded growth story of Lectric eBikes appeals to those seeking reliable and ethically operated companies. ( The Verge )
- Insights from the CEO of Lectric eBikes highlight the enjoyment and utility of e-bikes, broadening the appeal to a wider audience. ( Autonocast )
These placements generated topically relevant and authoritative links and brand mentions related to the company and individual expertise.
Expert commentary and unique data appeal to journalists. Lectric could have used PR outreach to pitch Lectric’s sales data and CEO commentary to obtain media coverage.
I almost exclusively use unique data and expert commentary to secure media coverage in digital PR. This is a very effective technique.
Consideration
The company obtained mentions in articles that discussed market success, customer satisfaction, and endorsements from reputable sources. This helped build trust and positioned Lectric eBikes as a reliable choice.
Coverage included comparative discussions on pricing and quality, showing how Lectric stands out from competitors. This was crucial for audiences evaluating their options.
- Lectric eBikes’ market success and customer satisfaction offer social proof, encouraging new customers to consider an e-bike. ( Electrek article )
- Gaining trust from the audience by applying for awards from trusted sources (Arizona Tech Council).
- Media coverage and expert commentary discussing how they focus on a lower price over incentive programs ( Axios )
- Securing links and mentions in articles that evaluate options for e-bikes ( Earth911 )
Digital PR Insight
The Axios article is a great example of a technique I use in data campaigns. Find data about specific states or cities that relate to your niche. Then, use that data to pitch media about a given topic.
The website’s content was tailored to answer final questions and overcome objections. This included detailed product comparisons, reviews, and clear, transparent pricing information.
By this stage, Lectric eBikes focused on ranking for both non-brand and brand-specific keywords, facilitating easy access for users ready to make a purchase decision.
The audience is actively searching Lectric by name as a result of the digital PR.
Lectic’s site has comparison, reviews, and showroom information easily accessible in the main navigation.
It also has clear pricing and product options.
Pro tip: Brand search for a company or product seems to have an impact on a site’s ability to rank in the top three for non-brand keywords .
If you’re unfamiliar with the audience journey, here’s an overview.
What Is Full-Funnel PR & SEO?
It’s the stages of the audience journey.
A full-funnel strategy means that you create content for each stage in the audience’s journey and at the touchpoints where they are going for that type of information.
The audience journey has several stages:
- Awareness Stage: The customer becomes aware of a need, opportunity, or problem and starts looking for solutions.
- Consideration Stage: The customer evaluates different options and solutions to address their need or problem.
- Decision Stage: The customer decides on the best solution and buys or takes action.
A full-funnel strategy creates content for each stage of the audience journey.
Using e-bikes as an example:
- Situation: Consumers want to have less of a carbon footprint, and e-bikes are an option.
- Awareness: Provide graphics showing the amount of carbon an e-bike produces compared to a car.
- Considerations: Show how your e-bike compares to others in terms of carbon footprint.
- Decision: Provide information about pricing and maybe carbon savings during the checkout process.
It’s Wherever The Audience Is
The audience journey has touchpoints they use to learn or gather insights at different stages.
For example:
- Awareness Stage: The audience reads news sites, so you use digital PR to pitch unique data to journalists who cover environmental issues.
- Consideration Stage: The audience searches Google for [e-bikes with lowest carbon footprint], so you rank articles with data showing how your e-bike has the lowest carbon footprint.
- Decision Stage: The audience will search your e-bike’s brand name and purchase intent keywords, so you should focus on ranking your e-commerce pages for brand and non-brand keywords.
Targeting each stage of the audience’s journey can create topically relevant links at key touchpoints.
Designing A Full-Funnel Strategy
Designing a strategy means laying out a structured roadmap for businesses to effectively guide their target audience from awareness to decision-making.
I’m a big fan of templates that simplify processes. I created this React Workbook as part of my Digital PR for SEO Mini MBA course. You can use it to create an audience journey map, identify assets, and create an integrated PR and SEO strategy. Screenshots are below.
Create An Audience Journey Map
Start by mapping your audience’s journey, identifying key stages, touchpoints, and content needs. This will serve as the foundation for your strategy.
Understand and visualize the path your audience takes from first becoming aware of a need or problem to making a purchase decision.
The screenshot below is of an audience journey map template I created to make the process of mapping the audience journey more actionable.
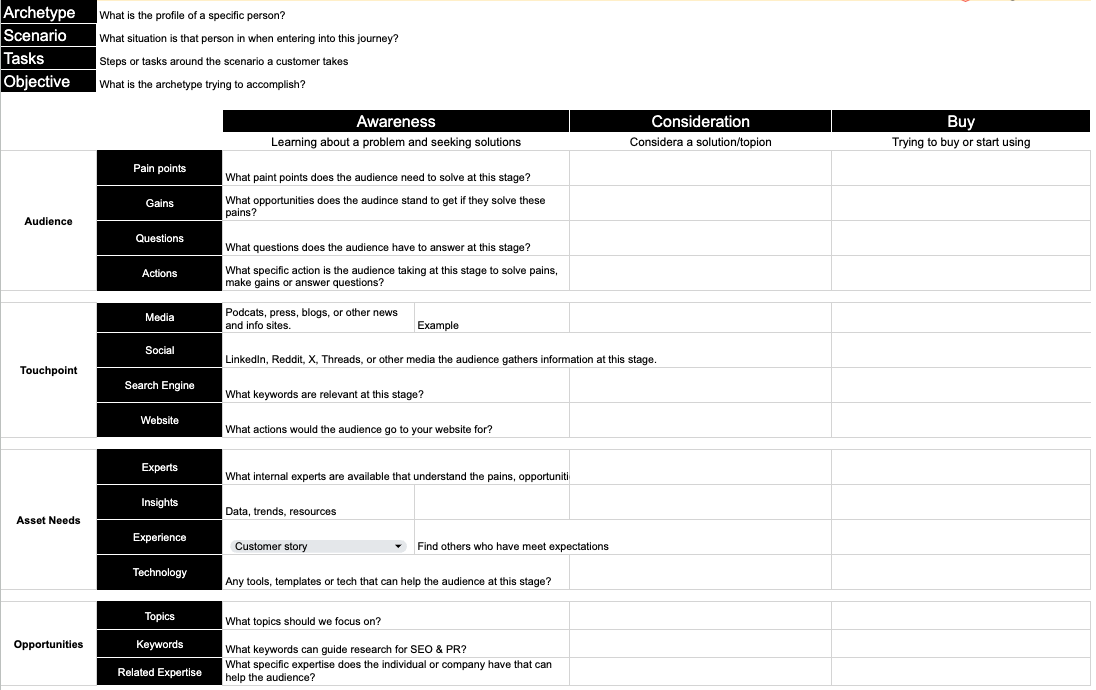
Create Owned Assets For Each Stage
Develop a variety of unique assets and resources tailored to each stage of the audience journey, designed to engage, inform, and convert your target audience. These assets should be useful for both digital PR and SEO.
Instead of creating endless blog articles, create assets that are linkable and shareable.
- Expert commentary: Leverage internal experts and the C-suite to provide commentary on trends in the media.
- Unique data: Research unique data and insights into trends or data about the company’s growth.
- Expert resources: Have internal experts identify resources that are helpful to the audience.
- Guides: Create easy-to-use guides that help your audience accomplish something at a stage in their journey
In my webinar with SEJ , I gave the example of how my digital PR team earned links by analyzing publicly available data in manufacturing around the outsourcing of manufacturing overseas due to increasing labor costs in the US.
This idea was a result of recent media trends discussing the idea that US manufacturing may be in a recession. We did this for a CFO consultancy that worked with manufacturing companies.
Thus, these assets can show your overall expertise in a given category.
With assets in hand, start an integrated digital PR and SEO program.
Implement Integrated Digital PR And SEO
Launch a coordinated digital PR and SEO campaign that leverages external media coverage (links and brand mentions) and optimized online content to improve organic search visibility and drive targeted traffic to your website.
I use this integrated topic tour canvas to simplify the planning process.
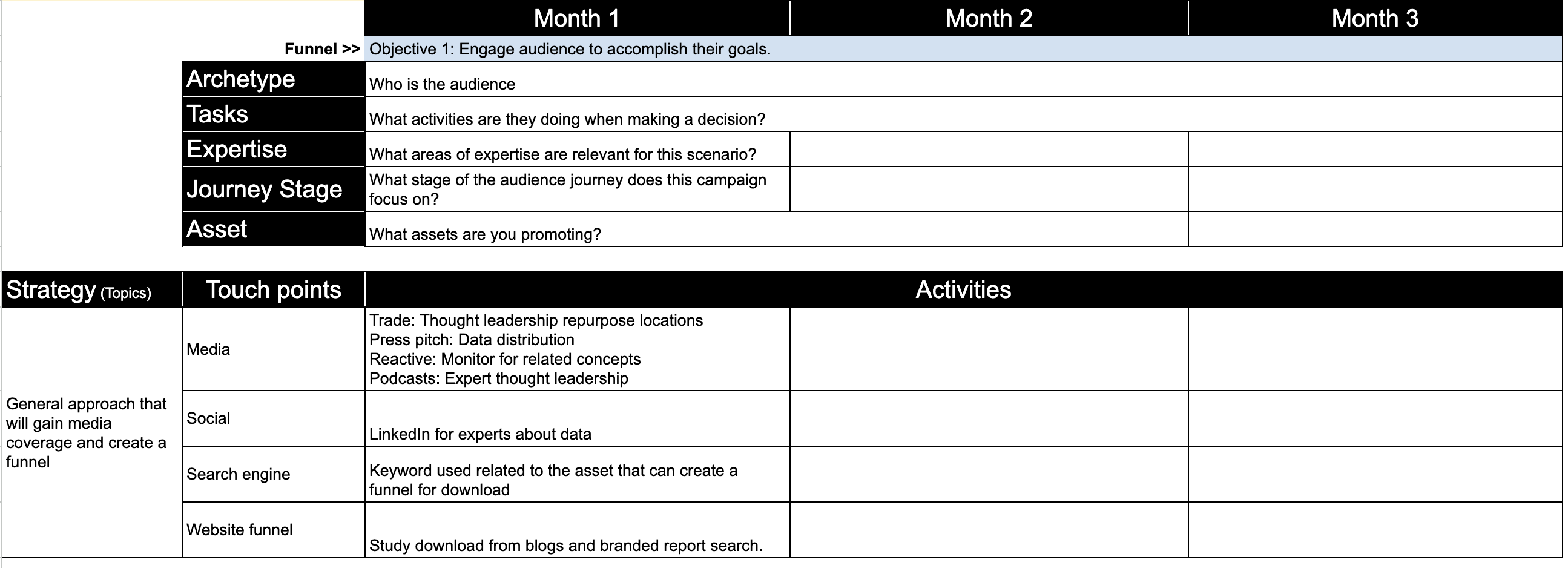
- Digital PR tactics: Pitch story ideas, unique data, and expert commentary to journalists and influencers to secure media mentions and backlinks.
- SEO integration: Align your digital PR efforts with SEO by targeting keywords and phrases that have high search volumes and are relevant to the content being pitched. Use the media coverage and backlinks obtained through digital PR to enhance your website’s E-E-A-T and ranking.
- Cross-channel promotion : Amplify the reach of your media coverage and owned content through social media, email marketing, and other digital channels, ensuring that your target audience sees your brand across multiple touchpoints.
- Use digital PR strategies instead of traditional link building as it builds your E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authority, and Trust) and the associated ranking factors.
- Have a technical expert or leadership contribute to on-site content and digital PR.
Leveraging Digital PR and SEO Builds A Powerful Online Presence
Implementing this full-funnel strategy requires ongoing collaboration between your PR, SEO, and content teams to ensure all efforts are aligned and focused on guiding the audience toward conversion.
By systematically mapping the audience journey, creating engaging content for each stage, and leveraging both digital PR and SEO, businesses can build a powerful online presence by ranking in the top three and driving brand search.
More resources:
- Why Brands Should Prioritize Bottom Of Funnel Keywords In SEO
- How To Use SEO To Target Your Audience Throughout The Funnel
- The Dark Side Of Link Building
Featured Image: eamesBot/Shutterstock
Kevin is the Founder & Head of Digital PR Strategy at PureLinq, a provider of digital PR for SEO services. After ...
Subscribe To Our Newsletter.
Conquer your day with daily search marketing news.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Literature Review Funnel The "literature review funnel" is a heuristic - a tool for discovering the broader audience and impact for your academic research project. Do not think of this funnel as a law that you must follow step-by-step. Rather, think of it as a way to visualize your introduction and literature review by considering the ...
Every literature review needs to show how the research problem you're investigating arose, and give a critical overview of how it, or aspects of it, have been addressed by other researchers to date. ... The funnel structure moves from the broad to the detailed, the general to the specific, or from the abstract to the concrete. ...
Every literature review needs to show how the research problem you're investigating arose, and give a critical overview of how it, or aspects of it, have been addressed by other researchers to date. ... The funnel structure moves from the broad to the detailed, the general to the specific, or from the abstract to the concrete. So you start ...
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
A literature review follows the same 'funnel' narrative, moving from general themes to more specific detail: Top tip: Sticky note shuffle To check the flow of your literature review, write the topic or theme of each paragraph on a post-it note and line them up.
As shown in Figure 2-3, the literature review funnel illustrates how the researcher conducted the reviewing process and remains a common approach in analysing heterogenous literature (Berthon et ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A funnel plot is designed to check for the existence of publication bias, other reporting biases, and systematic heterogeneity in a systematic review. These are biases caused by the absence of information from unpublished sources (missing studies), or selective outcome reporting of a study's result (missing outcomes).
Multi-funnel literature review structure by Academic Skills Service. To create a solid thematic structure in a literature review, the key is thinking carefully and critically about your groupings of literature and how they relate to one another. In some cases, your themes will fit in a single funnel. In other cases, it will make sense to group ...
A literature review ought to be a clear, concise synthesis of relevant information. A literature review should introduce the study it precedes and show how that study fits into topically related studies that already exist. Structurally, a literature review ought to be something like a funnel: start by addressing the topic broadly and gradually ...
Another way to think about structuring a literature review is a funnel model. A funnel model goes from broad topic, to sub-topics, to link to the study being undertaken. You can think of a literature review as a broad argument using mini-arguments. To use the funnel model, list your topic and the related subtopics, then design questions to ...
In other words, a literature review is a synthesis (more on synthesis below) of many articles and other published materials on a certain research topic. Depending on the field, the literature review might be a stand-alone piece or part of a larger research article. ... Organize your review like a funnel. Start by addressing the larger context ...
2. MOTIVATE YOUR RESEARCH in addition to providing useful information about your topic, your literature review must tell a story about how your project relates to existing literature. popular literature review narratives include: ¡ plugging a gap / filling a hole within an incomplete literature ¡ building a bridge between two "siloed" literatures, putting literatures "in conversation"
Thesis/Dissertation Tips #3: Writing the Literature Review. Watch on. 2. SECOND OF ALL: Structure the SCOPE of your study. Think of your theoretical background (or Literature review) as a FUNNEL. Yup, you heard it. A FUNNEL! You must structure it so that you can cover it from the broadest topic until the most specific!
Ellis and Levy describe the concept of the funnel in a research study from the perspective of 'research-worthy problem (P)' described as the input to choosing a research area; 'the valid peer-reviewed literature (L)' as 'key funnel (components) that limits the range of applicable research approaches, based on the body of knowledge ...
The recommendations are based on a detailed MEDLINE review of literature published up to 2007 and discussions among methodologists, who extended and adapted guidance previously summarised in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. 7 A funnel plot is a scatter plot of the effect estimates from individual studies against ...
As mentioned previously, there are a number of existing guidelines for literature reviews. Depending on the methodology needed to achieve the purpose of the review, all types can be helpful and appropriate to reach a specific goal (for examples, please see Table 1).These approaches can be qualitative, quantitative, or have a mixed design depending on the phase of the review.
An "express method" of writing a literature review for a research paper is as follows: first, write a one paragraph description of each article that you read. Second, choose how you will order all the paragraphs and combine them in one document. Third, add transitions between the paragraphs, as well as an introductory and concluding ...
History: The chronological progression of the field, the literature, or an idea that is necessary to understand the literature review, if the body of the literature review is not already a chronology. Methods and/or Standards: The criteria you used to select the sources in your literature review or the way in which you present your information ...
Points to remember from Machi and McEvoy (The literature review: Six steps to success. Corwin Press, 2016.) Do not take data out of context; Do your own research; Present only what you believe to be factual; Present all sides of the question; Plagiarism can easily sneak into a review unless it is carefully avoided
What a literature review for a research project should do. Position your research within the wider body of literature on the topic. Demonstrate an in-depth understanding of your topic area. Identify who the major thinkers are. Identify what research has already been done in that area. Find gaps or new directions to help you formulate your own ...
Download scientific diagram | 1: The funnel method of structuring a literature review (adapted from Hofstee 2006, p. 96) from publication: A Framework to Mitigate Phishing Threats | Within an ...
A literature review is a body of text that aims to review the critical points of current knowledge on a particular topic. Most often associated with science-oriented literature, such as a thesis, the literature review usually proceeds a research proposal, methodology and results section. Its ultimate goals is to bring the reader up to date with ...
Leveraging Digital PR and SEO Builds A Powerful Online Presence. Implementing this full-funnel strategy requires ongoing collaboration between your PR, SEO, and content teams to ensure all efforts ...