Presentation Description Mastery: A Step-by-Step Guide in 2024
Anh Vu • 05 April, 2024 • 8 min read
The correct presentation description is what makes it more interesting for the target audience.
It will provide an opportunity to make a text that will attract the attention of the target audience and help convey the key idea. But for this task to be completed, you need to make the description high quality. Let’s consider in more detail how to create an appealing presentation description.

Table of Contents
- Three Key Ideas
- Harmonious combination of speech and presentation
- Use the Services of Professionals
- The relationship of presentation elements
- Match the content of the presentation with its purpose
- Ignore the Myths About Ideal Scope
- Use the tips from the list below
- Put yourself in the audience place
- Frequently Asked Questions
Tips for Better Engagement
- How to start a presentation
- Script presentation

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
1. Three Key Ideas – Presentation Description
To make it easier for the audience to perceive the meaning of what was said, the thoughts outlined in the presentation should be structured. Therefore, it is worth asking yourself: “If the audience remembered only 3 ideas from my speech, what would they be about?”. Even if the presentation is voluminous, it should revolve around these 3 key ideas. This does not narrow the meaning of what has been said. On the contrary, you will be able to focus the attention of the target audience around a few basic messages.
2. Harmonious Combination of Speech and Presentation – Presentation Description
Often speakers use the presentation as a dubbing of what they are saying. But this option is completely ineffective. It makes no sense to give the same content in different forms. The presentation should be an addition, not just a repetition of what has been said. She can emphasize key ideas, but not duplicate everything. An option is appropriate when the main essence of what was said is briefly structured in the presentation.
3. Use the Services of Professionals – Presentation Description
The team of professional EssayTigers writers will create a great presentation text for you that will work for you. This description will strengthen the idea and reveal it from the best side.
4. The Relationship of Presentation Elements – Presentation Description
Those presentations, the components of which look too fragmented, do not inspire confidence. The audience gets the impression that the material is grouped randomly. It is very difficult to understand such material. And most importantly, the audience needs to understand why this information is being offered to them. When there is no single plot, there is no unifying meaning. People who will be introduced to the presentation will not understand what exactly they want to say. Work to ensure that the relationship between the components of your presentation is built correctly. Then, having read one slide, the audience will expect another.
The most significant vector of efforts should be directed to what arouses people’s interest. Winning the fight for attention is a major win that can help you win other people’s love.
5. Match the Content of The Presentation with Its Purpose – Presentation Description
The goals may be different. If the task is to convince people of the benefits of a product or the benefits of an affiliate program, you need numbers, research, facts, and comparative characteristics. Emotional arguments in this case, as a rule, do not work. And if you need to enhance the meaning of an artistic or literary presentation, the presentation may consist of slides with art objects and short quotes or aphorisms. In each case, you need to pay attention to the context of the situation. If it is an informal context where people are sharing something creative, the text for the presentation can be written in a more free form. And if you need to convincingly argue in a given situation, textual content requires a clear structure.
6. Ignore the Myths About Ideal Scope – Presentation Description
The description really shouldn’t be too overloaded. This is the only tip that applies to all presentations. But its exact volume cannot be inscribed in some universal formula. It all depends on:
- performance time;
- the number of facts that you want to convey to the audience;
- the complexity of the information presented and the need for it to be complemented by specific explanatory footnotes.
Focus on the topic, the specifics of the content, and the time you have to spend on the presentation.
7. Use the Tips from The List Below – Presentation Description
We offer recommendations that will help make the text more literate, concise, and capacious:
- On one slide, reveal only one thought, this will not scatter the attention of the audience.
- If one of the ideas you want to convey to people is not easy to understand, break it up into several slides and provide footnotes with explanations.
- If the text can be diluted with images without losing its meaning, do it. Excess textual information is very difficult to perceive.
- Don’t be afraid of brevity. A clearly stated idea is remembered much better than too abstract, long, and vague formulations.
- Ask the audience for feedback after concluding the presentation! You could use a live Q&A tool to make this process easier, to make people feel comfortable to give you a response for improvement later on!
These tips are simple, but they will help.
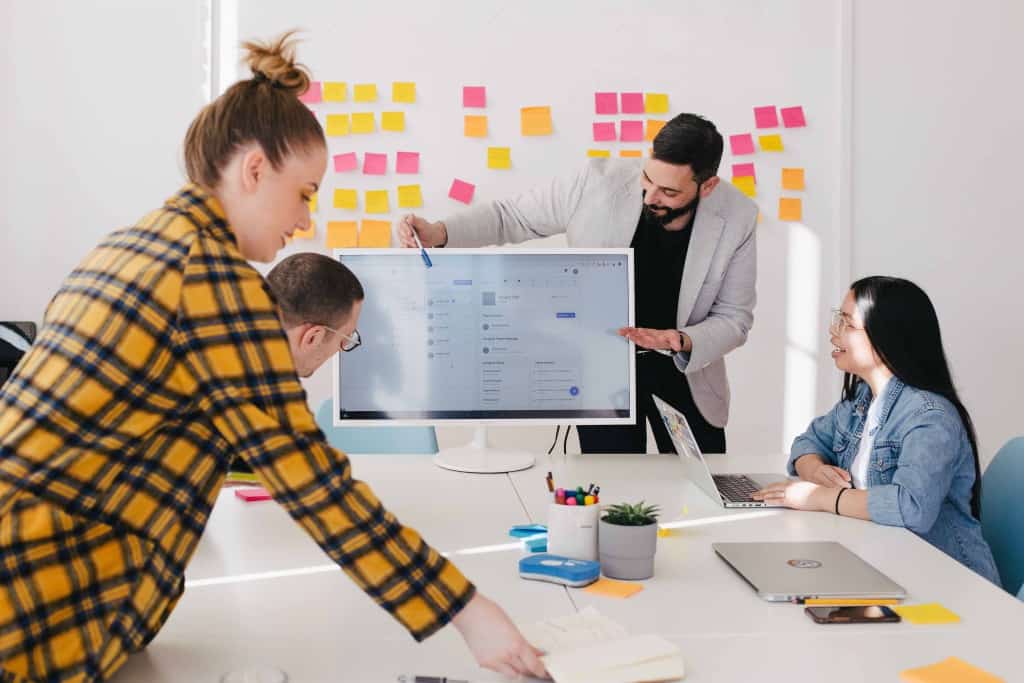

8. Put Yourself in The Audience Place – Presentation Description
If you don’t know how people will be able to perceive what you plan to convey to them, put yourself in the place of the audience. Consider whether it would be interesting for you to listen to such a talk and watch the accompanying presentation. If not, what could be improved? This approach will allow you to look at the situation critically and prevent shortcomings instead of facing their consequences.
You could utilize different interactive tools for online presentations, to make sure that your slides are interesting and attractive to participants. Few features you could try include:
- Divide your team into groups by AhaSlides random team generator , to gather more diverse responses!
- AhaSlides’ AI Online Quiz Creator brings sheer joy to any lesson, workshop or social event
- AhaSlides Live Word Cloud Generator adds sparks to your presentations, feedback and brainstorming sessions, live workshops and virtual events.
About The Author
Leslie Anglesey is a freelance writer, journalist, and author of various articles with a passion for telling stories about the economic and social situation in the world. In case of any inquiries or suggestions kindly reach out to her at [email protected].
Frequently Asked Questions:
How do you write a presentation description.
Presentation description helps the audience perceive easily the meaning and the structure of the presentation. It is the very basic information for a presentation, and before writing a presentation description, you should ask yourself: “If the audience remembered only 3 ideas from my speech, what would they be about?”. You could also use the AhaSlides idea board to organize thoughts and opinions better in the presentation!
How long should a presentation description be?
There is no fixed rule on the length of a presentation description, as long as it provides sufficient information so that the audience can have a comprehensive view of the topic, structure, and purpose of the presentation. A good presentation description could make the audience know what the presentation is about and why they should participate in it.

Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides


- Tips & Tricks
- PowerPoint Templates
- Training Programs
- Free E-Courses
Visualization in Presentations
Home > PowerPoint Slides > Visualization in Presentations
In this article, you’ll read about an important parameter for slide evaluation which is about visualization in presentations. Presenting your ideas and concepts visually increases clarity of your message for your audience.
Before we learn about the slide-o-meter parameter…
A quick word about the relationship between Assertion and Evidence:
In a PowerPoint slide, there is a clear place for assertion, evidence and explanation of the slide. Here is the pictorial representation of how assertion-evidence model works on slides:
Evidence is a combination of visual representation and verbal explanation.
For a presentation to be effective, the evidence needs to be easily understood. The best way to achieve this is by using visualization and build. We will talk about build in another article.
Why use visualization in presentations?
To answer that, I want you to look at the following two slides. Both of them present the same information. Which of these two slides is easier for you to understand?
Slide 2: Visual Slide with charts and Diagrams on Sales Performance
I am sure you chose the second slide.
Here are the two questions I want you to think about –
- What is the difference between the two slides in presenting the same information?
- What is the specific reason why the second slide is easier to understand?
Here is the difference:
The first slide provides data about sales performance. The second slide provides information about sales performance by capturing the relationship between the data .
- Visualization is the art of capturing relationship between objects
Why capture relationship between objects?
Human brain stores information by forming connection between objects. This web of connection is called ‘schema’. For example, the following may be the web of information in our mind about Mammals.
These connections help the brain to retrieve the stored information quickly, and learn new information by establishing the context easily.
When you use visualization in presentations, you help your audience connect your ideas and objects. This helps them ‘get’ your message and retain your information for a long time.
At this point, we wish to recommend our Visual Presentations eBook , which teaches you a simple yet remarkable process to convey your ideas as visual diagrams. It is a must have book, if you are serious about improving your business presentation skills.
Resouce: FREE DOWNLOAD: As a thank you for going through today’s article, you can download the first 3 chapters from the ‘Visual Presentations – eBook’ for free.
A primer on capturing relationship between objects:
While this short article doesn’t give us enough space to explain the detailed process of creating remarkable visual presentations (That’s why we came up with the eBook), we will give you a quick primer on how to capture relationship between objects.
Start with the information on your bulleted slides. Remove the unnecessary words in each of the bulleted sentences. This will help you find the keywords of your message.
For example:
If your bullet point is:
- Most people have a strange habit when it comes to reading on the net. They don’t follow any specific order in reading the pages. They read in a random order.
Keywords are:
- Most people have a strange habit when it comes to reading web pages on the net. They don’t follow any specific order in reading the pages. They read in a random order.
Gist: People read web pages in random order.
Once you are clear with the keywords, the next step is to capture the relationship between the keywords. This will help you create the right diagram to represent the relationship.
Here is an example of how to capture the relationship between the keywords:
There is an effective method to capture the relations to help you come up with insightful visuals. We teach you the 3 critical steps for visualization in presentations in the eBook.
You can also read about a rough and ready way to quickly identify the right relationship between objects using the 4 common types of relationships for a shortcut to diagrams .
To summarize the article on visualization in presentations:
- Since our mind stores information as connections, visual diagrams help your audience to ‘get’ your message fast and retain it longer
- To visualize information, start with bulleted sentences and remove the junk words to identify the keywords
- Once you identify the keywords, capture the relationship between keywords in the form of a diagram
Return to Top of Visualization in presentations Page
Read related article on Visual Chunking for effective PowerPoint Design
Return to Main PowerPoint Slides
Share these tips & tutorials
Get 25 creative powerpoint ideas mini course & members-only tips & offers. sign up for free below:.
Like what you're reading?
Presentation design guide: tips, examples, and templates
Get your team on prezi – watch this on demand video.
Anete Ezera January 09, 2023
Presentation design defines how your content will be received and remembered. It’s responsible for that crucial first impression and sets the tone for your presentation before you’ve even introduced the topic. It’s also what holds your presentation together and guides the viewer through it. That’s why visually appealing, easily understandable, and memorable presentation design is what you should be striving for. But how can you create a visually striking presentation without an eye for design? Creating a visually appealing presentation can be challenging without prior knowledge of design or helpful tools.
With this presentation design guide accompanied by Prezi presentation examples and templates, you’ll have no problem creating stunning and impactful presentations that will wow your audience.
In this guide, we’ll start by looking at the basics of presentation design. We’ll provide a simple guide on creating a presentation from scratch, as well as offer helpful tips for different presentation types. In addition, you’ll discover how to organize information into a logical order and present it in a way that resonates with listeners. Finally, we’ll share tips and tricks to create an eye-catching presentation, and showcase some great presentation examples and templates you can get inspired by!
With our comprehensive introduction to designing presentations, you will be able to develop an engaging and professional presentation that gets results!

What is presentation design?
Presentation design encompasses a variety of elements that make up the overall feel and look of the presentation. It’s a combination of certain elements, like text, font, color, background, imagery, and animations.
Presentation design focuses on finding ways to make the presentation more visually appealing and easy to process, as it is often an important tool for communicating a message. It involves using design principles like color, hierarchy, white space, contrast, and visual flow to create an effective communication piece.
Creating an effective presentation design is important for delivering your message efficiently and leaving a memorable impact on your audience. Most of all, you want your presentation design to support your topic and make it easier to understand and digest. A great presentation design guides the viewer through your presentation and highlights the most essential aspects of it.
If you’re interested in learning more about presentation design and its best practices , watch the following video and get practical insights on designing your next presentation:
Types of presentations
When creating a presentation design, you have to keep in mind several types of presentations that shape the initial design you want to have. Depending on the type of presentation you have, you’ll want to match it with a fitting presentation design.
1. Informative
An informative presentation provides the audience with facts and data in order to educate them on a certain subject matter. This could be done through visual aids such as graphs, diagrams, and charts. In an informative presentation, you want to highlight data visualizations and make them more engaging with interactive features or animations. On Prezi Design, you can create different engaging data visualizations from line charts to interactive maps to showcase your data.
2. Instructive
Instructive presentations teach the audience something new. Whether it’s about science, business strategies, or culture, this type of presentation is meant to help people gain knowledge and understand a topic better.
With a focus on transmitting knowledge, your presentation design should incorporate a variety of visuals and easy-to-understand data visualizations. Most people are visual learners, so you’ll benefit from swapping text-based slides for more visually rich content.

3. Motivational
Motivational presentations try to inspire the audience by giving examples of successful projects, stories, or experiences. This type of presentation is often used in marketing or promotional events because it seeks to get the audience inspired and engaged with a product or service. That’s why the presentation design needs to capture and hold the attention of your audience using a variety of animations and visuals. Go beyond plain images – include videos for a more immersive experience.
4. Persuasive
Persuasive presentations are designed to sway an audience with arguments that lead to an actionable decision (i.e., buy the product). Audiences learn facts and figures relevant to the point being made and explore possible solutions based on evidence provided during the speech or presentation.
In a persuasive presentation design, you need to capture your audience’s attention right away with compelling statistics wrapped up in interactive and engaging data visualizations. Also, the design needs to look and feel dynamic with smooth transitions and fitting visuals, like images, stickers, and GIFs.
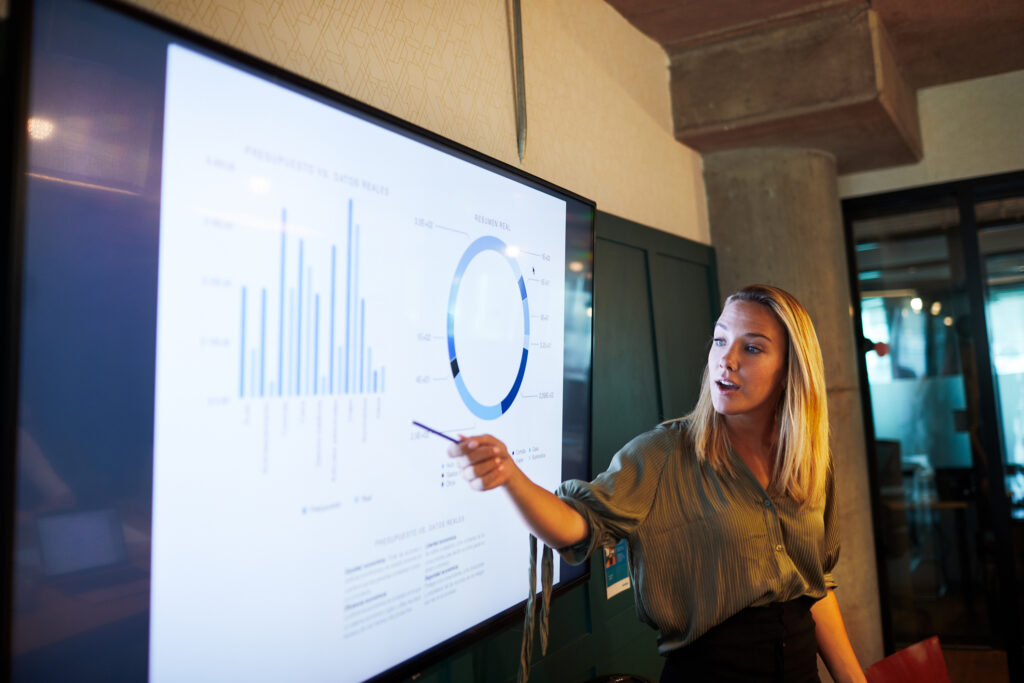

How to design a presentation
When you first open a blank presentation page, you might need some inspiration to start creating your design. For this reason, we created a simple guide that’ll help you make your own presentation from scratch without headaches.
1. Opt for a motion-based presentation
You can make an outstanding presentation using Prezi Present, a software program that lets you create interactive presentations that capture your viewer’s attention. Prezi’s zooming feature allows you to add movement to your presentation and create smooth transitions. Prezi’s non-linear format allows you to jump between topics instead of flipping through slides, so your presentation feels more like a conversation than a speech. A motion-based presentation will elevate your content and ideas, and make it a much more engaging viewing experience for your audience.
Watch this video to learn how to make a Prezi presentation:
2. Create a structure & start writing content
Confidence is key in presenting. You can feel more confident going into your presentation if you structure your thoughts and plan what you will say. To do that, first, choose the purpose of your presentation before you structure it. There are four main types of presentations: informative, instructive, motivational, and persuasive. Think about the end goal of your presentation – what do you want your audience to do when you finish your presentation – and structure it accordingly.
Next, start writing the content of your presentation (script). We recommend using a storytelling framework, which will enable you to present a conflict and show what could be possible. In addition to creating compelling narratives for persuasive presentations, this framework is also effective for other types of presentations.
Tip: Keep your audience in mind. If you’re presenting a data-driven report to someone new to the field or from a different department, don’t use a lot of technical jargon if you don’t know their knowledge base and/or point of view.
3. Research & analyze
Knowing your topic inside and out will make you feel more confident going into your presentation. That’s why it’s important to take the time to understand your topic fully. In return, you’ll be able to answer questions on the fly and get yourself back on track even if you forget what you were going to say when presenting. In case you have extra time at the end of your presentation, you can also provide more information for your audience and really showcase your expertise. For comprehensive research, turn to the internet, and library, and reach out to experts if possible.

4. Get to design
Keeping your audience engaged and interested in your topic depends on the design of your presentation.
Now that you’ve done your research and have a proper presentation structure in place, it’s time to visualize it.
4.1. Presentation design layout
What you want to do is use your presentation structure as a presentation design layout. Apply the structure to how you want to tell your story, and think about how each point will lead to the next one. Now you can either choose to use one of Prezi’s pre-designed templates that resemble your presentation structure the most or start to add topics on your canvas as you go.
Tip: When adding content, visualize the relation between topics by using visual hierarchy – hide smaller topics within larger themes or use the zooming feature to zoom in and out of supplementary topics or details that connect to the larger story you’re telling.
4.2. Color scheme
Now it’s time to choose your color scheme to give a certain look and feel to your presentation. Make sure to use contrasting colors to clearly separate text from the background, and use a maximum of 2 to 3 dominating colors to avoid an overwhelming design.
4.2. Content (visuals + text)
Add content that you want to highlight in your presentation. Select from a wide range of images, stickers, GIFs, videos, data visualizations, and more from the content library, or upload your own. To provide more context, add short-format text, like bullet points or headlines that spotlight the major themes, topics, and ideas in your presentation.
Also, here you’ll want to have a final decision on your font choice. Select a font that’s easy to read and goes well with your brand and topic.
Tip: Be careful not to turn your presentation into a script. Only display text that holds significant value – expand on the ideas when presenting.

4.3. Transitions
Last but not least, bring your presentation design to life by adding smooth, attractive, and engaging transitions that take the viewer from one topic to another without disrupting the narrative.
On Prezi, you can choose from a range of transitions that take you into the story world and provide an immersive presentation experience for your audience.
For more practical tips read our article on how to make a presentation .
Presentation design tips
When it comes to presentations, design is key. A well-designed presentation can communicate your ideas clearly and engage your audience, while a poorly designed one can do the opposite.
To ensure your presentation is designed for success, note the following presentation design tips that’ll help you design better presentations that wow your audience.

1. Keep it simple
Too many elements on a slide can be overwhelming and distract from your message. While you want your content to be visually compelling, don’t let the design of the presentation get in the way of communicating your ideas. Design elements need to elevate your message instead of overshadowing it.
2. Use contrasting text colors
Draw attention to important points with contrasted text colors. Instead of using bold or italics, use a contrasting color in your chosen palette to emphasize the text.
3. Be clear and concise.
Avoid writing long paragraphs that are difficult to read. Limit paragraphs and sections of text for optimum readability.
4. Make sure your slide deck is visually appealing
Use high-quality images and graphics, and limit the use of text to only the most important information. For engaging and diverse visuals, go to Prezi’s content library and discover a wide range of stock images, GIFs, stickers, and more.
5. Pay attention to detail
Small details like font choice and alignments can make a big difference in how professional and polished your presentation looks. Make sure to pay attention to image and text size, image alignment with text, font choice, background color, and more details that create the overall look of your presentation.
6. Use templates sparingly
While templates can be helpful in creating a consistent look for your slides, overusing them can make your presentation look generic and boring. Use them for inspiration but don’t be afraid to mix things up with some custom designs as well.
7. Design for clarity
Create a presentation layout that is easy to use and navigate, with clear labels and instructions. This is important for ensuring people can find the information they need quickly and easily if you end up sharing your presentation with others.
8. Opt for a conversational presentation design
Conversational presenting allows you to adjust your presentation on the fly to make it more relevant and engaging. Create a map-like arrangement that’ll encourage you to move through your presentation at your own pace. With a map-like design, each presentation will be customized to match different audiences’ needs. This can be helpful for people who have different levels of expertise or knowledge about the subject matter.
9. Be consistent
Design consistency holds your presentation together and makes it easy to read and navigate. Create consistency by repeating colors, fonts, and design elements that clearly distinguish your presentation from others.
10. Have context in mind
A great presentation design is always dependent on the context. Your audience and objective influence everything from color scheme to fonts and use of imagery. Make sure to always have your audience in mind when designing your presentations.
For more presentation tips, read the Q&A with presentation design experts and get valuable insights on visual storytelling.
Presentation templates
Creating a presentation from scratch isn’t easy. Sometimes, it’s better to start with a template and dedicate your time to the presentation’s content. To make your life easier, here are 10 useful and stunning presentation templates that score in design and engagement. If you want to start creating with any of the following templates, simply go to our Prezi presentation template gallery , select your template, and start creating! Also, you can get inspired by the top Prezi presentations , curated by our editors. There you can discover presentation examples for a wide range of topics, and get motivated to create your own.
Business meeting presentation
The work desk presentation templates have a simple and clean design, perfectly made for a team or business meeting. With all the topics visible from start, everyone will be on the same page about what you’re going to cover in the presentation. If you want, you can add or remove topics as well as edit the visuals and color scheme to match your needs.
Small business presentation
This template is great for an introductory meeting or pitch, where you have to summarize what you or your business does in a few, highly engaging slides. The interactive layout allows you to choose what topic bubble you’re going to select next, so instead of a one-way interaction, you can have a conversation and ask your audience what exactly they’re interested in knowing about your company.
Mindfulness at work presentation
How can you capture employees’ attention to explain important company values or practices? This engaging presentation template will help you do just that. With a wide range of impactful visuals, this presentation design helps you communicate your ideas more effectively.
Business review template
Make your next quarterly business review memorable with this vibrant business presentation template. With eye-capturing visuals and an engaging layout, you’ll communicate important stats and hold everyone’s attention until the end.
History timeline template
With black-and-white sketches of the Colosseum in the background, this timeline template makes history come alive. The displayed time periods provide an overview that’ll help your audience to grasp the bigger picture. After, you can go into detail about each time frame and event.
Storytelling presentation template
Share stories about your business that make a lasting impact with this stunning, customizable presentation template. To showcase each story, use the zooming feature and choose to tell your stories in whatever order you want.
Design concept exploration template
Not all meetings happen in person nowadays. To keep that face-to-face interaction even when presenting online, choose from a variety of Prezi Video templates or simply import your already-existing Prezi template into Prezi Video for remote meetings. This professional-looking Prezi Video template helps you set the tone for your meeting, making your designs stand out.
Employee perks and benefits video template
You can use the employee benefits video template to pitch potential job candidates the perks of working in your company. The Prezi Video template allows you to keep a face-to-face connection with potential job candidates while interviewing them remotely.
Sales plan presentation template
Using a clear metaphor that everyone can relate to, this football-inspired sales plan presentation template communicates a sense of team unity and strategy. You can customize this Prezi business presentation template with your brand colors and content.
Flashcard template
How can you engage students in an online classroom? This and many other Prezi Video templates will help you create interactive and highly engaging lessons. Using the flashcard template, you can quiz your students, review vocabulary, and gamify learning.
Great presentation design examples
If you’re still looking for more inspiration, check out the following Prezi presentations made by our creative users.
Social media presentation
This presentation is a great example of visual storytelling. The use of visual hierarchy and spatial relationships creates a unique viewing experience and makes it easier to understand how one topic or point is related to another. Also, images provide an engaging and visually appealing experience.
Leadership books presentation
Do you want to share your learnings? This interactive presentation offers great insights in an entertaining and visually compelling way. Instead of compiling leadership books in a slide-based presentation, the creator has illustrated each book and added a zooming feature that allows you to peek inside of each book’s content.
Remote workforce presentation
This is a visually rich and engaging presentation example that offers an interactive experience for the viewer. A noteworthy aspect of this presentation design is its color consistency and matching visual elements.
A presentation about the teenage brain
Another great presentation design example that stands out with an engaging viewing experience. The zooming feature allows the user to dive into each topic and choose what subject to view first. It’s a great example of an educational presentation that holds the students’ attention with impactful visuals and compelling transitions.
Remote work policy presentation
This presentation design stands out with its visually rich content. It depicts exactly what the presentation is about and uses the illustrated window frames in the background image as topic placements. This type of presentation design simplifies complex concepts and makes it easier for the viewer to understand and digest the information.
Everyone can create visually-appealing presentations with the right tools and knowledge. With the presentation design tips, templates, and examples, you’re equipped to make your next presentation a success. If you’re new to Prezi, we encourage you to discover everything it has to offer. With this presentation design guide and Prezi, we hope you’ll get inspired to create meaningful, engaging, and memorable content for your audience!

Give your team the tools they need to engage
Like what you’re reading join the mailing list..
- Prezi for Teams
- Top Presentations
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
Creating Effective Presentation Visuals
Connecting People With Your Message
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate.
Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids. He knew that slides are most effective when they tell a story rather than convey information, so his visuals were simple, elegant, and image-based. They complemented and reinforced his message, and they never competed with him for his audience's attention.
You don't have to be Steve Jobs to give a great presentation, but you do need great visuals. They convey a powerful message about your ideas and your brand, so it's essential to get them right. In this article, we'll look at how you can create effective presentation visuals – slides that connect your audience with your message.
Why Simplicity Speaks Volumes
The saying "A picture is worth a thousand words" is popular for a good reason: the human brain processes information more effectively when it is accompanied by images, or by short, memorable statements. This means that when you use simple, image-based slides to support your message, your audience can better grasp the information you're communicating.
However, many people use too many slides, or they build presentations around visual aids that are word-heavy or excessively complex.
These kinds of visual aids can negatively affect your presentation. Let's look at some examples:
- You're trying to convince the board to support a new product idea. Your slides are made up of graphs, numbers, and blocks of text from top to bottom, and board members spend most of their time reading the slides instead of listening to you. The result? You don't make a real connection, and your passion for the project is lost on them. They vote unanimously not to take the idea forward.
- You're pitching to a promising potential client. You spent a lot of time creating your slides, using many colors, animations, and fonts. However, the slides are so complex that your client has trouble understanding them. She leaves the presentation feeling overwhelmed and tired, and avoids using your firm because she fears, subconsciously, that dealing with your firm in the future could be similarly draining.
- You're giving a presentation to your department to highlight its good work. You want to feature everyone, so you make a slide detailing each person's accomplishments. Your department has dozens of people, so by the end, your team cares more about leaving than their results.
Now think about what happens when you use simple and engaging visuals. Instead of generating confusion or exhaustion, your slides create a positive connection with your audience. People might not remember exactly what you said, but they will remember a powerful image. They'll recall the positive emotions that they experienced during your presentation, and they'll start to associate your brand with clear, intelligent communication.
The results will be profound. You'll win new clients, convince colleagues to act on your ideas, and earn recognition for your team members' hard work. In short, you'll make positive impressions that will remain in people's minds long after the details of your presentation have faded.
Creating Great Visuals
Your visual aids have one job: to support your presentation . However, it takes considerable time, creativity, and effort to develop slides that do this well. Use the tips below to make the most of your preparation time.
1. Be Consistent
A common mistake is choosing different colors and fonts for each slide. This can confuse your audience and divert attention away from your message. Stay consistent with your slides, so that they form part of a seamless whole.
First, choose colors carefully, as color will affect your presentation's mood and tone. Also, think about the space that you'll be presenting in. If the room will be dark (with lights off), choose a darker background color, such as dark blue, black, or gray, with white or light-colored text. If the room will be light (with lights on or plenty of ambient light), choose a white or light-colored background, with black or dark-colored text.
You also need to match color with the tone and message of your presentation. Bright colors convey energy and excitement, while darker colors may seem more conservative and serious. Align the color palette you choose with your subject matter.
Microsoft® PowerPoint and Apple's Keynote are the most widely used presentation packages. They feature useful templates and tools, and most people are familiar with the layout of their presentations.
However, cloud-based presentation tools have features and templates that might be new to your audience, increasing the potential impact of your presentations.
2. Consider Culture
Before you create your visuals, make sure that you understand your audience. This is especially true if you're presenting to a culturally diverse group.
For example, not everyone reads from left to right, and people from some cultures may consider a particular color offensive or bad luck in business settings (look out for examples of this in our Managing Around the World articles). Additionally, jargon or slang may cause confusion with your audience.
When designing your visuals, use images and photographs that reflect the culture to which you're speaking. If you're presenting to a culturally diverse group, use pictures and images that reflect this diversity.
And keep graphics and phrases simple; remember, not everyone in the room will be a native English speaker. Whenever possible, use images to replace bullet points and sentences.
Our article on Cross-Cultural Communication has more tips for communicating with an ethnically diverse group.
3. Use Images Intelligently
When Steve Jobs unveiled the MacBook Air® , he needed to show just how small this new laptop was. The audience wasn't going to remember that it was 0.68 x 11.8 x 7.56 inches; those numbers don't create an emotional response. Instead, he showed them that the MacBook Air would fit easily into a standard manila envelope. This was a powerful way to show its size.
This kind of creativity is essential when choosing images. Your audience has probably seen plenty of bad clip-art and too many pictures of cross-cultural handshakes. Brainstorm creative, clever approaches with your imagery, and look for photographs or illustrations that tell a story in a less obvious way.
Thoughtful images will keep your audience engaged, reinforce your professionalism, and make a lasting impression.
4. Break Complex Data Down
When you have to communicate complex data or large chunks of information, avoid putting it all on one slide, as your audience may struggle to take in all of the details. Instead, either summarize the information, or split it up over several slides.
You can also use handouts to communicate complex information. Handouts allow your audience to look at data closely. This is especially important when you're presenting to analytical people, such as engineers, scientists, or finance professionals. They are trained to be skeptical about data, and a handout will give them a closer look. Once again, this kind of attention to the needs of your audience will highlight your professionalism and support your message.
5. Keep It Simple
Each slide should focus on one idea or concept. This allows your audience to grasp quickly what you want to communicate. Keep your text to a bare minimum (10 words or fewer if possible), and, where you can, use an image to convey a message rather than words: for example, consider using a graph instead of a list to show changing trends. Each slide should take three seconds or fewer to process. If it takes longer, the slide is probably too complex.
It can sometimes be helpful to follow a clear structure when creating your presentation; for example, if it is focused on a document or process with which audience members are familiar. This will help them make connections between your content and their existing knowledge.
Avoid bulleted lists whenever possible; they make it too easy to put several ideas on one slide, which can be overwhelming for your audience. If you do need to use bullets, don't use sentences; instead, simply list the fact, statistic, or idea you want to communicate. Then use your narrative to educate the audience about what these mean.
To simplify the wording on your slides further, highlight the key word in every sentence.
Next, look at the layout of your slides. Aim to use a plain background and plenty of blank space: this will help to focus audience members' eyes on your message. Avoid decorating slides with background pictures, logos or patterns that could distract attention.
Last, consider using blank slides when you need the audience's complete focus; a blank slide is equivalent to a pause, and it will add drama, tension, and focus to your words.
Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
First, take our interactive quiz, How Good Are Your Presentation Skills? to get an idea of how well you speak. Our articles on Delivering Great Presentations and Better Public Speaking contain tips and strategies that will help you communicate with clarity and intention.
When you practice your presentation, use your visuals. You should be able to glance at each slide and know exactly what you want to say.
If you're not confident in creating your own slides, think about outsourcing the task to a professional. This can be a smart option when a lot is at stake, or when you don't have the technical skills to create the type of presentation you want.
Consider using an outsourcing service such as Elance , Guru , or PeoplePerHour to find a suitable professional.
If you do, keep in mind that managing a freelancer requires a different approach from managing a regular staff member. Be clear about the project details, communicate your goals for the presentation, and set deadlines that give you plenty of time to revise and add as necessary.
Presentations that are too complex or lengthy can undermine your message. To create better visuals, do the following:
- Stay consistent.
- Consider culture.
- Use images intelligently.
- Break down complex data.
- Keep it simple.
If the stakes are high with your presentation and you don't feel confident with your technical skills, consider outsourcing slide preparation.
"iPhone," "Apple," "MacBook Air," and "Keynote" are trademarks of Apple Inc. (see www.apple.com ). "Microsoft" and "PowerPoint" are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation (see www.microsoft.com ). We have no association or connection with these organizations.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
The nervous presenter's survival guide.
Overcoming Seven Common Presentation Fears
Even Better Presentations
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Defining Benefits
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Up is not the only way: rethinking career mobility.
Beverly Kaye, Lindy Williams and Lynn Cowart
Book Insights
Managing Conflicting Priorities
Keeping People Satisfied
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
Self-Assessment
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Thomas davenport and larry prusak: working knowledge.
The Five Modes of Knowledge Generation According to Davenport and Prusak
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Mastering the Art of Presentation Visualization: Engaging Audiences with Impactful Visuals
July 18, 2023 - Updated on July 18, 2023
Table of Contents
In the realm of presentations, effective communication goes beyond words. Presentation visualization conveys information, ideas, and messages through visually compelling elements. By integrating engaging visuals into presentations, speakers can capture their audience’s attention, enhance understanding, and leave a lasting impact. This article explores the importance of presentation visualization, key techniques for creating impactful visuals, and the benefits it brings to both presenters and audiences.
The Power of Presentation Visualization
In today’s fast-paced and information-rich world, audiences are inundated with data and content. Presentation visualization helps presenters break through the noise and deliver information memorably and engagingly. Visuals can uniquely simplify complex concepts, evoke emotions, and enhance the presentation experience. Here are some reasons why presentation visualization is essential.
Capturing Attention
One of the most effective ways to capture and maintain the interest of an audience is by using engaging visuals. Whether through striking images, informative graphs, detailed charts, or captivating infographics, incorporating these elements into presentations can instantly capture the audience’s attention and create a visual hook that sparks their curiosity.
Enhancing Comprehension
Visuals aid in conveying information more effectively than text alone. They simplify complex ideas, break down data into digestible chunks, and provide visual cues that aid understanding. Visual representations help the audience grasp concepts faster, leading to increased comprehension and retention of information.
Creating Emotional Connection
Well-designed visuals have the power to evoke emotions and create a connection with the audience. Images, videos, and illustrations can elicit emotional responses, making the presentation more memorable and impactful. Emotionally engaged audiences are likelier to resonate with the message and retain the information presented.
Techniques for Creating Impactful Presentation Visualization
When it comes to creating impactful presentation visualizations, there are a few techniques that can make a difference. One of the most important things to remember is to keep things simple and easy to understand.
Choose Appropriate Visual Formats
Select visual formats that align with the content and objectives of the presentation. Use charts and graphs to present data, images, illustrations to convey concepts, and videos to demonstrate processes or tell a story. Consider the message you want to share and the audience’s preferences to determine the most effective visual format.
Simplify Complex Information
When you’re trying to communicate complex ideas to an audience, it can be easy to overwhelm them with too much information at once. That’s why it’s important to break those ideas down into simpler components and represent them visually using diagrams, flowcharts, or metaphors. Doing this can make the information more accessible and easier to digest.
Utilize Color and Contrast
Colors have a significant impact on the visual appeal and comprehension of information. Choose a color palette that complements the message and ensures legibility. Use contrast to make important elements stand out and guide the audience’s focus. However, maintain a balance and avoid overwhelming the audience with excessive colors or distracting visuals.
Incorporate Storytelling Elements
Weaving storytelling elements into visuals can enhance engagement and make the presentation more compelling. Use images that evoke emotions, incorporate relevant narratives, or showcase real-life examples. Visual storytelling captivates the audience’s imagination and enables them to connect with the presentation more deeply.
Keep it Consistent and Clean
Maintain visual consistency throughout the presentation to create a cohesive and professional look. Use consistent fonts, colors, and visual styles to ensure a harmonious visual experience. Avoid cluttered visuals and excessive text, as they can overwhelm the audience and dilute the impact of the presentation.
Benefits of Presentation Visualization
Presentations that use visualization can effectively convey complex information clearly and concisely.
Improved Audience Engagement
Engaging visuals capture and maintain the audience’s attention, preventing boredom and distractions. Visuals break the monotony of text-heavy slides and create a dynamic and interactive presentation experience. Engaged audiences are likelier to retain information, actively participate, and respond positively to the message.
Enhanced Retention and Comprehension
Presentation Visualization aid in information processing and retention. The combination of visual and verbal communication enhances comprehension and recall. Presenters who effectively utilize presentation visualization are likelier to leave a lasting impact and ensure their key messages resonate with the audience.
Increased Persuasiveness
It’s no secret that visuals have a lot of power when it comes to persuasion. A compelling image or graphic can evoke all sorts of emotions in you, from awe to anger to joy. And when those visuals are well-designed and thoughtfully crafted, they can enhance the credibility of the person presenting them. After all, if someone takes the time and effort to create something that looks great and makes sense, it’s much easier to trust what they say.
Improved Clarity and Message Delivery
Visuals simplify complex information, making it easier for the audience to understand and follow the presenter’s message. Clear and concise visuals reinforce the key points, ensuring the audience grasps the main ideas effectively. This clarity enhances the overall effectiveness of the presentation.
Presentation visualization is a powerful tool that enables presenters to engage and captivate audiences. Presenters can enhance comprehension, evoke emotions, and make a lasting impact by incorporating visually compelling elements. Techniques such as choosing appropriate visual formats, simplifying complex information, utilizing color and contrast, incorporating storytelling elements, and maintaining visual consistency contribute to the effectiveness of presentation visualization. By embracing the art of presentation visualization, speakers can elevate their communication skills, create memorable experiences, and deliver impactful presentations that resonate with their audiences.
Software Review
VComply: Simplifying Compliance Management for Modern Organizations
Archer: Empowering Organizations with Integrated Risk Management (IRM) Solutions

SAP Risk Management: Enhancing Business Resilience through Comprehensive Risk Mitigation
Secureframe: Revolutionizing Compliance Automation and Cybersecurity

Successfully Navigating a BI Project: Key Considerations and Best Practices

Maximizing Efficiency with the Accounting Firm Service Catalog Management

Supply Chain Management in E-commerce: Driving Efficiency and Customer Satisfaction

The Impact of Advanced Research Planning Software to Accelerate Scientific Discovery
Related Articles

SoftwareAnalytic team is committed to providing accurate, trustworthy, and comprehensive evaluations to help make informed decisions and does not endorse any vendor, product, or service.
[email protected]
[email protected], [email protected], whatsapp: +8801400819895, opening hours.
- Monday - Friday:
- 10:00AM - 7:00PM (UTC)
- Saturday - Sunday:
- 2:00PM - 6:00PM (UTC)
ADVERTISEMENT
Build brand awareness across our networks! Our product-based specialist team provides effective advertising solutions for high-quality products to generate leads and boost sales.
COPYRIGHT © 2023 SOFTWAREANALYTIC | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
There was a problem reporting this post.
Block Member?
Please confirm you want to block this member.
You will no longer be able to:
- See blocked member's posts
- Mention this member in posts
- Invite this member to groups
Please allow a few minutes for this process to complete.
SOFTWARE ARTICLES
Vendor reviews, user activity.
- Accounting Practice Management
- Business intelligence
- Customer Relationship Management
- Cyber Security Solutions
- Data Management Platforms
- Data Visualization Tools
- Enterprise resource planning
- Governance, Risk and Compliance
- Human Resource Management
- Sales Intelligence
- Subscription Management
- Supply Chain & Logistics
Expert Opinions
Software in-depth, software reviews, about softwareanalytic, article submission, it consulting, privacy policy, terms of service, [email protected], advertise here.
Easy Render

Architectural visualizations are a powerful tool that can help you understand what a project would look like well before it’s finished. Whether they’re used in interior or exterior design, for civil engineering projects, or for small apartment remodels, they can bring any design to life and help you communicate your idea flawlessly.
Although visualizations are most commonly used to get your architectural teams on the same page, communicate design changes with the clients, or put designs in context, they’re handy for perfecting your presentations. Learn how to use them to create stunning presentations that demand attention and highlight your talents.
What are 3D visualizations?
Before you can understand how to use 3D visualizations in your presentations, you need to know what they are. They’re an advanced version of architectural models.
Traditionally, architects and designers would use blueprints, complex illustrations, and 2D drawings to communicate their ideas and present their designs. While they can be effective, they require much technical expertise to understand – a client with no prior experience with architectural drawings would struggle to decipher them.
An alternative is creating scaled architectural models – a miniature physical representation of a project. Much better at communicating what the final design would look like, the architectural model still has shortcomings. Creating it is a painstaking process, and taking it with you to your presentations can be next to impossible.
Hence the growing popularity of architectural visualizations.
3D visualizations are computer-generated representations of architectural designs. They can be created as still images, animations, or interactive videos that enable you to explore every nook and cranny of an architectural project in a virtual environment.
They’re true to life, often even photorealistic. As their name would suggest, they allow you to visualize the final design before the construction team has even been assembled. You don’t have to use your imagination to envision what a red brick facade, green shrubbery, and a pool in a backyard would look like. You can see it all clearly with the help of 3D visualizations.
How do they work?
Although the finished 3D visualization might make it seem like creating it was a piece of cake, that rarely happens. Architectural visualizations need to be created by experienced artists who are well-versed in some of the most powerful 3D rendering software solutions .
The artist can create a design from scratch or use the information from architectural blueprints and 2D drawings to bring a project to life. They can add realistic textures, design elements, furnishings, lighting, and more to make their work seem more life-like. Moreover, they can create anything from a small interior design project to a full-blown neighborhood to make the architectural projects stand out.
What’s truly fascinating is that with the help of 3D rendering software, the artists can quickly identify design errors and construction issues and even simulate conditions such as earthquakes and strong winds to understand how resilient a building would be in real life.
Creating an atmosphere
Using architectural visualizations in your presentations presents unique advantages. First and foremost, it allows you to create an immersive atmosphere that engages your audiences and will enable you to present your designs in the best light.
With a single button click, you can set an intimate, romantic atmosphere by changing the lighting or adjusting the shadows.
You can make your audiences feel more energized and excited about your project by adding people to your presentations and showing them walking around your building. You can highlight the scale of your design by switching up the perspective, doing an aerial view of the building, and injecting movement.
Architectural visualizations enable you to set the mood for your audiences and let them experience your designs exactly as you envisioned them.
Complementing your story
The best architectural presentations will always have a story. Storytelling allows you to connect with your clients and show them how they can enjoy your designs to the fullest.
You’ll find selling your office building design easier if you show your clients the building in use, highlighting how they can build their brand in the space you’ve created. You’ll have more success convincing a client doing a family home remodel to work with you if you show them how your designs adapt to their lifestyle.
Architectural visualizations can easily complement your story and make it seem more realistic. You can add any visual element you need to move your clients and make them feel more at home in your designs.
Explaining design elements and architectural solutions
Architectural visualizations allow you to examine every nook and cranny of your designs, making them the perfect solution for answering any question your clients may have.
If a client is worried about the natural light in their building, you can render a whole neighborhood and show them exactly how much light they’d get during different times of the day. If they aren’t sure whether the furniture you want to include will fit in their available space, you can quickly test it out and show them a realistic representation. After all, architectural designs always use accurate proportions and measurements.
There’s no room for misunderstandings or confusion with a photorealistic architectural visualization. Your clients can see what they’re getting.
Creating an emotional reaction
Finally, architectural visualizations can help you get an emotional reaction from your clients. With virtual reality (VR) tours or augmented reality (AR) designs, you can help your audience see themselves in the space you’ve created. They can “walk-around” their new home before the construction process has even begun. They can take a tour of their new commercial property directly from your office chair.
You’ll bring your ideas to life and help your clients experience everything that your designs have to offer long before they’re completed in real life. Architectural visualizations are the perfect tool for creating an emotional response and establishing a strong relationship with every client.
Architectural visualization offers unique advantages to architects and designers alike. Using them in your presentations will help you make a strong impression on your audiences and showcase your talents in ways never before imaginable.
- Design & deliver
Data visualization: A detailed guide to visualizing data in your presentation
- Last Updated : October 20, 2023
- 15 Min Read

"The greatest value of a picture is when it forces us to notice what we never expected to see." - John W. Tukey, mathematician and statistician
Visualization helps decipher or break down information that is challenging to understand in text or numeric form. It's mostly used for data storytelling, as it is a great way to simplify information and present it in a format that is understandable, insightful, and actionable.
Whether you're a data analyst, a graphic designer, a content strategist or a social media manager, expertise in data visualization can help you solve a wide range of business challenges and tell impactful stories. In this blog post, we will look at a step-by-step approach to using data visualizations in your presentation.
What is data visualization?
Data visualization is the process of presenting data in a visual format, such as a chart, graph, or map. It helps users identify patterns and trends in a data set, making it easier to understand complex information. Visualizations can be used to analyze data, make predictions, and even communicate ideas more effectively.
Some examples of data visualizations include dashboards to track analytics, infographics for storytelling, or even word clouds to highlight the crux of your article or script.
Why do we have to visualize data?
In today's information-rich world, audiences are often bombarded with vast amounts of data and complex information. This is where data visualization comes into play—it transforms raw data into visually appealing and comprehensible formats, allowing audiences to grasp key insights and trends at a glance.
Consider the picture below:
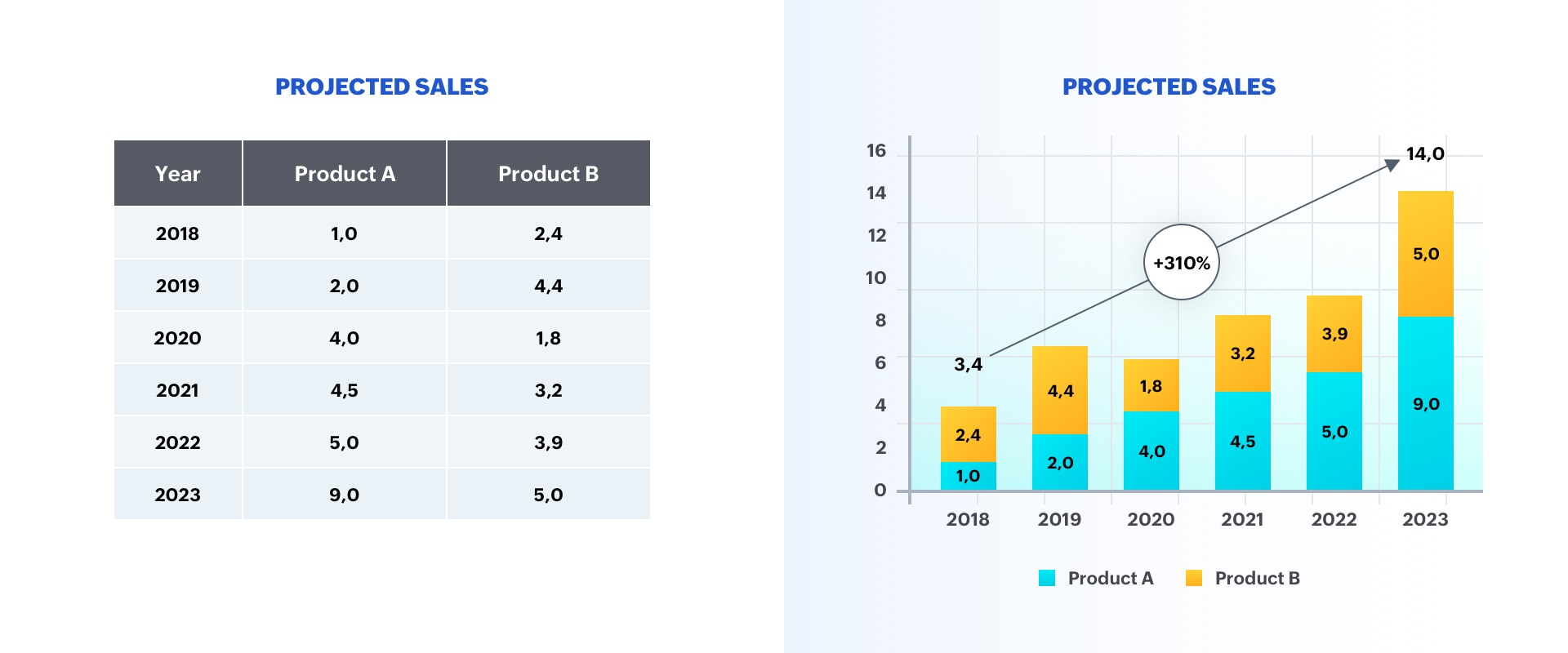
The option on the left is a table displaying two categories of data, whereas the option on the right is a graph representing sales growth. As you can see, the chart is more insightful, and makes it easier to identify trends in the numbers.
A good visualization typically represents some form of collected data as a picture, and can help with:
- Faster decision-making
- Identification of patterns and trends
- Presentation of an argument or story
Why is data visualization important in presentations?
Whether it's a business pitch, a campaign report, or a research presentation, data visualizations help you engage viewers on both rational and emotional levels.
They can be used to evoke empathy, urgency, or excitement, making the content more relatable and compelling. This is particularly crucial in decision-making contexts, where data-driven insights can sway opinions, drive actions, and guide strategic choices.
Ultimately, by incorporating data visualizations into presentations, you can benefit in the following ways:
- Elevate communication and convey impactful, data-centric narratives.
- Tell your story using visuals in a clear and meaningful way.
- Foster a deeper understanding of your data to make a stronger impact on the audience.
- Support idea generation and help derive business insights.
- Simplify data and business processes.
Step-by-step approach to data visualizations in presentations:
There are several factors to consider before adding a data visualization to your presentation. Here's a detailed guide:
Step 1: Define your purpose
The first step to visualizing data in your presentation is to determine your key message and decide on the type of story you are going to tell. Whether you plan to reveal trends, compare data, or explain a concept, a well-defined purpose will guide your data selection and visualization design, ensuring your visuals play a meaningful role in conveying your message.
Step 2: Understand your audience
Identify who your visualization is meant for and then make sure it fits their needs. Tailor your approach to suit your audience's familiarity with the topic and preferred level of detail. Knowing their expectations will help you fine-tune the complexity and depth of your visualizations, ensuring your presentation truly resonates with your audience.
Step 3: Choose your visualization type
Different data types and relationships call for different visualization formats. Selecting the appropriate chart, graph, or diagram is essential for accurately conveying your information. Here are some visualization types commonly used in presentations:
Tables: These consist of rows and columns and are used to compare variables in a structured way. Tables display data as categorical objects and make comparative data analysis easier. Example use: Pricing vs. feature comparison table.
Bar charts: Also known as column charts, these chart types use vertical or horizontal bars to compare categorical data. They are mainly used for analyzing value trends. Example use: Measure employee growth within a year.
Pie charts: These graphs are divided into sections that represent parts of a whole. They are used to compare the size of each component and are usually used to determine a percentage of the whole. Example use: Display website visitors by country.
Area charts: These are similar to bar and line graphs and show the progress of values over a period. These are mostly used to showcase data with a time-series relationship, and can be used to gauge the degree of a change in values. Example use: Show sales of different products in a financial year.
Histograms: Similar to bar charts (but with no space in between), histograms distribute numerical data. They are mainly used to plot the distribution of numbers and analyze the largest frequencies within a particular range. Example use: Measure app users by age.
Scatter charts: Also know as scatter plots, these graphs present the relationship between two variables. They are used to visualize large data sets, and show trends, clusters, patterns, and outliers. Example use: Track performance of different products in a suite.
Heat maps: These are a graphical way to visualize data in the form of hot and cold spots to identify user behavior. Example use: Present visitor behavior on your webpage.
Venn diagrams: These are best for showcasing similarities and differences between two or more categories. They are incredibly versatile and great for making comparisons, unions and intersections of different categories.
Timelines: These are best used for presenting chronological data. This is the most effective and efficient way to showcase events or time passage.
Flowcharts: These types of charts are ideal for showcasing a process or a workflow.
Infographics: These are a visual representation of content or data in a graphic format to make it more understandable at a glance.
Bonus: In addition to the above mentioned visualization types, you can use Gantt charts, word clouds, and tree maps. Gantt charts are used in project management presentations to demonstrate the work completed in a given period. Word clouds are a graphical representation of word frequency that gives greater prominence to the words that appear most within content. Tree maps display hierarchical data as a set of nested shapes, typically in the shape of rectangles.
Step 4: Use an appropriate chart
Once you're familiar with the different chart types available, the next step is to select the one that best conveys your key message. Knowing when and how to use each chart type empowers you to represent your data accurately and enhances the persuasiveness of your presentation. The best chart type for your needs depends more on the kind of analysis you are targeting than the type of data you've collected. Let's take a look at some of the most-used data visualization approaches in presentations.
Display changes over time: One of the most common applications of data visualizations is to show changes that have occurred over time. Bar or line charts are helpful in these instances.
Illustrate a part-to-whole composition: There might be times when you need to analyze the different components of a whole composition. Use pie, doughnut, and stacked bar charts for these part-to-whole compositions.
Visualize data distribution: Another important use of data visualization is to show how data has been distributed. Scatter plots, bar charts, and histograms help identify the outliers and demonstrate the range of information in the values.
Explore variable relationships: When you want to understand the relationship between two variables, use scatter plots or bubble charts. These can help you depict relationships between two variables, and observe trends and patterns between them.
Compare values between groups: Another common application of data visualization is in comparing values between two distinct groups. Using a grouped bar or line chart makes it easy to understand and compare trends.
There are several types of charts available in Zoho Show, each offering their own advantages. Learn how you can add and edit these charts in Show .
Step 5: Pick the right visualization tool
Utilize visualization software or tools that align with your proficiency and presentation needs. Factors such as ease of use, customization options, and compatibility with your data source should influence your choice of tool, enabling you to create impactful visualizations efficiently.
Zoho Show's charts are customizable, easy to use and come with wide range of options to make your data visualization easier. Some of the other prominent data visualization tools include Zoho Analytics , Tableau , Power Bi , and Infogram . These tools support a variety of visual styles and are capable of handling a large volume of data.
Step 6: Follow design best practices
Applying design principles will help you make sure your visualization is both aesthetically pleasing and easy to understand. You may apply these principles by choosing appropriate font colors and styles, or by effectively labeling and annotating your charts. By adhering to design best practices, you can create polished visuals and amplify the impact of your data-driven narrative.
Keep it simple: Data overload can quickly lead to confusion, so it’s important to include only the important information and simplify complex data. As a rule of thumb, don't crowd your slides with too much data, and avoid distracting elements.
Choose colors wisely: Use colors to differentiate and highlight information. The best practice is to use contrasting colors. You can also use patterns or texture to convey different types of information—but remember not to distort the data by applying 3D or gradient effects.
Add titles, labels, and annotations: Be sure to add a title, label, and description to your chart so your audience knows what they are looking at. Remember to keep it clear and concise.
Use proper fonts and text sizes: Use proper font styles and sizes to label and describe your charts. Your font choices may be playful, sophisticated, attention-grabbing, or elegant. Just be sure to choose a font that is easy to read and appropriate for your key message.
Closing thoughts
Human brains are naturally attuned to processing visual patterns and imageryUsing visuals not only helps you simplify complex information, but also makes your information more memorable. By leveraging charts and graphs, presenters can convey information to their audiences in a highly comprehensible manner. This helps them offer key insights and contribute to the decision-making process.
Ultimately, by incorporating data visualizations into presentations, presenters can elevate their communication from mere data sharing to impactful storytelling, fostering a deeper understanding of information among their audiences.
Related Topics
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked
You may also like
Streamline project presentations with Show's project management templates

Top five HR presentation templates

Mastering nonverbal communication in public speaking: A detailed guide
- + The Vault , Stuff Presenters Like
Presentation Preparation: How to Visualize Your Presentation
- By: Scott Schwertly
What do high-powered CEO’s, athletes like Michael Jordan and creative types like David Lynch all have in common? It may be hard to imagine that these disparate types could share common ground, but they do: They all use creative visualization. The term creative visualization goes by many names – and includes numerous approaches – but one thing is for sure, it works!
Simply speaking, creative visualization is a sort of meditation technique that can help you achieve more from your next presentation by encouraging you to create better clarity, focus and sense of purpose when it comes to achieving excellence the next time you take the stage. Without getting too complicated, we all want to do well when it comes to presenting, but we simply cannot do well until we actually believe we can.
Presenting is not easy. It pushes all kinds of buttons that we aren’t used to having pushed and it challenges us in ways our day-to-day jobs and lives usually don’t. For most of us, presenting casts us in a situation where we are fish-out-of-water, and like these hapless creatures our first reaction to being hit with a spotlight is to hyperventilate and flop around for a bit. Why? Because we don’t understand where we are and we can’t for the life of us imagine how to deal with the task at hand.
Creative visualization allows you to clarify your goal, imagine your best possible performance, and essentially “walk through it” time and time again before you ever step into that boardroom or walk up on that stage. Most of us allow our lives to be controlled by our unconscious expectations. Why not take control of those expectations and create the outcomes we truly desire?
Here’s how it works:
Set Your Goal Sure, you think you want the best possible outcome for your presentation, but do you really ? Most of our best intentions are also shot through with strong doubts and even self-destructive beliefs. Do you really want to be have a great presentation or do you just want to survive the trauma you fear? Take some time to really work through your goal for your presentation. Acknowledge negative feelings and attitudes but don’t let them stand between you and your best.
Picture Your Best This can be tough. Once you really know what you want out of your next presentation, you need to create that picture in your mind. See every detail. Hear every sound. What are you wearing? What does the room look like? See the faces in the audience as you deliver your best possible presentation.
Focus Often Take your visualization practice seriously and make it a priority in your preparations. Take time to be alone, be still and be in the moment with your thoughts as you run through your visualization again and again. As you practice, the image will become clearer and your focus will be easier to achieve.
By using creative visualization you are actually training your subconscious mind for greatness. This is just a basic rundown on the practice. Take the time to investigate creative visualization. You’ll find that there are countless resources to assist you as well as many mainstream research studies that support the effectiveness of this knockout preparation technique.
Scott Schwertly
Join our newsletter today.
© 2006-2024 Ethos3 – An Award Winning Presentation Design and Training Company ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Diversity and Inclusion
Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
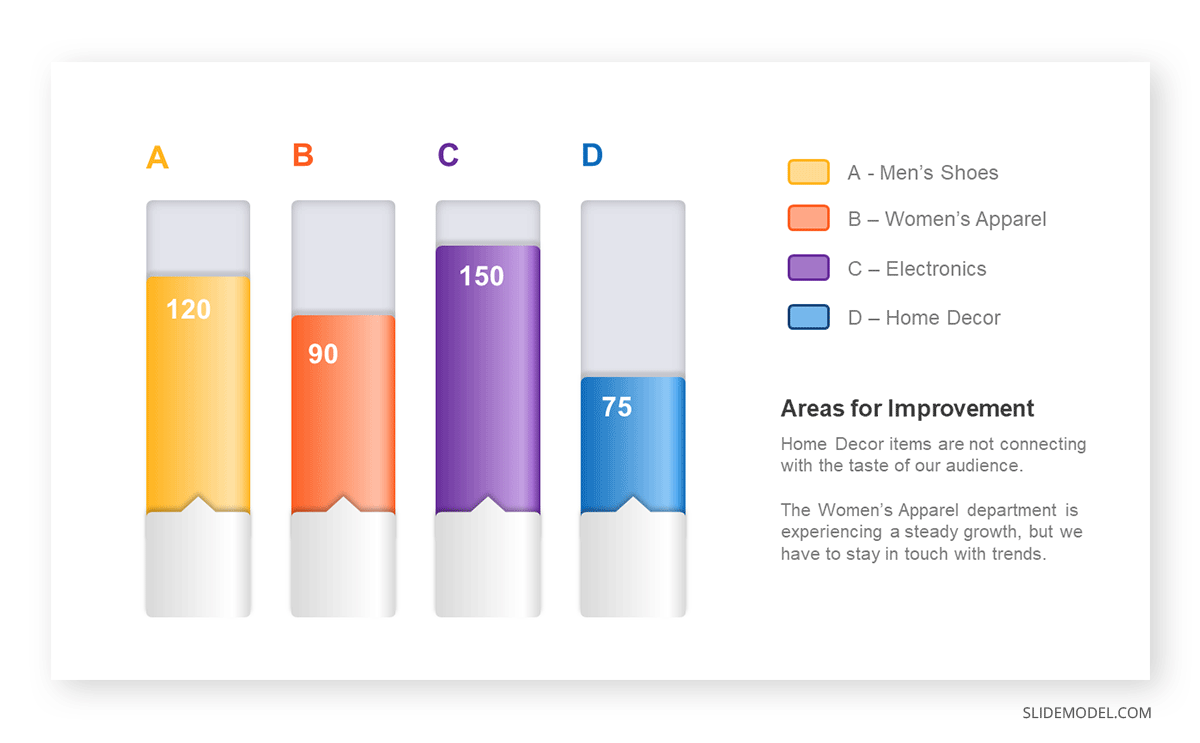
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
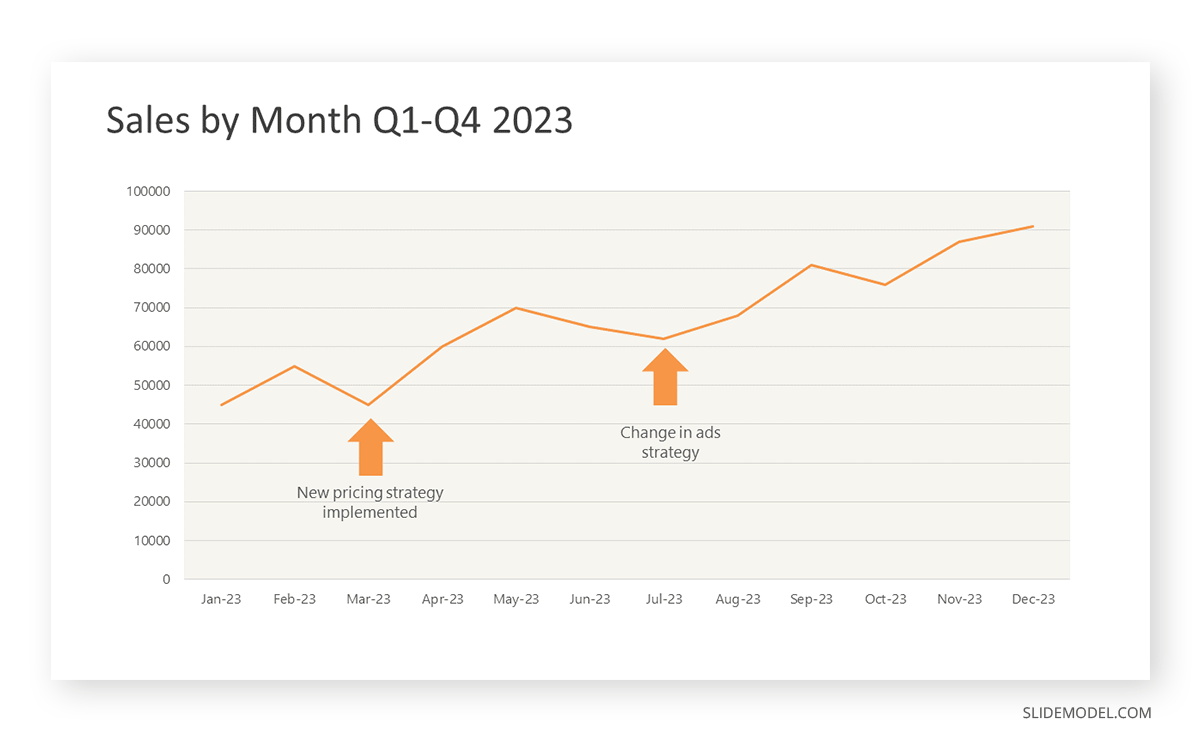
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
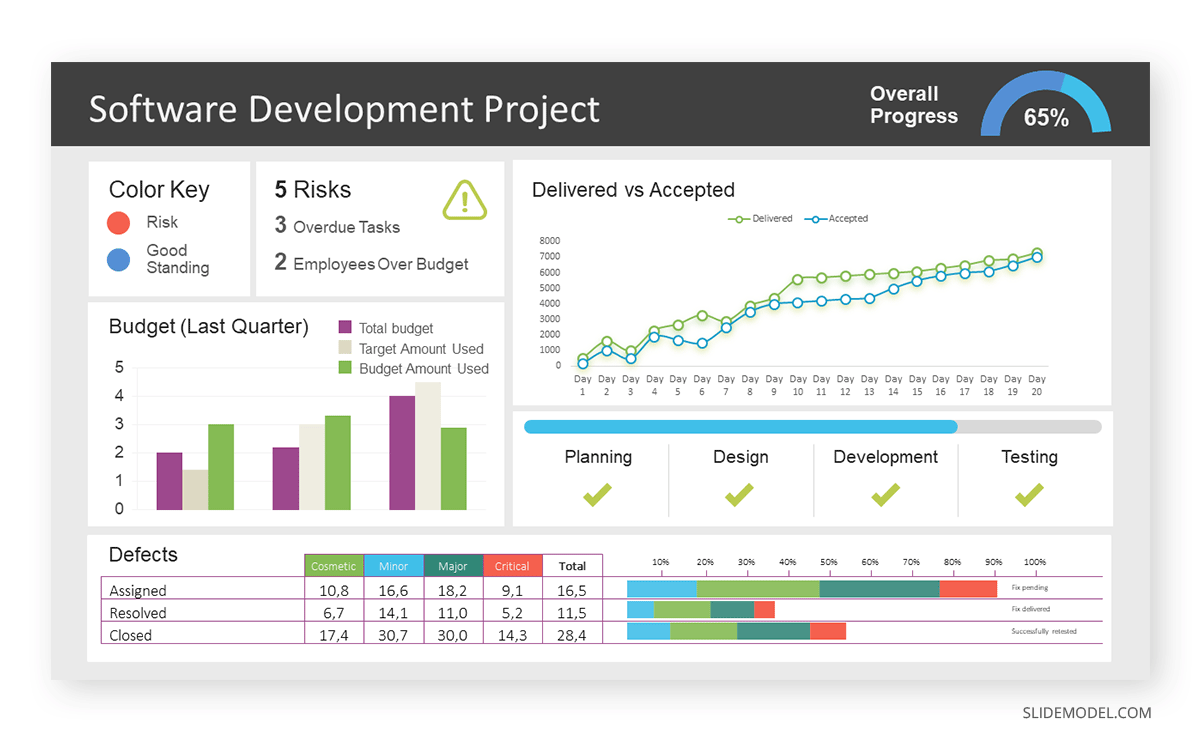
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
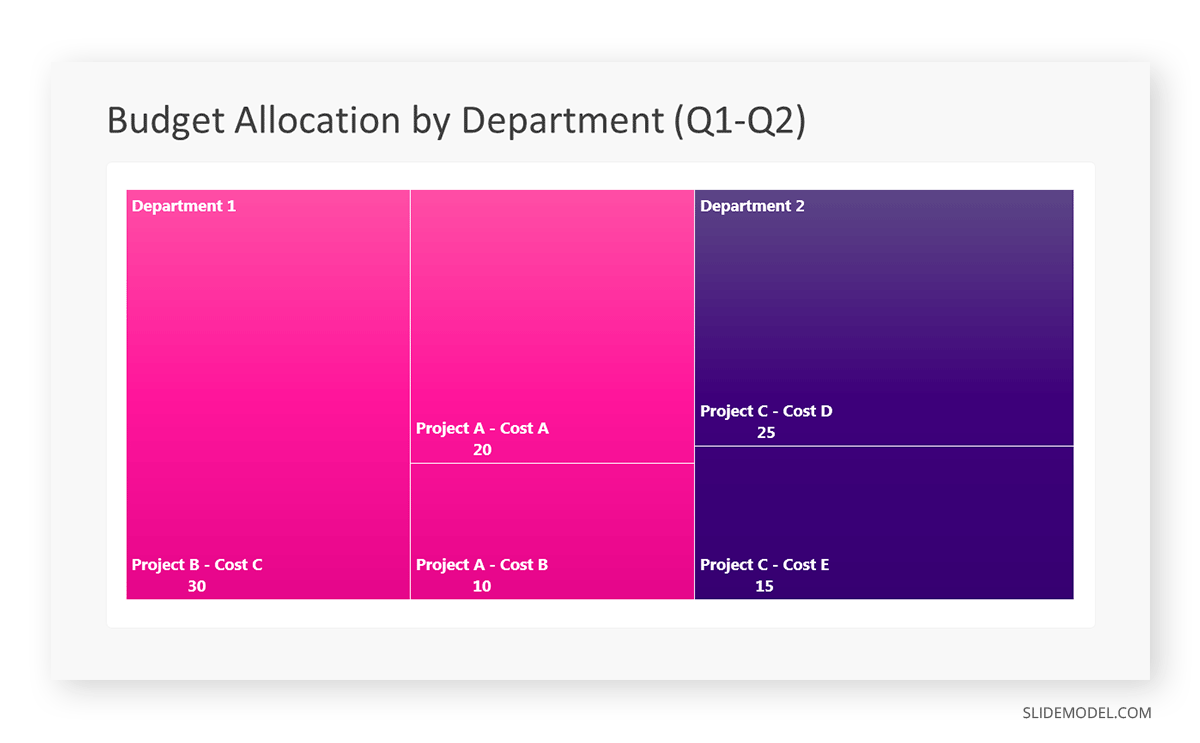
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
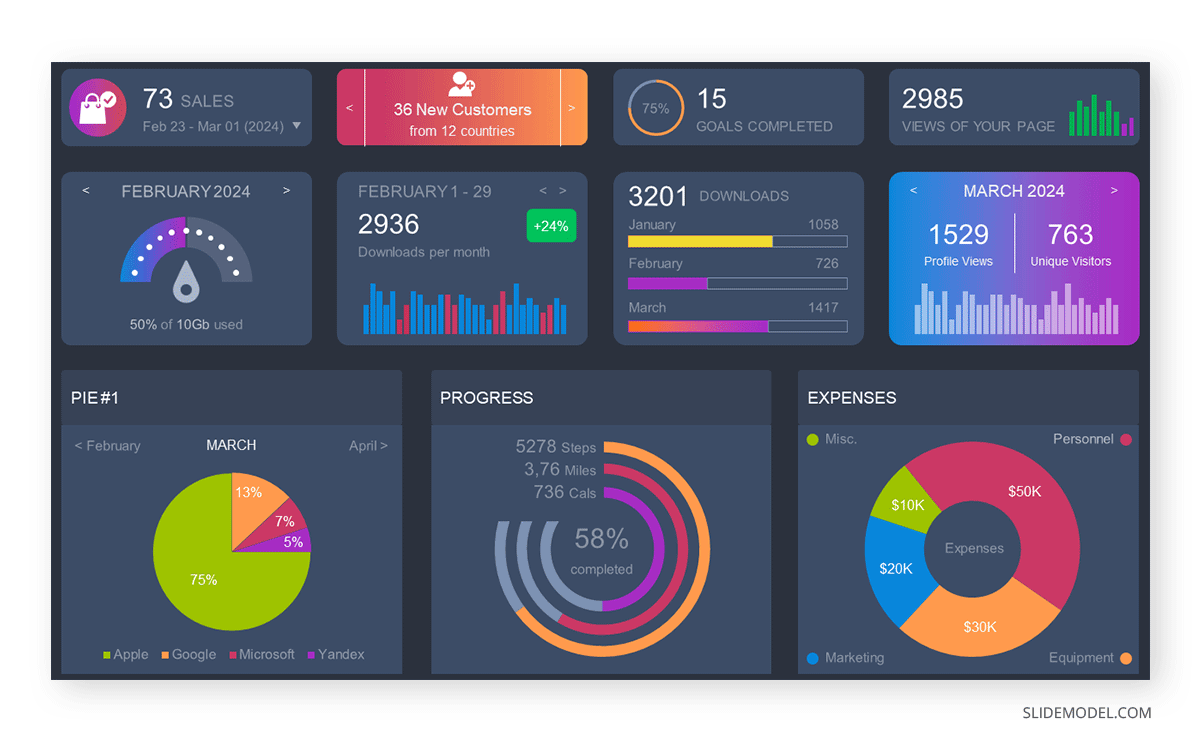
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
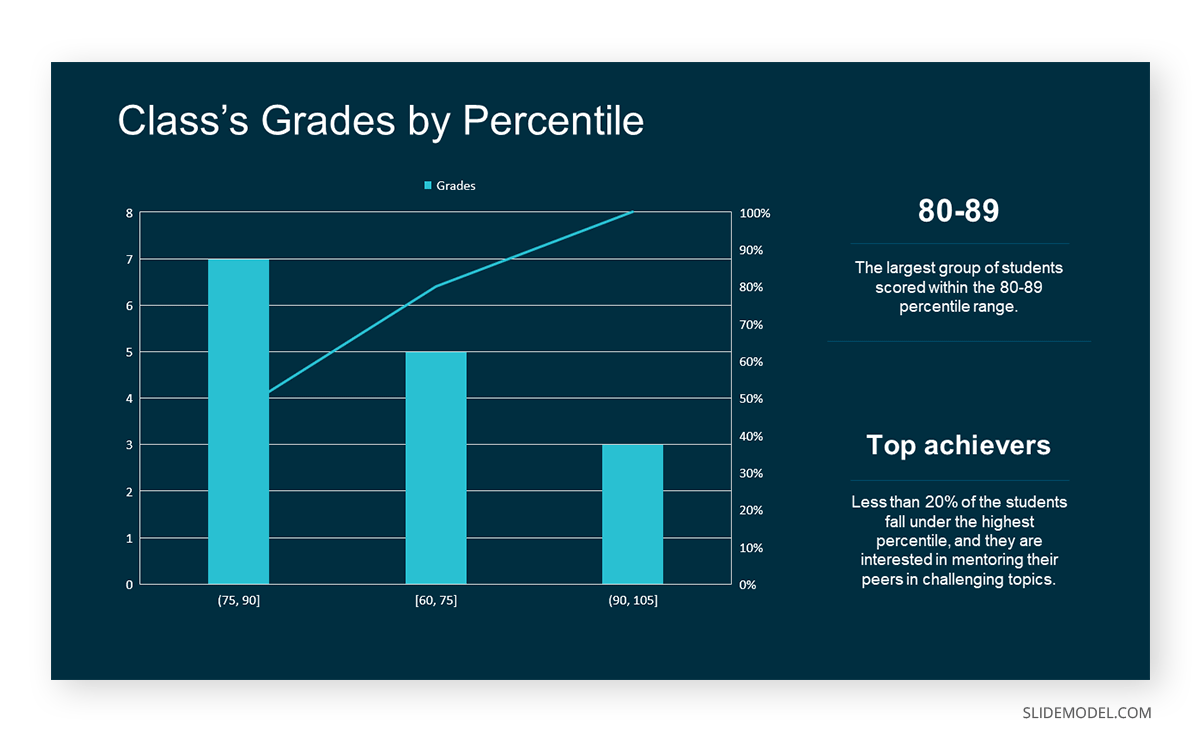
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
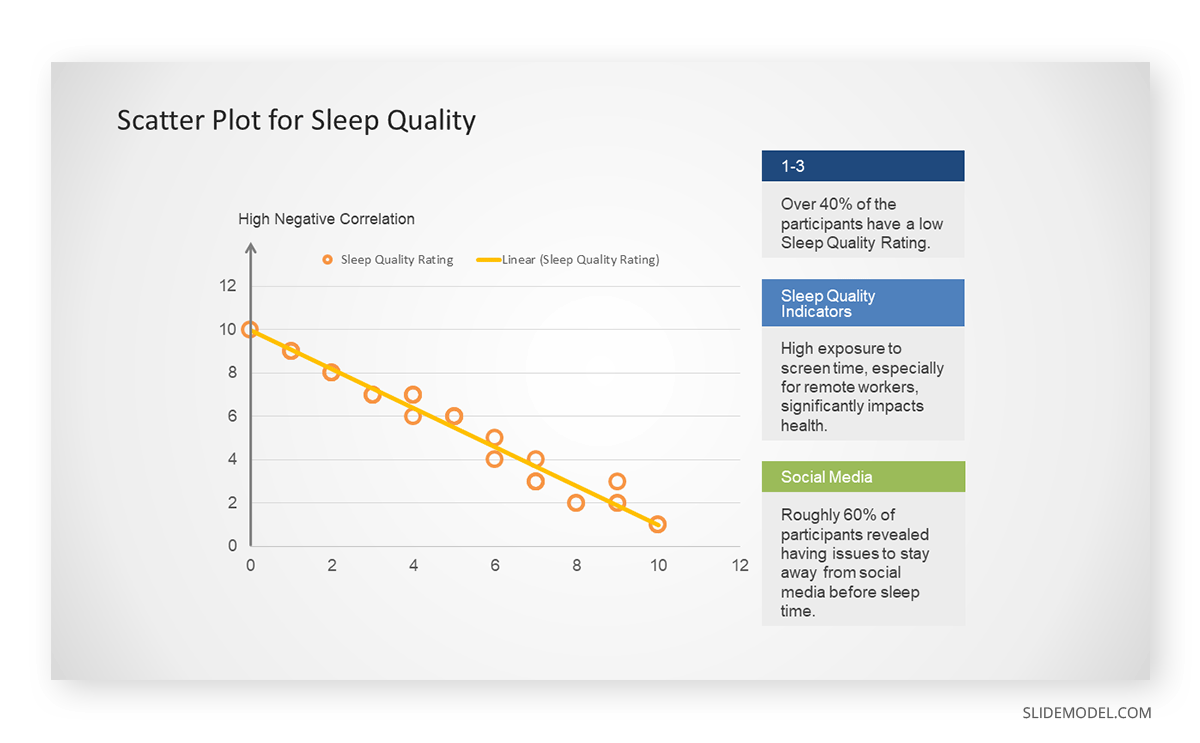
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
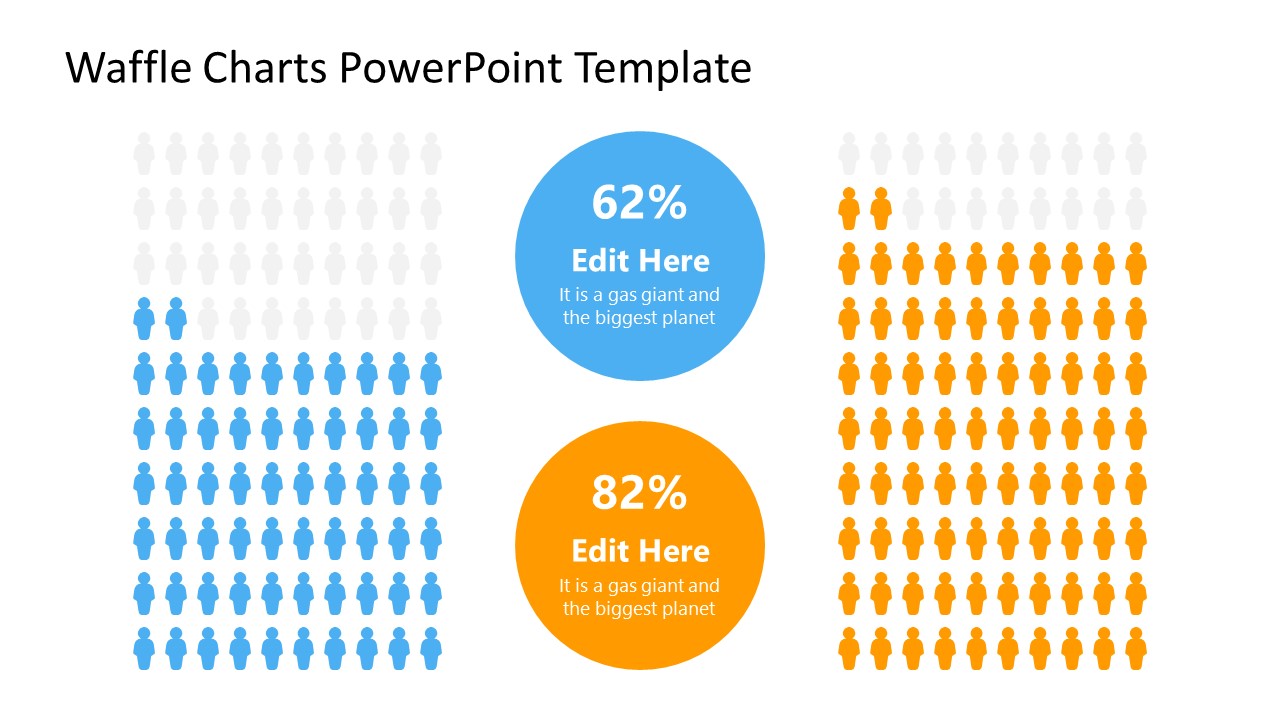
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
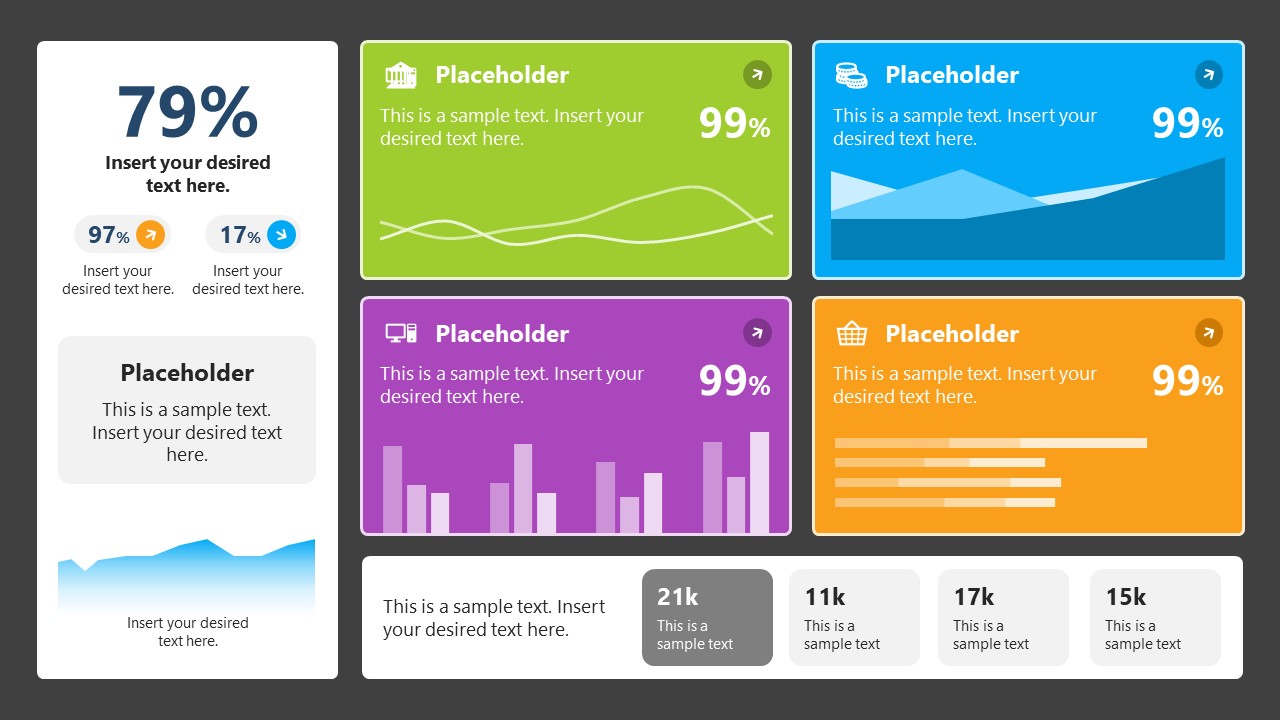
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
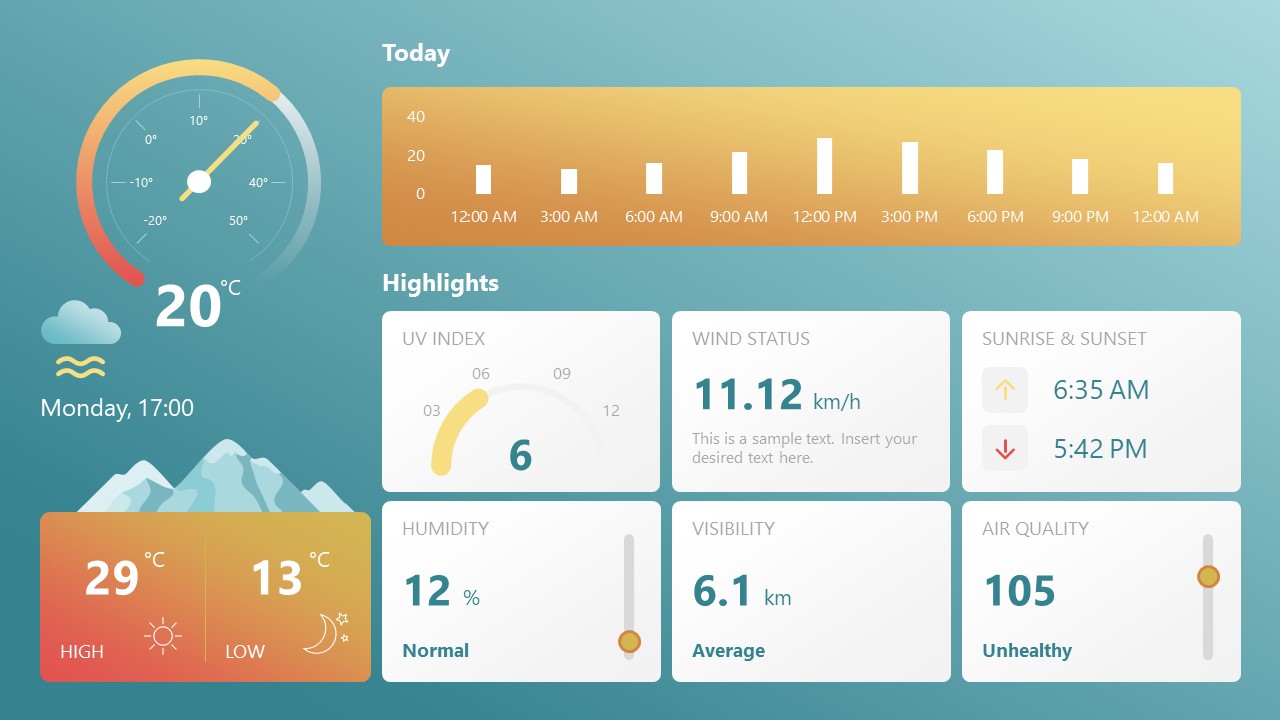
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
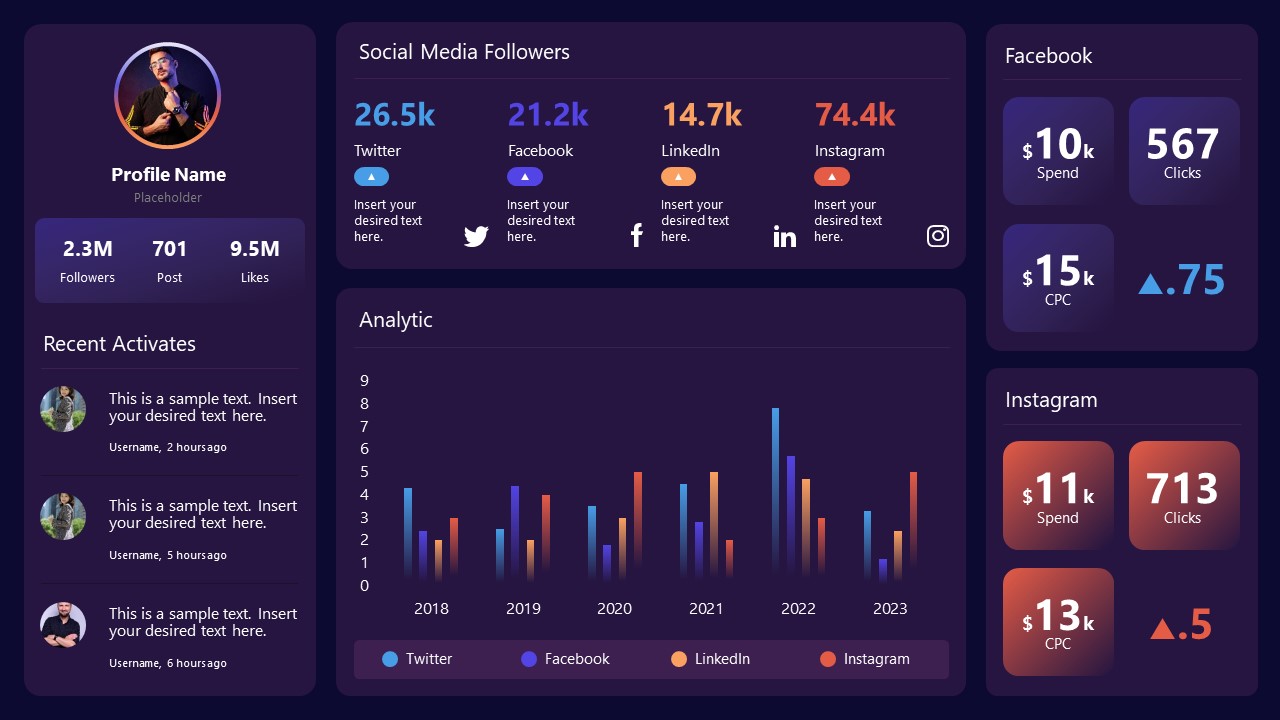
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
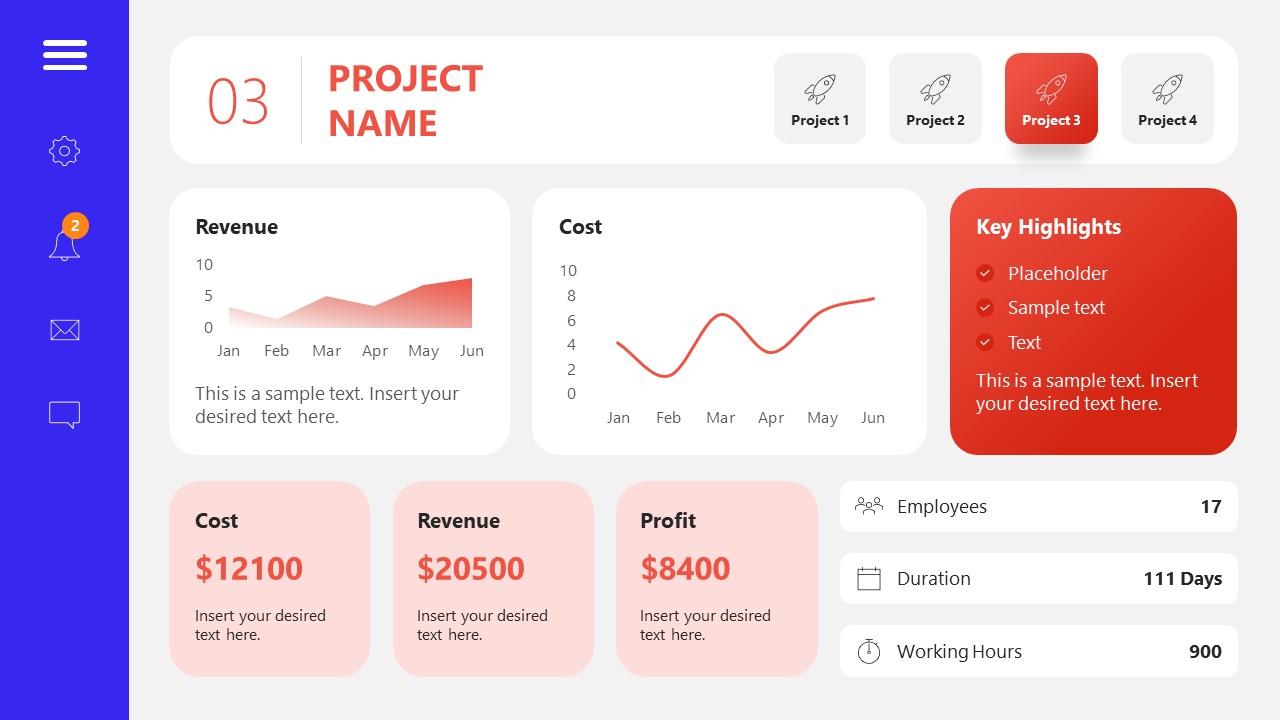
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
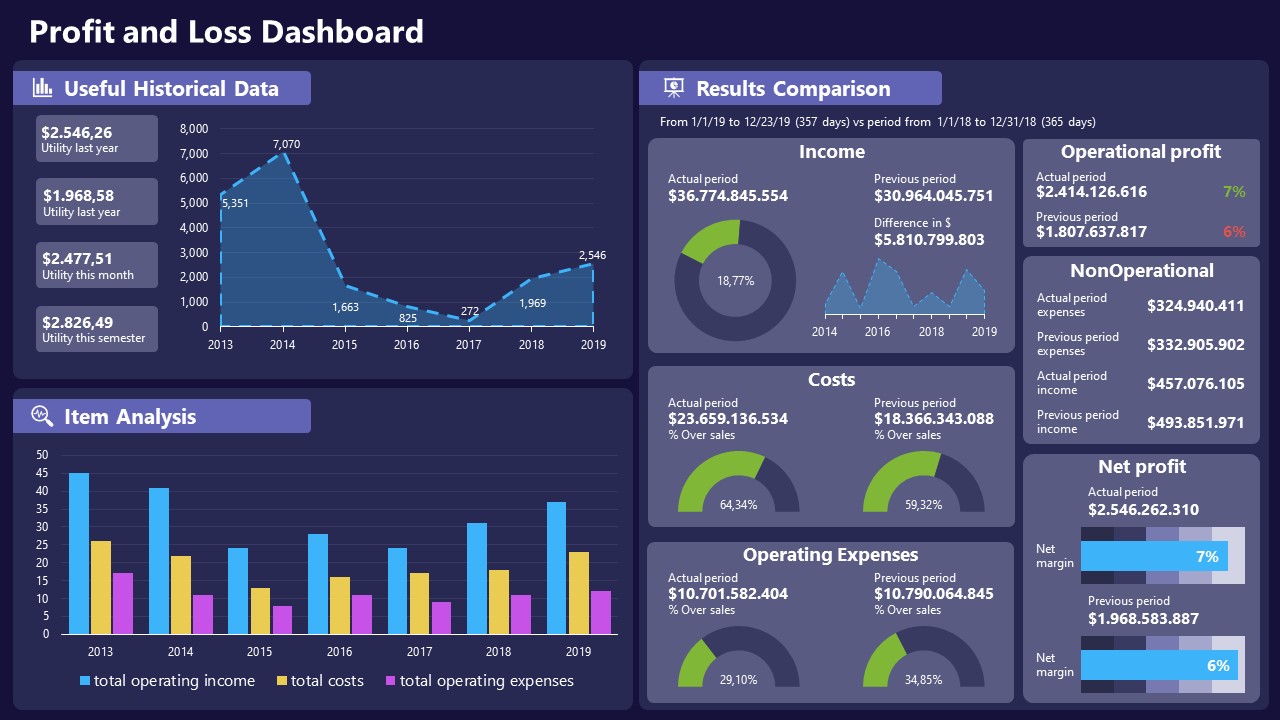
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides 8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]

8 Types of Presentations You Should Know [+Examples & Tips]
Written by: Krystle Wong Aug 11, 2023

From persuasive pitches that influence opinions to instructional demonstrations that teach skills, the different types of presentations serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences.
Presentations that are tailored to its objectives and audiences are more engaging and memorable. They capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
Don’t worry if you’re no designer — Whether you need data-driven visuals, persuasive graphics or engaging design elements, Venngage can empower you to craft presentations that stand out and effectively convey your message.
Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop interface, extensive presentation template library and customizable design options make it a valuable tool for creating slides that align with your specific goals and target audience.
Click to jump ahead:
8 Different types of presentations every presenter must know
How do i choose the right type of presentation for my topic or audience, types of presentation faq, 5 steps to create a presentation with venngage .

When it comes to presentations, versatility is the name of the game. Having a variety of presentation styles up your sleeve can make a world of difference in keeping your audience engaged. Here are 8 essential presentation types that every presenter should be well-acquainted with:
1. Informative presentation
Ever sat through a presentation that left you feeling enlightened? That’s the power of an informative presentation.
This presentation style is all about sharing knowledge and shedding light on a particular topic. Whether you’re diving into the depths of quantum physics or explaining the intricacies of the latest social media trends, informative presentations aim to increase the audience’s understanding.
When delivering an informative presentation, simplify complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples. Organize your content logically, starting with the basics and gradually delving deeper and always remember to keep jargon to a minimum and encourage questions for clarity.
Academic presentations and research presentations are great examples of informative presentations. An effective academic presentation involves having clear structure, credible evidence, engaging delivery and supporting visuals. Provide context to emphasize the topic’s significance, practice to perfect timing, and be ready to address anticipated questions.
2. Persuasive presentation
If you’ve ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you’ve experienced a persuasive presentation .
This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective. Expect to encounter solid evidence, logical reasoning and a dash of emotional appeal.
With persuasive presentations, it’s important to know your audience inside out and tailor your message to their interests and concerns. Craft a compelling narrative with a strong opening, a solid argument and a memorable closing. Additionally, use visuals strategically to enhance your points.
Examples of persuasive presentations include presentations for environmental conservations, policy change, social issues and more. Here are some engaging presentation templates you can use to get started with:

3. Demonstration or how-to presentation
A Demonstration or How-To Presentation is a type of presentation where the speaker showcases a process, technique, or procedure step by step, providing the audience with clear instructions on how to replicate the demonstrated action.
A demonstrative presentation is particularly useful when teaching practical skills or showing how something is done in a hands-on manner.
These presentations are commonly used in various settings, including educational workshops, training sessions, cooking classes, DIY tutorials, technology demonstrations and more. Designing creative slides for your how-to presentations can heighten engagement and foster better information retention.
Speakers can also consider breaking down the process into manageable steps, using visual aids, props and sometimes even live demonstrations to illustrate each step. The key is to provide clear and concise instructions, engage the audience with interactive elements and address any questions that may arise during the presentation.

4. Training or instructional presentation
Training presentations are geared towards imparting practical skills, procedures or concepts — think of this as the more focused cousin of the demonstration presentation.
Whether you’re teaching a group of new employees the ins and outs of a software or enlightening budding chefs on the art of soufflé-making, training presentations are all about turning novices into experts.
To maximize the impact of your training or instructional presentation, break down complex concepts into digestible segments. Consider using real-life examples to illustrate each point and create a connection.
You can also create an interactive presentation by incorporating elements like quizzes or group activities to reinforce understanding.
5. Sales presentation
Sales presentations are one of the many types of business presentations and the bread and butter of businesses looking to woo potential clients or customers. With a sprinkle of charm and a dash of persuasion, these presentations showcase products, services or ideas with one end goal in mind: sealing the deal.
A successful sales presentation often has key characteristics such as a clear value proposition, strong storytelling, confidence and a compelling call to action. Hence, when presenting to your clients or stakeholders, focus on benefits rather than just features.
Anticipate and address potential objections before they arise and use storytelling to showcase how your offering solves a specific problem for your audience. Utilizing visual aids is also a great way to make your points stand out and stay memorable.
A sales presentation can be used to promote service offerings, product launches or even consultancy proposals that outline the expertise and industry experience of a business. Here are some template examples you can use for your next sales presentation:

6. Pitch presentation
Pitch presentations are your ticket to garnering the interest and support of potential investors, partners or stakeholders. Think of your pitch deck as your chance to paint a vivid picture of your business idea or proposal and secure the resources you need to bring it to life.
Business presentations aside, individuals can also create a portfolio presentation to showcase their skills, experience and achievements to potential clients, employers or investors.
Craft a concise and compelling narrative. Clearly define the problem your idea solves and how it stands out in the market. Anticipate questions and practice your answers. Project confidence and passion for your idea.
7. Motivational or inspirational presentation
Feeling the need for a morale boost? That’s where motivational presentations step in. These talks are designed to uplift and inspire, often featuring personal anecdotes, heartwarming stories and a generous serving of encouragement.
Form a connection with your audience by sharing personal stories that resonate with your message. Use a storytelling style with relatable anecdotes and powerful metaphors to create an emotional connection. Keep the energy high and wrap up your inspirational presentations with a clear call to action.
Inspirational talks and leadership presentations aside, a motivational or inspirational presentation can also be a simple presentation aimed at boosting confidence, a motivational speech focused on embracing change and more.
8. Status or progress report presentation
Projects and businesses are like living organisms, constantly evolving and changing. Status or progress report presentations keep everyone in the loop by providing updates on achievements, challenges and future plans. It’s like a GPS for your team, ensuring everyone stays on track.
Be transparent about achievements, challenges and future plans. Utilize infographics, charts and diagrams to present your data visually and simplify information. By visually representing data, it becomes easier to identify trends, make predictions and strategize based on evidence.

Now that you’ve learned about the different types of presentation methods and how to use them, you’re on the right track to creating a good presentation that can boost your confidence and enhance your presentation skills .
Selecting the most suitable presentation style is akin to choosing the right outfit for an occasion – it greatly influences how your message is perceived. Here’s a more detailed guide to help you make that crucial decision:
1. Define your objectives
Begin by clarifying your presentation’s goals. Are you aiming to educate, persuade, motivate, train or perhaps sell a concept? Your objectives will guide you to the most suitable presentation type.
For instance, if you’re aiming to inform, an informative presentation would be a natural fit. On the other hand, a persuasive presentation suits the goal of swaying opinions.
2. Know your audience
Regardless if you’re giving an in-person or a virtual presentation — delve into the characteristics of your audience. Consider factors like their expertise level, familiarity with the topic, interests and expectations.
If your audience consists of professionals in your field, a more technical presentation might be suitable. However, if your audience is diverse and includes newcomers, an approachable and engaging style might work better.

3. Analyze your content
Reflect on the content you intend to present. Is it data-heavy, rich in personal stories or focused on practical skills? Different presentation styles serve different content types.
For data-driven content, an informative or instructional presentation might work best. For emotional stories, a motivational presentation could be a compelling choice.
4. Consider time constraints
Evaluate the time you have at your disposal. If your presentation needs to be concise due to time limitations, opt for a presentation style that allows you to convey your key points effectively within the available timeframe. A pitch presentation, for example, often requires delivering impactful information within a short span.
5. Leverage visuals
Visual aids are powerful tools in presentations. Consider whether your content would benefit from visual representation. If your PowerPoint presentations involve step-by-step instructions or demonstrations, a how-to presentation with clear visuals would be advantageous. Conversely, if your content is more conceptual, a motivational presentation could rely more on spoken words.

6. Align with the setting
Take the presentation environment into account. Are you presenting in a formal business setting, a casual workshop or a conference? Your setting can influence the level of formality and interactivity in your presentation. For instance, a demonstration presentation might be ideal for a hands-on workshop, while a persuasive presentation is great for conferences.
7. Gauge audience interaction
Determine the level of audience engagement you want. Interactive presentations work well for training sessions, workshops and small group settings, while informative or persuasive presentations might be more one-sided.
8. Flexibility
Stay open to adjusting your presentation style on the fly. Sometimes, unexpected factors might require a change of presentation style. Be prepared to adjust on the spot if audience engagement or reactions indicate that a different approach would be more effective.
Remember that there is no one-size-fits-all approach, and the best type of presentation may vary depending on the specific situation and your unique communication goals. By carefully considering these factors, you can choose the most effective presentation type to successfully engage and communicate with your audience.
To save time, use a presentation software or check out these presentation design and presentation background guides to create a presentation that stands out.
What are some effective ways to begin and end a presentation?
Capture your audience’s attention from the start of your presentation by using a surprising statistic, a compelling story or a thought-provoking question related to your topic.
To conclude your presentation , summarize your main points, reinforce your key message and leave a lasting impression with a powerful call to action or a memorable quote that resonates with your presentation’s theme.
How can I make my presentation more engaging and interactive?
To create an engaging and interactive presentation for your audience, incorporate visual elements such as images, graphs and videos to illustrate your points visually. Share relatable anecdotes or real-life examples to create a connection with your audience.
You can also integrate interactive elements like live polls, open-ended questions or small group discussions to encourage participation and keep your audience actively engaged throughout your presentation.
Which types of presentations require special markings
Some presentation types require special markings such as how sales presentations require persuasive techniques like emphasizing benefits, addressing objections and using compelling visuals to showcase products or services.
Demonstrations and how-to presentations on the other hand require clear markings for each step, ensuring the audience can follow along seamlessly.
That aside, pitch presentations require highlighting unique selling points, market potential and the competitive edge of your idea, making it stand out to potential investors or partners.
Need some inspiration on how to make a presentation that will captivate an audience? Here are 120+ presentation ideas to help you get started.
Creating a stunning and impactful presentation with Venngage is a breeze. Whether you’re crafting a business pitch, a training presentation or any other type of presentation, follow these five steps to create a professional presentation that stands out:
- Sign up and log in to Venngage to access the editor.
- Choose a presentation template that matches your topic or style.
- Customize content, colors, fonts, and background to personalize your presentation.
- Add images, icons, and charts to enhancevisual style and clarity.
- Save, export, and share your presentation as PDF or PNG files, or use Venngage’s Presentation Mode for online showcasing.
In the realm of presentations, understanding the different types of presentation formats is like having a versatile set of tools that empower you to craft compelling narratives for every occasion.
Remember, the key to a successful presentation lies not only in the content you deliver but also in the way you connect with your audience. Whether you’re informing, persuading or entertaining, tailoring your approach to the specific type of presentation you’re delivering can make all the difference.
Presentations are a powerful tool, and with practice and dedication (and a little help from Venngage), you’ll find yourself becoming a presentation pro in no time. Now, let’s get started and customize your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
The Role of Data Visualization in Presentations
Data visualization in presentations: types and advantages.
Sep 19, 2022
Your presentation should inspire, persuade, and inform your audience without boring them to tears. However, even with a creative mind and polished design skills, infusing life into sticky and data-populated presentation topics can be a tall order. But not if you leverage data visualization.

Data visualization is the representation of data through visual displays such as charts, histograms, maps, tables, dashboards, graphs, and infographics. Integrating data visualization into your presentation makes it easy for your audience to digest, absorb, and remember complex information and data. The American Management Association says visuals and actions make written information 70% more memorable .
Thus, if you want to design a stellar presentation that delights your audience from start to finish, utilize graphical displays to your advantage. Fortunately, as we discuss below, you can employ several types of data visualization in your presentation.
The Different Types of Interactive Data Visualizations
Interactive information visualization helps your audience quickly gather your presentation’s primary insights and takeaways by analyzing the visuals.
Interactive visualizations create a synergetic interaction between your audience and the data, empowering them to summarize and correlate findings more efficiently. They’re especially effective in the corporate world, for instance, when delivering a business process improvement presentation.
While interactive visualizations can take many forms, these are the most prevalent in presentations:
Pie Charts To Show Important Percentages

Pie charts are by far the most effective way of representing data in percentages. A pie chart denotes individual percentages of a whole figure, making it easier to interpret data since percentages tally up to 100%.
The full circle represents the whole figure, while each slice of the pie portrays the individual percentages. Ideally, you should use the pie chart to visualize five to six parts utmost, so it’s legible and not too populated. If you have seven or more sections to compare, go for the donut chart .
Lastly, make good use of color coding to differentiate each wedge of your pie chart as color schemes make your data more memorable. Research has shown that colors improve human memory by boosting concentration and focus.
Bar Chart or Scatter Plots for Easy Data Comparison
Bar charts contrast data along a vertical axis (y-axis) and a horizontal axis (x-axis). The graphical representation created by bar charts makes it easy to compare correlative data. For instance, when comparing the yearly profit revenues of a company, you can display the revenue numbers on the x-axis and the years on the y-axis.
Complete Dashboard Design With Multiple Graphs and Maps

When you need to display geographical data and protracted metrics, a dashboard design that integrates maps and graphs will suffice. You may need multiple graphs to present overlapping information like sales, revenue, and marketing data. Maps are handy when displaying geographical data like election results or meteorological data.
You need ample graphic design knowledge to create aesthetic data visualization designs — like business process flowcharts — to integrate them smoothly into your presentation. Good thing you can hire graphic design experts who understand the assignment inside out and are flexible and prompt.
Why Data Visualization Tools Are Necessary for a Presentation
You need data visualization tools to create all types of visual displays. These tools are software applications designed to render and present raw data in graphical formats, such as pie charts, graphs, and bar charts. Besides handling data rendering, data visualizations tools offer the following benefits:
Tells Your Data Story in an Elegant and Meaningful Way
Data in its raw form is complex and challenging to interpret and understand. It’s hard to tell a perceptive data story using blocks of text only. Given that the attention span for a typical audience is seven minutes , you’ll lose your audience sooner if your presentation is crammed with lots of raw data and statistics.
Conversely, visuals help you tell a compelling data story that your audience can follow without being at sea. Good thing you’ll find a suitable data visualization tool no matter your field of expertise. For instance, you’ll find a tool for creating complex scientific visualizations if you’re a scientist and one for creating simple pie charts if you’re a motivational speaker.
Supports Idea Generation Beyond Just Those in the Field of Statistics
It’s easier for your audience to derive business insights and spot data inaccuracies from a presentation with a lot of data visualizations. By assessing and probing these insights, your audience may get a light-bulb moment that births a conceptual idea with a real-world transformational impact.

With a graphical representation of data, it’s easier for a discerning eye to spot marginal differences in cycles and patterns. These are the subtle insights that decision-makers and top professionals need to implement innovative ideas. Without data visualization tools, it would take a great deal of time to structure raw data in an easy-to-read format that can foster idea generation.
Simplifies Data and Business Processes
If you had to draw all the data visualization examples you need in a presentation by yourself, it would be a huge undertaking that would tie up most of your productive time. But with data visualization tools, it’s simple and less time and resource-intensive. This has multifold benefits for you and your audience.
On the one hand, you’ll prepare your presentation visuals more swiftly. Faster preparation gives you more time to complete other tasks on your tab. On the other hand, your audience will access real-time data in a digested form, making it more valuable to their business processes.
Visualize Data With Ease By Outsourcing Your Presentations
Admittedly, adding data visualizations in your presentations isn’t a no-sweat job. Particularly, when dealing with large-scale data that needs multiple visual and graphic representations, the workflow can easily overwhelm you as there's much design thinking needed. But, creating data visualizations shouldn’t be overwhelming since you can hire presentation design experts like GhostRanch Communications to do all the heavy lifting.
At GhostRanch Communications, we design any graphical and visual representations you need for your presentation. Whether you want 3-D maps, bar graphs, or simple pie charts, we have the tools and talent to deliver exquisite designs that’ll turn heads, close deals, and save you time.
Contact us today , and let us help you visualize your next presentation.
You May Also Like…
Move content from an ugly table into a pretty table.
Feb 27, 2024
How do you write a powerful personal story? (Even when you don’t have a story to tell)
You don’t have to launch Xbox 360 in Europe or tour with rock bands to have a tale worth telling.
Feb 13, 2024
Transferring Themes - Colors and Fonts - from PowerPoint to Word and Excel and Vice Versa
Feb 12, 2024
A Top 5 Shortcut That Works in PowerPoint and Google Slides
The 2 secret powers of the redo shortcut

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Presentation Specialist Job Description: A Complete Guide
This blog will explore the Presentation Specialist Job Description in detail and help you understand how to design visually compelling Presentations. This helps you to enhance communication. It will also discuss how to create polished layouts, Data Visualisations, and impactful graphics using tools like PowerPoint. Read more!

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Business Writing Course
- Data Analysis Skills
- Presenting with Impact Training
- Blended Learning Essentials

Do you love creating Presentations and setting your projects apart from the rest? Does creating different infographics, animation and content for your business entice you? Then, a career as a Presentation Specialist is for you. If you want to know how to become one, this detailed Presentation Specialist Job Description will help you.
Presentation Specialists create slides, Data Visualisations, and graphics that simplify storytelling and are adapted to our brand needs. Together, they work with marketing, sales, and strategic teams to transform complex information into something that makes sense to the audience and helps them achieve their objectives. This blog covers the job description for a Presentation Specialist. Read on to find out more.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Presentation Specialist?
2) Job Description of a Presentation Specialist
3) Presentation Specialist qualifications
4) Responsibilities of a Presentation Specialist
5) Software utilised by Presentation Specialists
6) Conclusion
What is a Presentation Specialist?
A Presentation Specialist is responsible for making a visual Presentation that is both relevant and interesting by focusing on the meaning of the information with high accuracy. They use robust software tools like PowerPoint that help you harness narrative and vital data. They collaborate with the marketing, sales, and top management to build Presentations that communicate project objectives, satisfy audience needs, and conform to the brand norms of a company.
First, one of their strengths is presenting complicated data in an exciting and eye-catching way, leaving a vivid memory and effectively portraying the message. However, digital marketers stem their creativity from strategic thinking to ensure Presentations stand out and match the brand, and eventually, customers find it natural to relate to them.

Job Description of a Presentation Specialist
Let’s have a look at the Job Description of a Presentation Specialist:
Presentation Specialist qualifications
Let's look at some of the essential Qualifications that are required to become a Presentation Specialist:
Educational background
Generally, Presentation Specialists can major in Graphic Design, Visual Communication, marketing, or a related field. Of course, their first and most important education is their higher education, where they are grounded in some basic design, brand creation, and compelling storytelling.
Professional experience
A critical requirement is earlier exposure to making visually pleasing Presentations in many industries. They are usually considered to have established a reputation for being great at meeting the needs of marketing, sales, and executive teams. Such teams typically pay them to create content that aligns with the company's goals and those of their audiences.
Software competence
Familiarity with widely used tools like PowerPoint and graphic design tools like Adobe Creative Suite is necessary. Consequently, they are competent enough to create professional-level designs, charts, Data Visualisations, and images, contributing to my organisation's smooth communication.
Attention to detail
Foresight for details counts a lot for us to ascertain harmony and precise placing of elements and for data exploitation to be effective. Presentation Specialists are assigned to proofread the documents to remove errors and show that we are competent.
Learn how you can engage your audience with our Presentation Skills Courses – register today!
Responsibilities of a Presentation Specialist
The role of a Presentation Specialist is to present enticing visuals that successfully transmit what a company tries to convey using a message. Their duties incorporate creativity, skills and strategy, which assists the organisations.

Crafting engaging Presentations
One key responsibility is effectively making highly polished, concise, and audience-centered Presentations. This involves determining the correct layouts, colours, and fonts that correspond with the company's brand and help these elements stand out instead of the content.
Data Visualisation
Presentation Experts simplify complex data through visualisation tools such as graphs, charts, and infographics. This process includes finding vital pieces of data and creating visually appealing and well-structured Data Visualisations using tools like Excel and Tableau.
Content collaboration and refinement
Marketing, sales, and executive teams are their close partners, who provide them with feedback and help refine the Presentation content. Among them are knowing the core of customising the speech, remaining coherent, and tailoring the Presentation to the audience's demands. They could make recommendations for editing scripts and ensure that data is presented logically, among others.
Software proficiency
PowerPoint, Keynote, and Prezi are perfect examples of Presentation software; the ability to use them skillfully is necessary. These designers have also mastered using graphics design tools like Adobe Creative Suite and are competent enough to produce superior visuals.
Brand consistency
Keeping every Presentation in line with the brand is of the utmost importance. They ensure that the organisation follows its guidelines, using the correct logos, fonts, and colour schemes.
Project Management
Managing several projects at a time is an essential part of their work. Along with meeting deadlines, they need to be very average in terms of quality, so this implies excellent time-keeping skills.
Continuous improvement
In addition to remaining ahead of the latest design trends and being familiar with new Presentation software, they will always be on the set to enhance their expertise and generate new ideas for their company.
Enhance your understanding of Business Writing with our Business Writing Course – Join now!
Software utilised by Presentation Specialists
To achieve attractive, visually appealing Presentations, Presentation experts use the whole toolset of software instruments to fulfil all creative desires and effective communication ideas. The following are Google Slides, Microsoft PowerPoint, Apple Keynote, Adobe Creative Suite, etc. Here’s an in-depth look at each one:
1) Google Slides
Google Slides is a truly web-based Presentation tool that allows simultaneous contributions from collaborators with effortless online accessibility. Here’s how it benefits Presentation Specialists:
a) Collaboration: The cloud version of Google Slides allows many team members to work together while making a Presentation. Experts can amend, comment, and provide critical remarks immediately, which increases productivity and simplifies the workflow.
b) Accessibility: Lectures can be viewed from any device the specialists have through the web. This is key during collaborations with different units and across various locations.
c) Integration: Google Slides is excellently integrated with other Google Workspace applications, such as Docs and Sheets, thus facilitating the process of adding outside documented data, spreadsheets, or charts to the slides. It offers a colourful inventory of Presentations on various subjects and topics and much more.
d) Customisation: Although it is less popular than the more resourceful tools, Google Slides still provides templates, shapes, and basic animations that are good enough for covering simple Presentations.
2) Microsoft PowerPoint
MS PowerPoint continues to be a must-have for Presentation Specialists with diverse creative skills, as it provides myriad tools to build appealing Presentation designs. Its notable strengths include:
a) Templates and themes: PowerPoint offers a set of choices among templates and themes that establish the visual tone for a Presentation. The Presentation Specialists are capable of quickly personalising company logos.
b) Advanced animations and transitions: Its huge animations and transitions require specialists to create click animations that highlight crucial points and capture the audience's attention.
c) Data Visualisation: Another strength is the experts' capacity to combine PowerPoint with Excel for Data Visualisation. They can create live charts and graphs that self-refresh with any modifications executed in the source Excel documents.
d) Customisation: Arranging all these things individually (slide layouts, infographics, and charts), as needed, is a task for experts only. The program also has a feature that registers multimedia content like video and audio to make it more complete.
e) Add-ins: The third-party add-in PowerPoint also gives room for diagramming tools, timeline development, and other features that improve its functionality.
3) Apple Keynote
Apple’s Keynote is renowned for its slick, easy-to-use interface and impressive visual templates, which are very important for people who specialise in Presentations and focus on decor.
a) Templates: Using Keynote’s professionally designed templates in this Presentation mode allows experts to develop a beautiful document efficiently. The collection includes templates in different styles, from minimalistic to vivid and designer.
b) Animation: The "Magic Mov" feature makes the program move objects smoothly by changing slides and adding cinematic transitions. Keynote features an array of animations that enable the animator to add dynamics to the text and shapes to give them prominence.
c) Multimedia integration: Keynote has embedded features that can accommodate mixed media, including video, audio, and live feeds, making this Presentation extremely interactive.
d) Export Options: Experts can export their shots into different formats, including PDF and PowerPoint, to be compatible with all other platforms.
4) Adobe Creative Suite
The Adobe Creative Suite includes multiple applications that Presentation Specialists use to refine their Presentations:
a) Adobe Illustrator: This design tool is used for illustrations, icons, and vector graphics. Specialists can build custom forms, signs, and works of art that guarantee the Presentations are one-of-a-kind and identify the brand.
b) Adobe Photoshop: Photoshop is the most commonly used software for retouching and enhancing images inserted into PowerPoint Presentations. Skilled artists can, for instance, cut out backgrounds, play with colours, and adapt effects to create a unified visual storyline.
c) Adobe InDesign: This software is also used for desktop publishing and provides layout tools for complex Presentations of multiple content formats. It is beneficial for those who design multimedia Presentations.
d) Adobe After Effects: Complex Presentations with high-end animations or video aftereffects are indispensable. In other words, it enables the Presentation Specialists to apply custom motion graphics, effects, and astonishing intros and transitions that will picture-perfect their Presentations as if they were taken from the big screen.
Do you want to improve your Data Analysis skills? Register now for our Data Analysis Skills Course today!
Conclusion
We hope you understand what is required to become a Performance Specialist. This blog discussed the Presentation Specialist Job Description, which will help you understand the necessary qualifications and responsibilities to become a successful professional.
Learn how to become an expert professional by learning the art of Presentation – sign up now for our Presenting with Impact Training!
Frequently Asked Questions
Effective Presentation skills enhance your professional career by enabling clear communication of ideas, persuading stakeholders, and showcasing expertise.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Presentation Skills Training , including the Presentation Skills Training, Presenting with Impact Training, and Business Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Key Elements of Presentation .
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Presentation, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Presentation skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 5th Jul 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 6th Sep 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 1st Nov 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- A Complete Guide on Product Presentations
- Advanced Presentation Techniques
Using Data Visualization to Tell a Story

Aayush Jain
Choosing the right chart type for your data.

Understanding the Importance of Chart Selection
Choosing the right chart type for your data is crucial for effective data visualization. The appropriate chart not only makes the data more comprehensible but also enhances the overall impact of your presentation. Different types of charts are suited for different kinds of data and objectives. For instance, bar charts are excellent for comparing quantities, while line charts are ideal for showing trends over time. Understanding how to present product features using the right chart can transform complex data into compelling visual stories.
Deep Dive into Chart Types
There are several types of charts, each serving a unique purpose. Bar charts and column charts are best for comparing categories of data, making them ideal for product comparison presentations. Line charts are used to display data over a continuous period, making them perfect for showing trends and changes. Pie charts and donut charts are useful for illustrating proportions and parts of a whole. Scatter plots and bubble charts are excellent for showing relationships between variables. Selecting the right chart type involves understanding the nature of your data and the message you want to convey. For product managers, choosing the right chart type can aid in communicating key benefits and product features effectively.
Real-World Examples of Effective Chart Use
An excellent example of effective chart use is seen in Google's annual reports template, which utilize a variety of chart types to present data on user growth, market share, and financial performance. Another example is the product comparison powerpoint templates used by companies like Microsoft to showcase the differences between their product offerings. These templates often feature bar charts and line charts to highlight key differences and benefits. Using the right charts helps in simplifying complex data and making it accessible to a broader audience. It also aids in emphasizing the most critical aspects of the data, ensuring that the audience grasps the key points quickly.
Research and References Supporting Chart Selection
Research from the Journal of Data Visualization highlights that the correct choice of chart type can improve data comprehension by up to 40%. A study by the Nielsen Norman Group found that audiences are more likely to retain information presented in a well-chosen chart compared to text-only presentations. Additionally, data from the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction suggests that using appropriate chart types can significantly enhance user engagement and understanding. These findings underscore the importance of selecting the right chart type to create effective and impactful product presentations.
Simplifying Complex Data for Audience Understanding

Making Complex Data Accessible
Simplifying complex data is essential for ensuring that your audience can understand and engage with your presentation. Complex data can be overwhelming and difficult to process, but by breaking it down and presenting it in a clear and concise manner, you can make it accessible to a broader audience. Simplifying data involves using straightforward visuals, clear language, and focusing on key points to effectively communicate your message. This approach is particularly important when you need to convey product features or compare different products.
Techniques for Simplifying Data
Several techniques can be employed to simplify complex data. One effective method is to use summary statistics and visuals like infographics that highlight the key benefits and insights without overwhelming the audience with raw data. Grouping related data points and using visual aids such as charts and graphs can help in illustrating trends and patterns clearly. Tools like presentation templates can assist in organizing information logically and coherently. For product comparison presentations, side-by-side comparisons using tables or simplified charts can help in highlighting differences and similarities succinctly.
Practical Applications and Examples
A practical example of simplifying complex data is seen in the annual reports of companies like IBM, where large datasets are distilled into key takeaways using visual aids and summary sections. Another example is the use of Google Slides by educational institutions to present research findings. These presentations often employ bullet points, charts, and infographics to simplify complex data and highlight the most important aspects. For product managers, using product comparison PowerPoint templates can help in creating clear and concise presentations that focus on the key benefits and features of different products, making it easier for potential customers to make informed decisions.
Research and References Supporting Data Simplification
Research from the Data Visualization Society indicates that simplifying complex data can enhance audience understanding and retention by up to 30%. A study by the Harvard Business Review found that presentations that simplify data effectively are more likely to engage and persuade audiences. Additionally, data from the Journal of Business Research highlights that using visual aids to simplify complex information can significantly improve the organization, clarity and impact of presentations. These findings underscore the importance of making complex data accessible to ensure effective communication and audience engagement.
Storytelling Through Timelines and Journey Maps

The Power of Timelines and Journey Maps in Presentations
Timelines and journey maps are powerful tools for storytelling in product presentations. They help in visualizing the progression of events, milestones, or processes over time, making it easier for the audience to understand and engage with the narrative. By using timelines and journey maps, presenters can create a structured and compelling story that highlights the development, impact, and benefits of a product. This approach is particularly effective in illustrating the entire product development process and showcasing key milestones.
Understanding Timelines and Journey Maps
Timelines are linear visual representations of events in chronological order, commonly used to show the history or evolution of a product. Journey maps, on the other hand, focus on the customer experience, illustrating the steps a customer goes through when interacting with a product or service. Both tools are essential for breaking down complex information into a more digestible format, helping the audience follow the story and understand the key benefits. For product managers, using these tools can effectively communicate the product development process and the value it brings to potential customers.
Real-World Examples and Applications
An excellent example of using timelines is seen in Apple's product launch events. Apple often uses timelines to highlight the history and evolution of their products, demonstrating innovation and progress over time. Another example is journey maps used by companies like Airbnb to illustrate the customer experience from booking to check-out, highlighting key touchpoints and benefits. For product comparison presentations, timelines can be used to show the development stages of different products, while journey maps can illustrate how each product meets customer needs at various stages. These examples demonstrate the effectiveness of timelines and journey maps in creating engaging and informative presentations.
Research and References Supporting Storytelling Tools
Research from the company the Nielsen Norman Group indicates that using timelines and journey maps can increase audience engagement and understanding by up to 40%. A study by the Content Marketing Institute found that visual storytelling tools like timelines and journey maps are highly effective in conveying complex information and enhancing recall. Additionally, data from the Journal of Consumer Research highlights that customers are more likely to engage with and remember presentations that use structured storytelling methods. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating timelines and journey maps into product presentations to create a compelling narrative and enhance audience engagement.
Interactive Data Visualizations for Online Presentations

Enhancing Engagement with Interactive Visualizations
Interactive data visualizations have become an essential tool for online presentations, offering a dynamic and engaging way to present complex information. Unlike static charts or graphs, interactive visualizations allow the audience to explore data in real-time, providing a more immersive experience. This interactivity can significantly enhance audience engagement, making the data more accessible and understandable. Utilizing interactive data visualizations can be particularly effective in product comparison presentations, where detailed data exploration is often required.
The Benefits of Interactive Visualizations
Interactive visualizations offer several key benefits. They enable users to drill down into specific data points, customize their views, and gain insights tailored to their interests. This level of interactivity helps in simplifying complex data and making it more relatable. Tools like Tableau, Power BI, and Google Data Studio offer robust features for creating interactive visualizations that can be embedded into online presentations. For product managers, these tools can help illustrate key benefits, product features, and comparative analyses effectively, providing a comprehensive view that static slides cannot achieve.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
A notable example of effective use of interactive data visualizations is the New York Times, which often uses interactive graphics in its online articles to help readers explore complex data sets. Another example is how companies like IBM use interactive dashboards in their product presentations to showcase performance metrics, trends, and forecasts. For product comparison PowerPoint templates, incorporating interactive elements like clickable charts and dynamic graphs can help potential customers engage with the data and make more informed decisions. These applications demonstrate how interactive visualizations can enhance the storytelling aspect of presentations and provide a richer experience for the audience.
Research and References Supporting Interactive Visualizations
Research from the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction indicates that interactive data visualizations can increase audience engagement and comprehension by up to 60%. A study by the Data Visualization Society found that interactive elements in presentations significantly improve user satisfaction and data recall. Additionally, data from the Harvard Business Review highlights that companies using interactive data tools report higher levels of audience engagement and decision-making effectiveness. These findings emphasize the importance of integrating interactive data visualizations into online presentations to enhance engagement and provide deeper insights.
Incorporating Infographics for Summary Insights

The Power of Infographics in Presentations
Infographics are an effective way to summarize and present data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format. They combine visuals, text, and data to tell a cohesive story, making complex information more accessible to the audience. In product presentations, infographics can be used to highlight key benefits, compare product features, and provide a quick overview of important data. By incorporating infographics, presenters can enhance their message and ensure that the audience retains the most critical insights.
Understanding the Role of Infographics
Infographics are designed to convey information quickly and clearly. They are particularly useful for presenting data that might be too detailed or cumbersome to explain verbally. Infographics can include various design elements such as charts, icons, and illustrations that help break down information into manageable chunks. For product managers, using infographics in presentations can simplify the explanation of product benefits, features, and comparisons, making it easier for potential customers to understand and engage with the content. Infographics can also be used to illustrate the entire product development process or to present a product comparison PowerPoint presentation template effectively.
A prime example of effective infographic use is seen in annual reports by companies like Salesforce, which use infographics to present sales data, market trends, and key performance indicators in a concise and visually appealing manner. Another example is HubSpot’s marketing materials, which frequently incorporate infographics to explain marketing strategies, customer journey maps, and product benefits. For product comparison presentations, infographics can be used to provide a side-by-side comparison of different products, highlighting the key features and benefits in an easy-to-read format. These applications show how infographics can enhance the clarity and impact of presentations.
Research and References Supporting Infographic Use
Research from the Nielsen Norman Group indicates that infographics can improve comprehension and retention by up to 80%. A study by the Visual Communication Journal found that presentations incorporating infographics are more likely to engage the audience and convey complex information effectively. Additionally, data from the Content Marketing Institute highlights that infographics are among the most shared and liked content on social media, emphasizing their effectiveness in communication. These findings underscore the importance and success of incorporating infographics into product presentations to enhance understanding and engagement.
Using Animation to Highlight Key Data Points

Enhancing Presentations with Animation
Animation can be a powerful tool in product presentations, helping to highlight key data points and draw attention to important information. When used effectively, animation can make data more engaging and easier to access and understand, guiding the audience through the narrative of your presentation. By animating elements such as graphs, charts, and infographics, presenters can create a dynamic experience that keeps the audience’s attention and emphasizes critical insights.
The Role of Animation in Data Visualization
Animation in data visualization involves the use of movement to illustrate changes in data over time or to draw focus to specific elements. This can include transitions between slides, animated charts that update in real-time, or highlighting parts of a graph to emphasize trends or comparisons. For product managers, using animation in product comparison presentations can effectively showcase differences in product features and benefits, making complex data more accessible. Tools like PowerPoint, Google Slides, and specialized software like After Effects can be used to create these animations.
A notable example of using animation to deliver more effectively is seen in TED Talks presentations, where speakers often use animated graphics to illustrate key points and make their data more engaging. Another example is in corporate presentations by companies like Apple, which use smooth transitions and animated elements to highlight new product features and updates. In product comparison PowerPoint templates, animation can be used to compare products side-by-side dynamically, showing real-time changes and updates. These examples demonstrate how animation can enhance the storytelling aspect of presentations and make complex data more digestible.
Research and References Supporting Animation Use
Research from the Journal of Educational Psychology indicates that animated graphics can improve understanding and retention of information by up to 30%. A study by the Association for Computing Machinery found that presentations with animated data visualizations are more engaging and effective in communicating complex information. Additionally, data from the International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction highlights that animation can significantly enhance user experience and focus on product details. These findings underscore the importance of incorporating animation into product presentations to highlight key data points and maintain audience engagement.
Best Practices for Data Comparisons and Benchmarks

Effective Data Comparison Techniques
Data comparisons and benchmarks are essential for providing context and evaluating performance in product presentations. Effective comparison techniques help to highlight differences, similarities, and trends, making the data more meaningful and actionable for the audience. By following best practices for data comparisons, presenters can ensure their audience understands the key takeaways and the implications of the data. This is particularly important in product comparison presentations, where clear and accurate comparisons can influence decision-making.
Principles of Effective Data Comparisons
To effectively compare data, it is important to use consistent scales and units, clear labeling, and appropriate chart types. Consistent scales ensure that comparisons are accurate and easy to understand. Clear labeling helps to avoid confusion and ensures that the audience knows what each data point represents. Choosing the right chart type, such as bar charts for categorical comparisons or line charts for trends over time, is crucial for presenting data effectively. Product managers can use these principles to create compelling product benefits presentations that highlight the advantages of their products over competitors.
A practical example of effective data comparison is seen in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant reports, which use a standardized grid to compare technology providers based on their ability to execute and completeness of vision. Another example is the use of comparison tables in consumer electronics reviews, where features, specifications, and prices of different products are compared side-by-side. For product comparison PowerPoint templates, using similar techniques can help in presenting product features and benefits clearly, making it easier for potential customers to evaluate their options. These examples demonstrate how following best practices in data comparison can enhance the clarity and impact of presentations.
Research and References Supporting Best Practices
Research from the Data Visualization Society indicates that following best practices in data comparison can improve audience comprehension and retention by up to 25%. A study by the Harvard Business Review found that clear and accurate data comparisons are critical for effective decision-making in business contexts. Additionally, data from the International Journal of Business Communication highlights the idea that well-executed benchmarks and comparisons can significantly enhance the persuasiveness of presentations. These findings underscore the importance of adhering to best practices for data comparisons and benchmarks to create impactful and informative product presentations.
Techniques for Live Data Presentation and Updates

The Importance of Live Data in Presentations
Presenting live data can significantly enhance the relevance and impact of a product presentation. Live data presentations involve displaying data that is updated in real-time, providing the audience with the most current information available. This technique is particularly useful for showcasing ongoing trends, performance metrics, and other time-sensitive information. By incorporating live data, presenters can demonstrate transparency and provide a dynamic and engaging experience for their audience.
Methods for Incorporating Live Data
There are several methods to incorporate live data into presentations. Using tools like Google Sheets or Microsoft Excel with live data feeds, presenters can embed dynamic charts and graphs into their slides. Platforms like Tableau and Power BI offer advanced capabilities for real-time data visualization and integration with various data sources. These tools allow product managers to display up-to-date metrics, customer feedback, and sales figures during their presentations. Additionally, leveraging APIs can enable the integration of live data from external sources, such as social media feeds or financial markets, into your presentation.
A notable example of live data presentation is seen in financial news networks like Bloomberg and CNBC, where live stock market data is continuously updated on screen. Another example is in corporate board meetings, where companies like Amazon use live dashboards to present key performance indicators (KPIs) and operational metrics in real-time. For product comparison presentations, using live data can help demonstrate the current performance and customer feedback of various products, providing a compelling and up-to-date comparison. These examples illustrate how live data can add value and immediacy to presentations, making them more engaging and informative.
Research and References Supporting Live Data Use
Research from the International Journal of Information Management indicates that live data presentations can improve audience engagement and decision-making by up to 35%. A study by the Data Visualization Society found that real-time data visualizations are perceived as more credible and impactful. Additionally, data from the Journal of Business Research highlights that incorporating live data into presentations can significantly enhance the perceived transparency and reliability of the information presented. These findings emphasize the importance of using live data to create dynamic and impactful product presentations.
Visualizing Qualitative Data

The Challenge of Visualizing Qualitative Data
Visualizing qualitative data presents unique challenges compared to quantitative data, as it involves non-numeric information such as opinions, experiences, and narratives. However, effectively visualizing qualitative data is essential for providing context and insights in product presentations. By using appropriate visualization techniques, presenters can make qualitative data more accessible and engaging, helping the audience understand the underlying themes and patterns. This approach is particularly useful for showcasing customer feedback, market research findings, and user experiences.
Techniques for Visualizing Qualitative Data
Several techniques can be used to visualize qualitative data. Word clouds are a popular method for displaying the frequency of words in a body of text, highlighting the most common themes. Heat maps can show the intensity of responses across different categories, while affinity diagrams can organize and cluster qualitative data into meaningful groups. Additionally, narrative visualizations, such as storyboards or journey maps, can illustrate customer experiences or product development processes. These techniques help in transforming qualitative data into visual formats that are easier to interpret and present.
An example of effective qualitative data visualization is seen in customer feedback reports by companies like Amazon, which use word clouds and sentiment analysis to highlight common themes and customer sentiments. Another example is the use of journey maps by UX design firms to illustrate user experiences and interactions with delivering a product. For product comparison presentations, using qualitative data visualization techniques can help showcase customer testimonials, market research insights, and user experiences, providing a comprehensive view of the product’s impact. These examples demonstrate how qualitative data visualization can enhance the storytelling aspect of presentations.
Research and References Supporting Qualitative Visualization
Research from the Journal of Qualitative Research highlights that visualizing qualitative data can improve understanding and retention by up to 40%. A study by the Nielsen Norman Group found that qualitative data visualizations are more effective in conveying complex ideas, narratives and experiences. Additionally, data from the Content Marketing Institute indicates that presentations incorporating qualitative visualizations are perceived as more engaging and informative. These findings underscore the importance of using visualization techniques to effectively present qualitative data and enhance audience engagement in product presentations.
Tools and Software for Advanced Data Visualization

Leveraging Advanced Tools for Data Visualization
Utilizing advanced tools and software for data visualization can greatly enhance the quality and effectiveness of product presentations. These tools offer sophisticated features that enable users to create interactive, dynamic, and visually appealing visualizations. By leveraging these advanced tools, presenters can better convey complex data, highlight key insights, and engage their audience more effectively. Understanding the capabilities of these tools and how to use them can transform the way data is presented.
Overview of Advanced Visualization Tools
Several advanced data visualization tools stand out for their capabilities and ease of use. Tableau is renowned for its interactive dashboards and ability to connect to multiple data sources. Power BI by Microsoft offers robust data integration and real-time analytics features, making it ideal for business presentations. Google Data Studio provides an accessible platform for creating interactive reports and visualizations, integrating seamlessly with other Google services. For those requiring more customization, D3.js is a powerful JavaScript library solution that allows for the creation of complex, custom visualizations. These tools enable product managers to present product features, comparisons, and benefits in a compelling and understandable manner.
A practical example of using advanced visualization tools is seen in financial services companies like Goldman Sachs, which use Tableau to create interactive financial dashboards that help clients understand market trends and investment opportunities. Another example is how marketing teams at companies like Unilever use Power BI to analyze and present consumer data, showcasing key insights and trends. For product comparison presentations, tools like Google Data Studio can be used to create dynamic reports that update in real-time, providing the most current data to potential customers. These applications demonstrate the effectiveness of advanced tools in creating impactful data visualizations.
Research and References Supporting Advanced Tool Use
Research from the Data Visualization Society indicates that using advanced visualization tools can improve data comprehension and decision-making by up to 50%. A study by the Business Application Research Center (BARC) found that companies using advanced data visualization tools reported higher levels of data-driven decision-making and business performance. Additionally, data from Gartner highlights that organizations leveraging tools like Tableau and Power BI see significant improvements in their ability to communicate complex data effectively. These findings underscore the importance of utilizing advanced tools and software for data visualization to enhance the impact of product presentations.
Frequently Asked Questions

1. How to present a product feature?
To present a product feature effectively, start by clearly explaining what the feature is and how it works. Use visuals such as diagrams or screenshots to illustrate the feature. Highlight the benefits of the feature, focusing on how it solves a problem or enhances the user experience. Finally, provide real-world examples or customer testimonials to demonstrate the feature's value in action.
2. How to represent features of a product?
Representing features of a product involves using a combination of text, visuals, and demonstrations. Create detailed descriptions for each feature, supplemented with high-quality images or videos showing the feature in use. Use comparison tables or charts to highlight how these features stand out against competitors. Incorporate infographics to summarize key benefits and provide a clear, visual representation of the product’s capabilities.
3. How do you present the features and benefits of a product?
To present the features and benefits of a product, start with a brief overview of the product and its purpose. List the key features and describe each one in detail, emphasizing how they function. Follow this with a discussion of the benefits, explaining how each feature contributes to solving a problem or improving the user experience. Use customer testimonials, case studies, and real-world examples to reinforce the benefits.
4. How do you introduce a new product feature?
Introducing a new product feature involves a clear and engaging presentation. Begin by explaining the context or problem that the new feature addresses. Provide a detailed description of the feature and how it works, using visuals and demonstrations. Highlight the key benefits and impact of the feature on the user experience. Finally, showcase any early feedback or testimonials from users who have tested the feature.
5. What is an example of a product benefit?
An example of a product benefit could be increased efficiency. For instance, a software product might automate repetitive tasks, saving users time and effort and reducing the potential for errors. This benefit can be highlighted by showing how the product streamlines workflows and allows users to focus on more critical tasks, ultimately enhancing productivity.
6. What should be included in a product presentation?
A product presentation and marketing team should include the following elements:
- Introduction: Overview of the product and its purpose.
- Problem Statement: The issue the product solves.
- Features and Benefits: Detailed explanation of the product’s features and their advantages.
- Demonstration: Visual or live demo of the product in action.
- Testimonials: Customer feedback or case studies.
- Call to Action: Clear next steps for the audience, such as purchasing the product or requesting a demo.
7. What is the benefit slide of a product?
The benefit slide of a product presentation highlights the key advantages of the product. It summarizes how the product improves the user’s life or business operations, focusing on the tangible outcomes such as time savings, cost reduction, increased productivity, or enhanced user experience. This slide should be visually appealing and clearly communicate the primary benefits.
8. How to identify product benefits?
Identifying product benefits involves understanding the needs and pain points of your target audience. Conduct market research and gather customer feedback to identify common challenges and desired outcomes. Analyze how your product’s features address these needs and translate these features into specific, tangible benefits. Highlight how the product improves efficiency, saves time, reduces costs, or enhances the user experience.
9. How do you make a successful product presentation?
To make a successful product presentation:
- Know Your Audience: Tailor the presentation to the interests and needs of your audience.
- Clear Structure: Organize the content logically with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion.
- Engaging Visuals: Use high-quality images, videos, and infographics to illustrate key points.
- Interactive Elements: Incorporate demos, Q&A sessions, and interactive visualizations to engage the audience.
- Practice: Rehearse the presentation multiple times to ensure smooth delivery and build confidence.
10. What are the 5 rules needed for presenting a presentation?
The five rules for presenting a presentation are:
- Clarity: Ensure your message is clear and easily understood.
- Engagement: Use visuals, stories, and examples to keep the audience engaged.
- Simplicity: Avoid clutter and keep slides simple, focusing on key points.
- Relevance: Tailor your content to the interests and needs of your audience.
- Practice: Rehearse your presentation multiple times to ensure smooth delivery and build confidence.
Discover how we can create magic in your communication
%20(1).jpg)
Best Presentation Design Agencies in Mumbai
TL;DRIn the competitive landscape of presentation design, finding the right agency is crucial for effective communication. This guide highlights the top 10 presentation design agencies in Mumbai, showcasing their unique strengths and services. Among them, INK PPT stands out for its innovative approach, global delivery capability, and exceptional quality,
Different Types of Special Presentations
Investor Pitches and Fundraising Decks Crafting Effective Investor Pitches and Fundraising Decks Creating a compelling investor pitch and fundraising deck is crucial for startups and businesses seeking to secure investment. These presentations aim to convince potential investors of the viability and profitability of a business idea or product. The key
Sustainability in Presentation Design and Delivery
Eco-Friendly Materials for In-Person Presentation Handouts Embracing Eco-Friendly Materials for Presentations In today’s environmentally conscious world, using eco-friendly materials for in-person presentation handouts is a crucial step towards sustainability. Traditional handouts often result in significant paper waste and contribute to environmental degradation. By choosing sustainable alternatives, presenters can reduce
- UC Berkeley
- Sign Up to Volunteer
- I School Slack
- Alumni News
- Alumni Events
- Alumni Accounts
- Career Support
- Academic Mission
- Diversity & Inclusion Resources
- DEIBJ Leadership
- Featured Faculty
- Featured Alumni
- Work at the I School
- Subscribe to Email Announcements
- Logos & Style Guide
- Directions & Parking
The School of Information is UC Berkeley’s newest professional school. Located in the center of campus, the I School is a graduate research and education community committed to expanding access to information and to improving its usability, reliability, and credibility while preserving security and privacy.
- Career Outcomes
- Degree Requirements
- Paths Through the MIMS Degree
- Final Project
- Funding Your Education
- Admissions Events
- Request Information
- Capstone Project
- Jack Larson Data for Good Fellowship
- Tuition & Fees
- Women in MIDS
- MIDS Curriculum News
- MICS Student News
- Dissertations
- Applied Data Science Certificate
- ICTD Certificate
- Citizen Clinic
The School of Information offers four degrees:
The Master of Information Management and Systems (MIMS) program educates information professionals to provide leadership for an information-driven world.
The Master of Information and Data Science (MIDS) is an online degree preparing data science professionals to solve real-world problems. The 5th Year MIDS program is a streamlined path to a MIDS degree for Cal undergraduates.
The Master of Information and Cybersecurity (MICS) is an online degree preparing cybersecurity leaders for complex cybersecurity challenges.
Our Ph.D. in Information Science is a research program for next-generation scholars of the information age.
- Info 247. Information Visualization and Presentation
- Spring 2024 Course Schedule
- Summer 2024 Course Schedule
- Fall 2024 Course Schedule
The School of Information's courses bridge the disciplines of information and computer science, design, social sciences, management, law, and policy. We welcome interest in our graduate-level Information classes from current UC Berkeley graduate and undergraduate students and community members. More information about signing up for classes.
- Ladder & Adjunct Faculty
- MIMS Students
- MIDS Students
- 5th Year MIDS Students
- MICS Students
- Ph.D. Students

- Publications
- Centers & Labs
- Computer-mediated Communication
- Data Science
- Entrepreneurship
- Human-computer Interaction (HCI)
- Information Economics
- Information Organization
- Information Policy
- Information Retrieval & Search
- Information Visualization
- Social & Cultural Studies
- Technology for Developing Regions
- User Experience Research
Research by faculty members and doctoral students keeps the I School on the vanguard of contemporary information needs and solutions.
The I School is also home to several active centers and labs, including the Center for Long-Term Cybersecurity (CLTC) , the Center for Technology, Society & Policy , and the BioSENSE Lab .
- Why Hire I School?
- Request a Resume Book
- Leadership Development Program
- Mailing List
- For Nonprofit and Government Employers
- Jobscan & Applicant Tracking Systems
- Resume & LinkedIn Review
- Resume Book
I School graduate students and alumni have expertise in data science, user experience design & research, product management, engineering, information policy, cybersecurity, and more — learn more about hiring I School students and alumni .
- Press Coverage
- I School Voices

The School of Information’s May 2024 Commencement presented an opportunity to honor faculty and student achievements...

A group of scholars from the School of Information are tackling the issue of illegal sand mining with the help of a...

When the Bancroft Library received over 100,000 Japanese-American internment “individual record” forms (WRA-26) from...

On the March 27th episode of PBS’s documentary series Nova titled “A.I. Revolution,” correspondent Miles O’Brien...
- Distinguished Lecture Series
- I School Lectures
- Information Access Seminars
- CLTC Events
- Women in MIDS Events

Information Visualization and Presentation
Course description.
Information visualization is widely used in media, business, and engineering disciplines to help people analyze and understand the information at hand. The industry has grown exponentially over the last few years. As a result there are more visualization tools available, which have in turn lowered the barrier of entry for creating visualizations.
This course provides an overview of the field of Information Visualization. It follows a hands-on approach. Readings and lectures will cover basic visualization principles and tools. Labs will focus on practical introductions to tools and frameworks. We will discuss existing visualizations and critique their effectiveness in conveying information. Finally, guest speakers from the industry will give an insight into how information visualization is used in practice.
All students are expected to participate in class discussion, complete lab assignments, and create an advanced interactive data visualization as a semester project.
Priority for attending this class is given to I School students. The semester project involves programming; therefore students are expected to have some coding experience. Interested students from other departments are invited to join the class if they can demonstrate the required skills.
Note: This course is offered for a letter grade only.
Note: Until 2014, this course was offered for 3 units.
Prerequisites
Requirements satisfied, signing up for i school classes.
Instructions for Berkeley undergrads, graduate students, and community members
Course History
Spring 2023, spring 2022, spring 2021, spring 2020, spring 2019, spring 2018, spring 2017, spring 2016, spring 2015, spring 2014, spring 2013, spring 2012, spring 2010, project gallery, last updated:.
- Application
What Is Data Visualization: Brief Theory, Useful Tips and Awesome Examples
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
By Al Boicheva
in Insights , Inspiration
3 years ago
Viewed 10,427 times
Spread the word about this article:
Updated: June 23, 2022
To create data visualization in order to present your data is no longer just a nice to have skill. Now, the skill to effectively sort and communicate your data through charts is a must-have for any business in any field that deals with data. Data visualization helps businesses quickly make sense of complex data and start making decisions based on that data. This is why today we’ll talk about what is data visualization. We’ll discuss how and why does it work, what type of charts to choose in what cases, how to create effective charts, and, of course, end with beautiful examples.
So let’s jump right in. As usual, don’t hesitate to fast-travel to a particular section of your interest.
Article overview: 1. What Does Data Visualization Mean? 2. How Does it Work? 3. When to Use it? 4. Why Use it? 5. Types of Data Visualization 6. Data Visualization VS Infographics: 5 Main Differences 7. How to Create Effective Data Visualization?: 5 Useful Tips 8. Examples of Data Visualization
1. What is Data Visualization?
Data Visualization is a graphic representation of data that aims to communicate numerous heavy data in an efficient way that is easier to grasp and understand . In a way, data visualization is the mapping between the original data and graphic elements that determine how the attributes of these elements vary. The visualization is usually made by the use of charts, lines, or points, bars, and maps.
- Data Viz is a branch of Descriptive statistics but it requires both design, computer, and statistical skills.
- Aesthetics and functionality go hand in hand to communicate complex statistics in an intuitive way.
- Data Viz tools and technologies are essential for making data-driven decisions.
- It’s a fine balance between form and functionality.
- Every STEM field benefits from understanding data.
2. How Does it Work?
If we can see it, our brains can internalize and reflect on it. This is why it’s much easier and more effective to make sense of a chart and see trends than to read a massive document that would take a lot of time and focus to rationalize. We wouldn’t want to repeat the cliche that humans are visual creatures, but it’s a fact that visualization is much more effective and comprehensive.
In a way, we can say that data Viz is a form of storytelling with the purpose to help us make decisions based on data. Such data might include:
- Tracking sales
- Identifying trends
- Identifying changes
- Monitoring goals
- Monitoring results
- Combining data
3. When to Use it?
Data visualization is useful for companies that deal with lots of data on a daily basis. It’s essential to have your data and trends instantly visible. Better than scrolling through colossal spreadsheets. When the trends stand out instantly this also helps your clients or viewers to understand them instead of getting lost in the clutter of numbers.
With that being said, Data Viz is suitable for:
- Annual reports
- Presentations
- Social media micronarratives
- Informational brochures
- Trend-trafficking
- Candlestick chart for financial analysis
- Determining routes
Common cases when data visualization sees use are in sales, marketing, healthcare, science, finances, politics, and logistics.
4. Why Use it?
Short answer: decision making. Data Visualization comes with the undeniable benefits of quickly recognizing patterns and interpret data. More specifically, it is an invaluable tool to determine the following cases.
- Identifying correlations between the relationship of variables.
- Getting market insights about audience behavior.
- Determining value vs risk metrics.
- Monitoring trends over time.
- Examining rates and potential through frequency.
- Ability to react to changes.
5. Types of Data Visualization
As you probably already guessed, Data Viz is much more than simple pie charts and graphs styled in a visually appealing way. The methods that this branch uses to visualize statistics include a series of effective types.
Map visualization is a great method to analyze and display geographically related information and present it accurately via maps. This intuitive way aims to distribute data by region. Since maps can be 2D or 3D, static or dynamic, there are numerous combinations one can use in order to create a Data Viz map.
COVID-19 Spending Data Visualization POGO by George Railean
The most common ones, however, are:
- Regional Maps: Classic maps that display countries, cities, or districts. They often represent data in different colors for different characteristics in each region.
- Line Maps: They usually contain space and time and are ideal for routing, especially for driving or taxi routes in the area due to their analysis of specific scenes.
- Point Maps: These maps distribute data of geographic information. They are ideal for businesses to pinpoint the exact locations of their buildings in a region.
- Heat Maps: They indicate the weight of a geographical area based on a specific property. For example, a heat map may distribute the saturation of infected people by area.
Charts present data in the form of graphs, diagrams, and tables. They are often confused with graphs since graphs are indeed a subcategory of charts. However, there is a small difference: graphs show the mathematical relationship between groups of data and is only one of the chart methods to represent data.
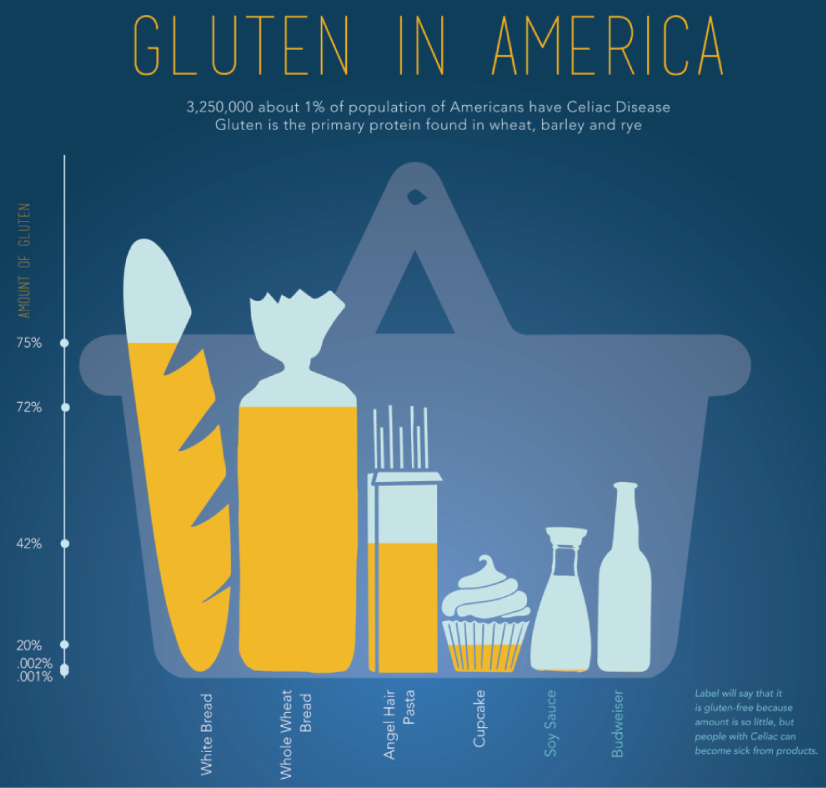
Infographic Data Visualization by Madeline VanRemmen
With that out of the way, let’s talk about the most basic types of charts in data visualization.
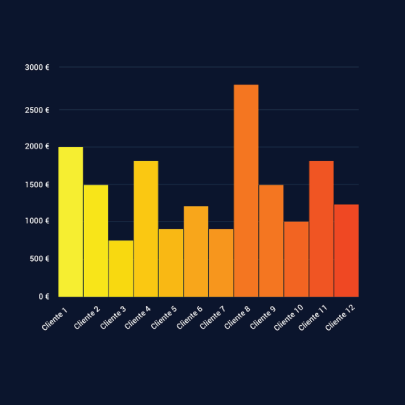
They use a series of bars that illustrate data development. They are ideal for lighter data and follow trends of no more than three variables or else, the bars become cluttered and hard to comprehend. Ideal for year-on-year comparisons and monthly breakdowns.
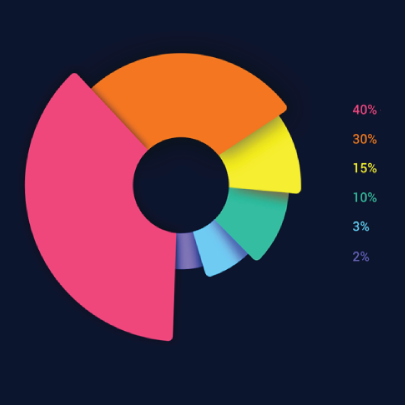
These familiar circular graphs divide data into portions. The bigger the slice, the bigger the portion. They are ideal for depicting sections of a whole and their sum must always be 100%. Avoid pie charts when you need to show data development over time or lack a value for any of the portions. Doughnut charts have the same use as pie charts.
They use a line or more than one lines that show development over time. It allows tracking multiple variables at the same time. A great example is tracking product sales by a brand over the years. Area charts have the same use as line charts.
Scatter Plot
These charts allow you to see patterns through data visualization. They have an x-axis and a y-axis for two different values. For example, if your x-axis contains information about car prices while the y-axis is about salaries, the positive or negative relationship will tell you about what a person’s car tells about their salary.
Unlike the charts we just discussed, tables show data in almost a raw format. They are ideal when your data is hard to present visually and aim to show specific numerical data that one is supposed to read rather than visualize.
Data Visualisation | To bee or not to bee by Aishwarya Anand Singh
For example, charts are perfect to display data about a particular illness over a time period in a particular area, but a table comes to better use when you also need to understand specifics such as causes, outcomes, relapses, a period of treatment, and so on.
6. Data Visualization VS Infographics
5 main differences.
They are not that different as both visually represent data. It is often you search for infographics and find images titled Data Visualization and the other way around. In many cases, however, these titles aren’t misleading. Why is that?
- Data visualization is made of just one element. It could be a map, a chart, or a table. Infographics , on the other hand, often include multiple Data Viz elements.
- Unlike data visualizations that can be simple or extremely complex and heavy, infographics are simple and target wider audiences. The latter is usually comprehensible even to people outside of the field of research the infographic represents.
- Interestingly enough, data Viz doesn’t offer narratives and conclusions, it’s a tool and basis for reaching those. While infographics, in most cases offer a story and a narrative. For example, a data visualization map may have the title “Air pollution saturation by region”, while an infographic with the same data would go “Areas A and B are the most polluted in Country C”.
- Data visualizations can be made in Excel or use other tools that automatically generate the design unless they are set for presentation or publishing. The aesthetics of infographics , however, are of great importance and the designs must be appealing to wider audiences.
- In terms of interaction, data visualizations often offer interactive charts, especially in an online form. Infographics, on the other hand, rarely have interaction and are usually static images.
While on topic, you could also be interested to check out these 50 engaging infographic examples that make complex data look great.
7. Tips to Create Effective Data Visualization
The process is naturally similar to creating Infographics and it revolves around understanding your data and audience. To be more precise, these are the main steps and best practices when it comes to preparing an effective visualization of data for your viewers to instantly understand.
1. Do Your Homework
Preparation is half the work already done. Before you even start visualizing data, you have to be sure you understand that data to the last detail.
Knowing your audience is undeniable another important part of the homework, as different audiences process information differently. Who are the people you’re visualizing data for? How do they process visual data? Is it enough to hand them a single pie chart or you’ll need a more in-depth visual report?
The third part of preparing is to determine exactly what you want to communicate to the audience. What kind of information you’re visualizing and does it reflect your goal?
And last, think about how much data you’ll be working with and take it into account.
2. Choose the Right Type of Chart
In a previous section, we listed the basic chart types that find use in data visualization. To determine best which one suits your work, there are a few things to consider.
- How many variables will you have in a chart?
- How many items will you place for each of your variables?
- What will be the relation between the values (time period, comparison, distributions, etc.)
With that being said, a pie chart would be ideal if you need to present what portions of a whole takes each item. For example, you can use it to showcase what percent of the market share takes a particular product. Pie charts, however, are unsuitable for distributions, comparisons, and following trends through time periods. Bar graphs, scatter plots,s and line graphs are much more effective in those cases.
Another example is how to use time in your charts. It’s way more accurate to use a horizontal axis because time should run left to right. It’s way more visually intuitive.
3. Sort your Data
Start with removing every piece of data that does not add value and is basically excess for the chart. Sometimes, you have to work with a huge amount of data which will inevitably make your chart pretty complex and hard to read. Don’t hesitate to split your information into two or more charts. If that won’t work for you, you could use highlights or change the entire type of chart with something that would fit better.
Tip: When you use bar charts and columns for comparison, sort the information in an ascending or a descending way by value instead of alphabetical order.
4. Use Colors to Your Advantage
In every form of visualization, colors are your best friend and the most powerful tool. They create contrasts, accents, and emphasis and lead the eye intuitively. Even here, color theory is important.
When you design your chart, make sure you don’t use more than 5 or 6 colors. Anything more than that will make your graph overwhelming and hard to read for your viewers. However, color intensity is a different thing that you can use to your advantage. For example, when you compare the same concept in different periods of time, you could sort your data from the lightest shade of your chosen color to its darker one. It creates a strong visual progression, proper to your timeline.
Things to consider when you choose colors:
- Different colors for different categories.
- A consistent color palette for all charts in a series that you will later compare.
- It’s appropriate to use color blind-friendly palettes.
5. Get Inspired
Always put your inspiration to work when you want to be at the top of your game. Look through examples, infographics, and other people’s work and see what works best for each type of data you need to implement.
This Twitter account Data Visualization Society is a great way to start. In the meantime, we’ll also handpick some amazing examples that will get you in the mood to start creating the visuals for your data.
8. Examples for Data Visualization
As another art form, Data Viz is a fertile ground for some amazing well-designed graphs that prove that data is beautiful. Now let’s check out some.
Dark Souls III Experience Data
We start with Meng Hsiao Wei’s personal project presenting his experience with playing Dark Souls 3. It’s a perfect example that infographics and data visualization are tools for personal designs as well. The research is pretty massive yet very professionally sorted into different types of charts for the different concepts. All data visualizations are made with the same color palette and look great in infographics.
My dark souls 3 playing data by Meng Hsiao Wei
Greatest Movies of all Time
Katie Silver has compiled a list of the 100 greatest movies of all time based on critics and crowd reviews. The visualization shows key data points for every movie such as year of release, oscar nominations and wins, budget, gross, IMDB score, genre, filming location, setting of the film, and production studio. All movies are ordered by the release date.
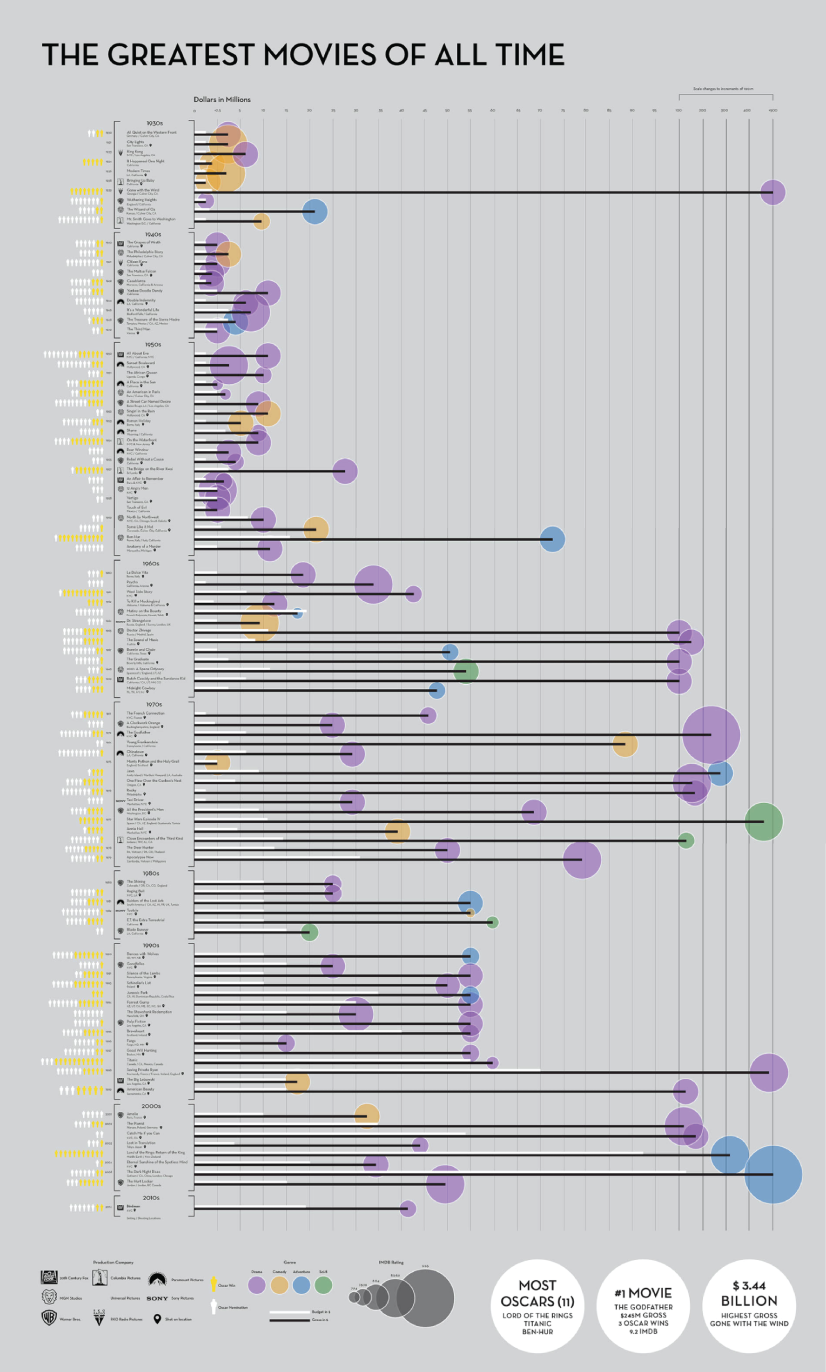
100 Greatest Movies Data Visualization by Katie Silver
The Most Violent Cities
Federica Fragapane shows data for the 50 most violent cities in the world in 2017. The items are arranged on a vertical axis based on population and ordered along the horizontal axis according to the homicide rate.
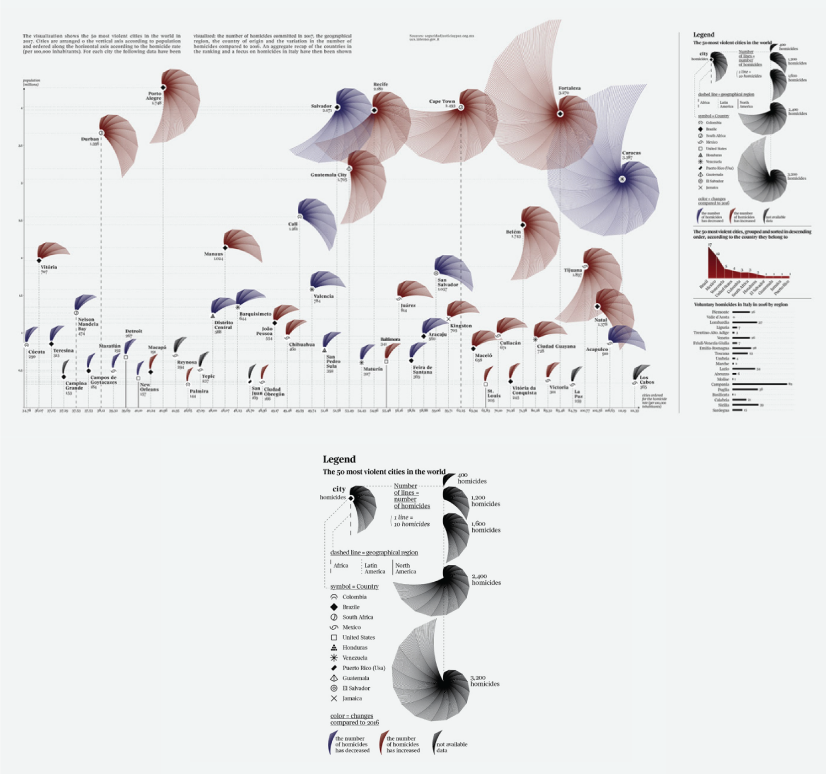
The Most Violent Cities by Federica Fragapane
Family Businesses as Data
These data visualizations and illustrations were made by Valerio Pellegrini for Perspectives Magazine. They show a pie chart with sector breakdown as well as a scatter plot for contribution for employment.
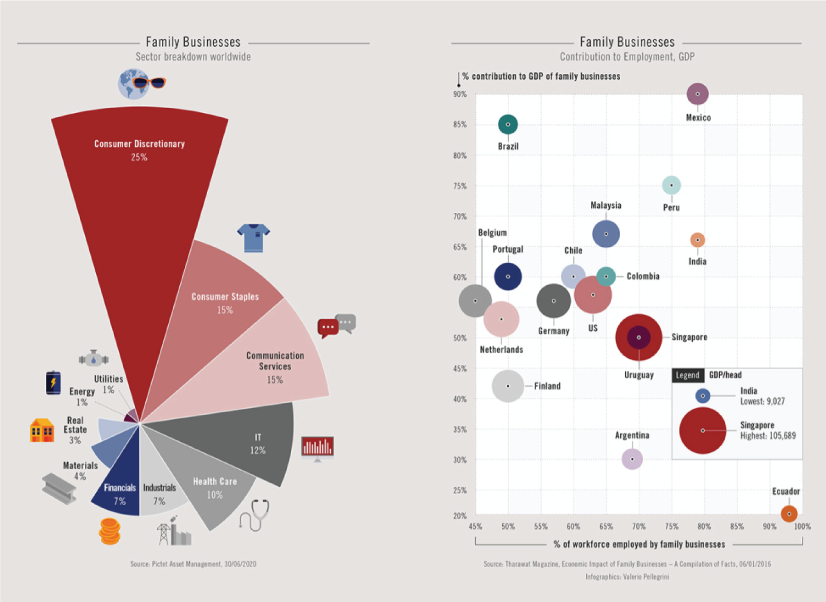
PERSPECTIVES MAGAZINE – Family Businesses by Valerio Pellegrini
Orbit Map of the Solar System
The map shows data on the orbits of more than 18000 asteroids in the solar system. Each asteroid is shown at its position on New Years’ Eve 1999, colored by type of asteroid.
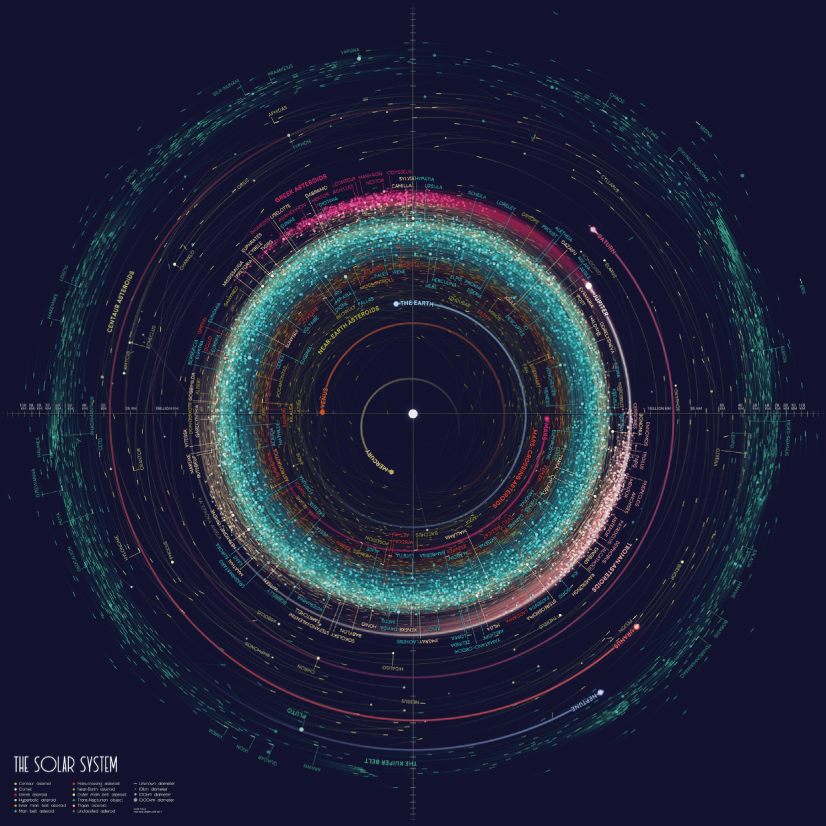
An Orbit Map of the Solar System by Eleanor Lutz
The Semantics Of Headlines
Katja Flükiger has a take on how headlines tell the story. The data visualization aims to communicate how much is the selling influencing the telling. The project was completed at Maryland Institute College of Art to visualize references to immigration and color-coding the value judgments implied by word choice and context.
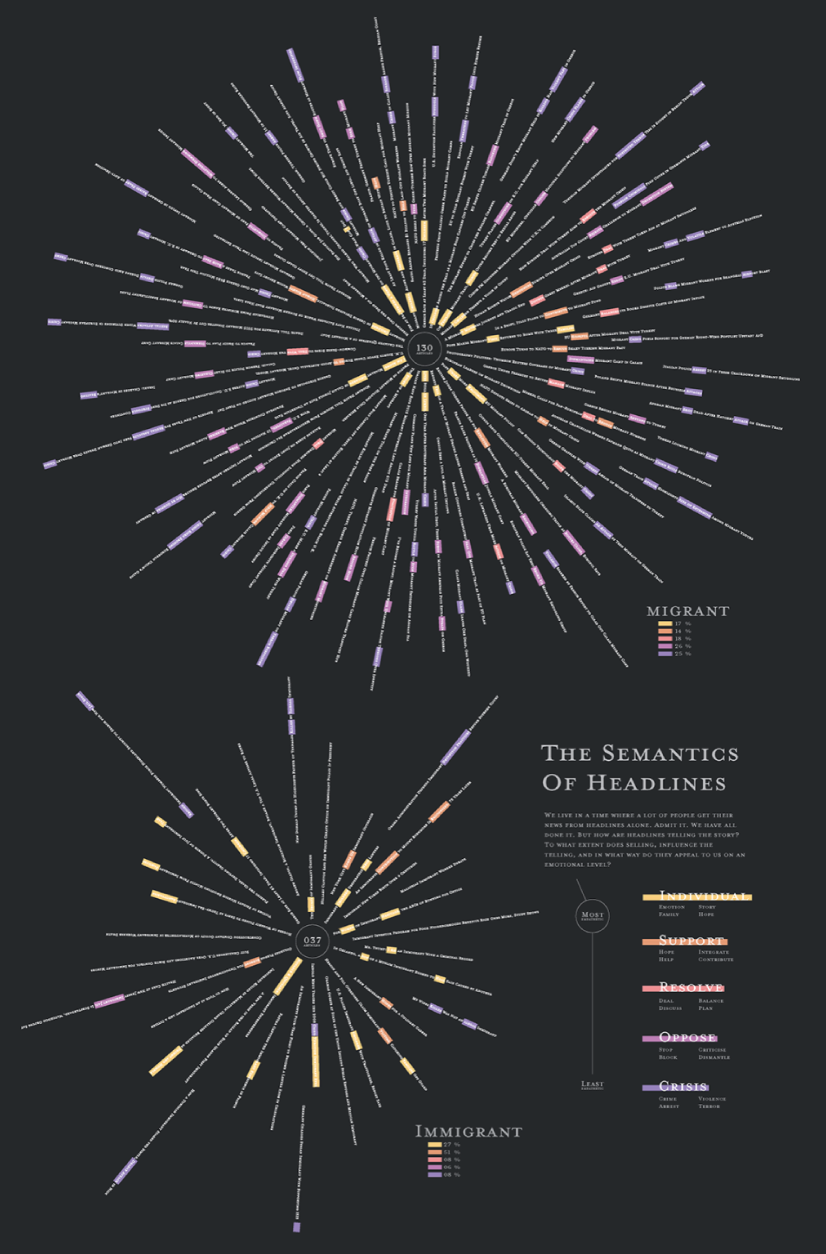
The Semantics of Headlines by Katja Flükiger
Moon and Earthquakes
This data visualization works on answering whether the moon is responsible for earthquakes. The chart features the time and intensity of earthquakes in response to the phase and orbit location of the moon.

Moon and Earthquakes by Aishwarya Anand Singh
Dawn of the Nanosats
The visualization shows the satellites launched from 2003 to 2015. The graph represents the type of institutions focused on projects as well as the nations that financed them. On the left, it is shown the number of launches per year and satellite applications.
WIRED UK – Dawn of the by Nanosats by Valerio Pellegrini
Final Words
Data visualization is not only a form of science but also a form of art. Its purpose is to help businesses in any field quickly make sense of complex data and start making decisions based on that data. To make your graphs efficient and easy to read, it’s all about knowing your data and audience. This way you’ll be able to choose the right type of chart and use visual techniques to your advantage.
You may also be interested in some of these related articles:
- Infographics for Marketing: How to Grab and Hold the Attention
- 12 Animated Infographics That Will Engage Your Mind from Start to Finish
- 50 Engaging Infographic Examples That Make Complex Ideas Look Great
- Good Color Combinations That Go Beyond Trends: Inspirational Examples and Ideas

Add some character to your visuals
Cartoon Characters, Design Bundles, Illustrations, Backgrounds and more...
Like us on Facebook
Subscribe to our newsletter
Be the first to know what’s new in the world of graphic design and illustrations.
- [email protected]
Browse High Quality Vector Graphics
E.g.: businessman, lion, girl…
Related Articles
How to use pinterest: tips & ideas for the pinner, 25 landing page examples with eye-candy illustrations, 20 storyboard examples for different uses of storyboarding [apps, ux, animation, commercials], mascot design – 10 brilliant transformations of famous mascots, 33 peculiar character design styles of the modern day, check out our infographics bundle with 500+ infographic templates:, enjoyed this article.
Don’t forget to share!
- Comments (2)

Al Boicheva
Al is an illustrator at GraphicMama with out-of-the-box thinking and a passion for anything creative. In her free time, you will see her drooling over tattoo art, Manga, and horror movies.

Thousands of vector graphics for your projects.
Hey! You made it all the way to the bottom!
Here are some other articles we think you may like:

Inspiration
Mood board examples and mega inspiration for your upcoming projects.
by Al Boicheva

Top Graphic Design Trends 2019: Fresh Hot & Bold
by Iveta Pavlova

37 Amazing Websites with Illustrations that Will Steal Your Heart
Looking for design bundles or cartoon characters.
A source of high-quality vector graphics offering a huge variety of premade character designs, graphic design bundles, Adobe Character Animator puppets, and more.
- Presentation Design
13 Best Free Presentation Websites Alternatives to PowerPoint in 2023
What is a presentation website?
Presentation websites are applications created to present information as a slide show. Slideshows are presentations that comprise charts, images, videos, and the standard text. They ensure that data is displayed clearly, summarized, and readable to the audience.
Slideshows work best when presented on a projector or a big screen. Intermittently, some users might print out slide shows as documents, but this is ill-suited for that purpose.
Any presentation tool must have three fundamental functions:
- A text editor: to input the contents of the presentation.
- An import function: to insert and manipulate images and other content.
- A slide-show or presenter mode: that displays the content in a nice, formatted way.
Slide shows often consist of a combination of text, video, images and charts. Their primary function is displaying clear, readable and summarized data to an audience.
Most presentations are shared and presented on a larger screen or through a digital projector. In rare occasions, slide presentations are printed out as a replacement for text documents, but this is a really inefficient way to review data, that Garr Reynolds calls ‘ PresDocs ’ (Garr Reynolds is the author of Presentation Zen, one of the most important go-to reference for successful presentations).
Related Read: What Makes Up the Best Presentation Templates?
What makes the best presentation website?
When looking for the best presentation apps, there is a need to consider not just pitch decks but also school lectures, religious sermons, and adverts. Therefore, an excellent presentation app should be affordable, have enough sharing and collaboration options, have a range of pre-built templates, and be flexible.
Visualization in presentations
A presentation without visual aids can be very boring. It's hard to remember things if they are just words on a page or screen. But with visuals, people retain information much better. So, ensure you have some great images to help your audience understand what you're talking about.
Consider using infographics if you want to add some spice to your presentations. Infographics are visually appealing ways to present complex information in a simple way. They can include charts, graphs, maps, diagrams, timelines, etc. Many online tools are available to create them, including Piktochart , Visually, and Canva .
Presentation or visualization names of websites
Presentation websites allow you to create amazing presentations through the use of web technologies.
There are many cases when you might need to create a presentation for a particular purpose. Creating a presentation on PowerPoint is easy, but that doesn't mean it's the best option. That's why we'll talk about how to create a presentation without PowerPoint and how to get the best out of these presentation website alternatives.
However, there exist today, numerous applications, software, and websites that can help create stunning designs and art for presentations other than PowerPoint. From Slidebean to Google Slides, there are more than enough presentation apps to help you. No matter your tastes, needs, and specifications, there is always one that fits your bill. Read on to find out more.
What makes a great PowerPoint Alternative?
Not everyone prefers PowerPoint. Why? Because it can feel and look clunky at times. But not every PowerPoint alternative works the same way. To find the best one for you, look out for features such as:
- Ability to present online and offline.
- Sharing and collaboration features.
- Features that allow for easy interpretation and assimilation of data.
- Highly customizable templates.
- Good transition and animation capabilities.
- Work import capabilities.
What are some good presentation websites
Here's a list of the best 10 powerpoint alternatives for 2023:.
Check out our top 10 presentation software tools that we believe are great alternatives to PowerPoint. We've curated this list based on our own interests and research. Let's dive right in and get started:
1. Slidebean presentation builder
Key Differentiator: Time Efficiency and Design
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $199/year
Slidebean tops our list for its impressive time efficiency and design capabilities. This presentation software harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to calculate new slide designs in seconds. The platform offers a vast array of professional templates, each equipped with text suggestions tailored to various industries, making presentation creation a breeze. Slidebean also allows logo integration, enhancing your branding. Moreover, the tracking feature provides valuable insights into audience engagement, giving you the opportunity to improve your content and drive success in your presentations.
TRY SLIDEBEAN PRESENTATIONS
2. google slides.
Key Differentiator: Collaborative Convenience
Pricing: Free
Google Slides is an excellent choice for those seeking seamless collaboration and cloud-based convenience. With a reliable internet connection, multiple collaborators can work on a single project simultaneously without any need for downloads. The platform also allows sharing via email, facilitating easy dissemination of your presentations. Although Google Slides offers some impressive templates, it could benefit from more diverse design options for a truly personalized touch.
TRY GOOGLE SLIDES
Key Differentiator: "Zooming" into Creativity
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $5/month)
Prezi's zoom function sets it apart, creating engaging and dynamic presentations. It boasts a unique smart structure technology that impresses audiences. However, using Prezi's exceptional features might require training and design skills. While the free version offers significant benefits, remember that it comes with privacy limitations. Consider opting for the paid plans if confidentiality is crucial for your presentations.
4. Apple Keynote
Key Differentiator: Sleek and Sophisticated
Pricing: Free with Mac devices, standalone versions available for macOS at $19.99
Designed for Apple users, Keynote brings sleekness and sophistication to your presentations. The software is versatile, allowing you to work on floor plans and text slides alike. While it may lack some collaborative features of other platforms, Keynote excels in creating aesthetically pleasing and professional presentation materials.
TRY KEYNOTE
5. haiku deck.
Key Differentiator: Simplified Storytelling
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $9.99/month
Haiku Deck focuses on visual storytelling, providing an array of visually appealing templates and high-quality images to captivate your audience. The software streamlines the presentation process, making it ideal for those seeking simplicity and elegance. With its user-friendly interface, Haiku Deck enables you to create impressive slides in minutes.
TRY HAIKU DECK
Key Differentiator: Design Flexibility
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $9.95/month)
Though primarily known for graphic design, Canva also offers powerful presentation tools. With a vast library of design elements, templates, and stock images, Canva allows you to fully customize your slides. Its collaborative features and easy sharing options make it a go-to choice for teams working on presentations.

Key Differentiator: Visual Content Creation
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $25/month
Visme excels in visual content creation, offering impressive charts, graphs, and infographics. This platform goes beyond conventional presentations, making it ideal for educational and business purposes. It enables you to create interactive and engaging content that will leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Key Differentiator: Animated Presentations
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $19/month
If you want to bring your presentations to life with animation, Powtoon is the software for you. Its dynamic and animated slides add flair to your content, keeping your audience engaged throughout the presentation. Powtoon's easy-to-use interface and extensive library of animated assets make it perfect for creating captivating animated presentations.
TRY POWTOON
Key Differentiator: Multi-dimensional Presentations
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $12/month
Emaze stands out with its multi-dimensional presentation capabilities. It offers 3D templates, virtual reality integration, and immersive slides, making your presentations stand out. For those seeking innovative ways to captivate audiences, Emaze is a powerful choice.
10. Zoho Show
Key Differentiator: Collaborative Creation
Pricing: Free with limited features, paid plans start at $5/month
Zoho Show offers collaborative features that make teamwork seamless. It allows multiple users to collaborate in real time, making it an excellent choice for group projects and presentations. The platform also provides a variety of templates and customization options to suit your presentation needs.
TRY ZOHO SHOW
A presentation software launched in 2020, Pitch is already referred to as a “PowerPoint killer”. It was created to help non-designers (or beginners) create excellent pitch decks.
Pitch has an extensive library of presentation templates, but this is just one of its benefits. This software emphasizes collaboration and even includes built-in video collaboration for remote teams to work together. Pitch presentations can also be integrated with Google Analytics, Google Sheets, and similar applications.

This cloud-based presentation tool proffers a user-friendly alternative to PowerPoint. Its sleek editor interface allows you to add your preferred background images, import a variety of designs, and collaborate easily with others. It is known to be very user-friendly.
Slides offers access and edit features from any device, as long as it is internet-connected. It also helps manage privacy rights, allows presentations offline, offers analytics management, and allows for adding GIFs and images.
However, it is limited in slide options and templates and does not offer graphic inclusions.
Gamma is a user-friendly web tool designed to make creating presentations easier for both educators and students. Its standout feature is its AI technology, which handles design tasks, allowing users to focus on their content. With Gamma, anyone can quickly create visually appealing presentations without needing advanced design skills.
How do I create a presentation without PowerPoint?
Numerous alternatives to PowerPoint are on the Internet. The issue is not about creating a presentation without PowerPoint but getting that presentation tool or software that can help achieve your goal.
While many tools offer free accounts to peruse and utilize online and offline presentations, some do not. This does not mean the free tools are not good, rather, it is just a marketing idea.
What can I use instead of PowerPoint for free?
Here are some presentation tools you can make use of instead of PowerPoint;
WPS Office boasts functionality and a well-designed, along with offline document capabilities. Sometimes accused of having very similar features to Microsoft Office, users can efficiently work on PowerPoint files. It also offers many templates. However, collaboration might be a bit stressful.
WPS Office is available on Android, Web Windows, iOS, Linux, and macOS.
If there is one thing Canva has, it is templates. Canva makes PowerPoint look simple with a vast array of templates for every specification. If you have a problem with making decisions, do not use Canva.
However, that is its Achilles heel; many people find themselves scrolling for so long. Not all templates are free but, it helps narrow down your options.
- Bonus Tool: InVideo
InVideo is considered a cloud-based online video editing tool with the feature of creating slideshow videos. it contains a huge selection of slideshow templates, stock footage, photos, and music to make great slideshow videos without a watermark. Although it is available for free, some features require a premium subscription.
Without a doubt, it can be stressful to get that one presentation software that can fit your exact specifications and give the required output. Although utilizing Slidebean can be very flexible, it can also be use to produce the best infographic presentation that compares data in an easily-understood manner.
Popular Articles

Pitch Deck Structure: What Investors Want To See

AirBnb Pitch Deck: Teardown and Redesign (FREE Download)
Upcoming events, financial modeling crash course, how to close a funding round.
The Startup Financial Model Template by Slidebean

Let’s move your company to the next stage 🚀
Ai pitch deck software, pitch deck services.
Financial Model Consulting for Startups 🚀

Raise money with our pitch deck writing and design service 🚀
The all-in-one pitch deck software 🚀

Check out our list of the top free presentation websites that offer unique features and design options. Discover the best platform for your next presentation now.

This is a functional model you can use to create your own formulas and project your potential business growth. Instructions on how to use it are on the front page.
Book a call with our sales team
In a hurry? Give us a call at
What Does an Entry-Level Data Analyst Do?

An entry-level data analyst gathers, processes, and analyzes data, utilizing statistical tools and visualization techniques to provide actionable insights and support business decisions.
Over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated daily, and the need for data analytics professionals is only increasing.
This information alone explains the importance of knowing precisely what an entry-level data analyst does today.
Let’s see what these professionals do, their business roles, and what skills they should possess.
Definition of a Data Analyst
A data analyst collects and processes large datasets before conducting various statistical analyses. In this case, data analysts utilize their technical expertise to maintain the accuracy and quality of data and convert it to value-added information that can assist an organization in making desired decisions.
A data analyst possesses several job opportunities in business, finance, healthcare, technology, marketing, and government, among other areas, with responsibilities such as strategy, process improvement, or enhancing customer understanding.
Key Responsibilities of a Data Analyst

Understanding the responsibilities of a data analyst is paramount in outlining the day-to-day operations that a person in this position is involved in and the role thereof in an organization. Below, I identify the key responsibilities of an entry-level data analyst that define what this person does in the organization.
Data Collection and Management
- Gather Data: Collect data from various sources to ensure accuracy and relevancy.
- Data Storage: Ensure efficiency in storing the collected data while ensuring integrity and accessibility.
Data Cleaning and Preparation
- Data Cleaning: Identifying data inaccuracy and inconsistency to correct them to maintain data quality.
- Data Preparation: Organize raw data and transform it into a format that can be analyzed.
Data Analysis
- Statistical Analysis: Interpret data using statistical tools and techniques and make predictions.
- Mathematical Modeling: Use mathematical models to solve problems and optimize, critical in data-informed decision-making.
Data Visualization
- Visual Representation: Create visuals that communicate data insights efficiently with technical and non-technical audiences.
- Dashboard Development: Use tools like PowerBI, Tableau, or Google Data Studio to develop dashboards that give real-time data insights.
Reporting and Communication
- Report Generation: Compile detailed reports of findings that outline clear and actionable insights.
- Presentation: Communicate data and analysis in an understandable and value addition way to the organization.
Decision Support
- Strategic Recommendations : Offer recommendations based on data analysis findings for strategic decision-making.
- Problem-Solving: Use analytical skills to solve problems, increasing operational efficiency.
Collaboration and Team Interaction
- Work Across Teams: Working with different departments to understand their data requirements and provide relevant insights.
- Stakeholder Management: Constant communication with stakeholders to ensure alignment and consolidate the value of data insights.
Continuous Learning and Development
- Skill Enhancement: Regularly hone analytical skills and knowledge and identify new data analysis tools and how they are used.
- Trend Watching : Keeping up with industry trends ensures the organization stays ahead of its competition.
Essential Skills and Tools You Need To Know As A Data Analyst

Now, let’s discover what skills and tools you must know as an entry-level data analyst. Let’s start with Math!
Math and Statistics
Maths and statistics form the backbone of data analysis. As an entry-level data analyst, it is crucial to be able to work with essential to intermediate maths.
- Math : Math includes familiar concepts such as algebra and derivatives; the latter is beneficial because optimizing functions is a classic requisite of data modeling.
- Statistics : Knowledge of statistics includes both descriptive statistics used in the summary of data and inferential statistics used to make predictions from the data
- Probability Theorem : The Probability Theorem makes you aware of the role of chance in your work and may help you assess risk, make predictions, and test hypotheses.
- Linear Algebra: Linear Algebra allows for the handling and manipulation large datasets and operations on multi-dimensional data arrays.
These skills are necessary to analyze data effectively, making insights from large, complex databases. They are the fundamental skills upon which all other more advanced techniques are based.
Coding Skills
As an entry-level data analyst, coding will be critical to efficiently processing and interpreting the data. The tools and skills to develop expertise in programming include:
Python is a general-purpose language with libraries that have made different areas of data activities more accessible.
These include:
- Data Cleaning: With tools like Pandas and NumPy
- Data Manipulations: Using Pandas to transform and structure raw data
- Data Analysis: Using SciPy for more sophisticated statistical actions
- Data Visualization: With Matplotlib and Seaborn to create graphical representations
It is a statistical language that can analyze a wide range of data.
- Statistical Analysis with help from ggplot2 to visualize data and dplyr to manipulate data
- Data Cleaning using tidyr and dplyr to ensure data is tidy
- Data Manipulation using dplyr to structure designed data for specific actions
- Data Visualization is done with ggplot2 for visual representations
- Using statistical functions and built-in tools to analyze data
- Functionalities to use pre-installed functions to calculate data at a glance
- Pivot tables are used to summarize data sets into manageable information
- Data Import and Export to enable importing and exporting of data to and from other platforms
- Ability to use SQL functions to extract and manipulate data
- Writing a concise high-level query to return the fastest data
- Database management procedures to maintain and optimize database systems
- Data integration merging of databases to provide a broad scope of information.
These skills and the tool-specific libraries are standard practice for a wide range of data analytics functions a data analyst will use.
High-Level Data Visualization Tools
Given the growing intricacy of data, high-level data visualization tools have become necessary to translate complicated data sets into comprehensive visual stories. Some of the tools that any entry-level data analyst should be familiar with are as follows.
- Interactive Visualizations: Data analysts can create dashboards, reports that include real-time data, and interactive visualizations.
- Data Integration: seamlessly integrates various data sources and synthesizes information.
- Customization: the user can customize visualizations to suit unique business needs or emphasize critical metrics.
- Ease of Design: Tableau is user-friendly and allows rapid learning and deployment.
- Advanced Analytics: Perform complex calculations, visualizations, and manipulation within the tool.
- Collaboration: Tableau Server and Tableau Online aid the spread of insights across teams or with stakeholders.
- Reporting: Tableau software provides a consolidated view of relevant data, which users can access to represent their analysis.
Google Data Studio
- Accessibility: It is free to use, and the user can use it with multiple Google services, such as Google Sheets and Google Analytics.
- Real-time Reporting Activity: The software provides data in real-time, which is helpful for time-bound decisions.
- Collaboration: It performs similarly to Google Docs, allowing multiple users to view and edit the report simultaneously.
Proficient use of these software tools is beneficial in making data more enticing and digestible and unraveling concealed patterns and connections that can change the whole decision-making process.
These are versatile accompaniments to any data analyst as they increase the depth and breadth of data exploration and presentation.
Soft Skills
As much as technical skills are fundamental in your career as an entry-level data analyst, soft skills are equally crucial to get the best out of you to communicate your insights and work with others.
The following five soft skills are essential and must be achieved by every data scientist entering this field; every data analyst should possess these soft skills:
Communication
- Effective communication: Able to explain complex data insights in an understandable way to non-techie demography.
- Presentation: Create and deliver a presentation that presents data and suggests what should be done to improve the current status.
A problem-solving attitude:
- Solutions-driven: Able to break down a significant problem and solve each part separately
Time management
- Strict with deadlines: Time-management, focus, and prioritize work to meet the delivery schedule
- Resilient: Keep focus on crucial tasks while adapting to unexpected changes
- Collaboration : The willingness to answer other people’s questions
- Demand management: Should respond to requests from one person while guiding data requests to another responsible person
Responsibility
- Mistakes/ Solutions: Capable of taking responsibility for own mistakes and work not to repeat the same in the future
- Innovative Approach: Suggest changes based on your observation and take new tasks and improvement suggestions
Entry-level vs. Experienced Data Analysts
One critical distinction between entry-level and experienced data analysts concerns the technical skills and complexity associated with their job roles. Below are the competencies of entry-level and professional data analysts.
Entry-Level data analyst
- Basic to intermediate math
- Descriptive and inferential statistics
- Basic probability Theorems and Linear Algebra
Experienced data analyst
- Advanced mathematical modeling and statistics
- Deep understanding of theories with real-world applications
- Proficiency in advanced statistics and probability models.
- Programming in Python in data cleaning, manipulation, analysis, and visualization with libraries Pandas, NumPy, Matplotlib, and Seaborn
- Basic R programming
- Familiarity with SQL
- Advanced programming in Python and R, basics of custom libraries,
- Advanced SQL and other database technologies
- Advanced database architecture and optimization and automation abilities.
- Beginning use of PowerBI, Tableau, and Google Data Studio.
- Data integration skills and ability to customize visualizations for specific business needs.
- Advanced data transformation and significant visualization high-level tools implementation
- Ability to deploy and manage enterprise-level data visualization platforms.
- Communication with colleagues
- Understanding of business needs
- Ability to set priorities.
- Advanced communicative skills
- Problem-solving
- Continuous learning.
The shift from an entry-level to an experienced data analyst involves increased technical skills and a better understanding of the business context. The analyst must also be able to host projects, deploy and manage high-level visual platforms, and engage in strategic decision-making based on available data.
The differences refer to broader responsibilities with deep scope and complexity that require more professionalism and softer skills.
Educational Background and Certifications
Back then, no university degree was explicitly dedicated to data analysis. The skills we referred to were collected from various sources.
However, after data-related jobs became more famous and attractive, the first online courses became available on platforms like Coursera, Datacamp, and Udemy. After completing a few courses, you can take classes, work on data projects, and become a junior analyst.
Yet, nowadays, since tools like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude have been implemented, the responsibilities of data analysts may have changed because these tools significantly speed up the data analysis process.
However, suppose you plan to be a data analyst and have second thoughts about these LLMs. In that case, the available versions are less capable than even entry-level data analysts because, for example, the mathematical capabilities of these models are minimal right now.
Career Path
After completing courses, your first step should be undertaking a portfolio data project. Remember, this project will set you apart from other junior analysts, so investing significant effort is crucial. Take your time to create a portfolio project that may include:
- Dashboards: Developed using tools like PowerBi , Tableau , or Google Data Studio( Free Course ).
- Website: Which hosts the dashboard.
- Data Visualizations: These should ideally be integrated into your website.
If your portfolio project successfully addresses a business problem, it might position you to hire talent while you are job searching!
Additionally, if you are on the verge of securing a job or preparing for interviews, consider reviewing interview questions from our platform. These resources are designed to help you prepare for your interview scenarios.
If you still have questions about what a data analyst is, read this one → “ What is a Data Analyst? Everything You Need to Know ”.
Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Now, after all these, you might dream that Google is looking for you to hire! And I hope they are, but sometimes things go differently than you dream of.
So, for your first job, look for something more manageable and smaller, such as freelancing from platforms like Upwork or Fiverr . Here, you can find more straightforward tasks, which is an excellent fit for you to grow confidence in Data Analytics.
In the meantime, you can continue applying to corporate companies like Meta, Apple, or Google, but you should also keep sharpening your skills and developing confidence by doing freelance jobs.
Finally, if you want to build something more significant and have a dream that can dedicate yourself for a long time, maybe you can be an entrepreneur/data analyst, where you are the brain and the founder of a company, which maybe will be the next Meta or Apple, who knows?
Here are the data analyst interview questions to see whether you have some skills to improve or not.
In this article, we discovered the complex profile of an entry-level data analyst and elaborated on the primary responsibilities from data collection and analysis to decision support and communication.
By acquiring the vital skills and competencies mentioned, you can improve your career potential and support any firm with considerable benefit. If you plan to prepare for an interview, don’t forget to visit our platform , where you can find interview questions from firms like Meta, Google, and Amazon.
Latest Posts:

Simplifying SQL Queries with Aliases: A How-To Guide

Self-Supervised Learning Guide: Super simple way to understand AI
Become a data expert. Subscribe to our newsletter.
PNW Wins in 2024 “Best of the Region”
Thank you for helping to vote PNW Best College/University in The Times of Northwest Indiana’s 2024 “Best of the Region” ballot, published May 19, 2024.
- myPNW Login
- Brightspace Login
- PNW Calendar
- Scholarships
- Tuition and Fees
CIVS Showcases Steel Research at AISTech 2024

On May 6-8, CIVS researchers and collaborators delivered various technical presentations at the AISTech 2024 Conference in Columbus, Ohio, which is the major Annual Internal Iron & Steel Technology Conference and Exposition. There were record-high attendees with over 8,400 professionals and students. The CIVS presentations included 1 panel discussion, 6 technical presentations, 3 undergraduate oral presentations, and 11 graduate poster presentations in the topics of blast furnace, electric arc furnace, reheating furnace, ladle, and safety.
CIVS research quality and efforts were recognized with 6 awards . CIVS also won the AISTech attendance challenge and was selected to receive an AISTech 2024 Material Advantage Chapter Travel Grant.
CIVS Director, Chenn Zhou, served as a panelist at the Energy & Utilities Panel Discussion at AISTech 2024. Four panelists discussed the importance of high energy efficiency and greener fuels for reheating furnaces. CIVS Senior Research Engineer Kyle Toth presented “Hazard Recognition Scenario Builder for On-Site Customizable Virtual Training” with co-author and Senior Research Scientist Jack Moreland.
It was exciting to see so many people interested in our project (we had about 80 attendees for our talk). It shows the importance of hazard recognition for safety and the need for our project to help create custom scenarios for site specific training. John “Jack” Moreland, Senior Research Scientist
AISTech gave a positive outlook on the steel industry and my place in it. Sustainability and decarbonization were huge topics in the technical presentations and town hall forum. Speakers emphasized how important it is for the students and young professionals of today to do research and lead change that will shape the steel industry over the next 25 years on its path to net zero. I came away from the conference excited about the future of steel and the direction the industry is headed. Veronica Pitt-Payne, undergraduate student majoring in Civil Engineering at PNW, 1st place winner of the undergraduate student contest
The following is a list of CIVS technical presentations:
1) “CFD Modeling of the Refining Process in an Industry-Scale Electric Arc Furnace: Analysis of Decarburization Efficiency and Model Validation,” presented by Orlando Ugarte, Post-Doctoral Researcher
2) “Scale Thickness Prediction for Steel Reheating,” presented by Nicholas Walla, Senior Research Engineer
3) “The Integrated Virtual Blast Furnace: Enabling Physics-Based Operational Guidance,” presented by Tyamo Okosun, Associate Director for Research
4) “Image-Based Casting Rate Estimation for Molten Iron Jet Released from Blast Furnace,” presented by Weixiao Shang, Post-Doctoral Researcher, Purdue University
5) “A CFD Study of Refractory Brick Erosion and Corrosion in Ladle Metallurgy Furnace,” presented by Xipeng Guo, Ph.D. Research Assistant
6) “Hazard Recognition Scenario Builder for On-Site Customizable Virtual Training,” presented by Kyle Toth, Senior Research Engineer
AISTech is North America’s largest annual iron and steel technology conference and exposition. It provides a global perspective on today’s marketplace by featuring technologies from all over the world that help steelmakers to compete more effectively. AISTech is hosted by The Association for Iron & Steel Technology.
The Association for Iron & Steel Technology (AIST) is a non-profit organization with over 18,500 members from over 70 countries. AIST represents a large network of steel industry professionals with tremendous knowledge and expertise.

2024 Chlorinated Conference 17+
Designed for ipad, screenshots, description.
Conference App For 13th International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds. The app will allow you to sign-in and favorite sessions or presentations allowing you to create your own custom itinerary. Filter the sessions, presentations, or participants to drill down and find the information you are looking for. Update your profile and create virtual badge. Post on the social feed for the conference to engage with your community and presenters. View the exhibit hall to find exhibitors descriptions.
App Privacy
The developer, Battelle , indicated that the app’s privacy practices may include handling of data as described below. For more information, see the developer’s privacy policy .
Data Linked to You
The following data may be collected and linked to your identity:
- Contact Info
- Identifiers
Privacy practices may vary, for example, based on the features you use or your age. Learn More
Information
- Developer Website
- App Support
- Privacy Policy
More By This Developer
Climate 2024

COMMENTS
The correct presentation description makes it more interesting for the target audience. 6. Ignore the Myths About Ideal Scope - Presentation Description. The description really shouldn't be too overloaded. This is the only tip that applies to all presentations. But its exact volume cannot be inscribed in some universal formula. It all ...
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls. To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It's like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable. 8.
Visualization is the art of capturing relationship between objects. Since our mind stores information as connections, visual diagrams help your audience to 'get' your message fast and retain it longer. To visualize information, start with bulleted sentences and remove the junk words to identify the keywords.
1. Opt for a motion-based presentation. You can make an outstanding presentation using Prezi Present, a software program that lets you create interactive presentations that capture your viewer's attention. Prezi's zooming feature allows you to add movement to your presentation and create smooth transitions.
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
6. Prepare. Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
Presentation visualization conveys information, ideas, and messages through visually compelling elements. By integrating engaging visuals into presentations, speakers can capture their audience's attention, enhance understanding, and leave a lasting impact. This article explores the importance of presentation visualization, key techniques for ...
3D visualizations are computer-generated representations of architectural designs. They can be created as still images, animations, or interactive videos that enable you to explore every nook and cranny of an architectural project in a virtual environment. They're true to life, often even photorealistic. As their name would suggest, they ...
Data visualization in presentations help decipher or break down information and present in a format that is understandable, insightful, and actionable. ... Add titles, labels, and annotations: Be sure to add a title, label, and description to your chart so your audience knows what they are looking at. Remember to keep it clear and concise.
Simply speaking, creative visualization is a sort of meditation technique that can help you achieve more from your next presentation by encouraging you to create better clarity, focus and sense of purpose when it comes to achieving excellence the next time you take the stage.
A simple definition of data visualization: Data visualization is the visual presentation of data or information. The goal of data visualization is to communicate data or information clearly and effectively to readers. Typically, data is visualized in the form of a chart, infographic, diagram or map. The field of data visualization combines both ...
By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding. References [1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart, 5.2 Bar chart. https://www150 ...
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
Data visualization is the representation of data through visual displays such as charts, histograms, maps, tables, dashboards, graphs, and infographics. Integrating data visualization into your presentation makes it easy for your audience to digest, absorb, and remember complex information and data. The American Management Association says ...
Responsibilities of a Presentation Specialist. The role of a Presentation Specialist is to present enticing visuals that successfully transmit what a company tries to convey using a message. Their duties incorporate creativity, skills and strategy, which assists the organisations.
The Power of Infographics in Presentations. Infographics are an effective way to summarize and present data in a visually appealing and easily digestible format. They combine visuals, text, and data to tell a cohesive story, making complex information more accessible to the audience.
The design and presentation of digital information. Use of graphics, animation, sound, visualization software, and hypermedia in presenting information to the user. Methods of presenting complex information to enhance comprehension and analysis. Incorporation of visualization techniques into human-computer interfaces. Three hours of lecture and one hour of laboratory per week.
Data Visualization is a graphic representation of data that aims to communicate numerous heavy data in an efficient way that is easier to grasp and understand. In a way, data visualization is the mapping between the original data and graphic elements that determine how the attributes of these elements vary. The visualization is usually made by ...
Prezi powers the best presenters to do their best presentations. Welcome to Prezi, the presentation software that uses motion, zoom, and spatial relationships to bring your ideas to life and make you a great presenter.
<p>One of the most influential data visualization books—updated with new techniques, technologies, and examples <p><i>Visualize This</i> demonstrates how to explain data visually, so that you can present and communicate information in a way that is appealing and easy to understand. Today, there is a continuous flow of data available to answer almost any question. Thoughtful charts ...
Data visualization is the representation of information and data using charts, graphs, maps, and other visual tools. These visualizations allow us to easily understand any patterns, trends, or outliers in a data set. Data visualization also presents data to the general public or specific audiences without technical knowledge in an accessible ...
PRESENTATION / VISUALIZATION What is Presentation? Presentation is a graphics program that allows you to create slide shows presenting a topic, lecture, demonstration to enlighten, educate, communicate, or persuade the audience. A presentation program allows you to organize, Zoho
You need high-quality business presentation software to take your slides to the next level. Some of the best presentation software include Visme, Haiku Deck, Prezi, Microsoft Powerpoint, Canva and Google Slides. In this comparison guide, we'll analyze each of these tools and many more to understand what the difference is between them so you ...
Presentation or visualization names of websites. Presentation websites allow you to create amazing presentations through the use of web technologies. There are many cases when you might need to create a presentation for a particular purpose. Creating a presentation on PowerPoint is easy, but that doesn't mean it's the best option.
Data Visualization.pptx. Data visualization is the graphical representation of information and data using visual elements like charts, graphs, and maps to provide an accessible way to see and understand trends and patterns in data. It allows massive amounts of information to be analyzed and data-driven decisions to be made. Data visualization ...
1 Nasa's Eyes on Asteroids. Image Source. If you are interested in exploring data visualization topics in space exploration, check out this striking data visualization created by NASA. NASA's Eyes on Asteroids is one of the best data visualizations due to its exceptional design and functionality.
An entry-level data analyst gathers, processes, and analyzes data, utilizing statistical tools and visualization techniques to provide actionable insights and support business decisions. Over 2.5 quintillion bytes of data are generated daily, and the need for data analytics professionals is only increasing. This information alone explains the ...
Use Canva's free online map maker and create your maps you can add to infographics, documents, presentations, and even websites. Better data visualization with our easy-to-use map maker. Canva's map creator is easy to use and highly intuitive so that anyone can create their own personalized maps, even with no design or cartography ...
On May 6-8, CIVS researchers and collaborators delivered various technical presentations at the AISTech 2024 Conference in Columbus, Ohio, which is the major Annual Internal Iron & Steel Technology Conference and Exposition. There were record-high attendees with over 8,400 professionals and students.
Description. Conference App For 13th International Conference on Remediation of Chlorinated and Recalcitrant Compounds. The app will allow you to sign-in and favorite sessions or presentations allowing you to create your own custom itinerary. Filter the sessions, presentations, or participants to drill down and find the information you are ...