Child Marriage Essay
500 words child marriage essay.
Child Marriage continues to be a prevalent practice in many parts of the world . Even though the world is evolving at a fast pace, there are some regions that can’t seem to move on with times. What’s sad is the dark reality of child marriage which is not considered often. Child marriage is basically the formal or informal marriage of a child with or without their consent, under the age of 18. In most cases, the boy or man is older than the girl. Through a child marriage essay, we will throw light on this social issue.


Causes and Impact of Child Marriage
Child marriage is no less than exploitation of right. In almost all places, the child must be 18 years and above to get married. Thus, marrying off the child before the age is exploiting their right.
One of the most common causes of child marriage is the tradition which has been in practice for a long time. In many places, ever since a girl is born, they consider her to be someone else’s property.
Similarly, the elders wish to work out their family’s expansion so they marry off the youngsters to characterize their status. Most importantly, poor people practice child marriage to get rid of their loans, taxes, dowry and more.
The impact of child marriage can be life-changing for children, especially girls. The household responsibilities fall on the children. They are not mentally or physically ready for it, yet it falls on them.
While people expect the minor boys to bear the financial responsibilities, the girls are expected to look after the house and family. Their freedom to learn and play is taken away.
Further, their health is also put at risk due to the contraction of sexually transmitted diseases like HIV and more. Especially the girls who get pregnant at a young age, it becomes harmful for the mother as well as the baby.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
How to End Child Marriage
Ending child marriage is the need of the hour. In order to end this social evil, everyone from individuals to world leaders must challenge the traditional norms. Moreover, we must do away with ideas that reinforce that girls are inferior to boys.
We must empower the children, especially girls, to become their own agents of change. To achieve this, they must get access to quality education and allow them to complete their studies so they can lead an independent life later on.
Safe spaces are important for children to be able to express themselves and make their voices heard. Thus, it is essential to remove all forms of gender discrimination to ensure everyone is given equal value and protection.
Conclusion of Child Marriage Essay
To sum it up, a marriage must be a sacred union between mature individuals and not an illogical institution which compromises with the future of our children. The problem must be solved at the grassroots level beginning with ending poverty and lack of education. This way, people will learn better and do better.
FAQ on Child Marriage Essay
Question 1: What are the causes of child marriage?
Answer 1: The causes of child marriages include poverty, dowry, cultural traditions, religious and social pressures, illiteracy, and supposed incapability of women to work for money.
Question 2: How can we end child marriage?
Answer 2: To end child marriage we must also raise awareness about this issue and educate both parents and kids. Further, we must encourage them to be independent first and then search for a partner only after attaining a specific age. Laws should be introduced to tackle this social issue.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Essay on Child Marriage
Students are often asked to write an essay on Child Marriage in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Introduction.
Child marriage is a global issue where a child, usually under 18 years, is married off. This practice affects both girls and boys but it’s more prevalent among girls.
Causes of Child Marriage
Many factors contribute to child marriage. Poverty, cultural traditions, and lack of education often drive families to marry off their children at a young age.
Consequences
Child marriage has severe consequences. It often leads to early pregnancies, health risks, and limits opportunities for education and career growth.
To end child marriage, we need to focus on education, enforce laws against it, and change societal attitudes.
Also check:
- 10 Lines on Child Marriage
250 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Child marriage, a deeply entrenched social issue, is a practice that involves the marriage of one or both parties before they reach the age of 18. Globally, it is considered a violation of human rights, yet it continues to persist in many societies due to a complex interplay of socio-economic and cultural factors.
The roots of child marriage are multifaceted. Poverty is a significant driver, with families marrying off young daughters to reduce their economic burden. Traditional norms and gender stereotypes also play a role, perpetuating the belief that a girl’s value lies in her ability to become a wife and mother. Furthermore, in some societies, child marriage is used as a strategy to strengthen familial ties or secure political alliances.
Consequences of Child Marriage
The consequences of child marriage are profound and far-reaching. It often results in early pregnancy, posing substantial health risks to young girls whose bodies are not yet mature enough for childbirth. It also hinders girls’ education and personal development, limiting their opportunities and perpetuating cycles of poverty.
Efforts to Combat Child Marriage
Efforts to combat child marriage span from local to global levels. They encompass law enforcement, advocacy for girls’ education, and initiatives to empower girls. However, for these efforts to be effective, it is crucial to address the underlying socio-economic factors that give rise to child marriage.
Child marriage is a complex issue that requires comprehensive, multi-faceted approaches to eradicate. By promoting education, gender equality, and economic stability, societies can help ensure that every child is afforded the right to a safe and fulfilling childhood.
500 Words Essay on Child Marriage
Child marriage, a prevalent practice in many cultures and societies, is a complex issue that infringes upon the rights and development of children, particularly girls. It is a deep-rooted practice, often perpetuated by poverty, gender inequality, traditions, and lack of education. This essay delves into the implications, causes, and potential solutions to child marriage.
The Implications of Child Marriage
Child marriage poses significant risks to the physical, psychological, and emotional well-being of children. It often leads to early pregnancies, which present health risks for both the mother and the child. Moreover, child brides are more likely to experience domestic violence and are less likely to receive proper education. This practice also perpetuates the cycle of poverty, as child brides are less likely to contribute economically to their communities.
Underlying Causes
The causes of child marriage are multifaceted and deeply entrenched in societal norms and structures. Poverty is a significant factor, with families marrying off their daughters to lessen financial burdens. Gender inequality also plays a crucial role, with girls often valued less in societies, leading to their early marriage. Additionally, traditional beliefs and lack of education contribute to the persistence of this practice.
Legislation and Its Limitations
Many countries have enacted laws to prevent child marriage, setting the minimum age for marriage at 18. However, the enforcement of these laws often proves challenging due to societal norms and lack of awareness. Moreover, in some societies, legal loopholes allow child marriage to continue under the guise of cultural or religious practices.
Addressing Child Marriage
Addressing child marriage requires a multifaceted approach. Education is a powerful tool in this regard. Empowering girls through education can help them understand their rights and resist early marriage. Furthermore, educating communities about the detrimental effects of child marriage can foster change in societal attitudes.
Economic empowerment is also crucial. By providing families with financial stability, the economic incentive for child marriage decreases. Social protection measures, such as cash transfers, can help achieve this.
Lastly, legal measures need to be strengthened. Laws against child marriage should be enforced strictly, and legal loopholes need to be addressed.
Child marriage is a violation of children’s rights and a practice that hampers societal development. While it is deeply entrenched in many societies, a combination of education, economic empowerment, and legal measures can help combat this practice. It is crucial for all stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and communities, to work together to end child marriage and ensure a better future for all children.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Arranged Marriage
- Essay on Army Officer
- Essay on Army Man
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Child marriage - Free Essay Examples And Topic Ideas
Child marriage is a global issue where minors are married off, often before they are physically or emotionally mature. Essays on child marriage could explore the sociocultural or economic factors contributing to its prevalence, the legal frameworks surrounding it, or its impact on individuals and communities. Analyzing efforts to combat child marriage, the role of education, and the impact of global advocacy can provide a nuanced understanding of the challenges and potential solutions associated with addressing child marriage. We’ve gathered an extensive assortment of free essay samples on the topic of Child Marriage you can find at PapersOwl Website. You can use our samples for inspiration to write your own essay, research paper, or just to explore a new topic for yourself.
Child Marriage: Legal Dilemmas and Cultural Clash
Child marriage is the marriage that an individual performs without reaching the physical and mental maturity necessary to act as an adult. Child marriage usually means the marriage of a 18-year-old child. Early marriage, these minors are from their families, friends and future; education, deprives the school of life and pushes it under very difficult responsibilities. We see such marriages more especially in developing and underdeveloped countries. In our country's legal system; According to the Turkish Civil Code, the Turkish […]
Child Marriage: Uncovering the Causes and Consequences in Contemporary Society
Child marriage is a formal or informal marriage of a child under the age of 18. Generally it is a marriage of a young girl with older man. There are approximately 700 million women around the world today who got married at young age. There would be a few factors that lead to child marriage and the effect that it gave to our society. Firstly, unwanted early pregnancies contribute to the ubiquity of child marriage in Malaysia. A high number […]
What we Do: Economic Empowerment
Abstract : Education is widely understood as an indicator of women status and even more importantly as a factor for the empowerment of women. Women have such unexplored potential which has never been tapped. For centuries women were not treated equal to men in many ways. Today we can see that women occupies respectable positions in all walks of life. Yet, they are not absolutely free, due to discriminations and harassments of the society. A few number of women have […]
We will write an essay sample crafted to your needs.
Essay about Gender Segregation
The developing world has encountered various forms of gender inequality or segregation. In education, when discrimination is mentioned, most people happen to think about African or Middle Eastern. The question commonly asked is how often women can be involved in this issue of segregation in education? Recently, women have gone through tremendous struggles for them to be granted the same rights for education like those given to men. Gender segregation can be defined as the concentration of one gender in […]
India and Muslims
Presentation: India has a historical significance and, according to some estimates, Indian civilization dates back to over five thousand years. Therefore, it is natural that its society is also very old and complex. Throughout its long-spanning history, India has witnessed and absorbed several waves of immigrants including Aryans, Muslims etc. These immigrants brought their own ethnicities and cultures, contributing to the country's diversity, richness, and vitality. As such, Indian society is a complex mix of diverse cultures, people, beliefs, and […]
A Marriage that Means Nothing but Necessities
Marriages of convenience are undertaken for many other reasons than that of a relationship of love and affection. Instead, the marriages are based upon personal gain for either one or both people in the marriage. In most cases, people typically marry only so one of them can have a visa. Women in poor countries often marry men in exchange for a better life, uprooting themselves and leaving their families, children, and everything they have ever known behind. First, I will […]
Beyond Tradition: Analyzing Global Efforts to Combat Child Marriage
Stepping into the global arena, the battle against child marriage intensifies, challenging longstanding norms and traditions. This pervasive issue, involving the union of individuals before the age of 18, has triggered a synchronized international effort to dismantle its foundations and usher in a more equitable future. The discourse surrounding child marriage now transcends cultural confines, evolving into a universal call for action. It goes beyond the mere overhaul of legal frameworks, delving into the complexities of societal attitudes that sustain […]
The Impact of Early Unions: Examining the Causes and Consequences of Child Marriage
Child marriage, an enduring societal dilemma, casts a lengthy shadow over the destinies of numerous young souls globally. This practice, involving the union of individuals before the age of 18, unfolds against a tapestry of cultural traditions, economic pressures, and gender imbalances. The repercussions of early unions are profound, shaping the trajectories of those involved and perpetuating a cycle of disadvantage. In this exploration, we delve into the labyrinth of causes and consequences surrounding child marriage, striving for a comprehensive […]
Rethinking Love and Relationships in the Battle against Child Marriage
In a world steeped in age-old traditions and norms, the mere mention of redefining love and relationships to combat the blight of child marriage might sound like a whimsical fairy tale. Yet, here we are, delving into the labyrinth of change armed with skepticism. As a psychologist, I find myself navigating through the unexplored corridors of human behavior, questioning the efficacy of rewriting the narrative of love in the fight against an entrenched social ill. Love, an elusive emotion, has […]
Skeptic’s Perspective on Digital Guardians: Rethinking Technology in the Battle against Child Marriage
Child marriage, a deeply entrenched societal issue, has stirred global conversations and efforts aimed at finding innovative solutions. Advocates often champion technology as a digital guardian capable of combating this grave problem. However, as a skeptic psychologist, I approach this notion with caution, questioning the effectiveness and potential unintended consequences of relying solely on technology to address such a complex and deeply rooted cultural phenomenon. The proponents of utilizing technology in the fight against child marriage argue that digital tools […]
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

- High contrast
- Press Centre
Search UNICEF
- Child marriage
Child marriage threatens the lives, well-being and futures of girls around the world.

- Harmful practices
- Available in:
Child marriage refers to any formal marriage or informal union between a child under the age of 18 and an adult or another child.
Despite a steady decline in this harmful practice over the past decade, child marriage remains widespread, with approximately one in five girls married in childhood across the globe. Today, multiple crises – including conflict, climate shocks and the ongoing fallout from COVID-19 – are threatening to reverse progress towards eliminating this human rights violation. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals call for global action to end child marriage by 2030.

Child marriage is often the result of entrenched gender inequality, making girls disproportionately affected by the practice. Globally, the prevalence of child marriage among boys is just one sixth that among girls.
Child marriage robs girls of their childhood and threatens their well-being. Girls who marry before 18 are more likely to experience domestic violence and less likely to remain in school. They have worse economic and health outcomes than their unmarried peers, which are eventually passed down to their own children, straining a country’s capacity to provide quality health and education services.
Child brides often become pregnant during adolescence, when the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth increases. The practice can also isolate girls from family and friends, taking a heavy toll on their mental health.
UNICEF's response
Addressing child marriage requires recognition of the factors that enable it. While the roots of the practice vary across countries and cultures, poverty, lack of educational opportunities and limited access to health care perpetuate it. Some families marry off their daughters to reduce their economic burden or earn income. Others may do so because they believe it will secure their daughters’ futures or protect them.
Norms and stereotypes around gender roles, as well as the socio-economic risk of pregnancy outside of marriage, also uphold the practice.

Because UNICEF works with a range of stakeholders – from grassroots organizations to high-level decision makers – across a scope of rights issues, we are uniquely positioned to identify and address the systemic barriers to reproductive health and gender equality.
In 2016, UNICEF, together with UNFPA , launched the Global Programme to End Child Marriage . Empowering young girls at risk of marriage or already in union, the programme have reached more than 21 million adolescent girls with life-skills training, comprehensive sexuality education and school attendance support since 2016. Over 353 million people, including key community influencers as well as men and boys specifically, have also engaged in dialogue and communication campaigns to support adolescent girls, or other efforts to end child marriage.
Last updated July 2023
More from UNICEF

UNFPA-UNICEF Global Programme
Learn how UNICEF and UNFPA are reaching the girls at greatest risk.

UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador David Beckham promotes equality and empowerment for girls on his first visit to India

Global polycrisis creating uphill battle to end child marriage – UNICEF

UNICEF Goodwill Ambassador Angélique Kidjo celebrates resilience of girls and young people during visit to Benin
Technical notes and fact sheets
- Battling the perfect storm: Adapting programmes to end child marriage during COVID-19 and beyond
- LEADS approach to ending child marriage
- Review of the African Union Campaign to End Child Marriage
Research, data and evaluations
- Leveraging large scale sectoral programmes to prevent child marriage
- Four areas of influence driving child marriage
- UNICEF data on child marriage
Online capacity-strengthening courses
- Exploring the drivers of behaviour: The case of child marriage
- Adolescent girls' agency, safety and well-being (with a specific module on programmes to end child marriage)
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Rev Obstet Gynecol
- v.2(1); Winter 2009
Child Marriage: A Silent Health and Human Rights Issue
Marriages in which a child under the age of 18 years is involved occur worldwide, but are mainly seen in South Asia, Africa, and Latin America. A human rights violation, child marriage directly impacts girls’ education, health, psychologic well-being, and the health of their offspring. It increases the risk for depression, sexually transmitted infection, cervical cancer, malaria, obstetric fistulas, and maternal mortality. Their offspring are at an increased risk for premature birth and, subsequently, neonatal or infant death. The tradition, driven by poverty, is perpetuated to ensure girls’ financial futures and to reinforce social ties. One of the most effective methods of reducing child marriage and its health consequences is mandating that girls stay in school.
Child marriage, defined as marriage of a child under 18 years of age, is a silent and yet widespread practice. Today, over 60 million marriages include girls under the age of 18 years: approximately 31 million in South Asia, 14 million in sub-Saharan Africa, and 6.6 million in Latin America and the Caribbean ( Figure 1 ). Each day, 25,000 girls are married and an anticipated 100 million girls will be married in 2012. 1 Over 60% of girls are married under the age of 18 in some sub-Saharan countries and Bangladesh, and 40% to 60% of girls undergo child marriage in India ( Figure 2 ).

Number of women aged 20–24 who were married or in union before age 18, by region (2006). CEE/CIS, Central and Eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States. Reproduced with permission from United Nations Children’s Fund. Progress for Children: A World Fit for Children Statistical Review. New York: UNICEF; 2007. http://www.unicef.org/publications/files/Progress_for_Children_No_6_revised.pdf .

Percentage of women aged 20–24 who were married or in union before age 18 (1987–2006). Reproduced with permission from United Nations Children’s Fund. Progress for Children: A World Fit for Children Statistical Review. New York: UNICEF; 2007. http://www.unicef.org/publications/files/Progress_for_Children_No_6_revised.pdf .
Child marriage has been referred to as early marriage or child brides , but these terms are not optimal. Early marriage does not imply that children are involved, and the term is vague because an early marriage for one society may be considered late by another. The term child brides glorifies the tradition by portraying an image of joy and celebration. Most of these marriages are arranged by parents, and girls rarely meet their future husband before the wedding. The girls know that after the wedding they will move to their husband’s household, become the responsibility of their in-laws, and might not see their own family or friends for some time.
Although child marriage includes boys, most children married under the age of 18 years are girls. In Mali, the ratio of married girls to boys is 72:1; in Kenya, it is 21:1; in Indonesia, it is 7.5:1; in Brazil, it is 6:1; and even in the United States, the ratio is 8:1. 2 – 4
Human and Children’s Rights
The United Nations and other international agencies have declared that child marriage violates human rights and children’s rights. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights states that individuals must enter marriage freely with full consent and must be at full age. In 1979, the Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination Against Women stated that child marriage is illegal. In 1989, the Convention on the Rights of the Child defined children as persons under the age of 18 years. Many countries passed laws changing the legal age of marriage to 18 years, but enforcement of these laws, and of laws requiring marriages to be registered, is weak. 5 For example, although the legal age of marriage is 18 years, in Mali 65% of girls are married at a younger age; in Mozambique, it is 57%; and in India, it is 50% ( Figure 3 ). In some parts of Ethiopia, although the legal age of marriage is 15 years, 50% of younger girls are married, and in Mali, 39% of younger girls are married. Furthermore, in some regions, an arranged marriage occurs at birth. 6

(A) Percentage of girls (aged 15–19 years) who are currently married. (B) Percentage of women aged 20 to 24 years married before age 18. Reproduced with permission from Mathur S, Greene M, Malhotra A. Too Young to Wed: The Lives, Rights, and Health of Young Married Girls. Washington, DC: International Center for Research on Women; 2003. http://www.icrw.org/docs/tooyoungtowed_1003.pdf .
Factors Driving Child Marriage
Three main forces drive child marriages: poverty, the need to reinforce social ties, and the belief that it offers protection. Child marriage is predominantly seen in areas of poverty. Parents are faced with 2 economic incentives: to ensure their daughter’s financial security and to reduce the economic burden daughters place on the family.
Child marriage is first and foremost a product of sheer economic need. Girls are costly to feed, clothe, and educate, and they eventually leave the household. Marriage brings a dowry to the bride’s family. The younger the girl, the higher the dowry, and the sooner the economic burden of raising the girl is lifted.
By marrying their daughter to a “good” family, parents also establish social ties between tribes or clans and improve their social status. Parents also believe that marrying their daughters young protects them from rape, premarital sexual activity, unintended pregnancies, and sexually transmitted infections, especially human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and AIDS. 5
Health Consequences of Child Marriage
Isolation and depression.
Once married, girls are taken to their husband’s household, where they assume the role of wife, domestic worker, and, eventually, mother. These new homes can be in a different village or town. Because of the high dowry paid, husbands are usually much older than the girls (and thus have little in common with them) and their new brides are expected to reproduce. Polygamy may also be acceptable in some of these regions. As a result, the girls feel rejected, isolated, and depressed. Some girls realize that survival requires embracing their new environment and proving their fertility. They lose their childhood and miss the opportunity to play, develop friendships, and be educated.
Risk of Sexually Transmitted Infection and Cervical Cancer
Parents believe that marrying their daughters early protects them from HIV/AIDS. Research has shown the opposite: marriage by the age of 20 years is a risk factor for HIV infection in girls. 7 In Kenya, married girls are 50% more likely than unmarried girls to become infected with HIV. In Zambia, the risk is even higher (59%). And in Uganda, the HIV prevalence rate of married girls and single girls between the ages of 15 and 19 years is 89% and 66%, respectively. Their husbands infected these girls. Because the girls try to prove their fertility, they had high-frequency, unprotected intercourse with their husbands. Their older husbands had prior sexual partners or were polygamous. In addition, the girls’ virginal status and physical immaturity increase the risk of HIV transmission secondary to hymenal, vaginal, or cervical lacerations. 5 Other sexually transmitted infections, such as herpes simplex virus type 2, gonorrhea, and chlamydia, are also more frequently transmitted and enhance the girls’ vulnerability to HIV. Research demonstrates that child marriage also increases the risk of human papillomavirus transmission and cervical cancer. 8
Risks During Pregnancy
Pregnant girls in malaria regions were found to be at higher risk for infection. Of the 10.5 million girls and women who become infected with malaria, 50% die. Their highest risk is during their first pregnancy. Pregnancy not only increases the risk of acquiring malaria, but pregnant girls under the age of 19 have a significantly higher malaria density than pregnant women over the age of 19. 9 They are also at significant risk of malaria-related complications such as severe anemia, pulmonary edema, and hypoglycemia.
Rates of HIV and malaria coinfection are highest in Central African Republic, Malawi, Mozambique, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, where more than 90% of the population is exposed to malaria and more than 10% are HIV positive. Having both diseases complicates the management and treatment of each. HIV-infected patients have a higher likelihood of getting a more severe form of the malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum . They are less likely to respond as well to antimalaria medication. Malaria increases HIV viral load and increases the mother-to-child HIV transmission rate. Data demonstrate that the combination of these diseases proves deadly to the young pregnant mother. 10
Risks During Labor and Delivery
Deliveries from child marriages are “too soon, too close, too many, or too late.” 11 Forty-five percent of girls in Mali, 42% in Uganda, and 25% in Ethiopia have given birth by the age of 18. In Western nations, the rates are 1% in Germany, 2% in France, and 10% in the United States ( Figure 4 ). Girls between the ages of 10 and 14 years are 5 to 7 times more likely to die in childbirth; girls between the ages of 15 and 19 years are twice as likely. 12 High death rates are secondary to eclampsia, postpartum hemorrhage, sepsis, HIV infection, malaria, and obstructed labor. Girls aged 10 to 15 years have small pelvises and are not ready for childbearing. Their risk for obstetric fistula is 88%. 13

Percentage of women, aged 20 to 24 years, married and giving birth by age 18. Reproduced with permission from Mathur S, Greene M, Malhotra A. Too Young to Wed: The Lives, Rights, and Health of Young Married Girls. Washington, DC: International Center for Research on Women; 2003. http://www.icrw.org/docs/tooyoungtowed_1003.pdf .
Risks for Infants
Mothers under the age of 18 have a 35% to 55% higher risk of delivering a preterm or low-birthweight infant than mothers older than 19 years. The infant mortality rate is 60% higher when the mother is under the age of 18 years. Data demonstrate that even after surviving the first year, children younger than 5 years had a 28% higher mortality rate in the young mothers cohort. 14 This morbidity and mortality is due to the young mothers’ poor nutrition, physical and emotional immaturity, lack of access to social and reproductive services, and higher risk for infectious diseases.
Disheartening as this information may be, there is encouraging news. Data show that in countries where poverty has decreased, such as Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand, the incidence of child marriage has also declined.
Media attention raises awareness of the issue and can prompt change. After a highly publicized story in 2008, in which a 10-year-old Yemeni girl fled her husband 2 months after being married and successfully obtained a divorce, Yemen increased the legal age for marriage from 15 to 18 years. More importantly, numerous children, inspired by this case, have sued for divorce. 15
Research has long enforced the importance of education for girls and their families. Child marriage truncates girls’ childhood, stops their education, and impacts their health and the health of their infants. Governmental and nongovernmental policies aimed at educating the community, raising awareness, engaging local and religious leaders, involving parents, and empowering girls through education and employment can help stop child marriage. Programs that have shown success are those that give families financial incentives to keep their daughters in school, those that feed children during school hours so parents do not have to bear that responsibility, and those that promise employment once girls have completed their schooling. 1 Education not only delays marriage, pregnancy, and childbearing, but school-based sex education can be effective in changing the awareness, attitudes, and practices leading to risky sexual behavior in marriage.
Main Points
- Over 60 million marriages include a girl under the age of 18 years.
- The main forces that drive child marriage are poverty, the need to reinforce social ties, and the belief that marriage at an early age protects girls from rape, unintended pregnancy, and sexually transmitted infection.
- Marriage before the age of 18 increases the rate of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection in girls.
- High death rates during pregnancy are secondary to eclampsia, postpartum hemorrhage, sepsis, HIV infections, and obstructed labor. The infant mortality rate is 60% higher when the mother is under the age of 18 years.
- Education not only delays marriage, pregnancy, and childbearing, but school-based sex education can be effective in changing the awareness, attitudes, and practices leading to risky sexual behavior in marriage.
- Open access
- Published: 14 February 2022
The health consequences of child marriage: a systematic review of the evidence
- Suiqiong Fan 1 &
- Alissa Koski 1 , 2
BMC Public Health volume 22 , Article number: 309 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
32k Accesses
29 Citations
19 Altmetric
Metrics details
Child marriage, defined as marriage before 18 years of age, is a violation of human rights and a marker of gender inequality. Growing attention to this issue on the global development agenda also reflects concerns that it may negatively impact health. We conducted a systematic review to synthesize existing research on the consequences of child marriage on health and to assess the risk of bias in this body of literature.
Methods and findings
We searched databases focused on biomedicine and global health for studies that estimated the effect of marrying before the age of 18 on any physical or mental health outcome or health behaviour. We identified 58 eligible articles, nearly all of which relied on cross-sectional data sources from sub-Saharan Africa or South Asia. The most studied health outcomes were indicators of fertility and fertility control, maternal health care, and intimate partner violence. All studies were at serious to critical risk of bias. Research consistently found that women who marry before the age of 18 begin having children at earlier ages and give birth to a larger number of children when compared to those who marry at 18 or later, but whether these outcomes were desired was not considered. Across studies, women who married as children were also consistently less likely to give birth in health care facilities or with assistance from skilled providers. Studies also uniformly concluded that child marriage increases the likelihood of experiencing physical violence from an intimate partner. However, research in many other domains, including use of contraception, unwanted pregnancy, and sexual violence came to divergent conclusions and challenge some common narratives regarding child marriage.
Conclusions
There are many reasons to be concerned about child marriage. However, evidence that child marriage causes the health outcomes described in this review is severely limited. There is more heterogeneity in the results of these studies than is often recognized. For these reasons, greater caution is warranted when discussing the potential impact of child marriage on health. We provide suggestions for avoiding common biases and improving the strength of the evidence on this subject.
Trial registration
The protocol of this systematic review was registered with PROSPERO (CRD42020182652) in May 2020.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Marriage before the age of 18, often referred to as child marriage, is a violation of human rights that hinders educational attainment and literacy and may increase the likelihood of living in poverty in adulthood [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Girls are far more likely to marry than boys, and these consequences contribute to existing gender gaps in educational outcomes in some settings [ 6 , 7 ]. The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals list child marriage as an indicator of gender inequality and call for an end to the practice by the year 2030 [ 8 ]. Child marriage remains ongoing throughout much of the world despite intensifying efforts to eliminate it [ 9 ].
In addition to its consequences on education, growing attention to child marriage as a global development issue also seems to reflect increasing consideration of its potential impacts on population health. Multinational organizations including the World Bank, the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) include the potential for harmful consequences on health among the foremost concerns regarding this practice [ 2 , 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. These organizations highlight relationships between child marriage and early childbearing [ 11 , 12 , 13 ], obstetric complications [ 12 , 13 ], violence [ 2 , 12 ], and sexually transmitted infections [ 12 ], among other adverse outcomes.
We undertook this systematic review to synthesize the results of existing research regarding the impact of child marriage on the health of persons who marry before the age of 18. We evaluated the range of health outcomes that have been studied and the geographic distribution of those studies. We also assessed the risk of bias in individual studies and the likelihood that their results reflect causal relationships.
We searched three databases for literature on the relationship between child marriage and health: MEDLINE, Embase, and Ovid Global Health. These databases were chosen because they focus on biomedicine and human health. We aimed to include as broad a range of health outcomes as possible and focusing our search within these databases allowed us to avoid defining specific health outcomes within our search terms. Instead, we searched for studies of child marriage within these databases. This approach made our search terms more concise and the range of outcomes more inclusive. Specific search terms used for each database are included in Supplementary File 1 . We registered our protocol with PROSPERO (CRD42020182652) in May 2020 and conducted our database searches shortly afterward.
We also searched Google Scholar to identify relevant grey literature. Haddaway et al. [ 14 ] found that the majority of grey literature tends to appear within the first 200 citations returned by Google Scholar and recommend focusing on the first 200-300 records. We followed this recommendation and evaluated the first 300 records returned, as sorted by relevance. Search terms used in Google Scholar are also included in Supplementary File 1 . We reviewed the bibliographies of all included studies in an effort to identify any relevant citations not picked up through searches of the databases described above. The search strategy was developed with assistance from a research librarian at McGill University.
Citations returned from searches of all four databases were imported into EndNote X9 and duplicate citations removed [ 15 ]. We transferred all unique citations into Rayyan to facilitate the review process [ 16 ]. A single reviewer (SF) examined the title and abstract of each unique citation for eligibility according to pre-defined criteria specified in the registered protocol. Articles were brought forward for full-text review if they described etiologic studies that used quantitative methods to estimate the effect of child marriage on one or more health outcomes. We defined child marriage as formal or informal union prior to the age of 18. If the title and abstract did not specify the age thresholds used to define child marriage, they were brought forward for full-text review. For example, abstracts that referred to the effect of adolescent or teen marriage without explicitly stating how those exposures were defined were brought forward. Eligible health outcomes included physical or mental health disorders or symptoms of those disorders, as well as health behaviours. Eligible health behaviours included actions like smoking or dietary habits as well as health care seeking, such as prenatal care. We restricted our review to studies in which outcomes were measured at the individual level and to those that measured the effect of child marriage on the individuals married; studies that examined the effect of age at marriage on the offspring of the persons who married were excluded. Studies written in English, French or Chinese were eligible for inclusion.
We excluded studies that used solely qualitative methods and quantitative studies that relied exclusively on hypothesis testing to indicate differences between groups. For example, studies that used chi-squared tests to indicate whether the distribution of some characteristic differed between persons married before the age of 18 and those married at older ages were excluded, even if the authors seemed to interpret their results as causal, because such testing does not result in a comparative effect measure (e.g., a risk difference or an odds ratio) and does not account for potential biases. We also excluded studies in which persons who married before the age of 18 were incorporated into a larger aggregate age category, making the effect of child marriage unidentifiable. For example, comparisons of outcomes among persons who married between 15 and 19 years of age with those who married between 20 and 24 years of age were not eligible for inclusion. Conference presentations and abstracts were also excluded.
Both authors read the full text of each article brought forward from the title and abstract review and independently judged their eligibility according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria described above. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion. The following information was extracted from each included study: authors, title, year of publication, the language of publication, country/region in which the study was conducted, study design, study population, sample size, data sources, statistical methods, outcomes, and results.
Risk of bias assessment
We assessed the risk of bias within each included study using the Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies - of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool developed by members of the Cochrane Bias Methods Group and the Cochrane Non-Randomised Studies Methods Group [ 17 ]. ROBINS-I is designed to evaluate the risk of bias in non-randomized studies by considering how closely the study’s design and methods approximate an ideal randomized trial. To illustrate, in a hypothetical cluster-randomized trial to estimate the causal effect of child marriage on a specified health outcome, the treatment or intervention would be marriage before the age of 18 years. All children in a specific area (a region, a state, a community, etc.) would be randomized at a very young age to one of two treatment groups: those randomized to the intervention would marry at some point prior to their 18th birthdays (a = 1), while those randomized to the control group would marry on their 18th birthday or any later age (a = 0). All children would then be followed up over a period of time sufficient to observe the specified outcome of interest. In the ideal randomized trial, all persons would adhere to their assigned treatment (i.e., remain married) and would remain in the study until follow-up was complete. After the follow-up period, the probability of the outcome among those assigned to a = 1 would be compared with the same probability among those assigned to a = 0. Under these conditions, we could expect that there would be no differences between those children who married before the age of 18 and those who married afterward aside from age at marriage. As a result, if the probability of the outcome among those randomly assigned to marry as children differed from the probability among those randomly assigned to marry after their 18th birthdays, one could interpret that difference as the causal effect of child marriage [ 18 ].
Of course, a randomized trial like this would be unethical and could never actually be conducted. Researchers interested in the effects of child marriage on health must rely on non-randomized study designs to estimate the causal effect of interest. Without the benefit of randomization, it becomes challenging to identify the causal effect of child marriage because those who marry as children are different from those who marry at later ages in many ways. For example, girls who marry before the age of 18 come from poorer households and from communities with greater gender inequality, on average, compared to those who marry at later ages. These differences are likely to affect their health through causal pathways other than age at marriage, such as the experience of violence or limited ability to access education or health care. This means that a naïve comparison of health outcomes between those who marry as children and those who marry as adults is likely to mix up the consequences of age at marriage with the consequences of childhood poverty and gender inequality.
The ROBINS-I tool requires assessors to carefully consider the potential for multiple sources of bias including confounding, inappropriate selection of participants into the study (i.e., selection bias), mishandling of missing data, and problems with the measurement of exposures and outcomes (i.e., information bias). The potential for bias in each domain is assessed through a series of signaling questions and a summary judgement of low, moderate, serious, or critical risk of bias is then made within each domain. A cross-domain judgement of the risk of bias for the entire study is made based on the risk within each individual domain. Both authors independently assessed the risk of bias in each included study. Disagreements in any single domain or across domains were resolved by discussion.
We identified a set of variables likely to confound estimates of the effect of child marriage on a wide range of health outcomes in advance to facilitate assessment of bias in this domain. These variables and their relationships to child marriage and health, broadly defined, are illustrated in the simplified Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) in Fig. 1 . The prevalence of child marriage has fallen over time in many countries, which means that the likelihood of marrying before the age of 18 differs across birth cohorts [ 6 , 19 ]. As discussed above, childhood socioeconomic conditions and gender inequality may lead to child marriage. They may also influence health later in life through a variety of causal pathways. We also considered spousal characteristics a source of confounding because the presence of an available spouse may drive child marriage. For example, a potential husband willing to pay a bride price for a young wife may motivate a family to marry a girl child. The same characteristics of the spouse that may motivate the marriage, such as his age, wealth, and attitudes regarding gender equity, may influence the married child’s health later in life through mechanisms like controlling behaviour. In studies that use pooled data from across multiple regions or countries, it is also important to control for confounding by country/regional-level variables that affect both the probability of child marriage and health. The DAG also illustrates our assumption that the effects of child marriage on health are often mediated through educational attainment and socioeconomic conditions after marriage.
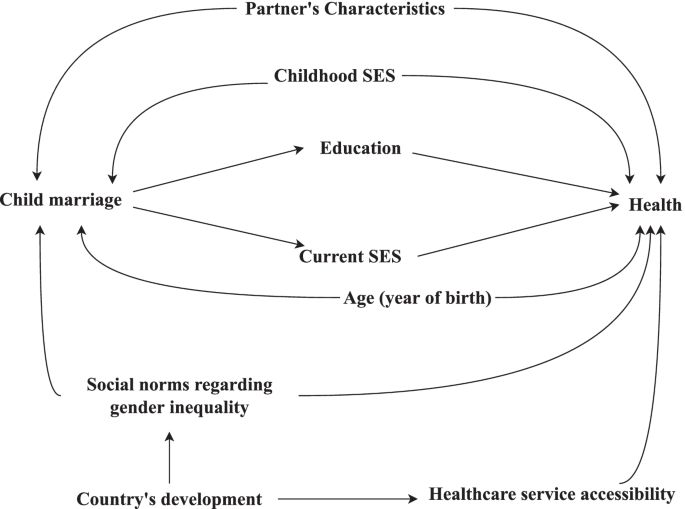
Directed acyclic graph illustrating assumed causal relationships between child marriage and a wide range of health outcomes
We synthesized results narratively. Included studies considered a wide range of health outcomes, as intended given our search strategy. We found it most intuitive and pragmatic to synthesize results within broad outcome categories, such as the effects of child marriage on contraceptive use, on maternal health care, and on mental health. These categories emerged from the data and were not pre-specified. Meta-analyses were not conducted because the studies examined a wide range of health outcomes that were measured in different ways. The serious risk of bias in all included studies, discussed below, also made quantitative synthesis inappropriate.
Our search strategy returned a total of 2767 unique records from MEDLINE, Embase, Ovid Global Health and Google Scholar, as shown in Fig. 2 . After title and abstracting screening, the full text of 126 articles was reviewed. Fifty-six of these studies met our inclusion criteria and two additional eligible studies were identified through citation tracking, for a total of 58 included articles.
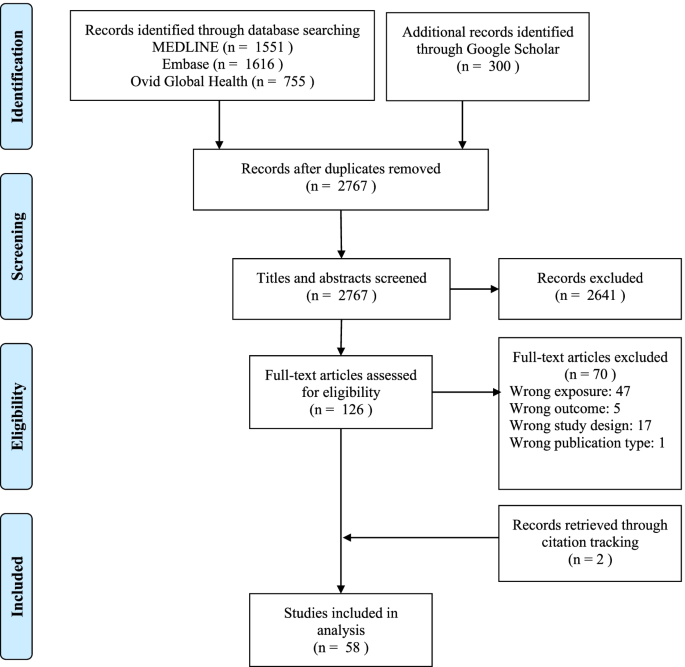
PRISMA flow diagram illustrating the process used to identify eligible studies
Selected characteristics of all 58 studies included in our review are presented in Table 1 . These studies were published between 1989 and 2020 but the vast majority ( n = 55, 95%) were published in 2010 or later and more than half ( n = 31, 53%) were published between 2016 and 2020, which reflects the relatively recent rise of child marriage on global health and development agendas. Included studies were based in 70 countries across the globe, as illustrated in Fig. 3 . Nearly all studies, 57 of 58, were based in low- and middle-income countries according to World Bank classifications [ 20 ]; the single exception was a study based in the United States [ 21 ]. The geographic distribution of studies included in our review was heavily focused in South Asia ( n = 30, 52%) and Sub-Saharan Africa ( n = 27, 47%), which is perhaps unsurprising given that countries in these regions have some of the highest rates of child marriage in the world [ 9 ]. However, more than half of the studies included in our review were based in just three countries: India ( n = 13), Bangladesh ( n = 8) and Ethiopia ( n = 11). Studies from regions other than South Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa were nearly all included in a handful of studies that analyzed survey data from multiple countries simultaneously [ 22 , 23 , 24 ].
Nearly all included studies, 55 of 58 (95%), were based on the analysis of cross-sectional survey data. More than half ( n = 34, 59%) relied on data from a single source, the Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS), or their precursor, the World Fertility Surveys (WFS).
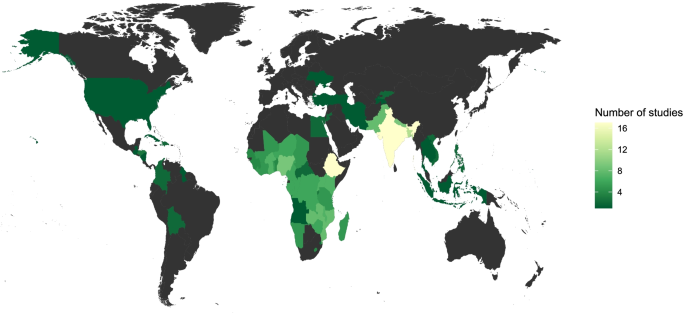
Geographic distribution of included studies
Bias assessment
All studies included in our review were determined to be at serious or critical risk of bias based on assessment using ROBINS-I. The summary risk of bias assessment for each study is listed in Table 1 ; risk of bias within each ROBINS-I domain in each study is detailed in Supplementary File 2 . Confounding was the most prevalent concern. Every study was deemed to be at serious to critical risk of bias in this domain, most often because of failure to account for important sources of confounding and inappropriate adjustment for variables affected by age at marriage that are on the causal pathway. Cross-sectional surveys like the DHS often do not collect information necessary to control for confounding. Failure to control for major sources of confounding like childhood poverty and gender inequality may result in overestimation of the harmful effects of child marriage. The second common source of bias was adjustment for variables measured after marriage that are likely on the causal pathway between age at marriage and the health outcomes being studied. To illustrate, the authors of many studies included in this review acknowledged that age at marriage may dictate how long a girl stays in school and that her educational attainment may subsequently influence a wide range of health outcomes. Unfortunately, they then adjusted for educational attainment in regression analyses. This will very likely result in biased estimates because educational attainment was measured after marriage and is more likely to be a mediator than a confounder (Fig. 1 ) [ 79 , 80 ]. Adjusting for it may remove some of the effect of child marriage on health and lead to underestimates of effect. Given that these two issues may bias results in different directions, predicting the net direction of confounding within studies is challenging. Other sources of bias also affected many of the studies in this review, including selection and measurement biases. Few authors discussed the potential influence of bias on their estimates or their conclusions.

The health consequences of child marriage
Studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on a variety of health outcomes. The most common outcomes were measures of reproductive health, such as fertility and fertility control, maternal health care utilization, intimate partner violence, mental health, and nutritional status. The following paragraphs synthesize the literature in each of these categories. In light of the serious risk of bias in all included studies, we interpreted these results with a high degree of caution. We assessed the direction of effect measures, meaning whether the study found that child marriage increased or decreased the probability of experiencing the outcome, and the consistency of directionality across studies within each outcome category. We also assessed the precision of effect measures by evaluating the width of confidence intervals surrounding those measures. We did not interpret the magnitude of the effect estimates from individual studies due to the risk of bias.
The effect of child marriage on the number and timing of births
Eleven studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the number of children born, though this outcome was not consistently measured. Some studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the odds of having given birth to any children [ 34 , 50 , 63 ], the odds of having three or more children [ 24 , 46 , 50 , 63 , 75 ], four or more children [ 34 ], five or more children [ 37 , 69 ], or a continuous measure of the total number of children ever born [ 24 , 25 , 30 , 46 , 54 ]. The age ranges of the people included in these studies also differed, leading to variation in the time frame over which these births could have occurred. Child marriage was correlated with higher fertility in nearly all studies regardless of how the outcome was defined. The only exception was a study from Ethiopia that found no effect [ 30 ]. Ten of these studies focused on fertility exclusively among women. Misunas et al. [ 24 ] focused on men and came to similar conclusions: child marriage increased the odds that men aged 20-29 had fathered three or more children and increased the average number of children fathered by the ages of 40-49 [ 24 ].
A second commonly examined outcome was the likelihood of giving birth within the first year of marriage. Four studies based on data from South Asia [ 39 , 46 , 50 , 63 ] and one study based on pooled data from multiple countries in Africa [ 75 ] examined this outcome. Three of these studies [ 46 , 50 , 75 ] reported that marriage before the age of 18 decreased the odds of giving birth within the first year of marriage. The remaining two [ 39 , 63 ] did not find any evidence of a relationship between child marriage and this outcome.
We also identified five studies that estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of giving birth before a specified age, often referred to as early, teen, or adolescent pregnancy [ 23 , 26 , 31 , 32 , 34 ]. Three of these studies found that child marriage increased the odds of giving birth before the age of 20 [ 26 , 31 , 32 ], the other two reported that child marriage increased the odds of giving birth before the age of 18 [ 23 , 34 ]. Two studies also estimated the effect of child marriage on mean age at first birth and found that those who married before the age of 18 gave birth for the first time at younger ages, on average, than those who married at older ages [ 32 , 46 ].
Collectively, this evidence indicates that women who marry as children often begin having children of their own at earlier ages when compared to their peers who marry after their 18th birthdays, and that they tend to have a larger number of children over their lifetimes. This is not surprising, given that marriage changes sexual behavior in ways that increase the risk of pregnancy. Essentially, girls who marry at earlier ages spend a longer time at risk of pregnancy than those who marry later.
The effect of child marriage on birth intervals
The World Health Organization recommends an interval of at least 24 months between a live birth and a subsequent pregnancy to reduce the risk of poor maternal health outcomes [ 81 ]. Five studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of repeated childbirths in less than two years [ 39 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. All five used samples of women between the ages of 20 and 24 who were included in DHS. A sixth study based on a small cross-sectional sample of women aged 15-49 from Ethiopia estimated the effect on repeated childbirth in less than three years [ 27 ]. These studies came to different conclusions. Two studies by the same author reported that child marriage increased the odds of repeated childbirth within two years in India [ 62 , 63 ] but another study based on the same data source found that women who married as children were less likely to have two births within a two-year period than those who married at older ages [ 39 ]. There were also differences in the results of research from Pakistan: one study reported that child marriage made it more likely that women would have two births within two years [ 50 ] while another found no evidence that child marriage influenced this outcome [ 39 ]. Child marriage protected against short birth intervals in Nepal [ 39 ] and in an analysis of data from 34 African countries [ 75 ]. There was no evidence that child marriage influence the likelihood of short birth intervals in Bangladesh [ 39 ].
These results, which range from harmful to protective effects, indicate that child marriage is not clearly or consistently correlated with short birth intervals.
Child marriage, unwanted or mistimed pregnancy, and pregnancy termination
Seven studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing a mistimed or unwanted pregnancy [ 39 , 46 , 47 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. All seven were based on analyses of DHS data. The DHS typically asks women whether pregnancies were wanted at the time they occurred, wanted later (i.e., mistimed), or not wanted. Interestingly, six of the seven studies that examined this outcome reduced these categorical responses into a binary measure: women were categorized as having an unwanted pregnancy if they reported that they had a mistimed pregnancy or if they became pregnant when they did not want any more children [ 39 , 46 , 50 , 62 , 63 , 75 ]. The rationale for doing this was not explained in any of the studies. The remaining study [ 47 ] only categorized instances in which a woman became pregnant at a time when she did not want any more children as unwanted.
Estimates of the effect of child marriage on this outcome are mixed. A study from 34 countries in Africa reported that child marriage protected against mistimed/unwanted pregnancies [ 75 ]. Studies from India, Pakistan, and Nepal concluded that child marriage increased the odds of experiencing mistimed/unwanted pregnancy [ 39 , 50 ]. Three studies from Bangladesh came to different conclusions. One found no relationship between child marriage and this outcome [ 39 ] while another reported that child marriage increased the odds of mistimed/unwanted pregnancy [ 46 ]. The third used a different definition of the outcome and found that marriage before the age of 15 was positively associated with unwanted pregnancy (mistimed pregnancies were treated as wanted) but no evidence that marriage between the ages of 15 and 17 affected the likelihood of unwanted pregnancy [ 47 ].
Three of these studies also estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing two or more mistimed or unwanted pregnancies [ 39 , 62 , 63 ]. Godha et al. reported a large effect of child marriage on having multiple mistimed/unwanted pregnancies in India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan but results were inconclusive in Nepal [ 39 ]. Two studies by the same author reported that child marriage increased the odds of having multiple mistimed/unwanted pregnancies in India [ 62 , 63 ].
We identified eight studies of the effect of child marriage on pregnancy outcomes [ 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 57 , 63 , 66 , 75 ]. Six of these relied on the DHS, which typically asks female respondents, “Have you ever had a pregnancy that miscarried, was aborted, or ended in a stillbirth?” [ 82 ]. The wording of this question makes it impossible to examine these outcomes separately. As a result, most studies based on the DHS used a composite outcome that grouped these three events despite differences in their intendedness. Five studies based on the DHS concluded that child marriage increased the odds of having a pregnancy end in either miscarriage, abortion, or stillbirth [ 39 , 48 , 50 , 63 , 75 ]. Exceptionally, the 2007 Bangladesh DHS asked a yes or no question regarding whether a woman had ever terminated a pregnancy. Using responses to this question, Kamal reported that marriage before the age of 15 was correlated with higher odds of termination but no evidence that marriage between 15 and 17 years of age influenced this outcome [ 47 ].
Two studies from India used other cross-sectional data sources and defined their outcomes differently. Santhya et al. used a combined outcome of miscarriage and stillbirth and found that child marriage increased the likelihood of experiencing either of these birth outcomes. [ 66 ]. Paul considered stillbirth and miscarriage separately. Marriage before the age of 15 increased the odds of stillbirth and miscarriage, but marriage between the ages of 15-17 was no less risky in this regard than marriage at 18 or later [ 57 ].
Child marriage and contraceptive use
Fifteen of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on various aspects of contraceptive use [ 23 , 24 , 32 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 43 , 46 , 53 , 56 , 62 , 63 , 65 , 66 , 75 ]. All were based on cross-sectional data and thirteen used data from the DHS.
Of these fifteen studies, eight estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood that women were using contraception at the time the surveys were conducted [ 32 , 39 , 40 , 46 , 53 , 62 , 63 , 65 ]. As with other outcomes, results were mixed. Child marriage reportedly increased the likelihood of using modern contraception in India and Bangladesh [ 39 ]. Results from Pakistan and Nepal indicate that the same may be true in those countries but the estimates were imprecise [ 39 ]. A second study from Nepal concluded that child marriage led to lower odds of using modern contraception [ 65 ]. The two studies from Nepal used different samples of women, which may partially explain the differences in their results. A study based on pooled data from 18 African countries found that child marriage was correlated with a lower likelihood of using modern contraception [ 53 ]. However, results varied markedly between countries and across geographic regions; in some, child marriage appeared to increase the likelihood of using modern contraception [ 53 ]. In Ghana, de Groot et al. found that child marriage was not correlated with the odds of using any form of contraception or with the use of modern contraceptives [ 32 ].
Two other studies investigated the effect of child marriage on the use of any method of contraception, including those not classified as modern [ 40 , 46 ]. Marriage prior to the age of 15 led to lower odds of contraceptive use in Rwanda, but there was no indication that those who married between 15 and 17 years of age were any more or less likely to use contraception than those who married at older ages [ 40 ]. In Bangladesh, women who married as children were more likely to be using some form of contraception at the time of the survey than those who married at the age of 18 or older [ 46 ]. In yet another iteration of this outcome, Yaya [ 75 ] reported that women who married as children were more likely to have ever used modern contraception. A single study estimated the effect of child marriage among men on the likelihood that they were using modern contraception [ 24 ]. In five of ten countries studied, child marriage was not related to modern contraceptive use. In two (Honduras and Nepal), child marriage seemed to slightly increase the odds of contraceptive use, but it decreased the likelihood in Madagascar [ 24 ].
A second outcome that has received particular focus is whether a woman used contraception before her first pregnancy. All four studies that examined the effect of child marriage on this outcome were based on data from South Asia [ 39 , 56 , 63 , 66 ] and concluded that marrying as a child decreased the likelihood that a woman used contraception prior to her first pregnancy [ 39 , 56 , 63 , 66 ]. The authors of these studies frequently interpreted their results as an indicator of uncontrolled fertility that may place girls and their children at risk of poor health outcomes [ 39 , 56 , 63 ]. However, this relationship is more challenging to interpret because the outcome variables used did not capture whether pregnancies were desired shortly after marriage or the outcomes of those pregnancies.
Four studies estimated the impact of child marriage on the likelihood that a woman had an unmet need for contraception [ 23 , 32 , 41 , 43 ]. This outcome was conceptually defined as a woman who is sexually active but not using contraception and who reports a desire to delay the next birth (a need for spacing), have no more births (a need for limiting), or a combination of the two. Once again, conclusions differ between studies. Using pooled DHS data from 47 countries, Kidman and Heymann found that marrying as a child increased the likelihood that women had an unmet need for contraception to either space or limit births [ 23 ]. An analysis of DHS data from Ethiopia found that women who married as children were less likely to have an unmet need for spacing and less likely to have an unmet need for limiting births compared to women who married at older ages [ 41 ]. In Zambia, child marriage was correlated with a greater unmet need for spacing and for limiting [ 43 ]. In Ghana, de Groot et al. found that child marriage was not correlated with an unmet need for limiting [ 32 ]. These studies all used different samples, which may partially explain the differences in their results.
Child marriage and use of maternal health care
Nine of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on the use of health care during pregnancy, at the time of delivery, and during the post-partum period, which we collectively refer to as maternal health care [ 33 , 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 62 , 66 , 67 , 74 ].
Studies of prenatal care defined their outcomes as the receipt of at least one prenatal checkup [ 49 , 62 ], the receipt of four or more prenatal checkups [ 49 , 58 , 67 ], or a count of the total number of prenatal checkups received [ 39 , 53 ]. Once again, results within countries come to different conclusions. In Nepal, one study found that women who married as children were less likely to receive four or more prenatal checkups [ 67 ] while another found no evidence that child marriage influenced this outcome [ 39 ]. A study from India found no indication that child marriage affected prenatal care [ 39 ] but two others concluded that child marriage decreased the likelihood of receiving at least one checkup and of receiving at least four checkups [ 58 , 62 ]. In one study from Pakistan, women who married as children were less likely to receive any prenatal care than those who married at older ages, but there was no difference in the likelihood of receiving four or more checkups [ 49 ]. A separate study from the same country reported that child marriage had no effect on the number of prenatal care checkups [ 39 ]. The effect of child marriage on the number of prenatal care visits varied between geographic regions in Africa. In some, child marriage appeared correlated with a decrease the number of visits while in others there was no effect [ 53 ].
Compared to other outcomes, the results of studies that estimated the impact of child marriage on the likelihood of delivering in a health care facility were remarkably consistent. Across geographic locations, all seven studies that examined this outcome concluded that child marriage reduced the likelihood of delivery in a health care facility [ 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 66 , 67 , 74 ]. Six of the same studies also found that women who married as children were less likely to have a skilled health care provider present during delivery [ 39 , 49 , 53 , 58 , 67 , 74 ].
Only two studies considered post-natal care [ 58 , 67 ]. One reported that child marriage led to lower likelihood of a post-natal checkup within 42 days of delivery in India [ 66 ] while the other found a lower likelihood of a checkup within 24 h of delivery in Nepal [ 75 ].
Child marriage and intimate partner violence
Sixteen studies estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of experiencing intimate partner violence [ 22 , 23 , 29 , 35 , 38 , 42 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 66 , 70 , 71 , 77 ]. Fifteen of these studies were based on cross-sectional data [ 22 , 23 , 29 , 35 , 38 , 42 , 51 , 53 , 55 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 66 , 70 , 71 ] and eight (50%) were based on the DHS [ 22 , 23 , 51 , 53 , 60 , 62 , 64 , 70 ]. The DHS measures intimate partner violence by asking female respondents a series of questions regarding their experience of specific acts. For example, physical violence is assessed by asking women whether they have been slapped, kicked, or pushed, among other actions. Sexual violence is assessed by asking whether the respondent’s husband has forced her to have sex or perform sex acts when she did not want to. Emotional violence is measured by asking whether her spouse has humiliated or threatened her [ 83 ]. Studies based on data from sources other than the DHS tended to use the same or very similar questions to measure the experience of violence.
Physical violence was the most frequently examined outcome but was measured over different time frames across studies. Some estimated the likelihood of ever having experienced physical violence from a husband or partner while others considered only the year prior to the survey. Still, others focused on the 3 months prior to the survey [ 35 ], the 9 months between survey waves [ 77 ], or during pregnancy [ 38 ]. Regardless of the time period during which violence was measured, the conclusions of these studies were fairly consistent: nearly all reported that marrying as a child increased the likelihood of experiencing physical violence [ 22 , 38 , 51 , 55 , 60 , 64 , 66 , 71 , 77 ]. A study from Ethiopia found no indication that child marriage had an effect on this outcome but it considered a relatively short time period of 3 months [ 35 ].
Estimates of the effect of child marriage on the experience of sexual violence were much less consistent. Two studies from India came to conflicting conclusions. Raj et al. found that child marriage did not increase the likelihood of experiencing sexual violence at any point or in the year prior to the 2005-06 National Family Health Survey [ 64 ]. However, a study by Santhya et al. based on survey data collected from five Indian states between 2006 and 2008 found that child marriage did increase the likelihood of ever experiencing sexual violence [ 66 ]. Studies from Bangladesh and Ghana reported that women who married as children were no more or less likely to experience sexual violence than those who married at later ages [ 60 , 71 ]. Two studies that pooled DHS data across multiple countries also found mixed results [ 22 , 53 ]. Olamijuwon used data from 18 African countries and found that child marriage increased the odds of experiencing sexual violence in Central, East, and Southern Africa, but there was no evidence of a statistical relationship in West Africa [ 53 ]. Kidman used DHS data from 34 countries across the globe and reported that child marriage seemed to increase the odds of experiencing sexual violence in the year prior to the surveys in all included geographic regions except Europe and Central Asia [ 22 ]. Erulkar found that women who married as children in Ethiopia were more likely to report that their first sexual experience was forced [ 35 ].
Only two studies, one from Pakistan and one from Ghana, considered emotional violence as a stand-alone outcome. Both concluded the child marriage led to an increase in the likelihood of ever experiencing emotional violence from an intimate partner [ 51 , 71 ].
Five studies considered only combined outcomes that mixed indicators of physical and sexual violence [ 62 , 70 ], or physical, sexual, and emotional violence [ 23 , 29 , 42 ]. All of these found that child marriage was associated with increased reporting of these composite measures of violence, but some results were sensitive to the sample used and were inconsistent across locations [ 70 ]. Hong Le et al. considered whether child marriage affected the likelihood of violence among boys but was underpowered to detect any effect [ 42 ].
Child marriage and mental health
Five of the studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on various aspects of mental health. These studies relied on cross-sectional data collected from Ghana, Iran, Ethiopia, Niger and the United States [ 21 , 32 , 36 , 44 , 45 ]. Women in the United States who married before the age of 18 were more likely to report experiencing a wide range of mood, anxiety, and other psychiatric disorders in adulthood when compared to those who married at later ages [ 21 ]. The authors of a small study from a single county in Iran found that women who married as children reported more depressive symptoms than those who married at the age of 18 or older [ 36 ]. John, Edmeades, and Murithi examined the relationship between child marriage and multiple domains of psychological well-being in Niger and Ethiopia [ 44 ]. The authors found that marriage before the age of 16 was correlated with poorer overall psychological well-being, but no evidence that marriage between the ages of 16 and 17 was associated with poorer outcomes when compared to women who married at the age of 18 or later [ 44 ]. In Ghana, child marriage seemed to protect against measures of stress. The Ghanaian study also found no indication of differences in levels of social support between women who married before the age of 18 and those who married after their 18th birthdays, though these odds ratio estimates were very imprecise [ 32 ].
Child marriage and nutritional status
Six studies included in our review estimated the effect of child marriage on indicators of nutritional status [ 28 , 34 , 52 , 61 , 76 , 78 ]. Four focused exclusively on pregnant women. Two studies from Ethiopia examined the relationship between child marriage and mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) [ 52 , 76 ]. One reported that pregnant women who married before the age of 18 were more likely to have an MUAC less than 22 cm, often interpreted as a marker of undernutrition [ 84 , 85 ], compared to those who married later on [ 52 ]. The other found that marrying before the age of 15 increased the likelihood of MUAC <22 cm but no evidence that marrying between the ages of 15 and 17 affected this outcome [ 76 ]. A third study from Ethiopia reported that child marriage led to an increase in the prevalence of Vitamin A deficiency among pregnant or recently post-partum women [ 28 ].
Two other studies focused on women who were not pregnant and used body mass index (BMI) as the indicator of nutritional status [ 34 , 78 ]. Their results diverge. Yusuf et al. found that women in Nigeria who married as children were more likely to have a BMI less than 18.5, frequently interpreted as underweight among adults. However, in a study of 35 African countries, Efevbera et al. reported that child marriage was protective against being underweight (BMI<18.5) [ 44 ]. Interestingly, the authors of these studies offered plausible explanations for effects in either direction. Efevbera et al. hypothesize that girls who marry as children may gain access to more plentiful food at an earlier age and that repeated pregnancies during adolescence might result in greater weight gain relative to those who marry at later ages [ 34 ]. In contrast, Nigatu et al. note that repeat pregnancies in quick succession may have a detrimental impact on cumulative nutritional status [ 52 ]. This suggests that the mechanisms through which age at marriage may affect subsequent nutritional status have not been thoroughly considered.
Other health consequences of child marriage
A few of the studies included in our review examined outcomes other than those discussed above. We note them briefly here. A case-control study from India reported that women diagnosed with cervical cancer were more likely to have been married before the age of 18 [ 72 ]. A large, pooled analysis of DHS data from 47 countries reported that child marriage was associated with symptoms of sexually transmitted infections [ 23 ]. A small, cross-sectional study from a single Indian state found no evidence that child marriage led to an increase in the odds of obstetric fistula [ 68 ]. A third study from India examined the effect of child marriage on the odds of experiencing at least one complication during pregnancy, delivery, or within two months after delivery [ 57 ]. Marriage before the age of 15 seemed to increase the likelihood of pregnancy complications, but there was no evidence of an effect for marriage between 15 and 17 years. Child marriage was not associated with delivery complications, but was associated with postnatal complications [ 57 ]. A study from Ghana found no indication that child marriage influenced the likelihood of self-reported poor health, of being ill in the two weeks prior to the survey, or of having a health insurance card but did report that child marriage increased the odds of having difficulty with activities of daily living, such as bending or walking [ 32 ].
Our systematic review synthesized research on the health consequences of marrying before the age of 18. Studies almost uniformly found that women who married before the age of 18 began having children of their own at earlier ages and gave birth to more children over the course of their reproductive lives when compared to those who married at the age of 18 or later. Whether these outcomes, considered alone, are harmful to health is not clear. Though there are many reasons to be concerned about adolescent childbearing, none of the studies of the effect of child marriage on the timing of births considered whether those pregnancies were planned or desired or whether they resulted in obstetric complications or maternal morbidity or mortality [ 23 , 26 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 39 , 46 , 50 , 63 , 75 ]. Similarly, having multiple births, especially at short intervals, may increase the risk of obstetric complications and subsequent morbidity or mortality. However, studies that compared the number of children born to women who married before the age of 18 with the number born to those who married at later ages also did not measure whether those pregnancies were planned or whether they led to harm [ 24 , 25 , 30 , 34 , 37 , 46 , 50 , 54 , 63 , 69 , 75 ]. Rather, studies seemed to assume that these are negative outcomes without directly measuring intentions or harms.
A separate set of studies that estimated the effect of child marriage on the experience of mistimed or unwanted pregnancies came to divergent conclusions: some found that child marriage increased the likelihood of these outcomes but others found that child marriage protected against them or had no effect. Studies of whether child marriage affected the likelihood of obstetric complications, miscarriage or stillbirth did not consider maternal age when those events occurred [ 39 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 57 , 63 , 66 , 75 ]. Moreover, the fact that child marriage corresponds with a larger number of pregnancies means that girls who married prior to the age of 18 had more opportunities to experience these events compared to those who married later; this was not discussed in any of the studies we identified.
The results of studies in other outcome domains are very mixed and challenge some common narratives regarding child marriage. To illustrate, studies included in this review came to conflicting conclusions regarding whether child marriage increases or decreases the use of modern contraception, the likelihood of giving birth within the first year of marriage, and the likelihood of repeated childbirth within two years. Conclusions regarding mistimed and unwanted pregnancies were also mixed, as noted above. Collectively, these results suggest that child marriage is not uniformly characterized by an inability to control the number or timing of births and suggests that a more cautious approach to discussions of agency within these marriages is warranted, at least regarding fertility and fertility control.
Across studies, women who married as children were less likely to give birth in a health care facility or with assistance from a skilled health care provider. These findings raise concerns about access to emergency obstetric care and subsequent birth outcomes for both mother and child. However, we found only one study that estimated the effect of child marriage on the likelihood of complications during pregnancy, delivery, and the postpartum period [ 57 ] and consideration of the consequences for the infants born was beyond the scope of this review. This statistical relationship could be confounded by lack of access due to geographic distance. Child marriage is more common in rural areas, where health care facilities and skilled health care providers may be more spread out. It may also be a function of gender inequality, which may manifest as an inability to seek care without permission. Future research should consider the potential for confounding by these and other variables and investigate whether place modifies this relationship.
Child marriage could plausibly affect many aspects of maternal and reproductive health through complex causal pathways. However, most of the studies included in our review did not discuss causal mechanisms in detail, which may have hindered their ability to identify and account for various sources of bias. More thorough consideration and discussion of these mechanisms would strengthen the theoretical underpinnings of this body of literature and help mitigate biases. For example, use of Directed Acyclic Graphs to illustrate assumed causal relationships would help to clarify the causal pathways being studied and identify sources of bias [ 86 ].
The effects of child marriage among boys have been almost entirely overlooked. Only 2 of the 58 studies included in this review considered boys or men and one of them was underpowered to generate informative estimates [ 42 ]. This intense focus on child marriage among girls reflects the gendered nature of the practice. However, a substantial proportion of boys also marry before the age of 18 in some countries [ 7 , 24 ] and further inquiry into the health consequences among boys is warranted.
The geographic distribution of research on child marriage and health is highly skewed. The focus on South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa may be justified since these regions have some of the highest rates of child marriage in the world. However, it is unclear why just three countries, India, Bangladesh, and Ethiopia, have received such focused attention while other countries in these regions have received very little. Child marriage is certainly ongoing in many other regions of the world that have received little or no research attention, including high-income countries [ 9 , 87 , 88 ].
The geographic distribution of these studies and the range of outcomes considered is clearly reflective of heavy reliance on the DHS. The DHS is appealing because it collects information on age at marriage that is comparable across settings and over time, data are readily accessible and of high quality, and samples are typically nationally representative. However, defaulting to this data source may also have restricted the range of outcomes studied. The DHS focuses primarily on reproductive health and our review included many studies of the effect of child marriage on fertility, contraceptive use, and intimate partner violence. Far less attention has been paid to other potential harms of child marriage that are not included in the surveys, such as indicators of mental health. Importantly, the DHS does not collect information on some of the strongest confounders of many relationships between child marriage and health, including childhood socioeconomic conditions and measures of gender equality. Other data sources will be necessary to increase the geographic scope of this body of research and to overcome some of the limitations inherent in the use of cross-sectional data to estimate causal effects.
All studies included in our review were at serious to critical risk of bias. Quantification of the net magnitude of different biases on the results of each study would have made the project untenable. Considering pervasive bias, we avoided interpreting the magnitude of reported estimates from individual studies and instead took only the directionality of the estimates at face value. This allowed us to assess the (in)consistency of conclusions within domains of health. However, it is entirely possible that bias could lead to a reversal of effects, i.e., estimating a positive effect when the true effect is negative or vice versa. The bias in these studies means that it is unclear whether any of the relationships described are causal.
Nearly all studies included in our review relied on cross-sectional data. There are severe limitations to using cross-sectional research designs to estimate causal effects, and more rigorous designs are needed to further our understanding of the consequences of child marriage. Quasi-experimental designs that more effectively mitigate confounding would strengthen this body of literature and have already been used to study the effect of child marriage on educational attainment and literacy. For example, Field and Ambrus and Sunder used age at menarche as an instrumental variable to study the effect of child marriage on these outcomes [ 3 , 4 ]. Encouragement trials that randomly assign exposure to interventions meant to prevent child marriage could also be used to estimate the effects of child marriage on health outcomes, though such trials are more resource intensive to conduct [ 89 ]. However, given that the DHS and other cross-sectional data sources will likely continue to be used to investigate these relationships, the use of quantitative bias analyses to examine how sensitive estimates are to various sources of bias would be an improvement [ 90 ].
There are several limitations to this systematic review. First, to capture as wide a range of health outcomes as possible, we searched databases focused on human health and biomedicine. Relevant studies from other academic disciplines such as economics and sociology may have been missed using this approach. Second, our search was conducted in English and all included studies were published in English. Eligible studies published in other languages may have been missed, which could influence our conclusions regarding the geographic distribution of research. Finally, as noted in the introduction, child marriage may have consequences beyond the domain of health. We focused our systematic review on the health consequences of child marriage in response to growing rhetoric regarding child marriage as a population health concern. Rigorous systematic reviews of the effect of child marriage on educational and economic outcomes would be a valuable addition to the literature.
Availability of data and materials
The PROSPERO protocol and the data extraction form are publicly available through the Open Science Foundation at https://osf.io/32mu7/ .
Abbreviations
Body Mass Index
Cross-Sectional
Directed Acyclic Graph
Demographic and Health Surveys
Mid-Upper Arm Circumference
Risk Of Bias In Non-randomised Studies - of Interventions tool
Socio-Economic Status
United Nations Population Fund
United Nations Children’s Fund
United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights. Recommendations for Action Against Child and Forced Marriages [Internet]. 2017. Report No.: UNICEF/UN05222/Dragaj. Available from: https://www.ohchr.org/Documents/Issues/Women/WRGS/CEFM/RecommendationsForActionEbook.pdf
UNICEF. Early marriage: a harmful traditional practice. New York: UNICEF; 2005.
Google Scholar
Field E, Ambrus A. Early Marriage, Age of Menarche, and Female Schooling Attainment in Bangladesh. J Polit Econ. 2008;116(5):881–930.
Sunder N. Marriage age, social status, and intergenerational effects in Uganda. Demography. 2019;56(6):2123–46.
Dahl GB. Early teen marriage and future poverty. Demography. 2010;47(3):30.
Article Google Scholar
Koski A, Clark S, Nandi A. Has child marriage declined in sub-Saharan Africa? An analysis of trends in 31 countries. Popul Dev Rev. 2017;43(1):7–29.
Gastón CM, Misunas C, Cappa C. Child marriage among boys: a global overview of available data. Vulnerable Child Youth Stud. 2019;14(3):219–28.
United Nations. The Sustainable Development Goals Report 2018. New York, NY; 2018.
Girls Not Brides. Child Marriage Atlas. [cited 2021 Jul 3]. Available from: https://atlas.girlsnotbrides.org/map/
UNICEF. Ending Child Marriage: Progress and Prospects. New York; 2014. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/media/files/Child_Marriage_Report_7_17_LR.pdf
Wodon Q. Child marriage: A persistent hurdle to health and prosperity. World Bank. 2015 [cited 2020 Jul 28]. Available from: https://blogs.worldbank.org/health/child-marriage-persistent-hurdle-health-and-prosperity
United Nations Population Fund. Marrying too young: end child marriage [Internet]. New York, NY: United Nations Population Fund; 2012 [cited 2020 Apr 27]. Available from: http://www.unfpa.org/webdav/site/global/shared/documents/publications/2012/MarryingTooYoung.pdf
UNICEF. Child Marriage. 2021 [cited 2020 Jul 30]. Available from: https://www.unicef.org/protection/child-marriage
Haddaway NR, Collins AM, Coughlin D, Kirk S. The Role of Google Scholar in Evidence Reviews and Its Applicability to Grey Literature Searching. PLOS ONE. 2015;17(9):e0138237.
Clarivate Analytics. EndNote. 2019 [cited 2020 May 11]. Available from: https://endnote.com/
Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016;5(1):210.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016 [cited 2020 Apr 27];355. Available from: https://www.bmj.com/content/355/bmj.i4919
Hernán MA, Robins JM. Causal Inference: What If. Boca Raton: Chapman & Hall/CRC; 2020.
Male C, Wodon Q. Girls’ Education and Child Marriage in West and Central Africa: Trends, Impacts, Costs, and Solutions. Forum Soc Econ. 2018;47(2):262–74.
World Bank. World Bank Country and Lending Groups [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Aug 17]. Available from: https://datahelpdesk.worldbank.org/knowledgebase/articles/906519-world-bank-country-and-lending-groups
Le Strat Y, Dubertret C, Le Foll B. Child marriage in the United States and its association with mental health in women. Pediatrics. 2011;128(3):524–30.
Kidman R. Child marriage and intimate partner violence: a comparative study of 34 countries. Int J Epidemiol. 2016;dyw225.
Kidman R, Heymann J. Prioritising action to accelerate gender equity and health for women and girls: Microdata analysis of 47 countries. Glob Public Health. 2018;13(11):1634–49.
Misunas C, Gastón CM, Cappa C. Child marriage among boys in high-prevalence countries: an analysis of sexual and reproductive health outcomes. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2019;19(1):25.
Agyei WKA, Mbamanya J. Determinants of cumulative fertility in Kenya. J Biosoc Sci. 1989;21(2):135–44.
Ali M, Alauddin S, Khatun MostF, Maniruzzaman Md, Islam SMS. Determinants of early age of mother at first birth in Bangladesh: a statistical analysis using a two-level multiple logistic regression model. J Public Health. 2020 [cited 2020 Jul 2]; Available from: http://link.springer.com/ https://doi.org/10.1007/s10389-020-01228-9
Ayane GB, Desta KW, Demissie BW, Assefa NA, Woldemariam EB. Suboptimal child spacing practice and its associated factors among women of child bearing age in Serbo town, JIMMA zone, Southwest Ethiopia. Contracept Reprod Med. 2019;4(1):4.
Baytekus A, Tariku A, Debie A. Clinical vitamin-A deficiency and associated factors among pregnant and lactating women in Northwest Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019 Dec;19(1):506.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Begum S, Donta B, Nair S, Prakasam C. Socio-demographic factors associated with domestic violence in urban slums, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. Indian J Med Res. 2015;141(6):783.
Berlie AB, Alamerew YT. Determinants of Fertility Rate among Reproductive Age Women (15-49) in Gonji-Kollela District of the Amhara National Regional State, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Dev.:12.
Birhanu BE, Kebede DL, Kahsay AB, Belachew AB. Predictors of teenage pregnancy in Ethiopia: a multilevel analysis. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):601.
de Groot R, Kuunyem MY, Palermo T. Child marriage and associated outcomes in northern Ghana: a cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):285.
Delprato M, Akyeampong K. The Effect of Early Marriage Timing on Women’s and Children’s Health in Sub-Saharan Africa and Southwest Asia. Ann Glob Health. 2017;83(3–4):557.
Efevbera Y, Bhabha J, Farmer P, Fink G. Girl child marriage, socioeconomic status, and undernutrition: evidence from 35 countries in Sub-Saharan Africa. BMC Med. 2019;17(1):55.
Erulkar A. Early marriage, marital relations and intimate partner violence in Ethiopia. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2013 Mar;39(01):006–13.
Fakhari A, Farahbakhsh M, Azizi H, Esmaeili ED, Mirzapour M, Rahimi VA, et al. Early Marriage and Negative Life Events Affect on Depression in Young Adults and Adolescents. Arch Iran Med. 2020;23(2):10.
Gebremedhin S, Betre M. Level and differentials of fertility in Awassa town, Southern Ethiopia. Afr J Reprod Health. 2009;13(1):93–112.
PubMed Google Scholar
Gebrezgi BH, Badi MB, Cherkose EA, Weldehaweria NB. Factors associated with intimate partner physical violence among women attending antenatal care in Shire Endaselassie town, Tigray, northern Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study, July 2015. Reprod Health. 2017;14(1):76.
Godha D, Hotchkiss DR, Gage AJ. Association between child marriage and reproductive health outcomes and service utilization: A multi-country study from South Asia. J Adolesc Health. 2013;52(5):552–8.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Habyarimana F, Ramroop S. The Analysis of Socio-Economic and Demographic Factors Associated with Contraceptive Use Among Married Women of Reproductive Age in Rwanda. Open Public Health J. 2018;11(1):348–59.
Hailemariam A, Haddis F. Factors Affecting Unmet Need for Family Planning In Southern Nations, Nationalities and Peoples Region, Ethiopia. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2011;21(2):77–90.
Hong Le MT, Tran TD, Nguyen HT, Fisher J. Early marriage and intimate partner violence among adolescents and young adults in Viet Nam. J Interpers Violence. 2014;29(5):889–910.
Imasiku ENS, Odimegwu CO, Adedini SA, Ononokpono DN. VARIATIONS IN UNMET NEED FOR CONTRACEPTION IN ZAMBIA: DOES ETHNICITY PLAY A ROLE? J Biosoc Sci. 2014;46(3):294–315.
John NA, Edmeades J, Murithi L. Child marriage and psychological well-being in Niger and Ethiopia. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):1029.
John NA, Edmeades J, Murithi L, Barre I. Child marriage and relationship quality in Ethiopia. Cult Health Sex. 2019;21(8):853–66.
Kamal SM. Decline in Child Marriage and Changes in Its Effect on Reproductive Outcomes in Bangladesh. J Health Popul Nutr. 2012;20(3):317–30.
Kamal SMM. Domestic Violence, Unwanted Pregnancy and Pregnancy Termination among Urban Women of Bangladesh. J Fam Reprod Health. 2013;7(1):11–22.
Kamal SMM, Hassan CH. Child Marriage and Its Association With Adverse Reproductive Outcomes for Women in Bangladesh. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2015;27(2):NP1492-506.
Nasrullah M, Zakar R, Krämer A. Effect of Child Marriage on Use of Maternal Health Care Services in Pakistan: Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122(3):517–24.
Nasrullah M, Muazzam S, Bhutta ZA, Raj A. Girl Child Marriage and Its Effect on Fertility in Pakistan: Findings from Pakistan Demographic and Health Survey, 2006–2007. Matern Child Health J. 2014;18(3):534–43.
Nasrullah M, Zakar R, Zakar MZ. Child Marriage and Its Associations With Controlling Behaviors and Spousal Violence Against Adolescent and Young Women in Pakistan. J Adolesc Health. 2014;55(6):804–9.
Nigatu M, Gebrehiwot TT, Gemeda DH. Household Food Insecurity, Low Dietary Diversity, and Early Marriage Were Predictors for Undernutrition among Pregnant Women Residing in Gambella, Ethiopia. Adv Public Health. 2018;2018:1–10.
Olamijuwon EO, Chisumpa VH, Akinyemi JO. Unveiling the realities of marrying too young: implications of child marriage on sexual and reproductive health of girls and infant survival in sub-Sahara Africa. (Special issue on family demography in Africa: determinants and consequences.). Afr Popul Stud. 2017;31(1):3594–610.
Onagoruwa A, Wodon Q. Measuring the impact of child marriage on total fertility: a study for fifteen countries. J Biosoc Sci. 2018;50(5):626–39.
Oshiro A, Poudyal AK, Poudel KC, Jimba M, Hokama T. Intimate Partner Violence Among General and Urban Poor Populations in Kathmandu, Nepal. J Interpers Violence. 2011;26(10):2073–92.
Pandey A, Singh KK. Contraceptive use before first pregnancy by women in India (2005–2006): determinants and differentials. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(1):1316.
Paul P. Maternal Age at Marriage and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes: Findings from the India Human Development Survey, 2011-2012. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2018;31(6):620–4.
Paul P, Chouhan P. Association between child marriage and utilization of maternal health care services in India: Evidence from a nationally representative cross-sectional survey. Midwifery. 2019;75:66–71.
Prakash R, Singh A, Pathak PK, Parasuraman S. Early marriage, poor reproductive health status of mother and child well-being in India. J Fam Plann Reprod Health Care. 2011;37(3):136–45.
Rahman M, Hoque MdA, Mostofa MdG, Makinoda S. Association Between Adolescent Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence: A Study of Young Adult Women in Bangladesh. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2014;26(2):160–8.
Rahman ML, Kile ML, Rodrigues EG, Valeri L, Raj A, Mazumdar M, et al. Prenatal arsenic exposure, child marriage, and pregnancy weight gain: Associations with preterm birth in Bangladesh. Environ Int. 2018;112:23–32.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Raj A. When the mother is a child: the impact of child marriage on the health and human rights of girls. Arch Dis Child. 2010 Nov 1;95(11):931–5.
Raj A, Saggurti N, Balaiah D, Silverman JG. Prevalence of child marriage and its effect on fertility and fertility-control outcomes of young women in India: a cross-sectional, observational study. The Lancet. 2009;30(9678):1883–9.
Raj A, Saggurti N, Lawrence D, Balaiah D, Silverman JG. Association between adolescent marriage and marital violence among young adult women in India. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2010;110(1):35–9.
Raj A, Vilms RJ, McDougal L, Silverman JG. Association between having no sons and using no contraception among a nationally representative sample of young wives in Nepal. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2013;121(2):162–5.
Santhya KG, Ram U, Acharya R, Jejeebhoy SJ, Ram F, Singh A. Associations Between Early Marriage and Young Women’s Marital and Reproductive Health Outcomes: Evidence from India. Int Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2010;36(03):132–9.
Sekine K, Carter DJ. The effect of child marriage on the utilization of maternal health care in Nepal: A cross-sectional analysis of Demographic and Health Survey 2016. Wilunda C, editor. PLOS ONE. 2019;14(9):e0222643.
Singh JP, Gupta SD, Khanna A, Sharma LS. Prevalence of Obstetric Fistula and Associated Factors in Rajasthan, India. J Health Manag. 2019;21(2):193–8.
Solanke BL. Maternal socio-demographic factors associated with low parity and grand multiparity in Nigeria. Women Health. 2019;59(7):730–47.
Speizer IS, Pearson E. Association between Early Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence in India: A Focus on Youth from Bihar and Rajasthan. J Interpers Violence. 2011;26(10):1963–81.
Tenkorang EY. Explaining the links between child marriage and intimate partner violence: Evidence from Ghana. Child Abuse Negl. 2019;89:48–57.
Thakur A, Gupta B, Gupta A, Chauhan R. Risk factors for cancer cervix among rural women of a hilly state: A case-control study. Indian J Public Health. 2015;59(1):45.
Thekdi KP, Mehta PI, Thekdi PI, Kartha GP. Fertility profile, anxiety, depression of married women and its association with reproductive tract infections in the rural area of Surendranagar district. Sch J Appl Med Sci. 2014;2(1):104–8.
Uddin J, Pulok MH, Johnson RB, Rana J, Baker E. Public Health. 2019;171:6–14.
Yaya S, Odusina EK, Bishwajit G. Prevalence of child marriage and its impact on fertility outcomes in 34 sub-Saharan African countries. BMC Int Health Hum Rights. 2019;19(1):33.
Yimer B. Under Nutrition and Associated Factors among Adolescent Pregnant Women in Shashemenne District, West Arsi Zone, Ethiopia: A Communitybased Study. J Nutr Food Sci [Internet]. 2016 [cited 2020 Jul 2];06(01). Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/under-nutrition-and-associated-factors-among-adolescent-pregnantwomen-in-shashemenne-district-west-arsi-zone-ethiopia-a-communityb-2155-9600-1000454.php?aid=66531
Yount KM, Crandall A, Cheong YF, Osypuk TL, Bates LM, Naved RT, et al. Child Marriage and Intimate Partner Violence in Rural Bangladesh: A Longitudinal Multilevel Analysis. Demography. 2016;53(6):1821–52.
Yusuf OB, Gbadebo BM, Afolabi RF, Adebowale AS. Trends, pattern and socioeconomic predictors of underweight among young married women in Nigeria. Public Health Res. 2018;8(2):35–45.
Elwert F, Winship C. Endogenous Selection Bias: The Problem of Conditioning on a Collider Variable. Annu Rev Sociol. 2014;40(1):31–53.
Schisterman EF, Cole SR, Platt RW. Overadjustment Bias and Unnecessary Adjustment in Epidemiologic Studies. Epidemiol Camb Mass. 2009;20(4):488–95.
World Health Organization. Report of a WHO technical consultation on birth spacing: Geneva, Switzerland 13-15 June 2005. 2007;(WHO/RHR/07.1). Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/69855
ICF International. Demographic and Health Surveys Methodology - Questionnaires: Household, Woman’s, and Man’s. [Internet]. Calverton, Maryland, USA; 2011. (MEASURE DHS Phase III). Available from: http://www.measuredhs.com/publications/publication-DHSQ6-DHS-Questionnaires-and-Manuals.cfm
ICF International. DHS Questionnaire Modules: Domestic Violence [Internet]. Calverton, Maryland, USA; 2019 [cited 2021 Jul 3]. Available from: https://dhsprogram.com/publications/publication-DHSQM-DHS-Questionnaires-and-Manuals.cfm
Kumar P, Sareen N, Agrawal S, Kathuria N, Yadav S, Sethi V. Screening Maternal Acute Malnutrition Using Adult Mid-Upper Arm Circumference in Resource-Poor Settings. Indian J Community Med Off Publ Indian Assoc Prev Soc Med. 2018;43(2):132–4.
Ververs M, Antierens A, Sackl A, Staderini N, Captier V. Which Anthropometric Indicators Identify a Pregnant Woman as Acutely Malnourished and Predict Adverse Birth Outcomes in the Humanitarian Context? PLoS Curr [Internet]. 2013 Jun 7 [cited 2020 Aug 19];5. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3682760/
Shrier I, Platt RW. Reducing bias through directed acyclic graphs. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2008;8(1):70.
Koski A, Clark S. Child Marriage in Canada. Popul Dev Rev. 2021;47(1):57–78.
Koski A, Heymann J. Child marriage in the United States: How common is the practice, and which children are at greatest risk? Perspect Sex Reprod Health. 2018;50(2):59–65.
Baird S, Chirwa E, McIntosh C, Özler B. The short-term impacts of a schooling conditional cash transfer program on the sexual behavior of young women. Health Econ. 2010;19(S1):55–68.
Lash T, Fox M, MacLehose R. Applying Quantitative Bias Analysis to Epidemiologic Data [Internet]. 2nd ed. Springer International Publishing; 2021 [cited 2021 Jul 6]. (Statistics for Biology and Health). Available from: https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9783030826727
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Genevieve Gore at the McGill University Library for her assistance in developing the search terms used in this review.
No funding was received for the study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Epidemiology, Biostatistics and Occupational Health, McGill University, 2001 McGill College Avenue, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 1G1, Canada
Suiqiong Fan & Alissa Koski
Institute for Health and Social Policy, McGill University, 2001 McGill College Avenue, Montreal, Quebec, H3A 1G1, Canada
Alissa Koski
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
SF and AK were responsible for the study conception and design. SF conducted database searches. SF and AK screened eligible studies and extracted data from included studies. SF and AK conducted the analysis, interpreted the results, and collaboratively wrote the manuscript. SF prepared the tables and figures. AK supervised the study. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Alissa Koski .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., additional file 2., additional file 3., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fan, S., Koski, A. The health consequences of child marriage: a systematic review of the evidence. BMC Public Health 22 , 309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12707-x
Download citation
Received : 16 September 2021
Accepted : 31 January 2022
Published : 14 February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-12707-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Child marriage
- Social determinants of health
- Systematic review
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Entertainment
- Environment
- Information Science and Technology
- Social Issues
Home Essay Samples Crime Child Abuse
The Dangerous And Harmful Act Of Child Marriage
*minimum deadline
Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below

- Serial Killer
- Criminal Behavior
- Gun Violence
- Sexual Harassment
- White Collar Crime
Related Essays
Need writing help?
You can always rely on us no matter what type of paper you need
*No hidden charges
100% Unique Essays
Absolutely Confidential
Money Back Guarantee
By clicking “Send Essay”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement. We will occasionally send you account related emails
You can also get a UNIQUE essay on this or any other topic
Thank you! We’ll contact you as soon as possible.
- Skip to main content
India’s Largest Career Transformation Portal
Essay on Child Marriage for Students in English [Easy Words*]
January 16, 2021 by Sandeep
Essay on Child Marriage: A banned social practice in India where young girls below adolescent age are married off to older men with or without their consent is called child marriage. India has set the record for the 14th highest rate of child marriages globally. Rajasthan, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are child marriage hotspots in the country. Poverty, social customs and traditions are the main reasons for the existence of child marriages even today.
Essay on Child Marriage 500 Words in English
Below we have provided Child Marriage Essay in English, suitable for class 6, 7, 8, 9 & 10.
Child marriage is a marriage that takes place either between two children or an adult and a child. In most cases, the adult is a man, and the child is a small girl. Child marriage was common throughout history, but it is still prevalent in developing countries. In a survey, it was found that in countries like Niger and Bangladesh, around 20 percent of the girls under the age of 15 are married. The legal age for marriage in India for women is 18, and for men, it is 21. Many organisations like UNICEF (United Nations Children’s Funds) and CRY (Child Rights and You) are working towards preventing child marriage.
Causes of Child Marriage
Child marriage is sometimes simply followed as a tradition. People follow the practice just because it has been going on from generations in their community. In many countries, there still exists prominent gender inequality. Girls are considered a burden on their family. They are bounded by patriarchal values. Child marriage is more widespread among people who live in poverty . They feel that by marrying their daughter young, they would have one less person to educate, feed and clothe.
Impact of Child Marriage
Child marriage can have serious negative repercussions on the physical as well as the mental health of a girl. It denies her fundamental rights that every person is entitled to include the right to education, the right to rest and leisure and the right to protection from sexual abuse and exploitation. When girls are married young, they are forced to take up household responsibilities. This deprives them of a chance to educate and empower themselves. They remain dependent on their male counterparts throughout their life.
The most physiologically and psychologically draining situation for a young girl is if she attains early motherhood. It is found that girls below the age of 15 who give birth are five times more likely to die during delivery than those who are above the age of 20. The bodies of these girls are not even fully developed and capable of giving birth at such a tender age. This puts the health of the mother and the child in grave danger.
There have been more studies on how child marriage affects young girls and very few on how it distresses young boys. However, two main adverse effects of child marriage on boys are related to education and poverty. As soon as boys get married, they are burdened with the responsibility of supporting their new family. Because of this, they stop their education and take up menial jobs that do not even pay well. This behaves like a vicious cycle of poverty.
Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006
Realising the plight of young brides and grooms, the government of India came out with The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act in the year 2006. Under this act, the legal age to get married is 21 for males and 18 for females. In case an adult is found marrying a girl below the age of 18, he will be severely punished. In cases where two minor children are forcibly married, the punishment will fall upon their parents or legal guardians. Punishment includes a fine up to Rs. 1 Lakh and imprisonment for up to 2 years.
Ways to Prevent Child Marriage
To stop this practice of forced marriage, not only girls, but even their parents should be made aware of the negative consequences that child marriage brings with it. The thinking of parents that a daughter is a burden on the family needs to be changed. This mindset has a very negative impact on the self-esteem of the girl. Girls should be encouraged to make themselves literate and independent. They should be given the opportunity of getting empowered and living life on their own terms.
- Bibliography
- More Referencing guides Blog Automated transliteration Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Automated transliteration
- Relevant bibliographies by topics
- Referencing guides
Dissertations / Theses on the topic 'Child marriage'
Create a spot-on reference in apa, mla, chicago, harvard, and other styles.
Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Child marriage.'
Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the chosen work in the citation style you need: APA, MLA, Harvard, Chicago, Vancouver, etc.
You can also download the full text of the academic publication as pdf and read online its abstract whenever available in the metadata.
Browse dissertations / theses on a wide variety of disciplines and organise your bibliography correctly.
Ali, Anjum Ashraf. "Child marriage in Islamic law." Thesis, McGill University, 2000. http://digitool.Library.McGill.CA:80/R/?func=dbin-jump-full&object_id=31082.
Sabel, Johanna. "Child marriage, only for some - An argumentation analysis of the arguments regarding child marriage in the Swedish political arena." Thesis, Malmö universitet, Fakulteten för kultur och samhälle (KS), 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:mau:diva-23406.
Johansson, Nathalie. "Child Marriage : The underlying reasons and possible solutions." Thesis, Linnéuniversitetet, Institutionen för samhällsstudier (SS), 2015. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:lnu:diva-45021.
Alking, Alaa. "CHILD MARRIAGE PRACTICES IN THE SYRIAN REFUGEE CAMPS." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Teologiska institutionen, 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-396789.
Adeniyi, Olayinka Oluwakemi. "Legal protection of the girl child against child marriage (Aure Yarinya) in Nigeria." Thesis, University of Pretoria, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/64609.
Nasrullah, Muazzam [Verfasser]. "Child marriage and its impact on maternal and child health in Pakistan / Muazzam Nasrullah." Bielefeld : Universitätsbibliothek Bielefeld, 2015. http://d-nb.info/1077605277/34.
Sanmartin, Beatrice <1996>. "The violation of child brides’ human rights: the possible solutions to tackle child marriage." Master's Degree Thesis, Università Ca' Foscari Venezia, 2021. http://hdl.handle.net/10579/20483.
Kim-Im, Julia. "Children's developing social cognitions on love and marriage." CSUSB ScholarWorks, 1993. https://scholarworks.lib.csusb.edu/etd-project/474.
Sjösvärd, Eira. "Legal Approaches to Child Marriage Concluded Abroad : A Comparison between Swedish Private International Law and English and Scottish Private International Law on Child Marriage." Thesis, Uppsala universitet, Juridiska institutionen, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:uu:diva-431944.
Slighting, Sadie Andrews. "Post-birth Marriage, White-Hispanic Families, and Child Academic Achievement." BYU ScholarsArchive, 2020. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/etd/8483.
Olaborede, Adebola Olufunmi. "The cultural practice of child marriage as a challenge to the realisation of the human rights of the girl –child: a comparative study of South Africa and Nigeria." Thesis, University of Fort Hare, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/10353/2578.
Annor, Euphemia Nyantakyiwaah. "The impact of child marriage on the sub-Saharan African economy." Diss., University of Pretoria, 2017. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/64631.
Grime, Jill. "Children in between : child rights and child placement in Sri Lanka." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2000. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/3675/.
Kelly, Nancy. "Decision making in child protection practice." Thesis, University of Huddersfield, 2000. http://eprints.hud.ac.uk/id/eprint/4845/.
Lalonde, Simon. "Child rearing practices and attitudes of adolescent fathers." Thesis, University of Nottingham, 1988. http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/11500/.
Katz, Emma. "Surviving together : domestic violence and mother-child relationships." Thesis, University of Nottingham, 2015. http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/28456/.
Cartwright, Kim. "The relationship between child ADHD and maternal expressed emotion : a longitudinal analysis of child and family effects." Thesis, University of Southampton, 2013. https://eprints.soton.ac.uk/365631/.
Mgidlana, Roberta Hlalisa. "Should South Africa criminalise ukuthwala leading to child and forced marriages?" University of the Western Cape, 2020. http://hdl.handle.net/11394/7607.
Kohno, Ayako. "Exploring the Background Factors of Child Marriage in Malaysia: A Qualitative Study." Kyoto University, 2020. http://hdl.handle.net/2433/254511.
Eng, Jessica. "Addressing discourses in manuals/texts on male engagement in ending child marriage." Thesis, Malmö universitet, Fakulteten för kultur och samhälle (KS), 2019. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:mau:diva-23757.
Owohunwa, Folayemi Oluwatosin. "Extent, experiences and perceptions on the practice of child marriage in northern Nigeria." Thesis, University of Leeds, 2018. http://etheses.whiterose.ac.uk/22777/.
Worugji, Nheoma Eme. "Media portrayal of Child marriage in Nigeria in the light of existing laws." Master's thesis, Faculty of Law, 2018. http://hdl.handle.net/11427/30427.
Lackovich-Van, Gorp Ashley N. "Positive Deviance and Child Marriage by Abduction in the Sidama Zone of Ethiopia." Antioch University / OhioLINK, 2014. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=antioch1412885500.
Moschetti, Carole Olive. "Conjugal wrongs dont make rights : international feminist activism, child marriage and sexual relativism /." Connect to thesis, 2005. http://repository.unimelb.edu.au/10187/3135.
Phillips, Shannon. "Essays on HIV, Marriage and Education in Sub Saharan Africa." Thesis, Boston College, 2011. http://hdl.handle.net/2345/1993.
Bakhtibekova, Zulfiya. "Early girls' marriage in Tajikistan : causes and continuity." Thesis, University of Exeter, 2014. http://hdl.handle.net/10871/17438.
Mafhala, Vhangani Richard. "Child marriage : a violation of human rights of girls in a free South Africa." Diss., University of Pretoria, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/53428.
Wrightson, Mary. "Feminism and the practice of marriage, family, and child counseling in two California counties." Scholarly Commons, 1991. https://scholarlycommons.pacific.edu/uop_etds/2950.
Guhman, Kiran Kaur. "Violence within the family : risk factors associated with child maltreatment." Thesis, University of Birmingham, 2014. http://etheses.bham.ac.uk//id/eprint/5320/.
López, Melonio María Noel. "Asking “the child question” : - an analysis of the child perspective of Swedish legislation concerning child marriage with special focus on the recognition of those enacted in other countries." Thesis, Umeå universitet, Juridiska institutionen, 2020. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:umu:diva-175438.
Goisis, Alice. "Childbearing postponement and child wellbeing in the U.K. : reconciling and integrating different perspectives." Thesis, London School of Economics and Political Science (University of London), 2013. http://etheses.lse.ac.uk/844/.
Piper, Christine. "'Making-sense' of child neglect : an exploration of child welfare professionals' practice." Thesis, University of Huddersfield, 2013. http://eprints.hud.ac.uk/id/eprint/20345/.
Walsh, Kieran. "Risk and reflexivity in the development of Irish child protection law and policy, 1919-2017." Thesis, University of Nottingham, 2018. http://eprints.nottingham.ac.uk/51649/.
Crowe, Rachel. "Living with a child with autism spectrum disorder : sibling and parental." Thesis, University of Birmingham, 2014. http://etheses.bham.ac.uk//id/eprint/5383/.
Cheng, Can. "Parental Involvement and Child Achievement in School Among Interracial Marriage and Same-race Marriage: Comparison of White-White, Asian-Asian, and White-Asian Families." BYU ScholarsArchive, 2016. https://scholarsarchive.byu.edu/etd/5938.
Badzis, Mastura. "Teachers' and parents' understanding of the concept of play in child development and education." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2003. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/2502/.
Kavari, Elizabeth Ikka Tjipetekera. "The impact of early marriage on the education attainment of the San-girl child in Omaheke Region, Namibia." Thesis, Nelson Mandela Metropolitan University, 2013. http://hdl.handle.net/10948/d1020052.
Sharp-Jeffs, Nicola. "A lot going on : the links between going missing, forced marriage and child sexual exploitation." Thesis, University of Bedfordshire, 2016. http://hdl.handle.net/10547/622097.
Zaher, Zulfia. "The Problematic Socialization of Child Marriage in Afghanistan: Perceptions, Challenges, and Possibilities for Social Change." Ohio University / OhioLINK, 2013. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=ohiou1375720048.
Ramnath, Prudence. "Are traditional African practices relating to child marriages in the face of HIV/AIDS in violation to the South African legal framework?" Thesis, University of the Western Cape, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/11394/5124.
Boodhoo, Amanda. "An examination of collaborative working in child protection." Thesis, University of Greenwich, 2010. http://gala.gre.ac.uk/7134/.
Mawodza, Obdiah. "An assessment of the legal framework on the protection of girls from child marriages in Malawi." Thesis, University of the Western Cape, 2015. http://hdl.handle.net/11394/5151.
Valentine, Marguerite Mary. "Developing a critical theory of child abuse : a discussion of the nature of child abuse as a manifestation of the social order." Thesis, University of Warwick, 1989. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/34822/.
Kotze, Marthé. "Is the difference in minimum legal ages of marriage for girls and boys in South Africa a violation of equality?" Diss., University of Pretoria, 2019. http://hdl.handle.net/2263/73472.
Alfano, Marco. "Female and child welfare in India : an empirical analysis." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2011. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/50806/.
Chung, Yee-har Ida. "An exploratory study of marital adjustment of mothers with a first born child /." [Hong Kong : University of Hong Kong], 1992. http://sunzi.lib.hku.hk/hkuto/record.jsp?B13418075.
Coulombe, Harold. "Child labour and schooling in West Africa : a three country study." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2000. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/36635/.
Arsene, Camelia V. "The quality of parent-child relationship and health in later life." Thesis, University of Warwick, 2009. http://wrap.warwick.ac.uk/3112/.
Sayeed, Yeasmin. "Child Marriage, Human Development and Welfare : Using Public Spending, Taxation and Conditional Cash Transfers as Policy Instruments." Doctoral thesis, Örebro universitet, Handelshögskolan vid Örebro Universitet, 2016. http://urn.kb.se/resolve?urn=urn:nbn:se:oru:diva-47122.
Melchiorre, Angela. "The right balance : The minimum age for marriage and the convention on the rights of the child." Thesis, University of London, 2011. http://ethos.bl.uk/OrderDetails.do?uin=uk.bl.ethos.536783.
Child Marriages in Modern India Essay
Case study: rajasthan community; the shaikh, extent of the practice of child marriage, effects of child marriage in the community, fight against child marriages, works cited.
The aspect of child marriages is common among the Muslim communities especially among those living in South Asia and sub- Saharan Africa. Early marriage entails the marriage of children and young people who are below the age of 18 years. It is, however, predominant among those living traditional lifestyles especially in the rural areas.
There are various reasons why parents may opt to marry their children while they are still very young, for instance, poverty where parents view marriage as an opportunity for the young girl and her family at large as a source of protection against sexual assault and unwanted pregnancies among others. This paper discusses early marriages through a case study of an ethnic group in India, the Shaikh of the Rajasthan community.
The Shaikh of Rajasthan is a constituent of the larger Shaikh community present in South Asia. It is the largest Muslim community in Rajasthan. The Shaikh community faces adverse effects of child marriages in addition to parallel cousin and cross-cousin marriages as it is being practiced to great extent. There have been many incidents of child marriages among this community for instance a marriage occurred between a five-year-old girl and a ten-year-old boy in the community.
Other child marriages have also been witnessed. These two victims are far below the adult age as they should be at least eighteen years for the girl and twenty one years of age for the boy. The laws enacted in regard to marriages especially on child marriages seem ineffective due to the contradicting customs among the Muslim communities for example the prevention of Child Marriages Act.
There have been instances where people come to homesteads and demand for girls who are underage stating that they want to marry them. Most of the people get married when they are too young without the knowledge of what marriage really entails.
Most communities other than the Shaikh also practice child marriages especially days that are deemed to be of religious importance for example the Dev Uthni Ekadashi.
The practice of child marriage continue to take place among the communities due absence of political will as some politicians view their actions of restricting the practice as a threat to their political prosperity. They fear their stand could make them lose votes and support from the people who value and appreciate the practice and would do anything to safeguard its existence.
The practice of child marriages among the Shaikh and the Rajasthan community at large has been exacerbated by the government’s reluctance in preventing it and to make the matter worst, it seems to be very supportive of the same. This can be seen from its attempt to register all marriages including the child marriages.
This action raises heated debate among citizens of India and also outside the country as many people who are against early or child marriages can not comprehend the reason behind its registration.
The government fights back by saying that the registration of such marriages does not mean their legalization but instead it is a positive step towards keeping a record of the number of the existing marriages of such kind for easy detection.
The Child marriage Prevention Act also seem to be ineffective as it does not provide for punishment of individuals and parents who plan and advocate for child marriages. This makes it more comfortable to execute this practice as those involved do not fear the legal consequences that may befall them as a result of their actions (Mahan 1).
The concept of child marriage in the Indian communities has been promoted by the Indian culture which places women in very low status and their roles in the family institution stipulate they should be submissive and be good wives to their husbands.
They do not have many rights like men. Early marriages are a major cause of increased population in the community as the young people add to the number of people through child bearing (India planning commission 51).
Child marriages also deny the victims their childhood and adolescence as they experience sexual relationships very early in life hence lacking freedom. This leads to poor performances in marriage and in general life of the victims as their social development is interfered with.
The girls that get married during their early age also do not pursue their education and hence they become incompetent in various aspects of life like critical decision making. There is also some health issues associated with child marriages, for instance, sexually transmitted diseases and premature pregnancies that lead to high rates of maternal and infant mortality.
Despite increased practices among the various communities in Rajasthan like the Shaikh, there are many people who are against the practice and are ready to fight it.
A good example is the establishment of a group, the Mali community, which is set to completely do away with the practice of child marriages through taking necessary actions against those who are involved in promoting it, for instance, parents who let their underage children to engage in marriage and also those who coordinate them. Some people have also pledged not to take part in any action tends to support child marriages.
A social boycott seem to be the only option left of ending this impunity as others like the use of threats and educating the society of the bad effects of child marriages has previously failed. To fight this problem, there should be educational campaigns to increase the legal age of marriage and educate people of the adverse effects of child marriages and also establishment of an effective marriage registration system.
It is evident the practice of child marriages has been in existence in many parts of India and other Muslim communities. The policy makers have also been keen to the details associated with child marriages but it has proved difficult and almost impossible to enforce laws that govern the issue. Various studies show that the Indian government is usually not good when handling personal laws that affect particular communities and do not hail from grassroots movements.
There is, however, efforts to solve the problem for instance, bills passed like the Marriage Bill which advocated for enactment of a uniform law in regard to marriages and compulsory registration of marriages introduced in 1994 to prevent practices of polygamy and child marriages. Unfortunately, the law did not pass. Other laws as mentioned above are also present but they are not effective since they have been implemented to end child marriages.
India Planning Commission. Rajasthan Development Report. New Delhi: Academic Foundation, 2006.
Mahan, Rajan. “Rajasthan endorsing child marriage?” NDTV News. 2010. Web.
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, January 23). Child Marriages in Modern India. https://ivypanda.com/essays/child-marriages-in-modern-india/
"Child Marriages in Modern India." IvyPanda , 23 Jan. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/child-marriages-in-modern-india/.
IvyPanda . (2024) 'Child Marriages in Modern India'. 23 January.
IvyPanda . 2024. "Child Marriages in Modern India." January 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/child-marriages-in-modern-india/.
1. IvyPanda . "Child Marriages in Modern India." January 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/child-marriages-in-modern-india/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Child Marriages in Modern India." January 23, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/child-marriages-in-modern-india/.
- Tourism: Shaikh Zayed Mosque in UAE
- Indian Culture: Dances of Rajasthan
- The Science of Hadith
- Interior Design: Indian Art, Craft and Color
- The History of Jainism in India
- Rainwater Harvesting to Replenish Underground Water in India
- Underage Drinking in a College Campus
- Research Project: Underage Drinking
- Public Health Challenge: Underage Drinking
- Underage Drinking and Teen Alcohol Abuse
- Importance of Volunteerism Essay
- Survey in Research studies
- Rebuilding Families and Marriage in America’s Society
- Cultural Influences on Personality
- Single Parenthood: History and Economic Implication
- How It Works
- Topic Generator
- United States
- View all categories

Child Marriage: Causes, Effects and Prevention - Essay Sample
Introduction.
Child marriage refers to the formal or informal marriage of a child under 18 years. Child marriage mostly occurs for young girls who are married off to an older man or boy. Girls who are forced into marriage at a younger age tend to be denied the right to access education because they are married off at school-going age. These young brides under 18 years tend to experience domestic violence. This paper will provide a discussion on child marriage, focusing on the causes, effects, and preventive measures.
Is your time best spent reading someone else’s essay? Get a 100% original essay FROM A CERTIFIED WRITER!
In India, there are high percentages of child marriage. Regardless of setting the legal marriage age at 18 years. New brides are anticipated to demonstrate their fertility after marriage through the reproduction of a male firstborn child. Child brides are physically immature, and being their early pregnancy, they are at risk of dying while giving birth or develop childbirth complications. According to UNICEF's report, India has the most significant number of child marriages in the world (Lal, 2995). Child marriage has been in existence in India for decades, where young girls are married off before they mature mentally and physically. In many instances, child marriages are worse for girls than for boys because boys are usually older than the girls.
Causes of Child Marriage
Causes of child marriage are propelled by first, gender inequality where male children are perceived as being superior to the girl child. Women who are married off at a younger age tend to experience domestic violence because of the age difference between the partners in which the man is older than the wife hence resulting in family misunderstanding (Mahato 698). Generally, families tend to discriminate boys and girls when giving them an opportunity of acquiring education. Girls are perceived as a burden to the family and someone else property because, in the end, they will get married. While the boy is viewed as prospective economic family assets. Therefore, early marriages of girls seem to be the solution to avoiding educational expenditure.
Secondly, in India, child marriage is driven by betrothal, where a girl is promised to be married before they are born to secure a future. At the puberty level, the guana ceremony takes place, and this children's bride is send off to their husbands to begin marriage life( Mahato, 700). The betrothals occur for young boys and girls who are not aware of the activities taking place; thus, plans for betrothals are made without their consent.
Thirdly, gender norms, and traditional customs leads to young girls being married off to older men. Girls tend to have a low value attached to them since society expects them to be hardworking and docile. Thus child marriage is used as a means of controlling female sexuality. Customary laws in India, which are religion-based acts as a barrier to curbing child marriage.
The other cause of child marriage in India is to minimizing marriage expenditure. According to the Indian culture, the girl’s family pays the dowry to the man’s family because of this reason. When the bridegroom is highly educated, the amount of dowry required is higher. Hence, early marriage is perceived as the only solution in the reduction of marriage expenses because when a girl is educated, the husband’s family claims that she will be a dictator in the house.
Also, high rates of child marriage in India is to avoid giving the female a share of the ancestral property. Females are supposed to be given a share of the ancestry property. Early marriages for girls heirs deprive them of an opportunity to ask for ancestry share because they will be having their own families (Mahato 701). Additionally, a high level of poverty. Female children and women are denied equivalent access to resources if the family has a low social status. Low-income families ought to use child marriage as a scapegoat for the female child burden.
Effects of Child Marriage
Child marriage has a lot of effects. Foremost, the inability to manage and planning families. Research has shown that women who are married at a younger age tend to bear more children. The young mothers are incapable of controlling their children based adequately on nutrition, healthcare, as well as management of the household (Raj 932). Secondly, Indian culture prioritizes male children; thus, whenever a girl is married and does not sire a male child as the firstborn, she will be forced to conceive until when she will give birth to a male child.
Thirdly, child marriage may result in exposure to HIV infection. Young women are prone to contracting HIV as compared to their male counterparts because her vagina is not well aligned with protective cells. Married adolescent girls are at the risk of getting infected because their older spouses may engage in extramarital sexual affairs with other women.
Preventive Measures
To curb child marriage world leaders, lawmakers, individuals as well as parents need to challenge to empower girls and question norms that positions boys as superior beings than girls. India is on the fight to curb early, child and forced marriages according to its vision of 2030, which targets 5.3 sustainable development goals. First, the government has used cash incentives like Dhan Laxmi scheme and programs for teenage empowerment to motivate change in behavior associated with child marriage.
Secondly, girls should be provided with equal opportunities to pursue their education and give them a chance to live fully independent lives after completing their studies (Ghosh 60). Thirdly, there is a need to establish and implement laws and policies which are against child marriages, and stringent measures should be put in place for those who are found involving themselves in child marriage. Fines and imprisonment are some of the steps that can be applied to those lawbreakers.
Also, to end child marriage, the community, as well as the parents, need to be educated on the importance of girl child in the society. Additionally, child marriage can be eliminated through the provision of economic support and incentives to families. Lastly, through empowering girls with support networks, information as well as skills.
In conclusion, child marriage is one of the problems facing India .regardless of stating the marriage age as 18 years, young girls and boys tend to be married off at the younger generation, and child marriage tends to affect mostly the girls. The causes of childbirth include poverty, denial of the right to share ancestry property, reduction in marriage expenditure, and avoiding female education expenses. The effects of child marriage include vulnerability to HIV infection, incapability of managing and planning the household, early pregnancy, and health complications as well as frequent giving birth in search of a male child. Child marriage can be prevented through the establishment and implementation of policies, empowering girls, offering incentives and economic support, providing essential services to the girls, and creating awareness of the effects of child marriage on the community and families.
Works Cited
Ghosh, Biswajit. "Child marriage and its prevention: Role of adolescent girls." Indian Journal of Development Research and Social Action 7.1-2 (2011): 49-62.
Lal, B. Suresh. "Child marriage in India: factors and problems." International Journal of Science and Research 4.4 (2015): 2993-2998.
Mahato, Santosh K. "Causes and consequences of child marriage: A perspective." International Journal of Scientific and Engineering Research 7.7 (2016): 697-702.
Raj, Anita. "When the mother is a child: the impact of child marriage on the health and human rights of girls." (2010): 931-935.
Cite this page
Child Marriage: Causes, Effects and Prevention - Essay Sample. (2023, Aug 10). Retrieved from https://proessays.net/essays/child-marriage-causes-effects-and-prevention-essay-sample
so we do not vouch for their quality
If you are the original author of this essay and no longer wish to have it published on the ProEssays website, please click below to request its removal:
- How Social Movement, Women's Movement, and the Civil Rights Movement Affect Democracy
- Article Analysis Essay on Ban the Bike! How Cities Made a Huge Mistake in Promoting Cycling
- Essay Example on Managerial Communication & Job Satisfaction: Examining the Link
- Behold! A Parent's Dream: My Son Achieves Milestone at Finals! - Essay Sample
- Essay Example on Exploring Positive Youth Justice: Assessing Claims of Uniqueness and Robustness
- Fostering Private-Public Partnerships: The People Concern's Mission to Address Social Challenges - Free Paper
- Paper Example on Women's Role in the Bible
Liked this essay sample but need an original one?
Hire a professional with VAST experience and 25% off!
24/7 online support
NO plagiarism
Submit your request
Sorry, but it's not possible to copy the text due to security reasons.
Would you like to get this essay by email?
Interested in this essay?
Get it now!
Unfortunately, you can’t copy samples. Solve your problem differently! Provide your email for sample delivery
You agree to receive our emails and consent to our Terms & Conditions
Sample is in your inbox
Avoid editing or writing from scratch! Order original essay online with 25% off. Delivery in 6+ hours!
- About Project
- Testimonials
Business Management Ideas

Essay on Child Marriage in India
List of essays on child marriage in india, essay on child marriage in india – short essay (essay 1 – 150 words), essay on child marriage in india (essay 2 – 250 words), essay on child marriage in india – written in english (essay 3 – 300 words), essay on child marriage in india – causes, effects and prevention (essay 4 – 400 words), essay on child marriage in india – for school students (class 7, 8, 9 and 10 standard) (essay 5 – 500 words), essay on child marriage in india – facts (essay 6 – 600 words), essay on child marriage in india – for college and university students (essay 7 – 750 words), essay on child marriage in india – long essay for competitive exams like ias, ips and upsc (essay 8 – 1000 words).
Child marriage in India is still a prevalent practice. So far, we can’t seem to overcome the dark reality of child marriage in India. In a layman’s language, child marriage in India means involving a boy and girl to get into the marital bond, with or without their consent.
Audience: The below given essays are exclusively written for school students (Class 7, 8, 9 and 10 standard) and college students. Furthermore, those students preparing for competitive exams like IAS, IPS, Civil Services and UPSC can also increase their knowledge by reading these essays.
Child marriage in India is one of the most baffling of all problems which the Indian society faces. There was a time when most children were married at a very premature age. There have been several instances wherein children less than 10 years of age got married. They barely understood the meaning of marriage and yet they were tied to a bond they could do nothing about.
Causes of Child Marriage in India:
In earlier times, Child marriage in India was an age old tradition. Some of the many other causes of Child Marriage in India include poverty, illiteracy, social pressure, etc.
The Perils of Child Marriage in India:
Of course, child marriage in India is filled with too many perils. A lot of innocent lives were lost and children who should be taught the basics of education ended up being chained to family pressure. This affected the children mentally as well as physically.
The Remedial Measures:
The right thing to do is to create awareness about this issue. If we want to solve the problem of child marriage in India, we should educate both parents and children and encourage them to be independent first and then look for a partner only after attaining a certain age. Laws should also be put in place in order to get rid of this social issue.
Conclusion:
Children of today are the future of tomorrow. They must be provided with proper education in order to build a strong nation. It’s time to put an end to Child Marriage in India.
Introduction:
Child Marriage in India basically originated to prevent the girl child from being taken away by the conquerors of the nation. Child Marriage means that a girl or a boy gets betrothed to her partner even as a child purely at the consent of the parents. Even though the lawful age for a person to be married is set at 18 by UNICEF, it is not practiced in many places.
Reasons & Consequences:
Two primary reasons for Child Marriages in India is lack of education and poverty . The appalling consequences of child marriages include pregnancy- related deaths , child mothers not able to provide proper infant care, subjected to domestic violence .
Government & Laws:
Although there were laws in existence since 1929 to protect children from Child Marriages in India, it is unfortunate that “Allowance of Child Marriages without police Intervention” is being announced as Election promises in this Country. Every Citizen in this country has a role to protect and uphold the future citizens, the now Children. Many Government programs such as ApniBeti, Apna Dhan (ABAD), which translates to “My daughter, My wealth,” focus on delaying the Child marriages in India. Balika Vadhu one of the most watched melo-drama, showcased how Child Marriages are a bane to human race and the country.
As a dutiful citizen, each of us should make the children understand their human rights . Create awareness and give the child appropriate contact information to seek contacts when their cry of refusal is denied ears. This would therefore abolish child marriage in India and create a safe environment to nurture the future of the country.
Marriage is a very responsible and sacred way of uniting two people who are matured and ready to accept each other. But child marriage in India is something that is a really unethical way of uniting people, who are not only immature but also does not understand the real responsibility behind the phenomenon.
Indian law has assigned a minimum age of eighteen for girls and twenty-one for boys to legally get married. This law was passed due to the increased reporting of child marriages in India. While at one side everyone is trying to make the most out of our nation’s growth, at the other side it is too much annoying to think how children are getting mislead to lead a responsible life at their childhood.
Mainly girl children are forced to fall into child marriage in India as they are discriminated in the society because of their gender. Child marriages in India were considered by parents as a way of saving their child from abuses and other difficulties they face from the outside world. But on the other hand child marriage in India is a real spoiler of a kid’s childhood. They get on with handling more responsibilities than they even know about and many cases have been reported against this child marriage in India.
They are forced to live a life they don’t have any idea about due to this inhuman child marriage in India. The girl child is made to move out of her own house at such a young age due to child marriage in India, and live completely among strangers. She is forced to do all the household chores and other more difficult responsibilities. Child marriage in India ruins a child’s life.
Domestic violence and forced sexual abuses are also major problems due to child marriage in India. Not only girls but boys are also forced for such inhumanity. Child marriage in India is more dominant in rural areas where proper education and awareness should be spread to stop this cruelty.
Child Marriage in India is a centuries old tradition. When the 1921 census reported 600 brides in the age group of one to twelve months, Mahatma Gandhi was shocked. He became instrumental in introducing the Sarda Act or the Child Marriage Restraint Act in 1929. That was the first step taken against child marriage in India. It fixed the age of marriage for girls at 14 years and boys at 18 years. Since then many reformers and stakeholders have been advocating against child marriage in India.
Since bygone days, the dignity and reputation of families in India were heavily dependent on the chastity of their daughters. To uphold the honour, child marriage in India was prevalent at a tender age before puberty.
Due to poverty, many poor parents wished to see off their daughters through marriage at early years. Some even received monetary benefits from the groom’s family in lieu of marriage. Further, poor families also found it cheaper to conduct child marriages than adult marriages.
So, the various reasons for child marriage in India include tradition, poverty, illiteracy and social pressures.
The victims of child marriage in India are often uneducated. They do not have a broad view of their life with respect to the world. So, they often tend to pass this tradition to future generations, out of ignorance.
Due to the early marriage, these children often experience unprecedented responsibilities, suffer discontinuation of education, deterioration of health etc. Since they are physically and psychologically not ready for a married life, their childhood is frustrated with hardships of life.
Prevention:
The latest effort to prevent child marriage in India is the landmark judgment of the Supreme Court in October 2017. All along, men who raped their minor wives were protected by the law. But, according this latest judgment, sexual act with a child bride has been criminalised. This is a definite step to curb child marriage in India.
Since 2014, it has become mandatory to register marriages in order to prevent child marriage in India. The public has been encouraged to report child marriages and non-registered marriages in order to keep violations in check.
Various sensitization programs are carried out to educate the parents and the public against child marriage in India.
UNICEF sees child marriage practice as violation of human rights. One of United Nations’ sustainable goals is to eradicate child marriage in the world by 2030. Studies indicate that more than 40% child marriages of the world, happen in India. So, the International community expects a radical change in India than any other country. With dreams to become a superpower in the near future, it has become imperative to put an end to child marriage in India.
India is surging on its way to become a superpower, but it is a startling reality that an age old evil practice called child marriage still prevails in the country. India has the second highest number of child marriages according to a United Nations report. According to the statistics the State of Bihar has the highest incidence of child marriage at 68% followed by Rajasthan and Jharkhand.
Causes of Child Marriage:
According to the law in India marriageable age is18 years for girls and 21 years for boys. Child marriage in India should be seen as an exploitation of human right. This evil tradition has existed in India for a long time. From the time of the birth of a girl child she was treated as someone else’s property and hence was married at a very tender age. Another social reason to initiate child marriages was that the elders wanted to see the growth of their family with respect to the number of children as it characterized their status. Poor people practiced child marriage to get rid of their loans, taxes, whereas some people instigated it to fetch lump sum dowry.
Impact of Child Marriage:
Child marriage in India imposes huge household responsibilities, especially on innocent girl children who are not mentally and physically prepared for it. Boys who are still minors are forced to bear critical financial responsibilities and the whole family. Child marriage in India snatches the innocent childhood and the freedom to play and learn from these kids. This evil practice incubates a greater risk of contracting sexual diseases like HIV. Girls who get married at a very young age are less likely to be aware about pregnancy and correlated topics. A baby born to such mother is more likely to suffer from ailments like malnutrition.
Prevention of Child Marriages in India:
The Indian Constitution and Law prohibit Child Marriage in India in any shape or form. The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006 eradicate the flaws in previously present laws. The act strictly prohibits the marriage of a girl under eighteen years of age and a boy below twenty-one years of age. Under this law, the children have the choice to declare their marriage as annulled up to two years of reaching adulthood. Apparently, a major shortcoming of the law is that it doesn’t cover the Muslims, as this law is binding to all citizens of India. A foremost hindrance in curbing the evil practice is that most of these marriages are not registered and are carried out informally.
Marriage is a sacred union between two mature individuals who are in consensus with each other to share responsibilities and take care of each other for a lifetime. Child Marriages happen to be an illogical institution that has prevailed in the country, despite all the development and growth that the country has witnessed over the time. It needs to be understood that poverty and lack of education are the major factors that undermine the efforts to end this menace. The Government of India and different NGOs’ are working meticulously to spread awareness about child marriage in India. As a responsible citizen of India we must contribute to the fullest to eradicate this evil practise by immediately reporting to the police when one hears of child marriage taking place.
Child marriage in India is a disturbing truth that still exists in the nation. Marriage is an institution in which two mature persons agree to live with each other by sharing their responsibilities equally. But, child marriage in India is totally opposed to it.
What is child marriage in India and its history?
Child marriage in India is an informal or formal wedding amongst two persons in which the male is below 21 years of age and the girl is below 18 years of age. It is also considered as the misuse of civil rights because it is a kind of an involuntary wedding.
There is a long history behind the child marriage in India. It exists from the eras when the empire structure was predominant.
The child marriage in India was also utilized as a weapon to keep the girls safe from rapes and kidnap by foreign sovereigns. One more social motive to start child marriage in India was that the aging people in the families desired to see their grandchildren’s faces before dying.
Effects of Child Marriage In India:
The following are the effects of child marriage in India:
1. During child marriage in India, the immature girl kid needs to leave her home forcefully and have to live in a new home with lots of responsibilities. At such a small age, the girl who is not mentally mature has to take the huge responsibilities of the home.
2. Child marriage in India also results in a depression in the kids. Besides the girl child, the male child is also not so much capable of taking full responsibility of her wife and also the expenses of running a family.
3. Childhood gets vanished at the time of child marriage in India. In fact, the independence of playing and learning is also stolen in the practice.
4. There are extreme risk aspects that are associated with child marriage in India, such as, getting STDs (sexually transmitted diseases) like HIV. Girl child does not have much knowledge about pregnancy and babies of these small girls are more probable to health issues like low birth weights malnutrition, etc.
How to spread social awareness about Child Marriage in India?
The following steps should be taken to spread social awareness about child marriage in India:
1. Children have to be taught regarding their civil rights. They should know that when to decline and protest against the forceful child marriage.
2. Media can also play an important role in making people aware of child marriage in India. They can telecast some television programs or shows about this monstrous ritual which can create a massive change in the attitude of the people.
3. There should be strict laws and legal provision against the child marriage in India that can stop this evil from occurring. People indulging in such marriages should be punished reasonably by the law.
4. Government organizations and NGOs should work together to decelerate the practice of child marriage in India.
5. The current provision of punishment for child marriage in India is a few months along with some amount of fine which is completely insufficient. The severity of punishment should also increase to tackle this problem.
6. There should be an appointment of officers for the anti-child wedding in every single Indian State. There should be a rule that anybody who appears in child marriage in India must inform about it to the concerning officer for stopping this disaster to happen.
Child marriage in India should be abolished and this can only be done if people become aware of the massive consequences of this evil. Child marriage not only spoils the childhood of the kids but also their coming future.
As per Indian law, a girl before the age of 18 and a boy before the age of 21 are not considered eligible to marry. Any such disobedience is considered as child marriage and is regarded as unlawful and is a punishable offence. However, the law of terming child marriage as a punishable offence is relatively new with having come into existence just a few years before India gained independence from the British rule. Prior to it, child marriage was an accepted social practice prevalent in almost all parts of the country.
Historical Reference of Child Marriage:
The origin of the practice of child marriage is not known, though it is believed to have been commonly practised across the world before the 19 th century. Girls, as soon as they attained puberty were required to be married off. This finds a reference in the Dharamsatra as well. Additionally, there is a mention in Manusmriti that it is an offence on part of the parents to marry off a girl before she has attained puberty or if it has been more than three years after she has attained puberty. Similarly, a boy is required to be married off before he attained the age of 16 years.
Association of Dowry with Child Marriage:
The offering of gifts and wealth to the groom’s family by the bride’s family is called dowry. It has long been associated with child marriage in India. A common practice across all religions in India, it is often correlated to the age of the bride. In other words, more the age of the bride, more the demand of the dowry will be. This fear of more dowry has led to more prevalence of child marriage in India. Additionally, poverty has also been a major factor driving people towards child marriage.
Child Marriage Laws in India:
The first law against the child marriage in India came during the British rule. In the year 1929, the then British Government came up with the Child Marriage Restraint Act, which was later referred to as the Sarda Act. This law prohibited the marriage of boys under the age of 21 years and girls under the age of 18 years. Except for some states such as Jammu and Kashmir and Hyderabad, this act was enacted upon the entire country on 1 April 1930. Initially, the act proposed an imprisonment of up to three months in case of disobedience which was further amended in the years 1940 and 1978.
The Child Marriage Restraint act had some shortcomings. These shortcomings were addressed with the introduction of the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act in the year 2006. Under this law, the boys and the girls forced into marriage were provided with the option of terming their marriage as void and the dowry so given was returned to the bride’s family.
Initiatives by the Government:
According to the information of the National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), an aggregate number of 169, 222 and 280 cases have been enlisted under the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006 in the year 2012, 2013 and 2014 individually.
As per the information provided by the Government in the Lok Sabha, it is concerned about the pervasiveness of Child Marriages in the nation and has set up essential enactment viz. Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA) 2006 to handle the issue. The States/UTs now and again is as a rule routinely sought after for compelling usage of the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006. Further, State Governments are asked to take the unique activity to postpone marriage by facilitated endeavours on Akha Teejthe customary day for such marriages. Advertisements in the press and electronic media instructing people groups about the issue of Child Marriage and so forth are additionally being taken up. Stages, for example, the International Women’s Day and the National Girl Child Day are utilized to make mindfulness on issues identified with ladies and to convey to the inside stage issues, for example, kid marriage. Through the Sabla program of this Ministry, girls in the age gathering of 11 to 18 years are conferred preparing with respect to legitimate privileges of women which additionally incorporates the Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006.
Not all practices prevalent in the society were meant to benefit the people. Some of them need to be changed with time. Child Marriage is one such practice which should be stopped altogether. However, this cannot be possible only by enacting laws. The people of the country should equally support the government and oppose whenever they encounter such practices. Then only we can be successful in abolishing this practice altogether throughout the country.
Child Marriage Concept:
However, that is not the only case for child marriage in India. Most of the time, a minor girl is married off to an adult male. Such incidences are plenty and fall under the category of child marriage in India. And though most child marriages in India take place in villages, their occurrence in the urban areas cannot be denied.
In technical terms, if the girl is below eighteen years and the boy is below twenty-one years of age, then, their marriage would be considered a child marriage in India. It is believed that the youngsters below the respective ages are not mature enough.
In the case of child marriage in India, both the candidates can neither understand, give a genuine viewpoint, nor make a decision on the serious matter of marriage. Hence, such wedlock is regarded as child marriage in India. The practice of child marriage in India is highest in Bihar and lowest in Himachal Pradesh.
Factors Responsible:
Child marriage in India is practiced mostly in the rural parts of the country. There are many important factors which contribute to the existence of child marriage in India. Preference of boys over girls among rural people causes them to see the female child as a burden. Consequently, parents often marry off their daughters at an early age, resulting in child marriage in India.
Child marriage in India is also related to poverty. As the people in villages and small towns do not have sufficient sources of income, to them, marrying the girl child would mean fewer mouths to feed. Not only that, but child marriage in India also involve selling the minor girl to the groom’s family.
Lack of education has an equal role in child marriage in India. When adults are not well-educated, they are unaware of the severe impacts of child marriage in India. The absence of awareness for the mental, physical, and emotional repercussions of this malpractice leads to the perpetuation of child marriage in India.
Social customs and traditions still define the mindset of particular castes and communities in the society. Child marriage in India has been practiced since the invasion by the Mughals and then the Britishers. It was performed to protect the young girls from abduction and sexual abuses.
Nonetheless, the modern scenario of child marriage in India revolves around the patriarchal system. Girls do not have much say when it comes to their sexual rights and freedom. It is the male who possesses more power in such matters.
Consequences of Child Marriage:
Child marriage in India imposes many untimely hardships upon both girls and boys. The male child has to take up the role of breadwinner for his wife. The female child has to indulge in sex and motherhood, even when she is not prepared for it mentally, physically and psychologically.
In many ways, child marriage in India steals childhood away from the minors. It crushes their dreams and innocence. Child marriage in India has gruesome effects on the mind and body of the girl child. The body of a young girl is not fully developed. She is also vulnerable emotionally. An early marriage disturbs her whole health poorly.
Unwanted and multiple pregnancies suck the life out of her. Sometimes, the painful process of childbirth may also cause the death of the young mother. Miscarriages are common in the young brides. Child marriage in India is the major cause of child mortality.
Even if the childbirth is without any complications, both mother and child suffer from malnutrition and poor weight. Their immunity is low and so, they are more prone to falling sick frequently. The child marriage in India also takes a toll on the girl as they have to carry out all the household works at such a young age.
Obviously, due to child marriage in India, the girl’s basic right to education is violated which ultimately drives her to a hopeless future. Bereaved of education and awareness, the couple has higher chances to acquire sexually transmitted diseases, like AIDS and HIV, etc. They are ill-informed about the use of contraceptives and benefits of family planning.
Dealing with the Issue:
The first step toward ending the child marriage in India is to create awareness through every possible medium. Expectations from the government and official systems are understandable but without the support of the common public, child marriage in India would continue to happen.
Basic level of education for boys and girls should be mandatory because the absence of knowledge is the prime cause of child marriage in India. When our younger generation in the rural areas would be well educated, they would be less likely to fall into the trap of child marriages.
Info-graphic posters, interesting radio advertisements, folk songs, and folklores are quite effective in catching the attention of adults as well as young ones. Academic teachings have very limited use in the personal lives of people. Young ones must be informed of their basic human rights to refuse child marriages and to call it void, if at all.
Spreading awareness through various financial and non-financial campaigns can do wonders to throw off the system of child marriage in India on the root level. Street plays also known as Nukkad Natak , are entertaining ways to educate the rural population about the drawbacks of child marriages.
Enough laws have been made to protect the children from this evil malpractice. The problem is that of effective implementation. Unless and until the system would be prompt in its response, the child marriages in India would be difficult to catch hold of. Both public and NGOs have an essential role to play in the proper functioning of the government system.
Child Marriage , Social Issues
Get FREE Work-at-Home Job Leads Delivered Weekly!

Join more than 50,000 subscribers receiving regular updates! Plus, get a FREE copy of How to Make Money Blogging!
Message from Sophia!
Like this post? Don’t forget to share it!
Here are a few recommended articles for you to read next:
- Essay on Child Labour
- Essay on Gender Equality in India
- Which is More Important in Life: Love or Money | Essay
- Essay on My School
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Billionaires
- Donald Trump
- Warren Buffett
- Email Address
- Free Stock Photos
- Keyword Research Tools
- URL Shortener Tools
- WordPress Theme
Book Summaries
- How To Win Friends
- Rich Dad Poor Dad
- The Code of the Extraordinary Mind
- The Luck Factor
- The Millionaire Fastlane
- The ONE Thing
- Think and Grow Rich
- 100 Million Dollar Business
- Business Ideas
Digital Marketing
- Mobile Addiction
- Social Media Addiction
- Computer Addiction
- Drug Addiction
- Internet Addiction
- TV Addiction
- Healthy Habits
- Morning Rituals
- Wake up Early
- Cholesterol
- Reducing Cholesterol
- Fat Loss Diet Plan
- Reducing Hair Fall
- Sleep Apnea
- Weight Loss
Internet Marketing
- Email Marketing
Law of Attraction
- Subconscious Mind
- Vision Board
- Visualization
Law of Vibration
- Professional Life
Motivational Speakers
- Bob Proctor
- Robert Kiyosaki
- Vivek Bindra
- Inner Peace
Productivity
- Not To-do List
- Project Management Software
- Negative Energies
Relationship
- Getting Back Your Ex
Self-help 21 and 14 Days Course
Self-improvement.
- Body Language
- Complainers
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality
Social Media
- Project Management
- Anik Singal
- Baba Ramdev
- Dwayne Johnson
- Jackie Chan
- Leonardo DiCaprio
- Narendra Modi
- Nikola Tesla
- Sachin Tendulkar
- Sandeep Maheshwari
- Shaqir Hussyin
Website Development
Wisdom post, worlds most.
- Expensive Cars
Our Portals: Gulf Canada USA Italy Gulf UK
Privacy Overview

The Modern Love Issue
Can a Sexless Marriage Be a Happy One?
Experts and couples are challenging the conventional wisdom that sex is essential to relationships.
Credit... Tonje Thilesen for The New York Times
Supported by
- Share full article
By Amanda Montei
- Published April 17, 2024 Updated April 18, 2024
Will and Rose met online 10 years ago. His screen name was professorparsley, and he looked the part — tall and thin, with glasses, features that Rose found attractive. On their first date, Rose learned that Will was a college student living with his mother, and his handle came from a nickname given to him by a child at an art camp where he worked. They laugh about it now, as they do with most things. Will thought Rose was exciting and direct. He grew up in suburban Ontario, and she was from Southern California, which was like another world to him. Right away, what they loved about each other were their differences.
Listen to this article, read by Julia Whelan
Rose was drawn to how stable Will seemed — so unlike the other men she had dated, who dreaded commitment. Their relationship survived multiple moves, about a year of long-distance dating and the challenges of finding time to be together while living with parents and roommates. Now, seven years into their marriage, they have their own place: a one-bedroom apartment in Los Angeles, where Rose sees Pilates clients. Will is gone during the day, teaching, and at night they cuddle in bed and watch television. “It’s my favorite part of the day,” Rose says. (Rose and Will are middle names. All subjects asked to be referred to by their first names, middle names or a nickname, out of concerns for their privacy.)
As much as Will grounds her, Rose feels that the familiar calm of their relationship also shuts her down sexually. They go months without sex, but they don’t lack intimacy. They have a policy of never refusing a hug, something they instituted to resolve the minor disagreements that inevitably crop up in any relationship. They have also talked candidly about how, for her, the safe predictability of their marriage — the quality she loves about their lives together — dulls her sex drive. She knows that can be confusing, even frustrating, for Will, but she doesn’t like the idea of forcing herself to have sex. Rose’s mother, now divorced, felt obligated to have sex with Rose’s father once a week. That’s not the kind of relationship Rose wants.
To get into a sexual mood, Rose relies on a set of rituals to help build anticipation — doing her hair and makeup, shaving her legs, having a glass of wine over dinner or, when their schedules allow, going on vacation to break out of their routines. Will doesn’t need to do anything to feel ready for sex, and Rose sees this as another way in which they’re different. Over the years, they have accepted that this is what their sex life looks like, and will look like, if they want to be together, which they do.
During the pandemic, the couple went more than a year without having sex, but they savored their extra time together. Rose used to spend hours driving in traffic to different workout studios, coming home late, not seeing her husband much. Stuck at home, they took walks around their neighborhood. They talked constantly. They started taking online yoga classes together, a hobby that stuck. Will appreciates these smaller opportunities to connect. Rose thinks she’s not the nurturing type, but Will disagrees. “She’s not stingy in spirit or time,” he says.
Sometimes they shower together and hold each other naked, without any expectation of sex. Though Will remains hopeful that these moments will lead to something else, he doesn’t push it.
Cultural attitudes about the role sex plays in a marriage have evolved significantly over time. Where once marital sex was primarily a means for bearing children, in recent decades, the conventional wisdom was that frequent sex was integral to a happy union. During the 1990s, a new wave of sex positivity coincided with the ascendancy of different forms of therapy, including couples counseling. Experts coached couples on how to strengthen their marriages, often relying on the belief that healthy relationships included consistent sex with partners. By the 2010s, appointment sex had become one popular method for maintaining intimacy and, somewhat implicitly, safeguarding against separation.
In more recent years, however, both relationship experts and couples themselves have been gradually dismantling some of these commonly held views, working to destigmatize the unconventional approaches that some take to stay together. Online groups have sprung up for couples who challenge basic assumptions that spouses should share a bedroom or even a home. Sharon Hyman, who runs a Facebook group called Apartners for couples who have chosen to live separately, told me that many of the members in her community find their sex lives improve when they don’t spend every minute together. “My goal is to show that there are healthy options for relationships,” Hyman says. “No one size fits all.”
One effect of the ever-changing sexual climate is that many couples today are simply less willing to tolerate what the psychotherapist Esther Perel calls “boredom” in the bedroom. Perel has made a career of articulating how domestic overexposure saps eroticism, which requires some intrigue, mystery and unfamiliarity. That’s not to suggest that long-term love and desire are impossible, but according to Perel, keeping sexual interest alive requires getting creative. In her podcast, “Where Should We Begin?” Perel helps couples explore and articulate their fantasies, honor each other as individuals and experiment with new approaches to fulfilling their desires together.
For Perel, as for many other relationship experts, that sometimes means re-examining investment in another foundational premise of marriage: monogamy. The advice columnist Dan Savage, too, has argued that monogamy isn’t entirely plausible, or pleasurable, for everyone, and is critical of Americans’ obsession with moralizing infidelity. He encourages married people to be honest with each other about how hard it is to carry the responsibility of fulfilling their partner’s sexual and emotional needs for decades on end.

While some are questioning the standard of monogamous sex in marriage by exploring polyamorous and open relationships, others are pushing back against the pressure to have sex at all. In fact, Americans on the whole are having less sex than they used to — across race, gender, region, educational level and work status. One study found that American adults born in the 1990s are having less sex than older generations; they are in fewer steady partnerships, and those who are partnered are also having less sex. The 2021 General Social Survey found that about 50 percent of all adults polled had sex once a month or less , with half of those people reporting they hadn’t had sex for a year. Researchers have speculated about the reasons for this 30-year sexual low, from isolation caused by technology to cultural conversations about consent.
Many younger women, for instance, shaped in part by the #MeToo movement, are engaging in intentional abstinence. There are trends on TikTok about going “boysober,” a word coined by the comedian Hope Woodard, who says that taking a break from sex can be empowering for women who previously altered their desires to accommodate men. The digital feminist 4B movement, which originated in South Korea but has spread globally through social media, advocates a rejection of childbearing, as well as heterosexual dating, marriage and sex. “Platonic life partners,” meanwhile — friends who commit to owning a home and even raising children together — insist that sex and romance are not necessary to lifelong unions.
The sex educator and researcher Emily Nagoski is resistant to the idea that frequent sex should be a chief component of every committed relationship. Nagoski — who has been open about her own hiatus from marital sex — doesn’t endorse obligatory sex, nor does she encourage aiming for any sexual base line in terms of regularity or behavior. Drawing on the work of the Canadian sexologist Peggy Kleinplatz, Nagoski believes that low desire can sometimes be evidence of good judgment. “It’s not dysfunctional not to want sex you don’t like,” Nagoski says.
In her new book, “Come Together,” Nagoski urges couples who want to explore their sexualities and deepen their sexual bond to begin by figuring out what each person wants when they want sex. For many, sex represents freedom from the ordinary, but what it takes to get there will look different for every couple and is likely to change over time. After all, desires don’t always align, or they evolve in unexpected ways.
Michelle and John met in 2005 at a party, and in the early years of their relationship, they couldn’t keep their hands off each other. Four years ago, however, after experiencing what she calls a “traumatic” childbirth, Michelle began to worry that intercourse would cause her pain.
She and John did not have sex for a year after they became parents. Now they can go months without it. Friends of theirs, too, seem to be experiencing new chapters in their own sex lives and opening up their marriages, which has sparked conversations between Michelle and John about the possibilities for reinvigorating their sex life. But they don’t always agree on what they want, or what they’re comfortable with.
John knows, however, that having sex outside the marriage is a red line for Michelle. She witnessed infidelity tear apart her parents’ relationship. “I think there’s a big fear about ‘I have an urge that may be resolved in a minute or two,’ but the sense of what could be broken is not worth the risk,” John says.
Love, for both, is about much more than fulfilling those momentary desires. After almost two decades together, they consider themselves best friends and “soul mates.” When they first began dating, Michelle was reeling from the loss of her brother, who died in a car accident. She talked with John about the experience on an early date, and they were inseparable after that. John thought she was beautiful and wanted to spend as much time with her as he could. Michelle thought he was a welcome distraction, someone who could lift her out of her grief. They went to concerts. He made her mixtapes. But there were also times when she broke down crying, and he was there for her.
John used to try to comfort Michelle by saying he understood how she felt, but when he lost his own brother in 2012, he realized how wrong he had been. As he mourned, Michelle “just knew what to do in the unspoken moments — whether it was knowing when to give me space, or knowing when I needed a hug, or I just needed her to be next to me,” John says. Today, Michelle remains the “central piece” of his happiness.
Michelle and John share a one-bedroom with their daughter, and while they get some privacy during the day, they’re busy working from home. Now, most days, Michelle masturbates in the morning, while John takes their daughter to preschool. He masturbates at night in the bathroom, while watching porn on his phone. For John, it’s merely a physical release, but for Michelle, pleasuring herself serves a different purpose: She is trying to figure out what makes her feel good. Exploring her changed body alone eliminates the guilt she has when she can’t climax with her husband. She doesn’t want him to think it has anything to do with him. “I want to get there, but it’s not getting there,” she says.
Of the more than 30 married people I interviewed, many, like Michelle, told me that becoming parents irrevocably changed their sex lives. Camille, who lives in California, felt her marriage was the most solid and caring relationship she had ever experienced, but becoming a mother distanced her from her desire. “It feels like something I can’t quite touch, like in another room, or another part of me that I don’t know how to access,” she says.
Other mothers started to see sex as one more chore, another line item on their list of responsibilities. Keti, a mother of a neurodivergent child who craved being held, found that sex with her husband had become “robotic” as she began to see it as “one more demand.” Her husband was doing everything he could to support her, but she felt an obligation to get back to their old sex life, even though she wanted “desperately to go into a forest and just lie down and not hear anyone or anything.”
Lilien, who has two kids, says becoming a mother was a turning point for her. She had to leave her previous career and didn’t know who she was or what she wanted. “My identity was totally eviscerated,” she says. “I was really confused about what my worth was.” Her history of sexual assault also resurfaced in profound ways. She thought she needed to be “permeable” to nurture her children. She didn’t have the capacity to extend that physical openness to her husband. She couldn’t stand soft caresses from him, which felt like the tickling of her child’s hands.
Lilien’s husband, Philip, never pressured her to be intimate, for which she is grateful. “The most important thing for me was to maintain a place where the sex you have is very positive, very consensual, very understood and mutually enjoyed,” he says. Five years later, Philip knows she is still coming to terms with everything motherhood has brought into her life. Recently they started having more sex, about once every other month. Lilien loves her husband’s firm back rubs, which he’s happy to give.
Other couples, much like Rose and Will, confessed to feeling sexually misaligned with their partners as their desires shifted in different directions. Jean, a 38-year-old mother living in Virginia, told me that her husband’s interest in sex has dropped off gradually over the course of their 13-year marriage. She, on the other hand, experienced what she called “a secondary puberty” as her kids grew older and became less dependent on her. She felt “so sexually charged” that she visited her gynecologist to confirm she wasn’t having a hormonal issue. She’s now trying to figure out how to navigate her husband’s low desire. “I feel like I’m living in the upside-down a lot of the time,” she says. “My friends complain about their husbands grabbing their butt while they wash dishes, and I think, Wow, I would love to feel wanted like that.”
Another mother, Emily, says that sex gradually became less important over the course of her 34-year marriage. When her kids were little, intimacy with her husband stalled briefly, but as their children grew older, they had a “revival of a good sex life,” Emily says. Now she is 59 and has had several operations resulting from a battle with cancer, including a hysterectomy and mastectomy. As a result, her desire lessened, and sex began to feel like “vacuuming the house” — something she did to make her husband happy. And he noticed. “If you are used to somebody responding to you in a certain way, you can tell when they are acting,” she says. “I wasn’t the same person.”
One night in bed, about 10 years after she went on a hormone treatment for her cancer that put her into early menopause, they had a frank conversation about their sex life. “We discussed my lack of desire, and he said that if I’m not turned on, then he’s not either,” Emily says. He admitted that his sex drive had dipped, too. So they decided not to force it. She feels there’s some cultural pressure for older people to keep up their sex lives into their 80s. She’s read, with skepticism, articles claiming that maintaining sex later in life is healthy. “Is it?” she said. “I don’t know.”
Emily feels their marriage has progressed naturally: They experienced decades of passion, and while they remain affectionate outside of the bedroom, their relationship now transcends sex in many ways. It’s about the life they’ve built together. “We’ve been in a sexless relationship for years now,” Emily says. “We get along great, but we’re more like best buds than lovers.”
Despite their insistence that sex isn’t essential in their marriages, most of the couples I spoke with still keep track of how often they have sex. They also appear haunted by how far they deviate from perceived norms. John, for instance, hopes he and his wife can work back up to having sex two or three times a week, but admits he has no idea where that figure came from.
Numbers, Nagoski believes, can be a counterproductive metric. It’s impossible to hear such statistics and not judge one’s relationship against them. Numbers also don’t account for whether participants are enjoying the sex they are having. “You’re comparing yourself — you’re judging yourself as OK or inadequate — compared to a whole bunch of people you’re not having sex with, who are not having sex with you,” Nagoski says.
For couples measuring themselves against what Nagoski calls the “fictions” of sex, or for those worried that their relationship is on the line whenever they enter the bedroom or don’t meet some monthly number, there may be too much pressure for sex to be enjoyable. It’s more important that couples establish what kind of sex is worth having.
‘There are people who tell you all the sex they’re having. I feel like it’s a lot more common that a lot of people are not.’
Rose admits to feeling the weight of societal expectations. Recently she decided that since she and Will were rarely having sex, she would have her birth-control implant removed from her arm. During the procedure, the nurse intimated there was something wrong with Rose’s marriage. Rose felt shamed and angry. The idea that she should be living in a constant state of arousal with her husband after a decade together is, to her, ridiculous, but also part of a facade she thinks many married couples maintain.
“There are people who tell you all the sex they’re having,” she says. “I feel like it’s a lot more common that a lot of people are not.” With the help of her therapist, Rose is exploring whether her A.D.H.D. may play a role in her need to seek new stimuli — not because she sees it as a problem but because she is interested in understanding her desire more fully. “Apparently the partner fatigue I experience is not so uncommon because our ‘special’ brains are always seeking out what’s new,” she says.
Will sometimes turns to Buddhist writings on restraint to explore his sexuality. He jokes there may be some confirmation bias at work, but he thinks his wife’s self-awareness — and her unwillingness to force herself into sex that she doesn’t want to have — has matured him. For Will, intimacy is less about completion and more about connection. “I’ve learned, even just about the act of sex itself, the ending is not always the best part,” Will says. “There’s pleasure throughout the spectrum.”
In March, for Rose’s 40th birthday, they took a trip to Hawaii. She switched off her phone for hours as they sprawled out by the ocean. Will remembers turning toward his wife and staring at her, watching her relaxing, her body loose. In that moment, he wasn’t thinking about sex or how beautiful Rose looked under the sun. He was thinking about how similar they actually are. More than anything, they want to enjoy themselves in their own way, to savor the small moments when they can let the rest of the world fade away.
Amanda Montei is the author of “Touched Out: Motherhood, Misogyny, Consent and Control.” She is based in California.
Read by Julia Whelan
Narration produced by Anna Diamond and Tanya Pérez
Engineered by Joel Thibodeau
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Child marriage is basically the formal or informal marriage of a child with or without their consent, under the age of 18. In most cases, the boy or man is older than the girl. Through a child marriage essay, we will throw light on this social issue. Causes and Impact of Child Marriage. Child marriage is no less than exploitation of right.
Child marriage, a prevalent practice in many cultures and societies, is a complex issue that infringes upon the rights and development of children, particularly girls. It is a deep-rooted practice, often perpetuated by poverty, gender inequality, traditions, and lack of education. This essay delves into the implications, causes, and potential ...
Child marriage remains a deeply concerning issue that violates the rights and well-being of children worldwide. This practice, which involves marrying individuals under the age of 18, often results in profound physical, emotional, and psychological consequences.This essay explores the compelling reasons why child marriage should be banned, considering the detrimental impact on health ...
2 pages / 692 words. Child marriage remains a deeply concerning issue that violates the rights and well-being of children worldwide. This practice, which involves marrying individuals under the age of 18, often results in profound physical, emotional, and psychological consequences. This essay explores the compelling reasons why child marriage...
Child marriage, a concerning and pervasive issue in various parts of the world, represents a severe violation of human rights and dignity. This essay aims to delve into the complex topic of child marriage, exploring its causes, consequences, and the critical need for its eradication.
Words: 2031 Pages: 7 5306. Child marriage is the marriage that an individual performs without reaching the physical and mental maturity necessary to act as an adult. Child marriage usually means the marriage of a 18-year-old child. Early marriage, these minors are from their families, friends and future; education, deprives the school of life ...
Child marriage refers to any formal marriage or informal union between a child under the age of 18 and an adult or another child. Despite a steady decline in this harmful practice over the past decade, child marriage remains widespread, with approximately one in five girls married in childhood across the globe. Today, multiple crises ...
Child marriage, defined as marriage of a child under 18 years of age, is a silent and yet widespread practice. Today, over 60 million marriages include girls under the age of 18 years: approximately 31 million in South Asia, 14 million in sub-Saharan Africa, and 6.6 million in Latin America and the Caribbean (Figure 1).Each day, 25,000 girls are married and an anticipated 100 million girls ...
Save the Children's Global Girlhood Report estimates that an additional 2.5 million girls are at risk of child marriage globally between 2020 and 2025, as a result of reported increases in all types of gender-based violence due to the COVID-19 pandemic. We project that up to 15 million girls and boys will never return to school following ...
BACKGROUND. Child marriage is defined as a formal or informal union before the age of 18. The practice affects mostly girls. While child marriage is especially prevalent in low and lower-middle income countries, it is also observed in other countries. It endangers the life trajectories of girls in multiple ways.
Marriage before the age of 18, often referred to as child marriage, is a violation of human rights that hinders educational attainment and literacy and may increase the likelihood of living in poverty in adulthood [1,2,3,4,5].Girls are far more likely to marry than boys, and these consequences contribute to existing gender gaps in educational outcomes in some settings [6, 7].
The prevalence of child marriage was 70.50% with average age of marriage and early marriage were 16.82±3.63 years and 14.95±1.17 years, respectively. About 43% early married women were in ...
Child marriage is a harmful and despicable global practice that violates children's basic human rights. In the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, it states in articles 1,3,4,16, states that everyone has the right to equality, liberty, freedom from slavery and the right to marry and have a family when legally old enough.
Essay on Child Marriage: A banned social practice in India where young girls below adolescent age are married off to older men with or without their consent is called child marriage. India has set the record for the 14th highest rate of child marriages globally. Rajasthan, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka are child marriage hotspots in the country.
By misfortune, child marriage arises from many factors including poverty, limited education, traditions, and safety, which tend to result in premature pregnancy, maternal mortality, infant mortality, abuse, and multiple health conditions. To begin, poverty and limited education are only two of the numerous factors which influence the existence ...
833 Words. 4 Pages. Open Document. Child marriage, defined as "a formal marriage or informal union before age 18, is a common phenomenon for both boys and girls, although girls are disproportionately more affected than boys". (author, 2016) Child marriage is a widespread issue and it has a grave affection on the society and children's life.
Create a spot-on reference in APA, MLA, Chicago, Harvard, and other styles. Consult the top 50 dissertations / theses for your research on the topic 'Child marriage.'. Next to every source in the list of references, there is an 'Add to bibliography' button. Press on it, and we will generate automatically the bibliographic reference to the ...
There have been many incidents of child marriages among this community for instance a marriage occurred between a five-year-old girl and a ten-year-old boy in the community. Other child marriages have also been witnessed. These two victims are far below the adult age as they should be at least eighteen years for the girl and twenty one years of ...
Argumentative Essay On Child Forced Marriage Every two minutes a child is married. Approximately 15 million girls are married before they reach the age of 18. Child marriage is often the end product of a girl's education, economic prospects, constrained social engagement and increased health risks including physical, emotional and sexual ...
"Child marriage and its prevention: Role of adolescent girls." Indian Journal of Development Research and Social Action 7.1-2 (2011): 49-62. Lal, B. Suresh. "Child marriage in India: factors and problems." International Journal of Science and Research 4.4 (2015): 2993-2998. Mahato, Santosh K. "Causes and consequences of child marriage: A ...
Child marriage, a deeply ingrained practice in many parts of the world, represents a grave violation of human rights and dignity. This essay seeks to shed light on the disturbing phenomenon of child marriage, exploring its root causes, dire consequences, and the urgent need for its eradication.By delving into the complexities surrounding this issue, we aim to underscore the importance of ...
Besides the girl child, the male child is also not so much capable of taking full responsibility of her wife and also the expenses of running a family. 3. Childhood gets vanished at the time of child marriage in India. In fact, the independence of playing and learning is also stolen in the practice. 4.
Now, seven years into their marriage, they have their own place: a one-bedroom apartment in Los Angeles, where Rose sees Pilates clients. Will is gone during the day, teaching, and at night they ...
A new tool called Writable, which uses ChatGPT to help grade student writing assignments, is being offered widely to teachers in grades 3-12. Why it matters: Teachers have quietly used ChatGPT to grade papers since it first came out — but now schools are sanctioning and encouraging its use. Driving the news: Writable, which is billed as a ...