

Article Critique
Ai generator.
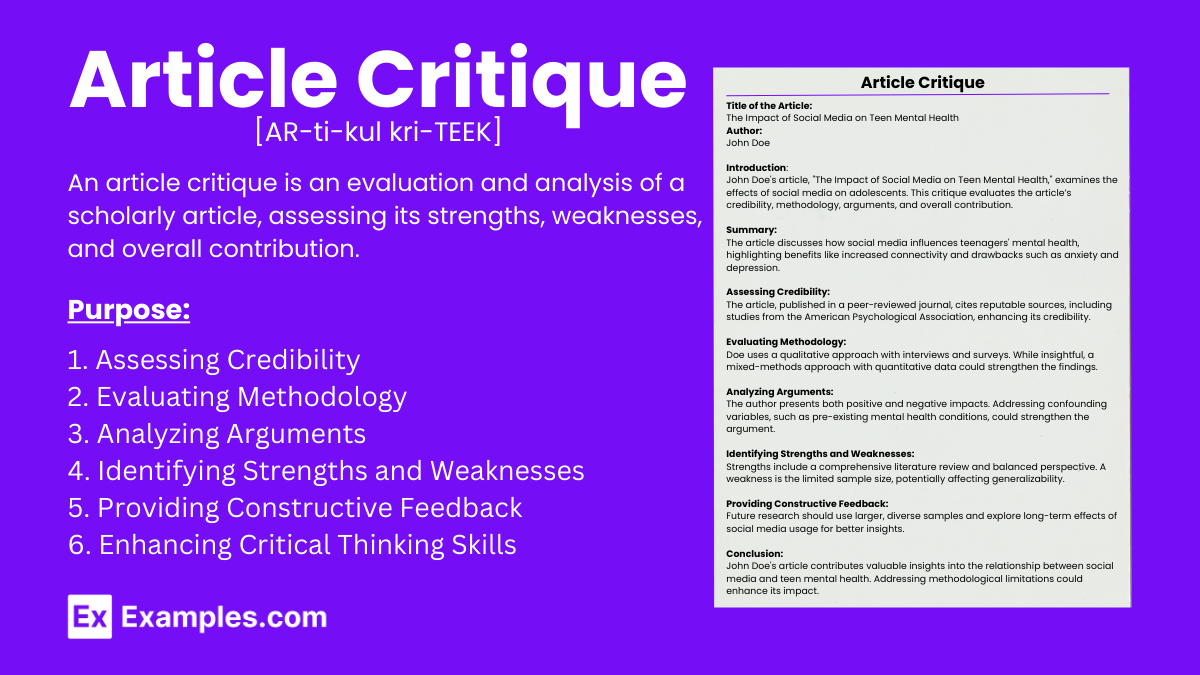
In the realm of academia and intellectual discourse, the art of critiquing articles holds significant importance. It not only refines one’s skills but also contributes to the growth of knowledge. A well-executed article critique showcases your ability to analyze, evaluate, and engage with scholarly work. This article delves into the concept of article critiques, offering insights into their purpose and benefits, along with a step-by-step guide on how to craft one effectively.
What is an Article Critique?
An article critique is a detailed evaluation and analysis of a scholarly article or research paper . It involves an objective assessment of the author’s arguments, evidence, methodology, and conclusions. An effective critique goes beyond summarizing the content; it delves into the strengths, weaknesses, and implications of the article. Developing this skill allows you to identify the characteristics that contribute to a compelling scholarly work, while also honing your ability to engage critically with academic literature.
Article Critique Format
1. introduction.
- Article Information : Mention the title of the article, the author’s name, the source ( journal , magazine , etc.), and the publication date.
- Thesis Statement : Summarize the main argument or purpose of the article.
- Scope of the Critique : Briefly outline the main points you will discuss in your critique.
2. Summary of the Article
- Main Points : Summarize the key points and arguments presented by the author.
- Purpose and Scope : Explain the purpose of the article and the main topics covered.
- Findings and Conclusions : Highlight the primary findings and conclusions drawn by the author.
3. Critical Analysis
A. structure and organization.
- Introduction : Evaluate the effectiveness of the introduction. Does it set the stage for the article?
- Body : Assess the organization of the main sections. Are the arguments and evidence presented logically?
- Conclusion : Examine the conclusion. Does it effectively summarize the article and provide closure?
b. Content and Arguments
- Clarity : Determine if the article is clear and easy to understand.
- Evidence : Analyze the evidence used to support the arguments. Is it relevant and convincing?
- Consistency : Check for logical consistency in the arguments.
c. Research Methodology
- Approach : Evaluate the research methods used in the article. Are they appropriate for the research question ?
- Data Collection : Assess the reliability and validity of the data collection methods.
- Analysis : Examine the thoroughness and accuracy of the data analysis .
d. Writing Style
- Tone : Assess the appropriateness of the tone for the target audience.
- Language : Evaluate the use of language. Is it precise and concise?
- Grammar and Syntax : Check for grammatical correctness and syntactical clarity.
e. Contribution to the Field
- Originality : Determine the originality of the article. Does it offer new insights?
- Impact : Assess the potential impact of the article on the field. Does it advance knowledge or understanding?
4. Personal Response
- Strengths : Identify the strengths of the article. What did the author do well?
- Weaknesses : Point out the weaknesses or areas for improvement.
- Overall Impression : Provide your overall impression of the article.
5. Conclusion
- Summary : Summarize your main points of critique.
- Recommendation : Offer any recommendations for future research or improvements to the article.
6. References
- Citation : Provide a full citation of the article in the appropriate format (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Additional Sources : Include citations for any additional sources referenced in your critique.
Examples of Article Critique For Students
Psychology article critique.
Reference: Smith, J. A., & Brown, R. L. (2022). The impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance. Journal of Psychological Research , 34(2), 123-135. https://doi.org/10.1001/jpsychres.2022.01.001 Introduction In their article “The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Cognitive Performance,” Smith and Brown (2022) examine the effects of sleep deprivation on various cognitive functions. The authors aim to highlight the importance of adequate sleep for maintaining cognitive health and performance. Summary Smith and Brown (2022) conducted a series of cognitive tests on participants who were sleep-deprived for 24 hours. The results indicated significant declines in memory retention, attention span, and problem-solving skills among the sleep-deprived group. The article also discusses potential long-term consequences of chronic sleep deprivation on brain health. Critique Smith and Brown (2022) provide compelling evidence linking sleep deprivation to cognitive decline. Their methodology is robust, featuring a well-defined participant group and controlled variables. However, the study’s sample size is relatively small, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the article does not sufficiently explore potential confounding factors, such as stress and caffeine intake, which could influence cognitive performance. Conclusion Overall, Smith and Brown (2022) effectively underscore the critical role of sleep in cognitive health. Despite some methodological limitations, their findings contribute valuable insights to the field of sleep research. Future studies should aim to address the identified limitations to strengthen the generalizability and applicability of the results.
Education Article Critique
Reference: Johnson, L. M., & White, P. D. (2023). The impact of technology integration on student learning outcomes. Journal of Educational Technology , 29(1), 45-59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeduc.2023.01.002 Introduction In the article “The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes,” Johnson and White (2023) explore how incorporating digital tools and resources in the classroom affects students’ academic performance. The authors aim to identify both the benefits and challenges of technology integration in education. Summary Johnson and White (2023) evaluate various forms of technology integration, including interactive whiteboards, educational software, and online resources. They analyze the effects of these tools on student engagement, motivation, and achievement across different subjects and grade levels. The study presents data from several schools that have implemented these technologies, showing improvements in test scores and classroom participation. Critique The article by Johnson and White (2023) provides a comprehensive analysis of the positive impacts of technology on student learning. The use of multiple case studies strengthens the validity of their conclusions. However, the study’s focus on urban schools may not reflect the experiences of students in rural or underfunded schools, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the reliance on short-term data does not capture the long-term effects of technology integration on student learning. Conclusion Johnson and White (2023) make a compelling case for the positive impact of technology on student learning outcomes. While the article effectively demonstrates the benefits of digital tools, addressing the identified limitations would provide a more comprehensive understanding of technology integration in education. Future research should focus on long-term effects, diverse educational settings, and the challenges of teacher training and equitable access to technology.
Business Article Critique
Reference: Davis, K. L., & Roberts, J. H. (2021). Corporate social responsibility and business success: A review of recent research. Journal of Business Ethics , 38(4), 220-235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbuseth.2021.02.003 Introduction In their article “Corporate Social Responsibility and Business Success: A Review of Recent Research,” Davis and Roberts (2021) explore how corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives impact business performance. The authors aim to demonstrate the benefits of CSR in enhancing corporate reputation and customer loyalty. Summary Davis and Roberts (2021) review several studies that analyze the outcomes of CSR initiatives across different industries. The article highlights positive correlations between CSR activities and financial performance, as well as improvements in brand reputation and customer satisfaction. The authors also discuss the potential challenges businesses face when implementing CSR programs. Critique Davis and Roberts (2021) provide a thorough review of the literature on CSR and its impact on business success. The article effectively synthesizes findings from various studies, supporting their argument that CSR can be beneficial for companies. However, the article could be improved by including more critical perspectives on CSR, such as potential drawbacks or instances where CSR initiatives have failed. Additionally, the authors do not provide detailed guidelines on how companies can measure the effectiveness of their CSR efforts. Conclusion Overall, Davis and Roberts (2021) make a strong case for the positive impact of CSR on business success. Their review underscores the importance of socially responsible practices in building a positive corporate image and achieving long-term profitability. Future research should address the limitations noted, particularly by exploring the challenges and failures of CSR initiatives and providing actionable metrics for evaluating their success.
Health Sciences Article Critique
Reference: Nguyen, M. T., & Kim, H. S. (2020). The effects of a plant-based diet on cardiovascular health: A systematic review. Journal of Nutritional Science , 17(3), 95-110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutrsci.2020.03.005 Introduction In the article “The Effects of a Plant-Based Diet on Cardiovascular Health: A Systematic Review,” Nguyen and Kim (2020) investigate the impact of plant-based diets on heart disease prevention and management. The authors aim to provide evidence supporting dietary recommendations for cardiovascular health. Summary Nguyen and Kim (2020) review multiple studies comparing the cardiovascular outcomes of individuals on plant-based diets versus those on omnivorous diets. Their findings suggest that plant-based diets are associated with lower cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and decreased incidence of heart disease. The authors discuss potential mechanisms, such as reduced intake of saturated fats and increased consumption of fiber and antioxidants. Critique Nguyen and Kim (2020) present a comprehensive review of the cardiovascular benefits of plant-based diets. The inclusion of various studies strengthens the validity of their conclusions. However, the review would benefit from a more balanced discussion of potential challenges, such as the risk of nutrient deficiencies and the social and cultural barriers to adopting a plant-based diet. Additionally, the article focuses primarily on short-term studies, and more research on the long-term sustainability of these diets is needed. Conclusion Overall, Nguyen and Kim (2020) provide strong evidence supporting the cardiovascular benefits of plant-based diets. Their systematic review contributes valuable insights to the field of nutritional science. Future research should address the limitations identified, particularly regarding long-term sustainability and potential challenges in adhering to plant-based diets.
Social Sciences Article Critique
Reference: Lopez, G. R., & Thompson, S. L. (2021). Urban poverty and social policy: Examining the effectiveness of welfare programs. Journal of Social Policy , 43(2), 180-195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsp.2021.04.007 Introduction In the article “Urban Poverty and Social Policy: Examining the Effectiveness of Welfare Programs,” Lopez and Thompson (2021) analyze the impact of various welfare programs on reducing urban poverty. The authors aim to assess the effectiveness of these programs in improving the socioeconomic conditions of urban populations. Summary Lopez and Thompson (2021) evaluate several welfare programs, including food assistance, housing subsidies, and employment training initiatives. Their analysis reveals mixed outcomes, with some programs showing significant positive effects on poverty reduction, while others have minimal impact. The authors discuss factors contributing to these varied results, such as program design, implementation quality, and participant engagement. Critique Lopez and Thompson (2021) provide a detailed analysis of the effectiveness of welfare programs in addressing urban poverty. The article’s strength lies in its comprehensive evaluation of multiple programs and consideration of various influencing factors. However, the study relies on data from a limited number of cities, which may not be representative of broader urban contexts. Additionally, the authors could have included more qualitative data to provide deeper insights into the lived experiences of program participants. Conclusion Overall, Lopez and Thompson (2021) offer valuable insights into the effectiveness of welfare programs in reducing urban poverty. Their findings highlight the need for well-designed and effectively implemented programs to achieve meaningful poverty reduction. Future research should aim to include a more diverse range of urban settings and incorporate qualitative data to enrich the understanding of program impacts.
Examples of Thesis Statements for Article Critiques
Psychology article critique thesis statements.
- “The article successfully links mindfulness practices to reduced anxiety levels, yet it overlooks the potential variability in individual responses, which could affect the generalizability of the results.”
- “While the study provides significant insights into the effects of social media on adolescent self-esteem, its cross-sectional design limits the ability to infer causality.”
Literature Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article provides a nuanced analysis of the themes of isolation in ‘Frankenstein,’ but its limited engagement with contemporary critical perspectives reduces its impact.”
- “Although the article offers a compelling interpretation of symbolism in ‘Moby Dick,’ its narrow focus on literary devices neglects the broader socio-political context of the novel.”
Business Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article effectively highlights the benefits of agile project management in tech startups, but it fails to consider the potential downsides, such as the risk of scope creep and resource strain.”
- “Despite presenting a well-researched argument for the advantages of remote work, the article’s lack of empirical data on long-term productivity effects weakens its conclusions.”
Health Sciences Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article convincingly argues for the role of gut microbiota in mental health, though it would benefit from a more thorough exploration of the mechanisms underlying this relationship.”
- “While the study provides strong evidence for the benefits of intermittent fasting on metabolic health, its reliance on short-term studies limits the understanding of long-term effects.”
Education Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article makes a strong case for the use of gamification in education to enhance student motivation, yet it neglects to address potential challenges related to accessibility and equity.”
- “Despite effectively demonstrating the positive impacts of project-based learning on student engagement, the article lacks consideration of the additional resources and training required for successful implementation.”
Environmental Science Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article offers a comprehensive review of the impacts of deforestation on climate change, but it would be strengthened by incorporating more case studies from diverse geographic regions.”
- “While the article effectively discusses the potential of urban green spaces to mitigate air pollution, it underestimates the complexities of urban planning and maintenance costs.”
Social Sciences Article Critique Thesis Statements
- “The article provides valuable insights into the influence of cultural norms on gender roles, but its limited geographic focus restricts the applicability of its findings to a global context.”
- “Although the study sheds light on the relationship between economic inequality and crime rates, its reliance on correlational data makes it difficult to draw definitive causal conclusions.”
Example of Article Critique About Education
Article Title : The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes Introduction The article “The Impact of Technology Integration on Student Learning Outcomes” investigates how the use of digital tools and resources in the classroom influences students’ academic performance. The research aims to identify the benefits and potential drawbacks of incorporating technology into educational settings. Summary The study evaluates various forms of technology integration, including interactive whiteboards, educational software, and online resources. It examines their effects on student engagement, motivation, and achievement across different subjects and grade levels. The article presents data from several schools that have implemented these technologies, showcasing improvements in test scores and classroom participation. Critique The article provides a comprehensive analysis of the positive impacts of technology on student learning. The use of multiple case studies strengthens the validity of its conclusions. However, the article could improve by addressing some critical aspects: Sample Size and Diversity : The study primarily focuses on schools in urban areas, which may not reflect the experiences of students in rural or underfunded schools. Expanding the sample size to include a more diverse range of schools would enhance the generalizability of the findings. Longitudinal Data : The research relies heavily on short-term data, which may not capture the long-term effects of technology integration on student learning. Longitudinal studies are necessary to understand the sustained impact of these tools. Teacher Training and Support : While the article highlights the benefits of technology, it overlooks the challenges teachers face in integrating these tools effectively. Providing adequate training and ongoing support is crucial for the successful implementation of technology in the classroom. Equity and Access : The article briefly mentions the digital divide but does not delve into how disparities in access to technology can affect educational outcomes. A more thorough examination of equity issues would provide a balanced perspective on the advantages and limitations of technology integration. Conclusion Overall, the article makes a compelling case for the positive impact of technology on student learning outcomes. It effectively demonstrates how digital tools can enhance engagement and academic performance. However, to provide a more comprehensive understanding, future research should address the limitations identified, particularly regarding sample diversity, long-term effects, teacher support, and equity issues. By doing so, the research could offer more actionable insights for policymakers and educators striving to harness the full potential of technology in education.
More Examples & Samples Article Critique in PDF
1. quantitative article critique.

2. Article Critique Guidelines
4. Critiquing Research Articles

4. Article Review & Critiques

5. Instructions for Article Critiques

6. Critique of an Academic Article
7. Critique and Review of Research Articles

8. Article Critique Assignment

9. Book Review or Article Critique

10. Press Article Critique
Purpose of Article Critique
An article critique serves multiple essential purposes in both academic and professional contexts. Below, we delve into the primary objectives of conducting an article critique, which are vital for developing critical thinking, analytical skills, and subject-specific knowledge.
1. Developing Critical Thinking Skills
Critical Evaluation:
- Encourages students and professionals to go beyond surface-level reading.
- Promotes a deeper understanding of the material by questioning the validity and reliability of the arguments presented.
Analytical Reasoning:
- Helps in identifying logical fallacies, biases, and unsupported claims.
- Facilitates the assessment of evidence and methodologies used in the article.
2. Enhancing Understanding of Subject Matter
In-Depth Analysis:
- Requires a thorough examination of the article’s content, including the main arguments, evidence, and conclusions.
- Enhances comprehension of complex concepts and theories within a specific field.
Contextual Awareness:
- Places the article within the broader context of existing literature.
- Identifies gaps in the research and suggests areas for further investigation.
3. Improving Academic Writing Skills
Structured Writing:
- Teaches students how to organize their thoughts coherently.
- Develops skills in writing clear, concise, and structured critiques.
Evidence-Based Arguments:
- Encourages the use of evidence to support evaluations and opinions.
- Helps in the practice of citing sources correctly and ethically.
4. Facilitating Peer Review and Feedback
Constructive Criticism:
- Provides a framework for giving and receiving constructive feedback.
- Enhances collaborative learning by engaging in discussions about the strengths and weaknesses of an article.
Quality Assurance:
- Plays a crucial role in academic publishing and professional fields by ensuring the quality and credibility of published work.
- Helps maintain high standards in research and scholarship.
5. Encouraging Lifelong Learning
Continual Improvement:
- Fosters a habit of continuous learning and improvement.
- Keeps individuals updated with the latest research, trends, and advancements in their field.
Adaptability:
- Prepares students and professionals to adapt to new information and changing paradigms.
- Cultivates a mindset that is open to questioning and re-evaluating established knowledge.
Components of an Article Critique
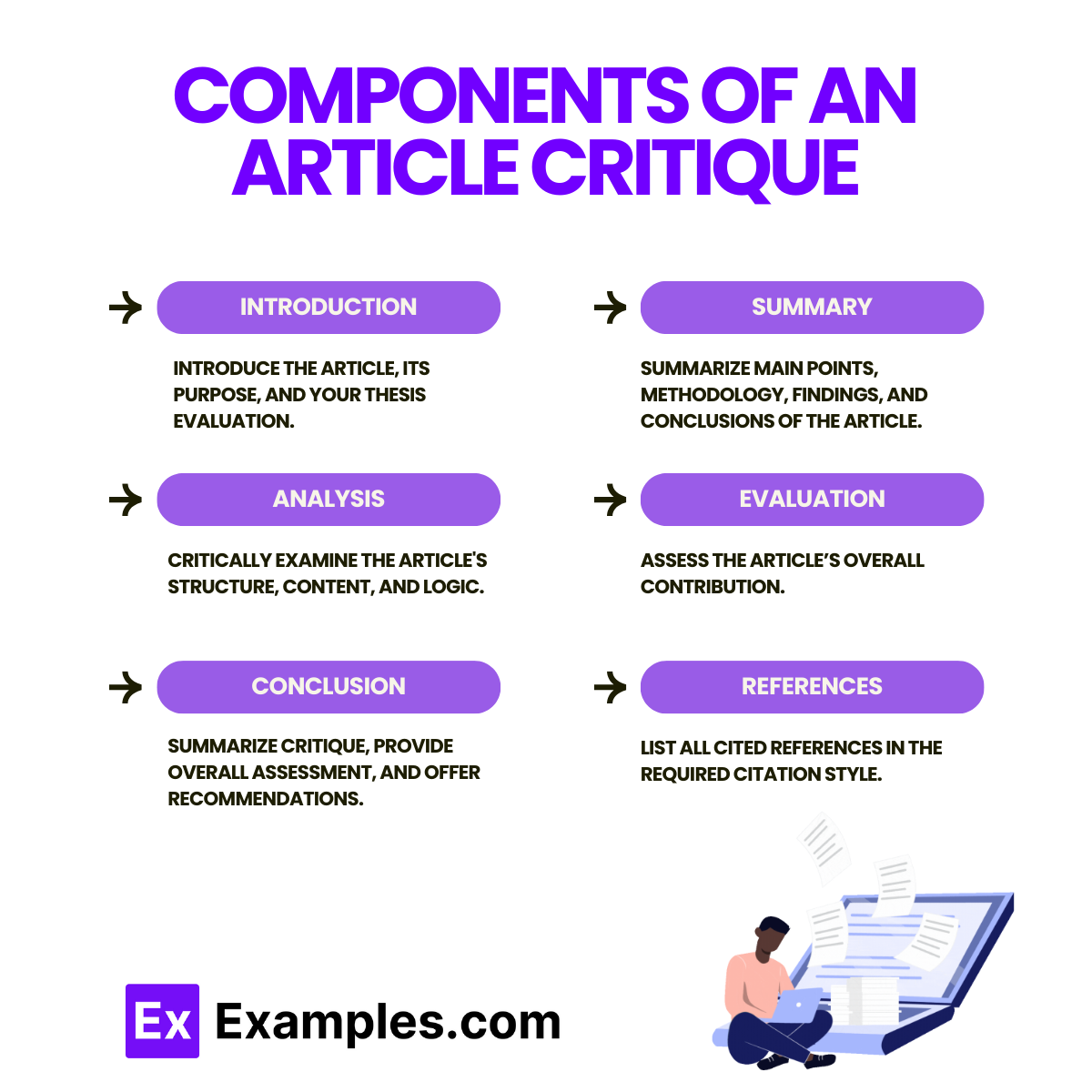
An effective article critique includes several key components to ensure a thorough evaluation and analysis. Below are the main components:
- Provide an overview of the article.
- Introduce the main thesis and key points.
Components:
- Title and Author: State the article’s title and author.
- Publication Details: Include publication name, date, etc.
- Thesis Statement: Summarize the article’s main argument.
- Purpose of the Critique: Explain your objective.
- Summarize the article’s content.
- Main Points: Highlight key arguments.
- Methodology: Describe research methods briefly.
- Findings and Conclusions: Outline main findings and conclusions.
3. Analysis
- Critically examine the article’s structure, content, and logic.
- Structure and Organization: Evaluate clarity and coherence.
- Content Evaluation: Assess relevance and depth.
- Argumentation: Analyze logical flow and evidence strength.
- Methodology: Critique research methods and identify biases.
- Sources and References: Evaluate quality and relevance of cited sources.
4. Evaluation
- Assess the article’s overall contribution.
- Strengths: Highlight strengths such as originality and depth.
- Weaknesses: Identify weaknesses like gaps and biases.
- Contribution to the Field: Discuss the article’s impact.
- Summarize the critique and provide final thoughts.
- Summary of Evaluation: Recap key points.
- Overall Assessment: Provide a final judgment.
- Recommendations: Suggest future research or improvements.
- List sources cited in your critique.
- Citations: Format according to the appropriate style (e.g., APA, MLA).
How to Write an Article Critique
Mastering the art of crafting an effective article critique requires a systematic approach. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you navigate this process with finesse.
Step 1: Reading and Observation
Before diving into the critique, thoroughly read the article. Take notes on the main points, observation , objectives , and tone of the article. Identify the author’s goals and the case study , if applicable. This step is crucial for grasping the nuances of the work.
Step 2: Analyzing Structure and Content
Evaluate the structure of the article. Identify the introduction, main arguments, supporting evidence, and conclusion. Examine the use of verbs and analogies , as well as the cause-and-effect relationships presented. Analyze how effectively the author communicates their ideas.
Step 3: Assessing Methodology and Evidence
Scrutinize the methodology used by the author. Is it appropriate for the objectives of the article? Evaluate the quality and relevance of the evidence presented. Consider whether the evidence supports the author’s claims adequately.
Step 4: Critical Evaluation
Engage in a critical evaluation of the article. Identify its strengths and weaknesses. Does the author effectively address counterarguments? Are there any gaps in the logic? Assess the overall coherence and effectiveness of the article’s presentation.

Why is article critique important?
It develops critical thinking, enhances understanding of the subject, improves academic writing skills, and provides constructive feedback.
What are the main components of an article critique?
Introduction, Summary, Analysis, Evaluation, Conclusion, and References.
How do I start an article critique?
Begin with an introduction that provides the article’s title, author, publication details, and a brief summary of its thesis and purpose.
What should be included in the summary?
Key points, research methods, findings, and conclusions of the article.
How do I analyze an article?
Examine the structure, content, logic, argumentation, methodology, and sources for clarity, relevance, and evidence strength.
What makes a good evaluation?
Balanced assessment of the article’s strengths and weaknesses, and its contribution to the field.
How should I conclude an article critique?
Summarize your findings, provide an overall assessment, and offer suggestions for improvement or future research.
How do I cite sources in an article critique?
Follow the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) and ensure all references are correctly formatted.
What are common pitfalls to avoid in an article critique?
Avoid biased or overly negative reviews, lack of evidence for claims, and failure to provide a balanced perspective.
How can I ensure my critique is objective?
Use evidence to support your points, acknowledge both strengths and weaknesses, and avoid personal biases.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing an article SUMMARY
- Writing an article REVIEW
Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author’s argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher’s claims.
Introduction
Give an overview of the author’s main points and how the author supports those points. Explain what the author found and describe the process they used to arrive at this conclusion.
Body Paragraphs
Interpret the information from the article:
- Does the author review previous studies? Is current and relevant research used?
- What type of research was used – empirical studies, anecdotal material, or personal observations?
- Was the sample too small to generalize from?
- Was the participant group lacking in diversity (race, gender, age, education, socioeconomic status, etc.)
- For instance, volunteers gathered at a health food store might have different attitudes about nutrition than the population at large.
- How useful does this work seem to you? How does the author suggest the findings could be applied and how do you believe they could be applied?
- How could the study have been improved in your opinion?
- Does the author appear to have any biases (related to gender, race, class, or politics)?
- Is the writing clear and easy to follow? Does the author’s tone add to or detract from the article?
- How useful are the visuals (such as tables, charts, maps, photographs) included, if any? How do they help to illustrate the argument? Are they confusing or hard to read?
- What further research might be conducted on this subject?
Try to synthesize the pieces of your critique to emphasize your own main points about the author’s work, relating the researcher’s work to your own knowledge or to topics being discussed in your course.
From the Center for Academic Excellence (opens in a new window), University of Saint Joseph Connecticut
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
Writing an Article Critique (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
How to Critique an Article (from Essaypro.com)
How to Write an Article Critique (from EliteEditing.com.au)
- << Previous: Writing an article REVIEW
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries

Journal Article Critique Guide and Example in 2025.
Journal article critiques are essential tools in academic and professional fields, providing a structured method to analyze and evaluate scholarly work. As we move into 2025, the importance of critical analysis in an age of information overload has only increased. This guide will walk you through the process of crafting a comprehensive journal article critique, highlighting key components and offering practical tips for success.
A journal article critique goes beyond mere summarization, delving into the strengths and weaknesses of the research presented. It requires a careful examination of the article’s methodology, findings, and conclusions, all while considering its relevance and contribution to the field. By mastering the art of critique, you’ll develop crucial skills in critical thinking, analytical writing, and scholarly discourse.
In this Journal Article Critique Guide. we’ll explore the step-by-step process of creating a journal article critique, from initial reading strategies to final presentation. We’ll also provide a detailed example to illustrate these concepts in action, ensuring you have a clear understanding of how to apply these principles to your own work.

What You'll Learn
Understanding the Purpose and Structure of a Journal Article Critique
The primary purpose of a journal article critique is to provide a balanced and objective evaluation of a scholarly work. This evaluation serves multiple functions in the academic community:
- Quality control: Critiques help maintain high standards in research by identifying strengths and weaknesses in published work.
- Knowledge advancement: By analyzing existing research, critiques contribute to the ongoing dialogue within a field and can inspire new avenues of inquiry.
- Skill development: Writing critiques hones critical thinking, analytical, and communication skills essential for academics and professionals.
A well-structured journal article critique typically includes the following components:
- Introduction: Provides an overview of the article and your main assessment.
- Summary: Concisely presents the key points of the original article.
- Critique: Offers a detailed analysis of the article’s strengths and weaknesses.
- Conclusion: Summarizes your overall evaluation and the article’s significance.
Understanding this structure is crucial for organizing your thoughts and presenting a coherent critique. Each section builds upon the previous one, guiding the reader through your analysis and supporting your final assessment.
As we move into 2025, the ability to critically evaluate research has become increasingly important. With the rapid dissemination of information and the growing interdisciplinary nature of many fields, a well-crafted critique can serve as a valuable resource for researchers, students, and professionals alike.
Preparing to Write: Initial Reading and Note-Taking Strategies
Before diving into the critique itself, it’s essential to approach the journal article with a strategic reading and note-taking process. This preparation phase sets the foundation for a thorough and insightful critique.
First Reading: Begin with a quick, overall read of the article to grasp its main ideas and structure. Pay attention to the abstract, introduction, headings, and conclusion. This initial pass helps you understand the article’s general argument and methodology without getting bogged down in details.
Second Reading: During your second, more careful reading, focus on the following elements:
- Research question or hypothesis
- Methodology and data collection
- Results and analysis
- Conclusions and implications
- References and citations
As you read, take detailed notes on each of these aspects. Use a system that works for you, whether it’s digital note-taking tools, handwritten notes, or a combination of both. Consider using a template or table to organize your observations systematically.
Critical Questions: While reading, ask yourself critical questions such as:
- Is the research question clearly stated and relevant?
- Does the methodology appropriately address the research question?
- Are the results presented clearly and interpreted accurately?
- Do the conclusions logically follow from the results?
- Is the article well-organized and clearly written?
By 2025, advanced AI-powered tools may be available to assist in this process, potentially offering automated summaries or highlighting key points. However, developing your own critical reading skills remains crucial for producing insightful critiques.
Analyzing the Article’s Content and Methodology
Once you’ve thoroughly read and taken notes on the article, it’s time to delve deeper into your analysis. This section of your critique should focus on evaluating the content and methodology of the research.
Content Analysis: Examine the article’s arguments, evidence, and theoretical framework. Consider the following:
- Clarity and coherence of the main argument
- Quality and relevance of evidence presented
- Logical flow of ideas and reasoning
- Appropriate use of relevant literature and theories
- Identification and addressing of potential counterarguments
Methodology Evaluation: Assess the research design and methods used in the study:
- Appropriateness of the chosen methodology for the research question
- Sample size and selection process (if applicable)
- Data collection techniques and their potential limitations
- Validity and reliability of measurements or instruments used
- Ethical considerations in the research process
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Scrutinize how the authors analyzed their data and interpreted the results:
- Suitability of statistical tests or qualitative analysis methods
- Clarity and accuracy of data presentation (tables, graphs, etc.)
- Thoroughness of the analysis in addressing all aspects of the research question
- Consideration of alternative explanations for the findings
- Acknowledgment of limitations in the study design or results
As you analyze these elements, remember to balance criticism with recognition of the article’s strengths. A fair and balanced critique acknowledges both the positive aspects and areas for improvement in the research.
Evaluating the Article’s Contribution to the Field
An essential aspect of your critique is assessing the article’s overall contribution to its field of study. This evaluation helps contextualize the research within the broader academic landscape and highlights its significance.
Relevance and Originality: Consider how the article advances knowledge in its area:
- Does it address a gap in existing literature?
- Does it challenge or confirm previous findings?
- Does it introduce new concepts, methodologies, or theoretical frameworks?
- How does it build upon or diverge from established research in the field?
Practical and Theoretical Implications: Examine the potential impact of the research:
- What are the practical applications of the findings?
- How might the results influence future research directions?
- Does the study have implications for policy or practice in its field?
- Are there potential interdisciplinary connections or applications?
Comparison with Similar Research: Place the article in context with related studies:
- How does this research compare to similar studies in terms of methodology and findings?
- Does it offer any unique perspectives or insights?
- Are there any contradictions with established research that need to be addressed?
Long-term Significance: Consider the lasting impact of the research:
- Is the topic likely to remain relevant in the coming years?
- Does the article lay groundwork for future studies?
- How might technological advancements or societal changes affect the relevance of this research?
By thoroughly evaluating these aspects, you can provide a comprehensive assessment of the article’s contribution and significance within its field. This analysis not only adds depth to your critique but also demonstrates your understanding of the broader academic context.
Crafting Your Critique: Writing Tips and Best Practices
Now that you’ve thoroughly analyzed the article, it’s time to translate your insights into a well-structured critique. Follow these writing tips and best practices to ensure your critique is clear, comprehensive, and professional.
Organization:
- Follow the standard structure: introduction, summary, critique, and conclusion.
- Use clear headings and subheadings to guide your reader through each section.
- Ensure a logical flow of ideas within and between paragraphs.
Tone and Style:
- Maintain an objective and scholarly tone throughout your critique.
- Use precise language and avoid unnecessary jargon.
- Strike a balance between formal academic writing and accessibility.
Supporting Your Arguments:
- Provide specific examples from the article to support your points.
- Use direct quotes sparingly and always cite them properly.
- Reference relevant literature to contextualize your critique.
Balancing Criticism and Praise:
- Acknowledge the article’s strengths as well as its weaknesses.
- Offer constructive criticism rather than merely pointing out flaws.
- Provide suggestions for improvement or future research directions.
Clarity and Concision:
- Be clear and direct in your assessments.
- Avoid repetition and unnecessary elaboration.
- Use transition sentences to connect different points and sections.
Proofreading and Editing:
- Review your critique for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors.
- Ensure consistency in formatting and citation style.
- Consider having a peer review your critique for additional feedback.
By following these guidelines, you’ll create a polished and professional critique that effectively communicates your analysis. Remember, the goal is to provide a fair and insightful evaluation that contributes to the academic discourse surrounding the article’s topic.
Example: A Sample Journal Article Critique
To illustrate the principles discussed in this guide, let’s examine a sample critique of a hypothetical journal article titled “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Workplace Dynamics in 2025” by J. Smith and A. Lee, published in the Journal of Future Work Studies.
Introduction: This critique evaluates Smith and Lee’s (2025) article on the influence of AI in contemporary workplaces. The study provides valuable insights into the changing nature of work but has some methodological limitations that warrant discussion.
Summary: Smith and Lee conducted a mixed-methods study involving surveys of 500 employees across various industries and in-depth interviews with 50 managers. They argue that AI integration in workplaces has led to significant shifts in job roles, skill requirements, and organizational structures. Key findings include:
- 60% of surveyed employees reported changes in their job responsibilities due to AI implementation.
- Managers identified critical thinking and AI literacy as essential skills for future workforce.
- Organizations are increasingly adopting flatter structures to facilitate human-AI collaboration.
Critique: Strengths:
- Timely and relevant topic addressing a critical aspect of modern work environments.
- Comprehensive mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative data with qualitative insights.
- Clear presentation of findings with well-designed graphs and tables.
Weaknesses:
- Limited sample size for the qualitative component may not capture the full range of managerial perspectives.
- Potential selection bias in the survey sample, with a skew towards tech-savvy respondents.
- Lack of longitudinal data to support claims about long-term trends.
The authors provide a compelling argument for the transformative impact of AI on workplace dynamics. However, their conclusions could be strengthened by addressing the limitations in their methodology and considering alternative explanations for their findings.
Conclusion: Despite its limitations, this study offers valuable insights into the evolving relationship between AI and human workers. It lays a foundation for future research and has important implications for workforce development and organizational planning in the AI era.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid in Journal Article Critiques
When writing a journal article critique, be aware of these common pitfalls that can diminish the quality and effectiveness of your analysis:
- Summarizing without critiquing: While a summary is important, the bulk of your critique should focus on analysis and evaluation. Avoid simply restating the article’s content without offering your own insights.
- Personal bias: Maintain objectivity in your critique. Don’t let your personal opinions or preconceptions about the topic unduly influence your evaluation of the research.
- Nitpicking: Focus on significant aspects of the article rather than minor issues. Critiquing every small detail can detract from your main arguments.
- Lack of balance: Avoid focusing solely on either strengths or weaknesses. A good critique acknowledges both positive aspects and areas for improvement.
- Unsupported claims: Always provide evidence or reasoning to support your critiques. Avoid making broad statements without backing them up.
- Misunderstanding the article: Ensure you fully understand the article’s content and methodology before critiquing it. Misinterpretations can lead to irrelevant or inaccurate criticisms.
- Ignoring context: Consider the article within its broader academic and historical context. Don’t critique it based on current knowledge if it was groundbreaking at the time of publication.
- Overreliance on direct quotes: While quotes can be useful, overusing them can make your critique seem unoriginal. Paraphrase and synthesize information where appropriate.
- Lack of structure: Organize your critique logically. A disorganized critique can be confusing and less impactful.
- Offering vague suggestions: When proposing improvements or future research directions, be as specific as possible. Vague suggestions add little value to your critique.
By avoiding these pitfalls, you can ensure that your critique is focused, balanced, and contributes meaningfully to the academic discourse surrounding the article’s topic.
The Future of Journal Article Critiques: Trends and Technologies
As we look ahead to 2025 and beyond, several trends and technologies are shaping the landscape of journal article critiques:
- AI-assisted analysis: Advanced AI tools are emerging to help researchers identify patterns, inconsistencies, and potential biases in academic articles. These tools can complement human analysis, offering additional insights and saving time.
- Interactive critiques: Digital platforms are enabling more dynamic and interactive forms of critique. Readers can engage with critiques through comments, annotations, and real-time discussions, fostering a more collaborative approach to academic discourse.
- Data visualization: As research becomes increasingly data-driven, critiques are incorporating more sophisticated data visualization techniques to illustrate key points and analyses.
- Open peer review: There’s a growing trend towards transparency in the peer review process. This may influence how critiques are written and shared, with a focus on constructive feedback and open dialogue.
- Interdisciplinary approaches: As research becomes more interdisciplinary, critiques are increasingly drawing on diverse fields of knowledge to provide comprehensive evaluations.
- Emphasis on reproducibility: With the replication crisis in various fields, critiques are placing greater emphasis on evaluating the reproducibility of research findings.
- Real-time updates: In fast-moving fields, critiques may need to be updated as new information emerges. Dynamic publishing platforms could allow for ongoing refinement of critiques.
- Accessibility and inclusivity: There’s a growing focus on making academic discourse more accessible to diverse audiences, which may influence the language and format of critiques.
- Ethical considerations: As research tackles more complex and sensitive topics, critiques are paying increased attention to the ethical implications of studies.
- Integration with systematic reviews: Critiques may become more closely linked with systematic review processes, contributing to broader syntheses of research in particular fields.
Related Article: Literature Topics and Research
FAQs on Journal Article Critique Guide
How do you write a journal critique?
To write a journal critique, start by thoroughly reading the article and taking notes. Then, structure your critique with an introduction, summary, detailed analysis of strengths and weaknesses, and a conclusion. Focus on evaluating the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions. Provide evidence for your assessments and maintain an objective tone throughout.
What are some examples of critiques?
Examples of critiques include book reviews, film critiques, art criticism, and academic peer reviews. In an academic context, journal article critiques, literature reviews, and research proposal evaluations are common forms of critique.
How to write a critique example?
To write a critique example, choose a specific article or work to analyze. Follow the structure outlined in this guide: introduce the work, summarize its main points, provide a detailed analysis of its strengths and weaknesses, and conclude with your overall assessment. Use specific examples from the work to support your points.
Start by filling this short order form order.studyinghq.com
And then follow the progressive flow.
Having an issue, chat with us here
Cathy, CS.
New Concept ? Let a subject expert write your paper for You
Post navigation
Previous post.
📕 Studying HQ
Typically replies within minutes
Hey! 👋 Need help with an assignment?
🟢 Online | Privacy policy
WhatsApp us
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Unintended Pregnancy and Its Adverse Social and Economic Consequences on Health System: A Narrative Review Article
Mansureh yazdkhasti, abolghasem pourreza, arezoo pirak, fatemeh abdi.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
* Corresponding Author: Email: [email protected]
Received 2014 Jul 16; Accepted 2014 Nov 23.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 3.0 Unported License which allows users to read, copy, distribute and make derivative works for non-commercial purposes from the material, as long as the author of the original work is cited properly.
Unintended pregnancy is among the most troubling public health problems and a major reproductive health issue worldwide imposing appreciable socioeconomic burden on individuals and society. Governments generally plan to control growth of births (especially wanted births as well as orphans and illegitimate births) imposing extra burden on public funding of the governments which inevitably affects economic efficiency and leads to economic slowdown, too. The present narrative review focuses on socioeconomic impacts of unintended pregnancy from the health system perspective. Follow of Computerized searches of Academic, 53 scientific journals were found in various databases including PubMed, EMBASE, ISI, Iranian databases, IPPE, UNFPA (1985-2013). Original articles, review articles, published books about the purpose of the paper were used. During this search, 20 studies were found which met the inclusion criteria. Unintended pregnancy is one of the most critical challenges facing the public health system that imposes substantial financial and social costs on society. On the other hand, affecting fertility indicators, it causes reduced quality of life and workforce efficiency. Therefore lowering the incidence of intended pregnancies correlates with elevating economic growth, socio-economic development and promoting public health. Regarding recent policy changes in Iran on family planning programs and adopting a new approach in increasing population may place the country at a higher risk of increasing the rate of unintended pregnancy. Hence, all governmental plans and initiatives of public policy must be regulated intelligently and logically aiming to make saving in public spending and reduce healthcare cost inflation.
Keywords: Unintended pregnancy, Economic burden, Cost, Health indicators, Reproductive health
Introduction
Unintended pregnancies are pregnancies that are mistimed, unplanned or unwanted at the time of conception. Unintended pregnancies include unwanted pregnancies at least for one of couples. Unintended pregnancy is among the most troubling public health problems and a major reproductive health issue including accidental pregnancy and defined as a pregnancy that was undesired for one or both of the partners ( 1 ). Regarding the World Health Organization (2005) approximately 210 million pregnancies occur each year worldwide of which 87 million are unplanned and 41 million continue to birth. According to the reports ( 2 ) the total number of unsafe abortion in 2008 was 21-22 million worldwide and there were 22 unsafe abortions per 1000 women aged 15-44 years. While the report on mortality due to unsafe abortion estimates 47000 maternal deaths (that is 13% of maternal mortality in 2008. Approximately fifty percent of pregnancies in United States of America are unintended and about 48% of reproductive-age American women ( 15 – 44 ) have experienced at least one unintended pregnancy ( 2 , 3 ).
Contrary to extensive coverage of family planning in Iran and the efforts in this regard unplanned pregnancies are common problem as well. A research in different parts of Iran revealed the prevalence of unintended pregnancies to be 22% while in Ardebil it was 61% ( 3 , 4 ). Another survey reported it to be 31% (of which 56% were unwanted and 44% were unplanned ( 5 ). Unintended pregnancy is also considered as a high-risk pregnancy associated with high rates of negative consequences for mother, partner and the baby. These groups of women are more exposed to suicide ( 6 ) and depression rate, poor nutrition during gestation ( 7 ), mental health issues, unstable family relationships, experiencing physical and psychological violence, risk of miscarriage and having low birth weight infants ( 8 ) and delayed onset of prenatal care ( 9 ).
Statistics show that when compared to wanted ones, unwanted children are exposed to greater risk factors, so that they more likely experience negative psychological and physical health issues and dropout of high school and tend to show delinquent behavior during adolescence ( 2 ). The participants of a research in Australia reported higher level of depression, anxiety and delinquency than compared with those in wanted children group thus child smoking were self-reported at 14-years ( 10 ).
According to several micro-level studies, a child’s overall health has an impact on his or her ability to achieve academic success. Existing studies at the macro level suggest population health has a significant effect on a nation’s economic performance and growth ( 11 ). Overall, the evidence suggests that unintended pregnancy is one of the most critical challenges facing the public health system and imposes significant financial and social costs on society. Long-term studies confirm that reducing unintended pregnancy incidences would increase labor force participation rates, improve academic achievement, have better economic efficiency, increase the level of health and reduce in crime rates among vulnerable groups ( 2 , 10 ). Thus in this paper we focus on the socio-economic impacts of unwanted pregnancy from the viewpoint of health system.
The present narrative review focuses on socioeconomic impacts of unintended pregnancy from the health system perspective. Follow of Computerized searches of Academic, 1245 scientific journals were found in various databases including Pub-Med, EMBASE, ISI, Iranian databases, IPPE, UNFPA (1985-2013). Related keywords included unwanted pregnancy, economic outcomes, social outcomes, cost, socio-economic consequences, health indicators, Reproductive health. After reading to topics, 53 relevant articles were identified. During this search, 20 studies were found which met the inclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria: 1-published articles in English and Persian (Original articles, review articles, published books about the purpose of the paper were used). 2-coordination between articles and Research Goals (Socio-economic consequences of unintended pregnancy). Socio-economic variables influencing unintended pregnancy were selected based on Socio-economic determinants of reproductive health (2010). Socio-economic determinants of reproductive (2010) that affect unintended pregnancy including: age, educational level of the spouses, the economic situation, employment of women, number of children, type of contraception, abortion and the number of children are living or dead.
Unintended pregnancy and unsafe abortion: An economic approach
Unintended pregnancies are classified as the high-risk gestations and occur across society regardless of race are socioeconomic status and its rates are highest among poor and low-income women ( 12 ). Furthermore, the number of illegal abortion is rising dramatically. According to global statistics annually 19 million women in developing countries and more than 15 million in Asia experience unsafe abortion, it is estimated that each year about 500000 women in developing countries die because of pregnancy complications. Therefore, unsafe and illegal abortion is among the main causes of death worldwide. The annual cost of treating a woman for complications of unsafe and illegal abortion is considerably higher than the cost of providing medical and safe abortion ( 13 ). The incidence of induced abortion is an important indicator of the frequency with which women experience unintended pregnancies ( 14 ). In 2008, 43.8 million abortions occurred worldwide while nearly half of all was unsafe and 98% of all unsafe abortions occurred in developing countries ( 15 ).
Forty percent of pregnancies are unplanned in Iran ( 16 ). Abortion is illegal due to religious, cultural and social beliefs in Iran and most of the unwanted pregnancies are terminated by clandestine and unsafe abortion procedures. This can cause irreparable damage to mother including death and serious disabilities; an unsuccessful abortion may influence the child’s health, too. These can negatively influence quality of life and impose heavy expenditures on the health system that are not defined or recorded in the balance sheet ( 2 ). Regarding the allocation of funds the health sector, problems related to pregnancies place heavy financial burden on governments (especially federal government). Most of money spent by taxpayers to comply with the health system may be spent for issues associated with unintended pregnancies.
Economic analysis shows that U.S. taxpayers spend more than 12 billion each year on unintended pregnancy ( 17 ). In the analysis of medical costs Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) reported that 12.1 billion is spent each year for as estimated 1.25 million unwanted pregnancies that 103 million is allocated to abortion services. On the other hand studies suggest that eliminating medical costs by preventing unwanted pregnancies can help to save about three- quarters of the budget allocated by the federal government allocated for UNICEF projects in 2010.
Reducing the incidence of unintended pregnancies can lead to reducing maternal mortality. Maternal mortality ratios is a major indicator of development in the world and according to the Millennium Development Goals, it should be reduced by three- quarters (75%) between 1990 and 2015. In our country the maternal mortality ratio is 21 per on hundred thousand live birth. Indeed any decrease in the rate of unintended pregnancy will significantly affect mortality rate. In developing countries including Iran it is somehow impossible to find out the exact number of unintended pregnancies and the statistics are ambiguous and, therefore, increase the tax burden on taxpayers and subsequent economic costs are unknown, too ( 2 ).
Family planning policy has recently been changed in Iran so adopting a new approach in increasing population in our country may place the country at a higher risk of increasing the unintended childbirth rate. Variables of quantitative economics, micro and macro socio-economic interactions on social variables such as unemployment, dropout and social harm to restate that this is considered in this paper ( 12 ).
Review literature: Unintended pregnancies and population, from a socio economic perspective
Demographic changes in the last two centuries, along with fundamental changes in lifestyle, technology development and various rising of expectations in promoting physical, mental and social welfare have led to the further consideration of population issues and developing strategies to manage the population ( 18 ).
Health status of a population is affected by various factors such as age structure, exposing to risk of different carriers, and also level of population welfare behavior and characteristics as well as reproductive behaviors healthcare needs do affect a country’s economic performance. Commission on the Macroeconomics and Health reports that population health has a significant impact on different aspects of microeconomics and health labor market and saving variables that will eventually affect the macroeconomic outcomes of a country ( 19 ). The problem of unwanted pregnancy is one of the main challenges facing developing countries due to its effect on uncontrollable population growth and mother and child health. The world population doubles every 40 years while in poor countries it will probably happen in less than 20 years. Thus unintended pregnancy can be among the factors negatively affects the growth of population. This issue can be approached in two ways: prevention of uncontrolled excessive population growth and its impact on both mother and baby ( 14 ). The risk factors associated with unintended pregnancy include unwanted pregnancy in adolescents, inadequate family planning services, low socio economic status, lack of or improper use of family planning methods and unawareness of it. Unwanted pregnancy rate among low-income American teens is reported to be about 60%. Teenage (15-19 yr) unintended pregnancy often leads to academic failure and school dropout. It is also associated with a greater risk of psychological distress, suicide and unsafe abortion and may threaten the health of the individual ( 17 ). Health is the basis of job and learning efficiency increasing physical — mental and intellectual abilities development and is essential for productive adulthood. So the incidence of unplanned pregnancy, affecting health of children and adults, leaves costs and financial burden to the governments ( 20 ).
Unintended pregnancies are more common among poor adolescents. Poverty and disease are the major causes of suffering that accelerates population growth and unequal distribution of health services and health inequalities ( 13 , 21 ). “Health inequalities” is a term used to socioeconomic and health inequalities. Many epidemiological studies have shown that developing countries grapple with the poor health consequences and higher burdens of diseases compared to countries that are more affluent. This kind of pregnancies will lead to decline in welfare of couples, reducing socio-economic development ( 22 ). Unintended pregnant teens will be more exposed to risk factors including lower education and income levels and being focused to take low status jobs. Gini coefficient based on Lorenz curve is used measure of inequality income, which is a cumulative frequency graph that compares distribution, which represents equality of incomes. In this regard, there is a range of problems associated with data sources on health status of population that can potentially cause serious bias in the measurement of health in equalities. There is also a risk of serious bias due to the lack of definitive statistics concerning health status of Iranians ( 23 ).
In a system of public financing and in the systems that medical bills are paid by third-party payers (employer- based insurance systems) insured groups or people put pressure to meet its demand that rising budgetary pressure for the state is its minimal impact. These additional costs will eventually be reflected in Consumer Price Index (CPI) ( 24 , 25 ). Budgetary pressures resulting from unintended pregnancies and taxpayers costs are high so that the average cost per unintended pregnancy in United States is calculated to be about 10 thousands of public funds ( 2 , 26 ). Clearly, the incidence of unplanned pregnancies can impose a significant burden on taxpayers. Use strategy to prevent unintended pregnancy (Method of family planning and contraceptive methods such as condoms, pills, etc.) will reduce the financial burden on taxpayers. Because of economic and social variables on the interaction, so improving economic variables, social variables can also be improved.
Unintended pregnancy and Health: Socioeconomic approach
Health and safety issues are intertwined with comprehensive progress and development including economic growth. Healthy people are more happy and motivated ones that increase productivity and economic development by reducing direct and indirect costs. Therefore, most of the communities have paid special attention to promotion of health indicators Health indicators are quantifiable characteristics of a population, which researchers use as supporting evidence for describing the health of a population ( 21 , 27 ). Indeed the most important factors affecting economic growth are labor, physical and human capital ( 28 ).
The concept of human capital in economic literature defined by including education, training, health, skills, expertise, experience, migration and other investments that enhance an individual’s productivity and improve economic growth ( 29 ). When speaking of improving the quality of labor productivity the issue is not unique to education, skill or experience but the impact of public health should also be considered as an important factor in the accumulation of human capital. Unplanned pregnancy interferes with health and wellness in different ways ( 30 ). Unintended pregnancy not only effects on various aspects of individual and family health state, but also reduces the labor productivity ( 31 ). In the regards different domains relevant to quality of life: socio economic, familial, psychological, spiritual, health and performance aspects ( 32 , 33 ). Unintended pregnancy due to complications that can reduce quality of life ( 34 , 35 ). Several reports suggest that incidence of unintended pregnancy predicts a range of negative outcomes like labor market challenges and increasing the number of working days lost ( 2 , 36 ). There is a reciprocal relationship between them so the level of public health (especially Health promotion labor force) is directly related to the economic growth and consequently socio economic development. Reciprocally economic growth is associated with increasing level of public health ( 23 , 37 ). Implementation of public health interventions to reduce unintended pregnancy can cause growth and economic development ( 26 ).
Unplanned pregnancies can reduce labor productivity through declining health stock for individuals that in turn lowers the standards of living) 32). According to Myrdal cumulative causation theory low-income leads to lower levels of life, so human productivity level will be limited and the vicious circle will be repeated because of low incomes ( 22 , 38 ).
Unintended pregnancy and reproductive health from a socioeconomic perspective
Health development is driven by public health that in turn driven by reproductive health ( 39 ). Reproductive health can be divided into some subcategories: consultations, information, education and communication about family planning, promoting right to freely choose marriage (partner), contributing gender equality and equity in decision making for marriage, family planning services, improving reproductive decisions, providing prenatal care and healthcare for women, securing reproductive and sexual health, preventing infertility, inappropriate treatment of infertility and abortion and treating its complications as well as treating reproductive tract infections, dealing with sexually transmitted diseases and appropriate treatment ( 40 – 42 ).
Demographic studies in the second half of the 20 th century indicate progression in fertility transition in different parts of the world, especially in developing countries. Studies showed a correlation between fertility transition and the rate of unintended pregnancy. Model of Bongaart, suggested that with the onset of the fertility transition, unwanted fertility typically rises substantially that will stabilize at the end of the phase and will not decrease. Then he argues that the reason for increase unplanned pregnancy rate during the first half of the transition is a decrease in desired family size (or ideal number of children). Unplanned pregnancy is the major reproductive health issue that seriously affects its indicators ( 44 ).
Infant mortality rate, as one of the major indicators, is affected by unintended pregnancy incidence. According to a number of studies infant mortality and malnutrition levels and the rate of abuse and mental illnesses including schizophrenia are high among the babies from unwanted pregnancies and they are more likely fail in academic achievements in later life. Unintended pregnancy increases the risk of low birth weight and affects the infant growth indicators ( 43 ). Mortality rate of children under 5 years of age is an important indicator for reproductive health that can be affected by incidence of unplanned pregnancy. This kind of pregnancy is the leading cause for death of 14 million children under 4 years worldwide ( 45 , 46 ).
Maternal death indicator is affected by unplanned gestation due to unsafe and criminal abortions. The results of “Reasons women give for contemplating or undergoing abortion”, indicate that the private decision of the mother, number of children she has, opinion of the partner and people significant in her life have direct impact on her abortion decision ( 16 ).
43.8 million abortions occurred worldwide, of which 86% occurred in low-/middle-income countries. Between 2003 and 2008, the proportion of unsafe abortions increased and they were believed to account for 13% of maternal deaths, with the majority of these concentrated in countries with restrictive laws on abortion ( 15 , 47 ). Nevertheless, global studies have mostly focused on psychological impact of induced abortion on the woman however; there have been few studies on the issues of the ones choose to continue their pregnancy.
Women with unintended pregnancy did high-risk activities when facing unwanted childbearing including hitting, lifting heavy objects, using unhealthy vulva objects, using injections and eating herbal and chemical medicines ( 47 , 48 , 50 ). A research on reproductive health indicators including prenatal care and stated concluded that average weight gain in women with unintended pregnancy is significantly less than the ones with wanted gestation ( 18 , 48 ).
There are significant differences between women with intended and unintended pregnancies in the indicators for family planning in reproductive health services. Ineffective use of family planning methods are associated with increased rates of maternal mortality due to pregnancy that is a health equity indicator ( 39 ).
The life expectancy indicator is one of the indicators heavily influenced by infant mortality rate (IMR) that is the best indicator of socio-economic development. Accurate statistics on the number of unintended pregnancies resulted in fetal death, is not exist ( 6 ). The stock and investment in health human capital (health expenditures) influenced the growth rate of per capita income positively and were in a significant level of, respectively, 99 and 90 percent ( 22 ). Results from the analysis of reproductive health indicators and impact of unplanned pregnancies on them suggest that this condition leads to more health expenditures and family responsibilities and limits women’s participation in economic activities. Labor force and its productivity lead to increase human capital inventory and it can be said that health expenditures are one of the most effective factors on production. The overall state of the economy (including current and future growth rates) can affect both actual and expected values of variables that are the determinants of health and change health state of community ( 52 ). Then it is necessary to initiatives public policy intelligently aimed at reducing and preventing unwanted pregnancies that will generate significant savings in the governments’ budget ( 2 ). This has resulted in economic growth, increased government revenue especially taxes and income from profit- making activities which may prove useful for development of treatment and in improving the public health ( 52 ).
Prevention of Unintended pregnancy: By separating economic and social variables
Out-of-pocket health care spending imposes a substantial financial burden on government and households and in many countries, health expenditure per capita has risen faster than the rise in Gross Domestic Product (GPD) ( 10 ). Almost all countries with advanced economics are striving to control soaring health costs along with achieving the goals of health care and Medicaid. Reining the healthcare costs is a major priority for policymakers and stimulating healthcare reform ( 11 , 19 ). In order to achieve better outcomes and reduce the costs, it is essential to implement preventive measures, promote health information, advance evidence-based self-care behaviors and improve performance of information systems and electronic applications aimed at treatment detection and follow up.
Prevention is an effective way of dealing with socioeconomic burden of unwanted pregnancies imposed to health sector. Some of the leading causes of unintended pregnancies are non-use and also improper use of contraceptive services and contraceptive failure ( 1 ). Social pressures and expectations overshadowed the needs of women and so they are not allowed to prevent pregnancy. Social sanctions and inequality between men and women, husband’s disapproval of contraceptive methods, inadequate family planning, lack of effective consultation make recommendations incompatible with their conditions that would make them not use contraceptives ( 36 , 52 ).
The costs of unintended pregnancy are classified as the intangible costs, which are not just financial but can indeed cause a decrease in the quality of life of these mothers and their families. In fact, the real damage to quality of life is incalculable. Unintended pregnancies result in a range of adverse consequences including labor market struggles, higher crime rates, more abortions, increased levels of household stress and others that have nothing to do with public balance sheets and creates a huge financial burden for taxpayers given the initial value of the nominal. Prevention of unplanned pregnancies will help to increase national savings and lead to higher rates of economic growth ( 39 ). Obviously, adoption of policies such as: adolescent pregnancy prevention, improving family health literacy based on socio-economic welfare ( 2 ), launching programs promoting contraceptive use. Promotion of consultation and men’s participation, reduction in unprotected sex and implementing programs to improve the quality of family planning services ( 39 ) can lead to significant savings in public spending and many health expenditure inflation rate ( 9 ).
However, unintended pregnancy can be reduced using quality improvement programs. Among socio economic factors, training and education has been proven to be the most effective factors affecting fertility behavior. Women with higher education are more likely to succeed in controlling their fertility advancing their opportunities for childbearing ( 52 , 53 ).
Individual health is considered as a key factor in the accumulation of human capital, reducing the welfare of couples and socio economic development. Briefly concluding the economic analysis, it can be inferred that unintended pregnancy is one of the major challenges facing public health and safety that imposes significant economic and social costs on society.
WHO Report, Poverty and health inequalities are important factors in unintended pregnancy ( 13 , 21 ). Many epidemiological studies have shown that developing countries grapple with the poor health consequences and higher burdens of diseases compared to countries that are more affluent. This kind of pregnancies will lead to decline in welfare of couples, reducing socio-economic development ( 22 , 23 ).
Social stratification ranks individuals based on their education, income and employment status and therefore consolidates their position in the system. Unintended pregnant teens will be more exposed to risk factors including lower education and income levels and being focused to take low status jobs ( 23 , 24 ). In many studies, reducing coverage for family planning is an important factor in unwanted pregnancy ( 3 – 5 , 40 – 42 ). Contrary to extensive coverage of family planning in Iran and the efforts, in this regard unplanned pregnancies are common problem as well. The prevalence of unintended pregnancy is reported 22% in Iran ( 3 ) and 61% in Ardabil ( 4 ).
Unintended pregnancy has a range of negative consequences—abridged educational careers ( 23 , 24 ), labor-market struggles ( 19 , 47 ), higher crime rates ( 2 , 53 ), more abortions ( 48 ), increased levels of household stress ( 47 , 48 ), and other related outcomes—that have nothing to do with public balance sheets and are therefore not incorporated into our analysis. Similarly, due to practical data limitations, we do not account for the likelihood that delaying some mistimed pregnancies will reduce the likelihood that they will require taxpayer support when they eventually occur. Thus, our estimates are inherently conservative ( 47 ).
Overall, the evidence suggests that unintended pregnancy is one of the most critical challenges facing the public health system and imposes significant financial and social costs on society. Long-term studies confirm that reducing unintended pregnancy incidences would increase labor force participation rates, improve academic achievement, have better economic efficiency, increase the level of health and reduce in crime rates among vulnerable groups.
Ethical considerations
Ethical issues (Including plagiarism, Informed Consent, misconduct, data fabrication and/or falsification, double publication and/or submission, redundancy, etc.) have been completely observed by the authors.
Acknowledgments
This project was granted by the Tehran University of Medical Sciences. The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
- Finer LB, Zolna MR (2011). Unintended pregnancy in the United States: Incidence and disparities, 2006. Contraception, 84(5): 478–485. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sonfield A, Kost K, Gold RB, Finer LB (2011). The Public Costs of Births Resulting from Unintended Pregnancies: National and State-Level Estimates. Perspect Sex Reprod Health, 43(2): 94–102. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Amani F, Bashiri J, Nahan Moghadam N, Tabarraie Y(2010). Applicdation of logistic regression model in surveying effective causes of unwanted pregnancy (Persian). Qom University of Medical Sciences Journal 4(1): 32–6. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jahanfar S, Ramazani TehraniI F, Sadat Hashemi S (2002). The prevalence of unwanted cities in Iran 2000 (Persian). TUMJ, 60(4): 334–40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pourheydari M, Souzani A, Shamaiian N (2007). Prevalence of unwanted pregnancy and their correlates in pregnant women in Shahrood, Iran (Persian). Payesh, 6(1): 63–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Afshar M, Delavardevin N, Kianfar S (2004). Comparison of neonatal growth indices in unwanted pregnancies with gestational asked (Persian). Goums, 13(83): 40–5. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fourn L, Ducic S, Seguin L (1999). Factors associated with low birth weight: a ultivariate analysis. Sante, 9(1): 7–11. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sereshti M, Delaram M, Rafieian M (2005). [Prevalence and causes of unwanted pregnancy from the perspective of pregnant women (Persian)]. JRHS, 13(24)8–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Karacam Z, Onel K, Gercek E (2011). Effects of unplanned pregnancy on maternal health in Turkey. Midwifery, 27(2): 288–93. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hayatbakhsh MR, Najman JM, Khatun M, Al Mamun A, Bor W, Clavarino A(2011). A longitudinal study of child mental health and problem behaviours at 14 years of age following unplanned pregnancy. Psychiatry Res, 185(1-2): 200–4. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fogel R (2004). Health, Nutrition, and Economic growth. Economic Development & Cultural Change, 52(3): 643–58. [ Google Scholar ]
- Thomas A, Emily M (2011). The High Cost of Unintended Pregnancy. CCF Brief, 45(5): 2–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Carlin EM, Boag FC (1995). A study on the effective factors of unwanted regnancies in pregnant women of Tehran city. Int J STD AIDS, 6(6): 373–886.8845393 [ Google Scholar ]
- Moss MCN (2003). Unintended pregnancies: Acall for nursing action. Am J Matern Child Nurs, 28(1): 24–30. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heather W (2012). Indigenous Women of Latin America: Unintended Pregnancy, Unsafe Abortion, and Reproductive Health Outcomes. Pimatisiwin, 10(3): 271–282. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kirkman M, Rosenthal D, Mallett S, Rowe H, Annarella H (2010). Reasons women give for contemplating or undergoing abortion: A qualitative investigation in Victoria, Australia. Sex Reprod Healthc, 1(4): 149–55. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morgan LM, Roberts EFS (2012). Reproductive governance in Latin America. Anthropol Med, 19(2): 241–254. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Abazari F, Arab M, Abbasszadeh A (2003). Relationship of unwanted pregnancy and fertility behavior in pregnant women who visited maternity wards of Kerman hospitals (Persian). J Reprod Infertil, 4(1): 39–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- Poorreza A, Khosravi M, Alipoor V, Jafari S (2007). What Should Macroeconomists Know about Health Care Policy? Eds, Heller PS and Hsiao W, 2nd ed, New York, pp.40–5. [ Google Scholar ]
- Spence M, Lewise M (2009). Health and growth. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development. The World Bank. [ Google Scholar ]
- World Health Organization, World health & Statistics; 2009, 2010. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lotfalipoor M, Falahi MA, Borji M (2011). The effect of health indicators and economic growth in Iran (Persian). Health Management, 14(46): 70–5. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ameryoun A, Meskarpour-Amiri M, Lorgard Dezfuli-Nejad M, Khoddami-ishteh HR, Tofighi Sh (2011). The Assessment of Inequality on Geographical Distribution of Non-Cardiac Intensive Care Beds in Iran. Iran J Public Health, 40(2): 25–33. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Halpern NA, Pastores SM, Thaler HT, Green-stein RJ (2006). Changes in critical care beds and occupancy in the United States 1985– 2000: Differences attributable to hospital size. Crit Care Med, 34(8): 2105–2112. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Carr BG, Addyson DK, Kahn JM (2010). Variation in critical care beds per capita in the United States: implications for pandemic and disaster planning. JAMA, 3(14): 1371–1372. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gipson JD, Koenig MA and Hindin MJ (2008). The effects of unintended pregnancy on infant, child, and parental health: a review of the literature. Stud Fam Plann, 39(1): 18–38. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kasule OH (2003). Social and religious dimensions of unwanted pregnancy: an Islamic perspective. Med J Malaysia, 58(3): 49–60. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fears CS (2013). Teenage Pregnancy Prevention: Statistics and Programs. CSR Report for congress, www.crs.gov . [ Google Scholar ]
- Frankenberg E, Thomas D (2009). Reproductive Health, Empowerment of Women, and Economic Prosperity. POP POV, Research Network, poppov.org/Portals/1/documents/papers/5.Frankenberg.pdf You visited this page on 2/3/14.
- Frankenberg E1, Buttenheim A, Sikoki B, Suriastini W (2009). Do Women Increase Their Use of Reproductive Health Care When It Becomes More Available? Evidence From Indonesia, Stud Fam Plann, 41(1): 27–40. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Greene M, Mehta M, Pulrwitz J, Wulf D, Bankole A, Singh S. Involving men in reproductive health: contributes to development. Background paper to the public choices, private decisions: sexual and reproductive health and the millennium development goals. United Nation Millennium Development project 2004.[CITED SEP 5 2009]. Available at: URL: http://www.unmillenniumproject.org/d ocuments/Greene_et_al-final.pdf .
- Skevington SM (2002). Advancing cross-cultural research on quality of life: observations drawn from the WHOQOL development. World Health Organisation Quality of Life Assessment. Qual Life Res, 11(2): 135–44. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yazdkhasti M, Keshavarz M, Khoei EM et al. (2012). The Effect of Support Group Method on Quality of Life in Post-menopausal Women. Iran J Public Health, 41(11): 78–84. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yazdkhasti M, Keshavarz M, Mahmoodi Z, Hosseini AF (2014). Self-directed Learning and Its Impact on Menopausal Symptoms. Ircm J, 16(5): 32–9. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- King J.T, Tsevat J, Moossy J, Roberts M. Preference-Based Quality of Life Measurement in Patients with Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy. Spine, 2004; 29: 1271–80. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khang YH, Lynch JW, Yun S, Lee SI (2004). Trends in socioeconomic health inequalities in Korea: use of mortality and morbidity measyres. J Epidemiol Community Health, 58(4): 308–14. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kardesler E, Yetkiner I H. (2009). The Impact of Corruption on FDI: An Application of Efficient Grease Hypothesis to EU Countries. The Empirical Economics Letters, 8(8): 409–429. [ Google Scholar ]
- Laporte A (2004). Do Economic Cycles Have a Permanent Effect on Population Health? Revisit-ingthe Brenner Hypothesis. Health Economics, 13(8): 767–79. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Khakki SI, Khani H, Halimi SS, Monemi A (2011). Best practice of comparison of Reproductive health Indicators on the bases on design checklist of family physicians and current guidelines of health Ministry Chaharbid rural health and medical centers in 2011. International Journal of Optimal Experience and Functioning Primary Health Care System, 2(1): 1–8. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sadeghi H, AminiSani N, Arshi S, Sezavar Sh (2003). Reproductive factors among migrant tribes (Ashayer) women in Ardabil province (Persian). JAUMS, 3(9): 38–41. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mazlumi Mahmudabad SS, Shasidi F, AbbasiShavazi M, Shahrizadeh F (2007). Evaluating knowledge, attitude and behavior of women on reproductive health subject in seven central cities of Iran (Persian). JRI, 4(29): 391–400. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohammadi A, Eftekhar Ardebffi H, Akbari Haghighi F, Mahmoudi M, Poorreza A (2004). Evaluations of services quality based on the pations’expectations and perceptions in Zanjan hospitals. Sjsph, 2(2): 71–84 [ Google Scholar ]
- Bongaarts J. Trends in unwanted childbearing in the developing world (1997). Stud Fam Plan, 28(4): 267–77. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jourabchi Z, Ranjkesh F, Asefzadeh S, Sann LM (2013). Impact of integrated maternal health care on reducing pregnancy and delivery complication in Qazvin province (2009-2011) (Persian). JQUMS, 16(4): 47–53. [ Google Scholar ]
- Minnesota Department of Health (2002). Strategies for Public Health: A Compendium of Ideas, Experiences, and Research from Minnesota’s Public Health Professionals. Available from: http://www.health.state.mn.us/strategies/toc.pdf [accessed on July4, 2011].
- Aghababaei S, Bakht R, Moien R(2010). Study of Contraceptives Used in Unwanted Pregnancies (Persian). Journal of Shaheed Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences, 18 (3): 307–314. [ Google Scholar ]
- Le Hoa H, Connolly Mark P, Bahamondes Luis et al. (2014). The burden of unintended pregnancies in Brazil: a social and public health system cost analysis. Int J Womens Health, 16(6): 663–70. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Major B, Appelbaum M, Beckman L, Dutton MA, Russo NF, West C(2009). Abortion and mental health: evaluating the evidence. Am Psychol, 64(9): 863. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corbin J, Strauss AL (2008). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 3 rd ed, Sage publication, Inc. www.sagepub.com/corbinstudysite [ Google Scholar ]
- Wilson EK, McQuiston C (2006). Motivations for pregnancy planning among Mexican immigrant women in North Carolina. Matern Child Health J, 10(3): 311–20. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beheshti M, Sojudi S (2007). [Empirical Analysis of the Relationship between Health Expenditure and GDP in Iran (Persian)]. Slname-Barresi Ha Ye Eghtesadi, 4(4): 115–135. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shovazi MJ, Hoseini Chavoshi M, Delavar B (2003). Unwanted pregnancy and its influencing factors in Iran (Persian). J Reprod Infertil, 1(5): 62–7. [ Google Scholar ]
- Weinberger MB (1987). The relationship between women’s education and fertility:selected findings from the World Fertility Surveys. Int Fam Plan Perspec, 1987;13(2): 35–46. [ Google Scholar ]
- PDF (473.2 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
Home > Articles > Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper 2025
Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper 2025

Updated on 17th October, 2024 , 2 min read
The Central Board of Secondary Education has released the Class 12th Physical Education Sample Paper on its official website. The students can download the Physical Education Sample Paper in PDF format. To prepare well for their exams, the students must practice the Sample Papers provided by the Board. Moreover, the CBSE has also released the Class 12th Physical Education Marking Scheme. Students can download the Sample Papers to overview the exam pattern and mark distribution.
Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper 2025: Preparation Tips
- Students should take time-bound test papers to maintain their speed in the exam.
- Students can also join online courses which can assist them in their preparation
- Taking mock tests regularly to evaluate preparation and enhance time management.
- Learn from video tutorials on challenging subjects to gain a variety of viewpoints. Utilize applications to learn new ideas and for practice.
- To prepare well for their Board Exams, students are advised to follow some preparatory strategies. The preparation tips are mentioned in the points listed below:
- Students should practice regularly with whatever material is available to them. However, practicing the books recommended by the Board should be initially done.
- To improve their score in the English section, students should stress more on improving their English by reading, writing and speaking.
- Students can start their preparations with the simpler subjects. Next, they can tackle the challenging ones. When the simpler topics are finished, they feel accomplished and more confident.
- Scoring good marks is simple when students use diagrams. Regularly practice diagrams and label them neatly. Students should practice regularly drawing the diagrams as it helps them immensely during the exams.
- Understanding the syllabus: Students can obtain the most recent syllabus from their school or download it from the Bihar Board's official website.
- Collect Study Materials: Students should make sure that they practice the previous year's questions and sample papers so that they may know about the test format.

Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper 2025 PDF Download
The table presented below provides the Class 12th Physical Education Sample Papers of the current academic year (i.e. 2024-25). Students can access the Sample papers from the given table:
| CBSE 12th Sample Papers 2025 |
|
| ISC Physical Education Specimen Question Paper 2025 | Not Announced Yet |
Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper 2024 PDF Download
The table presented below provides the Class 12th Physical Education Sample Papers. Students can access the Sample papers from the given table:
| CBSE 12th Sample Papers 2024 |
|
| ISC Physical Education Specimen Question Paper 2024 | |
| PSEB 12th Physical Education Sample Paper 2024 |
Advantages Of Solving The Class 12th Physical Education Sample Papers 2025
Solving the Sample Papers can be extremely helpful for the students who will appear for their Class 12th Board exams soon. The advantages of solving the Class 12th Physical Education Sample Paper are mentioned in the points listed below:
- By solving the sample papers, students learn about the marks distribution and exam pattern.
- It helps the students to increase their question-solving speed and finish the exam within the allotted time.
- Students get to know about the difficulty of the exam.
- It boosts their confidence.
- It helps them identify weak areas where they need to focus on.
- It enhances their accuracy.
- It improves their overall understanding of the subject.
Similar Articles
Difference Between BE and BTech: What should be your pick?
Biotechnology Courses After 12th: Eligibility & Top Colleges
Software Engineering Courses After 12th - Fees Eligibility & Top Colleges
PDF Preview
Popular searches, popular colleges/universities, top colleges by courses, top courses.
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers
CBSE Class 12 Home Science Sample Paper and Marking Scheme 2024-25: Download Free PDF
Cbse home science class 12 sample paper 2025: cbse class 12 students download the sample question paper for home science along with the marking scheme from direct links given in this article. .

CBSE Class 12 Home Science Sample Paper 2024-25: Are you a CBSE Class 12 student, looking for the sample question paper for Home Science for 2024-25? Well then don’t worry as we have got you covered. The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) has made available the sample question papers for all the subjects for class 12 students. Students must solve these model papers to give a boost to their exam preparation. Students can find the CBSE Class 12 Home Science Sample Paper and Marking Scheme here .
Benefits of Solving Sample Papers
Sample question papers increase confidence in students and make them understand their strengths and weaknesses. When students solve sample question papers, they get an idea of how much they have actually understood from what they have learned. Sample papers also help them to understand the typology and level of difficulty of questions that they can expect in the examination. It also helps to develop writing practice and teaches speed and time management.
CBSE Class 12 Home Science Question Paper Instructions 2024-25
1. All questions are compulsory.
2. There are total 35 questions.
3. Question paper is divided into four sections-A, B, C and D.
4. Section A has question no.1 to 14 are Multiple choice questions and are of 1 mark each.
5. Section B has question no.15 to 18 are Case-based questions and are of 1 mark each.
6. Section C has question no. 19 to 25 are of 2 marks each and question no. 26 to 29 and are of 3 marks each.
7. Section D has question no. 30 to 33 are of 4 and question no. 34 and 35 and are of 5 marks each.
8. Internal choices are given in some questions.
CBSE Class 12 Home Science Sample Paper 2024-25
Section a (multiple choice questions).
Q1. Which of the following is the guiding principles of ECCE?
(A) Blend of modern and traditional sources
(B) Mix of formal and informal interactions
(C) Based on only informal interaction
(D) Use of expensive materials, arts and knowledge
Q2. The set of methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into finished and semi-finished products is-
(A) Food Science
(B) Food Processing
(C) Food Technology
(D) Food Manufacturing
Q3. Which of the following is the main aim of social entrepreneur?
(A) Changing the pattern of design of a product / commodity
(B) Achieving large scale benefits through entrepreneurship for a specific group
(C) Attempting new technological methods for producing a commodity
(D) Attaining full employment and self-reliance for women workers
Q4. Which of the following is a visible biological hazard in food?
(A) Virus
(B) Stones
(C) Protozoa
(D) Caterpillars
Q5. Frozen peas are an example of:
(A) Functional food
(B)Formulated food
(C)Preserved food
(D)Minimally processed food
The process of conversion of oil to Vanaspati is called as _____________.
(A)hydrogenation
(B)fortification
(C)preservation
(D)supplementation
Q6. Which of the following is short term strategy to combat malnutrition?
(A)Ensuring food security
(B)Control of micronutrient deficiencies
(C)Employment generation schemes
(D)Prevention of food adulteration
Q7. If the food gets spoiled during transportation, then it shows a lack of control in which of the food safety management system?
(A) ISO
(B) GMP
(C) GHP
(D) GDP
Q8. Choose the correct pair of craft with its State.
(A) Shola craft: Maharashtra
(B) Channapatna dolls: Karnataka
(C) Warli painting: Assam
(D) Bamboo craft: Odisha
Q9. When the height of the child is less than adequate for age, this is termed as-
(A) Underweight
(B) Stunting
(C) Wasting
(D) Obesity
Q10. Which of the following organization supported in implementation of Red Ribbon Express (RRE) project?
(A) NYKS
(B) SARI
(C) CRS
| List I (Colour Harmony) | List II (Description) |
| i. Monochromatic harmony | 1. Two pairs of complementary |
| ii. Achromatic harmony | 2. Only neutrals |
| iii. Double Complementary harmony | 3. Combination of three colours |
| iv. Split complementary harmony | 4. Single hue |
Choose the correct option from the following-
(A) i-4, ii-2, iii-1, iv-3
(B) i-2, ii-3, iii-4, iv-1
(C) i-1, ii-2, iii-3, iv-4
(D) i-3, ii-4, iii-1, iv-2
| List I(Types of establishments offering hospitality services) | List II(Feature) |
| i. Hotel | 1. Only lodging |
| ii. Motel | 2. Lodging, meals and other services |
| iii. Resort | 3. Lodging and parking near the room |
| iv. Lodge | 4. Lodging with range of amenities |
(A) i-4, ii-3, iii-2, iv-1
Q13. Which of the following career options are advised for DCJ professional?
(i) Community Media
(ii) Analyst for testing
(iii) Research Scholar
(iv) Quality Control Manager
Choose the correct option from the following-
(A) (i) and (iii)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iv)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Q14. Which of the following are features of SOS children’s home?
(i)Grow with biological families
(ii)Supports till child becomes independent
(iii)Family based long term care to orphan children
(iv)Government social organization which has family approach
(A) (i) and (ii)
(B) (ii) and (iii)
(C) (ii) and (iv)
(D) (i) and (iv)
Which of the following services are offered by ICDS?
(i) Non-formal pre-school education
(ii) Supplementary feeding
(iii) Establishment of youth clubs
(iv) Social defense and protection
SECTION B (CASE STUDY- BASED QUESTIONS)
Read the passage carefully and answer Question no. 15 to 18.
The medical nutrition therapist takes into account the food pattern and frequency of intake of different types of food, diagnosis of disease and prescription given by the doctor, the health status and physical condition including ability to eat, chew, swallow, digest and absorb the food eaten, feeling of hunger, physical activity and life style, dietary and other supplements consumed, cultural/ethnic practices and religious beliefs.
Q15. In the context of medical nutrition therapy choose the correct pair.
(A)Antioxidants: Low sodium salt
(B)Nutraceuticals: Beta-carotene
(C) Medical foods: Lactose free milk
(D)Phyto chemicals: Amla powder
| List I (Type of Diets) | List II(Examples) |
| i. Mechanical soft diet | 1. Buttermilk |
| ii. Liquid diet | 2. Sago kheer |
| iii. Soft diet | 3. Strained soup |
| iv. Clear liquid diet | 4. Pureed apple |
(A) i-1, ii-2, iii-3, iv-4
(B) i-4, ii-3, iii-2, iv-1
(C) i-3, ii-4, iii-2, iv-1
(D) i-4, ii-1, iii-2, iv-3
Q17. Given below are two statements labeled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
ASSERTION (A): Intravenous feeds are preferred over tube feeds.
REASON (R): In intravenous feeds the patients are nourished with the special solutions that are given through a drip in the vein.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true.
Q18. Given below are two statements labeled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
ASSERTION (A): High consumption of convenience and processed foods increases the incidence of Hypertension.
REASON (R): It is attributed to the presence of high sodium content.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(C) A is true but R is false.
(D) A is false but R is true
Online Test Series for CBSE Class 12 Students
Class 12 students can prepare effectively for the exams with the help of online test series prepared by the subject matter experts. These test series will help students to check their exam preparation. Refer to the links below:
CBSE Class 12 Humanities Online Test Series
CBSE Class 12 Science Online Test Series
CBSE Class 12 Commerce Online Test Series
Also, check
CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers 2024-2025
CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024-2025: Download PDF of All Subjects
CBSE Additional Practice Questions for CBSE Board Exam 2024
CBSE Class 12 Deleted Syllabus 2025
CBSE Class 12 Competency Based Questions 2024-25 PDFs
NCERT Books for CBSE Class 12 - Latest Edition
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
MOCK TEST 1
CBSE Class XII Humanities 2024-25
English/Hindi
MOCK TEST 2
MOCK TEST 3
- TSPSC Group 1 Hall Ticket 2024
- IBPS PO Admit Card 2024
- ADRE Grade 4 Admit Card 2024
- UGC NET Result 2024
- RSMSSB CET Admit Card 2024
- HSSC Group C, D Result 2024
- ugcnet.nta.ac.in Result 2024
- Moon Timing Today
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Paper 2024-25
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers 2024-25
Latest Education News
BJP Candidate List 2024 Jharkhand: बीजेपी ने किस सीट से किसे दिया टिकट? देखें यहां
Haryana Cabinet Ministers List 2024: सैनी कैबिनेट में किसे मिला कौन-सा मंत्रालय? देखें यहां
[OUT] इंडिया पोस्ट जीडीएस 3rd मेरिट लिस्ट 2024: indiapostgdsonline.gov.in पर जारी, ये रहा रीजन वाइज पीडीएफ डाउनलोड लिंक
IQ Test: Only someone with an IQ above 140 can solve this math puzzle in 9 seconds!
IRCTC ने ट्रेन टिकट बुकिंग के कौन-कौन से नियम बदले, और कब से होंगे लागू? जानें
CM अब्दुल्ला या LG, जम्मू-कश्मीर में किसके आदेश का पालन करेगी राज्य पुलिस? जानें
Personality Test: Your Pinky Finger Reveals Your Hidden Personality Traits
IGNOU June 2024 Results Announced at ignou.ac.in, Get Direct Link
IGNOU December TEE 2024 Deadline Extended Till Oct 27, Apply at iop.ignouonline.ac.in
Brain Teaser IQ Test: Are you smart enough to find the diamond in 7 seconds?
Rajju Bhaiya University Result 2024 OUT at prsuniv.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Main and Back Paper Exam Marksheet PDF
ICC Women's T20 World Cup Winners List till 2024
IBPS PO Exam Analysis 2024 Live: Shift 1, 2, 3 and 4 Prelims Paper Review, Difficulty Level, Topics Asked & Good Attempts
Brain Teaser IQ Test: Can You Spot The Thief In This Party Picture In 5 Seconds?
Diwali Holidays: TN Government Announces 2 Day Holiday, Check Details Here
Picture Puzzle IQ Test: Only Geniuses Can Crack This 23-Second Thief Puzzle!
ICAI CA Intermediate, Foundation September 2024 Results in November, Check Details Here
IGNOU June TEE Result 2024 OUT at ignou.ac.in; Direct Link to Download Term End Exam UG and PG Grade Card
IBPS PO Cutoff 2024: Check Category Wise Previous Year Minimum Qualifying Marks
Find 3 Differences in 28 Seconds in Cute Kitten Picture

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
many examples of work written by those who have written on this subject in the past. Pesch cites people like Locke, Montesquieu, and Machiavelli. These are good, well-‐known examples. and authors and I think it adds a great deal credibility to the piece as a whole.
Introduction. Article Information: Mention the title of the article, the author's name, the source (journal, magazine, etc.), and the publication date. Thesis Statement: Summarize the main argument or purpose of the article. Scope of the Critique: Briefly outline the main points you will discuss in your critique. 2.
The results wer e discussed appropriat ely- No misinterpretation. 11. Streng ths motioned are the true strengths. 12. Limitations are r eported do not aff ec t the applicability of the study-. 13 ...
A procedure for writing a critical review. Step 1: Skim read the article to get a general idea of what it is about. (This should. take you about 1 0-1 5 minutes or less. See Chapter 5, Reading: A ...
1. Begin of briefly critique by identifying the article's title, author(s), date of publication, and the name. researchers. (see the your journal other publication in which app ared. In your introduction, you should also of the Table publication describe 1). or the If the in paper purpose which was it appeared and the credentials and not ...
1. This is author version of book chapter published as: Danby, Susan J. (2004) A Critic's Review of Educational Research, in McWilliam, Erica and Danby, Susan and Knight, John, Eds. Performing ...
Summaries and critiques are two ways to write a review of a scientific journal article. Both types of writing ask you first to read and understand an article from the primary literature about your topic. The summary involves briefly but accurately stating the key points of the article for a reader who has not read the original article.
Critiques generally follow this structure, but variations do exist, so always ask your instructors about their preference: introduce the name of the article/book and name of author(s) summarize the article/book's main claim, goals, methods, and findings. show how the article/book supports its claims. indicate the main position or claim that ...
ould be the purpose of our multiple accountability systems.Education systems, mainly formal, from pre-school to higher education face social, cultural, environmental, technical, and political challenges, a. well as other developments at both local and global level. Countries should be able to react proper. sity, [ORCID 0000-0001-9391-5856 ...
ABSTRACT. This review summarizes the relevant research on the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in education. Specifically, it reviews studies that have touched upon the merits of ICT integration in schools, barriers or challenges encountered in the use of ICT, factors influencing successful ICT integration, in-service and ...
A critique asks you to evaluate an article and the author's argument. You will need to look critically at what the author is claiming, evaluate the research methods, and look for possible problems with, or applications of, the researcher's claims. ... Evaluate the sample group. Can you detect any problems in terms of size, composition, or ...
Box 1. Descriptive Analysis Is a Critical Component of Research Box 2. Examples of Using Descriptive Analyses to Diagnose Need and Target Intervention on the Topic of "Summer Melt" Box 3. An Example of Using Descriptive Analysis to Evaluate Plausible Causes and Generate Hypotheses Box 4.
interpretations it remains heavily contested. (See, for example, Illich, 1974; Postman & Richter, 1998; von Hentig, 1996; Harber, 2004.) The importance of this distinction underpins a paper by Sayed (1997), who argues that „the concept „quality‟ in education is elusive and … frequently used but never defined‟ and goes on
Writing a Critical Review The advice in this brochure is a general guide only. We strongly recommend that you also follow your assignment instructions and seek clarification from your lecturer/tutor if needed. Purpose of a critical review The critical review is a writing task that asks you to summarise and evaluate a text. The critical review can
Agreeing with, defending or confirming a particular point of view. Proposing a new point of view. Conceding to an existing point of view, but qualifying certain points. Reformulating an existing idea for a better explanation. Dismissing a point of view through an evaluation of its criteria. Reconciling two seemingly different points of view.
This research is a case study on the effects of an instructional EFL L2 writing. model for blended learning (BL) in a higher education environment in Korea. The. authors investigate the use of a ...
Part One, Section B. Choose one of the articles named below (both available in pdf versions on the D2L community page). Write an essay on the strengths and weaknesses of its research and the conclusions drawn from it, and identify the article's relation to other work in its area(s) of inquiry. Harper, C. and Yeung, F. (2013).
How to Write an A. ticle CritiqueRead the article. Try not to make any notes when you rea. the article for the first time.2 Read the article again, paying close attention to the main point or thesis of the article and the support. points that the article. ses.o3 Read the article again. To write a thorough article critique you must have t.
Example: A Sample Journal Article Critique. To illustrate the principles discussed in this guide, let's examine a sample critique of a hypothetical journal article titled "The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Workplace Dynamics in 2025" by J. Smith and A. Lee, published in the Journal of Future Work Studies.
Writing an article critique is often confused with an article summary where the article's contents ... Education of a Reluctant President." This claim, although stated as ... For example, the article states, "Since the war in Syria began, Obama has repeatedly denounced the killing of innocent civilians - more than 100,000 people have ...
1. Issues of Reflective Practice in Teacher Education According to a literature review, reflective practice is a notion that has developed over time. The first part of its evolution elicited from the review is the changes in the reflective practice paradigm, and the second part of its evolution concerns the process of reflective practice.
During this search, 20 studies were found which met the inclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria: 1-published articles in English and Persian (Original articles, review articles, published books about the purpose of the paper were used). 2-coordination between articles and Research Goals (Socio-economic consequences of unintended pregnancy).
Download Sociology Sample Paper Class 12 with marking scheme in pdf format from the direct links given in this article. CBSE Class 12 Sociology Question Paper Instructions 2024-25 1.
The students can download the Physical Education Sample Paper in PDF format. To prepare well for their exams, the students must practice the Sample Papers provided by the Board. Moreover, the CBSE has also released the Class 12th Physical Education Marking Scheme. Students can download the Sample Papers to overview the exam pattern and mark ...
CBSE Class 12 Home Science Question Paper Instructions 2024-25. 1. All questions are compulsory. 2. There are total 35 questions. 3. Question paper is divided into four sections-A, B, C and D.