Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved August 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is your plagiarism score.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

How To Write A Research Proposal
A Straightforward How-To Guide (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewed By: Dr. Eunice Rautenbach | August 2019 (Updated April 2023)
Writing up a strong research proposal for a dissertation or thesis is much like a marriage proposal. It’s a task that calls on you to win somebody over and persuade them that what you’re planning is a great idea. An idea they’re happy to say ‘yes’ to. This means that your dissertation proposal needs to be persuasive , attractive and well-planned. In this post, I’ll show you how to write a winning dissertation proposal, from scratch.
Before you start:
– Understand exactly what a research proposal is – Ask yourself these 4 questions
The 5 essential ingredients:
- The title/topic
- The introduction chapter
- The scope/delimitations
- Preliminary literature review
- Design/ methodology
- Practical considerations and risks
What Is A Research Proposal?
The research proposal is literally that: a written document that communicates what you propose to research, in a concise format. It’s where you put all that stuff that’s spinning around in your head down on to paper, in a logical, convincing fashion.
Convincing is the keyword here, as your research proposal needs to convince the assessor that your research is clearly articulated (i.e., a clear research question) , worth doing (i.e., is unique and valuable enough to justify the effort), and doable within the restrictions you’ll face (time limits, budget, skill limits, etc.). If your proposal does not address these three criteria, your research won’t be approved, no matter how “exciting” the research idea might be.
PS – if you’re completely new to proposal writing, we’ve got a detailed walkthrough video covering two successful research proposals here .

How do I know I’m ready?
Before starting the writing process, you need to ask yourself 4 important questions . If you can’t answer them succinctly and confidently, you’re not ready – you need to go back and think more deeply about your dissertation topic .
You should be able to answer the following 4 questions before starting your dissertation or thesis research proposal:
- WHAT is my main research question? (the topic)
- WHO cares and why is this important? (the justification)
- WHAT data would I need to answer this question, and how will I analyse it? (the research design)
- HOW will I manage the completion of this research, within the given timelines? (project and risk management)
If you can’t answer these questions clearly and concisely, you’re not yet ready to write your research proposal – revisit our post on choosing a topic .
If you can, that’s great – it’s time to start writing up your dissertation proposal. Next, I’ll discuss what needs to go into your research proposal, and how to structure it all into an intuitive, convincing document with a linear narrative.
The 5 Essential Ingredients
Research proposals can vary in style between institutions and disciplines, but here I’ll share with you a handy 5-section structure you can use. These 5 sections directly address the core questions we spoke about earlier, ensuring that you present a convincing proposal. If your institution already provides a proposal template, there will likely be substantial overlap with this, so you’ll still get value from reading on.
For each section discussed below, make sure you use headers and sub-headers (ideally, numbered headers) to help the reader navigate through your document, and to support them when they need to revisit a previous section. Don’t just present an endless wall of text, paragraph after paragraph after paragraph…
Top Tip: Use MS Word Styles to format headings. This will allow you to be clear about whether a sub-heading is level 2, 3, or 4. Additionally, you can view your document in ‘outline view’ which will show you only your headings. This makes it much easier to check your structure, shift things around and make decisions about where a section needs to sit. You can also generate a 100% accurate table of contents using Word’s automatic functionality.

Ingredient #1 – Topic/Title Header
Your research proposal’s title should be your main research question in its simplest form, possibly with a sub-heading providing basic details on the specifics of the study. For example:
“Compliance with equality legislation in the charity sector: a study of the ‘reasonable adjustments’ made in three London care homes”
As you can see, this title provides a clear indication of what the research is about, in broad terms. It paints a high-level picture for the first-time reader, which gives them a taste of what to expect. Always aim for a clear, concise title . Don’t feel the need to capture every detail of your research in your title – your proposal will fill in the gaps.
Need a helping hand?
Ingredient #2 – Introduction
In this section of your research proposal, you’ll expand on what you’ve communicated in the title, by providing a few paragraphs which offer more detail about your research topic. Importantly, the focus here is the topic – what will you research and why is that worth researching? This is not the place to discuss methodology, practicalities, etc. – you’ll do that later.
You should cover the following:
- An overview of the broad area you’ll be researching – introduce the reader to key concepts and language
- An explanation of the specific (narrower) area you’ll be focusing, and why you’ll be focusing there
- Your research aims and objectives
- Your research question (s) and sub-questions (if applicable)
Importantly, you should aim to use short sentences and plain language – don’t babble on with extensive jargon, acronyms and complex language. Assume that the reader is an intelligent layman – not a subject area specialist (even if they are). Remember that the best writing is writing that can be easily understood and digested. Keep it simple.

Note that some universities may want some extra bits and pieces in your introduction section. For example, personal development objectives, a structural outline, etc. Check your brief to see if there are any other details they expect in your proposal, and make sure you find a place for these.
Ingredient #3 – Scope
Next, you’ll need to specify what the scope of your research will be – this is also known as the delimitations . In other words, you need to make it clear what you will be covering and, more importantly, what you won’t be covering in your research. Simply put, this is about ring fencing your research topic so that you have a laser-sharp focus.
All too often, students feel the need to go broad and try to address as many issues as possible, in the interest of producing comprehensive research. Whilst this is admirable, it’s a mistake. By tightly refining your scope, you’ll enable yourself to go deep with your research, which is what you need to earn good marks. If your scope is too broad, you’re likely going to land up with superficial research (which won’t earn marks), so don’t be afraid to narrow things down.
Ingredient #4 – Literature Review
In this section of your research proposal, you need to provide a (relatively) brief discussion of the existing literature. Naturally, this will not be as comprehensive as the literature review in your actual dissertation, but it will lay the foundation for that. In fact, if you put in the effort at this stage, you’ll make your life a lot easier when it’s time to write your actual literature review chapter.
There are a few things you need to achieve in this section:
- Demonstrate that you’ve done your reading and are familiar with the current state of the research in your topic area.
- Show that there’s a clear gap for your specific research – i.e., show that your topic is sufficiently unique and will add value to the existing research.
- Show how the existing research has shaped your thinking regarding research design . For example, you might use scales or questionnaires from previous studies.
When you write up your literature review, keep these three objectives front of mind, especially number two (revealing the gap in the literature), so that your literature review has a clear purpose and direction . Everything you write should be contributing towards one (or more) of these objectives in some way. If it doesn’t, you need to ask yourself whether it’s truly needed.
Top Tip: Don’t fall into the trap of just describing the main pieces of literature, for example, “A says this, B says that, C also says that…” and so on. Merely describing the literature provides no value. Instead, you need to synthesise it, and use it to address the three objectives above.

Ingredient #5 – Research Methodology
Now that you’ve clearly explained both your intended research topic (in the introduction) and the existing research it will draw on (in the literature review section), it’s time to get practical and explain exactly how you’ll be carrying out your own research. In other words, your research methodology.
In this section, you’ll need to answer two critical questions :
- How will you design your research? I.e., what research methodology will you adopt, what will your sample be, how will you collect data, etc.
- Why have you chosen this design? I.e., why does this approach suit your specific research aims, objectives and questions?
In other words, this is not just about explaining WHAT you’ll be doing, it’s also about explaining WHY. In fact, the justification is the most important part , because that justification is how you demonstrate a good understanding of research design (which is what assessors want to see).
Some essential design choices you need to cover in your research proposal include:
- Your intended research philosophy (e.g., positivism, interpretivism or pragmatism )
- What methodological approach you’ll be taking (e.g., qualitative , quantitative or mixed )
- The details of your sample (e.g., sample size, who they are, who they represent, etc.)
- What data you plan to collect (i.e. data about what, in what form?)
- How you plan to collect it (e.g., surveys , interviews , focus groups, etc.)
- How you plan to analyse it (e.g., regression analysis, thematic analysis , etc.)
- Ethical adherence (i.e., does this research satisfy all ethical requirements of your institution, or does it need further approval?)
This list is not exhaustive – these are just some core attributes of research design. Check with your institution what level of detail they expect. The “ research onion ” by Saunders et al (2009) provides a good summary of the various design choices you ultimately need to make – you can read more about that here .
Don’t forget the practicalities…
In addition to the technical aspects, you will need to address the practical side of the project. In other words, you need to explain what resources you’ll need (e.g., time, money, access to equipment or software, etc.) and how you intend to secure these resources. You need to show that your project is feasible, so any “make or break” type resources need to already be secured. The success or failure of your project cannot depend on some resource which you’re not yet sure you have access to.
Another part of the practicalities discussion is project and risk management . In other words, you need to show that you have a clear project plan to tackle your research with. Some key questions to address:
- What are the timelines for each phase of your project?
- Are the time allocations reasonable?
- What happens if something takes longer than anticipated (risk management)?
- What happens if you don’t get the response rate you expect?
A good way to demonstrate that you’ve thought this through is to include a Gantt chart and a risk register (in the appendix if word count is a problem). With these two tools, you can show that you’ve got a clear, feasible plan, and you’ve thought about and accounted for the potential risks.
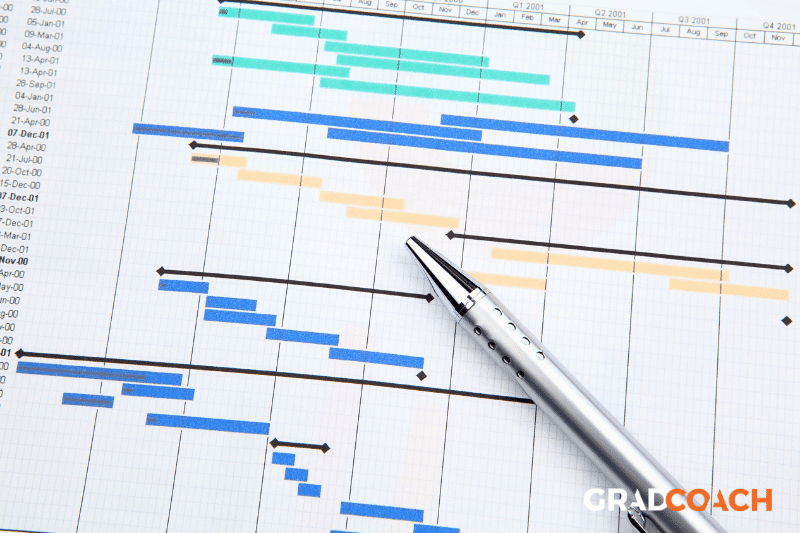
Tip – Be honest about the potential difficulties – but show that you are anticipating solutions and workarounds. This is much more impressive to an assessor than an unrealistically optimistic proposal which does not anticipate any challenges whatsoever.
Final Touches: Read And Simplify
The final step is to edit and proofread your proposal – very carefully. It sounds obvious, but all too often poor editing and proofreading ruin a good proposal. Nothing is more off-putting for an assessor than a poorly edited, typo-strewn document. It sends the message that you either do not pay attention to detail, or just don’t care. Neither of these are good messages. Put the effort into editing and proofreading your proposal (or pay someone to do it for you) – it will pay dividends.
When you’re editing, watch out for ‘academese’. Many students can speak simply, passionately and clearly about their dissertation topic – but become incomprehensible the moment they turn the laptop on. You are not required to write in any kind of special, formal, complex language when you write academic work. Sure, there may be technical terms, jargon specific to your discipline, shorthand terms and so on. But, apart from those, keep your written language very close to natural spoken language – just as you would speak in the classroom. Imagine that you are explaining your project plans to your classmates or a family member. Remember, write for the intelligent layman, not the subject matter experts. Plain-language, concise writing is what wins hearts and minds – and marks!
Let’s Recap: Research Proposal 101
And there you have it – how to write your dissertation or thesis research proposal, from the title page to the final proof. Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- The purpose of the research proposal is to convince – therefore, you need to make a clear, concise argument of why your research is both worth doing and doable.
- Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper.
- Title – provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms
- Introduction – explains what you’ll be researching in more detail
- Scope – explains the boundaries of your research
- Literature review – explains how your research fits into the existing research and why it’s unique and valuable
- Research methodology – explains and justifies how you will carry out your own research
Hopefully, this post has helped you better understand how to write up a winning research proposal. If you enjoyed it, be sure to check out the rest of the Grad Coach Blog . If your university doesn’t provide any template for your proposal, you might want to try out our free research proposal template .

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
30 Comments
Thank you so much for the valuable insight that you have given, especially on the research proposal. That is what I have managed to cover. I still need to go back to the other parts as I got disturbed while still listening to Derek’s audio on you-tube. I am inspired. I will definitely continue with Grad-coach guidance on You-tube.
Thanks for the kind words :). All the best with your proposal.
First of all, thanks a lot for making such a wonderful presentation. The video was really useful and gave me a very clear insight of how a research proposal has to be written. I shall try implementing these ideas in my RP.
Once again, I thank you for this content.
I found reading your outline on writing research proposal very beneficial. I wish there was a way of submitting my draft proposal to you guys for critiquing before I submit to the institution.
Hi Bonginkosi
Thank you for the kind words. Yes, we do provide a review service. The best starting point is to have a chat with one of our coaches here: https://gradcoach.com/book/new/ .
Hello team GRADCOACH, may God bless you so much. I was totally green in research. Am so happy for your free superb tutorials and resources. Once again thank you so much Derek and his team.
You’re welcome, Erick. Good luck with your research proposal 🙂
thank you for the information. its precise and on point.
Really a remarkable piece of writing and great source of guidance for the researchers. GOD BLESS YOU for your guidance. Regards
Thanks so much for your guidance. It is easy and comprehensive the way you explain the steps for a winning research proposal.
Thank you guys so much for the rich post. I enjoyed and learn from every word in it. My problem now is how to get into your platform wherein I can always seek help on things related to my research work ? Secondly, I wish to find out if there is a way I can send my tentative proposal to you guys for examination before I take to my supervisor Once again thanks very much for the insights
Thanks for your kind words, Desire.
If you are based in a country where Grad Coach’s paid services are available, you can book a consultation by clicking the “Book” button in the top right.
Best of luck with your studies.
May God bless you team for the wonderful work you are doing,
If I have a topic, Can I submit it to you so that you can draft a proposal for me?? As I am expecting to go for masters degree in the near future.
Thanks for your comment. We definitely cannot draft a proposal for you, as that would constitute academic misconduct. The proposal needs to be your own work. We can coach you through the process, but it needs to be your own work and your own writing.
Best of luck with your research!
I found a lot of many essential concepts from your material. it is real a road map to write a research proposal. so thanks a lot. If there is any update material on your hand on MBA please forward to me.
GradCoach is a professional website that presents support and helps for MBA student like me through the useful online information on the page and with my 1-on-1 online coaching with the amazing and professional PhD Kerryen.
Thank you Kerryen so much for the support and help 🙂
I really recommend dealing with such a reliable services provider like Gradcoah and a coach like Kerryen.
Hi, Am happy for your service and effort to help students and researchers, Please, i have been given an assignment on research for strategic development, the task one is to formulate a research proposal to support the strategic development of a business area, my issue here is how to go about it, especially the topic or title and introduction. Please, i would like to know if you could help me and how much is the charge.
This content is practical, valuable, and just great!
Thank you very much!
Hi Derek, Thank you for the valuable presentation. It is very helpful especially for beginners like me. I am just starting my PhD.
This is quite instructive and research proposal made simple. Can I have a research proposal template?
Great! Thanks for rescuing me, because I had no former knowledge in this topic. But with this piece of information, I am now secured. Thank you once more.
I enjoyed listening to your video on how to write a proposal. I think I will be able to write a winning proposal with your advice. I wish you were to be my supervisor.
Dear Derek Jansen,
Thank you for your great content. I couldn’t learn these topics in MBA, but now I learned from GradCoach. Really appreciate your efforts….
From Afghanistan!
I have got very essential inputs for startup of my dissertation proposal. Well organized properly communicated with video presentation. Thank you for the presentation.
Wow, this is absolutely amazing guys. Thank you so much for the fruitful presentation, you’ve made my research much easier.
this helps me a lot. thank you all so much for impacting in us. may god richly bless you all
How I wish I’d learn about Grad Coach earlier. I’ve been stumbling around writing and rewriting! Now I have concise clear directions on how to put this thing together. Thank you!
Fantastic!! Thank You for this very concise yet comprehensive guidance.
Even if I am poor in English I would like to thank you very much.
Thank you very much, this is very insightful.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
How to write a good research proposal (in 9 steps)

A good research proposal is one of the keys to academic success. For bachelor’s and master’s students, the quality of a research proposal often determines whether the master’s program= can be completed or not. For PhD students, a research proposal is often the first step to securing a university position. This step-by-step manual guides you through the main stages of proposal writing.
1. Find a topic for your research proposal
Finding a topic for your research is a crucial first step. This decision should not be treated lightly.
How to find a research topic? Start broadly: Which courses did you enjoy? What issues discussed during seminars or lectures did you like? What inspired you during your education? And which readings did you appreciate?
Take a blank piece of paper. Write down everything that comes to your mind. It will help you to reflect on your interests.
Then, think more strategically. Maybe you have a rough idea of where you would like to work after graduation. Maybe a specific sector. Or even a particular company. If so, you could strategically alight your thesis topic with an issue that matters to your dream employer. Or even ask for a thesis internship.
2. Develop your research idea
Once you pinpoint your general topic of interest, you need to develop your idea.
Second, writing a research proposal is not a linear process. Start slowly by reading literature about your topic of interest. You have an interest. You read. You rethink your idea. You look for a theoretical framework. You go back to your idea and refine it. It is a process.
Remember that a good research proposal is not written in a day.
And third, don’t forget: a good proposal aims to establish a convincing framework that will guide your future research. Not to provide all the answers already. You need to show that you have a feasible idea.
3. Conduct a literature review for your research proposal
Academic publications (journal articles and books) are the foundation of any research. Thus, academic literature is a good place to start. Especially when you still feel kind of lost regarding a focused research topic.
Download interesting-sounding articles and read them. Repeat but be cautious: You will never be able to read EVERYTHING. So set yourself a limit, in hours, days or number of articles (20 articles, for instance).
4. Define a research gap and research question
Once you read academic publications on your topic of interest, ask yourself questions such as:
Asking yourself these questions helps you to formulate your research question. In your research question, be as specific as possible.
5. Establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal
A theory is a general principle to explain certain phenomena. No need to reinvent the wheel here.
6. Specify an empirical focus for your research proposal
There are only very few master’s and PhD theses that are entirely theoretical. Most theses, similar to most academic journal publications, have an empirical section.
It is also possible to start the whole research proposal idea with empirical observation. Maybe you’ve come across something in your environment that you would like to investigate further.
7. Emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal
Societal relevance is increasingly important in academia, too.
Do the grandparent test: Explain what you want to do to your grandparents (or any other person for that matter). Explain why it matters. Do your grandparents understand what you say? If so, well done. If not, try again.
Always remember. There is no need for fancy jargon. The best proposals are the ones that use clear, straightforward language.
8. Develop a methodology in your research proposal
Methods of data analysis are used to make sense of this data. This can be done, for instance, by coding, discourse analysis, mapping or statistical analysis.
9. Illustrate your research timeline in your research proposal
Master academia, get new content delivered directly to your inbox, phd thesis types: monograph and collection of articles, ten reasons not to pursue an academic career, related articles, the 11 best ai tools for academic writing, why and how to conduct a systematic literature review, the best online courses for phd researchers in 2024, 10 powerful methodology courses for phd students [online].

Write A Research Proposal: Follow Our Step-by-Step Guide
A research project begins with a compelling proposal, a document that not only outlines your plan but also persuades its readers of its merit.
Whether you’re aiming for a Ph.D or securing funding, our step-by-step guide provides you with the essential tools and insights to craft a persuasive research proposal.
From formulating a clear hypothesis to detailing your methodology, follow along to ensure your proposal is both thorough and convincing.
Research Proposal Writing Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| – Sets the stage for your proposal. – Include title, your name, affiliation, date. – Must meet institutional formatting guidelines. | |
| – Briefly covers the key aspects of your proposal. – Details research problem, objectives, methodology, implications. | |
| – Demonstrates your knowledge and identifies the research gap. – Involves critical analysis of important literature. – Use AI tools to speed up the process. | |
| – Helps you to focus your study based on identified gaps. – Includes specific research questions and objectives. | |
| – Outlines how your research will be conducted. – Includes research design, methods, data analysis, and tools. – Address potential issues and solutions in the process. | |
| – Clarify why your research matters. – Show implications and contributions to knowledge. | |
| – Shows how you’ll manage the research phases. – Break down into phases, possibly visualized with a Gantt chart. – Highlights feasibility and time management. | |
| – Shows extensive research and academic integrity. – Includes all sources used in your research proposal. Use citation software for ease. – Follow field-specific citation guidelines. |
Why Write A Research Proposal?
A research proposal for postgraduate studies is a detailed plan that outlines your research question, methodology, and objectives. A well written research proposal:
- sets the scope of your study,
- demonstrates your knowledge of existing research, and
- shows how your work will contribute to your field.
Writing a research proposal for your postgraduate studies might seem daunting, but there are many reasons you should spend time to produce one:
Allows You To Define Your Research Question Clearly
A well-thought-out research proposal allows you to define your research question clearly. This means you pinpoint exactly what you want to explore, avoiding broad or vague topics.
Your research question acts as the guiding star throughout your entire research process, keeping your thesis, research paper, or dissertation focused and on track.

Develop Literature Familiarity & Identify Research Gap
Delving into a literature review as part of your proposal helps you understand the existing research and identify any gaps.
This isn’t just about summarising what others have done; it’s your chance to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the field and to build on the foundation others have laid. You get to show how your research will add new insights or challenge established beliefs.
Refine Your Methodology
Your proposal must outline your research methodology, detailing how you plan to collect and analyze data.
This isn’t just about stating what tools and procedures you will use; it’s about convincing the reader that your project is feasible and your methods are sound.
If you’re conducting research involving human subjects, you’ll need to describe how you will ensure ethical standards are met.
Supports Your Funding Application
Creating a concise and coherent proposal with a clear problem statement and defined research objectives also positions you well for securing research funding.
Funding bodies want to support projects with clearly defined aims and potential implications that contribute significantly to their field.
Initial Pitch To Interested Parties
Your proposal acts as an initial pitch of your research idea. It helps you clarify the purpose of your research and align your goals with academic expectations.
This is where you get to argue the significance of your study and outline practical steps you will take to answer your research questions. You can then take your research proposal and shop it around for:
- university placement,
- supervisors,
- funding, or
- other potential supports you may need.
Steps To Write A Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal can seem overwhelming, but breaking it down into structured steps can demystify the process.
Here’s a detailed guide to help you craft an effective proposal that communicates your research idea compellingly and clearly.
Step 1: Create a Captivating Title Page
The title page serves as the introduction to your proposal. It should feature a title that succinctly conveys the essence of your research project.
The title must grab attention while accurately reflecting the content of your study. This page should also include your:
- institutional affiliation, and
These details need to be presented in a professional format that adheres to the specific requirements of your academic or funding institution.
Step 2: Summarize with a Strong Abstract
Following the title page, the abstract should succinctly summarize the critical aspects of your proposal in about 100 to 150 words. It should outline:
- the research problem,
- main objectives,
- proposed methodology, and
- potential implications of your research.
Although brief, the abstract is powerful, providing a snapshot that encourages further reading. See it as a movie trailer – it should be able to attract the attention of those that are interested in your research, and repel those that dont.
Step 3: Conduct a Thorough Literature Review
The literature review is where you show you are well-versed in the field. This section demonstrates your understanding of the existing research and highlights the gap your study will address.
It involves a critical analysis of the key literature and situates your research question in the context of what has already been explored, establishing the foundation for your research.
Literature review used to be a nightmare, but with the power of AI tools, you can easily find relevant papers easily and quickly. Here’s a few to help you get started:
Step 4: Define Clear Research Questions and Objectives
From the literature review, distill your research questions. These should be clear, focused, and directly related to the gaps you’ve identified in the literature.
The research aims and objectives should be specific outcomes that your study aims to achieve, guiding the direction of your research.
This step transforms the general interest of your study into a precise plan of inquiry, worthy of an academic or researcher’s time to study and understand. Get this right, and you will have an easier time on the later process of your research.
Step 5: Argue Your Research Design, Detail Your Research Methodology
The methodology section is crucial as it lays out the blueprint for how you will conduct your research. This should detail the research design and methods, including how data will be collected and analysed.
Explain the choice of qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods, and justify these choices based on the nature of your research question.
Argue strongly and with passion here, as you need to show confidence that your research method of choice is the best way to answer the research question.
Once you have proposed a research approach, discuss how you intend to conduct data analysis. List out the potential software or tools you plan to use for the process, and how you would ensure your research is:
- valid and reliable (quantitative)
- credible (qualitative)
This section should also discuss any potential challenges and how you plan to address them, showcasing your preparedness and realistic approach to the research process.
Step 6: Articulate the Significance of Your Research
In this part of the proposal, you need to articulate why your proposed research is important.
Discuss the potential implications of your research topic and how it will contribute to existing knowledge or theory.

Highlighting the significance can engage your reader and justify the need for your study, often influencing the decision of funding bodies or academic committees.
Step 7: Include a Realistic Timeline
Project management is key in research, and outlining a timeline demonstrates your organisational skills and realistic understanding of the research process.
Break down your research into phases, from initial data collection to analysis and reporting results. A Gantt chart may be useful here, as it is a good visual representation of your research timeline.
This schedule not only helps gauge the project’s feasibility but also shows that you can efficiently manage time, a critical aspect of conducting successful research.
Step 8: Compile a Comprehensive Bibliography
Finally, a detailed bibliography is essential. It should list every source that has informed your research proposal, demonstrating a thorough and rigorous approach to your preparatory work.
This section underlines your scholarly diligence and ensures that all intellectual debts are acknowledged, reinforcing the academic integrity of your proposal.
Look at research papers within your field, and see the citation style common with the field for an idea how to approach this.
There are formats such as APA, MLA, Chicago and more, which means you want to be sure to follow the conventions in your field of research.

You can also use a wide range of software to help manage and write out your bibliography. Here’s a few free citation tools you can use.
By following these steps, you craft a proposal that not only presents your research plan but also persuasively argues its worth.
Your proposal becomes not just a plan for a study, but a convincing argument for why it should be undertaken and how it will contribute to the field.
Common Mistakes When Writing A Research Proposal
To ensure your proposal stands out for the right reasons, be aware of common pitfalls and how to avoid them. Here are five typical mistakes and how to correct them:
Mistake 1: Vague Objectives
A common issue is unclear aims and objectives. Your proposal needs to specify exactly what you intend to investigate and what you hope to achieve.
Vague objectives can make your proposal seem unfocused and unrealistic.
Be specific here: instead of saying you aim to “explore the effects of social media,” say you will “quantify the impact of targeted social media advertising on consumer purchasing decisions among 18-24 year-olds.”
Mistake 2: Inadequate Literature Review
Skipping the thorough review of existing literature is a serious oversight. Your research proposal can be easily rejected, without a proper literature review.

A good literature review not only shows you’re familiar with the field but also justifies the necessity of your research. It highlights the gap in existing knowledge that your project will address.
To fix this, dedicate time to summarising previous research and discuss how your work will build on or challenge the existing knowledge.
Mistake 3: Poorly Defined Methodology
Another frequent error is a methodology section that lacks clarity and detail. This part of your proposal outlines how you will answer your research questions.
A common mistake is not specifying data collection tools and procedures. Make sure you explain the methodology clearly:
- what methods will you use,
- why are they best suited to your research question, and
- how will you handle data analysis?
If you are planning to conduct a survey, describe the demographic, how samples will be selected, and the type of analysis you’ll use, like regression analysis.
Mistake 4: Ignoring Potential Pitfalls
Often, proposals fail to discuss potential limitations and risks associated with the research design.
Addressing these issues proactively shows that you are prepared and realistic about your research capabilities. Outline potential challenges and your strategies for mitigating them.
If there’s a possibility of low participant turnout, explain how you will recruit participants and ensure sufficient sample size.
Mistake 5: Overlooking the Significance and Impact
Many proposals do not adequately convey the significance of the study or its potential implications. Your proposal should make it clear why your research is important and how it will contribute to the field.
This means explicitly stating the potential implications of your findings. Say, if your research could influence policy, describe how it could lead to changes in legislation or practice within the relevant field.
By addressing these common mistakes, you ensure your research proposal is not only comprehensive but also compelling.
Research Proposal – Get It Right For A Smoother Dissertation
Writing a research proposal requires a clear and methodical approach, from crafting an eye-catching title to compiling a comprehensive bibliography.
By following the steps outlined in our guide, you ensure that each component of your proposal is thoughtfully considered and well-presented.
This not only boosts the persuasiveness of your proposal but also significantly enhances the likelihood of gaining approval or funding for your research project.
Remember, a well-structured proposal is your first step towards a successful research endeavour.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a research proposal

What is a research proposal?
What is the purpose of a research proposal , how long should a research proposal be, what should be included in a research proposal, 1. the title page, 2. introduction, 3. literature review, 4. research design, 5. implications, 6. reference list, frequently asked questions about writing a research proposal, related articles.
If you’re in higher education, the term “research proposal” is something you’re likely to be familiar with. But what is it, exactly? You’ll normally come across the need to prepare a research proposal when you’re looking to secure Ph.D. funding.
When you’re trying to find someone to fund your Ph.D. research, a research proposal is essentially your “pitch.”
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research.
You’ll need to set out the issues that are central to the topic area and how you intend to address them with your research. To do this, you’ll need to give the following:
- an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls
- an overview of how much is currently known about the topic
- a literature review that covers the recent scholarly debate or conversation around the topic
➡️ What is a literature review? Learn more in our guide.
Essentially, you are trying to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into.
It is the opportunity for you to demonstrate that you have the aptitude for this level of research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas:
It also helps you to find the right supervisor to oversee your research. When you’re writing your research proposal, you should always have this in the back of your mind.
This is the document that potential supervisors will use in determining the legitimacy of your research and, consequently, whether they will invest in you or not. It is therefore incredibly important that you spend some time on getting it right.
Tip: While there may not always be length requirements for research proposals, you should strive to cover everything you need to in a concise way.
If your research proposal is for a bachelor’s or master’s degree, it may only be a few pages long. For a Ph.D., a proposal could be a pretty long document that spans a few dozen pages.
➡️ Research proposals are similar to grant proposals. Learn how to write a grant proposal in our guide.
When you’re writing your proposal, keep in mind its purpose and why you’re writing it. It, therefore, needs to clearly explain the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. You need to then explain what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
Generally, your structure should look something like this:
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Research Design
- Implications
If you follow this structure, you’ll have a comprehensive and coherent proposal that looks and feels professional, without missing out on anything important. We’ll take a deep dive into each of these areas one by one next.
The title page might vary slightly per your area of study but, as a general point, your title page should contain the following:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- The name of your institution and your particular department
Tip: Keep in mind any departmental or institutional guidelines for a research proposal title page. Also, your supervisor may ask for specific details to be added to the page.
The introduction is crucial to your research proposal as it is your first opportunity to hook the reader in. A good introduction section will introduce your project and its relevance to the field of study.
You’ll want to use this space to demonstrate that you have carefully thought about how to present your project as interesting, original, and important research. A good place to start is by introducing the context of your research problem.
Think about answering these questions:
- What is it you want to research and why?
- How does this research relate to the respective field?
- How much is already known about this area?
- Who might find this research interesting?
- What are the key questions you aim to answer with your research?
- What will the findings of this project add to the topic area?
Your introduction aims to set yourself off on a great footing and illustrate to the reader that you are an expert in your field and that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge and theory.
The literature review section answers the question who else is talking about your proposed research topic.
You want to demonstrate that your research will contribute to conversations around the topic and that it will sit happily amongst experts in the field.
➡️ Read more about how to write a literature review .
There are lots of ways you can find relevant information for your literature review, including:
- Research relevant academic sources such as books and journals to find similar conversations around the topic.
- Read through abstracts and bibliographies of your academic sources to look for relevance and further additional resources without delving too deep into articles that are possibly not relevant to you.
- Watch out for heavily-cited works . This should help you to identify authoritative work that you need to read and document.
- Look for any research gaps , trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions.
- Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal.
This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal. It should be a discussion about the overall approach you plan on taking, and the practical steps you’ll follow in answering the research questions you’ve posed.
So what should you discuss here? Some of the key things you will need to discuss at this point are:
- What form will your research take? Is it qualitative/quantitative/mixed? Will your research be primary or secondary?
- What sources will you use? Who or what will you be studying as part of your research.
- Document your research method. How are you practically going to carry out your research? What tools will you need? What procedures will you use?
- Any practicality issues you foresee. Do you think there will be any obstacles to your anticipated timescale? What resources will you require in carrying out your research?
Your research design should also discuss the potential implications of your research. For example, are you looking to confirm an existing theory or develop a new one?
If you intend to create a basis for further research, you should describe this here.
It is important to explain fully what you want the outcome of your research to look like and what you want to achieve by it. This will help those reading your research proposal to decide if it’s something the field needs and wants, and ultimately whether they will support you with it.
When you reach the end of your research proposal, you’ll have to compile a list of references for everything you’ve cited above. Ideally, you should keep track of everything from the beginning. Otherwise, this could be a mammoth and pretty laborious task to do.
Consider using a reference manager like Paperpile to format and organize your citations. Paperpile allows you to organize and save your citations for later use and cite them in thousands of citation styles directly in Google Docs, Microsoft Word, or LaTeX.
Your project may also require you to have a timeline, depending on the budget you are requesting. If you need one, you should include it here and explain both the timeline and the budget you need, documenting what should be done at each stage of the research and how much of the budget this will use.
This is the final step, but not one to be missed. You should make sure that you edit and proofread your document so that you can be sure there are no mistakes.
A good idea is to have another person proofread the document for you so that you get a fresh pair of eyes on it. You can even have a professional proofreader do this for you.
This is an important document and you don’t want spelling or grammatical mistakes to get in the way of you and your reader.
➡️ Working on a research proposal for a thesis? Take a look at our guide on how to come up with a topic for your thesis .
A research proposal is a concise and coherent summary of your proposed research. Generally, your research proposal will have a title page, introduction, literature review section, a section about research design and explaining the implications of your research, and a reference list.
A good research proposal is concise and coherent. It has a clear purpose, clearly explains the relevance of your research and its context with other discussions on the topic. A good research proposal explains what approach you will take and why it is feasible.
You need a research proposal to persuade your institution that you and your project are worth investing their time and money into. It is your opportunity to demonstrate your aptitude for this level or research by showing that you can articulate complex ideas clearly, concisely, and critically.
A research proposal is essentially your "pitch" when you're trying to find someone to fund your PhD. It is a clear and concise summary of your proposed research. It gives an outline of the general area of study within which your research falls, it elaborates how much is currently known about the topic, and it highlights any recent debate or conversation around the topic by other academics.
The general answer is: as long as it needs to be to cover everything. The length of your research proposal depends on the requirements from the institution that you are applying to. Make sure to carefully read all the instructions given, and if this specific information is not provided, you can always ask.

How to Write a Research Proposal

Seeking guidance on crafting an effective research proposal? It’s a pivotal concern within academic circles today. Understanding the composition of a research proposal is fundamental because it determines the success and effectiveness of a research.
Table of Contents
What is a Research Proposal?
If you want to learn how to write a research proposal then at first understand what a research proposal is a key part of studying and exploring a topic academically. It’s like a blueprint for your project, outlining the main ideas and how you will approach it.
If you are familiar with how to write a proposal essay, understanding research proposals gets easier. The record of research’s actual origin is unknown but the known accounts date back to 1577. Research is common practice for higher educational levels like PHD, Masters, Bachelors. With the advancement of the educational system, research is introduced to high school students and lower grades as well.
Who Needs To Know About Research Proposal Guide?
- Students studying in research rich fields such as science, humanities, medicine, law, and computers are most likely to write research proposals.
- Students studying for Bachelors, Masters, and PHD needs to be well practiced in writing research proposals for their research papers, assignments, and projects.
- Beginners who want to be professional researchers.
Resources to Learn More About Research Proposal Guide
| University Websites | The official websites of your respective universities have the guidelines for research proposals. |
| Research Gate | Research gate is an online community that is dedicated to help students in research. |
| Grammerly.com | A tool that helps you maintain the accuracy of your paper and provides blogs to help students understand the guidelines of research papers. |
| Indeed.com | A Job seeking platform that provides comprehensive blogs and guides to enable people to learn professional instructions. |
| Scriber.com | A platform that provides academic research guidelines and services for the students. |
Importance Of Writing A Research Proposal For Students
Research is not an easy task and many of the students struggle with it. Even the author of this guide shared, “My first research proposal got rejected and I was baffled. But with time I realized that my writing process was flawed entirely. It took me a lot of time to practice and perfect my research proposal writing process and when I invested all my efforts in understanding the right procedure, my proposal got accepted and appreciated.”
Let’s understand the importance of learning how to write a research proposal like a pro.
- To articulate and solidify research intentions.
- For skill development in research design and writing.
- As a precursor to future extensive research projects.
- To showcase academic competence and planning ability.
- To gain insights into different research methodologies.
- For feedback and refinement of research ideas.
- To cultivate effective time management skills.
- Identifying and managing required resources.
- For enhancing critical analysis and evaluation abilities.
- Preparing for careers valuing research skills.
How to Start Writing a Research Proposal – Quick Tips
- Understand the guidelines provided by your institution or the target audience. Clarify expectations regarding research brief format, length, and content.
- Identifying a strong research question statement is the most important step of how to write a research proposal process.
- Conduct a comprehensive literature review to get a better understanding of the context.
- Outline Your Methodology and lay out the ways and strategies you plan on using in your investigation. Understand how to organize a research paper in terms of those evidences.
- Consider feasibility and resources and make sure it’s doable within the limits you have.
- Seek feedback and revise to make it more understandable, consistent, and better overall.

Common challenges that student face while writing Research Proposal
To get a clear idea of major issues that students face during the process of writing a research proposal, a university of indonesia conducted a research. They observed the major issues that students of different categories face. They collected data through 32 questionnaires. Below we are going to share some statistics from the research.
| Having difficulty to find current sources for literature review | 77.58% |
| Having difficulty to critically analyze works of literature | 76.04% |
| Having difficulty to be critical about proposal writing | 75.82% |
| Having difficulty to decide techniques of data analysis | 75.82% |
| Having difficulty to review words of literature | 73.63% |
| Having difficulty convincing the reader that the said researched problem needs to be addressed. | 72.97% |
| Having difficulty to identify the main topic | 72.09% |
| Having difficulty to write a conceptual framework | 70.99% |
| Having difficulty to cite studies in background section | 69.67% |
| Having difficulty to decide data collection techniques | 68.35% |
Source: Research Gate
Expert Steps to Write a Research Proposal By Tackling Challenges
These are 11 steps of how to write a research proposal. You can follow some research proposal examples for perfecting your research proposal writing skills. These steps together can also be termed as the research proposal format.
Step 1: Title
Create a clear, concise, and descriptive title that encapsulates the essence of your proposed research.
The title of a research proposal serves as its initial point of engagement, offering a glimpse into the focus and significance of the study. Crafting a title requires precision to convey the essence of the research succinctly. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Clarity and Conciseness
The title should be clear and concise, providing a snapshot of the research’s primary focus without unnecessary wording or jargon. It should be easily comprehensible to both experts and non-experts in the field.
Original Title: “An Investigation into the Effects of Environmental Factors on Child Development in Urban Areas”
Revised Title: “Environmental Influences on Urban Child Development”
Specificity
The vital tip on how to write a research proposal is that the title should be specific enough to indicate the particular aspect or angle of the research being addressed. Vague or broad titles may fail to capture the uniqueness of the study.
Original Title: “Healthcare Challenges in Developing Countries”
Revised Title: “Access to Healthcare Services in Rural India: A Case Study”
Descriptive and Informative
The title should provide a glimpse of what the research aims to explore or uncover, giving readers an idea of the subject matter. It’s all important part of research brief format
Original Title: “Social Media’s Impact on Society”
Revised Title: “Navigating Digital Spaces: Exploring the Social Impact of Instagram Influencers”
Keywords and Key Concepts
Incorporating relevant keywords and key concepts can enhance the discoverability of the research and its alignment with the field’s terminology.
Original Title: “Technology in Education”
Revised Title: “Integrating Virtual Reality: Enhancing STEM Education in High Schools”
Reflective of Research Scope
Ensure the title accurately reflects the scope and depth of the proposed research without overpromising or underrepresenting its objectives.
Original Title: “Solving Global Poverty”
Revised Title: “Microfinance Initiatives: Empowering Rural Communities in Sub-Saharan Africa”
Avoid Ambiguity
Steer clear of ambiguous or misleading titles that may lead to misconceptions about the research’s purpose or scope.
Original Title: “Uncovering Secrets of the Mind”
Revised Title: “Cognitive Psychology: Investigating Memory Retention in Alzheimer’s Patients”
Step 2: Introduction
The introduction is the most important step of how to write a research proposal process. The introductory paragraph is the foundation that starts the discussion section of a research paper and enforces the main idea. It aims to engage readers, provide necessary background information, and establish the rationale for the research. Here’s an in-depth explanation with examples:
Introducing the Research Problem or Question
This section should begin by highlighting the specific issue or question your research seeks to address. It serves as a hook to grab the reader’s attention and clarify the focus of your study.
In recent years, there has been a growing concern regarding the declining access to clean water in rural areas of Southeast Asia. This study aims to investigate the socio-economic factors contributing to this issue and propose sustainable solutions to improve water accessibility in these regions.
Providing Context and Background Information
Contextualizing the research problem involves discussing existing knowledge, theories, or previous studies relevant to your topic. This helps situate your research within the broader field and highlights the gaps or limitations in current understanding.
“Studies by Smith et al. (2018) and Johnson (2020) have shed light on the challenges faced by rural communities in accessing clean water. However, while these studies acknowledge the problem, a comprehensive analysis of the socio-economic factors influencing this issue remains lacking.”
Clearly Stating Objectives and Purpose
This part is mandatory in how to write a research proposal because it articulates the specific goals or aims of your research. It should clearly outline what you intend to achieve and why your study is significant in addressing the identified problem or gap.
This research endeavors to:
Identify the socio-economic barriers hindering access to clean water.
Assess the impact of community-based initiatives on water accessibility.
Propose sustainable strategies to improve water availability in rural Southeast Asian communities.
The purpose of this study is to contribute valuable insights and practical recommendations to alleviate the water scarcity crisis prevalent in these areas.
Step 3: Literature Review
The literature review section of a research proposal is a critical component that demonstrates your understanding of the existing scholarship related to your topic. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Conducting a Comprehensive Review
The expert tip for how to write a research proposal is to begin by extensively exploring scholarly works, research papers, books, proposal essay examples, and other relevant sources that discuss your research topic. Summarize and synthesize this body of literature, organizing it in a coherent manner.
A review of the literature reveals a multitude of studies examining the impact of climate change on coastal ecosystems. Works by Johnson (2017), Smith et al. (2019), and Garcia (2020) analyze the effects of rising sea levels on biodiversity and local communities in coastal regions.
Identifying Gaps, Debates, or Areas for Further Exploration
While reviewing existing literature, identify gaps or contradictions in the research. Highlight areas where conflicting viewpoints exist or where studies haven’t sufficiently addressed certain aspects of the topic.
Despite the extensive research on the ecological effects of climate change on coastal areas, there remains a dearth of studies focusing on the socio-economic ramifications of these environmental shifts. Moreover, the existing literature primarily emphasizes the impact on flora and fauna, neglecting the human dimension and community resilience in these regions.
Justifying the Need for Your Research
How to write a research proposal to justify the significance and relevance of your proposed research? Use the gaps identified in the literature. Explain how your study will contribute to filling these gaps or addressing the unanswered questions in the field. This is where a professional research paper writing service provider does well.
Given the limited attention to socio-economic aspects in current literature, this proposed research aims to bridge this gap by investigating the adaptive strategies employed by coastal communities facing environmental challenges. By examining both ecological shifts and community responses, this study seeks to provide a holistic understanding of the complexities surrounding climate change impacts.
Step 4: Research Questions or Hypothesis
The formulation of research questions or hypotheses is a pivotal aspect of a research proposal. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Clearly Stating Research Questions or Hypotheses
Begin by articulating the specific queries or hypotheses that your research aims to address. These questions or hypotheses serve as the guiding framework for your study, directing the focus of your investigation. you can go through some proposal essay examples for practice.
Example – Research Questions
What is the impact of technological integration in classroom settings on student engagement in STEM education?
How does socioeconomic status influence access to healthcare services in underserved urban communities?
Example – Hypotheses :
Increased integration of virtual reality tools in STEM classrooms will positively correlate with higher student engagement levels.
Lower socioeconomic status will be associated with reduced accessibility and utilization of healthcare services in urban areas.
Ensuring SMART Criteria
Your research questions or hypotheses should align with the SMART criteria to ensure their effectiveness and feasibility. This practice helps you become an expert on how to write a research proposal process.
The questions/hypotheses should be well-defined and focused on a particular aspect of the research topic.
Example – Specificity
What factors contribute to the decline in pollinator populations in agricultural areas?
Does the implementation of mindfulness-based interventions reduce stress levels among college students?
They should be quantifiable or have observable outcomes, allowing for empirical testing and measurement.
Example – Measurability
To what extent does exposure to air pollution correlate with respiratory health complications among children?
Is there a significant difference in academic performance between students who receive traditional teaching methods versus those exposed to experiential learning?
The questions/hypotheses should be realistic and feasible to explore within the scope of the study.
Example – Achievability
Can the effectiveness of a new vaccine be adequately assessed within a six-month research period?
Is it feasible to conduct a nationwide survey on consumer behavior within the allocated budget and time frame?
They should directly relate to the research topic and contribute to addressing the research problem or objectives.
Example – Relevance
How does social media usage impact mental health outcomes among adolescents in suburban areas?
Do mentoring programs significantly influence career advancement in underrepresented groups within the tech industry?
They should have a clear timeframe or indicate when the outcomes or answers will be assessed.
Example – Time-Bound
Within what timeframe can the short-term effects of a new drug on disease progression be determined?
Will the effects of climate change on crop yields be noticeable within a five-year observational study?
Step 5: Methodology
The methodology section is the backbone of how to write a research proposal process. The method section in a research paper outlines the strategies, techniques, and procedures you intend to employ to gather and analyze data. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Data Collection
Describe the specific methods you’ll use to gather information. This might include surveys, interviews, observations, experiments, or secondary data collection from existing sources.
Example – Data Collection Methods
A mixed-methods approach will be utilized, involving semi-structured interviews with healthcare professionals and a quantitative survey among patients.
Data will be collected through ethnographic fieldwork, including participant observation and in-depth interviews in the selected communities.

Data Analysis
Explain the techniques or tools you’ll apply to analyze the collected data. This could involve statistical analysis, thematic coding, content analysis, or qualitative interpretation methods. Please make sure to follow the recommended research project template for students of your educational level.
Example – Data Analysis Technique :
Quantitative data will be analyzed using SPSS software to conduct regression analysis, while qualitative data will undergo thematic coding to identify recurring patterns.
Thematic analysis will be employed to identify key themes from interview transcripts, followed by cross-comparison for data triangulation.
Justifying Methodology Choice
How to write a research proposal with absolute accuracy? Explain how your chosen methodology is appropriate and aligns with addressing your research questions or hypotheses. Justify why these methods are best suited to achieve your objectives.
Example – Justification
The use of surveys and interviews enables a comprehensive exploration of both patient perspectives and healthcare professionals’ insights, allowing for a multifaceted understanding of the healthcare service gaps.
The ethnographic approach is ideal as it facilitates immersive observation and in-depth engagement with community members, essential for capturing the nuanced socio-cultural dynamics affecting environmental practices.
Previous Research Support
Reference existing studies or literature that validate the effectiveness of the chosen methodology in similar research contexts. Highlight how this methodology has been successfully utilized in relevant studies.
Example – Previous Research Support
Similar studies by Jones et al. (2019) and Smith (2020) have utilized mixed-methods approaches in healthcare settings, demonstrating its efficacy in capturing diverse viewpoints and generating comprehensive insights.
Ethnographic studies conducted by Johnson (2018) in similar communities have shown its efficacy in understanding local perspectives and cultural nuances related to environmental behaviors.
Step 6: Timeline
A well-defined timeline in a research proposal demonstrates your planning and organization skills, indicating how you intend to progress through various stages of the research process. You need to know how long a research paper can be according to your guidelines.. Here’s an in-depth breakdown with examples:
Structure of the Timeline
Begin with the proposed start date of the research project and the anticipated end date. This provides a clear timeframe for the entire study.
Divide the research process into distinct stages, such as literature review, data collection, analysis, and writing. Allocate specific durations to each stage.
Considerations for Flexibility
Incorporate buffer periods or contingency time in case of unexpected delays or revisions required in any stage.
Consultation and Feedback: Allocate time for seeking feedback from supervisors, advisors, or peers at different stages of the research.
Realism and Feasibility
Ensure the proposed timeline is realistic and feasible within the available resources, considering factors like access to data, participant availability, and the complexity of analysis.
Step 7: Resources
In how to write a research proposal process, the resources section outlines the necessary tools, materials, funding, and access required to conduct the proposed study. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Identifying Required Resources
Specify the databases, archives, or sources needed to access relevant information or datasets for your research.
Access to peer-reviewed journals via academic databases like PubMed, Scopus, and JSTOR for literature review.
Government census data and regional health records for demographic analysis.
Equipment or Tools
Outline any specialized equipment, software, or tools necessary for data collection, analysis, or experimentation.
High-resolution microscopes for cellular imaging in biology research.
Statistical software packages like SPSS or R for data analysis.
Funding Requirements
Mention any financial support needed for conducting the research, including expenses for travel, participant compensation, or purchasing materials.
Funding for conducting surveys and interviews, including participant incentives.
Travel grant to attend conferences or conduct fieldwork.
Explanation of Resource Acquisition
Describe how you plan to gain access to specific databases, libraries, or archives, whether through institutional subscriptions, collaborations, or memberships.
Access to academic databases will be facilitated through the university’s library subscription, supplemented by interlibrary loan services for specialized journals.
Collaboration with research institutions or organizations granting access to proprietary datasets.
Equipment Procurement or Usage
Explain whether the required equipment will be sourced internally, borrowed, or rented, or if you’ll seek collaborations with laboratories or facilities possessing the necessary tools. Such practices help polishing your skills for how to write a research proposal in future.
Utilizing laboratory facilities within the university for conducting experiments, including shared equipment available within the department.
Collaborating with external research centers possessing specialized equipment on a collaborative basis.
Funding Acquisition
Specify the funding sources you plan to apply for or how you intend to secure the necessary financial support for your research.
Applying for research grants offered by government agencies, foundations, or academic institutions.
Seeking sponsorship from industry partners interested in the research topic.
Step 8: Ethical Considerations
Addressing ethical considerations in a research proposal is crucial to ensure that the study complies with ethical standards, safeguards participant rights, and minimizes any potential risks. Here’s a detailed breakdown with examples:
Participant Consent
Explain how you plan to obtain informed consent from participants. Discuss the process of informing participants about the research, their rights, and the voluntary nature of their participation.
Participants will be provided with detailed information sheets explaining the purpose of the study, their involvement, and their rights. Written consent will be obtained prior to their participation.
Confidentiality and Anonymity
To make the entire how to write a research proposal process more authentic, address how you’ll maintain confidentiality and ensure participant anonymity. Describe measures to protect sensitive information and ensure that participants’ identities remain undisclosed.
All data collected will be coded and stored securely, using anonymized identifiers to safeguard participant identities. Only authorized researchers will have access to the data.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Discuss any potential risks participants might face and how you plan to mitigate these risks. Additionally, outline the potential benefits of participating in the research.
While minimal, participants may experience discomfort discussing sensitive topics. To mitigate this, support services will be available, and participants can withdraw at any time without consequences.
The study aims to contribute valuable insights to the field of medicine, potentially improving healthcare practices and benefiting the wider community.
Research Approval and Compliance
Mention any ethical review boards or institutions where you’ll seek approval for conducting the research. Emphasize your commitment to complying with ethical guidelines and regulations.
The research protocol has been submitted to the Institutional Review Board (IRB) for ethical approval. The study will adhere to the guidelines set by the IRB and relevant regulatory bodies.
Informed Consent with Vulnerable Groups
If involving vulnerable populations (such as minors, the elderly, or individuals with cognitive impairments), special considerations are taken to ensure their informed consent and well-being. It will help add more ethical value in overall how to write a research proposal process.
In cases involving minors, parental consent and assent from the child will be obtained. The research will be conducted in an age-appropriate and non-invasive manner.
Step 9: Expected Outcomes
- Clearly articulate the expected outcomes of your research.
- Explain how these outcomes will contribute to the field or address the research problem.
Step 10: Conclusion
You need to understand the basics of how to write conclusion for a research paper , which usually includes summarizing the key points of your proposal and reinforcing the significance of your research and its potential impact.
Step 11: References
Include a comprehensive list of all sources referenced in your proposal using the appropriate citation style. You can go through the format of how to write a proposal essay in order to understand how referencing is added in a proposal.
Best Proposal Essay Topics
Proposal essays are focused on elaborating an issue and then providing solutions to tackle it. Such topics are highly preferred in the research proposal assignments and projects. We have shared some of the best proposal essay topics below. You can go through it to pick a topic related to your interests.
- How to control food waste?
- How to encourage people to recycle?
- Measures to take for endangered species
- How to conserve water?
- Does pollution impact the water cycle?
- Discovering the dark side of the internet
- How does biometric system change security measures?
- How to come up with a business plan?
Important Take Away
Here is what you need to keep in mind regarding research proposal:
- Go through the guidelines of the university or institute you are going to submit the research at.
- Ensure that your proposal has clear objectives and aims.
- Be mindful of the ethical considerations of your research.
- Take help from research guides and paper writing service tools in order to practice writing.
- All the sources of information need to be cited properly.
- Title and introduction will determine the success of your proposal, so make it highly compelling.
Concluding Remarks on Crafting a Research Proposal
Crafting a research proposal demands meticulous attention and deliberate contemplation. Within this comprehensive guide on formulating a research proposal, we have encountered various challenges inherent in its composition. These challenges encompass:
- Understanding the research proposal
- The basic elements of writing one
- Quick tips for crafting a good research proposal
- Ensuring a complete understanding of all the elements
Moreover, a practical approach has been employed to efficiently understand how a beginner can get started with writing a research proposal. Such that he won’t have to search for how to write a research proposal again.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
- Locations and Hours
- UCLA Library
- Research Guides
- Research Tips and Tools
Advanced Research Methods
- Writing a Research Proposal
- What Is Research?
- Library Research
What Is a Research Proposal?
Reference books.
- Writing the Research Paper
- Presenting the Research Paper
When applying for a research grant or scholarship, or, just before you start a major research project, you may be asked to write a preliminary document that includes basic information about your future research. This is the information that is usually needed in your proposal:
- The topic and goal of the research project.
- The kind of result expected from the research.
- The theory or framework in which the research will be done and presented.
- What kind of methods will be used (statistical, empirical, etc.).
- Short reference on the preliminary scholarship and why your research project is needed; how will it continue/justify/disprove the previous scholarship.
- How much will the research project cost; how will it be budgeted (what for the money will be spent).
- Why is it you who can do this research and not somebody else.
Most agencies that offer scholarships or grants provide information about the required format of the proposal. It may include filling out templates, types of information they need, suggested/maximum length of the proposal, etc.
Research proposal formats vary depending on the size of the planned research, the number of participants, the discipline, the characteristics of the research, etc. The following outline assumes an individual researcher. This is just a SAMPLE; several other ways are equally good and can be successful. If possible, discuss your research proposal with an expert in writing, a professor, your colleague, another student who already wrote successful proposals, etc.
- Author, author's affiliation
- Explain the topic and why you chose it. If possible explain your goal/outcome of the research . How much time you need to complete the research?
- Give a brief summary of previous scholarship and explain why your topic and goals are important.
- Relate your planned research to previous scholarship. What will your research add to our knowledge of the topic.
- Break down the main topic into smaller research questions. List them one by one and explain why these questions need to be investigated. Relate them to previous scholarship.
- Include your hypothesis into the descriptions of the detailed research issues if you have one. Explain why it is important to justify your hypothesis.
- This part depends of the methods conducted in the research process. List the methods; explain how the results will be presented; how they will be assessed.
- Explain what kind of results will justify or disprove your hypothesis.
- Explain how much money you need.
- Explain the details of the budget (how much you want to spend for what).
- Describe why your research is important.
- List the sources you have used for writing the research proposal, including a few main citations of the preliminary scholarship.
- << Previous: Library Research
- Next: Writing the Research Paper >>
- Last Updated: Aug 22, 2024 3:43 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.ucla.edu/research-methods
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Write a Research Proposal
Last Updated: March 20, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Christopher Taylor, PhD . Christopher Taylor is an Adjunct Assistant Professor of English at Austin Community College in Texas. He received his PhD in English Literature and Medieval Studies from the University of Texas at Austin in 2014. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 785,361 times.
The exact format and requirements for a research proposal can vary slightly depending on the type of research being proposed and the specific demands of the institution you plan to submit your proposal to, but there are a few basics that are almost always needed. Overall, a good research proposal takes time to write and must identify what the proposed research will address and why the proposed research is so important. Here is a brief explanation of the sections needed to complete a standard research proposal as well as the writing timeline you should strive to follow.
Research Proposal Help

Sections of a Proposal

- For example, try a short, informative title like, “Medieval Plagues and the Movement Towards Humanism,” or “The Negative Impact of Alcohol on Liver Function.”
- Avoid phrases like “An Investigation of…” or “A Review of the…”

- Each sponsoring agency may specify a format for the title page. If an agency does not, apply the APA style. [2] X Research source
- Include a "running head" in the upper left corner. The running head will appear on all pages of the document and should be a shortened version of the title.
- Include the page number in the upper right corner. The page number should appear on all pages of the proposal.
- Center the full title of your research proposal roughly 1/3 of the way down the page. Double space it, and immediately below the title, insert your name. Below your name, list the institution you are affiliated with and the names and affiliations of any co-investigators you’re working with. In some styles, you may include their contact information as well.

- Center the word "Abstract" at the top of the page.
- Begin the text of your abstract directly below the word "Abstract." Do not indent the paragraph.
- The text of you abstract will usually be between 150 and 250 words.

- For example, if your proposal is about heart diseases, you might use phrases like circulatory system, blood, heart attack, etc.
- Your keywords can be single words, or phrases of 2-4 words.

- Brief proposals that only span a few pages do not often need a table of contents. Leaving out a table of contents is common, but depends on the type of research you’re doing and the institution you’re submitting the proposal to.
- Especially long proposals may also need a list of illustrations, figures, or tables.
- List all major parts and divisions of the proposal.

- Restate and center the title of your paper before moving into your introduction. Include a quick note about the topic being discussed and a definition of the theory from which your proposed research will be based.
- Write "Statement of Problem" before moving into a paragraph detailing the problem. When writing this part of the introduction, seek to answer the question: why does this research need to be conducted and what new issues does this research raise?
- Type "Purpose of Study" before writing this section of the introduction. Identify the goal of the study in one precise terms.
- Type "Significance of Research." In the paragraph below, answer why the area of research is important and identify the type of research or analysis proposed.

- If desired, you can break this section into multiple subsections.
- Under a header reading "Research Question" or "Research Hypothesis," describe the relationship between variables in the research or predict the relationship between variables. This essentially identifies the research problem.
- Under a header reading "Definition of Terms," define the central ideas that will be utilized in the proposed research.
- Also provide evidence supporting your competence or expertise in the field.

- Don’t turn this section into a list or a bland summary. Sum up existing research in a story-like manner that draws readers in while exposing the hole that your research will attempt to fill.

- This section can also be titled "Methodology."
- Provide a complete explanation of your proposed research. Address the explanation to experts in the field rather than laymen.
- The set up and information in this section will depend on whether your research is qualitative and quantitative. You’ll likely have subsections like "Research Design," "Instrumentation," "Data Collection and Analysis Procedures." You may include information about what you will do to protect the rights of human subjects, if necessary, under a section called "Protection of Human Rights.” Other possible subsections might include “Rigor,” “Neutrality,” “Consistency,” and “Applicability.”
- You should also demonstrate your knowledge of alternative methods, while making the case that your approach is the most effective way to tackle your research question.
- Be realistic about what you hope to accomplish, clear about your focus, and explicit about everything the research relies on. The description should also include a detailed schedule of the proposed work and thorough about all groundwork and materials needed.
- Also include information about sample size and target populations, if applicable.

- Identify information like the institution's past competence or contributions within the field of research, the university's supportive services, or the institution's research facilities.

- Note that this section is not always included, especially for shorter proposals.
- State the expertise and responsibilities of each contributor.

- Each cost should include justifying information.
Writing Timeline

- At 26 weeks, review administrative requirements for the foundations and organizations you plan to submit your proposal to. Double-check due dates and submission requirements.
- At 23 to 25 weeks, create a one to two page preliminary statement defining your proposed research.
- If working with an adviser or colleagues, present this short version of your proposal at 23 weeks. Use any feedback you receive to further focus your research in week 22.
- Research the context, history, and background of your research problem at 21 weeks.
- At 19 weeks, write a two to three page document exploring questions and possible methodological approaches.
- Contact experts in the field at 17 weeks to learn about the feasibility and relevance of each potential methodological approach.
- Continue your research during week 16 and refine your research question by week 14.

- At 20 weeks, identify and contact any relevant sources of information, including experts, archives, and organizations.
- Begin researching your budget needs by 18 weeks and your protocol process by 14 weeks.
- Request any necessary transcripts by 13 weeks.

- Create a single 5-page document containing your research question, framework, and proposed research design by week 13.
- Gather any additional data needed to complete a draft during week 12.
- Reconnect with collaborators and organizations. Determine which will be most helpful.
- Add the remaining details needed to complete your draft. Use the above guidelines or guidelines provided by the provider of the grant provider. Complete this between weeks 10 and 12.
- Ask your colleagues or adviser for more feedback by the 9 week mark.
- Revise your draft at 8 weeks. Create a tentative budget and ask advisers for letters of recommendation.

- At 5 weeks, review specific requirements addressed by the application and revise your proposal to meet this requirements and incorporate adviser suggestions.
- Give yourself a break during week 4 to let things settle.
- Remind your adviser and other faculty about your letters of recommendation during week 3.
- At 2 weeks, assemble your materials, review your proposal, and finalize your proposal.
- Ask colleagues to help you copy-edit 10 days in advance.
- Print your final copy and collect your materials 3 to 4 days in advance.
- Submit your research proposal 2 to 3 days before the due date.
Community Q&A
- Include images, charts, and diagrams in your methodology section if allowed and if applicable. The resources can structure the information in an easy-to-digest format while also breaking up otherwise long, monotonous blocks of text. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 0
- Be objective. Throughout the entire research proposal, you must strive to maintain an objective tone. Identify the importance of your research using broad academic reasons instead of narrow personal reasons. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185911
- ↑ https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/paper-format/title-page
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/abstract
- ↑ https://libguides.lvc.edu/c.php?g=333843&p=2247147
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- ↑ https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185916
- ↑ https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/literaturereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3282423/
- ↑ https://academicanswers.waldenu.edu/faq/72739
About This Article

To write a research proposal, start by writing an introduction that includes a statement of the problem that your research is trying to solve. After you've established the problem, move into describing the purpose and significance of your research within the field. After this introduction, provide your research questions and hypotheses, if applicable. Finally, describe your proposed research and methodology followed by any institutional resources you will use, like archives or lab equipment. To learn how to construct a realistic writing timeline, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Juan C. Ruiz
Jan 17, 2019
Did this article help you?

Whitney Roberts
Nov 12, 2019
Felix Adegbile
Dec 18, 2019
Mahlako Bapela
Jan 25, 2020
JACKIE STEVENSON
Feb 10, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
10 Helpful Steps for Writing a Graduate Research Proposal
The road to obtain a graduate degree is unquestionably long. But we have ten incredibly helpful steps for writing your graduate research proposal. When you finally reach your destination, it will all be worthwhile.
As a graduate student, when you start your journey, you must write, present and defend a graduate research proposal in front of a committee of professors, also known as a graduate advisory committee.
A research proposal is usually short, with only fewer than ten pages, but it has to cover the proposed research in detail. After the committee approves it, you should follow the research plan explained in the research proposal to complete your research project.

Figure 1. The typical timeline in graduate school.
Why is it important to write a research proposal?
There are eight major reasons for graduate students to write a research proposal in graduate school:
- It's required by the graduate school before performing research.
- Students become more familiar with the research project
- They develop research skills and academic writing skills.
- Students develop literature review skills.
- Students learn how to identify the research problem, objective, research questions and hypothesis.
- They learn to explore different methods to collect and analyze data, and to select the most appropriate methods for solving research problems.
- They learn to design research experiments based on logical and chronological steps.
- The process nurtures critical thinking and logical reasoning skills.
What to include in a research proposal
The common elements to include in a good research proposal are:
- Title : The title of a research proposal should be clear and brief.
- Introduction : This part contains the background information of the proposed study leading to the research problem.
- Statement of purpose : This element should include the research objectives.
- Literature review : It should include an overview of findings from the previous studies, the gaps in the previous studies and the findings from a preliminary study.
- Research questions and hypothesis : This includes the research questions and hypothesis.
- Methodology : This element contains a full description of the research procedures, possible problems and alternatives strategies.
- The significance and impact of the study : This part shows how the proposed research will contribute to the field of study.
The 10 steps to writing an incredible research proposal
Below are ten steps for writing a research proposal:
1.Choose a research topic and develop a working title
Having a strong interest in your research topic will certainly help you to keep going when the journey becomes more challenging. The research topic is the subject of your research, which is a part of a broader field of study.
When you pick a research topic, find a topic that is not too narrow nor too broad. You can limit your topic, for example, by focusing on a certain treatment, population group, species, geographical area, period, methodology, or other specific factors.

After selecting a research topic, develop a working title to help you focus on your topic. As you write the proposal, you can keep changing the working title to formulate the perfect title.
2.Perform a literature review
The next step is to conduct a literature review. This step is important because when you write out the background information and knowledge gaps in your topic area, it will help you become more familiar with your research topic.
In addition, performing a literature review will direct you to a research problem . A research problem is a specific area of concern serving as the focus of your proposed research.
When performing a literature review, a graduate student can also discover some ideas for designing their research plan.
To help you conduct a literature review, answer the following questions below:
What have others done so far to solve the research problem?
Some helpful steps to answer this question:
- Understand the experimental designs from previous studies to help you design your own research experiments.
- Learn about appropriate sample sizes, data collection, and statistical analyses from previous studies.
- Investigate and make a list the reagents and equipment you’ll possibly need for your research.
- Learn the research questions, the findings, the impact and the significance of previous studies.
- Find out about any ethical concerns.
What additional studies are still needed to solve the research problem?
- Pay attention to the strength and limitation part of the discussion section of scientific articles. From this part, make notes about the limitations of previous studies to give you an idea about a potential research problem.
- Read the suggestions for future research part of scientific articles. That can serve as a call to action for you to solve those unanswered questions from previous studies.

3.Write an introduction
The introduction of your research proposal builds a framework for the research. This framework is the structure that supports your study and contains the background information. Its function is similar to the role of a foundation in supporting a building—if it is weak, a building will fall apart. Likewise, if your research lacks a strong background as a framework, it’s hard for others to see why it matters.
Writing your introduction can feel a little overwhelming. Where do you begin? How do you know you’re not missing anything?
You might want to read over our article:
How to Write an Effective Introduction Section of a Scientific Article
While the article is more specific to the introduction section of a formal research paper, there are some parts and tips you might find helpful.
4. Write research objectives or aims
In the next step, include research objectives or aims in the research proposal. A research objective is a goal you want to achieve in your research project ( Al-Riyami, 2008 ). Your research objectives must have a strong connection with your research problem.
When developing research objectives, identify all variables associated with the research problem. A variable in the research is a characteristic that you manipulate or observe in your experiment.
There are different types of variables, including an independent variable and dependent variable (Al-Riyami, 2008). An independent variable is a variable you can change in your experiment, whereas a dependent variable is a variable you observe in response to the independent variable. After identifying the variables, connect them to the research objective.
An example of a research objective: to determine the effect of different doses of a novel antibiotic X on the growth rate of some resistant bacterial strains . In this example, the independent variable is the treatment (the different doses of antibiotic X), and the dependent variable is the growth rate of some bacterial strains.

5.State a research question
The next step is to identify a research question. A research question is the key question you want to answer in your proposed study ( Farrugia et al ., 2010 ). A research project can contain several research questions.
Keep in mind that your research question must meet the criteria of a good research question, including specific, feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant (Farrugia et al ., 2010).
In term of feasibility, use current methods and technology to answer the question during your limited time in the graduate school.
An example of a research question : What doses of the antibiotic X are effective to inhibit the growth of some resistant bacterial strains?

6.Formulate a research hypothesis
After developing the research objectives and question, the next step is to formulate a research hypothesis. A research hypothesis is a statement of a possible research outcome.
Some criteria of a good hypothesis ( Prasad et al., 2010 ; Al-Riyami, 2008):
- Logical, precise, and clear
- Testable with research experiments
- Makes a prediction about the relationship between variables
An example of a research hypothesis: The new antibiotic X will significantly prevent the growth of some resistant bacterial strains.

7.Explain research methods
The methodology section containing proposed experimental procedures is required for a research proposal. This section has the detailed plan to solve the research problem. It also reflects the research questions and hypothesis.
After reviewing the credibility and validity of your research methods, your advisory committee will make a decision about the fate of your proposed study. Therefore, when writing the methodology section, keep in mind that others should be able to follow each step in the research design to perform the same experiment.
In this section, you should include these following key points:
- Experimental design : This is the research strategy you choose to solve your problem.
- Samples : It contains the description about the samples for each group of treatment in the proposed study.
- Sample size : This information is important to make sure your sample size is sufficient.
- Materials : It contains the reagents and chemicals needed in the proposed study.
- Equipment : This has the list of equipment needed for the proposed study.
- Protocols of data collection : It contains the procedures needed before collecting your data.
- Ethical issues and consent forms : You may need to include these if your proposed studies will need human participants.
- Data analysis : This part should include the steps to analyze the data.
- Gantt chart : This chart contains tasks in each research project with the timeline for each task.
8.Include potential problems and alternative strategies
When performing your study, you may encounter potential problems. Therefore, include some of the possible problems that may occur during your study and the potential solution for them. By doing so, you can use your backup plan to solve each potential problem when the problems actually occurs.
9.Conduct and include a preliminary study
Perform and include the findings from a preliminary study in your research proposal. A preliminary study is a small-scale pilot study, conducted to test the experimental design ahead of time and increase the likelihood of success. By including the findings from a preliminary study, your advisory committee can visualize and assess the feasibility of your large-scale study.
10.State the potential impact and significance
In the last paragraph of your research proposal, include the potential impact and significance of your proposed study.
The potential impact of your study means the changes that your proposed research would make. These changes can be positive or negative, immediate or long-term, and direct or indirect.
Whereas, the potential significance of your study means the contribution that your proposed research would make. For example, you can explain its contribution to the knowledge in your field of study.
After putting it all together, evaluate the entire proposal to make sure it is strong and well written.
Al-Riyami, A. (2008). How to prepare a Research Proposal. Oman Medical Journal, 23(2), 66–69. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC32824...
Benedetti, A. (n.d.). Research Guides: Advanced Research Methods: Writing a Research Proposal. Guides.library.ucla.edu. Retrieved March 17, 2021, from https://guides.library.ucla.edu/c.php?g=180334&p=1289236.
Crawford, L. (2020). LITERATURE-BASED DEFINITIONS OF CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORKS. https://us.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-assets/105274_book_item_105274.pdf.
Farrugia, P., Petrisor, B. A., Farrokhyar, F., & Bhandari, M. (2010). Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Canadian Journal of Surgery. Journal Canadien de Chirurgie, 53(4), 278–281. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC29120...
How to choose a research area. (2016, April 8). ASCB. https://www.ascb.org/careers/choose-research-area/
How to Select a Research Topic | University of Michigan-Flint. (2019). Umflint.edu; UM-Flint. https://www.umflint.edu/library/how-select-research-topic.
How To Write a Proposal | Science & Quantitative Reasoning. (n.d.). Science.yalecollege.yale.edu. Retrieved March 17, 2021, from https://science.yalecollege.yale.edu/fellowships/how-write-proposal.
Jacobs, R. L. (2013). Developing a dissertation research problem: A guide for doctoral students in human resource development and adult education. New Horizons in Adult Education and Human Resource Development, 25(3), 103–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/nha3.20034.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between Theory, Theoretical Framework, and Conceptual Framework: A Systematic Review of Lessons from the Field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7(6), 44. https://doi.org/10.5430/ijhe.v7n6p44.
LibGuides: Writing a Research Proposal: Parts of a Proposal. (2017). Illinois.edu. https://guides.library.illinois.edu/c.php?g=504643&p=3454882.
LibGuides: Research Process: Finding a Research Topic. (2019). Libguides.com. https://ncu.libguides.com/researchprocess/researchtopic.
LibGuides: Research Process: Literature Gap and Future Research. (2012). Libguides.com. https://ncu.libguides.com/researchprocess/literaturegap.
Pajares, F. (n.d.). THE ELEMENTS OF A PROPOSAL. https://www.uky.edu/~eushe2/Pajares/ElementsOfaProposal.pdf.
Prasad, S., Rao, A., & Rehani, E. (2001). DEVELOPING HYPOTHESES & RESEARCH QUESTIONS DEVELOPING HYPOTHESIS AND RESEARCH QUESTIONS. https://www.public.asu.edu/~kroel/www500/hypothesi...
Shardlow, M., Batista-Navarro, R., Thompson, P., Nawaz, R., McNaught, J., & Ananiadou, S. (2018). Identification of research hypotheses and new knowledge from scientific literature. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making, 18(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-018-0639-1
Steps in Developing a Research Proposal. Open.lib.umn.edu; University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing edition, 2015. This edition adapted from a work originally produced in 2010 by a publisher who has requested that it not receive attribution. https://open.lib.umn.edu/writingforsuccess/chapter...
Vining, S. (2019, July 22). Dissertation Proposal | Genetics and Genomics. https://genetics.mcb.uconn.edu/dissertation-propos...
Writing a Research Plan. (2017, December 11). Science | AAAS. https://www.sciencemag.org/careers
Related Articles

The road to obtain a graduate degree is unquestionably long. But we have ten incredibly helpful step...

Guide to Writing the Results and Discussion Sections of a Scientific Article
A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing (Bordage, 200...

Building a Clear Path and Finishing Graduate School Even When You’re Ready to Give Up
Obtaining a graduate degree can be an arduous, long, and unpredictable journey. Sometimes when this...

How to Master Collaboration Skills in the Graduate School
It’s common for researchers to collaborate in science. By doing so, scientists can share expertise,...
Join our list to receive promos and articles.

- Competent Cells
- Lab Startup
- Z')" data-type="collection" title="Products A->Z" target="_self" href="/collection/products-a-to-z">Products A->Z
- GoldBio Resources
- GoldBio Sales Team
- GoldBio Distributors
- Duchefa Direct
- Sign up for Promos
- Terms & Conditions
- ISO Certification
- Agarose Resins
- Antibiotics & Selection
- Biochemical Reagents
- Bioluminescence
- Buffers & Reagents
- Cell Culture
- Cloning & Induction
- Competent Cells and Transformation
- Detergents & Membrane Agents
- DNA Amplification
- Enzymes, Inhibitors & Substrates
- Growth Factors and Cytokines
- Lab Tools & Accessories
- Plant Research and Reagents
- Protein Research & Analysis
- Protein Expression & Purification
- Reducing Agents
Stanford Research Development Office
Guidance for Writing Proposal Sections
Most recent content update: July 2, 2024
The following proposal sections, listed in alphabetical order, are commonly required by a variety of funders. For each, we have provided resources to assist in preparing content; some have been developed by RDO, while others are curated from trusted internal and external sources.
The resources below are intended to be a starting point. Solicitations will often specify unique requirements for each of these sections. Always check the requirements from your specific agency and call.
We encourage you to check this page regularly, as additional content will be added over time. Email us at [email protected] if you have suggestions.
Biographical Sketches
These documents provide evidence of an individual's qualifications for the role played in a proposed project and are generally requested in specific formats based on sponsor. For most STEM sponsors, RDO recommends using SciEnCV for generating and saving your biosketch as it will be easier to update and the interface allows reformatting for use in proposals for different sponsors.
- Start here : Stanford ORA Biosketch Resource Page - Stanford resource with links to NSF and NIH biosketch guidance as well as SciEnCV resources
- SciEnCV - a tool for assembling biographical information for federal sponsors that can easily be ported into multiple sponsor formats. It is quickly becoming an accepted (and often required) biosketch format for many sponsors including NIH, NSF, and DOE
- NSF SciEnCV FAQs and Guide - start here if you need help setting up your SciEnCV account or run into questions along the way
Broader Impacts
Broader Impacts requirements generally ask for the answer to the question "how does your research benefit society?" This term and requirement are commonly associated with NSF, but other agencies can also have similar requirements. The resources below help to describe the breadth of what broader impacts can be as well as give advice on how to develop a vision and craft a compelling story about the broader impacts of your work.
- Stanford Grant Writing Academy Broader Impacts Resources - Among other information, includes a short video explaining NSF's BI requirement and suggestions on crafting a strong BI element for your proposal
- Stanford Office of Education and STEM Outreach - A part of the Office of Community Engagement, ESO serves as a nexus connecting Stanford faculty, students, and postdocs with youth, schoolteachers, nonprofit organizations, and the broader community with the goals of increasing engagement, participation, equity and inclusion in STEM fields
- ARIS Broader Impacts Toolkit - resources from the Center for Advancing Research Impact in Society designed to assist proposal teams as they develop broader impact projects
Budget and Budget Justifications
Budgets are an integral part of proposals that have a direct effect on how monies can be used, are tracked, and are audited in the post award period.
- Start here : Stanford ORA Budget Resource Page - find templates and helpful links and information including California's partial sales and use tax exemption for research and development equipment
- Stanford VPDoR Rates page - tables, policies, and information on F&A rates, fringe benefit rates, and others
Conflicts of Interest
Often sponsors require a list of collaborators and other affiliates in a form that allows the agency to ensure that no conflicts exist in the process of selecting reviewers or to check for PI conflict of interest in various areas. These can be in the form of "COA", "Collaborator", "COI" or other documents. Be sure to check and follow your sponsor's guidelines for these documents; many provide their own specific required templates.
- Stanford Global Engagement Review Program coordinates input from multiple offices that advise on various aspects of foreign engagements to assess risks related to undue foreign influence, research security, and integrity
Data Management Plans
Many funding agencies will require a data management plan (DMP) as part of a proposal. The DMP describes the types of data you expect to collect, how they will be managed, and how access and preservation will be accomplished over time.
- Start here : Stanford Libraries has a Resource Page with information about DMPs including access to an Online Data Management Plan Tool for creating a ready-to-use plan for your proposal
- DMP Self Assessment Questionnaire (Stanford Libraries)
- Stanford Libraries Data Management Services assists researchers with data preservation and access and has other data tools and services available
- Lane Medical Library NIH DMSP Checklist
- Stanford University IT data Storage Recommendations
- DOE suggested elements for a DMP
- NASA DMP guidance
- NEH guidelines for digital humanities
- NIH DMS Plan policy (new guidelines effective January 25, 2023)
- NIH Sample Plans for different contexts
- NSF DMP requirements (also includes links to directorate-specific guidances)
- NSF FAQs for public access
- RDO has prepared a guide to creating NSF Data Management Plans (current guide reflects NSF PAPPG 23-1; to be updated after PAPPG 24-1 goes into effect May 20, 2024)
- Effective practices for making research data discoverable and citable (NSF Dear Colleague Letter, March 2022)
Diversity Plans
Sponsors sometimes require demonstration that a project team will make specific efforts to promote diversity, equity, and inclusion. These requirements vary by sponsor and it is important to understand the level at which the activities are to take place. For example, does the sponsor want to see activities that are community-focused or targeted to the researchers and staff you will have on the project? In any case, a strong diversity plan also includes evaluation strategies and metrics for success.
- Stanford RDO's thought starter for DOE PIER Plan
- Stanford SoM PDO template for NIH PEDP
- DOE CBP: Community Benefits Plans (page includes links to templates)
- DOE PIER: Promoting Inclusive and Equitable Research Plans
- DOE DEI Informational Resources
- NIH PEDP: Plan for Enhancing Diverse Perspectives
Evaluation Plans
Often addressed in multiple sections of a proposal, evaluation plans are an important component of understanding whether a project or strategy is effective and successful. Developing robust evaluation plans at the proposal stage can demonstrate to the reviewers and funders that you have thought about what "success" means and how you will be certain you will achieve it or adjust practices to course correct along the way. These are commonly requested for educational activities, outreach plans, workforce development strategies, and management plans.
- American Evaluation Association Find an Evaluator Tool - a directory that can be searched by location, area of expertise, or name
Institutional Support
Funding agencies may request that cost sharing, details on facilities, equipment, and other resources available to the proposal team, and other forms of institutional support be included with proposals. The scope and format of these requirements will depend on the specific funding opportunity or call. RDO recommends starting early in your proposal development process and working in collaboration with department or school leadership to identify and request appropriate institutional support for your proposal.
- RDO's Thought Starter: Stanford Institutional Support for Large, Strategic Grant Proposals - a list of support that may be appropriate for large, strategic proposals that are beyond the usual scale for a given discipline. Contains notes on how to start the conversations necessary to secure different types of institutional support, relevant policies set by the University, and other factors to consider.
Management Plans
Management plans are common elements of large collaborative or center grants. This section is intended to demonstrate to reviewers how teams will work together to accomplish the various goals of a project. Some plans also require detailed administrative information as well as plans for evaluation of project activities (see section on Evaluation Plans above).
- Start here : RDO Management Plan Guidelines - six common topics for consideration when devising a management plan for STEM center grants
- RDO resources for collaboration and team science
- DOE's EFRC Good Management Practices - while it originated from a specific DOE program, this document contains excellent advice that is generalizable to other research center management strategies
Postdoctoral Mentoring Plans
Postdoctoral mentoring plans (PMPs) are often required in STEM-focused proposals where a postdoctoral researcher's involvement is indicated. These serve as roadmaps for both mentor and mentee to navigate the key aspects of mentorship and professional development of postdocs. It's best to avoid using a boilerplate approach and instead tailor the Plan to the specific program you are proposing, institution you are with, and/or postdoc(s) to be mentored.
- Start here : RDO's Postdoctoral Mentoring Plan Guidelines - an NSF-focused document with prompts and suggestions for writing an effective PMP that is also useful in thinking of strategies to fulfill PMP requirements for other sponsors. Note: Proposals due or submitted on or after May 20, 2024 will be required to submit a Mentoring Plan applicable to both graduate students and postdoctoral researchers, in lieu of the prior Postdoctoral Mentoring Plan requirement. Please see NSF PAPPG 24-1 for details.
- National Postdoc Association Institutional Guide to Postdoc Mentorship - includes specific guidance on PMPs as well as links to resources on mentorship
Sponsors sometimes request information on protocols and plans related to safety in various context including in the laboratory, at field sites, or any off-campus work environment. The university has policies and procedures related to these topics which can be found in addition to other resources linked below.
- Start here : Stanford EH&S website - central website for Stanford safety services and support which also includes information on training, standard operating procedures, and many safety related resources for the campus community
- Stanford ORA template for NSF Plans for Safe and Inclusive Working Environments for Off-campus Research - an NSF-focused document with instructions, applicable University policy information, and fillable fields for PIs to complete their project-specific information
Created: 10/06/22
Updated: 08/22/24
Proposal Development Services

💡 Grant Writing Tip: Proposal Brainstorming
- by Stephanie F Etting
- August 20, 2024
You want to write a grant but are not sure where to begin. Or you have ideas but need help narrowing them down and developing them into a project plan. If either is true for you, read on for steps to take towards building your next proposal.
Step 1: What do you want to do?
If you have many ideas but are not sure how to focus your efforts, start here. If you have a clear research objective already, feel free to skip this step. Spend time writing down all of your ideas, giving yourself a time limit so you don’t get too carried away. For each idea, write only a sentence or two of description. Once you’ve reached your time limit, narrow down your ideas into a related set of goals (say 3-4). Be sure to save the others for future grant ideas!
Step 2: What are your goals and objectives?
With your set of cohesive research ideas, spend time expanding each of them into the research objectives (aims) that each will target. Again, limit the time you spend on each.
Step 3: What research activities are required to address the objectives?
For each research objective from the previous step, map out specific activities required to address those goals. Make notes about potential personnel, equipment, and money needed for each. It helps to include approximately how long each task might take.
Step 4: What is innovative about the project?
You’ve now got your basic research plan outlined, so it is time to reflect on what is important about the proposed work. What about your project is innovative (novel) and urgent (fills a necessary gap)?
Step 5: What is the research impact?
When developing a research plan, it is critical to remember how the work will impact the broader community. Spend time brainstorming about the potential impacts of the objectives and activities. Imagine what the world will look like if you succeed.
Step 6: How will you evaluate your progress?
Each activity should move you towards your overall research goals, so how will you measure your progress during the research process (formative assessments) and overall (summative assessments)? What deliverables are expected, and when during the project these should happen? Also, plan for potential pitfalls in your research and how you will handle them.
Next Step: Integrating your plan
If you have completed the above steps, congratulations! The hardest part is done. The next step is to find a funding opportunity, then take your notes and integrate them into a cohesive pitch. We suggest forming your pitch as a One-Pager that you can use to approach program officers and, later, to develop your full proposal! For UC Davis faculty interested in a downloadable a full template of this brainstorming activity .
Scholarship competition resources

Federal and provincial scholarships support high-caliber graduate students demonstrating strong academic excellence, research ability/potential, and outstanding professional or personal achievements.
Each competition has its own specific eligibility criteria. Prior to applying, you are encouraged to visit each scholarship website to confirm your eligibility. After your review, if you have specific scholarship questions, contact your department graduate co-ordinator . If you are a prospective graduate student and have questions, please connect with the program contact as identified on each graduate program page .
Jump to: Fall 2024 scholarship events | Checklist for applying | Academic input of your research proposal | Writing and Communication Centre
Fall 2024 scholarship events
The major federal and provincial scholarships are highly competitive. We strongly encourage you to attend the scholarship events below to learn more about the application processes, and have your questions answered!
Additional scholarship events will be added below as they are confirmed.

NSERC Doctoral and Postdoctoral Information Session (Aug 27 session)
NSERC is hosting question and answer sessions for the doctoral scholarships and postdoctoral fellowships programs which will be hosted as live Q&A MS Teams events. These sessions are supported by a series of informational videos available on the NSERC YouTube channel so that you can watch videos in advance and come to the Q&A session with specific questions in mind.
- Current students ,
- Current graduate students ,
- Future students ,
- Future graduate students
NSERC Doctoral and Postdoctoral Information Session (Sept 6 session)

Creating a Competitive Graduate Scholarship Application Webinar
Join our experts to receive recommended tips and suggestions for putting together a strong scholarship application package.
This webinar will focus on the content and writing of your application. For scholarship eligibility, please visit the external awards page on our website.
Registration is required.
- Current undergraduate students ,
NSERC Doctoral and Postdoctoral Information Session (Sept 12 session)
Nserc doctoral and postdoctoral information session (sept 13 session).

Tri-Agency Doctoral Scholarship Workshop
Receive advice and feedback on your CV, lay abstract, and/or research proposal from faculty members and postdoctoral scholars. Students at any stage in the Tri-Agency scholarship application process are welcome to join.
- Future graduate students ,
Checklist for applying - critical steps in the application process
Each scholarship application requires you to follow the steps below. It is important to start the process as soon as possible!
- Confirm your eligibility and read the application instructions.
- Familiarize yourself with the transcript instructions and determine if you need to order transcripts. If you do, order them now.
- Talk to prospective referees about reference letters, provide them with the appropriate deadline and detailed information to assist them with writing an informed assessment.
- Work on your research proposal/program statement.
- Apply for admission to a graduate program at Waterloo, if applicable.
- Complete the application and all components/attachments and submit it by the deadline.
Academic input of your research proposal and/or CV drafts
If you have drafted your proposal and want to have it reviewed by an academic in your area, we encourage you to reach out to:
- Your current/prospective supervisor
- Your department graduate chair/officer
- A faculty member in your area of research as suggested by the graduate chair/officer
Writing and Communication Centre (WCC)
The Writing and Communication Centre (WCC) is a hub of communication and writing practice, support, and research on campus. Students are encouraged to utilize the services offered by the Centre which include one-on-one appointments, workshops, writing cafes, etc.

COMMENTS
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let's look at the explanation for each of the steps here: Step 1: Title and Abstract. Step 2: Introduction. Step 3: Research objectives. Step 4: Literature review.
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components : Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Conduct a literature review for your research proposal. 4. Define a research gap and research question. 5. Establish a theoretical framework for your research proposal. 6. Specify an empirical focus for your research proposal. 7. Emphasise the scientific and societal relevance of your research proposal.
Create a Captivating Title Page. - Sets the stage for your proposal. - Include title, your name, affiliation, date. - Must meet institutional formatting guidelines. 2. Summarize with a Strong Abstract. - Briefly covers the key aspects of your proposal. - Details research problem, objectives, methodology, implications. 3.
A step-by-step guide to writing a research proposal #1 Introduction. Researchers who wish to obtain grant funding for a project often write a proposal when seeking funding for a research-based postgraduate degree program, or in order to obtain approval for completing a thesis or PhD.
Key Takeaways. Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the ...
Look for any research gaps, trends and patterns, common themes, debates, and contradictions. Consider any seminal studies on the topic area as it is likely anticipated that you will address these in your research proposal. 4. Research Design. This is where you get down to the real meat of your research proposal.
Step 1: Title. Create a clear, concise, and descriptive title that encapsulates the essence of your proposed research. The title of a research proposal serves as its initial point of engagement, offering a glimpse into the focus and significance of the study.
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
Develop an Outline. Create a clear and logical structure: Divide your proposal into sections or headings that will guide your readers through the content. Introduction: Provide a concise overview of the problem, its significance, and the proposed solution. Background/Context: Offer relevant background information and context to help the readers ...
Lecturers, request your electronic inspection copy. This is your step-by-step guide to success with your research proposal. The new Third Edition covers every section of the proposal, telling you all you need to know on how to structure it, bring rigor to your methods section, impress your readers, and get your proposal accepted.
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
A research proposal is a short piece of academic writing that outlines the research a graduate student intends to carry out. It starts by explaining why the research will be helpful or necessary, then describes the steps of the potential research and how the research project would add further knowledge to the field of study.
Academic Research Proposal. This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review, methodology, and expected outcomes.
Include the page number in the upper right corner. The page number should appear on all pages of the proposal. Center the full title of your research proposal roughly 1/3 of the way down the page. Double space it, and immediately below the title, insert your name.
INTRODUCTION. A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under 'Research methodology II' section [Table 1] in this issue of IJA) and to ...
Style: If space allows, provide a clear project title. Structure your text - if allowed use section headings. Present the information in short paragraphs rather than a solid block of text. Write short sentences. If allowed, provide images/charts/diagrams to help break up the text.
1.Choose a research topic and develop a working title. Having a strong interest in your research topic will certainly help you to keep going when the journey becomes more challenging. The research topic is the subject of your research, which is a part of a broader field of study.
STEP (2): Provide relevant personal and professional detai ls. STEP (3): Provide a short abstract or summary of around 300 words. STEP (4): Supply six keywords to describe the research proposal ...
that a research proposal is the backbone of any research work that guide us throughout the research work. and helps to come up with new knowledge in the researcher's interest area. A good research ...
Budgets are an integral part of proposals that have a direct effect on how monies can be used, are tracked, and are audited in the post award period. Start here: Stanford ORA Budget Resource Page - find templates and helpful links and information including California's partial sales and use tax exemption for research and development equipment
You want to write a grant but are not sure where to begin. Or you have ideas but need help narrowing them down and developing them into a project plan. If either is true for you, read on for steps to take towards building your next proposal. Step 1: What do you want to do? If you have many ideas but are not sure how to focus your efforts, start ...
Talk to prospective referees about reference letters, provide them with the appropriate deadline and detailed information to assist them with writing an informed assessment. Work on your research proposal/program statement. Apply for admission to a graduate program at Waterloo, if applicable.
About 68 percent and 66 percent of voters, respectively, were in favor of canceling the opening of the Tel Aviv Global Center and the University's dual degree program with Tel Aviv University. April 24, 2024 House Speaker Mike Johnson (R-La.) held a press conference on Low Steps alongside Foxx and demanded Shafik step down. House Speaker Mike ...