- [email protected]

Education System in Nepal: Structure, Challenges and Solutions
Article 12 Feb 2023 25222

Education is a critical aspect of human development and progress, and it is no different in the case of Nepal. With a rich history and cultural heritage, Nepal is a fascinating country with a diverse population. The education system in Nepal has undergone significant changes and developments over the years, and this article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the current state of education in Nepal.
Overview of the Education System in Nepal:
The education system in Nepal is governed by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology, and it is structured into primary, secondary, and higher education. The education system in Nepal is free and compulsory for children aged 5 to 16 years. The Nepalese government has made significant efforts to improve access to education, particularly in rural and remote areas, and the results have been encouraging.
Historical Background and Evolution of Education in Nepal:
The history of education in Nepal can be traced back to ancient times when the Gurukula system was prevalent. This traditional system of education was based on apprenticeship, where students would live with their teachers and learn various subjects, including religion, philosophy, and practical skills. As Nepal opened to the influence of other countries, including Britain, the education system underwent significant changes, and modern schools were introduced. As the country has maintained its sovereignty throughout history.
During the Rana dynasty (1846-1951), the education system in Nepal was confined to the ruling class, and the majority of the population was illiterate. It wasn't until the 1950s, after the fall of the Rana dynasty and the introduction of democratic governance, that the education system in Nepal began to expand. During this period, the Nepalese government made efforts to improve access to education and to provide education to all sections of the population. The education system in Nepal was further expanded in the 1960s when the government introduced a policy of compulsory education, making primary education free and compulsory for all children.
Over the next few decades, the education system in Nepal continued to evolve and expand. In the 1980s, the government introduced a policy of extending free education to the secondary level, and in the 1990s, the government established a number of universities, which helped to expand access to higher education in Nepal.
Structure of the Education System in Nepal:
Primary Education: Primary education in Nepal is mandatory for children aged 5 to 11 years, and it lasts for six years. The primary education curriculum covers subjects such as Nepali, mathematics, science, and social studies.
Secondary Education: Secondary education in Nepal lasts for five years and is divided into two stages, lower secondary and upper secondary. The lower secondary stage lasts for three years, while the upper secondary stage lasts for two years. The curriculum at the secondary level includes subjects such as Nepali, mathematics, science, and social studies, as well as elective subjects such as arts, music, and physical education.
Higher Education: Higher education in Nepal includes colleges and universities, and it is optional for students who have completed their secondary education. The higher education system in Nepal offers a wide range of programs, including bachelor's degrees in arts, science, and commerce, as well as master's and PhD programs.
Current State of Education in Nepal:
The current state of education in Nepal is a mixed picture, with both positive developments and ongoing challenges. On the one hand, there has been significant progress in increasing access to education and improving the quality of education in Nepal in recent years. On the other hand, there are still significant disparities in access to education and in the quality of education, particularly in rural areas and for children from disadvantaged backgrounds.
- Enrollment and Literacy Rates: The enrollment rate in primary education in Nepal has increased in recent years, reaching 85% in 2019, according to the World Bank. Additionally, the literacy rate in Nepal has increased from 65% in 2015 to 72% in 2019.
- Access to Education: The Nepalese government has made significant efforts to increase access to education, particularly in rural areas. Programs such as the Community Schools Program have successfully enrolled over 50,000 students from underprivileged backgrounds.
- Quality of Education: Despite progress in increasing access to education, the quality of education remains a concern. Many schools lack basic infrastructure and qualified teachers, and the quality of education received by students in rural areas is often lower than that received by urban students.
- Teacher Training and Availability: The Nepalese government has made efforts to improve teacher training and increase the availability of qualified teachers, particularly in rural areas. However, there is still a shortage of qualified teachers in many areas, and many teachers remain inadequately trained.
- Gender Disparities: Despite progress in increasing access to education for girls in Nepal, significant disparities remain. Girls are still less likely to attend school and to complete their education than boys, particularly in rural areas.
Challenges Faced by the Education System in Nepal:
Despite the progress made in recent years, the education system in Nepal still faces several challenges. One of the biggest challenges is the lack of resources, particularly in rural and remote areas, where infrastructure and facilities are limited. Another challenge is the quality of education, which is often poor, and teacher training and development are also lacking. Furthermore, there are significant disparities in access to education between urban and rural areas, and between different socio-economic groups.
Some of the major challenges facing the education system in Nepal include:
- Low Enrollment and Attendance Rates: Despite the introduction of compulsory education, many children in Nepal, especially in rural areas, do not attend school. According to the latest data from the World Bank, the net enrollment rate in primary education in Nepal was only 85% in 2019. Additionally, many children who do enroll in school drop out before completing their education.
- Poor Quality of Education: The quality of education in Nepal remains a major concern. Many schools lack basic infrastructure, such as toilets and drinking water facilities, and the teacher-student ratio is often high, leading to overcrowded classrooms and inadequate attention for individual students. Additionally, many teachers in Nepal are poorly trained, and there is a shortage of qualified teachers in many rural areas.
- Lack of Resources: The Nepalese government faces significant challenges in providing sufficient resources for the education system. The government budget allocation for education remains low, and many schools lack adequate funding for basic supplies and infrastructure. This has a negative impact on the quality of education and student outcomes.
- Inequality: Despite the government's efforts to provide education to all sections of the population, significant disparities remain in access to education and in the quality of education. Children from disadvantaged backgrounds, including those from low-income families and from rural areas, face significant barriers to accessing education, and the quality of education they receive is often lower than that of their urban peers.
- Political Instability: Political instability and frequent changes in government have had a negative impact on the education system in Nepal. This has led to a lack of consistency in policy and has hindered the government's ability to effectively implement reforms and initiatives aimed at improving the education system.
Government Initiatives and Policies to Improve the Education System:
The Nepalese government has taken various initiatives and implemented policies to improve the education system in Nepal. One of the most successful government-led initiatives is the Community Schools Program, which has enrolled over 50,000 students from underprivileged backgrounds. The program provides free education, as well as other resources such as textbooks, uniforms, and meals to students in rural areas where access to education is limited. The program has been instrumental in increasing enrollment and reducing dropout rates, and it serves as a model for other initiatives aimed at improving access to education in Nepal.
Another initiative that has been introduced in recent years is the implementation of digital classrooms in some schools in Nepal. This has not only improved the quality of education by providing students with access to digital resources and educational technology, but it has also helped to reduce the burden on teachers, who are now able to use digital tools to enhance their teaching methods.
Despite these efforts, the education system in Nepal still faces a number of challenges. One of the major challenges is the shortage of trained and qualified teachers. Many schools in rural areas lack trained teachers, which leads to low-quality education and high dropout rates. In addition, the lack of adequate infrastructure and facilities in many schools is another challenge, as this makes it difficult for students to receive a proper education.
Another challenge facing the education system in Nepal is the lack of funding and resources. The government has limited resources to invest in education, and this has resulted in a lack of investment in infrastructure, teacher training, and other resources necessary to provide quality education to students. As a result, many schools in Nepal are under-resourced and are unable to provide students with the education they need to succeed.
Despite these challenges, the future prospects for the education system in Nepal are positive. The Nepalese government has demonstrated a commitment to improving the education system, and it has taken a number of important steps towards achieving this goal. Additionally, international organizations and non-governmental organizations have been providing support and resources to help the Nepalese government achieve its goals.
Recommendations
Given the challenges faced by the education system in Nepal, it is clear that a comprehensive approach is needed to address these issues and improve the quality of education in Nepal. Improving the education system in Nepal requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing investment in education, teacher training and support, promoting gender equality, improving the quality of education, and encouraging private sector involvement. With the right investments and policies, it is possible to build a strong and effective education system in Nepal that will provide all children with access to quality education.
Here are a few recommendations that could help to achieve this goal:
- Increase investment in education: The Nepalese government should increase investment in the education sector, to provide better infrastructure, teacher training and support, and educational materials for students. This will improve the quality of education and increase access to education for all children, especially those in rural areas.
- Address teacher shortages: The Nepalese government should take steps to address the shortage of qualified teachers, particularly in rural areas, by providing teacher training and support programs and increasing incentives for teachers to work in rural areas.
- Promote gender equality: The Nepalese government should take steps to promote gender equality in education, by providing girls with equal access to education and by addressing the social and cultural barriers that prevent girls from attending school and completing their education.
- Improve quality of education: The Nepalese government should work to improve the quality of education by implementing national curriculum standards, ensuring that all schools have adequate resources and infrastructure, and providing regular teacher training and support programs.
- Emphasize early childhood education: The Nepalese government should place a strong emphasis on early childhood education, to provide children with the foundation they need for future academic success and to help break the cycle of poverty.
- Encourage private sector involvement: The Nepalese government should encourage private sector involvement in the education sector, through public-private partnerships and other initiatives, to help provide additional resources and support for education in Nepal.
In conclusion, the education system in Nepal has come a long way since its inception, and it has made significant progress in recent years. However, it still faces a number of challenges, including a shortage of trained teachers, lack of adequate infrastructure and facilities, and lack of funding and resources. The Nepalese government and international organizations have demonstrated a commitment to improving the education system, and with the right resources and support, the future prospects for education in Nepal are bright.
Empowering First Nations Youth: Teaching and Learning in the Yukon's Communities
20 essential questions to ask before choosing your college, key consider while studying it course: skills & resources guide, what should i consider when choosing a college, can a commerce student do bit, top 10 essential time management tips for students, student success: 10 proven strategies for academic excellence, top 10 benefits of a good study environment, 10 tips to create a good study environment at home, how to study for exam last minute: effective & easy tips to ace it, time management skills every student needs to succeed, global innovation collaborations for economic growth and problem-solving, impact of social media influencers on consumer markets & economy, exploring the benefits of mind mapping for effective study techniques, impact of e-commerce evolution on small businesses & local economies, effective study techniques to boost learning & memory retention, economic measures to promote sustainable agriculture, social learning theory of albert bandura: a complete guide for educators.
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Education system of Nepal: impacts and future perspectives of COVID-19 pandemic
Khadka bahadur pal, buddha bahadur basnet, ramesh raj pant, kiran bishwakarma, kopila kafle, namraj dhami, motee lal sharma, lal b thapa, binod bhattarai, youb raj bhatta.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author. [email protected]
Received 2021 May 25; Revised 2021 Aug 17; Accepted 2021 Sep 14; Collection date 2021 Sep.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
The academic sectors are badly affected by the COVID-19 pandemic globally. The studies regarding the implications of COVID-19 in education in Nepal were minimal, thus, this paper aims to highlight the impacts of the pandemic on the education sector of Nepal. It is revealed that the Nepalese academia has been facing problems due to lack of adequate and appropriate sustainable infrastructure for the online system, including skilled human resources. In addition, limited internet facilities in remote and rural areas were the other challenging tasks for virtual academic activities. Therefore, the concerned stakeholders should provide necessary services and appropriate strategies for virtual means of the education system to compensate the repercussion caused by the pandemic. This study could be helpful to identify the critical needs emerged due to the pandemic at present and in future and also contribute to adopt appropriate policy for the revival of educational institutions.
Keywords: COVID-19, Pandemic, Virtual education, Online education, Nepal
COVID-19; Pandemic; Virtual education; Online education, Nepal.
1. Introduction
The year 2020 was started with the terror of the COVID-19 and witnessed the indelible imprints of the pandemic on the global community ( WHO, 2020 ). The global health emergency due to COVID-19 was declared by the World Health Organization (WHO) on 30 th January 2020. Subsequently, it was declared a pandemic after more than 118,000 infected population by COVID-19 from 114 countries with 4,291 deaths up to 11 th March 2020. Globally, up to 6 th August 2021, there have been over 200 million confirmed cases, including the deaths over 42 million ( WHO, 2021 ).
WHO recommended the countries across the world to take precautionary measures to break the transmission chain of the coronavirus ( Barkur and Vibha Kamath, 2020 ). Among the different prevention strategies, the lockdown was considered as one of the best approaches for interrupting transmission, which was widely adopted by the global community ( Flaxman et al., 2020 ). Therefore, many of the countries in the world imposed lockdown throughout the national and regional levels. In the same line, the Government of Nepal (GoN) also announced the first lockdown on 24 th March 2020 and continued for about six months ( Basnet et al., 2021a , 2021b ). Besides the lockdown, effective tracking, tracing, quarantine, social distancing, and hygienic behaviours of some countries such as China controlled the disease spread successfully ( Basnet et al., 2021c ). However, the lockdown has not been sufficient in many countries ( Zhu et al., 2020 ).
The lockdown imposed noxious impacts affecting the psycho-sociological and livelihoods of people. On one side, the new cases of the virus around the globe are increasing and on the other side, the commencement of lockdown has affected a more significant number of sectors, including academia ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). Importantly, the academia victimized severely from the lockdowns owing to the COVID-19 pandemic. Most academic institutions such as schools, colleges, and universities remained closed during the lockdown period. Still, the academic activities have not been resumed fully as usual with face-to-face instructions.
The pandemic challenges in the education systems have been the greatest ever faced by the world community ( Azzi-Huck and Shmis, 2020 ). According to the United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), the closures of academic institutions have impacted more than 1.5 billion students and youth across the globe directly/indirectly ( UNESCO, 2020 ). The COVID-19 pandemic has changed the world, creating the need for new actions from society, including universities and academia ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2021 ). Cease of the physical presence of students and teachers in the classroom for teaching and learning have switched the academic institutions to online teaching and virtual education. The educational institutions faced an economic crisis due to less number enrollment of students, delay in fee collection, and the management of alternate methods for teaching and learning. The institutions tried to adopt the alternate methods for teaching and learning such as online or virtual methods which are not likely to provide the quality of education as delivered in the classroom ( Panthee et al., 2020 ; Viner et al., 2020 ). Such challenges of the COVID-19 to the education sector especially in the developing countries like Nepal are the severer than the developed countries as the former countries have limited facilities of online systems (e.g., internet, devices, and skilled human resources) ( Poudel and Subedi, 2020 ). In the case of Nepal, the academic institutions remained closed for a long time during the lockdown, and some of them started to manage alternate ways of teaching with the prolongation of lockdown. The government institutions were affected mainly in two ways: firstly, they were turned into quarantine stations, and secondly, there were limited facilities including internet access, computer devices, and a skilled workforce. After the lockdown, the government of Nepal has given authority to the local governments to decide on resuming the academic institutions as usual, and many of the institutions are partially or fully reopened, but the health experts have warned that this decision has increased the risk of the virus transmission ( Poudel and Subedi, 2020 ).
The number of darks sides of the COVID-19 pandemic has given opportunities to the researchers to explore new avenues of cure and treatments and other several facts related to the disease. Many of the researchers have engaged in analyzing the consequences of this pandemic, focusing on different sectors such as environment, agriculture, business, tourism, economy, and education, etc ( Pant et al., 2021 ; Azzi-Huck and Shmis, 2020 ; Barkur and Vibha Kamath, 2020 ; Flaxman et al., 2020 ; IAU, 2020 ). Such analysis, findings, and recommendations have contributed to the nations making policies and strategies to combat future pandemics. However, it has been felt that the studies regarding the implications of COVID-19 in the education sector are minimal. In the context of Nepal, the publications related to the facts are almost naught. Thus, this paper aims to highlight the impacts of COVID-19 on the education sector of Nepal.
This study is based on both primary and secondary data. The electronic databases through Google Scholar, Science Direct, and published reports of national and international organizations were the secondary sources of information on COVID-19. A manual search was conducted to search related articles to gather relevant literature ( Kapasia et al., 2020 ). A survey was also conducted by preparing a short questionnaire (open-ended) to collect primary data. The questionnaire was formatted to collect information on the impacts of COVID-19 in academic institutions. Altogether 35 academic institution heads [10 government schools, 10 private boarding schools, 5 Council for Technical Education and Vocational Training (CTEVT) institutions, 5 university constituent campuses, and 5 university-affiliated campuses] were requested to respond to the questionnaire. Authorities of the Federal GoN, Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, provincial and local governments, and universities were consulted as the key informants. The questionnaire was validated with the help of a review by two experts from medical sciences and two experts from the education sector in Nepal. In addition, before the review, the questionnaire was subjected to purposive sampling of 10 respondents from the Kathmandu valley for the pilot test.
3. Education system in Nepal
In Nepal, the school-level education comprises the primary level (1–8) and secondary level (9–12). There are a total of 35,055 schools in Nepal, of which 27,728 are public schools (community schools), 6,206 private schools, and 1,121 religious schools (Muslim religious schools, Gumbas/Vihar , and Hindu A shrams schools) ( DoE 2018 , Figure 1 ). Thus, there are 7,214,525 students enrolled in school level (grade 1–12) in the year 2018/19. Out of the total enrolment, 77% of students are at the primary level and 23% at the secondary level. Meanwhile, 4,124,478; 1,368,620; and 62,281 students were enrolled in public, private, and religious schools at the primary level, respectively. Similarly, 1,152,674; 294,732; and 610 students were enrolled in public, private, and religious schools at the secondary level, respectively ( DoE 2018 ).
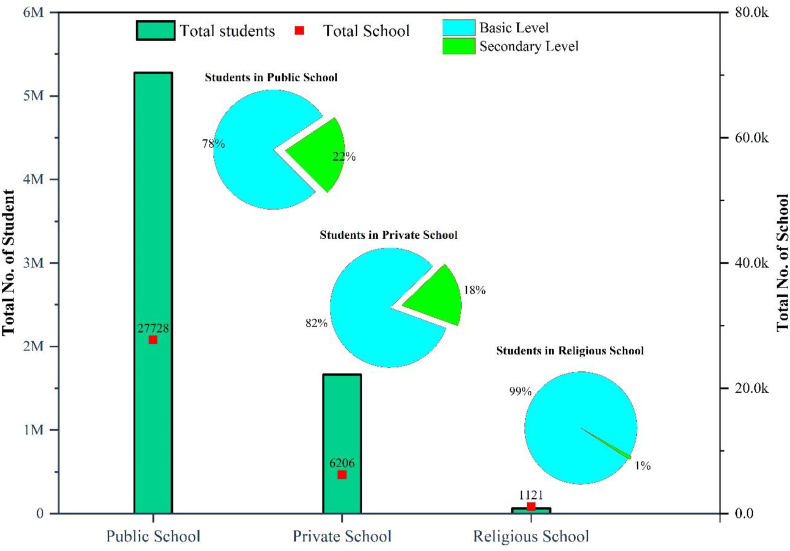
Students enrollment in public, private and religious schools in Nepal ( DoE 2018 ).
The education imparted after the secondary level is considered higher education (tertiary education) in Nepal. According to a report of the University Grants Commission (UGC), Nepal, there are 11 universities and six autonomous medical academies that offer higher education in Nepal ( UGC, 2020 , Table 1 ). Higher education is offered at the universities, of which the Tribhuvan University (TU) is the oldest and largest one. The universities in Nepal currently provide courses on sciences and technology; education; management; social sciences and humanities; law; engineering; forestry; medicine; agriculture and animal sciences; Ayurved; Sanskrit, etc. These academic programs run based on annual and semester systems at bachelor, master, MPhil, and PhD levels. Depending upon the nature of the courses, the time duration allocated to accomplish the programs varies with universities. For example, the bachelors, masters, MPhil, and PhD courses require 3–4, 2, 1.5, and 3 years, respectively, in most of the academic institutions in Nepal. The academic, research, and administrative activities are governed by the rules and regulations of the concerned institutions.
Status of students and Universities in Nepal (2017) ( UGC, 2020 ).
Under the umbrella of Higher education in Nepal, 1,425 campuses and 423,996 students enrolled in different academic programs ( UGC, 2020 ). According to the office of planning directorate (TU), it has 1,124 campuses (62 constituents and 1,062 affiliated campuses). Open and distance learning programs have been adopted by the National Open University (NOU). The NOU programs are designed for e-based learning for interested students. The relevance and need for such open and distance learning programs markedly increased under the context of pandemic situations. Regarding the enrollment percentage, the TU has the highest i.e., 79.04 % while Pokhara University, Purbanchal University, and Kathmandu University have the enrollment 6.94 %, 6.16 %, and 4.23% students, respectively ( UGC, 2020 ). Among the enrolled students, 78.6% and 21.4% were enrolled in general and technical programs, respectively. The students in management; education; and humanities and social sciences were 46.78%, 17.88%, and 13.20%, respectively. There are 7.11% of students in science and technology, and only 6.08% and 6.55% of students are in medicine and engineering, respectively ( Figure 2 ).
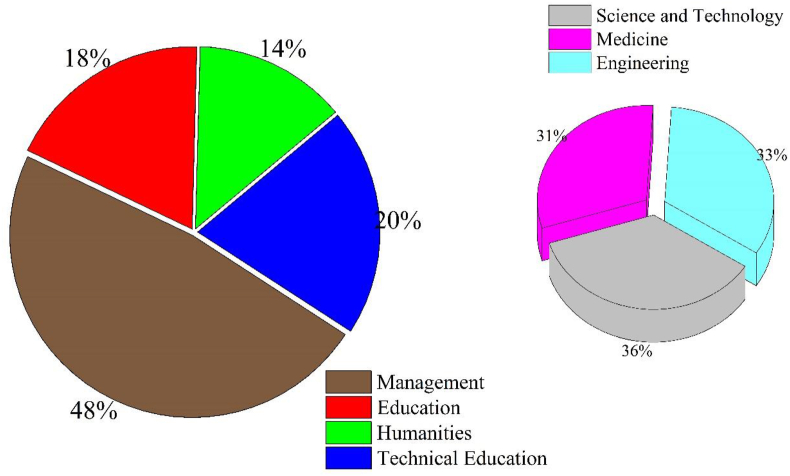
Current scenario of students distributions in different faculties at higher education level ( UGC, 2020 ).
The provincial-level distribution of students in tertiary education revealed that >50% of students are concentrated in the Bagmati Province only while the least number of students (3.31%) are studying in the Karnali Province. The dominancy order of number of students is Bagmati Province > Lumbini Province > Province no. 1 > Gandaki Province > Province no. 2 > Sudurpaschim Province > Province no. 1 > Karnali Province ( Figure 3 ). The share of student enrollment in the community campuses is 30.29%, whereas constituent campuses and private campuses have received 32.41% and 37.30%, respectively ( UGC, 2020 ). The data shows that private campuses have relatively higher number of students enrolled in Nepal.
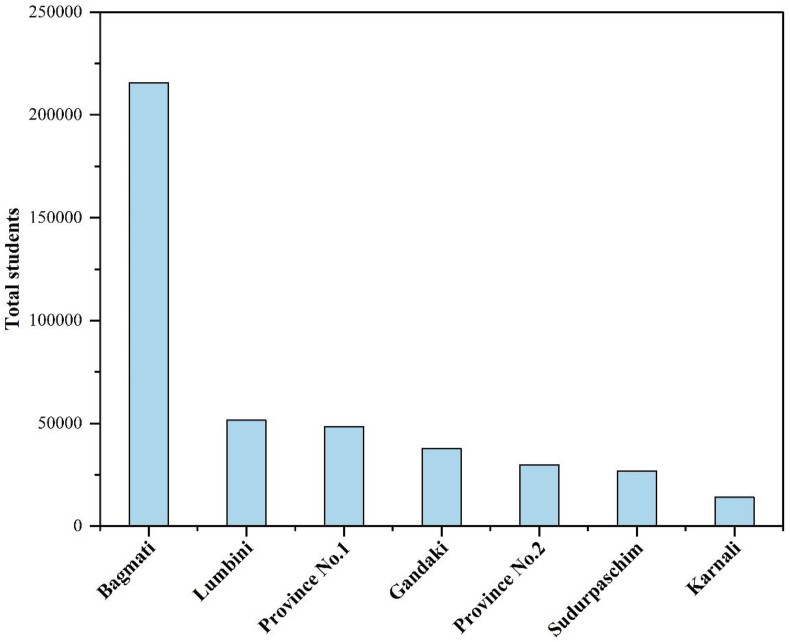
Provincial status of students at higher education level ( UGC, 2020 ).
Regarding the academic institutions' student evaluation and monitoring system, schools and universities have different provisions in Nepal. There is an annual examination system with midterm and internal evaluations for the basic level students under the direct supervision of respective schools and local governments. Furthermore, students are evaluated by annual examinations for the school level, including internal and midterm evaluations by the respective schools and the local government. However, the final examination of grade XII is provisioned to be examined by the National Education Board (NEB). In tertiary education, both the internal evaluations and final examinations are held at the end of each semester or year. Tribhuvan University has reintroduced the semester systems from 2012 onwards, and students are evaluated internally (40%) by the respective campuses/departments and externally (60%) by the concerned office of the dean under the Office of the Controller of the Examinations ( TU, 2012 ). The Council for Technical Education and Vocational Training (CTEVT) has adopted semester systems from the beginning of all programs ( DoE, 2018 ). Notably, most of the school and tertiary level examinations are held in a conventional system with physical presence and there was no application of virtual means of teaching and learning.
4. Appraisal of COVID-19 impacts in Nepalese education system
Regarding the recent gloom and doom scenario created by the COVID-19 pandemic in academia, many countries have tried to adopt various virtual media for learning and teaching activities. The COVID-19 lockdown was implemented at the end of the academic session (March, 2020), which directly hindered both school and university academic calendars in Nepal. The nationwide lockdown immediately impacted the pre-scheduled examinations of the grade 10 to 12. In addition, the scheduled semester examinations of many universities had been postponed. As the lockdown prolonged, almost all the academic activities, including examinations halted. It has directly affected the teaching-learning activities of nearly 8,796,624 students belonging to pre-primary (11%), primary (28%), secondary (39%), and tertiary (5%) levels nationwide, as estimated by UNESCO ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). The questionnaire survey and key informant interviews in this study have highlighted the several aspects of impacts of COVID-19 lockdown on academia in Nepal.
The impacts of COVID-19 on academia has directly affected the students, teachers, and parents. The challenges and impacts of the pandemic highlighted by the respondents were cancellation of board exams, irregularity in learning and skills development, assessments, restriction to study abroad, disrupted the enrollment cycle, inequality in access to education, anxiety to start schools and universities, etc. In higher education, laboratory-based research and field works are greatly hindered. In addition, there may also be decreased funding to continue or undertake new research and innovative activities in the universities in Nepal ( Michael and Murphy, 2020 ).
The lockdown has reduced the enrollment of students and increased the risk of dropout rate. In addition, it has created the obligation for the academic institutions to switch on the virtual media to maintain the pre-announced academic calendars. A transition phase of the traditionaleducational system to the digital system appeared and the Nepalese academia started partially or fully digital system with prolongation of the lockdown. The academic institutions became engagged on transformations in policy formulation, infrastructure development, searching appropriate online methods of teaching, and conducting assessments. As there was a lack of proper planning and educational guidelines previously for online teaching and learning, most of the universities and schools could not run any online models of pedagogical approaches in the initial phase ( MWU, 2020 ).
A handful number of colleges and schools launched online classes in urban areas. The majority of the respondents highlighted that comparing to the physical classes, the online methods are relatively less effective due to more absenteeism and irregularities of the students. It has been estimated that only 9% of the total students from Nepal are getting online classes, and >90% of the students from rural and urban areas are still out of such virtual courses. Currently, 12% of schools and 56% of households have internet facilities, while 51% of students are using media such as radio and TV ( Dawadi et al., 2020 ). It shows that the remaining 44% of students are unlikely to regularly access online or other media, which could be one of the serious concerns for the policymakers of the academic sectors ( Marahatta et al., 2020 ).
Meanwhile, the greatly impacted sector by the COVID-19 pandemic is the research activities in higher education, according to the respondents. The research activities such as field researches had been postponed, and the laboratory research activities remained suspended by the universities. According to the informants, the numbers of chemical reagents and enzymes prepared for upcoming experiments basically in the laboratory based research were worthless due to the closer of the laboratories for an extended period. Master and PhD level dissertations were delayed, and the time-bound research grants and scholarships were cancelled. In such a situation, academia and the policymakers were in dilemmas to design a clear roadmap about the commencement of academic activities. Limited internet facilities, computer devices, and lack of skilled human resources hindered running virtual classes and other activities. It was a challenging to connect the studnets from the rural and remote areas of Nepal in the online classes. The virtual courses are even more challenging for those learners who are differently able students which is consistent around the globe ( Manzoor, 2020 ; Chalise and Dhungana, 2020 ). Notably, the closures of academic institutions have resulted in multi-faceted implications such as disrupting completion of the syllabus on time, the regular cycle of academic intakes, semester end examinations required for graduation.
Despite the pandemic situation, there were some positive impacts on academia at the same time. It had allowed reshaping the of pedagogical strategies and adapt to innovative e-learning techniques. Schools and universities decided to introduce a digital education system. Several platforms, such as Zoom, Google Meet, Microsoft Teams, and Social Media including Viber, WhatsApp, Facebook, were given priority by the academia to run the academic activities online. For instance, with the help of Microsoft Teams, TU initiated its virtual academic activities with 500,000 users (teachers and students) ( TU, 2020 ). In the history of Nepalese academia, this was one of the most outstanding achievements for the paradigm shift of the conventional pedagogical approaches. The learners and education provider institutions used media such as television, radio networks, YouTube, and other social media. Interestingly, the literacy and expertise on computers, apps, and virtual platforms have improved at the grass-root level. The universities conducted training for teachers and students for the online system of joining in academic activities.
The schools and higher education institutions expanded ICT infrastructures to support ICT associated teaching/learning. Most of the institutions have also prepared their guideline for facilitating online classes and assessment systems under the direction of the GoN and the University Grants Commission (UGC). Academic institutions have also initiated collaborations with local to national media such as Radios, FMs, and TVs. The virtual media have significant positive impacts on providing educational content and lives call with teachers in support of students ( Hiltz and Wellman, 1997 ). As the cases of COVID-19 are still increasing globally, the public policies significantly, the academic policies should be revised and strictly follow with the epidemiological alerts ( Yáñez et al., 2020 ). Precisely, the COVID-19 situation compelled all the academic institutions and stakeholders for redesigning and reconsidering their teaching-learning and research approaches.
5. Future perspectives and conclusion
The schools and HEIs in Nepal have limited digital services, including electronic libraries, relevant online scientific publications, and other resources. The major challenge for the institutions was conducting assessments and exams online. In the context of Nepal, many children from low-income families and disadvantaged groups do not afford even the necessities of learning, such as textbooks, notebooks, and other required stationaries. Modern digital devices, including smartphones, iPad, iPods, laptops, computers, the internet, etc., are far from their expectations ( UNESCO and IESALC, 2020 ). On the other side, the people in the remote and rural areas are deprived of online access due to limited internet facilities. In this context, providing equal opportunity for virtual learning to all groups of people and all parts of the country has become challenging. Therefore, the federal, provincial, and local governments are urged to switch their strategies and programs towards modern virtual education systems. For this purpose, different programs for enhancing the capacities of human resources, students, institution authorities, management, and parents are recommended. It is essential to understand the behaviour of learners about online and face-to-face academic activities to ensure the best academic outcomes ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2020b ).
Due to the lack of adequate and appropriate sustainable infrastructure in Nepalese academia for the online system, developing such infrastructure is indispensable. The infrastructures for virtual education (internet facilities and digital devices) should be affordable to institutions of remote and rural areas. Especially the poor and disadvantaged groups should be prioritized, clustered, and trained in low/no cost by the government. The international and national organizations anduniversity graduates could be mobilized as volunteers to teach in rural areas. The school education boards and universities should prioritize to revise their curricula including internship or community services for their students to share the knowledge and expertise to the needy people in rural and remote areas in Nepal. The institutions should consider adjustments in terms of accessibility, infrastructure, and equipment from a long term perspective.
Additionally, within traditional pedagogical approaches, the blended modes of education system could be implemented to improve the quality of education at an affordable cost with limited trained human resources. The activities such as homework assignments, open-book exams, home take exams, quizzes, or small projects can be considered as the options of conventional paper-based examinations. Moreover, some modes of communication such as chat channels and discussion groups in social media could also benefit to the learners. There is limited preparedness to cope with such pandemic in Nepal, thus, there must be cooperation and coordination among the different sectors to combat the impacts of COVID-19. There could be a multifactorial fight during the pandemic to increase health literacy, develop better detection tools, and enable action by local, provincial and federal governments ( Alvarez-Risco et al., 2020c ). Continuous awareness and sensitization about the risks of COVID-19 also play a vital role to reduce the havoc created by the pandemic ( Quispe-Cañari et al., 2021 ).
Overall, this study comprises the education system in Nepal and COVID-19 imprints in the school and university education in Nepal. Also, we have tried to highlight the pros and cons of the pandemic on academia during the lockdown and suggested the possible way forwards. In this context, the concerned stakeholders should provide necessary services and develop appropriate strategies for virtual means of the education system to compensate for the repercussion caused by COVID-19 lockdown. Sustainable solutions are essential to manage the crisis and build a resilient education system in the long run. Thus, the insights from this study could be helpful to cope with the problem due to the pandemic and contribute to adopting an appropriate policy for the revival of educational institutions. Also, the present work contributes to the necessary way forward to tackle the crisis in academia in Nepal in the future.
Declarations
Author contribution statement.
All authors listed have significantly contributed to the development and the writing of this article.
Funding statement
This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency.
Data availability statement
All data are available described in the article.
Declaration of interests statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Not applicable.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (MoEST), Department of Education (DoE), GoN and University Grants Commission (UGC), Nepal for supporting data in this research.
- Alvarez-Risco A., Mejia C.R., Delgado-Zegarra J., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Arce-Esquivel A.A., Valladares-Garrido M.J., The Peru approach against the COVID-19 infodemic: insights and strategies. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020;103(2):583–586. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.20-0536. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Risco A., Estrada-Merino A., de las Mercedes Anderson-Seminario M., Mlodzianowska S., García-Ibarra V., Villagomez-Buele C., Carvache-Franco M. ITSE; 2020. Multitasking Behaviour in Online Classrooms and Academic Performance: the Case of university Students in Ecuador during COVID-19 Outbreak. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alvarez-Risco A., Del-Aguila-Arcentales S., Rosen M.A., García-Ibarra V., Maycotte-Felkel S., Martínez-Toro G.M. Expectations and interests of university students in covid-19 times about sustainable development goals: evidence from Colombia, Ecuador, Mexico, and Peru. Sustainability. 2021;13(6):3306. [ Google Scholar ]
- Azzi-Huck K., Shmis T. 2020. Managing the Impact of COVID-19 on Education Systems Worldwide: How Countries Are Preparing, Copying, and Planning for Recovery. https://blogs.worldbank.org/education/managing-impact-COVID-19-education-systems-around-world-how-countries-are-preparing [ Google Scholar ]
- Barkur G., Vibha Kamath G.B. Sentiment analysis of nationwide lockdown due to COVID 19 outbreak: evidence from India. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2020;51:102089. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2020.102089. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Bishwakarma K., Pant R.R., Dhakal S., Pandey N., Gautam D., Ghimire A., Basnet T.B. Combating the COVID-19 pandemic: experiences of the first wave from Nepal. Front. Public Health. 2021;12(9):613402. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2021.613402. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Pant R.R., Bishwakarma K., Paudel S., Pandey N., Adhikari S.K., Ranabhat K., Ghimire A. A year trend analysis and spatial distribution of COVID-19 cases in Nepal. Asia Pac. J. Publ. Health. 2021 doi: 10.1177/10105395211012233. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Basnet B.B., Basnet R., Panday R. Prospects for controlling future pandemics of SARS in highlights of SARS-CoV-2. VirusDis. 2021 doi: 10.1007/s13337-021-00715-1. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chalise H.N., Dhungana H.N. Fears of COVID-19 catastrophe as Nepal reports death from new Coronavirus. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Disabil. 2020;6:47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dawadi S., Giri R., Simkhada P. Sage submissions; 2020. Impact of COVID-19 on the Education Sector in Nepal- Challenges and Coping Strategies. [ Google Scholar ]
- Department of Education . 2018. Flash Report I (2017-2018), Sanothimi, Bhaktapur, Nepal. https://www.doe.gov.np/assets/uploads/files/cbe2b2b1ae68bb5bdaa93299343e5c28.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Flaxman S., Mishra S., Gandy A., Unwin H.J.T., Mellan T.A., Coupland H., Bhatt S. Estimating the effects of non-pharmaceutical interventions on COVID-19 in Europe. Nature. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2405-7. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hiltz S.R., Wellman B. Vol. 40. 1997. Asynchronous Learning Networks as a Virtual Classroom; pp. 44–49. (9) [ Google Scholar ]
- International Association of Universities . 2020. The Impact of COVID-19 on Higher Education Worldwide Resources for Higher Education Institutions. https://www.iau-aiu.net/IMG/pdf/COVID-19_and_he_resources.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Kapasia N., Paul P., Roy A., Saha J., Zaveri A., Mallick R., Barman B., Das P., Chouhan P. Impact of lockdown on learning status of undergraduate and postgraduate students during COVID-19 pandemic in West Bengal, India. Child. Youth Serv. Rev. 2020;116:105194. doi: 10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105194. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Manzoor A. 2020. Online Teaching and Challenges of COVID-19 for Inclusion of PWDs in Higher Education. https://dailytimes.com.pk/595888/online-teaching-and-challenges-of-covid-19-for-inclusion-of-pwds-in-higher-education/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Marahatta S., Paudel S., Aryal N. COVID-19 Pandemic: what can Nepal do to curb the potential public health disaster? JKAHS. 2020;3(1):1–14. https://www.jkahs.org.np/jkahs/index.php/jkahs/article/view/213 [ Google Scholar ]
- Michael P., Murphy A. COVID-19 and emergency e-Learning: consequences of the securitization of higher education for post-pandemic pedagogy. Contemp. Secur. Pol. 2020;41(3) [ Google Scholar ]
- Mid-Western University . 2020. Digital, Virtual and Alternative Teaching-Learning and Operating Systems Policy Guidelines (2020) https://www.mwu.edu.np/mwu-dvatlosp-guideline-2020/news/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Poudel K., Subedi P. Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on socioeconomic and mental health aspects in Nepal. Int. J. Soc. Psychiatr. 2020;66(8):748–755. doi: 10.1177/0020764020942247. 2020 12. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Panthee B., Dhungana S., Panthee N., Paudel A., Gyawali S., Panthee S. COVID-19: the current situation in Nepal. New Microbes New Infect. 2020;37:100737. doi: 10.1016/j.nmni.2020.100737. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Pant R.R., Bishwakarma K., Qaiser F.U.R., Pathak L., Jayaswal G., Sapkota B., Pal K.B., Thapa L.B., Koirala M., Rijal K., Maskey R. Imprints of COVID-19 lockdown on the surface water quality of Bagmati river basin, Nepal. J. Environ. Manang. 2021;289:112522. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112522. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Quispe-Cañari J.F., Fidel-Rosales E., Manrique D., Mascaró-Zan J., Huamán-Castillón K.M., Chamorro–Espinoza S.E., Mejia C.R. Self-medication practices during the COVID-19 pandemic among the adult population in Peru: a cross-sectional survey. Saudi Pharmaceut. J. 2021;29(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2020.12.001. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Tribhuvan University Online Class Nirdeshika. 2020. https://neporesult.com/news_notices/tribhuwan-university-online-class-nirdeshika/ [ Google Scholar ]
- TU . B.S. Tribhuvan University; Kathmandu, Nepal: 2012. Tribhuvan University, TU semester system operational guideline - 2070. [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO . UNESCO; 2020. COVID-19: Impact on Education. https://en.unesco.org/covid19/educationresponse [ Google Scholar ]
- UNESCO and IESALC COVID-19 and higher education: today and tomorrow. Impact analysis, policy responses and recommendations. Isaac. 2020;(9):1–46. http://www.iesalc.unesco.org/en/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/COVID-19-EN-090420-2.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- University Grant Commission . 2020. Education Management Information System (EMIS), UGC Report on Higher Education 2017-2018. https://www.ugcnepal.edu.np/uploads/publicationsAndReports/b6ABmh.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Viner R.M., Russell S.J., Croker H., Packer J., Ward J., Stansfield C., Mytton O., Bonell C., Booy R. School closure and management practices during coronavirus outbreaks including COVID-19: a rapid systematic review. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health. 2020;4(5):397–404. doi: 10.1016/S2352-4642(20)30095-X. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . 2020. World health organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. https://www.who.int. [ Google Scholar ]
- WHO . 2021. World health organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak. https://covid19.who.int/ [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Yáñez J.A., Alvarez-Risco A., Delgado-Zegarra J. Covid-19 in Peru: from supervised walks for children to the first case of Kawasaki-like syndrome. BMJ. 2020;369:m2418. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m2418. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zhu N., Zhang D., Wang W., Li X., Yang B., Song J., Tan W. A novel coronavirus from patients with pneumonia in China 2019. NEJM. 2020;382:723–733. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001017. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
- View on publisher site
- PDF (679.5 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections
- Essay Samples
- College Essay
- Writing Tools
- Writing guide

↑ Return to College Essay
Education system in Nepal – Research Essay
Introduction
In my research essay, I explore the education system in Nepal. I am already aware that the education system in Nepal was based on home schooling and Gurukula, but since they become a democracy in 1951, they have made many improvements. It is my intention to find out what those improvements are.
Methodology
My main methodology will include reading written research on the subject from local libraries, University libraries, and trusted online resources. I will also research and read records and websites relating to trusted statistics. They have school and higher education, where a student has to apply for higher education as people have to in other countries.
A student gets a school-leaving certificate for completing school and getting their education. Grades 11 and 12 are considered higher secondary education, for which a student gets a certificate for completing by the HSEB, which is the Higher Secondary Education Board.
If you opt for higher education, then you may earn your bachelor degree, masters and PhD in a Nepal college. There is also vocational education that starts in lower school and allows a person to work towards a trade and get a “Technical School leaving Certificate”. Research
The first school in Nepal was made only for elite learners and was opened in 1853. More have come about since democracy broke out in Nepal, and again in 1971 when the country built its education department and started allowing and funding schools in Nepal.
In 1971, there was a literacy rate of 5%. There were also a total of 10,000 students spread across 300 schools. Now much of the population receives some sort of education and the number of schools, big and small, is 49,000. The adult literacy rate has jumped from just 5% to 60.3%.
Nepal has done a good job to come so far in such as short space of time, but there is still a long way to go. Poverty and social exclusion are two very big restraints on people and their ability to get a good (or usable) education. There are also more males getting an education than females. There are 46.3% of females getting an education, whereas there are 73% of males getting an education. These are very good figures and show that the government in Nepal has been working towards improving the education system in Nepal. Conclusion
The education system in Nepal is not as bad as it was, but there are still massive holes in their education system. They really need to up the pace if they want to get anywhere near to the quality levels of many other countries.
There are clearly more opportunities for students in Nepal these days than there was, and they have certainly created a good structure on which to build a good education system, but it needs a lot of work. Too many people are excluded from school because of poverty or social exclusion, and females are not getting as good of an education than male students are (especially since fewer females attend school).

Follow Us on Social Media
Get more free essays

Send via email
Most useful resources for students:.
- Free Essays Download
- Writing Tools List
- Proofreading Services
- Universities Rating
Contributors Bio

Find more useful services for students
Free plagiarism check, professional editing, online tutoring, free grammar check.
The Status of School Education in Nepal: Educating the Nation Through Schooling
- Living reference work entry
- Latest version View entry history
- First Online: 04 December 2020
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Pramod Bhatta 3 &
- Archana Mehendale 4
Part of the book series: Global Education Systems ((GES))
77 Accesses
1 Citations
Nepal, once seen as an “education virginland,” has made rapid progress over the years in establishing an education system. After Nepal emerged from the Rana rule in 1951, one of the first ambitions of the new, multiparty democratic regime was to institute a national, uniform, and universal system of education in the country. The establishment of the Ministry of Education with external assistance and the National Education Planning Commission laid the foundation of an education system that brought together diverse schools being run by local communities. The structure of school education and the policy frameworks governing them has been gradually evolving in tandem with the global norms and policy influence of development partners.
This chapter provides a critical-historical overview of the development and institutionalization of modern education in Nepal. The developments made with regards to improving access to education, equity, and quality of education are presented. The chapter also presents the constitutional and legal frameworks that make education a right of every citizen of Nepal and discusses the institutional evolution of the governance structures related to regulation and funding of school education. Critical issues related to education privatization and the role of donor agencies is highlighted.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

The Status of School Education in Nepal

The Education System of Mexico
School education systems and policies in south asia.
ActionAid Nepal and Norad. (2017). Nepal citizens’ education report . Retrieved from https://nepal.actionaid.org/sites/nepal/files/nepal_national_citizens_education_report.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Aryal, K. R. (1970). Education for the development of Nepal . Kathmandu: Shanti Prakashan.
Google Scholar
Basnet, K. (2003). 100 years of Nepal-Nippon. Nepali Times . Issue # 175 (19 Dec 2003–25 Dec 2003). Retrieved from http://archive.nepalitimes.com/news.php?id=6142#.Xml_bahKhPY on 11 Mar 2020.
Bhatta, P. (2011). Aid agency influence in national education policy-making: A case from Nepal’s ‘education for all’ movement. Globalisation, Societies and Education, 9 (1), 11–26.
Article Google Scholar
Bhatta, P. (2014). Public desire for private schooling in Nepal. In I. Macpherson, S. Robertson, & G. Walford (Eds.), Education, privatisation and social justice: Case studies from Africa, South Asia and South East Asia . Oxford: Symposium.
Bhatta, P. (2015). Privatization through affiliation: Trajectories of higher education expansion in post-1990 Nepal. Studies in Nepali History and Society, 20 (2), 303–333. Retrieved from http://www.martinchautari.org.np/files/SINHAS-Articles/SINHAS-Vol.20-No.2_Pramod-Bhatta.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Bhatta, P., & Budhathoki, S. (2013). Understanding private education scapes in Nepal . London: Privatisation in Education Research Initiative (PERI)/Open Society Foundations.
Bhatta, P., & Pherali, T. (2017). Nepal: Patterns of privatisation in education. A case study of low-fee private schools and private chain schools . Education International. Retrieved from https://download.ei-ie.org/Docs/WebDepot/Research_Nepal_final.pdf on 16 Mar 2020.
Central Bureau of Statistics. (2011). Nepal living standards survey 2010/11. Statistical report Vol 2 . National Planning Commission Secretariat. Government of Nepal. Retrieved from https://time.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/statistical_report_vol2.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Constituent Assembly Secretariat. (2015). Constitution of Nepal 2015 . Unofficial translation by Nepal Law Society, IDEA and UNDP. Retrieved from http://extwprlegs1.fao.org/docs/pdf/nep155698b.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Constitution of the Kingdom of Nepal 2047. (1990). Dated 9 Nov 1990. Retrieved from https://www.refworld.org/docid/3ae6b4fa10.html on 11 Mar 2020.
Department of Education. (2005). Flash I report 2005/06 . Sanothimi/Bhaktapur: Department of Education.
Department of Education. (2015). Flash II report 2015–16 . Sanothimi/Bhaktapur: Department of Education.
Education Review Office. (2015). Report on National Assessment of Student Achievement (NASA) 2013 (Grade 8: Mathematics, Nepali and Science) . Kathmandu: Education Review Office. Retrieved from http://www.ero.gov.np/assets/uploads/files/NASA_2013_Grade_8_Report.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Eide, A. H., Neupane, S., & Hem, K. G. (2016). Living conditions among people with disability in Nepal. SINTEF Technology and Society, Department of Health Research. Retrieved from https://www.sintef.no/globalassets/sintef-a27656-nepal-printversionfinal.pdf on 16 Mar 2020.
Fuller, B. (1991). Growing up modern: The Western state builds third world schools . New York: Routledge.
Interim Constitution of Nepal 2063. (2007) (repealed). Dated 15 Jan 2007. Retrieved from https://www.refworld.org/docid/46badd3b2.html on 11 Mar 2020.
Kushiyait, B. K. (n.d.). Research report on financing gap in education . National Campaign for Education Nepal (NCE-Nepal). Retrieved from http://ncenepal.org.np/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Education-Financing-Gap-research-report.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Mihaly, E. B. (2002). Foreign aid and politics in Nepal: a case study. 2nd edition. Kathmandu: Himal Books.
Ministry of Education. (1971). The national education system plan for 1971–76 . Kathmandu: Ministry of Education.
Ministry of Education. (2014). Nepal education in figures 2014 at-a-glance . Kathmandu: Government of Nepal.
Ministry of Education. (2015). Nepal education in figures 2015 at-a-glance . Kathmandu: Government of Nepal.
Ministry of Education. (2016a). Nepal education in figures 2016 at-a-glance . Kathmandu: Government of Nepal.
Ministry of Education. (2016b). School sector development plan 2016/17-2022/23 (BS 2073/74-2079/80) . Retrieved from https://www.globalpartnership.org/content/nepal-school-sector-development-plan-2016-2023 on 16 Mar 2020.
Ministry of Education. (2016c). School Sector Development Program - Teacher Rationalization and Redeployment Plan (2016/17-2023) . p.6. Retrieved from: https://www.doe.gov.np/assets/uploads/files/18fe973c8531bccad18c000e217eb37e.pdf on 13 May 2020.
Ministry of Education, Science and Technology. (2017). Nepal education in figures 2017 at-a-glance . Kathmandu: Government of Nepal.
Ministry of Finance. (2018). Economic survey 2017/18 . Kathmandu: Government of Nepal. Retrieved from https://mof.gov.np/uploads/document/file/for%20web_Economic%20Survey%202075%20Full%20Final%20for%20WEB%20_20180914091500.pdf on 9 Apr 2020.
National Education Planning Commission (NEPC). (1955). Education in Nepal: Report of the National Education Planning Commission . Kathmandu: Bureau of Publications.
National Institute for Research and Training. (2017). Nepal education sector analysis . Kathmandu. Retrieved from https://www.globalpartnership.org/sites/default/files/2019-05-nepal-education-sector-analysis.pdf on 13 Mar 2020.
Nepal Law Commission. (2018). The act relating to compulsory and free education, 2075 . Retrieved from http://www.lawcommission.gov.np/en/archives/category/documents/prevailing-law/statutes-acts/education-act-2028-1971 on 16 Mar 2020.
New Era. (2014). Nepal education studies 2012/13 school and household survey . Kathmandu: World Bank.
Parajuli, L. R. (2012). From controlling access to crafting minds: Experiments in education in Late Rana Era. Studies in Nepali History and Society, 17 (2), 297–331.
Pherali, T. (2011). Education and conflict in Nepal: Possibilities for reconstruction. Globalisation Societies and Education, 9 (1), 135–154.
Pradhan, U. (2018). National education system in Nepal: Between the ‘local’ and the ‘global’. In Education in South Asia (pp. 165–183). London: Bloomsbury Publications.
Rappleye, J. (2019). Origins of the faith: The untold story of Hugh Wood, American Development Assistance in the 1950s, and Nepal’s Modern Education System. Studies in Nepali History and Society, 24 (1), 105–141.
Savada, A. M. (1991). Nepal: A country study . Washington: Government Publishing Office for the Library of Congress.
Skerry, C. A., Moran, K., & Calavan, K. M. (1992). Four decades of development. The history of U.S. assistance to Nepal 1951–1991 . Kathmandu: United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Retrieved from https://pdf.usaid.gov/pdf_docs/PNABR755.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Sharma, S. (2002). Half a century of foreign aid. In Mihaly, E.B. (ed.) Foreign aid and politics in Nepal: a case study. p. xix-lx. Kathmandu: Himal Books.
Thapa, A. (2015). Public and private school performance in Nepal: An analysis using the SLC examination. Education Economics, 23 (1), 47–62. https://doi.org/10.1080/09645292.2012.738809 .
UNESCO/IIEP-US and Global Partnership for Education. (2016). National education accounts in Nepal: Expenditure for education 2009–2015 . Retrieved from http://uis.unesco.org/sites/default/files/nepal-nea-report.pdf on 11 Mar 2020.
Van Wessel, M., & van Hirtum, R. (2013). Schools as tactical targets in conflict: What the case of Nepal can teach us. Comparative Education Review, 57 (1), 1–21.
Wood, H. B. (1987). Nepal diary . Oregon: American Nepal Education Foundation.
Wright, D. (1877). History of Nepal . New Delhi/Madras: Asian Educational Services. Reprint 1990. Translated from the Parbatiya by Munshi Shew Shunker Singh Pandit Shri Gunachand.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Martin Chautari and Tribhuvan University, Kathmandu, Nepal
Pramod Bhatta
Centre for Education Innovation and Action Research, Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Mumbai, India
Archana Mehendale
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pramod Bhatta .

Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Mumbai, Maharashtra, India
Padma M. Sarangapani
Tata Institute of Social Sciences, Hyderabad, India
Rekha Pappu
Section Editor information
No affiliation provided
Tatsuya Kusakabe
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Bhatta, P., Mehendale, A. (2021). The Status of School Education in Nepal: Educating the Nation Through Schooling. In: Sarangapani, P.M., Pappu, R. (eds) Handbook of Education Systems in South Asia. Global Education Systems. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3309-5_16-2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3309-5_16-2
Received : 07 April 2020
Accepted : 13 April 2020
Published : 04 December 2020
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-13-3309-5
Online ISBN : 978-981-13-3309-5
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Education Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Education
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
Chapter history
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3309-5_16-2
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3309-5_16-1
- Find a journal
- Track your research

- Special Stories
- Coronavirus
- Entertainment
- Immigration
- Nepali Mahila
- Inspirational
- Events in Nepal
- Events in USA
- Global Events
- Interesting Facts
- Nepal Photos
Nepal Education System – An Overview of Challenges and Opportunities

In the run for qualitative education and the resultant good job prospects, many students across the globe prefer pursuing higher education in foreign destinations. And Nepali foreign education aspirants are no exception here.
The scenario in Nepal is such that Nepalis with a foreign degree are preferred over a Nepali student with a national degree.
This throws light on the existing curriculum and teaching methodology in the country. An overview of the past few generations knowledge gaining shows that the younger has not learned anything new than the older generations.
The Nepali education system has failed to provide the same educational standards that the global industry demands.
The current knowledge trend in Nepal is such that students are pursuing degrees not for the sake of knowledge gaining but for the sake of earning an undergraduate certification.

This in turn is creating a generation of individuals lacking self-confidence. Their lack of satisfaction in the jobs they take up in line with their stream of education is resulting in a lot of educated unemployment in Nepal.
While this trend is on the rise, Nepali employers are finding it equally difficult to find qualitative candidates who own problem solving and critical thinking skills.
Nepal Vs International Education System

Looking at what foreign universities have to offer , courses in foreign countries are research based, training students to be problem solvers. Research propels knowledge gaining and problem solving. The credit for such courses and curriculum goes to experts who design them after a lot of research and insight into the future and the current job industry requirements.
With this research-based approach, students who study at a foreign university are motivated to look for two or more references, enabling them to come up with unique documentation, supported with substantial proof.
On the other hand, the curriculum in Nepal doesn’t promote research and most of the knowledge gaining is done through model papers, referring to old Q&As and other learning material. Nepali students who produce material based on research are given lower grades in Nepal, when compared to their valuation in international universities.

However, this scenario is slowly changing and there is a steady rise of Nepali education institutions affiliated with foreign universities. The demand for students studying in such universities is very high as they are in a position to compete nationally and internationally.
International degrees challenge the intellect of students by getting them to work on a particular project or work area and gain a hands-on experience well in advance.
Even if students fail to secure higher grades, they at least have the knowledge, confidence and skill to tackle and manage complex situations at the work front.
Factors Challenging Nepal’s Education System

The following factors pose a challenge to Nepal’s education system:
1) Political Instability and bureaucracy
Nepal has witnessed a series of political upheavals in the last three decades. This has impacted the education system and has held it back from working independently.
Government support and the freedom for the education system to make critical decisions pertaining to the sector can majorly uplift the education system in Nepal.
2) Lack of Practical learning approach
Although the curriculum of Nepal is not completely backward, it lacks a practical approach to learning, where students are motivated to research, create and learn from their own experience.
Additionally, the education system is not strict with plagiarism and encourages students to rely and study only from limited material. Students in Nepal should be made to conduct research, gain hand-on experience and be given the choice to make their own decisions.
3) Job-driven knowledge gaining
Many Nepali graduates are educating themselves only to get jobs. Instead, the education system in Nepal should encourage students to develop entrepreneurial skills and critical thinking skills and enable to become free thinkers.
Nepal’s education system should enable students to develop entrepreneurial skills and others to help them become more proactive in self-growth and national building in the larger picture.
4) Nepalis Permanently Settling Abroad
The situation in Nepal is such that the society is divided into well-to do students whose families are financially sound and they go to foreign countries only to study a particular course and come back to run family businesses. However, this is a smaller majority.
On the other hand, there are a number of students who go abroad to seek permanent residence and then take up jobs in those destinations to payback their loans.
Students should come back to Nepal to help support the development of the nation. Foreign destinations are highly developed due to the knowledge and skill individuals receive in their respective nations’ educational institutions. These skills in return are utilized in the development of their countries.
Conclusion It’s high time that Nepal considered a review of its curriculum and teaching methodologies. Only then will it be at par with the international education standards and provide a generation of capable, self-confident and knowledgeable individuals.
For more Nepal education news, visit NepaliSansar’s Education page.
Related Articles:-
- Nepal Medical Education Commission Increases Scholarship Quota by 65 Percent
- The World University Rankings 2020: Nepal’s TU Enters Top World Universities
- Nepal Education Loan – Eligibility & Documents for Student Loan

Nepal Jumps 16 Places to Secure 94th Rank in World Business Index

Tihar 2076 (2019) Celebrations In Nepal
Related " Education " Stories
- Nepal Launches Nurturing Excellence in Higher Education Program!
- Nepal’s Mid-West University Signs MoU with India’s Chandigarh University!
- Pandemic Mayhem: 4.5 Million Girls at Risk of Missing School!
- SEE 2079 Registration Dates Announced! Register Now!
- SEE 2078 Application Date Released! Apply Now!
- 2021 Nepal-EU Film Festival Kick Starts!
- Nepal’s 12th Class Examinations Kickoff Today
- Grade XI Supplementary Exam Routine 2078 Released! Check Now!
Related Posts

Most Discussed

Nepal Budget FY 2078/79 (2021/22): Highlights and Key Takeaways!

- Most Recent
- DFW-Himalayas Football Club bags the 7thNepali New Year Cup
- 7 Budgetary Highlights Which Are Set to Spruce Up Nepali Tourism
- Activists Demand Chief Justice of Nepal to be Investigated
- Nepal witnesses COVID-19 uptick with 220 new cases
- 5 Cafés Which Reflect the Serene Nature of Kathmandu
- Nepal Bars Entry for South Africans
- Nepali trade deficit widens to NPR 568.17 billion
- Trek or vacation? Do Both at these Nepali Basecamps
- NEB Board Grade 12th Exam Routine 2078
- SEE Exam 2078 Routine Class 10 2078
- NEB Class 12 Results 2077 with Marksheet
- Public Holidays in Nepal 2021
- Live Updates! Gold Price Rates
- Best Nepali Short Films on YouTube Watch For Free
- Best Jobs for Nepalese in the United States!
- Visit Nepal 2020 Tourist Arrivals
- Miss Nepal Winners List From 1994-2020
- 2020 Nepal Tourist Arrivals
- Nepal, China Announces New Height of Mt Everest at 8,848.86M

Subscribe to our Newsletter
Sign up for more inspiring latest news, events, tourism, and more from Nepalisansar.
Privacy Overview

- Nepal Gallery
Recent Posts
Recent comments.
- January 2022
- December 2021
- November 2021
- October 2021
- September 2021
- August 2021
- February 2021
- January 2021
- December 2020
- November 2020
- October 2020
- September 2020
- August 2020
- February 2020
- January 2020
- December 2019
- November 2019
- October 2019
- September 2019
- August 2019
- February 2019
- January 2019
- December 2018
- November 2018
- October 2018
- September 2018
- August 2018
- February 2018
- January 2018
- December 2017
- November 2017
- October 2017
- September 2017
- August 2017
- February 2017
- Uncategorized
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
Switch to the dark mode that's kinder on your eyes at night time.
Switch to the light mode that's kinder on your eyes at day time.
Nepal Educational System Landscape: Recent Reforms and Ongoing Challenges.
Nepal education system navigates a dynamic terrain, balancing tradition with modern aspirations. Recent years have witnessed significant changes, presenting both opportunities and challenges for learners across the country.
Structure and Reform:
Nepal’s education system offers a minimum of 12 years of foundational education, spanning pre-primary to secondary levels. The landmark School Leaving Certificate (SLC) exam remains a crucial gateway to higher education. However, recent reforms have introduced vocational and technical streams, diversifying pathways for student success. The curriculum itself is undergoing revisions, aiming to foster critical thinking, practical skills, and local relevance.

Winds of Progress:
The Nepalese government has made strides towards educational inclusivity. The Constitution guarantees free and compulsory basic education, and initiatives like community schools are expanding access in remote areas. Technology is also playing an increasingly central role, with digital platforms bridging geographical divides and offering innovative learning opportunities.
Persistent Obstacles:
Despite these commendable advancements, obstacles remain. Rural areas grapple with inadequate infrastructure, teacher shortages, and limited resources. Gender disparities persist, with girls facing higher dropout rates. Additionally, while the growth of private schools offers more options, it can exacerbate affordability issues.

The Road Ahead:
As Nepal education system navigates its evolving landscape, ensuring equitable access to quality education for all students remains paramount. Addressing structural inequalities, continuously improving learning environments, and harnessing the potential of technology will be crucial in scaling the remaining peaks.
Challenges Faced by the Nepal Education System :
1. access and enrollment:.
- Discuss challenges related to access to education, especially in rural areas.
- Highlight disparities in enrollment rates among different demographics.
2. Quality of Education:
- Explore issues related to the quality of education.
- Discuss efforts to improve teacher training and curriculum development.
- Some schools, especially in the countryside, don’t have enough teachers or materials. This can make it harder to learn.
3. Infrastructure and Resources:
- Address challenges related to inadequate infrastructure and resources.
- Discuss the impact on the learning environment and student outcomes.
4. Gender Disparities:
- Explore gender-related challenges in education.
- Discuss efforts to promote gender equality and empower female students.
- Some kids, especially girls or those from poor families, still have trouble getting to school.
5. Technological Integration:
- Evaluate the integration of technology in education.
- Discuss challenges and opportunities in adopting digital learning methods.
6. Language of Instruction:
- Discuss the role of language in education.
- Explore challenges related to language barriers and their impact on learning outcomes.
Ongoing Efforts and Solutions:
1. government initiatives:.
- Highlight specific government programs aimed at addressing educational challenges.
- Discuss their impact and potential for improvement.
2. Community Involvement:
- Explore the role of communities and NGOs in supporting education.
- Highlight successful community-driven initiatives.
Learn more about how organizations like UNICEF are working to address these inequities: https://www.unicef.org/nepal/education
Check out this cool video about a community school in Nepal: https://www.thedigitalbiography.com/top-seven-community-schools-in-nepal/
Nepal education system is at a crucial juncture, with significant progress alongside persistent challenges. By investing in teacher training, embracing technology, and fostering local ownership, Nepal can move closer to ensuring equitable access to quality education for all its citizens.
Written by Gunjan
What do you think.

Udhauli: Celebrating the Harvest in Nepal.

Nepal Waterfalls: Top 10 Must-Visit Waterfall Places in Nepal.
Copyright © 2022 O.M.G. Media Pvt. Ltd.
Username or Email Address
Forgot password?
Enter your account data and we will send you a link to reset your password.
Your password reset link appears to be invalid or expired.
Privacy policy.
To use social login you have to agree with the storage and handling of your data by this website. %privacy_policy%
Add to Collection
Public collection title
Private collection title
No Collections
Here you'll find all collections you've created before.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The education system in Nepal is governed by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology, and it is structured into primary, secondary, and higher education. The education system in Nepal is free and compulsory for children aged 5 to 16 years.
Overall, this study comprises the education system in Nepal and COVID-19 imprints in the school and university education in Nepal. Also, we have tried to highlight the pros and cons of the pandemic on academia during the lockdown and suggested the possible way forwards.
This country profile describes current trends in education and student mobility in Nepal and provides an overview of the Nepali education system. It replaces an earlier version by Nick Clark, published in 2013. Nepal is an increasingly important sending country for international students.
Primary education in Nepal is called Basic Education and consists of grades one through eight. Secondary levels are grades nine to twelve. In 2021, the literacy rates of the country were 71.2% (81% for males and 63.3% for females). [3]
In my research essay, I explore the education system in Nepal. I am already aware that the education system in Nepal was based on home schooling and Gurukula, but since they become a democracy in 1951, they have made many improvements.
The chapter traces the rise of modern education in Nepal, examines the current status of such education by looking at access and equity, and quality of education. It also describes the institutional evolution of school governance and concludes by highlighting a number of policy issues affecting the growing crisis of legitimacy of the public ...
Many Nepali graduates are educating themselves only to get jobs. Instead, the education system in Nepal should encourage students to develop entrepreneurial skills and critical thinking skills and enable to become free thinkers.
Nepal education system is at a crucial juncture, with significant progress alongside persistent challenges. By investing in teacher training, embracing technology, and fostering local ownership, Nepal can move closer to ensuring equitable access to quality education for all its citizens.
Neupane (2019) argues that Nepal’s public education―both school education and university education―are in disadvantage state due to the lack of resources, especially the lack of advanced educational technology.
The main goal of education in Nepal is to contribute to workforce development and poverty reduction. Indeed, the public expect an education to provide better life outcomes for themselves and their children.