
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

About the Research and Synthesis Tables
Research Tables and Synthesis Tables are useful tools for organizing and analyzing your research as you assemble your literature review. They represent two different parts of the review process: assembling relevant information and synthesizing it. Use a Research table to compile the main info you need about the items you find in your research -- it's a great thing to have on hand as you take notes on what you read! Then, once you've assembled your research, use the Synthesis table to start charting the similarities/differences and major themes among your collected items.
We've included an Excel file with templates for you to use below; the examples pictured on this page are snapshots from that file.
- Research and Synthesis Table Templates This Excel workbook includes simple templates for creating research tables and synthesis tables. Feel free to download and use!
Using the Research Table

This is an example of a research table, in which you provide a basic description of the most important features of the studies, articles, and other items you discover in your research. The table identifies each item according to its author/date of publication, its purpose or thesis, what type of work it is (systematic review, clinical trial, etc.), the level of evidence it represents (which tells you a lot about its impact on the field of study), and its major findings. Your job, when you assemble this information, is to develop a snapshot of what the research shows about the topic of your research question and assess its value (both for the purpose of your work and for general knowledge in the field).
Think of your work on the research table as the foundational step for your analysis of the literature, in which you assemble the information you'll be analyzing and lay the groundwork for thinking about what it means and how it can be used.
Using the Synthesis Table

This is an example of a synthesis table or synthesis matrix , in which you organize and analyze your research by listing each source and indicating whether a given finding or result occurred in a particular study or article ( each row lists an individual source, and each finding has its own column, in which X = yes, blank = no). You can also add or alter the columns to look for shared study populations, sort by level of evidence or source type, etc. The key here is to use the table to provide a simple representation of what the research has found (or not found, as the case may be). Think of a synthesis table as a tool for making comparisons, identifying trends, and locating gaps in the literature.
How do I know which findings to use, or how many to include? Your research question tells you which findings are of interest in your research, so work from your research question to decide what needs to go in each Finding header, and how many findings are necessary. The number is up to you; again, you can alter this table by adding or deleting columns to match what you're actually looking for in your analysis. You should also, of course, be guided by what's actually present in the material your research turns up!
- << Previous: Synthesizing Research
- Next: Additional Resources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics
- Research Guides
- Vanderbilt University Libraries
- Peabody Library
Literature Reviews
Literature review table.
- Steps to Success: The Literature Review Process
- Literature Reviews Webinar Recording
- Writing Like an Academic
- Publishing in Academic Journals
- Managing Citations This link opens in a new window
- Literature Review Table Template Peabody Librarians have created a sample literature review table to use to organize your research. Feel free to download this file and use or adapt as needed.
- << Previous: Literature Reviews Webinar Recording
- Next: Writing Like an Academic >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 4:20 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.vanderbilt.edu/peabody/litreviews

- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
Published on 22 February 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 7 June 2022.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research.
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarise sources – it analyses, synthesises, and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Why write a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1: search for relevant literature, step 2: evaluate and select sources, step 3: identify themes, debates and gaps, step 4: outline your literature review’s structure, step 5: write your literature review, frequently asked questions about literature reviews, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a dissertation or thesis, you will have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position yourself in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your dissertation addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
You might also have to write a literature review as a stand-alone assignment. In this case, the purpose is to evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of scholarly debates around a topic.
The content will look slightly different in each case, but the process of conducting a literature review follows the same steps. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research objectives and questions .
If you are writing a literature review as a stand-alone assignment, you will have to choose a focus and develop a central question to direct your search. Unlike a dissertation research question, this question has to be answerable without collecting original data. You should be able to answer it based only on a review of existing publications.
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research topic. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list if you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can use boolean operators to help narrow down your search:
Read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
To identify the most important publications on your topic, take note of recurring citations. If the same authors, books or articles keep appearing in your reading, make sure to seek them out.
You probably won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on the topic – you’ll have to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your questions.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models and methods? Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- How does the publication contribute to your understanding of the topic? What are its key insights and arguments?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible, and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can find out how many times an article has been cited on Google Scholar – a high citation count means the article has been influential in the field, and should certainly be included in your literature review.
The scope of your review will depend on your topic and discipline: in the sciences you usually only review recent literature, but in the humanities you might take a long historical perspective (for example, to trace how a concept has changed in meaning over time).
Remember that you can use our template to summarise and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using!
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It’s important to keep track of your sources with references to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography, where you compile full reference information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
You can use our free APA Reference Generator for quick, correct, consistent citations.
To begin organising your literature review’s argument and structure, you need to understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly-visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat – this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organising the body of a literature review. You should have a rough idea of your strategy before you start writing.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarising sources in order.
Try to analyse patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organise your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text, your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
If you are writing the literature review as part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate your central problem or research question and give a brief summary of the scholarly context. You can emphasise the timeliness of the topic (“many recent studies have focused on the problem of x”) or highlight a gap in the literature (“while there has been much research on x, few researchers have taken y into consideration”).
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, make sure to follow these tips:
- Summarise and synthesise: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole.
- Analyse and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole.
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources.
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transitions and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts.
In the conclusion, you should summarise the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasise their significance.
If the literature review is part of your dissertation or thesis, reiterate how your research addresses gaps and contributes new knowledge, or discuss how you have drawn on existing theories and methods to build a framework for your research. This can lead directly into your methodology section.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a dissertation , thesis, research paper , or proposal .
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarise yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, June 07). What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a dissertation proposal | a step-by-step guide, what is a theoretical framework | a step-by-step guide, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
Reference management. Clean and simple.
Literature review

How to write a literature review in 6 steps
How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.

How to write a systematic literature review [9 steps]
How do you write a systematic literature review? What types of systematic literature reviews exist and where do you use them? Learn everything you need to know about a systematic literature review in this guide

What is a literature review? [with examples]
Not sure what a literature review is? This guide covers the definition, purpose, and format of a literature review.

About Systematic Reviews
Summary of Findings Table in a Systematic Review

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
What is a summary of findings table.
The Cochrane Review defines the “summary of findings table” as a structured tabular format in which the primary findings of a review, particularly information related to the quality of evidence, the magnitude of the effects of the studied interventions, and the aggregate of available data on the main outcomes, are presented. It includes multiple pieces of data derived from both quantitative and qualitative data analysis in systematic reviews . These include information about the main outcomes, the type and number of studies included, the estimates (both relative and absolute) of the effect or association, and important comments about the review, all written in a plain-language summary so that it’s easily interpreted. It also includes a grade of the quality of evidence; i.e., a rating of its certainty.
Most systematic reviews are expected to have one summary of findings table. But some studies may have multiple, if the review addresses more than one comparison, or deals with substantially different populations that require separate tables. The studies in a table can also be grouped in terms of applied intervention type, type of outcome measure, the type of participants, the study design etc..
How Do You Make A Summary Of Findings Table For A Systematic Review?
Learn more about distillersr.
(Article continues below)
What Does A Summary Of Findings Table Include?
A summary of findings table typically includes the following information:
- A description of the population and setting addressed by the available evidence
- A description of comparisons addressed in the table, including all interventions
- A list of the most important outcomes, whether desirable or undesirable (limited to seven)
- A measure of the burdens of each outcome
- The magnitude of effect measured for each outcome (both absolute and relative)
- The participants and studies analyzed for each outcome
- An assessment of the certainty of the evidence for each outcome (typically using GRADE)
- Explanations
It’s best to include evidence profiles, i.e. additional tables that support the data in the summary of findings, to which the review may be linked. It also may be neat to have a study descriptor table different from a results table. The study descriptor table shows information about the characteristics of included studies, like study design, study region, participant information, etc. The results table mostly contains outcomes, outcome measures, study results, etc. These can help provide readers with more context about the review, and its conclusions.
Final Takeaway
3 reasons to connect.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
Literature Review Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Literature Review Template
If you’re working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction . We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template . This includes:
- The literature review opening/ introduction section
- The theoretical framework (or foundation of theory)
- The empirical research
- The research gap
- The closing section
We then progress to the sample literature review (from an A-grade Master’s-level dissertation) to show how these concepts are applied in the literature review chapter. You can access the free resources mentioned in this video below.
PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Literature Review Example
Literature review example: frequently asked questions, is the sample literature review real.
Yes. The literature review example is an extract from a Master’s-level dissertation for an MBA program. It has not been edited in any way.
Can I replicate this literature review for my dissertation?
As we discuss in the video, every literature review will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your literature review to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a literature review here .
Where can I find more examples of literature reviews?
The best place to find more examples of literature review chapters would be within dissertation/thesis databases. These databases include dissertations, theses and research projects that have successfully passed the assessment criteria for the respective university, meaning that you have at least some sort of quality assurance.
The Open Access Thesis Database (OATD) is a good starting point.
How do I get the literature review template?
You can access our free literature review chapter template here .
Is the template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the template and you are free to use it as you wish.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .

You Might Also Like:

What will it take for you to guide me in my Ph.D research work?
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Harvey Cushing/John Hay Whitney Medical Library
- Collections
- Research Help
YSN Doctoral Programs: Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
- Biomedical Databases
- Global (Public Health) Databases
- Soc. Sci., History, and Law Databases
- Grey Literature
- Trials Registers
- Data and Statistics
- Public Policy
- Google Tips
- Recommended Books
- Steps in Conducting a Literature Review
What is a literature review?
A literature review is an integrated analysis -- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question. That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
A literature review may be a stand alone work or the introduction to a larger research paper, depending on the assignment. Rely heavily on the guidelines your instructor has given you.
Why is it important?
A literature review is important because it:
- Explains the background of research on a topic.
- Demonstrates why a topic is significant to a subject area.
- Discovers relationships between research studies/ideas.
- Identifies major themes, concepts, and researchers on a topic.
- Identifies critical gaps and points of disagreement.
- Discusses further research questions that logically come out of the previous studies.
APA7 Style resources
APA Style Blog - for those harder to find answers
1. Choose a topic. Define your research question.
Your literature review should be guided by your central research question. The literature represents background and research developments related to a specific research question, interpreted and analyzed by you in a synthesized way.
- Make sure your research question is not too broad or too narrow. Is it manageable?
- Begin writing down terms that are related to your question. These will be useful for searches later.
- If you have the opportunity, discuss your topic with your professor and your class mates.
2. Decide on the scope of your review
How many studies do you need to look at? How comprehensive should it be? How many years should it cover?
- This may depend on your assignment. How many sources does the assignment require?
3. Select the databases you will use to conduct your searches.
Make a list of the databases you will search.
Where to find databases:
- use the tabs on this guide
- Find other databases in the Nursing Information Resources web page
- More on the Medical Library web page
- ... and more on the Yale University Library web page
4. Conduct your searches to find the evidence. Keep track of your searches.
- Use the key words in your question, as well as synonyms for those words, as terms in your search. Use the database tutorials for help.
- Save the searches in the databases. This saves time when you want to redo, or modify, the searches. It is also helpful to use as a guide is the searches are not finding any useful results.
- Review the abstracts of research studies carefully. This will save you time.
- Use the bibliographies and references of research studies you find to locate others.
- Check with your professor, or a subject expert in the field, if you are missing any key works in the field.
- Ask your librarian for help at any time.
- Use a citation manager, such as EndNote as the repository for your citations. See the EndNote tutorials for help.
Review the literature
Some questions to help you analyze the research:
- What was the research question of the study you are reviewing? What were the authors trying to discover?
- Was the research funded by a source that could influence the findings?
- What were the research methodologies? Analyze its literature review, the samples and variables used, the results, and the conclusions.
- Does the research seem to be complete? Could it have been conducted more soundly? What further questions does it raise?
- If there are conflicting studies, why do you think that is?
- How are the authors viewed in the field? Has this study been cited? If so, how has it been analyzed?
Tips:
- Review the abstracts carefully.
- Keep careful notes so that you may track your thought processes during the research process.
- Create a matrix of the studies for easy analysis, and synthesis, across all of the studies.
- << Previous: Recommended Books
- Last Updated: Jan 4, 2024 10:52 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.yale.edu/YSNDoctoral
MSU Libraries
- Need help? Ask a Librarian
Nursing Literature and Other Types of Reviews
- Literature and Other Types of Reviews
- Starting Your Search
- Constructing Your Search
- Selecting Databases and Saving Your Search
- Levels of Evidence
- Creating a PRISMA Table
- Literature Table and Synthesis
- Other Resources
About Literature Tables and Writing a Synthesis
A literature table is a way to organize the articles you've selected for inclusion in your publication. There are many different types of literature tables-the main thing is to determine the important pieces that help draw out the comparisons and contrasts between the articles included in your review. The first few columns should include the basic info about the article (title, authors, journal), publication year, and the purpose of the paper.
While the table is a step to help you organize the articles you've selected for your research, the literature synthesis can take many forms and can have multiple parts. This largely depends on what type of review you've undertaken. Look back at the examples under Literature and Other Types of Reviews to see examples of different types of reviews.
- Example of Literature Table
Examples of Literature Tables

Camak, D.J. (2015), Addressing the burden of stroke caregivers: a literature review. J Clin Nurs, 24: 2376-2382. doi: 10.1111/jocn.12884

Balcombe, L., Miller, C., & McGuiness, W. (2017). Approaches to the application and removal of compression therapy: A literature review. British Journal of Community Nursing , 22 , S6–S14. https://doi-org.proxy1.cl.msu.edu/10.12968/bjcn.2017.22.Sup10.S6
- << Previous: Creating a PRISMA Table
- Next: Other Resources >>
- Last Updated: Mar 27, 2024 3:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.lib.msu.edu/nursinglitreview
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is a Literature Review? How to Write It (with Examples)

A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing how your work contributes to the ongoing conversation in the field. Learning how to write a literature review is a critical tool for successful research. Your ability to summarize and synthesize prior research pertaining to a certain topic demonstrates your grasp on the topic of study, and assists in the learning process.
Table of Contents
- What is the purpose of literature review?
- a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
- b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
- c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
- d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
- How to write a good literature review
- Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Select Databases for Searches:
- Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Review the Literature:
- Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Frequently asked questions
What is a literature review?
A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the existing literature, establishes the context for their own research, and contributes to scholarly conversations on the topic. One of the purposes of a literature review is also to help researchers avoid duplicating previous work and ensure that their research is informed by and builds upon the existing body of knowledge.

What is the purpose of literature review?
A literature review serves several important purposes within academic and research contexts. Here are some key objectives and functions of a literature review: 2
- Contextualizing the Research Problem: The literature review provides a background and context for the research problem under investigation. It helps to situate the study within the existing body of knowledge.
- Identifying Gaps in Knowledge: By identifying gaps, contradictions, or areas requiring further research, the researcher can shape the research question and justify the significance of the study. This is crucial for ensuring that the new research contributes something novel to the field.
- Understanding Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks: Literature reviews help researchers gain an understanding of the theoretical and conceptual frameworks used in previous studies. This aids in the development of a theoretical framework for the current research.
- Providing Methodological Insights: Another purpose of literature reviews is that it allows researchers to learn about the methodologies employed in previous studies. This can help in choosing appropriate research methods for the current study and avoiding pitfalls that others may have encountered.
- Establishing Credibility: A well-conducted literature review demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with existing scholarship, establishing their credibility and expertise in the field. It also helps in building a solid foundation for the new research.
- Informing Hypotheses or Research Questions: The literature review guides the formulation of hypotheses or research questions by highlighting relevant findings and areas of uncertainty in existing literature.
Literature review example
Let’s delve deeper with a literature review example: Let’s say your literature review is about the impact of climate change on biodiversity. You might format your literature review into sections such as the effects of climate change on habitat loss and species extinction, phenological changes, and marine biodiversity. Each section would then summarize and analyze relevant studies in those areas, highlighting key findings and identifying gaps in the research. The review would conclude by emphasizing the need for further research on specific aspects of the relationship between climate change and biodiversity. The following literature review template provides a glimpse into the recommended literature review structure and content, demonstrating how research findings are organized around specific themes within a broader topic.
Literature Review on Climate Change Impacts on Biodiversity:
Climate change is a global phenomenon with far-reaching consequences, including significant impacts on biodiversity. This literature review synthesizes key findings from various studies:
a. Habitat Loss and Species Extinction:
Climate change-induced alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns contribute to habitat loss, affecting numerous species (Thomas et al., 2004). The review discusses how these changes increase the risk of extinction, particularly for species with specific habitat requirements.
b. Range Shifts and Phenological Changes:
Observations of range shifts and changes in the timing of biological events (phenology) are documented in response to changing climatic conditions (Parmesan & Yohe, 2003). These shifts affect ecosystems and may lead to mismatches between species and their resources.
c. Ocean Acidification and Coral Reefs:
The review explores the impact of climate change on marine biodiversity, emphasizing ocean acidification’s threat to coral reefs (Hoegh-Guldberg et al., 2007). Changes in pH levels negatively affect coral calcification, disrupting the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
d. Adaptive Strategies and Conservation Efforts:
Recognizing the urgency of the situation, the literature review discusses various adaptive strategies adopted by species and conservation efforts aimed at mitigating the impacts of climate change on biodiversity (Hannah et al., 2007). It emphasizes the importance of interdisciplinary approaches for effective conservation planning.

How to write a good literature review
Writing a literature review involves summarizing and synthesizing existing research on a particular topic. A good literature review format should include the following elements.
Introduction: The introduction sets the stage for your literature review, providing context and introducing the main focus of your review.
- Opening Statement: Begin with a general statement about the broader topic and its significance in the field.
- Scope and Purpose: Clearly define the scope of your literature review. Explain the specific research question or objective you aim to address.
- Organizational Framework: Briefly outline the structure of your literature review, indicating how you will categorize and discuss the existing research.
- Significance of the Study: Highlight why your literature review is important and how it contributes to the understanding of the chosen topic.
- Thesis Statement: Conclude the introduction with a concise thesis statement that outlines the main argument or perspective you will develop in the body of the literature review.
Body: The body of the literature review is where you provide a comprehensive analysis of existing literature, grouping studies based on themes, methodologies, or other relevant criteria.
- Organize by Theme or Concept: Group studies that share common themes, concepts, or methodologies. Discuss each theme or concept in detail, summarizing key findings and identifying gaps or areas of disagreement.
- Critical Analysis: Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of each study. Discuss the methodologies used, the quality of evidence, and the overall contribution of each work to the understanding of the topic.
- Synthesis of Findings: Synthesize the information from different studies to highlight trends, patterns, or areas of consensus in the literature.
- Identification of Gaps: Discuss any gaps or limitations in the existing research and explain how your review contributes to filling these gaps.
- Transition between Sections: Provide smooth transitions between different themes or concepts to maintain the flow of your literature review.
Conclusion: The conclusion of your literature review should summarize the main findings, highlight the contributions of the review, and suggest avenues for future research.
- Summary of Key Findings: Recap the main findings from the literature and restate how they contribute to your research question or objective.
- Contributions to the Field: Discuss the overall contribution of your literature review to the existing knowledge in the field.
- Implications and Applications: Explore the practical implications of the findings and suggest how they might impact future research or practice.
- Recommendations for Future Research: Identify areas that require further investigation and propose potential directions for future research in the field.
- Final Thoughts: Conclude with a final reflection on the importance of your literature review and its relevance to the broader academic community.

Conducting a literature review
Conducting a literature review is an essential step in research that involves reviewing and analyzing existing literature on a specific topic. It’s important to know how to do a literature review effectively, so here are the steps to follow: 1
Choose a Topic and Define the Research Question:
- Select a topic that is relevant to your field of study.
- Clearly define your research question or objective. Determine what specific aspect of the topic do you want to explore?
Decide on the Scope of Your Review:
- Determine the timeframe for your literature review. Are you focusing on recent developments, or do you want a historical overview?
- Consider the geographical scope. Is your review global, or are you focusing on a specific region?
- Define the inclusion and exclusion criteria. What types of sources will you include? Are there specific types of studies or publications you will exclude?
Select Databases for Searches:
- Identify relevant databases for your field. Examples include PubMed, IEEE Xplore, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar.
- Consider searching in library catalogs, institutional repositories, and specialized databases related to your topic.
Conduct Searches and Keep Track:
- Develop a systematic search strategy using keywords, Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT), and other search techniques.
- Record and document your search strategy for transparency and replicability.
- Keep track of the articles, including publication details, abstracts, and links. Use citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to organize your references.
Review the Literature:
- Evaluate the relevance and quality of each source. Consider the methodology, sample size, and results of studies.
- Organize the literature by themes or key concepts. Identify patterns, trends, and gaps in the existing research.
- Summarize key findings and arguments from each source. Compare and contrast different perspectives.
- Identify areas where there is a consensus in the literature and where there are conflicting opinions.
- Provide critical analysis and synthesis of the literature. What are the strengths and weaknesses of existing research?
Organize and Write Your Literature Review:
- Literature review outline should be based on themes, chronological order, or methodological approaches.
- Write a clear and coherent narrative that synthesizes the information gathered.
- Use proper citations for each source and ensure consistency in your citation style (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Conclude your literature review by summarizing key findings, identifying gaps, and suggesting areas for future research.
The literature review sample and detailed advice on writing and conducting a review will help you produce a well-structured report. But remember that a literature review is an ongoing process, and it may be necessary to revisit and update it as your research progresses.
Frequently asked questions
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive analysis of existing literature (published and unpublished works) on a specific topic or research question and provides a synthesis of the current state of knowledge in a particular field. A well-conducted literature review is crucial for researchers to build upon existing knowledge, avoid duplication of efforts, and contribute to the advancement of their field. It also helps researchers situate their work within a broader context and facilitates the development of a sound theoretical and conceptual framework for their studies.
Literature review is a crucial component of research writing, providing a solid background for a research paper’s investigation. The aim is to keep professionals up to date by providing an understanding of ongoing developments within a specific field, including research methods, and experimental techniques used in that field, and present that knowledge in the form of a written report. Also, the depth and breadth of the literature review emphasizes the credibility of the scholar in his or her field.
Before writing a literature review, it’s essential to undertake several preparatory steps to ensure that your review is well-researched, organized, and focused. This includes choosing a topic of general interest to you and doing exploratory research on that topic, writing an annotated bibliography, and noting major points, especially those that relate to the position you have taken on the topic.
Literature reviews and academic research papers are essential components of scholarly work but serve different purposes within the academic realm. 3 A literature review aims to provide a foundation for understanding the current state of research on a particular topic, identify gaps or controversies, and lay the groundwork for future research. Therefore, it draws heavily from existing academic sources, including books, journal articles, and other scholarly publications. In contrast, an academic research paper aims to present new knowledge, contribute to the academic discourse, and advance the understanding of a specific research question. Therefore, it involves a mix of existing literature (in the introduction and literature review sections) and original data or findings obtained through research methods.
Literature reviews are essential components of academic and research papers, and various strategies can be employed to conduct them effectively. If you want to know how to write a literature review for a research paper, here are four common approaches that are often used by researchers. Chronological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the chronological order of publication. It helps to trace the development of a topic over time, showing how ideas, theories, and research have evolved. Thematic Review: Thematic reviews focus on identifying and analyzing themes or topics that cut across different studies. Instead of organizing the literature chronologically, it is grouped by key themes or concepts, allowing for a comprehensive exploration of various aspects of the topic. Methodological Review: This strategy involves organizing the literature based on the research methods employed in different studies. It helps to highlight the strengths and weaknesses of various methodologies and allows the reader to evaluate the reliability and validity of the research findings. Theoretical Review: A theoretical review examines the literature based on the theoretical frameworks used in different studies. This approach helps to identify the key theories that have been applied to the topic and assess their contributions to the understanding of the subject. It’s important to note that these strategies are not mutually exclusive, and a literature review may combine elements of more than one approach. The choice of strategy depends on the research question, the nature of the literature available, and the goals of the review. Additionally, other strategies, such as integrative reviews or systematic reviews, may be employed depending on the specific requirements of the research.
The literature review format can vary depending on the specific publication guidelines. However, there are some common elements and structures that are often followed. Here is a general guideline for the format of a literature review: Introduction: Provide an overview of the topic. Define the scope and purpose of the literature review. State the research question or objective. Body: Organize the literature by themes, concepts, or chronology. Critically analyze and evaluate each source. Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of the studies. Highlight any methodological limitations or biases. Identify patterns, connections, or contradictions in the existing research. Conclusion: Summarize the key points discussed in the literature review. Highlight the research gap. Address the research question or objective stated in the introduction. Highlight the contributions of the review and suggest directions for future research.
Both annotated bibliographies and literature reviews involve the examination of scholarly sources. While annotated bibliographies focus on individual sources with brief annotations, literature reviews provide a more in-depth, integrated, and comprehensive analysis of existing literature on a specific topic. The key differences are as follows:
References
- Denney, A. S., & Tewksbury, R. (2013). How to write a literature review. Journal of criminal justice education , 24 (2), 218-234.
- Pan, M. L. (2016). Preparing literature reviews: Qualitative and quantitative approaches . Taylor & Francis.
- Cantero, C. (2019). How to write a literature review. San José State University Writing Center .
Paperpal is an AI writing assistant that help academics write better, faster with real-time suggestions for in-depth language and grammar correction. Trained on millions of research manuscripts enhanced by professional academic editors, Paperpal delivers human precision at machine speed.
Try it for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime , which unlocks unlimited access to premium features like academic translation, paraphrasing, contextual synonyms, consistency checks and more. It’s like always having a professional academic editor by your side! Go beyond limitations and experience the future of academic writing. Get Paperpal Prime now at just US$19 a month!
Related Reads:
- Empirical Research: A Comprehensive Guide for Academics
- How to Write a Scientific Paper in 10 Steps
- Life Sciences Papers: 9 Tips for Authors Writing in Biological Sciences
- What is an Argumentative Essay? How to Write It (With Examples)
6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Self-plagiarism in research: what it is and how to avoid it, you may also like, academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , measuring academic success: definition & strategies for excellence, what is academic writing: tips for students, why traditional editorial process needs an upgrade, paperpal’s new ai research finder empowers authors to..., what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college....
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 14: completing ‘summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence.
Holger J Schünemann, Julian PT Higgins, Gunn E Vist, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Nicole Skoetz, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group (formerly Applicability and Recommendations Methods Group) and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group
Key Points:
- A ‘Summary of findings’ table for a given comparison of interventions provides key information concerning the magnitudes of relative and absolute effects of the interventions examined, the amount of available evidence and the certainty (or quality) of available evidence.
- ‘Summary of findings’ tables include a row for each important outcome (up to a maximum of seven). Accepted formats of ‘Summary of findings’ tables and interactive ‘Summary of findings’ tables can be produced using GRADE’s software GRADEpro GDT.
- Cochrane has adopted the GRADE approach (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) for assessing certainty (or quality) of a body of evidence.
- The GRADE approach specifies four levels of the certainty for a body of evidence for a given outcome: high, moderate, low and very low.
- GRADE assessments of certainty are determined through consideration of five domains: risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision and publication bias. For evidence from non-randomized studies and rarely randomized studies, assessments can then be upgraded through consideration of three further domains.
Cite this chapter as: Schünemann HJ, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, Guyatt GH. Chapter 14: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
14.1 ‘Summary of findings’ tables
14.1.1 introduction to ‘summary of findings’ tables.
‘Summary of findings’ tables present the main findings of a review in a transparent, structured and simple tabular format. In particular, they provide key information concerning the certainty or quality of evidence (i.e. the confidence or certainty in the range of an effect estimate or an association), the magnitude of effect of the interventions examined, and the sum of available data on the main outcomes. Cochrane Reviews should incorporate ‘Summary of findings’ tables during planning and publication, and should have at least one key ‘Summary of findings’ table representing the most important comparisons. Some reviews may include more than one ‘Summary of findings’ table, for example if the review addresses more than one major comparison, or includes substantially different populations that require separate tables (e.g. because the effects differ or it is important to show results separately). In the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), all ‘Summary of findings’ tables for a review appear at the beginning, before the Background section.
14.1.2 Selecting outcomes for ‘Summary of findings’ tables
Planning for the ‘Summary of findings’ table starts early in the systematic review, with the selection of the outcomes to be included in: (i) the review; and (ii) the ‘Summary of findings’ table. This is a crucial step, and one that review authors need to address carefully.
To ensure production of optimally useful information, Cochrane Reviews begin by developing a review question and by listing all main outcomes that are important to patients and other decision makers (see Chapter 2 and Chapter 3 ). The GRADE approach to assessing the certainty of the evidence (see Section 14.2 ) defines and operationalizes a rating process that helps separate outcomes into those that are critical, important or not important for decision making. Consultation and feedback on the review protocol, including from consumers and other decision makers, can enhance this process.
Critical outcomes are likely to include clearly important endpoints; typical examples include mortality and major morbidity (such as strokes and myocardial infarction). However, they may also represent frequent minor and rare major side effects, symptoms, quality of life, burdens associated with treatment, and resource issues (costs). Burdens represent the impact of healthcare workload on patient function and well-being, and include the demands of adhering to an intervention that patients or caregivers (e.g. family) may dislike, such as having to undergo more frequent tests, or the restrictions on lifestyle that certain interventions require (Spencer-Bonilla et al 2017).
Frequently, when formulating questions that include all patient-important outcomes for decision making, review authors will confront reports of studies that have not included all these outcomes. This is particularly true for adverse outcomes. For instance, randomized trials might contribute evidence on intended effects, and on frequent, relatively minor side effects, but not report on rare adverse outcomes such as suicide attempts. Chapter 19 discusses strategies for addressing adverse effects. To obtain data for all important outcomes it may be necessary to examine the results of non-randomized studies (see Chapter 24 ). Cochrane, in collaboration with others, has developed guidance for review authors to support their decision about when to look for and include non-randomized studies (Schünemann et al 2013).
If a review includes only randomized trials, these trials may not address all important outcomes and it may therefore not be possible to address these outcomes within the constraints of the review. Review authors should acknowledge these limitations and make them transparent to readers. Review authors are encouraged to include non-randomized studies to examine rare or long-term adverse effects that may not adequately be studied in randomized trials. This raises the possibility that harm outcomes may come from studies in which participants differ from those in studies used in the analysis of benefit. Review authors will then need to consider how much such differences are likely to impact on the findings, and this will influence the certainty of evidence because of concerns about indirectness related to the population (see Section 14.2.2 ).
Non-randomized studies can provide important information not only when randomized trials do not report on an outcome or randomized trials suffer from indirectness, but also when the evidence from randomized trials is rated as very low and non-randomized studies provide evidence of higher certainty. Further discussion of these issues appears also in Chapter 24 .
14.1.3 General template for ‘Summary of findings’ tables
Several alternative standard versions of ‘Summary of findings’ tables have been developed to ensure consistency and ease of use across reviews, inclusion of the most important information needed by decision makers, and optimal presentation (see examples at Figures 14.1.a and 14.1.b ). These formats are supported by research that focused on improved understanding of the information they intend to convey (Carrasco-Labra et al 2016, Langendam et al 2016, Santesso et al 2016). They are available through GRADE’s official software package developed to support the GRADE approach: GRADEpro GDT (www.gradepro.org).
Standard Cochrane ‘Summary of findings’ tables include the following elements using one of the accepted formats. Further guidance on each of these is provided in Section 14.1.6 .
- A brief description of the population and setting addressed by the available evidence (which may be slightly different to or narrower than those defined by the review question).
- A brief description of the comparison addressed in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, including both the experimental and comparison interventions.
- A list of the most critical and/or important health outcomes, both desirable and undesirable, limited to seven or fewer outcomes.
- A measure of the typical burden of each outcomes (e.g. illustrative risk, or illustrative mean, on comparator intervention).
- The absolute and relative magnitude of effect measured for each (if both are appropriate).
- The numbers of participants and studies contributing to the analysis of each outcomes.
- A GRADE assessment of the overall certainty of the body of evidence for each outcome (which may vary by outcome).
- Space for comments.
- Explanations (formerly known as footnotes).
Ideally, ‘Summary of findings’ tables are supported by more detailed tables (known as ‘evidence profiles’) to which the review may be linked, which provide more detailed explanations. Evidence profiles include the same important health outcomes, and provide greater detail than ‘Summary of findings’ tables of both of the individual considerations feeding into the grading of certainty and of the results of the studies (Guyatt et al 2011a). They ensure that a structured approach is used to rating the certainty of evidence. Although they are rarely published in Cochrane Reviews, evidence profiles are often used, for example, by guideline developers in considering the certainty of the evidence to support guideline recommendations. Review authors will find it easier to develop the ‘Summary of findings’ table by completing the rating of the certainty of evidence in the evidence profile first in GRADEpro GDT. They can then automatically convert this to one of the ‘Summary of findings’ formats in GRADEpro GDT, including an interactive ‘Summary of findings’ for publication.
As a measure of the magnitude of effect for dichotomous outcomes, the ‘Summary of findings’ table should provide a relative measure of effect (e.g. risk ratio, odds ratio, hazard) and measures of absolute risk. For other types of data, an absolute measure alone (such as a difference in means for continuous data) might be sufficient. It is important that the magnitude of effect is presented in a meaningful way, which may require some transformation of the result of a meta-analysis (see also Chapter 15, Section 15.4 and Section 15.5 ). Reviews with more than one main comparison should include a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table for each comparison.
Figure 14.1.a provides an example of a ‘Summary of findings’ table. Figure 15.1.b provides an alternative format that may further facilitate users’ understanding and interpretation of the review’s findings. Evidence evaluating different formats suggests that the ‘Summary of findings’ table should include a risk difference as a measure of the absolute effect and authors should preferably use a format that includes a risk difference .
A detailed description of the contents of a ‘Summary of findings’ table appears in Section 14.1.6 .
Figure 14.1.a Example of a ‘Summary of findings’ table
Summary of findings (for interactive version click here )
a All the stockings in the nine studies included in this review were below-knee compression stockings. In four studies the compression strength was 20 mmHg to 30 mmHg at the ankle. It was 10 mmHg to 20 mmHg in the other four studies. Stockings come in different sizes. If a stocking is too tight around the knee it can prevent essential venous return causing the blood to pool around the knee. Compression stockings should be fitted properly. A stocking that is too tight could cut into the skin on a long flight and potentially cause ulceration and increased risk of DVT. Some stockings can be slightly thicker than normal leg covering and can be potentially restrictive with tight foot wear. It is a good idea to wear stockings around the house prior to travel to ensure a good, comfortable fit. Participants put their stockings on two to three hours before the flight in most of the studies. The availability and cost of stockings can vary.
b Two studies recruited high risk participants defined as those with previous episodes of DVT, coagulation disorders, severe obesity, limited mobility due to bone or joint problems, neoplastic disease within the previous two years, large varicose veins or, in one of the studies, participants taller than 190 cm and heavier than 90 kg. The incidence for the seven studies that excluded high risk participants was 1.45% and the incidence for the two studies that recruited high-risk participants (with at least one risk factor) was 2.43%. We have used 10 and 30 per 1000 to express different risk strata, respectively.
c The confidence interval crosses no difference and does not rule out a small increase.
d The measurement of oedema was not validated (indirectness of the outcome) or blinded to the intervention (risk of bias).
e If there are very few or no events and the number of participants is large, judgement about the certainty of evidence (particularly judgements about imprecision) may be based on the absolute effect. Here the certainty rating may be considered ‘high’ if the outcome was appropriately assessed and the event, in fact, did not occur in 2821 studied participants.
f None of the other studies reported adverse effects, apart from four cases of superficial vein thrombosis in varicose veins in the knee region that were compressed by the upper edge of the stocking in one study.
Figure 14.1.b Example of alternative ‘Summary of findings’ table
14.1.4 Producing ‘Summary of findings’ tables
The GRADE Working Group’s software, GRADEpro GDT ( www.gradepro.org ), including GRADE’s interactive handbook, is available to assist review authors in the preparation of ‘Summary of findings’ tables. GRADEpro can use data on the comparator group risk and the effect estimate (entered by the review authors or imported from files generated in RevMan) to produce the relative effects and absolute risks associated with experimental interventions. In addition, it leads the user through the process of a GRADE assessment, and produces a table that can be used as a standalone table in a review (including by direct import into software such as RevMan or integration with RevMan Web), or an interactive ‘Summary of findings’ table (see help resources in GRADEpro).
14.1.5 Statistical considerations in ‘Summary of findings’ tables
14.1.5.1 dichotomous outcomes.
‘Summary of findings’ tables should include both absolute and relative measures of effect for dichotomous outcomes. Risk ratios, odds ratios and risk differences are different ways of comparing two groups with dichotomous outcome data (see Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1 ). Furthermore, there are two distinct risk ratios, depending on which event (e.g. ‘yes’ or ‘no’) is the focus of the analysis (see Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1.5 ). In the presence of a non-zero intervention effect, any variation across studies in the comparator group risks (i.e. variation in the risk of the event occurring without the intervention of interest, for example in different populations) makes it impossible for more than one of these measures to be truly the same in every study.
It has long been assumed in epidemiology that relative measures of effect are more consistent than absolute measures of effect from one scenario to another. There is empirical evidence to support this assumption (Engels et al 2000, Deeks and Altman 2001, Furukawa et al 2002). For this reason, meta-analyses should generally use either a risk ratio or an odds ratio as a measure of effect (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Correspondingly, a single estimate of relative effect is likely to be a more appropriate summary than a single estimate of absolute effect. If a relative effect is indeed consistent across studies, then different comparator group risks will have different implications for absolute benefit. For instance, if the risk ratio is consistently 0.75, then the experimental intervention would reduce a comparator group risk of 80% to 60% in the intervention group (an absolute risk reduction of 20 percentage points), but would also reduce a comparator group risk of 20% to 15% in the intervention group (an absolute risk reduction of 5 percentage points).
‘Summary of findings’ tables are built around the assumption of a consistent relative effect. It is therefore important to consider the implications of this effect for different comparator group risks (these can be derived or estimated from a number of sources, see Section 14.1.6.3 ), which may require an assessment of the certainty of evidence for prognostic evidence (Spencer et al 2012, Iorio et al 2015). For any comparator group risk, it is possible to estimate a corresponding intervention group risk (i.e. the absolute risk with the intervention) from the meta-analytic risk ratio or odds ratio. Note that the numbers provided in the ‘Corresponding risk’ column are specific to the ‘risks’ in the adjacent column.
For the meta-analytic risk ratio (RR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the corresponding intervention risk is obtained as:
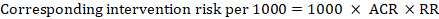
As an example, in Figure 14.1.a , the meta-analytic risk ratio for symptomless deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is RR = 0.10 (95% CI 0.04 to 0.26). Assuming a comparator risk of ACR = 10 per 1000 = 0.01, we obtain:
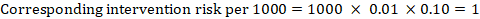
For the meta-analytic odds ratio (OR) and assumed comparator risk, ACR, the corresponding intervention risk is obtained as:
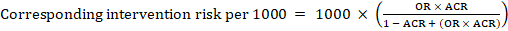
Upper and lower confidence limits for the corresponding intervention risk are obtained by replacing RR or OR by their upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.10 with 0.04, then with 0.26, in the example). Such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator risks.
When dealing with risk ratios, it is critical that the same definition of ‘event’ is used as was used for the meta-analysis. For example, if the meta-analysis focused on ‘death’ (as opposed to survival) as the event, then corresponding risks in the ‘Summary of findings’ table must also refer to ‘death’.
In (rare) circumstances in which there is clear rationale to assume a consistent risk difference in the meta-analysis, in principle it is possible to present this for relevant ‘assumed risks’ and their corresponding risks, and to present the corresponding (different) relative effects for each assumed risk.
The risk difference expresses the difference between the ACR and the corresponding intervention risk (or the difference between the experimental and the comparator intervention).
For the meta-analytic risk ratio (RR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the corresponding risk difference is obtained as (note that risks can also be expressed using percentage or percentage points):
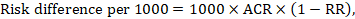
As an example, in Figure 14.1.b the meta-analytic risk ratio is 0.41 (95% CI 0.29 to 0.55) for diarrhoea in children less than 5 years of age. Assuming a comparator group risk of 22.3% we obtain:
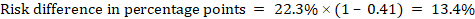
For the meta-analytic odds ratio (OR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the absolute risk difference is obtained as (percentage points):
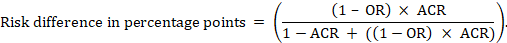
Upper and lower confidence limits for the absolute risk difference are obtained by re-running the calculation above while replacing RR or OR by their upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.41 with 0.28, then with 0.55, in the example). Such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator risks.
14.1.5.2 Time-to-event outcomes
Time-to-event outcomes measure whether and when a particular event (e.g. death) occurs (van Dalen et al 2007). The impact of the experimental intervention relative to the comparison group on time-to-event outcomes is usually measured using a hazard ratio (HR) (see Chapter 6, Section 6.8.1 ).
A hazard ratio expresses a relative effect estimate. It may be used in various ways to obtain absolute risks and other interpretable quantities for a specific population. Here we describe how to re-express hazard ratios in terms of: (i) absolute risk of event-free survival within a particular period of time; (ii) absolute risk of an event within a particular period of time; and (iii) median time to the event. All methods are built on an assumption of consistent relative effects (i.e. that the hazard ratio does not vary over time).
(i) Absolute risk of event-free survival within a particular period of time Event-free survival (e.g. overall survival) is commonly reported by individual studies. To obtain absolute effects for time-to-event outcomes measured as event-free survival, the summary HR can be used in conjunction with an assumed proportion of patients who are event-free in the comparator group (Tierney et al 2007). This proportion of patients will be specific to a period of time of observation. However, it is not strictly necessary to specify this period of time. For instance, a proportion of 50% of event-free patients might apply to patients with a high event rate observed over 1 year, or to patients with a low event rate observed over 2 years.
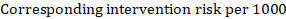
As an example, suppose the meta-analytic hazard ratio is 0.42 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.72). Assuming a comparator group risk of event-free survival (e.g. for overall survival people being alive) at 2 years of ACR = 900 per 1000 = 0.9 we obtain:
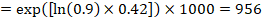
so that that 956 per 1000 people will be alive with the experimental intervention at 2 years. The derivation of the risk should be explained in a comment or footnote.
(ii) Absolute risk of an event within a particular period of time To obtain this absolute effect, again the summary HR can be used (Tierney et al 2007):
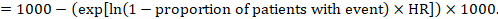
In the example, suppose we assume a comparator group risk of events (e.g. for mortality, people being dead) at 2 years of ACR = 100 per 1000 = 0.1. We obtain:
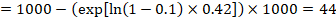
so that that 44 per 1000 people will be dead with the experimental intervention at 2 years.
(iii) Median time to the event Instead of absolute numbers, the time to the event in the intervention and comparison groups can be expressed as median survival time in months or years. To obtain median survival time the pooled HR can be applied to an assumed median survival time in the comparator group (Tierney et al 2007):
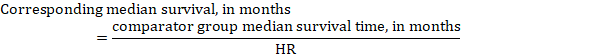
In the example, assuming a comparator group median survival time of 80 months, we obtain:
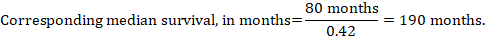
For all three of these options for re-expressing results of time-to-event analyses, upper and lower confidence limits for the corresponding intervention risk are obtained by replacing HR by its upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.42 with 0.25, then with 0.72, in the example). Again, as for dichotomous outcomes, such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator group risks. This is of special concern for long-term survival with a low or moderate mortality rate and a corresponding high number of censored patients (i.e. a low number of patients under risk and a high censoring rate).
14.1.6 Detailed contents of a ‘Summary of findings’ table
14.1.6.1 table title and header.
The title of each ‘Summary of findings’ table should specify the healthcare question, framed in terms of the population and making it clear exactly what comparison of interventions are made. In Figure 14.1.a , the population is people taking long aeroplane flights, the intervention is compression stockings, and the control is no compression stockings.
The first rows of each ‘Summary of findings’ table should provide the following ‘header’ information:
Patients or population This further clarifies the population (and possibly the subpopulations) of interest and ideally the magnitude of risk of the most crucial adverse outcome at which an intervention is directed. For instance, people on a long-haul flight may be at different risks for DVT; those using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) might be at different risk for side effects; while those with atrial fibrillation may be at low (< 1%), moderate (1% to 4%) or high (> 4%) yearly risk of stroke.
Setting This should state any specific characteristics of the settings of the healthcare question that might limit the applicability of the summary of findings to other settings (e.g. primary care in Europe and North America).
Intervention The experimental intervention.
Comparison The comparator intervention (including no specific intervention).
14.1.6.2 Outcomes
The rows of a ‘Summary of findings’ table should include all desirable and undesirable health outcomes (listed in order of importance) that are essential for decision making, up to a maximum of seven outcomes. If there are more outcomes in the review, review authors will need to omit the less important outcomes from the table, and the decision selecting which outcomes are critical or important to the review should be made during protocol development (see Chapter 3 ). Review authors should provide time frames for the measurement of the outcomes (e.g. 90 days or 12 months) and the type of instrument scores (e.g. ranging from 0 to 100).
Note that review authors should include the pre-specified critical and important outcomes in the table whether data are available or not. However, they should be alert to the possibility that the importance of an outcome (e.g. a serious adverse effect) may only become known after the protocol was written or the analysis was carried out, and should take appropriate actions to include these in the ‘Summary of findings’ table.
The ‘Summary of findings’ table can include effects in subgroups of the population for different comparator risks and effect sizes separately. For instance, in Figure 14.1.b effects are presented for children younger and older than 5 years separately. Review authors may also opt to produce separate ‘Summary of findings’ tables for different populations.
Review authors should include serious adverse events, but it might be possible to combine minor adverse events as a single outcome, and describe this in an explanatory footnote (note that it is not appropriate to add events together unless they are independent, that is, a participant who has experienced one adverse event has an unaffected chance of experiencing the other adverse event).
Outcomes measured at multiple time points represent a particular problem. In general, to keep the table simple, review authors should present multiple time points only for outcomes critical to decision making, where either the result or the decision made are likely to vary over time. The remainder should be presented at a common time point where possible.
Review authors can present continuous outcome measures in the ‘Summary of findings’ table and should endeavour to make these interpretable to the target audience. This requires that the units are clear and readily interpretable, for example, days of pain, or frequency of headache, and the name and scale of any measurement tools used should be stated (e.g. a Visual Analogue Scale, ranging from 0 to 100). However, many measurement instruments are not readily interpretable by non-specialist clinicians or patients, for example, points on a Beck Depression Inventory or quality of life score. For these, a more interpretable presentation might involve converting a continuous to a dichotomous outcome, such as >50% improvement (see Chapter 15, Section 15.5 ).
14.1.6.3 Best estimate of risk with comparator intervention
Review authors should provide up to three typical risks for participants receiving the comparator intervention. For dichotomous outcomes, we recommend that these be presented in the form of the number of people experiencing the event per 100 or 1000 people (natural frequency) depending on the frequency of the outcome. For continuous outcomes, this would be stated as a mean or median value of the outcome measured.
Estimated or assumed comparator intervention risks could be based on assessments of typical risks in different patient groups derived from the review itself, individual representative studies in the review, or risks derived from a systematic review of prognosis studies or other sources of evidence which may in turn require an assessment of the certainty for the prognostic evidence (Spencer et al 2012, Iorio et al 2015). Ideally, risks would reflect groups that clinicians can easily identify on the basis of their presenting features.
An explanatory footnote should specify the source or rationale for each comparator group risk, including the time period to which it corresponds where appropriate. In Figure 14.1.a , clinicians can easily differentiate individuals with risk factors for deep venous thrombosis from those without. If there is known to be little variation in baseline risk then review authors may use the median comparator group risk across studies. If typical risks are not known, an option is to choose the risk from the included studies, providing the second highest for a high and the second lowest for a low risk population.
14.1.6.4 Risk with intervention
For dichotomous outcomes, review authors should provide a corresponding absolute risk for each comparator group risk, along with a confidence interval. This absolute risk with the (experimental) intervention will usually be derived from the meta-analysis result presented in the relative effect column (see Section 14.1.6.6 ). Formulae are provided in Section 14.1.5 . Review authors should present the absolute effect in the same format as the risks with comparator intervention (see Section 14.1.6.3 ), for example as the number of people experiencing the event per 1000 people.
For continuous outcomes, a difference in means or standardized difference in means should be presented with its confidence interval. These will typically be obtained directly from a meta-analysis. Explanatory text should be used to clarify the meaning, as in Figures 14.1.a and 14.1.b .
14.1.6.5 Risk difference
For dichotomous outcomes, the risk difference can be provided using one of the ‘Summary of findings’ table formats as an additional option (see Figure 14.1.b ). This risk difference expresses the difference between the experimental and comparator intervention and will usually be derived from the meta-analysis result presented in the relative effect column (see Section 14.1.6.6 ). Formulae are provided in Section 14.1.5 . Review authors should present the risk difference in the same format as assumed and corresponding risks with comparator intervention (see Section 14.1.6.3 ); for example, as the number of people experiencing the event per 1000 people or as percentage points if the assumed and corresponding risks are expressed in percentage.
For continuous outcomes, if the ‘Summary of findings’ table includes this option, the mean difference can be presented here and the ‘corresponding risk’ column left blank (see Figure 14.1.b ).
14.1.6.6 Relative effect (95% CI)
The relative effect will typically be a risk ratio or odds ratio (or occasionally a hazard ratio) with its accompanying 95% confidence interval, obtained from a meta-analysis performed on the basis of the same effect measure. Risk ratios and odds ratios are similar when the comparator intervention risks are low and effects are small, but may differ considerably when comparator group risks increase. The meta-analysis may involve an assumption of either fixed or random effects, depending on what the review authors consider appropriate, and implying that the relative effect is either an estimate of the effect of the intervention, or an estimate of the average effect of the intervention across studies, respectively.
14.1.6.7 Number of participants (studies)
This column should include the number of participants assessed in the included studies for each outcome and the corresponding number of studies that contributed these participants.
14.1.6.8 Certainty of the evidence (GRADE)
Review authors should comment on the certainty of the evidence (also known as quality of the body of evidence or confidence in the effect estimates). Review authors should use the specific evidence grading system developed by the GRADE Working Group (Atkins et al 2004, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011a), which is described in detail in Section 14.2 . The GRADE approach categorizes the certainty in a body of evidence as ‘high’, ‘moderate’, ‘low’ or ‘very low’ by outcome. This is a result of judgement, but the judgement process operates within a transparent structure. As an example, the certainty would be ‘high’ if the summary were of several randomized trials with low risk of bias, but the rating of certainty becomes lower if there are concerns about risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision or publication bias. Judgements other than of ‘high’ certainty should be made transparent using explanatory footnotes or the ‘Comments’ column in the ‘Summary of findings’ table (see Section 14.1.6.10 ).
14.1.6.9 Comments
The aim of the ‘Comments’ field is to help interpret the information or data identified in the row. For example, this may be on the validity of the outcome measure or the presence of variables that are associated with the magnitude of effect. Important caveats about the results should be flagged here. Not all rows will need comments, and it is best to leave a blank if there is nothing warranting a comment.
14.1.6.10 Explanations
Detailed explanations should be included as footnotes to support the judgements in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, such as the overall GRADE assessment. The explanations should describe the rationale for important aspects of the content. Table 14.1.a lists guidance for useful explanations. Explanations should be concise, informative, relevant, easy to understand and accurate. If explanations cannot be sufficiently described in footnotes, review authors should provide further details of the issues in the Results and Discussion sections of the review.
Table 14.1.a Guidance for providing useful explanations in ‘Summary of findings’ (SoF) tables. Adapted from Santesso et al (2016)
14.2 Assessing the certainty or quality of a body of evidence
14.2.1 the grade approach.
The Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group (GRADE Working Group) has developed a system for grading the certainty of evidence (Schünemann et al 2003, Atkins et al 2004, Schünemann et al 2006, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011a). Over 100 organizations including the World Health Organization (WHO), the American College of Physicians, the American Society of Hematology (ASH), the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technology in Health (CADTH) and the National Institutes of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) in the UK have adopted the GRADE system ( www.gradeworkinggroup.org ).
Cochrane has also formally adopted this approach, and all Cochrane Reviews should use GRADE to evaluate the certainty of evidence for important outcomes (see MECIR Box 14.2.a ).
MECIR Box 14.2.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
For systematic reviews, the GRADE approach defines the certainty of a body of evidence as the extent to which one can be confident that an estimate of effect or association is close to the quantity of specific interest. Assessing the certainty of a body of evidence involves consideration of within- and across-study risk of bias (limitations in study design and execution or methodological quality), inconsistency (or heterogeneity), indirectness of evidence, imprecision of the effect estimates and risk of publication bias (see Section 14.2.2 ), as well as domains that may increase our confidence in the effect estimate (as described in Section 14.2.3 ). The GRADE system entails an assessment of the certainty of a body of evidence for each individual outcome. Judgements about the domains that determine the certainty of evidence should be described in the results or discussion section and as part of the ‘Summary of findings’ table.
The GRADE approach specifies four levels of certainty ( Figure 14.2.a ). For interventions, including diagnostic and other tests that are evaluated as interventions (Schünemann et al 2008b, Schünemann et al 2008a, Balshem et al 2011, Schünemann et al 2012), the starting point for rating the certainty of evidence is categorized into two types:
- randomized trials; and
- non-randomized studies of interventions (NRSI), including observational studies (including but not limited to cohort studies, and case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, case series and case reports, although not all of these designs are usually included in Cochrane Reviews).
There are many instances in which review authors rely on information from NRSI, in particular to evaluate potential harms (see Chapter 24 ). In addition, review authors can obtain relevant data from both randomized trials and NRSI, with each type of evidence complementing the other (Schünemann et al 2013).
In GRADE, a body of evidence from randomized trials begins with a high-certainty rating while a body of evidence from NRSI begins with a low-certainty rating. The lower rating with NRSI is the result of the potential bias induced by the lack of randomization (i.e. confounding and selection bias).
However, when using the new Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool (Sterne et al 2016), an assessment tool that covers the risk of bias due to lack of randomization, all studies may start as high certainty of the evidence (Schünemann et al 2018). The approach of starting all study designs (including NRSI) as high certainty does not conflict with the initial GRADE approach of starting the rating of NRSI as low certainty evidence. This is because a body of evidence from NRSI should generally be downgraded by two levels due to the inherent risk of bias associated with the lack of randomization, namely confounding and selection bias. Not downgrading NRSI from high to low certainty needs transparent and detailed justification for what mitigates concerns about confounding and selection bias (Schünemann et al 2018). Very few examples of where not rating down by two levels is appropriate currently exist.
The highest certainty rating is a body of evidence when there are no concerns in any of the GRADE factors listed in Figure 14.2.a . Review authors often downgrade evidence to moderate, low or even very low certainty evidence, depending on the presence of the five factors in Figure 14.2.a . Usually, certainty rating will fall by one level for each factor, up to a maximum of three levels for all factors. If there are very severe problems for any one domain (e.g. when assessing risk of bias, all studies were unconcealed, unblinded and lost over 50% of their patients to follow-up), evidence may fall by two levels due to that factor alone. It is not possible to rate lower than ‘very low certainty’ evidence.
Review authors will generally grade evidence from sound non-randomized studies as low certainty, even if ROBINS-I is used. If, however, such studies yield large effects and there is no obvious bias explaining those effects, review authors may rate the evidence as moderate or – if the effect is large enough – even as high certainty ( Figure 14.2.a ). The very low certainty level is appropriate for, but is not limited to, studies with critical problems and unsystematic clinical observations (e.g. case series or case reports).
Figure 14.2.a Levels of the certainty of a body of evidence in the GRADE approach. *Upgrading criteria are usually applicable to non-randomized studies only (but exceptions exist).
14.2.2 Domains that can lead to decreasing the certainty level of a body of evidence
We now describe in more detail the five reasons (or domains) for downgrading the certainty of a body of evidence for a specific outcome. In each case, if no reason is found for downgrading the evidence, it should be classified as 'no limitation or not serious' (not important enough to warrant downgrading). If a reason is found for downgrading the evidence, it should be classified as 'serious' (downgrading the certainty rating by one level) or 'very serious' (downgrading the certainty grade by two levels). For non-randomized studies assessed with ROBINS-I, rating down by three levels should be classified as 'extremely' serious.
(1) Risk of bias or limitations in the detailed design and implementation
Our confidence in an estimate of effect decreases if studies suffer from major limitations that are likely to result in a biased assessment of the intervention effect. For randomized trials, these methodological limitations include failure to generate a random sequence, lack of allocation sequence concealment, lack of blinding (particularly with subjective outcomes that are highly susceptible to biased assessment), a large loss to follow-up or selective reporting of outcomes. Chapter 8 provides a discussion of study-level assessments of risk of bias in the context of a Cochrane Review, and proposes an approach to assessing the risk of bias for an outcome across studies as ‘Low’ risk of bias, ‘Some concerns’ and ‘High’ risk of bias for randomized trials. Levels of ‘Low’. ‘Moderate’, ‘Serious’ and ‘Critical’ risk of bias arise for non-randomized studies assessed with ROBINS-I ( Chapter 25 ). These assessments should feed directly into this GRADE domain. In particular, ‘Low’ risk of bias would indicate ‘no limitation’; ‘Some concerns’ would indicate either ‘no limitation’ or ‘serious limitation’; and ‘High’ risk of bias would indicate either ‘serious limitation’ or ‘very serious limitation’. ‘Critical’ risk of bias on ROBINS-I would indicate extremely serious limitations in GRADE. Review authors should use their judgement to decide between alternative categories, depending on the likely magnitude of the potential biases.
Every study addressing a particular outcome will differ, to some degree, in the risk of bias. Review authors should make an overall judgement on whether the certainty of evidence for an outcome warrants downgrading on the basis of study limitations. The assessment of study limitations should apply to the studies contributing to the results in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, rather than to all studies that could potentially be included in the analysis. We have argued in Chapter 7, Section 7.6.2 , that the primary analysis should be restricted to studies at low (or low and unclear) risk of bias where possible.
Table 14.2.a presents the judgements that must be made in going from assessments of the risk of bias to judgements about study limitations for each outcome included in a ‘Summary of findings’ table. A rating of high certainty evidence can be achieved only when most evidence comes from studies that met the criteria for low risk of bias. For example, of the 22 studies addressing the impact of beta-blockers on mortality in patients with heart failure, most probably or certainly used concealed allocation of the sequence, all blinded at least some key groups and follow-up of randomized patients was almost complete (Brophy et al 2001). The certainty of evidence might be downgraded by one level when most of the evidence comes from individual studies either with a crucial limitation for one item, or with some limitations for multiple items. An example of very serious limitations, warranting downgrading by two levels, is provided by evidence on surgery versus conservative treatment in the management of patients with lumbar disc prolapse (Gibson and Waddell 2007). We are uncertain of the benefit of surgery in reducing symptoms after one year or longer, because the one study included in the analysis had inadequate concealment of the allocation sequence and the outcome was assessed using a crude rating by the surgeon without blinding.
(2) Unexplained heterogeneity or inconsistency of results
When studies yield widely differing estimates of effect (heterogeneity or variability in results), investigators should look for robust explanations for that heterogeneity. For instance, drugs may have larger relative effects in sicker populations or when given in larger doses. A detailed discussion of heterogeneity and its investigation is provided in Chapter 10, Section 10.10 and Section 10.11 . If an important modifier exists, with good evidence that important outcomes are different in different subgroups (which would ideally be pre-specified), then a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table may be considered for a separate population. For instance, a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table would be used for carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high grade stenosis (70% to 99%) in which the intervention is, in the hands of the right surgeons, beneficial, and another (if review authors considered it relevant) for asymptomatic patients with low grade stenosis (less than 30%) in which surgery appears harmful (Orrapin and Rerkasem 2017). When heterogeneity exists and affects the interpretation of results, but review authors are unable to identify a plausible explanation with the data available, the certainty of the evidence decreases.
(3) Indirectness of evidence
Two types of indirectness are relevant. First, a review comparing the effectiveness of alternative interventions (say A and B) may find that randomized trials are available, but they have compared A with placebo and B with placebo. Thus, the evidence is restricted to indirect comparisons between A and B. Where indirect comparisons are undertaken within a network meta-analysis context, GRADE for network meta-analysis should be used (see Chapter 11, Section 11.5 ).
Second, a review may find randomized trials that meet eligibility criteria but address a restricted version of the main review question in terms of population, intervention, comparator or outcomes. For example, suppose that in a review addressing an intervention for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease, most identified studies happened to be in people who also had diabetes. Then the evidence may be regarded as indirect in relation to the broader question of interest because the population is primarily related to people with diabetes. The opposite scenario can equally apply: a review addressing the effect of a preventive strategy for coronary heart disease in people with diabetes may consider studies in people without diabetes to provide relevant, albeit indirect, evidence. This would be particularly likely if investigators had conducted few if any randomized trials in the target population (e.g. people with diabetes). Other sources of indirectness may arise from interventions studied (e.g. if in all included studies a technical intervention was implemented by expert, highly trained specialists in specialist centres, then evidence on the effects of the intervention outside these centres may be indirect), comparators used (e.g. if the comparator groups received an intervention that is less effective than standard treatment in most settings) and outcomes assessed (e.g. indirectness due to surrogate outcomes when data on patient-important outcomes are not available, or when investigators seek data on quality of life but only symptoms are reported). Review authors should make judgements transparent when they believe downgrading is justified, based on differences in anticipated effects in the group of primary interest. Review authors may be aided and increase transparency of their judgements about indirectness if they use Table 14.2.b available in the GRADEpro GDT software (Schünemann et al 2013).
(4) Imprecision of results
When studies include few participants or few events, and thus have wide confidence intervals, review authors can lower their rating of the certainty of the evidence. The confidence intervals included in the ‘Summary of findings’ table will provide readers with information that allows them to make, to some extent, their own rating of precision. Review authors can use a calculation of the optimal information size (OIS) or review information size (RIS), similar to sample size calculations, to make judgements about imprecision (Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann 2016). The OIS or RIS is calculated on the basis of the number of participants required for an adequately powered individual study. If the 95% confidence interval excludes a risk ratio (RR) of 1.0, and the total number of events or patients exceeds the OIS criterion, precision is adequate. If the 95% CI includes appreciable benefit or harm (an RR of under 0.75 or over 1.25 is often suggested as a very rough guide) downgrading for imprecision may be appropriate even if OIS criteria are met (Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann 2016).
(5) High probability of publication bias
The certainty of evidence level may be downgraded if investigators fail to report studies on the basis of results (typically those that show no effect: publication bias) or outcomes (typically those that may be harmful or for which no effect was observed: selective outcome non-reporting bias). Selective reporting of outcomes from among multiple outcomes measured is assessed at the study level as part of the assessment of risk of bias (see Chapter 8, Section 8.7 ), so for the studies contributing to the outcome in the ‘Summary of findings’ table this is addressed by domain 1 above (limitations in the design and implementation). If a large number of studies included in the review do not contribute to an outcome, or if there is evidence of publication bias, the certainty of the evidence may be downgraded. Chapter 13 provides a detailed discussion of reporting biases, including publication bias, and how it may be tackled in a Cochrane Review. A prototypical situation that may elicit suspicion of publication bias is when published evidence includes a number of small studies, all of which are industry-funded (Bhandari et al 2004). For example, 14 studies of flavanoids in patients with haemorrhoids have shown apparent large benefits, but enrolled a total of only 1432 patients (i.e. each study enrolled relatively few patients) (Alonso-Coello et al 2006). The heavy involvement of sponsors in most of these studies raises questions of whether unpublished studies that suggest no benefit exist (publication bias).
A particular body of evidence can suffer from problems associated with more than one of the five factors listed here, and the greater the problems, the lower the certainty of evidence rating that should result. One could imagine a situation in which randomized trials were available, but all or virtually all of these limitations would be present, and in serious form. A very low certainty of evidence rating would result.
Table 14.2.a Further guidelines for domain 1 (of 5) in a GRADE assessment: going from assessments of risk of bias in studies to judgements about study limitations for main outcomes across studies
Table 14.2.b Judgements about indirectness by outcome (available in GRADEpro GDT)
Intervention:
Comparator:
Direct comparison:
Final judgement about indirectness across domains:
14.2.3 Domains that may lead to increasing the certainty level of a body of evidence
Although NRSI and downgraded randomized trials will generally yield a low rating for certainty of evidence, there will be unusual circumstances in which review authors could ‘upgrade’ such evidence to moderate or even high certainty ( Table 14.3.a ).
- Large effects On rare occasions when methodologically well-done observational studies yield large, consistent and precise estimates of the magnitude of an intervention effect, one may be particularly confident in the results. A large estimated effect (e.g. RR >2 or RR <0.5) in the absence of plausible confounders, or a very large effect (e.g. RR >5 or RR <0.2) in studies with no major threats to validity, might qualify for this. In these situations, while the NRSI may possibly have provided an over-estimate of the true effect, the weak study design may not explain all of the apparent observed benefit. Thus, despite reservations based on the observational study design, review authors are confident that the effect exists. The magnitude of the effect in these studies may move the assigned certainty of evidence from low to moderate (if the effect is large in the absence of other methodological limitations). For example, a meta-analysis of observational studies showed that bicycle helmets reduce the risk of head injuries in cyclists by a large margin (odds ratio (OR) 0.31, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.37) (Thompson et al 2000). This large effect, in the absence of obvious bias that could create the association, suggests a rating of moderate-certainty evidence. Note : GRADE guidance suggests the possibility of rating up one level for a large effect if the relative effect is greater than 2.0. However, if the point estimate of the relative effect is greater than 2.0, but the confidence interval is appreciably below 2.0, then some hesitation would be appropriate in the decision to rate up for a large effect. Another situation allows inference of a strong association without a formal comparative study. Consider the question of the impact of routine colonoscopy versus no screening for colon cancer on the rate of perforation associated with colonoscopy. Here, a large series of representative patients undergoing colonoscopy may provide high certainty evidence about the risk of perforation associated with colonoscopy. When the risk of the event among patients receiving the relevant comparator is known to be near 0 (i.e. we are certain that the incidence of spontaneous colon perforation in patients not undergoing colonoscopy is extremely low), case series or cohort studies of representative patients can provide high certainty evidence of adverse effects associated with an intervention, thereby allowing us to infer a strong association from even a limited number of events.
- Dose-response The presence of a dose-response gradient may increase our confidence in the findings of observational studies and thereby enhance the assigned certainty of evidence. For example, our confidence in the result of observational studies that show an increased risk of bleeding in patients who have supratherapeutic anticoagulation levels is increased by the observation that there is a dose-response gradient between the length of time needed for blood to clot (as measured by the international normalized ratio (INR)) and an increased risk of bleeding (Levine et al 2004). A systematic review of NRSI investigating the effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events found that the summary estimate (RR) with rofecoxib was 1.33 (95% CI 1.00 to 1.79) with doses less than 25mg/d, and 2.19 (95% CI 1.64 to 2.91) with doses more than 25mg/d. Although residual confounding is likely to exist in the NRSI that address this issue, the existence of a dose-response gradient and the large apparent effect of higher doses of rofecoxib markedly increase our strength of inference that the association cannot be explained by residual confounding, and is therefore likely to be both causal and, at high levels of exposure, substantial. Note : GRADE guidance suggests the possibility of rating up one level for a large effect if the relative effect is greater than 2.0. Here, the fact that the point estimate of the relative effect is greater than 2.0, but the confidence interval is appreciably below 2.0 might make some hesitate in the decision to rate up for a large effect
- Plausible confounding On occasion, all plausible biases from randomized or non-randomized studies may be working to under-estimate an apparent intervention effect. For example, if only sicker patients receive an experimental intervention or exposure, yet they still fare better, it is likely that the actual intervention or exposure effect is larger than the data suggest. For instance, a rigorous systematic review of observational studies including a total of 38 million patients demonstrated higher death rates in private for-profit versus private not-for-profit hospitals (Devereaux et al 2002). One possible bias relates to different disease severity in patients in the two hospital types. It is likely, however, that patients in the not-for-profit hospitals were sicker than those in the for-profit hospitals. Thus, to the extent that residual confounding existed, it would bias results against the not-for-profit hospitals. The second likely bias was the possibility that higher numbers of patients with excellent private insurance coverage could lead to a hospital having more resources and a spill-over effect that would benefit those without such coverage. Since for-profit hospitals are likely to admit a larger proportion of such well-insured patients than not-for-profit hospitals, the bias is once again against the not-for-profit hospitals. Since the plausible biases would all diminish the demonstrated intervention effect, one might consider the evidence from these observational studies as moderate rather than low certainty. A parallel situation exists when observational studies have failed to demonstrate an association, but all plausible biases would have increased an intervention effect. This situation will usually arise in the exploration of apparent harmful effects. For example, because the hypoglycaemic drug phenformin causes lactic acidosis, the related agent metformin was under suspicion for the same toxicity. Nevertheless, very large observational studies have failed to demonstrate an association (Salpeter et al 2007). Given the likelihood that clinicians would be more alert to lactic acidosis in the presence of the agent and over-report its occurrence, one might consider this moderate, or even high certainty, evidence refuting a causal relationship between typical therapeutic doses of metformin and lactic acidosis.
14.3 Describing the assessment of the certainty of a body of evidence using the GRADE framework
Review authors should report the grading of the certainty of evidence in the Results section for each outcome for which this has been performed, providing the rationale for downgrading or upgrading the evidence, and referring to the ‘Summary of findings’ table where applicable.
Table 14.3.a provides a framework and examples for how review authors can justify their judgements about the certainty of evidence in each domain. These justifications should also be included in explanatory notes to the ‘Summary of Findings’ table (see Section 14.1.6.10 ).
Chapter 15, Section 15.6 , describes in more detail how the overall GRADE assessment across all domains can be used to draw conclusions about the effects of the intervention, as well as providing implications for future research.
Table 14.3.a Framework for describing the certainty of evidence and justifying downgrading or upgrading
14.4 Chapter information
Authors: Holger J Schünemann, Julian PT Higgins, Gunn E Vist, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Nicole Skoetz, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group (formerly Applicability and Recommendations Methods Group) and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group
Acknowledgements: Andrew D Oxman contributed to earlier versions. Professor Penny Hawe contributed to the text on adverse effects in earlier versions. Jon Deeks provided helpful contributions on an earlier version of this chapter. For details of previous authors and editors of the Handbook , please refer to the Preface.
Funding: This work was in part supported by funding from the Michael G DeGroote Cochrane Canada Centre and the Ontario Ministry of Health.
14.5 References
Alonso-Coello P, Zhou Q, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Mills E, Heels-Ansdell D, Johanson JF, Guyatt G. Meta-analysis of flavonoids for the treatment of haemorrhoids. British Journal of Surgery 2006; 93 : 909-920.
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Zaza S. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004; 328 : 1490.
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Norris S, Guyatt GH. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011; 64 : 401-406.
Bhandari M, Busse JW, Jackowski D, Montori VM, Schünemann H, Sprague S, Mears D, Schemitsch EH, Heels-Ansdell D, Devereaux PJ. Association between industry funding and statistically significant pro-industry findings in medical and surgical randomized trials. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2004; 170 : 477-480.
Brophy JM, Joseph L, Rouleau JL. Beta-blockers in congestive heart failure. A Bayesian meta-analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001; 134 : 550-560.
Carrasco-Labra A, Brignardello-Petersen R, Santesso N, Neumann I, Mustafa RA, Mbuagbaw L, Etxeandia Ikobaltzeta I, De Stio C, McCullagh LJ, Alonso-Coello P, Meerpohl JJ, Vandvik PO, Brozek JL, Akl EA, Bossuyt P, Churchill R, Glenton C, Rosenbaum S, Tugwell P, Welch V, Garner P, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 1: a randomized trial shows improved understanding of content in summary of findings tables with a new format. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 7-18.
Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Effect measures for meta-analysis of trials with binary outcomes. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG, editors. Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-analysis in Context . 2nd ed. London (UK): BMJ Publication Group; 2001. p. 313-335.
Devereaux PJ, Choi PT, Lacchetti C, Weaver B, Schünemann HJ, Haines T, Lavis JN, Grant BJ, Haslam DR, Bhandari M, Sullivan T, Cook DJ, Walter SD, Meade M, Khan H, Bhatnagar N, Guyatt GH. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing mortality rates of private for-profit and private not-for-profit hospitals. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2002; 166 : 1399-1406.
Engels EA, Schmid CH, Terrin N, Olkin I, Lau J. Heterogeneity and statistical significance in meta-analysis: an empirical study of 125 meta-analyses. Statistics in Medicine 2000; 19 : 1707-1728.
Furukawa TA, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE. Can we individualize the 'number needed to treat'? An empirical study of summary effect measures in meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002; 31 : 72-76.
Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgical interventions for lumbar disc prolapse: updated Cochrane Review. Spine 2007; 32 : 1735-1747.
Guyatt G, Oxman A, Vist G, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann H. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008; 336 : 3.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011a; 64 : 383-394.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, Devereaux PJ, Montori VM, Freyschuss B, Vist G, Jaeschke R, Williams JW, Jr., Murad MH, Sinclair D, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Whittington C, Thorlund K, Andrews J, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence--imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011b; 64 : 1283-1293.
Iorio A, Spencer FA, Falavigna M, Alba C, Lang E, Burnand B, McGinn T, Hayden J, Williams K, Shea B, Wolff R, Kujpers T, Perel P, Vandvik PO, Glasziou P, Schünemann H, Guyatt G. Use of GRADE for assessment of evidence about prognosis: rating confidence in estimates of event rates in broad categories of patients. BMJ 2015; 350 : h870.
Langendam M, Carrasco-Labra A, Santesso N, Mustafa RA, Brignardello-Petersen R, Ventresca M, Heus P, Lasserson T, Moustgaard R, Brozek J, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 2: a systematic survey of explanatory notes shows more guidance is needed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 19-27.
Levine MN, Raskob G, Landefeld S, Kearon C, Schulman S. Hemorrhagic complications of anticoagulant treatment: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest 2004; 126 : 287S-310S.
Orrapin S, Rerkasem K. Carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017; 6 : CD001081.
Salpeter S, Greyber E, Pasternak G, Salpeter E. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 4 : CD002967.
Santesso N, Carrasco-Labra A, Langendam M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Mustafa RA, Heus P, Lasserson T, Opiyo N, Kunnamo I, Sinclair D, Garner P, Treweek S, Tovey D, Akl EA, Tugwell P, Brozek JL, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 3: detailed guidance for explanatory footnotes supports creating and understanding GRADE certainty in the evidence judgments. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 28-39.
Schünemann HJ, Best D, Vist G, Oxman AD, Group GW. Letters, numbers, symbols and words: how to communicate grades of evidence and recommendations. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2003; 169 : 677-680.
Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook DJ, Bria WF, El-Solh AA, Ernst A, Fahy BF, Gould MK, Horan KL, Krishnan JA, Manthous CA, Maurer JR, McNicholas WT, Oxman AD, Rubenfeld G, Turino GM, Guyatt G. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006; 174 : 605-614.
Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Jaeschke R, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Kunz R, Craig J, Montori VM, Bossuyt P, Guyatt GH. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations for diagnostic tests and strategies. BMJ 2008a; 336 : 1106-1110.
Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Bossuyt P, Chang S, Muti P, Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH. GRADE: assessing the quality of evidence for diagnostic recommendations. ACP Journal Club 2008b; 149 : 2.
Schünemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J. [Diagnostic accuracy and linked evidence--testing the chain]. Zeitschrift für Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualität im Gesundheitswesen 2012; 106 : 153-160.
Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Reeves BC, Akl EA, Santesso N, Spencer FA, Shea B, Wells G, Helfand M. Non-randomized studies as a source of complementary, sequential or replacement evidence for randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews on the effects of interventions. Research Synthesis Methods 2013; 4 : 49-62.
Schünemann HJ. Interpreting GRADE's levels of certainty or quality of the evidence: GRADE for statisticians, considering review information size or less emphasis on imprecision? Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 75 : 6-15.
Schünemann HJ, Cuello C, Akl EA, Mustafa RA, Meerpohl JJ, Thayer K, Morgan RL, Gartlehner G, Kunz R, Katikireddi SV, Sterne J, Higgins JPT, Guyatt G, Group GW. GRADE guidelines: 18. How ROBINS-I and other tools to assess risk of bias in nonrandomized studies should be used to rate the certainty of a body of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018.
Spencer-Bonilla G, Quinones AR, Montori VM, International Minimally Disruptive Medicine W. Assessing the Burden of Treatment. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2017; 32 : 1141-1145.
Spencer FA, Iorio A, You J, Murad MH, Schünemann HJ, Vandvik PO, Crowther MA, Pottie K, Lang ES, Meerpohl JJ, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt GH. Uncertainties in baseline risk estimates and confidence in treatment effects. BMJ 2012; 345 : e7401.
Sterne JAC, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT, Boutron I, Carpenter JR, Chan AW, Churchill R, Deeks JJ, Hróbjartsson A, Kirkham J, Jüni P, Loke YK, Pigott TD, Ramsay CR, Regidor D, Rothstein HR, Sandhu L, Santaguida PL, Schünemann HJ, Shea B, Shrier I, Tugwell P, Turner L, Valentine JC, Waddington H, Waters E, Wells GA, Whiting PF, Higgins JPT. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016; 355 : i4919.
Thompson DC, Rivara FP, Thompson R. Helmets for preventing head and facial injuries in bicyclists. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000; 2 : CD001855.
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007; 8 .
van Dalen EC, Tierney JF, Kremer LCM. Tips and tricks for understanding and using SR results. No. 7: time‐to‐event data. Evidence-Based Child Health 2007; 2 : 1089-1090.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.
- UWF Libraries
Literature Review: Conducting & Writing
- Sample Literature Reviews
- Steps for Conducting a Lit Review
- Finding "The Literature"
- Organizing/Writing
- APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window
- MLA Style This link opens in a new window
Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts
Have an exemplary literature review.
- Literature Review Sample 1
- Literature Review Sample 2
- Literature Review Sample 3
Have you written a stellar literature review you care to share for teaching purposes?
Are you an instructor who has received an exemplary literature review and have permission from the student to post?
Please contact Britt McGowan at [email protected] for inclusion in this guide. All disciplines welcome and encouraged.
- << Previous: MLA Style
- Next: Get Help! >>
- Last Updated: Mar 22, 2024 9:37 AM
- URL: https://libguides.uwf.edu/litreview

- University of Texas Libraries
Literature Reviews
- What is a literature review?
- Steps in the Literature Review Process
- Define your research question
- Determine inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Choose databases and search
- Review Results
- Synthesize Results
- Analyze Results
- Librarian Support
What is a Literature Review?
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important past and current research and practices. It provides background and context, and shows how your research will contribute to the field.
A literature review should:
- Provide a comprehensive and updated review of the literature;
- Explain why this review has taken place;
- Articulate a position or hypothesis;
- Acknowledge and account for conflicting and corroborating points of view
From S age Research Methods
Purpose of a Literature Review
A literature review can be written as an introduction to a study to:
- Demonstrate how a study fills a gap in research
- Compare a study with other research that's been done
Or it can be a separate work (a research article on its own) which:
- Organizes or describes a topic
- Describes variables within a particular issue/problem
Limitations of a Literature Review
Some of the limitations of a literature review are:
- It's a snapshot in time. Unlike other reviews, this one has beginning, a middle and an end. There may be future developments that could make your work less relevant.
- It may be too focused. Some niche studies may miss the bigger picture.
- It can be difficult to be comprehensive. There is no way to make sure all the literature on a topic was considered.
- It is easy to be biased if you stick to top tier journals. There may be other places where people are publishing exemplary research. Look to open access publications and conferences to reflect a more inclusive collection. Also, make sure to include opposing views (and not just supporting evidence).
Source: Grant, Maria J., and Andrew Booth. “A Typology of Reviews: An Analysis of 14 Review Types and Associated Methodologies.” Health Information & Libraries Journal, vol. 26, no. 2, June 2009, pp. 91–108. Wiley Online Library, doi:10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x.
Meryl Brodsky : Communication and Information Studies
Hannah Chapman Tripp : Biology, Neuroscience
Carolyn Cunningham : Human Development & Family Sciences, Psychology, Sociology
Larayne Dallas : Engineering
Janelle Hedstrom : Special Education, Curriculum & Instruction, Ed Leadership & Policy
Susan Macicak : Linguistics
Imelda Vetter : Dell Medical School
For help in other subject areas, please see the guide to library specialists by subject .
Periodically, UT Libraries runs a workshop covering the basics and library support for literature reviews. While we try to offer these once per academic year, we find providing the recording to be helpful to community members who have missed the session. Following is the most recent recording of the workshop, Conducting a Literature Review. To view the recording, a UT login is required.
- October 26, 2022 recording
- Last Updated: Oct 26, 2022 2:49 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/literaturereviews

Literature Review
- First Online: 02 March 2021
Cite this chapter

- Konstantin Druker 2
3981 Accesses
Zusammenfassung
Der folgende Literature Review hat zum Ziel, den hierzu nachvollziehbar eingegrenzten Forschungsstand nach verschiedenen Kriterien einzuordnen, um somit eine Gesamtaussage zu unterschiedlichen Einzelaspekten wirtschaftlicher Krisen im europäischen Clubfußball zu erhalten. Darüber hinaus werden Forschungslücken anhand aus dem Literature Review abgeleiteten künftigen Forschungsfragen, -foki und -methoden dargestellt.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Dies ist ein leicht abgeändertes Zitat, das Cooper in einer seiner früheren Arbeiten (1982, S. 292) von Taveggia (1974) übernommen hatte.
Im Sinne von Whittemore und Knafl (2005) wäre es der Integrative Review, im Sinne von Weed (2005) der Systematic Review in Verbindung mit Elementen der Meta-interpretation (da hauptsächlich qualitative Arbeiten bzw. ausschließlich qualitative Aspekte der Arbeiten relevant sind) und im Sinne von Grant und Booth (2009) ebenfalls der Systematic Review mit Elementen des Critical Reviews (treten beide gemeinsam auf, so sprechen die Autoren von einem Systematic Search and Review) in Verbindung mit dem Qualitative Systematic Review.
Er beschreibt diese Schritte anhand von quantitativer Forschung. Aber die Vorgehensweise ist ebenso auf qualitative Forschung anwendbar, da diese Schritte die logische Struktur eines Reviews verdeutlichen und unabhängig von der Art der Daten sind. Lediglich Schritt vier kann nicht mehr aus dem Werk von Cooper (1998) übernommen werden, da hier spezifisch die (quantitativ orientierte) Meta-analysis beschrieben wird.
Kodierbogenkategorien: Konzeptualisierung des Untersuchungsgegenstandes, (geographische) Region, Datenart (primär/ sekundär)
Kodierbogenkategorien: Konzeptualisierung des Untersuchungsgegenstandes, Einordnung nach thematisch sinnvollen Rahmenkonzepten, Ebene der Untersuchung, Methodik (Datenerhebung/ Datenanalyse), Hauptergebnis; Zusatzangabe, wie die Informationen aus den Einzelbeiträgen zustande kommen
Kodierbogenkategorien: Verwendetet Theorien, Untersuchungszeitraum, (geographische) Region
Kodierbogenkategorien: Konzeptualisierung des Untersuchungsgegenstandes, verwendete Theorien, Datenart (primär/ sekundär/ mixed/ keine), Forschungsdesign (quantitative/ qualitative/ mixed), konkrete Datenerhebungs- und -analysemethoden, Stichprobendaten
Dies sind die einem Autor bekannten Beiträge auf seinem Forschungsgebiet (vgl. Cooper 1998, S. 46–49). Hier zählt auch der Kontakt zum Kollegium z. B. auf Konferenzen oder das aktuell in der einschlägigen Forschung aktiv ist. Insgesamt ist diese Methode als „informell“ und auch unsystematisch zu betrachten.
Vgl. z. B. Whitney (1993), Rapp (2004) oder Beech et al. (2010, S. 238). Jedoch betont Szymanski (vgl. 2015, S. 74), dass sich im Englischen der Begriff „bankruptcy“ eigentlich auf natürliche Personen bezieht.
Die Schreibweise mit „ß“ ergibt eine identische Anzahl an Treffern.
Dies ist aus zeitökonomischen und verfügbarkeitstechnischen Gründen nur selten in hohem Umfang möglich. In dieser Arbeit wurde anhand von vier Beiträgen (jeweils ein wirtschafts- und ein rechtswissenschaftlicher Beitrag jeweils als begutachtet und nicht begutachtet), im Hinblick auf fragliche Codierungskategorien, ein informelles „intercoder agreement“ mit einer akademisch ausgebildete Person (in einer sozialwissenschaftlichen Disziplin promovierter Professor) diskutiert.
Letzteres Problem kann, wie im oberen Abschnitt erwähnt, in gewissem Grade eingedämmt werden, wenn mehrere Personen die Codierung durchführen und ein „intercoder agreement“ angegeben werden kann (vgl. Cooper 1998, S. 109).
Die Wahl von „mindestens drei Beiträgen“ ergibt sich nur aufgrund der spezifischen Tatsache, dass nur wenige Autoren überhaupt auf mindestens drei Beiträge kommen (nur sieben von 121 verschiedenen Autoren; 15 kommen auf 2 Beiträge und 99 kommen auf einen Beitrag). D. h. ab drei Beiträgen ist man, zumindest in diesem Forschungsfeld, bereits überdurchschnittlich aktiv. In anderen Feldern kann eine ganz andere Anzahl für eine überdurchschnittliche Aktivität stehen. Bei ihrem Literature Review zum Thema „Konzeptualisierung der Partizipation im Fantasy Sport“ legen Tacon und Vainker (2017, S. 560–561) ebenfalls „mindestens drei Beiträge“ als untere Grenze für die Analyse der Autorenkonzentration fest.
Z.B. der jährliche Bundesligareport der Deutschen Fußballiga (DFL)
Z.B. der Annual Review of Football Finance
D. h. von den 39 Beiträgen mit Bezug zum deutschen Fußball sind 25 rechtswissenschaftlicher und die 14 übrigen wirtschaftswissenschaftlicher Natur.
Betrachtet man nur Artikel mit Erscheinungsjahr 2011-2018, dann liegt die Spitze im Jahr 2010. Wird das Erscheinungsjahr auf den Zeitraum 2007-2018 ausgeweitet, so liegt die Spitze im Jahr 2005.
Für die Feststellung einer „wirtschaftlichen Krise“ reicht es nicht, nominell ein Krisenstadium zu untersuchen. Es muss im Ergebnis des Beitrags klar argumentiert werden, warum im Kontext des Teamsports eine Krise vorliegt. Nur dann wird eine Klassifizierung als „wirtschaftliche Krise“ vorgenommen.
Die Kriterien für diese Kategorien waren sehr streng, d. h. es musste explizit auf einen systematischen Charakter der Krise verwiesen worden sein. Wenn nur eine „wirtschaftlichen Krise“ festgestellt wurde, dann heißt es nicht zwangsläufig, dass diese nicht auch systematisch sein kann, sondern nur, dass es nicht explizit erwähnt wurde.
Damit werden Unternehmen gemeint, deren Wertschöpfung (weitestgehend) dem Prinzip der klassischen Wertkette nach Porter (1985) folgt.
Wenn beispielsweise nur eine bestimmte Liga untersucht wird und herauskommt, dass eine wirtschaftliche Krise vorliegt, so bezieht sich das Ergebnis auch nur auf diese Liga und nicht etwa auf die ganze Nation oder den europäischen Fußball. Wenn der Beitrag dies nicht untersucht, so kann er eine solche Aussage auch nicht leisten.
Es wird eine wirtschaftliche Krise in Beiträgen mit Erscheinungsjahr 2003, 2004, 2009, 2012, und drei Mal in 2016 festgestellt. Wobei die systematische Krise drei Mal festgestellt wird (in den Jahren 2004, 2012 und 2016). Diese Verteilung ist somit nicht konzentriert und bedarf keiner besonderen Erläuterung.
Beispielsweise ist die fehlende Überschneidungsfreiheit deutlich erkennbar an den Inhalten der Kategorie „Aspekte von Anreiz- und Kontrolldefiziten“ (z. B. Institutionellen Regelungen) und den Inhalten der „Neuen Institutionenökonomie“ oder zwischen dem Ansatz „Fußballclubs als kulturelle Instanz“ und dessen Widerspiegelung als Bestandteil der Mikroökonomischen Theorie. Selbst innerhalb derselben Kategorie folgt die Einordnung v. a. funktionalen Kriterien und ist somit ebenfalls nicht immer überschneidungsfrei (z. B. haben „Umwegrenten“ Bezug zu „Zielfunktionen“).
Zum allgemeinen Begriff der Primär- und Sekundärdaten siehe z. B. Döring und Bortz (2016, S. 191–192).
Zum allgemeinen Begriff der Datenerhebung siehe z. B. Döring und Bortz (2016, 322 ff.).
Zum allgemeinen Begriff der Datenanalyse vgl. z. B. Döring und Bortz (2016, 597 ff.).
Zum Vergleich: Über alle 107 Beiträge lag der arithmetische Mittelwert bei 10,4 und der Median bei 6 Saisons/ Jahre.
Es könnte natürlich auch „‘gerade wegen‘ stetig wachsender Umsatzerlöse“ lauten. Denn durch die Annahme des Wachstums in der Zukunft könnten heutige Verlust durch morgige Erlöse ausgeglichen werden.
Siehe z. B. Dietl et al. (2003, S. 528)
Siehe z. B. Franck (1999, S. 541)
Siehe z. B. Daumann (2019, S. 174)
Der Begriff „Hyperaktivität“ wurde im Kontext des Teamsports erstmals von Alchian und Demsetz (1972, S. 791) verwendet. Sie umschrieben ihn zunächst auch als „reverse shirking“, d. h. als das Gegenteil von Drückebergerei.
Handelt es sich um gemeinnützige bzw. Non-Profit-Organisationen, so gibt es ein von Anfang an festgelegtes, also hartes, Budget in dessen Rahmen sich die Organisation finanziell bewegen muss.
Franck und Müller (vgl. 2000, S. 16–19) bezeichnen solche Mechanismen als Elemente eines „alles oder nichts“-Spiels. Sie lösen ein Glücksspielerverhalten aus (d. h. ein negativer Erwartungswerts wird ignoriert bzw. die Gewinnwahrscheinlichkeit wird überschätzt) und zwingen die Teilnehmer des Spiels (hier der Fußballclubs) in ein sogenanntes „entrapment-game“ (zurückzuführen auf Shubik 1971). Dabei entsteht die hochkompetitive Situation.
Die Ratten messen sich in einem Wettlauf um den größten Anteil am Käse. Wer schneller an diesem ankommt, verbraucht zwar mehr Kalorien, bekommt aber auch das größte Stück ab, um diese wieder aufzufüllen. Einige Ratten (ggf. auch alle) werden trotzdem ihre Kalorienbilanz nicht positiv gestalten können, da es insgesamt nicht genügend Käse gibt. Übertragen auf den Teamsport steht der Käse für die Belohnung in Form von Preisgeldern und höheren Vermarktungspotentialen und die Geschwindigkeit der Ratten steht für die Talentinvestitionen/ Spielergehälter der Clubs, die in Spielstärke übersetzt werden.
Budzinski (2017b) führt hierzu jedoch empirische Evidenz an, die das Gegenteil besagt. Mehr dazu weiter unten im aktuellen Kapitel.
Es gibt zwei Arten von externen Effekten, den pekuniären und den technologischen (vgl. z. B. Fritsch 2018, S. 84 ff.). Der (negative) pekuniäre Effekt entsteht grundsätzlich, wenn ein Wettbewerber stärker wird und einem anderen Marktanteile abnimmt bzw. ihm die Marktposition streitig macht. Dieser Art von externem Effekt ist Teil eines jeden natürlichen Wettbewerbs und wird durch den Preismechanismus aufgelöst. Hierzu zählt, dass ein Team ein anderes in der Tabelle überholt, da es stärker ist – dies indiziert kein Marktversagen und kommt in allen Branchen vor. Die zweite Form des negativen externen Effekts spiegelt ein Marktversagen wider und führt zu einer Wohlfahrtsminderung. Ein Beispiel hierzu ist die zunehmende Dominanz von einzelnen Teams auf Kosten der vermarktungsrelevanten Spannung des gesamten Wettbewerbs. Franck (vgl. 1995, S. 154 bezeichnet dies als „Dominanzexternalität“; passend hierzu wird auf die Aussage des „Louis-Schmelling-Paradoxons“ in Abschnitt 2.2.3.1 verwiesen). Nur die zweite Form externer Effekte begründet eine Korrektur.
Auch hier führt Budzinski (2017b) empirische Evidenz an, die das Gegenteil besagt. Mehr dazu weiter unten im aktuellen Kapitel.
In der Einleitung unter dem Abschnitt „Untersuchungsgegenstand“ wurde bereits darauf hingewiesen, dass es innerhalb der Neoklassik, die u. a. von streng rationalen, d. h. vollkommen informierten, Akteuren ausgeht, (Team-)Sport nicht geben dürfte.
Dieses Working Paper wurde später als Beitrag in einem Herausgeberband veröffentlicht als Budzinski (2017a). Im Rahmen des Systematic Reviews wurde dieser Beitrag zunächst nicht identifiziert. Da die Inhalte, bis auf ein paar ausführlichere Beispiele, aber identisch sind, wird das Working Paper als Quelle beibehalten.
Institutionelle Hebel können z. B. Auf- und Abstiegsregelungen, hohe Erlösdifferenzen zwischen den Ligen oder Qualifikationsränge zu übergeordneten Wettbewerben der UEFA sein (vgl. z. B. Dietl et al. 2008, S. 366; Storm 2012, S. 27). Ein medialer Hebel ermöglicht es, ausgestrahlten Output ohne nennenswerte Zusatzkosten beliebig oft zu vervielfältigen (denn Medien müssen den Output nur einmal „herstellen“). Die Marktnachfrage kann sich dadurch auf ganz wenige Superstar-Anbieter konzentrieren (vgl. z. B. Franck und Müller 2000, S. 21).
Dietl et al. (vgl. 2003, S. 530–532) zeigen, dass sich die Entscheidungsträger in einem spieltheoretischen Gefangenendilemma befinden und die dominante Strategie eine Überinvestition als Konsequenz nach sich zieht. Auch García Villar und Rodríguez (vgl. 2003, S. 264) und Solberg und Haugen (vgl. 2010, S. 340) argumentieren u. a. spieltheoretisch bezüglich einer dominanten Strategie und ihrer ruinösen Folgen für alle Teilnehmer.
Hierzu wurde in Abschnitt 2.2.3.3 von einem „Teufelskreis“ gesprochen, in den sich die Clubs begeben, wenn sie ihre Investitionen nicht refinanzieren können.
Mit dem Begriff „Zombierennen“ nimmt er zwar Bezug auf das „Rattenrennen“, meint damit aber die Überinvestitionssituation, die aus dem „Rattenrennen“ folgt. Im vorherigen Unterkapitel 3.6.2 wurde das „Rattenrennen“ als Erklärung für die Überinvestition abgelehnt. Der Begriff wird im Folgenden beschrieben.
In Deutschland ist die vorherrschende Clubverfassung aufgrund der „50 + 1“-Regel sowie der noch teilweise vorhandenen Vereinsstrukturen grundsätzlich, d. h. es gibt auch Ausnahmen wie z. B. Bayer Leverkusen, VfL Wolfsburg, TSG 1899 Hoffenheim oder RB Leipzig, nicht dafür geeignet (vgl. Franck 2010b, S. 6).
Zum Begriff siehe Fußnote 30.
Andreff (vgl. 2011, S. 24–25) bestätigt eine signifikante, kausale Beziehung zwischen Spielergehältern (exogen) und Erlösen aus der TV-Vermarktung (endogen) (anhand einer Untersuchung der ersten beiden französischen Profifußballligen). Gemäß seiner Argumentation entsteht ein „Teufelskreis“, der die Clubs (als Liga) dazu zwingt, den nächsten TV-Rechtevertrag stets so zu verhandeln, dass die angehäuften Verluste der Clubs – entstanden aufgrund der zu hoch angesetzten Spielergehältern, die aber nicht zu entsprechend hoher Produktivität führten – ausgeglichen werden können. Dies sieht er als eine Form der Überinvestition, die über das Konzept des „soft budget constraint“ (siehe nächstes Kapitel) erklärt werden kann.
Hier ist explizit auf die Verbindung zu dem Begriff „Auslöser“ (von Krisen) zu verweisen (siehe Abschnitt 2.1.2).
„(H)BC“ steht für „(hard) budget contraint“.
Sie werden an dieser Stelle nicht aufgezählt, da sie keine spezifische Relevanz für die weitere Argumentation aufweisen. Bei Interesse kann die angegeben Quelle konsultiert werden.
Unterschiedliche Möglichkeiten für die Gestalt „softer“ Budgets werden bei Kornai et al. (vgl. 2003, S. 1101–1104) beschrieben.
Die Motivation der zu rettenden Organisation kann letztendlich auf „Überlebenswille“ reduziert werden. Die rettende Organisation kann hingegen z. B. durch bereits getätigte Investitionen („sunk costs“) motiviert sein, um Ansteckungseffekte zu vermeiden, aus moralischen Gründen, um Popularität und öffentliches Ansehen zu steigern oder weil die Entscheidungsträger durch Bestechungen finanziell profitieren (vgl. Kornai 2014, S. 28–32). Die Motive der rettenden Organisation entsprechen dem, was unter dem Begriff „Umwegrente“ beschrieben wurde.
Budzinski und Müller (vgl. 2013, S. 10–11) sprechen von „too- prominent -to-fail“, d. h. Clubs können so prominent werden, dass sich immer jemand findet, der sie in der Krise rettet.
Diese Aussage bezieht sich auf die Wurzeln des Clubs, die eine besondere Bedeutung für die im 19. Jahrhundert eingewanderten katholischen Iren haben. Der Club wurde zunächst als Vehikel für Armutsbekämpfung gegründet und später in die schottische Liga aufgenommen. Er symbolisiert für seine Anhänger die Gruppe der katholischen Iren.
Z.B. ist die „Ligaorganisation als verbindliche Regelungsinstanz“ (Bereich Branchenstruktur/ Wertschöpfungslogik) eng verknüpft mit dem gesamten Bereich „Institutionelle Mechanismen“. Ebenfalls ist der Stakeholder „Fan“ (Bereich Branchenstruktur/ Wertschöpfungslogik) zentral für den Bereich „Club als ‚kulturelle Instanz‘“. Die Interdependenz zwischen den verbleibenden beiden Bereichen lässt sich beispielhaft an den „Umwegrenten“ und den Investitionsbeschränkungen (z. B. aufgrund von Verbandsvorgaben wie „der 50 + 1“-Regelung) darstellen.
In der folgenden Tabelle wie folgt abgekürzt: Mikroeben als „Mik“, Mesoeben als „Mes“ und Makroeben als „Mak“.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Stuttgart, Deutschland
Konstantin Druker
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
3.1 Elektronisches Zusatzmaterial
Zusatzmaterial 1 (docx 356 kb), rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Der/die Autor(en), exklusiv lizenziert durch Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, ein Teil von Springer Nature
About this chapter
Druker, K. (2021). Literature Review. In: Management wirtschaftlicher Krisen im deutschen Profifußball. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-32712-5_3
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-32712-5_3
Published : 02 March 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-32711-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-32712-5
eBook Packages : Business and Economics (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Advertisement
Supported by
Three Lives Entwined by Tragedy — and a Love of Literature
In Monica Wood’s rich new novel, “How to Read a Book,” death, prison and poetry become the catalyst for new beginnings.
- Share full article

By Helen Simonson
Helen Simonson is the author of “Major Pettigrew’s Last Stand” and “The Summer Before the War.” Her latest novel, “The Hazelbourne Ladies Motorcycle and Flying Club ,” is out now.
- Barnes and Noble
- Books-A-Million
When you purchase an independently reviewed book through our site, we earn an affiliate commission.
HOW TO READ A BOOK, by Monica Wood
”How to Read a Book” might be the perfect pick to really light a fire under my book club, and yours. It’s a charming, openhearted novel, deceptively easy to read but layered with sharp observations, hard truths and rich ideas.
Set in Portland, Maine, the novel opens in a women’s prison book club full of caustic inmates whose spirited discussions reveal a thick vein of humor and a weary compassion. According to Violet, a young woman with a manslaughter conviction and a gift for wicked turns of phrase, the weekly meetings are the highlight of a prison life so dull that “every day: same, same, same. The boredom feels like lice and you itch all over.” She and her fellow members have insulted every book choice but, she admits, “sometimes a sparkling sentence can really rip you up.”
Violet’s voice is self-aware, with a haunting fragility beneath the tough talk. And just as we fall for her we also meet Frank, a bookstore handyman still stunned by the death of his wife in a drunk-driving accident — caused by Violet. So much for easy! Wadsworth Books, a warm and welcoming independent bookstore full of young people and foster cats, is also the favorite haunt of our third narrative voice: the book club’s leader, Harriet, a widowed English teacher who is struggling to find purpose. “Retired people were often thought to be lonely, but it wasn’t that. It was the feeling of uselessness, of being done with it all,” she reflects. Harriet cultivates her prison book club as if gardening, “exposing the women to the open air of literature, to the sunshine of fresh ideas.” When Violet is released from prison, Harriet bumps into her at the bookstore and must hustle her to safety as Frank suffers a full meltdown.
Even after these three lives are neatly entangled (and recounted in alternating chapters), the heart of the story remains Violet, who stumbles into a job as an assistant at a research lab dedicated to proving that African gray parrots don’t just talk but also think (at last, real talking animals!). As she makes her fresh start, with the help of Harriet and occasional acts of random kindness from strangers, Violet still has to face Frank and the tragedy she caused.
Harriet instructs us that “stories have a ‘meanwhile’ — an important thing that’s happening while the rest of the story moves along,” and so the many layers of “meanwhile” delicately accrue. The novel asks us to stop and consider: Which kinds of people deserve second chances? Are people their worst acts, or a lifetime of better days? Is it possible to stop judging fictional characters (or each other in this divided, angry world) long enough to see that we are all “fellow creatures”? Personally, I want to talk about the parrots whose powers of cognition did nothing to free them from their life sentences.
Another “meanwhile”: The story here also serves as a meditation on the power of books. While Edgar Lee Masters’s 1915 poetry collection “Spoon River Anthology” plays a prominent role, works from J.D. Salinger, F. Scott Fitzgerald and William Butler Yeats to Zadie Smith and Maya Angelou underpin and suffuse every chapter.
“Harriet had always considered Angelou a tad pious,” Wood notes — a pot-calling-kettle moment that made me chortle, as “How to Read a Book” nudges the conscience as much as it pulls at the heartstrings. But it is also generously seasoned with unexpected twists and a wonderful wit. It’s never saccharine. In book clubs and in life, sometimes you just need a break from the sense of gritty hopelessness. This novel is a reminder that goodness, and books, can still win in this world.
HOW TO READ A BOOK | By Monica Wood | Mariner Books | 288 pp. | $28
Explore More in Books
Want to know about the best books to read and the latest news start here..
The complicated, generous life of Paul Auster, who died on April 30 , yielded a body of work of staggering scope and variety .
“Real Americans,” a new novel by Rachel Khong , follows three generations of Chinese Americans as they all fight for self-determination in their own way .
“The Chocolate War,” published 50 years ago, became one of the most challenged books in the United States. Its author, Robert Cormier, spent years fighting attempts to ban it .
Joan Didion’s distinctive prose and sharp eye were tuned to an outsider’s frequency, telling us about ourselves in essays that are almost reflexively skeptical. Here are her essential works .
Each week, top authors and critics join the Book Review’s podcast to talk about the latest news in the literary world. Listen here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empirical and theoretical literature to assess the strength of evidence, develop guidelines for practice and policymaking, and identify areas for future research.1 It is often essential and usually the first task in any research endeavour, particularly in masters or doctoral level education. For effective data extraction and rigorous synthesis ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Research Tables and Synthesis Tables are useful tools for organizing and analyzing your research as you assemble your literature review. They represent two different parts of the review process: assembling relevant information and synthesizing it. Use a Research table to compile the main info you need about the items you find in your research ...
As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter. Importantly, you must complete steps one and two before you start writing up your chapter.
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
Peabody Librarians have created a sample literature review table to use to organize your research. Feel free to download this file and use or adapt as needed. << Previous: Literature Reviews Webinar Recording; Next: Writing Like an Academic >> Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 4:20 PM;
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review. As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. There are five key steps to writing a literature review: Search for relevant literature. Evaluate sources. Identify themes, debates and gaps.
How to write a literature review in 6 steps. How do you write a good literature review? This step-by-step guide on how to write an excellent literature review covers all aspects of planning and writing literature reviews for academic papers and theses.
John's, NL A1C 5C4, Canada; various approaches for developing literature summary a y6133@ mun. ac Five tips for developing useful literature summary tables for writing review articles Ahtisham Younas ,1,2 Parveen Ali 3,4 Research made simple 10.1136/ebnurs-2021-103417 Introduction Literature reviews offer a critical synthesis of empir-
in the summary tables (see figure 1) demonstrates to. the readers that a robust method of data extraction and. synthesis has been followed. Tip 5: create your person alised template for lit ...
A formal literature review is an evidence-based, in-depth analysis of a subject. There are many reasons for writing one and these will influence the length and style of your review, but in essence a literature review is a critical appraisal of the current collective knowledge on a subject. Rather than just being an exhaustive list of all that ...
A summary of findings table is an essential component of a systematic review. This comprehensive synthesis of data analysis provides a simple, and transparent presentation of data, which makes it easier for readers to understand the study, the assessment of its reviewed literature, and the conclusions derived from its methodology.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications .For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively .Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every ...
If you're working on a dissertation or thesis and are looking for an example of a strong literature review chapter, you've come to the right place.. In this video, we walk you through an A-grade literature review from a dissertation that earned full distinction.We start off by discussing the five core sections of a literature review chapter by unpacking our free literature review template.
A literature review is an integrated analysis-- not just a summary-- of scholarly writings and other relevant evidence related directly to your research question.That is, it represents a synthesis of the evidence that provides background information on your topic and shows a association between the evidence and your research question.
There are many different types of literature tables-the main thing is to determine the important pieces that help draw out the comparisons and contrasts between the articles included in your review. The first few columns should include the basic info about the article (title, authors, journal), publication year, and the purpose of the paper.
A literature review is a critical analysis and synthesis of existing research on a particular topic. It provides an overview of the current state of knowledge, identifies gaps, and highlights key findings in the literature. 1 The purpose of a literature review is to situate your own research within the context of existing scholarship, demonstrating your understanding of the topic and showing ...
Review authors should provide time frames for the measurement of the outcomes (e.g. 90 days or 12 months) and the type of instrument scores (e.g. ranging from 0 to 100). Note that review authors should include the pre-specified critical and important outcomes in the table whether data are available or not.
Steps for Conducting a Lit Review; Finding "The Literature" Organizing/Writing; APA Style This link opens in a new window; Chicago: Notes Bibliography This link opens in a new window; MLA Style This link opens in a new window; Sample Literature Reviews. Sample Lit Reviews from Communication Arts; Have an exemplary literature review? Get Help!
A literature or narrative review is a comprehensive review and analysis of the published literature on a specific topic or research question. The literature that is reviewed contains: books, articles, academic articles, conference proceedings, association papers, and dissertations. It contains the most pertinent studies and points to important ...
Tabelle 3.9 und 3.10 (es sind zwei Teile einer längeren Tabelle) stellen die aus dem Literature Review abgeleiteten Forschungslücken als mögliche, künftige Forschungsfragen samt Forschungsfokus und dem entsprechenden Forschungsdesign/ -methode dar.
Cancer immunotherapy is a rapidly developing field of medicine that aims to use the host's immune mechanisms to inhibit and eliminate cancer cells. Antibodies targeting CTLA-4, PD-1, and its ligand PD-L1 are used in various cancer therapies. However, the most thoroughly researched pathway targeting PD-1/PD-L1 has many limitations, and multiple malignancies resist its effects. Human ...
In Monica Wood's rich new novel, "How to Read a Book," death, prison and poetry become the catalyst for new beginnings. By Helen Simonson Helen Simonson is the author of "Major Pettigrew ...