- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21 Answer Key
Engage ny eureka math 4th grade module 3 lesson 21 answer key, eureka math grade 4 module 3 lesson 21 sprint answer key.
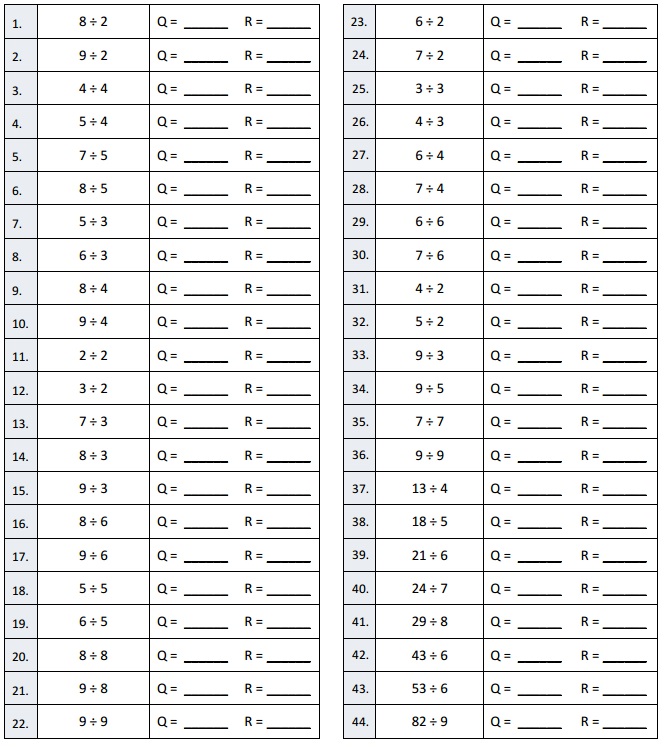
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 2 when 8 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 4, (2 X 4 = 8) and remainder is 0.
Question 2. 9 ÷ 2 Q = ___4___ R = ___1___ Answer: 9 ÷ 2 = quotient = 4 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 2 when 9 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 4, (2 X 4 = 8) and remainder is 1.
Question 3. 4 ÷ 4 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 4 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 4 ÷ 4 when 4 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 1, (4 X 1 = 4) and remainder is 0.
Question 4. 5 ÷ 4 Q = ___1___ R = ___1___ Answer: 5 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 5 ÷ 4 when 5 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 1, (4 X 1 = 4) and remainder is 1.
Question 5. 7 ÷ 5 Q = __1____ R = ___2___ Answer: 7 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 5 when 7 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 1, (5 X 1 = 5) and remainder is 2.
Question 6. 8 ÷ 5 Q = ___1___ R = __3____ Answer: 8 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 5 when 8 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 1, (5 X 1 = 5) and remainder is 3.
Question 7. 5 ÷ 3 Q = ___1___ R = __2____ Answer: 5 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 5 ÷ 3 when 5 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 1, (3 X 1 = 3) and remainder is 2.
Question 8. 6 ÷ 3 Q = __2____ R = __0__ Answer: 6 ÷ 3 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 6 ÷ 3 when 6 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 2, (3 X 2 = 6) and remainder is 0.
Question 9. 8 ÷ 4 Q = __2____ R = __0____ Answer: 8 ÷ 4 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 4 when 8 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 2, (4 X 2 = 8) and remainder is 0.
Question 10. 9 ÷ 4 Q = __2____ R = ___1___ Answer: 9 ÷ 4 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 4 when 9 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 2, (4 X 2 = 8) and remainder is 1.
Question 11. 2 ÷ 2 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 2 ÷ 2 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 2 ÷ 2 when 2 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 1, (2 X 1 = 2) and remainder is 0.
Question 12. 3 ÷ 2 Q = __1____ R = __1____ Answer: 3 ÷ 2 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 3 ÷ 2 when 3 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 1, (2 X 1 = 2) and remainder is 1.
Question 13. 7 ÷ 3 Q = __2____ R = __1____ Answer: 7 ÷ 3 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 3 when 7 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 2, (3 X 2 = 6) and remainder is 1.
Question 14. 8 ÷ 3 Q = ___2___ R = ___2___ Answer: 8 ÷ 3 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 3 when 8 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 2, (3 X 2 = 6) and remainder is 2.
Question 15. 9 ÷ 3 Q = __3____ R = __0____ Answer: 9 ÷ 3 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 3 when 9 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 3, (3 X 3 = 9) and remainder is 0.
Question 16. 8 ÷ 6 Q = ___1___ R = __2____ Answer: 8 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 6 when 8 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 1, (6 X 1 = 6) and remainder is 2.
Question 17. 9 ÷ 6 Q = __1____ R = __3____ Answer: 9 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 6 when 9 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 1, (6 X 1 = 6) and remainder is 3.
Question 18. 5 ÷ 5 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 5÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 5 ÷ 5 when 5 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 1, (5 X 1 = 5) and remainder is 0.
Question 19. 6 ÷ 5 Q = ____1__ R = __1____ Answer: 6 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 6 ÷ 5 when 6 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 1, (5 X 1 = 5) and remainder is 1.
Question 20. 8 ÷ 8 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 8 ÷ 8 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 8 when 8 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 1, (8 X 1 = 8) and remainder is 0.
Question 21. 9 ÷ 8 Q = ___1___ R = __1____ Answer: 9 ÷ 8 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 8 when 9 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 1, (8 X 1 = 8) and remainder is 1.
Question 22. 9 ÷ 9 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 9 ÷ 9 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 9 when 9 is divided by 9 we get quotient as 1, (9 X 1 = 9) and remainder is 0.
Question 23. 6 ÷ 2 Q = ___3___ R = __0____ Answer: 6 ÷ 2 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 6 ÷ 2 when 6 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 3, (2 X 3 = 6) and remainder is 0.
Question 24. 7 ÷ 2 Q = __3____ R = __1____ Answer: 7 ÷ 2 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 2 when 7 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 3, (2 X 3 = 6) and remainder is 1.
Question 25. 3 ÷ 3 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 3 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 3 ÷ 3 when 3 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 1, (3 X 1 = 3) and remainder is 0.
Question 26. 4 ÷ 3 Q = ___1___ R = __1____ Answer: 4 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 4 ÷ 3 when 4 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 1, (3 X 1 = 3) and remainder is 1.
Question 27. 6 ÷ 4 Q = ___1___ R = ___2___ Answer: 6 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 6 ÷ 4 when 6 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 1, (4 X 1 = 4) and remainder is 2.
Question 28. 7 ÷ 4 Q = __1____ R = __3____ Answer: 7 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 4 when 7 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 1, (4 X 1 = 4) and remainder is 3.
Question 29. 6 ÷ 6 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 6 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 6 ÷ 6 when 6 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 1, (6 X 1 = 6) and remainder is 0.
Question 30. 7 ÷ 6 Q = ___1___ R = __1____ Answer: 7 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 6 when 7 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 1, (6 X 1 = 6) and remainder is 1.
Question 31. 4 ÷ 2 Q = ___2___ R = ___0___ Answer: 4 ÷ 2 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 4 ÷ 2 when 4 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 2, (2 X 2 = 4) and remainder is 0.
Question 32. 5 ÷ 2 Q = __2____ R = __1____ Answer: 5 ÷ 2 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 5 ÷ 2 when 5 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 2, (2 X 2 = 4) and remainder is 1.
Question 33. 9 ÷ 3 Q = ___3___ R = __0____ Answer: 9 ÷ 3 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 3 when 9 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 3, (3 X 3= 9) and remainder is 0.
Question 34. 9 ÷ 5 Q = ___1___ R = ___4___ Answer: 9 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 4,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 5 when 9 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 1, (5 X 1 = 5) and remainder is 4.
Question 35. 7 ÷ 7 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 7 ÷ 7 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 7 when 7 is divided by 7 we get quotient as 1, (7 X 1 = 7) and remainder is 0.
Question 36. 9 ÷ 9 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 9 ÷ 9 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 37. 13 ÷ 4 Q = ___3___ R = __1____ Answer: 13 ÷ 4 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 13 ÷ 4 when 13 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 3, (4 X 3 = 12) and remainder is 1.
Question 38. 18 ÷ 5 Q = ___3___ R = __3____ Answer: 18 ÷ 5 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 18 ÷ 5 when 18 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 3, (5 X 3 = 15) and remainder is 3.
Question 39. 21 ÷ 6 Q = ____3__ R = __3____ Answer: 21 ÷ 6 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 21 ÷ 6 when 21 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 3, (6 X 3 = 18) and remainder is 3.
Question 40. 24 ÷ 7 Q = __3____ R = __3____ Answer: 24 ÷ 7 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 24 ÷ 7 when 24 is divided by 7 we get quotient as 3, (7 X 3 = 21) and remainder is 3.
Question 41. 29 ÷ 8 Q = __3____ R = __5____ Answer: 29 ÷ 8 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 29 ÷ 8 when 29 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 3, (8 X 3 = 24) and remainder is 5.
Question 42. 43 ÷ 6 Q = ___7___ R = __1____ Answer: 43 ÷ 6 = quotient = 7 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 43 ÷ 6 when 43 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 7, (6 X 7 = 42) and remainder is 1.
Question 43. 53 ÷ 6 Q = __8____ R = ___5___ Answer: 53 ÷ 6 = quotient = 8 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 53 ÷ 6 when 53 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 8, (6 X 8 = 48) and remainder is 5.
Question 44. 82 ÷ 9 Q = ___9___ R = ___1___ Answer: 82 ÷ 9 = quotient = 9 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 82 ÷ 9 when 82 is divided by 9 we get quotient as 9, (9 X 9 = 81) and remainder is 1.
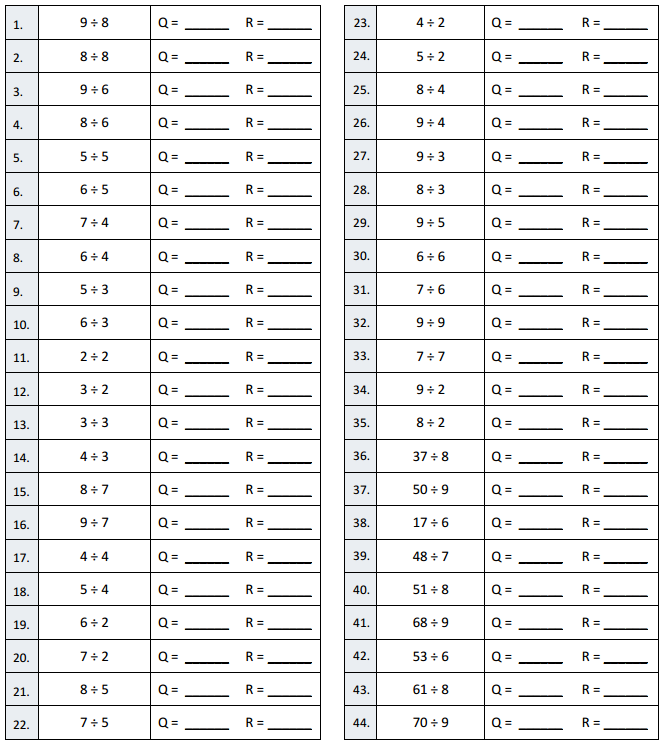
Question 2. 8 ÷ 8 Q = __1____ R = ___0___ Answer: 8 ÷ 8 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 3. 9 ÷ 6 Q = __1____ R = ___2___ Answer: 9 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Explanation: Given 9 ÷ 6 when 9 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 1, (6 X 1 = 6) and remainder is 2.
Question 4. 8 ÷ 6 Q = __1____ R = __2____ Answer: 8 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Question 5. 5 ÷ 5 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 5 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 6. 6 ÷ 5 Q = ___1___ R = __1____ Answer: 6 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Question 7. 7 ÷ 4 Q = ___1___ R = __3____ Answer: 7 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 7 ÷ 4 when 7 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 3, (4 X 1 = 4) and remainder is 3.
Question 8. 6 ÷ 4 Q = __1____ R = __2____ Answer: 6 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Question 9. 5 ÷ 3 Q = __1____ R = __2____ Answer: 5 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Question 10. 6 ÷ 3 Q = __2____ R = ___0___ Answer: 6 ÷ 3 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Question 11. 2 ÷ 2 Q = __1____ R = __0____ Answer: 2 ÷ 2 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 12. 3 ÷ 2 Q = ___1___ R = ___1___ Answer: 3 ÷ 2 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Question 13. 3 ÷ 3 Q = ___1___ R = __0____ Answer: 3 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 14. 4 ÷ 3 Q = __1___ R = ___1___ Answer: 4 ÷ 3 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Question 15. 8 ÷ 7 Q = __1____ R = ___1__ Answer: 8 ÷ 7 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 7 when 8 is divided by 7 we get quotient as 1, (7 X 1 = 7) and remainder is 1.
Question 16. 9 ÷ 7 Q = ___1___ R = __2____ Answer:
Question 17. 4 ÷ 4 Q = ___1___ R = ___0___ Answer: 4 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 18. 5 ÷ 4 Q = ___1___ R = __1____ Answer: 5 ÷ 4 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Question 19. 6 ÷ 2 Q = __3____ R = __0____ Answer: 6 ÷ 2 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 6÷ 2 when 6 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 3, (3 X 1 = 3) and remainder is 0.
Question 20. 7 ÷ 2 Q = __3____ R = __1____ Answer: 7 ÷ 2 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 1,
Question 21. 8 ÷ 5 Q = __1____ R = __3____ Answer: 8 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 3,
Question 22. 7 ÷ 5 Q = ___1___ R = __2____ Answer: 7 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 2,
Question 23. 4 ÷ 2 Q = __2____ R = __0____ Answer: 4 ÷ 2 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Explanation: Given 4 ÷ 2 when 4 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 2, (2 X 1 = 2) and remainder is 0.
Question 24. 5 ÷ 2 Q = __2____ R = __1____ Answer: 5 ÷ 2 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 1,
Question 25. 8 ÷ 4 Q = ___2___ R = ___0___ Answer: 8 ÷ 4 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 0,
Question 26. 9 ÷ 4 Q = ___2___ R = __1____ Answer: 9 ÷ 4 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 1,
Question 27. 9 ÷ 3 Q = ___3___ R = __0____ Answer: 9 ÷ 3 = quotient = 3 and remainder = 0,
Question 28. 8 ÷ 3 Q = ___2___ R = __2____ Answer: 8 ÷ 3 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 2,
Question 29. 9 ÷ 5 Q = __1____ R = ___4___ Answer: 9 ÷ 5 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 4,
Question 30. 6 ÷ 6 Q = ___1___ R = ___0___ Answer: 6 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 31. 7 ÷ 6 Q = __1____ R = ___1___ Answer: 7 ÷ 6 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 1,
Question 32. 9 ÷ 9 Q = __1____ R = ___0___ Answer: 9 ÷ 9 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 33. 7 ÷ 7 Q = ___1___ R = _0_____ Answer: 7 ÷ 7 = quotient = 1 and remainder = 0,
Question 34. 9 ÷ 2 Q = ___4___ R = ___1___ Answer: 9 ÷ 2 = quotient = 4 and remainder = 1,
Question 35. 8 ÷ 2 Q = ___4___ R = ___0___ Answer: 8 ÷ 2 = quotient = 4 and remainder = 0,
Question 36. 37 ÷ 8 Q = ___4___ R = ___5___ Answer: 37 ÷ 8 = quotient = 4 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 37 ÷ 8 when 37 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 4, (8 X 4 = 32) and remainder is 5.
Question 37. 50 ÷ 9 Q = ___5___ R = __5____ Answer: 50 ÷ 9 = quotient = 5 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 50 ÷ 9 when 50 is divided by 9 we get quotient as 5, (9 X 5 = 45) and remainder is 5.
Question 38. 17 ÷ 6 Q = ___2___ R = __5____ Answer: 17 ÷ 6 = quotient = 2 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 17 ÷ 6 when 17 is divided by 6 we get quotient as 2, (6 X 2 = 12) and remainder is 5.
Question 39. 48 ÷ 7 Q = __6____ R = __6____ Answer: 48 ÷ 7 = quotient = 6 and remainder = 6,
Explanation: Given 48 ÷ 7 when 48 is divided by 7 we get quotient as 6, (7 X 6 = 42) and remainder is 6.
Question 40. 51 ÷ 8 Q = ___6___ R = ___3___ Answer: 51 ÷ 8 = quotient = 6 and remainder = 3,
Explanation: Given 51 ÷ 8 when 51 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 6, (8 X 6 = 48) and remainder is 3.
Question 41. 68 ÷ 9 Q = __7____ R = ___5___ Answer: 68 ÷ 9 = quotient = 7 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 68 ÷ 9 when 68 is divided by 9 we get quotient as 7, (9 X 7= 63) and remainder is 5.
Question 42. 53 ÷ 6 Q = __8____ R = __5____ Answer: 53 ÷ 6 = quotient = 8 and remainder = 5,
Question 43. 61 ÷ 8 Q = ___7___ R = __5____ Answer: 61 ÷ 8 = quotient = 7 and remainder = 5,
Explanation: Given 61 ÷ 8 when 61 is divided by 8 we get quotient as 71, (8 X 7 = 56) and remainder is 5.
Question 44. 70 ÷ 9 Q = __7____ R = __7____ Answer: 70 ÷ 9 = quotient = 7 and remainder = 7,
Explanation: Given 70 ÷ 9 when 70 is divided by 9 we get quotient as 7, (9 X 7 = 63) and remainder is 7.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21 Problem Set Answer Key
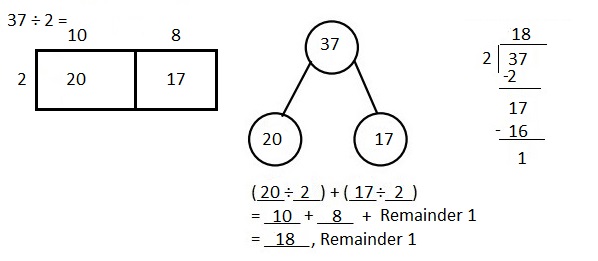
Explanation: Solved 76 ÷ 3 using an area model. Used long division and the distributive property to record your work.
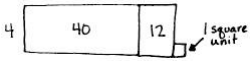
Explanation: Carolina solved the following division problem by using an area model as 40 + 12 + 1 = 53 divided by 4.
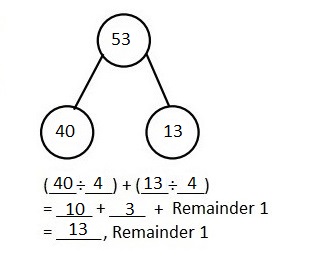
Solved the following problems using the area model. Supported the area model with long division or the distributive property.
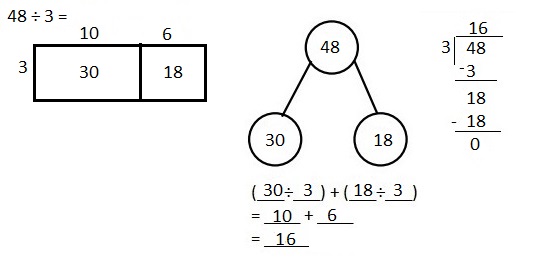
Explanation: Given 49 ÷ 3 when 49 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 16, (3 X 16 = 48) and remainder is 1. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
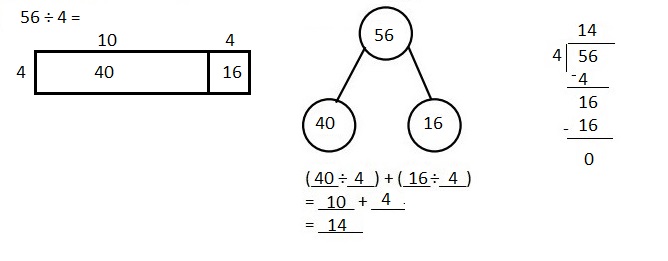
Explanation: Given 56 ÷ 4 when 56 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 14, (4 X 14 = 56) and remainder is 0. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
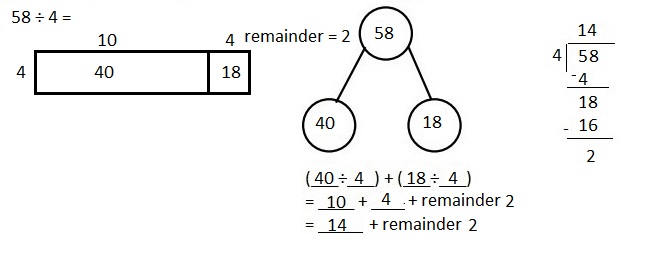
Explanation: Given 58 ÷ 4 when 58 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 14, (4 X 14 = 58) and remainder is 2. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
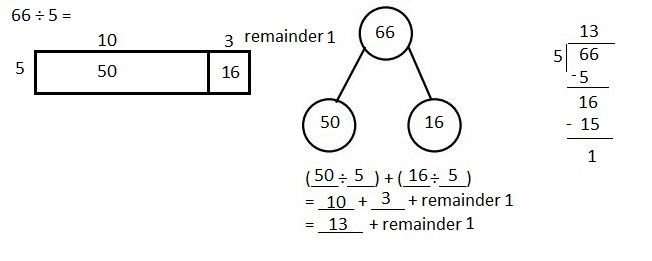
Explanation: Given 66 ÷ 5 when 66 is divided by 5 we get quotient as 13, (5 X 13 = 65) and remainder is 1. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
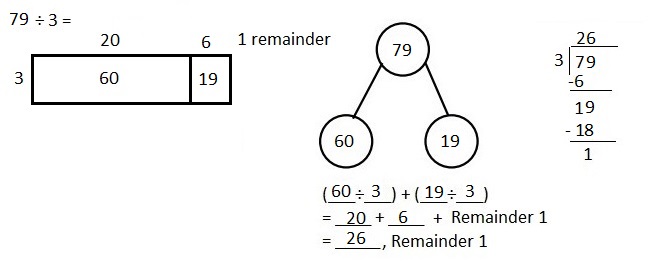
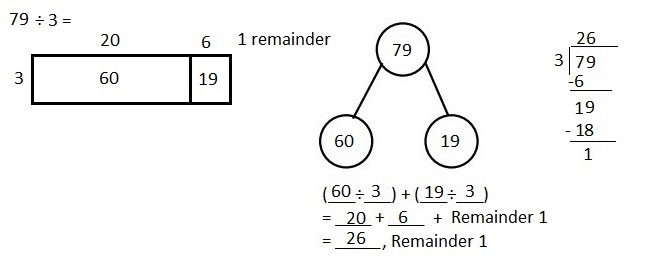
Explanation: Given 79 ÷ 3 when 79 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 26, (3 X 26 = 78 ) and remainder is 1. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
Question 10. Seventy-three students are divided into groups of 6 students each. How many groups of 6 students are there? How many students will not be in a group of 6?
Answer: There are 12 groups of 6 students are there, 1 student will not be in a group of 6,
Explanation: Given Seventy-three students are divided into groups of 6 students each. The number of groups of 6 students are 73 ÷ 6 = quotient = 12 and remainder = 1 means there are 12 groups of 6 students are there and 1 student will not be in a group of 6.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21 Exit Ticket Answer Key
Explanation: Kyle drew the following area model to find an unknown length. The division equation did he modeled is 59 ÷ 2 as (40 + 18 + 1) ÷ 2 = 59 ÷ 2.
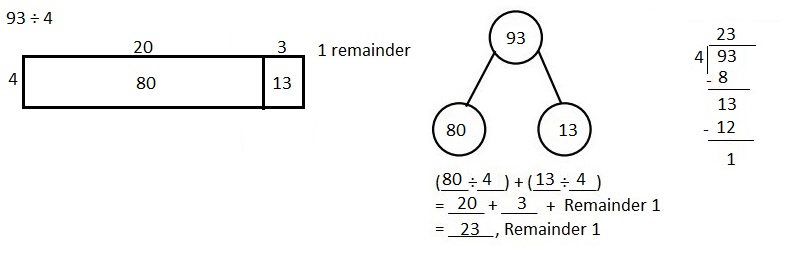
Explanation: Solved 93 ÷ 4 using the area model, long division, and the distributive property as shown above.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 22 Homework Answer Key
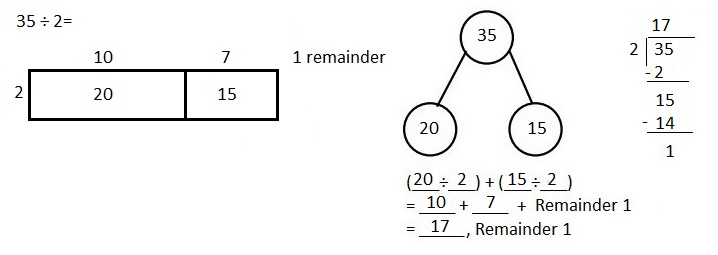
Explanation: Solved 35 ÷ 2 using an area model. Used long division and the distributive property to record my work as shown above.
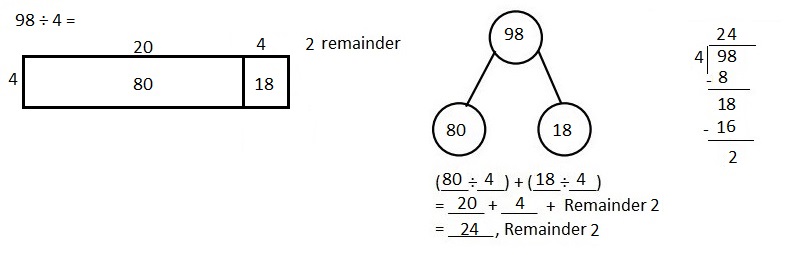
Explanation: Paulina solved the following division problem by drawing an area model as (40 + 40 + 16 + 2) ÷ 4 = 98 ÷ 4.
Solve the following problems using the area model. Support the area model with long division or the distributive property.
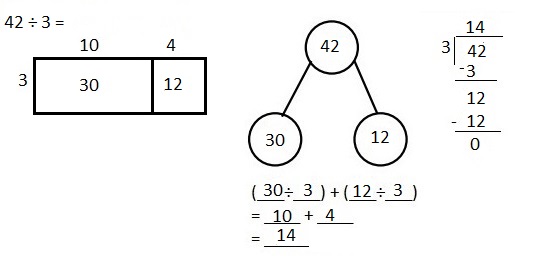
Explanation: Given 42 ÷ 3 when 14 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 14, (3 X 14 = 42) and remainder is 0. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
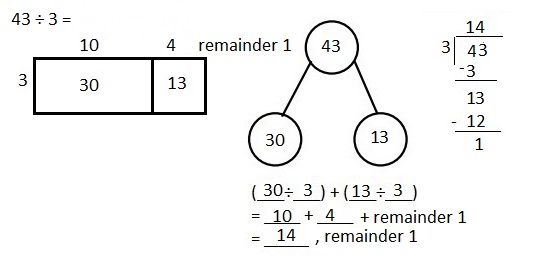
Explanation: Given 43 ÷ 3 when 43 is divided by 3 we get quotient as 14, (3 X 14 = 42) and remainder is 1. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
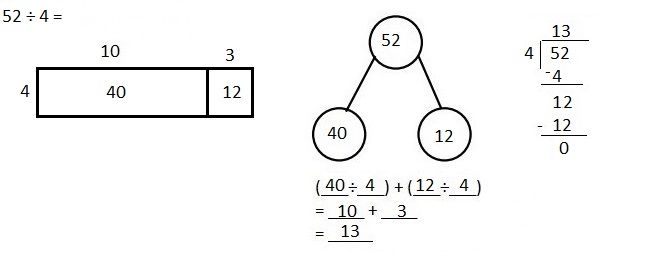
Explanation: Given 52 ÷ 4 when 52 is divided by 4 we get quotient as 13, (4 X 13 = 52) and remainder is 0. Solved the following problem using the area model. Supported the area model with long division and the distributive property.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Standards Alignment
Assessments, professional learning, family engagement, case studies.
NEW EUREKA MATH 2 ® PILOT PACKAGE
Are you looking for new ways to advance equity and build knowledge in your math classroom with high-quality instructional materials? EdReports recently reviewed Eureka Math 2 . Scan the QR code or access the final report .
Check out our special pilot package for only $10 per student.
Shop Online

SEE THE SCIENCE OF READING IN ACTION
At Great Minds ® , we’re committed to ensuring our curricula are aligned to the latest research on how students best learn to read, write, and build knowledge.
Explore webinars, blogs, research briefs, and more to discover how we incorporate this important body of research.

FREE CLASSROOM PRINTABLES
At Great Minds®, we’re committed to supporting educators with high-quality curricula and resources.
Explore resources designed to aid students in science and engineering and spark classroom conversation.
Webinar Library
Instructional resources, trending topics, knowledge-building, the science of reading, lesson design, universal design for learning (udl), background knowledge.
Palm Springs, CA
Houston, TX
New Orleans, LA


Eureka Math Print Materials
As the creator of Engage NY Math and Eureka Math , Great Minds is the only place where you can get print editions of the PK–12 curriculum. Our printed materials are available in two configurations: Learn, Practice, Succeed , or student workbooks, teacher editions, assessment and fluency materials.
The Learn, Practice, Succeed configuration is available for grades K–8 and offers teachers multiple ways to differentiate instruction, provide practice, and assess student learning. The Learn, Practice, Succeed configurations are also available in the following languages:
- Arabic (K–5)
- Armenian (K–6)
- French (K–6)
- Korean (K–6)
- Traditional Chinese (K–3)
- Simplified Chinese (4–6)
- Spanish (K–8)
In addition to our Learn, Practice, Succeed configuration you can get student workbooks, teacher editions, and assessment and fluency materials for Grades PK–12. These materials are also available in Spanish for Grades K–8.
Along with our curriculum print materials, Eureka Math Manipulative Kits and Study Guides are available exclusively from our partner, Didax. We also offer specially priced print bundles.
Our sales team is available to help you navigate our offerings and determine the best package for your school or district.
Learn, Practice, Succeed Configuration: K–5
- Application Problems
- Problem Sets
- Exit Tickets
Practice Book*
- Sprints & Fluency
- Additional Problems for Homework
Homework Helpers
* The Learn and Practice books provide all of the printed materials a student uses for core instruction.

Learn, Practice, Succeed Configuration: 6–8
Learn, Practice, Succeed Book*
* The same content found in the Learn , Practice , Succeed books but in one book per module.

Original Configuration: PK–12
Student Edition*
Printed Packets
* Available in Spanish (Grades K-8)

NOW AVAILABLE
Eureka Math in Other Languages
Eureka Math is now available in the following languages.

Traditional Chinese

Simplified Chinese

Bundles and Class Sets Available
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set.

every child is capable of greatness
- Job Openings
- Digital Support
- Print Support
- Media Inquiries
Let’s Connect
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- System Status
- CA Residents: Do Not Sell My Info

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Engage NY Eureka Math 4th Grade Module 3 Lesson 21 Answer Key Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21 Sprint Answer Key. Division with Remainders. Answer: Question 1. 8 ÷ 2 Q = ___4___ R = ___0___ Answer: 8 ÷ 2 = 4 quotient = 4 and remainder = 0, Explanation: Given 8 ÷ 2 when 8 is divided by 2 we get quotient as 4, (2 X 4 = 8) and remainder ...
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21For more Eureka Math (EngageNY) videos and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a me...
It's Homework Time! Help for fourth graders with Eureka Math Module 5 Lesson 21.
Eureka Essentials: Grade 4. An outline of learning goals, key ideas, pacing suggestions, and more! Fluency Games. Teach Eureka Lesson Breakdown. Downloadable Resources. Teacher editions, student materials, application problems, sprints, etc. Application Problems. Files for printing or for projecting on the screen.
Unit 1: Module 1: Place value, rounding, and algorithms for addition and subtraction. 0/2000 Mastery points. Topic A: Place value of multi-digit whole numbers Topic B: Comparing multi-digit whole numbers Topic C: Rounding multi-digit whole numbers. Topic D: Multi-digit whole number addition Topic E: Multi-digit whole number subtraction.
Multi-Digit Multiplication and Division. Eureka Essentials: Grade 4. An outline of learning goals, key ideas, pacing suggestions, and more! Fluency Games. Teach Eureka Lesson Breakdown. Downloadable Resources. Teacher editions, student materials, application problems, sprints, etc. Application Problems.
Eureka Essentials: Grade 4 URL An outline of learning goals, key ideas, pacing suggestions, and more! ... Lesson 1 Video Page. Lesson PDF Page. Homework Solutions Page. Promethean ... This work by EMBARC.Online based upon Eureka Math and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set.
As the creator of Engage NY Math and Eureka Math, Great Minds is the only place where you can get print editions of the PK-12 curriculum.Our printed materials are available in two configurations: Learn, Practice, Succeed, or student workbooks, teacher editions, assessment and fluency materials. The Learn, Practice, Succeed configuration is available for grades K-8 and offers teachers ...
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21. EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 21.
10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Eureka Math™ Grade 4, Module 4 Student File_A Contains copy-ready classwork and homework as well as templates (including cut outs) ... 1 Homework 4Lesson 3. a. Observe the familiar figures below. Label some points on each figure. b. Use those points to label and name representations of each of the following in the table ...
3. Step 1: Draw an area model for a fraction with units of thirds, fourths, or fifths. Step 2: Shade in more than one fractional unit. Step 3: Partition the area model again to find an equivalent fraction. Step 4: Write the equivalent fractions as a number sentence.
Eureka Math™. Grade 2, Module 4 Student File_A. Contains copy-ready classwork and homework as well as templates (including cut outs) A Story of Units®. Lesson 1 Problem Set 2 4. Lesson 1: 1Relate 1 more, 1 less, 10 more, and 10 less to addition and subtraction of 1 and 10. Name Date 1. Complete each moreor lessstatement.
Grade 4. Gr4General. Gr4Mod1. Grade 4 Module 1. Topic A: Place Value of Multi-Digit Whole Numbers. Lesson 1. Lesson 2. Lesson 3. Lesson 4. Topic B: Comparing Multi-Digit Whole Numbers. Lesson 5. Lesson 6. Topic C: Rounding Multi-Digit Whole Numbers. Lesson 7. Lesson 8. Lesson 9. Lesson 10. Mid-Module. Topic D: Multi-Digit Whole Number Addition ...
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 1 Module 4 Lesson 21For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/eurekapusdPLEASE leave a message if a video has a technical diffic...
A 4th grade resource for teachers using Eureka Math and EngageNY. G4M4: Angle Measure and Plane Figures. A 4th grade resource for teachers using Eureka Math and EngageNY. G4M5: Fraction Equivalence, Ordering, and Operations. A 4th grade resource for teachers using Eureka Math and EngageNY. G4M6: Decimal Fractions.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 21For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/engageportal