Faculty Resources
Assignments.

The assignments in this course are openly licensed, and are available as-is, or can be modified to suit your students’ needs. Selected answer keys are available to faculty who adopt Waymaker, OHM, or Candela courses with paid support from Lumen Learning. This approach helps us protect the academic integrity of these materials by ensuring they are shared only with authorized and institution-affiliated faculty and staff.
If you import this course into your learning management system (Blackboard, Canvas, etc.), the assignments will automatically be loaded into the assignment tool, where they may be adjusted, or edited there. Assignments also come with rubrics and pre-assigned point values that may easily be edited or removed.
The assignments for Introductory Psychology are ideas and suggestions to use as you see appropriate. Some are larger assignments spanning several weeks, while others are smaller, less-time consuming tasks. You can view them below or throughout the course.
You can view them below or throughout the course.

Discussion Grading Rubric
The discussions in the course vary in their requirements and design, but this rubric below may be used and modified to facilitate grading.
- Assignments with Solutions. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Pencil Cup. Authored by : IconfactoryTeam. Provided by : Noun Project. Located at : https://thenounproject.com/term/pencil-cup/628840/ . License : CC BY: Attribution

- Accessibility
- Main SQA Website
- Using the site
- > Subjects
- > Psychology
- > Higher
- > Assignment
In this section
Select a subject Accounting Administration and IT Applications of Mathematics Apprenticeships Art and Design Baccalaureates Barista Skills Biology Business Management Care Chemistry Childcare & Development Chinese Languages Classical Studies Computing Science Core Skills Dance Design and Manufacture Drama Economics Engineering Science English Environmental Science ESOL Fashion and Textiles French Gaelic (Learners) Gaidhlig Geography German Graphic Communication Health and Food Technology History HN Human Biology Italian Latin Mathematics Mathematics of Mechanics Media Modern Studies Music Music Technology National 1 & 2 NPA Philosophy Photography Physical Education Physics Politics Practical Cake Craft Practical Cookery Practical Electronics Practical Metalworking Practical Woodworking Psychology RMPS Scots Language Skills for Work Sociology Spanish Statistics SVQ Urdu
- Question paper
- Presentations
- Course Reports
- Additional resources for sessions 2020-22
Higher Psychology - assignment
Assignment 2022 (all links open as pdf files), complete assignments, usage of technology and its effect on sleep.
- Candidate 1 Evidence
- Candidate 1 Commentary
The impact of false high estimates on the participants estimated guess of sweets in the jar
- Candidate 2 Evidence
- Candidate 2 Commentary
1. Introduction (Aims and Hypotheses)
- Section 1 Candidate Evidence
- Section 1 Commentary
2. Method (Design)
- Section 2 Candidate Evidence
- Section 2 Commentary
3. Method (Ethics)
- Section 3 Candidate Evidence
- Section 3 Commentary
4. Discussion
- Section 4 Candidate Evidence
- Section 4 Commentary
Assignment 2021 (All links open to PDF files)
Please view these materials in conjunction with the higher Psychology webinar recording from April 2021 , available within the 2021 section of the Webinars page.
- Candidate Evidence 2021
- Commentary 2021
Assignment 2019 (All links open as PDF files)
Investigating how age affects conformity, how does prelim stress correlate with winter illnesses.
- Candidate 2 Evidence
Conformity Study - Sweets in a Jar
- Candidate 3 Evidence
Correlation between screen time and quantity/quality of sleep gained
- Candidate 4 Evidence
- Candidates 1 to 4 Commentaries
- Workshop - Candidate evidence and commentary
- Terms & Conditions
- Back To Top
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
50+ Research Topics for Psychology Papers
How to Find Psychology Research Topics for Your Student Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
- Specific Branches of Psychology
- Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
- Human Cognition
- Human Development
- Critique of Publications
- Famous Experiments
- Historical Figures
- Specific Careers
- Case Studies
- Literature Reviews
- Your Own Study/Experiment
Are you searching for a great topic for your psychology paper ? Sometimes it seems like coming up with topics of psychology research is more challenging than the actual research and writing. Fortunately, there are plenty of great places to find inspiration and the following list contains just a few ideas to help get you started.
Finding a solid topic is one of the most important steps when writing any type of paper. It can be particularly important when you are writing a psychology research paper or essay. Psychology is such a broad topic, so you want to find a topic that allows you to adequately cover the subject without becoming overwhelmed with information.
I can always tell when a student really cares about the topic they chose; it comes through in the writing. My advice is to choose a topic that genuinely interests you, so you’ll be more motivated to do thorough research.
In some cases, such as in a general psychology class, you might have the option to select any topic from within psychology's broad reach. Other instances, such as in an abnormal psychology course, might require you to write your paper on a specific subject such as a psychological disorder.
As you begin your search for a topic for your psychology paper, it is first important to consider the guidelines established by your instructor.
Research Topics Within Specific Branches of Psychology
The key to selecting a good topic for your psychology paper is to select something that is narrow enough to allow you to really focus on the subject, but not so narrow that it is difficult to find sources or information to write about.
One approach is to narrow your focus down to a subject within a specific branch of psychology. For example, you might start by deciding that you want to write a paper on some sort of social psychology topic. Next, you might narrow your focus down to how persuasion can be used to influence behavior .
Other social psychology topics you might consider include:
- Prejudice and discrimination (i.e., homophobia, sexism, racism)
- Social cognition
- Person perception
- Social control and cults
- Persuasion, propaganda, and marketing
- Attraction, romance, and love
- Nonverbal communication
- Prosocial behavior
Psychology Research Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
Exploring a psychological disorder or a specific treatment modality can also be a good topic for a psychology paper. Some potential abnormal psychology topics include specific psychological disorders or particular treatment modalities, including:
- Eating disorders
- Borderline personality disorder
- Seasonal affective disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Antisocial personality disorder
- Profile a type of therapy (i.e., cognitive-behavioral therapy, group therapy, psychoanalytic therapy)
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition
Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include:
- False memories
- Speech disorders
- Problem-solving
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Development
In this area, you might opt to focus on issues pertinent to early childhood such as language development, social learning, or childhood attachment or you might instead opt to concentrate on issues that affect older adults such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease.
Some other topics you might consider include:
- Language acquisition
- Media violence and children
- Learning disabilities
- Gender roles
- Child abuse
- Prenatal development
- Parenting styles
- Aspects of the aging process
Do a Critique of Publications Involving Psychology Research Topics
One option is to consider writing a critique paper of a published psychology book or academic journal article. For example, you might write a critical analysis of Sigmund Freud's Interpretation of Dreams or you might evaluate a more recent book such as Philip Zimbardo's The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil .
Professional and academic journals are also great places to find materials for a critique paper. Browse through the collection at your university library to find titles devoted to the subject that you are most interested in, then look through recent articles until you find one that grabs your attention.
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Famous Experiments
There have been many fascinating and groundbreaking experiments throughout the history of psychology, providing ample material for students looking for an interesting term paper topic. In your paper, you might choose to summarize the experiment, analyze the ethics of the research, or evaluate the implications of the study. Possible experiments that you might consider include:
- The Milgram Obedience Experiment
- The Stanford Prison Experiment
- The Little Albert Experiment
- Pavlov's Conditioning Experiments
- The Asch Conformity Experiment
- Harlow's Rhesus Monkey Experiments
Topics of Psychology Research About Historical Figures
One of the simplest ways to find a great topic is to choose an interesting person in the history of psychology and write a paper about them. Your paper might focus on many different elements of the individual's life, such as their biography, professional history, theories, or influence on psychology.
While this type of paper may be historical in nature, there is no need for this assignment to be dry or boring. Psychology is full of fascinating figures rife with intriguing stories and anecdotes. Consider such famous individuals as Sigmund Freud, B.F. Skinner, Harry Harlow, or one of the many other eminent psychologists .
Psychology Research Topics About a Specific Career
Another possible topic, depending on the course in which you are enrolled, is to write about specific career paths within the field of psychology . This type of paper is especially appropriate if you are exploring different subtopics or considering which area interests you the most.
In your paper, you might opt to explore the typical duties of a psychologist, how much people working in these fields typically earn, and the different employment options that are available.
Topics of Psychology Research Involving Case Studies
One potentially interesting idea is to write a psychology case study of a particular individual or group of people. In this type of paper, you will provide an in-depth analysis of your subject, including a thorough biography.
Generally, you will also assess the person, often using a major psychological theory such as Piaget's stages of cognitive development or Erikson's eight-stage theory of human development . It is also important to note that your paper doesn't necessarily have to be about someone you know personally.
In fact, many professors encourage students to write case studies on historical figures or fictional characters from books, television programs, or films.
Psychology Research Topics Involving Literature Reviews
Another possibility that would work well for a number of psychology courses is to do a literature review of a specific topic within psychology. A literature review involves finding a variety of sources on a particular subject, then summarizing and reporting on what these sources have to say about the topic.
Literature reviews are generally found in the introduction of journal articles and other psychology papers , but this type of analysis also works well for a full-scale psychology term paper.
Topics of Psychology Research Based on Your Own Study or Experiment
Many psychology courses require students to design an actual psychological study or perform some type of experiment. In some cases, students simply devise the study and then imagine the possible results that might occur. In other situations, you may actually have the opportunity to collect data, analyze your findings, and write up your results.
Finding a topic for your study can be difficult, but there are plenty of great ways to come up with intriguing ideas. Start by considering your own interests as well as subjects you have studied in the past.
Online sources, newspaper articles, books , journal articles, and even your own class textbook are all great places to start searching for topics for your experiments and psychology term papers. Before you begin, learn more about how to conduct a psychology experiment .
What This Means For You
After looking at this brief list of possible topics for psychology papers, it is easy to see that psychology is a very broad and diverse subject. While this variety makes it possible to find a topic that really catches your interest, it can sometimes make it very difficult for some students to select a good topic.
If you are still stumped by your assignment, ask your instructor for suggestions and consider a few from this list for inspiration.
- Hockenbury, SE & Nolan, SA. Psychology. New York: Worth Publishers; 2014.
- Santrock, JW. A Topical Approach to Lifespan Development. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

Resources: Course Assignments
Assignment: Motivation and Emotion
Theories of emotion.
STEP 1 : Using a stimulus of your choosing (not one found in your text) demonstrate the James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, Schachter-Singer, and cognitive-mediational theories of emotion. Describe each in just a few sentences.
CC licensed content, Original
- Theories of Emotion Assignment. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
General Psychology Copyright © by OpenStax and Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Browse Course Material
Course info.
- Prof. Jeremy Wolfe
Departments
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
As Taught In
- Cognitive Science
Learning Resource Types
Introduction to psychology, assignments, the general idea.
Over the course of the term, you need to write three different kinds of papers and revise one of them.
Each of these will be about 6 pages long (about 1800 words). The revision will be a bit longer.
On the server, there is a folder associated with each lecture and/or chapter. In the folder you will find pdfs of an article or two (sometimes a URL pointing to an article). The contents of the folder will be described on the handout for that lecture/chapter. The handouts are also on the web. Your work for each of the papers begins with one (or more) of these articles. What you do with the article(s) will depend on the kind of paper you are writing. (See below).
General Requirements: Sources
- Each of the first three papers must use at least one of the articles posted on the server.
- Each of the first three papers must use at least two sources beyond what is on the website.
- Those two sources must be published in the scholarly literature or in book form (College level textbooks are fine for one of the two sources. No…you can’t use Gleitman.)
- If you are in doubt about the scholarly nature of a source, ask your TA or ask the librarians (good reason to go to a library workshop).
- A random webpage found by ‘Googling’ cannot be counted toward the two scholarly resources; BUT it might be useful. You can use such sources. You can cite them (give the URL). You just can’t rely on them exclusively.
- Electronic versions of scholarly publications (like most of what I have put on the server) are just fine.
- When in doubt, ASK.

General Requirements: Writing
Always, always make sure you are using your own words. Direct quotation can be used but only very sparingly. It is rarely needed in this sort of writing. Direct quotes should be “in quotes” of course and a proper citation should be given. What we really want to avoid are papers where you read a paragraph and then write a paragraph that is a close paraphrase of your source. Changing “I discovered” to “She discovered” is not “using your own words”. Read your sources. Take notes on your sources. Think about the material. Then write something of your own. If your paper is a pastiche of near quotes, we are going to give you a really bad grade. You have been warned.
Citation: We are not particularly concerned about the form of citation that you use. I suggest following the model used in Gleitman. You put an author and year marker in the text at the relevant point (Wolfe, 2004) and a suitable bibliographic reference at the end of the paper.
Wolfe, J. M. “Writing Assignments for Intro.” Psych. Journal of Course Requirements 12, no. 4 (2004): 403-405.
The critical requirement is that we should be able to find the source of any facts and ideas that you gleaned in your reading. Again, when in doubt, ask.
The Four Papers
Paper 1: Writing for the Public ( PDF )
Paper 2: Taking the Next Step ( PDF )
Examples of Good and Bad Writing ( PDF )
Paper 3: Rewriting the Textbook ( PDF )
Paper 4: Revision ( PDF )

You are leaving MIT OpenCourseWare

What this handout is about
This handout discusses some of the common writing assignments in psychology courses, and it presents strategies for completing them. The handout also provides general tips for writing psychology papers and for reducing bias in your writing.
What is psychology?
Psychology, one of the behavioral sciences, is the scientific study of observable behaviors, like sleeping, and abstract mental processes, such as dreaming. Psychologists study, explain, and predict behaviors. Because of the complexity of human behaviors, researchers use a variety of methods and approaches. They ask questions about behaviors and answer them using systematic methods. For example, to understand why female students tend to perform better in school than their male classmates, psychologists have examined whether parents, teachers, schools, and society behave in ways that support the educational outcomes of female students to a greater extent than those of males.
Writing in psychology
Writing in psychology is similar to other forms of scientific writing in that organization, clarity, and concision are important. The Psychology Department at UNC has a strong research emphasis, so many of your assignments will focus on synthesizing and critically evaluating research, connecting your course material with current research literature, and designing and carrying out your own studies.
Common assignments
Reaction papers.
These assignments ask you to react to a scholarly journal article. Instructors use reaction papers to teach students to critically evaluate research and to synthesize current research with course material. Reaction papers typically include a brief summary of the article, including prior research, hypotheses, research method, main results, and conclusions. The next step is your critical reaction. You might critique the study, identify unresolved issues, suggest future research, or reflect on the study’s implications. Some instructors may want you to connect the material you are learning in class with the article’s theories, methodology, and findings. Remember, reaction papers require more than a simple summary of what you have read.
To successfully complete this assignment, you should carefully read the article. Go beyond highlighting important facts and interesting findings. Ask yourself questions as you read: What are the researchers’ assumptions? How does the article contribute to the field? Are the findings generalizable, and to whom? Are the conclusions valid and based on the results? It is important to pay attention to the graphs and tables because they can help you better assess the researchers’ claims.
Your instructor may give you a list of articles to choose from, or you may need to find your own. The American Psychological Association (APA) PsycINFO database is the most comprehensive collection of psychology research; it is an excellent resource for finding journal articles. You can access PsycINFO from the E-research tab on the Library’s webpage. Here are the most common types of articles you will find:
- Empirical studies test hypotheses by gathering and analyzing data. Empirical articles are organized into distinct sections based on stages in the research process: introduction, method, results, and discussion.
- Literature reviews synthesize previously published material on a topic. The authors define or clarify the problem, summarize research findings, identify gaps/inconsistencies in the research, and make suggestions for future work. Meta-analyses, in which the authors use quantitative procedures to combine the results of multiple studies, fall into this category.
- Theoretical articles trace the development of a specific theory to expand or refine it, or they present a new theory. Theoretical articles and literature reviews are organized similarly, but empirical information is included in theoretical articles only when it is used to support the theoretical issue.
You may also find methodological articles, case studies, brief reports, and commentary on previously published material. Check with your instructor to determine which articles are appropriate.
Research papers
This assignment involves using published research to provide an overview of and argument about a topic. Simply summarizing the information you read is not enough. Instead, carefully synthesize the information to support your argument. Only discuss the parts of the studies that are relevant to your argument or topic. Headings and subheadings can help guide readers through a long research paper. Our handout on literature reviews may help you organize your research literature.
Choose a topic that is appropriate to the length of the assignment and for which you can find adequate sources. For example, “self-esteem” might be too broad for a 10- page paper, but it may be difficult to find enough articles on “the effects of private school education on female African American children’s self-esteem.” A paper in which you focus on the more general topic of “the effects of school transitions on adolescents’ self-esteem,” however, might work well for the assignment.
Designing your own study/research proposal
You may have the opportunity to design and conduct your own research study or write about the design for one in the form of a research proposal. A good approach is to model your paper on articles you’ve read for class. Here is a general overview of the information that should be included in each section of a research study or proposal:
- Introduction: The introduction conveys a clear understanding of what will be done and why. Present the problem, address its significance, and describe your research strategy. Also discuss the theories that guide the research, previous research that has been conducted, and how your study builds on this literature. Set forth the hypotheses and objectives of the study.
- Methods: This section describes the procedures used to answer your research questions and provides an overview of the analyses that you conducted. For a research proposal, address the procedures that will be used to collect and analyze your data. Do not use the passive voice in this section. For example, it is better to say, “We randomly assigned patients to a treatment group and monitored their progress,” instead of “Patients were randomly assigned to a treatment group and their progress was monitored.” It is acceptable to use “I” or “we,” instead of the third person, when describing your procedures. See the section on reducing bias in language for more tips on writing this section and for discussing the study’s participants.
- Results: This section presents the findings that answer your research questions. Include all data, even if they do not support your hypotheses. If you are presenting statistical results, your instructor will probably expect you to follow the style recommendations of the American Psychological Association. You can also consult our handout on figures and charts . Note that research proposals will not include a results section, but your instructor might expect you to hypothesize about expected results.
- Discussion: Use this section to address the limitations of your study as well as the practical and/or theoretical implications of the results. You should contextualize and support your conclusions by noting how your results compare to the work of others. You can also discuss questions that emerged and call for future research. A research proposal will not include a discussion section. But you can include a short section that addresses the proposed study’s contribution to the literature on the topic.
Other writing assignments
For some assignments, you may be asked to engage personally with the course material. For example, you might provide personal examples to evaluate a theory in a reflection paper. It is appropriate to share personal experiences for this assignment, but be mindful of your audience and provide only relevant and appropriate details.
Writing tips for psychology papers
Psychology is a behavioral science, and writing in psychology is similar to writing in the hard sciences. See our handout on writing in the sciences . The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association provides an extensive discussion on how to write for the discipline. The Manual also gives the rules for psychology’s citation style, called APA. The Library’s citation tutorial will also introduce you to the APA style.
Suggestions for achieving precision and clarity in your writing
- Jargon: Technical vocabulary that is not essential to understanding your ideas can confuse readers. Similarly, refrain from using euphemistic phrases instead of clearer terms. Use “handicapped” instead of “handi-capable,” and “poverty” instead of “monetarily felt scarcity,” for example.
- Anthropomorphism: Anthropomorphism occurs when human characteristics are attributed to animals or inanimate entities. Anthropomorphism can make your writing awkward. Some examples include: “The experiment attempted to demonstrate…,” and “The tables compare…” Reword such sentences so that a person performs the action: “The experimenter attempted to demonstrate…” The verbs “show” or “indicate” can also be used: “The tables show…”
- Verb tenses: Select verb tenses carefully. Use the past tense when expressing actions or conditions that occurred at a specific time in the past, when discussing other people’s work, and when reporting results. Use the present perfect tense to express past actions or conditions that did not occur at a specific time, or to describe an action beginning in the past and continuing in the present.
- Pronoun agreement: Be consistent within and across sentences with pronouns that refer to a noun introduced earlier (antecedent). A common error is a construction such as “Each child responded to questions about their favorite toys.” The sentence should have either a plural subject (children) or a singular pronoun (his or her). Vague pronouns, such as “this” or “that,” without a clear antecedent can confuse readers: “This shows that girls are more likely than boys …” could be rewritten as “These results show that girls are more likely than boys…”
- Avoid figurative language and superlatives: Scientific writing should be as concise and specific as possible. Emotional language and superlatives, such as “very,” “highly,” “astonishingly,” “extremely,” “quite,” and even “exactly,” are imprecise or unnecessary. A line that is “exactly 100 centimeters” is, simply, 100 centimeters.
- Avoid colloquial expressions and informal language: Use “children” rather than “kids;” “many” rather than “a lot;” “acquire” rather than “get;” “prepare for” rather than “get ready;” etc.
Reducing bias in language
Your writing should show respect for research participants and readers, so it is important to choose language that is clear, accurate, and unbiased. The APA sets forth guidelines for reducing bias in language: acknowledge participation, describe individuals at the appropriate level of specificity, and be sensitive to labels. Here are some specific examples of how to reduce bias in your language:
- Acknowledge participation: Use the active voice to acknowledge the subjects’ participation. It is preferable to say, “The students completed the surveys,” instead of “The experimenters administered surveys to the students.” This is especially important when writing about participants in the methods section of a research study.
- Gender: It is inaccurate to use the term “men” when referring to groups composed of multiple genders. See our handout on gender-inclusive language for tips on writing appropriately about gender.
- Race/ethnicity: Be specific, consistent, and sensitive with terms for racial and ethnic groups. If the study participants are Chinese Americans, for instance, don’t refer to them as Asian Americans. Some ethnic designations are outdated or have negative connotations. Use terms that the individuals or groups prefer.
- Clinical terms: Broad clinical terms can be unclear. For example, if you mention “at risk” in your paper, be sure to specify the risk—“at risk for school failure.” The same principle applies to psychological disorders. For instance, “borderline personality disorder” is more precise than “borderline.”
- Labels: Do not equate people with their physical or mental conditions or categorize people broadly as objects. For example, adjectival forms like “older adults” are preferable to labels such as “the elderly” or “the schizophrenics.” Another option is to mention the person first, followed by a descriptive phrase— “people diagnosed with schizophrenia.” Be careful using the label “normal,” as it may imply that others are abnormal.
- Other ways to reduce bias: Consistently presenting information about the socially dominant group first can promote bias. Make sure that you don’t always begin with men followed by other genders when writing about gender, or whites followed by minorities when discussing race and ethnicity. Mention differences only when they are relevant and necessary to understanding the study. For example, it may not be important to indicate the sexual orientation of participants in a study about a drug treatment program’s effectiveness. Sexual orientation may be important to mention, however, when studying bullying among high school students.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. n.d. “Frequently Asked Questions About APA Style®.” APA Style. Accessed June 24, 2019. https://apastyle.apa.org/learn/faqs/index .
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Landrum, Eric. 2008. Undergraduate Writing in Psychology: Learning to Tell the Scientific Story . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Before you write your essay, it’s important to analyse the task and understand exactly what the essay question is asking. Your lecturer may give you some advice – pay attention to this as it will help you plan your answer.
Next conduct preliminary reading based on your lecture notes. At this stage, it’s not crucial to have a robust understanding of key theories or studies, but you should at least have a general “gist” of the literature.
After reading, plan a response to the task. This plan could be in the form of a mind map, a summary table, or by writing a core statement (which encompasses the entire argument of your essay in just a few sentences).
After writing your plan, conduct supplementary reading, refine your plan, and make it more detailed.
It is tempting to skip these preliminary steps and write the first draft while reading at the same time. However, reading and planning will make the essay writing process easier, quicker, and ensure a higher quality essay is produced.
Components of a Good Essay
Now, let us look at what constitutes a good essay in psychology. There are a number of important features.
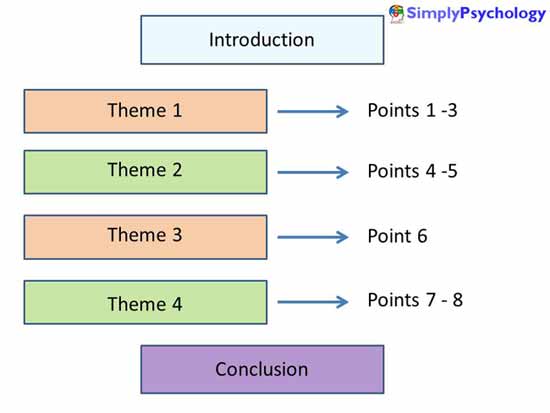
- Global Structure – structure the material to allow for a logical sequence of ideas. Each paragraph / statement should follow sensibly from its predecessor. The essay should “flow”. The introduction, main body and conclusion should all be linked.
- Each paragraph should comprise a main theme, which is illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
- Knowledge and Understanding – recognize, recall, and show understanding of a range of scientific material that accurately reflects the main theoretical perspectives.
- Critical Evaluation – arguments should be supported by appropriate evidence and/or theory from the literature. Evidence of independent thinking, insight, and evaluation of the evidence.
- Quality of Written Communication – writing clearly and succinctly with appropriate use of paragraphs, spelling, and grammar. All sources are referenced accurately and in line with APA guidelines.
In the main body of the essay, every paragraph should demonstrate both knowledge and critical evaluation.
There should also be an appropriate balance between these two essay components. Try to aim for about a 60/40 split if possible.
Most students make the mistake of writing too much knowledge and not enough evaluation (which is the difficult bit).
It is best to structure your essay according to key themes. Themes are illustrated and developed through a number of points (supported by evidence).
Choose relevant points only, ones that most reveal the theme or help to make a convincing and interesting argument.
Knowledge and Understanding
Remember that an essay is simply a discussion / argument on paper. Don’t make the mistake of writing all the information you know regarding a particular topic.
You need to be concise, and clearly articulate your argument. A sentence should contain no unnecessary words, a paragraph no unnecessary sentences.
Each paragraph should have a purpose / theme, and make a number of points – which need to be support by high quality evidence. Be clear why each point is is relevant to the argument. It would be useful at the beginning of each paragraph if you explicitly outlined the theme being discussed (.e.g. cognitive development, social development etc.).
Try not to overuse quotations in your essays. It is more appropriate to use original content to demonstrate your understanding.
Psychology is a science so you must support your ideas with evidence (not your own personal opinion). If you are discussing a theory or research study make sure you cite the source of the information.
Note this is not the author of a textbook you have read – but the original source / author(s) of the theory or research study.
For example:
Bowlby (1951) claimed that mothering is almost useless if delayed until after two and a half to three years and, for most children, if delayed till after 12 months, i.e. there is a critical period.
Maslow (1943) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs. When one need is fulfilled a person seeks to fullfil the next one, and so on.
As a general rule, make sure there is at least one citation (i.e. name of psychologist and date of publication) in each paragraph.
Remember to answer the essay question. Underline the keywords in the essay title. Don’t make the mistake of simply writing everything you know of a particular topic, be selective. Each paragraph in your essay should contribute to answering the essay question.
Critical Evaluation
In simple terms, this means outlining the strengths and limitations of a theory or research study.
There are many ways you can critically evaluate:
Methodological evaluation of research
Is the study valid / reliable ? Is the sample biased, or can we generalize the findings to other populations? What are the strengths and limitations of the method used and data obtained?
Be careful to ensure that any methodological criticisms are justified and not trite.
Rather than hunting for weaknesses in every study; only highlight limitations that make you doubt the conclusions that the authors have drawn – e.g., where an alternative explanation might be equally likely because something hasn’t been adequately controlled.
Compare or contrast different theories
Outline how the theories are similar and how they differ. This could be two (or more) theories of personality / memory / child development etc. Also try to communicate the value of the theory / study.
Debates or perspectives
Refer to debates such as nature or nurture, reductionism vs. holism, or the perspectives in psychology . For example, would they agree or disagree with a theory or the findings of the study?
What are the ethical issues of the research?
Does a study involve ethical issues such as deception, privacy, psychological or physical harm?
Gender bias
If research is biased towards men or women it does not provide a clear view of the behavior that has been studied. A dominantly male perspective is known as an androcentric bias.
Cultural bias
Is the theory / study ethnocentric? Psychology is predominantly a white, Euro-American enterprise. In some texts, over 90% of studies have US participants, who are predominantly white and middle class.
Does the theory or study being discussed judge other cultures by Western standards?
Animal Research
This raises the issue of whether it’s morally and/or scientifically right to use animals. The main criterion is that benefits must outweigh costs. But benefits are almost always to humans and costs to animals.
Animal research also raises the issue of extrapolation. Can we generalize from studies on animals to humans as their anatomy & physiology is different from humans?
The PEC System
It is very important to elaborate on your evaluation. Don’t just write a shopping list of brief (one or two sentence) evaluation points.
Instead, make sure you expand on your points, remember, quality of evaluation is most important than quantity.
When you are writing an evaluation paragraph, use the PEC system.
- Make your P oint.
- E xplain how and why the point is relevant.
- Discuss the C onsequences / implications of the theory or study. Are they positive or negative?
For Example
- Point: It is argued that psychoanalytic therapy is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority.
- Explain: Because psychoanalytic therapy involves talking and gaining insight, and is costly and time-consuming, it is argued that it is only of benefit to an articulate, intelligent, affluent minority. Evidence suggests psychoanalytic therapy works best if the client is motivated and has a positive attitude.
- Consequences: A depressed client’s apathy, flat emotional state, and lack of motivation limit the appropriateness of psychoanalytic therapy for depression.
Furthermore, the levels of dependency of depressed clients mean that transference is more likely to develop.
Using Research Studies in your Essays
Research studies can either be knowledge or evaluation.
- If you refer to the procedures and findings of a study, this shows knowledge and understanding.
- If you comment on what the studies shows, and what it supports and challenges about the theory in question, this shows evaluation.
Writing an Introduction
It is often best to write your introduction when you have finished the main body of the essay, so that you have a good understanding of the topic area.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your introduction.
Ideally, the introduction should;
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which “lie behind” the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. “Signpost” the essay’s key argument, (and, if possible, how this argument is structured).
Introductions are very important as first impressions count and they can create a h alo effect in the mind of the lecturer grading your essay. If you start off well then you are more likely to be forgiven for the odd mistake later one.
Writing a Conclusion
So many students either forget to write a conclusion or fail to give it the attention it deserves.
If there is a word count for your essay try to devote 10% of this to your conclusion.
Ideally the conclusion should summarize the key themes / arguments of your essay. State the take home message – don’t sit on the fence, instead weigh up the evidence presented in the essay and make a decision which side of the argument has more support.
Also, you might like to suggest what future research may need to be conducted and why (read the discussion section of journal articles for this).
Don”t include new information / arguments (only information discussed in the main body of the essay).
If you are unsure of what to write read the essay question and answer it in one paragraph.
Points that unite or embrace several themes can be used to great effect as part of your conclusion.
The Importance of Flow
Obviously, what you write is important, but how you communicate your ideas / arguments has a significant influence on your overall grade. Most students may have similar information / content in their essays, but the better students communicate this information concisely and articulately.
When you have finished the first draft of your essay you must check if it “flows”. This is an important feature of quality of communication (along with spelling and grammar).
This means that the paragraphs follow a logical order (like the chapters in a novel). Have a global structure with themes arranged in a way that allows for a logical sequence of ideas. You might want to rearrange (cut and paste) paragraphs to a different position in your essay if they don”t appear to fit in with the essay structure.
To improve the flow of your essay make sure the last sentence of one paragraph links to first sentence of the next paragraph. This will help the essay flow and make it easier to read.
Finally, only repeat citations when it is unclear which study / theory you are discussing. Repeating citations unnecessarily disrupts the flow of an essay.
Referencing
The reference section is the list of all the sources cited in the essay (in alphabetical order). It is not a bibliography (a list of the books you used).
In simple terms every time you cite/refer to a name (and date) of a psychologist you need to reference the original source of the information.
If you have been using textbooks this is easy as the references are usually at the back of the book and you can just copy them down. If you have been using websites, then you may have a problem as they might not provide a reference section for you to copy.
References need to be set out APA style :
Author, A. A. (year). Title of work . Location: Publisher.
Journal Articles
Author, A. A., Author, B. B., & Author, C. C. (year). Article title. Journal Title, volume number (issue number), page numbers
A simple way to write your reference section is use Google scholar . Just type the name and date of the psychologist in the search box and click on the “cite” link.
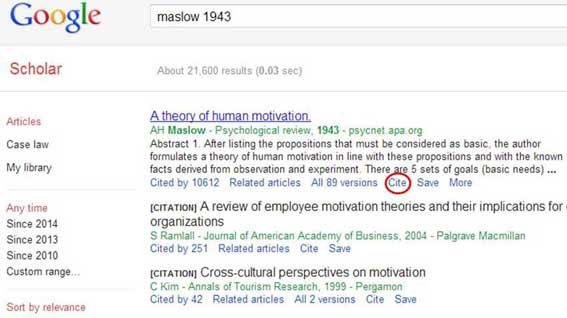
Next, copy and paste the APA reference into the reference section of your essay.

Once again, remember that references need to be in alphabetical order according to surname.

IMAGES
VIDEO