Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples

How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
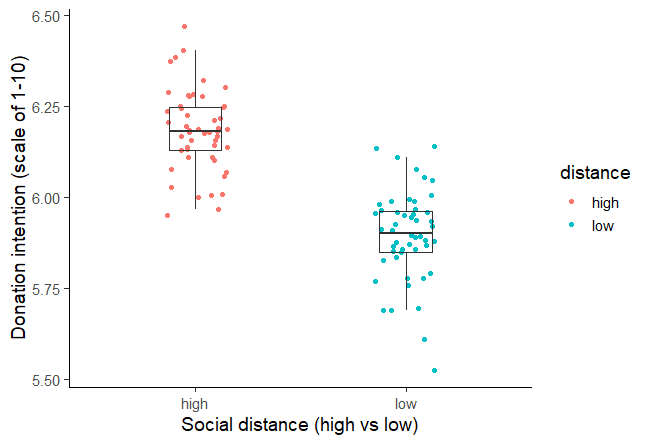
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing - try for free!
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Try for free
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Results
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Results Section in Research
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions.
In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings of the study. It is important to be objective and not interpret the data in this section. Instead, the researcher should report the data as accurately and objectively as possible.
Structure of Research Results Section
The structure of the research results section can vary depending on the type of research conducted, but in general, it should contain the following components:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the study, its aims, and its research questions. It should also briefly explain the methodology used to conduct the study.
- Data presentation : This section presents the data collected during the study. It may include tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help readers better understand the data. The data presented should be organized in a logical and coherent way, with headings and subheadings used to help guide the reader.
- Data analysis: In this section, the data presented in the previous section are analyzed and interpreted. The statistical tests used to analyze the data should be clearly explained, and the results of the tests should be presented in a way that is easy to understand.
- Discussion of results : This section should provide an interpretation of the results of the study, including a discussion of any unexpected findings. The discussion should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Limitations: This section should acknowledge any limitations of the study, such as sample size, data collection methods, or other factors that may have influenced the results.
- Conclusions: The conclusions should summarize the main findings of the study and provide a final interpretation of the results. The conclusions should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Recommendations : This section may provide recommendations for future research based on the study’s findings. It may also suggest practical applications for the study’s results in real-world settings.
Outline of Research Results Section
The following is an outline of the key components typically included in the Results section:
I. Introduction
- A brief overview of the research objectives and hypotheses
- A statement of the research question
II. Descriptive statistics
- Summary statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation) for each variable analyzed
- Frequencies and percentages for categorical variables
III. Inferential statistics
- Results of statistical analyses, including tests of hypotheses
- Tables or figures to display statistical results
IV. Effect sizes and confidence intervals
- Effect sizes (e.g., Cohen’s d, odds ratio) to quantify the strength of the relationship between variables
- Confidence intervals to estimate the range of plausible values for the effect size
V. Subgroup analyses
- Results of analyses that examined differences between subgroups (e.g., by gender, age, treatment group)
VI. Limitations and assumptions
- Discussion of any limitations of the study and potential sources of bias
- Assumptions made in the statistical analyses
VII. Conclusions
- A summary of the key findings and their implications
- A statement of whether the hypotheses were supported or not
- Suggestions for future research
Example of Research Results Section
An Example of a Research Results Section could be:
- This study sought to examine the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.
- Hypothesis : College students who report better sleep quality will have higher GPAs than those who report poor sleep quality.
- Methodology : Participants completed a survey about their sleep habits and academic performance.
II. Participants
- Participants were college students (N=200) from a mid-sized public university in the United States.
- The sample was evenly split by gender (50% female, 50% male) and predominantly white (85%).
- Participants were recruited through flyers and online advertisements.
III. Results
- Participants who reported better sleep quality had significantly higher GPAs (M=3.5, SD=0.5) than those who reported poor sleep quality (M=2.9, SD=0.6).
- See Table 1 for a summary of the results.
- Participants who reported consistent sleep schedules had higher GPAs than those with irregular sleep schedules.
IV. Discussion
- The results support the hypothesis that better sleep quality is associated with higher academic performance in college students.
- These findings have implications for college students, as prioritizing sleep could lead to better academic outcomes.
- Limitations of the study include self-reported data and the lack of control for other variables that could impact academic performance.
V. Conclusion
- College students who prioritize sleep may see a positive impact on their academic performance.
- These findings highlight the importance of sleep in academic success.
- Future research could explore interventions to improve sleep quality in college students.
Example of Research Results in Research Paper :
Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables and a binary churn outcome variable.
Our analysis revealed that all three algorithms performed well in predicting customer churn, with an overall accuracy of 85%. However, the Random Forest algorithm showed the highest accuracy (88%), followed by the Support Vector Machine (86%) and the Neural Network (84%).
Furthermore, we found that the most important predictor variables for customer churn were monthly charges, contract type, and tenure. Random Forest identified monthly charges as the most important variable, while Support Vector Machine and Neural Network identified contract type as the most important.
Overall, our results suggest that machine learning algorithms can be effective in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company, and that Random Forest is the most accurate algorithm for this task.
Example 3 :
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
Abstract : This study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use, body image, and self-esteem among young adults. A total of 200 participants were recruited from a university and completed self-report measures of social media use, body image satisfaction, and self-esteem.
Results: The results showed that social media use was significantly associated with body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem. Specifically, participants who reported spending more time on social media platforms had lower levels of body image satisfaction and self-esteem compared to those who reported less social media use. Moreover, the study found that comparing oneself to others on social media was a significant predictor of body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem.
Conclusion : These results suggest that social media use can have negative effects on body image satisfaction and self-esteem among young adults. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media use and to recognize the potential negative impact it can have on their mental health. Furthermore, interventions aimed at promoting positive body image and self-esteem should take into account the role of social media in shaping these attitudes and behaviors.
Importance of Research Results
Research results are important for several reasons, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research results can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field, whether it be in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, or humanities.
- Developing theories: Research results can help to develop or modify existing theories and create new ones.
- Improving practices: Research results can inform and improve practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and public policy.
- Identifying problems and solutions: Research results can identify problems and provide solutions to complex issues in society, including issues related to health, environment, social justice, and economics.
- Validating claims : Research results can validate or refute claims made by individuals or groups in society, such as politicians, corporations, or activists.
- Providing evidence: Research results can provide evidence to support decision-making, policy-making, and resource allocation in various fields.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper
Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper:
- Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
- Present the findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data and make the presentation more engaging.
- Describe the data: Describe the data in detail, including the sample size, response rate, and any missing data. Provide relevant descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and ranges.
- Interpret the findings: Interpret the findings in light of the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of the findings and the extent to which they support or contradict existing theories or previous research.
- Discuss the limitations : Discuss the limitations of the study, including any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that may have affected the results.
- Compare the results : Compare the results with those of previous studies or theoretical predictions. Discuss any similarities, differences, or inconsistencies.
- Avoid redundancy: Avoid repeating information that has already been presented in the introduction or methods sections. Instead, focus on presenting new and relevant information.
- Be objective: Be objective in presenting the results, avoiding any personal biases or interpretations.
When to Write Research Results
Here are situations When to Write Research Results”
- After conducting research on the chosen topic and obtaining relevant data, organize the findings in a structured format that accurately represents the information gathered.
- Once the data has been analyzed and interpreted, and conclusions have been drawn, begin the writing process.
- Before starting to write, ensure that the research results adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the intended audience, such as a scientific journal or academic conference.
- Begin by writing an abstract that briefly summarizes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Follow the abstract with an introduction that provides context for the research, explains its significance, and outlines the research question and objectives.
- The next section should be a literature review that provides an overview of existing research on the topic and highlights the gaps in knowledge that the current research seeks to address.
- The methodology section should provide a detailed explanation of the research design, including the sample size, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Present the research results in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and figures to illustrate the findings.
- Discuss the implications of the research results, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the topic and what further research is needed.
- Conclude the paper by summarizing the main findings, reiterating the significance of the research, and offering suggestions for future research.
Purpose of Research Results
The purposes of Research Results are as follows:
- Informing policy and practice: Research results can provide evidence-based information to inform policy decisions, such as in the fields of healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. They can also inform best practices in fields such as business, engineering, and social work.
- Addressing societal problems : Research results can be used to help address societal problems, such as reducing poverty, improving public health, and promoting social justice.
- Generating economic benefits : Research results can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that can create economic value and improve quality of life.
- Supporting academic and professional development : Research results can be used to support academic and professional development by providing opportunities for students, researchers, and practitioners to learn about new findings and methodologies in their field.
- Enhancing public understanding: Research results can help to educate the public about important issues and promote scientific literacy, leading to more informed decision-making and better public policy.
- Evaluating interventions: Research results can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as treatments, educational programs, and social policies. This can help to identify areas where improvements are needed and guide future interventions.
- Contributing to scientific progress: Research results can contribute to the advancement of science by providing new insights and discoveries that can lead to new theories, methods, and techniques.
- Informing decision-making : Research results can provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This can include decision-making at the individual, organizational, or governmental levels.
- Fostering collaboration : Research results can facilitate collaboration between researchers and practitioners, leading to new partnerships, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Research Results
Some Advantages of Research Results are as follows:
- Improved decision-making: Research results can help inform decision-making in various fields, including medicine, business, and government. For example, research on the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease can help doctors make informed decisions about the best course of treatment for their patients.
- Innovation : Research results can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. For example, research on renewable energy sources can lead to the development of new and more efficient ways to harness renewable energy.
- Economic benefits: Research results can stimulate economic growth by providing new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. For example, research on new materials or manufacturing techniques can lead to the development of new products and processes that can create new jobs and boost economic activity.
- Improved quality of life: Research results can contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals and society as a whole. For example, research on the causes of a particular disease can lead to the development of new treatments and cures, improving the health and well-being of millions of people.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
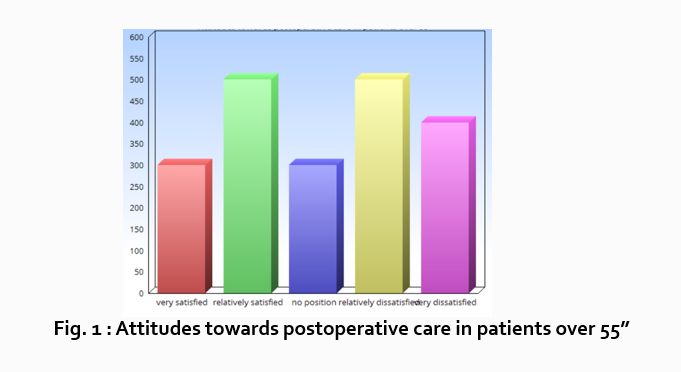
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
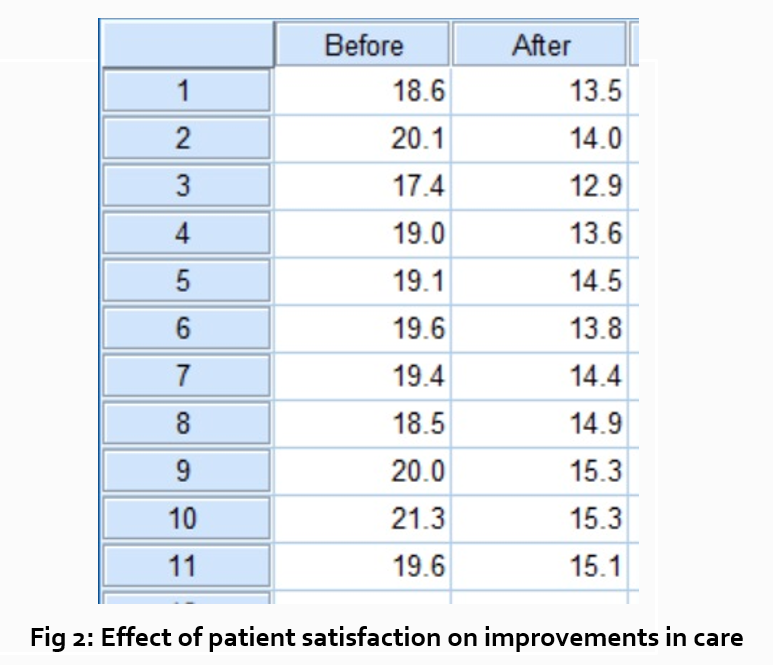
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
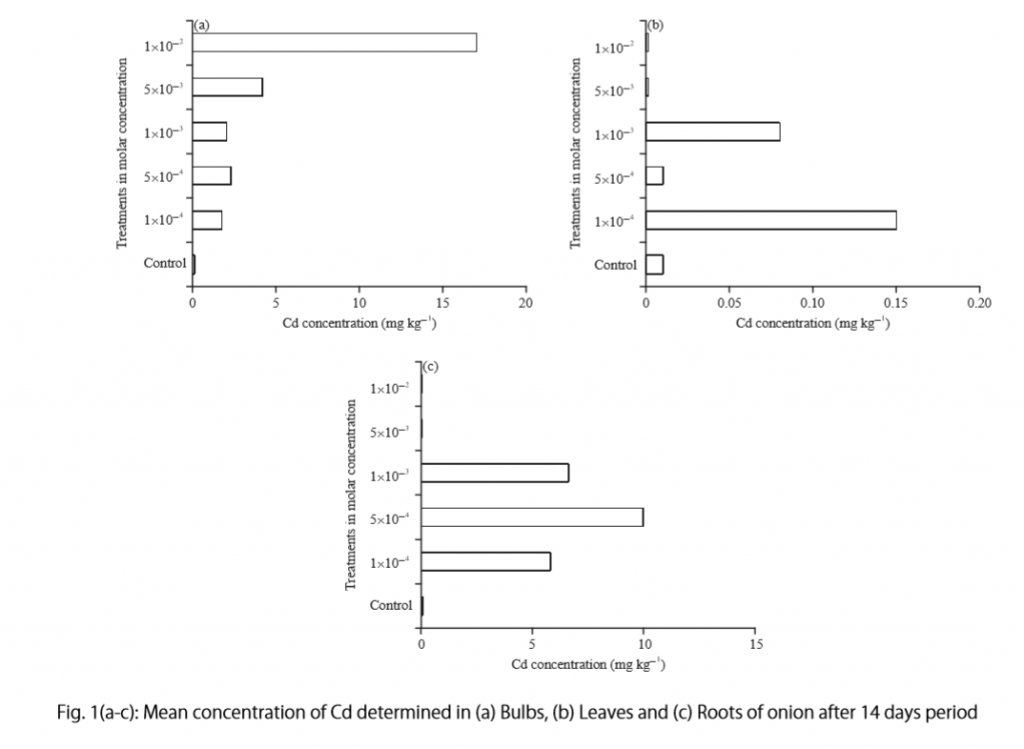
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers

- Manuscript Preparation
How to write the results section of a research paper
- 3 minute read
- 56.8K views
Table of Contents
At its core, a research paper aims to fill a gap in the research on a given topic. As a result, the results section of the paper, which describes the key findings of the study, is often considered the core of the paper. This is the section that gets the most attention from reviewers, peers, students, and any news organization reporting on your findings. Writing a clear, concise, and logical results section is, therefore, one of the most important parts of preparing your manuscript.
Difference between results and discussion
Before delving into how to write the results section, it is important to first understand the difference between the results and discussion sections. The results section needs to detail the findings of the study. The aim of this section is not to draw connections between the different findings or to compare it to previous findings in literature—that is the purview of the discussion section. Unlike the discussion section, which can touch upon the hypothetical, the results section needs to focus on the purely factual. In some cases, it may even be preferable to club these two sections together into a single section. For example, while writing a review article, it can be worthwhile to club these two sections together, as the main results in this case are the conclusions that can be drawn from the literature.
Structure of the results section
Although the main purpose of the results section in a research paper is to report the findings, it is necessary to present an introduction and repeat the research question. This establishes a connection to the previous section of the paper and creates a smooth flow of information.
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the questions. This ensures clarity and minimizes confusion while reading.
Consider representing your results visually. For example, graphs, tables, and other figures can help illustrate the findings of your paper, especially if there is a large amount of data in the results.
Remember, an appealing results section can help peer reviewers better understand the merits of your research, thereby increasing your chances of publication.
Practical guidance for writing an effective results section for a research paper
- Always use simple and clear language. Avoid the use of uncertain or out-of-focus expressions.
- The findings of the study must be expressed in an objective and unbiased manner. While it is acceptable to correlate certain findings in the discussion section, it is best to avoid overinterpreting the results.
- If the research addresses more than one hypothesis, use sub-sections to describe the results. This prevents confusion and promotes understanding.
- Ensure that negative results are included in this section, even if they do not support the research hypothesis.
- Wherever possible, use illustrations like tables, figures, charts, or other visual representations to showcase the results of your research paper. Mention these illustrations in the text, but do not repeat the information that they convey.
- For statistical data, it is adequate to highlight the tests and explain their results. The initial or raw data should not be mentioned in the results section of a research paper.
The results section of a research paper is usually the most impactful section because it draws the greatest attention. Regardless of the subject of your research paper, a well-written results section is capable of generating interest in your research.
For detailed information and assistance on writing the results of a research paper, refer to Elsevier Author Services.

- Research Process
Writing a good review article

Why is data validation important in research?
You may also like.

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②

The Essentials of Writing to Communicate Research in Medicine

Changing Lines: Sentence Patterns in Academic Writing
Input your search keywords and press Enter.

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" results section
Figures and Captions in Lab Reports
"Results Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
Additional tips for results sections.
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is the core of the paper. Don't start the results sections with methods you left out of the Materials and Methods section. You need to give an overall description of the experiments and present the data you found.
- Factual statements supported by evidence. Short and sweet without excess words
- Present representative data rather than endlessly repetitive data
- Discuss variables only if they had an effect (positive or negative)
- Use meaningful statistics
- Avoid redundancy. If it is in the tables or captions you may not need to repeat it
A short article by Dr. Brett Couch and Dr. Deena Wassenberg, Biology Program, University of Minnesota
- Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary.
- Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained.
- Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting results in chronological order rather than logical order; ignoring results that do not support the conclusions;
- Number tables and figures separately beginning with 1 (i.e. Table 1, Table 2, Figure 1, etc.).
- Do not attempt to evaluate the results in this section. Report only what you found; hold all discussion of the significance of the results for the Discussion section.
- It is not necessary to describe every step of your statistical analyses. Scientists understand all about null hypotheses, rejection rules, and so forth and do not need to be reminded of them. Just say something like, "Honeybees did not use the flowers in proportion to their availability (X2 = 7.9, p<0.05, d.f.= 4, chi-square test)." Likewise, cite tables and figures without describing in detail how the data were manipulated. Explanations of this sort should appear in a legend or caption written on the same page as the figure or table.
- You must refer in the text to each figure or table you include in your paper.
- Tables generally should report summary-level data, such as means ± standard deviations, rather than all your raw data. A long list of all your individual observations will mean much less than a few concise, easy-to-read tables or figures that bring out the main findings of your study.
- Only use a figure (graph) when the data lend themselves to a good visual representation. Avoid using figures that show too many variables or trends at once, because they can be hard to understand.
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion
- << Previous: METHODS
- Next: DISCUSSION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The results section is where you report the findings of your study based upon the methodology [or methodologies] you applied to gather information. The results section should state the findings of the research arranged in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation. A section describing results should be particularly detailed if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Findings can only confirm or reject the hypothesis underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise. Use non-textual elements appropriately, such as figures and tables, to present findings more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish information that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other content that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data that has not been summarized should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good strategy is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper that follows].
Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Brett, Paul. "A Genre Analysis of the Results Section of Sociology Articles." English for Specific Speakers 13 (1994): 47-59; Go to English for Specific Purposes on ScienceDirect;Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit; "Reporting Findings." In Making Sense of Social Research Malcolm Williams, editor. (London;: SAGE Publications, 2003) pp. 188-207.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Organization and Approach
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results . Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach.
- Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings . This approach can be used to highlight important findings. For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is appropriate to highlight this finding in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a result and then explain it, before presenting the next result then explaining it, and so on, then end with an overall synopsis . This is the preferred approach if you have multiple results of equal significance. It is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it is helpful to provide a brief conclusion that ties each of the findings together and provides a narrative bridge to the discussion section of the your paper.
NOTE : Just as the literature review should be arranged under conceptual categories rather than systematically describing each source, you should also organize your findings under key themes related to addressing the research problem. This can be done under either format noted above [i.e., a thorough explanation of the key results or a sequential, thematic description and explanation of each finding].
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following:
- Introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem underpinning your study . This is useful in re-orientating the reader's focus back to the research problem after having read a review of the literature and your explanation of the methods used for gathering and analyzing information.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate key findings, if appropriate . Rather than relying entirely on descriptive text, consider how your findings can be presented visually. This is a helpful way of condensing a lot of data into one place that can then be referred to in the text. Consider referring to appendices if there is a lot of non-textual elements.
- A systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation . Not all results that emerge from the methodology used to gather information may be related to answering the " So What? " question. Do not confuse observations with interpretations; observations in this context refers to highlighting important findings you discovered through a process of reviewing prior literature and gathering data.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported . However, focus on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem. It is not uncommon to have unanticipated results that are not relevant to answering the research question. This is not to say that you don't acknowledge tangential findings and, in fact, can be referred to as areas for further research in the conclusion of your paper. However, spending time in the results section describing tangential findings clutters your overall results section and distracts the reader.
- A short paragraph that concludes the results section by synthesizing the key findings of the study . Highlight the most important findings you want readers to remember as they transition into the discussion section. This is particularly important if, for example, there are many results to report, the findings are complicated or unanticipated, or they are impactful or actionable in some way [i.e., able to be pursued in a feasible way applied to practice].
NOTE: Always use the past tense when referring to your study's findings. Reference to findings should always be described as having already happened because the method used to gather the information has been completed.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save this for the discussion section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to the work of Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings. This should have been done in your introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need for additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Writing up research is rarely a linear process. Always revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . A negative result generally refers to a finding that does not support the underlying assumptions of your study. Do not ignore them. Document these findings and then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, can give you an opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be hesitant to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater than other variables..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...." Subjective modifiers should be explained in the discussion section of the paper [i.e., why did one variable appear greater? Or, how does the finding demonstrate a promising trend?].
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you want to highlight a particular finding, it is appropriate to do so in the results section. However, you should emphasize its significance in relation to addressing the research problem in the discussion section. Do not repeat it in your results section because you can do that in the conclusion of your paper.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. Don't call a chart an illustration or a figure a table. If you are not sure, go here .
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers. Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit ; Ng, K. H. and W. C. Peh. "Writing the Results." Singapore Medical Journal 49 (2008): 967-968; Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in scholarly social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings with a discussion about their significance and implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two distinct sections for each section in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret the information and answer the "So What?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you can consider melding the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
Driscoll, Dana Lynn and Aleksandra Kasztalska. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Insiderness
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 1:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
How to Present Results in a Research Paper
- First Online: 01 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Aparna Mukherjee 4 ,
- Gunjan Kumar 4 &
- Rakesh Lodha 5
626 Accesses
The results section is the core of a research manuscript where the study data and analyses are presented in an organized, uncluttered manner such that the reader can easily understand and interpret the findings. This section is completely factual; there is no place for opinions or explanations from the authors. The results should correspond to the objectives of the study in an orderly manner. Self-explanatory tables and figures add value to this section and make data presentation more convenient and appealing. The results presented in this section should have a link with both the preceding methods section and the following discussion section. A well-written, articulate results section lends clarity and credibility to the research paper and the study as a whole. This chapter provides an overview and important pointers to effective drafting of the results section in a research manuscript and also in theses.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Kallestinova ED (2011) How to write your first research paper. Yale J Biol Med 84(3):181–190
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
STROBE. STROBE. [cited 2022 Nov 10]. https://www.strobe-statement.org/
Consort—Welcome to the CONSORT Website. http://www.consort-statement.org/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Korevaar DA, Cohen JF, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP et al (2016) Updating standards for reporting diagnostic accuracy: the development of STARD 2015. Res Integr Peer Rev 1(1):7
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n160
Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups | EQUATOR Network. https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/coreq/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Aggarwal R, Sahni P (2015) The results section. In: Aggarwal R, Sahni P (eds) Reporting and publishing research in the biomedical sciences, 1st edn. National Medical Journal of India, Delhi, pp 24–44
Google Scholar
Mukherjee A, Lodha R (2016) Writing the results. Indian Pediatr 53(5):409–415
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lodha R, Randev S, Kabra SK (2016) Oral antibiotics for community acquired pneumonia with chest indrawing in children aged below five years: a systematic review. Indian Pediatr 53(6):489–495
Anderson C (2010) Presenting and evaluating qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ 74(8):141
Roberts C, Kumar K, Finn G (2020) Navigating the qualitative manuscript writing process: some tips for authors and reviewers. BMC Med Educ 20:439
Bigby C (2015) Preparing manuscripts that report qualitative research: avoiding common pitfalls and illegitimate questions. Aust Soc Work 68(3):384–391
Article Google Scholar
Vincent BP, Kumar G, Parameswaran S, Kar SS (2019) Barriers and suggestions towards deceased organ donation in a government tertiary care teaching hospital: qualitative study using socio-ecological model framework. Indian J Transplant 13(3):194
McCormick JB, Hopkins MA (2021) Exploring public concerns for sharing and governance of personal health information: a focus group study. JAMIA Open 4(4):ooab098
Groenland -emeritus professor E. Employing the matrix method as a tool for the analysis of qualitative research data in the business domain. Rochester, NY; 2014. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2495330 . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Download references
Acknowledgments
The book chapter is derived in part from our article “Mukherjee A, Lodha R. Writing the Results. Indian Pediatr. 2016 May 8;53(5):409-15.” We thank the Editor-in-Chief of the journal “Indian Pediatrics” for the permission for the same.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Studies, Trials and Projection Unit, Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India
Aparna Mukherjee & Gunjan Kumar
Department of Pediatrics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Rakesh Lodha
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rakesh Lodha .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Mukherjee, A., Kumar, G., Lodha, R. (2023). How to Present Results in a Research Paper. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an APA Results Section
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Verywell / Nusha Ashjaee
What to Include in an APA Results Section
- Justify Claims
- Summarize Results
Report All Relevant Results
- Report Statistical Findings
Include Tables and Figures
What not to include in an apa results section.
Psychology papers generally follow a specific structure. One important section of a paper is known as the results section. An APA results section of a psychology paper summarizes the data that was collected and the statistical analyses that were performed. The goal of this section is to report the results of your study or experiment without any type of subjective interpretation.
At a Glance
The results section is a vital part of an APA paper that summarizes a study's findings and statistical analysis. This section often includes descriptive text, tables, and figures to help summarize the findings. The focus is purely on summarizing and presenting the findings and should not include any interpretation, since you'll cover that in the subsequent discussion section.
This article covers how to write an APA results section, including what to include and what to avoid.
The results section is the third section of a psychology paper. It will appear after the introduction and methods sections and before the discussion section.
The results section should include:
- A summary of the research findings.
- Information about participant flow, recruitment, retention, and attrition. If some participants started the study and later left or failed to complete the study, then this should be described.
- Information about any reasons why some data might have been excluded from the study.
- Statistical information including samples sizes and statistical tests that were used. It should report standard deviations, p-values, and other measures of interest.
Results Should Justify Your Claims
Report data in order to sufficiently justify your conclusions. Since you'll be talking about your own interpretation of the results in the discussion section, you need to be sure that the information reported in the results section justifies your claims.
When you start writing your discussion section, you can then look back on your results to ensure that all the data you need are there to fully support your conclusions. Be sure not to make claims in your discussion section that are not supported by the findings described in your results section.
Summarize Your Results
Remember, you are summarizing the results of your psychological study, not reporting them in full detail. The results section should be a relatively brief overview of your findings, not a complete presentation of every single number and calculation.
If you choose, you can create a supplemental online archive where other researchers can access the raw data if they choose.
How long should a results section be?
The length of your results section will vary depending on the nature of your paper and the complexity of your research. In most cases, this will be the shortest section of your paper.
Just as the results section of your psychology paper should sufficiently justify your claims, it should also provide an accurate look at what you found in your study. Be sure to mention all relevant information.
Don't omit findings simply because they failed to support your predictions.
Your hypothesis may have expected more statistically significant results or your study didn't support your hypothesis , but that doesn't mean that the conclusions you reach are not useful. Provide data about what you found in your results section, then save your interpretation for what the results might mean in the discussion section.
While your study might not have supported your original predictions, your finding can provide important inspiration for future explorations into a topic.
How is the results section different from the discussion section?
The results section provides the results of your study or experiment. The goal of the section is to report what happened and the statistical analyses you performed. The discussion section is where you will examine what these results mean and whether they support or fail to support your hypothesis.
Report Your Statistical Findings
Always assume that your readers have a solid understanding of statistical concepts. There's no need to explain what a t-test is or how a one-way ANOVA works. Your responsibility is to report the results of your study, not to teach your readers how to analyze or interpret statistics.
Include Effect Sizes
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association recommends including effect sizes in your results section so that readers can appreciate the importance of your study's findings.
Your results section should include both text and illustrations. Presenting data in this way makes it easier for readers to quickly look at your results.
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
Only include tables and figures if you are going to talk about them in the body text of your results section.
In addition to knowing what you should include in the results section of your psychology paper, it's also important to be aware of things that you should avoid putting in this section:
Cause-and-Effect Conclusions
Don't draw cause-effect conclusions. Avoid making any claims suggesting that your result "proves" that something is true.
Interpretations
Present the data without editorializing it. Save your comments and interpretations for the discussion section of your paper.
Statistics Without Context
Don't include statistics without narration. The results section should not be a numbers dump. Instead, you should sequentially narrate what these numbers mean.
Don't include the raw data in the results section. The results section should be a concise presentation of the results. If there is raw data that would be useful, include it in the appendix .
Don't only rely on descriptive text. Use tables and figures to present these findings when appropriate. This makes the results section easier to read and can convey a great deal of information quickly.
Repeated Data
Don't present the same data twice in your illustrative materials. If you have already presented some data in a table, don't present it again in a figure. If you have presented data in a figure, don't present it again in a table.
All of Your Findings
Don't feel like you have to include everything. If data is irrelevant to the research question, don't include it in the results section.
But Don't Skip Relevant Data
Don't leave out results because they don't support your claims. Even if your data does not support your hypothesis, including it in your findings is essential if it's relevant.

More Tips for Writing a Results Section
If you are struggling, there are a few things to remember that might help:
- Use the past tense . The results section should be written in the past tense.
- Be concise and objective . You will have the opportunity to give your own interpretations of the results in the discussion section.
- Use APA format . As you are writing your results section, keep a style guide on hand. The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association is the official source for APA style.
- Visit your library . Read some journal articles that are on your topic. Pay attention to how the authors present the results of their research.
- Get a second opinion . If possible, take your paper to your school's writing lab for additional assistance.
What This Means For You
Remember, the results section of your paper is all about providing the data from your study. This section is often the shortest part of your paper, and in most cases, the most clinical.
Be sure not to include any subjective interpretation of the results. Simply relay the data in the most objective and straightforward way possible. You can then provide your own analysis of what these results mean in the discussion section of your paper.
Bavdekar SB, Chandak S. Results: Unraveling the findings . J Assoc Physicians India . 2015 Sep;63(9):44-6. PMID:27608866.
Snyder N, Foltz C, Lendner M, Vaccaro AR. How to write an effective results section . Clin Spine Surg . 2019;32(7):295-296. doi:10.1097/BSD.0000000000000845
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
Purdue Online Writing Lab. APA sample paper: Experimental psychology .
Berkeley University. Reviewing test results .
Tuncel A, Atan A. How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper ? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):16-19. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.048
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
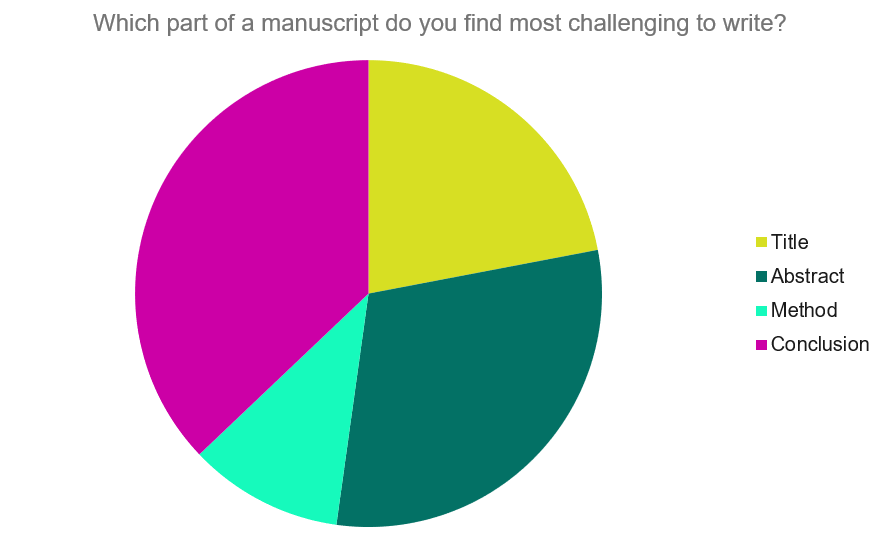
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
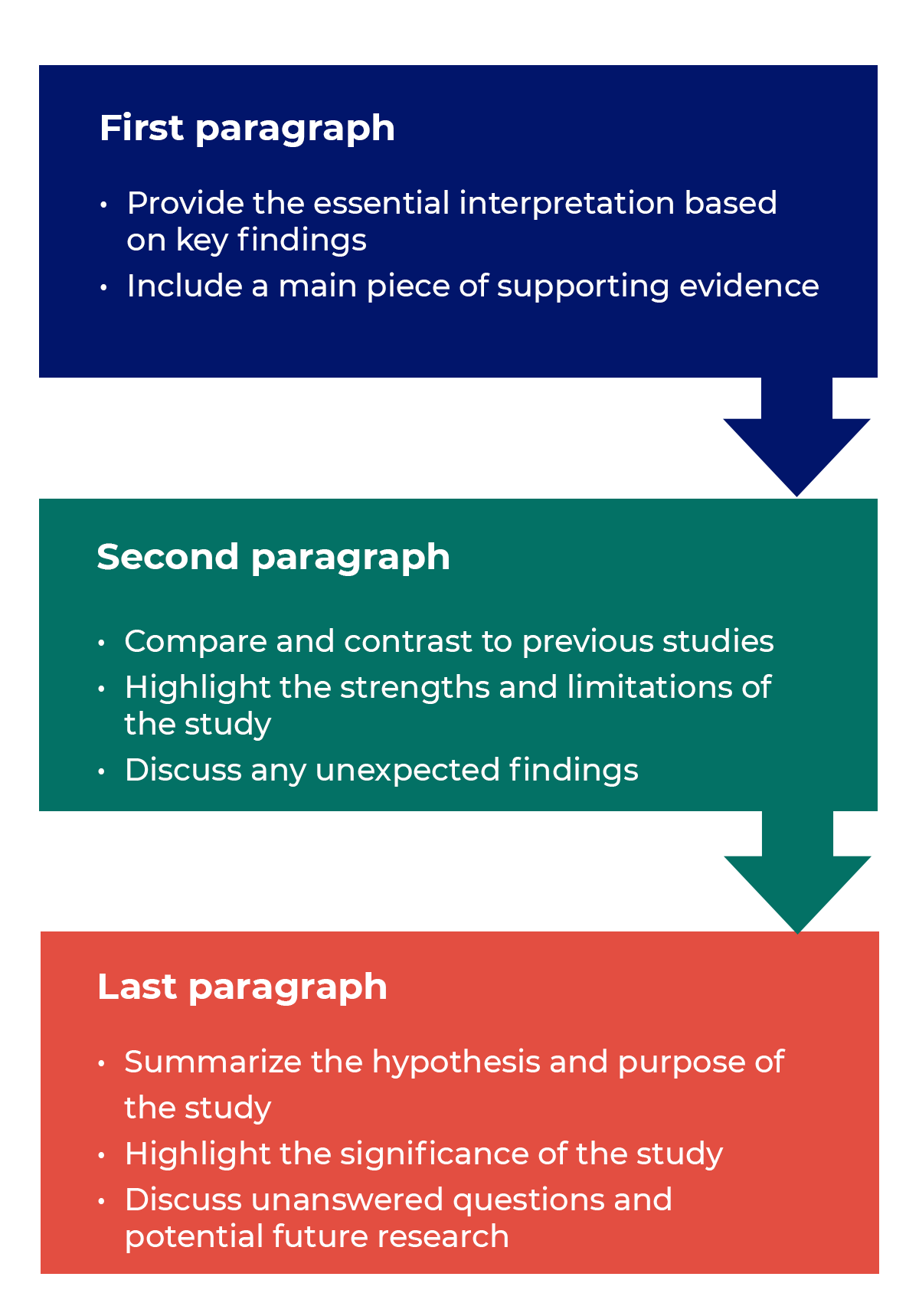
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper
Table of Contents
Laura Moro-Martin, freelance scientific writer on Kolabtree, provides expert tips on how to write the results section of a research paper .
You have prepared a detailed −but concise− Methods section . Now it is time to write the Results of your research article. This part of the paper reports the findings of the experiments that you conducted to answer the research question(s). The Results can be considered the nucleus of a scientific article because they justify your claims, so you need to ensure that they are clear and understandable. You are telling a story −of course, a scientific story− and you want the readers to picture that same story in their minds. Let’s see how to avoid that your message ends up as in the ‘telephone game’.
The Results Section: Goals and Structure
Depending on the discipline, journal, and the nature of the study, the structure of the article can differ. We will focus on articles were the Results and Discussion appear in two separate sections, but it is possible in some cases to combine them.
In the Results section, you provide an overall description of the experiments and present the data that you obtained in a logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. The Results section should simply state your findings without bias or interpretation. For example, in your analysis, you may have noticed a significant correlation between two variables never described before. It is correct to explain this in the Results section. However, speculation about the reasons for this correlation should go in the Discussion section of your paper.
In general, the Results section includes the following elements:
- A very short introductory context that repeats the research question and helps to understand your results.
- Report on data collection, recruitment, and/or participants. For example, in the case of clinical research, it is common to include a first table summarizing the demographic, clinical, and other relevant characteristics of the study participants.
- A systematic description of the main findings in a logical order (generally following the order of the Methods section), highlighting the most relevant results.
- Other important secondary findings, such as secondary outcomes or subgroup analyses (remember that you do not need to mention any single result).
- Visual elements, such as, figures, charts, maps, tables, etc. that summarize and illustrate the findings. These elements should be cited in the text and numbered in order. Figures and tables should be able to stand on its own without the text, which means that the legend should include enough information to understand the non-textual element.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper: Tips
The first tip −applicable to other sections of the paper too− is to check and apply the requirements of the journal to which you are submitting your work.
In the Results section, you need to write concisely and objectively, leaving interpretation for the Discussion section. As always, ‘learning from others’ can help you. Select a few papers from your field, including some published in your target journal, which you consider ‘good quality’ and well written. Read them carefully and observe how the Results section is structured, the type and amount of information provided, and how the findings are exposed in a logical order. Keep an eye on visual elements, such as figures, tables, and supplementary materials. Understand what works well in those papers to effectively convey their findings, and apply it to your writing.
Your Results section needs to describe the sequence of what you did and found, the frequency of occurrence of a particular event or result, the quantities of your observations, and the causality (i.e. the relationships or connections) between the events that you observed.
To organize the results, you can try to provide them alongside the research questions. In practice, this means that you will organize this section based on the sequence of tables and figures summarizing the results of your statistical analysis. In this way, it will be easier for readers to look at and understand your findings. You need to report your statistical findings, without describing every step of your statistical analysis. Tables and figures generally report summary-level data (for example, means and standard deviations), rather than all the raw data.
Following, you can prepare the summary text to support those visual elements. You need not only to present but also to explain your findings, showing how they help to address the research question(s) and how they align with the objectives that you presented in the Introduction . Keep in mind that results do not speak for themselves, so if you do not describe them in words, the reader may perceive the findings differently from you. Build coherence along this section using goal statements and explicit reasoning (guide the reader through your reasoning, including sentences of this type: ‘In order to…, we performed….’; ‘In view of this result, we ….’, etc.).
In summary, the general steps for writing the Results section of a research article are:
- Check the guidelines of your target journal and read articles that it has published in similar topics to your study.
- Catalogue your findings in relation to the journal requirements, and design figures and tables to organize your data.
- Write the Results section following the order of figures and tables.
- Edit and revise your draft and seek additional input from colleagues or experts.
The Style of the Results Section
‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor’, Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann said. Although the scope of the Results section −and of scientific papers in general− is eminently functional, this does not mean that you cannot write well. Try to improve the rhythm to move the reader along, use transitions and connectors between different sections and paragraphs, and dedicate time to revise your writing.
The Results section should be written in the past tense. Although writing in the passive voice may be tempting, the use of the active voice makes the action much more visualizable. The passive voice weakens the power of language and increases the number of words needed to say the same thing, so we recommend using the active voice as much as possible. Another tip to make your language visualizable and reduce sentence length is the use of verbal phrases instead of long nouns. For example, instead of writing ‘As shown in Table 1, there was a significant increase in gene expression’, you can say ‘As shown in Table 1, gene expression increased significantly’.
Get a Second (And Even Third) Opinion
Writing a scientific article is not an individual work. Take advantage of your co-authors by making them check the Results section and adding their comments and suggestions. Not only that, but an external opinion will help you to identify misinterpretations or errors. Ask a colleague that is not directly involved in the work to review your Results and then try to evaluate what your colleague did or did not understand. If needed, seek additional help from a qualified expert.
Common Errors to Avoid While Writing the Results Section
Several mistakes frequently occur when you write the Results section of a research paper. Here we have collected a few examples:
- Including raw results and/or endlessly repetitive data. You do not need to present every single number and calculation, but a summary of the results. If relevant, raw data can be included in supplementary materials.
- Including redundant information. If data are contained in the tables or figures, you do not need to repeat all of them in the Results section. You will have the opportunity to highlight the most relevant results in the Discussion .
- Repeating background information or methods , or introducing several sentences of introductory information (if you feel that more background information is necessary to present a result, consider inserting that information in the Introduction ).
- Results and Methods do not match . You need to explain the methodology used to obtain all the experimental observations.
- Ignoring negative results or results that do not support the conclusions. In addition to posing potential ethical concerns on your work, reviewers will not like it. You need to mention all relevant findings, even if they failed to support your predictions or hypotheses. Negative results are useful and will guide future studies on the topic. Provide your interpretation for negative results in the Discussion .
- Discussing or interpreting the results . Leave that for the Discussion , unless your target journal allows preparing one section combining Results and Discussion .
- Errors in figures/tables are varied and common . Examples of errors include using an excessive number of figures/tables (it is a good idea to select the most relevant ones and move the rest to supplementary materials), very complex figures/tables (hard-to-read figures with many subfigures or enormous tables may confuse your readers; think how these elements will be visualized in the final format of the article), difficult to interpret figures/tables (cryptic abbreviations; inadequate use of colors, axis, scales, symbols, etc.), and figures/tables that are not self-standing (figures/tables require a caption, all abbreviations used need to be explained in the legend or a footnote, and statistical tests applied are frequently reported). Do not include tables and figures that are not mentioned in the body text of your Results .
In summary, the Results section is the nucleus of your paper that justifies your claims. Take time to adequately organize it and prepare understandable figures and tables to convey your message to the reader. Good writing!
- The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. https://abacus.bates.edu/~ganderso/biology/resources/writing/HTWsections.html – methods (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Organizing Academic Research Papers: 7. The Results. https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803&p=185931 (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Kendra Cherry. How to Write an APA Results Section. https://www.verywellmind.com/how-to-write-a-results-section-2795727 (accessed on 30th September 2020)
- Chapin Rodríguez. Empowering your scientific language by making it “visualizable”. http://creaducate.eu/wp-content/uploads/2019/11/tipsheet36_visualizable-lang-tip-sheet.pdf (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- IMRaD Results Discussion. https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- Writing the Results Section for a Research Paper. https://wordvice.com/writing-the-results-section-for-a-research-paper/ (accessed on 1st October 2020)
- Scott L. Montgomery. The Chicago Guide to Communicating Science , Chapter 9. Second edition, The University of Chicago Press, 2017.
- Hilary Glasman-Deal . Science Research Writing for Non-Native Speakers of English, Unit 2 . Imperial College Press, 2010.
Unlock Corporate Benefits • Secure Payment Assistance • Onboarding Support • Dedicated Account Manager
Sign up with your professional email to avail special advances offered against purchase orders, seamless multi-channel payments, and extended support for agreements.
About Author
Ramya Sriram manages digital content and communications at Kolabtree (kolabtree.com), the world's largest freelancing platform for scientists. She has over a decade of experience in publishing, advertising and digital content creation.
Related Posts
Spotlight: kolabtree’s regulatory medical writer dr. nare simonyan, how healthcare writers can help your business , the benefits of outsourcing in continuing medical education (cme), leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER BRIEF
- 08 May 2019
Toolkit: How to write a great paper
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow:
1. Context — your introduction
2. Content — your results
3. Conclusion — your discussion
Plan your paper carefully and decide where each point will sit within the framework before you begin writing.

Collection: Careers toolkit
Straightforward writing
Scientific writing should always aim to be A, B and C: Accurate, Brief, and Clear. Never choose a long word when a short one will do. Use simple language to communicate your results. Always aim to distill your message down into the simplest sentence possible.
Choose a title
A carefully conceived title will communicate the single core message of your research paper. It should be D, E, F: Declarative, Engaging and Focused.
Conclusions
Add a sentence or two at the end of your concluding statement that sets out your plans for further research. What is next for you or others working in your field?
Find out more
See additional information .
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-019-01362-9
Related Articles
How to get published in high impact journals

So you’re writing a paper
Writing for a Nature journal

How I harnessed media engagement to supercharge my research career
Career Column 09 APR 24

How we landed job interviews for professorships straight out of our PhD programmes
Career Column 08 APR 24

Three ways ChatGPT helps me in my academic writing
Brazil’s postgraduate funding model is about rectifying past inequalities
Correspondence 09 APR 24
Declining postdoc numbers threaten the future of US life science
Junior Group Leader Position at IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
The Institute of Molecular Biotechnology (IMBA) is one of Europe’s leading institutes for basic research in the life sciences. IMBA is located on t...
Austria (AT)
IMBA - Institute of Molecular Biotechnology
Open Rank Faculty, Center for Public Health Genomics
Center for Public Health Genomics & UVA Comprehensive Cancer Center seek 2 tenure-track faculty members in Cancer Precision Medicine/Precision Health.
Charlottesville, Virginia
Center for Public Health Genomics at the University of Virginia
Husbandry Technician I
Memphis, Tennessee
St. Jude Children's Research Hospital (St. Jude)
Lead Researcher – Department of Bone Marrow Transplantation & Cellular Therapy
Researcher in the center for in vivo imaging and therapy.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Results Section
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
12 min read

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Have you ever felt stuck and confused when trying to share the results of your research in a paper? You're not alone!
Many students and researchers struggle with making their findings easy to understand while still sounding smart. It can get pretty frustrating when you're not sure how to talk about all the data and numbers in your research.
Without clear guidelines, it's easy to feel lost and unsure about how to make your results section both detailed and easy to read.
Don't worry! This guide is here to help you figure it all out.
We'll break down the process of writing a results section into simple steps. From explaining tricky stats to showing your data clearly, we've got your back.
Let's get started!
- 1. What Exactly is the Result Section of a Research Paper?
- 2. Importance of the Result Section of a Research Paper
- 3. How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper?
- 4. Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
- 5. How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper - Examples
- 6. Result vs Discussion Section vs Conclusion - What’s the Difference?
- 7. Mistakes to Avoid While Writing the Results Section
What Exactly is the Result Section of a Research Paper?
The results section of a research paper is where you get to showcase the findings of your study.
Think of it as the big reveal, where you share all the important information and data you've gathered. This section is crucial because it's where your reader learns about the outcomes of your research and whether your hypotheses were supported or not.
Importance of the Result Section of a Research Paper
The results section in a research paper is really important. It's like a hub where you put all the main findings and results from your study.
This part is crucial because it shows exactly what data you gathered and how you analyzed it.
In the academic world, the research results act as a kind of checkpoint. It lets other researchers and scholars review and confirm the reliability of your study methods. This helps ensure that your research is trustworthy and adds valuable information to the wider pool of knowledge in a specific field.
Also, the results section helps either prove or disprove the hypothesis you set up in your study. It's the part where the numbers and trends either support what you expected or reveal surprising insights.
What's Included in the Result Section of a Research Paper
When you're talking about the results of a research paper, it's important to know the key parts that make it clear and complete.
Let’s see what the results section of a research paper includes:
Key Points To Consider In The Result Section:
- Clarity: Present the results in a straightforward manner, making it easy for readers to comprehend.
- Objectivity: Avoid interpretation or discussion at this stage; stick to presenting the observed data.
- Consistency: Organize the results logically, following the same order as your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper?
The results section of a research paper is crucial for conveying the outcomes of your study in a clear and organized manner.
Follow these steps to learn how to write the findings section of a research paper:
Step 1: Start With a Clear Organization
Begin the results section with a brief introductory paragraph that outlines the purpose of the results. Mention the research questions or hypotheses that the study aimed to address.
- Order of Presentation
Present your results in a systematic and coherent order. Make sure the logical sequence with the research questions or hypotheses established in the earlier sections of your paper.
This helps readers follow a logical flow and easily locate information related to specific aspects of your study.
- Use of Subheadings
Divide the Results section into meaningful subsections using clear and descriptive subheadings.
Subheadings provide a roadmap for readers, guiding them through different parts of your results.
For example, if your research involves multiple variables or distinct analyses, create subheadings for each, making it easy for readers to navigate.
Step 2: Use Concise Text and Visuals
When writing the result section, use clear and concise language to communicate your results.
Avoid unnecessary details and focus on conveying the key research findings succinctly. Present each piece of data or result once, eliminating redundancy for a streamlined presentation.
- Utilize Tables and Figures : Tables and figures should be self-explanatory, with titles and captions providing essential context.
- Choose Appropriate Detail : Strike a balance between providing essential information and avoiding information overload.
Step 3: Be Objective and Specific
Present your findings without adding personal interpretation or analysis. Focus on conveying the observed outcomes in a straightforward and unbiased manner.
- Stick to the Facts : State what was found during the study without speculating on the reasons or implications.
- Include Numerical Data : Include means, medians, standard deviations, percentages, or any other statistical measures that accurately represent your results.
- Quantify Results : Use precise numbers to quantify your findings wherever possible. This adds clarity and concreteness to your presentation.

Tough Essay Due? Hire Tough Writers!
Step 4: Refer to Appendices
Evaluate the volume and complexity of your data to determine if it warrants inclusion in appendices. If your dataset is extensive and might overwhelm the main text, consider creating appendices.
Transfer detailed data, additional analyses, or supplementary information to appendices. Use separate appendices for different types of information, maintaining clarity.
- Highlight Relevance : Explain how the appendices supplement and enrich the content presented in the main text.
- Use Clear Labeling : Number or letter of each appendix for easy reference in the main text.
Step 5: Use Subheadings for Different Analyses
Recognize the various analyses conducted in your study, each addressing specific research questions or hypotheses. Introduce subheadings to distinguish and separate different analyses in the Results section.
Each subheading should correspond to a unique analysis, providing clarity to readers.
- Clearly Label Subsections : The subheading should succinctly convey the focus of the analysis without ambiguity.
- Guide Readers Effectively : The use of subheadings allows readers to locate specific information related to each analysis with ease.
Step 6: Highlight Patterns and Trends
Thoroughly examine your results to identify any recurring patterns or trends. Look for consistencies or variations in data points that are noteworthy for your study.
- Consider Multiple Analyses : Explore patterns across different analyses if applicable, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of your findings.
- Use Emphatic Language : Clearly convey the significance of identified trends in the context of your research questions.
- Connect to Research Questions: Explain how the observed trends contribute to answering the main queries of your study.
Step 7: Address Negative or Unexpected Results
Approach unexpected or negative results with transparency and honesty. Clearly state that the outcomes were not as anticipated.
Make sure to resist the temptation to downplay unexpected or negative results and acknowledge them as integral parts of the scientific process.
For Example:
Step 8: Relate to Research Questions/Hypotheses
At the last, revisit the research questions or hypotheses established at the beginning of your paper. This serves as a reminder of the primary objectives of your study.
Explicitly connect each set of findings to the corresponding research question or hypothesis. Make sure you clearly state how the results address the specific inquiries posed at the outset.
Differences Between Qualitative and Quantitative Data
Understanding the difference between qualitative and quantitative data is fundamental in research methodology.
These two distinct types of data collection offer unique insights, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of phenomena.
In this section, we explore the key characteristics that set qualitative and quantitative data apart.
Tips for Presenting Quantitative Data in the Results Section
- Use clear and concise tables or graphs to present numerical results.
- Include descriptive statistics (mean, median, etc.) to summarize central tendencies.
Tips for Presenting Qualitative Data in the Results Section
- Summarize key themes or patterns derived from qualitative analysis.
- Use quotes or excerpts to illustrate significant findings.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper - Examples
Here are a few examples that show how to write the results part of a research paper.
Results Section of a Research Paper - Apa
Results Section of a Qualitative Research Paper
Results Section of a Research Report
Result vs Discussion Section vs Conclusion - What’s the Difference?
The Results section presents a factual showcase of observed or measured outcomes.
In contrast, the discussion section goes beyond the facts, interpreting results, providing context to findings, and exploring their broader implications.
Finally, the conclusion section summarizes key points, discusses implications, and often suggests avenues for future research.
Mistakes to Avoid While Writing the Results Section
The results section of a research paper demands precision and clarity to communicate the study's outcomes effectively. However, several common mistakes can compromise the quality of this section.
To ensure an insightful results section, be mindful of the following pitfalls:
In summary, by following these tips and avoiding common mistakes, you can create a results section that meets academic standards and clearly shows why your research is important.
Remember, the results section sets the stage for the subsequent discussion. If you present your findings well, it makes your whole research paper better and easier to understand.
If you ever feel stuck while writing a research paper, especially in the results section, consider reaching out to MyPerfectWords.com!
Our experts can craft an outstanding result section that resonates with your whole research paper. We can also craft different parts of a research paper upon customized requests!
So, do not delay! Get your custom paper from a professional essay writing service now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long should the results section of a research paper be.
The length varies, but keep it concise. Include enough information to support your discussion and conclusion without unnecessary details. A balanced Results section enhances the overall flow of your research paper.
What is the Difference between Results And Discussion Sections?
The results section presents the raw findings of a study, focusing on data and observations.
In contrast, the Discussion section interprets and analyzes these results, offering insights, context, and help readers understand the significance of the findings.

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper?
The writing of the results section of a scientific paper is very important for the readers for clearly understanding of the study. This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures.
Introduction
Medical articles consist of review articles, case reports, and letters to the editor which are prepared with the intention of publishing in journals related to the medical discipline of the author. For an academician to be able to progress in carreer, and make his/her activities known in the academic environment, require preparation of the protocol of his/her academic research article, and acquiring sufficient information, and experience related to the composition of this article. In this review article, the information related to the writing of the ‘Results’ section, and use of tables, and figures will be presented to the attention of the readers.
Writing the ‘Results’ section
The ‘Results’ section is perhaps the most important part of a research article. In fact the authors will share the results of their research/study with their readers. Renown British biologist Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895) indicated his feelings as “The great tragedy of science: the slaying of a beautiful hypothesis by an ugly fact.” which emphasizes the importance of accurately, and impressively written results.
In essence results provide a response for the question” What is found in the research performed?”. Therefore, it is the most vital part of the article. As a priority, while drafting the ‘Results’ section of a manuscript one should not firstly write down methods in the ‘Material and Method’ section. The first sentence should give information about the number of patients who met the inclusion criteria, and thus enrolled in the study. [ 1 ] Besides information about the number of patients excluded from the study, and the reasons for exclusion is very important in that they will enlighten the readers, and reviewers who critically evaluate the manuscript, and also reflect the seriousness of the study. On the other hand, the results obtained should be recorded in chronological order, and without any comments. [ 2 ] In this section use of simple present tense is more appropriate. The findings should be expressed in brief, lucid, and explicable words. The writing style should not be boring for the reader. During writing process of a research article, a generally ill-conceived point is that positive, and significant findings are more important, attractive, and valuable, while negative, and insignificant findings are worthless, and less attractive. A scientific research is not performed to confirm a hypothesis, rather to test it. Not only positive, and significant results are worth writing, on the other hand negative or statistically insignificant result which support fallacy of a widely accepted opinion might be valuable. Therefore, all findings obtained during research should be inclıuded in the ‘Results’ section. [ 1 ]
While writing the ‘Results’ section, the sequence of results, tabulated data, and information which will be illustrated as figures should be definitively indicated. In indicating insignificant changes, do not use expressions as “decreased” or “increased”, these words should be reserved for significant changes. If results related to more than one parameter would be reported, it is appropriate to write the results under the subheading of its related parameter so as to facilitate reading, and comprehension of information. [ 2 ] Only data, and information concerning the study in question should be included in the ‘Results’ section. Results not mentioned in this section should not be included in the ‘Discussion’ and ‘Summary’ sections. Since the results obtained by the authors are cited in the ‘Results’ section, any reference should not be indicated in this section. [ 3 ]
In the ‘Results’ section, numerical expressions should be written in technically appropriate terms. The number of digits (1, 2 or 3 digits) to be written after a comma (in Turkish) or a point (in especially American English) should be determined The number of digits written after the punctuation marks should not be changed all throughout the text. Data should be expressed as mean/median ± standard deviation. Data as age, and scale scores should be indicated together with ranges of values. Absolute numerical value corresponding to a percentage must be also indicated. P values calculated in statistical analysis should be expressed in their absolute values. While writing p values of statistically significant data, instead of p<0.05 the actual level of significance should be recorded. If p value is smaller than 0.001, then it can be written as p <0.01. [ 2 ] While writing the ‘Results’ section, significant data which should be recalled by the readers must be indicated in the main text. It will be appropriate to indicate other demographic numerical details in tables or figures.
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23) is presented below:
“A total of 9 (56.2%) female, and 7 (43.8%) male patients with were included in this study. Mean age of all the patients was 44.3±13.8 (17–65) years, and mean dimensions of the adrenal mass was 4.5±3.4 (1–14) cm. Mean ages of the male, and female patients were 44.1 (30–65), and 42.4 (17–64) years, while mean diameters of adrenal masses were 3.2 (1–5), and 4.5 (1–14) cm (p age =0.963, p mass size =0.206). Surgical procedures were realized using transperitoneal approach through Chevron incision in 1 (6.2%), and retroperitoneal approach using flank incision with removal of the 11. rib in 15 (93.7%) patients. Right (n=6; 37.5%), and left (n=2; 12.5%) adrenalectomies were performed. Two (12.5%) patients underwent bilateral adrenalectomy in the same session because of clinical Cushing’s syndrome persisted despite transsphenoidal hipophysectomy. Mean operative time, and length of the hospital stay were 135 (65–190) min, and 3 (2–6) days, respectively. While resecting 11. rib during retroperitoneal adrenalectomy performed in 1 patient, pleura was perforated for nearly 1.5 cm. The perforated region was drained, and closed intraoperatively with 4/0 polyglyctan sutures. The patient did not develop postoperative pneumothorax. In none of the patients postoperative complications as pneumothorax, bleeding, prolonged drainage were seen. Results of histopathological analysis of the specimens retrieved at the end of the operation were summarized in Table 1 .” Table 1. Histopathological examination results of the patients Histopathological diagnosis Men n (%) Women n (%) Total n (%) Adrenal cortical adenoma 5 (31.3) 6 (37.6) 11 (68.8) Pheochromocytoma 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) 2 (12.6) Ganglioneuroma 1 (6.2) - 1 (6.2) Myelolipoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Adrenal carcinoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Total 7 (43.7) 9 (56.2) 16 (100) Open in a separate window
Use of tables, and figures
To prevent the audience from getting bored while reading a scientific article, some of the data should be expressed in a visual format in graphics, and figures rather than crowded numerical values in the text. Peer-reviewers frequently look at tables, and figures. High quality tables, and figures increase the chance of acceptance of the manuscript for publication.
Number of tables in the manuscript should not exceed the number recommended by the editorial board of the journal. Data in the main text, and tables should not be repeated many times. Tables should be comprehensible, and a reader should be able to express an opinion about the results just at looking at the tables without reading the main text. Data included in tables should comply with those mentioned in the main text, and percentages in rows, and columns should be summed up accurately. Unit of each variable should be absolutely defined. Sampling size of each group should be absolutely indicated. Values should be expressed as values±standard error, range or 95% confidence interval. Tables should include precise p values, and level of significance as assessed with statistical analysis should be indicated in footnotes. [ 2 ] Use of abbreviations in tables should be avoided, if abbreviations are required they should be defined explicitly in the footnotes or legends of the tables. As a general rule, rows should be arranged as double-spaced Besides do not use pattern coloring for cells of rows, and columns. Values included in tables should be correctly approximated. [ 1 , 2 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23).is shown in Table 1 .
Most of the readers priorly prefer to look at figures, and graphs rather than reading lots of pages. Selection of appropriate types of graphs for demonstration of data is a critical decision which requires artist’s meticulousness. As is the case with tables, graphs, and figures should also disploay information not provided in the text. Bar, line, and pie graphs, scatter plots, and histograms are some examples of graphs. In graphs, independent variables should be represented on the horizontal, and dependent variables on the vertical axis. Number of subjects in every subgroup should be indicated The labels on each axis should be easily understandable. [ 2 ] The label of the Y axis should be written vertically from bottom to top. The fundamental point in writing explanatory notes for graphs, and figures is to help the readers understand the contents of them without referring to the main text. Meanings of abbreviations, and acronyms used in the graphs, and figures should be provided in explanatory notes. In the explanatory notes striking data should be emphasized. Statistical tests used, levels of significance, sampling size, stains used for analyses, and magnification rate should be written in order to facilitate comprehension of the study procedures. [ 1 , 2 ]
Flow diagram can be utilized in the ‘Results’ section. This diagram facilitates comprehension of the results obtained at certain steps of monitorization during the research process. Flow diagram can be used either in the ‘Results’ or ‘Material and Method’ section. [ 2 , 3 ]
Histopathological analyses, surgical technique or radiological images which are considered to be more useful for the comprehension of the text by the readers can be visually displayed. Important findings should be marked on photos, and their definitions should be provided clearly in the explanatory legends. [ 1 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the ‘Results’ section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17–22.) are shown in Figures 1 , and and2 2 .

a The mean SHIM scores of the groups before and after treatment. SHIM sexual health inventory for male. b The mean IPSS scores of the groups before and after treatment. IPSS international prostate symptom score

Flowchart showing patients’ progress during the study. SHIM sexual health inventory for male, IIEF international index of erectile function, IPSS international prostate symptom score, QoL quality of life, Q max maximum urinary flow rate. PRV post voiding residual urine volume
In conclusion, in line with the motto of the famous German physicist Albert Einstein (1879–1955). ‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor .’ results obtained in a scientific research article should be expressed accurately, and with a masterstroke of a tailor in compliance with certain rules which will ensure acceptability of the scientific manuscript by the editorial board of the journal, and also facilitate its intelligibility by the readers.
Read our research on: Gun Policy | International Conflict | Election 2024
Regions & Countries
Political typology quiz.
Notice: Beginning April 18th community groups will be temporarily unavailable for extended maintenance. Thank you for your understanding and cooperation.
Where do you fit in the political typology?
Are you a faith and flag conservative progressive left or somewhere in between.

Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That’s OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if it isn’t exactly right.
About Pew Research Center Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 11.4.2024 in Vol 26 (2024)
Patients’ Experiences With Digitalization in the Health Care System: Qualitative Interview Study
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Christian Gybel Jensen 1 * , MA ;
- Frederik Gybel Jensen 1 * , MA ;
- Mia Ingerslev Loft 1, 2 * , MSc, PhD
1 Department of Neurology, Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen, Denmark
2 Institute for People and Technology, Roskilde University, Roskilde, Denmark
*all authors contributed equally
Corresponding Author:
Mia Ingerslev Loft, MSc, PhD
Department of Neurology
Rigshospitalet
Inge Lehmanns Vej 8
Phone: 45 35457076
Email: [email protected]
Background: The digitalization of public and health sectors worldwide is fundamentally changing health systems. With the implementation of digital health services in health institutions, a focus on digital health literacy and the use of digital health services have become more evident. In Denmark, public institutions use digital tools for different purposes, aiming to create a universal public digital sector for everyone. However, this digitalization risks reducing equity in health and further marginalizing citizens who are disadvantaged. Therefore, more knowledge is needed regarding patients’ digital practices and experiences with digital health services.
Objective: This study aims to examine digital practices and experiences with public digital health services and digital tools from the perspective of patients in the neurology field and address the following research questions: (1) How do patients use digital services and digital tools? (2) How do they experience them?
Methods: We used a qualitative design with a hermeneutic approach. We conducted 31 semistructured interviews with patients who were hospitalized or formerly hospitalized at the department of neurology in a hospital in Denmark. The interviews were audio recorded and subsequently transcribed. The text from each transcribed interview was analyzed using manifest content analysis.
Results: The analysis provided insights into 4 different categories regarding digital practices and experiences of using digital tools and services in health care systems: social resources as a digital lifeline, possessing the necessary capabilities, big feelings as facilitators or barriers, and life without digital tools. Our findings show that digital tools were experienced differently, and specific conditions were important for the possibility of engaging in digital practices, including having access to social resources; possessing physical, cognitive, and communicative capabilities; and feeling motivated, secure, and comfortable. These prerequisites were necessary for participants to have positive experiences using digital tools in the health care system. Those who did not have these prerequisites experienced challenges and, in some cases, felt left out.
Conclusions: Experiences with digital practices and digital health services are complex and multifaceted. Engagement in digital practices for the examined population requires access to continuous assistance from their social network. If patients do not meet requirements, digital health services can be experienced as exclusionary and a source of concern. Physical, cognitive, and communicative difficulties might make it impossible to use digital tools or create more challenges. To ensure that digitalization does not create inequities in health, it is necessary for developers and institutions to be aware of the differences in digital health literacy, focus on simplifying communication with patients and next of kin, and find flexible solutions for citizens who are disadvantaged.
Introduction
In 2022, the fourth most googled question in Denmark was, “Why does MitID not work?” [ 1 ]. MitID (My ID) is a digital access tool that Danes use to enter several different private and public digital services, from bank accounts to mail from their municipality or the state. MitID is a part of many Danish citizens’ everyday lives because the public sector in Denmark is digitalized in many areas. In recent decades, digitalization has changed how governments and people interact and has demonstrated the potential to change the core functions of public sectors and delivery of public policies and services [ 2 ]. When public sectors worldwide become increasingly digitalized, this transformation extends to the public health sectors as well, and some studies argue that we are moving toward a “digital public health era” that is already impacting the health systems and will fundamentally change the future of health systems [ 3 ]. While health systems are becoming more digitalized, it is important that both patients and digitalized systems adapt to changes in accordance with each other. Digital practices of people can be understood as what people do with and through digital technologies and how people relate to technology [ 4 ]. Therefore, it is relevant to investigate digital practices and how patients perceive and experience their own use of digital tools and services, especially in relation to existing digital health services. In our study, we highlight a broad perspective on experiences with digital practices and particularly add insight into the challenges with digital practices faced by patients who have acute or chronic illness, with some of them also experiencing physical, communicative, or cognitive difficulties.
An international Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development report indicates that countries are digitalized to different extents and in different ways; however, this does not mean that countries do not share common challenges and insights into the implementation of digital services [ 2 ].
In its global Digital Government Index, Denmark is presented as one of the leading countries when it comes to public digitalization [ 2 ]. Recent statistics indicate that approximately 97% of Danish families have access to the internet at home [ 5 ]. The Danish health sector already offers many different digital services, including web-based delivery of medicine, e-consultations, patient-related outcome questionnaires, and seeking one’s own health journal or getting test results through; “Sundhed” [ 6 ] (the national health portal) and “Sundhedsjournalen” (the electronic patient record); or the apps “Medicinkortet” (the shared medication record), “Minlæge” (My Doctor, consisting of, eg, communication with the general practitioner), or “MinSP” (My Health Platform, consisting of, eg, communication with health care staff in hospitals) [ 6 - 8 ].
The Danish Digital Health Strategy from 2018 aims to create a coherent and user-friendly digital public sector for everyone [ 9 ], but statistics indicate that certain groups in society are not as digitalized as others. In particular, the older population uses digital services the least, with 5% of people aged 65 to 75 years and 18% of those aged 75 to 89 years having never used the internet in 2020 [ 5 ]. In parts of the literature, it has been problematized how the digitalization of the welfare state is related to the marginalization of older citizens who are socially disadvantaged [ 10 ]. However, statistics also indicate that the probability of using digital tools increases significantly as a person’s experience of using digital tools increases, regardless of their age or education level [ 5 ].
Understanding the digital practices of patients is important because they can use digital tools to engage with the health system and follow their own health course. Researching experiences with digital practices can be a way to better understand potential possibilities and barriers when patients use digital health services. With patients becoming more involved in their own health course and treatment, the importance of patients’ health literacy is being increasingly recognized [ 11 ]. The World Health Organization defines health literacy as the “achievement of a level of knowledge, personal skills and confidence to take action to improve personal and community health by changing personal lifestyles and living conditions” [ 12 ]. Furthermore, health literacy can be described as “a person’s knowledge and competencies to meet complex demands of health in modern society, ” and it is viewed as a critical step toward patient empowerment [ 11 , 12 ]. In a digitalized health care system, this also includes the knowledge, capabilities, and resources that individuals require to use and benefit from eHealth services, that is, “digital health literacy (eHealth literacy)” [ 13 ]. An eHealth literacy framework created by Norgaard et al [ 13 ] identified that different aspects, for example, the ability to process information and actively engage with digital services, can be viewed as important facets of digital health literacy. This argument is supported by studies that demonstrate how patients with cognitive and communicative challenges experience barriers to the use of digital tools and require different approaches in the design of digital solutions in the health sector [ 14 , 15 ]. Access to digital services and digital literacy is becoming increasingly important determinants of health, as people with digital literacy and access to digital services can facilitate improvement of health and involvement in their own health course [ 16 ].
The need for a better understanding of eHealth literacy and patients’ capabilities to meet public digital services’ demands as well as engage in their own health calls for a deeper investigation into digital practices and the use of digital tools and services from the perspective of patients with varying digital capabilities. Important focus areas to better understand digital practices and related challenges have already been highlighted in various studies. They indicate that social support, assessment of value in digital services, and systemic assessment of digital capabilities are important in the use and implementation of digital tools, and they call for better insight into complex experiences with digital services [ 13 , 17 , 18 ]. Therefore, we aimed to examine digital practices and experiences with public digital health services and digital tools from the perspective of patients, addressing the following research questions: how do patients use digital services and digital tools, and how do they experience them?
We aimed to investigate digital practices and experiences with digital health services and digital tools; therefore, we used a qualitative design and adopted a hermeneutic approach as the point of departure, which means including preexisting knowledge of digital practices but also providing room for new comprehension [ 19 ]. Our interpretive approach is underpinned by the philosophical hermeneutic approach by Gadamer et al [ 19 ], in which they described the interpretation process as a “hermeneutic circle,” where the researcher enters the interpretation process with an open mind and historical awareness of a phenomenon (preknowledge). We conducted semistructured interviews using an interview guide. This study followed the COREQ (Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research) checklist [ 20 ].
Setting and Participants
To gain a broad understanding of experiences with public digital health services, a purposive sampling strategy was used. All 31 participants were hospitalized or formerly hospitalized patients in a large neurological department in the capital of Denmark ( Table 1 ). We assessed whether including patients from the neurological field would give us a broad insight into the experiences of digital practices from different perspectives. The department consisted of, among others, 8 inpatient units covering, for example, acute neurology and stroke units, from which the patients were recruited. Patients admitted to a neurological department can have both acute and transient neurological diseases, such as infections in the brain, stroke, or blood clot in the brain from which they can recover completely or have persistent physical and mental difficulties, or experience chronic neurological and progressive disorders such as Parkinson disease and dementia. Some patients hospitalized in neurological care will have communicative and cognitive difficulties because of their neurological disorders. Nursing staff from the respective units helped the researchers (CGJ, FGJ, and MIL) identify patients who differed in terms of gender, age, and severity of neurological illness. Some patients (6/31, 19%) had language difficulties; however, a speech therapist assessed them as suitable participants. We excluded patients with severe cognitive difficulties and those who were not able to speak the Danish language. Including patients from the field of neurology provided an opportunity to study the experience of digital health practice from various perspectives. Hence, the sampling strategy enabled the identification and selection of information-rich participants relevant to this study [ 21 ], which is the aim of qualitative research. The participants were invited to participate by either the first (CGJ) or last author (MIL), and all invited participants (31/31, 100%) chose to participate.
All 31 participants were aged between 40 to 99 years, with an average age of 71.75 years ( Table 1 ). Out of the 31 participants, 10 (32%) had physical disabilities or had cognitive or communicative difficulties due to sequela in relation to neurological illness or other physical conditions.
Data Collection
The 31 patient interviews were conducted over a 2-month period between September and November 2022. Of the 31 patients, 20 (65%) were interviewed face-to-face at the hospital in their patient room upon admission and 11 (35%) were interviewed on the phone after being discharged. The interviews had a mean length of 20.48 minutes.
We developed a semistructured interview guide ( Table 2 ). The interview questions were developed based on the research aim, findings from our preliminary covering of literature in the field presented in the Introduction section, and identified gaps that we needed to elaborate on to be able to answer our research question [ 22 ]. The semistructured interview guide was designed to support the development of a trusting relationship and ensure the relevance of the interviews’ content [ 22 ]. The questions served as a prompt for the participants and were further supported by questions such as “please tell me more” and “please elaborate” throughout the interview, both to heighten the level of detail and to verify our understanding of the issues at play. If the participant had cognitive or communicative difficulties, communication was supported using a method called Supported Communication for Adults with Aphasia [ 23 ] during the interview.
The interviews were performed by all authors (CGJ, FGJ, and MIL individually), who were skilled in conducting interviews and qualitative research. The interviewers are not part of daily clinical practice but are employed in the department of neurology from where the patients were recruited. All interviews were audio recorded and subsequently transcribed verbatim by all 3 authors individually.
a PRO: patient-related outcome.
Data Analysis
The text from each transcribed interview was analyzed using manifest content analysis, as described by Graneheim and Lundman [ 24 ]. Content analysis is a method of analyzing written, verbal, and visual communication in a systematic way [ 25 ]. Qualitative content analysis is a structured but nonlinear process that requires researchers to move back and forth between the original text and parts of the text during the analysis. Manifest analysis is the descriptive level at which the surface structure of the text central to the phenomenon and the research question is described. The analysis was conducted as a collaborative effort between the first (CGJ) and last authors (MIL); hence, in this inductive circular process, to achieve consistency in the interpretation of the text, there was continued discussion and reflection between the researchers. The transcriptions were initially read several times to gain a sense of the whole context, and we analyzed each interview. The text was initially divided into domains that reflected the lowest degree of interpretation, as a rough structure was created in which the text had a specific area in common. The structure roughly reflected the interview guide’s themes, as guided by Graneheim and Lundman [ 24 ]. Thereafter, the text was divided into meaning units, condensed into text-near descriptions, and then abstracted and labeled further with codes. The codes were categorized based on similarities and differences. During this process, we discussed the findings to reach a consensus on the content, resulting in the final 4 categories presented in this paper.
Ethical Considerations
The interviewees received oral and written information about the study and its voluntary nature before the interviews. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Participants were able to opt of the study at any time. Data were anonymized and stored electronically on locked and secured servers. The Ethics Committee of the Capitol Region in Denmark was contacted before the start of the study. This study was registered and approved by the ethics committee and registered under the Danish Data Protection Agency (number P2021-839). Furthermore, the ethical principles of the Declaration of Helsinki were followed for this study.
The analysis provided insights into 4 different categories regarding digital practices and experiences of using digital tools and services in health care systems: social resources as a digital lifeline, possessing the necessary capabilities, big feelings as facilitators or barriers, and life without digital tools.
Social Resources as a Digital Lifeline
Throughout the analysis, it became evident that access to both material and social resources was of great importance when using digital tools. Most participants already possessed and had easy access to a computer, smartphone, or tablet. The few participants who did not own the necessary digital tools told us that they did not have the skills needed to use these tools. For these participants, the lack of material resources was tied particularly to a lack of knowledge and know-how, as they expressed that they would not know where to start after buying a computer—how to set it up, connect it to the internet, and use its many systems.
However, possessing the necessary material resources did not mean that the participants possessed the knowledge and skill to use digital tools. Furthermore, access to material resources was also a question of having access to assistance when needed. Some participants who had access to a computer, smartphone, and tablet and knew how to use these tools still had to obtain help when setting up hardware, updating software, or getting a new device. These participants were confident in their own ability to use digital devices but also relied on family, friends, and neighbors in their everyday use of these tools. Certain participants were explicitly aware of their own use of social resources when expressing their thoughts on digital services in health care systems:
I think it is a blessing and a curse. I think it is both. I would say that if I did not have someone around me in my family who was almost born into the digital world, then I think I would be in trouble. But I feel sorry for those who do not have that opportunity, and I know quite a few who do not. They get upset, and it’s really frustrating. [Woman, age 82 years]
The participants’ use of social resources indicates that learning skills and using digital tools are not solely individual tasks but rather continuously involve engagement with other people, particularly whenever a new unforeseen problem arises or when the participants want a deeper understanding of the tools they are using:
If tomorrow I have to get a new ipad...and it was like that when I got this one, then I had to get XXX to come and help me move stuff and he was sweet to help with all the practical stuff. I think I would have cursed a couple of times (if he hadn’t been there), but he is always helpful, but at the same time he is also pedagogic so I hope that next time he showed me something I will be able to do it. [Man, age 71 years]
For some participants, obtaining assistance from a more experienced family member was experienced as an opportunity to learn, whereas for other participants, their use of public digital services was even tied directly to assistance from a spouse or family member:
My wife, she has access to mine, so if something comes up, she can just go in and read, and we can talk about it afterwards what (it is). [Man, age 85 years]
The participants used social resources to navigate digital systems and understand and interpret communication from the health care system through digital devices. Another example of this was the participants who needed assistance to find, answer, and understand questionnaires from the health care department. Furthermore, social resources were viewed as a support system that made participants feel more comfortable and safer when operating digital tools. The social resources were particularly important when overcoming unforeseen and new challenges and when learning new skills related to the use of digital tools. Participants with physical, cognitive, and communicative challenges also explained how social resources were of great importance in their ability to use digital tools.
Possessing the Necessary Capabilities
The findings indicated that possessing the desire and knowing how to use digital tools are not always enough to engage with digital services successfully. Different health issues can carry consequences for motor skills and mobility. Some of these consequences were visibly affecting how our participants interacted with digital devices, and these challenges were somewhat easy to discover. However, our participants revealed hidden challenges that posed difficulties. In some specific cases, cognitive and communicative inabilities can make it difficult to use digital tools, and this might not always be clear until the individual tries to use a device’s more complex functions. An example of this is that some participants found it easy to turn on a computer and use it to write but difficult to go through security measures on digital services or interpret and understand digital language. Remembering passwords and logging on to systems created challenges, particularly for those experiencing health issues that directly affect memory and cognitive abilities, who expressed concerns about what they were able to do through digital tools:
I think it is very challenging because I would like to use it how I used to before my stroke; (I) wish that everything (digital skills) was transferred, but it just isn’t. [Man, age 80 years]
Despite these challenges, the participants demonstrated great interest in using digital tools, particularly regarding health care services and their own well-being. However, sometimes, the challenges that they experienced could not be conquered merely by motivation and good intentions. Another aspect of these challenges was the amount of extra time and energy that the participants had to spend on digital services. A patient diagnosed with Parkinson disease described how her symptoms created challenges that changed her digital practices:
Well it could for example be something like following a line in the device. And right now it is very limited what I can do with this (iPhone). Now I am almost only using it as a phone, and that is a little sad because I also like to text and stuff, but I also find that difficult (...) I think it is difficult to get an overview. [Woman, age 62 years]
Some participants said that after they were discharged from the hospital, they did not use the computer anymore because it was too difficult and too exhausting , which contributed to them giving up . Using digital tools already demanded a certain amount of concentration and awareness, and some diseases and health conditions affected these abilities further.
Big Feelings as Facilitators or Barriers
The findings revealed a wide range of digital practices in which digital tools were used as a communication device, as an entertainment device, and as a practical and informative tool for ordering medicine, booking consultations, asking health-related questions, or receiving email from public institutions. Despite these different digital practices, repeating patterns and arguments appeared when the participants were asked why they learned to use digital tools or wanted to improve their skills. A repeating argument was that they wanted to “follow the times, ” or as a participant who was still not satisfied with her digital skills stated:
We should not go against the future. [Woman, age 89 years]
The participants expressed a positive view of the technological developments and possibilities that digital devices offered, and they wanted to improve their knowledge and skills related to digital practice. For some participants, this was challenging, and they expressed frustration over how technological developments “moved too fast ,” but some participants interpreted these challenges as a way to “keep their mind sharp. ”
Another recurring pattern was that the participants expressed great interest in using digital services related to the health care system and other public institutions. The importance of being able to navigate digital services was explicitly clear when talking about finding test answers, written electronic messages, and questionnaires from the hospital or other public institutions. Keeping up with developments, communicating with public institutions, and taking an interest in their own health and well-being were described as good reasons to learn to use digital tools.
However, other aspects also affected these learning facilitators. Some participants felt alienated while using digital tools and described the practice as something related to feelings of anxiety, fear, and stupidity as well as something that demanded “a certain amount of courage. ” Some participants felt frustrated with the digital challenges they experienced, especially when the challenges were difficult to overcome because of their physical conditions:
I get sad because of it (digital challenges) and I get very frustrated and it takes a lot of time because I have difficulty seeing when I look away from the computer and have to turn back again to find out where I was and continue there (...) It pains me that I have to use so much time on it. [Man, age 71 years]
Fear of making mistakes, particularly when communicating with public institutions, for example, the health care system, was a common pattern. Another pattern was the fear of misinterpreting the sender and the need to ensure that the written electronic messages were actually from the described sender. Some participants felt that they were forced to learn about digital tools because they cared a lot about the services. Furthermore, fears of digital services replacing human interaction were a recurring concern among the participants. Despite these initial and recurring feelings, some participants learned how to navigate the digital services that they deemed relevant. Another recurring pattern in this learning process was repetition, the practice of digital skills, and consistent assistance from other people. One participant expressed the need to use the services often to remember the necessary skills:
Now I can figure it out because now I’ve had it shown 10 times. But then three months still pass... and then I think...how was it now? Then I get sweat on my forehead (feel nervous) and think; I’m not an idiot. [Woman, age 82 years]
For some participants, learning how to use digital tools demanded time and patience, as challenges had to be overcome more than once because they reappeared until the use of digital tools was more automatized into their everyday lives. Using digital tools and health services was viewed as easier and less stressful when part of everyday routines.
Life Without Digital Tools: Not a Free Choice
Even though some participants used digital tools daily, other participants expressed that it was “too late for them.” These participants did not view it as a free choice but as something they had to accept that they could not do. They wished that they could have learned it earlier in life but did not view it as a possibility in the future. Furthermore, they saw potential in digital services, including digital health care services, but they did not know exactly what services they were missing out on. Despite this lack of knowledge, they still felt sad about the position they were in. One participant expressed what she thought regarding the use of digital tools in public institutions:
Well, I feel alright about it, but it is very, very difficult for those of us who do not have it. Sometimes you can feel left out—outside of society. And when you do not have one of those (computers)...A reference is always made to w and w (www.) and then you can read on. But you cannot do that. [Woman, age 94 years]
The feeling of being left out of society was consistent among the participants who did not use digital tools. To them, digital systems seemed to provide unfair treatment based on something outside of their own power. Participants who were heavily affected by their medical conditions and could not use digital services also felt left out because they saw the advantages of using digital tools. Furthermore, a participant described the feelings connected to the use of digital tools in public institutions:
It is more annoying that it does not seem to work out in my favour. [Woman, age 62 years]
These statements indicated that it is possible for individuals to want to use digital tools and simultaneously find them too challenging. These participants were aware that there are consequences of not using digital tools, and that saddens them, as they feel like they are not receiving the same treatment as other people in society and the health care system.
Principal Findings
The insights from our findings demonstrated that our participants had different digital practices and different experiences with digital tools and services; however, the analysis also highlighted patterns related to how digital services and tools were used. Specific conditions were important for the possibility of digital practice, including having access to social resources; possessing the necessary capabilities; and feeling motivated, secure, and comfortable . These prerequisites were necessary to have positive experiences using digital tools in the health care system, although some participants who lived up to these prerequisites were still skeptical toward digital solutions. Others who did not live up to these prerequisites experienced challenges and even though they were aware of opportunities, this awareness made them feel left out. A few participants even viewed the digital tools as a threat to their participation in society. This supports the notion of Norgaard et al [ 13 ] that the attention paid to digital capability demands from eHealth systems is very important. Furthermore, our findings supported the argument of Hjeltholt and Papazu [ 17 ] that it is important to better understand experiences related to digital services. In our study, we accommodate this request and bring forth a broad perspective on experiences with digital practices; we particularly add insight into the challenges with digital practices for patients who also have acute or chronic illness, with some of them also experiencing physical, communicative, and cognitive difficulties. To our knowledge, there is limited existing literature focusing on digital practices that do not have a limited scope, for example, a focus on perspectives on eHealth literacy in the use of apps [ 26 ] or intervention studies with a focus on experiences with digital solutions, for example, telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic [ 27 ]. As mentioned by Hjeltholt et al [ 10 ], certain citizens are dependent on their own social networks in the process of using and learning digital tools. Rasi et al [ 28 ] and Airola et al [ 29 ] argued that digital health literacy is situated and should include the capabilities of the individual’s social network. Our findings support these arguments that access to social resources is an important condition; however, the findings also highlight that these resources can be particularly crucial in the use of digital health services, for example, when interpreting and understanding digital and written electronic messages related to one’s own health course or when dealing with physical, cognitive, and communicative disadvantages. Therefore, we argue that the awareness of the disadvantages is important if we want to understand patients’ digital capabilities, and the inclusion of the next of kin can be evident in unveiling challenges that are unknown and not easily visible or when trying to reach patients with digital challenges through digital means.
Studies by Kayser et al [ 30 ] and Kanoe et al [ 31 ] indicated that patients’ abilities to interpret and understand digital health–related services and their benefits are important for the successful implementation of eHealth services—an argument that our findings support. Health literacy in both digital and physical contexts is important if we want to understand how to better design and implement services. Our participants’ statements support the argument that communication through digital means cannot be viewed as similar to face-to-face communication and that an emphasis on digital health literacy demonstrates how health systems are demanding different capabilities from the patients [ 13 ]. We argue that it is important to communicate the purposes of digital services so that both the patient and their next of kin know why they participate and how it can benefit them. Therefore, it is important to make it as clear as possible that digital health services can benefit the patient and that these services are developed to support information, communication, and dialogue between patients and health professionals. However, our findings suggest that even after interpreting and understanding the purposes of digital health services, some patients may still experience challenges when using digital tools.
Therefore, it is important to understand how and why patients learn digital skills, particularly because both experience with digital devices and estimation of the value of digital tools have been highlighted as key factors for digital practices [ 5 , 18 ]. Our findings indicate that a combination of these factors is important, as recognizing the value of digital tools was not enough to facilitate the necessary learning process for some of our participants. Instead, our participants described the use of digital tools as complex and continuous processes in which automation of skills, assistance from others, and time to relearn forgotten knowledge were necessary and important facilitators for learning and understanding digital tools as well as becoming more comfortable and confident in the use of digital health services. This was particularly important, as it was more encouraging for our participants to learn digital tools when they felt secure, instead of feeling afraid and anxious, a point that Bailey et al [ 18 ] also highlighted. The value of digital solutions and the will to learn were greater when challenges were viewed as something to overcome and learn from instead of something that created a feeling of being stupid. This calls for attention on how to simplify and explain digital tools and services so that users do not feel alienated. Our findings also support the argument that digital health literacy should take into account emotional well-being related to digital practice [ 32 ].
The various perspectives that our participants provided regarding the use of digital tools in the health care system indicate that patients are affected by the use of digital health services and their own capabilities to use digital tools. Murray et al [ 33 ] argued that the use of digital tools in health sectors has the potential to improve health and health delivery by improving efficacy, efficiency, accessibility, safety, and personalization, and our participants also highlighted these positive aspects. However, different studies found that some patients, particularly older adults considered socially vulnerable, have lower digital health literacy [ 10 , 34 , 35 ], which is an important determinant of health and may widen disparities and inequity in health care [ 16 ]. Studies on older adult populations’ adaptation to information and communication technology show that engaging with this technology can be limited by the usability of technology, feelings of anxiety and concern, self-perception of technology use, and the need for assistance and inclusive design [ 36 ]. Our participants’ experiences with digital practices support the importance of these focus areas, especially when primarily older patients are admitted to hospitals. Furthermore, our findings indicate that some older patients who used to view themselves as being engaged in their own health care felt more distanced from the health care system because of digital services, and some who did not have the capabilities to use digital tools felt that they were treated differently compared to the rest of society. They did not necessarily view themselves as vulnerable but felt vulnerable in the specific experience of trying to use digital services because they wished that they were more capable. Moreover, this was the case for patients with physical and cognitive difficulties, as they were not necessarily aware of the challenges before experiencing them. Drawing on the phenomenological and feministic approach by Ahmed [ 37 ], these challenges that make patients feel vulnerable are not necessarily visible to others but can instead be viewed as invisible institutional “walls” that do not present themselves before the patient runs into them. Some participants had to experience how their physical, cognitive, or communicative difficulties affected their digital practice to realize that they were not as digitally capable as they once were or as others in society. Furthermore, viewed from this perspective, our findings could be used to argue that digital capabilities should be viewed as a privilege tied to users’ physical bodies and that digital services in the health care system are indirectly making patients without this privilege vulnerable. This calls for more attention to the inequities that digital tools and services create in health care systems and awareness that those who do not use digital tools are not necessarily indifferent about the consequences. Particularly, in a context such as the Danish one, in which the digital strategy is to create an intertwined and user-friendly public digital sector for everyone, it needs to be understood that patients have different digital capabilities and needs. Although some have not yet had a challenging experience that made them feel vulnerable, others are very aware that they receive different treatment and feel that they are on their own or that the rest of the society does not care about them. Inequities in digital health care, such as these, can and should be mitigated or prevented, and our investigation into the experiences with digital practices can help to show that we are creating standards and infrastructures that deliberately exclude the perspectives of those who are most in need of the services offered by the digital health care system [ 8 ]. Therefore, our findings support the notions that flexibility is important in the implementation of universal public digital services [ 17 ]; that it is important to adjust systems in accordance with patients’ eHealth literacy and not only improve the capabilities of individuals [ 38 ]; and that the development and improvement of digital health literacy are not solely an individual responsibility but are also tied to ways in which institutions organize, design, and implement digital tools and services [ 39 ].
Limitations
This qualitative study provided novel insights into the experiences with public digital health services from the perspective of patients in the Danish context, enabling a deeper understanding of how digital health services and digital tools are experienced and used. This helps build a solid foundation for future interventions aimed at digital health literacy and digital health interventions. However, this study has some limitations. First, the study was conducted in a country where digitalization is progressing quickly, and people, therefore, are accustomed to this pace. Therefore, readers must be aware of this. Second, the study included patients with different neurological conditions; some of their digital challenges were caused or worsened by these neurological conditions and are, therefore, not applicable to all patients in the health system. However, the findings provided insights into the patients’ digital practices before their conditions and other challenges not connected to neurological conditions shared by patients. Third, the study was broad, and although a large number of informants was included, from a qualitative research perspective, we would recommend additional research in this field to develop interventions that target digital health literacy and the use of digital health services.
Conclusions
Experiences with digital tools and digital health services are complex and multifaceted. The advantages in communication, finding information, or navigating through one’s own health course work as facilitators for engaging with digital tools and digital health services. However, this is not enough on its own. Furthermore, feeling secure and motivated and having time to relearn and practice skills are important facilitators. Engagement in digital practices for the examined population requires access to continuous assistance from their social network. If patients do not meet requirements, digital health services can be experienced as exclusionary and a source of concern. Physical, cognitive, and communicative difficulties might make it impossible to use digital tools or create more challenges that require assistance. Digitalization of the health care system means that patients do not have the choice to opt out of using digital services without having consequences, resulting in them receiving a different treatment than others. To ensure digitalization does not create inequities in health, it is necessary for developers and the health institutions that create, design, and implement digital services to be aware of differences in digital health literacy and to focus on simplifying communication with patients and next of kin through and about digital services. It is important to focus on helping individuals meet the necessary conditions and finding flexible solutions for those who do not have the same privileges as others if the public digital sector is to work for everyone.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the people who gave their time to be interviewed for the study, the clinical nurse specialists who facilitated interviewing patients, and the other nurses on shift who assisted in recruiting participants.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
- Year in search 2022. Google Trends. URL: https://trends.google.com/trends/yis/2022/DK/ [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Digital government index: 2019. Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. URL: https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/content/paper/4de9f5bb-en [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Azzopardi-Muscat N, Sørensen K. Towards an equitable digital public health era: promoting equity through a health literacy perspective. Eur J Public Health. Oct 01, 2019;29(Supplement_3):13-17. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Digital practices. Umeå University. URL: https://www.umu.se/en/humlab/research/digital-practice/ [accessed 2024-04-02]
- It-anvendelse i befolkningen 2020. Danmarks Statistik. URL: https://www.dst.dk/da/Statistik/nyheder-analyser-publ/Publikationer/VisPub?cid=29450 [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Sundhed.dk homepage. Sundhed.dk. URL: https://www.sundhed.dk/borger/ [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Nøhr C, Bertelsen P, Vingtoft S, Andersen SK. Digitalisering af Det Danske Sundhedsvæsen. Odense, Denmark. Syddansk Universitetsforlag; 2019.
- Eriksen J, Ebbesen M, Eriksen KT, Hjermitslev C, Knudsen C, Bertelsen P, et al. Equity in digital healthcare - the case of Denmark. Front Public Health. Sep 6, 2023;11:1225222. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Digital health strategy. Sundhedsdatastyrelsen. URL: https://sundhedsdatastyrelsen.dk/da/english/digital_health_solutions/digital_health_strategy [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Hjelholt M, Schou J, Bojsen LB, Yndigegn SL. Digital marginalisering af udsatte ældre: arbejdsrapport 2. IT-Universitetet i København. 2018. URL: https://egv.dk/images/Projekter/Projekter_2018/EGV_arbejdsrapport_2.pdf [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Sørensen K, Van den Broucke S, Fullam J, Doyle G, Pelikan J, Slonska Z, et al. Health literacy and public health: a systematic review and integration of definitions and models. BMC Public Health. Jan 25, 2012;12(1):80. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Improving health literacy. World Health Organization. URL: https://www.who.int/activities/improving-health-literacy [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Norgaard O, Furstrand D, Klokker L, Karnoe KA, Batterham R, Kayser L, et al. The e-health literacy framework: a conceptual framework for characterizing e-health users and their interaction with e-health systems. Knowl Manag E Learn. 2015;7(4). [ CrossRef ]
- Kramer JM, Schwartz A. Reducing barriers to patient-reported outcome measures for people with cognitive impairments. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. Aug 2017;98(8):1705-1715. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Menger F, Morris J, Salis C. Aphasia in an internet age: wider perspectives on digital inclusion. Aphasiology. 2016;30(2-3):112-132. [ CrossRef ]
- Richardson S, Lawrence K, Schoenthaler AM, Mann D. A framework for digital health equity. NPJ Digit Med. Aug 18, 2022;5(1):119. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Hjelholt M, Papazu I. "De har fået NemID, men det er ikke nemt for mig” - Digital rum(me)lighed i den danske velfærdsstat. Social Kritik. 2021;2021-2(163). [ FREE Full text ]
- Bailey C, Sheehan C. Technology, older persons’ perspectives and the anthropological ethnographic lens. Alter. 2009;3(2):96-109. [ CrossRef ]
- Gadamer HG, Weinsheimer HG, Marshall DG. Truth and Method. New York, NY. Crossroad Publishing Company; 1991.
- Tong A, Sainsbury P, Craig J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. Dec 16, 2007;19(6):349-357. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Polit DF, Beck CT. Nursing Research: Generating and Assessing Evidence for Nursing Practice. Philadelphia, PA. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc; 2012.
- Kvale S, Brinkmann S. InterViews: Learning the Craft of Qualitative Research Interviewing. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications; 2009.
- Kagan A. Supported conversation for adults with aphasia: methods and resources for training conversation partners. Aphasiology. Sep 1998;12(9):816-830. [ CrossRef ]
- Graneheim UH, Lundman B. Qualitative content analysis in nursing research: concepts, procedures and measures to achieve trustworthiness. Nurse Educ Today. Feb 2004;24(2):105-112. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Krippendorff K. Content Analysis: An Introduction to Its Methodology. Thousand Oaks, CA. SAGE Publications; 1980.
- Klösch M, Sari-Kundt F, Reibnitz C, Osterbrink J. Patients' attitudes toward their health literacy and the use of digital apps in health and disease management. Br J Nurs. Nov 25, 2021;30(21):1242-1249. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Datta P, Eiland L, Samson K, Donovan A, Anzalone AJ, McAdam-Marx C. Telemedicine and health access inequalities during the COVID-19 pandemic. J Glob Health. Dec 03, 2022;12:05051. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rasi P, Lindberg J, Airola E. Older service users’ experiences of learning to use eHealth applications in sparsely populated healthcare settings in Northern Sweden and Finland. Educ Gerontol. Nov 24, 2020;47(1):25-35. [ CrossRef ]
- Airola E, Rasi P, Outila M. Older people as users and non-users of a video conferencing service for promoting social connectedness and well-being – a case study from Finnish Lapland. Educ Gerontol. Mar 29, 2020;46(5):258-269. [ CrossRef ]
- Kayser L, Kushniruk A, Osborne RH, Norgaard O, Turner P. Enhancing the effectiveness of consumer-focused health information technology systems through eHealth literacy: a framework for understanding users' needs. JMIR Hum Factors. May 20, 2015;2(1):e9. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Karnoe A, Furstrand D, Christensen KB, Norgaard O, Kayser L. Assessing competencies needed to engage with digital health services: development of the ehealth literacy assessment toolkit. J Med Internet Res. May 10, 2018;20(5):e178. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Nielsen AS, Hanna L, Larsen BF, Appel CW, Osborne RH, Kayser L. Readiness, acceptance and use of digital patient reported outcome in an outpatient clinic. Health Informatics J. Jun 03, 2022;28(2):14604582221106000. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Murray E, Hekler EB, Andersson G, Collins LM, Doherty A, Hollis C, et al. Evaluating digital health interventions: key questions and approaches. Am J Prev Med. Nov 2016;51(5):843-851. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chesser A, Burke A, Reyes J, Rohrberg T. Navigating the digital divide: a systematic review of eHealth literacy in underserved populations in the United States. Inform Health Soc Care. Feb 24, 2016;41(1):1-19. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Chesser AK, Keene Woods N, Smothers K, Rogers N. Health literacy and older adults: a systematic review. Gerontol Geriatr Med. Mar 15, 2016;2:2333721416630492. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mitra S, Singh A, Rajendran Deepam S, Asthana MK. Information and communication technology adoption among the older people: a qualitative approach. Health Soc Care Community. Nov 21, 2022;30(6):e6428-e6437. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ahmed S. How not to do things with words. Wagadu. 2016. URL: https://sites.cortland.edu/wagadu/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2017/02/v16-how-not-to-do-ahmed.pdf [accessed 2024-04-02]
- Monkman H, Kushniruk AW. eHealth literacy issues, constructs, models, and methods for health information technology design and evaluation. Knowl Manag E Learn. 2015;7(4). [ CrossRef ]
- Brørs G, Norman CD, Norekvål TM. Accelerated importance of eHealth literacy in the COVID-19 outbreak and beyond. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. Aug 15, 2020;19(6):458-461. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 14.03.23; peer-reviewed by G Myreteg, J Eriksen, M Siermann; comments to author 18.09.23; revised version received 09.10.23; accepted 27.02.24; published 11.04.24.
©Christian Gybel Jensen, Frederik Gybel Jensen, Mia Ingerslev Loft. Originally published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research (https://www.jmir.org), 11.04.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in the Journal of Medical Internet Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://www.jmir.org/, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Desalination system could produce freshwater that is cheaper than tap water
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
Engineers at MIT and in China are aiming to turn seawater into drinking water with a completely passive device that is inspired by the ocean, and powered by the sun.
In a paper appearing today in the journal Joule, the team outlines the design for a new solar desalination system that takes in saltwater and heats it with natural sunlight.
The configuration of the device allows water to circulate in swirling eddies, in a manner similar to the much larger “thermohaline” circulation of the ocean. This circulation, combined with the sun’s heat, drives water to evaporate, leaving salt behind. The resulting water vapor can then be condensed and collected as pure, drinkable water. In the meantime, the leftover salt continues to circulate through and out of the device, rather than accumulating and clogging the system.
The new system has a higher water-production rate and a higher salt-rejection rate than all other passive solar desalination concepts currently being tested.
The researchers estimate that if the system is scaled up to the size of a small suitcase, it could produce about 4 to 6 liters of drinking water per hour and last several years before requiring replacement parts. At this scale and performance, the system could produce drinking water at a rate and price that is cheaper than tap water.
“For the first time, it is possible for water, produced by sunlight, to be even cheaper than tap water,” says Lenan Zhang, a research scientist in MIT’s Device Research Laboratory.
The team envisions a scaled-up device could passively produce enough drinking water to meet the daily requirements of a small family. The system could also supply off-grid, coastal communities where seawater is easily accessible.
Zhang’s study co-authors include MIT graduate student Yang Zhong and Evelyn Wang, the Ford Professor of Engineering, along with Jintong Gao, Jinfang You, Zhanyu Ye, Ruzhu Wang, and Zhenyuan Xu of Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China.
A powerful convection
The team’s new system improves on their previous design — a similar concept of multiple layers, called stages. Each stage contained an evaporator and a condenser that used heat from the sun to passively separate salt from incoming water. That design, which the team tested on the roof of an MIT building, efficiently converted the sun’s energy to evaporate water, which was then condensed into drinkable water. But the salt that was left over quickly accumulated as crystals that clogged the system after a few days. In a real-world setting, a user would have to place stages on a frequent basis, which would significantly increase the system’s overall cost.
In a follow-up effort, they devised a solution with a similar layered configuration, this time with an added feature that helped to circulate the incoming water as well as any leftover salt. While this design prevented salt from settling and accumulating on the device, it desalinated water at a relatively low rate.
In the latest iteration, the team believes it has landed on a design that achieves both a high water-production rate, and high salt rejection, meaning that the system can quickly and reliably produce drinking water for an extended period. The key to their new design is a combination of their two previous concepts: a multistage system of evaporators and condensers, that is also configured to boost the circulation of water — and salt — within each stage.
“We introduce now an even more powerful convection, that is similar to what we typically see in the ocean, at kilometer-long scales,” Xu says.
The small circulations generated in the team’s new system is similar to the “thermohaline” convection in the ocean — a phenomenon that drives the movement of water around the world, based on differences in sea temperature (“thermo”) and salinity (“haline”).
“When seawater is exposed to air, sunlight drives water to evaporate. Once water leaves the surface, salt remains. And the higher the salt concentration, the denser the liquid, and this heavier water wants to flow downward,” Zhang explains. “By mimicking this kilometer-wide phenomena in small box, we can take advantage of this feature to reject salt.”
Tapping out
The heart of the team’s new design is a single stage that resembles a thin box, topped with a dark material that efficiently absorbs the heat of the sun. Inside, the box is separated into a top and bottom section. Water can flow through the top half, where the ceiling is lined with an evaporator layer that uses the sun’s heat to warm up and evaporate any water in direct contact. The water vapor is then funneled to the bottom half of the box, where a condensing layer air-cools the vapor into salt-free, drinkable liquid. The researchers set the entire box at a tilt within a larger, empty vessel, then attached a tube from the top half of the box down through the bottom of the vessel, and floated the vessel in saltwater.
In this configuration, water can naturally push up through the tube and into the box, where the tilt of the box, combined with the thermal energy from the sun, induces the water to swirl as it flows through. The small eddies help to bring water in contact with the upper evaporating layer while keeping salt circulating, rather than settling and clogging.
The team built several prototypes, with one, three, and 10 stages, and tested their performance in water of varying salinity, including natural seawater and water that was seven times saltier.
From these tests, the researchers calculated that if each stage were scaled up to a square meter, it would produce up to 5 liters of drinking water per hour, and that the system could desalinate water without accumulating salt for several years. Given this extended lifetime, and the fact that the system is entirely passive, requiring no electricity to run, the team estimates that the overall cost of running the system would be cheaper than what it costs to produce tap water in the United States.
“We show that this device is capable of achieving a long lifetime,” Zhong says. “That means that, for the first time, it is possible for drinking water produced by sunlight to be cheaper than tap water. This opens up the possibility for solar desalination to address real-world problems.”
“This is a very innovative approach that effectively mitigates key challenges in the field of desalination,” says Guihua Yu, who develops sustainable water and energy storage systems at the University of Texas at Austin, and was not involved in the research. “The design is particularly beneficial for regions struggling with high-salinity water. Its modular design makes it highly suitable for household water production, allowing for scalability and adaptability to meet individual needs.”
Funding for the research at Shanghai Jiao Tong University was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions, time magazine.
A number of MIT spinouts and research projects – including the MOXIE instrument that successfully generated oxygen on Mars, a new solar-powered desalination system and MIT spinout SurgiBox – were featured on TIME’s Best Inventions of 2023 list.
Insider reporter Katie Hawkinson explores how MIT researchers developed a new solar-powered desalination system that can remove the salt from seawater for less than the cost of U.S. tap water. Creating a device that relies on solar power, “eliminates a major financial barrier, especially for low-income countries experiencing water scarcity,” Hawkinson explains.
The Hill reporter Sharon Udasin writes that MIT researchers have developed a new solar-powered desalination device that “could last several years and generate water at a rate and price that is less expensive than tap water.” The researchers estimated that “if their model was scaled up to the size of a small suitcase, it could produce about 4 to 6 liters of drinking water per hour,” writes Udasin.
The Daily Beast
MIT researchers have developed a new desalination system that uses solar energy to convert seawater into drinkable water, reports Tony Ho Tran for the Daily Beast . The device could make it possible to, “make freshwater that’s even more affordable than the water coming from Americans’ kitchen faucets.”
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Evelyn Wang
- Lenan Zhang
- Device Research Lab
- Department of Mechanical Engineering
Related Topics
- Desalination
- Mechanical engineering
- Sustainability
Related Articles

Passive cooling system could benefit off-grid locations
Solar-powered system offers a route to inexpensive desalination

Solar-powered system extracts drinkable water from “dry” air

Simple, solar-powered water desalination
More mit news.

A biomedical engineer pivots from human movement to women’s health
Read full story →

MIT tops among single-campus universities in US patents granted

A new way to detect radiation involving cheap ceramics

A crossroads for computing at MIT

Growing our donated organ supply
New AI method captures uncertainty in medical images
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
Next, the results section needs to communicate the findings of your research in a systematic manner. The section needs to be organized such that the primary research question is addressed first, then the secondary research questions. If the research addresses multiple questions, the results section must individually connect with each of the ...
Tips to Write the Results Section. Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data. Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data. Write and highlight important findings in your results. Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting ...
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results. Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach. Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings. This approach can be used to highlight important findings.
The "Results" section is arguably the most important section in a research manuscript as the findings of a study, obtained diligently and painstakingly, are presented in this section. A well-written results section reflects a well-conducted study. This chapter provides helpful pointers for writing an effective, organized results section.
1. Context. The "results section" is the heart of the paper, around which the other sections are organized ().Research is about results and the reader comes to the paper to discover the results ().In this section, authors contribute to the development of scientific literature by providing novel, hitherto unknown knowledge ().In addition to the results, this section contains data and ...
Structure your results section around tables or figures that summarize the results of your statistical analysis. In many cases, the easiest way to accomplish this is to first create your tables and figures and then organize them in a logical way. Next, write the summary text to support your illustrative materials.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Build coherence along this section using goal statements and explicit reasoning (guide the reader through your reasoning, including sentences of this type: 'In order to…, we performed….'; 'In view of this result, we ….', etc.). In summary, the general steps for writing the Results section of a research article are:
A clear format will ensure that your research paper is understood by your readers. Follow: 1. Context — your introduction. 2. Content — your results. 3. Conclusion — your discussion. Plan ...
Step 1: Start With a Clear Organization. Begin the results section with a brief introductory paragraph that outlines the purpose of the results. Mention the research questions or hypotheses that the study aimed to address. Order of Presentation. Present your results in a systematic and coherent order.
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the 'Results' section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17-22.) are shown in Figures 1, and and2 2.
Here is an example for quantitative results of a research paper: Results Section Of A Quantitative Research Paper. Results Section for Qualitative Research. Writing the Results section for qualitative research involves presenting and interpreting the data collected through methods such as interviews, observations, or content analysis. ...
The "Results section" is the third most important anatomical structure of IMRAD (Introduction, Method and Material, Result, And Discussion) frameworks, the almost universally accepted framework in many journals in the late nineteenth century. 3 Before using a structured IMRAD format, research findings in scientific papers were presented in chronological order "First, I saw this, and then ...
Unlike essays, research papers usually divide the body into sections with separate headers to facilitate browsing and scanning. Use the divisions in your outline as a guide. Follow along your outline and go paragraph by paragraph. Because this is just the first draft, don't worry about getting each word perfect.
Then, it's key to consider that this is main section of your research paper where you present and explain the data you have collected or gathered and the findings of your data analysis and interpretation. The academic writing should be clear, impartial, and objective. Each result, which confirms or refutes your assumptions, should be noted in ...
Research papers rely on other people's writing as a foundation to create new ideas, but you can't just use someone else's words. That's why paraphrasing is an essential writing technique for academic writing.. Paraphrasing rewrites another person's ideas, evidence, or opinions in your own words.With proper attribution, paraphrasing helps you expand on another's work and back up ...
Take our quiz to find out which one of our nine political typology groups is your best match, compared with a nationally representative survey of more than 10,000 U.S. adults by Pew Research Center. You may find some of these questions are difficult to answer. That's OK. In those cases, pick the answer that comes closest to your view, even if ...
This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue: eHealth Literacy / Digital Literacy (328) Focus Groups and Qualitative Research for Human Factors Research (700) Adoption and Change Management of eHealth Systems (639) Health Care Quality and Health Services Research (211) Health Literacy, Health Numeracy, and Numeracy (14) Demographics of Users, Social & Digital Divide (651)
In a paper appearing today in the journal Joule, the team outlines the design for a new solar desalination system that takes in saltwater and heats it with natural sunlight. The configuration of the device allows water to circulate in swirling eddies, in a manner similar to the much larger "thermohaline" circulation of the ocean.
Abstract. In mainstream culture, the horror genre is frequently looked down upon as trivial, shocking and nasty - horror films are seen as being cheap to make, made for a younger, mass audience, and horror films tend to dwell on society's taboos, phobias and anxieties.