This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience. Learn more about DOAJ’s privacy policy.
Hide this message
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.

The Directory of Open Access Journals
Quick search.
Journal of Learning for Development (Jul 2023)
Collaborative Research Writing in the New Normal: Students’ Views, Challenges, Coping Strategies, and Takeaways
- Mark Joshua Roxas
Affiliations
Read online
The ‘new normal’ setup of education posed challenges on courses requiring learners’ collaboration. Despite the proven advantages of collaborative writing, several challenges still confront the learners which may affect the quality of their output. Collaboration per se is already a challenge for learners in face-to-face classes, more so in online distance learning. Thus, this study explored the views, challenges, coping strategies, and takeaways of senior high school students in collaborative research writing in the ‘new normal.’ Thirty (30) reflective essays written by senior high school students from three (3) academic strands, namely Humanities and Social Sciences, General Academic, and Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics were analysed. Ten (10) sample essays from each strand were selected through Critical Case Sampling. Findings revealed that students view collaborative research writing in general as easy, while some see it as difficult. The students met challenges in research technicalities, communication, and collaboration. Varied coping strategies were identified, such as having a positive mindset, being patient, considerate and determined, seeking help from others, maintaining proper communication and collaboration, seeking spiritual guidance, and taking a break. Ultimately, the takeaways of the students were not limited to academics or cognitive aspects—they were also able to gain important values.
WeChat QR code

Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
- Experts Say the ‘New Normal’ in 2025 Will Be Far More Tech-Driven, Presenting More Big Challenges
A plurality of experts think sweeping societal change will make life worse for most people as greater inequality, rising authoritarianism and rampant misinformation take hold in the wake of the COVID-19 outbreak. Still, a portion believe life will be better in a ‘tele-everything’ world where workplaces, health care and social activity improve
Table of contents.
- 1. Emerging change
- 2. Worries about life in 2025
- 3. Hopes about life in 2025
- About this canvassing of experts
- Acknowledgments
This is the 12th “ Future of the Internet ” canvassing Pew Research Center and Elon University’s Imagining the Internet Center have conducted together to get expert views about important digital issues. In this case, the questions focused on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020 on the evolution of humans-plus-technology. This is a nonscientific canvassing based on a nonrandom sample; this broad array of opinions about where current trends may lead in the next few years represents only the points of view of the individuals who responded to the queries.
Pew Research Center and Elon’s Imagining the Internet Center built a database of experts to canvass from a wide range of fields, choosing to invite people from several sectors, including professionals and policy people based in government bodies, nonprofits and foundations, technology businesses, think tanks and in networks of interested academics and technology innovators. The predictions reported here came in response to a set of questions in an online canvassing conducted between June 30 and July 27, 2020. In all, 915 technology innovators and developers, business and policy leaders, researchers and activists responded to at least one of the questions covered in this report. More on the methodology underlying this canvassing and the participants can be found in the final section.
When pandemics sweep through societies , they upend critical structures, such as health systems and medical treatments , economic life , socioeconomic class structures and race relations , fundamental institutional arrangements , communities and everyday family life . A new canvassing of experts in technology, communications and social change by Pew Research Center and Elon University’s Imagining the Internet Center finds that many expect similar impacts to emerge from the COVID-19 outbreak .
Asked to consider what life will be like in 2025 in the wake of the outbreak of the global pandemic and other crises in 2020, some 915 innovators, developers, business and policy leaders, researchers and activists responded. Their broad and nearly universal view is that people’s relationship with technology will deepen as larger segments of the population come to rely more on digital connections for work, education, health care, daily commercial transactions and essential social interactions. A number describe this as a “tele-everything” world.
Notable shares of these respondents foresee significant change that will:
- worsen economic inequality as those who are highly connected and the tech-savvy pull further ahead of those who have less access to digital tools and less training or aptitude for exploiting them and as technological change eliminates some jobs;
- enhance the power of big technology firms as they exploit their market advantages and mechanisms such as artificial intelligence (AI) in ways that seem likely to further erode the privacy and autonomy of their users;
- multiply the spread of misinformation as authoritarians and polarized populations wage warring information campaigns with their foes. Many respondents said their deepest worry is over the seemingly unstoppable manipulation of public perception, emotion and action via online disinformation – lies and hate speech deliberately weaponized in order to propagate destructive biases and fears. They worry about significant damage to social stability and cohesion and the reduced likelihood of rational deliberation and evidence-based policymaking.
At the same time, a portion of these experts express hope that changes spawned by the pandemic will make things better for significant portions of the population because of changes that:
- inaugurate new reforms aimed at racial justice and social equity as critiques of current economic arrangements – and capitalism itself – gain support and policymaker attention;
- enhance the quality of life for many families and workers as more flexible-workplace arrangements become permanent and communities adjust to them;
- produce technology enhancements in virtual and augmented reality and AI that allow people to live smarter, safer and more productive lives, enabled in many cases by “smart systems” in such key areas as health care, education and community living.
These six themes were commonly expressed by these experts in their responses to a question that asked them to consider the changes that were set in motion in 2020 by the COVID-19 outbreak and describe what the “new normal” might look like in 2025.
Some 47% of these respondents said life will be mostly worse for most people in 2025 than it was before the pandemic, while 39% said life will be mostly better for most people in 2025 than it was pre-pandemic. Another 14% said most people’s lives in 2025 will not be much different from the way things would have turned out if there had been no pandemic.
Among the 86% who said the pandemic will bring about some kind of change, most said they expect that the evolution of digital life will continue to feature both positives and negatives. These expert views link in interesting ways with public attitudes. A Pew Research survey in August 2020 found that 51% of U.S. adults said they expected their lives to remain changed in major ways even after the pandemic is over.
This is a nonscientific canvassing, based on a nonrandom sample. The results represent only the opinions of the individuals who responded to the queries and are not projectable to any other population.
The bulk of this report covers these experts’ written answers explaining their responses. They sounded many broad themes about the ways in which individuals and groups are adjusting in the face of the global crisis, describing the most likely opportunities and challenges emerging as humans accelerate their uses and applications of digital technologies in response. It is important to note that the responses were gathered in the summer of 2020, before the completion of the presidential election in the United States and before COVID-19 vaccines had been approved.
As these experts pondered what was happening in mid-2020 and the likely changes ahead, they used words like “inflection point,” “punctuated equilibrium,” “unthinkable scale,” “exponential process,” “massive disruption” and “unprecedented challenge.” They wrote about changes that could reconfigure fundamental realities such as people’s physical “presence” with others and people’s conceptions of trust and truth.
They wondered, too, if humans can cope effectively with such far-reaching changes, given that they are required to function with “paleolithic emotions, medieval institutions and god-like technology,” in the words of biologist E.O. Wilson .
Among the scores of changes they see is the emergence of: an “Internet of Medical Things” with sensors and devices that allow for new kinds of patient health monitoring; smart millimeter wave machines to diagnose people with disease symptoms; advances in synthetic biology and computational virology that improve drug testing and targeted disease therapies; diagnostic screenings that cover a person’s diet, genes and microbiome; handheld detection devices that citizen swarms use to address environmental problems; and a new class of tele-care workers.
Additionally, these experts forecast the creation of 3-D social media systems that allow for richer human interaction (sometimes via hologram avatars); mediated digital agents (interdigital agents) gradually taking over significantly more repetitive or time-consuming tasks; a “flying Internet of Things” as drones become more prolific in surveillance, exploration and delivery tasks; ubiquitous augmented reality; an expanded gig economy built around work-from-home free agents; urban farming that reaches industrial scale; advances in trusted cryptocurrency that enable greater numbers of peer-to-peer collaborations; locally based, on-demand manufacturing; “local in spirit and local in practice” supply chains; a robust marketplace of education choices that allow students to create personalized schooling menus; “tele-justice” advances that allow courts to handle large numbers of cases remotely; “truth valuation” protocols that diminish the appeal of disinformation; and small, safer nuclear reactors for energy production.
At the more everyday level, these experts also think there will be better speech recognition, facial recognition (including sentiment discernment from facial expressions), real-time language translation, captioning and autocorrect capacity, sensory suits, robust video search, body motion sensors, 3D glasses, multimedia databases and broader network bandwidth that will enable full 3D virtual experiences and developments in AI allowing it to serve more of people’s needs.
These themes and more are outlined in the accompanying tables.
Emerging change: As the global pandemic unfolds, experts predict people will develop greater reliance on swiftly evolving digital tools for good and for ill by 2025
The pandemic proves that world-upending phenomena can emerge from anywhere. The turn to living and working more intensively within digital communications networks shows the value of these complex systems. The pandemic brings more focus on both the upsides and the downsides of digital life.
- Tele-everything is embraced: The broad adoption of “remote” processes – telework, telemedicine, virtual schooling, e-commerce and more – is growing. In 2025, there will be more people working from home, more virtual social and entertainment interactions and fewer forays in public than has been in the case in recent years.
- Humans’ yearning for convenience and safety fuels reliance on digital tools: The pandemic has rearranged incentives so that consumers will be more willing to seek out smart gadgets, apps and systems. This will speed up adoption of new education and learning platforms, rearrange work patterns and workplaces, change family life and upend living arrangements and community structures.
- The best and worst of human nature are amplified: The crisis is enhancing digital interconnectedness that engenders empathy, better awareness of the ills facing humanity and positive public action. On the flip side, some individuals, cities and nation-states will become more insular and competitive as survival mode kicks in. Xenophobia, bigotry and closed communities will also increase.
- Worries: As the global pandemic unfolds, experts fear growing social and racial inequality, worsening security and privacy and the further spread of misinformation
- The advantaged enjoy more advantages; the disadvantaged fall further behind. Concerns particularly focus on the growing power of technology firms. Many suggested solutions have a double-edged quality because they threaten civil liberties. Automation could take many humans out of the work equation. And the spread of lies via social media and other digital platforms is likely to further damage all social, political and economic systems.
- Inequality and injustice are magnified: The pandemic and quick pivot to the use of digitally driven systems will widen racial and other divides and expand the ranks of the unemployed, uninsured and disenfranchised. Power imbalances between the advantaged and disadvantaged are being magnified by digital systems overseen by behemoth firms as they exploit big data and algorithmic decision-making that are often biased. More people will be pushed into a precarious existence that lacks predictability, economic security and wellness.
- As risk grows, security must also; privacy falls and authoritarianism rises: The health crisis spawned by the pandemic and broader dependence people have on the internet heighten threats of criminal activity, hacks and other attacks. Optimized security solutions may further reduce individuals’ privacy and civil liberties. They are likely to expand mass surveillance, as authoritarian states will use this as an opportunity to silence dissent and abuse citizens’ civil rights.
- Threats to work will intensify from automation, artificial intelligence, robotics and globalization: In order to survive, businesses are reconfiguring systems and processes to automate as many aspects as possible. While artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics will enhance some lives, they will damage others, as more work is taken over by machines. Employers may outsource labor to the lowest bidder globally. Employees may be asked to work for far less; they may have to shift to be gig and contract workers, supplying their own equipment, and they may be surveilled at home by employers.
- Misinformation will be rampant: Digital propaganda is unstoppable, and the rapidly expanding weaponization of cloud-based technologies divides the public, deteriorates social cohesion and threatens rational deliberation and evidence-based policymaking.
- People’s mental health will be challenged: Digital life was already high-stress for some people prior to the required social isolation brought on by the pandemic. The shift to tele-everything will be extensive and that will diminish in-person contact and constrict tech users’ real-world support systems and their social connections.
Hopes: As the global pandemic unfolds, experts urge that calls for social justice be heeded and that technology design focus on human well-being
People have the chance now to reconfigure major systems such as the structure of capitalism, education, health care and workplaces. Advances in technologies such as artificial intelligence, smart cities, data analytics and virtual reality could make all systems safer, more humane and more helpfully productive. Better communication of more-accurate information can dramatically improve emergency responses in crises and alleviate suffering.
- Social justice will get priority: The reawakening of public movements for social justice and economic equality may create more-responsive government and sociopolitical systems that are more attuned to diversity, equity and inclusion. This includes a focus on closing digital divides.
- People’s well-being will prevail over profit: Businesses may start to value serving the greater good above the typical goals of market capitalism. This could produce policies to fund broader safety nets such as universal health care, universal basic income and broadband as a basic utility. A reckoning for tech companies and their leaders might also occur.
- The quality of life will improve: The transition to home-based work will reduce urban air pollution, overcrowding and transportation gridlock. It will enhance the overall quality of life, create a better environment for family life, allow more accommodations for those with disabilities and inspire other enhancements.
- AI, VR, AR, ML will yield good : Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, augmented reality, deep learning, machine learning and natural language processing will make virtual spaces feel much more real, in-person, authentic and effective.
- Smarter systems will be created: Municipal, rural, state and independent services, especially in the health care sector, will be modernized to better handle future crises, quickly identifying and responding to emerging threats and sharing information with all citizens in more timely and helpful ways.
Source: Nonscientific canvassing of select experts conducted June 30-July 27, 2020. N=915. “Experts Say the ‘New Normal’ in 2025 Will Be Far More Tech-Driven, Presenting More Big Challenges”
Following is a selection of some of the most comprehensive overarching responses shared by a number of the 915 thought leaders participating in this canvassing.
Privacy was always a luxury in the past – only the rich enjoyed it. Then it spread to a large fraction of the population in the West. Now it is receding again, in a way that mirrors the rise in inequality and the inevitable fall in civil liberties.MARCEL FAFCHAMPS, PROFESSOR OF ECONOMICS AND SENIOR FELLOW AT THE CENTER ON DEMOCRACY, DEVELOPMENT AND THE RULE OF LAW AT STANFORD UNIVERSITY
Marcel Fafchamps, professor of economics and senior fellow at the Center on Democracy, Development and the Rule of Law at Stanford University, commented, “Here are some of the changes I anticipate. Please note that many of them were already in the background and could have occurred anyway, but I suspect less fast and less strongly.
- Economic and social inequality: The economic contrast between the ‘confined,’ the ‘essentials’ and the ‘unemployed’ will perdure. The confined are those who can work from home and be productive. Because employers save money on them, they will continue to prosper. Anyone who cannot work from home will as a result earn comparatively less than without the introduction of work-from-home as a normal way of life. Many workers will be displaced or made redundant by this change, e.g., all those who support work-life (restaurants, transport including car making, maintenance of office buildings, etc.). A gig economy will arise that caters to the same needs for those working from home but, because they will work in a very competitive industry (they will compete with each other for each home-worker-customer) and they will be much harder to organize in unions, strikes, etc., they will earn less. And they will become invisible, like domestic workers or gardeners today.
- The generalization of work-from-home will change where people live – possibly away from city centers, but this need not be the case if people value their social life, as is likely, especially for the young – possibly into small towns instead of big metropolis. This will in turn lead to more social segmentation/parochialism/segregation in terms of residential choice and social circle. Business districts force different people together by need rather than choice. If people can choose who they live with, they will sort on similar attributes, including wealth and all its correlates.
- By reducing the cost of congestion inherent to having a workforce in large office buildings, these changes will enable even larger firms, leading to an even stronger concentration of corporate power into a small number of key actors. The last wave saw the concentration of financial and service industry into a small number of world banks into a small number of geographical centers (e.g., New York, London, Shanghai, Singapore, etc.). We have already seen this with Amazon, Alibaba, Google and the like for their respective industries. We will now see this spread to other work-from-home industries: more agglomeration, but this time happening in the digital world, and not requiring geographical concentration itself.
- Civil liberties were severely curtailed during COVID-19. New tools and technologies were introduced to control people better, including phone apps that identify likely social interactions between people. These tools will be used by totalitarian regimes to control their population better, on the Chinese model. Furthermore, people working from home will be much harder to organize and much easier to target individually by repression. I therefore anticipate population control to become more efficient and effective, cutting down the productivity gap between autocratic regimes and democracies. As a result, democracy will be on the defensive, its spread will be reversed in many parts of the world, and democracies themselves will infringe more on civil liberties. We are entering a post-democratic era.
- Privacy was always a luxury in the past – only the rich enjoyed it. Then it spread to a large fraction of the population in the West. Now it is receding again, in a way that mirrors the rise in inequality and the inevitable fall in civil liberties. The poor never have privacy. COVID-19 has justified the loss of the last bit of privacy we had left, namely, our health data and who we meet in the park.
- In a not-too-distant future the Soviet Union will be seen as ahead of its time: Its main weakness was the inability to deal with the complexity of matching production and consumer demand. Now this can be achieved via Amazon or Alibaba, and the complex dispatch or matching algorithm that they and Google and Facebook have created. With concentration of corporate power, increase in inequality and weakening of civil liberties, it will be easy to recreate a post-democratic world that fulfills the Soviet promise, without necessarily requiring public ownership in the means of production: It will no longer matter who is formally the owner of capital, as China today demonstrates.”
Amy Webb, quantitative futurist and founder of the Future Today Institute , said: “We’ve entered a new Bioinformation Age, a new period in human history characterized by the shift from privacy and personal choice to new social, government and economic structures that require our data to operate. You can expect to see a Flying Internet of Things: smart drones equipped with object- and face-recognition, audio analytics, motion detection and sense-and-avoid systems that communicate with each other in the air and back down to a command center on the ground. The Flying Internet of Things will be used for surveillance and deliveries of small payloads, such as medicines, medical supplies and other necessities. Drones will transport specimens between buildings on hospital campuses, and they will move prescriptions between drugstores and homes.
“The availability of diagnostic testing will be far more ubiquitous. Drugstores, schools and large company offices will have compact COVID-19 testing machines and technicians. A specimen will be taken, put onto a cartridge and results will be delivered within minutes. Meanwhile, at airports, offices and event spaces, smart millimeter wave machines will be used to algorithmically diagnose people with COVID-19 symptoms. The machines will include a thermal imager and a powerful suite of AI algorithms that in seconds will scan someone’s heart rate, respiration rate, blood oxygen level and body temperature. Our new normal will include decentralized, persistent biometric surveillance. Within just a few years, biometric-recognition technology will transition from suspect, to reviled, to acceptable, to essential. Eventually, a massive biometric surveillance apparatus will become the invisible infrastructure enabling our economies to function again. …
“The fate of regulation, as national governments try to reconcile the desire for public safety with a reality in which algorithms are encoded with bias, could take many years to sort out, and the result is likely a patchwork of different protocols and permissions around the world. In the Bioinformation Age, transparency, accountability and data governance are paramount, but few organizations are ready. Everyone alive today is under persistent surveillance from a host of technologies, and what most people don’t realize is that tech companies don’t need cameras to see you. From Wi-Fi signals to single strands of hair, it is possible to recognize you without submitting to face scans.
“Catastrophe can be a catalyst for positive change. In a race to find a vaccine, important areas of science – synthetic biology, computational virology – are accelerating. This will result in more-efficient drug testing, new approaches to targeted therapies and, someday, a future in which we engineer life itself.
In a race to find a vaccine, important areas of science – synthetic biology, computational virology – are accelerating. AMY WEBB, QUANTITATIVE FUTURIST AND FOUNDER OF THE FUTURE TODAY INSTITUTE
“Many organizations in the public and private sectors had not invested in digital transformation. The virus provided an immediate impetus to change. On the other side of this, organizations should have better workflows, data management, information and cybersecurity, and new efficiencies. The virus could finally be an accelerant to healthcare equity in the U.S. The virus has highlighted the lack of broadband infrastructure in the U.S. and a growing digital divide. One of the coronavirus aftershocks will be a realization that American kids need internet access to perform well in school, and many families don’t have it. We could categorize internet access the way we categorize food security and emerge from the pandemic with federal programs to provide internet and device assistance to families in need.”
David Brin, physicist, futures thinker and author of “ Earth ” and “ Existence ,” commented, “Assuming we restore the basic stability of the Western Enlightenment Experiment, and that is a big assumption, then several technological and social trends may come to fruition in the next five to 10 years.
- Advances in cost-effectiveness of sustainable energy supplies will be augmented by better storage systems. This will both reduce reliance on fossil fuels and allow cities and homes to be more autonomous.
- Urban farming methods may move to industrial scale, allowing similar moves toward local autonomy (perhaps requiring a full decade or more to show significant impact). Meat use will decline for several reasons, ensuring some degree of food security, as well.
- Local, small-scale, on-demand manufacturing may start to show effects in 2025. If all of the above take hold, there will be surplus oceanic shipping capacity across the planet. Some of it may be applied to ameliorate (not solve) acute water shortages. Innovative uses of such vessels may range all the way to those depicted in my novel ‘Earth.’
- Full-scale diagnostic evaluations of diet, genes and microbiome will result in micro-biotic therapies and treatments. AI appraisals of other diagnostics will both advance detection of problems and become distributed to handheld devices cheaply available to all, even poor clinics.
- Handheld devices will start to carry detection technologies that can appraise across the spectrum, allowing NGOs and even private parties to detect and report environmental problems.
- Socially, this extension of citizen vision will go beyond the current trend of assigning accountability to police and other authorities. Despotisms will be empowered, as predicted in ‘Nineteen Eighty-four.’ But democracies will also be empowered, as in ‘The Transparent Society.’
- I give odds that tsunamis of revelation will crack the shields protecting many elites from disclosure of past and present torts and turpitudes. The Panama Papers and Epstein cases exhibit how fear propels the elites to combine efforts at repression. But only a few more cracks may cause the dike to collapse, revealing networks of blackmail. This is only partly technologically driven and hence is not guaranteed. If it does happen, there will be dangerous spasms by all sorts of elites, desperate to either retain status or evade consequences. But if the fever runs its course, the more transparent world will be cleaner and better run.
- Some of those elites have grown aware of the power of 90 years of Hollywood propaganda for individualism, criticism, diversity, suspicion of authority and appreciation of eccentricity. Counterpropaganda pushing older, more traditional approaches to authority and conformity are already emerging, and they have the advantage of resonating with ancient human fears. Much will depend upon this meme war.
“Of course, much will also depend upon short-term resolution of current crises. If our systems remain undermined and sabotaged by incited civil strife and distrust of expertise, then all bets are off. You will get many answers to this canvassing fretting about the spread of ‘surveillance technologies that will empower Big Brother.’ These fears are well-grounded, but utterly myopic. First, ubiquitous cameras and facial recognition are only the beginning. Nothing will stop them and any such thought of ‘protecting’ citizens from being seen by elites is stunningly absurd, as the cameras get smaller, better, faster, cheaper, more mobile and vastly more numerous every month. Moore’s Law to the nth degree. Yes, despotisms will benefit from this trend. And hence, the only thing that matters is to prevent despotism altogether.
“In contrast, a free society will be able to apply the very same burgeoning technologies toward accountability. We are seeing them applied to end centuries of abuse by ‘bad-apple’ police who are thugs, while empowering the truly professional cops to do their jobs better. I do not guarantee light will be used this way, despite today’s spectacular example. It is an open question whether we citizens will have the gumption to apply ‘sousveillance’ upward at all elites. But Gandhi and Martin Luther King Jr. likewise were saved by crude technologies of light in their days. And history shows that assertive vision by and for the citizenry is the only method that has ever increased freedom and – yes – some degree of privacy.
Handheld devices will start to carry detection technologies that can appraise across the spectrum, allowing NGOs and even private parties to detect and report environmental problems. David Brin, Author of “EartH” and “Existence”
“I would wager that I am almost alone in saying this in this canvassing. The hand wringers are totally right about the problem and the danger presented by surveillance tech! And they are diametrically wrong in the common prescription. Trying to ban technologies and create shadows for citizens to hide within is spectacularly wrongheaded and disastrous. See my book, ‘The Transparent Society: Will Technology Make Us Choose Between Privacy and Freedom?’ ”
Barry Chudakov, founder and principal of Sertain Research, commented, “The ‘new normal’ for the average person in 2025 will entail adapting to multiple simultaneous accelerations. … COVID-19 will be followed by other pandemics. Atmospheric climate change will accelerate. Wetlands deterioration will accelerate. The number of homeless refugees – due to soil, crop and weather devastation – will accelerate. Information speeds and content compression will accelerate. The invasiveness and accuracy of tracking, search and recognition technologies will accelerate. Our reliance on remote-distance technologies and interfaces will accelerate.
“The consequence of these accelerations is complexity: Problems and issues, programs and technologies, all are becoming more complex. The substrate of the new normal will be ineradicable complexity: Both our problems and our technologies (including how we deploy these technologies) have passed the stage of simple approaches. To quote McKinsey : ‘ Telemedicine experienced a tenfold growth in subscribers in just 15 days. Similar acceleration patterns can be seen in online education, nearshoring, and remote working, to name but a few areas. All these trends were clear before the crisis and have been amplified by it.’
“This is a fundamental amplification. The way people use and think about technology will progress further on the continuum of actual to virtual. We will become even more screen-dependent. We will see less of the world IRL (in real life) and more through interfaces and screens whose distancing will shield us from deadly viruses but also isolate us. Thus, the new normal with regard to the role of digital technologies in individuals’ personal and professional lives will be to usher in, and learn to navigate, the emerging metaverse. … What worries me most about the role of technology and technology companies in individuals’ lives in 2025 is the deliberate depreciation of complexity. The diminishment of complexity invites tyranny. It is the tyranny of simple-ism and reductionism papered over by happy talk, lies and distortions designed to distract us from real issues.
“We urgently need clarity and sound thinking. Simplistic clichés and slight-of-hand responses won’t solve the complex problems we face such as accelerating climate change, soil and shoreline erosion, global immigration or morphing pandemics. We must embrace transparency – make the science required to tackle this complexity easily understandable. To be clear: Complexity is not an end in itself; it is a fact of life that must be addressed, like the melting of the Greenland ice sheet. For example, Rana el Kaliouby, CEO of Affectiva, has written and spoken often about the need to embrace the complexity of gender, race, cultural context, accessibility, socioeconomic status and other variables that often are lacking in the environments that design the computer programs and algorithms that mediate our lives. We must humanize AI and make human variability the substrate of bits and qubits.
“A second level of complexity – and the more urgent one – is our engagement with our devices. We use them; we typically are not present with them. We don’t notice how they bend our perceptions and behaviors. As complexity accelerates, curiously, our ability to embrace and engage with that complexity diminishes. This is in no small measure due to the ergonomic design of our devices that makes them both indispensable and makes us more likely to adhere in our thinking and action to their compression logic: They compress time, distance, communication, relationships. We have an active and reactive relationship with our tools. Because of this we need a meta layer of awareness that monitors how we change and adapt. Merely adopting tool logic as our own – texting while we drive, ghosting, growing alone together – is hardly a healthy response. Further, our lack of presence with our tools effectively means we are at the mercy of the surveillance capitalism and interruptive logic that pervades their inception. These technologies and the companies that create them daily gain in sophistication; this is a new acceleration.
“Much of this accelerated sophistication is outstanding and useful. But we pick up and use our devices and, as it were, live our lives eyes wide shut. We don’t look at what we’re using and how we’re using it – we practice unconscious tech engagement. Our tools are so ergonomic, so easy to use, so quick to respond that we are seduced by the slick way they reorganize our thinking, our behavior and our lives. But we have reached a tipping point with our tools: They are now more sophisticated than our ability to fully appreciate their effects; those effects are hidden in the tool logic, the actions of the tool. We must become present with our tools; we must gain in meta-awareness, retool our understanding of how we think while tech-immersed versus how we think otherwise.
We have reached a tipping point with our tools: They are now more sophisticated than our ability to fully appreciate their effects; those effects are hidden in the tool logic, the actions of the tool. Barry Chudakov, founder and principal of Sertain Research
“Why is this a concern? In prior human history, the power to manipulate reality, facts, behaviors and lives was centered in visible entities with physical representatives: the king, the pope, the organizer, the leader. Institutions from churches to schools to governments were concrete entities with no metalife. If you couldn’t talk to the king or the pope every day, you knew where they lived in a castle or the Vatican. While many institutions can fossilize and grow weedy with bureaucratic complexity, newer technologies present the ability to avoid presence. More than absence, this is the ability to hide, to obfuscate, to distort. The more virtual we become, the more I worry that we abandon the concrete for becoming gadgeteers and, as Neil Postman put it, ‘amusing ourselves to death.’ The more we disembody, the more virtual our realities become, the more we exhibit antisocial, even psychopathic behaviors. Alone together we lose empathy; we lose compassion; we lose focus. As computing goes quantum, as algorithms and AI mediate more of our interactions, our educational structures have either lagged far behind or have given up altogether trying to prepare young minds for the world they will inherit. The more device dependent we become, the more incumbent it is upon all users to fully understand the tool logic and business model of the tool they pick up and use. Surveillance is a business model; exploitation of data exhaust is a business model; tracking is a business model; observation and analysis is a business model. In whose interest is it for us to embrace that business model? In ‘ Everybody Lies ’ Seth Stephens-Davidowitz says, ‘Google searches are the most important dataset ever collected on the human psyche.’ In other words, the human psyche is an emerging business model.”
Brad Templeton, internet pioneer, futurist and activist, a former president of the Electronic Frontier Foundation, said, “It has been suggested that this is the first battle in our last war on disease – that, partly as a result of this, we will come to understand viruses at a fundamental level. And now the budget will be there (due to the obvious benefit) to create the ability to make a vaccine or counter-agent to a virus on demand – just sequence the virus and quickly be able to generate agents that will be known to be safe and effective. It’s very likely we’ll get much better at diagnostics as well. These are tremendous goods, and one would even say worth the cost of the pandemic, except we were trying to make them before and this just kickstarts them. This could prevent the death of millions, and if you can attribute it to the pandemic, you would have to go into the ‘wildly, wildly positive’ camp on the pandemic.
“We’re learning a great deal about videoconferences and meetings, holding large events online, holding parties online. We still suck at it, but we’re learning lots and getting better. The video call was something that was going to be ‘the next thing’ since the 1950s. The pandemic made that finally happen, and it’s probably here to stay. We may even develop means to do pretty significant business travel without the travel, which has benefits in cost, time and pollution. …
“We may learn to do occasional ‘dry runs’ of all the technologies necessary for hard lockdown – online shopping, delivery, virtual meeting spaces and remote learning and more. We will probably learn that the right approach is to use those technologies to generate a very hard lockdown for a short time, rather than a moderate lockdown for a very long time. Delivery robots (in which I am involved) will gain more appreciation. Public transit will mostly recover but only because it has to; long-overdue changes away from its 20th-century models will be hastened in reaction to that decline, and fear for several years of cramped, packed spaces. This will slightly hasten the eventual replacement of most public transit with robotic group and solo transportation. The world will probably get a bit cleaner. Ultraviolet disinfection will become common. This may reduce the spread of other infections like flu.”
Digital technologies always mirror and magnify the good, bad and ugly. danah boyd, founder and president of the Data & Society Research Institute and principal researcher at Microsoft
danah boyd, founder and president of the Data & Society Research Institute and principal researcher at Microsoft, wrote, “Inequality will create a huge division between those who are thriving and those who are in dire straits. There will be plenty of high-status people who will come out of the pandemic with wealth, health and their life goals intact. But a large amount of society will be dealing with all sorts of ripple effects. There will be those who got sick and never fully recovered. There will be those who lost their jobs and precarity turned to poverty fast. But there will also be mothers whose careers took a left turn after multiple years of trying to be a stay-at-home parent plus a teacher while working at home. There will be so many people who will be facing tremendous post-traumatic stress disorder as they struggle to make sense of the domestic violence they experienced during the pandemic, the loss of family and friends and the tremendous amount of uncertainty that surrounded every decision. Digital technologies always mirror and magnify the good, bad and ugly. People will continue to use technology to get support and help, but they will also struggle with how technology becomes a place of hostility and information confusion. A cohort of young people will be accustomed to engaging friends through technology, but also struggle with a range of face-to-face encounters as the fears/confusion over illness persist. If we’re lucky, schools, conferences, mental health and general health care will be forever reimagined to consider hybrid ways of approaching services. But this is more likely to be something that magnifies inequality rather than actually doing the connective work that could be possible. The biggest unknown in the United States concerns political leadership.”
Douglas Rushkoff, media theorist and author, wrote, “2025 may be a whole lot more local in spirit and local in practice. As global supply chains falter and reveal their structural inadequacies, people will come to depend more on locally produced goods. This will also mean fewer ridiculous, meaningless, valueless cubicle jobs, and more time spent actually creating value. I’m thinking simple, real tasks like growing food, building houses, teaching kids, health care and providing energy may dominate what we now think of as ‘work.’ In other words, instead of developing careers in industries, people will learn how to do things – which could prove truly fulfilling and psychologically stabilizing.
“The climate and economic challenges may be bigger, but our resilience as people could be stronger. It’s only three or four years out, so I don’t anticipate we’ll be through the disillusionment at the failure of global corporate capitalism. As for the role of digital technologies? I don’t know if they will be quite as important in their own right. They’ll likely be more embedded into other stuff, and less fetishized on their own. The only tech-related change I’m really hoping for is less of it. It’s really draining. Even typing this right now I’m using tech to write to you about the future of tech? As for tech making life better? The obvious ones: solar, regenerative energy, less-industrial agriculture (more low- or light-tech solutions to topsoil depletion, air pollution, watershed destruction). More simple stuff that solves real problems. Less social networks designed to create new problems.
“My worries? Well, there are now trillions of dollars invested in companies that depend on addiction, isolation and fear to keep growing. That’s very dangerous, since these companies will spend their war chests on deliberately causing panic, pain and fear. They know the more upset and reactive we are, the more likely we are to engage with their platforms. So, when the wealthiest industry in the world is doing everything it can to attack our basic sense of well-being, I do get concerned we may not have the resilience as people to oppose these forces. Once they really get a handle on using AI for this purpose, I’m not sure how we get ourselves out of it. Even now, we see people on social media platforms attacking those with whom they should be allied. They cancel people rather than collaborate with them. If AIs determine that turning people against each other is the easiest way for them to deliver desired metrics, then we could be in great trouble.”
Esther Dyson, internet pioneer, journalist, entrepreneur and executive founder of Wellville, responded, “Things will be both better and worse. Many people will be dead and many others more will be permanently damaged, physically or mentally or economically. And those people will mostly be the ones who were worse-off in the first place, poor, Black or another minority, disabled or ill, or otherwise challenged. Yet at the same time, the U.S. and even the world at large are much more aware of the disparities and the unfairness of this situation.
“With luck, we will start to think long-term (to the next pandemic?) and realize how much better things could be for all (including rich employers who want educated, happy, productive employees and well-off customers) if we would invest in our greatest asset – human beings. The money one spends keeping pregnant/new mothers healthy, providing child care (and paying care workers’ wages that honor their work), educating children, keeping people healthy instead of trying to fix them when it’s too late – all that money delivers a huge return on investment. It’s just that the rewards don’t go directly to those who pay; they go to society as a whole and make the world a better place for both rich and poor (but with more impact on the poor because their condition has so much more room for improvement).
“That’s the optimistic view of things. I’m doing everything in my power to make it come true. The short version is that we need to think long-term and invest in everyone’s future versus grabbing what we can for our narrowly defined selves. Ah yes, and you were asking about ‘digital tech.’ We’re going to discover that it is getting cheaper to do a lot of things, including many varieties of telemedicine, less travel and jet lag for the rich, upper-class workers, and that we can actually afford to invest in human capital cost-effectively. We need to do that and we need to train a large new cadre of tele-care workers to help deal with the residual effects of COVID-19 (including contact tracing). The human communication skills needed for contact tracing now are the same skills that will also make for better child care, mental health and other care workers.
We need to do that and we need to train a large new cadre of tele-care workers to help deal with the residual effects of COVID-19 (including contact tracing). The human communication skills needed for contact tracing now are the same skills that will also make for better child care, mental health and other care workers. Esther Dyson, internet pioneer, journalist, entrepreneur and executive founder of Wellville
“One really interesting impact will be on privacy: Any stranger could be infectious, so there will be demands for testing and immunity passports and the like – and a similar demand for secrecy from (usually poor) people terrified of losing their physical-presence-required jobs, their ability to travel, etc., etc. It’s akin to issues around concealed weapons, etc., etc. A lot will depend on how immunity/vaccines/and other medical issues play out over the next year.
“There will be a lot less traveling and a lot more appreciation for face-to-face (or mask-to-mask) connections when we do make them. Much more telehealth and a healthier population. More self-aware use of social networks and an understanding of how addictive they can be. The use of all kinds of digital monitors should help people to manage their own health and resilience better (though they can be abused/addictive like everything else). I would love for every third grader in this country to get a continuous glucose monitor along with an age-appropriate scientific curriculum so that they could see for themselves how the food they eat affects their bodies and their mood. Or more cheaply, at least a Mouse House with four mice – two sedentary and two with a running wheel, orthogonally two on a healthy diet and two eating the kind of processed, overly sweetened junk still found in many schools’ cafeterias. Maybe PETA would sue, which would just help to make the point of how badly we feed so many children. Meanwhile, the kids could just watch and see the impact of the four combinations of choices. I worry that poor and minority people still will have limited access to all the tech and tools that the rich take for granted. … Disparities in access to tech can aggravate other disparities. I also worry that people will turn to tech rather than to other people for human comfort.”
Jamais Cascio, research fellow at the Institute for the Future, predicted, “Three big arenas of technological uncertainty we’re likely to see by 2025 emerge from social dynamics well underway now: the prevalence and availability of remote work and the technologies used to enable it; the manifestation of authority and policing, particularly in the balance of surveillance of citizens and surveillance by citizens; and the degree of trust and accountability of social media systems, in terms of both personal privacy and protections against manipulation. All three of these issues could have radically divergent outcomes in a relatively short amount of time, making it very difficult to pin down 2025.
- Remote work: The speed and stability of an actual recovery from the pandemic will shape how much we continue to rely upon remote work; there’s a very good chance that a significant portion of the pandemic remote workforce will want to continue to work from home, but the longer the forced isolation lasts, the greater the likelihood that people will be desperate to return to human contact at work. Increasing improvements in automation will eliminate some of the ‘essential’ delivery jobs. It’s possible that these may be semi-automated tasks, where a remote pilot controls the drone or robot used to make deliveries (to handle the unexpected and customer interaction).
- Policing and surveillance: The capacities of surveillance technologies are increasing rapidly, but their use against civilian populations and their use as a way to monitor authorities are not necessarily correlated. The degree to which institutions of authority adapt to changing social demands will shape the level to which surveillance could be imposed upon them; conversely, if authorities are able to suppress demands for change, the spread of top-down surveillance will likely accelerate.
- Social media networks: Even as Facebook demographics continue to age, Millennials desiring a more stable platform for social (and family) engagement will start to look beyond transient interaction apps. Facebook could remain the default if it manages to act as a bulwark against social manipulation and tighten up its privacy-related behavior, but since that’s not a highly likely scenario, we’ll probably see the emergence of something else that fills that role for younger adults. This ‘something’ will allow for both persistent interaction and advanced privacy protection; what that would look like remains to be seen. I’d like to see more systems that allow for improved privacy, accountability and insight.
“Beyond information technology, we could see major improvements in our lives through the acceleration of the shift away from fossil fuels: more electric cars and the corresponding infrastructure, more power-self-sufficient homes and much longer-lived energy storage/batteries. I also hope that the pandemic will trigger a variety of advances in medical and biotech systems, improving the overall quality of health and life for millions (or billions).”
Jim Spohrer, director of cognitive open technologies and the AI developer ecosystem at IBM, noted, “The new normal by 2025 will likely be better. 1) Dealing with pandemics will be improved, vaccine speed of development will be improved, preparedness for next pandemic will be improved. 2) Online education, health and government services will be improved, and more people will have experience with them. 3) Businesses will continue to encourage more online meetings (less travel) and more work from home (less travel). 4) There will be more retail robots, tele-presence robots and robots at home – all with more investment, deployments and success stories. 5) There will be a resurgence in community approaches to local jobs in service of community culture and development.”
Fernando Barrio, a lecturer in business law at Queen Mary University of London expert in AI and human rights, wrote, “More than 20 years ago we all had a very optimistic and naive view of the evolution of technology in people’s lives, so it was paramount to allow the technology to develop unhindered by regulatory intervention. The result is a vast and resilient network that allows us to do even more things than we envisioned. But it also means a world where wealth is more concentrated than ever, where science takes second place to charlatans and gossipers that cause serious damage to millions, where the political arena is hijacked by a combination of media and foreign interventions making a mockery of democracy, and the list of not very nice things is quite longer than the nice moments of the Arab Spring and #MeToo movements. And it seems that, yet again, we are planting the seeds for the new normal to be very nice in the surface, while creating a society more unequal, unfair and sharply divided about too many things that need social consensus. In 2025 the new normal will imply a society more sharply divided between those who have access and those who don’t. In this context, access is multi-pronged: access to food, access to wealth, access to connectivity and technology, access to power.
And it seems that, yet again, we are planting the seeds for the new normal to be very nice in the surface, while creating a society more unequal, unfair and sharply divided about too many things that need social consensus. In 2025 the new normal will imply a society more sharply divided between those who have access and those who don’t. Fernando Barrio, a lecturer in business law at Queen Mary University of London expert in AI and human rights
“When one thinks about people’s relationship with technology, one is thinking of the group of people that have access to it – unfettered access. If we restrict the view to that group, the new normal will be an enhanced form of what we are living today, where the economy, the education, the human relations and the politics are technologically mediated. Before the COVID-19 crisis, there was already a push by certain sectors of the media-IT corporations to normalize the use of certain technologies where the possibility of individuals’ control is purely theoretical. That push was supported in part by elite universities, academia, due to funding from those corporations or because the ideological shift had already taken place within them.
“Accordingly, it was possible to see all around the globe members of those groups advocating the change from text to voice, therefore encouraging voice-managed assistants in every room of people’s homes, disregarding the immense possibilities of surveillance and absolute control over people’s lives that those technologies introduce. Not focusing on the need to have better privacy agreements regardless of the countless examples of violations of agreements that discourage the use of the information for any purpose without individuals’ control and consent.
“The COVID-19 crisis showed that the resilience of the vast global network over which different layers of protocols, software and applications run is being used to exalt the upper applications layer because it is the one that made possible the tele-everything that we are experiencing. Thus, in the new normal hyper-intrusive technology is taken for granted. Instead of embedding privacy, security and protection of individual rights in every layer that runs over the network, in the crisis the new normal is that those concepts are modified to allow technologies to intrude in people’s lives (as they already do in certain nondemocratic countries). That paradigm shift will also blur the limits between people’s personal, professional and public lives. For example, instances of cyber-sacking – in which one loses a job for comments or information posted online – will become more common, having an impact on the quality of the discussions and information put forward by individuals, and even private conversation held in private groups or within hearing of voice-managed assistants at home might be also processed at that effect.”
Christine Boese, a consultant and independent scholar, wrote, “Thanks to the horrors of COVID-19, as we sit in our homes and take stock of our personal economic situations, make hard decisions, suddenly what is absolutely essential becomes clear. It is a reset, and – despite the horrors – it was long, long overdue. …
“It is in difficult times when we see the seams and frayed edges of our thin veneer of civilization, the illusions of the fractured U.S. health care system and even the severe limits to much-touted electronic medical records innovations. In times like this, we don’t have to look so hard to separate technology hype from reality. We face failing infrastructure across the U.S. Other countries have systems that work, at all levels, while ours falters. Without this horrific stress test, we would not be able to see, let alone correct for, these fault lines. That thin veneer of civilization balances precariously on a consumption engine, and American culture is literally consuming itself, even as Rush Limbaugh suggests we need to adapt to this self-consumption ‘like the Donner Party did.’ As with most absurdities, it comes with its own irony: Like the Roman Empire, we make little ourselves and instead consume the cheaply produced, slavery-inducing trifles created elsewhere, as if it fills some kind of deep emptiness inside. The extremis of the COVID-19 situation glaringly exposes several things that had previously been invisible:
- The actual power of mass media, even as channels multiply and become diffuse. One channel, Fox News, has created an entire class of people who are actively putting themselves at risk of death or lifelong health problems. As someone with relatives who have fallen prey to this external programming, I can attest that no rhetoric, no persuasion, no methods currently known to me can penetrate this closed belief set. What we are living in right now makes Leni Riefenstahl look like a mere piker.
- The manipulative panoptic power of interactive social media in the hands of malevolent agents. When I began to do internet research in the 1990s, I speculated that the active and interactive power of user-directed and navigated media would lead to a more aware and awake populace, even if not fully democratized. What I did not anticipate (and I am currently studying now) is the power of dark UX patterns driven by algorithmic assumptions, whether accurate or not, and, very soon, a real Pandora’s box of AI-driven machine learning.
- How dangerously hollowed out the U.S. infrastructure is, from endemic underfunding of systems and anything that requires attention to detail below the surface to business-school ‘top-line’ summaries of a management layer that flies above anything that takes more than five minutes to scan. Newspapers and universities were hollowed out first, the agents that created and fostered critical thinkers. The gutting of public education was the third leg of that stool. Remove anything that might question the status quo, that engages in detailed work (even engineering!) or requires long-term planning. Boeing itself fell prey to something that, from the outside, looks like the Agile-ification of all work, which must, despite protestations by the manifesto’s philosophy, degenerate into surface-level patch work and the delivery of marginal improvements called ‘features.’
- Lastly, how deeply distorted the cultural fabric of American life has become, when, upon being forced to actually live in our homes for extended months on end rather than merely using them as places to sleep and consume things because our primary away-from-home activity was work, we discovered how much our homes lacked in all those ‘things’ we own that actually enrich our lives. As livelihoods were put perilously at risk, many of us came to realize what we were being expected to die for and discovered that that was as hollowed out as everything else, driven by a churn to consume as a red herring to keep us from noticing how thin our lives were becoming, even as we all, as a society at large, have consumed ourselves into larger and larger sizes.”
Craig Silliman, an executive vice president for a major global company, wrote, “While COVID-19 has forced us to distance physically, it has brought individuals closer together. Many of us have spent years in countless meetings and meals and on airplanes with colleagues and yet never learned as much about them as we have in the past four months. When we lost our physical proximity, we created emotional bridges that connected us in new and profound ways. It turns out that it took forced distancing to bring out our most complete and authentic humanity. I believe that once we are together again physically, we will not forget what we learned while we were apart, and that will make for richer and deeper relationships for years to come.
When we lost our physical proximity, we created emotional bridges that connected us in new and profound ways. It turns out that it took forced distancing to bring out our most complete and authentic humanity. Craig Silliman, an executive vice president for a major global company
“On the technology front, most of the technologies that we are using daily are not new. What has changed is not the capability but our behavior. I have talked to numerous colleagues who have observed that they never again will board a six-hour flight for a two-hour meeting. We previously might have thought that this was highly inefficient but didn’t feel we had ‘permission’ to suggest video conferencing because we weren’t sure how a boss/client/customer might react. Because this was a simultaneous discontinuity in work patterns globally, it will have caused us all to change our work habits, particularly involving the use of technology to be more efficient. We will be working in very (positively) different ways in 2025 as a result of COVID-19. We previously have thought about the office as a place where one must go to ‘be at work’ or to ‘do work,’ even if the office environment wasn’t the most effective location for a particular task. We will increasingly think about a spectrum of locations where work can be done, and a spectrum of technologies that are a platform for work to be done, and start by asking what the task is that we seek to accomplish and then using the appropriate location and technology to best accomplish that task. That will allow us to design office spaces to serve as platforms for what shared, collaborative spaces do best while liberating workers to find the mode and place of working that makes them most effective.”
Abigail De Kosnik, associate professor and director of the Center for New Media at the University of California, Berkeley, predicted, “Climate change, invasive corporatized technologies and increasing economic precarity will all combine to give rise to a far more paranoid society in 2025 than we had at the start of 2020. In some ways, widespread fear and anxiety will have positive results, as people will be more environmentally conscious than ever before and will engage en masse in efforts to regulate corporate resource extraction and pollution, and will show a collective willingness to adopt less environmentally harmful lifestyles (for example, I expect a huge upsurge in mass transit use and a corresponding movement to improve the quality of mass transit in cities across the U.S.). However, the paranoia will be justified – there will be fewer opportunities for college graduates who do not have family connections, and climate change will make large regions uninhabitable. This will lead to huge problems in mental health and will negatively impact at least a couple of generations of Americans in terms of their relationships, sense of self and lifetime- happiness quotient.
“I am especially worried about the fact that technology companies are overall having a hugely negative effect on the environment and on humans’ ways of thinking about and understanding the world … and they don’t seem to care much about spreading misinformation and training hundreds of millions of people all over the world to think less critically about information are my biggest concerns. The tech industry will likely continue to produce technologies that either do nothing to improve everyday life or make it significantly worse. What can happen to improve technology is better organization on the part of users and tech workers who object to their companies’ negative social impact.
“I have hope that we will see a wave of activism and unionization and the formation of alternate types of organizations ( B Corps or P Corps for example) that will yield new technologies whose aim will not be profit but actual problem solving – mobilizing collective intelligence to solve the problems of environmental disaster, massive social inequity and lack of opportunity that we will face in 2025.”
Adam Clayton Powell III, senior fellow at the USC Annenberg Center on Communication Leadership and Policy, predicted, “The 2025 ‘new normal’ will be better, often much better, for the affluent and for other global elites. They have now and will continue to have access to and can afford the best technologies to serve them in their personal and professional lives. But 2020 has been such a setback for the hundreds of millions of people, most in Asia and Africa, who have just emerged from poverty and whose progress has now been reversed that it is difficult to imagine these reversals can be entirely cured by 2025. In the U.S. we had record employment – some said ‘full’ employment – as recently as February of this year. While one can hope that the sudden plunge to Depression-level unemployment can be temporary, there are so many changes – especially in any industry relying on people crowding together (transportation, entertainment) – that the shift to video communication and streaming home entertainment suggests these coping mechanisms for 2020 will not entirely recede.
“Many have said that the virus pandemic has accelerated changes in uses of digital technologies that were already underway. There does not seem to be any reason to believe we will return to 2019. For a start, why would I ever want to commute to an office again? For decades, we have said that the internet brings to our fingertips the riches of the world’s libraries. Now people around the world – people who are connected, that is – realize they have the riches of the world’s information and entertainment video and experiential technologies at their fingertips. This will not go away. Consider history: The Metropolitan Opera is streaming opera productions every day. It was during the Depression that the Met started transmitting its productions on radio. The Depression ended but the Met’s radio broadcasts didn’t.”
Susan Etlinger , an industry analyst for Altimeter Group, observed, “Technology is ultimately about power – about who frames a problem, what ‘solving’ it looks like, who benefits, who is overlooked. So, if anything would make post-pandemic life better, it would be a willingness to, as John Lewis has said, ‘get in good trouble.’ My main concern is that the large technology companies have far too much power to frame what we know and how we live, and that, ultimately, we are all assets to be leveraged for shareholder value. Technology should be a tool – not a weapon, a religion or a government. The biggest issue for technology is essentially a choice: Do we commit to building models that describe and classify people and the world without excluding, discriminating and amplifying inequality?
My main concern is that the large technology companies have far too much power to frame what we know and how we live, and that, ultimately, we are all assets to be leveraged for shareholder value. Technology should be a tool – not a weapon, a religion or a government. Susan Etlinger, an industry analyst for Altimeter Group
“In a year in which we mourn the deaths of George Floyd, Tony McDade, Breonna Taylor and too many others and again confront our long history of systemic racism can we finally acknowledge that technology has been deeply complicit? More to the point, can we stop hiding behind the fig leaf that data and technology are a) neutral and b) always the answer? Yes, people are messy, yes this is hard. But we need to stop hiding behind excuses. This isn’t to say we should toss our phones and flee to the hills. But we do have to ask the hard questions and make the harder choices about how we solve problems, and whether, in solving one set of problems, we’re creating others that are more insidious and longer-lasting.
“Will we, in the interest of public health and safety, increasingly surveil our employees, guests, customers, neighbors? Will we address the inevitable issues of discrimination and exclusion of vulnerable and marginalized populations? Do these technology solutions actually work, and are there other, less invasive ways to keep people safe? Did we leave anyone behind? I hope we can use this moment in our history as an opportunity to reflect on the choices we’ve made and what, finally, we value. If we say Black Lives Matter, are we willing to speak up in meetings where design decisions have the potential to put Black lives at risk? Are we willing to challenge cultural norms to ensure that we have representation from the people who are most affected by the decisions we make and whose talent we have overlooked? Are we willing to sit down so someone else can speak, and amplify their voices?”
Paul Jones, professor emeritus of information science at the University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, predicted, “Let’s look at changes that were underway and that will likely prevail by 2025:
- Cashless payments: No stopping them. COVID-19-era purchasing, whether retail or curbside pickup, is making cashless the norm. In the U.S. this was already apace. In China, cashless is already a done deal. Every phone, every new card, every over-the-phone purchase is cashless and checkless. Goodbye money, coins, etc. Too late for Harriet Tubman to replace Andrew Jackson on the $20 bill, except in the area – much needed – of symbolism in the U.S.
- Officeless organizations: They will proliferate. The organization of work within a physical location is, for the most part, done. At home, everyone has their own corner office with a view. Every day is Bring Your Pet to Work Day. Every day is – from the waist down anyway – Casual Friday. The toll paid to commute is fully recognized and rejected. All of this was underway but now the issues are resolved and normalized.
- Distributed access to education: This is much more complex that virtual offices or virtual organizations. Despite various rhetorical stances that education is actually job training or something of the sort, countries who provide actual education always take the lead in innovation and tech. That said, we have quickly gotten much better in the U.S. at pushing the limits of our skills to both educate and train, learning what we knew in the physical classroom that, as Marshall McLuhan quipped, ‘Anyone who tries to make a distinction between education and entertainment doesn’t know the first thing about either.’ A straightforward, traditional online lecture has limited educational utility. The reimagining of the classroom for digital life is still underway, but we can expect both the practice and expectations of learning to be changed radically by tech. Mentorship, whether in the classroom, laboratory, or at work, is indispensable. Tools for collaboration will be extended and embraced. Slack, Zoom, GitHub, Google Drive and cousins are already firmly in place and will be improved upon. If tech and policy align correctly, this will make our lives better.
- Transportation: Post-COVID-19 we will have seen this shift accelerated, but in which direction? In the near term, public transport (trains, buses, etc.), mass transport (air, cruises, ferries, etc.) and shared ride services including taxis are stagnated. Personal transport is also underused. We are realizing we need not drive, fly or float as much as we have been doing before. We may yearn to travel but not for work. The lack of traditional benefits for ride-share drivers will have to be better addressed – by their own organizing or by government advocacy and regulation. Transportation ownership by people under 35 was already on the decline – except for skateboards. Fewer people will own cars in the U.S. – this will have accelerated by 2025. Business air travel will have also decreased and perhaps become novel.
- Food: During COVID-19, people have learned to cook again and to enjoy doing so. We have turned in a few months from a nation of restaurant-goers to a nation of pickup and home cooking. Tech will continue to assist this trend which should continue through 2025. Instapot is only the first shot fired. Plant-based eating will continue to trend. Americans having gained weight during lockdown are looking in the mirror and thinking of carrots and salads. Our taste for vegetables has returned as quickly as our reluctance to eat as much meat. Thank you, Instagram, for making meal presentation, even of home cooking, into a visual art.
- Tech itself: Training in tech has had the attitude that tech is at worst neutral, that people will do with tech what they will (absolving tech from any responsibility), that ‘we just create this stuff then people used it or don’t.’ This concept of socially agnostic engineering was already under challenge but computer science departments in particular are slow at letting go. Father John Culkin said, ‘We become what we behold. We shape our tools and then our tools shape us.’ This is often incorrectly attributed to Marshal McLuhan. Techno-social scholars have been on the forefront of this concept, looking closely through qualitative and quantitative means at the tech landscape. This has led to overdue attention to diversity issues within tech and to inquiries into social limits as well as tech limits. I expect these inquiries to become much more important than, say, increasing the number of pixels rendered or megaflops produced. We used to teach people how to use tech, now we teach tech how to use people. Not just in information architecture, but in design, the tech business has learned that the lower the barriers to use, the more people will use a product and use it more often and be more engaged. We will see more engagement from sociology, psychology and other disciplines in what we now know as tech. Information science will be more significant than computer science or a disengaged data science.”
The use of AI to optimize the logistics of resource use could dramatically improve our nutrition, education, health and even our social interactions. The addition of sensor feedback into automation of all types, from traffic handling to regulatory regimes, could greatly improve the functionality of our systems. Jeanne Dietsch, New Hampshire senator and former CEO of MobileRobots Inc.
Jeanne Dietsch, New Hampshire senator and former CEO of MobileRobots Inc., said, “Disruption is always difficult. Until we task AI with the complex logistics needed to optimize the use of resources and the smart automation needed to perform low-skilled jobs, many workers will be overtaxed: teachers, bus drivers, health professionals, mental health professionals, caregivers, administrators, just to name a few. We face a vast amount of work that has been ignored over the past decades full of short-sighted decisions. We have failed to maintain our infrastructure, but more importantly, we have failed to care for the future of the next generation. To turn that work into jobs requires determination and the ability to stand up for our values, stand up against a system that rewards corporations seeking short-term profit over any other goal. Carbon fee and dividend is the first step toward shifting the structure of our economy toward a more egalitarian one, with better values. The use of AI to optimize the logistics of resource use could dramatically improve our nutrition, education, health and even our social interactions. The addition of sensor feedback into automation of all types, from traffic handling to regulatory regimes, could greatly improve the functionality of our systems. What concerns me most is technology’s ability to enable people to magnify ignorance and misinformation.”
Alexa Raad, co-founder and co-host of the TechSequences podcast and former chief operating officer at Farsight Security, commented, “The pandemic has already highlighted and exacerbated the gap between the haves and the have-nots, not only in terms of the cost of lives lost but also in terms of economic disparity. The policies of the current administration have accelerated that divide. … The pandemic also put a spotlight on broken systems and processes such as health care that require a significant effort and will to fix. …
“The pandemic highlighted the importance of internet connectivity. Many companies in the tech and service industries will realize that a work-at-home model is efficient and less costly for some or many of their workforce and that they do not need expensive commercial urban real estate. Therefore, more people will work from home, which affects everything from daily routines to the makeup of services offered to the home. However, this is a luxury for only a set of individuals who can work from home and can afford the set up (high-speed access, required space and internet-enabled equipment) to work from home. This of course sets a new and quite complex normal for managing cybersecurity threats. Large-scale industry events will be less prevalent, as will the frequency of corporate travel. All of these will have rippling affects across multiple industries like airlines, hospitality and event/exhibit management. Overall, there will be less economic security. One of the legacies of the pandemic is the realization that although many conveniences of modern life are predicated on the simple assumption that close proximity of people yields economic and social benefits, in an age of accelerating climate change and multiple pandemics (COVID-19 is likely a precursor of others yet to come) that will no longer hold true. Conveniences such as airplane travel, movies, amphitheater, subways, high-rise apartment units, shopping malls, were based on this assumption and as a result densely packed areas were sustained hotspots of infection. … Technologies to identify and manage the spread of infections will be intrusive in terms of privacy (example – contact-tracing apps) unless very thoughtful governance of data privacy is implemented. …
“The new normal will put a greater strain on our health care system. The pandemic highlighted how unprepared we as a nation are, not only in terms of our acceptance of scientific and evidence-based advice, but also in regard to having the means to efficiently and economically deal with a public health crisis. A beneficial tech-related change will be the delivery of some aspects of health care into the home. For example, people will continue to have online consultations with health professionals instead of an inconvenient in-person visit. This is already happening and will be the new normal.
Internet of Things-based devices will be more plentiful and will serve as a means to monitor everyday health and diagnose and in some cases remotely manage illnesses without the need for intrusive surgery. However, they will also pose a much greater threat in terms of privacy and cybersecurity. More and more private data will be generated, collected and used. Alexa Raad, co-founder and co-host of the TechSequences podcast and former chief operating officer at Farsight Security,
“Internet of Things-based devices will be more plentiful and will serve as a means to monitor everyday health and diagnose and in some cases remotely manage illnesses without the need for intrusive surgery. However, they will also pose a much greater threat in terms of privacy and cybersecurity. More and more private data will be generated, collected and used. Unless there are appropriate safeguards and controls as to how the data is handled, we will see an erosion of our privacy and further loss of control over our choices and decisions as a result. Internet of Things devices have the potential to greatly improve our well-being, and we will see AI-enabled IoT devices which will, for example, monitor our health, provide biological feedback, anticipate and warm of an impending health crisis, etc. But IoT devices increase the attack surface and vectors for bad actors. We will see rise of new cybersecurity threats. Imagine, for example, a nation-state targeting a public figure by hacking into his/her pacemaker. Given where we are now in terms of lacking a basic level of cyber hygiene for these devices, unless we make significant progress we will fall further and further behind the bad actors.
“A few of my concerns:
- The consolidation of services and power into very few largely unregulated companies worries me a great deal. If this trend continues, we will be beholden to very few companies for the many services our lives rely on. These companies will become ‘too big to fail.’ In the financial crisis of 2008, the government bailed out financial institutions who were deemed too big to fail, even though the actions of those same institutions were directly and indirectly responsible for the crisis. Many organizations use Amazon’s AWS cloud services for their web presence and mission-critical applications. Concentrated dependency has never been a harbinger of benefits.
- I also worry about the lack of proper governance for potential threats posed by AI. And by ‘threats’ I mean in regard to security (AI can also be used by our adversaries), economic impact (the loss of blue collar jobs without provisions for retraining or alternative employment will only increase the economic gap) loss of privacy, loss of agency, etc. Although the promise of the best of AI is probably likely to come to fruition beyond 2025, we need to be thinking of proper governance and risk mitigation now, and we are behind.
- I worry about the societal cost of social media. Social media platforms have become the breeding ground for disinformation campaigns, conspiracy theories, extremist groups, online bullying, anti-vaxxers and bots that manipulate opinions and sow division and discord. … When journalism and legitimate news media struggle to compete, we lose one of the fundamental bulwarks of democracy – a free press. And then there is the lack of proper guardrails and defined consequences for social media companies’ use of our personal data (example – Cambridge Analytica). Lastly, social media effects tap into the brain’s reward system and the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine. It is addictive, and its premise is that of addictive entertainment and not critical thinking. When critical thinking is eroded, so is trust in science – and we collectively pay the price.”
Maja Vujovic, a consultant for digital and ICT at Compass Communications, predicted, “If entire sectors – education, tourism and hospitality, food production, entertainment and more – continue to experience the deep freeze caused by COVID-19 through 2020 and beyond, the ‘new normal’ will likely not remain limited to benign disruptions, such as blended learning or continued work from home and the related office space redux. If the pandemic persists for many months or spills over into another year, the recession will go into free fall. Countries with strong social security systems and/or capital will activate a range of protective measures to prevent public disorder. Countries without such a safety net will be forced to choose between solidarity and oppression.
“If the pandemic persists longer than a year, it will affect the world’s economy like a global war; in that case, food rationing and other wartime measures will become inevitable. This will entail identification, allocation, distribution and delivery – all of it enabled by a range of digital tech. Identity control will therefore have to be enforced very strictly, to avoid fraud. Other previously inconceivable disruptions will occur, e.g., primary and secondary education will need to enter into public-private partnerships with commercial providers of automated instruction, learning and testing platforms at scale, able to instruct the majority of students, while teachers from formal schools deal with small numbers of exceptions, such as special-needs students etc.
A ‘marketplace’ will emerge, where students will be able to pick and choose courses from any university, to create unique, personalized schooling ‘menus.’ Maja Vujovic, a consultant for digital and ICT at Compass Communications
“Higher education will become a terrain where a small number of entertainment-savvy lecturers attract huge student audiences via tech-enabled remote learning, while professors unskilled in it become dispensable. A ‘marketplace’ will emerge, where students will be able to pick and choose courses from any university, to create unique, personalized schooling ‘menus.’ This will create a demand for a certification mechanism at a level above individual universities. Distinguished schools with vast traditions will thus have to reconsider and redefine their missions and their very purpose and a number of them may not prove sustainable. Overwhelmed health systems will become the reserve of emergency and infection treatments. Workplaces will become leaner and nimbler. Specialized teams will work on project-based assignments, often without the need for a large enterprise to sustain them. Taxation and labour laws will need to change, to enable individuals to participate in a more secure, more equitable digitally enabled gig economy.”
Jon Lebkowsky, CEO, founder and digital strategist at Polycot Associates, wrote, “My hopes:
- Technical innovations to address and mitigate anthropogenic climate change. Not just clean energies, but also technologies to balance CO2 in the air. Regarding clean energy, innovative battery technologies for energy storage.
- (related) Smarter and lighter transportation technologies, including proliferation of high-speed rail systems and smarter last mile travel, diminishing the number of individual automobiles and the use of fossil fuels.
- Improved space technology and potential colonization of the moon and Mars.
- Innovative methods for managing disease, including ways to combat viruses through genetic modifications and nanotech.
- Development of small, safer nuclear reactors as new sources for energy.
- Ongoing development of new food sources and evolution away from meat consumption as we can derive complete proteins from lab-developed sources.
- And I am most worried about technology-mediated indoctrination through propaganda and ‘managed alternate truths.’ And I am also concerned about the potential for the increasing and evolving use of AI-driven surveillance technologies.”
Mary Chayko, author of “ Superconnected ,” said, “In the absence of a national commitment and strategy to assist marginalized populations in attaining online access, skills and literacy, social inequalities will persist and deepen in the ‘new normal.’ This will exacerbate all current societal problems: racial and gender discrimination, poverty, health crises and complications, educational and work-related inequities, privacy and surveillance. Digital technologies can be employed to help to improve these conditions, but unless their benefits can be realized by all, social justice and equality will remain elusive. Digital technology, and the means to use and understand it, must be considered a primary social good. Technologies that will assist people in living productive, healthy lives – like online learning, working and telemedicine tools – should be freely and widely available, along with necessary and relevant information and support. I am most worried that the scope of tech companies’ impact on our lives will become so deep, sophisticated and far-reaching that we will fail to see and resist it or grow weary of doing so.”
Social media enabled us to connect with people anywhere in glancing ways; video conferencing in many forms – virtual conferences, happy hours and so on – will let us connect in more direct and meaningful ways. Jeff Jarvis, director of the Tow-Knight Center and professor of journalism innovation at City University of New York
Jeff Jarvis, director of the Tow-Knight Center and professor of journalism innovation at City University of New York, commented, “Yes, there may be unintended positive consequences, including greater awareness of racial inequities in society; less travel and thus less environmental damage; greater ability to work at home and remotely and be closer to family. But we cannot gloss over the still-unknown health repercussions that millions of needlessly infected people will have to deal with; the severe economic impact on so many sectors of a service economy permanently affecting the employment of people in lower-paid jobs; the likely permanent economic damage to universities and colleges as institutions; the lost educational time for children during the pandemic; and mental stress on everyone. As much we may now suffer Zoom fatigue, I believe that in the long run, having become accustomed to seeing people in online calls, we will find they provide richer interaction. At work we will still be addicted to having too many damned meetings but if we can waste less time traveling or commuting to them, all the better. Social media enabled us to connect with people anywhere in glancing ways; video conferencing in many forms – virtual conferences, happy hours and so on – will let us connect in more direct and meaningful ways. I would like to think that we would see the value in gathering and sharing health data at a level that would allow us to spot and treat problems early in their spread in the future, but I fear a growing moral panic around data may prevent that.”
Jillian York, director of international freedom of expression for the Electronic Frontier Foundation, wrote, “I expect that, when it comes to technology, our ‘new normal’ will be an even greater dependency on privately owned infrastructure and platforms, making us more beholden to Silicon Valley than before. I worry that the amount of time that we’re now spending at home has led us to this greater reliance on it, and that companies are not adapting along with us. When it comes to platforms, specifically, one of my biggest concerns is the impact they have on our speech and our well-being or dignity. On the one hand, hate speech is rampant and companies are responding piecemeal. On the other hand, at a time when many of us need platforms for our livelihoods, companies are cracking down prudishly on nudity, sexuality and the human body. The impact that this has on sex workers, burlesque performers and others whose work touches on these themes must not be ignored; by banning content around these topics without their consultation, we’ve essentially created an untouchable class of workers.
“I worry about the unaccountability of Silicon Valley and the ways in which corporate policymakers practice ‘both-sidesism’ in order to craft policies that benefit the lowest common denominator without upsetting too many others. I worry about the fact that so many people are willing to hand over the governance of their speech to unaccountable actors. I worry about the potential for technology companies to keep our own history from us – already we’ve seen images from U.S. protests taken down (often for violating rules on ‘graphic violence’ – even when it’s the Feds committing the violence – or in some cases, bans on nudity), echoing what Syrians have been pointing out for years about the erasure of videos, many of which contain documentation of war crimes, emerging from their country. I worry about the continued capture of data for no purpose other than to sell us more stuff we don’t need.”
Morgan G. Ames, associate director of the University of California, Berkeley’s Center for Science, Technology & Society, responded, “While I am heartened by the #BlackLivesMatter protest movement in the United States as well as protest movements in Hong Kong and elsewhere around the world, I look to previous disasters and broader trends as a probable guide to what will be coming. And what I see are too many opportunities for the powerful to retrench and expand their power. Ubiquitous surveillance, increasingly fascist policing tactics, the expansion of hate groups that amplify the worst state ideologies, and the widening chasm between the ultra-rich and everyone else are all global structural trends that will be incredibly difficult, and incredibly disruptive, to reverse. As much as I would like to hold out hope that the disruptions caused by the novel coronavirus can be turned toward social justice, the evidence so far that this is the case is really not good.”
Vint Cerf, Internet Hall of Fame member and vice president at Google, observed, “We may see more flexibility in work-from-home provisions. Travel may be less necessary thanks to video conferencing. I have maintained significant international interactions despite time zone challenges for the past three months. I further expect:
- Cloud computing and cloud commuting!
- We will see an Internet of Medical Things (sensors mostly), as remote doctor house calls escalate. There is an interesting tension involved in digitally linking a lot of one’s online life: calendar, messaging, travel, geo-tracking/location – all this information can be usefully correlated to make life easier but, if exposed, also erodes (destroys?) privacy. The more we rely on online resources, the more tempting it is to interlink information to take automatic and useful actions.
- Reminders and notifications, etc. For example, I am on email a lot of my time, and getting an email saying a FedEx package has arrived is actually very helpful. Of course, if there are too many ‘messaging’ applications all running at once they ‘self-pollute’ as in getting an email because you have a LinkedIn message (Aaaaargh!).
- I am optimistic about the use of information technology to automate chores and to facilitate cooperative work. Shared access to Google Docs has been a remarkably enabling capability – shared spreadsheets for tracking group activity for example. Still, there is the exposure of personal information, lax security leading to serious compromises, poor user attention to security. Reliance on autonomous software leading to unexpected failures and consequences.”
Christina J. Colclough, an expert on the future of work and the politics of technology and ethics in AI, observed, “Unless our governments step into another gear, we will:
- Become super-surveilled at the expense of our fundamental rights and human rights.
- Work will become more and more individualised and precarious as companies first cut costs by making working from home the norm and then by hiring contract workers rather than permanent employees.
- Mental health will suffer as loneliness, financial struggles and competitive forces pressure individuals.
- Innovation will decline as social capital declines due to the above.
- Workers who need to go to work (physically) will be segmented from the ‘others.’ I am tech optimist under the condition that it is regulated and governed.
“I would like the following to be regulated:
- Improved workers’ data rights. These are either weak in current regulation, or nonexistent.
- Collective data rights. All data regulations (bar some discussions currently held within Indian Parliament) are concerned with an individual’s rights. We need to think of communities, of workers, of citizens, of businesses and of the relationship between state, market and civil society and ask: How can we benefit from digital tech so it benefits people and planet?
- We must break up Big Tech. Its power is unfathomable and comes even at the expense of democracy and governments’ scope to regulate.
- Public procurement must include a demand that all data generated and produced is shared between public and private actors.
- We must globally enforce the principle of data minimisation and, preferably, data emphermality.
- We need to talk redistribution again and close tax havens. Probably tax revenue and not profit.
- We need vastly improved rights over data inferences.
“Among my worries are these:
- That we lose the right to be human, in as such that who you are, what you want, your dreams, desires and aspirations become subordinate to algorithms and algorithmically defined choices on your behalf.
- That we are monitored and surveilled at home, in the public space and at work without the means and power to resist.
- That democracy will suffer, as the public sector is fundamentally dependent on data from tech companies and all that that entails of desired versions of ‘reality.’”
The failures of social media and AI are not technology problems. They are problems of human design and execution. Alan D. Mutter, a consultant and former Silicon Valley CEO
Alan D. Mutter, a consultant and former Silicon Valley CEO, wrote, “We are not going to code our way out of the moral and political mess we are in. Technology will help if the right people do the right things. It will do epic damage if they don’t. The social media were hijacked by thugs and trolls to do incalculable damage. Their efforts were at once ignored and abetted by Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg and his ilk to amp up page views to boost ad revenues. Social media had great promise to level the intellectual playing field by giving everyone the power to give or get whatever information they wanted. Instead, the social media have become treacherous cesspools of mis- and mal-information. Artificial intelligence can do wondrous things so long as it is properly trained and deployed. That is its notable fail. For instance, AI often fails to accurately recognize the faces of people of color. When AI is used to recommend sentences for criminals, it tends to discriminate against people of color. The failures of social media and AI are not technology problems. They are problems of human design and execution. Technology is only as good as the people who devise and control it. I am less interested in potential technology advances; I am worried about whether new developments will be wisely and safely deployed.”
Kathleen M. Carley, director of the Center for Computational Analysis of Social and Organizational Systems at Carnegie Mellon University, commented, “More people will be able to work remotely, allowing companies access to greater pools of talent, and a possible leveling of pay across cities. There will be an increased understanding of viruses and how to create vaccines and improved technology to support health care. There will be regulation of and self-imposed constraints on social media platforms.
“There will also be: increased public understanding of the limits of, and problems with, machine learning; police-hiring reform; an international response to disinformation; improved technologies for group meetings online; new agile business models for technologies that mainly employ the web; improved health standards in schools and public places; improved sick leave policies; a decrease in business travel, possibly leading to a better carbon footprint; less middle management. There will be a small increase in automation, but more effort on designing and building even more automation for the home and small businesses that will become more ubiquitous and some type of certification for AI to show that it meets some ethical standards. There will be certification for online tools to show that they meet some privacy standard.
- Expect to see: increased access to the internet; more stores that operate only for pickup and returns; more mail-in voting, and experiments with online voting; increased provision of medical advice and appointments online; increased online services for legal issues.
- There will be: more jobs requiring more computer skills, or skills with online web tools; improved search routines; new parental control panels for online-group-meeting technologies; new toys that support interaction through the internet for very young children and grad school ‘children’; an increase in self-paced online master’s programs for those working remotely.
- There are some things that are likely to reduce the quality of life: a decrease in the variety of items carried by grocery stores and, indeed, all stores; a decrease in gourmet food items, specialty tools, and high-end fashion or a major increase in their cost; favorite restaurants will have closed; food prices will increase.
- There will be an emergence of an overwhelming number of stories, movies, songs dealing with the pandemic.
- In many countries, there will be fewer women in the workforce, and fewer women in schools.
- There will be an initial increase in income disparity, which should eventually be reduced through an increase in service jobs and greater access to the internet.
- Scams, fraud and price gouging will rise due to new internet services, delivery services and online shopping services.
“Other things – it is not clear if they will be good or bad, but are possible:
- There will be a new baby boom entering preschool and kindergarten in 2025.
- Expect to see mandatory health screening in organizations.
- I hope we will increase the national debate and create a shared perception about what level of regulation is acceptable on what type of technology.
- That there will be recognition that disinformation is like pornography and it has to be treated similarly in legal terms. There will be improved transparency through online access, etc., of health processes, legal and government processes and assorted other processes.
- There will be certification programs for privacy-preserving software and for ethical software and there will be international treaties relating to information on social media.
- There will be more funding for research on robotics for home use, and a consequent transition to market, improved technologies for measuring and removing particulates from the air, improvements in our understanding of how viruses and bacteria impact the human body, and so increased speed in generating and testing vaccines. If the cost of computing does not go down, it will slow down the development of the Internet of Things, however, we should expect to see more smart technology in the home and workplace.”
The U.S. court system has been all but shut down during the pandemic. Some jails have released large numbers of lesser offenders to prevent pandemic blooms. This pandemic straw will break the judicial backlog’s back, and a number of new approaches will take root. I predict this will also force legal reforms in how trials are conducted, which may even cause major changes in the legal profession. Sam S. Adams, a 24-year veteran of IBM now working as a senior research scientist in artificial intelligence for RTI International
Sam S. Adams, a 24-year veteran of IBM now working as a senior research scientist in artificial intelligence for RTI International, wrote, “The confluence of the global pandemic and the U.S. presidential election cycle is likely to accelerate a large number of large-scale changes in multiple domains and industries. Given the caveats of no multiple concurrent pandemics and no revolution-scale social unrest, these changes will likely accelerate a number of positive transitions that will improve life in general.
- Telework and resulting de-urbanization: The forced telework situation due to the pandemic has opened many eyes to new possibilities. Living in the city to avoid nasty commutes gives way to moving to the country and buying land vs. a high-priced apartment. If commuting patterns change drastically, then lots of other dominoes fall, including pollution and its impacts.
- Telehealth is here to stay: No way customer management systems will return to requiring in-person visits for practitioners to get paid. This will accelerate other forms of telehealth, expand the physician assistant and nurse practitioner ranks, and allow doctors and specialists to telework as well, resulting [in] more optimal use of medical resources without reducing quality of care. I expect quality of care by 2025 to actually improve because of this transition.
- Tele-justice: The U.S. court system has been all but shut down during the pandemic. Some jails have released large numbers of lesser offenders to prevent pandemic blooms. This pandemic straw will break the judicial backlog’s back, and a number of new approaches will take root. I predict this will also force legal reforms in how trials are conducted, which may even cause major changes in the legal profession.
- Tele-education: Forced virtual schooling (where most parents are also forced into part-time homeschooling as well) forces state public school systems to create virtual curricula, which is then available to non-local, non-physical attending students, including traditional homeschoolers. Competition for quality and the digital nature of the content transforms the education system into a hybrid physical-virtual system, where access and quality of content and instructors is better distributed. The MOOC revolution in college and professional training will accelerate into the primary/secondary grade levels, and commercial education content providers will grow dramatically as parents of even public school children are able to augment their kids’ education with high-quality commercial sources, cafeteria-style at low costs.
- Communication networks: In 2025, 5G deployment is widespread, driven by a national mandate to eliminate internet have-nots. Broadband access becomes a human right-level issue.”
J. Scott Marcus, an economist, political scientist and engineer who works as a telecommunications consultant, predicted, “The impact of the pandemic is large, but the world will eventually recover (assuming that the virus does not mutate to a still-more-dangerous form). This was the case in 1919 and there is no reason to expect anything different here. Changes such as remote work, teleconferencing, telemedicine and remote learning are mostly positive. The changes that have emerged were technically feasible for years but held up by institutional rigidities.
“Things will not go back to where they were – not entirely, anyway. As a whole, I think most people will be worse off, not solely because of the pandemic, but at least as much due to intensifying trade wars, a decline in international cooperation and more. The impact of climate change will still not be catastrophic, but it will continue to grow. I hope for the acceleration of trends toward remote work for jobs in the upper-income quartile or two. The greatly increased use of teleconferencing, with a corresponding decline in travel; tourism will take a long time to return to previous levels, if ever. Increased reliance on telemedicine. A major retooling of the education and training systems was needed anyway, not only to shift to remote learning (which is not simply the same as current practice done from afar), but also to lifelong learning.
“My worries are information bubbles, fake news and their negative impact on traditional (more reliable) news media and public broadcasting. I worry about the growing dominance of a small number of platforms. My worry for AI and big data is challenges with explainability.”
Glenn Edens, professor at Thunderbird School of Global Management, Arizona State University, previously a vice president at PARC, observed, “There is a good chance by 2025 society will have forgotten all about the current crisis. A key question is, how soon do we find a viable vaccine and how long does it take to put that into production, and when does it become part of the annual flu-season vaccine? If for some reason a vaccine and treatment continue to be elusive, then all bets are off for recovery by 2025.
“The economic fallout from the current crisis will likely take a decade to ‘fix’ – we should be prepared for five to seven years of lower growth prospects, higher taxes, continued failures of firms and an uneven recovery. It is reasonable to expect that some industries will find it harder to return to ‘pre-COVID-19’ status quo. Some will not recover – for example, e-commerce, on-demand delivery and working from home are not retreating. Many firms are realizing they don’t need huge commercial real estate or physical infrastructure – I’d predict a significant restructuring of commercial real estate. The displacement of brick-and-mortar retail by e-commerce, which has been steady and slow, has been kicked into high gear – how will the convenience of e-commerce versus the experience of physical retail unfold? My bet is that many brands and chains will not survive and the very nature of a ‘shopping mall’ will have to change dramatically – these facilities will survive, as will site-specific retail experiences. Consumption = convenience, so I’d suggest e-commerce is likely to jump to account for 50% or more of all retail sales and it will continue to grow.
“The conflict of the individual versus the good for the commons has been vividly brought to the forefront, and so far the results are not looking so good for the commons. While working from home (or remotely under different scenarios) is not perfect or anywhere near as good as it could be, it is here to stay. Many firms are discovering it is very cost-effective. The jury is still out on the true impact of productivity gains or losses due to working from home. Many of the firms I’ve talked to are seriously thinking about incorporating working from home as a long-term part of their human resources and commercial real estate strategy. This will continue to provide funding for more innovations in the communications technology sector – we are already seeing improved security and some small advances in user interface and user-experience improvements (we may finally get real spatialized audio).
“There is a dark side of these tools, which is not well understood yet – many managers I’ve spoken to are intrigued with (giddy about?) the increased tools for monitoring employees, their work output, productivity, work styles and intricate details of their behavior – this will be exploited and may lead to unintended consequences. At the same time, it is interesting that the ‘internet’ didn’t collapse – it held up pretty well, and it is pretty clear that investing in high-speed internet access is going to continue to set geographic areas apart economically. We seem to also be getting more serious about security. Longer-term it is clear, of course, that society will continue to increase its dependence on digitally intermediated systems for every facet of life: health care, education, shopping, groceries, entertainment, transportation, work and finance – that trend is unstoppable. At the same time, we are a social species and we crave social interaction – risks will not sway us. :)”
Gregory Shannon, chief scientist at the CERT division of Carnegie Mellon University’s Software Engineering Institute observed, “I see willingness to trust and flexibility in trust as a key element of the ‘new normal.’ Previous trust modes/models/habits/norms will evolve, and those most successful in the new normal will have adapted/optimized their approaches on trust. Those who don’t adapt/evolve their approach to trust will be hampered, inefficient and even isolated in the new normal.
I see willingness to trust and flexibility in trust as a key element of the ‘new normal.’ Previous trust modes/models/habits/norms will evolve, and those most successful in the new normal will have adapted/optimized their approaches on trust. Gregory Shannon, chief scientist at the CERT division of Carnegie Mellon University’s Software Engineering Institute
“The new normal will continue and accelerate the move towards digital spaces, which, without in-person interaction, are abstract and hard for many to grasp. I find it interesting that many modern efficiencies are based on getting many people physically close together. Transportation, sports events, restaurants, education, work teams, hospitals, city parks, gyms, places of worship, Fifth Avenue, etc. Who and where do we each trust to get close to others? Can we get ‘close’ in a meaningful way via technology? It’s not clear to me how.
“Will we see an exodus from cities as density becomes more of a bug than a feature? How will we meet new people? Will it be much more localized, like to our neighborhood? I expect a real increase in social isolation, especially for those older, or less tech savvy, or with few resources to connect virtually. I expect smart virtual avatars/agents will make and manage connections. They can suggest/negotiate introductions to new colleagues with relevant yet diverse perspectives. The agents could also warn/caution when new colleagues seem insincere, untrustworthy or even artificial.
“I expect we’ll see much better virtual collaboration technologies. From wikis and such to continuous virtual conferencing. I worry about the availability of accessible, stable and secure bandwidth. The current ‘best effort’ residential connectivity plans are failing. There are too many dropped calls, glitchy video, audio drops (every other word) and a lack of scalability for group discussions. Privacy is also certainly an issue. If these are not addressed well it will increase social isolation.”
Chris Arkenberg, research manager at Deloitte’s Center for Technology, Media and Telecommunications, predicted, “While a five-year horizon will see some classes of society claiming benefits from the COVID-19 discontinuity such as more remote-working arrangements, fewer commutes, better habits in many high-traffic institutions, etc., many will still be under the economic downturn. Many jobs are simply disappearing under the twin engines of small-business destruction and enterprise-scale automation. More job providers are already seeking the security of automation to hedge against the next crisis. Eventually COVID-19 will also likely accelerate the deconstructing of an aging capitalism that fails to allocate resources to teachers, workers, ‘essential services’ and many other economic sectors that have been undervalued while favoring rent-seekers and financial vaporware that adds no real value to society. This will take 10 years at least.
Eventually COVID-19 will also likely accelerate the deconstructing of an aging capitalism that fails to allocate resources to teachers, workers, ‘essential services’ and many other economic sectors that have been undervalued while favoring rent-seekers and financial vaporware that adds no real value to society. Chris Arkenberg, research manager at Deloitte’s Center for Technology, Media and Telecommunications
“At the same time, global political leaders who recently rode a far-right, nationalistic wave of anti-immigration will see more election cycles by 2025. With such strong economic challenges, it is unclear if nationalism will retain its influence or if there will be a mandate for a more technocratic and educated leadership. One might hope for the latter, given the [Trump] administration’s failure to manage COVID-19. In short, a five-year horizon will likely still feel disrupted and degraded for most, while a 10-year horizon may see some of the sea changes underway that were only amplified by COVID-19 start to yield meaningful results.
“The reality is that global, national and state institutions are being reconceived under the impact of globalization, the internet, global warming and, now, global pandemic. There will be a rocky transition to the next stable state.”
Kenneth Cukier, senior editor at The Economist and co-author of “ Big Data ,” said, “I see this for 2025: Economic crises, less global trade and constant international political conflict. Companies substituting technology (machines and algorithms) for human labor. A rise in populist or ‘infotainment’ governments means serious, long-term problems aren’t addressed by the state, and well-meaning civil institutions can’t have the impact they’d like.
“The educated, wealthy, moderates (aka ‘elites’) retreat even further from mainstream society, believing the situation unfixable and to avoid being a target of attack. Worthy social-justice issues like racism get hijacked by extremists, creating a ‘cultural revolution’ of intolerance that crimps free expression and ideas.
“New technologies will greatly improve the quality of life, such as AI in health care. We will be able to scale up productivity to new heights by applying software and data to all areas of economic activity. Tech will also be on the front lines of responding to climate change. But tech will continue to foment huge problems like misinformation and social platforms that drive people apart. It will create new problems, such as dominating the business landscape by dint of size and scale that offline players can’t compete against. And in tech will be the vital ingredient of a new class of weaponry without safeguards to control it well.”
Stephen Downes, senior research officer for digital technologies with the National Research Council of Canada, commented, “The net result of the pandemic will be an increased recognition of the role of governance and civil society, seen in an increased interest in social and economic support, including, for example, the need for public health care and for income support. It will also be seen in greater social and civic responsibility, including new controls on policing and greater access to services for minorities and underserved populations. And it will be seen in a wider recognition of social responsibility, for example a return to more progressive taxation, especially corporate taxation, as a response to income inequality.
“The most significant change could be summarized with the slogan ‘protocol, not platform,’ as Mike Masnick argued last year . The idea is that instead of depending on a specific social media application to connect with friends and colleagues, people could use the application of their choice and use a common messaging standard. This makes it more difficult for platforms to shape discourse using algorithms and to monetize discourse using tracking and advertising. The current structure of dialogue and media privileges extreme and provocative content, which tends to polarize society and to make it more difficult to come to consensus on social issues. Discourse that is more cooperative and creative enables constructive responses to be adopted society-wide to pressing issues of the day, including but not limited to equity, environment, prejudice and policing. With common communications protocols, solutions to pressing issues will begin to emerge. Common protocols also enable greater security, through such mechanisms of zero-knowledge proofs, for example. This allows better insight into the effectiveness of social programs and enables governments and critics to evaluate innovation on more than merely financial or economic criteria.
“Our experience during the pandemic showed clearly how even modest improvements in interoperable communications can have a significant effect. Before the pandemic, there was no incentive to support widely accessible cross-platform video conferencing. Then we had Zoom, a simple tool everyone could use, and suddenly we could work from home, learn remotely or host conferences online. Having learned how convenient and efficient so many online services have become, we will be much less likely to commute to work, attend residence-based campuses or fly to conferences. This makes the world of work, learning and commerce much more accessible to large populations who previously did not have the resources to participate, and greatly increases our efficiency and productivity.
When technology divides us, it also disempowers us, as everything about us becomes subservient to the conflict. Our agency, our identity, our activities – all these become the means and mechanisms for one faction to fight the other. Stephen Downes, senior research officer for digital technologies with the National Research Council of Canada
“My concern about the near future is that our technology choices will force us into mutually exclusive and competing factions. These factions may be defined politically or may be defined by class or race, by economic status or by power and control. Technological dystopia occurs when one faction uses technology against the other, perhaps by means of surveillance and spying, perhaps by means of manipulation and misinformation or ever by means of hacking and disruption. When technology divides us, it also disempowers us, as everything about us becomes subservient to the conflict. Our agency, our identity, our activities – all these become the means and mechanisms for one faction to fight the other. This is a worry about technological public spaces becoming private spaces: There’s no application we can use or no online space we can go that isn’t owned by some entity and designed to further the objectives of that entity, with the social goods of individual freedom and social cohesion taking a back seat to those objectives. It’s the sort of world where we no longer own things, but can merely lease them, subject to the terms, conditions and digital rights management of the technology company. It’s a world in which there is no space for creativity or free expression outside the constraints of end-user licensing agreements, and no public space for discussion, decision and action where the needs of society can prevail over private and corporate interests. By 2025 we will have a clear idea whether we are slipping into technological dystopia. The more difficult we find it to interact on an equal basis with people from other countries, other cultures, other political beliefs or even other platforms or social networks, the less likely we are to be able to find common solutions to global problems. The more prevalent surveillance and control through technological means becomes, the less likely a less-powerful people can redress the excesses of the more powerful. These, eventually, will manifest in physical symptoms of dystopia: shortages, outages, civil unrest, open conflict.”
A lawyer and former law school dean who specializes in technology issues predicted, “There will be greater awareness of need for broadscale safety nets for employees – workforce employment protections (such as those implemented by EU). There will be greater societal demands for public health and safety protections supported by governments. There will be a widespread demand for more effective leadership of government institutions. Just contrast how the leadership overseeing the COVID pandemic problems in New Zealand, much of Europe, Taiwan and South Korea with the anemic, chaotic leadership in the U.S. People will demand more and better leadership traits in their elected leaders. My hopes are for better social media ‘ethics’ by movements to constrain and reduce hate speech, overt hatred online and manifest dishonesty on social and political issues. A greater societal awareness of need to rely on truth-telling online, especially the major influential sources (Facebook, Twitter, etc.) while recognizing that some things are opinions and should be respected as long as not false, defamatory, hateful, likely to inspire hatred, etc. There will be a movement from the essential lawlessness of the internet to a demand for a more civil and civic discourse approach. I worry over the tech companies’ lack of respect for the importance of civic discourse on their platforms. Much of the social media space is essentially the Wild West: no laws, no rules, hate speech is permitted if it supports advertising revenues, etc. Those companies’ employees are revolting within the context of their employment, and they are demanding that the corporate leadership grow a spine and step up against the voices of discord, hatred, anarchy, etc.”
Amali De Silva-Mitchell, a futurist and consultant participating in multistakeholder internet-governance processes, said, “Technology will ease the work-life balance; increase productivity; help reduce carbon emissions; allow for savings on infrastructure expenditures such as roads, although there should be more spending on internet infrastructure and actions to enable universal access. Life may seem to speed up, and new technologies that were supposed to still be in development for a decade will become available sooner. In-person social life with a human touch will be restricted and perhaps even mistrusted. The packed pub or tea house will only be open to those who can provide proof of vaccination.
“Evidence-based identification to show ‘purity of health’ and even health histories will be required everywhere. Face coverings will be commonplace, and each person may be embedded with an ID chip that can be tracked on the street. Outward appearances may appear to be the same as today, but the underlying monitoring of each person will be much greater. People will trade privacy for a semblance of the old normal. People will become more aware of their actions and feelings and be knowledgeable about repercussions. It is possible that brain waves will be used to monitor the emotional space of the public so as to predict behavior of crowds. We may see new forms of safeguards or barriers in projections via holograms which will also be common at business meetings.
“AI will be everywhere, but there will be issues with the quality. The individual’s self-identity could decline, and the need to conform to a norm increase, as being out of step will create the need to sort out the exceptions. People will become more managed, spontaneous behavior will be discouraged, although creativity at work will be encouraged. Humans will be replaced in many settings by robots, forcing them to compete; economic security may become something of the past unless the state provides universal benefits. People will guard their minds as if they are a gold mine as that will be the ticket to their individual sustainability.
“Medical technologies may assist humans to live a full life, from telemedicine 24/7, to new medications from AI developments, to new monitoring devices and delivery devices, prosthetics, etc. Items such as clothing, footwear, nutrition, household goods, vehicles, etc., could be designed with technology to optimize output as well as service and be produced or delivered at reduced cost. Waste minimization, safekeeping, comfort, specification and adaptation will be key. Minimizing expenditures will be key for the average working person, hence technologies that assist with that goal to produce the product or service at little cost the consumer will do well, hence the trend to AI-driven technologies for production, etc. Wearable technologies will be important, as people keep all their possessions close to them for safekeeping, hence there will be more and more micro products and perhaps the use of holograms to assist with screen display. Voice and sound technology will assist the elderly and disabled in a very beneficial manner, as will text-to-speech and speech-to-text. These applications will be developed further to assist with everyday work productivity. The need to remember things will be something of the past.
“People are giving up a lot of privacy to receive the benefits of technology. Data risk management in an ethical manner is critical. Standards will lag behind new technical developments. The even greater risk will be the lack of transparency around emerging technologies, and thus the lack of feedback from the public to mitigate the risks of these new developments until an event occurs. A few companies will have data concentrated in their hands and any mismanagement, including poor ethical standards, could have serious outcomes.”
Greg Sherwin, vice president for engineering and information technology at Singularity University, responded, “The new normal will include a greater awareness of systemic dependencies and the need for social goods. Linear thinking and highly individualistic, reductionist approaches to society and the planet will shift towards communitarianism. The myth of social atomism is being broken and more will observe the harm of that model on individual belonging and health as well as social and planetary cohesion and survival. That being said, privacy will continue to slide away as a mythical value. Algorithms will continue to rule our lives but will be questioned as to their validity, bias and rules for human appeal. We will also have quickly discovered before 2021 that we over-indexed for how we thought the pandemic would change our view towards health in our surroundings. Instead of the overarching narratives about how offices and architecture will never be the same, we will have found common ground with the human experiences of 1919 – where everyone quickly returned to their normal social habits.”
Mike Godwin, former general counsel for the Wikimedia Foundation, wrote, “The ‘new normal’ has the potential to be more humane for workers in many ways. First, it seems clear that we are learning rapidly the extent to which ‘knowledge workers’ can work effectively from home, provided that they have the right informational infrastructure that supports such remote work. Cutting down on the need to commute, making schedules flexible and increasing the ability for employees to be caregivers and parents while working will be helpful.
“Second, there is a growing consensus that providing income security is the right approach to coping with abrupt economic downturns that can be caused by pandemics, by climate change, and by social unrest associated with both pandemics and unrest – including increased migration, which will be a major disruptor in this century. The greatest single improvement I hope for is increased access to reliable broadband internet for the purposes of remote work, as well as the more efficient coordination of aid and resources in response to weather crises or public-health crises. The digital devices at the endpoints of the broadband infrastructure (personal computers and phones, primarily, but more and more devices with other functions) already will have a great deal of local processing power, but the key point on the critical path will be the prioritization of broadband access that’s inexpensive, robust, capacious and widely available in small towns and rural areas. Enabling competition and appropriate government subsidies and other support will likely play a central role in keeping prices down and keeping capacity rising. I worry that processing power and widespread data sharing will make it increasingly easy for individual privacy to be eroded, not least through technologies like facial recognition but also through traffic analysis and aggregation of individual transactional patterns. The amount of processing power this kind of monitoring and tracking of individuals will require is already here.”
David Krieger, director of the Institute for Communication and Leadership, based in Switzerland, commented, “The growing need for a viable vision of a global future will (hopefully) shift political discourse away from traditional ideologies toward new horizons. Even if the impact of medical science on politics may be short-lived and ambiguous, the impact of digital technologies on society is enormous and will continue. Both in the private and the public sectors, in education, health care, research and other areas, organizations of all kinds have realized that home office, virtual delivery of services and products, virtual collaborative work, new work and decentralization function very well and reduce costs as well as solve pressing environmental problems.
“In the trade-off between liberty and security/health, security seems to have better cards. This becomes even more apparent when we consider that the shift of more governmental and business activities into the cyber realm will bring greater dangers of cyber criminality and cyber warfare, which in turn demand much greater investments in cybersecurity, or indeed, entirely new concepts of security and accompanying social and organizational changes. David Krieger, director of the Institute for Communication and Leadership, based in Switzerland
“Many digital immigrants have been quickly and even forcibly ‘naturalized’ into the digital world, and traditional top-down, command-and-control management has received perhaps a death blow. There is a clear need to reduce bureaucracy and cut red tape, not only in health care but in all areas of society. The virus has disabled not only many people, but also many traditional convictions about social and economic order, about the way things have to be done.
“A further impact of the pandemic will probably lead to increasing demands for transparency and open information. Already many accuse China of dangerous censorship and secrecy with regard to information about the outbreak. Scientists have joined in a worldwide exchange of data and research. Publishers have torn down paywalls. Open access to information of all kinds is considered a priority. Intellectual property claims are becoming suspect. In addition to this, governments are deploying tracking apps, and citizens are accepting more disclosure of so-called ‘personal information.’
“In the trade-off between liberty and security/health, security seems to have better cards. This becomes even more apparent when we consider that the shift of more governmental and business activities into the cyber realm will bring greater dangers of cyber criminality and cyber warfare, which in turn demand much greater investments in cybersecurity, or indeed, entirely new concepts of security and accompanying social and organizational changes. Taken together, it appears that in the wake of the pandemic, we are moving faster towards the data-driven global network society than ever before.
“Some have predicted that the pandemic will end the ‘techlash,’ since what we need to survive is more information and not less about everyone and everything. This information must be analyzed and used as quickly as possible, which spurs on investments in AI and big data analytics. Calls for privacy, for regulation of tech giants and for moratoriums on the deployment of tracking, surveillance and AI are becoming weaker and losing support throughout the world. Perhaps traditional notions of civil liberties need to be revised and updated for a world in which connectivity, flow, transparency and participation are the major values.”
The sections of this report that follow organize hundreds of additional expert quotes under the headings that follow the common themes listed in the tables at the beginning of this report. For more on how this canvassing was conducted, including full question wording, see “ About this canvassing .”
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Emerging Technology
- Future of the Internet (Project)
- Misinformation
Americans in both parties are concerned over the impact of AI on the 2024 presidential campaign
A quarter of u.s. teachers say ai tools do more harm than good in k-12 education, many americans think generative ai programs should credit the sources they rely on, americans’ use of chatgpt is ticking up, but few trust its election information, q&a: how we used large language models to identify guests on popular podcasts, most popular, report materials.
901 E St. NW, Suite 300 Washington, DC 20004 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan, nonadvocacy fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It does not take policy positions. The Center conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, computational social science research and other data-driven research. Pew Research Center is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts , its primary funder.
© 2024 Pew Research Center
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
Better Writing in Scientific Publications Builds Reader Confidence and Understanding
Zoë a doubleday, matthew j dry, carolyn semmler, sean d connell.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Edited by: Pei Sun, Tsinghua University, China
Reviewed by: Ying Wang, Tsinghua University, China; Loene Monique Howes, University of Tasmania, Australia
*Correspondence: Sean D. Connell, [email protected]
This article was submitted to Educational Psychology, a section of the journal Frontiers in Psychology
Received 2021 May 25; Accepted 2021 Jul 22; Collection date 2021.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
Scientific publications are the building blocks of discovery and collaboration, but their impact is limited by the style in which they are traditionally written. Recently, many authors have called for a switch to an engaging, accessible writing style. Here, we experimentally test how readers respond to such a style. We hypothesized that scientific abstracts written in a more accessible style would improve readers’ reported readability and confidence as well as their understanding, assessed using multiple-choice questions on the content. We created a series of scientific abstracts, corresponding to real publications on three scientific topics at four levels of difficulty—varying from the difficult, traditional style to an engaging, accessible style. We gave these abstracts to a team of readers consisting of 170 third-year undergraduate students. Then, we posed questions to measure the readers’ readability, confidence, and understanding with the content. The scientific abstracts written in a more accessible style resulted in higher readability, understanding, and confidence. These findings demonstrate that rethinking the way we communicate our science may empower a more collaborative and diverse industry.
Keywords: accessibility, confidence, interdisciplinarity, readability, scientific writing, traditional style, understanding
Introduction
Scientists belong to a global culture, and we are transforming our sector into one that is diverse, inclusive and equitable. We are moving beyond narrow fields and collaborating across disciplines to address the world’s biggest problems. And we are making science relevant and useful to medical practitioners, policy makers, and innovators to name just a few. Unfortunately, however, stubborn gaps persist in this age of diversity. Women and non-binary and transgender people remain underrepresented in science and senior positions ( Beemyn, 2015 ; Leslie et al., 2015 ), scientists still have trouble communicating across disciplines ( Winowiecki et al., 2011 ), and the uptake of science by the general public remains limited and skewed ( Suleski and Ibaraki, 2010 ; Herrando-Perez et al., 2019 ).
Scientific publications are the building blocks of knowledge and collaboration. Understanding them builds a reader’s confidence—both within a scientific discipline, and in their own ability to explore new frontiers across disciplines. Building confidence could also help reduce persistent gender gaps in science ( Leslie et al., 2015 ), reduce language barriers to people speaking English as a second language ( Hanauer and Englander, 2011 ), and assist people with learning disabilities like dyslexia, who also need the energy and determination that comes from the confidence of understanding ( Vellutino et al., 2004 ).
More accessible writing can help. Science has the opportunity to move beyond the traditional scientific writing style ( Pinker, 2015 ; Doubleday and Connell, 2017 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ). The traditional writing style strives for objectivity and distance from the subject, but also remains dense, formulaic and difficult to read. Similar to a pay-wall, it acts as a linguistic-wall. In a time of intense policy debate over open access publishing ( Tofield, 2019 ), we should also consider policies that build reader confidence and linguistic access to science ( Jeschke et al., 2019 ).
Scientific writing is explored in countless guides and manuals (e.g., Montgomery, 2003 ; Sword, 2012 ; Pinker, 2015 ). These books differ on many points, but they all agree that the essential characteristic of scientific writing is clarity ( Heard, 2014 ). However, clear scientific papers are rare. One study on over 7,00,000 scientific papers published in life, medical, social, and multidisciplinary sciences between 1881 and 2015 documented a rise in technical jargon; in fact, over one fifth of scientific abstracts were written at a level that even a college graduate would struggle to comprehend ( Plavén-Sigray et al., 2017 ). This study was successfully replicated using data on around 28,000 abstracts published in management research between 1991 and 2019 ( Graf-Vlachy, 2021 ). A similar study, which assessed around 12 million scientific abstracts from a multidisciplinary collection of publications from 1900 to 2018, also found that papers are becoming more difficult to read ( Vergoulis et al., 2019 ). Also, an analysis of 24 million article titles and 18 million abstracts published in health and medicine between 1950 and 2019 found an increasing use of obscure acronyms ( Barnett and Doubleday, 2020 ). The rise in jargon and reading difficulty may reflect the trend toward writing styles that are specific to, and isolated within, single disciplines ( Ngai et al., 2018 ).
This increasing impenetrability of science presents a paradox: peer-reviewed publications are the universal currency for creating and communicating scientific knowledge, but the language is increasingly ill-suited to this purpose ( Doubleday and Connell, 2017 ). Some solutions have been offered, such as lay-reader summaries for clinical findings in medical journals ( Kuehne and Olden, 2015 ). However, inaccessible language threatens the accessibility and reproducibility of new scientific findings ( Plavén-Sigray et al., 2017 ). Difficult-to-read papers can compromise readers’ ability to understand information and can threaten their support for new ideas ( Bullock et al., 2019 ). Furthermore, accessible information is critical for making decisions that depend on coordinating knowledge from multiple fields ( Millgram, 2015 ).
To address this problem, many scientists now advocate for an alternative: a scientific writing style that is clear and accessible. Doubleday and Connell (2017) promote scientific language that is clear, accessible, and even inspiring, while maintaining the objectivity critical to science. Sand Jensen (2007) argues that accessible language can attract scientists, unify our understanding, and promote timely debate and discussion. Hartley et al. (2002) write that clear scientific writing can encourage exchanges between researchers, practitioners, and the general public, and that making science accessible is actually the duty of taxpayer-supported scientists. Empirical studies also provide support for accessible scientific writing, with several studies finding correlations between writing style and impact ( Weinberger et al., 2015 ; Hillier et al., 2016 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ).
Is this boost in influence a result of how readers respond to more accessible writing? Indeed, in educational research it has long been established that more readable writing is more easily understood ( Dale and Chall, 1949 ), which, in turn, boosts a reader’s confidence in the message ( Galbraith and Alexander, 2005 ).
So, this study aimed to measure how more accessible scientific publications stimulate reader understanding and confidence. Specifically, we tested the hypotheses that better writing in scientific publications can enhance readability, reader confidence, and reader understanding.
Materials and Methods
Experimental manipulation.
To test the effect of reading style on readability, confidence, and understanding, we performed an experimental manipulation with randomized participants. We created a series of scientific abstracts corresponding to real, recent, peer-reviewed publications in three research topics: social anxiety (health sciences), solar cells (physics), and populist politics (social sciences). We used abstracts as a proxy for full articles, as abstracts follow a relatively consistent structure and reflect the content and writing style of the full publications ( Plavén-Sigray et al., 2017 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ).
Each abstract was manipulated to create four variants, ranging in readability from very difficult to very easy. We achieved this variation in difficulty by including different systematic combinations of nine measurable components known to affect writing style ( Table 1 ). We selected these components as a measure of clear, creative writing style following a recent observational study, which derived them from findings in psychology, English, and science communication literature ( Ryba et al., 2019 ). That study used a set of 11 measurable components, and here we adopted the nine that can be objectively manipulated when constructing new versions of the same abstract. Table 1 contains definitions for each component, and further details and references are provided in that study ( Ryba et al., 2019 ). The nine components signal either clear and inspiring writing, as with signposting and setting, or awkward and obscure prose that worsens the cognitive load on the reader, as with acronyms or extra words that dilute the central message ( Pinker, 2015 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ). (We excluded “consistent language” and “parallel phrasing” from Ryba et al. (2019) , as those two components cannot be readily added to abstracts without altering the flow of content and logic).
The combination of writing components that we used to generate new abstracts of a range of qualities (see Ryba et al., 2019 for further details on each writing component).
| ) at the start of a sentence or idea | ) | ||||||||
| Easiest | Yes | Yes | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 110 |
| Easy | Yes | No | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 160 |
| Hard | No | No | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 6 | 4 | 160 |
| Hardest | No | No | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 15 | 4 | 230 |
The first five components make for clear, engaging writing, while the latter four are typical of the traditional style and make for a dull, confusing read ( Ryba et al., 2019 ).
We took care to keep the range of writing components within the range that we have recorded from real-world publications. We also retained all content and logical flow across the different writing styles, meaning that the level of detail is the same across all styles for a given topic. This way, we generated writing styles that ranged from the traditional to the accessible, with two intermediate styles, while crossing each of the four styles orthogonally across the three topics. An example of the writing styles is given in Supplementary Table 1 .
Participants
We then asked teams of volunteer readers to read the abstracts. To obtain readers who were consistent in scientific background and age group, we approached four classes of third-year undergraduate science students (173 students in total). We offered all participants the opportunity to participate, and participants were permitted to opt out either verbally or by selecting the appropriate option on the consent form.
Each participant completed up to three readings. For a given participant, the topics and difficulty levels were randomly assigned using a random number generator, with the condition that the readings be of different topics ensuring that students could not learn any abstract content between readings. Participants were not made aware that there were multiple levels of difficulty.
We approached 173 individuals for participation in the full experiment, 170 of whom began the experiment. Thus, the data analysis included responses from 170 participants, meaning that we analyzed 347 responses for each of readability and confidence and 628 responses for understanding. We excluded the models from any observation with incomplete data for each model variable. The detailed participant flow is charted in Figure 1 . 87.1% of participants were native English speakers.
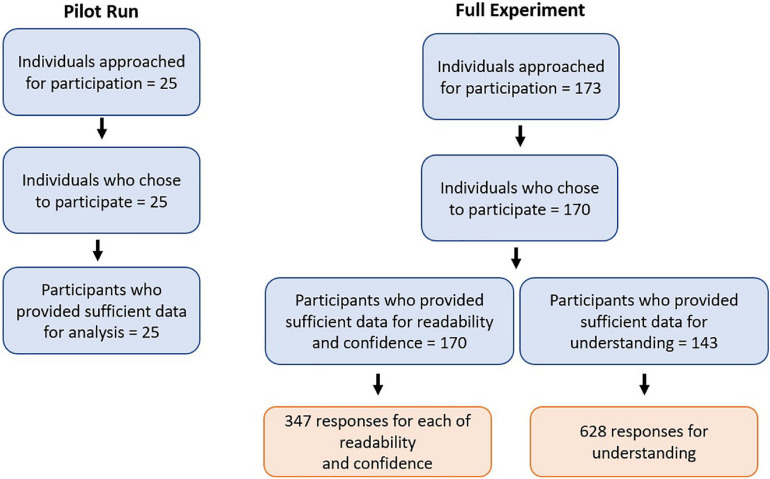
Flow of participants through the pilot run and the full experiment.
We asked our readers to read each abstract. Readers then answered two questions on a scale from one to five: “how easy was this abstract to read?” (readability) and “how confident are you that you understood the information present in the abstract?” (confidence). Each reader was then independently tested with two multiple-choice questions about the content of the abstract (understanding). Those multiple-choice questions were “Why was this research conducted?” and “What is the take-home message of this research?”; the multiple-choice answers differed depending on the topic (example in Supplementary Table 1 ). We acknowledge that the use of 1–2 questions for each variable is a limitation; we chose to ask fewer questions to allow us to obtain multiple readings from each participant, as the statistical power of the study was a priority. Using this approach, we could determine how writing style affected readability, confidence, and understanding, while also accounting for topic.
Ethics approval was obtained from the School of Psychology Human Research Ethics Committee at the University of Adelaide (approval number H-2019/18).
Each reader was given 5 min to read the abstract and answer the questions, although no reader used the entire duration. In total, we received 347 valid responses for each of readability and confidence, and 628 valid responses for understanding.
The experiment was performed during normal teaching hours in March 2019 and in March 2021. The experimental procedure differed between the 2 years only in that participants completed up to two readings each in 2019, and up to three in 2021. Prior to the experiment, we conducted a pilot run, used to estimate the effect size and calculate an appropriate sample size for the full study. We chose our sample size as 300 observations for each of reading and confidence and 600 for understanding, given the effect sizes for each response variable observed in our pilot study, yields a power above 0.99 at the significance level of 0.05. This calculation was performed using the R package simr ( Green and MacLeod, 2016 ), which uses Monte Carlo simulations to perform power analysis for generalized linear mixed models. Each session lasted approximately 30 min.
Data Analysis
We expressed each of the four levels of reading difficulty as a continuous variable. This continuous variable was calculated using a method from previous research on readability ( Hillier et al., 2016 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ). Firstly, we performed principal component analysis to reduce the nine writing components in each level of difficulty to a series of uncorrelated axes. Then, we identified which of these axes correlated positively with the “good” writing components and negatively with the “bad” components. This axis (the first—which also explained most of the variation in the writing components) was used as a continuous variable representing reading difficulty.
Mean confidence, readability, and understanding for each level of difficulty, averaged across all topics, is provided in Table 2 . For readability and confidence, we rescaled the predicted values to percentages (1.0 = 0; 5.0 = 100%). For understanding, we converted each multiple-choice question to a binary response (0 = incorrect; 1 = correct). We then rescaled the probabilities of obtaining a correct response to percentages.
The mean readability, reader confidence, and reader understanding observed in the experiment at each level of difficulty as generated from the responses of participants.
| Easiest | 66.29 (29.94) | 62.36 (29.71) | 57.87 (49.52) |
| Easy | 58.51 (28.53) | 57.98 (29.38) | 39.47 (49.04) |
| Hard | 52.31 (26.27) | 55.03 (26.01) | 40.79 (49.31) |
| Hardest | 44.44 (29.44) | 48.78 (30.56) | 47.95 (50.13) |
Standard deviations are given in brackets.
To estimate the effect of reading difficulty on confidence and readability, we generated linear mixed models. We used linear mixed models to account for the correlation that arises from taking multiple measurements from each participant ( Jostins et al., 2012 ). We included terms for fixed effects of reading difficulty and topic, and for random effects of participant. This random effect captures the effect of specific participants, which might include characteristics such as reading strength and familiarity with the topic, on the response variables. We allowed for random effects in the intercept, but not the slope, as there were only a few measurements from each participant. For the effect of reading difficulty on understanding, the response was binary. So, we generated a generalized linear mixed model using the binomial family with a logit link function. All data analysis was performed in R ( R Core Team, 2020 ). Models were generated using the R package lme4 ( Bates et al., 2015 ) and tabulated using the package sjPlot ( Lüdecke, 2020 ). We performed significance tests on the coefficients using the package lmerTest , which uses Satterthwaite’s degrees of freedom method ( Kuznetsova et al., 2017 ).
So, what does better writing mean for the reader? When we presented readers with abstracts written in the most traditional scientific writing style, mean readability was 44.4% (SD: 29.4%). In contrast, when we presented readers with abstracts written in an accessible, engaging style, mean readability was 66.3% (SD: 29.9%) ( Figure 2 ). A similar effect was found for understanding, which resulted in a mean of 47.9% (SD: 50.1%) for the traditional style and 57.9% (SD: 49.5%) for the accessible style. Likewise, confidence ratings were 44.1% (SD: 23.7%) and 58.3% (SD: 32.3%), respectively, for the traditional and accessible styles, respectively. The mean scores of readability and confidence increased consistently from the most difficult to the easiest writing styles.
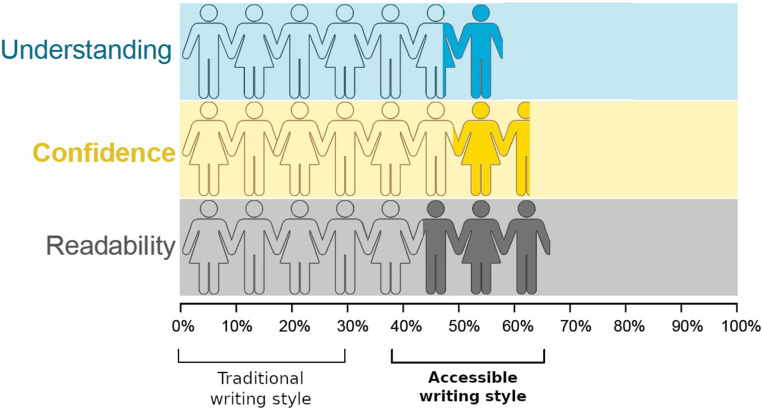
Accessible writing boosts readability ( p < 0.001), reader understanding ( p = 0.027), and reader confidence ( p = 0.001). The stick figures represent the proportional gain in readability, confidence and understanding by writing in the most accessible style (filled figures), compared to the most traditional style of writing (hollow figures). Each stick figure represents 5%.
The models ( Table 3 ) revealed statistically significant effects of writing style on readability, understanding, and confidence. The differences between each level of writing style, after accounting for the effects of topic and reader, are revealed by the effect sizes. For readability, the slope was 2.91 (confidence interval: 1.79–4.03), indicating that a one-unit increase in writing style was associated with a 2.91% increase in readability. For understanding, the odds ratio was 1.08 (1.01–1.15), indicating that a one-unit increase in writing style was associated with a 1.08-fold increase in odds of successful understanding. For confidence, the slope was 1.87 (0.75–2.99), indicating that a one-unit increase was associated with a 1.87% increase in confidence. As a continuous variable, writing style spanned approximately 5 units; as such, one can readily see how moving from the most difficult style to the most accessible style can boost readability, understanding, and confidence quite substantially. Likewise, the effect of topic was statistically significant on readability, understanding, and confidence. Alternative models found no evidence of an interaction between topic and difficulty, and no evidence of an effect of English as a second language ( Supplementary Table 2 ).
Model outputs for the effect of reading difficulty on readability, reader confidence, and reader understanding.
| (Intercept) | 71.87 | 67.39–76.35 | <0.001 | 341.00 | 0.89 | 66.30–75.47 | <0.001 | 341.00 | 0.85 | 0.65–1.11 | 0.234 | 623.00 |
| Difficulty | 2.91 | 1.79–4.03 | <0.001 | 341.00 | 1.87 | 0.75–2.99 | 0.001 | 341.00 | 1.08 | 1.01–1.15 | 623.00 | |
| Topic—populism | −14.24 | −20.23 to −8.25 | <0.001 | 341.00 | −15.19 | −21.05 to −9.33 | <0.001 | 341.00 | 1.81 | 1.24–2.64 | 0.002 | 623.00 |
| Topic—solar cells | −32.12 | −38.92 to −25.32 | 341.00 | −29.69 | −36.29 to −23.10 | 341.00 | 0.70 | 0.46–1.05 | 0.087 | 623.00 | ||
| σ | 593.71 | 544.76 | 3.29 | |||||||||
| τ | 73.97 | 160.45 | 0.05 | |||||||||
| ICC | 0.11 | 0.23 | 0.02 | |||||||||
| N | 170 | 170 | 143 | |||||||||
| Observations | 347 | 347 | 628 | |||||||||
| Marginal R /Conditional R | 0.244/0.327 | 0.186/0.372 | 0.053/0.068 | |||||||||
CI, confidence interval; df, degrees of freedom.
In this study, we sought to measure how accessible scientific writing can stimulate reader understanding and confidence. The findings reveal that writing in a more accessible style can enhance readability of and confidence with scientific publications, as well as understanding of the content. This study extends previous research on readability and confidence (e.g., Galbraith and Alexander, 2005 ) to the context of scientific publications. Furthermore, this study provides evidence that more readable writing is more easily understood ( Dale and Chall, 1949 ). So, the evidence supports the hypotheses that better writing in scientific publications can enhance readability, reader understanding, and reader confidence.
The magnitude of the effect is quite striking. The finding that mean reader confidence, for example, was 62% for the accessible style (compared to 49% for the traditional style) illustrates that the way publications are written can cause readers to be far more confident when digesting scientific advances. Indeed, the research described in the abstracts was complex, as scientific advances tend to be. With that in mind, it is easy to recognize the valuable opportunity before us.
Just as we aim to hone our science, we can also further that goal by honing our writing—in essence, writing with the comprehension of the reader in mind ( Doubleday et al., 2017 ). These findings indicate that we all have a concrete opportunity to boost the confidence of our readers and promote access to science through simple stylistic choices. Specifically, a setting can help ground the research in time and space; first-person narration can enhance clarity; punctuation marks can help guide the reader’s attention; conjunctions can help to link complex ideas; and the judicious use of signposts can help order and structure a piece of writing. Likewise, avoiding acronyms can ease the reader’s mental load; breaking up noun chunks can help the reader digest ideas; and hedging only where necessary can help emphasize the message ( Montgomery, 2003 ; Sand Jensen, 2007 ; Sword, 2012 ; Lindsay, 2013 ; Pinker, 2015 ; Weinberger et al., 2015 ; Hillier et al., 2016 ; Ryba et al., 2019 ; Barnett and Doubleday, 2020 ).
Future research can complement the subjective measures we report here by collecting further measures. In particular, since readability, confidence and understanding were collected from self-reported questions, objective measures could shine further light on how readers respond to different abstracts. For example, objective measures could be calculated from the time that readers take to read texts ( Maksymski et al., 2015 ); from existing metrics of writing style such as the Flesch Reading Ease ( Flesch, 1948 ) or the Dale–Chall Readability Formula ( Chall and Dale, 1995 ); and from more detailed tests on abstract content. Also, subjective measures could enable participants to report their attitudes and feelings toward the content ( Olney et al., 1991 ). These measures can enable future researchers to delve deeper into how readers respond to better scientific writing. Furthermore, this study detected no difference of lower readability, understanding or confidence for participants for whom English as a second language. These readers likely experience a greater burden in reading and writing research articles ( Hanauer and Englander, 2011 ), although this study and sample was not designed to test that question. A future study could replicate our analysis using a larger sample of readers for whom English is a second language; this would reveal how the findings here could reduce the burden on those readers.
Evidence can be a powerful motivator for the scientific community to revise the way they communicate science. This study signals two compelling avenues for research inquiry. First, it would be progressive to recognize the relative extent to which different disciplines benefit from writing in a more accessible style. Where readability is improved, to what extent does greater reader confidence and understanding also improve a scientist’s willingness to make connections between concepts, methods and interpretations? It is likely that progress, particularly in interdisciplinary research, will be more rapid where those searching for solutions have the confidence to engage with alternate approaches (e.g., disciplines) ( Brandt et al., 2013 ).
Second, we may benefit from recognizing how more accessible writing benefits the spectrum of expertise among science readers. Our study involved a sample of one particular audience of scientific publications—specifically, third-year undergraduate students. Students represent one group of readers of scientific papers, and so replicating the study with samples from different audiences (e.g., post-doctorate researchers, senior scientists, policymakers) would enable us to see whether the findings are generalizable to all readers ( Zahedi et al., 2014 ; Mohammadi et al., 2015 ). If society is to perceive science as relevant to their well-being, then scientific uptake not only relies on science literacy ( Ryder, 2001 ), but also the readability of science. Whilst there is a variety of science forums, namely those for members of the public and other non-expert groups, it would be insightful to research whether greater readability results in greater inclusion of readers from diverse groups.
Securing the boost in readability and confidence would mean updating the practice and teaching of scientific writing. Journal policies and university courses have, traditionally, promoted a writing style that is distant and formulaic ( Doubleday and Connell, 2017 ). But there is a wiser way. As we have found here, a boost in confidence can be made through better writing. Journal editors and teaching staff who encourage readable, accessible writing may help the new generation of scientists explore new topics and collaborate more easily across disciplines. Indeed, recent advances in this area have stimulated discussion on writing policy in scientific journals (e.g., Allen, 2019 ; Chaffey, 2019 ; Sayer, 2019 ). And there are published style guides that give instruction on writing scientific publications in an inspired way (e.g., Montgomery, 2003 ; Sword, 2012 ; Pinker, 2015 ). Our evidence suggests that the widespread adoption of these style guides could boost the confidence of people who read scientific publications.
By cultivating reader confidence in understanding, we could empower a more diverse readership, making science both more inclusive and connected. Developing our writing style to one that is more accessible and inclusive requires a bold and proactive approach. We are trying to open up access from behind the pay-wall through bold initiatives, such as Plan S which aims to ensure that publicly funded research is published in publicly accessible journals ( Tofield, 2019 ); likewise, we also need to open up access from behind the linguistic-wall ( Doubleday and Connell, 2017 ). We believe that scientists who write with the reader in mind will empower their readers to build confidence and challenge new boundaries. With a growing diversity of bright minds in research, we will be in the best position to develop major advances in the twenty-first century.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics Statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by H-2019/18. The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author Contributions
RR and SC performed investigation. RR performed data curation and formal analysis and wrote original draft. All authors contributed to review, editing, conceptualization, and methodology.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the experimental participants for contributing their time and effort, as well as the facilitators for contributing to the smoothly run experimental sessions.
Funding. RR was supported by an Australian Government Research Training Program Scholarship. SC was supported by an ARC grant (LP20020100).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.714321/full#supplementary-material
- Allen D. (2019). Encouraging citation through clear writing and april joe highlights. J. Extn. 57:2ed1. [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnett A., Doubleday Z. (2020). The growth of acronyms in the scientific literature. ELife 9:e60080. 10.7554/eLife.60080 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bates D., Machler M., Bolker B., Walker S. (2015). Fitting linear mixed-effects models using lme4. J. Stat. Softw. 67 1–48. 10.18637/jss.v067.i01 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beemyn G. (2015). Coloring outside the lines of gender and sexuality: the struggle of nonbinary students to be recognized. Educ. Forum 79 359–361. 10.1080/00131725.2015.1069518 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brandt P., Ernst A., Gralla F., Luederitz C., Lang D. J., Newig J., et al. (2013). A review of transdisciplinary research in sustainability science. Ecol. Econ. 92 1–15. 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2013.04.008 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bullock O. M., Colon Amill D., Shulman H. C., Dixon G. N. (2019). Jargon as a barrier to effective science communication: evidence from metacognition. Public Underst. Sci. 28 845–853. 10.1177/0963662519865687 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chaffey N. (2019). Science communication: getting it right botany one. Available online at: https://www.botany.one/2019/04/science-communication-getting-it-right/ [Accessed September 19, 2019]. [ Google Scholar ]
- Chall J. S., Dale E. (1995). Readability revisited: the New Dale-Chall readability formula. Cambridge: Brookline Books. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dale E., Chall J. S. (1949). The concept of readability. Element. Eng. 26 19–26. [ Google Scholar ]
- Doubleday Z. A., Connell S. D. (2017). Publishing with objective charisma: breaking science’s paradox. Trends Ecol. Evol. 32 803–805. 10.1016/j.tree.2017.06.011 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Doubleday Z. A., Connell S. D., Montgomery S. L. (2017). Creativity: the stronger. blacker sheep behind great papers . Trends Ecol. Evol. 32 895–896. 10.1016/j.tree.2017.09.008 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Flesch R. (1948). A new readability yardstick. J. Appl. Psychol. 32 221–233. 10.1037/h0057532 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galbraith A., Alexander J. (2005). Literacy, self-esteem and locus of control. Support. Learn. 20 28–34. 10.1111/j.0268-2141.2005.00357.x [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Graf-Vlachy L. (2021). Is the readability of abstracts decreasing in management research. Rev. Manag. Sci. 10.1007/s11846-021-00468-7 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Green P., MacLeod C. J. (2016). simr: an R package for power analysis of generalised linear mixed models by simulation. Methods Ecol. Evol. 7 493–498. 10.1111/2041-210X.12504 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanauer D. I., Englander K. (2011). Quantifying the burden of writing research articles in a second language: data from mexican scientists. Writ. Commun. 28 403–416. 10.1177/0741088311420056 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hartley J., Sotto E., Pennebaker J. (2002). Style and substance in psychology: are influential articles more readable than less influential ones? Soc. Stud. Sci. 32 321–334. 10.1177/0306312702032002005 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Heard S. (2014). On whimsy, jokes, and beauty: can scientific writing be enjoyed? Ideas Ecol. Evol. 7 64–72. 10.4033/iee.2014.7.14.f [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Herrando-Perez S., Bradshaw C. J. A., Lewandowsky S., Vieites D. R. (2019). Statistical language backs conservatism in climate-change assessments. Bioscience 69 209–219. 10.1093/biosci/biz004 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hillier A., Kelly R. P., Klinger T. (2016). Narrative style influences citation frequency in climate change science. PLoS One 11:e0167983. 10.1371/journal.pone.0167983 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jeschke J. M., Lokatis S., Bartram I., Tockner K. (2019). Knowledge in the dark: scientific challenges and ways forward. FACETS 4 423–441. 10.1139/facets-2019-0007 33356898 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Jostins L., Pickrell J. K., MacArthur D. G., Barrett J. C. (2012). Misuse of hierarchical linear models overstates the significance of a reported association between OXTR and prosociality. PNAS 109 E1048–E1048. 10.1073/pnas.1202539109 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuehne L. M., Olden J. D. (2015). Lay summaries needed to enhance science communication. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 112 3585–3586. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuznetsova A., Brockhoff P. B., Christensen R. H. B. (2017). lmerTest package: tests in linear mixed effects models. J. Stat. Softw. 82 1–26. 10.18637/jss.v082.i13 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leslie S.-J., Cimpian A., Meyer M., Freeland E. (2015). Expectations of brilliance underlie gender distributions across academic disciplines. Science 347 262–265. 10.1126/science.1261375 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Lindsay D. R. (2013). Scientific Writing = Thinking in Words. Collingwood: CSIRO Publishing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lüdecke D. (2020). sjPlot: Data Visualization for Statistics in Social Science . R package version 2.8.3 10.5281/zenodo.1308157 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Maksymski K., Gutermuth S., Hansen-Schirra S. (2015). Translation and Comprehensibility. Berlin: Frank & Timme GmbH. [ Google Scholar ]
- Millgram (2015). The Great Endarkenment: Philosophy for an Age of Hyperspecialization. New York.NY: Oxford University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mohammadi E., Thelwall M., Haustein S., Larivière V. (2015). Who reads research articles? An altmetrics analysis of Mendeley user categories. J. Assoc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 66 1832–1846. 10.1002/asi.23286 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Montgomery S. L. (2003). The Chicago Guide to Communicating Science. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ngai S. B. C., Singh R. G., Koon A. C. (2018). A discourse analysis of the macro-structure, metadiscoursal and microdiscoursal features in the abstracts of research articles across multiple science disciplines. PLoS One 13:0205417. 10.1371/journal.pone.0205417 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Olney T. K., Holbrook M. B., Batra R. (1991). Consumer responses to advertising: The effects of ad content, emotions, and attitude toward the ad on viewing time. J. Consum. Res. 17 440–453. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pinker S. (2015). The Sense of Style: The Thinking Person’s Guide to Writing in the 21st Century. New York: Penguin Books. [ Google Scholar ]
- Plavén-Sigray P., Matheson G. J., Schiffler B. C., Thompson W. H. (2017). The readability of scientific texts is decreasing over time. Elife 6:e27725. 10.7554/eLife.27725 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- R Core Team. (2020). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryba R., Doubleday Z. A., Connell S. D. (2019). How can we boost the impact of publications? try better writing . PNAS 116 341–343. 10.1073/pnas.1819937116 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ryder J. (2001). Identifying science understanding for functional scientific literacy. Stud. Sci. Educ. 36 1–44. 10.1080/03057260108560166 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sand Jensen K. (2007). How to write consistently boring scientific literature. Oikos 116 723–727. 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2007.15674.x [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sayer E. J. (2019). The essentials of effective scientific writing – A revised alternative guide for authors. Funct. Ecol. 33 1576–1579. 10.1111/1365-2435.13391 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suleski J., Ibaraki M. (2010). Scientists are talking, but mostly to each other: a quantitative analysis of research represented in mass media. Public Underst. Sci. 19 115–125. 10.1177/0963662508096776 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sword H. (2012). Stylish Academic Writing. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tofield A. (2019). The cOALition S and Plan S: explained. Eur. Heart J. 40 952–953. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz105 [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vellutino F. R., Fletcher J. M., Snowling M. J., Scanlon D. M. (2004). Specific reading disability (dyslexia): what have we learned in the past four decades? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 45 2–40. 10.1046/j.0021-9630.2003.00305.x [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vergoulis T., Kanellos I., Tzerefos A., Chatzopoulos S., Dalamagas T., Skiadopoulos S. (2019). “A Study on the Readability of Scientific Publications,” in Digital Libraries for Open Knowledge Lecture Notes in Computer Science, eds Doucet A., Isaac A., Golub K., Aalberg T., Jatowt A. (Springer: International Publishing; ), 136–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- Weinberger C. J., Evans J. A., Allesina S. (2015). Ten simple (empirical) rules for writing science. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11:e1004205. 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004205 [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Winowiecki L., Smukler S., Shirley K., Remans R., Peltier G., Lothes E., et al. (2011). Tools for enhancing interdisciplinary communication. Sustainability: Sci. Practice Policy 7 74–80. 10.1080/15487733.2011.11908067 [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zahedi Z., Costas R., Wouters P. (2014). Broad altmetric analysis of Mendeley readerships through the ‘academic status’ of the readers of scientific publications. in Proceedings of the science and technology Indicators Conference 2014 Leiden. Leiden: Universiteit Leiden. [ Google Scholar ]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
- View on publisher site
- PDF (836.4 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.

What is research writing?
The prominent socio-linguist and educator, Ken Hyland (as cited in Epting, 2018) stated that in academia, “we are what we write” (p. 561) . As new researchers preparing to join the research community we learn that writing both communicates particular content and embodies the “routines of [our] social communities” (Hyland as cited in Epting, 2018, p. 561). This means that writing for research is an act of ‘becoming’ a researcher and a crucial step in take an esteemed place in a research community.

It is important that as a n aspiring research writer , you too engage in the norms and conventions that define research in your field . Th is includes but is not limited to writing and publishing and involves any other form of communicating and disseminating your work.
As Kamler & Thomson (2006) state in a well-known book titled, Helping Doctorial Students Write: Pedagogies for Supervision:
“We see research writing as an institutionally-constrained social practice. It is about meaning making and learning to produce knowledge in particular disciplines and discourse communities” (p. 5) .
In joining your own research community and establishing yourself as a researcher within that field, you too will be following the cultural norms and behaviours that are well-established in that field.
Research and Writing Skills for Academic and Graduate Researchers Copyright © 2022 by RMIT University is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Teaching and Learning in the New Normal: Responding to Students’ and Academics’ Multifaceted Needs
- Conference paper
- First Online: 09 July 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Andriani Piki ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0376-1713 9 &
- Magdalena Brzezinska ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4213-8636 10
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNCS,volume 14026))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction
724 Accesses
Alongside the prolonged social and economic instability and the escalating demands for upskilling, Covid-19 pandemic had a detrimental impact on students’ and academics’ mental health and wellbeing. Social isolation and the emergency transition to remote education caused high levels of psychological distress, hindering students’ self-efficacy and academic performance. The pandemic also induced sudden changes affecting academics’ personal and professional lives, leading to mental disorders and risk of burnout. While recent research focuses on addressing the effects of the pandemic on either students or academics, this paper presents a collective analysis. The key themes that emerged by examining the experiences of both students and academics in higher education are framed in a multi-layered support system embracing qualities such as: self-efficacy, wellbeing, equality, diversity, and inclusion, social interactions, human-centred technologies, and authentic pedagogical methods. The findings are discussed with the aim to extract informed recommendations for enhancing teaching and learning experiences in the post-pandemic era.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Abu Elnasr, E.S., Hasanein, A.M., Abu Elnasr, A.E.: Responses to COVID-19 in higher education: Social media usage for sustaining formal academic communication in developing countries. Sustainability 12 (16), 6520 (2020)
Google Scholar
Al Miskry, A.S.A., Hamid, A.A.M., Darweesh, A.H.M.: The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic on University Faculty, Staff, and Students and Coping Strategies Used During the Lockdown in the United Arab Emirates. Frontiers in Psychology 12 (2021)
Al-Taweel, D., et al.: Multidisciplinary academic perspectives during the COVID‐19 pandemic. Int. J. Health Planning Manag. 35 (6), 1295–1301 (2020)
Aucejo, E.M., French, J., Araya, M.P.U., Zafar, B.: The impact of Covid-19 on student experiences and expectations: Evidence from a survey. Journal of public economics, 191 (2020)
Bates, A.W.: Teaching in a Digital Age, 2nd edn. Tony Bates Associates Ltd., Vancouver, B.C. (2019)
Berger, T.: How to Maslow Before Bloom, All Day Long. Edutopia (2020). https://www.edutopia.org/article/how-maslow-bloom-all-day-long/
Bożykowski, M., Izdebski, A., Jasiński, M., Konieczna-Sałamatin, J.: Nauczanie w dobie pandemii i perspektywa powrotu do normalności, Pracownia Ewaluacji Jakości Kształcenia Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego (University of Warsaw) (2021)
Brzezinska, M., Cromarty, E.: Emergency Remote Teaching in the University Context: Responding to Social and Emotional Needs During a Sudden Transition Online. In: Meiselwitz, G. (eds) Social Computing and Social Media: Applications in Education and Commerce. HCII 2022. LNCS, vol. 13316. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05064-0_3
Brzezinska, M.: Global skills in the global pandemic: how to create an effective bichronous learning experience during an emergency shift to remote instruction. In: Auer, M.E., Pester, A., May, D. (eds.) Learning with Technologies and Technologies in Learning. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol. 456. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-04286-7_32
Cassibba, R., Ferrarello, D., Mammana, M.F., Musso, P., Pennisi, M., Taranto, E.: Teaching mathematics at distance: a challenge for universities. Educ. Sci. 11 (1), 1 (2020)
Czaja, K., et al.: Zdalne kształcenie na Wydziale Humanistycznym Uniwersytetu Śląskiego w Katowicach. Report (March-April 2020). (A Report. Remote Education at the Department of Humanities of the University of Silesia in Katowice), Uniwersytet Śląski w Katowicach 2020, https://us.edu.pl/wydzial/wh/wp-content/uploads/sites/15/Nieprzypisane/ZDALNE-KSZTAŁCENIE-NA-WYDZIALE-HUMANISTYCZNYM-RAPORT.pdf
Darby, F., Lang, J.M.: Small Teaching Online: Applying Learning Science in Online Classes (1st ed.). Jossey-Bass (2019)
Dewey, J.: How we think: A restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process. DC Heath (1933)
Dinu, L.M., et al.: A case study investigating mental wellbeing of university academics during the COVID-19 pandemic. Educ. Sci. 11 (11), 702 (2021)
Article Google Scholar
Engelbrecht, J., Borba, M. C., Llinares, S., Kaiser, G.: Will 2020 be remembered as the year in which education was changed? ZDM – Math. Educ. 52 (5), 821–824 (2020)
Flaherty, C.: Faculty pandemic stress is now chronic. Inside Higher Ed, 19 (2020)
France, P.E.: Reclaiming Personalized Learning: A Pedagogy for Restoring Equity and Humanity in Our Classrooms (First). Corwin (2020)
France, P.E.: Humanizing Distance Learning: Centering Equity and Humanity in Times of Crisis (First). Corwin (2021)
Gewin, V.: Pandemic Burnout Is Rampant in Academia. Nature Publishing Group (2021). https://media.nature.com/original/magazine-assets/d41586-021-00663-2/d41586-021-00663-2.pdf
Gierdowski, D.C.: ECAR Study of Undergraduate Students and Information Technology (Research report). Louisville, CO: EDUCAUSE Center for Applied Research, October 2019 (2019). http://www.educause.edu/ecar
Halabieh, H., et al.: The future of higher education: identifying current educational problems and proposed solutions. Educ. Sci. 12 (12), 888 (2022)
Hodges, C., Moore, S., Lockee, B., Trust, T., Bond, A.: The difference between emergency remote teaching and online learning. EDUCAUSE Rev. 2020 , 3 (2020)
Hughes, G.J., Byrom, N.C.: Managing student mental health: the challenges faced by academics on professional healthcare courses. J. Adv. Nurs. 75 (7), 1539–1548 (2019)
Joosten, T., Weber, N., Baker, M., Schletzbaum, A.: Planning for a Blended Future: A Research-Driven Guide for Educators (2021). Available online: https://eduq.info/xmlui/handle/11515/38291
Kara, M.: Revisiting online learner engagement: exploring the role of learner characteristics in an emergency period. J. Res. Technol. Educ., 1–17 (2021)
Killen, C., Langer-Crame, M., Penrice, S.: Teaching Staff Digital Experience Insights Survey 2020: UK Higher Education Findings (2021). https://www.jisc.ac.uk/reports/teaching-staff-digital-experience-insights-survey-2020-uk-higher-education
Kita, Y., Yasuda, S., Gherghel, C.: Online education and the mental health of faculty during the COVID-19 pandemic in Japan. Sci. Rep. 12 (1), 1–9 (2022)
Kukulska-Hulme, A., et al.: Innovating Pedagogy 2022: Open University Innovation Report 10. Milton Keynes: The Open University (2022)
Kumar, S., Martin, F., Budhrani, K., Ritzhaupt, A.: Award-winning faculty online teaching practices: Elements of award-winning courses. Online Learning 23(4) (2019)
Leone, V., Brzezinska, M.: Transatlantic Educators Dialogue (TED) Program for Global Citizenship. Idee in Form@Zione, 99–115 (2021)
Leong, K., Sung, A., Au, D., Blanchard, C.: A review of the trend of microlearning. J. Work-Appl. Manage. 13 (1), 88–102 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/JWAM-10-2020-004
Ma, X., Liu, J., Liang, J., Fan, C.: An empirical study on the effect of group awareness in CSCL environments. Interactive Learning Environments, 1–16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1758730
Marinoni, G., van’t Land, H.: The Impact of COVID-19 on Global Higher Education. International Higher Education. Special Issue 102, pp. 7–9 (2020)
McGaughey, F., et al.: This can’t be the new norm’: academics’ perspectives on the COVID-19 crisis for the Australian university sector. Higher education research & development, 1–16 (2021)
McKee, C., Ntokos, K.: Online microlearning and student engagement in computer games higher education. Res. Learn. Technol. 30 (2022). https://doi.org/10.25304/rlt.v30.2680
McKenzie, L.: Bridging the Digital Divide: Lessons From Covid-19. Inside Higher Ed (2021). https://www.insidehighered.com/content/bridging-digital-divide-lessons-covid-19
Meletiou-Mavrotheris, M., Eteokleous, N., Stylianou-Georgiou, A.: Emergency remote learning in higher education in Cyprus during COVID-19 lockdown: a zoom-out view of challenges and opportunities for quality online learning. Educ. Sci. 12 (7), 477 (2022)
Muñoz-Carril, P.C., Hernández-Sellés, N., Fuentes-Abeledo, E.J., González-Sanmamed, M.: Factors influencing students’ perceived impact of learning and satisfaction in Computer Supported Collaborative Learning. Comput. Educ. 174 , 104310 (2021)
Peters, D., Calvo, R.A., Ryan, R.M.: Designing for motivation, engagement and wellbeing in digital experience. Front. Psychol. 9 , 797 (2018)
Piki, A.: An exploration of student experiences with social media and mobile technologies during emergency transition to remote education. In: The Proceedings of the 19th World Conference on Mobile, Blended and Seamless Learning (mLearn 2020), November 2–4, 2020, Cairo, Egypt (2020)
Piki, A.: Re-imagining the distributed nature of learner engagement in computer-supported collaborative learning contexts in the post-pandemic era. In: Meiselwitz, G. (eds.) Social Computing and Social Media: Applications in Education and Commerce. HCII 2022 (June 26-July 1, 2022). LNCS, vol. 13316. Springer, Cham (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05064-0_13
Piki, A., Andreou, L., Markou, M.: Students’ perspectives on the emergency transition to online education – a case study in mathematics education. In: 16th Annual International Technology, Education and Development Conference (INTED2022), March 7–2, 2022 (2022)
Raygoza, M., Leon, R. Norris, A.: Humanizing Online Teaching (2020). https://digitalcommons.stmarys-ca.edu/school-education-faculty-works/1805
Rifkin, J.: The Empathetic Civilization: The Race to Global Consciousness in a World of Crisis. Penguin, New York, NY (2009)
Shaw, A.: Authentic Assessment in the Online Classroom. Center for Teaching and Learning. Wiley Education Services (2020)
Stefan, I.A., Gheorghe, A.F., Stefan, A., Piki, A., Tsalapata, H., Heidmann, O.: Constructing seamless learning through game-based learning experiences. Int. J. Mob. Blended Learn. (IJMBL) 14 (4), 1–12 (2022)
UUK (Universities UK) (2021). Stepchange Mentally Healthy Universities. https://www.universitiesuk.ac.uk/what-we-do/policyand-research/publications/stepchange-mentally-healthy-universities
Urbina-Garcia, A.: What do we know about university academics’ mental health? a systematic literature review. Stress. Health 36 (5), 563–585 (2020)
Veluvali, P., Surisetti, J.: Learning management system for greater learner engagement in higher education—a review. High. Educ. Future 9 (1), 107–121 (2022)
Vijayan, R.: Teaching and learning during the COVID-19 pandemic: a topic modeling study. Educ. Sci. 11 , 347 (2021)
Vlachopoulos, D.: COVID-19: threat or opportunity for online education? High. Learn. Res. Commun. 10 (1), 16–19 (2020)
Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Gong, S., Wang, Z., Li, N., Ai, L.: Interaction and learning engagement in online learning: the mediating roles of online learning self-efficacy and academic emotions. Learn. Individ. Differ. 94 , 102128 (2022)
Watchorn, D., Heckendorf, E., Smith, C.: Locked down, burned out: Publishing in a pandemic: The impact of Covid on academic authors. De Gruyter, Germany (2020)
Watermeyer, R., Crick, T., Knight, C., Goodall, J.: COVID-19 and digital disruption in UK universities: afflictions and affordances of emergency online migration. High. Educ. 81 (3), 623–641 (2021)
Whitman, G., Kelleher, I.: Your Checklist for Virtual Project-Based Learning. Edutopia (2020). https://www.edutopia.org/article/your-checklist-virtual-project-based-learning
WHO/UNESCO (2021). Making every school a health-promoting school: implementation guidance. Geneva: World Health Organization and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (2021). https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240025073
Wray, S., Kinman, G.: Supporting Staff Wellbeing in Higher Education (ISBN 978-1-7399860-1-8). Education Support, London (2021)
Yiapanas, G., Constantinou, M., Marcoulli, E.: The readiness of higher education academic staff in cyprus for shifting the instructional delivery mode from face-to-face to emergency remote teaching. In: Handbook of Research on Digital Innovation and Networking in Post-COVID-19 Organizations, pp. 301–323. IGI Global (2022)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Central Lancashire – Cyprus, Larnaca, Cyprus
Andriani Piki
WSB University, Poznan, Poland
Magdalena Brzezinska
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Magdalena Brzezinska .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
University of Bucharest, Bucharest, Romania
Adela Coman
University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba, Japan
Simona Vasilache
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Piki, A., Brzezinska, M. (2023). Teaching and Learning in the New Normal: Responding to Students’ and Academics’ Multifaceted Needs. In: Coman, A., Vasilache, S. (eds) Social Computing and Social Media. HCII 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14026. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35927-9_9
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-35927-9_9
Published : 09 July 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-35926-2
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-35927-9
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Scientific Writing: Tips and Techniques for Researchers and Students
Don't just communcate findings
Scientific writing is not just about communicating your findings; it's about doing so in a way that is clear, concise, and compelling. This form of writing has the power to influence the scientific community, policymakers, and the public. At SciSummary, we recognize that strong scientific writing can transform complex research into something accessible and impactful.
Why You Should Care
For us at SciSummary, scientific writing is more than a necessity; it’s a way to showcase the value of research to a broader audience. Imagine the potential when your work is read and understood globally. That's the kind of impact proper scientific writing can generate.
Techniques to Enhance Your Scientific Writing
1. structure your manuscript effectively.
A well-structured manuscript can make your research more readable and easier to understand. Start with a clear introduction that sets up your research question or hypothesis, followed by your methodology, results, and a compelling conclusion. Each section should logically flow into the next, providing a seamless narrative of your research journey.
- Introduction: Establish your research question and the significance of your study.
- Methodology: Describe your methods clearly to enable replication.
- Results: Present your data succinctly with appropriate figures and tables.
- Discussion/Conclusion: Interpret the results, highlight the implications, and suggest future directions.
2. Writing with Precision and Clarity
Precision and clarity are crucial in scientific writing. Use simple language and avoid unnecessary jargon that might alienate your audience. At SciSummary, we value making complex scientific concepts accessible, and we encourage writers to prioritize clarity. Utilize straightforward sentences and define technical terms when necessary.
3. Mastering the Art of Persuasive Argument
Your discussion and conclusion sections should not only summarize your findings but also underscore their relevance. Clearly articulate the contribution of your work to the existing body of knowledge. To aid in this, build a persuasive argument by linking your data logically to your conclusions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. overgeneralizing results.
Avoid making broad claims that your data cannot support. Be careful to stay within the bounds of your study's findings and acknowledge the limitations. At SciSummary, our backing of robust summarization tools lies in presenting information accurately, a principle that extends to writing too.
2. Ignoring Feedback from Peers
Always seek feedback from colleagues and mentors. Peer reviews can provide insights and catch errors you might have overlooked. Scientific writing is a collaborative process, much like how we at SciSummary value collaborative efforts to ensure the quality of our summaries.
Tools and Resources to Support Scientific Writing
1. reference management software.
Tools like Zotero or EndNote can help manage citations efficiently, ensuring you're always giving credit where credit is due. These tools can save you countless hours and make your writing process more efficient.
2. Grammar and Style Tools
Apps like Grammarly or Hemingway can polish your writing by checking for grammatical errors and enhancing readability. These tools are incredibly beneficial, much as our SciSummary platform streamlines the task of summarizing extensive research papers.
3. SciSummary as a Resource
While honing your writing skills, let SciSummary assist in simplifying complex papers, making the core message of your work more focused. Our platform can serve as a useful stepping stone in ensuring your writing is precise and comprehensible.
Mastering scientific writing is an ongoing journey. It's a skill that enhances the dissemination of your research and builds credibility within your field. By incorporating these techniques, along with utilizing the right tools, you can elevate your writing to new heights. At SciSummary, we're passionate about supporting research communication, and our platform is here to complement your writing process by streamlining the summarization of scientific content. Whether you're a student starting out or an experienced researcher, these tips will empower you to communicate your findings effectively.
We invite you to explore SciSummary further to see how it can enhance your scientific writing endeavors. Visit our website to learn more.

About Al-Kindi
All journals
- Publish with us
- Our services
- Our Partners
Journal of World Englishes and Educational Practices
Article contents
Research, Writing, and Collaborative Skills, and Research Output Quality of Senior High School Students Under the New Normal
This survey-correlational research was conducted to determine the levels of research, writing, and collaborative skills and research output quality of Senior High School students under the new normal, S.Y. 2020-2021. The participants of this study were sixty-three (63) Grade 12 students and five (5) Senior High School teachers involved in research advising, paneling, and teaching, who are currently enrolled and employed respectively in Ochando National High School in the District of New Washington. The research skills of the students were measured using a 42-item objective type researcher-made Research Skills Test. The writing skills were evaluated through an adapted Writing Skills Test and were graded using a 20-point adapted rubric. The collaborative skills were assessed using a 50-item adapted and modified Collaborative Skills Questionnaire. The research output quality was assessed through a 60-point researcher-made Research Output Quality Rubric. The data-gathering instruments were subjected to face and content validation by a panel of experts, reliability testing, and item analysis. The statistical tools used in descriptive data analyses were frequency count, mean, and standard deviation. The Analysis of Variance and Pearson r were used as inferential statistical tools to determine the significant differences and relationships among the levels of the variables of the study. All inferential tests were set at a 5% alpha level of significance. The study revealed that students had developing research skills. Students possessed developing writing skills. Students had high collaborative skills. Their research output quality was poor. There was a significant difference in research output quality among the levels of research skills of Senior High School students. There was a significant difference in research output quality among the levels of writing skills of Senior High School students. There was a significant difference in research output quality among the levels of collaborative skills of Senior High School students. There were significant relationships among research skills, writing skills, collaborative skills, and research output quality of Senior High School students.
Article information
Volume (issue), https://doi.org/10.32996/jweep.2022.4.2.5.
Copyright (c) 2022 Journal of World Englishes and Educational Practices
Open access

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License .
How to Cite
Research skills, Writing skills, Collaborative skills, Collaboration skills, Research output quality, Research quality, Research output
Find out more

Further Information
Our partners
Propose a special issue
Publication ethics
Article processing charges
Keep up to date
Copyright © 2024 Al-Kindi Center for Research and Development 3 Dryden Avenue, W7 1ES, Hanwell, London, UK | Registered in England & Wales No. 13110099

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Findings revealed varied students’ views on collaborative research writing in the new normal. Various challenges encountered by the students such as those associated with research technicalities, communication, and collaboration were identified.
Findings revealed that students view collaborative research writing in general as easy, while some see it as difficult. The students met challenges in research technicalities, communication, and collaboration.
The machines will include a thermal imager and a powerful suite of AI algorithms that in seconds will scan someone’s heart rate, respiration rate, blood oxygen level and body temperature. Our new normal will include decentralized, persistent biometric surveillance.
During the month of March, amidst constantly shifting medical knowledge of the novel coronavirus and daily briefings by health and public officials, a “new normal” emerged. We learned to socially distance, work remotely, wash our hands more diligently, and wear masks around others (Maragakis 2020).
Specifically, a setting can help ground the research in time and space; first-person narration can enhance clarity; punctuation marks can help guide the reader’s attention; conjunctions can help to link complex ideas; and the judicious use of signposts can help order and structure a piece of writing.
Based on a literature review (primarily of UNESCO and OECD publications and their critics), the following question is posed: How can one resist the slide into passive technologization and seize the possibility of achieving a responsive, ethical, humane, and international-transformational approach to education?
As new researchers preparing to join the research community we learn that writing both communicates particular content and embodies the “routines of [our] social communities” (Hyland as cited in Epting, 2018, p. 561).
This paper undertakes to collectively investigate and analyse academics’ and students’ experiences and perspectives to inform pedagogical recommendations for teaching and learning in the new normal.
2. Ignoring Feedback from Peers. Always seek feedback from colleagues and mentors. Peer reviews can provide insights and catch errors you might have overlooked. Scientific writing is a collaborative process, much like how we at SciSummary value collaborative efforts to ensure the quality of our summaries.
This survey-correlational research was conducted to determine the levels of research, writing, and collaborative skills and research output quality of Senior High School students under the new normal, S.Y. 2020-2021.