
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science The Human Eye and Colourful World
Case study questions class 10 science chapter 11 the human eye and colourful world.

At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
Case study 1
As we know that, the ciliary muscles are responsible for change in focal length of the eye lens. And this ability of eye lens to change the focal length is referred as accommodation. The least distance of distinct vision of normal eye is a about 25 cm and the far point of normal eye is found to be at infinity. Because of refractive defects of vision in human being 3 defects are possible they are myopia, hypermetropia and presbyopia. In case of myopia, person is able to see nearby objects clearly but cannot able to see distant objects distinctly. In this defect, the image is formed in front of retina and hence to correct this defect concave lens which is a diverging lens of suitable power is used to form the image on the retina. In case of hypermetropia, the person is not able to see nearby objects clearly but he is able to see distant objects distinctly. And hence in this case, the image is formed behind the retina because of that to correct this defect convex lens which is converging lens of suitable power is used to form the image on the retina.
Presbyopia is the defect of vision which occurs with ageing. Such person is not able to see nearby objects clearly and distinct objects distinctly without proper eye glasses. The persons which are suffering from both myopia and hypermetropia uses bi-focal lenses.
Questions :
1) Which reasons are responsible for myopia?
2) Hypermetropia is also called as?
3) A student who is sitting on the first bench in the class is not able to see what is written on the board. The student is suffering from which defect and which type of lens is suitable for him?
4) What is cataract?
1) The defect myopia occurs because of excessive curvature of eye lens and elongation of the eye balls.
2) Hypermetropia is also called as far-sightedness because person suffering from hypermetropia is able to see distant objects clearly but cannot able to see nearby objects clearly.
3) The student sitting on the first bench in the class is not able to see what is written in the board because that student is suffering from hypermetropia in which person is able to see distant objects distinctly but cannot able to see nearby objects clearly. And hence to correct his defect he should have to use convex lens of suitable power.
4) Sometimes, at old age the crystalline lens of people becomes cloudy and milky and that condition is called as cataract because of which the person may lose partial or complete vision. And it is cured by cataract surgery only.
Case study 2
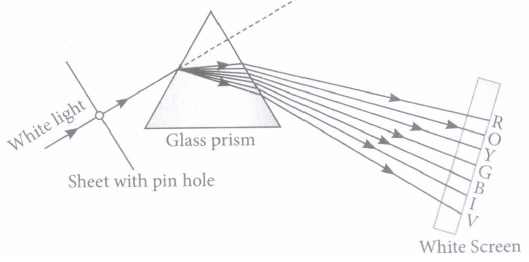
There are various natural phenomenon associated with light. Refraction of light is the phenomenon in which when light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium it changes its direction. The change in direction of light is due to the change in velocity of light in different media. And hence the path of the light also changes in different media. In case of refraction of light through rectangular glass slab we must observe that the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. We can see the pencil immersed in water as bent at the water air interface only because of the refraction of light. Again second phenomenon is dispersion of light in which white light when passed through the prism it splits into seven coloured spectrum. And these seven colours are VIBGYOR. We can see here the angle of deviation is different for different colour because different wavelengths of different colour. Also, Newton observed that when second prism is placed inverted to first prism the white light incident on the first prism will come out as white light only when emerges out from second prism. The phenomenon of formation of rainbow is also because of the dispersion of light. In that case the tiny water droplets acts as prism.
But most importantly, the refraction of light occurs only because of the change in refractive index of medium. The twinkling of stars is due to the atmospheric refraction of light.
1) Rainbow formation takes place because of which phenomenon related to light?
2) What is mean by total internal reflection?
3) Why atmospheric refraction occurs?
4) For which colour the angle of deviation is more in case of dispersion?
1) Rainbow is formed because of total internal reflection of light, dispersion of light and refraction of light.
2) When a ray of light travels from one medium to other, if the angel of incidence is greater than the critical angle then the incident light get reflected totally in the same medium is called as total internal reflection.
3) The atmosphere contains different layers which contains hot and cold air. The hotter air is lighter than the cooler air. And hence the refractive index of hot air is less than the cooler air. As there is continuous change in refractive index of different layers of atmosphere, the atmospheric refraction takes place.
4) The angel of deviation is more for violet colour. And it decreases from violet to red in VIBGYOR.
Case study 3
The Tyndall effect is related to scattering of light. The blue colour of the sky, colour of water in the deep sea, the reddish colour of sun at sunrise and sunset are the colourful phenomenon of light related to scattering. The spreading of light when it strikes to small dust particles, smoke particles which are present in the air is called as scattering of light. When we will send the beam of light through the true solution we will observe the path of beam is not visible. While in case of colloidal solution the path of the beam is visible because of colloidal particles which are somewhat larger in size. We know that atmosphere contains large number of very small particles it means it is a heterogeneous mixture which contains smoke particles, tiny water droplets, suspended particles of dust and air. When light passes through such a heterogeneous mixture the path of the light becomes visible because it strikes with such particles. This effect is called as Tyndall effect. Sometimes we can see the visible beam of light entering into the smoke filled room through a small hole. In canopy of dense forest also, the light coming shows the visible path. Here the scattering of light is due to the water droplets present in the mist. In case of scattering of light, if the particles are having very small size then the light scattered more is of shorter wavelength that is blue colour and scattered red light is less of longer wavelength.
1) The reddening of the sun at sunset and sunrise is because of
a) Dispersion of light
b) scattering of light
c) refraction of light
d) total internal reflection of light
2) Which colour is having longest wavelength?
3) The advance sunrise and delayed sunset are because of
a) Scattering of light
b) dispersion of light
c) reflection of light
d) atmospheric Refraction of light
4) Which coloured light scatter more and why?
2) The red colour is having longest wavelength and wavelength increases from violet to red in the sequence VIBGYOR.
4) The blue coloured light scatter more because the wavelength of blue colour light is shortest. And scattering of light increases as the wavelength of light decrease.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Telangana scert class 5 evs chapter 13 energy solution, telangana scert class 5 evs chapter 12 historical sites – wanaparti fort solution, new mathematics today class 6 solutions chapter 11 – speed, time and distance, maharashtra board class 4 math chapter 9 word problems : addition and subtraction solution.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11

Last Updated on August 30, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 11 The Human Eye and the Colourful World.
| The Human Eye and the Colourful World | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 10 | |
| Science | |
| Class 10 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on The Human Eye and the Colourful World
Question 1:
Read the following and answer the questions given below:
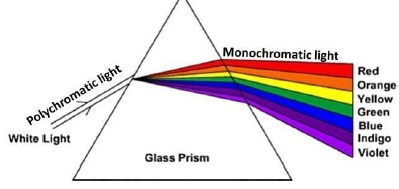
Light of all the colour travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium (glass or water), the light of different colours travel with different speeds for different wavelength that means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelength. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colour bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light.
λ r > λ v and r n < v n . Also frequency, ν = c/λ.
(i) Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air? (a) Red light moves fastest. (b) Blue light moves faster than green light. (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed. (d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: All the colours of the white light move with the same speed in air.
(ii) Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength? (a) Red > Green > Yellow (b) Red > Violet > Green (c) Yellow > Green > Violet (d) Red > Yellow > Orange
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: The increasing order of wavelength of visible spectrum is Violet < Indigo < Blue < Green < Yellow < Orange < Red So, the correct order is Yellow > Green > Violet
(iii) Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass? (a) Red > Green > Blue (b) Blue > Green > Red (c) Violet > Red > Green (d) Green > Red > Blue
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: The more be the wavelength, more be the speed.
(iv) Which colour which has maximum frequency (a) Red (b) Violet (c) Blue (d) Green
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Frequency is inversely proportional to the wavelength. Violet has minimum wavelength among all these colours, so violet has maximum frequency.
(v) Which of the following is the correct order of angle of deviation? (a) Red > Green > Blue (b) Blue > Yellow > Orange (c) Orange > Red > Green (d) Blue > Green > Violet
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: The angle of deviation is more for more refractive index.
Question 2:
The spreading of light by the air molecules is called scattering of light. The light having least wavelength scatters more. The sun appears red at sunrise and sunset, appearance of blue sky it is due to the scattering of light. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of particles. The smaller the molecules in the atmosphere scatter smaller wavelengths of light. The amount of scattering of light depends on the wavelength of light. When light from sun enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets scattered by the dust particles and air molecules present in the atmosphere. The path of sunlight entering in the dark room through a fine hole is seen because of scattering of the sun light by the dust particles present in its path inside the room.
(i) To an astronaut in a spaceship, the colour of earth appears (a) red (b) blue (c) white (d) black
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Light is scattered by the air molecules present in atmosphere.
(ii) At the time of sunrise and sunset, the light from sun has to travel. (a) longest distance of atmosphere (c) both (a) and (b) (b) shortest distance of atmosphere (d) can’t say
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: As the distance between us and sun is more at the time of sunrise and sunset.
(iii) The colour of sky appears blue, it is due to the (a) refraction of light through the atmosphere (b) dispersion of light by air molecules (c) scattering of light by air molecules (d) all of these.
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Due to the more scattering of blue colour by molecules of air.
(iv) At the time of sunrise and sunset (a) Blue colour scattered and red colour reaches our eye (b) Red colour scattered and blue colour reaches our eye (c) Green and blue scattered and orange reaches our eye (d) None of these
Ans. Option (a) is correct. Explanation: Red light being of largest wavelength blue scatter more, red scattered least.
(v) The danger signs made red in colour, because (a) the red light can be seen from farthest distance (b) the scattering of red light is least (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Scattering is least but velocity of red light is more.
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
- Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
Acids Bases and Salts Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 2
Chemical reactions and equations class 10 case study questions science chapter 1, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Structure of the Human Eye
- Functioning of the Eye
- Defects of Vision and Their Correction
- Prism and the Refractive Index
- Dispersion of Light
- Atmospheric Refraction
- Scattering of Light
Case study questions from the above topics may be asked.
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on The Human Eye and the Colourful World Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.
Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on The Human Eye and the Colourful World for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on The Human Eye and the Colourful World class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of The Human Eye and the Colourful World.
Q7: What is the power of accommodation of a normal eye?
Ans. A normal eye has a power of accommodation which enables objects as far as infinity and as close as 25 cm to be focussed on the retina.
Q8: What is meant by spherical aberration of a lens?
A8: The inability of a lens to bring all the rays coming from a point object to focus at a single point is known as spherical aberration.
Q9: Is the focal length of our eye lens fixed?
Q10: what is astigmatism how is it corrected.
A10: It is that defect of the eye due to which the image of a distant point source of light is formed, not as a point but as a vertical or a horizontal line. It can be corrected by using cylindrical lenses.
Q11: White light consists of seven colours. Is the refractive index of glass same for all colours?
A11: The refractive index of glass is different for each of the colours.
Q12: When a monochromatic light passes through a prism, will it show dispersion?
A12: No, it will not show any dispersion but will show only deviation.
Q13: When does an object appear black?
A13: When it absorbs all the colours incident on it.
Q14: Why does a rose appear red in daylight?
A14: Because it reflects only red colour to our eye, out of all the seven colours of sun light falling on it.

Related Posts


Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Study Questions Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Re a son . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
The Human Eye and The Colourful World Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
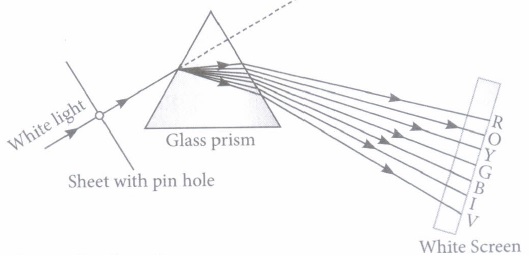
(i) The splitting of white light can be done by
| (a) lens | (b) prism |
| (c) mirror | (d) none of these |
Answer: (b) prism
(ii) Which property of light is used by prism to form a spectrum?
| (a) Reflection | (b) Refraction |
| (c) Dispersion | (d) Scattering |
Answer: (b) Refraction
(iv) When a red light passes through a prism, it (a) will not split (b) will split into seven colours (c) will split into white colour (d) will split into many different colours
Answer: (a) will not split
(v) The spectrum produced by the white light by a prism is called
| (a) pure spectrum | (b) impure spectrum |
| (c) monochromatic spectrum | (d) none of these. |
Answer: (b) impure spectrum
Question 2:
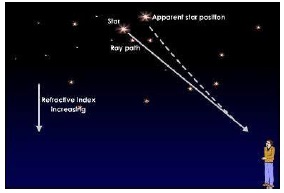
Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light on passing through the earth’s atmosphere. As we move above the surface of the earth, the density of air goes on decreasing. Local conditions like temperature etc. also affect the optical density of the earth’s atmosphere. On account of atmospheric refraction, stars seen appear higher than they actually are; advanced sunrise; delayed sunset, the oval appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset; stars twinkle, planets do not.
(i) Due to atmospheric refraction, the apparent length of the day (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same (d) all of these
Answer: (a) Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day increases by 4 minutes.
(ii) Apparent position of the star appears raised due to (a) atmospheric refraction (b) scattering of light (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Answer: (a) Apparent position of the stars appears raised due to atmospheric refraction.
(iii) The sun appears oval-shaped or flattened due to (a) dispersion (b) scattering (c) atmospheric refraction (d) cannot say
Answer: (c) atmospheric refraction
(iv) Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is accounted for by (a) scattering of light (b) dispersion of light (c) atmospheric refraction (d) none of these
(v) In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears (a) blue (b) black (c) red (d) yellow
Answer: (d) yellow
Case Study 3: The human eye is a complex organ that enables us to perceive the world around us. It consists of various parts that work together to provide vision. The cornea is the transparent outer covering of the eye that helps in focusing light. The iris, the colored part of the eye, controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. The lens, located behind the iris, further focuses the light onto the retina, which contains light-sensitive cells called rods and cones. These cells convert light into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the optic nerve. The brain processes these signals and interprets them as visual images. The eye is capable of adjusting its focal length through a process called accommodation, allowing us to see objects at different distances clearly. The eye is also sensitive to different colors due to the presence of cones that respond to specific wavelengths of light. Understanding the functioning of the human eye and the properties of light helps us comprehend vision, perception, and phenomena such as refraction, dispersion, and the formation of images.
What is the function of the cornea? a) Controlling the amount of light entering the eye b) Focusing light onto the retina c) Transmitting electrical signals to the brain d) Providing vision Answer: b) Focusing light onto the retina
What part of the eye controls the amount of light entering the eye? a) Cornea b) Iris c) Lens d) Retina Answer: b) Iris
Where are the light-sensitive cells called rods and cones located? a) Cornea b) Iris c) Lens d) Retina Answer: d) Retina
How are visual images transmitted to the brain? a) Via the cornea b) Via the iris c) Via the optic nerve d) Via the lens Answer: c) Via the optic nerve
What is the process called that allows the eye to adjust its focal length? a) Accommodation b) Refraction c) Dispersion d) Reflection Answer: a) Accommodation
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World with Answers Pdf free download have been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science The Human Eye and The Colourful World Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Class 10 english first flight mcq with answers pdf download, extra questions of class 10 social science civics chapter 7 outcomes of democracy pdf download.

Class 10 Social Science History Notes by Toppers – Download PDF
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 9 Minutes
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World .
Question 1:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v).
The spreading of light by the air molecules is called scattering of light. The light having least wavelength scatters more. The sun appears red at sunrise and sunset, appearance of blue sky it is due to the scattering of light. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of particles. The smaller the molecules in the atmosphere scatter smaller wavelengths of light. The amount of scattering of light depends on the wavelength of light. When light from sun enters the earth’s atmosphere, it gets scattered by the dust particles and air molecules present in the atmosphere. The path of sunlight entering in the dark room through a fine hole is seen because of scattering of the sun light by the dust particles present in its path inside the room.
(i) To an astronaut in a spaceship, the colour of earth appears (a) red (b) blue (c) white (d) black
(ii) At the time of sunrise and sunset, the light from sun has to travel. (a) longest distance of atmosphere (b) shortest distance of atmosphere (c) both (a) and (b) (d) can’t say
(iii) The colour of sky appears blue, it is due to the (a) refraction of light through the atmosphere (b) dispersion of light by air molecules (c) scattering of light by air molecules (d) all of these.
(iv) At the time of sunrise and sunset (a) Blue colour scattered and red colour reaches our eye (b) Red colour scattered and blue colour reaches our eye (c) Green and blue scattered and orange reaches our eye (d) None of these
(v) The danger signs made red in colour, because (a) the red light can be seen from farthest distance (c) both (a) and (b) (b) the scattering of red light is least (d) none of these
Question 2:
Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v)
Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light on passing through earth’s atmosphere. As we move above the surface of earth, density of air goes on decreasing. Local conditions like temperature etc. also affect the optical density of earth’s atmosphere. On account of atmospheric refraction, stars seen appear higher than they actual are; advanced sunrise; delayed sunset, oval appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset; stars twinkle, planets do not.
(i) Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same (d) all of these
(ii) Apparent position of the star appears raised due to (a) atmospheric refraction (b) scattering of light (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
(iii) The sun appears oval shaped or flattened due to (a) dispersion (b) scattering (c) atmospheric refraction (d) cannot say
(iv) Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is accounted for by (a) scattering of light (b) dispersion of light (c) atmospheric refraction (d) none of these
(v) In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears (a) blue (b) black (c) red (d) yellow
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
2 thoughts on “ Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World ”
In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears Black
the question is asking about the colour of the earth, not the sky!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions Class 10
Students who are studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to get the knowledge about the Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions. Case based questions are generally based on the seen passages from the chapter Human Eye and Colourful World. Through solving the case based questions, students can understand each and every concept.
With the help of Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions, students don’t need to memorise each answer. As answers for these case studies are already available in the given passage. Questions are asked through MCQs so student’s won’t take time to mark the answers. These multiple choice questions can help students to score the weightage of Human Eye and Colourful World.
Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions with Solutions
Selfstudys provides case studies for the Class 10 Science chapter Human Eye and Colourful World with solutions. The Solutions can be helpful for students to refer to if there is a doubt in any of the case studies problems. The solutions from the Selfstudys website are easily accessible and free of cost to download. This accessibility can help students to download case studies from anywhere with the help of the Internet.
Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions with solutions are in the form of PDF. Portable Document Format (PDF) can be downloaded through any of the devices: smart phone, laptop. Through this accessibility, students don't need to carry those case based questions everywhere.
Features of Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions
Before solving questions, students should understand the basic details of Human Eye and Colourful World. Here are the features of case based questions on Human Eye and Colourful World are:
- These case based questions start with short or long passages. In these passages some concepts included in the chapter can be explained.
- After reading the passage, students need to answer the given questions. These questions are asked in the Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ).
- These case based questions are a type of open book test. These case based questions can help students to score well in the particular subject.
- These Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions can also be asked in the form of CBSE Assertion and Reason .
Benefits of Solving Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions
According to the CBSE board, some part of the questions are asked in the board exam question papers according to the case studies. As some benefits of solving Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions can be obtained by the students. Those benefits are:
- Through solving case studies students will be able to understand every concept included in the chapter Human Eye and Colourful World
- Passages included in the case study are seen passages, so students don’t need to struggle for getting answers. As these questions and answers can be discussed by their concerned teacher.
- Through these students can develop their observation skills. This skill can help students to study further concepts clearly.
- Case studies covers all the concepts which are included in the Human Eye and Colourful World
How to Download Human Eye and Colourful World Case Based Questions?
Students studying in CBSE class 10 board, need to solve questions based on case study. It is necessary for students to know the basic idea of Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions. Students can obtain the basic idea of case based questions through Selfstudys website. Easy steps to download it are:
- Open Selfstudys website.
- Bring the arrow towards CBSE which is visible in the navigation bar.
- A pop-up menu will appear, Select case study from the list.
- New page will appear, select 10 from the list of classes.
- Select Science from the subject list.
- And in the new page, you can access the Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions.
Tips to solve Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Questions-
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science.
- Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
- Students should start solving the case based questions through reading the given passage.
- Identify the questions and give the answers according to the case given.
- Read the passage again, so that you can easily answer the complex questions.
- Answer according to the options given below the questions provided in the Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

CBSE Expert
Class 10 Science: Case Study Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World PDF Download
In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given.

Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Case Study Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:

(i) The splitting of white light can be done by
| (a) lens | (b) prism |
| (c) mirror | (d) none of these |
Answer: (b) prism
(ii) Which property of light is used by prism to form a spectrum?
| (a) Reflection | (b) Refraction |
| (c) Dispersion | (d) Scattering |
Answer: (b) Refraction
(iv) When a red light passes through a prism, it (a) will not split (b) will split into seven colours (c) will split into white colour (d) will split into many different colours
Answer: (a) will not split
(v) The spectrum produced by the white light by a prism is called
| (a) pure spectrum | (b) impure spectrum |
| (c) monochromatic spectrum | (d) none of these. |
Answer: (b) impure spectrum
Question 2:
Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light on passing through the earth’s atmosphere. As we move above the surface of the earth, the density of air goes on decreasing. Local conditions like temperature etc. also affect the optical density of the earth’s atmosphere. On account of atmospheric refraction, stars seen appear higher than they actually are; advanced sunrise; delayed sunset, the oval appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset; stars twinkle, planets do not.
(i) Due to atmospheric refraction, the apparent length of the day (a) increases (b) decreases (c) remains the same (d) all of these
Answer: (a) Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day increases by 4 minutes.
(ii) Apparent position of the star appears raised due to (a) atmospheric refraction (b) scattering of light (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Answer: (a) Apparent position of the stars appears raised due to atmospheric refraction.
(iii) The sun appears oval-shaped or flattened due to (a) dispersion (b) scattering (c) atmospheric refraction (d) cannot say
Answer: (c) atmospheric refraction
(iv) Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is accounted for by (a) scattering of light (b) dispersion of light (c) atmospheric refraction (d) none of these
(v) In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears (a) blue (b) black (c) red (d) yellow
Answer: (d) yellow
You can also practice Class 10 Science MCQ Questions for Board Exams.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free
Case Study Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World
Please refer to Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines. These case based questions are expected to come in your exams this year. Please practise these case study based Class 10 Science Questions and answers to get more marks in examinations.
Case Study Questions Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World
Case/Passage – 1 Human eye is spherical in shape and has diameter of about 2.5 cm. Sclerotic is a tough, opaque and white substance forming the outermost coating of the eyeball. The front portion is sharply curved and covered by a transparent protective membrane called the ‘cornea’. Inner to the sclerotic there is a layer of black tissue called as choroids consisting of a mass of blood vessels, which nourishes the eye. The black colour does not reflect the light and hence rules out the blurring of image by reflection within the eyeball. Behind the cornea, the space is filled with a liquid called the aqueous humour and behind that a crystalline lens. ‘Iris’ is a muscular diaphragm lying between the aqueous humour and the crystalline lens. Iris has an adjustable opening in the middle called the pupil of the eye. The pupil appears black because all the light entering is absorbed by the ‘retina’, which covers the inside of the rear part of the ball. Iris controls the amount of light entering because the retina absorbs nearly all the light, which falls upon it. This is done by varying the aperture of the pupil with the help of the iris. In dim light the iris dilates the pupil so that more light can enter in. When the light is bright the pupil contracts. The crystalline lens divides the eyeball into two chambers.The chamber between the cornea and the lens is called the anterior chamber filled with a fluid called aqueous humour while the chamber between the lens and the retina is called the posterior chamber which is filled with a transparent gelatinous substance called vitreous humour. The refractive indices of the cornea, pupil lens and fluid portion of the eye are quite similar. So, when a ray of light enters the eye, it is refracted at the cornea. This refraction produces a real inverted and diminished image of distant objects on the retina. When the object is kept at different distances then, we may expect the image to be formed at different distances from the lens. It means, it may not form on the retina always. But in reality it is not so. Image is always formed on the retina. This is possible because the curvature of the crystalline lens is altered by ciliary muscles. When the eye is focused on infinity the muscles are relaxed and the eye lens remains thin. If the object is brought near by, the curvature increases so that the image can be formed on the retina. This property of the eye lens is called accommodation.
Question: The fluid between the retina and the lens is called ______ (a) aqueous humour (b) vitreous humour (c) aqua (d) humus
Question: The part of the eye where optic nerves enter the eye (a) pupil (b) ciliary muscles (c) retina (d) blind spot
Question: The change in focal length of an eye lens to focus the image of objects at varying distances is done by the action of _______ (a) pupil (b) ciliary muscles (c) retina (d) blind spot
Question: The inner back surface of the eyeball is called (a) pupil (b) ciliary muscles (c) retina (d) blind spot
Case/Passage – 2
The phenomenon of decomposition of the white light into its seven component colours when passing through a prism or through a transparent object delimited by non parallel surfaces is called dispersion of light. A beam of light containing all the visible spectrum of the light is white, because the sum of all the colors generates the white color. The light is decomposed in all the component colours, Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange and Red, called as VIBGYOR. The band of the coloured components of a light beam is call d its spectrum. The phenomenon can be explained by thinking that light of different colours (different wavelengths) has different velocities while travelling in a medium vm = f λm. Hence, the change in velocity of light observed when the light passes from the air to the glass, depends on the wavelength.
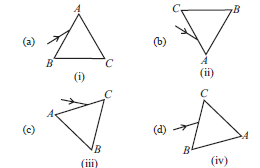
Question: A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in figure. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
Question: When white light is allowed to pass through a glass prism, which colour deviates the most? (a) Indigo (b) Green (c) Red (d) Violet
Question: Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air? (a) Red light moves fastest (b) Blue light moves faster than green light (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed (d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light
Question: For a prism material,refractive index is highest for (a) Red (b) Yellow (c) Orange (d) Violet Passage Based Questions
Question: When white light is allowed to pass through a glass prism,which colour deviates the least? (a) Violet (b) Red (c) Green (d) Orange
Case/Passage – 3
The ciliary muscles of eye control the curvature of the lens in the eye and hence can alter the effective focal length of the system. When the muscles are fully relaxed, the focal length is maximum. When the muscles are strained the curvature of lens increases (that means radius of curvature decreases) and focal length decreases. For a clear vision the image must be on retina. The image distance is therefore fixed for clear vision and it equals the distance of retina from eye-lens. It is about 2.5 cm for a grown-up person. A person can theoretically have clear vision of objects situated at any large distance from the eye. The smallest distance at which a person can clearly see is related to minimum possible focal length. The ciliary muscles are most strained in this position. For an average grown-up person minimum distance of object should be around 25 cm. A person suffering for eye defects uses spectacles (Eye glass). The function of lens of spectacles is to form the image of the objects within the range in which person can see clearly. The image of the spectacle-lens becomes object for eye-lens and whose image is formed on retina. The number of spectacle-lens used for the remedy of eye defect is decided by the power of the lens required and the number of spectacle-lens is equal to the numerical value of the power of lens with sign. For example power of lens required is +3D (converging lens of focal length 100/3 cm) then number of lens will be +3. For all the calculations required you can use the lens formula and lens maker’s formula. Assume that the eye lens is equiconvex lens. Neglect the distance between eye lens and the spectacle lens.
Question: Maximum focal length of eye lens of normal person is (a) 25 cm (b) 2.5 cm (c) 25/9 cm (d) 25/11 cm
Question: Minimum focal length of eye lens of a normal person is (a) 25 cm (b) 2.5 cm (c) 25/9 cm (d) 25/11 cm
Question: A nearsighted man can clearly see object only upto a distance of 100 cm and not beyond this. The number of the spectacles lens necessary for the remedy of this defect will be (a) +1 D (b) –1 D (c) + 3 D (d) – 3 D

Related Posts

CBSE Class 10 English The Ball poem Summary

The Bangle Sellers Summary by Sarojini Naidu

Consumer Rights Class 10 Social Science Notes And Questions
Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Case Based Questions - Human Eye and Colourful World
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Case study - 1
The Tyndall effect is related to scattering of light. The blue colour of the sky, colour of water in the deep sea, the reddish colour of sun at sunrise and sunset are the colourful phenomenon of light related to scattering. The spreading of light when it strikes to small dust particles, smoke particles which are present in the air is called as scattering of light. When we will send the beam of light through the true solution we will observe the path of beam is not visible. While in case of colloidal solution the path of the beam is visible because of colloidal particles which are somewhat larger in size. We know that atmosphere contains large number of very small particles it means it is a heterogeneous mixture which contains smoke particles, tiny water droplets, suspended particles of dust and air. When light passes through such a heterogeneous mixture the path of the light becomes visible because it strikes with such particles. This effect is called as Tyndall effect. Sometimes we can see the visible beam of light entering into the smoke filled room through a small hole. In canopy of dense forest also, the light coming shows the visible path. Here the scattering of light is due to the water droplets present in the mist. In case of scattering of light, if the particles are having very small size then the light scattered more is of shorter wavelength that is blue colour and scattered red light is less of longer wavelength.
Q1: The reddening of the sun at sunset and sunrise is because of (a) dispersion of light (b) scattering of light (c) refraction of light (d) total internal reflection of light Ans: (b) Explanation: When the sun is close to the horizon during sunrise or sunset, its light passes through a larger portion of Earth's atmosphere than when it's directly overhead. This increased path length through the atmosphere leads to a phenomenon called scattering of light. Q2: Which colour is having longest wavelength? Ans: The red colour is having longest wavelength and wavelength increases from violet to red in the sequence VIBGYOR. Q3: The advance sunrise and delayed sunset are because of (a) Scattering of light (b) dispersion of light (c) reflection of light (d) atmospheric Refraction of light Ans: (d) Explanation: The advance sunrise and delayed sunset are primarily due to the atmospheric refraction of light. Atmospheric refraction is the bending of light as it passes through the Earth's atmosphere, which causes the apparent position of the Sun to be slightly different from its actual position. This bending of light is a result of the varying density of the Earth's atmosphere. Q4: Which coloured light scatter more and why? Ans: The blue coloured light scatter more because the wavelength of blue colour light is shortest. And scattering of light increases as the wavelength of light decrease.
Case study - 2
There are various natural phenomenon associated with light. Refraction of light is the phenomenon in which when light travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium it changes its direction. The change in direction of light is due to the change in velocity of light in different media. And hence the path of the light also changes in different media. In case of refraction of light through rectangular glass slab we must observe that the incident ray and the emergent ray are parallel to each other. We can see the pencil immersed in water as bent at the water air interface only because of the refraction of light. Again second phenomenon is dispersion of light in which white light when passed through the prism it splits into seven coloured spectrum. And these seven colours are VIBGYOR. We can see here the angle of deviation is different for different colour because different wavelengths of different colour. Also, Newton observed that when second prism is placed inverted to first prism the white light incident on the first prism will come out as white light only when emerges out from second prism. The phenomenon of formation of rainbow is also because of the dispersion of light. In that case the tiny water droplets acts as prism. But most importantly, the refraction of light occurs only because of the change in refractive index of medium. The twinkling of stars is due to the atmospheric refraction of light.
Q1: Rainbow formation takes place because of which phenomenon related to light? Ans: Rainbow is formed because of total internal reflection of light, dispersion of light and refraction of light. Q2: What is mean by total internal reflection? Ans: When a ray of light travels from one medium to other, if the angel of incidence is greater than the critical angle then the incident light get reflected totally in the same medium is called as total internal reflection. Q3: Why atmospheric refraction occurs? Ans: The atmosphere contains different layers which contains hot and cold air. The hotter air is lighter than the cooler air. And hence the refractive index of hot air is less than the cooler air. As there is continuous change in refractive index of different layers of atmosphere, the atmospheric refraction takes place. Q4: For which colour the angle of deviation is more in case of dispersion? Ans: The angel of deviation is more for violet colour. And it decreases from violet to red in VIBGYOR.
Case study - 3
As we know that, the ciliary muscles are responsible for change in focal length of the eye lens. And this ability of eye lens to change the focal length is referred as accommodation. The least distance of distinct vision of normal eye is a about 25 cm and the far point of normal eye is found to be at infinity. Because of refractive defects of vision in human being 3 defects are possible they are myopia, hypermetropia and presbyopia. In case of myopia, person is able to see nearby objects clearly but cannot able to see distant objects distinctly. In this defect, the image is formed in front of retina and hence to correct this defect concave lens which is a diverging lens of suitable power is used to form the image on the retina. In case of hypermetropia, the person is not able to see nearby objects clearly but he is able to see distant objects distinctly. And hence in this case, the image is formed behind the retina because of that to correct this defect convex lens which is converging lens of suitable power is used to form the image on the retina. Presbyopia is the defect of vision which occurs with ageing. Such person is not able to see nearby objects clearly and distinct objects distinctly without proper eye glasses. The persons which are suffering from both myopia and hypermetropia uses bi-focal lenses.
Q1: Which reasons are responsible for myopia? Ans: The defect myopia occurs because of excessive curvature of eye lens and elongation of the eye balls. Q2: Hypermetropia is also called as? Ans: Hypermetropia is also called as far-sightedness because person suffering from hypermetropia is able to see distant objects clearly but cannot able to see nearby objects clearly. Q3: A student who is sitting on the first bench in the class is not able to see what is written on the board. The student is suffering from which defect and which type of lens is suitable for him? Ans: The student sitting on the first bench in the class is not able to see what is written in the board because that student is suffering from hypermetropia in which person is able to see distant objects distinctly but cannot able to see nearby objects clearly. And hence to correct his defect he should have to use convex lens of suitable power.
Q4: What is cataract? Ans: Sometimes, at old age the crystalline lens of people becomes cloudy and milky and that condition is called as cataract because of which the person may lose partial or complete vision. And it is cured by cataract surgery only.
Top Courses for Class 10
| Last updated |
video lectures
Mock tests for examination, viva questions, practice quizzes, shortcuts and tricks, study material, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, objective type questions, past year papers, sample paper, semester notes, extra questions.

Case Based Questions: The Human Eye and the Colourful World Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: the human eye and the colourful world, case based questions: the human eye and the colourful world notes, case based questions: the human eye and the colourful world class 10, study case based questions: the human eye and the colourful world on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.

Forgot Password
Change country.

- Neet Online Test Pack
12th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material
தமிழ் subjects.

Computer Applications

Computer Science
Business maths.

Computer Technology

Accountancy

English Subjects

Business Maths and Statistics

11th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

உயிரியல் - தாவரவியல்

Computer applications

9th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

Social Science
6th standard stateboard question papers & study material.

10th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

7th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

8th Standard stateboard question papers & Study material

கணிதம் - old

12th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Introductory Micro and Macroeconomics

Business Studies

Indian Society

Physical Education

Bio Technology

Engineering Graphics

Entrepreneurship

Hindi Elective

Home Science

Legal Studies

Political Science

11th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

Mathematics

Enterprenership

Applied Mathematics
10th standard cbse subject question paper & study material.

9th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

8th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

7th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

6th Standard CBSE Subject Question Paper & Study Material

School Exams

Tamil Nadu State Board Exams

Scholarship Exams

Study Materials , News and Scholarships

Stateboard Tamil Nadu

Free Online Tests

Educational News

Scholarships

Entrance Exams India

Video Materials

10th Standard CBSE
Class 10th Science - Human Eye and the Colourful World Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Class 10th Science - Human Eye and the Colourful World Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023 Study Materials Sep-09 , 2022
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Science Subject - Human Eye and the Colourful World, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.

A PHP Error was encountered
Severity: Warning
Message: in_array() expects parameter 2 to be array, null given
Filename: material/details.php
Line Number: 1436
Message: Use of undefined constant EXAM - assumed 'EXAM' (this will throw an Error in a future version of PHP)
Line Number: 1438
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Human eye and the colourful world case study questions with answer key.
Final Semester - June 2015
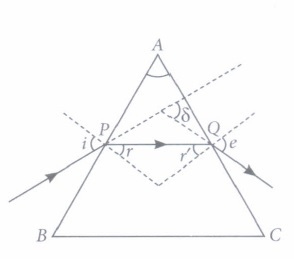
(ii) The angle between the incident ray and the emergent ray is called
(iii) When a ray is refracted through a prism, then
| i=\(\angle\)\(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\) | i=\(\angle\)e+\(\angle\)\(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\) |
| \(\begin{equation} \delta \end{equation}\)= \(\angle\)e | i > \(\angle\)r |
(iv) The angle of deviation depends on
(v) The rectangular surfaces of a prism are known as
(ii) Which property of light is used by prism to form a spectrum?
(iii) Which of the following dispersion is correct?
(iv) When a red light passes through a prism, it (a) will not split (b) will split into seven colours (c) will split into white colour (d) will split into many different colours. (v) The spectrum produced by the white light by a prism is called
Light of all the colour travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths. But in any transparent medium (glass or water), the light of different colours travel with different speeds for different wavelength that means that the refractive index of a particular medium is different for different wavelength. As there is a difference in their speeds, the light of different colour bend through different angles. The speed of violet colour is maximum and the speed of red colour is minimum in glass so, the red light deviates least and violet colour deviates most. Hence, higher the wavelength of a colour of light, smaller the refractive index and less is the bending of light. \(\begin{equation} \lambda \end{equation}\) r > \(\begin{equation} \lambda \end{equation}\) v and r n < v n , \(\begin{equation} v=\frac{c}{\lambda} . \end{equation}\) (i) Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air? (a) Red light moves fastest. (b) Blue light moves faster than green light. (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed. (d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light. (ii) Which of the following is the correct order of wavelength?
(iii) Which of the following is the correct order of speed of light in glass?
(iv) Which colour which has maximum frequency
(v) Which of the following is the correct order of angle of deviation?
The spreading of light by the air molecules is called scattering of light. The light having least wavelength scatters more. The sun appears red at sunrise and sunset, appearance of blue sky it is due to the scattering of light. The colour of the scattered light depends on the size of particles. The smaller the molecules in the atmosphere scatter smaller wavelengths of light. The amount of scattering of light depends on the wavelength of light. When light from sun enters the earth's atmosphere, it gets scattered by the dust particles and air molecules present in the atmosphere. The path of sunlight entering in the dark room through a fine hole is seen because of scattering of the sun light by the dust particles present in its path inside the room. (i) To an astronaut in a spaceship, the colour of earth appears
(ii) At the time of sunrise and sunset, the light from sun has to travel. (a) longest distance of atmosphere (b) shortest distance of atmosphere (c) both (a) and (b) (d) can't say (iii) The colour of sky appears blue, it is due to the (a) refraction oflight through the atmosphere (b) dispersion of light by air molecules (c) scattering of light by air molecules (d) all of these. (iv) At the time of sunrise and sunset (a) Blue colour scattered and red colour reaches our eye (b) Red colour scattered and blue colour reaches our eye (c) Green and blue scattered and orange reaches our eye (d) None of these (v) The danger signs made red in colour, because (a) the red light can be seen from farthest distance (b) the scattering of red light is least (c) both (a) and (b) (d) none of these
Atmospheric refraction is the phenomenon of bending of light on passing through earth's atmosphere. As we move above the surface of earth, density of air goes on decreasing. Local conditions like temperature etc. also affect the optical density of earth's atmosphere. On account of atmospheric refraction, stars seen appear higher than they actual are; advanced sunrise; delayed sunset, oval appearance of the sun at sunrise and sunset; stars twinkle, planets do not. (i) Due to atmospheric refraction, apparent length of the day
(ii) Apparent position of the star appears raised due to
(iii) The sun appears oval shaped or flattened due to
(iv) Twinkling of stars and non-twinkling of planets is accounted for by
(v) In absence of atmosphere, the colour of sky appears
| (a) violet | (b) red | (c) green | (d) blue |
(ii) The colour of white light which suffers the maximum bending (or maximum refraction) on passing through a glass prism is :
| (a) yellow | (b) orange | (c) red | (d) violet |
(iii) Which of the following colour of white light is least deviated by the prism ?
| (a) green | (b) violet | (c) indigo | (d) yellow |
(iv) The colour of white light which is deviated the maximum on passing through the glass prism is :
| (a) blue | (b) indigo | (c) red | (d) orange |
(v) The splitting up of white light into seven colours on passing through a glass prism is called :
| (a) refraction | (b) deflection | (c) dispersion | (d) scattering |
| (a) Reflection of light | (b) Refraction of light |
| (c) Scattering of light | (d) Inference of light |
(ii) Stars appear to twinkle because of :
| (a) Atmospheric refraction | (b) Movement of air |
| (c) Both (a) and (b) | (d) None of these |
(iii) At noon the Sun appears white as : (a) Light is least scattered (b) All the colours of the white light are scattered away (c) Blue colour is scattered the most (d) Red colour is scattered the most (iv) Which of the following phenomena of light is involved in the formation of rainbow? (a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion (b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection (c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection (d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection (v) Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of light of different colours of white light in air? (a) Red light moves with the fastest speed (b) Blue light moves faster than green light (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed. (d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet light
*****************************************
- Previous Class 10th Science - Our Environment Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 202...
- Next Class 10th Science - Magnetic Effects of Electric Current Case Study Questions a...
Reviews & Comments about Class 10th Science - Human Eye and the Colourful World Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023

Write your Comment

10th Standard CBSE Science Videos
CBSE 10th Science Sample Model Question Paper with Answer Key 2023
10th Standard CBSE Science Usefull Links

- 10th Standard
Other 10th Standard CBSE Subjects

Other 10th Standard CBSE Science Study material
Class 10th science - our environment case ... click to view, class 10th science - magnetic effects of ... click to view, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - human eye and ... click to view, class 10th science - light reflection and ... click to view, class 10th science - heredity and evolution ... click to view, class 10th science - how do organisms ... click to view, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023 click to view, class 10th science - periodic classification of ... click to view, class 10th science - carbon and its ... click to view, class 10th science - metals and non-metals ... click to view, class 10th science - acids, bases and ... click to view, class 10th science - chemical reactions and ... click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper iii 2019-2020 click to view, 10th standard cbse science board exam model question paper ii 2019-2020 click to view, register & get the solution for class 10th science - human eye and the colourful world case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

COMMENTS
Important Case Study Questions for Class 10 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions The Human Eye and Colourful World.
Case Study Questions on The Human Eye and the Colourful World. Questions. Question 1: Read the following and answer the questions given below: Light of all the colour travel at the same speed in vacuum for all wavelengths.
The Human Eye and The Colourful World Case Study Questions With Answers. Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World
Here, we have provided case based/passage based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World. Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions from (i) to (v). The spreading of light by the air molecules is called scattering of light.
CBSE 10th Standard Science Subject Human Eye and the Colourful World Chapter Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions .
Students should follow some basic tips to solve Human Eye and Colourful World Case Study Based Questions. These tips can help students to score good marks in CBSE Class 10 Science. Generally, the case based questions are in the form of Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
Here we are providing you with Class 10 Science Chapter 11 The Human Eye and The Colourful World Case Study Questions, by practicing these Case Study and Passage Based Questions will help you in your Class 10th Board Exam.
Please refer to Chapter 11 Human Eyes and Colourful World Case Study Questions with answers provided below. We have provided Case Study Questions for Class 10 Science for all chapters as per CBSE, NCERT and KVS examination guidelines.
Information about Case Based Questions: The Human Eye and the Colourful World covers topics like Case study - 1, Case study - 2, Case study - 3 and Case Based Questions: The Human Eye and the Colourful World Example, for Class 10 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Case ...
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 10th Science Subject - Human Eye and the Colourful World, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.