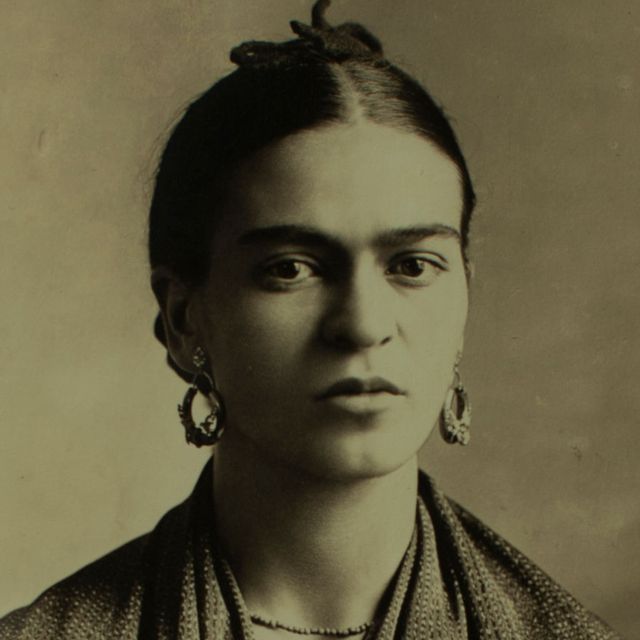
Frida Kahlo
Painter Frida Kahlo was a Mexican artist who was married to Diego Rivera and is still admired as a feminist icon.

We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back.
(1907-1954)

Quick Facts:
Who was frida kahlo, family, education and early life, frida kahlo's accident, frida kahlo's marriage to diego rivera, artistic career, frida kahlo's most famous paintings, frida kahlo’s death, movie on frida kahlo, frida kahlo museum, book on frida kahlo.
FULL NAME: Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón BORN: JULY 6, 1907 BIRTHPLACE: Coyoacán, Mexico City, Mexico ASTROLOGICAL SIGN: Cancer
Artist Frida Kahlo was considered one of Mexico's greatest artists who began painting mostly self-portraits after she was severely injured in a bus accident. Kahlo later became politically active and married fellow communist artist Diego Rivera in 1929. She exhibited her paintings in Paris and Mexico before her death in 1954.
Kahlo was born Magdalena Carmen Frieda Kahlo y Calderón on July 6, 1907, in Coyoacán, Mexico City, Mexico.
Kahlo's father, Wilhelm (also called Guillermo), was a German photographer who had immigrated to Mexico where he met and married her mother Matilde. She had two older sisters, Matilde and Adriana, and her younger sister, Cristina, was born the year after Kahlo.
Around the age of six, Kahlo contracted polio, which caused her to be bedridden for nine months. While she recovered from the illness, she limped when she walked because the disease had damaged her right leg and foot. Her father encouraged her to play soccer, go swimming, and even wrestle — highly unusual moves for a girl at the time — to help aid in her recovery.
In 1922, Kahlo enrolled at the renowned National Preparatory School. She was one of the few female students to attend the school, and she became known for her jovial spirit and her love of colorful, traditional clothes and jewelry.
While at school, Kahlo hung out with a group of politically and intellectually like-minded students. Becoming more politically active, Kahlo joined the Young Communist League and the Mexican Communist Party.
On September 17, 1925, Kahlo and Alejandro Gómez Arias, a school friend with whom she was romantically involved, were traveling together on a bus when the vehicle collided with a streetcar . As a result of the collision, Kahlo was impaled by a steel handrail, which went into her hip and came out the other side. She suffered several serious injuries as a result, including fractures in her spine and pelvis.
After staying at the Red Cross Hospital in Mexico City for several weeks, Kahlo returned home to recuperate further. She began painting during her recovery and finished her first self-portrait the following year, which she gave to Gómez Arias.
In 1929, Kahlo and famed Mexican muralist Diego Rivera married. Kahlo and Rivera first met in 1922 when he went to work on a project at her high school. Kahlo often watched as Rivera created a mural called The Creation in the school’s lecture hall. According to some reports, she told a friend that she would someday have Rivera’s baby.
Kahlo reconnected with Rivera in 1928. He encouraged her artwork, and the two began a relationship. During their early years together, Kahlo often followed Rivera based on where the commissions that Rivera received were. In 1930, they lived in San Francisco, California. They then went to New York City for Rivera’s show at the Museum of Modern Art and later moved to Detroit for Rivera’s commission with the Detroit Institute of Arts.
Kahlo and Rivera’s time in New York City in 1933 was surrounded by controversy. Commissioned by Nelson Rockefeller , Rivera created a mural entitled Man at the Crossroads in the RCA Building at Rockefeller Center. Rockefeller halted the work on the project after Rivera included a portrait of communist leader Vladimir Lenin in the mural, which was later painted over. Months after this incident, the couple returned to Mexico and went to live in San Angel, Mexico.
Never a traditional union, Kahlo and Rivera kept separate, but adjoining homes and studios in San Angel. She was saddened by his many infidelities, including an affair with her sister Cristina. In response to this familial betrayal, Kahlo cut off most of her trademark long dark hair. Desperately wanting to have a child, she again experienced heartbreak when she miscarried in 1934.
Kahlo and Rivera went through periods of separation, but they joined together to help exiled Soviet communist Leon Trotsky and his wife Natalia in 1937. The Trotskys came to stay with them at the Blue House (Kahlo's childhood home) for a time in 1937 as Trotsky had received asylum in Mexico. Once a rival of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin , Trotsky feared that he would be assassinated by his old nemesis. Kahlo and Trotsky reportedly had a brief affair during this time.
Kahlo divorced Rivera in 1939. They did not stay divorced for long, remarrying in 1940. The couple continued to lead largely separate lives, both becoming involved with other people over the years .
While she never considered herself a surrealist, Kahlo befriended one of the primary figures in that artistic and literary movement, Andre Breton, in 1938. That same year, she had a major exhibition at a New York City gallery, selling about half of the 25 paintings shown there. Kahlo also received two commissions, including one from famed magazine editor Clare Boothe Luce, as a result of the show.
In 1939, Kahlo went to live in Paris for a time. There she exhibited some of her paintings and developed friendships with such artists as Marcel Duchamp and Pablo Picasso .
Kahlo received a commission from the Mexican government for five portraits of important Mexican women in 1941, but she was unable to finish the project. She lost her beloved father that year and continued to suffer from chronic health problems. Despite her personal challenges, her work continued to grow in popularity and was included in numerous group shows around this time.
In 1953, Kahlo received her first solo exhibition in Mexico. While bedridden at the time, Kahlo did not miss out on the exhibition’s opening. Arriving by ambulance, Kahlo spent the evening talking and celebrating with the event’s attendees from the comfort of a four-poster bed set up in the gallery just for her.
After Kahlo’s death, the feminist movement of the 1970s led to renewed interest in her life and work, as Kahlo was viewed by many as an icon of female creativity.
Many of Kahlo’s works were self-portraits. A few of her most notable paintings include:
'Frieda and Diego Rivera' (1931)
Kahlo showed this painting at the Sixth Annual Exhibition of the San Francisco Society of Women Artists, the city where she was living with Rivera at the time. In the work, painted two years after the couple married, Kahlo lightly holds Rivera’s hand as he grasps a palette and paintbrushes with the other — a stiffly formal pose hinting at the couple’s future tumultuous relationship. The work now lives at the San Francisco Museum of Modern Art.
'Henry Ford Hospital' (1932)
In 1932, Kahlo incorporated graphic and surrealistic elements in her work. In this painting, a naked Kahlo appears on a hospital bed with several items — a fetus, a snail, a flower, a pelvis and others — floating around her and connected to her by red, veinlike strings. As with her earlier self-portraits, the work was deeply personal, telling the story of her second miscarriage.
'The Suicide of Dorothy Hale' (1939)
Kahlo was asked to paint a portrait of Luce and Kahlo's mutual friend, actress Dorothy Hale, who had committed suicide earlier that year by jumping from a high-rise building. The painting was intended as a gift for Hale's grieving mother. Rather than a traditional portrait, however, Kahlo painted the story of Hale's tragic leap. While the work has been heralded by critics, its patron was horrified at the finished painting.
'The Two Fridas' (1939)
One of Kahlo’s most famous works, the painting shows two versions of the artist sitting side by side, with both of their hearts exposed. One Frida is dressed nearly all in white and has a damaged heart and spots of blood on her clothing. The other wears bold colored clothing and has an intact heart. These figures are believed to represent “unloved” and “loved” versions of Kahlo.
'The Broken Column' (1944)
Kahlo shared her physical challenges through her art again with this painting, which depicted a nearly nude Kahlo split down the middle, revealing her spine as a shattered decorative column. She also wears a surgical brace and her skin is studded with tacks or nails. Around this time, Kahlo had several surgeries and wore special corsets to try to fix her back. She would continue to seek a variety of treatments for her chronic physical pain with little success.
DOWNLOAD BIOGRAPHY'S FRIDA KAHLO FACT CARD

About a week after her 47th birthday, Kahlo died on July 13, 1954, at her beloved Blue House. There has been some speculation regarding the nature of her death. It was reported to be caused by a pulmonary embolism, but there have also been stories about a possible suicide.
Kahlo’s health issues became nearly all-consuming in 1950. After being diagnosed with gangrene in her right foot, Kahlo spent nine months in the hospital and had several operations during this time. She continued to paint and support political causes despite having limited mobility. In 1953, part of Kahlo’s right leg was amputated to stop the spread of gangrene.
Deeply depressed, Kahlo was hospitalized again in April 1954 because of poor health, or, as some reports indicated, a suicide attempt. She returned to the hospital two months later with bronchial pneumonia. No matter her physical condition, Kahlo did not let that stand in the way of her political activism. Her final public appearance was a demonstration against the U.S.-backed overthrow of President Jacobo Arbenz of Guatemala on July 2nd.
Kahlo’s life was the subject of a 2002 film entitled Frida , starring Salma Hayek as the artist and Alfred Molina as Rivera. Directed by Julie Taymor, the film was nominated for six Academy Awards and won for Best Makeup and Original Score.
The family home where Kahlo was born and grew up, later referred to as the Blue House or Casa Azul, was opened as a museum in 1958. Located in Coyoacán, Mexico City, the Museo Frida Kahlo houses artifacts from the artist along with important works including Viva la Vida (1954), Frida and Caesarean (1931) and Portrait of my father Wilhelm Kahlo (1952).
Hayden Herrera’s 1983 book on Kahlo, Frida: A Biography of Frida Kahlo , helped to stir up interest in the artist. The biographical work covers Kahlo’s childhood, accident, artistic career, marriage to Diego Rivera, association with the communist party and love affairs.
Watch the 2024 documentary, titled Frida , about the artist's life on Amazon Prime Video.
We strive for accuracy and fairness. If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
- I never paint dreams or nightmares. I paint my own reality.
- My painting carries with it the message of pain.
- I paint self-portraits because I am so often alone, because I am the person I know best.
- I think that, little by little, I'll be able to solve my problems and survive.
- The only thing I know is that I paint because I need to, and I paint whatever passes through my head without any other consideration.
- I was born a bitch. I was born a painter.
- I love you more than my own skin.
- I am not sick, I am broken, but I am happy as long as I can paint.
- Feet, what do I need you for when I have wings to fly?
- I tried to drown my sorrows, but the bastards learned how to swim, and now I am overwhelmed with this decent and good feeling.
- There have been two great accidents in my life. One was the trolley and the other was Diego. Diego was by far the worst.
- I hope the end is joyful, and I hope never to return.
The Biography.com staff is a team of people-obsessed and news-hungry editors with decades of collective experience. We have worked as daily newspaper reporters, major national magazine editors, and as editors-in-chief of regional media publications. Among our ranks are book authors and award-winning journalists. Our staff also works with freelance writers, researchers, and other contributors to produce the smart, compelling profiles and articles you see on our site. To meet the team, visit our About Us page: https://www.biography.com/about/a43602329/about-us

Famous Painters

Jean-Michel Basquiat

Georgia O'Keeffe

11 Notable Artists from the Harlem Renaissance

Fernando Botero

Gustav Klimt

The Surreal Romance of Salvador and Gala Dalí

Salvador Dalí

Margaret Keane

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

Frida Kahlo summary

Frida Kahlo , (born July 6, 1907, Coyoacán, Mex.—died July 13, 1954, Coyoacán), Mexican painter. The daughter of a German Jewish photographer, she had polio as a child and at 18 suffered a serious bus accident. She subsequently underwent some 35 operations; during her recovery, she taught herself to paint. She is noted for her intense self-portraits, many reflecting her physical ordeal. Like many artists working in post-revolutionary Mexico, Kahlo was influenced by Mexican folk art; this is apparent in her use of fantastical elements and bold use of colour, and in her depictions of herself wearing traditional Mexican, rather than European-style, dress. Her marriage to painter Diego Rivera (from 1929) was tumultuous but artistically rewarding. The Surrealists André Breton and Marcel Duchamp helped arrange exhibits of her work in the U.S. and Europe, and though she denied the connection, the dreamlike quality of her work has often led historians to identify her as a Surrealist. She died at 47. Her house in Coyoacán is now the Frida Kahlo Museum.

Encyclopedia of Humanities
The most comprehensive and reliable Encyclopedia of Humanities
Frida Kahlo
We explain who Frida Kahlo was, and explore her childhood and the development of her works. In addition, we discuss her style and death.
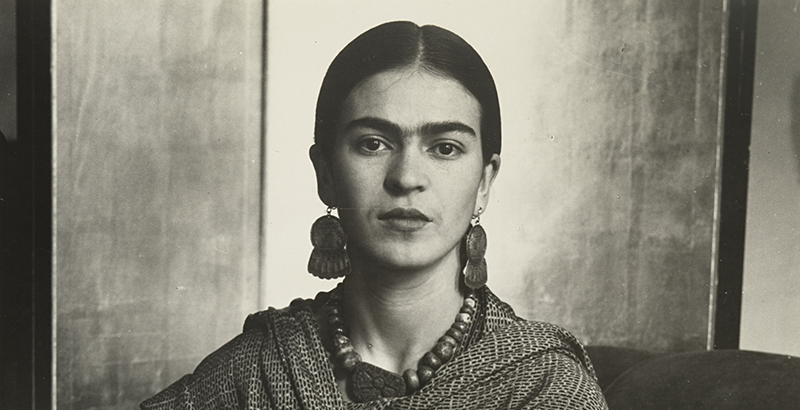
Who was Frida Kahlo?
Frida Kahlo, original name Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón, was a Mexican painter born in Coyoacán on July 6, 1907 . She died on July 13, 1954.
As a child, Frida contracted polio and, at the age of 18, she suffered a severe bus accident that nearly took her life . As a result, she had to undergo 32 surgeries over the years. The hardships she faced are vividly reflected in her artwork.
She was the wife of renowned Mexican painter Diego Rivera , who introduced her to the circle of the most prominent artists of the time, and received acclaim from notable art figures such as Marcel Duchamp, André Breton, Wassily Kandinsky, and Pablo Picasso.
Frida Kahlo’s works also convey her political and social commitment. Widespread recognition came posthumously , especially from the 1970s onward, and she is now regarded as one of the major artists in Latin America .
- See also: Eva Perón
Birth and childhood of Frida Kahlo
Frida Kahlo was born in Coyoacán, Mexico, on July 6, 1907. Her father, German photographer Guillermo Kahlo, was of Hungarian-Jewish descent, and her mother, Matilde Calderón, was Mexican of Spanish and indigenous ancestry, born in Mexico City.
As a child, Frida learned to develop, retouch, and color photographs under her father's guidance , which later influenced her passion for painting.
At the age of six, she contracted polio , and her father took care of her during the six months of her recovery. As a consequence of the disease, she was afflicted with a limp throughout her life.
Accident and painting of Frida Kahlo
In 1922, Frida entered the National Preparatory School in Mexico City, her intention being to study medicine. However, on September 17, 1925, the bus in which she was traveling collided with a streetcar , and Frida was severely injured.
Although she managed to survive, she suffered multiple injuries that would shape her life. Her spine suffered several fractures and, over the years, she underwent over 30 surgeries and had to wear plaster corsets. During the initial months of convalescence, she was bedridden; she abandoned the idea of studying medicine and began painting . In 1926, she painted her first self-portrait.
Frida Kahlo and the Communist Party
Two years after the accident, Frida had recovered sufficiently to reconnect with friends and associate with personalities in the fields of art, thought, and politics. She identified with a cultural movement seeking to recover elements of the Mexican popular tradition , including indigenous influences.
In 1928, her friend Germán del Campo introduced her to Cuban communist leader Julio Antonio Mella, who was in exile in Mexico with his partner, Italian photographer Tina Modotti. Frida began attending meetings of the Mexican Communist Party and became romantically involved with Diego Rivera, who had been a member of the party since 1922.
Following a stay in the United States between 1930 and 1933 with Rivera, whom she had married in 1929, she returned to Mexico City. Between 1937 and 1939, she provided refuge to Russian communist exile Leon Trotsky , persecuted by the Stalinist government, who was eventually assassinated in 1940.
Frida maintained her adherence to communism for the rest of her life . Upon her death, her coffin was draped with the flag of the Mexican Communist Party.
Frida Kahlo's marriage to Diego Rivera
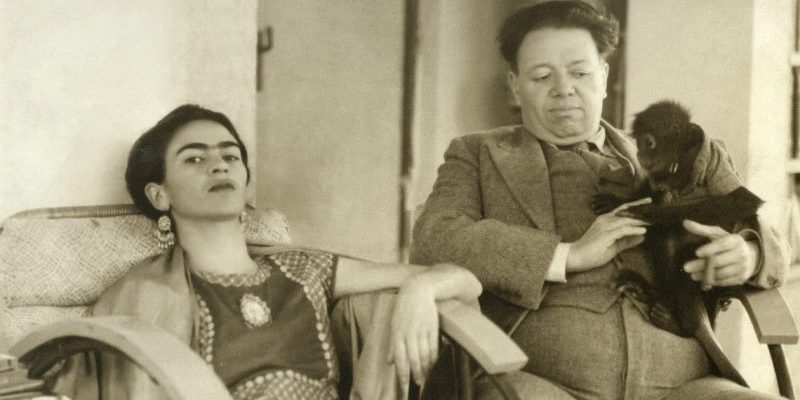

Frida met muralist Diego Rivera in 1922 , when he was painting a mural at the National Preparatory School she attended. However, their romantic relationship only began in 1928 when they were introduced by communist activists Julio Antonio Mella and Tina Modotti.
Frida shared her artwork with Rivera, who encouraged her to continue painting. They married in 1929. She was 22 years old and he was 42 . The marriage was tumultuous, marred by extramarital affairs from both parties, most notably Rivera's relationship with Frida's younger sister, which led to their divorce in 1939. However, they remarried at the end of 1940.
Frida's relationship with Rivera influenced not only her artistic style but also the way she dressed. She usually wore colorful garments characteristic of indigenous women in some regions of Mexico, particularly the Tehuana dresses, which pleased her husband. These included necklaces, ornamental combs, or flower headdresses, which became a hallmark of Frida Kahlo's image.
Attempts at motherhood and death
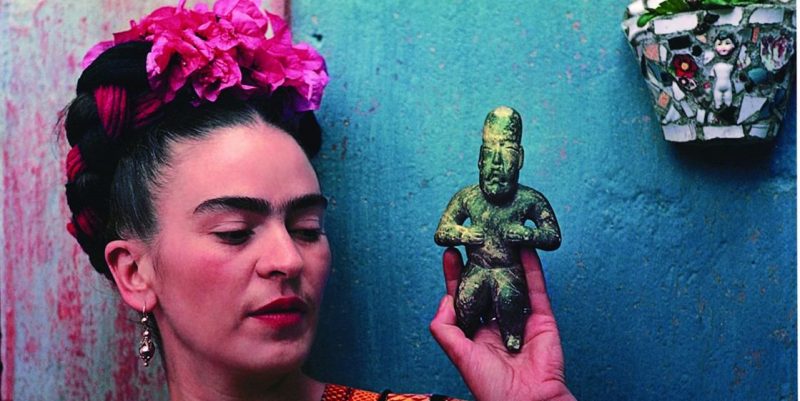

Frida became pregnant with Rivera's child on three occasions but, due to her health problems, she lost each pregnancy . Some of her artwork conveys her thwarted desire for motherhood and the pain from the lost pregnancies.
Throughout her life, Frida continued to suffer from ailments and medical treatments. Her health deteriorated towards 1950, and she eventually died on July 13, 1954 at the age of 47 , due to a pulmonary embolism. Some versions suggested it might have been a suicide, but no evidence has ever appeared to support this theory.
She had expressed her wish not to be buried , on the grounds that she had been bedridden for many years. Her body was cremated and her ashes were placed in a pre-Columbian urn at The Blue House (La Casa Azul) in Coyoacán, where she had lived most of her life and which today houses the Frida Kahlo Museum.
The Blue House
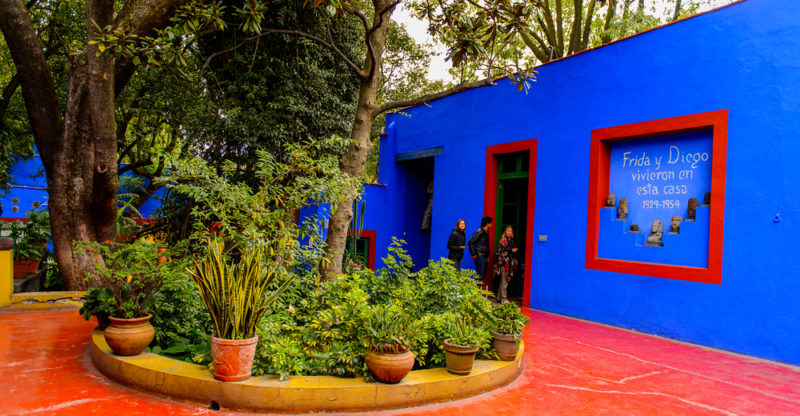

In the famous Blue House (La Casa Azul) in Coyoacán (Mexico City), on the corner of Londres and Allende streets , Frida Kahlo was born, grew up, and produced much of her great artistic work.
Diego Rivera also lived in this house during the time they were married, and it was frequented by artists and intellectuals . Moreover, the Blue House sheltered communist militant refugees, among them Leon Trotsky and his wife.
Following Frida's death, the Blue House and its gardens became home to the Frida Kahlo Museum , which opened on July 12, 1958. Today, it exhibits paintings and personal objects of Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera, as well as documents, books, furniture, dresses, and pre-Columbian sculptures that were the environment in which Frida created her works.
The work of Frida Kahlo
Her artistic style.
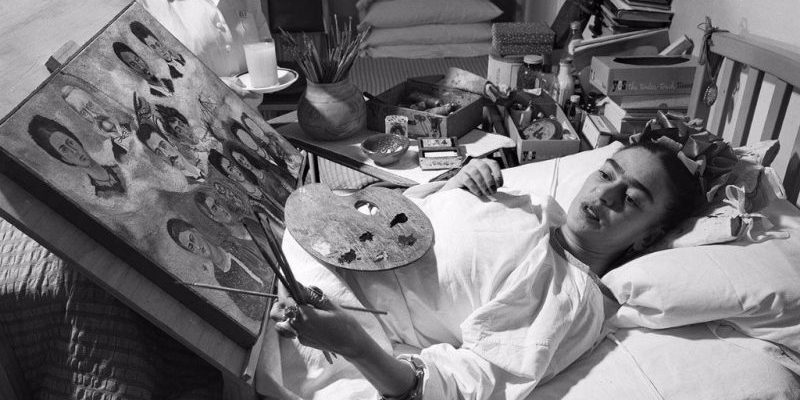

Frida Kahlo's art largely consisted of paintings that conveyed the suffering and torments she experienced throughout her life. She painted numerous self-portraits in which she crudely expressed her personal experiences and also distanced herself from the artistic stereotypes about femininity, which later influenced her image's revival by feminist movements after her death.
In her nearly 200 works, in addition to self-portraits, she painted still lifes and touched upon social and political themes . Her art often portrayed Mexican folklore since, like many artists and intellectuals following the Mexican Revolution, she was concerned with rescuing aspects of Mexican folk art.
She also incorporated into her art symbolism and images from the recent history of communism , which had made an international impact after the Bolshevik revolution of 1917 and whose ideology was embraced by Frida.
Frida Kahlo's style is difficult to classify. On one occasion, her work was defined as surrealist , which she rejected claiming that her art dealt with her own real life. She has also been associated with primitivism and expressionism.
Her most renowned works include Self-Portrait in a Velvet Dress (1926), Henry Ford Hospital (1932), The Frame (1938), The Two Fridas (1939), The Broken Column (1944), Moses (1945), The Wounded Deer (1946), and Diego and I (1949).
Her color choice
In her works, Frida used bright vibrant colors, which became hallmarks of her style. According to the artist, the colors she used bore specific meanings:
- Good warm light.
- Blood (the red color in her paintings and some of her frames may have symbolized the blood she shed throughout her life: in the accident, surgeries, and miscarriages).
- Madness, fear, illness, mystery.
- Love, purity, electricity, distance, and tenderness.
Exhibition of her artworks
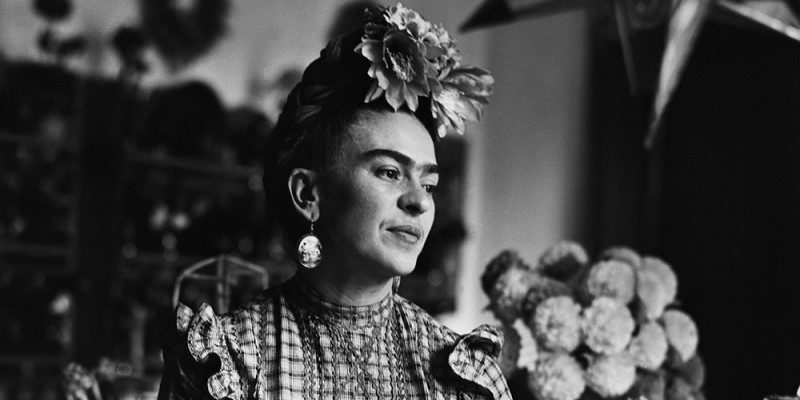

Frida Kahlo's first solo exhibition took place in November 1938 at the Julien Levy Gallery in New York. Her work had been promoted by surrealist writer André Breton , who had traveled to Mexico and had been impressed by her work. In 1939, she exhibited in Paris, and the Louvre Museum acquired her piece "The Frame" ( El marco ). In subsequent years, she exhibited in other cities, especially in the United States.
Frida had only one solo exhibition in her home country . On the opening day, April 13, 1953, her health was so deteriorated that her doctor advised against getting out of bed. Nonetheless, Frida chose to arrive by ambulance and attended the event lying on a hospital bed.
Following her death, and particularly from the 1970s onward, her work acquired widespread recognition, and her paintings have been exhibited in galleries and museums worldwide .
Explore next:
- Che Guevara
- Nelson Mandela
- Thales of Miletus
- Jean Monnet (1888-1979)
- Kahlo 1907-1954. Dolor y pasión . Kettenmann, A. (1999). Taschen.
- "Frida Khalo" en Museo Frida Kahlo .
- "Frida Kahlo. Un ícono del siglo XX" Sadurní, J. M. (2021) en Historia National Geographic .
- "Frida Kahlo" Zelazko, A. (2022) en Encyclopedia Britannica .

Was this information useful to you?
Updates? Omissions? Article suggestions? Send us your comments and suggestions
Thank you for visiting us :)
Articles and Features
Female Iconoclasts: Frida Kahlo
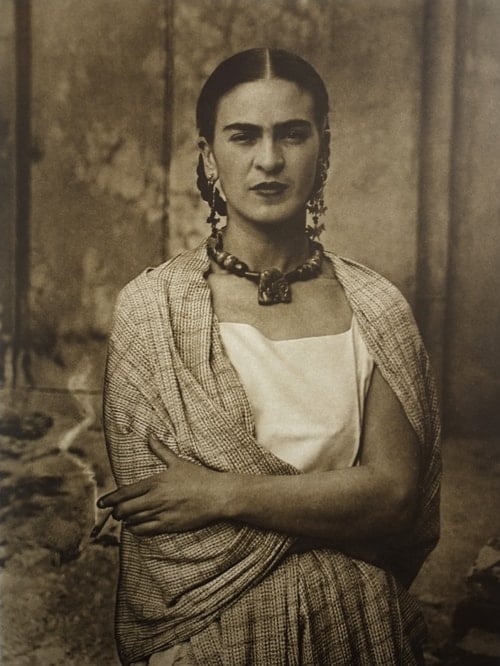

By Shira Wolfe
“I never painted dreams. I painted my own reality. The only thing I know is that I paint because I need to, and I paint whatever passes through my head without any other consideration.” Frida Kahlo
Who is Frida Kahlo?
Our “Female Iconoclasts” series highlights some of the most boundary-breaking works of our time, crafted by women who defied conventions in contemporary art and society in order to pursue their passion and contribute their unique vision to the world. This week, we focus on Frida Kahlo, one of the greatest artistic icons ever to have lived, whose life has become just as iconic as her body of work. Her art was deeply personal and political, reflecting her own turbulent personal life, her physical ailments, her relationship with the great muralist Diego Rivera , and the Mexico she so loved and fought for. Since the 1970s she has grown into a feminist icon and the past decade has seen her persona and art become co-opted by pop culture.
During her lifetime she was called a ‘surrealist’ by André Breton, and a ‘realist’ by her husband Diego Rivera. Kahlo, however, eschewed labels; in fact, one of the most famous quotes by the artist reads: “I paint my own reality. The only thing I know is that I paint because I need to, and I paint whatever passes through my head without any other consideration.”
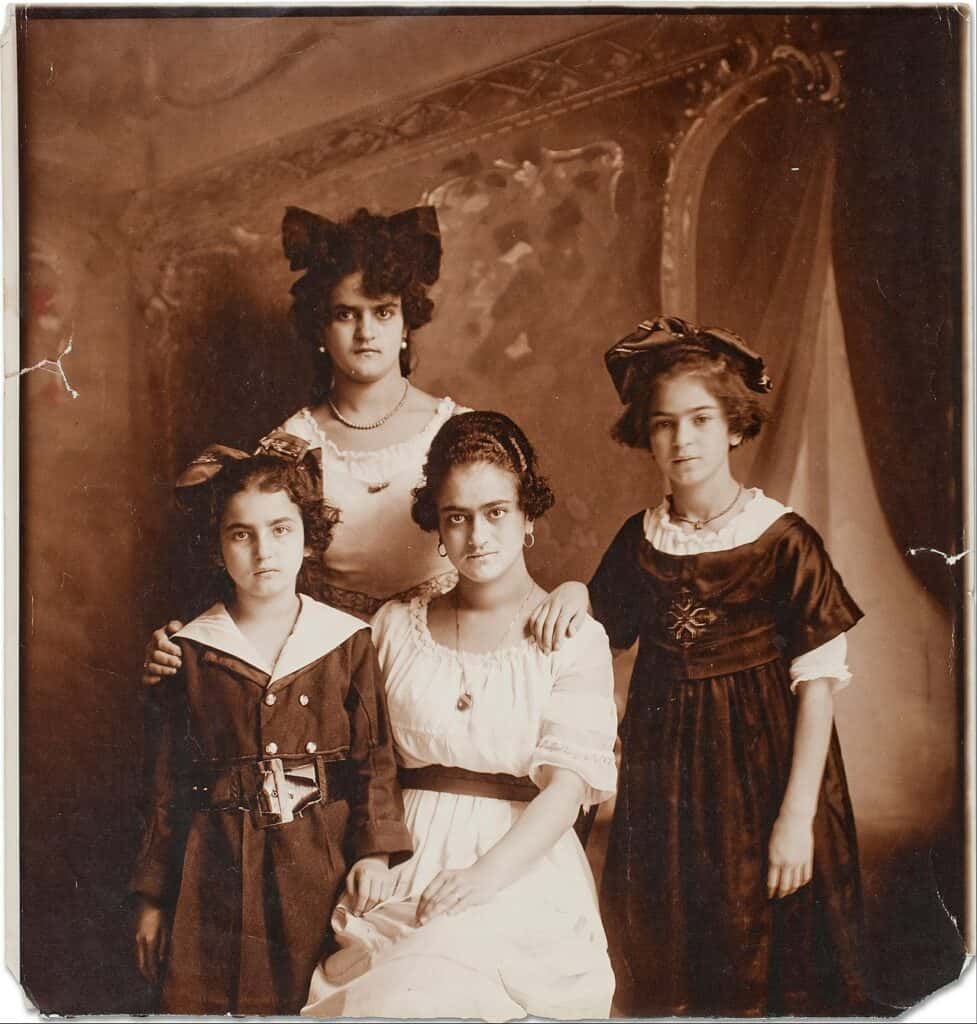
Biography of Frida Kahlo
Frida Kahlo was born as Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo Calderón on 6 July 1907 in the Casa Azul, her family home in the Mexico City municipality Coyoacán.
The Family of Frida Kahlo
Frida Kahlo’s father, Wilhelm (Guillermo) Kahlo, was a photographer of German-Jewish descent who had immigrated to Mexico. Her mother was the Mexican Matilde Calderón. Frida had three sisters, Matilde, Adriana, and Cristina.
The Early Life of Frida Kahlo
Frida’s early life was marked by severe health issues. At the age of 6, she contracted polio, causing her right leg to remain slightly shorter than the left one. At 18, she suffered a tragic accident that would haunt her for the rest of her life: a streetcar crashed into the bus she was travelling in, and she was terribly injured: she was impaled by the metal bannister, fractured many bones, suffered severe damage to her spinal cord, and dislocated her shoulder and foot. During the hard recuperation period, she lay practically immobilized in her bed and took up painting. Her mother had an easel built that allowed her to paint while lying in bed and mounted a mirror above her bed so she could paint herself.
For Frida, painting became a mode of survival and self-expression, which helped her to cope with her tortuous chronic pain, prolonged periods of bed rest and physical fragility that frustrated the enigmatic woman with such a lust for life. Throughout her life, Frida underwent several intense operations in order to attempt to improve the quality of her life following the accident. These operations were followed by long convalescences and had serious consequences, including having to wear corsets to correct her posture and suffering three miscarriages.
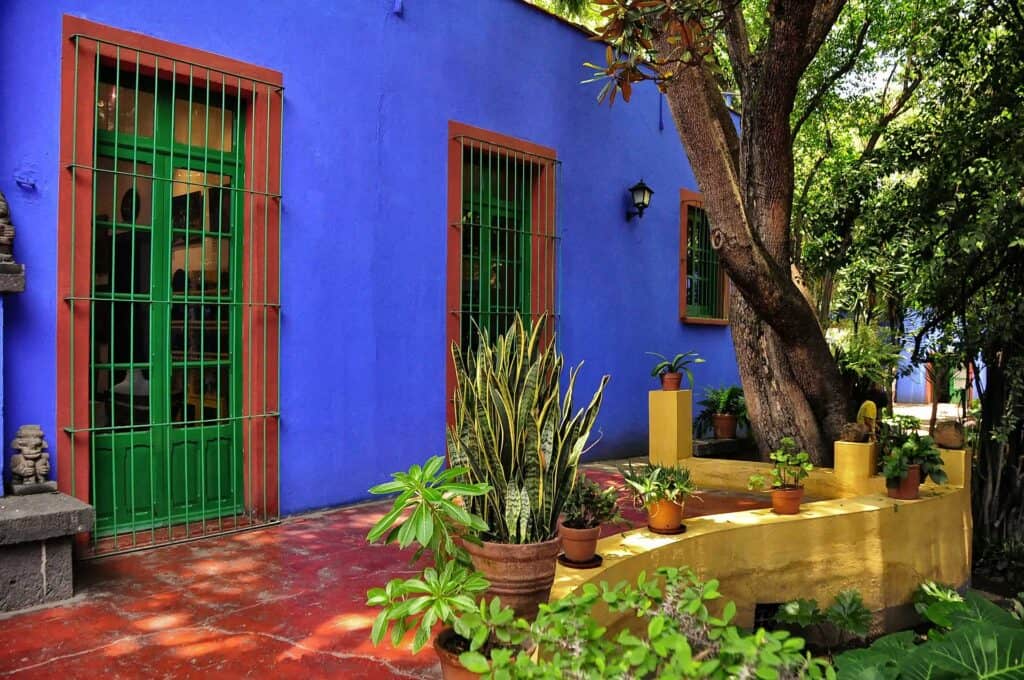

The Relationship with Diego Rivera
The other event that shook Frida’s life to the core was her meeting and forming a relationship with renowned artist Diego Rivera. Diego was a huge supporter of her art and started frequenting the Casa Azul. The couple married in 1929, when Rivera was 43 years old, and Frida just 22. Their marriage was described by Frida’s mother as “the wedding between an elephant and a dove.” The love between Frida and Diego was strong and passionate, yet their relationship was also volatile and tumultuous, with many affairs on both sides shaking things up. On an artistic level, they supported each other unconditionally and each considered the other to be the greatest living Mexican painter. They also shared a passion for politics and the revolutionary ideals of the time. Both were affiliated with the Communist Party of Mexico, and they even took in the Russian dissident Leon Trotsky for two years, between 1937 and 1939, who was being persecuted by Stalin. The couple resided in different intervals at the Casa Azul, at Diego’s studio in San Ángel, in Cuernavaca, and in various cities in the United States. Frida and Diego spent three years in the United States from 1930 to 1933, living in New York, Detroit and San Francisco.
Following deep emotional crises as a result of Diego’s many infidelities, Frida divorced him in 1939, only to remarry him one year later with a mutual agreement that they would lead autonomous sex lives.
How Frida Kahlo Died
Toward the end of her life, Frida’s health deteriorated and she was confined to the Hospital Inglés from 1950 to 1951. Her right leg was amputated in 1953, due to a threat of gangrene, and Frida died at the Casa Azul on 13 July 1954. The National Institute of Fine Arts was just in the process of preparing a retrospective exhibition as a national tribute to her. Following her wishes, the Casa Azul was turned into a museum several years after her death, and it remains one of the most important spaces in Mexico, filled with her being and her objects.
“ I paint self-portraits because I am the person I know best. I paint my own reality. The only thing I know is that I paint because I need to and I paint whatever passes through my head without any consideration .” Frida Kahlo

Themes, styles and approach
Frida Kahlo found a way to express herself and survive the difficult episodes in her life through art. She was determined to paint her own reality, and two-thirds of her paintings are self-portraits, revealing her keen interest in exploring her own being and identity in depth. She once said: “I paint self-portraits because I am the person I know best. I paint my own reality. The only thing I know is that I paint because I need to and I paint whatever passes through my head without any consideration.” Her self-portraits are beautiful and honest, showing images of herself with her signature moustache and unibrow, and in moments of suffering and pain, as such boldly defying conventional beauty norms.
At the same time, Frida was interested in reclaiming the roots of Mexican folk art and culture through her daily life and her art. She dressed in indigenous Mexican attire and avidly collected Mexican folk art. All these influences were reflected in her painting. Although the Surrealists tried to claim her as one of their own and Frida was interested in their work, she preferred to avoid any labels when it came to her art. For her, the surrealist images in her paintings were actually her reality. She never painted her dreams, but painted what was happening to her and passing through her mind at that very moment.
The Most Famous Art by Frida Kahlo
The two fridas.

Frida painted The Two Fridas in 1939, the year she divorced Diego Rivera. The painting shows two Frida Kahlos sitting side by side. Both their hearts are revealed, and they are distinguished from one another through their clothing. The one on the left wears a traditional Tehuana costume and her heart is torn open; the one on the right wears a more modern outfit. The main artery leading from the torn open heart of the traditional Frida connects to the modern Frida’s heart, wraps around her arm, and is cut off with a pair of scissors by the traditional Frida. The modern Frida holds a pendant with a portrait of a young Diego Rivera. This powerful painting shows two sides of Frida Kahlo, suffering from heartache while also remembering the good aspects of her love for Diego.
Diego on My Mind (Self-Portrait as a Tehuana)

Frida started painting Diego on My Mind (Self-Portrait as a Tehuana) in 1940 when the couple were still divorced, and finished it in 1943, at which point they had reconciled. The painting shows Frida wearing a traditional Tehuana costume, with the face of Diego as a third eye in her forehead. The painting shows how she cannot stop thinking about him, despite his betrayals and their separation.
The Broken Column

The Broken Column is a painting from 1944. It depicts Frida after spinal surgery, bound and constrained by a cage-like body brace. She is missing flesh, and a broken column is exposed where her spine should be. Metal nails pierce Frida’s face, breasts, arms, torso and upper thigh, and tears are streaming down her face. This is one of her most brutally revealing self-portraits where she deals with her physical suffering.
The Wounded Deer

The Wounded Deer is a 1946 painting, which Frida painted following another spinal operation in New York that same year. We see Frida as a young deer in the forest, fatally wounded by several arrows. She had hoped that the New York surgery would free her from her severe physical pain, but it failed, and this painting expresses her disappointment following the procedure.
Where to Find Frida Kahlo’s Work
During her lifetime, Frida held several exhibitions internationally: at the Julien Levy Gallery in New York, at the Renou et Colle Gallery in Paris, and at the Lola Álvarez Bravo Gallery in Mexico. She also participated in the Group Surrealist Show at the Mexican Art Gallery. In 1939, The Louvre acquired her painting The Frame (1938). Today, Frida Kahlo’s paintings can be found in numerous private collections in Mexico, the United States, and Europe. A current exhibition at the Cobra Museum in Amstelveen, the Netherlands, brought together an impressive selection of works by Frida Kahlo, Diego Rivera and several other Mexican contemporaries of theirs. But by far the most moving experience is to experience the full essence of Frida Kahlo in her Casa Azul in Mexico City, which is still left almost exactly in the same condition as when Frida herself lived there. Several of her and Diego Rivera’s paintings are on display there, as well as the Mexican folk art that they collected, and the many objects that were important to Frida.
Frequently Asked Questions
Frida Kahlo was born in Casa Azul, her family home in the Mexico City Coyoacán.
Frida Kahlo died at an age of 47.
Relevant sources to learn more
The excellent exhibition “Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera: A Love Revolution” is on show at the Cobra Museum of Modern Art in Amstelveen, the Netherlands through 26 September 2021
Discover the art of María Izquierdo, a contemporary of Kahlo and Rivera who was far less known but also made an important contribution to Mexican art
Read more about Art Movements and Styles Throughout History here
You may also like: The Fantastic Women of Surrealism

My painting carries with it the message of pain.
- Frida Kahlo
Frida Kahlo and her paintings

Mexican artist Frida Kahlo is remembered for her self-portraits, pain and passion, and bold, vibrant colors. She is celebrated in Mexico for her attention to Mexican and indigenous culture and by feminists for her depiction of the female experience and form.
Kahlo, who suffered from polio as a child, nearly died in a bus accident as a teenager. She suffered multiple fractures of her spine, collarbone and ribs, a shattered pelvis, broken foot and a dislocated shoulder. She began to focus heavily on painting while recovering in a body cast. In her lifetime, she had 30 operations.
Life experience is a common theme in Kahlo's approximately 200 paintings, sketches and drawings. Her physical and emotional pain are depicted starkly on canvases, as is her turbulent relationship with her husband, fellow artist Diego Rivera , who she married twice. Of her 143 paintings, 55 are self-portraits.
The devastation to her body from the bus accident is shown in stark detail in The Broken Column . Kahlo is depicted nearly naked, split down the middle, with her spine presented as a broken decorative column. Her skin is dotted with nails. She is also fitted with a surgical brace.
Kahlo's first self-portrait was Self-Portrait in a Velvet Dress in 1926. It was painted in the style of 19th Century Mexican portrait painters who themselves were greatly influenced by the European Renaissance masters. She also sometimes drew from the Mexican painters in her use of a background of tied-back drapes. Self-Portrait - Time Flies (1929), Portrait of a Woman in White (1930) and Self-Portrait Dedicated to Leon Trotsky (1937) all bear this background.
I paint self-portraits because I am so often alone, because I am the person I know best." - Frida Kahlo
In her second-self portrait, "Time Flies," Kahlo uses a folk style and vibrant colors. She wears peasant clothing, and the red, white and green in the painting are the colors of the Mexican flag.
During her life, self portrait is a subject that Frida Kahlo always returns to, as artists have always returned to their beloved themes - Rembrandt his Self Portrait , Vincent van Gogh his Sunflowers , and Claude Monet his Water Lilies .
Frida and Diego: Love and Pain
Kahlo and Rivera had a tumultuous relationship, marked by multiple affairs on both sides. Self-Portrait With Cropped Hair (1940), Kahlo is depicted in a man's suit, holding a pair of scissors, with her fallen hair around the chair in which she sits. This represents the times she would cut the hair Rivera loved when he had affairs.
The 1937 painting Memory, the Heart , shows Kahlo's pain over her husband's affair with her younger sister Christina. A large broken heart at her feet shows the intensity of Kahlo's anguish. Frida Kahlo and Diego Rivera divorced in 1939, but reunited a year later and remarried. The Two Fridas (1939) depicts Kahlo twice, shortly after the divorce. One Frida wears a costume from the Tehuana region of Mexico, representing the Frida that Diego loved. The other Frida wears a European dress as the woman who Diego betrayed and rejected. Later, she is back in Tehuana dress in Self-Portrait as a Tehuana (1943) and Self Portrait (1948).
Pre-Columbian artifacts were common both in the Kahlo/Rivera home (Diego collected sculptures and idols, and Frida collected Jewelry) and in Kahlo's paintings. She wore jewelry from this period in Self-Portrait - Time Flies (1926), Self-Portrait With Monkey (1938) and Self-Portrait With Braid (1941), among others. Other Pre-Columbian artifacts are found in The Four Inhabitants of Mexico City (1938), Girl With Death Mask (1938) and Self-Portrait With Small Monkeys (1945).
My painting carries with it the message of pain." - Frida Kahlo
Surreal or Realist?
Frida Kahlo participated in the "International Exhibition of Surrealism" in 1940 at the Galeria de Arte, Mexicano. There, she exhibited her two largest paintings: The Two Fridas and The Wounded Table (1940). Surrealist Andrew Breton considered Kahlo a surrealistic, a label Kahlo rejected, saying she just painted her reality. However, In 1945, when Don Jose Domingo Lavin asked Frida Kahlo to read the book Moses and Monotheism by Sigmund Freud - whose psychoanalysis works Surrealism is based on - and paint her understanding and interpretation of this book. Frida Kahlo painted Moses , and this painting was recognized as second prize at the annual art exhibition in the Palacio de Bellas Artes.
Kahlo did not sell many paintings in her lifetime, although she painted occasional portraits on commission. She had only one solo exhibition in Mexico in her lifetime, in 1953, just a year before her death at the age of 47.
Today, her works sell for very high prices. In May 2006, Frida Kahlo self-portrait, Roots , was sold for $5.62 million at a Sotheby's auction in New York, sets a record as the most expensive Latin American work ever purchased at auction, and also makes Frida Kahlo one of the highest-selling woman in art.
Widely known for her Marxist leanings, Frida, along with Marxism Revolutionary Che Guevara and a small band of contemporary figures, has become a countercultural symbol of the 20th century, and created a legacy in art history that continues to inspire the imagination and mind. Born in 1907, dead at 47, Frida Kahlo achieved celebrity even in her brief lifetime that extended far beyond Mexico's borders, although nothing like the cult status that would eventually make her the mother of the selfie, her indelible image recognizable everywhere.
At the Frida Kahlo Museum in Mexico City, her personal belongings are on display throughout the house, as if she still lived there. Kahlo was born and grew up in this building, whose cobalt walls gave way to the nickname of the Blue House. She lived there with her husband for some years, and she died there. The facility is the most popular museum in the Coyoacan neighborhood and among the most visited in Mexico City.
The Two Fridas
Self-portrait with thorn necklace & hummingbird, viva la vida, watermelons, the wounded deer, self portrait with monkeys, without hope, me and my parrots, what the water gave me, frida and diego rivera, the wounded table, diego and i, my dress hangs there, my grandparents, my parents, and me, self portrait as a tehuana, fulang chang and i.

COMMENTS
Learn about the life and work of Frida Kahlo, a Mexican painter known for her self-portraits and Surrealist style. Explore her early years, bus accident, marriage to Diego Rivera, and notable paintings such as Self-Portrait Wearing a Velvet Dress and The Two Fridas.
Who Was Frida Kahlo? Artist Frida Kahlo was considered one of Mexico's greatest artists who began painting mostly self-portraits after she was severely injured in a bus accident.
Learn about Frida Kahlo, one of Mexico's greatest artists, who painted her own life, emotions, and experiences. Discover her tragic accident, her turbulent marriage, her surreal style, and her impact on the art world.
Learn about the life and work of Frida Kahlo, a Mexican painter known for her self-portraits, surrealism, and folk art. Explore her biography, artistic career, and legacy as a symbol of Mexican and Indigenous culture and feminism.
Learn about the life and work of Frida Kahlo, a Mexican painter known for her self-portraits and folk art influences. Find out about her marriage to Diego Rivera, her surreal style, and her legacy.
Explore the life and art of Frida Kahlo, a Mexican painter who used self-portraits to express her identity, pain, and politics. See examples of her surrealist and magic realist style, and learn about her influences, themes, and legacy.
Frida Kahlo's marriage to Diego Rivera Frida and Diego married in 1929. She was 22 years old and he was 42. Frida met muralist Diego Rivera in 1922, when he was painting a mural at the National Preparatory School she attended.However, their romantic relationship only began in 1928 when they were introduced by communist activists Julio Antonio Mella and Tina Modotti.
Learn about the life and work of Frida Kahlo, one of Mexico's most celebrated and well-known artists, renowned for her surrealistic paintings and self-portraits. See her timeline, exhibitions, and awards, including her nomination for six Academy Awards for the movie Frida.
Learn about the life and work of Frida Kahlo, one of the greatest artistic icons ever to have lived, whose art was deeply personal and political. Explore her self-portraits, themes, styles and approach, and her relationship with Diego Rivera.
Mexican artist Frida Kahlo is remembered for her self-portraits, pain and passion, and bold, vibrant colors. She is celebrated in Mexico for her attention to Mexican and indigenous culture and by feminists for her depiction of the female experience and form.