Sales | How To

How to Create a Sales Plan in 10 Steps (+ Free Template)
Published March 9, 2023
Published Mar 9, 2023
REVIEWED BY: Jess Pingrey
WRITTEN BY: Jillian Ilao
This article is part of a larger series on Sales Management .
- 1 Establish Your Mission Statement
- 2 Set Sales Goals & Objectives
- 3 Determine Your Ideal Customer
- 4 Set Your Sales Budget
- 5 Develop Sales Strategies & Tactics
- 6 Implement Sales Tools
- 7 Develop Your Sales Funnel
- 8 Create Your Sales Pipeline
- 9 Assign Roles & Responsibilities
- 10 Monitor Progress & Adjust Accordingly
- 11 Examples of Other Free Small Business Sales Plan Templates
- 12 Sales Planning Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 13 Bottom Line
Sales plans enable businesses to set measurable goals, identify resources, budget for sales activities, forecast sales, and monitor business progress. These all contribute to guiding the sales team toward the company’s overall strategy and goals. In this article, we explore how to create a sales plan, including details on creating an action plan for sales, understanding the purpose of your business, and identifying your ideal customers.
What Is a Sales Plan? A sales plan outlines the strategies, objectives, tools, processes, and metrics to hit your business’ sales goals. It entails establishing your mission statement, setting goals and objectives, determining your ideal customer, and developing your sales strategy and sales funnel. To effectively execute your sales plan, assign roles and responsibilities within your sales team and have metrics to measure your outcomes versus your goals and objectives.
Ten steps to creating an effective sales plan
Download and customize our free sales planning template and follow our steps to learn how to create a sales plan to reach your company’s revenue goals.
FILE TO DOWNLOAD OR INTEGRATE
Free Sales Plan Template

Thank you for downloading!
💡 Quick Tip:
Once you’ve created a sales plan, give your sales team the tools to execute it effectively with robust customer relationship management (CRM) software.
Use a CRM like HubSpot CRM to help your sales team collaborate on deals, develop sales reports, track deals, and create custom sales dashboards
1. Establish Your Mission Statement
A mission statement summarizing why you’re in business should be part of your action plan for sales. It should include a broad overview of your business’ products or services and your brand’s unique selling proposition. For example, you wouldn’t say, “We provide customers with insurance policies.” Instead, you might frame it as “We provide customers with cost-effective financial risk management solutions.”
It’s essential to fully understand your unique selling proposition before creating a mission statement. This allows you to learn why you’re different from competitors in your industry. It also helps you determine how your unique proposition suits a niche market better.
Steps on how to create a unique selling proposition
For instance, using the same insurance example above, you may realize specific markets are easier to sell based on that selling proposition. Therefore, it’s a good idea to narrow in on your mission statement by saying, “We provide startup businesses with cost-effective risk management solutions.”
2. Set Sales Goals & Objectives
Once you have summarized why you’re in business in a mission statement, begin setting sales goals . Typically, business goals will include one year, but may also include three- or five-year projections.
Steps on how to set sales goals
Here are a few options for how to set sales revenue goals for your business:
- Set sales amount: You may have a specific amount in mind for a sales goal. For instance, you may determine that $200,000 is a reasonable sales goal based on prior sales and your company’s ability to generate new business.
- Desired profitability: First, calculate the total anticipated expenses for the set time period to find the break-even point. From there, you can calculate how much revenue your team needs to bring in to make a certain profit margin. For example, if annual operating costs are expected to be $100,000, and you want to make a 30% profit, your sales goal is $130,000.
- Projected sales forecast: Based on an industry-standard or estimates you attained by running a sales forecast, you may find it’s better to use a projected sales forecast as your sales goal.
Pro tip: Projecting sales can be challenging without a suitable sales forecasting model. Our free sales forecast templates help you create simple, long-term, budget-based, multi-product, subscription-based, and month-to-month business sales forecasts. Some customer relationship managers (CRMs) like Freshsales have sales goal-tracking functionalities that allow you to set and assign sales goals for your team.
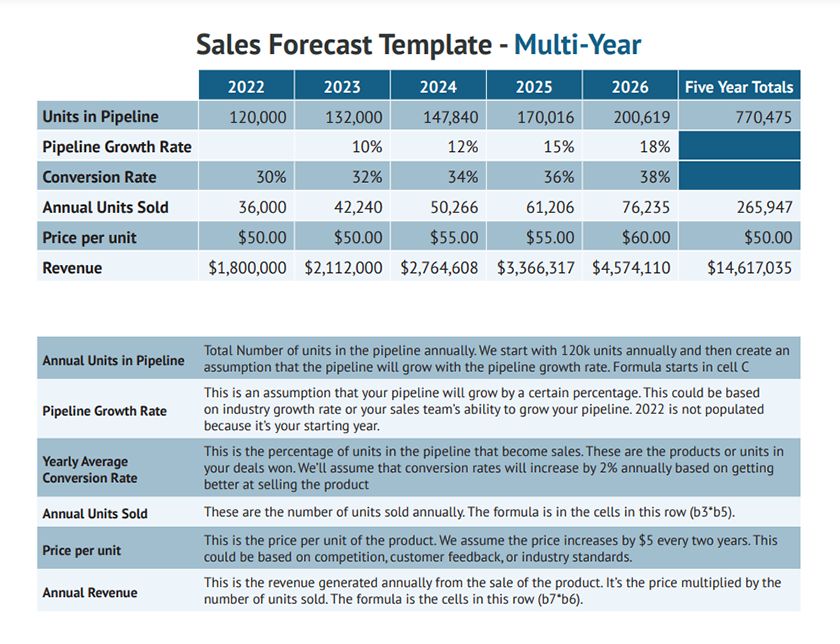
Five-year sales forecast template example (Source: Fit Small Business )
Sales goal tracking in Freshsales (Source: Freshsales )
Sales goals must reflect new business revenue and sales from existing or recurring customers. Then, you must add specific sales objectives that identify and prioritize the sales activities your team needs to complete to meet sales goals. This creates an objective way to measure success in hitting goals at all levels: organizational, sales department, team, and individual sales rep, which is an essential part of sales management .
For example, imagine your total revenue goal is $200,000 in year two and $300,000 in year three. You then add an objective, such as stating you want your business’ revenue from existing customers to grow 15% in year three. This can be measured by evaluating your percentage of revenue from existing customers in year three compared to year two.
3. Determine Your Ideal Customer
Determining the ideal customer or target market is the next step of your business plan for sales reps. It may have been accomplished when you developed your mission statement, but also when you set your sales goals and discovered how broad your market needs to be to reach them. Describing your ideal customer helps dictate who you’re selling to and your selling approach.
One way to establish your ideal customer is by creating a series of unique customer profiles . Each profile specifies key demographics, behaviors, interests, job positions, and geographic information about one of your ideal buyer types. Based on your customer profiles, you can then develop more targeted marketing strategies for lead generation and nurturing to move leads through the sales process more efficiently and close more deals.
Pro tip: Making a customer persona can be challenging, especially if it is based on the wrong data or if you just focus on the demographics. Check out our article on creating a customer persona to help you define your company’s ideal buyer types and guide your lead generation and marketing activities.
4. Set Your Sales Budget
After establishing your objectives and identifying your ideal customer personas—and before developing your actual strategies and tactics—you must identify a sales budget to work with. It should include estimated expenses for salaries, travel expenses, and the cost of any software tools or service providers used to help with sales and marketing. While these are meant to be estimates, research and due diligence should be done to avoid financial errors.
One way to set your sales budget, particularly for software tools and services you may be interested in, is to create and issue a request for proposal (RFP). Issuing an RFP allows you to post a summary of your needs to solicit proposals on potential solutions. In addition to providing accurate budget estimates from various qualified vendors and contractors, it may also help you discover cost-effective or high-performing options you were previously unaware of.
5. Develop Sales Strategies & Tactics
A sales strategy explains how you plan to outsell your competitors and accomplish your sales goals. It defines specific, detailed tactics your team will use to pursue your sales goals. These may involve using Google Ads, cold calling, and drip email marketing campaigns as part of a lead generation strategy. Available strategies differ depending on your company’s resources, skill sets, sales operation, and product or service offerings.
Strategies and tactics should be personalized for your ideal customers based on their unique interests, behaviors, and the best ways to connect with them. For example, some customer profiles show your ideal buyer generally only makes purchases based on trusted referrals. In this case, you could implement a referral strategy that provides incentives to generate more customer referrals .
Plus, different sales strategies will be needed to acquire new business vs keeping existing customers. When selling to existing customers, for example, your strategy could include cross-selling tactics where additional products are recommended based on prior purchases. The short-term cross-selling tactics could require customer service reps to send 30 emails per week recommending a complementary product to existing customers.
For a new business strategy, sales reps might rely on emotional selling methods when using cold calling as a tactic. Instead of product features, cold calling scripts would be geared to evoke feelings that lead to buying decisions. Tactics could reflect the objective of having reps make 15 cold calls each week. They could use a script that opens with a story about how a purchase made a customer feel or how someone felt because they didn’t purchase the product.
Pro tip: Ensuring your strategies are properly executed requires excellent sales leadership and a healthy environment for sales reps to operate in. Our how-to guide for building a positive sales culture shows you how to create an environment that promotes high job satisfaction, low employee turnover, and profitability.
6. Implement Sales Tools
Your sales strategy template should reference the software, hardware, and materials you use to manage the sales operation and make each team member more efficient. One of the most notable tools to include is the customer relationship management (CRM) system . It allows your team to organize contact information, streamline sales tasks, and facilitate communication with customers and leads.
HubSpot CRM , for instance, makes it easy to organize information about leads, contacts, and deal opportunities. Additionally, from a HubSpot CRM lead profile, you can initiate a conversation with that contact by calling, emailing, or scheduling an appointment.
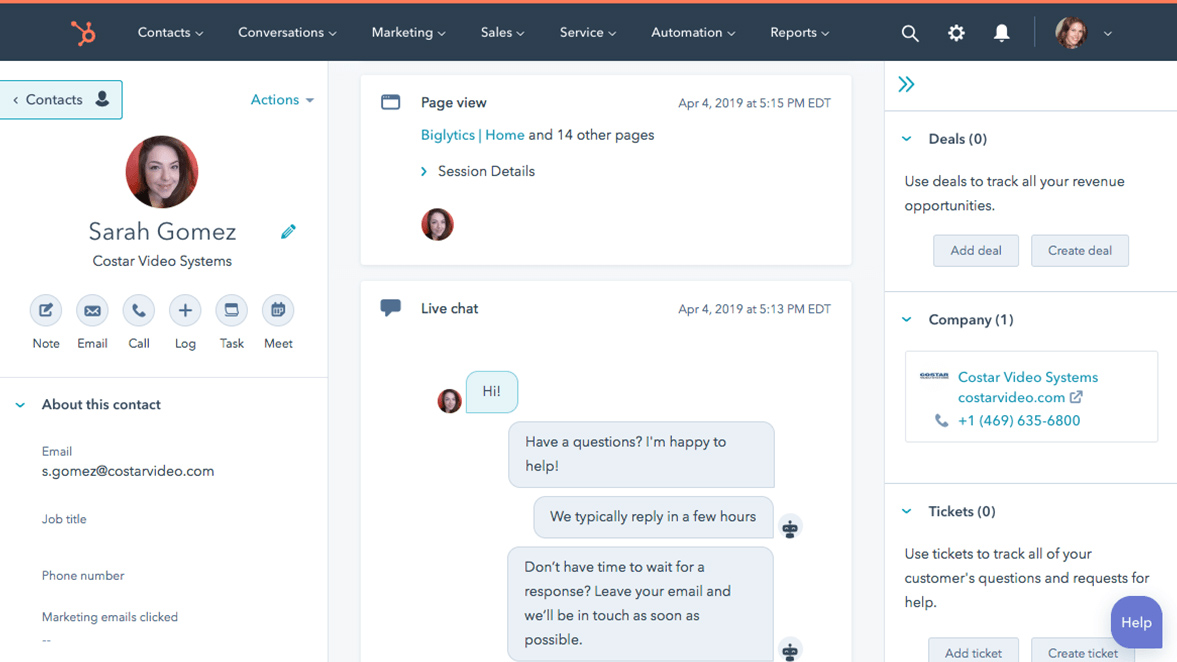
HubSpot CRM contact profile (Source: HubSpot )
CRMs are also used to monitor and report sales progress. For example, many have dashboards and functionality, such as alerts, which make it easy to identify where your team may be underperforming. These could also tell you which leads are most likely to convert and should be focused on. Sales information such as deals closed, revenue generated, and leads created can be presented in a detailed report .
These types of insights can also be shown on the CRM’s system dashboard . Pipedrive is an example of a CRM that has a customizable dashboard that displays both activity information and performance-based data. Activity data include emails sent, received, and outstanding tasks to be completed. Performance-based data, on the other hand, have deals lost or the average value of won deals.
Pipedrive’s customizable dashboard (Source: Pipedrive )
Other sales enablement tools can make your sales team more effective. These include voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone systems , lead generation platforms, email campaign tools, content creation platforms, and task automation software. These tools can be found within CRM software or through CRM integrations and standalone applications.
In addition to technology tools, sales and marketing templates should be used to streamline outreach initiatives. Scenario-based, premade sales email templates , for instance, allow salespeople to have an email already crafted for their specific situation.
Creating and storing business proposal templates in your CRM also streamlines the contact procurement and business proposal generation process . This way, whenever a prospect says they’d like to receive a quote or you’re responding to a request for a proposal, you already have a customizable template ready to go.
Pro tip: Effective cold calling scripts sales reps can use as a guide when placing calls to new leads is a tremendous sales tool to include in your action plan for sales. Get started using our guide for writing a cold calling script , which includes examples and free templates.
7. Develop Your Sales Funnel
Setting up a sales funnel within your sales strategy template lets you visualize the stages of the customer journey, from becoming aware of your business to buying from it. By creating and understanding the different statuses of your leads, you can track progress and determine how effective you are at converting leads to the next stages in the funnel.
Using a sales funnel with conversion rates also makes it easier for you to adjust your sales strategies and tactics based on how effectively you’re getting leads through the funnel. For instance, let’s say you have 100 leads in the awareness stage of the funnel. You decide to cold call 50 of them and write a sales email to the other 50 to qualify leads by setting up a product demonstration.
After each campaign, you find you were able to qualify seven of the leads that were cold-called and only two of the leads you had emailed. Based on these funnel conversion rates of 14% (7/50) from cold calling and 4% (2/50) from emailing, you would likely adjust your tactics to focus more on calling instead of emailing.
Do you need help creating a sales funnel for your business? Our guide to creating a sales funnel explains the step-by-step sales funnel creation process and provides free templates and specific examples.
8. Create Your Sales Pipeline
Once your sales process’ sales funnel stages are identified, develop the sales pipeline stages . These stages include your team’s sales activities to move leads through the funnel. For example, you need to get a lead from the sales funnel stage of brand awareness to show interest in learning more about one of your services. To do this, you could add a sales pipeline activity like setting up a demo or presentation appointment through a cold call.
Adding your sales pipeline to your sales strategy is essential because it describes all the activities your sales reps need to do to close a sales deal. CRM systems like Freshsales allow you to create and track the pipeline stages for each lead or deal within the lead record.
Funnel view of Freshsales’ deal pipeline (Source: Freshsales )
Listing each pipeline stage also helps you identify tools and resources needed to perform the activities for each stage. For example, if you use phone calls to initiate contact with or introduce a product to a lead, you could develop outbound sales call scripts for your team.
After the initial contact by phone, you may use email to follow up after a call and then nurture leads throughout the sales process. As part of your follow-up, create and automate a sales follow-up email template to get them to the next pipeline stage.
The sales funnel shows where a lead is in the sales process. The sales pipeline, on the other hand, lists activities needed to drive leads to the next stage in the sales funnel. Both should be used in your sales strategy when defining the repeatable steps required to generate leads and close deals. Check out our article to learn how to create a winning sales process with insights on both creating a sales process and measuring its success.
9. Assign Roles & Responsibilities
Regardless of the size of your business or sales operation, your business plan for sales reps should include the role and responsibility of each person in the sales team. Each role should have a name, such as someone being a sales development representative (SDR). There should also be a summary of their responsibilities, such as “the SDR is responsible for setting up sales appointments using the activities listed in the sales pipeline.”
Measuring the performance of any sales position is simple through key performance indicators (KPIs). Specific KPIs should be used to measure performance for each role and should be included in your plan. Below are some examples of KPIs that can be used by the members of the sales team and their respective responsibility:
- Sales development representative: Responsible for introducing products and services, qualifying leads, and setting up appointments for the account executive. Performance is measured by calls placed, emails sent, and appointments generated.
- Account executive: Responsible for nurturing qualified leads, delivering the sales pitch , sending quotes, and closing deals. Performance is measured by business proposals sent, the average time in the proposal consideration stage, deals closed, and deal closing rate.
- Customer service representative: Responsible for managing customer needs, handling billing, and managing service tickets by assisting customers. Performance is measured by customer satisfaction, retention rates, and total tickets resolved.
- Sales manager: Responsible for the entire sales operation or team for a specific region or product/service line. Performance is measured by job satisfaction rates of sales reps, pipeline and funnel conversion rates, team sales deals closed, and team revenue growth.
While assigning roles in your plan, a sales rep’s territory could be based on geography, industry, potential deal size, or product/service line, creating more specialization for better results. Our six-step process on proper sales territory management is an excellent resource for segmenting, creating, and assigning sales territories.
This section of the business plan is also a prime spot for individually setting sales quotas for each rep or team needed to hit your organizational sales goals. Sales quotas should be a specific KPI for that sales role and be set based on the experience, skill level, and resources of that individual or team. These quotas should also be based on your organizational, department, and team goals and objectives.
10. Monitor Progress & Adjust Accordingly
Once the strategic business plan is in motion, monitor its progress to make any required adjustments. For instance, while your sales operation is running, you may find certain sales tactics are working better than expected, and vice versa. Your sales goal template should account for using that tactic more, as well as any new sales tools, budgetary changes, new roles, and possibly even a new sales goal.
As in the earlier example, if you found that cold calling was significantly more effective than emailing, reduce or abandon the email method in favor of cold calling. You could also invest in sales tools especially useful for cold calling, such as power dialing using a voice-over-internet-protocol (VoIP) phone system, or hire additional staff to place calls. All of these will be part of your updated business plan.
Pro tip: Focusing on the big picture by creating, executing, and adjusting a strategic business plan is one of the most critical traits of an effective sales leader. For more insights on what it means to be a sales leader and how to become one, check out our ultimate guide to sales leadership .
Examples of Other Free Small Business Sales Plan Templates
Apart from our free downloadable sales strategy template, other providers have shared their version of a free strategic sales plan examples. Click on our picks below to see if these templates fit your business process better:
HubSpot’s free sales planning template helps users outline their company’s sales strategy. It contains sections found in most sales plans, as well as prompts for you to fill out your company’s tactics and information. These include company history and mission, team structure, target market, tools and software used, positioning, market strategy, action plan, goals, and budget.

HubSpot sales strategy template (Source: HubSpot )

HubSpot’s sales goals template with the mission, vision, and story of the company (Source: HubSpot )
Visit HubSpot
Asana’s free sales plan template helps organizations analyze their current sales process, establish their sales objectives, identify success metrics, and plan actionable steps. The sales business plan template is embedded within Asana’s platform, automatically integrating aspects such as goals and measuring them against results or sales performance.
Asana sales plan example (Source: Asana )
Visit Asana
Sales Planning Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is sales planning.
Sales planning is creating a document that outlines your sales strategy, objectives, target audience, potential obstacles, and tools to achieve goals within a specified period. This may include your daily, monthly, quarterly, yearly, and long-term revenue objectives.
What is included in a sales plan?
A sales strategy plan template typically includes the following key elements:
- Target customers, accounts, or verticals
- Stock-keeping units (SKUs)
- Revenue targets or forecasts
- Strategies and tactics
- Pricing and promotions
- Deadlines and directly responsible individuals (DRIs)
- Team structure and coordination
- Market conditions
What are the different types of strategic sales planning?
The type of strategic planning for sales that you choose for your team ultimately depends on different factors. These include your revenue goals, available resources, the ability and bandwidth of your sales team, and your personal commitment to your plans. Once you have determined the details of these factors, you can choose from these types of strategic sales planning:
- Revenue-based sales action plan template: This is ideal for teams aiming for a specific revenue goal. It focuses on in-depth sales forecasting, improvement of conversion rates, and closing more deals.
- Sales business plan based on the target market: This plan is best for businesses that cater to several markets that are different from each other. In this situation, you must create separate sales goal templates for enterprise companies and small businesses.
- Sales goals plan: This focuses on other goals such as hiring, onboarding, sales training plans, or sales activity implementation.
- New product sales business plan: This plan is developed for the launch and continued promotion of a new product.
Bottom Line
While any business can set bold sales goals, creating a sales plan outlines how your team will achieve them. By following the best practices and 10-step process laid out above, your sales goal template defines what your sales process will look like. It will help establish baselines for accountability and identify optimal strategies, tactics, and the tools needed to make your team as efficient as possible.
About the Author

Jillian Ilao
Jill is a sales and customer service expert at Fit Small Business. Prior to joining the company, she has worked and produced marketing content for various small businesses and entrepreneurs from different markets, including Australia, the United Kingdom, the United States, and Singapore. She has extensive writing experience and has covered topics on business, lifestyle, finance, education, and technology.
Join Fit Small Business
Sign up to receive more well-researched small business articles and topics in your inbox, personalized for you. Select the newsletters you’re interested in below.
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
- How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small Business Resources
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions

Online only.

How to Write a Sales Plan

Table of Contents
Every business needs a business plan as well as more detailed road maps that offer guidance to each department working toward that common goal. As the revenue-generating engine of your company, the sales department should be a top priority for this type of document, aptly named the “sales plan.” This guide introduces the concept of a sales plan and gives you all the guidance you need to create a sales plan that works for your business.
What is a sales plan?
A sales plan details the overall sales strategy of a business, including the revenue objectives of the company and how the sales department will meet those goals. This may also include revenue goals, the target audience and tools the team will use in their day-to-day. In addition, the sales plan should include examples of the hurdles and pain points the team might encounter, as well as contingency plans to overcome them.
“[A sales plan] is essential to support the growth of an organization,” said Bill Santos, vice president of the ITsavvy Advanced Solutions Group. “A sales plan helps individual reps understand the priorities of the business as well as the measurements by which they will be evaluated.”
Business plans vs. sales plans
Business plans and sales plans are closely linked. A sales plan, though, should outline the actions that the sales department will take to achieve the company’s broader goals. A sales plan differs from a business plan, though both work toward the same end.
“A business plan is a ‘what’ [and] a sales plan is a ‘how,'” said James R. Bailey , professor of management and Hochberg Professional Fellow of Leadership Development at the George Washington University School of Business. “Business plans are where a firm wants to go. A sales plan is a part of how they can achieve that. A business plan is direction; a sales plan is execution.”
For example, a software company that developed a new mobile application might state in its business plan that the app will be installed by 1 million users within a year of launch, while the sales plan describes how that will actually be achieved.
How to write a sales plan
Every sales plan should suit the individual needs of a different company, so they come in all shapes and sizes. There is no one-size-fits-all sales plan; the one you create will be unique to your business. With careful planning, you’ll have a much clearer vision of what you need to accomplish and a road map for how to get there.
Chris Gibbs, vice president of global sales at Centripetal Networks, named some additional items that every sales plan should include.
- Targeted accounts: Assign each salesperson a few key accounts to focus on, and grow from that base.
- Targeted verticals: Sales teams might focus on specific market segments or verticals, such as a particular industry.
- SKUs: Salespeople should emphasize certain SKUs or inventory items rather than get lost in a broad catalog of merchandise to sell.
- Sales and marketing coordination: Sales and marketing teams should work together to create promotions to help generate sales.
- Product road maps: Every company has a road map, and each product should have a road map that shows the plan and direction for a product offering over time to chart out when a product will launch and when it might sunset or be replaced by a newer model.
- Forecasts: Sales forecasting is projecting sales volumes and expectations by comparing them historically to sales of previous years, and then conducting market comparison to determine where sales will fall against the competition.
“Sales plans are extremely important to ensure there is cohesiveness between product teams, sales and marketing,” Gibbs said. “In addition, they’re important for ensuring that timing of new products and/or new version releases coincide with sales objectives and forecasts.”
What are the steps to create a sales plan?
A sales plan is necessary for businesses of every size, from an individual entrepreneur to a Fortune 500 company. When you’re ready to actually write your sales plan, follow these steps:
1. Define the objectives.
Clearly outlining your goals and stating your objectives should always be the first step in creating a sales plan or any other business venture. You should include the expected sales volume and any markets or territories you expect to reach.
For example, let’s say you own a retail store selling household goods and electronics. If your purpose is to establish yourself as a trusted local retailer, ask yourself the following questions:
- If so, are they purchasing anything or just browsing?
- Was it word of mouth?
- Was it through marketing efforts, such as email marketing, direct mail or social media?
- How many are new customers?
- How many are repeat customers?
- Where do you want your sales to come from?
- What are some external and internal factors that could impact your sales? These include industry trends and economic conditions.
When you can precisely state your key objectives, you are setting yourself up to plan later steps around achieving your goals.
2. Assess the current situation.
The next step is to create an honest overview of your business situation in relation to the goal you set in the first step.
Review your strengths and assets. Take a look at your resources and how you can apply them to your goal. This can include personal relationships and competitive advantages like new products or services.
For example, if your goal is to enhance your relationship with your customers, you’d need to ask yourself some questions to examine your current situation:
- What is your current relationship with your customers?
- Where did most of your sales come from?
- Where would you like to expand your sales?
When examining your strengths and opportunities, conduct a SWOT analysis to get a clearer picture of where your business stands.
3. Determine and outline the sales strategies.
Sales strategies are the actual tactics your team will use to reach customers. They can include marketing channels as well as procedures for lead generation and client outreach employed by your salespeople.
Here are two examples of potential sales strategies:
- Use your POS system to retain customer information so you can track current and new customers.
- Employ email marketing, text message marketing , social media, outbound call center services and direct mail marketing campaigns.
4. Define roles for the sales team.
Each member of the sales team should be assigned clear roles, whether they vary from person to person or everyone performs the same functions.
Defining the sales direction of the team is crucial, as it shows the focus of the company and helps the team target and execute sales most effectively.
The plan of attack for the sales team should be communicated clearly by leadership, whether it is from team leaders or the CEO.
5. Inform other departments of sales objectives.
A sales plan shouldn’t just update a company president or C-suite; it should inform the whole organization of the sales team’s objectives.
Clearly outline your plan for the rest of the company to help them understand the goals and procedures of the sales team. Other departments become more efficient when interacting with the sales team and clients. This also conveys a certain level of quality and professionalism to the clients about the company.
6. Provide tools for the sales team.
Provide the tools each member of the sales team needs to achieve the stated goals, such as customer relationship management (CRM) software. The best CRM software is customizable to meet a company’s needs, making it much easier for your team to use the software and work efficiently.
7. Detail how the department will track progress.
Offer strategic direction and insight on how progress will be monitored. Having a quarterly review to assess whether the company is on target is just as important as the plan itself.
Markets change, and so should your sales plan. Keeping it up to date will help you capitalize on the market and achieve your goals. Tracking progress is made easier by the tools you use to collect data. That data will then have to be analyzed and presented in a way which all departments can understand and use for future growth.
Key elements of a sales plan
Every sales plan should also include the following elements.
Realistic goals
You need to set achievable goals . Challenge your sales team, but don’t push too hard. Bailey said that these “deliverables” are among the key points to include in a sales business plan.
“Deliverables need to be as specific as possible and moderately difficult to achieve – specific inasmuch as being measurable in a manner that is uncontested [and] moderately difficult inasmuch as making sales goals too difficult can lead to failure and discouragement.”
Midpoint goals also help build morale and keep the team working toward a larger goal. Instead of having one giant goal, creating smaller goals to achieve along the way will keep your team focused.
Set milestones that give you the opportunity to regularly determine whether you are on track to achieve your sales goals or need to make adjustments.
Sales tools
Tracking sales throughout the term is helpful, and you can employ tools to keep track of each team member as well as the department overall. It also helps establish a culture of accountability among salespeople.
“Tools can help, especially project management and CRM software,” Santos said. “Having a weekly cadence of update and review is also important, as it sends a message that ownership and updates are important.”
Clear expectations and a defined commission structure
Assign goals and responsibilities to each team member to make expectations clear. This is true whether or not each team member has the same goals.
“We meet with each individual to come up with a plan that works for them so that they can reach their goals,” said Leah Adams, director of client success at Point3 Security. “We measure results based on numbers. Each team member has his own plan and how they’re going to get there.”
It’s also necessary to spell out the commission structure in full detail.
“The only real difference is how sales count,” Bailey said. “In petroleum-based products … a few big clients are necessary. Compensation needs to be structured not just in contract value, but in graduated terms: Above $1 million, commissions move from 5% to 9%, and so forth. In smaller-volume enterprises, commissions might be front-loaded with higher percentages early, then graduated down. You have to reward what you want.”
Training programs
Along the way, some training might be necessary to maintain the momentum.
“What’s important to us is that we’re teaching these individuals to be the best salesperson they can be,” Adams said. “We help them do that by constantly training them and giving them knowledge of what’s going on in our industry. Everything stays on track because each member of the team knows their individual goal; though each person has a number, they also know the ultimate goal is for the entire team to hit.”
Adams said that an effective CRM keeps things organized and helps delegate tasks and responsibilities on a schedule that uses the company’s lead information.
Key steps to follow when devising a sales plan
Here are some best practices for creating a sales plan:
- Refer to the business plan. The sales plan should directly address the objectives of the business plan and how those objectives can be achieved.
- Advance clear objectives. The clearer the objectives are, the easier it will be to reach your goals.
- Reference prior sales data. Chart sales over the previous few terms, and project the trend for the current term. New businesses can create sales projections based on expectations.
- Outline the commission structure. This will help motivate your team and help you calculate anticipated costs.
- Be clear about how progress is measured. There should be no dispute about this. If larger clients carry more weight than lower-volume buyers, that should be stated upfront.
The benefits of a sales plan
A sales plan keeps the sales department on track, considering the details of how they must operate to hit their targets and achieve company objectives. Because the sales team is the primary driver of revenue, it is an incredibly important document. [Related article: Adopting a CRM? How to Get Buy-in From Your Sales Department ]
“It’s extremely important to have a sales plan in place, almost a must,” Adams said. “Without this plan, it’s almost impossible to get through the year and hit the company’s sales goals.”
It’s not uncommon to encounter obstacles along the way, however. A good sales plan accounts for that.
“Almost always, you’ll run into the speed bumps along the way, but with a plan in place, it makes it a whole lot easier to navigate through it all,” Adams said. “The sales plan allows you to adjust when necessary so the goal can still be hit. I strongly believe a plan allows you to stay in control and reduce the risk while being able to measure the team’s results along the way to that finish line.”
A solid sales plan helps you deal with unexpected events and acts as a benchmark for where your company is and where you want it to go.
Sales plan templates
Sales templates are helpful in that many of them are based on tried-and-true formats that have been used by businesses across several industries. They can also provide structure so that it is clear to each employee what their role and responsibilities are.
Create your own sales plan by downloading our free template .
“A template helps plan each individual’s daily activities in a structured way,” Adams said. “If you know what each person is doing daily, it’s easier to help correct what’s going wrong. It helps with things like conversion rates, etc. Yes, these templates can be customized in any way a team’s manager sees fit, based on how he believes the team will perform better.”
Sales plans should be unique to the company; however, there are key components they should always include. Because there is somewhat of a formula, you can use a template.
Templates are extremely helpful, Gibbs said. “It creates uniformity for the team, as well as a yearly or quarterly sales plan to present to senior management.”
Gibbs added that templates can easily be customized to meet the needs of a particular business or sales team.
Keeping your team on track with a sales plan
Planning is vital for any business, especially when dealing with sales targets. Before selling your product or service, you must outline your goals and ways to execute them. Essentially, a sales plan enables you to mitigate problems and risks. When there is a clear plan of action, you will know how to proceed in order to attain your goals.
Enid Burns contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
How To Build a Strategic Sales Plan + 10 Examples
- March 28, 2024
Every sales team has some sort of plan, even if it’s just “sell more of the product/service that you’re employed to sell.”
A sales plan is a portfolio that includes a layout of your processes, target audience, objectives and tactics. It’s used to guide your sales strategy and predict cost and returns.
Yet without a codified sales plan, it can be difficult to give a sales team the motivation and purpose they need to successfully engage customers and continue to generate revenue.
Not having a sales plan that’s written down and signed off on by stakeholders can lead to confusion around what sales reps should and shouldn’t be doing , which can be demotivating.
It might seem daunting or time-consuming to put together an entire sales plan, but it doesn’t need to be. Here’s how to create a thorough sales plan in 10 simple steps.
What Is a Sales Plan?
A successful sales plan defines your target customers, business objectives, tactics, obstacles and processes. An effective plan will also include resources and strategies that are used to achieve target goals. It works similarly to a business plan in the way it’s presented, but only focuses on your sales strategy.
A sales plan should include the following three components:
- Ideas: If you use specific business methodologies, you may choose to outline key principles and examples of them in action within your sales plan. An example could be conversation tactics when pitching your product to your target customer.
- Processes: In order to streamline productivity and business strategy, you’ll want to make sure your processes are defined within your sales plan. Your sales team should be able to refer to the sales plan when they’re in need of direction.
- Tools and tactics: The most effective sales plans include not only high-level business strategies, but also step-by-step approaches for your sales team to utilize. These tools can include key conversation pieces for your sales reps to use when pitching a product or content to close out a deal.
Solidifying a sales plan is crucial for a strong business model. Taking the time to narrow in on the components above will set you and your business up for success down the road.
Sales Planning Process
It’s important to keep in mind that sales planning isn’t just about creating a sales plan document. A sales plan should be a go-to item that’s used every day by your team, rather than sitting on your desk collecting dust. Creating an effective sales plan requires high-level strategy.
You should:
- Decide on a timeline for your goals and tactics
- Outline the context
- Write out the company mission and values
- Describe the target audience and product service positioning
- Include sales resources
- Draw out an overview of concurrent activities
- Write an overview of your business road map
- Outline your goals and KPIs
- Outline an action plan
- Create a budget
Below we dive into each of these steps to create your ideal sales plan.
1. Decide on Your Timeline
Setting goals and outlining tactics is not going to be productive if you’re not working toward a date by which you’ll measure your efforts.
Determining the timeline of your sales plan should therefore be your number one consideration. When will you be ready to kick-start your plan, and when is a reasonable time to measure the outcomes of your plan against your SMART goals?
Remember that you need to give the plan a chance to make an impact, so this timeline shouldn’t be too restrictive. However, you also want to make sure that you’re flexible enough to adjust your plan if it’s not producing the desired results.
Most sales plan timelines cover about a year, which may be segmented into four quarters and/or two halves to make it a little more manageable.
2. Outline the Context
Use the first page of your sales plan to outline the context in which the plan was created.
What is the current state of the organization? What are your challenges and pain points? What recent wins have you experienced?
Do you have tighter restrictions on cash flow, or does revenue appear to be growing exponentially? How is your sales team currently performing?
While you’ll discuss your business plan and road map later in the document, you can also outline the long-term vision for your business in this section. For example, where do you want to see the business in five years?
Tip: Comparing the current situation with your vision will emphasize the gap between where you are now and where you need to be.
3. Company Mission and Values
It’s essential that you put your mission and values at the heart of your business. You need to incorporate them into every function – and this includes your sales plan.
Outlining your mission and values in your sales plan ensures that you remember what the company is striving for, and in turn helps ensure that your approach and tactics will support these objectives.
Remember: A strong brand mission and authentic values will help boost customer loyalty, brand reputation and, ultimately, sales.
4. Target Market and Product/Service Positioning
Next, you’ll need to describe the market or markets that you’re operating in.
What is your target market or industry? What research led you to conclude that this was the optimal market for you?
Who within this industry is your ideal customer? What are their characteristics? This could be a job title, geographical location or company size, for example. This information makes up your ideal customer profile .
If you’ve delved further into audience research and developed personas around your target market, then include them in here, too.
5. Sales Team and Resources
This step is simple: Make a list of your sales resources, beginning with a short description of each member of your sales team.
Include their name, job title, length of time at the company and, where appropriate, their salary. What are their strengths? How can they be utilized to help you hit your goals?
You should also include notes around the gaps in your sales team and whether you intend to recruit any new team members into these (or other) roles.
Tip: Communicate the time zones your team members work in to be mindful of designated work hours for scheduling meetings and deadlines.
Then, list your other resources. These could be tools, software or access to other departments such as the marketing team – anything that you intend to use in the execution of your sales plan. This is a quick way to eliminate any tools or resources that you don’t need.
6. Concurrent Activities
The next step in creating your sales plan involves providing an overview of non-sales activities that will be taking place during the implementation of your sales plan.
Any public marketing plans, upcoming product launches, or deals or discounts should be included, as should any relevant events. This will help you plan sales tactics around these activities and ensure that you’re getting the most out of them.
7. Business Road Map
For this step, write up an overview of your business’s overall road map, as well as the areas where sales activities can assist with or accelerate this plan. You’ll need to collaborate with the CEO, managing director or board of directors in order to do this.
In most cases, the business will already have a road map that has been signed off on by stakeholders. It’s the sales manager’s job to develop a sales plan that not only complements this road map, but facilitates its goals.
Tip: Highlight areas of the road map that should be touchpoints for the sales team.
Ask yourself what your department will need to do at each point in the road map to hit these overarching company goals.
8. Sales Goals and KPIs
Another important part of the sales plan involves your sales goals and KPIs.
Outline each goal alongside the KPIs you’ll use to measure it. Include a list of metrics you’ll use to track these KPIs, as well as a deadline for when you project the goal will be achieved.
It’s vital to make these goals tangible and measurable.
A bad example of a goal is as follows:
Goal 1: Increase sales across company’s range of products and services.
A better goal would look something like:
Goal 1: Generate $500,000+ in revenue from new clients through purchases of X product by X date.
9. Action Plan
Now that you’ve laid out your goals, you need to explain how you will hit them.
Your action plan can be set out week by week, month by month, or quarter by quarter. Within each segment, you must list out all of the sales activities and tactics that you will deploy – and the deadlines and touchpoints along the way.
Tip: Organize your action plan by department – sales, business development and finance.
While this is arguably the most complex part of the sales plan, this is where sales leaders are strongest. They know which approach will work best for their team, their company and their market.
Budgets vary from team to team and company to company, but whatever your situation, it’s important to include your budget in your sales plan.
How are you going to account for the money spent on new hires, salaries, tech, tools and travel? Where the budget is tight, what are your priorities going to be, and what needs to be axed?
The budget section should make references back to your action plan and the sales team and resources page in order to explain the expenditures.
6 Strategic Sales Plan Examples
You can create different types of strategic sales plans for your company, depending on how you want to structure your sales plan. Here are a few examples.
Customer Profile
A customer profile outlines your ideal customer for your service or product. It will usually include industry, background, attributes and decision-making factors.
Creating a customer profile helps narrow in on the target customer your sales team should focus on while eliminating unproductive leads.
Buyer’s Guide
A buyer’s guide is an informational sheet that describes your company’s services or products, including benefits and features. This document is useful both for your sales team but also for a potential customer who requires more information on the product before purchasing.
30-60-90-Day Plan
This plan is organized based on time periods. It includes outlines of goals, strategy and actionable steps in 30-day periods. This is a useful sales plan model for a new sales representative tracking progress during their first 90 days in the position or meeting quotas in a 90-day period.
This type of sales plan is also ideal for businesses in periods of expansion or growth. It’s helpful to minimize extra effort in onboarding processes.
Market Expansion Plan
A market expansion plan clarifies target metrics and list of actions when moving into a new territory or market. This sales plan model is typically used with a target market that resides in a new geographical region.
You’ll want to include a profile of target customers, account distribution costs and even time zone differences between your sales representatives.
Marketing-alignment Plan
Creating a marketing-alignment sales plan is useful if your organization has yet to align both your sales and marketing departments. The goal of the sales plan is finalizing your target customer personas and aligning them with your sales pitches and marketing messages.
New Product/Service Plan
If your organization is launching a new service or product, it’s best to create a sales plan to track revenue and other growth metrics from the launch. You’ll want to include sales strategy, competitive analyses and service or product sales positioning.
Sales Plan Template
4 additional sales plan templates.
Here are some additional templates you can use to create your own unique sales plan.
- Template Lab
- ProjectManager
5 Tips for Creating a Sales Plan
Now that you’ve seen and read through a few examples and a sales plan template, we’ll cover some easy but useful tips to create a foolproof sales plan.
- Create a competitive analysis: Research what sales strategies and tactics your close competitors are using. What are they doing well? What are they not doing well? Knowing what they are doing well will help you create a plan that will lead to eventual success.
- Vary your sales plans: First create a base sales plan that includes high-level goals, strategies and tactics. Then go more in depth on KPIs and metrics for each department, whether it’s outbound sales or business development .
- Analyze industry trends: Industry trends and data can easily help strengthen your sales approach. For example, if you’re pitching your sales plan to a stakeholder, use current market trends and statistics to support why you believe your sales strategies will be effective in use.
- Utilize your marketing team: When creating your sales plan, you’ll want to get the marketing department’s input to align your efforts and goals. You should weave marketing messages throughout both your sales plan and pitches.
- Discuss with your sales team: Remember to check in with your sales representatives to understand challenges they may be dealing with and what’s working and not working. You should update the sales plan quarterly based on feedback received from your sales team.
When Should You Implement a Strategic Sales Plan?
Does your organization currently not have a sales plan in place that is used regularly? Are you noticing your organization is in need of structure and lacking productivity across departments? These are definite signs you should create and implement a sales plan.
According to a LinkedIn sales statistic , the top sales tech sellers are using customer relationship management (CRM) tools (50%), sales intelligence (45%) and sales planning (42%) .
Below are a few more indicators that you need an effective sales plan.
To Launch a New Product or Campaign
If you’re planning to launch a new service or product in six months, you should have a concrete marketing and sales strategy plan to guarantee you’ll see both short- and long-term success.
The sales plan process shouldn’t be hasty and rushed. Take the time to go over data and competitor analysis. Work with your team to create objectives and goals that everyone believes in. Your sales plan should be updated formally on a quarterly basis to be in line with industry trends and business efforts.
To Increase Sales
If your team is looking to increase revenue and the number of closed sales, you may need to widen and define your target audience. A sales plan will help outline this target audience, along with planning out both sales and marketing strategies to reach more qualified prospects and increase your sales conversion rate.
Now that you’ve seen sales plan examples and tips and tricks, the next step after creating your sales plan is to reach those ideal sales targets with Mailshake . Connect with leads and generate more sales with our simple but effective sales engagement platform.

- Content Marketing
- Practical Prospecting Podcast
- Success Stories
Continue reading

Getting Practical with Julia Carter

Accelerate: Sales Landscape in 2024

29 Sales Email Templates Plus Examples
Grow your revenue faster, automate all your sales outreach with mailshake..

- Mailshake Blog
- Cold Email Masterclass
- Cold Email Academy
- Prospecting Podcast
- Accelerate Newsletter
- Follow-Up Strategy
- Email Analyzer
- Live Training
- Data Finder
- LinkedIn Automation
- AI Email Writer
- Email Deliverability
- Lead Catcher
- Chrome Extension
- Integrations
How to Create a Sales Plan: A Complete Guide (Tips + Examples)

Write a sales plan that can adjust to change, and zero in on the actions that will hit your goals.

Paul Bookstaber
Share article.
- Link Copied
There is a world where sales planning happens once a year. You draw it up in January — “Whew, I’m glad that’s done!” — and everything goes as you planned. You hit your goals.
Meanwhile, on Earth, you create a sales plan, start to act on it — and everything hits the fan. A competitor launches a new product, an analyst switches up their report, and your best sales rep quits. Now what?
Below we share tips for how to create a sales plan that can bend to change and not break. You’ll learn why a sales plan is so important, see examples of the different types, and discover how to create one that brings you closer to your big hairy revenue goals — while also driving down costs.
Make sales plans that deliver more revenue
Our Sales Planning solution can help you align your targets, budget, and headcount — with just a few clicks.

What is a sales plan?
A sales plan is a blueprint for hitting revenue targets. It begins when sales leaders define long-term company goals. Then, sales managers create an annual sales plan to achieve those goals, adjusting it as market conditions change. They make decisions around hiring, quotas, compensation, territories, and customer segments. Finally, sellers translate the annual sales plan into account plans to close individual deals.
What are the benefits of creating a sales plan?
The key benefits of creating a sales plan are about hitting your targets with the resources you already have . First, it allows you to spot the gaps in your sales process that block you from your goals and address them with the best actions. Second, it sets you up to adapt fast to changing business and market conditions.
Let’s take a closer look.
Finding the actions to achieve your goals
A sales plan lets you test and measure how different actions will affect your numbers, so you can choose the right path forward to hit your goal.
You begin by adding up the numbers you know — how much your team will likely sell (based on past performance) and how much it will cost (based on your current resources). You’ll arrive at a prediction of the numbers you’ll hit.
If the prediction falls short of your targets, a sales plan helps you test different scenarios so you can find the action that forces the equation to spit out your target number in the most cost-effective way.
What if you hire more people? Increase your quotas? Level up your enablement program to increase win rates (the number of deals that close)? A sales plan gives you the framework to crunch the numbers until you find the reality that matches your dream.
Your business is more resilient to change
The traditional sales plan is something you create once a year. An agile sales plan is something you revisit, test, and adjust continually. The benefit is that even as market conditions change or surprises happen within your company, you can study the impacts of those changes and adapt to stay on track.
The path to agility is to do away with your disconnected tools and bring all of your sales plan data into the same system — your customer relationship management (CRM) system — where you sell. With this in place, changes in the real world show up as threats to your target within your plan. You can react in real-time, studying the data, testing different scenarios, and adjusting your sales plan to get back on track.

Map a clear path to success with annual planning
Set goals, target metrics, and key responsibilities during yearly planning with sales operations. Discover how on Trailhead, the free learning platform from Salesforce.
Annual Planning with Sales Operations

Sales plan types and examples
The different types of sales plans are meant to bring together your company’s long-term vision, short-term tactics that get you there, and everything in between. Leaders set a five-year track for where the company is heading. Then, sales managers step into a new time frame — the year — with sales forecasts and territory plans that help sellers hit their numbers. They come up with capacity plans to make sure teams are running lean and mean. Finally, sellers create account plans for every deal.
Let’s take a closer look at these different types of sales plans with the examples below.
Long-Range Sales Plan
This is where leadership comes together — people like the CEO, chief revenue officer, CFO, and VP of sales — and set the long-term path for the company. They’re thinking about where the opportunities are and how to seize them. For example, they might decide to grow annual contract value (ACV) by $30 million in the next five years, while also slowing the rate of hiring — because they want to make existing sellers more productive instead.
Annual Sales Plan
The sales manager creates an annual sales plan to set immediate targets and decisions that will help the company get closer to the goals established in the long-range sales plan. This plan begins with an understanding of the team’s capacity, or how much revenue they’re likely to produce. From there, territories, quotas, and compensation plans are set to ensure that sellers hit their numbers.
If, for example, the long-range sales plan is to achieve $30 million in ACV over the next five years while also making sellers more productive. Then a sales manager might set targets of $4 million in ACV in the first year and increase the quotas that sellers carry to hit that goal rather than hire more people.
Territory Plan
Don’t just segment customers based on geography. You should also segment them based on categories meaningful to the business. For example, if you want to sell to more enterprises, you might want to segment customers based on their size, and match sellers with enterprise expertise to enterprise companies. You can also segment customers based on industry and assign them to sellers with industry expertise.
Account Plan
Now that sellers know their targets and their territories, they take on planning of their own — customer by customer — with account plans. They strategize how to bring more value to every conversation and close individual deals . They research the needs of the customer, identify obstacles that stand in the way of selling, and list action items for how to build relationships to move each deal forward. Then, they work with different people within their company to execute on their account plans. They might connect with business development representatives (BDRs) to get a foot in the door with new leads, or with solution engineers to create demos for presentations.
How to create a sales plan
To create your annual sales plan for the year and make sure it can adapt to change, bring all of your sales data into one place. Then, study how much your people can sell (based on historical data), and set targets and incentives that will make your goal a reality. Use technology that can update all your sales plan data in real-time, so you can measure the impact of change and adjust to stay on track.
Ready to create your sales plan? Here’s how to take it one step at a time.
1. Connect sales plan data with your CRM
It’s important to build your sales plan in customer relationship management (CRM) software. When you have all your sales data in one central place, updated in real-time, real world changes show up as misalignments in the data. You have visibility into changes that put your targets at risk.
Without this single source of truth, you’d be spending weeks manually pulling in data from different systems, trying to understand the impact of the disruption. With every passing day, the gap between your plan and your reality widens.
Imagine that you begin an enterprise sales push with 50 sellers in January, but two have quit by March. A CRM can send you an alert that you’re under target. That real-time data is critical if you want to adjust your plan quickly to stay on track.
2. Understand your team’s capacity (how much they can sell)
Using your CRM data, take a look at capacity — that’s how much revenue you predict your team can sell during the coming year. To calculate capacity, look at all metrics that affect sales output, including hiring data, a review of quotas and targets, and historical sales rep performance data to predict future sales.
Following the example above, you might determine that based on the previous year’s performance, each seller, on average, can bring in $120,000 worth of revenue. However, now that you’re short two sellers, you’re short $240,000 in your capacity.
3. Measure the gap between your reality and your dream
Now that you understand the reality of who’s under your roof — and how much you think your team can sell — determine the gap between your revenue predictions and your revenue targets.
For example, imagine your target from the long-range sales plan is to hit $6 million in ACV this year. With $240,000 down in your capacity, as we showed above, you’ll need to figure out how to still meet the goal.
4. Find the actions to fill the gap and reach your goal
It’s time to write your sales plan to achieve your targets. Begin with the backbone — your team — and outline what’s expected (quotas), what the rewards are (compensation), how to organise customers (segments), and how to assign the reps (territories).
Then, to close the gap and hit your targets, create “What if?” scenarios to test the impact of different possible actions. The guideposts here should be cost savings and efficiency — how to hit your target by making the most of what you have. What if you hire two more people? (Straight-forward, sure, but hardly cost-effective.) What if you assign your highest performers to more lucrative territories? What if you create an enablement program that trains your sellers in a strategic industry?
In the example above, you’re trying to find a way to add $240,000 to your capacity without adding cost. One of the scenarios you tested shows that a new enablement program might do the trick, because training your sellers to sell more effectively can help you close more and bigger deals. This can be your Plan A. But since it will require investing in a new enablement program, you might want to come up with a Plan B as well that doesn’t require additional budget. For example, you might propose increasing each seller’s quota.
5. Present your proposed actions to leadership and execute
Make your case to leadership to get the rubber stamp on your proposed best action. Show them the data in your sales plan to demonstrate why your proposed solution will hit your targets and be cost-effective at the same time.
You might make the case for Plan A: investing in a new enablement program. If leadership balks because of cost, then it’s time to roll out Plan B: Increase each seller’s quota instead. Sales reps might protest at first, but you can reframe it as an opportunity to make more money. You’re in sales, remember? Finding the positive spin is what you do.
6. Keep adjusting and stay on target even as market conditions change
Change will come — whether from outside forces (think a disruption in your customer base) or inside forces (think a pivot in your product roadmap). The mindset shift is to take your sales plan off the shelf, dust it off, and reimagine it as a living, breathing thing. It’s something you adjust continually throughout the year — with your sights pinned to your goal.
Ready to turn your sales plan into a reality?
With the steps above, you’re ready to go. Study the real-time sales plan data in your CRM, measure the impact of the change on your goals, test different possible actions, and go with the best one. This is agile sales planning. It says, “Bring it on!” to change.
Learn how thousands of sales pros are driving productivity — today

Just For You

What Is a Sales Pipeline and How Do You Build One? A Complete Guide

Your Sales Tech Stack Is About to Get a Whole Lot Smaller

Explore related content by topic

Paul Bookstaber is a writer at Salesforce. He has a decade of experience in content marketing in B2B tech. Before that, he published a magazine and ran a tabloid blog. Today, he splits his time between Florida and the Mountain West, and loves to hike, ski, and watch Bravo. He is in a polyamorous relationship with Luke and Roger, who are cats.
Want Trailblazer tips and thought leadership straight to your inbox?

Predictive Analytics: Shaping the Future with Salesforce

Understanding Process Automation: Examples and Benefits

From Service to Sales: How Field Service Can Drive Revenue Growth

7 Sales Dashboards Every Team Needs (With Examples)

Mastering Lead Management: The Ultimate Guide for Success

What is Sales Automation? A Complete Guide

What is a Sales Process?

How Will Generative AI Affect Sales Reps’ Jobs?

New to Salesforce?
- Why Salesforce
- What is CRM
- Explore All Products
- Customer Success
- Product Pricing
About Salesforce
- Security and Performance
- Salesforce.org
- Best CRM Software
- Sustainability
- Give us your Feedback
Popular Links
- New Release Features
- Salesforce Mobile App
- Business App Store
- CRM Software
- Salesforce Plus
- Salesforce for Startups
- América Latina (Español)
- Brasil (Português)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- España (Español)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- Sverige (Svenska)
- United Kingdom (English)
- All other countries (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- ประเทศไทย (ไทย)
© Copyright 2024 Salesforce, Inc. All rights reserved . Various trademarks held by their respective owners. Salesforce.com Singapore Pte Ltd. 5 Temasek Boulevard #13-01 Suntec Tower 5 Singapore 038985
How to Create a Sales Plan: Tips, Examples & Free Sales Plan Template
Tactics and strategies are great. But when you create a sales plan, you set a clear path to success, with each step mapped out ahead of you.
The Internet is full of people who will tell you all about the success they’ve found from their strategies, whether it's personalizing a newsletter subject line or changing the color of the 'Buy Now' button.
But, news flash—these tips and tricks aren’t actual sales strategies .
To create real, lasting growth for you and your company, you need to create your own grand strategy. And that starts with a solid sales plan .
So, what’s your plan? How do you build it (and stick to it)?
We’re about to take a deep dive into sales plans. By the end of this guide, you’ll be completely equipped to win the fight for business growth. And we can't recommend it enough—grab our free sales plan template here in the Sales Success Kit today:
GET THE SALES SUCCESS KIT →
What is a Sales Plan? (And What Makes for Successful Sales Planning?)
Armed with the information you'll compile within your sales plan, you can quickly identify any upcoming problems, sales droughts, or opportunities—and then do something about them.
If done correctly, the right sales plan template empowers you to spend even more time growing and developing your business, rather than responding reactively to the day-to-day developments in sales.
Sound exciting? Let’s jump right in.
Download Your Free Sales Plan Templates Today
Want to build your own sales plan template that'll clarify your business plan and accelerate your growth? Grab the Sales Success Kit , including...
...and more to help you set up strategic sales planning and quotas for your team.
Want to stand out in the competitive market? Explore the insights of challenger selling .
What’s in a Sales Plan? 6 Elements Every Sales Plan Needs
In basic terms, a sales plan template includes:
- Sales forecasting and goal-setting
- Market and customer research
- Prospecting and partnerships
Each part of the sales plan naturally works itself into the next, starting with your high-level goals, then considering market factors, and finally looking at who you know, and how to find more prospects to help hit your sales goals .
Here are the key elements to include in your plan:
1. Mission Statement
What gets your sales reps out of bed in the morning? What’s the clear mission that pushes your team to keep fighting for that win?
Your mission statement is a concise statement of the ‘big picture’—the main idea and goal you want to achieve. Think about your company mission and how the sales team forms part of that overarching goal.
2. Sales Goals and Revenue Targets
A sales plan must include achievable sales goals and the targets your sales reps will be working to reach. Use previous years' results to tell you what's reasonably possible for your team to do. Include specific metrics and KPIs , how these are performing currently, and what you plan to do to improve them.
This may also include information about your product’s pricing , planned discounts, and how your team can focus on the right customers to get the most revenue possible. Link these sales goals to the business goals your company is working to achieve.
3. Analysis of the Target Market
Your plan should clearly identify your ideal customer profile and information about the target market and demographic you plan to sell to. Are you breaking into a new market? Are you targeting small business or enterprise customers ? Give a concise description of your target audience and the stakeholders you’ll need to sell to.
4. Sales Strategy Overview and Methods to Reach Target Customers
This should include a brief overview of the customer journey , pain points , and how your salespeople will engage and follow up with new prospects throughout their journey to purchase. You'll likely outline specific sales activities you'll focus on, such as improving referral numbers, testing new cold-calling email strategies, or dipping your toe in social selling.
You may also include information about the marketing strategy and lead generation methods used to gather new leads and how sales managers will support the team.
5. Use of Resources and Sales Tools
How much does it cost your team to close a new deal? What is your budget for the sales team, or for sales tools ?
Inside your plan, list the resources you have available to you, and how you plan to use them during the year. This includes monetary resources, as well as human resources.
Next, show how your resources will be used. For example, how much will you spend on sales tools? Which CRM software is your team depending on? Briefly explain how you plan to use each tool and why you’ve allocated resources in that way.
6. Sales Team Structure
The structure of your sales team includes which reps are available during what times of the year, their specialties and skills, and where they focus in the sales process .

Also, include information about the sales managers, their teams, and the incentives you offer your reps.
The Benefits of Sales Planning: Why You Need a Sales Plan
Creating a sales plan from scratch can be daunting, even with the right sales planning template. So, why should you have your sales strategy written down and ready to act on?
Let’s talk about the benefits of sales planning to attract new business and grow your market share.
Clear, Time-Bound Goals Help You Reach Revenue Targets
There’s a reason they say, “A goal without a plan is just a wish.”
If you want your sales team to execute on and accomplish your sales goals, you need to have a plan in place. When targets are linked to specific timeframes and actions, your whole team will see how their individual work is involved in reaching your sales goals.
Prioritize Time and Resources
Without a specific action plan in place , your team won’t be able to prioritize their time with the right sales tactics and strategies to hit their targets.
With a clear outline of the tactics that bring the most significant ROI for your team, each rep can get the best results for the time they spend selling.
Clear Action Plan to Reach Your Goals
With an action plan in place, each team member knows what they’re supposed to be doing, and why they’re doing it. This keeps them motivated and helps them see how their individual efforts make a difference.
4 Types of Sales Plans (How to Choose Which Planning Style is Right for Your Sales Team)
It’s difficult to templatize a good sales plan since every plan is unique to the business and team it applies to. So, what are some examples of the types of sales plans you might create, and how can you choose between them?
- Revenue-based sales plan: If you’re aiming for a specific revenue goal, this type of sales plan will be focused on in-depth sales forecasting and specific actions to improve conversion rates and close more deals.
- Sales plan based on the target market: If you’re selling to vastly different markets, you may want to create a different sales plan based on the market you’re targeting. For example, your sales plan for enterprise companies would differ from your sales plan for selling to SMBs.
- Sales goals plan: A plan that’s focused on goals (other than revenue) may include hiring and onboarding, sales training plans, or plans to implement a new type of sales activity into your process.
- New product sales plan: When launching a new product, it’s a good idea to develop a specific business plan around its launch and continued promotion. This plan may include finding and contacting strategic partners, building a unique value prop in the market, and creating new sales enablement content for the team to use when selling this product. This type of sales plan can also apply to launching new features in your SaaS product.

How to Choose the Right Sales Planning Style
Ultimately, this will depend on factors such as:
- Your revenue goals
- The resources at your disposal
- Your sales team’s abilities and bandwidth
- Your personal commitment to seeing this plan through
When you’ve determined who is involved in sales planning, how committed they are, and the resources you can use to make this plan happen, you can start building your own sales plan.
9 Steps to Create a Sales Plan to 10x Your Sales Team’s Results
It may seem like a lot of work to develop a sales plan at this point. But once you do, you’ll be in a place to take your sales (and brand) to the next level.
Let’s break down this process, step-by-step, so you can start achieving greater results.
1. Define Your Sales Goals and Milestones
With a sales plan, we begin at the end: an end goal.
Start by choosing the sales metrics that matter most to your overall business. This could be:
- Annual or monthly recurring revenue (ARR or MRR)
- Retention or churn rates
- Average conversion time
- Average conversion rate
- Customer lifetime value (CLV)
It doesn’t matter so much which metric you choose —the important point is that it can tell you whether your work has succeeded.
Next, look at last year’s forecast and results . Were you being realistic? How did sales revenue increase annually? How does that compare your company to the industry standards? Use this information to determine what realistically you can bring in based on the size of the market, your company goals, and the experience and resources available to your sales team .
After setting clear sales goals, it’s time to set milestones . This involves breaking that big number down into smaller expectations with strict deadlines. These should challenge and motivate your sales team , without being so difficult they kill morale.

Lean on your sales team during this process. After all, they’re in the trenches with you and probably have the best knowledge about your customers. Learn about what they do during the workweek to close deals. Ask how much they’re currently doing, and how much bandwidth they have to do more. This will give you a real, frontline take on what goals and milestones to set in your sales plan template.
Finally, create specific targets with clear deadlines . For example, to achieve a sales goal of increasing revenue by 15% YOY, you might set the milestone of increasing your customer base by 20%, or increasing sales by 50% for a specific product.
Brought together, these milestones inform and support your overall sales plan, giving you a clear, actionable workflow to hit your overall goals for the year.
2. Clearly Define Your Target Market or Niche
You need to know the market you’re in and the niche you’re going to occupy so you can properly position your business for growth.
What’s a business niche? It’s more than just what your business specializes in—a niche is the space your business occupies, with your products, content, company culture, branding, and message. It’s how people identify with you and search you out over the competition.
As serial entrepreneur Jason Zook explains: “ When you try to create something for everyone, you end up creating something for no one. ”
Don’t do that.
Instead, start by looking at a niche and asking yourself these questions:
- How big is the market?
- Is there a built-in demand for what you're selling?
- What’s your current market position?
- Who are your competitors? What are their strengths, weakness, opportunities, and threats?
If you’re stuck, start by going back to your own strengths . List out your strongest interests and passions. Pick a field where the odds are already in your favor—where you have a proven track record, more expertise to offer, an extensive contact base, and people who can provide you with intros.
These kinds of strategic advantages will help you clarify your buyer persona and amplify the results of your planning.
Start with one product in one niche—you can always branch out to a complementary niche later. Sell beautiful, handcrafted tea cups? How about a booming doily business? Or customizable teaspoons?
A niche doesn’t limit you. It focuses you.
3. Understand Your Target Customers
Chasing the wrong customers will only waste your time and money, so don't allow them to sneak into your sales plan.
Your best customers are the ones that are successful with your product and see the ROI of it. Talk to them, and find out what they have in common.
While defining ideal customers depends on your company and market, here are some basic characteristics you’ll want to identify:
- Company size (number of employees, number of customers, yearly revenue)
- Size of the relevant department
- Geographical information
- Job title of your POC
- Buying process
- The goal they’re trying to achieve with your product or service
Also, don’t forget to think about whether they will be a good ‘fit’. If this is a long-term relationship you’re developing rather than a one-night stand, you want to ensure you speak the same language and share a similar culture and vision.
Use this information to build out an ideal customer profile . This fictitious organization gets significant value from using your product/service and provides significant value to your company. A customer profile helps you qualify leads and disqualify bad-fit customers before you waste time trying to sell to them.

Once you know the type of company you want to target with your sales team, it’s time to get inside their head. Start by hanging out where they hang out:
- Are they on social media? What’s their network of choice?
- Are they members of any Facebook or LinkedIn groups?
- Can you answer industry questions for them on Quora or Reddit?
- What podcasts do they listen to or what resources do they read?
Get in your customers’ heads and you’ll be in a much better position to sell to them.
GET THE IDEAL CUSTOMER PROFILE KIT →
4. Map Out Your Customer’s Journey
The next part of an effective sales plan must address how that ideal customer becomes your customer. Do this by mapping out their journey, including actions and events during the different stages of the sales funnel :
- Consideration
Conduct a customer survey , or chat directly with your current, happy customers to gather valuable sales planning insights. Ask them:
- When you became a customer, what did you want our product to do for you?
- What features were important to you? Why?
- What was your budget?
- How were you solving this problem before using our product?
To fully understand their journey as a customer, you can also ask about past buying experiences:
- When was the last time you bought something similar?
- Was that a good or bad experience? Why?
- What was the decision-making process like?
- How did you evaluate different offers?
- Which factors made you choose that particular solution?
Once you’ve identified the awareness, interest, and consideration stages, let your prospects and new customers build the rest of their roadmap by asking them: ‘what’s next?’
"What needs to happen to make you a customer?"
If, for example, they say they’ll have to get approval from the VP of Finance. Ask:
"Ok, and let's say he agrees that we're the right fit, what's next?"
We call this the virtual close , a way to put your prospect in a future-thinking state of mind that makes them imagine buying from you. Asking this question to several high-quality prospects will tell you those final few steps in the customer journey until they’ve signed on the dotted line.
Finally, piece together the post-sale journey. Once a prospect becomes a customer, what’s next? How do you enable them to use your product and be successful with it? What happened to create your most loyal customers? Understanding this piece of the sales process is essential to managing and increasing customer retention .
5. Define Your Value Propositions
You know your customers. You know their journey. Now, define where you fit in by looking at your competitive advantage . Fully articulating what sets you apart from the competition is a crucial element of your sales plan template.
Start by asking a few simple questions:
- Why do customers buy from us?
- Why do customers buy from our competitors and not us?
- Why do some potential customers not buy at all?
- What do we need to do to be successful in the future?
Remember that customers buy benefits, not features. When describing your value proposition , it’s easy to get caught up in talking about you. What you’ve made. What you do. Instead, flip the script and talk about what your product will do for your customers . A strong competitive advantage:
- Reflects the competitive strength of your business
- Is preferably, but not necessarily, unique
- Is clear and simple
- May change over time as competitors try to steal your idea
- Must be supported by ongoing market research
For example, the competitive advantage of help desk software has nothing to do with its social media integrations and real-time ticket tracking. It’s the fact that it allows its customers to focus on creating a great customer experience.
Here’s the point: Focus on value, not features in your sales plan template.

Your competitive advantage will inform everything your company does moving forward, from marketing to product development. It’s a great example of where sales can influence the development of a product and the direction of a business.
6. Organize Your Sales Team
The way your sales team is organized can enable them to better serve their customers and bring new revenue into your business faster.
Here are three basic structures for your sales team :
- The island: Individual reps work alone.
- Assembly line: Each sales rep is assigned a specialized role such as lead generation, SDR (qualifier), Account Executive (closer), or Customer Success (farmer).
- Pods: Each sales rep is assigned a specialized role in a pod, or group, that’s responsible for the entire journey of specific customers.
Think about the strengths and weaknesses of your sales team members, and how they will truly thrive as part of the team.
7. Outline the Use of Sales Tools
Now it’s time to think about the tools you’re using. Building out your sales stack takes time and effort, but listing out that stack in your sales plan will help you avoid getting caught up with new tech that may or may not help your sales team.
Basically, you’ll need tools for these areas to cover all aspects of the sales process:
- CRM software (like Close )
- Lead generation and prospecting tools
- Internal communication software
- Engagement and outreach tools
- Documentation software
- Sales enablement stack
Think about how all of your sales tools work together through integrations and where automation comes into play to save your team time, and how you'll drive CRM adoption across your team members.
8. Build a Prospecting List
A prospect list is where we take all the theory and research of the last few sections of our sales plan template and put them into action.
At its core, a prospect list is a directory of real people you can contact who would benefit from your product or service. This can be time-consuming, but it's essential for driving your sales plan and company growth.
First, use your ideal customer profile to start finding target companies:
- Search LinkedIn
- Check out relevant local business networks
- Attend networking events and meetups
- Do simple Google searches
- Check out the member list of relevant online groups
Target up to 5 people at each organization. Targeting more than one individual will give you better odds of connecting by cold email outreach as well as a better chance that someone in your network can connect you personally.
Remember, this isn’t just a massive list of people you could sell to. This is a targeted list based on the research you’ve done previously in your sales plan.
Once you have your list, keep track of your leads and how you found them using a sales CRM. This will keep historical context intact and make sure you don’t overlap on outreach if you’re working with teammates.
9. Track, Measure, and Adjust As Needed
Just because you’ve made a solid sales plan template to follow, doesn’t mean you get to sit back and watch the cash roll in.
Remember what Basecamp founder Jason Fried said about plans:
“A plan is simply a guess you wrote down.”
You’re using everything you know about the market, your unique value, target customers, and partners to define the ideal situation for your company. But yes, try as we might, very few of us actually see anything when we gaze deep into the crystal ball.
Instead, remember that your sales plan is a living, breathing document that needs to account for and adapt to new features, marketing campaigns, or even new team members who join.
Set regular meetings (at least monthly) to review progress on your sales plan, identify and solve issues, and align your activities across teams to optimize your plan around real-world events and feedback. Learn from your mistakes and victories, and evolve your sales plan as needed.

Create a Strategic Sales Plan to Grow Your Business
You’ve just discovered the basics—but I’ll bet you’re ready to go beyond that. Here are some final ideas to take your sales plan from a simple foundation to a strategic, actionable one.
Avoid Moving the Goalpost
Avoid making adjustments to the goals outlined in your sales plan—even if you discover you’ve been overly optimistic or pessimistic in your sales planning. When you're developing your very first sales plan template, it's natural to be wrong in some of your assumptions—especially around goals and forecasting .
Instead of letting it get you down, remember your plan serves as a benchmark to judge your success or failure. As you see places where your assumptions were wrong, carefully document what needs updating when it's time to revise your sales plan.
Invite Your Others to Challenge Your Sales Plan
Never finalize a plan without another set of eyes (or a few sets.) Get an experienced colleague—an accountant, senior salesperson, or qualified friend—to review the document before solidifying your sales plan.
Your sales team is another strong resource for reviewing your sales plan. Ask their opinions, give them time to think about how it relates to their daily work, and agree on the key points that go into your sales plan.
Set Individual Goals and Milestones for Your Sales Team
We talked about creating milestones for your business, but you can take your sales plan to the next level by setting individual milestones for your sales team as well.

These individual goals need to consider the differences in strengths, weaknesses, and skills among your salespeople.
For example, if someone on your team is making a ton of calls but not closing, give them a milestone of upping their close rate . If someone’s great at closing but doesn’t do much outreach, give them a milestone of contacting 10 new prospects a month.
Doing this will help your individual reps build their skills and contribute to their company and career growth.
Ready to Hit Your Sales Goals?
In most sales situations, the biggest challenge is inertia. But with a solid, detailed sales plan and a dedicated team with clear milestones, you’ll have everything you need to push through any friction and keep on track to hit your goals!
All jazzed up and ready to put together your own sales plan? Download our free Sales Success Kit and access 11 templates, checklists, worksheets, and guides.
They're action-focused and easy to use, so you can have your best sales year yet.
Actionable sales advice
Get actionable sales advice read by over 200,000 sales professionals every week.

Ready to up your game? Subscribe now.

Create a Sales Plan That Actually Works (Tips + Template)
- January 21, 2021
True success always starts with a plan. And for sales success, nothing beats a strategic sales plan.
Designed specifically to help your sales team drive more sales, a sales plan can show you where you’re at, where you want to be, and even more important, how to get there.
The question, of course, is how to create a sales plan that actually impacts sales. Keep reading for tips and a template to quickly and confidently create a strategic sales plan for your business.
Table of Contents
What is a sales plan, what is included in a sales plan, sales plan examples: there’s no one right way, the benefits of a sales plan, how to write a sales plan, 7 tips to help you create a sales plan, sales strategy template, selling your sales plan, final remarks.
A sales plan is a strategy document that lays out a company’s plan for improving sales results in a specified time period. A sales plan makes it possible for everyone on the sales team to see the big picture, share the same overall objectives, and work the same plan to achieve them.
It usually includes:
- Specific revenue and performance goals for a given period
- The strategies for achieving them
- The resources and activities required to carry out those strategies
A sales plan covers a lot of important aspects of business growth: revenue goals, selling methods and metrics, target customers, current sales force capabilities, and more.
Specifically, it covers 9 pieces of strategic information.
1. Executive Summary and Scope of The Sales Plan
This section gives a short summary of the document, focusing on goals and the strategies to achieve them. It also states the specific period and other parameters covered by the plan.
2. Business Goals and Revenue Targets
This section clearly establishes revenue targets and may include associated business goals (e.g., optimize lifecycle value through customer success programs, etc). Classifying revenue figures based on different categories (such as line and territory) helps clarify the document.
3. Review of Prior Period Performance
This section presents a recap of the prior period’s performance, identifying mistakes as well as decisive actions that led to a positive outcome. The overarching goal is to optimize the sales plan by adopting inputs and techniques that work.
4. Market and Industry Conditions
This section provides a summary of the market trends that have a high likelihood of influencing sales performance.
5. Strategies, Methodologies, and Tactics
This section recommends the best selling techniques, communication sequences, and playbooks for the specific company.
6. Customer Segments
This section cites all the potential revenue-generating, omnichannel opportunities available for the brand, such as the following:
- Cross-sells
- New Prospects
- New Segments
The document should describe new segments of the addressable market when they arise.
7. Team Capabilities, Resources, and Upgrades
This section provides a summary and describes the current state of all production inputs (human resources, tech software, specialized sales team, etc.,) required to process and close sales details.
8. Action Plan For Teams and Individuals
This section assigns tasks, activities, and responsibilities to different teams and individuals. Tasks include prospecting activities, meeting appointments, and product demos/presentations.
9. Performance Benchmarks & Monitoring
This section lays out performance metrics to track the systems and processes that help monitor these metrics.
What usually comes to mind when you think about sales plans?
If you’re like most people, it’s the annual sales plan or weekly sales plan — broad strategic and tactical documents mapping out the plan for everything sales-related.
But there are as many different types of sales plans as there are needs for a sales plan.
We’ll go over a few sales plan examples to get you started in the right direction.
30-60-90-day Sales Plan
There’s the 30-60-90-day sales plan. This is designed to help a new salesperson or sales manager get up to speed quickly in their first quarter on the job. The plan includes milestones they’d need to achieve at the 30th, 60th, and 90th day of their ramp-up.
Generally, the 30-60-90-day sales plan can be broken down into 3 sections:
Day 1 to 30:
Learn and understand everything you can about a company from their processes, customers, products, the competition to procedures.
Day 31 to 60:
Evaluate and put your plan into action. Analyze their current processes and assess changes.
Day 61 to 90:
Optimize and make the plan better. It is time to take action. Initiate an action plan. Implement any new strategies and procedures you’ve come up with.
Sales Plan For Specific Sales
A sales process involves using different tactics to approach and convert a prospect into a paying customer.
Another type of sales plan you’ll see a lot is an individual sales plan for specific sales tactics, such as prescribed call sequences, email follow-up frequency, and meeting appointments. This type of plan is similar to an annual/weekly sales plan, but it focuses on measuring and improving results for just one goal or task.
Territory Sales Plan
Meanwhile, sales managers who oversee a geo-location or region often use territory sales plans to give sales directors and VPs more visibility into their sales efforts.
This is a workable plan used to target the right customers and implement goals to increase the income generated and sales over time.
A good territory sales plan will:
- Make your team more productive
- Reduce operational costs
- Increase the number of generated sales
- Improve your customer coverage
- Improve working relationships between clients and managers
Note: It is essential to work on your territory sales plan and avoid making constant changes. Unnecessary changes can tamper with your productivity and your ‘territory’ in general.
Sales Training Plan
And there are sales plans for every area of sales. Sales Enablement might have a sales training plan, for example, and Revenue Ops might have a sales compensation plan.
A sales training plan can be used as a roadmap for different sales training programs. It can be grouped according to positions held in an organization, assets, sales record etc.
A sales compensation plan is an umbrella for base salary, incentives and commission that make up a sales representative earnings.
Therefore, you can schedule a sales training plan to talk to your sales team about the importance of a sales compensation plan and how they can use it to increase revenue and drive performance.
Sales Budget Plan
Lastly, a sales budget plan gives you a sales forecast for a given period based on factors that could impact revenue — like industry trends and entry to a new market segment. Similar to a traditional sales plan, they cover the staff, tools, marketing campaigns, and other resources needed to generate the target revenue.
A good sales budget plan should include the following:
Sales forecasting:
The process of estimating future sales by predicting the number of units a salesperson or team can sell over a certain period, i.e. week, month, year, etc.
Anticipated expenses:
Include the number of costs your team is likely going to incur. Remember to have even the smallest expenses to estimate the average sales.
Expect the unexpected:
Always leave room for unforeseen circumstances in your sales budget. For example, new packaging expenses, new competitive market strategies etc.
A sales plan does deliver side benefits (such as promoting discipline and diligence), but it’s really about making sure your sales don’t dry up over time. Which means it’s not optional.
The reality is this: Most of us aren’t planners. We talk a good game, but nothing happens until we’re accountable.
Without a written plan, it’s just talk.
So the first benefit of a sales plan is that it helps you execute on all your best ideas. But that’s not all. A good sales plan will also help you:
- Keep your sales team on the same page, aiming for the same target and focusing on the same priorities.
- Clarify your goals and revenue objectives for a given period.
- Give your team direction, focus, and purpose.
- Adopt a unified set of strategies and playbooks to reach your business and revenue goals.
- Know what your team capabilities are and be able to isolate your needs, from tools to talent and other resources.
- Inspire and motivate stakeholders.
- Track your progress and optimize performance over time.
A sales plan is a pretty straightforward document. It doesn’t need to be written in a formal language or pass your compliance review. It just needs to outline your plans for the coming period, whether that’s a year, a quarter, or a month.
While there are 9 sections in the sales plan template, much of the document simply validates your ideas. The most important pieces of information are:
1. Your goals
Setting smart goals for you and your team is an essential part of creating a sales plan. I believe the biggest mistake you can make when setting goals is solely focusing on numbers.
Smart sales goals should be actively focused on. If it helps, use goal-setting and planning frameworks such as SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound). Create goals that stretch your capabilities, but that seems doable based on your new strategy.
2. Your SWOT analysis
SWOT — short for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats — is one of the best frameworks for analyzing your sales team’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and strengths. It helps you to build a bulletproof wall around your plan.
You’ll be able to address what you’re lacking, the areas that need improvement, identify your USP (Unique Selling Point), come up with Value-Based Selling , and your most vital points and how you can exploit them to your advantage.
3. Your strategy
Your sales strategy should be documented to help position your products and services to differentiate your solution from competitors.
A good strategy will help you address your customers’ needs in every stage of your sales plan. For better sales, you can balance inbound and outbound sales strategies for even higher sales.
4. Your tactics
Be aware, though, it’s not just a wish list or a collection of ideas. Your sales plan should be based on actual field data and only use benchmarks and quantities that are measurable. Be clear. Be specific. Be actionable.
Which brings me to another point: A good sales plan is realistic.
It’s fine to have a 5-year goal of hitting $10B. But what about now? Figure out exactly what your current numbers are, and set your targets based on those numbers.
I already mentioned that your sales plan doesn’t have to be a formal document. But it does need to be clearly written, so all team members and stakeholders understand the plan.
Tip #1: Base it on in-depth and up-to-date research
You need relevant statistics and trends in your niche, industry, and ideal customers. Remember, markets and customers are in a constant state of flux. There’s nothing worse than stubbornly chasing prospects who aren’t a good fit anymore while ignoring entire market segments that show a rising demand for your solutions.
Tip #2: Use data and statistics
Use the data from your in-depth research to identify problem areas, find points of opportunity in your sales process, and validate your assumptions and ideas.
You can also use the data to come up with accurate metrics and figures to help predict your sales plan’s outcome.
Tip #3: Verify your facts
Accuracy matters!
Don’t rush! Facts and figures are essential, especially to stakeholders. One simple mistake and your entire plan come tumbling down.
Ensure you take time to review your facts, figures, and forecasts before finalizing the document.
Tip #4: Get tactical
Break the overall sales action plan into tactical plans for individual areas of sales:
- SDRs and account executives
- Sales operations
- Sales enablement
- Customer success
This may require collaboration with cross-functional teams such as marketing, customer support, and product teams.
Tip #5: Use Historical Performance Data
In sales, you can use the past to dictate the future. Historical data will help you set targets for the current period. For example, what were your previous revenue targets? Did you hit them? Why or why not? This information can help you set achievable goals for your current sales plan and know the mistakes to avoid.
Tip #6: List The Tracking Methods You’ll Use
Highlight the tracking methods you’ll use to keep your plan moving forward. That includes performance metrics, monitoring techniques, software, tools, and selling strategies for your business model.
Tip #7: Build a Strong Case For Your Proposed Budget
Stakeholders and superiors are impressed with cold-hard facts. Therefore, having a strong detailed case for your budget will help your sales plan smoothly sail through.
Not only will you outline your plans for the coming period for your budget, but you’ll also need to detail the costs. Be sure to include an ROI analysis for any new tools or talent you think you’ll need.
Are you ready to write your own sales strategy? Here is a sales plan template to help you get started. Here’s how to use the sales plan template to make it useful to you:
Start by using the Sales Plan Template we’ll give you in the next section. Just follow the prompts in the template, so you know what information is needed in each section. Don’t try to be fancy. Use simple language. Focus on being specific and clear.
Then share information in whatever format works best. That may be text paragraphs, tables, lists, charts, graphics, or screenshots. You can also adapt it as needed to suit your business, your sales team, and your needs.
A sales plan should contain the following sections:
1. Executive Summary
This is your opening ‘statement’. It is a formal summary that sum ups the contents of your strategy.
When writing your executive summary , keep it short, and precise. It should be one page or two. Ensure it gives an overview of what is included in your plan. It should talk about:
- The strategies you’ll implement to achieve your goals
- The time-frame you expect to achieve your plan
- The scope of your plans
2. Business Goals With Revenue Targets
This section talks about the revenue target and associated business goals. You can classify revenue figures according to different categories to clarify the sales strategy.
For example, for each goal, you can enter the current outcome and targeted outcome as illustrated in the table below:
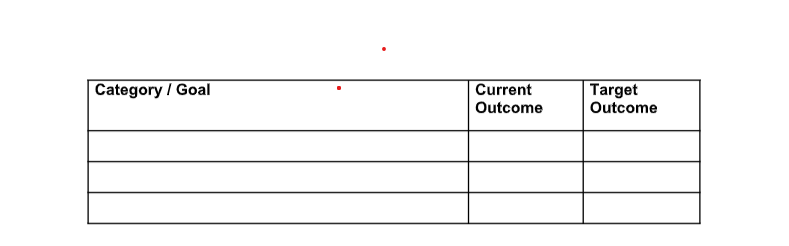
3. Review of Past Performance
Take a trip down prior period performance . Note the mistakes that negatively affected the outcome and their strengths which positively impacted the general outcome.
Your goal is to identify the strategies and tactics that work.
4. Specific Strategies, Methods, and Playbooks
List the specific sales strategies, methods, and playbooks you’ll use to achieve the goals listed above.
5. Customer Segments/ Buyers Persona
This section talks about potential revenue-generating streams and different opportunities available for the company and new markets. Remember to include upsells, referrals, and renewals.
6. Team Capabilities and Resources
Here, provide a summary and describe the current production inputs required in the sales process , i.e., human resources, specialized software, sales team, etc.
7. Action Plan
The action plan requires you to set specific strategies and supporting tactics that will be used to achieve a particular goal, i.e. new acquisition. Assign different activities and responsibilities to teams who will run that particular action.
Below is an example of an action plan table:
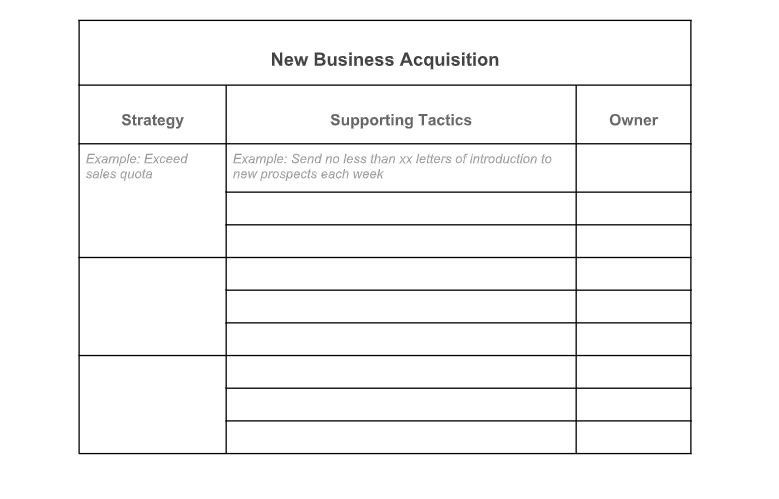
8. Sales Tools
Go ahead and list the tools you’ll use to ensure the sales plan runs smoothly and all sales processes will be managed using these tools.
9. Performance Benchmarks
This is the last section of your sales plan. It lays out the performance metrics to track the process systems to help and monitor these metrics.
Also, list and provide links to used sources. Explain how the report will be generated and stored. Finally, talk about how the report will be used to review the progress made.
Okay, your sales plan is written. Great! But you’re not done yet.
Your next step is to present it to the sales team, management, and stakeholders. That’s because you need buy-in to make it happen.
When your sales team is on board, they’ll be pumped about doing their assigned tasks. When management is on board, they’ll be excited about giving you the budget you need to turn your plan into a reality. With buy-in as your top priority, it’s important to be prepared to give a solid presentation. In other words, sell it.
One final note: There are lots of reasons you may not get everything you ask for. There may be plans in the works you don’t know anything about yet. Or the budget may need to favor another initiative.
If you don’t get the budget you asked for, be sure to update your sales plan accordingly. The goal is to stretch your team’s capabilities, not do the impossible.
Sales don’t happen without a good sales plan. Fortunately, they’re not as hard as they might seem.
Take your time identifying your biggest challenges and problem-solving to overcoming them. Once that’s done, your sales plan is simply the document that organizes your ideas.
What’s your biggest hang-up when it comes to creating a sales plan? Have you found any tricks that help? Let me know in the comments below.
Max Altschuler
More like this....
- 4 Common Mistakes SaaS Companies Make While Scaling Revenue
- Ten Sales Kickoff (SKO) Insights You Can’t Afford to Miss
GTM 88: Know Your Numbers to Create Alignment and Unlock Scale with Kyle Lacy
Join us today, insider access to the gtm network and the best minds in tech., you may also like....

Want insider access? Sign up here.

Experience, strategy, and insights to help take you from 0 to IPO.
- Customer Success
Watch This Live Event
2023 Playbook: How to Create a Revenue-Generating Sales Plan [Template + Examples]
![how to do a business plan for a sales company 2023 Playbook: How to Create a Revenue-Generating Sales Plan [Template + Examples]](https://www.yesware.com/blog/_next/image/?url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.yesware.com%2Fwp-content%2Fuploads%2F2021%2F05%2Fsales-plan-yesware.jpg&w=1984&q=75)
Casey O'Connor
What Is a Sales Plan?
Why do i need a sales plan, how to create a sales plan: 7 steps + what to include, types of sales plans, how to measure sales progress, what to include in a sales plan template, sales plan template, sales plan examples, tips for creating a winning sales plan.
A sales plan is a detailed, A – Z roadmap for salespeople that outlines the various stages, executable actions, methodologies, outcomes, and goals of the sales process.
The document provides the sales team with an action plan for executing their roles and responsibilities in supporting your company goals.
In this article, we’ll go over all the steps you need to take (and exactly what to include) in order to create an effective sales plan as well as examples, templates, and proven tips.
Here’s what we’ll cover:
- How to Create a Sales Plan
A sales plan is very similar to a business plan , except that it focuses entirely on sales activities. It’s an all-encompassing playbook that spells out everything a salesperson might need to know about what they’re working toward within their company, including:
- Strategies or methods to adopt
- Action steps to follow
- Team players, their specific responsibilities, and the skills required to do their jobs
- Potential pitfalls and challenges
- Individual and team-wide, short-term, and long-term goals
An effective sales plan should be very thorough, and should outline for your salespeople all the various steps — and their potential outcomes — they will need to take in order to play their part in meeting the company’s targets.
A sales plan is meant to help sales reps understand their specific roles and responsibilities, and how their actions and outcomes contribute to the bigger picture.
Like a business plan, a sales plan is a customizable document and should reflect the specifics of your company or small business. What you include in the document — and how you go about creating it — will be unique to your scenario.
With that being said, there are some guidelines and best practices to follow to ensure your sales plan is as effective as possible. We’ll go over all of those later in this article.
First, let’s look at some of the reasons why it’s so important to make a sales plan.
For many sales reps, the name of the game is closing deals . It can be easy to lose sight of the process in favor of converting as many leads as quickly as possible.
But solidifying and systemizing the sales process is critically important. Creating a sales plan will help you:
- Maximize the efficiency of your sales process by determining which strategies and methods are most effective with your target market
- Identify a variety of targets and goals, and encourage your sales reps to continually strive to meet them
- Track individual and collective performance data from every stage of the sales process, which will help fine-tune your sales process and determine your budgeting needs
Though it may require some time and effort on the front end, creating a sales plan will pay off in spades in the long run.
It doesn’t matter how skilled or talented your sales team is — if they’re not efficient in their sales activities, they will never reach peak performance.
In fact, most top-performing companies report that their sales activities are carefully structured , far more so than average or underperforming companies.
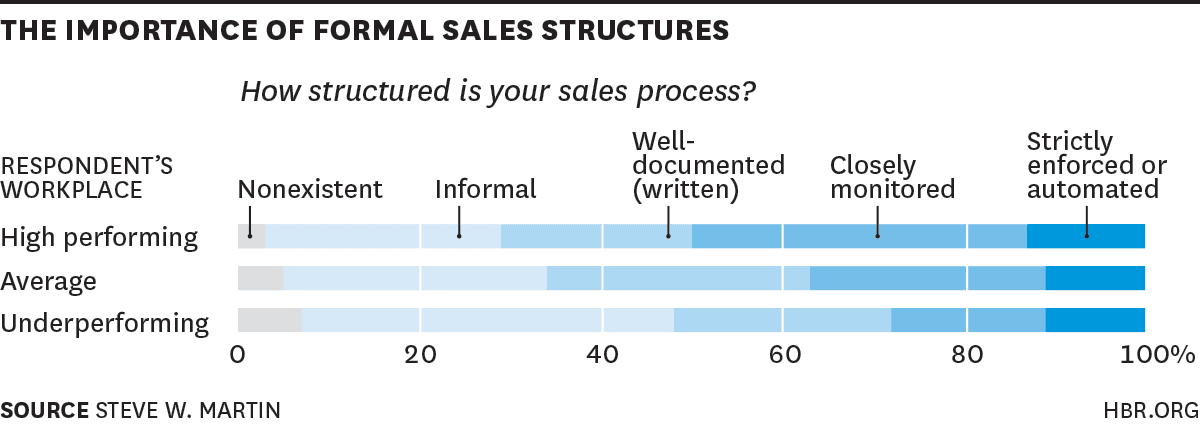
Having a structured system allows your sales team to meet their sales goals more quickly and easily. The detailed roadmap of the sales plan enables your reps to waste no time deciding what to do next, wondering whether what they’re doing is working, or how close they are to meeting their goals.
One of the most effective ways to motivate a sales rep is through expertly crafted sales goals . It’s important that your goals are lofty, and will drive your business forward, but they should also be achievable.
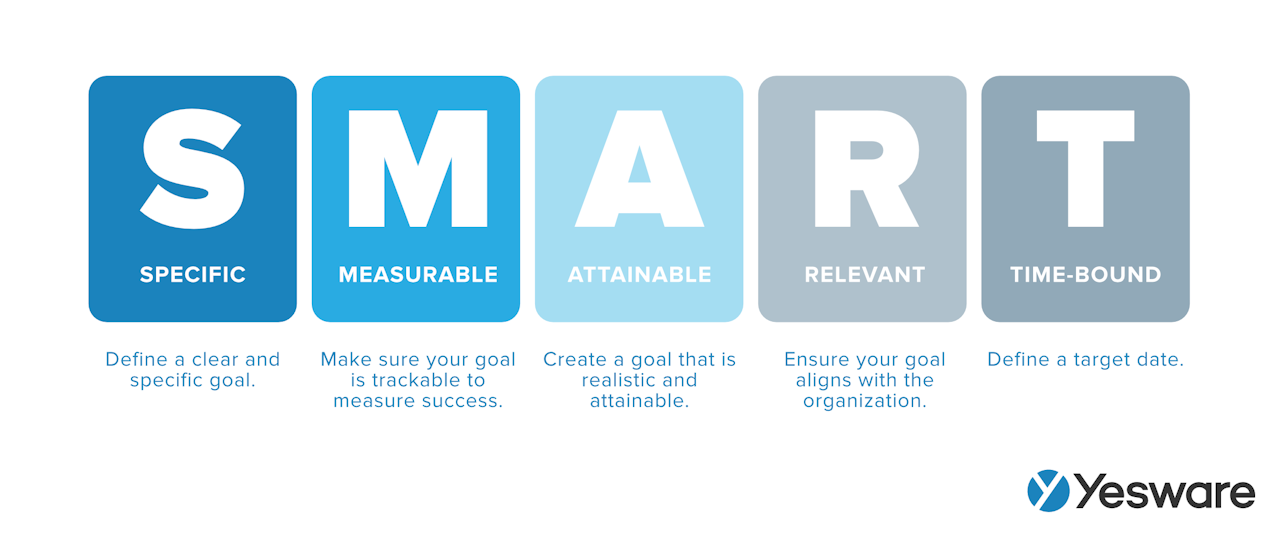
Once you’ve set effective goals, you also need to be able to see what steps and actions are helping you meet them, and which need some fine-tuning.

Although your sales plan will be unique to your company’s current operating status and future goals, there is a relatively standard process that will help most sales managers create one to suit their needs.
These seven steps will help you know where to start — and what all to include — in your sales plan.
1. Mission Statement & Positioning
Before you start nailing down the specifics of your goals and sales actions, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the big picture. What is your company’s purpose? What do you do and why do you do it? What are your company values? All of these things come together to form a company’s mission.
Creating a mission statement is an all-hands-on-deck exercise. Your company’s mission is developed by and given contributions from many departments. Be sure to consult with your marketing, account management, and content management teams, along with any other stakeholders that are impacted by the company’s larger purpose (in other words, everyone!).
It’s also important during this step to acknowledge your company’s current position in the market. Who are your main competitors? What is the value you offer that sets you apart ? This isn’t necessarily part of your mission statement, but it does help your sales team understand where they currently fit in the bigger market picture.
Once you’ve zoomed out and gotten a handle on the higher-level ideals and values of your company, it’s time to dive into the nitty-gritty.

Do not cut corners in this step. The more specific, the better, and you should consider setting smaller, highly targeted goals for every stage of the sales pipeline .
For example, a high-level goal may be to close 100 deals in a month. That’s a good start at a SMART goal, but challenge yourself to go several steps further . Reverse engineer those 100 deals, and look at all of the steps that happened before close that helped you arrive there.
How many cold emails did it take to close a single deal? How many phone calls are reps making before qualifying a prospect ? How is your social media engagement ? Your sales process map can help you identify and target each individual step in the process, so you can create smaller, stepping-stone goals.
Here’s a general structure:
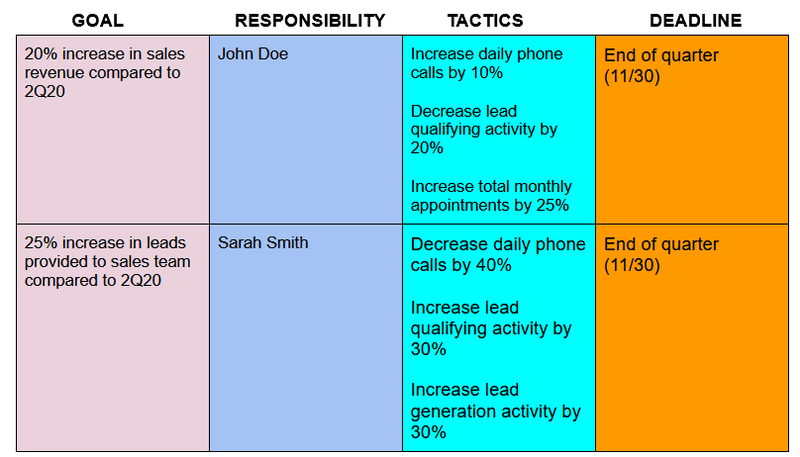
One last tip: make sure to set goals for activities that are directly within a sales rep’s control — things like how many phone calls they make in a day, or how long their demo takes to present — and the outcomes that are driven by those activities (like revenue or number of deals closed).
3. Sales Team Organization & Structure
Here is where you’ll outline your team roster , so to speak. This section of your sales plan should start with an overview of your current sales team, as well as the specific roles and responsibilities of each team member.
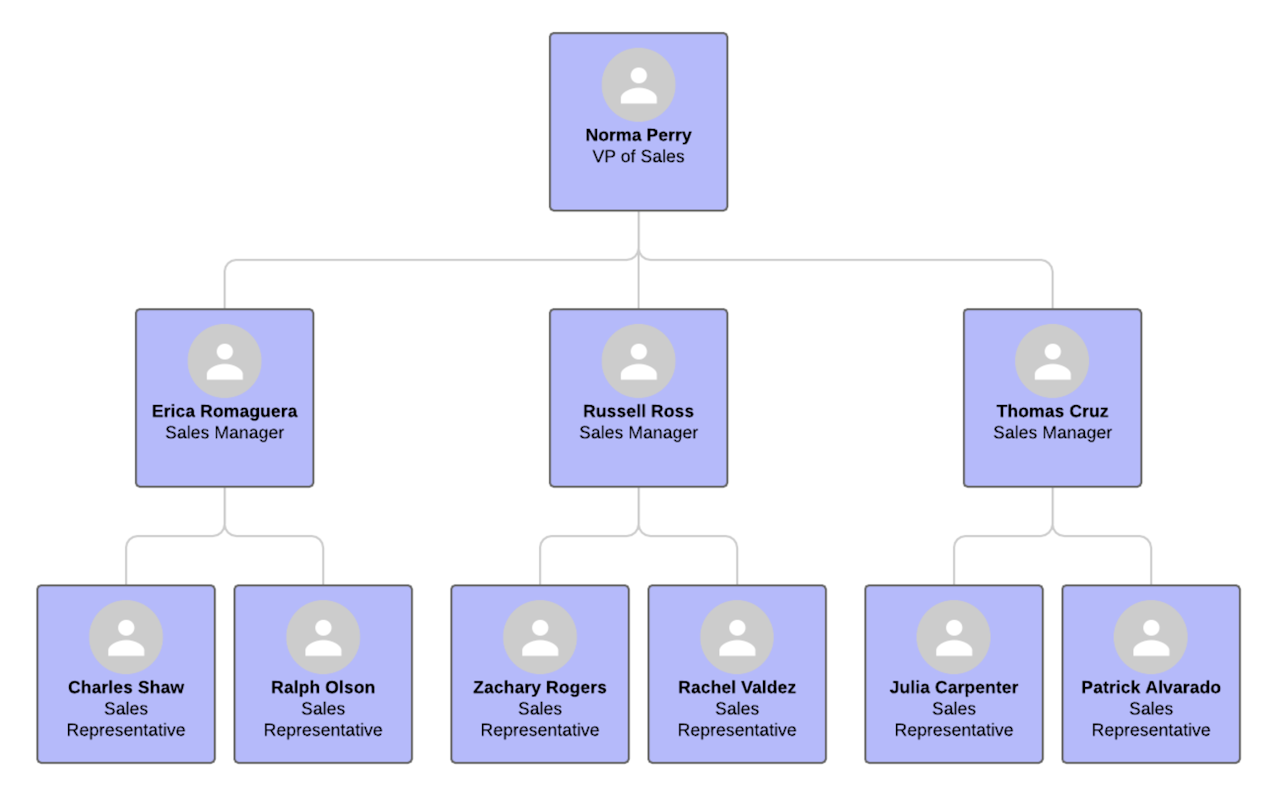
Beyond that, it should also outline the specific skills and/or training that your sales reps currently possess, and what they (ideally) still need in order to be successful. You should also consider including projections for future growth or openings on the sales team. Similarly, you may consider including your compensation plan within the sales plan.
Some of this section will be forward-looking and dependent on your sales budget — don’t exclude something just because it’s not happening now or seems too expensive. These projections will help further shape your revenue goals and allow you to budget appropriately.
This section should rely heavily on self-reports from your sales reps. Take the time to interview them individually about how they view their role and what they currently take responsibility for within the sales process .
There are no right or wrong answers here, so be sure to let your reps know that this isn’t a performance evaluation. The point of gathering this kind of input is to see, from a high-level perspective, which responsibilities are currently well-served, and which need more attention.
4. Target Market & Buyer Persona
As important as it is to clearly understand the internal workings of your sales process, it’s just as important to outline things from the customer’s perspective.

5. Sales Strategies & Methodologies
In this section, you’ll want to give an overview of the various sales methodologies that are most successful for your target market, as well as the actionable steps required for each one.
This doesn’t mean that you need to adopt one approach and stick with it. Many top-tier sales teams use a hybrid approach to sales strategies, combining a variety of methods depending on the rep and the customer.
For example, you may find that inbound leads respond best to a value-selling approach.
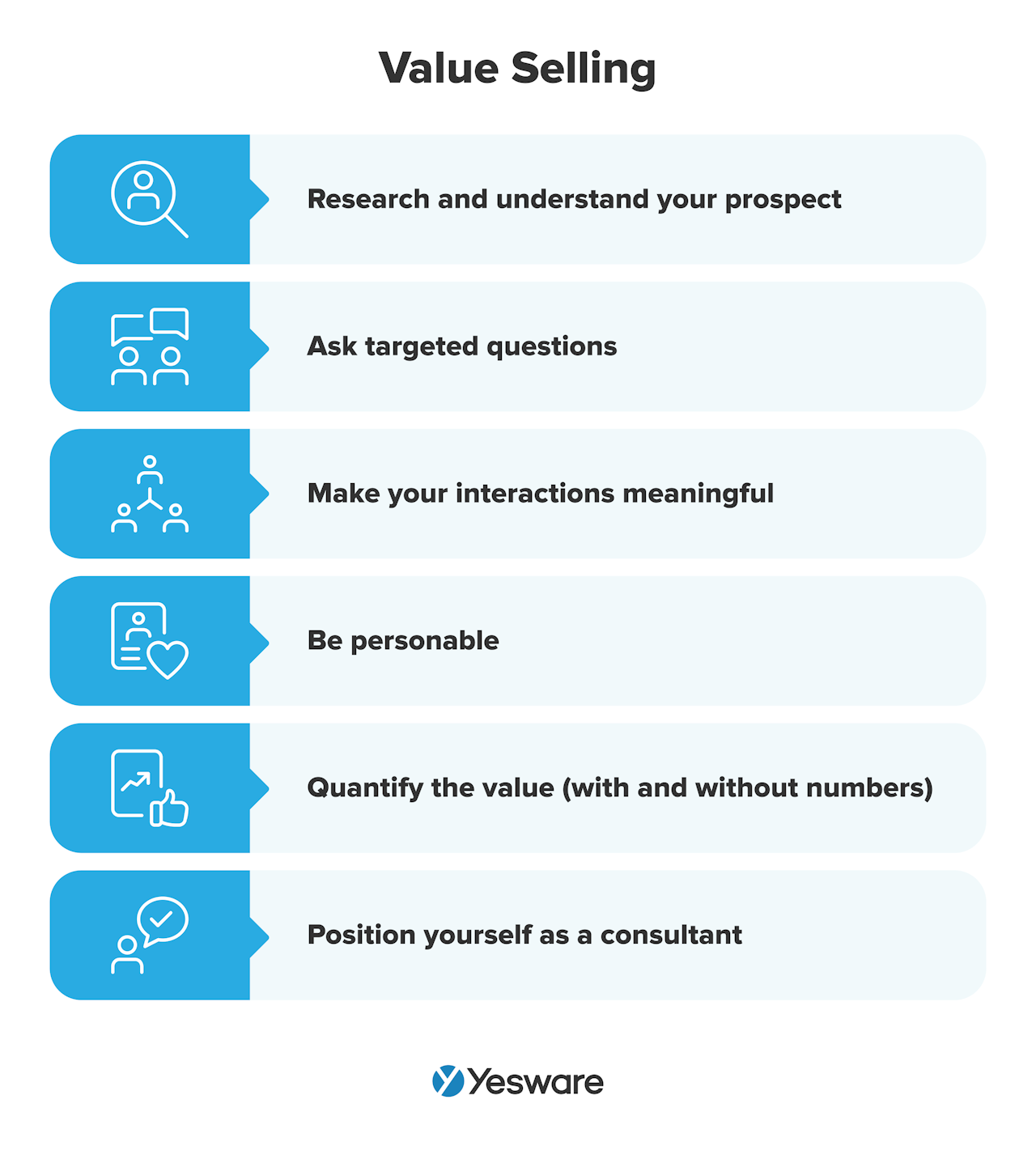
This section works best when it’s laid out according to each stage of the sales cycle .
The sales landscape is changing faster than ever, particularly with the rise of social selling . With that in mind, here’s another reminder to update this section with best practices as you continue to adopt and practice new strategies.
6. Sales Execution & Action Plan
If the sales organization structure section is your roster, then the execution & action plan is your playbook.
Here is the real “meat” of your sales plan. This section is where you will outline the very specific sales activities, timelines, deadlines, and milestones that you expect to take place throughout the sales process.
Be as specific as possible here. “Make 200 cold calls” is far more executable than “Call prospects.” The SMART goals and sales strategies you outlined will drive your execution plan. Include all relevant deadlines, as well as the individuals directly responsible for meeting them. It can be beneficial to break this section down into monthly, quarterly, and yearly timelines.
Tip: Grab this free interactive worksheet that helps you identify the number of calls, conversations, new opportunities, and deals needed to hit your quota each month.

The specificity here will serve two primary purposes.
First, it will be an enormous help to your sales team. There’s no better way to learn on the job than with a step-by-step manual. It also makes the onboarding process very smooth.
It will also allow you to pinpoint which stages of your sales process are converting well, and which need help. It can show you where your sales team’s energy is currently going and where it’s most needed. If, for example, you see that most reps are spending 70% of their time prospecting and still not meeting their quotas, you may want to reconsider your marketing plan.
7. Measure KPIs
The last part of your sales plan involves measuring and analyzing your sales KPIs . What you measure and how you measure it will depend on your specific company, but it’s important to standardize them across the company so that everyone is working toward — and knows exactly how to achieve — the same sales targets.
Most companies choose to track both primary metrics — the ones that measure your overall, big-picture progress — and secondary ones that indicate levels of success throughout the various stages of selling. We’ll go over some of these in the next section.
A robust CRM can help you manage and track the many moving pieces of the sales process.
One of the most useful things about sales plans is that you can create one for just about any scenario your sales team might encounter.
Whether you’re entering a new market, launching a new product, or simply wanting to grow your revenue, a sales plan specific to your goals can make all the difference in your success.
Here are a few examples of the different types of sales plans your team might create.
Annual/Quarterly/Weekly Sales Plan
One straightforward way to write a sales plan is by determining goals for a specific time period.
Most sales teams create weekly/monthly/quarterly/annual goals; a sales plan can help everyone involved achieve those goals.
A sales plan created around a specific time period should include revenue goals, specific sales strategies and tactics, and a means for measuring progress.
Here’s an example of a quarterly sales plan :
New Product Sales Plan
A new product sales plan details the goals, strategies, tactics, and people involved in launching a new product. It’s essentially a blueprint for how to generate sustainable revenue from the launch.
A new product sales plan should also include competitive analysis, details or ideas about any potential strategic partnerships, information about your unique selling points, and a sales enablement strategy for the launch.
Customer Segment Sales Plan
A customer segment sales plan helps sales reps understand the many different sub-groups in their target market, and how to sell most effectively to each.
Your customer segments may be determined by geographic area. They may also be segmented by other demographic information, like company size or revenue bracket. A customer segment plan outlines the specifics of each of those segments and helps you optimize your sales strategies and tactics for each one.
30-60-90 Day Sales Plan
A 30-60-90 day sales plan is a popular option for new sales hires. This kind of sales plan outlines the approach and specific strategies that a new sales rep will take in their first 90 days on the job.

Days 30 through 60 are for putting the plan into action. Sales reps should jump into the sales process and track their progress, challenges, and successes. These will be analyzed later in order to optimize the process.
Days 61 through 90 are all about fine-tuning the plan. Sales reps should take the data they gathered through the first two phases and use any insights gained to create a new and improved iteration of the sales plan.
Market Expansion Sales Plan
If you’re hoping to start selling to a bigger market, a market expansion sales plan might help structure the process and improve productivity and results.
A market expansion sales plan outlines what a sales team must do in order to successfully expand into a new market or territory. Most often, this kind of plan addresses expanding into a new geographic market.
A market expansion plan should address distribution efforts to the new territory, as well as time zone issues and other logistical considerations.
Revenue-Based Sales Plan
A revenue-based sales plan is based on — no surprise here — revenue.
This type of sales plan focuses on sales forecasting and strategies to improve conversion rates in order to close more deals and improve the bottom line.
There are a number of ways to use your sales plan to measure your sales progress. Remember, your sales plan is a living, breathing document and should be scrutinized and updated as often as needed to reflect your current sales team, product pricing, market conditions, and sales tactics.
As your sales plan changes over time, your measurable metrics may need updating, as well. Consider tracking some of the following KPIs to keep your finger on the pulse of your team’s progress.
Revenue is one of the most straightforward metrics to track, but keep in mind that there are many ways to approach this. You can measure revenue in one or several of the following ways:
- Overall revenue
- Revenue by product
- Revenue from new customers vs. existing ones
- Revenue by territory or market
If you only track overall revenue, you lose out on valuable insights for growth. Your total revenue, for example, might look healthy, but a closer look could reveal that it’s streaming almost entirely from existing customers. Tracking revenue from new customers would highlight the fact that your company needs to focus on customer acquisition in order to continue generating new business.
Sales Activities
You can also track the day-to-day behavior and sales activities of your sales team. Consider monitoring things like:
- Social media engagement
- Scheduled meetings
- Demos and presentations
Remember, none of this is meant to spy on your sales team or micromanage their progress. Instead, the goal is to promote growth and efficiency.
Funnel Metrics
The sales cadence is another lens through which to analyze your team’s progress. Take a bird’s eye view of your sales pipeline and start tracking some of the following:
- Length of sales cycle
- Number of closed deals
- Number of deals that didn’t close after reaching a certain stage
- Value of the pipeline by individual and team, by month and by quarter
- Average contract value
- Conversion rate
Tracking these metrics will help you see any kinks in the overall process.
Lead Generation Metrics
When you track your lead generation progress, you can get valuable data about how effectively you’re reaching your target customers. The following data will help you set benchmarks and reach your business goals.
- Volume of new opportunities
- Lead response time
- Percentage of follow up
- Dropped leads
- Qualified leads
- Customer acquisition cost
If any of these metrics are lagging, you may want to work with your marketing or content teams and reconsider your marketing strategy.
Sales Productivity Metrics
Sales productivity metrics are great for seeing where your reps’ sales efforts are going. These metrics can be a bit more tedious to measure and track, but are well worth studying in the long run.
- Entering data
- Creating content
- Number of sales tools used
- Percentage of lead follow-up
Time is money, and knowing where your time is going has a direct impact on your bottom line.
Ultimately, it’s up to sales teams (ideally in collaboration with marketing) to decide what information will be most useful to them within a sales plan.
Here are some of the more common components that teams include in their sales plans.
Mission Statement
A company’s mission statement gives a high-level, goal-oriented synopsis of its purpose and how it serves the market.
Although this isn’t necessarily an actionable component of the sales process, it’s good to include it in the plan so that it’s front of mind as your team works to meet the goals laid out in the sales plan.
Target Customers
Your sales plan should always outline who your offer is best-fit to serve.
At a minimum, your sales and marketing teams should collaborate to define the ICP and buyer personas. But certain sales plans need to go beyond the basics and define their target market into subgroups. Some examples of customer segments might include:
- Upsells and cross-sells
Your target customer segments can also be defined by geography, demographics, and company size — just to name a few.
Team Structure
Many teams also include a section that succinctly outlines the people involved in the sales process, and their specific roles and responsibilities.
Effective sales plans outline roles and DRIs, so it’s a good idea to ensure that everyone has access to the roster, so to speak, as they execute the sales plan. This is especially important for larger sales teams.
Sales Goals and Revenue Targets
Every sales plan needs to include the goals it aims to achieve.
Remember to follow the SMART goal framework; our goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
It’s especially important to make clear in your sales plan how your team plans to track your progress toward those goals. How and when will you monitor/measure performance? What are the performance benchmarks you’re hoping to achieve in a given time period? These specifics should be outlined in full in your sales plan.
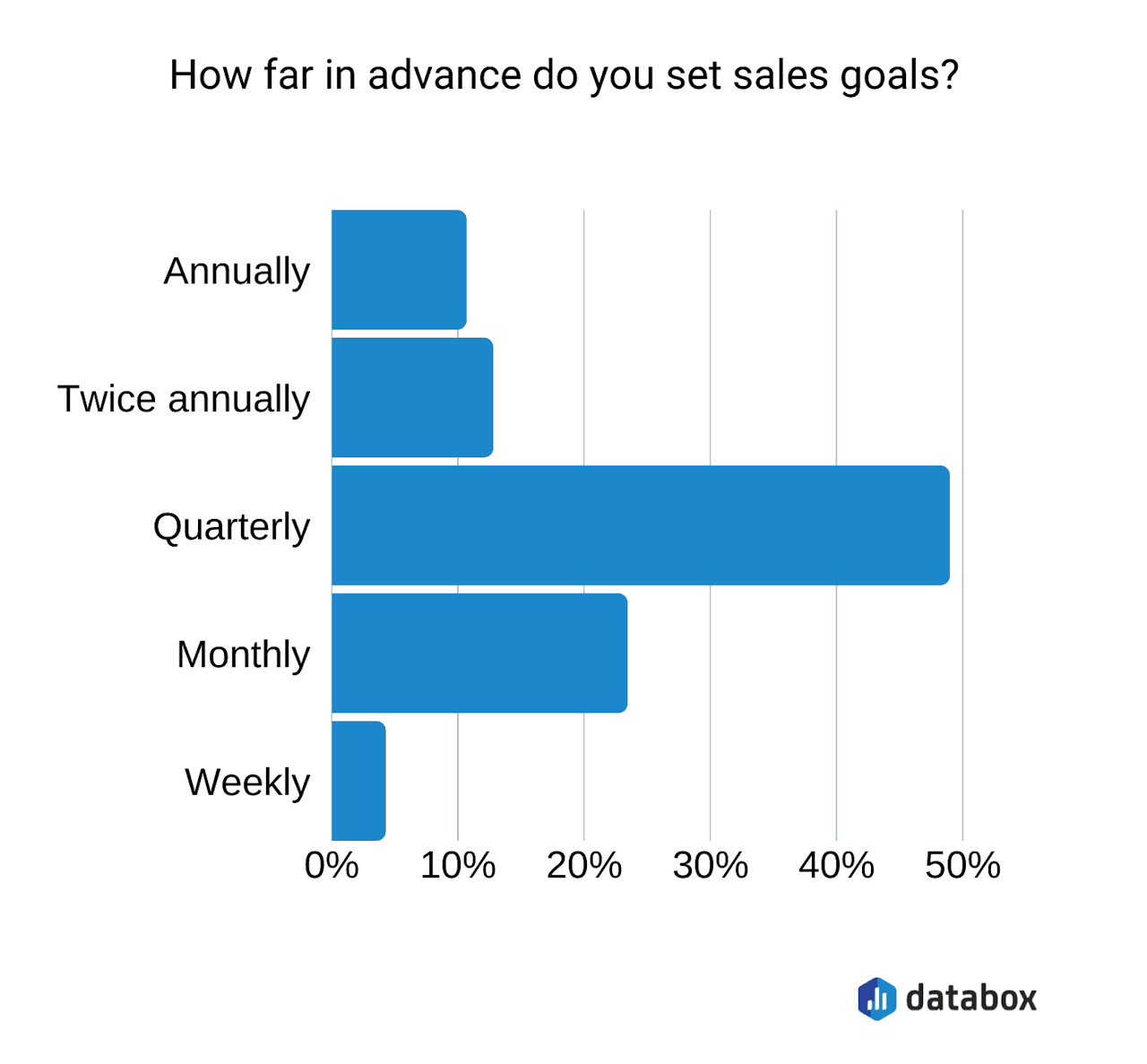
Performance During the Prior Period
You can give your sales plan context by including data about your team’s past performance in your goal areas. This helps salespeople understand how much of a gap they need to fill in order to succeed.
Strategies and Tactics
Your sales plan must include details about the specific strategies, tactics, and/or methodologies your team will use to reach their goals. This section should be action-oriented and aligned with the unique buyer’s journey of the target market.
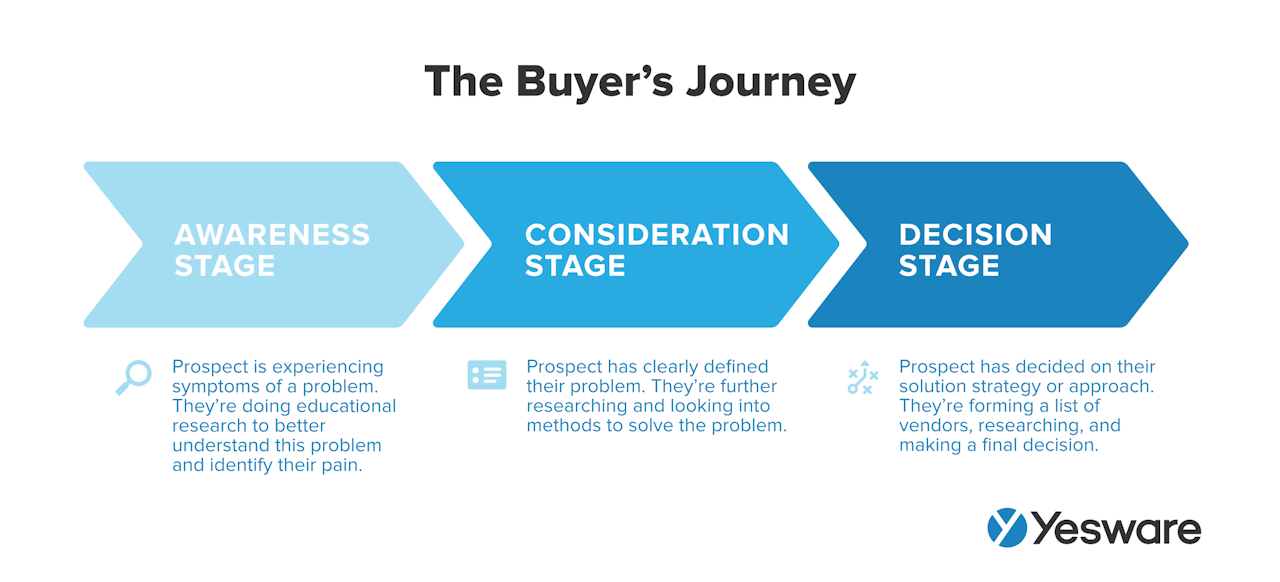
You’ll also want to include details and actionable insights about any specific sales strategies you want your team to use.
Pricing and Promotions
Most sales plans will also need to include at least basic information about your offer’s pricing structure , and whether or not you plan to offer any promotions.
Be thoughtful about these numbers, especially promotions. Sales teams need to strike a fine balance between attracting customers with hard-to-refuse deals and making enough profit to affect the bottom line in a meaningful way.
Deadlines and DRIs
Every sales plan needs to include clear information about who is responsible for which deliverables, and when those deliverables are due.
Everyone on the team needs to be clear on the DRIs (directly responsible individuals) for each step of the plan.
A timeline can also be a very helpful visual component of a sales plan.
It’s also a good idea to include an overview of the resources and/or tools your team will need to use in order to execute the plan successfully.
Resources might include a CRM system, project management software, sales enablement tools, forecasting software, or a sales dashboard . You should also include a breakdown of the budget.
Market Conditions
You can also add some context to your sales plan by including insights about the current state of the market.
Information about general trends and potential disruptions in the industry can help motivate your sales reps to buy into your sales plan, as well as help them know how to approach their responsibilities. You’ll also want to include an in-depth competitive analysis.
Below you’ll find a basic sales plan template that you can copy and paste as a starting point. Remember, the sales plan is meant to be highly specific to your company, so it’s likely that the template here will not meet all of your needs. Instead, treat it as a jumping-off point and customize it until it captures all of the pertinent information.
[COMPANY NAME]
SALES PLAN [YEAR]
1. Mission Statement
3. Sales Team Organization
4. Target Market
- Demographics (Age, Marital Status, Location, Profession, Etc.):
- Challenges:
- Pain Points:
- Objections:
5. Sales Methodologies
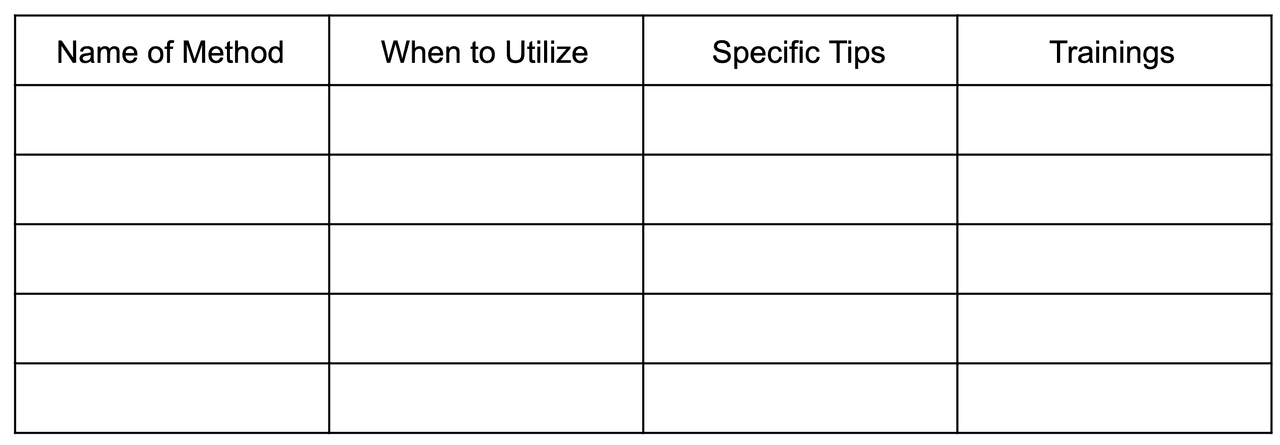
6. Action Plan
[This section is highly specific to your preference. Consider formatting as a list, table, or flowchart.]
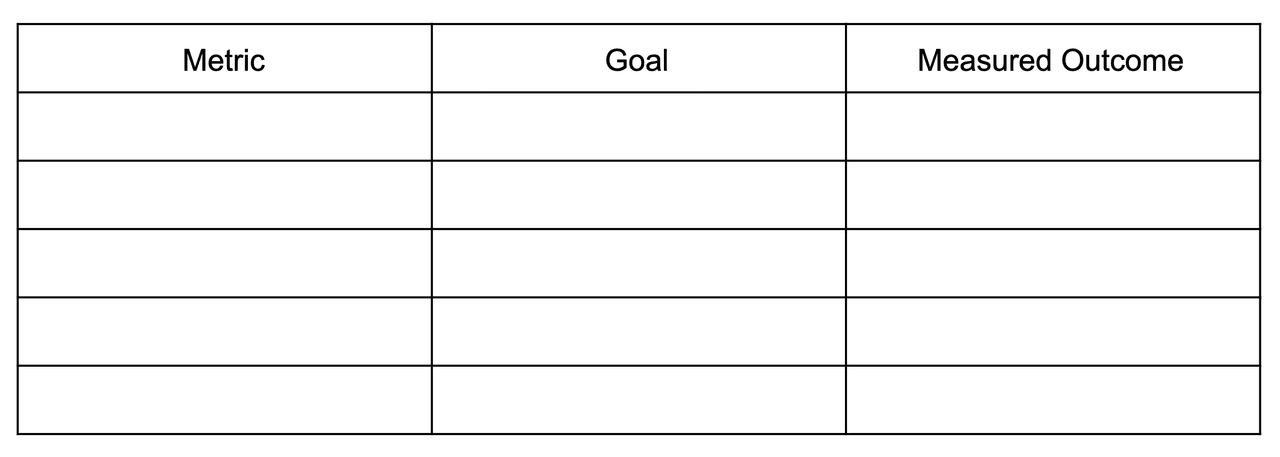
Here are a few examples of sales plans to fit a variety of scenarios. Remember, these are intended to be templates or starting points; they should be tweaked or changed to fit the unique needs and goals of your team.

Basic Sales Plan Template
Best Templates offers a comprehensive and straightforward sales template that can be adapted to fit just about any sales goal.

Simply download the template and fill in each section with relevant data and information. This template includes sections for goals, lead demand generation, implementation, and progress tracking.
Single Page Sales Plan
If you’re going for brevity, a one-sheet sales plan might be a good fit for your team.

This template gets right down to brass tacks; it includes space for budget details, deliverables, and KPIs.
Customizable and Design-Forward
For a sales plan that’s custom to your needs and looks great to boot, try Venngage . Venngage is an online sales plan creation software that helps sales teams create actionable, visually engaging sales plans.
Venngage offers users the ability to choose from dozens of layout templates that they can further customize with charts, photos, and illustrations.

Tip: If you’re interested in the checklist above — grab the Google Docs version of it here.
Microsoft Word Sales Plan
This template allows sales teams to tackle multiple goals at the same time, making it easy to get a bird’s-eye view of how close your team is to achieving both individual targets and big-picture goals.
Tip: Grab more sales plans here –> 13 Strategic Sales Plan Templates
Here are some of our best tips for creating a sales plan that gets results.
Get Input From Marketing
Your sales plan will only be effective if your marketing team can attract the right leads.
It’s essential that sales and marketing teams remain in close collaboration as they create, track, and manage sales plans.
Understand Your Sales Rep’s Challenges
You can enable your sales reps to be most successful by creating your sales plans around their strengths, and taking their challenges into account.
Of course, sales reps will likely always encounter challenges during a deal — that’s to be expected. But the best sales plans are the ones that leverage their team’s strengths to get the job done and have built-in workarounds to address the team’s needs and potential challenges.
Don’t Move the Goal Posts Once It’s Complete
Although it can be tempting, it’s important to finalize your sales plan and refrain from editing it until the given time period is complete.
Your team will be best-served if you stick to the plan, collect data on the process, and use those insights to further optimize your next sales plan.
Get Feedback
Share your sales plan in draft form with members of other teams. Customer success , marketing, and finance teams can all offer valuable insights into how the proposed sales plan fits into the bigger picture of the company’s goals.
Set Individual Goals and Milestones for Your Team
All sales plans should include SMART goals for the sales team. But some of the most effective plans also include SMART goals for each individual sales rep that’s involved. This helps keep everyone on the team accountable.
This guide was updated on November 30, 2022.
Get sales tips and strategies delivered straight to your inbox.
Yesware will help you generate more sales right from your inbox. Try our Outlook add-on or Gmail Chrome extension for free, forever!
Hit your number every month
Works on Outlook or Gmail (+ many more integrations)
Related Articles

The Future of Sales AI
12 Proven Sales Approaches to Boost Performance

How to Write an Introduction Email That Wins You an In
Melissa Williams
Sales, deal management, and communication tips for your inbox
We're on a mission to help you build lasting business relationships.
75 Kneeland Street, Floor 15 Boston, MA 02111

How to Create a Sales Plan: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you looking to develop a solid sales plan that drives business growth and sets your team up for success? You’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through the essentials of how to create a sales plan, from understanding its importance to leveraging technology and tools for continuous improvement. Let’s dive in and unlock the full potential of your sales team!
Short Summary
- A sales plan is essential for business growth , setting goals, and optimizing operations.
- Creating a successful sales plan requires strategic thinking, careful planning, and ongoing refinement involving stakeholders.
- Leveraging technology & tools to track progress & make data-driven decisions encourages continuous learning & improvement among the sales team members.
Understanding the Importance of a Sales Plan
A sales plan is a document that outlines target customers, business objectives, tactics, obstacles, and processes, as well as resources and strategies to help achieve the desired goals. It plays a vital role in business growth by providing direction, establishing objectives, and delineating strategies to accomplish revenue targets.
Furthermore, a well-defined sales plan helps identify the right sales tools to be used by the sales team, ensuring that they operate at their highest potential.
However, creating a successful sales plan is no easy feat. It requires a clear understanding of your target market , a well-defined sales strategy, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. The good news is that with the right approach and tools, sales managers can develop a winning sales plan that drives business growth and keeps their team focused on achieving their goals.
So let’s explore the key components of an effective sales plan.
The role of a sales plan in business growth
Sales plans play an essential role in business growth by setting targets, allocating resources, and optimizing operations. Regularly reviewing a sales plan helps identify growth opportunities, prioritize customers, maintain competitiveness, and adapt to changes in market conditions. By having a clear sales plan in place, your team can focus on the most critical tasks and maximize their efforts to generate revenue.
A strategic sales plan for business development zeroes in on securing new business opportunities by engaging in activities such as networking, sponsoring events, and outreach. Organizing a sales team and focusing on business development is vital for long-term success, as it helps your organization stay competitive and plan for future growth. The right sales tools play a significant role in organizing a sales team and supporting business development.
Benefits of having a sales plan
A sales plan has numerous advantages, including enhanced efficiency, sound decision-making, and augmented revenue. A well-defined sales plan helps motivate your sales team and allows them to recognize the impact of their individual contributions on overall business success. Moreover, delineating roles and responsibilities in a sales plan facilitates efficient task delegation, enhances collaboration, reduces overlap, and increases accountability among team members.
Pricing and promotions also play a crucial role in your sales plan, as they have the power to attract customers and drive them to purchase. By considering the needs of your target customers and adjusting your pricing and promotional strategies accordingly, you can maximize the potential of your sales plan and, ultimately, boost your bottom line.
Key Components of an Effective Sales Plan
Now that we understand the importance of a sales plan let’s explore its key components. An effective sales plan typically includes setting SMART objectives, defining target markets, developing strategic sales approaches, and allocating budgets and resources. By focusing on these essential elements, you can create a comprehensive sales plan that keeps your team on track and drives business growth.
It’s important to remember that the investment required to devise a sales plan is primarily time-based, not monetary. By dedicating the necessary time and effort to develop your sales plan, you can ensure that your team has a clear roadmap for success, complete with the tools and support they need to achieve their goals.
Setting SMART sales objectives
Establishing SMART sales objectives ensures that your goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound. When setting realistic and attainable sales targets, it is prudent to review past and current data to gain an understanding of your current position as well as what can be achieved in the short term and longer-term.
By setting SMART objectives, you provide your team with clear, actionable goals that drive them toward success.
Defining your target market
Defining your target market is crucial in focusing your sales efforts on the most profitable customer segments. This involves identifying factors such as industry, company size, and common challenges that your ideal customers face.
By understanding the needs and preferences of your target customers, you can tailor your sales strategies to effectively address their pain points and maximize the potential of your sales plan.
Developing strategic sales approaches
Developing strategic sales approaches involves creating tactics to reach and engage potential customers. Examples of sales strategies include outlining potential buyer pain points and how to address them, detailing the various ways to connect with the target customer and disseminate information about a new product, and implementing a lead scoring model to identify high-quality leads. By incorporating these strategies, your sales plan will be more effective and targeted.
The action plan is another indispensable component of a sales plan. It delineates the precise steps and tactics that will be employed to accomplish the established goals. Include concrete actions in your sales plan provides guidance and ensures that your team takes definite steps to attain the objectives outlined in the document. This, in turn, helps keep your sales team focused and accountable for their actions.
Allocating budgets and resources
Allocating budgets and resources is essential to guarantee financial feasibility and adequate support for your sales plan. This involves allocating resources according to the goals and objectives outlined in the plan and ensuring that your team has access to the necessary tools, software, and resources to achieve success in their roles.
By effectively allocating budgets and resources, you can create a sales plan that is both well-supported and financially viable within your overall business plan.
Steps to Create a Sales Plan
Creating a sales plan involves a series of steps, including analyzing past performance, identifying gaps, setting up team structure, coordinating sales and marketing efforts, and monitoring progress. By following these steps, you can develop a comprehensive sales plan that keeps your team focused on achieving their goals and drives business growth through an effective sales process.
It’s important to note that the sales planning process should be repeated annually to ensure that your organization’s sales excellence is maintained. By regularly reviewing and updating your sales plan, you can stay on top of industry trends, adapt to changing market conditions, and continually improve your sales strategies.
Analyzing past performance and industry trends
Analyzing past performance and industry trends is crucial in identifying areas for improvement and capitalizing on potential opportunities. This involves examining your sales data, conducting competitive analysis, and understanding buyer personas to gain insights into your current market position and areas where you can improve.
Regularly reviewing your sales plan allows you to adapt to changes in the market and maintain a competitive edge.
Identifying gaps and opportunities
Identifying gaps and opportunities in your sales plan allows you to make strategic adjustments to maximize your potential for success. By analyzing your past performance, industry trends, and customer feedback, you can pinpoint areas where your sales plan may be lacking and opportunities that can be exploited to drive growth.
Once you’ve identified these gaps and opportunities, you can adjust your sales plan accordingly to make the most of your resources and capitalize on new market trends.
Establishing sales team structure and roles
Establishing a clear sales team structure and defining individual roles is essential for ensuring efficient operations and maximizing the impact of your sales plan. By delineating roles and responsibilities, you can facilitate efficient task delegation, enhance collaboration, and ensure that each team member is accountable for their performance.
This also helps in the proper allocation of sales tools to each team member. This ensures that each team member has the resources they need to be successful in their role and that each team member has the resources they need to be successful in their role.
Aligning sales and marketing efforts
Aligning sales and marketing efforts is crucial for maximizing the overall impact of both departments on revenue generation. By coordinating your sales and marketing initiatives, you can ensure that your sales team has the necessary support and resources to effectively reach and engage your target customers.
This, in turn, helps to drive growth and increase your bottom line.
Monitoring progress and adjusting the plan
Monitoring progress and adjusting your sales plan is essential for ensuring continuous improvement and adaptability to changing market conditions. By regularly evaluating your sales performance and making necessary adjustments to your plan, you can stay on top of industry trends and continually refine your sales strategies to maximize your potential for success.
This approach also enables you to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive edge in your industry.
Sales Plan Templates and Examples
Templates and examples can serve as a foundation for generating individualized plans that are tailored to the specific needs of your business. By utilizing these templates, you can create a customized sales plan that addresses your unique business goals and objectives, ensuring that your sales team is well-equipped to drive growth and achieve success.
In this section, we’ll explore four types of sales plan templates that can provide a starting point for creating your own customized plan: the 30-60-90 day sales plan template, the territory sales plan template, the market expansion sales plan template, and the new product launch sales plan template. Each of these templates addresses specific business needs and can help you develop a comprehensive sales plan that drives growth and success.
30-60-90 day sales plan template
A 30-60-90 day sales plan template is ideal for new salespeople or businesses that are just starting to establish their sales objectives. This template breaks down your sales plan into short-term goals and action steps, allowing you to focus on immediate priorities and track your progress as you work towards achieving your long-term objectives.
By using a 30-60-90-day sales plan template, you can set realistic goals and create a clear roadmap for success in the early stages of your sales journey.

Territory sales plan template
A territory sales plan template focuses on targeting specific regions and maximizing sales within those areas. This template is particularly useful for businesses that operate in multiple locations or have a geographically diverse customer base.
By using a territory sales plan template, you can ensure that your sales team’s efforts are focused on the most profitable regions and effectively allocate resources to drive growth in those areas.
Market expansion sales plan template
A market expansion sales plan template is designed to outline strategies for entering new markets and growing your market share. This template is ideal for businesses looking to expand their reach and tap into new customer segments.
By using a market expansion sales plan template, you can develop a comprehensive plan that addresses the unique challenges and opportunities associated with entering new markets, ensuring that your business is well-positioned for success.
New product launch sales plan template
A new product launch sales plan template provides a framework for successfully introducing new products to the market. This template includes sections for market research, target audience analysis, pricing strategy, promotional activities, sales goals, and timelines, ensuring that all necessary aspects of the product launch are taken into account and executed effectively.
By using a new product launch sales plan template, you can streamline the product launch process and maximize the potential for success.
Tips for Creating a Successful Sales Plan
Creating a successful sales plan requires a combination of strategic thinking, careful planning, and ongoing refinement. In this section, we’ll share some tips that can help you develop a sales plan that drives growth and keeps your team focused on achieving its goals. By following these tips, you can foster a culture of continuous improvement and adaptability, ensuring that your sales plan remains relevant and effective in an ever-changing market.
Some strategies for creating a successful sales plan include involving stakeholders, regularly reviewing and updating the plan, fostering collaboration between departments, leveraging technology and tools, and encouraging continuous learning and improvement. By incorporating these strategies into your sales planning process, you can create a sales plan that drives growth, maximizes the potential of your team, and positions your business for long-term success.
Involving stakeholders
Involving stakeholders in the sales planning process is crucial for ensuring buy-in and support from all relevant parties. This can be achieved by soliciting feedback from experienced associates, such as accountants, senior salespeople, or knowledgeable acquaintances, and requesting input from your sales team, including sales reps.
By incorporating the insights and perspectives of various stakeholders, you can create a sales plan that is well-rounded and addresses the diverse needs of your organization.
Regularly reviewing and updating the plan.
Regularly reviewing and updating your sales plan is essential for keeping it relevant and aligned with changing market conditions and business goals. This involves assessing your current performance, identifying any gaps or opportunities, and making adjustments to the plan as needed.
By regularly reviewing your sales plan, you can stay on top of industry trends, adapt to changing market conditions, and continually refine your sales strategies.
Fostering collaboration between departments
Fostering collaboration between departments, such as sales and marketing, is crucial for maximizing the overall impact on revenue generation. By promoting open communication, establishing clear goals and objectives, and providing resources and support to assist teams in working together, you can create a collaborative working environment that drives growth and success.
This, in turn, helps break down silos and encourages the sharing of knowledge, resources, and ideas across your organization.

Leveraging technology and tools
Leveraging technology and tools, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems, can streamline sales processes and improve efficiency. By implementing these tools and technologies, you can automate repetitive tasks, allowing your sales team to focus on more critical activities and drive growth.
Additionally, technology and tools can help you track progress and make data-driven decisions to refine your sales plan and maximize its effectiveness.
Encouraging continuous learning and improvement
Encouraging continuous learning and improvement among your sales team promotes skill development and adaptability, allowing them to stay competitive and provide superior customer service. This can be achieved by providing access to training materials, offering incentives for completing training, and fostering a culture of learning and development within your organization.
By promoting continuous learning and improvement, you can ensure that your sales team remains at the top of their game and is well-equipped to drive business growth.
In conclusion, creating a successful sales plan is crucial for driving business growth and maximizing the potential of your sales team. By understanding the importance of a sales plan, incorporating key components, following a step-by-step process, and utilizing various templates and examples, you can develop a comprehensive sales plan that keeps your team focused on achieving their goals. Remember to involve stakeholders, regularly review and update your plan, foster collaboration, leverage technology, and encourage continuous learning and improvement to ensure long-term success. Now it’s time to take action and create a winning sales plan for your business!
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you write a brief sales plan.
To create an effective sales plan, outline realistic goals, set deadlines and milestones, build traction in the industry, define a value proposition, establish a list of prospects, and track and measure progress.
This plan should include realistic goals that are achievable within a certain timeframe. Deadlines and milestones should be set to ensure that progress is made in a timely manner. Building traction in the industry is also important, as it will help to create a larger customer base. A value proposition should be made.
What is the creation of a sales plan?
A sales plan is a blueprint for achieving revenue targets, where sales leaders define long-term company goals and create an annual plan with strategies and resources necessary for achieving them. It includes information on the business’s target customers, revenue goals, team structure, and more.
What is the importance of a sales plan in business growth?
A sales plan is essential for business growth, providing direction, setting objectives, and outlining strategies to reach revenue goals. It also assists in recognizing the appropriate sales tools to be used by the sales team.
Having a well-defined sales plan is critical for any business that wants to succeed. It helps to ensure that the sales team is focused on the right goals and objectives and that they have the right tools.
What are the key components of an effective sales plan?
An effective sales plan should include setting SMART objectives, defining target markets, developing strategic sales approaches, and allocating budgets and resources.
SMART objectives are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound goals. Defining target markets involves researching customer needs and preferences and understanding the competitive landscape. Strategic sales approaches involve creating a plan to reach a target audience.
How can I ensure continuous improvement and adaptability in my sales plan?
Regularly review and update your sales plan, foster inter-departmental collaboration, leverage technology and tools, and prioritize continuous learning to ensure continuous improvement and adaptability in your sales plan.
Leave a Comment Cancel
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Email Address:
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Generate Leads
Find quality leads and discover new lead sources
- Email Finder
- LI Prospect Finder
- Chrome Extension
- Email Verifier
Close Deals
Automate outreach with personalized emails to grow sales
- Drip Campaigns
- Email Deliverability Check
- Email Warm-up
- Gmail Email Tracker
Manage Sales
Keep your lead base organized and your clients buying
Snovio Academy
Expert-led crash courses on growing sales.
Case Studies
Stories of growth from real businesses who use Snov.io
News, analysis, growth tips, tutorials and more
Sales Cheats
First-aid solutions to the most common sales problems
Help Center
Find answers to all your Snov.io questions with detailed guides
Beginner-friendly articles on all things sales and marketing
Security Center
See which audits and certifications ensure top-level protection of your data
Integrations
Sync Snov.io with over 5,000 of your favorite tools and apps
- Pipedrive Integration
- Hubspot integration
Integrate Snov.io features directly into your platform
How To Create A Sales Plan: Steps, Templates, And Examples
Want your sales to skyrocket?
You’ll need a strategy. And for the sales success, nothing works better than a strategic sales plan. The key concern, of course, is how to design a plan that impacts sales.
We’ve collected the necessary steps and sales plan examples so that you can promptly create a document that’s right for your organization.
What is a sales plan?
Advantages of a sales plan.
- Strategic steps to create an efficient sales plan
- Strategic sales plan templates
What sales plan to choose?
Let’s deal with the definition and sales plan elements first.
A sales plan is a strategy document that lays out a company’s plan for improving sales results over a particular period.
Its components may differ. But they all focus on the business’ growth: profit plans, sales strategies, analytics, target market, existing sales force potentials, and much more. +
To make things easier, we narrowed them down to 9 main elements that lead to smooth selling. But feel free to use as many of them as you like.
1. Revenue targets and business goals
Without goals, you won’t know if your sales strategy was successful, right? This is the part where you can set a specific number to shoot for or create multiple goals for your sales team.
If you are in doubt about what to include, here are some examples to spark a thought:
- Specific sales numbers;
- Number of new clients you want to convert;
- Number of existing customers you plan to nurture and retain;
- Sales goals around a new product or service you are offering.

If you write an annual sales plan, you can briefly recap the previous year, its goals, scope of work, and results. Identify the mistakes and actions that led to positive results and draw a lesson from them.
3. Your ideal customer profile and their user journey
Ask yourself a question: who do you want to attract and convert? Demographics, purchasing habits, and other factors will help you create your buyer persona .
But you shouldn’t stop here. It’s useful to outline the customer journey of your clients and suggest ways to improve their experience at every step of the sales funnel.
4. Customer segmentation and tactics to work with each segment
In this section, you can describe all segments of the leads you get from your channels and ways to communicate with them to boost profit generation. If new segments might appear in the future, describe them as well.
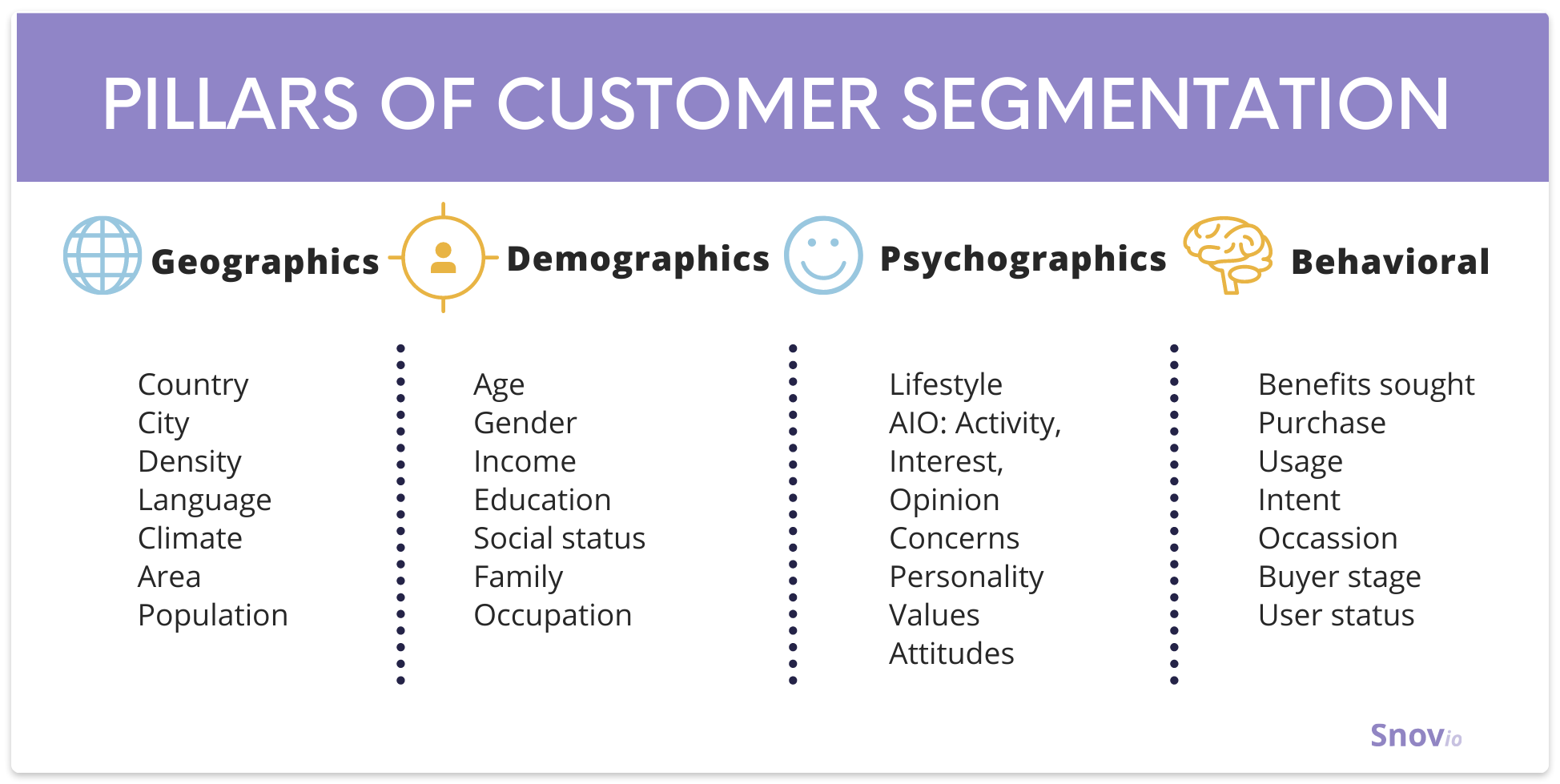
Research market trends that can strongly affect your sales and suggest ways to use them to boost your performance.
Without a budget set in place, you risk spending more resources than you intended to. Think of the team size and operational tools you need to process and close the deals.
7. Strategies and tactics
Suggest the best approaches for your company and describe their implementation.
8. Action plan for individuals and teams
Here, you can determine the roles and responsibilities of specific staff members, assign tasks, and set deadlines for them.
9. Performance criteria and analytics benchmarks
Describe the tracked metrics and systems that help monitor them.
You might now think, “That’s too many components to describe, do I need a sales plan at all?” Yes, you do. Let us explain why.
Of course, a sales plan promotes self-discipline and diligence, but it also ensures that your sales don’t dry up over time. Which means it’s not optional.
We all tend to talk a lot, but without a plan, your goals might never turn into reality. So, the first advantage of a sales plan is that it helps you realize all of your greatest ideas.
Besides, with it, you can determine the demand for your solution and identify new product areas to predict the growth of your business. It’s also a great tool in analyzing your rivals and competitive advantage to distinctly position your company in the market and specify your product niche.
Without the sales plan, it would be hard to choose strategies and metrics for your sales team. And, as a result, it would be more difficult to measure your progress, optimize your performance over time, and motivate stakeholders.
Here are all the benefits summarized:

8 strategic steps to create an efficient sales plan
If you only start in sales and have neither sales planning experience, nor previous statistics, the following extensive guide will help you organize your work at every step, be it a small startup or a big corporation.
Each aspect of the sales plan moves gradually into the next, beginning with the team’s high-level objectives, then considering market conditions, checking your existing audience, and discovering more leads to help you meet your sales demands.
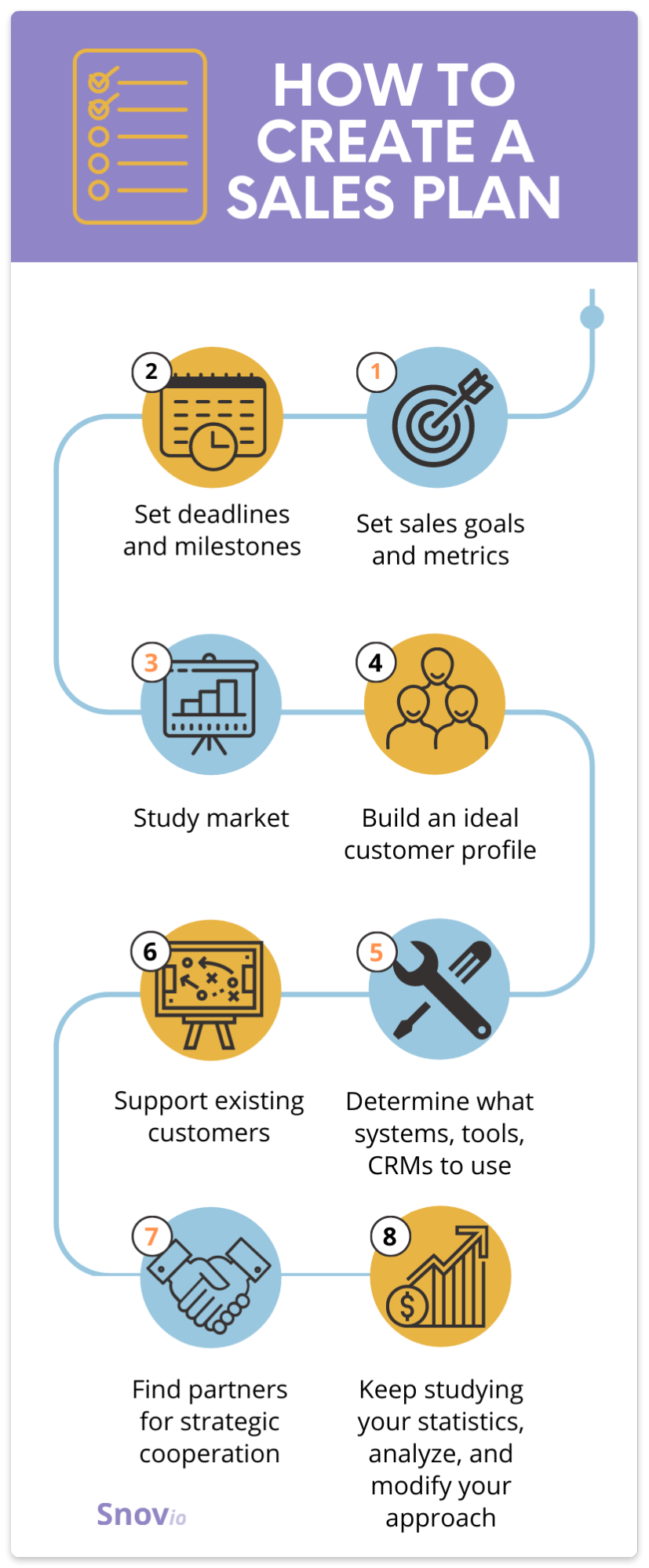
1. Set sales goals and metrics
Your sales plan structure needs an end goal . Identify what you can yield based on the size of the market, skills, and tools available to your sales team.
The biggest mistake you can make here is to set unrealistic goals. Yes, we know, you might be over-optimistic. But if you assume, for example, that the market’s going to go down and you’re going to lose a certain share, it won’t make any sense to forecast an increase in sales, right?
Another piece of advice is to ask your sales team what they think your goals should be. These people closely work with your clients and have the best understanding of them. Ask their opinion, give them enough time to think it over, and then discuss it together. Or, you can get a more experienced person to analyze the plan and help set metrics before approving it.
Remember, your goals must be SMART !
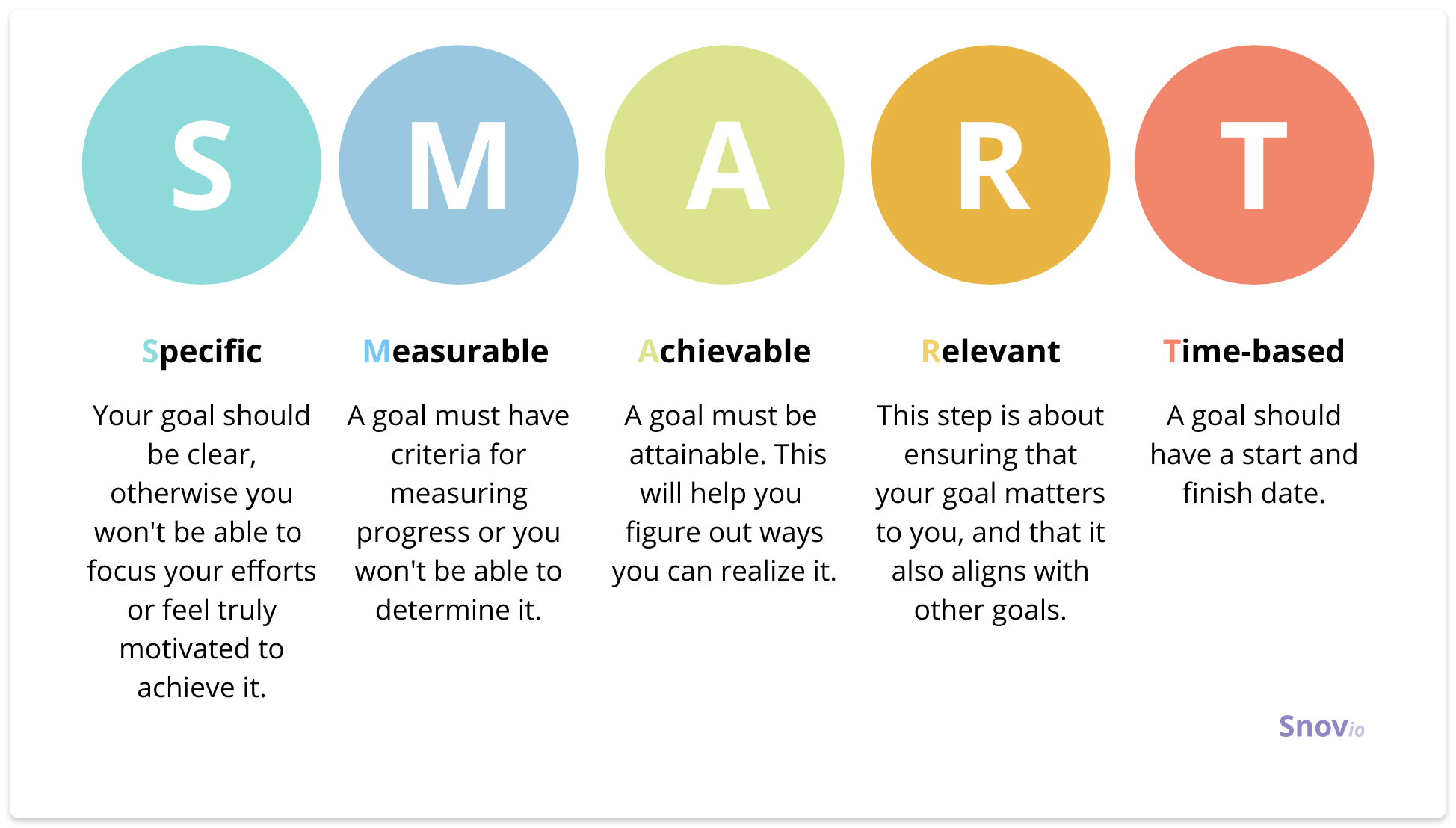
What metrics should you track while analyzing the success of your sales department? There are plenty of them to monitor:
- Sales growth
- Sales target
- Current opportunities
- Product performance
- Sales to date
- Quote-to-close
- Lead conversion rate
- Sell-through rate
It would be great for a team to have all the metrics displayed on one clear, intuitive dashboard . You can include screenshots of such dashboards in your sales plan for a more effective demonstration. For this task, such free tools as PowerPoint, Google Sheets, or Excel can be of great help. Or you can use any other software, as in the example:
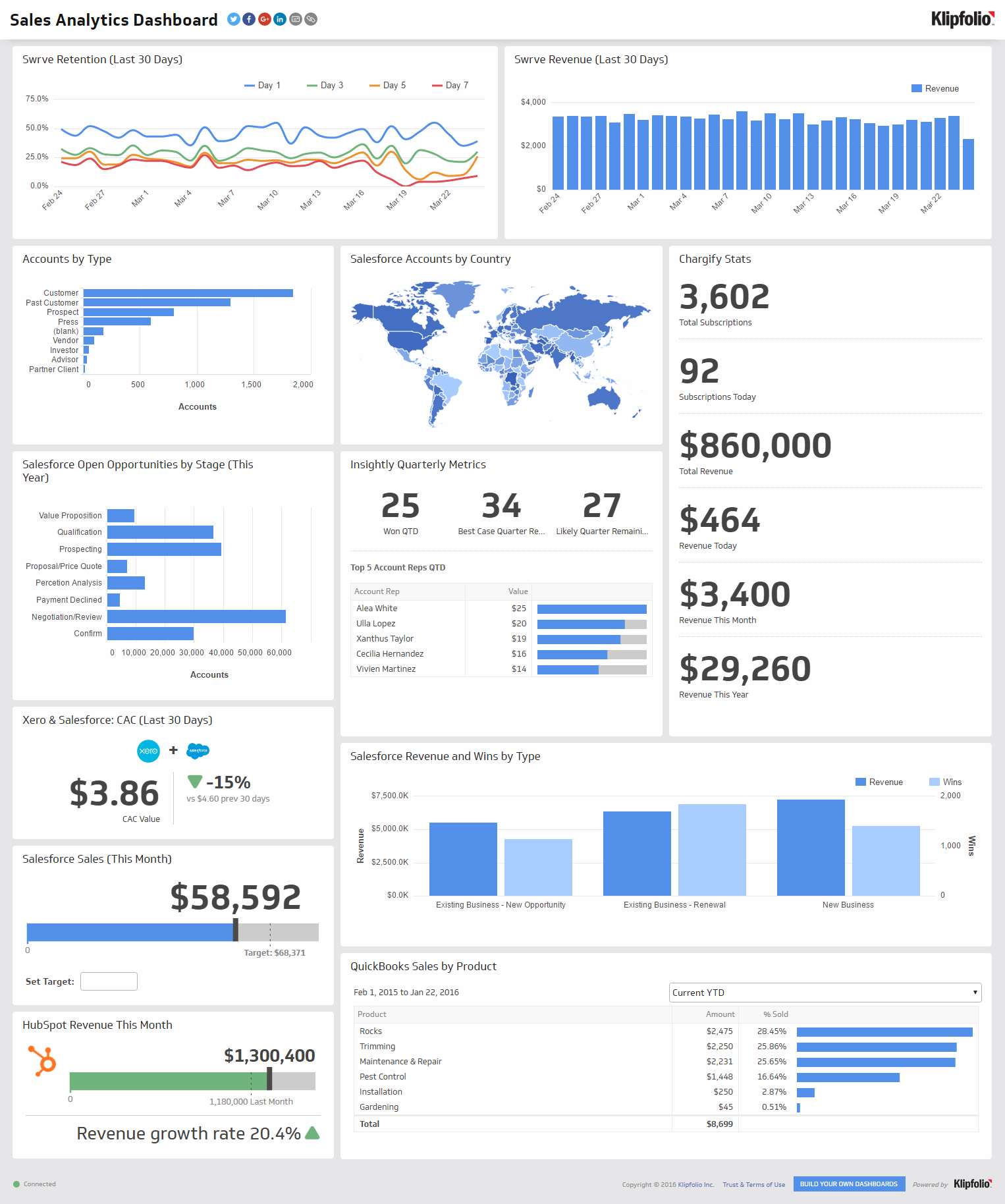
“But what if it turns out I was wrong in some of my assumptions around the sales plan objectives?”
Don’t worry. If you’re developing a template for the first time, this is perfectly normal. But what’s essential is that you’ll be able to learn what needs to be improved when it’s time for the next version of your sales plan.
2. Set deadlines and milestones
It will take a while to achieve your goals, so why not split them into smaller sized milestones with deadlines to track the progress? These targets are extremely convenient in checking if your sales plan is on the right track.
Use last year’s statistics . Observe how sales earnings improved and compare your company to the market criteria. Again, talk to your sales team about their work, how they generate leads, and how they convert them into clients. What is the current conversion rate? How many deals do they expect to close in the future? This will show you what objectives to set.
Your milestones need to be precise with definite deadlines . For instance, you might want to increase your client base by 25% or boost your revenue by 40% for a specified product by the end of Q3. No matter what the milestone is, set clear objectives and a tough deadline.
This is not it. It’s better to also set personalized milestones for your sales professionals, considering differences among your employees.
For example, if somebody on your team is sending a lot of emails but not getting deals, give them the task of increasing the number of their closed deals. If someone’s awesome at closing deals but doesn’t do much outreach, give them the task of generating at least 20 new leads a month.
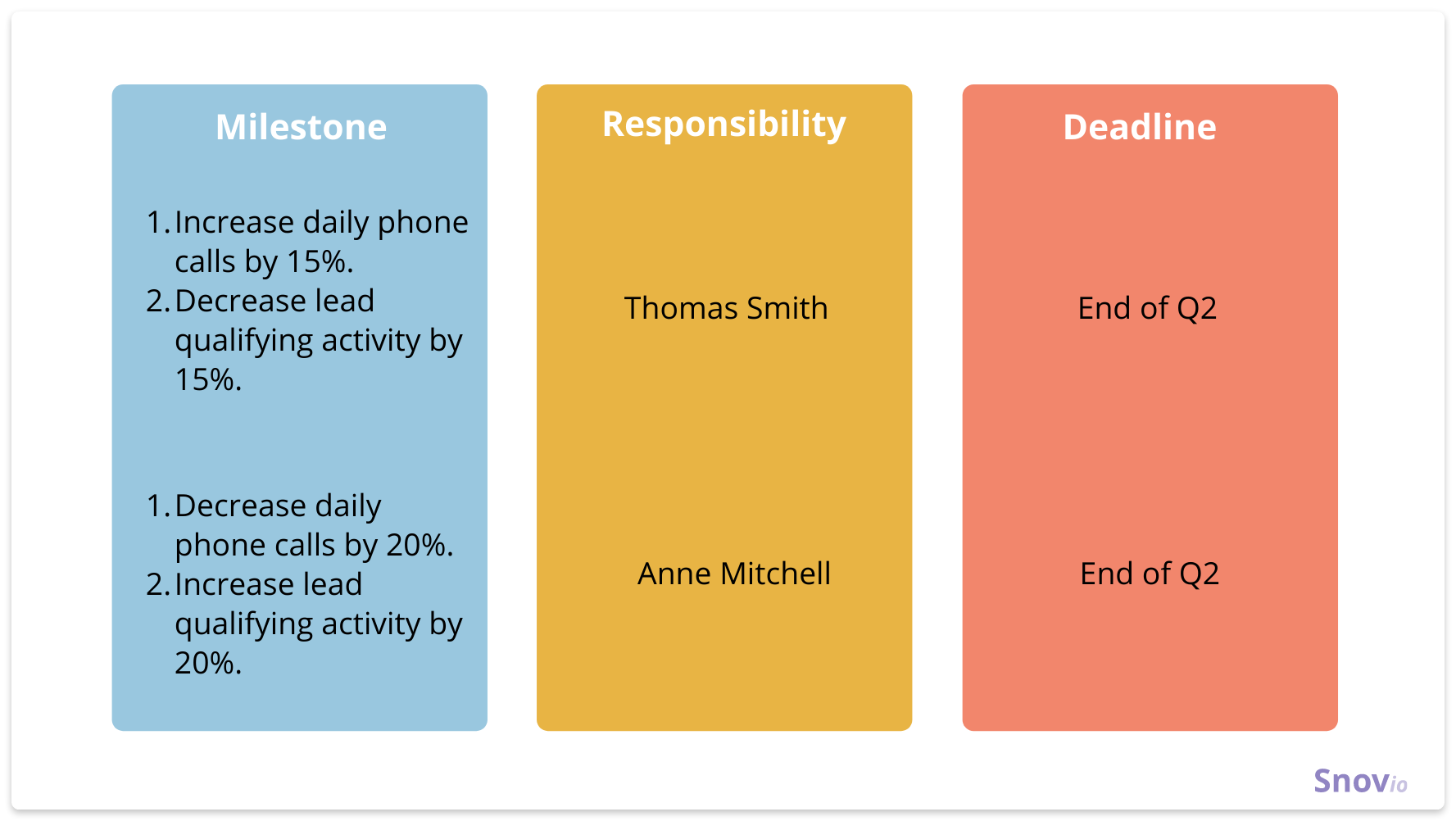
Oh, and set the budget as well! It usually includes:
- Sales training
- Salary and commission
- Tools, software, and resources
- Travel costs
3. Study market
You now know what you want. It’s high time to define the market niche you’re in so that you can accurately position your business to achieve the best results.
What’s a market niche? It’s what your company specializes in and also the place your business occupies, not only with your solution but also with generated content, corporate culture, and branding. It’s the way your audience identifies with you and recognizes you among competitors.
To analyze your niche, answer the following questions:
- How big is your potential market?
- Is there an inherent demand for your product?
- What’s your market situation today? ( SWOT analysis will be awesome here)
- Who are your competitors? (Again, SWOT analysis)
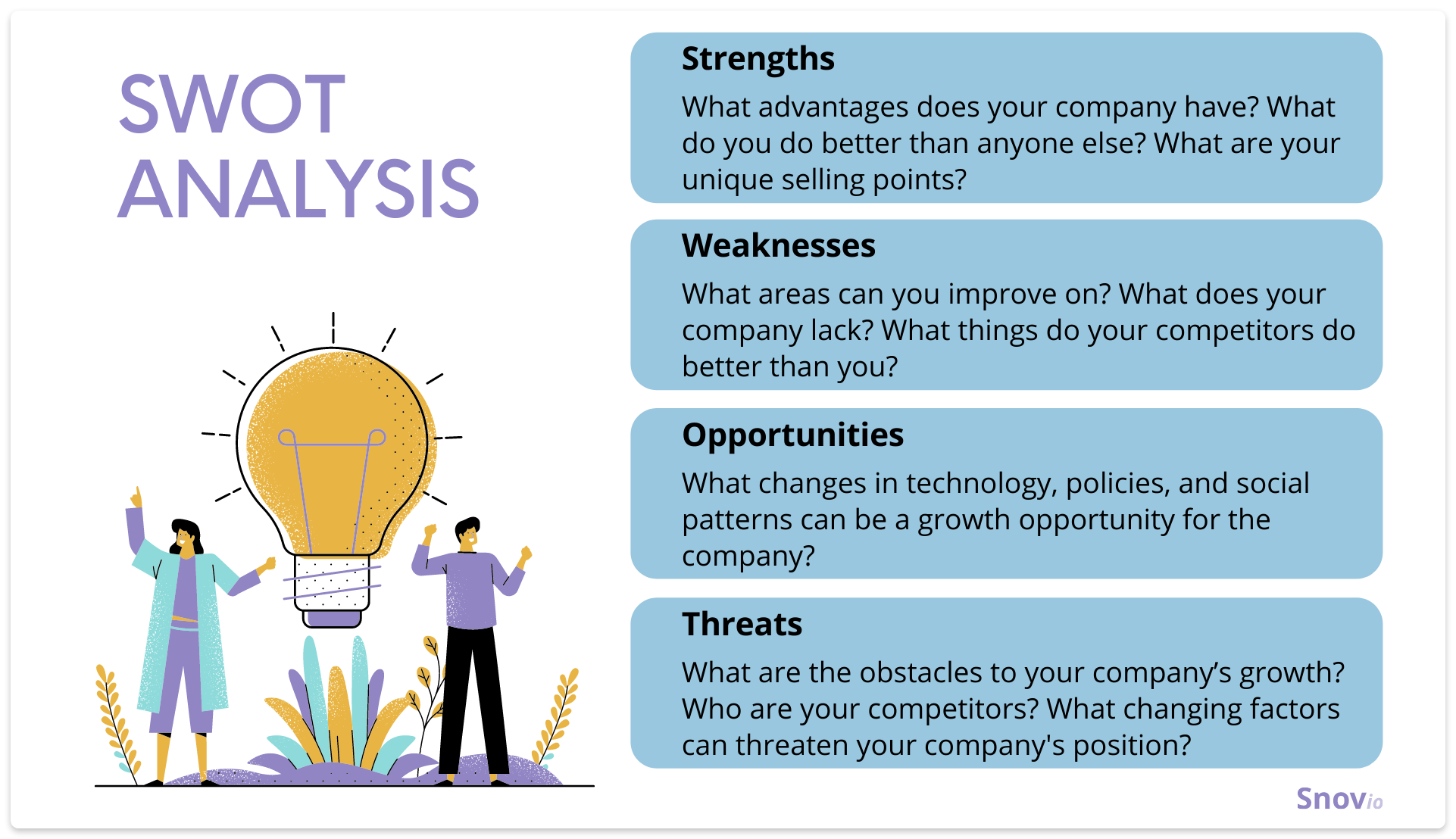
The key here is to find what your competitive benefit is:
- Why do clients decide to purchase from you?
- Why do customers buy from your rivals and never from you?
- How come some prospective leads do not purchase at all?
- What must you do to achieve success with time?
Keep in mind that clients purchase advantages, not characteristics. Whenever explaining your value proposition , it’s an easy task to get trapped in talking about your business too much. Put the script aside and mention exactly what your solution does for clients.
A good competitive advantage :
- Shows the competitive power of the organization
- Is ideally, although not always, unique
- Is obvious and simple
- May change over time
Your competitive advantage isn’t just a fundamental component of your sales strategy, it will determine everything your organization does, from advertising to product enhancement.
4. Build an ideal customer profile
Before you get inside your potential clients’ heads, you need to define who your target market is. Ask yourself questions:
- What do your best customers look like?
- What’s their personality like?
- What are their age, level of income, and living situation?
- What does their career journey look like?
- What industry do they belong to?
- Do they have the same pain points ?
- What are these challenges preventing them from achieving?
- What influences their decision-making?
- What content and information is most useful when communicating convincingly with them?
- What sorts of social networking platforms do they normally use?
5. Determine what systems, tools, CRMs to use
It will be hard to do everything without the right resources for the job. And that’s where CRM software and sales automation tools come in handy.
CRM is a technology for managing all business relationships and interactions with existing and potential customers within a company. It helps gather information on how many emails your team is sending, how much time they’re spending on qualifying leads, and how much revenue they are bringing in.
Meanwhile, with sales automation software, you will be able to standardize and automate the entire sales process. There are lots of professional tools for sales teams, these are just some of the examples:
- Salesforce,
- Freshsales,
- Insightly,
- Pipedrive,
- Microsoft Dynamics 365,
For example, a tool like Snov.io helps you fill your marketing funnel with quality targeted leads and close them easier. You can focus on every stage of the sales funnel and business growth: market research, lead generation, nurturing, conversion, statistics, analysis, and business forecasting for scaling and future growth.
6. Support existing customers
Don’t underestimate your current dedicated customers. References, word-of-mouth, client feedback, and existing connections are your best sources that ensure additional growth.
Check if anybody you know on social media can recommend you to one of your desired prospects. Contact loyal clients and offer them a discount or a referral bonus if they know someone who would profit from your products or services.
7. Find partners for strategic cooperation
Many entrepreneurs, startups, and big organizations might target the same types of customers. But oftentimes, they are not your competitors but rather offer services that can complement your solution (this is why they can be called CSPs or Complementary Service Providers).
You can engage with them in different ways:
- Writing for their website or blog;
- Delivering speeches at webinars or offline seminars;
- Offering valuable resources for their platforms;
- Creating a mastermind group where you can exchange contacts.
The more value you provide to your business partners and target audiences, the more connections you will have. All these services are provided for free and included as an additional investment in your sales strategy plan.
8. Keep studying your statistics, analyze, and modify your approaches
Don’t forget that your sales plan is a flexible document and needs to be regularly updated according to new market trends, outreach campaigns, features, or even staff members. Return to the document from time to time to see if your prognosis is close to reality.
Organize regular meetings to discuss progress, discover and solve problems, align the work across teams, get experience from your failures and success, and enhance your plan accordingly.
Strategic sales plan templates
If you want to find more inspiration, check out these simple yet helpful sales plan template examples.
- HubSpot Sales Plan Template
- Sales Plan by Asana
- BestTemplates Sample Sales Plan
- Venngage Online Sales Plan Maker Map
- BestTemplates Simple Plan
- Creately Sales Strategy Plan
- FitSmallBusiness Sales Plan
- BestTemplates Sales Action Plan
- TemplateLab Sales Plan Template in Microsoft Word
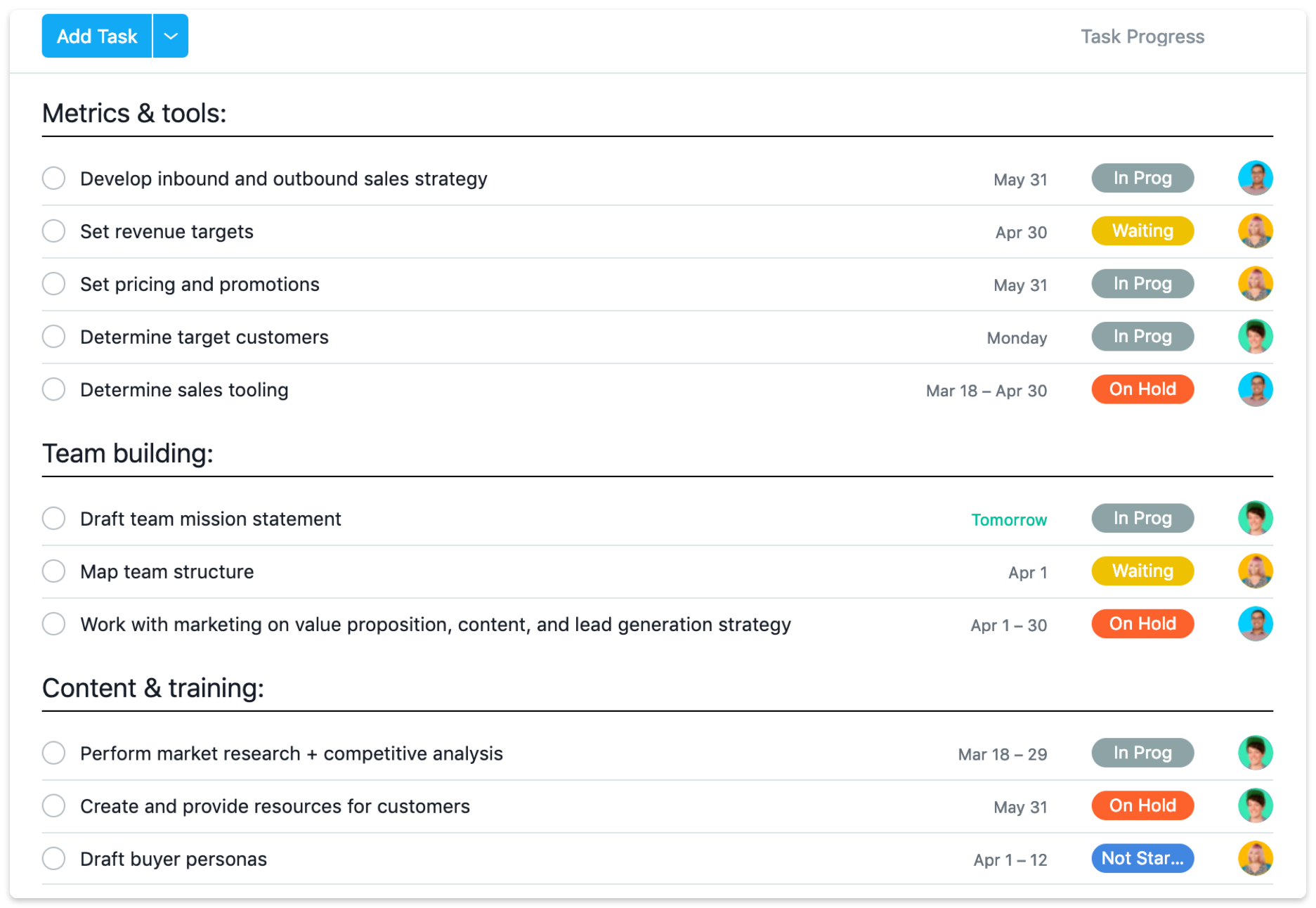
There might be one more question unanswered – what template to choose? It all depends on your particular business goals:
- The most common one is the 30-60-90 day sales plan with milestones that need to be achieved by each period.
- A weekly or yearly sales plan is also an option.
- You can create a sales plan for specific sales tactics , such as email drip campaigns, prescribed calls, and appointments. It sort of resembles a yearly/weekly sales plan, but it focuses on assessing and increasing gains for a single objective or task.
- In the meantime, sales professionals who manage a specific market region typically use region sales plans to present CMOs and VPs with more clarity of their sales initiatives.
Wrapping up
In many product sales circumstances, the greatest challenge is passiveness. However, with a great, step-by-step product sales plan and a passionate team with distinct milestones in mind, you’ll have everything you need to endure any resistance and carry on hitting your targets!
Leave a Reply (0) Cancel reply
Most Popular

How To Handle Sales Objections And Avoid The Backfire Effect
14 November 2023
Grow Your Business With Targeted Email Marketing
31 January 2024

How To Improve Customer Experience With Email
13 December 2022
Copied to clipboard
Thanks for subscribing 🎉
You will now receive the freshest research and articles from Snov.io Labs every month!
We've seen you before 👀
It looks like you've already subscribed to Snov.io Labs. Be patient - our next newsletter is already in the works!
For Sales Manager:
For sales reps:, 10 steps to create an effective sales plan for your growing business.
Updated On: 11 Mar, 2024
It’s no secret that in order to succeed, your business needs a good sales plan. Sales success is one of the most critical components of the long-term growth and profitability of any company.
But crafting a successful sales plan can be tricky – it’s not as simple as putting together a few goals and hoping for the best. It takes time, effort, and a lot of planning.
That said, don’t worry – we’ve put together a 10-step guide to help you create a successful sales plan for your business. From defining your target market to setting achievable goals , this guide will help you map out a plan that will help you achieve your sales targets.
1. Establish Your Company’s Mission Statement
- 2. Set Sales Goals
- 3. Understand Your Target Customers
- 4. Develop Sales Strategies and Tactics
- 5. Implement Sales Tools
6. Create your Sales Pipeline
- 7. Leverage Existing Customer Relationship
- 8. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
- 9. Set Your Sales Budget
- 10. Measure Progress and Adjust Accordingly
- Bottomline
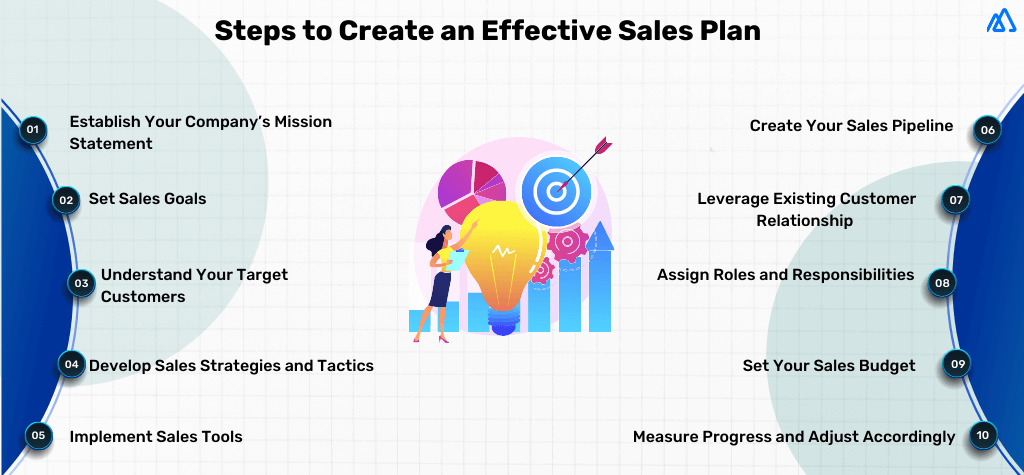
Your company’s mission statement is the foundation of your branding and marketing efforts. It communicates the heart of your company and its purpose to the world. A well-crafted mission statement can also help you make decisions about your products, services, and marketing.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when creating your company’s mission statement. First, make sure it’s clear and concise. Your mission statement should be easy to remember and understand.
Second, make sure it reflects your company’s values. The statement should be something you believe in and are passionate about. Finally, make sure it’s realistic. It should be something you can achieve and that provides a guide for your company’s future.
Some mission statements are short and sweet, while others are more in-depth. But they all share a few common traits. They are concise, clear, and inspiring. They also communicate the company’s values and goals.
Here are a few examples of simple, yet effective company mission statements:
Apple: “To bring the best experience to people in their lives.”
Netflix: “To connect people globally with great entertainment and communications experiences.”
Facebook: “To give people the power to share and make the world more open and connected.”
Google: “To organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.”
2. Set Sales Goals
Setting realistic goals is important to the success of your sales plan. You need to shoot for the stars, but also be grounded in reality. That way you’ll set a goal that’s challenging, yet achievable while avoiding building castles in the air.
When creating your goals, keep these factors in mind:
- Your past performance
- The market potential for your product or service
- Competitor activity
- Your company’s objectives and mission
- The resources (budget, manpower, tools, and training) you have at your disposal
You will also need to ensure your goals are S.M.A.R.T (specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and time-bound) .
Be specific about:
- your overall sales targets
- the timeframe to achieve them
- how you will track and measure your sales performance (key performance indices)
- individual targets for your sales team members
Here are a few SMART sales goals to include in your sales plan:
“We will increase monthly sales turnover by $20,000 for the next 6 months. To do this, we will acquire 4 new customers every month, the average value of each customer being $5000.
“We will reduce sales overheads by cutting down on non-essential travel by 50 percent over the next 9 months. We will strengthen our video conferencing capabilities to achieve this goal.”
Remember to set individual goals for your sales team members.
Points to consider when setting up goals:
-The size of your sales team
-How motivated they are
-Work environment/culture
-Amount of resources available to support the sales function
Consider your sales team members’ personalities and differences before assigning individual goals. For instance, one salesperson may be great at outreach but may be struggling with the closing ratio. Another salesperson may be good with closing ratio but not so successful with outreach.
3. Understand Your Target Customers
Defining your target market involves understanding who your customers are, what needs and wants they have, and how you can reach them. It’s important to be as specific as possible when defining your target market, as this will help you better understand who your customers are.
This will also help you understand what type of messaging and marketing efforts will be most effective in reaching them.
To do this, you’ll need to answer some key questions:
- What are their ages?
- Who is your product or service aimed at?
- What needs or problems does your product or service solve?
- What kind of people make up your target market?
- Where do they live?
- What are their incomes?
- What kind of lifestyle do they lead?
At this stage, it is important to get into the granular details of your target audience including the preferred networks, social media channels, and sources of information.
When you have a good understanding of who your target market is, you can start developing marketing materials and strategies that will appeal to them.
Once you have defined your target market, you need to understand what needs and wants they have.
This means researching your industry and marketplace, identifying trends, and understanding what motivations drive people to buy products or services like yours. It’s also important to understand the different segments within your target market, as not all customers will want or need the same things.
Evaluating the purchase history and purchase drivers of your targets will give you rich insights that you can use to create a foolproof sales plan.
Ask these questions to evaluate their purchase behavior and purchase drivers:
- How often do you buy products or services similar to ours?
- What problem/needs do they solve?
- Why you purchased those products or services?
- What factors (offers, reviews, comments, price, and so on) did you consider before choosing the product or service?
- How was the purchase experience?
- What features or benefits are most important in a product or service and why?
- What price are you willing to pay for a product/service that has these features or benefits?
4. Develop Sales Strategies and Tactics
A sales strategy is a roadmap for your sales team, setting out how you plan to achieve your targets and grow your customer base. It covers the key decisions you have made about how to position your products and services, how you will attack your rivals and the selling processes you will use.
A well-executed sales strategy can result in market dominance, while a poor one can lead to missed opportunities and financial distress.
There are many factors to consider when crafting or tweaking a sales strategy, including the target market, product, pricing, distribution channels, and promotion . It is essential that all of these pieces work together in order for the sales strategy to be successful.
While your sales strategies can include both inbound and outbound sales tactics, some of the most popular strategies include:
- Product demonstration
- Thought leadership through articles, webinars, and blog posts to share your niche expertise, best practices, and evidence-based solutions.
- Social media marketing
- Cold calls and emails
- Direct mail marketing
- TV, print, and radio ads
- Partnering with complementary service providers
5. Implement Sales Tools
For your sales plan to succeed, you will need the right tools. Sales tools reduce the time required for salespeople to understand their customers, their needs, and most importantly, their pain points. They save time by taking over time-consuming, repetitive administrative tasks, freeing up your time and resources to focus on offering value to customers.
While there are diverse sales tools, here are some of the most important ones:
CRM : A CRM ( Customer Relationship Management ) tool helps you get rid of manual work while streamlining sales data and sales activity. It provides updated information on prospects to your sales team to help them:
- Efficiently manage the sales pipeline
- Track emails easily
- Create granular sales reports
- Communicate efficiently with prospects
- Integrate seamlessly with other apps and tools
Sales Intelligence: These are technologies salespeople use to find, understand and monitor their existing clients and prospects.
The tool lets your sales team know who they should reach out to, when, and what they should talk about with the prospects. With contextual information about these contacts (digital footprint, purchase history, and business objectives), these tools make it easy to acquire leads and close deals.
Sales Acceleration: Examples of tools that accelerate sales include email tracking software, coaching tools, predictive analytics, outbound sales dialers, and sales engagement software.
Lead Acquisition: A range of advanced lead acquisition tools is available that include features such as autoresponders, chatbots, and sentiment analysis to feedback surveys. One such tool is offered by LinkedIn that makes it easy to acquire leads:
With this tool, you can
- Get custom lead recommendations.
- Leverage advanced search to look for the right leads
- Utilize InMail to send messages to any LinkedIn member.
- Track the results of your sales efforts
A sales pipeline is a visual representation of your sales process. It is a system that helps you track and manage your opportunities, and it also allows you to measure your success over time.
The most important part of creating a sales pipeline is understanding your sales process. Once you know what steps are involved in the sale, you can create a pipeline that accurately reflects those steps. The steps in your process may vary depending on your industry/offerings, but there are some basic steps that are common to most sales.
- Lead generation -The first step is usually identifying potential customers or leads. leads can be sourced from a variety of places, including advertising, networking, or referrals.
- Qualification of leads -Once you have a leads list, you need to qualify those leads to determine if they are actually interested in your product or service.
- Contacting leads and submitting proposals -The next step is to create proposals and pitch them to them. If a lead is interested in what you have to offer, they will usually request a proposal. At this point, you will need to create a proposal that meets their needs and submit it for approval.
- Closing the deal -If the proposal is approved, the next step is to close the sale. This may involve signing a contract, setting up an appointment for delivery or installation, or some other action that finalizes the sale.
You can use Funnel charts to gain clarity on multiple stages in the sales pipeline including the sales prospects you have.
7. Leverage Existing Customer Relationship
You have probably read that acquiring new customers is costlier than retaining the existing ones. Some estimates also suggest that loyal customers spend ten times more than new leads and account for 80 percent of a business’s sales revenue.
For growing businesses that have limited high-value clients, staying in touch with them on a personal basis may be possible. But for most companies, one-on-one outreach is not feasible.
You can nurture your existing clients in multiple ways:
- Send regular newsletters, special offers, and invites to events/webinars to your current customer base.
- Offer seasonal tips, free samples of new products, or other useful information
- Leverage opportunities on LinkedIn or other platforms to connect and engage with your current clients
- Ask for referrals and offer discounts or referral rewards
8. Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Sales roles and responsibilities within a company will vary depending on the company’s size, products, and target market.
The various roles that are involved in sales include:
- Account Executive
- Sales Specialist
- Development Rep
- Sales Manager
- Customer Success Rep
The most important factor to consider when assigning sales roles is determining which members of the team have the best skills and experience for the job. Once the right people have been identified, the next step is to define their specific duties and responsibilities.
This should be done in consultation with the team members themselves, in order to ensure that everyone is clear on their job duties and expectations.
It is important to provide regular feedback to team members on their sales performance. This can help them to track their progress and identify areas where they need to continue improving. everyone is clear on what is expected of them.
Finally, it’s important to establish some basic ground rules for how team members should work together. This includes setting expectations around communication, cooperation, and conflict resolution. By establishing a clear and mutually agreed-upon set of guidelines, team members will be more likely to collaborate effectively and produce positive results.
9. Set Your Sales Budget
Setting a sales budget is one of the most important steps in effective sales forecasting . Without accurate sales projections, it’s difficult to determine whether your team is on track to meet its goals and objectives. Moreover, it can be challenging to optimize spending and resources if you’re not aware of your company’s average sales cycle or customer acquisition costs.
There are a few key things to keep in mind when setting a sales budget:

- Know your historical sales volume and average sale size. This information will help you establish a realistic sales budget for your business.
- Determine your desired sales growth percentage. This will help you set goals for how much you want to increase your sales volume over time.
- Estimate your marketing expenses. Your marketing budget should be proportional to the amount of new business you expect to generate as a result of your marketing efforts.
- Calculate your expected return on investment (ROI) . Divide your marketing expenses by the increase in sales you expect to achieve as a result of your marketing efforts. This will give you an estimate of how much profit you can expect to make on each dollar you spend on marketing.
10. Measure Progress and Adjust Accordingly
It is easy to measure the progress of your sales efforts because you set SMART goals in the initial stage of your sales plan. There are a variety of ways to measure how well your sales team is performing.
One common way is to track how much revenue your team generates over a period of time. This can be done by dividing the total revenue by the number of days in the period. You can also calculate how much revenue each salesperson generates by dividing the total revenue by the number of salespeople.
Another way to measure sales performance is to track the number of leads that your team is able to convert into customers. This can be done by dividing the number of leads by the number of customers. Other metrics to track are customer lifetime value, customer churn, and gross margin.
Customer acquisition is the number of new customers that a business acquires in a given period of time. This metric is important because it measures how well the business is attracting new customers.
Customer lifetime value is the average amount of money that a customer spends with a business. This metric is important because it measures how much profit a business generates from each customer.
To calculate customer lifetime value, subtract the cost of acquiring a customer from the average amount of money that the customer spends with the business. This gives you the net profit generated from each customer. Divide this number by the number of times that customer has been active with the business to get the average lifetime value per customer.
Bottomline
Now that you understand the basic steps to creating your sales plan, it’s time to start putting it all together. Put your sales plan into action with a CRM. While sales plans are planned typically on a yearly basis, creating a monthly sales plan and using a Sales CRM can help you respond quickly to any changes to your financial objectives, company goals, or market dynamics.
Click here to find out more about how Kylas Sales CRM can help you ace your sales goals with ease.
Priyanka Mohanty
Priyanka is a marketer with over 13 years of experience in content curation. She has extensive blogging experience and has worked with many companies in the US. She is known to bring practical knowledge to the table. However, besides writing, Priyanka is also passionate about dancing, drawing, and reading.
- Sales CRM for Small Businesses
Sales Effectiveness
Sales Strategy
Recommended Articles
How To Build An Ideal B2B Customer Profile For Lead Generation?
Knowing your customer is at the centre of selling successfully. But who exactly is the customer? This is the million-dollar…
Published On: March 15, 2022
How CRM Solves Common Sales Territory Management Challenges?
In a market where competition is at an all-time high, organizations want to make the most of their sales teams.…
Published On: July 11, 2023
How to Manage your Sales Team without Micromanaging it?
Micromanagement is one of the most common challenges organizational leaders face and try to overcome. Thanks to Sales CRM, which…
Published On: August 06, 2021
Enterprise-grade CRM designed for your growing business
Kylas is easy to use, quick to deploy & comes with expert help
Why you will love Kylas!
Quick to Deploy
Easy to Use
Onboarding by Experts

4000+ growing businesses have signed up for Kylas!
Existing user? Login here.
An account with the given contact details already exists. Please proceed to log in or try signing up with a different email id or phone number.
By clicking on "Sign up for free", you agree to our terms and you acknowledge having read our privacy policy
Thank you for your interest in Kylas. Our experts will connect with you shortly.
22 Best Sales Strategies, Plans, & Initiatives for Success [Templates]
Discover sales strategy examples, templates, and plans used by top sales teams worldwide.

FREE SALES PLAN TEMPLATE
Outline your company's sales strategy in one simple, coherent plan.

Updated: 03/07/24
Published: 03/07/24
A strong sales strategy plan creates the foundation for a cohesive and successful sales organization.
Sales strategies and initiatives also align salespeople on shared goals and empower them to do their best work — keeping them happy and successful, too.
In this guide, I’ll dig into some sales strategies and initiatives that I’ve found can help you generate more leads and close more deals. But first, let’s define what a sales strategy is.

Table of Contents
What is a sales strategy?
Why is a sales strategy important, the most effective sales strategies, sales strategy types, sales planning: how to build a sales strategy plan, sales initiatives, sales strategy examples from successful sales teams.
A sales strategy is a set of decisions, actions, and goals that inform how your sales team positions the organization and its products to close new customers. It acts as a guide for sales reps to follow, with clear goals for sales processes, product positioning, and competitive analysis.
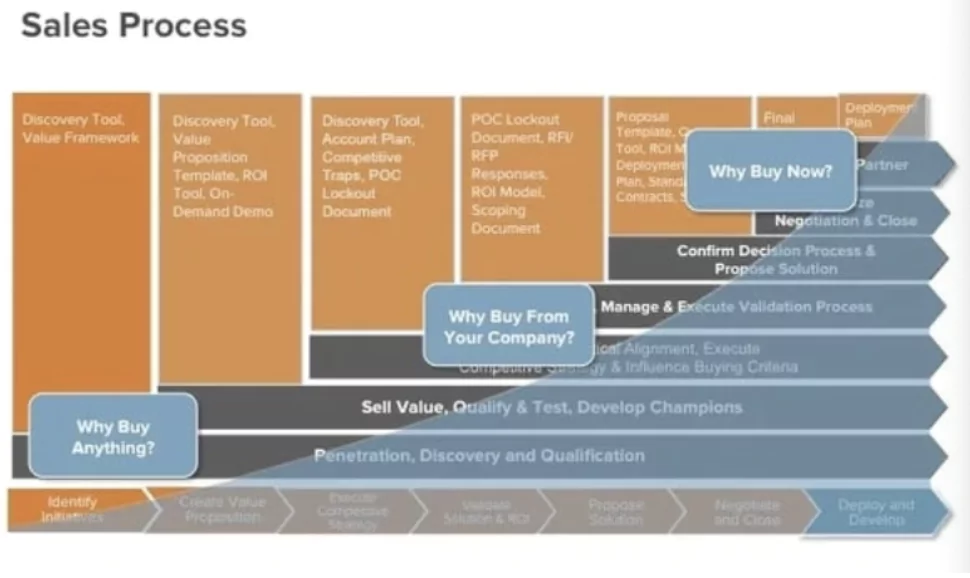
A clear sales strategy serves as a map for the growth of your business. Your sales strategy is key to future planning, problem-solving, goal-setting, and management.
An effective sales strategy can help you:
- Give your team direction and focus. Strategic clarity can help your sales reps and managers understand which goals and activities to prioritize. This can lead to improved productivity and outcomes.
- Ensure consistent messaging. Your sales strategy can help your team deliver a consistent message to prospects, partners, and customers. This can increase both trust and effectiveness.
- Optimize opportunities. Strong sales strategies will help you target the right prospects and customize your approach. This can help your team make the most of every sales opportunity.
- Improve resource allocation. Your sales strategy outlines your priorities and resources. In turn, this can help your sales team use their time, effort, and other resources more efficiently, boosting your team’s ability to focus on high-potential deals.
Next, let’s cover some of the sales strategies that I’ve found can be most effective.

50+ for Social Selling on LinkedIn and Beyond
Use this guide to improve your social selling efforts and close more deals from platforms like...
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
2. Become a thought leader.
Sharing your advice, tried-and-true best practices, and niche expertise are some of the most long-lasting ways to build your personal brand and lend more credibility to your organization. After all, nobody wants to feel like they’re being sold to. Instead, it’s better to help people by offering solutions to their problems.
That’s what thought leaders do. Indeed, a recent report found that “Thought leadership is one of the most effective tools an organization can use to demonstrate its value to customers during a tough economy — even more so than traditional advertising or product marketing, according to B2B buyers.”
According to the study, 61% of decision-makers believed that thought leadership could be moderately or very effective in demonstrating the value of a company’s products. Moreover, more than half of C-suite executives in the study believed that thought leadership has a greater impact on purchases during an economic downturn, making this an even more important element of a sales strategy in today’s uncertain economic times.
So what’s the catch?
Not all thought leadership content is created equal.
When done right, thought leadership can have a huge positive impact, but poor thought leadership can be devastating to a company’s sales goals. So, before you plan a spree of LinkedIn posts to drive leads, consider who your audience is, what they need to know, and how your organization can help.
Also, it may not hurt to have a second set of eyes from your marketing, communication, and PR departments review your plan first to make sure everything is on-brand (and trackable!).
3. Prioritize inbound sales calls as hot leads.
There’s an age-old question in sales: “Should I discuss product pricing with a prospect on the first sales call?” The honest answer is: It depends.
You and your sales team know your process better than anyone. So take it from me — if you’ve seen success with pitching with pricing first, last, or somewhere in between, stick with what’s working for you.
But beyond that, your team should always prioritize the prospects who come to you. These hot leads are definitely interested in what you have to sell, and before they make a decision, they want to get the information they need about how it will benefit them.
By prioritizing talking to these prospects as soon as they call in or send an email, you’re putting your best foot forward and showing them that you’re helpful, solutions-oriented, and considerate of their time. And if that means closing a deal on the first call, there’s nothing wrong with that — as long as the customer has the information they need to make an informed decision.
4. Properly research and qualify prospects.
I’ve personally discovered that even the strongest sales strategy can’t compensate for targeting the wrong customers. To ensure your team is selling to the right type of customer, encourage reps to research and qualify prospects before attempting to discuss your product. Indeed, throughout my career, I’ve found that more work on the front end can lead to smoother closing conversations later on.
Outline the criteria a prospect needs to meet to be qualified as a high-probability potential customer. These criteria will depend on your unique business and target audience, but they should generally be based on a prospect’s engagement history and demographics.
.png)
Free Guide: 101 Sales Qualification Questions
101 Questions to Ask Contacts When Qualifying, Closing, Negotiating, and Upselling.
- Budget Questions
- Business Impact Questions
- Competitor Questions
5. Implement a free trial.
Offering a free trial or freemium version of your product can be a highly effective way to convert prospects. In fact, HubSpot’s sales strategy report found that 76% of sales professionals feel that free trials are effective in converting prospects into paying customers, while 69% of professionals believe that freemium offerings are effective.
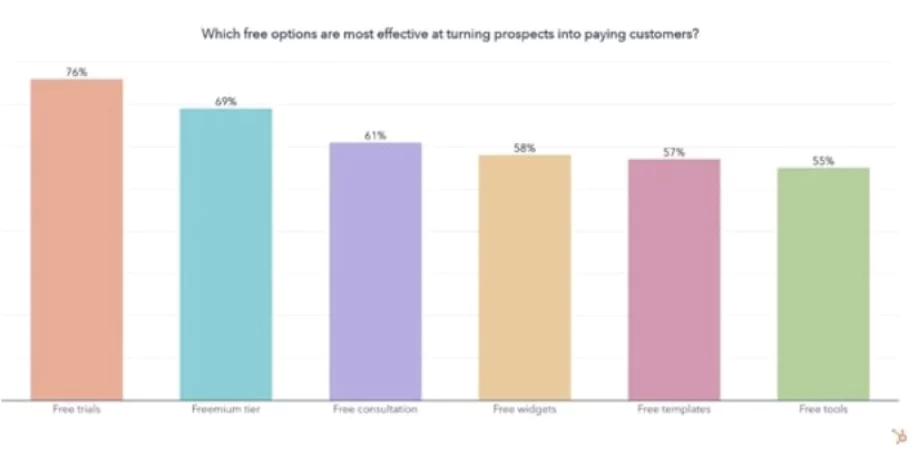
Keeping a list of proven, go-to closing techniques will help salespeople routinely win deals. Some of my favorite techniques include the ‘now or never close’ — i.e., “If you commit now, I can get you a 20% discount” — or the ‘question close,’ i.e., “In your opinion, does what I am offering solve your problem?”
.png)
Free Sales Closing Guide
An easy-to-use sales closing guide with three tactics you can use right away.
- Using an ROI calculator for your prospects
- How to ask confirmation questions
- Sales question templates you can use today
To further improve your closing techniques and learn to close deals with confidence, check out this free, downloadable Sales Closing Guide .
11. Nurture existing accounts for future selling opportunities.
Once a deal is done, there’s no need for a sales strategy, right? Wrong.
Account management is an incredibly important part of the sales process, as this is how you foster loyal, happy customers and identify cross-selling and upselling opportunities.
So, after your sales team sees success with its sales strategy, it’s vital to form a partnership between the sales team and customer service/success teams.
Remember: Ensuring customers’ continued satisfaction with your product or service will make them more likely to do business with your company again. You may even inspire them to advocate for it proactively.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

9 Bad Sales Habits (& How to Break Them In 2024), According to Sales Leaders

9 Key Social Selling Tips, According to Experts
![how to do a business plan for a sales company 7 Social Selling Trends to Leverage This Year [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/social%20selling%20trends.png)
7 Social Selling Trends to Leverage This Year [New Data]
![how to do a business plan for a sales company How Do Buyers Prefer to Interact With Sales Reps? [New Data]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/person%20phone%20or%20online%20sales%20FI.png)
How Do Buyers Prefer to Interact With Sales Reps? [New Data]
![how to do a business plan for a sales company 7 Sales Tips You Need to Know For 2024 [Expert Insights]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Sales%20Tips%202024%20FI.png)
7 Sales Tips You Need to Know For 2024 [Expert Insights]

What is Sales Planning? How to Create a Sales Plan

Sales Tech: What Is It + What Does Your Team Really Need?
![how to do a business plan for a sales company 10 Key Sales Challenges for 2024 [+How You Can Overcome Them]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales%20challenges%20FI.png)
10 Key Sales Challenges for 2024 [+How You Can Overcome Them]
![how to do a business plan for a sales company The Top Sales Trends of 2024 & How To Leverage Them [New Data + Expert Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales-trends-2023.png)
The Top Sales Trends of 2024 & How To Leverage Them [New Data + Expert Tips]
![how to do a business plan for a sales company 5 Predictions on the Future of Sales [Data & Expert Insights from Bardeen, Aircall, and HubSpot]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales%20predictions%20pillar%20%282%29.png)
5 Predictions on the Future of Sales [Data & Expert Insights from Bardeen, Aircall, and HubSpot]
All fields are required.

- Leadership Development
- Sales Coaching
- Sales Hiring and Retention
- Sales Performance
- Prospecting
- Sales Strategy
- Negotiation
- Sales Training
- Sales Culture
- See All Blogs
- Why The Brooks Group
- Meet Our Team
- Meet Our Sales Training Facilitators
- Awards & Press
- White Papers & Guides
- Success Stories
- Sales Performance Research
- See All Resources
- Agriculture
- Construction
- Distribution
- Energy & Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Professional Services
- Software & Technology
- Transportation
- See All Industries
- Coaching to IMPACT
- Sales Leadership Accelerator
- Train the Trainer
- Sales Training Reinforcement
- Sales Consulting Services
- Sales Team Insights
- Sales Culture Insights
- See All Sales Leadership Programs
- IMPACT Selling®
- IMPACT for Customer Service
- IMPACT Refresher
- Sales Negotiations
- Strategic Account Management
- Sales Territory Planning
- Conversations with Confidence
- Sales Skills Workshops
- Open Enrollment Training Programs
- See All Sales Training Programs
- Sales Training Programs
- Sales Leadership Training
- Sales Assessment Solutions
- Training Delivery Methods
- Keynotes & Workshops
- See All Solutions
6 Steps to Create a Successful Sales Business Plan

Written By Michelle Richardson
Michelle Richardson
Join over 17,000 sales leaders getting the best content right in their inbox.
- Presentation Skills
- Prospecting Skills
- Sales Assessments
- Sales Compensation
- Sales Goals
- Sales Leader Blog
- Sales Meetings
- Sales Performance Improvement
- Sales Performance Research Center
- Sales Pitches
- Sales Prospects
- Sales Team Motivation
- Time Management
- Virtual Sales
You may also like

Highly Effective Prospecting Techniques for Your Sales Team
Apr 10, 2024
In baseball, “keep your eye on the ball” means watch where the ball is at all times. In sales, it means staying...

Top Tactics for Selling to a Buying Committee
Apr 9, 2024
Finance, operations, and management, oh my! The B2B buying journey is getting longer and more complex. The average B2B...

Strategies for Effective Sales Coaching Conversations
Apr 3, 2024
Sales success hinges not only on strategy and skill but also on continuous improvement and development. This is where...
Ready to maximize the performance of your sales team? A representative from The Brooks Group can help get you started.
Should You Stick to the Business Plan or Change It?
5 min. read
Updated April 9, 2024
Is it time for plan B?
The best and most useful kind of business planning is not just a use-once business plan, but rather a continuous process.
The first business plan is just the first step. For the rest of your business’s life, you review the plan once a month. Compare actual results to what you had planned, determine what steps to take to optimize, and revise the plan.
You’ll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways:
- It helps maintain focus
- You’ll be able to align the team with priorities
- You can address changes in the marketplace as they happen
- It helps you tune strategy and tactics to what’s working and what’s not working
- It starts with knowing what happened
Review means comparing what actually happened to what you expected. Business plans are always wrong, so there will always be a difference between the plan and the actual results.
For the actual business numbers, such as sales, expenses, and such, accountants call the difference between the estimates in the plan and the actual results variance. Variance analysis looks at these differences to determine where the numbers are different, and in what direction.
What’s important here is not the accounting or the calculations, but rather the resulting management. You look for indications of problems or unexpected positives, so you can react.
In the illustration above, revenue is lower than planned and expenses are higher. Operating income is less than planned. Cash and cash flow are improving, which is good news. However, that may be because this company is stretching out its payments, averaging about six months, which is seven times more than in their plan. So accounts payable is 25 percent higher than planned. That’s good because it’s helping with financing and keeping money in the bank, but may also be bad because it could be spoiling reputation and relations with vendors.
The point is the management, not the hard numbers. What should be done, given these results, to make the company better?
- The monthly review meeting
The monthly review meeting is absolutely essential to real business planning— Lean Planning . The real value of business planning is the decisions it causes, and the management that results; and for that, you need not just a plan but a regular monthly review to track results and revise as necessary.
And the toughest part of the review meeting is this crucial question: Do we stick to the plan, or do we change it?
That comes up often because in the real world things never go exactly as planned. Business plans are supposed to set goals, tracking, milestones, and expectations.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
The review meeting is when you ask:
- What happened? What went right and what went wrong?
- If I change the plan, then is my plan (forecast) versus actual result valid?
- Doesn’t it take consistent execution to make strategy work?
You won’t find some set of best practices to make this easy. You’ll end up deciding on a case-by-case basis.
- The arguments for staying the course with your plan
I consider this an awkward, difficult fact about business strategy:
It’s better to have a mediocre strategy consistently applied over three or more years, than a series of brilliant strategies, each applied for six months or so.
Too often, management teams get bored with strategy before it’s had a chance to be effective. I was consulting with Apple Computers during the 1980s when the Macintosh platform became the foundation for what we now call “desktop publishing.” We take it for granted today, but back in 1985 when the first laser printers came out, it was like magic. Suddenly, a single person in a home office could produce documents that looked professional.
What I saw in Apple at that time was smart young managers getting bored with desktop publishing long before the market even understood what it was. They started looking at multimedia instead. They were attracted to new technologies and innovation. As a result, they lost the concentration on desktop publishing and lost a lot of market potential as Windows vendors moved in with competitive products.
That argues for staying the course. Strategy takes time.
- The arguments for revising the plan
On the other hand, this is also true:
There is no virtue in sticking to the plan for its own stake. Nobody wants the futility of trying to implement a flawed plan.
Generally accepted best practices have changed over the three decades I’ve been focusing on business planning.
Back in the 80s, business timeframes stretched longer and many business leaders recommended sticking to the plan. But times have changed. You’ve probably dealt with the problem of people doing something “because that’s the plan” when in fact it just isn’t working. I certainly have. That kind of thinking is one reason why some web companies survived the first dotcom boom and others didn’t. It also explains why some business experts question the value of the business plan.
This is sloppy thinking, in my opinion—confusing the value of the planning with the mistake of implementing a plan without change or review, just because it’s the plan.
- How to decide: Stay the course, or revise the plan?
This consistency versus revision dilemma is one of the best and most obvious reasons for having people—owners and managers—run the business planning, rather than algorithms or artificial intelligence. It takes people to deal with this critical judgment.
One good way to deal with it is by focusing on the assumptions. Identify the key assumptions and whether or not they’ve changed. When assumptions have changed, there is no virtue whatsoever in sticking to the plan you built on top of them.
Use your common sense . Were you wrong about the whole thing, or just about timing? Has something else happened, like market problems, disruptive technology, or new competition, that has changed your basic assumptions?
Do not revise your plan glibly . Remember that some of the best strategies take longer to implement. Remember also that you’re living with it every day; it is naturally going to seem old and boring to you long before the target audience gets it. But do revise your plan if it is out of date, inaccurate, or based on false assumptions.
That’s why you have the plan in the first place: to manage your business better.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.

Table of Contents
- You’ll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways:
Related Articles

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Real Estate Business Plan + Example Templates
8 Min. Read
How to Write a Home Health Care Business Plan

How to Create A Digital Marketing Plan and Strategy

13 Min. Read
How to Write a Nonprofit Business Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Tax Season Savings
Get 40% off LivePlan
The #1 rated business plan software
Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

- Credit cards
- View all credit cards
- Banking guide
- Loans guide
- Insurance guide
- Personal finance
- View all personal finance
- Small business
- Small business guide
- View all taxes
You’re our first priority. Every time.
We believe everyone should be able to make financial decisions with confidence. And while our site doesn’t feature every company or financial product available on the market, we’re proud that the guidance we offer, the information we provide and the tools we create are objective, independent, straightforward — and free.
So how do we make money? Our partners compensate us. This may influence which products we review and write about (and where those products appear on the site), but it in no way affects our recommendations or advice, which are grounded in thousands of hours of research. Our partners cannot pay us to guarantee favorable reviews of their products or services. Here is a list of our partners .
How to Get Student Loan Forgiveness in 2024

Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This influences which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list of our partners and here's how we make money .
Student loan forgiveness has a mixed track record. Last summer, the Supreme Court struck down a broad plan that would’ve erased up to $20,000 per borrower. Still, student loan forgiveness is more accessible now than ever before. A handful of existing federal student loan forgiveness programs have erased $143.6 billion in student debt for 3.96 million borrowers as of March 21, according to the Education Department, with more to come this year.
The White House is currently trying to push through a narrower forgiveness ‘Plan B’ version of its failed broad forgiveness plan. The proven paths to forgiveness, however, include programs that range from income-driven repayment (IDR) plans — which cap monthly bills at a percentage of your income and forgive your remaining balance after 10 to 25 years — to niche programs for borrowers with certain loan types, jobs or school circumstances.
Here’s how to get student loan forgiveness in 2024 — and what you need to know before pursuing this path.
Check your eligibility
You must have federal student loans to qualify for a forgiveness program. Private student loans aren’t eligible.
To verify you have federal loans, go to StudentAid.gov , and try to log in or recover your account.
Next, check which types of federal student loans you have. If you have certain types of loans, like commercially held FFELP or Perkins loans, you may have to consolidate them before going after forgiveness .
Income-driven repayment
The newest IDR plan — Saving on a Valuable Education, or SAVE — is the most accessible path to forgiveness. All borrowers with federal direct loans are eligible to enroll.
The SAVE plan forgives remaining student debt in as little as 10 years if you have an original balance of $12,000 or less, and in up to 20 or 25 years for other borrowers. While working toward forgiveness, your monthly bills could be $0 per month if you earn less than $32,800 as an individual or $67,500 as a family of four; otherwise, they’ll be capped at 5%-10% of your income.
Public Service Loan Forgiveness
If you work for a qualifying government or nonprofit employer, you could be eligible for Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) . This program erases your remaining balance after a decade of repayment.
“Generally, the PSLF program is the best one if you have access to it,” says Scott Stark, a financial coach and certified financial planner at Financial Finesse, a workplace financial wellness company.
Other forgiveness programs
Outside of IDR and PSLF, your student loan forgiveness options may include:
Teacher Loan Forgiveness , if you work in a qualifying low-income school.
Borrower defense to repayment , if you think your school defrauded you.
Closed school discharge , if your school closed during or shortly after your time there.
Perkins loan cancellation , if you have Perkins loans and work in public service.
State-based student loan payment assistance , if you work in health care or are willing to relocate to a new area.
Do the math
Use the Education Department’s loan simulator to see how much debt you could get erased under various forgiveness programs and repayment plans, how much your monthly payments could be and how long you’ll be in repayment.
If an IDR plan will result in you paying more interest for a longer period or paying off your debt before getting forgiveness, then it may not be a good choice for you. (Public Service Loan Forgiveness also requires enrollment in an IDR plan.)
“It really is a case-by-case kind of thing, but generally speaking, for people whose income is relatively high compared to their student debt loads, the income-driven repayment plans can be pretty unattractive,” says Tisa Silver Canady, founder of the Maryland Center for Collegiate Financial Wellness. “It might behoove them to just stay on a balance-driven plan and pay extra when they feel it makes sense.” Making extra payments toward the principal while on a balance-driven plan — like the standard 10-year plan , which splits your loan into 120 payments — allows you to shrink your debt faster and reduce total interest costs.
On the other hand, if the math for IDR works out such that borrowers can have smaller payments and keep more of their money to reach other financial goals, pursuing forgiveness is a good option, Stark says.
Prepare for a future tax bomb
IDR student loan forgiveness is exempt from federal taxes through 2025. After that, any amount forgiven could result in a student loan tax bomb . A small number of states tax IDR forgiveness, too.
It’s important to plan for a tax bomb if your forgiveness timeline will extend past 2025. Put a small amount of money aside each month to cover your future tax bill, Stark says.
Use the loan simulator to determine how much forgiveness you could ultimately receive: Your taxable income will increase by that amount in the year you get forgiveness. In some cases, the forgiveness could push you into a higher tax bracket, which could further increase your tax burden. If the amount you have to set aside each month to cover the tax bill is larger than the amount you’d save on the IDR plan, it might not be worth it.
Loan balances forgiven through PSLF, Teacher Loan Forgiveness, borrower defense to repayment, closed school discharge and Perkins loan cancellation are exempt from federal taxation.
Change your repayment plan
If you decide IDR forgiveness is the right choice, you must switch to an IDR plan like SAVE.
To sign up for an IDR plan, submit an online application at StudentAid.gov/IDR or call your student loan servicer.
You must also sign up for an IDR plan if you’re striving for PSLF. Choose the plan that gives you the smallest monthly bill to maximize the amount you could get forgiven after 10 years. It’s a good idea to submit your PSLF employer verification form each year to stay on track for forgiveness, Canady says. You can do this through the Education Department’s online PSLF Help Tool .
On a similar note...
99 Cents Only to close all 371 stores and wind down its business

- Show more sharing options
- Copy Link URL Copied!
99 Cents Only Stores will close all 371 of its stores and wind down its business operations after more than four decades, the City of Commerce discount chain announced Thursday.
“This was an extremely difficult decision and is not the outcome we expected or hoped to achieve,” interim Chief Executive Mike Simoncic said in a statement. “Unfortunately, the last several years have presented significant and lasting challenges in the retail environment.”
He cited multiple factors, including the “unprecedented impact” of the COVID-19 pandemic, shifting consumer demand, persistent inflationary pressures and rising levels of shrink — an industry term that refers to loss of inventory attributed to reasons such as shoplifting, employee theft and administrative errors.
Combined, those issues “have greatly hindered the company’s ability to operate,” Simoncic said.
99 Cents Only has stores in California, Arizona, Nevada and Texas and has about 14,000 employees. The privately held company said it had reached an agreement with Hilco Global to liquidate all of its merchandise and dispose of fixtures, furnishings and equipment at its stores. Sales are expected to begin Friday.
Hilco Real Estate is managing the sale of the company’s real estate assets, which are owned or leased.
99 Cents Only may turn into 99 cents mostly
Chain is expected to announce some items won’t stay under $1.
Sept. 5, 2008
The announcement by 99 Cents Only reflects a larger weakness in the dollar-store category, said Brad Thomas, equity research analyst at KeyBanc Capital Markets.
Dollar Tree, a Chesapeake, Va., retailer, announced last month that it was closing 600 of its Family Dollar stores this year and an additional 370 in the next few years, he noted.
“It’s been trying times for many, many retailers,” he said. “What’s interesting is that what started out as a boon to retailers in the pandemic, with all those stimulus checks, quickly turned into a very troublesome time.”
Rising wages, inflation and higher losses due to shrinkage have reduced profits for retailers in a deep-discount sector where margins are already extremely low.
99 Cents Only, with its large base of California stores, has been under particular wage pressure, he said. And it’s at a disadvantage compared with larger chains such as market leader Dollar General, which has a store count close to 20,000 — “a sales base and a store base that is multiple times larger than 99 Cents,” Thomas said.

Last week, Bloomberg reported that 99 Cents Only was considering a bankruptcy filing as it contended with a liquidity shortfall.
Founded in Los Angeles in 1982 by David Gold , 99 Cents Only popularized the single-price retail concept. At the time, dollar stores were seen as dumping grounds for undesirable products, but the Gold family made the stores bright and well-organized, with good-quality merchandise including groceries and household supplies.
“It was an instant success,” Howard Gold, one of David Gold’s sons, recalled Friday; he and his three siblings all worked at 99 Cents Only. “People thought it was government-subsidized because they couldn’t believe the prices.”
For years, it remained one of the few true “dollar” stores, with items priced at 99 cents or less or grouped to sell for a total of 99 cents.
That changed in 2008 when, faced with fast-rising inflation, soaring food and fuel prices, and a higher minimum wage, 99 Cents Only announced that it was straying from its long-standing price strategy.
Three years later, the company announced that it had agreed to be sold in a deal valued at about $1.6 billion, as investors eyed dollar stores that had grown in popularity during the Great Recession. In 2013, Howard Gold and the rest of the family management team departed the company.
Today, with stores scattered around Los Angeles County — among them in Hollywood, Silver Lake, Mid-Wilshire, Santa Monica, Thai Town, North Hollywood and Glendale — the closure of 99 Cents Only will leave a number of large vacant properties in prime locations.

“It’s very sad on many levels, and I’ll just leave it at that,” Gold, now retired and living in Studio City, said of the decision to close the chain his father built.
Other major retailers have also announced store closures in the region lately, including REI in Santa Monica , Macy’s in Simi Valley and several Rite Aid locations .
99 Cents Only did not respond to requests for comment.
Nicolas Kolesnikow, a retired teacher who lives in Westchester, said he was shocked to hear the chain was going out of business. He shops at a 99 Cents Only about four blocks from his house several times a week.
“It’s almost like a corner store for me,” said Kolesnikow, 82.
He might stop by and pick up milk if he runs out, and for longer trips will buy household items and produce such as tomatoes, cucumbers and cilantro before visiting a traditional supermarket with a larger selection.
Kolesnikow said he noticed that some products had become much more expensive in the last year, though there were still bargains.
“I found their prices were working their way up to regular prices,” he said, “and there were fewer shoppers.”
More to Read

99 Cents Only was an L.A. icon. Inside the fall of the popular chain
April 10, 2024

Column: More than just a store, 99 Cents Only gave a fair shake to all who entered
April 9, 2024

San Francisco’s iconic Union Square Macy’s will close
Feb. 27, 2024

Andrea Chang is a wealth reporter for the Los Angeles Times. She was previously a Column One editor, the deputy Food editor and an assistant Business editor, and has covered beats including technology and retail. Chang joined the paper in 2007 after graduating from the Medill School of Journalism at Northwestern University. She grew up in Cupertino, Calif.

Laurence Darmiento covers wealth and dealmakers in Southern California for the Los Angeles Times. He joined the paper in 2015 as an assistant business editor and has overseen finance, real estate and Washington business coverage. Darmiento previously had been the managing editor of the Los Angeles Business Journal and was a reporter for the Los Angeles Daily News and other outlets. A New York native, he is an alumnus of Cornell University.
More From the Los Angeles Times

Wall Street falls after hot inflation report burns hopes for a June rate cut

Company Town
Margot Robbie boards Lionsgate and Hasbro’s ‘Monopoly’ movie as producer

‘Joker 2’ trailer: Joaquin Phoenix and Lady Gaga lead twisted, musical fever dream

Why Biden is getting little credit for the economy, especially in California
Tesla shares down after report on company scrapping plans to build a low-cost EV
- Entry-level Tesla car won’t be built, three sources tell Reuters
- Tesla to focus on self-driving taxis instead, sources said
- Strategy shift comes as Tesla faces competition from China EV makers including BYD
Tesla has canceled the long-promised inexpensive car that investors have been counting on to drive its growth into a mass-market automaker, according to three sources familiar with the matter and company messages seen by Reuters.
The automaker will continue developing self-driving robotaxis on the same small-vehicle platform, the sources said.
The decision represents an abandonment of a longstanding goal that Tesla chief Elon Musk has often characterized as its primary mission: affordable electric cars for the masses. His first “master plan” for the company in 2006 called for manufacturing luxury models first, then using the profits to finance a “low cost family car.”
Tesla shares were down about 3% in early afternoon trading after the Reuters report.
Tesla going 'all in on robotaxi'
Musk has since repeatedly promised such a vehicle to investors and consumers. As recently as January, Musk told investors that Tesla planned to start production of the affordable model at its Texas factory in the second half of 2025, following an exclusive Reuters report detailing those plans.
Tesla’s cheapest current model, the Model 3 sedan, retails for about $39,000 in the United States. The now-defunct entry-level vehicle, sometimes described as the Model 2, was expected to start at about $25,000.
Tesla did not respond to requests for comment. After the story was published, Musk posted on his social media site X that "Reuters is lying (again)." He did not identify any specific inaccuracies.
The stark reversal comes as Tesla faces fierce competition globally from Chinese electric-vehicle makers flooding the market with cars priced as low as $10,000. The plan for driverless robotaxis, which could take longer to deliver, presents a stiffer engineering challenge and more regulatory risk.
Two sources said they learned of Tesla's decision to scrap the Model 2 in a meeting attended by scores of employees, with one of them saying the gathering happened in late February.
“Elon’s directive is to go all in on robotaxi,” that person said.
The third source confirmed the cancellation and said new plans call for robotaxis to be produced, but in much lower volumes than had been projected for the Model 2.
Tesla sales: Delivery numbers are down and stock prices are falling as a result
Several company messages reviewed by Reuters about the decision included one on March 1 from an unnamed program manager for the affordable car discussing the project’s demise with engineering staff and advising them to hold off on telling suppliers “about program cancellation.”
A fourth person with knowledge of Tesla’s plans expressed optimism about the decision to pivot away from the cheap-car strategy in favor of robotaxis, a segment Musk has envisioned as the future of mobility. The source cautioned that Tesla’s product plans could change again based on economic conditions.
EV competition heats up
Squeezing profits from entry-level vehicles is a challenge for any automaker. But Tesla’s delay in pursuing the car Musk once called his dream made it much tougher because it now faces far more competition in that price range.
While Tesla spent years developing its highly experimental Cybertruck, a pricey electric pickup, Chinese automakers have raced ahead on affordable EVs, grabbing market share, gaining economies of scale and offering consumers bargain prices that Western automakers are struggling to match.
As Chinese EVs surged to challenge Tesla’s dominance, Musk was tending to his sprawling empire, which includes rocket-maker SpaceX, brain-chip developer Neuralink, and social media giant X, which Musk acquired in 2022. Formerly called Twitter, the platform has foundered under Musk’s volatile management, shedding most of its value as the company has lost revenue and advertisers.
Plans for the affordable Tesla have been seen as key to delivering on Musk’s stratospheric ambitions for sales growth. Musk said in 2020 that Tesla aspired by 2030 to sell 20 million vehicles – twice as many as the world’s largest automaker, Toyota, sells today. With the death of the Model 2, it’s unclear how he’ll get there.
Expectations for a $25,000 vehicle have underpinned Wall Street analysts’ more modest, but still ambitious, forecasts for Tesla sales. Those forecasts, according to a Tesla investor-relations document, call for vehicle sales rising to 4.2 million by 2028 from 1.8 million last year.
Musk has wavered on the project before. In a biography of the entrepreneur released last year, author Walter Issacson reported that Musk in 2022 “put a hold on” the entry-level EV plans, reasoning that a Tesla robotaxi would make the car irrelevant. Musk’s advisors urged him to stay the course, the book said.
‘Halt all further activities'
Tesla called the affordable-car project NV91 internally and H422 externally when discussing it with suppliers, according to two of the sources and company messages reviewed by Reuters.
Messages from the unnamed Tesla program manager to staffers referenced those code names in discussing the project’s termination. One of those messages sent March 1 said that “suppliers should halt all further activities related to H422/NV91.”
The sources said they did not know all the reasons behind the decision to kill the project.
In another March 1 message, the manager thanked engineering staffers for their efforts and urged them to document what they had learned.
“I’d like to thank everyone for all your hard work and dedication to pushing boundaries and executing the best design possible given the aggressive constraints we had to work within,” the message said. “We would not want all our hard work to go to waste, so it’s important that we tie things off and document things properly.”
The messages showed meetings on the affordable-car project being canceled. The two sources said some engineers have been reassigned.
Robotaxi timeline unclear
Tesla’s timeline and business model for robotaxis remain unclear. Musk has publicly predicted a future of mobility in which driverless taxis could eventually become a more common mode of transport than human-driven cars. He has said Tesla, the world’s most valuable automaker, would be "worth basically zero" without achieving full self-driving capability.
Currently, self-driving cars have only been approved by U.S. and Chinese regulators for tightly limited, experimental use on public roads.
Tesla has yet to prove it can produce an autonomous car despite years of predictions by Musk that one was just around the corner, an expectation that partly underpinned Tesla’s soaring valuation. The automaker faces lawsuits and investigations into crashes involving its Autopilot and Full Self-Driving driver-assistance systems, which are not fully autonomous. Tesla has blamed the accidents on inattentive drivers.
Tesla's Autopilot woes are among a number of problems that have drawn scrutiny. The automaker faces another investigation into the driving-range estimates of its cars, launched after Reuters reported last year that Tesla had rigged the in-dash range meters in its vehicles to give rosy projections. Reuters reported in December that the automaker blamed “driver abuse” for chronic failures of suspension and steering parts it long knew were defective.
Tesla's image as a climate-friendly innovator has also suffered with Musk’s tilt toward right-wing politics and polarizing public statements, which have turned away some prospective Tesla buyers, according to surveys and experts.
The automaker reported an 8% year-over-year drop in deliveries on Tuesday , just after its chief Chinese competitor, BYD, reported a 13% gain. Tesla shares dropped 5% on the news, deepening a slide of more than 40% since last July, amounting to a loss of about $400 billion in market value.
Still, Tesla’s market capitalization of $545 billion is higher than the combined worth of the next three most valuable carmakers, Toyota, Porsche and Mercedes-Benz MBGn.DE. Tesla’s stock value has long been based on future expectations for mass-market sales and driverless cars rather than its current sales and profits.
Running late
The affordable-car project’s cancellation comes as Tesla and other established automakers have been rocked by slowing EV demand growth in the United States and Europe, and cut-throat competition in China.
If Tesla had moved forward with the low-cost car, it wouldn’t have arrived on the market until the latter half of 2025, by the company’s estimate. But the entry-level EV segment is already crowded with compelling models from BYD and many other Chinese brands.
Tesla is late to the segment in part because of a pivotal decision by Musk. In 2020, after releasing its hit crossover, the Model Y, Tesla focused on the highly experimental Cybertruck instead of an affordable car.
Musk unveiled a prototype of the angular, stainless steel-clad truck in 2019 and predicted a starting price of about $40,000. The vehicle finally arrived last year , but the lowest price version of the truck won't be available until 2025, at a price of about $61,000.
The company has also struggled to work through manufacturing problems, particularly with the truck's pioneering battery technology. Musk hopes to sell the vehicle in high volumes but warned investors last fall about "enormous challenges" ramping up production and making the vehicle profitable.
"We dug our own grave with the Cybertruck," he said.
During the same period, BYD has seen its electric-vehicle sales soar in China, growing from about 130,000 to more than 1.5 million, not including its thriving business in plug-in hybrids or its fast-growing exports.
BYD already offers a slew of low- and mid-range models, including its Seagull hatchback for less than $10,000. The Chinese automaker now plans to export that car for more than double that price - but still lower than the target for the cheap car Tesla had planned to build.
Tesla shares are down about 40% since July.
- Share full article
For more audio journalism and storytelling, download New York Times Audio , a new iOS app available for news subscribers.

- April 10, 2024 • 22:49 Trump’s Abortion Dilemma
- April 9, 2024 • 30:48 How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
- April 8, 2024 • 30:28 The Eclipse Chaser
- April 7, 2024 The Sunday Read: ‘What Deathbed Visions Teach Us About Living’
- April 5, 2024 • 29:11 An Engineering Experiment to Cool the Earth
- April 4, 2024 • 32:37 Israel’s Deadly Airstrike on the World Central Kitchen
- April 3, 2024 • 27:42 The Accidental Tax Cutter in Chief
- April 2, 2024 • 29:32 Kids Are Missing School at an Alarming Rate
- April 1, 2024 • 36:14 Ronna McDaniel, TV News and the Trump Problem
- March 29, 2024 • 48:42 Hamas Took Her, and Still Has Her Husband
- March 28, 2024 • 33:40 The Newest Tech Start-Up Billionaire? Donald Trump.
- March 27, 2024 • 28:06 Democrats’ Plan to Save the Republican House Speaker
How Tesla Planted the Seeds for Its Own Potential Downfall
Elon musk’s factory in china saved his company and made him ultrarich. now, it may backfire..
Hosted by Katrin Bennhold
Featuring Mara Hvistendahl
Produced by Rikki Novetsky and Mooj Zadie
With Rachelle Bonja
Edited by Lisa Chow and Alexandra Leigh Young
Original music by Marion Lozano , Diane Wong , Elisheba Ittoop and Sophia Lanman
Engineered by Chris Wood
Listen and follow The Daily Apple Podcasts | Spotify | Amazon Music
When Elon Musk set up Tesla’s factory in China, he made a bet that brought him cheap parts and capable workers — a bet that made him ultrarich and saved his company.
Mara Hvistendahl, an investigative reporter for The Times, explains why, now, that lifeline may have given China the tools to beat Tesla at its own game.
On today’s episode

Mara Hvistendahl , an investigative reporter for The New York Times.

Background reading
A pivot to China saved Elon Musk. It also bound him to Beijing .
Mr. Musk helped create the Chinese electric vehicle industry. But he is now facing challenges there as well as scrutiny in the West over his reliance on China.
There are a lot of ways to listen to The Daily. Here’s how.
We aim to make transcripts available the next workday after an episode’s publication. You can find them at the top of the page.
Fact-checking by Susan Lee .
The Daily is made by Rachel Quester, Lynsea Garrison, Clare Toeniskoetter, Paige Cowett, Michael Simon Johnson, Brad Fisher, Chris Wood, Jessica Cheung, Stella Tan, Alexandra Leigh Young, Lisa Chow, Eric Krupke, Marc Georges, Luke Vander Ploeg, M.J. Davis Lin, Dan Powell, Sydney Harper, Mike Benoist, Liz O. Baylen, Asthaa Chaturvedi, Rachelle Bonja, Diana Nguyen, Marion Lozano, Corey Schreppel, Rob Szypko, Elisheba Ittoop, Mooj Zadie, Patricia Willens, Rowan Niemisto, Jody Becker, Rikki Novetsky, John Ketchum, Nina Feldman, Will Reid, Carlos Prieto, Ben Calhoun, Susan Lee, Lexie Diao, Mary Wilson, Alex Stern, Dan Farrell, Sophia Lanman, Shannon Lin, Diane Wong, Devon Taylor, Alyssa Moxley, Summer Thomad, Olivia Natt, Daniel Ramirez and Brendan Klinkenberg.
Our theme music is by Jim Brunberg and Ben Landsverk of Wonderly. Special thanks to Sam Dolnick, Paula Szuchman, Lisa Tobin, Larissa Anderson, Julia Simon, Sofia Milan, Mahima Chablani, Elizabeth Davis-Moorer, Jeffrey Miranda, Renan Borelli, Maddy Masiello, Isabella Anderson and Nina Lassam.
Katrin Bennhold is the Berlin bureau chief. A former Nieman fellow at Harvard University, she previously reported from London and Paris, covering a range of topics from the rise of populism to gender. More about Katrin Bennhold
Mara Hvistendahl is an investigative reporter for The Times focused on Asia. More about Mara Hvistendahl
Advertisement

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Many business leaders see their sales plan as an extension of the traditional business plan. The business plan contains strategic and revenue goals across the organization, while the sales plan lays out how to achieve them. ... For example, a SaaS company that relies on inbound leads may do much of the heavy lifting during the initial meeting ...
Business Development Strategic Sales Plan. Download Now: Free Strategic Business Planning Template. A strategic sales plan for business development will focus on attracting new business to your company by networking with other companies, sponsoring events, and doing outreach. In your sales plan, you'll want to choose the right KPIs that best ...
3. Determine Your Ideal Customer. Determining the ideal customer or target market is the next step of your business plan for sales reps. It may have been accomplished when you developed your mission statement, but also when you set your sales goals and discovered how broad your market needs to be to reach them.
2. Assess the current situation. The next step is to create an honest overview of your business situation in relation to the goal you set in the first step. Review your strengths and assets. Take ...
A bad example of a goal is as follows: Goal 1: Increase sales across company's range of products and services. A better goal would look something like: Goal 1: Generate $500,000+ in revenue from new clients through purchases of X product by X date. 9. Action Plan.
Here's how to take it one step at a time. 1. Connect sales plan data with your CRM. It's important to build your sales plan in customer relationship management (CRM) software. When you have all your sales data in one central place, updated in real-time, real world changes show up as misalignments in the data.
Here's the point: Focus on value, not features in your sales plan template. Your competitive advantage will inform everything your company does moving forward, from marketing to product development. It's a great example of where sales can influence the development of a product and the direction of a business. 6.
2. Organize the team and roles within the team. Part of the planning includes organizing a group of people that will work together to meet the goals laid out in the plan. Create a branded org chart visualizing team roles and responsibilities. Include this chart on a page in your sales plan; make it part of the process.
Tip #2: Use data and statistics. Use the data from your in-depth research to identify problem areas, find points of opportunity in your sales process, and validate your assumptions and ideas. You can also use the data to come up with accurate metrics and figures to help predict your sales plan's outcome.
Start with the figures from last year; track the exponential increase in sales and compare them with your industry's present realities. This should be able to inform the milestones you'll need to set. 3. Select a suitable niche and focus on it. The previous steps have helped set a "bullseye" that you want to hit.
4. Target Market & Buyer Persona. As important as it is to clearly understand the internal workings of your sales process, it's just as important to outline things from the customer's perspective. Your sales plan should include detailed information about your target market and buyer persona.
Steps to Create a Sales Plan. Creating a sales plan involves a series of steps, including analyzing past performance, identifying gaps, setting up team structure, coordinating sales and marketing efforts, and monitoring progress. By following these steps, you can develop a comprehensive sales plan that keeps your team focused on achieving their ...
The Elements of a Strong Business Plan. Aside from outlining your goals, a strong sales business plan template is fleshed out by a few other pivotal elements: A thought-out marketing strategy accompanied by a thorough description of your target market. Know who you are selling to, and how you are going to sell to them.
Here are a few helpful tips for creating your sales plan: 1. Gather sales data and search for trends. To create a sales plan, you need to plan for the present and future. And in order to do that, your sales leaders need to look at past performance to identify any impactful sales trends.
Number of new clients you want to convert; Number of existing customers you plan to nurture and retain; Sales goals around a new product or service you are offering. 2. Review of goals, tactics, and performance from a prior period. If you write an annual sales plan, you can briefly recap the previous year, its goals, scope of work, and results.
Step 7: Create an Action Pan. Once you know your destination, you need to find a way to get there. This section is where you must outline the sales activities, deadlines, timeline and milestones that will take place throughout the sales process. Create action plans according to your sales goals and objectives.
From defining your target market to setting achievable goals, this guide will help you map out a plan that will help you achieve your sales targets. Table of Contents. 1. Establish Your Company's Mission Statement. 2. Set Sales Goals. 3. Understand Your Target Customers. 4.
4. Properly research and qualify prospects. I've personally discovered that even the strongest sales strategy can't compensate for targeting the wrong customers. To ensure your team is selling to the right type of customer, encourage reps to research and qualify prospects before attempting to discuss your product.
Step 4: Establish an Action Plan. Once your sales reps understand what numbers need to be met and where the opportunities and obstacles lie, they can work to identify an action plan. Have your reps identify specific strategies or projects they can execute to move them towards their goals. Then, be sure they list out the high-gain activities ...
Follow these steps to successfully create a strong business plan: 1. Gather key documents. You should plan out your document before officially writing it by gathering key information to reference and detail. Collect sales data from the previous year or two and identify any key trends.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Consider the following steps to create an effective business plan for a sales interview: 1. Conduct research. Before creating a business plan, it's important to understand the current processes, goals and team members of the company to which you're applying. Consider researching the company's current sales tactics, target market, leadership ...
1. Regular reviews and updates. Markets shift, consumer behavior changes, and your business will grow. Your plan must evolve with these factors, which makes regular reviews and updates a must-do ...
The first business plan is just the first step. For the rest of your business's life, you review the plan once a month. Compare actual results to what you had planned, determine what steps to take to optimize, and revise the plan. You'll find that continuous business planning helps in many ways: It helps maintain focus
This section is the most important for most businesses, as it can make or break a lender's confidence and willingness to extend credit. Always include the following documents in the financial ...
The SAVE plan forgives remaining student debt in as little as 10 years if you have an original balance of $12,000 or less, and in up to 20 or 25 years for other borrowers. While working toward ...
The deep-discount chain was founded in Los Angeles in 1982. 99 Cents Only Stores will close all 371 of its stores and wind down its business operations after more than four decades, the City of ...
During the same period, BYD has seen its electric-vehicle sales soar in China, growing from about 130,000 to more than 1.5 million, not including its thriving business in plug-in hybrids or its ...
29. Hosted by Katrin Bennhold. Featuring Mara Hvistendahl. Produced by Rikki Novetsky and Mooj Zadie. With Rachelle Bonja. Edited by Lisa Chow and Alexandra Leigh Young. Original music by Marion ...