What is phenomenology in qualitative research?
Last updated
7 February 2023
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Take a closer look at this type of qualitative research along with characteristics, examples, uses, and potential disadvantages.

Analyze your phenomenological research
Use purpose-built tools to surface insights faster
- What is phenomenological qualitative research?
Phenomenological research is a qualitative research approach that builds on the assumption that the universal essence of anything ultimately depends on how its audience experiences it .
Phenomenological researchers record and analyze the beliefs, feelings, and perceptions of the audience they’re looking to study in relation to the thing being studied. Only the audience’s views matter—the people who have experienced the phenomenon. The researcher’s personal assumptions and perceptions about the phenomenon should be irrelevant.
Phenomenology is a type of qualitative research as it requires an in-depth understanding of the audience’s thoughts and perceptions of the phenomenon you’re researching. It goes deep rather than broad, unlike quantitative research . Finding the lived experience of the phenomenon in question depends on your interpretation and analysis.
- What is the purpose of phenomenological research?
The primary aim of phenomenological research is to gain insight into the experiences and feelings of a specific audience in relation to the phenomenon you’re studying. These narratives are the reality in the audience’s eyes. They allow you to draw conclusions about the phenomenon that may add to or even contradict what you thought you knew about it from an internal perspective.
- How is phenomenology research design used?
Phenomenological research design is especially useful for topics in which the researcher needs to go deep into the audience’s thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
It’s a valuable tool to gain audience insights, generate awareness about the item being studied, and develop new theories about audience experience in a specific, controlled situation.
- Examples of phenomenological research
Phenomenological research is common in sociology, where researchers aim to better understand the audiences they study.
An example would be a study of the thoughts and experiences of family members waiting for a loved one who is undergoing major surgery. This could provide insights into the nature of the event from the broader family perspective.
However, phenomenological research is also common and beneficial in business situations. For example, the technique is commonly used in branding research. Here, audience perceptions of the brand matter more than the business’s perception of itself.
In branding-related market research, researchers look at how the audience experiences the brand and its products to gain insights into how they feel about them. The resulting information can be used to adjust messaging and business strategy to evoke more positive or stronger feelings about the brand in the future.
Free AI content analysis generator
Make sense of your research by automatically summarizing key takeaways through our free content analysis tool.
- The 4 characteristics of phenomenological research design
The exact nature of phenomenological research depends on the subject to be studied. However, every research design should include the following four main tenets to ensure insightful and actionable outcomes:
A focus on the audience’s interpretation of something . The focus is always on what an experience or event means to a strictly defined audience and how they interpret its meaning.
A lack of researcher bias or prior influence . The researcher has to set aside all prior prejudices and assumptions. They should focus only on how the audience interprets and experiences the event.
Connecting objectivity with lived experiences . Researchers need to describe their observations of how the audience experienced the event as well as how the audience interpreted their experience themselves.
- Types of phenomenological research design
Each type of phenomenological research shares the characteristics described above. Social scientists distinguish the following three types:
Existential phenomenology —focuses on understanding the audience’s experiences through their perspective.
Hermeneutic phenomenology —focuses on creating meaning from experiences through the audience’s perspective.
Transcendental phenomenology —focuses on how the phenomenon appears in one consciousness on a broader, scientific scale.
Existential phenomenology is the most common type used in a business context. It’s most valuable to help you better understand your audience.
You can use hermeneutic phenomenology to gain a deeper understanding of how your audience perceives experiences related to your business.
Transcendental phenomenology is largely reserved for non-business scientific applications.
- Data collection methods in phenomenological research
Phenomenological research draws from many of the most common qualitative research techniques to understand the audience’s perspective.
Here are some of the most common tools to collect data in this type of research study:
Observing participants as they experience the phenomenon
Interviewing participants before, during, and after the experience
Focus groups where participants experience the phenomenon and discuss it afterward
Recording conversations between participants related to the phenomenon
Analyzing personal texts and observations from participants related to the phenomenon
You might not use these methods in isolation. Most phenomenological research includes multiple data collection methods. This ensures enough overlap to draw satisfactory conclusions from the audience and the phenomenon studied.
Get started collecting, analyzing, and understanding qualitative data with help from quickstart research templates.
- Limitations of phenomenological research
Phenomenological research can be beneficial for many reasons, but its downsides are just as important to discuss.
This type of research is not a solve-all tool to gain audience insights. You should keep the following limitations in mind before you design your research study and during the design process:
These audience studies are typically very small. This results in a small data set that can make it difficult for you to draw complete conclusions about the phenomenon.
Researcher bias is difficult to avoid, even if you try to remove your own experiences and prejudices from the equation. Bias can contaminate the entire outcome.
Phenomenology relies on audience experiences, so its accuracy depends entirely on how well the audience can express those experiences and feelings.
The results of a phenomenological study can be difficult to summarize and present due to its qualitative nature. Conclusions typically need to include qualifiers and cautions.
This type of study can be time-consuming. Interpreting the data can take days and weeks.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 24 October 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Phenomenology In Qualitative Research
Saul McLeod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul McLeod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
What is phenomenology?
Phenomenology in qualitative research is characterized by a focus on understanding the meaning of lived experience from the perspective of the individual.
Instead of testing hypotheses or seeking to generalize findings to a larger population, phenomenological research aims to illuminate the specific and to challenge structural or normative assumptions by revealing the subjective experiences and perceptions of individuals.
This approach is particularly valuable for gaining insights into people’s motivations and actions, and for cutting through taken-for-granted assumptions and conventional wisdom.
Aim of Phenomenological Research
The aim of phenomenological research is to arrive at phenomenal understandings and insights into the meaning of lived experience.
These insights should be “impressively unique” and “primordially meaningful”, illuminating the specific experience being studied.
Phenomenological research attempts to uncover the meaning in lived experiences that are often overlooked in daily life. In other words, phenomenology asks the basic question: “What is this (primal) experience like?
To do this, phenomenological research examines experience as it appears to consciousness, seeking to avoid any preconceptions or assumptions.
Rather than simply describing what participants say, phenomenological research seeks to go deeper, to uncover implicit meanings and reveal the participant’s lifeworld.
This is not a matter of making generalized statements, but of understanding the experience from the individual’s perspective.
The aim is not to provide causal explanations or to theorize about the experience, but to “restore to each experience the ontological cipher which marks it internally.
Characteristics of Phenomenology
Phenomenology is best understood as a radical, anti-traditional style of philosophising that emphasizes describing phenomena as they appear to consciousness. It is not a set of dogmas or a system, but rather a practice of doing philosophy.
Here are some key characteristics of phenomenology:
- Focus on Experience: Phenomenology is concerned with the “phenomena,” which refers to anything that appears in the way that it appears to consciousness. This includes experiences, perceptions, thoughts, feelings, and meanings.
- First-Person Perspective: Phenomenology emphasizes the importance of the first-person, subjective experience. It seeks to understand the world as it is lived and experienced by individuals.
- Intentionality: A central concept in phenomenology is intentionality, which refers to the directedness of consciousness toward an object. This means that consciousness is always consciousness of something, and this directedness shapes how we experience the world.
- Bracketing (Epoche): Phenomenological research often involves “bracketing” or setting aside preconceived notions and assumptions about the world. This allows researchers to approach phenomena with an open mind and focus on how they appear in experience.
- Descriptive Emphasis: Phenomenology prioritizes description over explanation or interpretation. The aim is to provide a rich and nuanced account of experience as it is lived, without imposing theoretical frameworks or seeking to explain it in terms of external factors.
- Search for Essences: Phenomenology is interested in uncovering the essential structures and meanings of experience. This involves going beyond the particularities of individual experiences to grasp the shared features that make them what they are.
- Holistic Approach: Phenomenology seeks to understand experience in a holistic way , recognizing the interconnectedness of mind, body, and world. It rejects reductionist approaches that attempt to explain experience solely in terms of its parts.
- Use of Examples: Phenomenological researchers often use concrete examples to illustrate and explore the meaning of experience. These examples can be drawn from personal narratives, literature, or other sources that provide rich descriptions of lived experience.
Is phenomenology an epistemology or ontology?
Phenomenology straddles or undermines the traditional distinction between epistemology and ontology. Traditionally, epistemology is understood as the study of how we come to understand and have knowledge of the world, while ontology is the study of the nature of reality itself.
- Phenomenology investigates both how we understand the world and the nature of reality through its focus on phenomena . By examining how things appear to us, phenomenology analyzes our way of experiencing and understanding the world, simultaneously addressing questions about the objects themselves and their modes of appearance.
- Heidegger suggests that ontology is only possible through phenomenology . According to this view, analyzing our being-in-the-world is key to understanding the nature of reality itself.
Instead of separating subject and object, or the knower and the known, phenomenology highlights their interrelation, arguing that the mind is essentially open to the world, and reality is essentially capable of manifesting itself to us.
Exploring Phenomenology: Three Key Perspectives
1. husserl’s transcendental phenomenology.
Edmund Husserl viewed phenomenology as the “science of the essence of consciousness”, emphasizing the intentional structure of conscious acts. Central for phenomenological psychology was phenomenological philosopher Husserl’s understanding of “intentionality,” the idea that whenever we are conscious we are conscious of something, making the job of the researcher to better understand people’s experiences of things “in their appearing” (Langdridge, 2007, p. 13).
- Intentionality: This key concept describes consciousness’s directedness towards objects—our experiences are always about something. This “aboutness” isn’t limited to physical objects and encompasses mental acts like remembering, imagining, or even fearing.
- Essence over Existence: Husserl’s phenomenology focuses on uncovering the invariant structures of consciousness, aiming to reveal the essence of experiences like perception, thought, or emotion. It is not concerned with whether the object of an experience actually exists in the world.
- Transcendental Reduction: To grasp these essences, Husserl introduces the “epoché,” a methodological tool to bracket our natural attitude towards the world. This doesn’t mean denying the world’s existence; it’s about shifting focus from the objects themselves to how they appear in our consciousness.
- Example: When perceiving a table, we experience it through different profiles or perspectives. We can’t see all sides simultaneously, yet we grasp the table as a unified object. Transcendental phenomenology investigates the structures of consciousness that enable this constitution of objects from a multitude of appearances.
2. Heidegger’s Hermeneutical Phenomenology:
Martin Heidegger, while influenced by Husserl, diverged by emphasizing the importance of hermeneutics—the art of interpretation—in phenomenological inquiry.
- Being-in-the-World: Unlike Husserl’s focus on pure consciousness, Heidegger grounds his phenomenology in the concrete existence of Dasein—a term he uses to describe human existence’s inherent being-in-the-world.
- Facticity and Historicity: Heidegger recognizes that our understanding of the world is shaped by our historical and cultural contexts. We don’t encounter the world as a neutral observer, but through a lens of pre-existing interpretations and practices.
- Self-Concealing Nature of Phenomena: Heidegger contends that things don’t always reveal themselves fully. Our understanding is often clouded by biases, assumptions, or simply the inherent ambiguity of existence. Phenomenology, therefore, becomes a process of uncovering hidden meanings and questioning taken-for-granted assumptions.
- Example: Consider the act of using a hammer. For Heidegger, this isn’t just a neutral interaction with an object. It reveals a whole network of meanings related to our practical engagement with the world, our understanding of “for-the-sake-of-which” (building something), and our shared cultural practices.
3. Merleau-Ponty’s Idea of Perception
Maurice Merleau-Ponty further developed phenomenology by emphasizing the centrality of embodiment in our experience of the world.
- The Primacy of Perception: Merleau-Ponty challenges the traditional view of perception as a passive reception of sensory data. He argues that perception is an active and embodied engagement with the world.
- Body-Subject: Merleau-Ponty rejects the Cartesian mind-body dualism. For him, our body is not just an object in the world, but the very medium through which we experience and understand the world. The body is the “vehicle of being-in-the-world”.
- Perception as Foundation: Merleau-Ponty places perception at the heart of his phenomenology. He sees it as the foundation for all other cognitive activities, including thought, language, and intersubjectivity.
- Example: Consider the experience of touching a piece of velvet. It’s not simply that we receive tactile sensations. Our hand actively explores the fabric, and the perceived texture emerges from the dynamic interplay between our moving hand and the resistant surface. This experience can’t be reduced to purely mental representations or objective properties of the velvet; it arises from the embodied engagement between the perceiving subject and the world.
Data Collection in Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research focuses on understanding lived experience, and therefore relies on qualitative data that can illuminate the subjective experiences of individuals.
Because phenomenology aims to examine experience on its own terms, it is wary of imposing pre-defined categories or structures on the data.
Many phenomenological philosophers and researchers avoid using the term “method” in favor of talking about the phenomenological “approach.”
Interviews are a common method for collecting data in phenomenological research.
Researchers typically use semi-structured or unstructured interviews, which prioritize open-ended questions and allow participants to describe their experiences in their own words.
These interviews aim to elicit detailed, concrete descriptions of specific experiences rather than abstract generalizations.
For instance, instead of asking “What does friendship mean to you?”, a researcher might ask: “Can you describe a time you felt particularly connected to a friend?”.
This shift from the abstract to the concrete helps researchers access the pre-reflective, lived experience of the phenomenon, revealing its texture and nuanc
Researchers may also use follow-up questions to clarify or gain a deeper understanding of participants’ responses.
Phenomenological interviews often explore experiences across multiple dimensions:
- Bodily sensations: The interviewer might ask: “What was happening in your body during that experience?” or “How did that situation make you feel physically?” These questions help uncover the embodied aspects of experience often overlooked in more cognitively-focused approaches.
- Thoughts and cognitions: Questions like “What sense did you make of that experience?” or “What thoughts went through your head?” help explore the cognitive interpretations participants make about their experiences.
- Emotional responses: The interviewer may ask: “What feelings were present during that time?” or “How did that situation make you feel emotionally?” Allowing participants to articulate their feelings without judgment or interpretation is crucial.
- Relational dynamics: When exploring interpersonal experiences, interviewers might ask: “What was it like to be with that person during that event?” or “How did your relationship with that person shape your experience?” Recognizing that experiences are not confined to the individual but are shaped by social and relational contexts is central to phenomenological inquiry
Beyond interviews, phenomenological research may draw upon a variety of other methods, including :
- Discussions: Open-ended discussions among participants who share an experience can shed light on commonalities and differences in how the phenomenon is lived.
- Participant observation: This method involves the researcher immersing themselves in a particular setting or community to gain firsthand experience of the phenomenon being studied.
- Analysis of personal texts: Participants’ diaries, letters, or other written accounts of their experiences can provide valuable insights into their subjective lifeworlds.
- Creative media: Researchers may use art, dance, literature, photography, or other creative media to encourage participants to express their experiences in non-verbal ways.
“Examples” are particularly important in phenomenological research. Rather than treating individual experiences as mere illustrations of general concepts, phenomenology understands examples as offering a unique window into the essence of a phenomenon.
Researchers carefully select and analyze examples to uncover and articulate the essential features of a lived experience.
Number of Participants in Phenomenological Studies
There is no prescribed number of participants required for a phenomenological study. Some researchers may choose to include a larger number of participants.
Phenomenological research emphasizes in-depth understanding of lived experiences rather than statistical generalization.
Therefore, sample size is less important than the richness and depth of the data obtained from the participants.
However, phenomenological studies that include more than a handful of participants risk being superficial and may miss the spirit of phenomenology.
Here are some examples of approaches to the number of participants in a phenomenological study:
- Three to six participants are considered to give sufficient variation.
- One participant can be used for a case study.
- Researchers can also use autobiographical reflection .
- Single-case studies can identify issues that illustrate discrepancies and system failures and illuminate or draw attention to “different” situations, but positive inferences are less easy to make without a small sample of participants.
- The strength of inference increases rapidly once factors start to recur with more than one participant .
Analyzing Data in Phenomenological Research
There are a variety of approaches to conducting phenomenological research and analyzing data.
The variety of approaches within phenomenological research can make it challenging for students to navigate, as there are no fixed rules or procedures
The specific analytic strategies used in a phenomenological study depend on the researcher’s chosen approach and the nature of the phenomenon being investigated.
Some researchers advocate for a more orthodox approach to phenomenological research that prioritizes rigorous description and aims to uncover essential structures of experience.
Descriptive Phenomenology
This approach, exemplified by the work of Giorgi and Wertz, emphasizes a rigorous, descriptive approach to capturing the essential structures of experience. It involves bracketing assumptions, focusing on pre-reflective experience, and seeking generalizable insight
For example, Giorgi’s descriptive phenomenological method involves a multi-step procedure for analyzing descriptions of lived experience:
- Read the entire description to gain a holistic understanding.
- Divide the description into smaller units of meaning.
- Explicate the psychological significance of each meaning unit.
Hermeneutic Phenomenology
Other researchers, while still grounding their work in phenomenological philosophy, emphasize the importance of interpretation in understanding the unique, lived experience of individuals.
This approach, embraced by researchers like van Manen, prioritizes interpretation and dialogue in understanding the unique, lived experience of individuals.
For example, van Manen’s hermeneutic phenomenology emphasizes the role of interpretation and reflection in uncovering meaning in lived experience.
It acknowledges the researcher’s role in shaping interpretations and emphasizes the transition from pre-reflective experience to conceptual understanding.
Van Manen suggests that researchers should explicate their own assumptions and biases in order to better understand how they might be shaping their interpretations of the data.
His approach also highlights the importance of understanding the transition from pre-reflective experience to conceptual understanding.
Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis
If you are learning phenomenology, struggling with the material is expected.
Interpretive Phenomenological Analysis (IPA) has become popular because it offers novice researchers a concrete structure, but its set structures may cause researchers to get caught up in method and lose the essence of the phenomenon being studied.
Developed by Jonathan Smith, IPA is a qualitative research method designed to gain an in-depth understanding of how individuals experience and make sense of specific situations.
It focuses on individual experiences and interpretations rather than aiming to uncover universal essences. IPA draws on a broader range of phenomenological thinkers than just Husserl.
It differs from descriptive phenomenology by incorporating an interpretive component, acknowledging that individuals are inherently engaged in meaning-making processes.
Critical Phenomenology
Critical phenomenology expands upon traditional phenomenology by examining the impact of social structures on lived experiences of power and oppression.
Critical phenomenology acknowledges that societal structures like capitalism, colonialism, and patriarchy shape our lifeworlds and cannot be fully put aside
A key goal of critical phenomenology is to identify practical strategies for challenging oppressive structures and fostering liberatory ways of being in the world.
In psychology, phenomenology is linked with a critical realist epistemology; here, the real world exists, but it cannot be fully discovered because our experiences of it are always mediated (Shaw, 2019).
Regardless of the specific approach, several key principles should guide data analysis in phenomenological research:
- Focus on description : Phenomenological research aims to describe the lived experience of a phenomenon, rather than explain or theorize about it.
- Attend to pre-reflective experience : Researchers should strive to move beyond participants’ initial, surface-level descriptions to uncover the deeper, often implicit, meanings embedded in their experiences.
- Adopt a holistic perspective : A thorough analysis considers various aspects of experience, including embodiment, intersubjectivity, and the influence of social and cultural factors.
Reflexivity in Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research acknowledges that researchers are active participants who bring their own perspectives and experiences to the research process.
It’s important for researchers to practice reflexivity by setting aside their own assumptions and previous knowledge in order to see the world anew through the lens of the participants’ lived experiences.
This process, known as bracketing , is an attempt to approach the research with “fresh eyes,” free from contaminating assumptions. It involves:
- Adopting a self-critical, reflexive meta-awareness: This means questioning “common sense” and taken-for-granted assumptions to reveal more about the nature of subjectivity.
- Abstaining from judgments about the truth or reality of objects in the world: For example, if a participant mentions seeing a ghost, the researcher focuses on what the ghost means to the person and how they experienced it subjectively rather than questioning the existence of ghosts.
- Recognizing the impossibility of completely removing subjectivity: Rather than trying to eliminate subjectivity, researchers should actively recognize its impact and engage with their own (inter-)subjectivity to better understand the other.
Bracketing is an ongoing process that requires mindfulness, curiosity, compassion, and a “genuinely unknowing stance” to remain open to new understandings and avoid imposing the researcher’s own biases on the data.
This is essential for rigorous phenomenological research, as subjectivity is central to the investigation.
However, different schools of thought within phenomenology emphasize different aspects of bracketing:
- Descriptive phenomenologists focus on reflexively setting aside previous understandings to prioritize the participant’s perspective.
- Hermeneutic phenomenologists strive for transparency in their interpretations.
- Critical phenomenology acknowledges that societal structures like capitalism, colonialism, and patriarchy shape our lifeworlds and cannot be fully put aside.
By acknowledging the researcher’s role and emphasizing reflexivity, phenomenological research aims to ensure that findings remain grounded in the participants’ lived experiences, avoiding the imposition of the researcher’s own assumptions or biases.
Pitfalls of Phenomenology Research
A common pitfall of phenomenology research is failing to fully grasp the nuances of phenomenological philosophy.
For example, some studies that use Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis (IPA) do not adequately acknowledge their hermeneutic foundations or the need to engage in the Epoché, which helps limit the researcher’s pre-understandings.
Without this philosophical anchoring, the research is merely thematic analysis instead of phenomenology.
Other pitfalls in phenomenology research include:
- Missing the Phenomenon: Researchers should not solely focus on what is observed or said, or merely reproduce participant statements. Instead, they must uncover implicit meanings and insights into the participant’s lifeworld, providing an idiographic or general description of the phenomenon. Focusing too heavily on analysis can obscure the phenomenon, while excessive thematic structures can result in presenting “results” rather than phenomenological description.
- Misunderstanding the Phenomenological Attitude: Husserl’s bracketing is often misinterpreted as striving for objectivity, when in reality it is a profoundly subjective act to perceive the world from a fresh perspective. The focus should not be on judging reality, but on exploring experiential appearances and uncovering taken-for-granted aspects of experience. Reproducing participants’ words without going beyond their taken-for-granted understandings can cause research to get stuck in the “natural attitude”.
- Presenting an Insufficiently Holistic Account: Phenomenological studies should not just explore one aspect of consciousness or experience without considering intersubjectivity. A study that only examines an individual’s thoughts or feelings without considering the body or social context misses the point of phenomenology. Good analysis acknowledges existential being and lifeworldly dimensions like embodiment, relationships, time, and space.
- Seeing Subjectivity as Located Within an Individual: Ascribing cognition or emotion solely within individuals perpetuates the dualisms that phenomenology aims to dismantle, such as individual/social, body/mind, self/other, and internal/external. Phenomenology emphasizes a worldly matrix of meaning formed through relationships, shared language, and cultural history, highlighting the interconnectedness of individuals and the world.
- Killing the Phenomenon in Trying to be Scientifically Rigorous: Phenomenological studies that include a large number of participants in a misguided attempt to generalize findings risk being superficial and missing the essence of phenomenology. Similarly, reports that use overly intellectualized language or a detached “scientific” voice compromise the description of the lived experience.
Convincing phenomenological research should:
- Provide a rich and evocative description of the phenomenon.
- Focus on pre-reflective experience and consciousness rather than reproducing participant statements or researcher assumptions.
- Be grounded in phenomenological philosophy.
- Engage with the layered complexity and ambiguity of embodied, intersubjective, and lifeworldly meanings.
Despite ongoing debates among scholars about the best way to apply phenomenology, they share a commitment to an approach of openness and wonder.
This requires discipline, practice, and patience throughout the research process. Phenomenology has the potential to reveal new insights into the nature of lived experience.
Further Information
- Dorfman, E. (2009). History of the lifeworld: From Husserl to Merleau-Ponty. Philosophy Today , 53 (3), 294–303.
- Hanna, R. (2014). Husserl’s crisis and our crisis. International Journal of Philosophical Studies , 22 (5), 752–770.
- Held, K. Husserl’s Phenomenology of the Life-World. In D. Welton (Ed.), The New Husserl: A Critical Reader (pp. 32–62). Bloomington, IN: Indiana University Press.
- Nenon, T. (2015). Husserl and Heidegger on the Social Dimensions of the Life-World. In L. Učník, I. Chvatík, & A. Williams (Eds.), The Phenomenological Critique of Mathematisation and the Question of Responsibility (pp. 175–184). Heidelberg: Springer.
- Dillon, M. C. (1997). Merleau-Ponty’s Ontology . 2nd edition. Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press.
- Overgaard, S. (2007). Wittgenstein and Other Minds: Rethinking Subjectivity and Intersubjectivity with Wittgenstein, Levinas, and Husserl . New York and London: Routledge.
- Steinbock, A. (1995). Home and Beyond: Generative Phenomenology after Husserl . Evanston, IL: Northwestern University Press.
- Theunissen, M. (1986). The Other: Studies in the Social Ontology of Husserl, Heidegger, Sartre and Buber , trans. C. Macann. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- Berger, P. L., & Luckmann, T. (1991). The Social Construction of Reality: A Treatise in the Sociology of Knowledge . Harmondsworth: Penguin.
- Ferguson, H. (2006). Phenomenological Sociology: Insight and Experience in Modern Society . London: SAGE Publications.
- Garfinkel, H. (1984). Studies in Ethnomethodology . Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Heritage, J. (1984). Garfinkel and Ethnomethodology . Cambridge: Polity Press.
- Schutz, A. (1972). The Problem of Social Reality: Collected Papers I . The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff.
- Broome, M. R., Harland, R., Owen, G. S., & Stringaris, A. (Eds.). (2012). The Maudsley Reader in Phenomenological Psychiatry . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Finlay, L. (2009). Debating phenomenological research methods. Phenomenology & Practice , 3 (1), 6–25.
- Gallagher, S., & Zahavi, D. (2012). The Phenomenological Mind . 2nd edition. London: Routledge.
- Katz, D. (1989). The World of Touch , trans. L.E. Krueger. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
- Fodor, J. (1987). Psychosemantics . Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
- From, F. (1953). Om oplevelsen af andres adfærd: Et bidrag til den menneskelige adfærds fænomenologi . Copenhagen: Nyt Nordisk Forlag.
- Galileo, G. (1957). Discoveries and Opinions of Galileo . New York: Anchor House.
- Gadamer, H. (1991). Truth and method (J. Weinsheimer & D. Marshall, Trans.; 2nd ed.). New York: Crossroads. (Original work published 1975)
- Herman, J. (1992). Trauma and recovery . New York: Basic Books.
- Kohut, H. (1984). How does analysis cure? (A. Goldberg & P. Stepansky, Eds.). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Orange, D., Atwood, G., & Stolorow, R. (1997). Working intersubjectively: Contextualism in psychoanalytic practice . Hillsdale, NJ: Analytic Press.
- Stolorow, R., & Atwood, G. (1992). Contexts of being: The intersubjective foundations of psychological life . Hillsdale, NJ: Analytic Press.
- Connell, R. W. (1985). Teachers’ Work . Sydney, Allen & Unwin.
- Glaser, B., & Strauss, A. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Chicago, Aldine.
- Gorden, R. L. (1969). Interviewing: Strategy, Techniques and Tactics . Homewood Ill, Dorsey Press.
- Husserl, E. (1970) trans D Carr Logical investigations . New York: Humanities Press.
- Hycner, R. H. (1985). Some guidelines for the phenomenological analysis of interview data. Human Studies , 8 , 279–303.
- Measor, L. (1985). Interviewing: A Strategy in Qualitative Research. In R Burgess (Ed.) Strategies of Educational Research: Qualitative Methods . Lewes, Falmer Press.
- Shaw, R. (2019). Interpretative phenomenological analysis. In M. Forrester & C. Sullivan (Eds.), Doing qualitative research in psychology: A practical guide (2nd ed., pp. 185–208). SAGE.
- Landridge D. (2007). Phenomenological Psychology . Harlow, UK: Pearson Education.
Qualitative study design: Phenomenology
- Qualitative study design
Phenomenology
- Grounded theory
- Ethnography
- Narrative inquiry
- Action research
- Case Studies
- Field research
- Focus groups
- Observation
- Surveys & questionnaires
- Study Designs Home
Used to describe the lived experience of individuals.
- Now called Descriptive Phenomenology, this study design is one of the most commonly used methodologies in qualitative research within the social and health sciences.
- Used to describe how human beings experience a certain phenomenon. The researcher asks, “What is this experience like?’, ‘What does this experience mean?’ or ‘How does this ‘lived experience’ present itself to the participant?’
- Attempts to set aside biases and preconceived assumptions about human experiences, feelings, and responses to a particular situation.
- Experience may involve perception, thought, memory, imagination, and emotion or feeling.
- Usually (but not always) involves a small sample of participants (approx. 10-15).
- Analysis includes an attempt to identify themes or, if possible, make generalizations in relation to how a particular phenomenon is perceived or experienced.
Methods used include:
- participant observation
- in-depth interviews with open-ended questions
- conversations and focus workshops.
Researchers may also examine written records of experiences such as diaries, journals, art, poetry and music.
Descriptive phenomenology is a powerful way to understand subjective experience and to gain insights around people’s actions and motivations, cutting through long-held assumptions and challenging conventional wisdom. It may contribute to the development of new theories, changes in policies, or changes in responses.
Limitations
- Does not suit all health research questions. For example, an evaluation of a health service may be better carried out by means of a descriptive qualitative design, where highly structured questions aim to garner participant’s views, rather than their lived experience.
- Participants may not be able to express themselves articulately enough due to language barriers, cognition, age, or other factors.
- Gathering data and data analysis may be time consuming and laborious.
- Results require interpretation without researcher bias.
- Does not produce easily generalisable data.
Example questions
- How do cancer patients cope with a terminal diagnosis?
- What is it like to survive a plane crash?
- What are the experiences of long-term carers of family members with a serious illness or disability?
- What is it like to be trapped in a natural disaster, such as a flood or earthquake?
Example studies
- The patient-body relationship and the "lived experience" of a facial burn injury: a phenomenological inquiry of early psychosocial adjustment . Individual interviews were carried out for this study.
- The use of group descriptive phenomenology within a mixed methods study to understand the experience of music therapy for women with breast cancer . Example of a study in which focus group interviews were carried out.
- Understanding the experience of midlife women taking part in a work-life balance career coaching programme: An interpretative phenomenological analysis . Example of a study using action research.
- Holloway, I. & Galvin, K. (2017). Qualitative research in nursing and healthcare (Fourth ed.): John Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Rodriguez, A., & Smith, J. (2018). Phenomenology as a healthcare research method . Journal of Evidence Based Nursing , 21(4), 96-98. doi: 10.1136/eb-2018-102990
- << Previous: Methodologies
- Next: Grounded theory >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 11:46 AM
- URL: https://deakin.libguides.com/qualitative-study-designs
An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Phenomenological psychology and qualitative research
Magnus englander, james morley.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author.
Accepted 2021 Sep 23; Issue date 2023.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
This article presents the tradition of phenomenologically founded psychological research that was originally initiated by Amedeo Giorgi. This data analysis method is inseparable from the broader project of establishing an autonomous phenomenologically based human scientific psychology. After recounting the history of the method from the 1960’s to the present, we explain the rationale for why we view data collection as a process that should be adaptable to the unique mode of appearance of each particular phenomenon being researched. The substance of the article is then devoted to a detailed outline of the method’s whole-part-whole procedure of data analysis. We then offer a sample analysis of a brief description of an ordinary daydream. This is an anxiety daydream in response to the recent Covid-19 pandemic. We present this daydream analysis in full to show the concrete hands-on 5 step process through which the researcher explicated the participants’ expressions from the particular to the general. From this brief sample analysis, the researcher offers a first-person reflection on the data analysis process to offer the reader an introduction to the diacritical nature of phenomenological psychological elucidation.
Keywords: Phenomenology, Psychology, Qualitative research
Pure phenomenology's tremendous significance for any concrete grounding of psychology is clear from the very beginning. If all consciousness is subject to essential laws in a manner similar to that in which spatial reality is subject to mathematical laws, then these essential laws will be of most fertile significance in investigating facts of the conscious life of human and brute animals.—Husserl 1917 . 1 The natural sciences were never intended to study man as a person. One need not leave the realm of science to study man adequately. We need only to broaden science itself.—Giorgi, 1970 2
Introduction
Recently, there has been a healthy and long overdue discussion over how best to appraise the many new qualitative methods and how they contribute to scientific knowledge in psychology. For phenomenological psychologists the crucial challenge is, as expressed by Edmund Husserl (quoted above), to show how phenomenology provides a " concrete grounding " and " fertile significance " to the development of psychology as a science. Historically, it is well known that psychology, by and large, has imitated the methodology of the natural sciences. As expressed by Amedeo Giorgi (quoted above), by emulating physical science, psychology gave up studying human beings "as persons ." In response to this critical flaw at the heart of modern psychology, phenomenological psychologists endeavor to redirect psychology toward a more phenomenologically based direction. The centerpiece of this project has been the development of a qualitative research methodology that would make a phenomenological psychological science possible. What follows is an outline of the original research method, where we also offer an example of data analysis as carried out by the researcher.
Historical context: the project of a human science psychology
Before we launch into our main presentation, we believe that it is important to offer a brief historical review to illustrate the unique way in which this method developed in close collaboration with phenomenological philosophy. The following section is a synthesis that draws from historical accounts by Smith ( 2002 ), ( 2010 ), Cloonan ( 1995 ), and Churchill and Wertz’s ( 2015 ), as well as from the past experience of the authors.
In the early 1960’s Giorgi found phenomenology to be practiced in an ambivalent and often methodologically contradictory manner in European academic psychology. Similarly, American humanistic psychologists, sympathetic to phenomenology, were active critics of the deterministic approaches of mainstream psychology. But they, nonetheless, like their European counterparts, also defaulted to non-phenomenological measurement techniques when it came to their own research designs. It was as a response to this situation that the first systematically phenomenological psychology program was founded at Duquesne University in the early 1960’s. In this context Giorgi and his colleagues articulated this distinctly phenomenological way of doing psychological research—a methodology consistent with its phenomenological foundations. While Giorgi took the lead role in the development of this methodology, it needs to be stressed that this a was also an interdisciplinary community endeavor that took place between the philosophy and psychology departments at Duquesne University spanning the 1960’s to the late 1980’s. John Scanlon, the translator of Husserl’s phenomenological psychology lectures, was particularly supportive as a consultant to Giorgi and his colleagues during this period—as was Richard Rojcewicz, Al Lingis, Lester Embree, and several non-Duquesne but sympathetic scholars such as Martin Dillon, William Richardson and many others whom, records show, were often invited as guest speakers and consultants. Also, the psychology curriculum required students to take a minimum of two courses in modern philosophy, whereas the psychology faculty consistently audited philosophy courses.
In 1970 Giorgi launched the Journal of Phenomenological Psychology , which was at the outset a joint venture with European phenomenologically oriented psychologists and psychiatrists, as well as phenomenological philosophers. The journal was initially co-edited by Georges Thines and Carl F. Graumann. Serving on the first editorial board were Europeans such as Blankenburg, Buytendijk, Gurwitsch, van den Berg, van Breda, and Straus. The key point here is that the work being done on the development of the research methodology was part of a radically interdisciplinary and international project from the very beginning. As part of the overall project, Giorgi also founded the Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center . This research center also carries a copy of Husserl’s unpublished papers from the archives in Leuven, as well as the archives of Gurwitsch, Straus, Strasser, Bouman, Heidegger’s Marburg lectures, Buytendijk’s Pensée Repensée , and over 20,000 volumes, making it the largest collection of existential-phenomenological literature in the world. At the official inception of the center, Giorgi invited John Salis as his co-director.
Giorgi's seminal work, Psychology as a Human Science: A Phenomenology-Based Approach ( 1970 ) expressed a phenomenological response to the historical situation of psychology as a natural science. This also served as a foundational text for the psychology curriculum at Duquesne. Here, as a psychologist, he first proposed the necessity of a rigorously procedural, qualitative research method for a human scientific psychology. It made the appeal for an overall paradigmatic unity of “approach, method, and content” as the basis for a non-naturalistic psychology—an authentic Geisteswissenschaft or ‘human scientific’ psychology. Giorgi insisted that if psychology is to be true to its own subject matter, the scientific study of humans as persons, then the meaning of term 'empirical' in psychology must by necessity be 'broadened' beyond empiricism’s restriction to the sensory (see also, Giorgi, 1971 , 2009 ). A phenomenologically empirical science would be inclusive of all experience. This would include (in Husserl’s terms) the ir-real, or the more than sensory aspects of experience, not just the real or sense-based measurables of classical empiricism. The vision was to employ the overall phenomenological paradigm to ground a human scientific psychology, a scientific enterprise autonomous from the naturalistic juggernaut of mainstream psychology.
Over this 50-year history this methodological approach has been known by various names: the phenomenological psychological method, the existential-phenomenological psychological method, the qualitative phenomenological method, human science psychology and even “the Duquesne method.” The founding Duquesne faculty mostly preferred the term “ Existential-Phenomenological Psychology ” to highlight the influence of all main continental thinkers: Heidegger, Sartre and Merleau-Ponty—as well as Husserl and many others. The term “existential” also expressed their emphasis on concrete psychological situatedness in contrast to transcendental phenomenological philosophy. Phenomenological psychologists who received their graduate training from within the Duquesne research tradition, such as, Frederick Wertz (Wertz et al., 2011 ) used the term “Phenomenological Psychological Method,” whereas Scott Churchill ( 2022 ) maintains the original Duquesne term “Existential Phenomenological Research.” As we will see ahead, it was only in 2009 that Giorgi committed to the nomenclature of “the descriptive phenomenological method in psychology.” The emphasis on description was done to offer a counterpoint to the penchant among qualitative researchers, often influenced by cultural postmodernism, to take the extreme position that 'everything is an interpretation'—something rejected by Giorgi as the imposition of a hermeneutic universalism (Giorgi, 1992 ). 3 However, while generally based on Husserl’s approach, it is very important to highlight how in his 2009 text he never claimed his method to be identical to Husserl's. It was instead it was a modification of Husserlian philosophical methodology to adapt to the human scientific context of the discipline of psychology (Giorgi, 2014 , 2021 ). 4 In addition, Giorgi ( 2006 , 2010 , 2018 ) has also made several critical comparisons with other qualitative phenomenological methods as well as replies to philosophers (Giorgi, 2017 , 2020 , 2021 ). Several of his psychology colleagues and ex-students have developed variations of the method. Davidson ( 1988 , 2003 , 2021 ), for example, offers such a variation, to which both Giorgi ( 2020 , 2021 ) and Wertz ( 2016 ) are sympathetic. Churchill ( 2022 ) maintains the core Husserlian elements while complimenting them with Heideggerian insights. But all such variations maintain most of the key components of the overall method—as shall be outlined ahead.
Across the development of this research tradition, there have been innumerable studies published in various psychology journals and books based on this overall approach. This research tradition is cited as a significant development within the history of modern psychology (see Brennan & Houde, 2017 ). Important theoretical and original qualitative research findings were published in the four volume, Duquesne Studies in Phenomenological Psychology (Giorgi et al., 1971 , 1975 , 1979 , 1983 ), as well as the edited volume Phenomenology and Psychological Research (Giorgi, 1985 ). The latter contains paradigmatic empirical studies on learning (by Giorgi) criminal victimization (by Wertz), thinking while playing chess (by Aanstoos), and self-deception (by Fischer). A brief representative sampling that illustrates the range of recent research outputs is as follows: Living through positive experiences of psychotherapy (Giorgi & Gallegos, 2005 ), Lived persistent meaning of early emotional memories (Englander, 2007 ), Art appreciation (Roald, 2008 ), Pivotal moments in therapy (B. Giorgi, 2011 ), Postpartum depression (Røseth et al., 2011 ), Autism and culture (Desai et al., 2012 ), Leading a police vehicle pursuit (Broomé, 2013 ), Social anxiety (Beck, 2013 ), The suffering of older adults (Morrissey, 2015 ), The beginning of an extra-marital affair (Zapien, 2016 ), Mental health and the workplace (Tangvald-Pedersen and Bongaardt, 2017 ) Disturbances in maternal affection (Røseth and Bongaardt, 2019 ) Cross cultural learning (DeRobertis, 2017 , 2020 ), and Black men’s experience of police harassment (Vogel, 2021 ).
Data collection
Since this research tradition is oriented toward data analysis, this section on data collection will be brief and limited to some basic principles. Because psychologists are usually already well trained in interview techniques (Englander, 2020 ; Giorgi, 2020 ), it is natural that interviews will be commonly used to collect descriptive material. However, we stress that the method is not, by itself, an interview method. 5 Instead, each data collection strategy is developed in an idiosyncratic way by first understanding how each phenomenon best reveals itself in its own unique mode of appearance (Englander, 2020 ). For instance, when studying ‘thinking while playing chess’ Aanstoos ( 1985 ), found interviewing, by itself, to be insufficient for accessing the subtle psychological nuances of playing chess. To accommodate this phenomenon, Aanstoos ( 1983 ), developed a 'think aloud method' where one player freely spoke his thoughts into a recorder during a chess game while the opponent had his ears covered. In other words, the principle here was to design the data collection process by attending closely to the particularity of the phenomenon. Typically, the phenomenon is carefully circumscribed in advance through pilot studies, field work and clinical contexts from which the researcher can uncover the ways to best solicit descriptions and expressions that can most successfully reveal deeper psychological meanings.
Our main point here is that there should be a ‘custom fit’ between the phenomenon and the data collection design to solicit maximally good descriptions of the phenomenon within the context of everyday life. Strategies for collecting such descriptions should not be presumed beforehand and imposed on the phenomenon. The data collection design should fit the phenomenon instead of the phenomenon being forced to fit the design . Concretely, the phenomenon or related phenomena should be carefully studied through the trial-and-error process of pilot studies before any final decisions are made regarding data collection strategies.
Having made these points, some general recommendations have been laid out for data collection procedures. Drawing from existential-phenomenological philosophers such as Sartre ( 1962 , 28–29) and Merleau-Ponty ( 1962 ), phenomenological psychologists acknowledge that a person is always in a situation. At the start of any data collection, the research focus is on a concrete situation in which the participant has directly experienced the phenomenon under investigation. A concrete situation is not an idea, an attitude or anything abstract and conceptual—it is an experience that is directly lived. This acknowledgement of the situated concrete nature of psychological phenomena is another reason why data collection designs, again, need to be unique to the phenomenon and independently ‘custom-designed’ by the researcher. Or put another way, each study seeks the mode of investigation that allows the phenomenon to best express itself in its own distinctive way.
Data analysis 6
This is a ‘whole-part-whole’ qualitative method that includes steps where the researcher adopts the phenomenological psychological attitude and applies the technique of eidetic variation. Again, in contrast to philosophical analysis, phenomenological psychology begins and ends with meanings as lived and contextualized within the mundane, everyday lifeworld.
Concrete 5 step method of data analysis
The data analysis has five steps. Over the course of nearly five decades of experience we have learned that success with this method is best achieved by applying each step in a generally sequential relation to the other steps. In this way, all five steps work as an integral whole. The steps that follow where adopted from a recent publication by Giorgi et al. ( 2017 ). Having said this, it is important to also point out that these steps have both a linier and non-linier dimension to them. The linear sequential ‘steps’ offers an initial structure and organization that can also liberate the researcher to move back and forth, reviewing previous steps and revising them in relation to new discoveries and intuitions. In actual concrete practice, the process becomes more like a working draft or scaffold to work from. Ahead, in our discussion of the case analysis, this non-linier dimension will be more fully addressed.
Step 1. Initial reading for a sense of the whole
As this is a whole-part-whole method, the procedure begins with the ‘sense of the whole,’ proceeds with an analysis of the parts, and concludes with a newly elucidated ‘sense of the whole.’ Thus, the preliminary ‘appreciation’ of the entire description is important because it prepares and assists the researcher for the next steps where one studies its parts. This ‘sense of a whole’ should not be confused with hypothesis, conclusions or theorizations. Instead, it should be seen as a tentative understanding that is only an opening prelude to a relationship with the descriptive material. Importantly, it is this ‘sense of the whole,’ provided by the participant’s full descriptive account, that will act as the background to the diacritical figure-ground analysis carried out during the latter steps. In concrete practical terms, the researcher reviews the transcription (or audio or video) several times before starting Step 2. Again, this first step establishes the figure-ground framework that will drive the part-whole analysis of the entire method as every part, or meaning unit, will usually be explicated in terms of its relationship with the whole of the description.
Step 2. Adopting the phenomenological psychological attitude
Adopting the overall phenomenological attitude or ‘way of seeing’ is what distinguishes this method from other forms of non-phenomenological qualitative research. Importantly, and this can’t be stressed enough from the onset, in our work as social scientists doing life-world qualitative research, the epoché and the reduction function in a different context then in philosophy. 7 So, modified to accommodate the psychological sphere of interest, this attitude is essential to the next steps of the data analysis. Most would agree that time needs to be dedicated to the study authoritative primary sources in phenomenology to fully understand the nature of this phenomenological approach to research. This involves, (1) the epoché (or suspension) of the natural attitude, and (2) an assumption of the phenomenological psychological reduction.
With the practice of the epoché we try to just let the experience of something arise in its “givenness.” 8 In Husserl’s terms this is a ‘putting out of play’ or ‘parenthesizing’ of any positions of belief or doubt toward the world as independent of our consciousness of the world. This ordinary everyday position towards reality is what phenomenologists call the ‘natural attitude.’ A corollary of the natural attitude is the naturalistic attitude which is the commonsense belief that all things are ultimately explained by the physical causes of natural science. So, the psychologist appropriates the epoché for several reasons, (1) it clears the way for us to better understand how the participants are experiencing the world, self and others, and (2) it liberates us to better describe other people’s experiences without falling back on physical explanations, rationalizations, stereotypes or explaining them away with hypothetical models and concepts. (3). It allows researchers to become more aware of how, as Merleau-Ponty ( 1962 , p xiii) put it, one’s own ‘intentional threads’ are themselves influencing the phenomenon. (4). It invites researchers to overcome prejudices and doubts with regard to their own aptitudes for intuitive imagination. Put another way, the epoché opens us to see how the world is profusely intertwined with both the researchers and the research participant's experience of it, characterizing a radically non-dogmatic and open-minded perspective towards psychological research.
We will next go into some detail on the nature of the reduction in phenomenological psychology because it is here that phenomenological psychologists make significant and necessary modifications to the reduction, and in turn the epoché , as originally expressed by Husserl and philosophical phenomenologists. The phenomenological psychological reduction is what one does after first understanding the perspective of the epoché. Here we ‘reduce’ or restrict our frame of reference to a particular region of meaning. The psychological, in this sense, can be viewed as a particular region of science that is a psychological reduction. In the human scientific context of a qualitative psychology, a psychological reduction takes on a different meaning than Husserl’s original incomplete depiction of the psychological reduction. Husserl saw the psychological reduction as both a propaedeutic steppingstone towards the transcendental (or philosophical) reduction, 9 as much as he also saw it as the basis for new kind of psychological science—as we are applying it here. However, not being a psychologist, Husserl was not able to offer detail on how to apply the psychological reduction in an applied human science context. It is here where Giorgi's modification of the psychological reduction incorporates the doings of science to qualitative psychological research. The psychological region pertains to a particular domain of lived experience—an experience that is neither abstractly conceptual, nor objectively physical; it is concretely and personally lived, by a particular person, always socially engaged, in a particular situation in everyday social life, in space, time and history.
In this sense, the psychological reduction maintains an intimate but distinctively delicate, even tricky, relationship with the natural attitude. While philosophers may be disinterested in the natural attitude in order to pursue other matters, the phenomenological psychologist is studying exactly the natural attitude itself. This mundane world of everyday common-sense beliefs is precisely the subject matter of the phenomenological psychologist—and any other phenomenologically identified social scientists. In this sense, the psychological position transforms the nature of the epoché. Instead of the philosopher’s full suspension of the world of the natural attitude, the psychologist takes strong interest in exactly this world of the natural attitude. This means that the psychologist performs an epoché that is both in and out of the natural attitude. Within the psychological reduction we ‘step back’ from the natural attitude in order to study its structures. Again, the phenomenological psychologist is cognizant of the faith of the assumed world of the natural attitude but still studies this worldview not unlike the empathic manner of an anthropologist, doing field work, who both spontaneously participates in village life, like a fellow villager, while also maintaining his social scientific perspective. So, unlike the faith of the participant, the researcher’s is a faith that regularly, and methodically, steps back and questions itself. These points will be further developed in our reflection on how this attitude, particular to the phenomenological psychologists, was applied to the data analysis process performed on our sample case description.
Another aspect of this circumscribed 'psychological' region is that it pertains to the domain of relevance that is, itself, the ‘discipline’ of psychology 10 and what Giorgi ( 2009 ) has referred to as the 'disciplinary perspective'. Giorgi suggests that this ‘disciplinary’ reduction to the domain of the psychological (2009) should be most accurately depicted as a human scientific reduction. 11 In stark contrast to the empirical theory of science that drives mainstream psychology, the approach provided here allows researchers to explicate psychological meanings in their morphological, provisional, phenomenological sense.
Step 3. Dividing data into meaning units
This next step is motivated by practicality. Attempting to analyze, for example, 30–40 pages of transcribed interview material all at once is a daunting task. This is precisely why a data analysis method is helpful. Nevertheless, to stay consistent with a phenomenological theory of science, Step 3 is carried out from within the phenomenological attitude. For example, while reading through the recorded material, the researcher breaks down the material into smaller manageable parts to allow for a closer and more detailed focus in the upcoming Step 4. By phenomenologically elucidating the parts, the researcher is also able to begin distinguishing the participants’ meanings from how these appear in the natural attitude. This allows the expression by the participants to later (i.e., in Step 4) be explicated into phenomenologically psychologically sensitive description. The material is thus broken into manageable sections referred to as “meaning units.” The length of a meaning unit can vary from one sentence to an entire paragraph or (on rare occasions) a whole page of material. The length of meaning units can also vary from researcher to researcher, and such variation does not necessarily have any bearing on the general findings at the end of the analysis. Often the material can be easily differentiated. The main point is that too large a meaning unit can be unwieldy to analysis. It is also important to point out that not all meaning units are essential to the general structure of the phenomenon. However, all meaning units need to be analyzed (in Step 4). This last point is important, because sometimes when the researcher relaxes the epoché and returns to the natural attitude, some meaning units might mistakenly appear redundant. Nevertheless, when analyzed carefully, there is always the possibility of discovery.
Typically, researchers break this into two side-by-side columns that are written out in text form, referred to as Column 1 and Column 2 . This two-column transcription procedure serves several purposes. It conveniently organizes the process for the researcher and, importantly, it makes the data analysis process transparent and thus open for critique by other phenomenological researchers. As an additional procedure to this step, Giorgi also suggests that one modifies the participants’ expression into third person expressions. However, this is only a suggestion intended for researchers who are having difficulty in seeing the difference between the individual (or the idiographic level) and the phenomenon (the nomothetic level). Another discretionary modification is to extend columns, beyond the usual two, into three or even four columns. This was employed in the daydream analysis ahead where the researcher found a third column to be of value as it allowed him to visually check his more generalized transformations with the original meaning units—right before his eyes.
Step 4. Transformation of everyday expression to psychological meaning
The relationship between Column 1 (i.e., everyday expression, or naive description, of the participant) and Column 2 (i.e., phenomenological description of psychological meaning) is distinctive to this method. Here one carefully elucidates the participants’ essential meanings into generalizable terms within the domain of psychological relevance—as expressed above. We grasp and draw out the fuller psychological meanings embedded within the everyday description. Now, it is in this particular step that the phenomenological attitude takes center stage and is explicitly put into practice for the purpose of a phenomenological psychological analysis. In addition, in order to seek the general meanings within the lived experience this step also includes the tool of eidetic variation . This means that the researcher needs to maintain a general focus on the phenomenon under investigation while carrying out this detailed analysis. In this context, phenomenological elucidation is not a matter of mere notetaking, summarizing, annotating or just condensing meanings. It is more about how the researcher adjusts one’s mindset so as to allow the psychologically relevant meanings to emerge to one’s consciousness. In a certain sense, one opens oneself, or renders oneself a vehicle to the fuller meanings of the participant’s naive description, but always with a focus on the phenomenon. This is a receptive or ‘discovery’ mode of consciousness—not one of actively applying ideas, theories or concepts. One can understand this position as a contemplative openness to the givens of the other’s experience as it emerges through the participants’ expressions. There is an imaginative participation in the subjects’ descriptions not unlike the engagement one experiences when reading a novel, a poem, or any act of expressive art. There is here an ironically 'focused openness' or put another way: a resolute receptiveness. One converts the participant’s expressions (as conveyed within the natural attitude) into phenomenologically clarified psychological meanings by carefully following the intentionality in the participants' expression. The watchwords here are: elucidation, illumination, and explication. Here, we do not add to what our participants say, instead we bring forth the fuller meanings.
In addition, one does not need to restrict oneself to only one column during the analysis. It is perfectly feasible for the researcher to extend the analysis of the initial meaning unit into several levels of elucidation—such as a column 3 or 4. As noted in the previous section on Step 3, this 4th step is also about the spirit of transparency in science (similar to how one shows one's work when doing mathematics). By extending the analysis into stages or levels of analysis, one is showing colleagues exactly how one has reached these extended levels of generalization.
Step 5. Returning to the whole and moving toward the general structure
It is at this phase that the researcher moves from a part-whole eidetic analysis to a new focus on the whole again. But now we have a new whole, a whole that is the end result of this entire procedure. Remaining within the phenomenological psychological attitude, as described above, the researcher’s intimate engagement with the meaning unit analysis now becomes an act of synthesis of the parts together into what is usually a temporally sequential narrative. The watchword here is structure. A structure is understood in gestalt terms as a whole, but a whole composed only of essential parts. The idea here is that if one where to hypothetically remove one of the parts, then the rest of the structure would fall apart. Therefore, the researcher wants to be prudent to not overstuff a structure. A good structure should follow the elegance of simplicity—as much as reasonable. Furthermore, the features or constituent parts should be invariant. By invariant we do not mean universal or absolute. We are fully aware that human phenomena are contingent to history and culture. We only mean that an invariant psychological structure should “hold together” within this culture at this point in history. Within these parameters we think it reasonable that generalized psychological claims can be made. 12
It is important to note that most other qualitative research methods present their conclusions in terms of ‘themes.’ But because this approach emphasizes phenomena as totalities, i.e. as structures, we avoid any overemphasis on themes and prefer to comment on the structure of the phenomenon as a totality as much as possible. When we do discuss parts, we prefer the term ‘constituents’ to stress their relatedness to the whole of the structure. It is conventional for many other methods to present to readers curated direct quotes from their participants. But because we have already performed a very close analysis of the direct expressions of the participants in the earlier steps of the data analysis, we prefer to offer readers the more structural, or general, levels of meaning in any discussion of our results as will be seen ahead when we discuss the results of our analysis of an experience of daydreaming. In short, our inclination is to offer readers prepared or explicated data instead of curated raw data.
Situated structures
As an optional procedure one can add an extra step between the meaning unit analysis (step 4) and the General Structure (step 5). While Giorgi stressed the general structure, most advanced researchers find it effective to add this intermediary step—as demonstrated in the analysis offered ahead. 13 This can support the eventual goal of generality and can be an extremely helpful ‘bridge step’ toward the general structural description. But it must be stressed that to remain only on the level of situated individual experience would miss the key purpose of the method—which is to achieve a general (inter-subjective) structural description of the phenomenon. Having said this, a situated structure can be very rich in life world details and remarkably illuminative in its own right. One could depict this as a structure on the idiographic or individual level. This is often popular with clinical psychologists who prefer an individual ‘case-study’ level of understanding. But unlike ‘clinical’ case-studies, this is a research phenomenon which is different from a diagnostic, or therapeutic relationship. Here the research intention is paramount—not the clinical intention. Again, this is the elucidation of an individual participant’s experience performed as a step before moving to the general structure. This would be an essential structure of the invariant aspects of an individual person’s experience of the phenomenon. In more simple language this is a basic summary of the psychologically relevant aspects of this particular person’s experience of the phenomenon. Developing situated structures from three or more research participants can be a very helpful way to eidetically scrutinize the phenomenon as experienced by all of the participants. But when it comes to groups, it is important to emphasize that within the phenomenological approach to science, eidetic comparison (Wertz, 2010 ) should not be confused with statistical comparison. Though more challenging (especially for newcomers), in phenomenological psychology an eidetic analysis could just as well be performed on a single participant as on a group. But having made this qualification, a group of any number of situated structures is always a great support to one’s eidetic analysis towards generalizability. 14
The general structure
At this point, these phenomenologically elucidated ‘parts’ of the data analysis (including the situated structures) are brought back together into a new whole . Phenomenological psychology is definitively a search for psychological essences or what we prefer to call general invariant structures. Husserl called this ‘eidetic analysis’ and the primary technique he used for this level of analysis he called eidetic or ‘imaginary variation.’ In this analysis, one imaginatively reviews the phenomenologically clarified parts of the previous analysis as achieved in step 4, with an eye for intuiting a new whole. Again, this is a discovery frame of mind where I render myself open to the continually emerging intuitions and patterns in the elucidated data as they give themselves to my awareness. In other words, it is not an empirical summary or the common denominator of facts across the cases, but another level of the analysis. Specific to this level of the analysis is the technique of imagining the phenomenon in its various profiles, angles or possibilities. For example, as a researcher I can ask myself if the structure of this phenomenon is possible without any of the particular constituent parts that I have discovered during my analysis in Step 4? I may even imagine adding new parts that were not explicitly expressed in the data but ‘apperceptively’ or intuitively suggested by the data. To reiterate, in contrast to most other qualitative approaches, the general structure is an integral whole and is never just a series of separate themes. The key idea here is that a structure is a full gestalt , a whole, or a totality that dissipates when a part is removed. Therefore, it is important to edit a general structure with rigor and integrity and to delete all that is unessential to the systemic pattern that makes the phenomenon what it is. The general structure is typically narrated in the present tense—though not always. Sometimes a phenomenon may split off into types or variants. In such cases one could have two or three general structures, representing different ‘types.’ Therefore, forcing a closure by applying a psychological theory is not an option. The findings, as supported by the analysis, can at a later stage in the discussion section (of the research report) be presented in dialogue with established psychological theories (‘backloading’ in current nomenclature) and other research results (See Fig. 1 ).
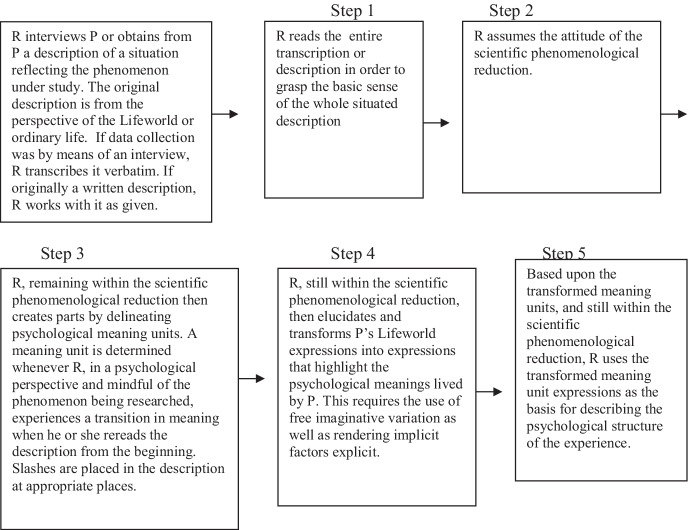
Overview—flowchart of data analysis process (from Giorgi et al., 2017 ). R researcher, P participant
Case example
What follows is a brief case example of a phenomenological psychological data analysis. Again, unlike philosophy where the research is done in a solitary first person manner, in phenomenological psychology we take a second person position. We see ourselves as participants —not mere observers—as we try to grasp the fuller meaning of other people’s concrete descriptions as expressed within the natural attitude of everyday life (Englander, 2020 ; Giorgi, 2009 ). We make no demands on our participants to take the reflective attitude of the practicing phenomenologist. Instead, only the researcher is responsible for taking the phenomenological stance as he or she reads the expressions of the participant. Here the data analysis is conducted within the tension of two intertwined goals: to be faithful to the intentional meanings as expressed while also deepening their meaning through their re-expression within the phenomenological psychological attitude—as performed in meaning unit analysis (step 4) and the development of structures (step 5). This, again, is what we call elucidation or explication . This is a fidelity that also takes us into a deeper understanding of the expressed intentions our participants. This is exactly the power of the epoché (within the psychological standpoint) as applied to the grasping or bringing-forth of psychological meaning. Like the way certain artists can transform the taken-for-granted experience of an ordinary object, such as an apple in a still-life painting, into an apple seen afresh ‘as if for the first time,’ so does the phenomenological psychologist strive to bring out the psychological meaning of the participant’s experience of the phenomenon.
The sample presented here is taken from the context of an ongoing research project on daydreaming that is currently replicating and updating a previously published study (Morley, 1998 , 1999 , 2003 ) through fresh interview material. As explained above, the data collection process was customized to suit the unique nature of the phenomenon. Here, in this particular research context, the procedure for collecting daydream reports has been to first request a self-written protocol from persons who are not themselves directly involved with psychology. A formal protocol question prompt (see below) was given to the participant to help guide the written description. As mentioned above, the reason for beginning with a written description is that, as an imaginary phenomenon, daydreaming can become unwieldy and difficult to articulate during an interview. Through pilot trials we have learned that written descriptions help the participant to ground or anchor their memory of the daydream. It then serves as an organizing point of reference for the interview—without imposing any leading external influences. Then, the researcher and participant begin the interview itself by re-reading the written protocol together to refresh their memories of the event. The researcher initiates the interview by asking the participant to take the initiative to express what, in the written description, he or she feels is most in need of elaboration or expansion. After the participants have offered further elaborations on what stands out as most important to them, the researcher will then pose questions from an informal semi-structured check-list of points of special phenomenological interest to the researcher. Specifically, the researcher asks for fuller descriptions of existential constants such as space, time, embodiment, social relations, sense of reality, and sense of self as experienced during the various temporal phases of the daydream. The actual interview approach, for this particular phenomenon, will vary across a spectrum from a gentle reiterative style to intensive and challenging inquiries 15 —depending on circumstances. As described above, this data collection method was developed through the researcher’s intimate relationship with the phenomenon over time.
A full data analysis of an entire interview would surfeit the space of this presentation. So it is for this reason that we chose to offer a concise sample of the analysis process drawn from material that was recently collected in the form of an initial written protocol. While not as detailed and spontaneous as the interview that followed, the written protocol still offers the reader a rich “sense of the whole’ that allows for a faithful sample the data analysis process. So, though brief, this was still a reasonably good description that offers a worthy example of the whole-part-whole dynamic central to the analysis process of this method. Choosing a brief sample also expresses the authors’ confidence that even the smallest fragment of an everyday type of description will explode in meaning when approached from within the phenomenological psychological attitude. Not unlike how the sensory empirical world burst open with the introduction of telescopes and microscopes, so does the human life world open up before us when beheld from within the openness provided by the lens of the overall phenomenological perspective as expressed above.
Having said this, we again caution that as a sample data analysis it does not benefit from the detail offered by the follow-up interview. This small sample is offered for strictly didactic reasons. More importantly, it also stands alone without the fuller dimensionality offered by the intersubjective eidetic analysis at least two other individual case examples to which it’s whole and constituent parts could be eidetically compared. It was for this reason that we restricted the title of the phenomenon from “daydreaming” to “an anxiety daydream” to reflect the particularity of the one sample. But even without the intersubjective corroboration of at least two other daydream descriptions, we hope readers will agree that it can be surprising to see what can emerge when using only one case example.
To reiterate, in brief, we begin with the whole daydream description as depicted in the written protocol. After reading for the whole we then break it into parts—or meaning units. Then, we phenomenologically elucidate each of the parts, or meaning units, though the technique of using columns—in this case we used 3 columns (most researchers only use two). Finally, we return to a renewed sense of the whole in both of the situated and general structures. The situated structure, like a case study, is idiographic to the particular description while the general structure is an attempt to achieve a nomothetic statement on the phenomenon of anxious daydreaming. In this instance, the general structure will be restricted to the meanings elicited from this single, and very brief, case example and will therefore be somewhat limited and tentative. It’s very important to note that in most research instances the general structure will be an eidetic analysis based on the various other individual situated structures. The general structure corresponds to what one could call the results of the research process. While the constituent parts of the whole structure will be discussed in most research reports, unlike most other qualitative methods that discuss themes , typically supported with selected quotes, we prefer to keep the whole structure of the experience as the primary reference point.
Ahead, within the analysis we will refer to the participant as ‘P.’ Later, in the discussion, we will address the participant through the pseudonym of Ashling.
Written daydream protocol—initial protocol prompt to the participant (P)
Please concretely describe a situation in which you experienced a daydream. Please describe what was happening when the daydream began, what the daydream was about, what it was like while having the daydream, and how the daydream came to an end. Please try to be as concrete and detailed in your description as possible.
Ashling’s written protocol description—including step 3, marking the meaning units
On March 14, 2020, I was in Tepoztlán, Mexico. Trump had recently announced he would be suspending travel from Europe to the US due to COVID-19. I had just moved to Mexico a few months prior. I feared if the closure was happening with Europe it would most likely be happening with Mexico very soon, a golden moment for Trump to assert his plan for the border with Mexico to be even more impenetrable. As we drove back from Tepoztlán to Mexico City and night was falling, I started to gaze out the window, daydreaming, as we passed the silhouetted Popocatépetl volcano in the distance.
I started thinking about how I would get back to my family in the US if flights were suspended with Mexico. As we continued to drive I thought about if we didn’t stop in Mexico city but just continued all the way to the border (about a 15 h drive). In my daydream I imagined arriving at the border and that there would be mayhem, cars piled up for miles and the border patrol not allowing anyone across. The border agents were armed and aggressive and unreachable. I imagined the reasons I would give, that my family needed me etc., but reasoning with them was not working. And I envisioned somehow managing to get past them as they were distracted by the chaos, and the relief felt by speeding into the US away from the border and onward towards home.
I felt anxious imagining the border patrol and their dominance, their potential to shoot us when we sped past, defying their rules of closure. But I then felt relief at the outcome of getting past, of fighting our way in and across and making it to a place of safety.
When my partner and I later got to the apartment in Mexico City that night I looked into flights to get to Boston where we would be in a familiar place during this most intensive and uncertain time. My good friend called me from Rennes in France and told me how bad it was, that death rates were rising, and how she wasn't leaving the house at all. She advised me to leave quickly and that to have a garden was a saving grace for her, and that at least in Boston I would have a garden. I booked my flight and packed a small case. I daydreamed again as I looked around the apartment, that 10 or so years would pass, and I would finally be able to come back and all my things would be here but between and around old weeds and crumbled walls and cobwebs, a scene left untouched and abandoned.
Meaning unit analysis
Situated structure of an anxiety daydream.
Daydreaming for this person was an imaginary manifestation of her feelings of anxiety. By manifesting this anxiety as a dramatically staged scenario, she was able to live-out or play-out the enactment of her anxiety and its eventual resolution. This particular daydream occurred as a person’s affective response to the threat of having her freedom of movement, across international borders, curtailed or restricted by political forces beyond her control. In particular she feared being cut-off and separated from her home and family during a time of great uncertainty. These strongly felt emotions around the experience of constraint or restriction had no means of expression within the context of a long road trip in a car. Turning her gaze, away from the car interior, out the window towards the twilight horizon of the landscape, P entered into an imagined scenario where she is in the same car but has arrived at the international border between her foreign country of residence and her desired home country. The daydream manifests the person’s own momentary existential situation as a scene of chaos and mayhem enforced by the imposing, threatening and impersonal agents of power i.e. the border guards who refuse to allow her to cross the border into her home country. P imagines trying to reason or negotiate with the guards but realizes that dialogue is futile in this situation. Again, these are circumstances out of her control. As a staged enactment or ‘metaphorization’ of her actual existential situation, the daydream is both the expression and revelation of her life situation. It allows her to “express” her immersion in the situation which also, in a reversible way, offers her a reflective distance to “see” the feeling of restriction that has occupied her. As both the expression and revelation of her present life situation the daydream is, in this sense, lived ambiguously as both an active and passive experience. These ambiguously dual, yet interwoven, perspectives are implicit to her daydreaming experience. Next, within the imaginary narrative of the daydream, the daydreaming/daydreamed person commits an act of defiant transgression. P shifts the narrative from that of passive casualty of powers beyond her control, to one where she takes charge, or assumes agency, by choosing the extreme risk of speeding past the distracted guards and thus flouting their overbearing authority by driving across the border without their sanctioned permission. By taking matters into her own hands and transgressing the rules, P escapes confinement and experiences the satisfaction that comes with the security of having returned to her home country. The daydream concludes with feelings of relief. The experience of this daydream allowed P to articulate her desire to return home to her native country during this time of uncertainty—a desire that was converted into an actual concrete decision to eventually book an airline flight home to family and friends.
Tentative general structure of an anxiety daydream
Daydreaming emerges in a situation of unfulfilling circumstances. In the case of anxiety, it appears in the form on an ominous and yet opaque threat to one’s well-being. This feeling presents itself as a demand for action—to seek the source of the threat and to overcome it. However, this demand for action cannot be achieved in the current situation as it is impeded by circumstances where no real behavioral action is possible. This becomes a tension between the feeling’s demand for action, regarding the ominous threat, and its restraining context. The person turns attention away from the immediately restraining situation by seeking out and shifting attention to another horizonal field of focus. It is here that the emotion takes the course of expressing itself through the medium of an imaginary scenario that opens up an opportunity for the fulfillment of the emotion. The emotion transforms into a world scenario where it is expressed in the form of an enacted narrative drama. The person assumes a dual intentional role as both the author/narrator of the dramatic scenario and well as the actor immersed within the dramatic action. The emotion is now lived in a narrative context that allows the possibility of its fulfilment. As a staged enactment the daydream can become a living metaphor of the person’s actual existential situation. The daydream scenario can be both the expression and revelation of one’s emotional situation. Its expression makes it possible to “see” one’s immersion in the emotional dramatic scenario. It can offer the opportunity for a reflective distance from the feeling of restriction that had previously occupied the person. As both expression and revelation of the person’s present life situation daydreaming reveals an ambiguous interplay between both active and passive aspects of experience. These ambiguously interwoven perspectives vary between being implicit or explicit to the daydreamer. Though daydreaming takes place within an imaginary region of experience, this region is always also interfused within one’s life historical horizons—always expressing one’s life projects and goals.
Commentary on the analysis
In any phenomenological psychological research report, there is an extensive theoretical discussion of the results (i.e. the constituent parts of general and situated structures) with the phenomenological and natural scientific literature. We have much to say here, especially with regard to such constituents as ‘dual intentionality’ ‘multiple realities, the ‘affective-imaginary dynamic,’ the “linkage of expression with revelation’ and, of course, the comparison of these findings with current studies in cognitive science (such as the default mode network). But alas, as the purpose of this essay is didactic with regard to the method, and due to the limits of space, we must defer this full dialogue to a future publication.
Due to the brevity of the written description, and the very fact of there being only a single participant, the researcher can only modestly offer a highly tentative sample general structure. However, despite its brevity, the participant, whom we will here call ‘Ashling,’ offered a rich and full description and the researcher feels confident that the situated structure was faithful to the participants experience.
The non-linier dimension of data analysis
While the researcher initially worked with fidelity to the 5 step method, it is also important to note that there was a significantly non-linier dimension to this process. This was especially the case when it came to the composition of the situated and general structures. Once the meaning units were demarcated, the process towards the situated and eventual general structures took on a life of its own. In other words, while the meaning units established a framework for data analysis, once the 3 column framework was established, and the participant’s expressions were laid out before his eyes , the researcher began a back-and-forth process of checking, rechecking, reflecting and intuitively linking the meanings into fuller wholes and patterns. To use an imperfect metaphor, we can compare this explication process to what is called a detective’s “crazy wall” that is used to help interpret and understand a crime case. From detective stories and movies, we are familiar with how the investigator will post pieces of data and information across a wallboard, or sometimes a city map. The detective can then use this to meaningfully link the information and datapoints with connecting strings. Seeing the constituent parts ‘before his eyes’ helps the investigator to make the ‘meaningfully intuitive connections’ that lead to better understanding of the case. Obviously, this helps the investigator to step back and see the dynamic relation between the parts and the whole and it is from this perspective that insights and discoveries can arise. This is exactly the benefit of meaning unit analysis.
The diacritical aspect of data analysis
To reiterate, the psychological phenomenological attitude is focused on understanding the particular experience of a particular person. Obviously, as evidenced by the general structure, we do not stop a the particular—but this is where we begin. While this attitude undoubtedly suspends the naturalistic attitude of physical science, its disposition towards the more global natural attitude, as discussed above, contains a strategic ambiguity. Very importantly, unlike phenomenological philosophy, phenomenological psychology directly takes up the naively believed world of the natural attitude as a subject of inquiry. Ours is, as Maurice Natanson, citing Alfred Schutz, calls it: “a phenomenology of the natural attitude” ( 1973 , p107). In other words, while we ourselves as researchers are trained to be aware of our own natural attitude, and ‘step back’ from it as best we can, it is also true that we do not entirely put it aside. So, for example, when reading Ashling’s description of her daydream, the researcher imaginatively participated with the description of her daydream and, for that moment, may have been empathically engrossed within the world of her natural attitude. In a recent publication this is well described by Scott Churchill as a ‘disciplined fascination’ (Churchill, 2022 ). Also, as a denizen of the natural attitude oneself, the researcher may well have applied his background stock of knowledge of daydreaming, garnered from personal experiences as well as professional readings on the subject; all of this in order to better understand Ashling’s experience and intentional structures. Hence, as discussed above, this is not a pure epoché or a pure reduction as practiced by the philosopher. On the other hand, unlike Ashling, or any research participant, the researcher continually practices a ‘stepping back’ from that believed world, again, in order to better understand her world. There is, in this way, a weaving process that is unique to the phenomenological psychological attitude.
The figure-ground metaphors used by Merleau-Ponty are very helpful here. Throughout his works he explicitly describes what we are calling the phenomenological psychological attitude, as a ‘ diacritical ’ process (Kearney, 2011 ) that is, like the act of breathing—both inhaling and exhaling as one whole act. This is precisely what we mean by the strategic ambiguity of the phenomenological psychological position. In his well-known discussion on methodology Merleau-Ponty describes the attitude of the researcher as follows: “Reflection does not withdraw us from the world…’ “…it steps back to watch the forms of transcendence fly up like sparks from a fire; it slackens the intentional threads which attach us to the world and thus brings them to our notice…” ( 1962 , p xiii). As psychologists these threads or tethers to the natural attitude are never cut, they are “loosened or slackened” to enable us to see the intentions of others—as well as one’s own. Seeing my own intentional threads can reveal fore-understandings that could either inhibit or enhance my analysis.
In this case, a young woman is learning about the encroaching covid pandemic, wants to return to the security of her home and family, and becomes upset about the closing international borders that could restrict, and become an obstacle, to her desire to return home. This was the big picture to which the researcher returned, in a circular manner, throughout the analysis.
The researcher came to see how Ashling was originally overcome with a desire to go home while simultaneously experiencing a feeling of being impeded from that intention. Though she did not explicitly say this, one could easily imagine how, as more borders closed, Ashling’s desire to return home would only intensify. The beginning part of the daydream narrative reflected this distressing and overwhelming devils circle where she is impeded by powers beyond her control. But in meaning unit 7 we see a turn.
Another diacritical element is the weaving between the whole of the description and its parts. As a reader one could say that I am “zooming-in” on the unique and minute details of the participants expressions as much as I am continually “zooming-out” to use the whole as the context for understanding these details. For example, Ashling’s use of key expressions in Meaning Unit 7 (MU7) such as “envisioned,” “getting past” and “the relief felt” all offered a basis for enhanced eidetic exploration and fuller illumination. They allowed the researcher to come to the insight of Ashling’s shift in position, from that of passive victim of overpowering circumstances to that of an active agent of an imaginary act of courageous transgression—driving past the armed and aggressive border guards to cross the border. Understanding the “whole” of her situation is what brought to light the essential meaning of the daydream.
Spelling out tacit meanings
By explication, or elucidation, we mean the process of spelling-out latent or tacit meanings. To offer an example, Ashling, of course, never explicitly said that she experienced a ‘dual intentional structure.’ It was the task of the researcher to cull out this structural component that was implicit to the description and likely lived-out in a pre-thematic way by Ashling. The researcher’s recognition of this constituent happened during the researcher’s transition from the meaning unit analysis to the whole of the situated structure. It was in this process of “putting the whole story back together again” that the researcher saw how this double intentionality was experienced by Ashling. Here, there were two distinct but related intentions, (1). the intention to deal with the practical frustrations of booking a flight home during an uncertain period of international crisis (the actual world), and (2). the daydreamed intention of getting past imaginary border guards (the daydreamed world scenario). The researcher came to see Ashling as experiencing both intentions and both corresponding world relations—the actual car scenario and the other being the daydreamed car scenario. Hence, the dual intentional structure. One could call this a “generalizing process” but, in actual practice, it was a much fuzzier and more unclear event than any such nominalizations can portray. Once again, we can understand this as a diacritical process: (1). The insight came ‘as given’ in the discovery manner of a direct phenomenological intuition, and (2). This pattern was ‘recognized’ from the researcher’s background stock of knowledge (or fore-understanding) as a daydream researcher and reader of phenomenological literature. Because this elucidation process is itself somewhat pre-reflective, one can never have absolute certainty over whether it was an intuitive given or a pre-understanding.
Again, Merleau-Ponty’s diacritical approach helps to illuminate this elucidation process. In describing Merleau-Ponty’s ( 1968 ) diacritical approach to grasping meaning, Kearney cites James Joyce’s statement that it is possible to have “two thinks at a time.” ( 2011 , p 1). Directly addressing psychological research, Merleau-Ponty says: “One may say indeed that psychological knowledge is reflection but that it is at the same time an experience. According to the phenomenologist (Husserl) it is a material apriori . Psychological reflection is a “constatation” (a finding). Its task is to discover the meaning of behavior through an effective contact with my own behavior and that of others. Phenomenological psychology is therefore a search for the essence, or meaning, but not apart from the facts.” (Merleau-Ponty, 1964 , p.95).
With the term “constatation’ Merleau-Ponty is suggesting that both observing , (receiving the intuitive givens) and asserting (actively applying one’s stock of knowledge) can be at play in the same act of psychological understanding. Both are one whole movement within the same act—in the chiasmatic, reversable manner of a figure-ground dynamic. While space does not allow us to develop this issue in the detail it deserves, we raise this matter to try to bring some light to the act of elucidation that is so central to this method. The take home point here is that, while the method highlights the significance of description, this does not mean that one needs to choose between stark antinomies such as description and interpretation, or phenomenology and hermeneutics as within this elucidation process of ‘disciplined fascination’ both movements come together.
Towards dual disciplinary citizenship
This method was designed to give psychological researchers an organized and structured framework for doing second person research. The whole-part-whole process, in itself, is not complicated or difficult to understand and learn. What is difficult for those who are beginning this style of research, is the assumption of the phenomenological psychological attitude. This attitude, which distinguishes this method from non-phenomenological qualitative research methods, can’t be taken for granted and requires training, study, and the support of a like-minded research community. Because it is founded in phenomenological epistemology, phenomenological psychology is a hybrid discipline. The practice of phenomenological psychology requires a kind of ‘dual citizenship’ in both psychology and phenomenological philosophy. Those trained solely in philosophy’s orthodox emphasis on textual exegesis may often lack experience in practical professional life-world applications as well as an overall knowledge of the literature and scientific history psychology. On the other hand, those trained solely in psychology, with little to no exposure to philosophy, coupled with the field’s strictly naturalist experimental orientation—which underscores the natural/naturalistic attitude—come to phenomenology with this resilient attitudinal disadvantage that can take effort to overcome. What we have here, in the current academic world, is a set-up for mutual misunderstanding between these disciplines. While the sharp disciplinary divides of the current academic world make such ‘dual citizenship’ training difficult and rare, this is possible, but only with special effort and unique pedagogical interventions. There are institutionalized training programs, usually schools of psychotherapy, that are open to such interdisciplinary training. Yet, these programs are few and far-ranging in their offerings. Most independent researchers entering this field need to supplement their training in naturalistic psychology with an intense period of philosophical study of primary sources and guidance in this study is too often lacking. Then, on the other hand, it is encouraging to see the increasing number of philosophers who are taking an interest in “applied phenomenology.” Yet, we currently see little cognizance, in much of this recent literature, of the 50-year phenomenological psychological research tradition. We mention this, as a friendly invitation to psychologically interested philosophical researchers to acquaint themselves with their predecessors to avoid re-inventing the wheel and duplicating research results and techniques that have already been developed within the phenomenological psychological research tradition. In the same breath, we would just as strongly urge our colleagues in the social sciences to give more serious study to the phenomenological philosophical tradition.
Open access funding provided by Malmö University.
From Husserl’s inaugural lecture in Freiburg given 1917 and published in Husserl—Shorter Works ( 1981 , 17).
This quote is from a talk that Giorgi gave at the Symposium on science and scientism: the human sciences Trinity College, May 15–16, 1970 and documented by Maurice Friedman ( 1984 ) Contemporary Psychology: revealing and obscuring the human . Pittsburgh: Duquesne University Press. (p.30).
To Giorgi, relativism is as much a dogmatism to be avoided in psychology as is reductionism. Giorgi's ( 2009 ) method, hence, became known as the descriptive phenomenological psychological research method. With the emphasis on description Giorgi intended to apply the phenomenological attitude by staying true to discoveries from the everyday lifeworld. So even though discoveries may sometimes be incomplete, he preferred that they were described in their incompleteness rather than forced into unnecessary closure for aesthetic or ideological reasons (ibid.). Hence, both psychologically relevant aspects of Husserl's phenomenology as well as the discovery-oriented spirit of science became essential influences on Giorgi's approach to the project of a qualitative research method in psychology.
Initially influenced by Merleau-Ponty’s psychologically oriented thought, Giorgi turned more to Husserl’s methodological emphasis in his pursuit of a phenomenological theory of science to support a qualitative psychological research method (see Giorgi, 2009 ). As Giorgi ( 2014 , 236) recently stated "…I use Husserl because he confronts the issue directly and he contrasts his position with that of the empiricists." In the late 90’s, several other qualitative methods using a phenomenological approach started to emerge, most had a stronger emphasis on postmodernism or hermeneutics. Giorgi differentiated his method from the newer ones by stressing that his was a more descriptive emphasis as opposed to an interpretative one (Giorgi, 1992 , see also, Giorgi 2006 , 2010 , 2018 ). Of course, the distinction should not be understood too literally, because in certain settings the use of the word ‘interpretation’ could synonymously refer to the act of ‘description.’ However, with the term ‘description’ Giorgi ( 1992 ) simply meant to stay true, or rooted, to what appeared in the data . This is similar to what is called a “close reading of the text” in literary studies. The intention was to avoid the kind of intrusive and overly imposing 'interpretations' where gaps in the qualitative data would be 'filled' with theoretical explanations, abstractions or even speculations.
Developing phenomenological interviewing skills requires practice and training that is often already present in the education of most clinical psychologists and health care workers. However, phenomenological psychologists have been recently applying the insights of philosophical phenomenology to better articulate the role of empathic reflection in participant observation (Englander, 2020 ; Churchill 2010 ) and designing phenomenologically inspired teaching methods (Englander 2014 ; Churchill, 2018 ) for improving quality of psychological interviewing and qualitative phenomenological research generally.
For a chronological development of the methodology, see Giorgi ( 1975a , 1975b , 1985 , 1997 , 2009 , 2018 ).
Referring to Schutz, Michal Barber points out how these terms are “analogous to the phenomenological prototype.” In other words, again, as social scientists we apply them with a different purpose than that of the philosopher. See: Barber, Michael, "Alfred Schutz", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2021 Edition, Edward N. Zalta (ed.),
URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2021/entries/schutz/ > .
The history of phenomenology could be considered one big ongoing deliberation about the meaning and possibility of the epoché. We hope readers will forgive us for sidestepping these discussions for the purposes of this presentation where space only permits us to present the epoché as practically applied to the research process in phenomenological psychology. But we will make this one brief point. All major phenomenological themes such as embodiment, temporality, intersubjectivity and even the hermeneutic circle were developed by philosophers thorough their initial employment of the epoché —or awareness of the natural attitude. It is therefore important, we believe, for one to understand the practice of the epoché to, in turn, fully grasp these phenomenological concepts. We find it inconceivable that one could proficiently comprehend basic phenomenological concepts such as the lived body or intersubjectivity while remaining unreflectively within the influence of the natural attitude. Similarly, we have learned through experience that success with the method we are presenting here is often in direct proportion to one’s awareness of their natural attitude.
The relation between the transcendental and the psychological reduction is another long-deliberated issue in the history of phenomenology which we can’t develop here. In brief, because the transcendental “philosophical” reduction is a non-personal and non-situated level of reflection it is simply not appropriate for performing qualitative psychological research—at the moment that we are doing it. To our knowledge, no phenomenological psychologist would claim to be doing both standpoints at once. But this does not mean that psychologists must, or should, ignore the insights of transcendentally derived philosophical concepts when we design our research or reflect on the results of our psychological analysis. Phenomenological philosophy can be a perfectly compatible basis from which to deepen our understandings of the results of our descriptive analysis. In short, psychologists may visit the transcendental position, but we do not unpack our bags, and we always remember our return ticket.
This is very similar to the relevance structure of a world as suggested by Schutz ( 1962 ).
As Giorgi ( 2009 , 99–100) writes, “The researcher does, of course, assume the human scientific (psychological) reduction. Everything in the raw data is taken to be how the objects were experienced by the describer, and no claim is made that the events described really happened as they were described. The personal past experiences of the researcher and all his or her past knowledge about the phenomenon are also bracketed. This bracketing results in a fresh approach to the raw data and the refusal to posit the existential claim allows the noetic-noematic relation to come to the fore so that the substratum of the psychologist's reality can be focused upon. That is, the particular way in which the describer's personal acts of consciousness were enacted to allow the phenomenal intentional objects to appear from the basis of the sense determination that the psychologist is interested in uncovering.”.
For a more elaborate discussion on general knowledge claims in qualitative research and its relation to a phenomenological theory of science, see for example, Englander ( 2019 ).
Giorgi originally included situated structures but later dropped them to emphasize the nomothetic (or generalized knowledge) aspect of the method. But most Giorgi’s colleagues and ex-students prefer to include situated structures as a transition to the general. As teachers we have learned that this psychologically rich transitional step is of great pedagogical value. For most newcomers to the method, it is intuitively much easier to construct situated structures before moving on to develop general structures. We also find situated structures to be of great psychological value in their own right—as we hope is demonstrated in our case example ahead.
It is important to note that research participants are not considered from the stance of an empirical theory of science. Any qualitative methodology, grounded in a phenomenological theory of science, cannot naively adopt the concept of the population (and sampling methods ) as its ground for making general knowledge claims (see for example, Englander, 2019 ).
At points in the interview when a more active questioning is called for, evocation techniques like those from the explication interview, or the micro phenomenological interview method, can be very effective. (see Petitmengin et al., 2018 ) Here, we invoke the daydream so that both the interviewer and the participant can, in an almost trance-like way, imaginatively re-live the daydream together. These techniques can provoke profoundly rich description. Here is another example of how we approach data collection as always contingent to the manner in which the phenomenon best expresses itself. Again, this is why we endorse an adaptable approach to data collection.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
Springer Nature's version of this paper was updated to present the corrected funding note.
Contributor Information
Magnus Englander, Email: [email protected].
James Morley, Email: [email protected].
- Aanstoos CM. The think aloud method in descriptive research. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1983;14:243–266. doi: 10.1163/156916283X00117. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Aanstoos C. The structure of thinking in chess. In: Giorgi A, editor. Phenomenology and psychological research. Duquesne University Press; 1985. pp. 23–85. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beck TJ. A phenomenological analysis of anxiety as experienced in social situations. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2013;44(2):179–219. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341255. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Brennan JF, Houde KA. History and systems of psychology. Cambridge University Press; 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Broomé R. The lived-experience of leading a successful police vehicle pursuit: A descriptive phenomenological psychological inquiry. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2013;44(2):220–243. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341256. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Churchill SD. “Second person” perspectivity in observing and understanding emotional expression. In: Embree L, Barber M, Nenon T, editors. Phenomenology: Selected essays from North America. Part 2: Phenomenology beyond philosophy. Zeta Books; 2010. pp. 81–106. [ Google Scholar ]
- Churchill SD. Explorations in teaching the phenomenological method: Challenging psychology students to “grasp at meaning” in human science research. Qualitative Psychology. 2018;5:207–227. doi: 10.1037/qup0000116. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Churchill SD. Essentials of existential phenomenological research. American Psychological Association; 2022. [ Google Scholar ]
- Churchill SD, Wertz F. An introduction to phenomenological research in psychology: Historical, conceptual, and methodological foundations. In: Schneider KJ, Pierson JF, editors. The handbook of humanistic psychology: Leading edges in theory, research, and practice. 2. Sage; 2015. pp. 275–295. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cloonan T. The early history of phenomenological psychological research methods in America. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1995;26:46–126. doi: 10.1163/156916295X00033. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson L. Husserl’s refutation of psychologism and the possibility of a phenomenological psychology. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1988;19(1):1–17. doi: 10.1163/156916288X00103. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson L. Living outside mental illness: Qualitative studies of recovery in schizophrenia. New York University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson L. Overcoming psychologism: Husserl and the transcendental reform of psychology. Springer International Publishing; 2021. [ Google Scholar ]
- DeRobertis E. From personal threat to cross cultural learning: An eidetic investigation. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2020;51(1):1–15. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341368. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- DeRobertis EM. The phenomenology of learning and becoming. Palgrave McMillan; 2017. [ Google Scholar ]
- Desai MU, Divan G, Wertz FJ, Patel V. The discovery of autism: Indian parents’ experience of caring for their child with an autism spectrum disorder. Transcultural Psychiatry. 2012;49:613–637. doi: 10.1177/1363461512447139. [ DOI ] [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Englander M. Persistent psychological meaning of early emotional memories. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2007;38(2):181–216. doi: 10.1163/156916207X234275. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Englander M. Empathy training from a phenomenological perspective. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2014;45(1):5–26. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341266. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Englander M. General knowledge claims in qualitative research. The Humanistic Psychologist. 2019;47(1):1–14. doi: 10.1037/hum0000107. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Englander M. Phenomenological psychological interviewing. The Humanistic Psychologist. 2020;48(1):54–73. doi: 10.1037/hum0000144. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedman M. Contemporary psychology: Revealing and obscuring the human. Duquesne University Press; 1984. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Psychology as a human science: A phenomenologically based approach. Harper & Row; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Phenomenology and experimental psychology II. In: Giorgi A, Fischer W, von Eckartsberg R, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology I. Duquesne University Press; 1971. pp. 17–19. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. An application of phenomenological method in psychology. In: Giorgi A, Fischer C, Murray E, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological Psychology II. Duquesne University Press; 1975. pp. 82–103. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Divergence of qualitative and quantitative methods in psychology. In: Giorgi ACF, Murray E, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological Psychology II. Duquesne University Press; 1975. pp. 72–79. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, editor. Phenomenology and psychological research. Duquesne University Press; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Description versus interpretation: Competing alternative strategies for qualitative research. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1992;23(2):119–135. doi: 10.1163/156916292X00090. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. The theory, practice, and evaluation of the phenomenological method as a qualitative research procedure. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1997;28:235–260. doi: 10.1163/156916297X00103. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Concerning variations in the application of the phenomenological method. The Humanistic Psychologist. 2006;34:305–319. doi: 10.1207/s15473333thp3404_2. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. The descriptive phenomenological method in psychology: A modified Husserlian approach. Duquesne University Press; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Phenomenology and the practice of science. Existential Analysis. 2010;21:3–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Phenomenological philosophy as the basis for a human scientific psychology. The Humanistic Psychologist. 2014;42(3):233–248. doi: 10.1080/08873267.2014.933052. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. A response to the attempted critique of the scientific phenomenological method. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2017;48(1):83–144. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341319. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. Reflections on certain qualitative and phenomenological psychological methods. University Professor’s Press; 2018. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. In defense of scientific phenomenologies. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2020;51(2):135–161. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341375. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A. The necessity of the epochē and reduction for a Husserlian phenomenological science of psychology. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2021;52(1):1–18. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341382. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi B. A phenomenological analysis of the experience of pivotal moments in therapy as defined by clients. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2011;42(1):61–106. doi: 10.1163/156916211X567497. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Gallegos N. Living through some positive experiences of psychotherapy. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2005;36(2):195–218. doi: 10.1163/156916205774651096. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Barton A, Maes C, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology IV. Duquesne University Press; 1983. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Fischer C, Murray E, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology II. Duquesne University Press; 1975. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Fischer W, von Eckartsberg R, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology I. Duquesne University Press; 1971. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Giorgi B, Morley J. The descriptive phenomenological psychological method. In: Willig C, Staiton-Rogers W, editors. The SAGE handbook of qualitative research in psychology. Sage; 2017. pp. 176–192. [ Google Scholar ]
- Giorgi A, Knowles R, Smith DL, editors. Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology III. Duquesne University Press; 1979. [ Google Scholar ]
- Husserl, E. (1981). Pure phenomenology, its method, and its field of investigation. In: P. McCormick & F. Elliston (Eds.) Husserl Shorter Works (R.W. Jordan, Trans.) University of Notre Dame Press/Harvester Press.
- Husserl, E. (1991). On the phenomenology of the consciousness of internal time (1893–1917). (J.B. Brough Trans.) Kluwer Academic Publishers. (German original, 1966).
- Kearney R. What is diacritical hermeneutics? Journal of Applied Hermeneutics. 2011 doi: 10.11575/jah.v0i0.53187. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Merleau-Ponty M. Phenomenology of perception. Routledge; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Merleau-Ponty, M. (1964). The primacy of perception. In: J. Eddie (eds.) (J. Wild Trans.). Northwestern University Press.
- Merleau-Ponty, M. (1968). The visible and the invisible C. Lefort (Eds.) (A. Lingus Trans.). Northwestern University Press.
- Morley J. The private theatre: A phenomenological investigation of daydreaming. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 1998;29:116–134. doi: 10.1163/156916298X00049. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morley J. The sleeping subject: Merleau-Ponty on dreaming. Theory and Psychology. 1999;9(1):89–101. doi: 10.1177/0959354399091005. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Morley J. The texture of the real: Merleau-Ponty, imagination, and psychopathology. In: Morley J, Phillips J, editors. Imagination and its pathologies. Cambridge: M.I.T. Press; 2003. pp. 93–108. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morrissey MB. Suffering narratives of older adults: A phenomenological approach to serious illness, chronic pain, recovery and maternal care. Routledge; 2015. [ Google Scholar ]
- Natanson M. Edmund Husserl: Philosopher of infinite tasks. Northwestern University Press; 1974. [ Google Scholar ]
- Petitmengin C, Van Beek M, Bitbol M, Nissou J-M, Roepstorff A. Studying the experience of meditation through micro-phenomenology. Current Opinions in Psychology. 2018;28:54–59. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2018.10.009. [ DOI ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Roald T. Toward a phenomenological psychology of art appreciation. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2008;39(2):189–212. doi: 10.1163/156916208X338783. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Røseth I, Bongaardt R. “I don’t love my baby?!”: A descriptive phenomenological analysis of disturbances in maternal affection. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2019;50(1):90–111. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341355. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Røseth I, Binder P-E, Malt UF. Two ways of living through postpartum depression. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2011;42(2):174–194. doi: 10.1163/156916211X599753. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Sartre J-P. A sketch for a theory of the emotions. Methuen; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schutz A. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality. Martinus Nijhoff; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith D. Fearfully and wonderfully made: The history of Duquesne University’s graduate psychology programs. Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center, Duquesne University; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith DL. A history of Amedeo P. Giorgi’s contribution to the psychology department and phenomenology center of Duquesne University in his twenty-five years there. In: Cloonan TF, Thiboutot C, editors. The redirection of psychology: Essays in honor of Amedeo P. Giorgi. Duquesne University Press; 2010. pp. 329–351. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tangvald-Pedersen O, Bongaardt R. The interconnection between mental health, work and belonging: A phenomenological investigation. Indo-Pacific Journal of Phenomenology. 2017;17(2):1–11. doi: 10.1080/20797222.2017.1392759. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Vogel EB. Black men’s experience of police harassment a descriptive phenomenological study. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2021;52(1):96–117. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341385. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wertz FJ. The method of eidetic analysis for psychology. In: Cloonan TF, Thiboutot C, editors. The redirection of psychology: Essays in honor of Amedeo P. Giorgi. CIRP; 2010. pp. 371–398. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wertz FJ. Outline of the relationship among transcendental phenomenology, phenomenological psychology, and the sciences of persons. Schutzian Research. 2016;8:139–162. doi: 10.5840/schutz201688. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wertz FJ, Charmaz K, McMullen LM, Josslson R, Anderson R, McSpadden E. Five ways of doing qualitative analysis: Phenomenological psychology, grounded theory, discourse analysis, narrative research, and intuitive inquiry. The Guilford Press; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Zapien N. The beginning of an extra-marital affair: A descriptive phenomenological study and clinical implications. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology. 2016;47(2):134–155. doi: 10.1163/15691624-12341311. [ DOI ] [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (732.8 KB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 6: Phenomenology
Darshini Ayton
Learning outcomes
Upon completion of this chapter, you should be able to:
- Identify the key terms, concepts and approaches used in phenomenology.
- Explain the data collection methods and analysis for phenomenology.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of phenomenological research.
What is phenomenology ?
The key concept in phenomenological studies is the individual .
Phenomenology is a method and a philosophical approach, influenced by different paradigms and disciplines. 1
Phenomenology is the everyday world from the viewpoint of the person. In this viewpoint, the emphasis is on how the individual constructs their lifeworld and seeks to understand the ‘taken for granted-ness’ of life and experiences. 2,3 Phenomenology is a practice that seeks to understand, describe and interpret human behaviour and the meaning individuals make of their experiences; it focuses on what was experienced and how it was experienced. 4 Phenomenology deals with perceptions or meanings, attitudes and beliefs, as well as feelings and emotions. The emphasis is on the lived experience and the sense an individual makes of those experiences. Since the primary source of data is the experience of the individual being studied, in-depth interviews are the most common means of data collection (see Chapter 13). Depending on the aim and research questions of the study, the method of analysis is either thematic or interpretive phenomenological analysis (Section 4).
Types of phenomenology
Descriptive phenomenology (also known as ‘transcendental phenomenology’) was founded by Edmund Husserl (1859–1938). It focuses on phenomena as perceived by the individual. 4 When reflecting on the recent phenomenon of the COVID-19 pandemic, it is clear that there is a collective experience of the pandemic and an individual experience, in which each person’s experience is influenced by their life circumstances, such as their living situation, employment, education, prior experiences with infectious diseases and health status. In addition, an individual’s life circumstances, personality, coping skills, culture, family of origin, where they live in the world and the politics of their society also influence their experience of the pandemic. Hence, the objectiveness of the pandemic is intertwined with the subjectiveness of the individual living in the pandemic.
Husserl states that descriptive phenomenological inquiry should be free of assumption and theory, to enable phenomenological reduction (or phenomenological intuiting). 1 Phenomenological reduction means putting aside all judgements or beliefs about the external world and taking nothing for granted in everyday reality. 5 This concept gave rise to a practice called ‘bracketing’ — a method of acknowledging the researcher’s preconceptions, assumptions, experiences and ‘knowing’ of a phenomenon. Bracketing is an attempt by the researcher to encounter the phenomenon in as ‘free and as unprejudiced way as possible so that it can be precisely described and understood’. 1(p132) While there is not much guidance on how to bracket, the advice provided to researchers is to record in detail the process undertaken, to provide transparency for others. Bracketing starts with reflection: a helpful practice is for the researcher to ask the following questions and write their answers as they occur, without overthinking their responses (see Box 1). This is a practice that ideally should be done multiple times during the research process: at the conception of the research idea and during design, data collection, analysis and reporting.
Box 6.1 Example s of bracketing prompts
How does my education, family background (culture), religion, politics and job relate to this topic or phenomenon?
What is my previous experience of this topic or phenomenon? Do I have negative and/or positive reactions to this topic or phenomenon? What has led to this reaction?
What have I read or understood about this topic or phenomenon?
What are my beliefs and attitudes about this topic or phenomenon? What assumptions am I making?
Interpretive or hermeneutic phenomenology was founded by Martin Heidegger (1889–1976), a junior colleague of Husserl. It focuses on the nature of being and the relationship between an individual and their lifeworld. While Heidegger’s initial work and thinking aligned with Husserl’s, he later challenged several elements of descriptive phenomenology, leading to a philosophical separation in ideas. Husserl’s descriptive phenomenology takes an epistemological (knowledge) focus while Heidegger’s interest was in ontology 4 (the nature of reality), with the key phrase ‘being-in-the-world’ referencing how humans exist, act or participate in the world. 1 In descriptive phenomenology, the practice of bracketing is endorsed and experience is stripped from context to examine and understand it.
Interpretive or hermeneutic phenomenology embraces the intertwining of an individual’s subjective experience with their social, cultural and political contexts, regardless of whether they are conscious of this influence. 4 Interpretive or hermeneutic phenomenology moves beyond description to the interpretation of the phenomenon and the study of meanings through the lifeworld of the individual. While the researcher’s knowledge, experience, assumptions and beliefs are valued, they do need to be acknowledged as part of the process of analysis. 4
For example, Singh and colleagues wanted to understand the experiences of managers involved in the implementation of quality improvement projects in an assisted living facility, and thus they conducted a hermeneutic phenomenology study. 6 The objective was to ‘understand how managers define the quality of patient care and administrative processes’, alongside an exploration of the participant’s perspectives of leadership and challenges to the implementation of quality improvement strategies. (p3) Semi-structured interviews (60–75 minutes in duration) were conducted with six managers and data was analysed using inductive thematic techniques.
New phenomenology , or American phenomenology , has initiated a transition in the focus of phenomenology from the nature and understanding of the phenomenon to the lived experience of individuals experiencing the phenomenon. This transition may seem subtle but fundamentally is related to a shift away from the philosophical approaches of Husserl and Heidegger to an applied approach to research. 1 New phenomenology does not undergo the phenomenological reductionist approach outlined by Husserl to examine and understand the essence of the phenomenon. Dowling 1 emphasises that this phenomenological reduction, which leads to an attempt to disengage the researcher from the participant, is not desired or practical in applied research such as in nursing studies. Hence, new phenomenology is aligned with interpretive phenomenology, embracing the intersubjectivity (shared subjective experiences between two or more people) of the research approach. 1
Another feature of new phenomenology is the positioning of culture in the analysis of an individual’s experience. This is not the case for the traditional phenomenological approaches 1 ; hence, philosophical approaches by European philosophers Husserl and Heidegger can be used if the objective is to explore or understand the phenomenon itself or the object of the participant’s experience. The methods of new phenomenology, or American phenomenology, should be applied if the researcher seeks to understand a person’s experience(s) of the phenomenon. 1
See Table 6.1. for two different examples of phenomenological research.
Advantages and disadvantages of phenomenological research
Phenomenology has many advantages, including that it can present authentic accounts of complex phenomena; it is a humanistic style of research that demonstrates respect for the whole individual; and the descriptions of experiences can tell an interesting story about the phenomenon and the individuals experiencing it. 7 Criticisms of phenomenology tend to focus on the individuality of the results, which makes them non-generalisable, considered too subjective and therefore invalid. However, the reason a researcher may choose a phenomenological approach is to understand the individual, subjective experiences of an individual; thus, as with many qualitative research designs, the findings will not be generalisable to a larger population. 7,8
Table 6.1. Examples of phenomenological studies
Phenomenology focuses on understanding a phenomenon from the perspective of individual experience (descriptive and interpretive phenomenology) or from the lived experience of the phenomenon by individuals (new phenomenology). This individualised focus lends itself to in-depth interviews and small scale research projects.
- Dowling M. From Husserl to van Manen. A review of different phenomenological approaches. Int J Nurs Stud . 2007;44(1):131-42. doi:10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2005.11.026
- Creswell J, Hanson W, Clark Plano V, Morales A. Qualitative research designs: selection and implementation. Couns Psychol . 2007;35(2):236-264. doi:10.1177/0011000006287390
- Morse JM, Field PA. Qualitative Research Methods for Health Professionals. 2nd ed. SAGE; 1995.
- Neubauer BE, Witkop CT, Varpio L. How phenomenology can help us learn from the experiences of others. Perspect Med Educ . 2019;8(2):90-97. doi:10.1007/s40037-019-0509-2
- Merleau-Ponty M, Landes D, Carman T, Lefort C. Phenomenology of Perception . 1st ed. Routledge; 2011.
- Singh J, Wiese A, Sillerud B. Using phenomenological hermeneutics to understand the experiences of managers working with quality improvement strategies in an assisted living facility. Healthcare (Basel) . 2019;7(3):87. doi:10.3390/healthcare7030087
- Liamputtong P, Ezzy D. Qualitative Research Methods: A Health Focus . Oxford University Press; 1999.
- Liamputtong P. Qualitative Research Methods . 5th ed. Oxford University Press; 2020.
- Abbaspour Z, Vasel G, Khojastehmehr R. Investigating the lived experiences of abused mothers: a phenomenological study. Journal of Qualitative Research in Health Sciences . 2021;10(2)2:108-114. doi:10.22062/JQR.2021.193653.0
- Engberink AO, Mailly M, Marco V, et al. A phenomenological study of nurses experience about their palliative approach and their use of mobile palliative care teams in medical and surgical care units in France. BMC Palliat Care . 2020;19:34. doi:10.1186/s12904-020-0536-0
Qualitative Research – a practical guide for health and social care researchers and practitioners Copyright © 2023 by Darshini Ayton is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Phenomenological psychology and qualitative research
- Open access
- Published: 30 October 2021
- Volume 22 , pages 25–53, ( 2023 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Magnus Englander ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-1211-8829 1 &
- James Morley 2
26k Accesses
36 Citations
4 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This article has been updated
This article presents the tradition of phenomenologically founded psychological research that was originally initiated by Amedeo Giorgi. This data analysis method is inseparable from the broader project of establishing an autonomous phenomenologically based human scientific psychology. After recounting the history of the method from the 1960’s to the present, we explain the rationale for why we view data collection as a process that should be adaptable to the unique mode of appearance of each particular phenomenon being researched. The substance of the article is then devoted to a detailed outline of the method’s whole-part-whole procedure of data analysis. We then offer a sample analysis of a brief description of an ordinary daydream. This is an anxiety daydream in response to the recent Covid-19 pandemic. We present this daydream analysis in full to show the concrete hands-on 5 step process through which the researcher explicated the participants’ expressions from the particular to the general. From this brief sample analysis, the researcher offers a first-person reflection on the data analysis process to offer the reader an introduction to the diacritical nature of phenomenological psychological elucidation.
Similar content being viewed by others

Investigating modes of being in the world: an introduction to Phenomenologically grounded qualitative research

Qualitative Research Methods in Peace Psychology

Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Pure phenomenology's tremendous significance for any concrete grounding of psychology is clear from the very beginning. If all consciousness is subject to essential laws in a manner similar to that in which spatial reality is subject to mathematical laws, then these essential laws will be of most fertile significance in investigating facts of the conscious life of human and brute animals.—Husserl 1917 . Footnote 1 The natural sciences were never intended to study man as a person. One need not leave the realm of science to study man adequately. We need only to broaden science itself.—Giorgi, 1970 Footnote 2
1 Introduction
Recently, there has been a healthy and long overdue discussion over how best to appraise the many new qualitative methods and how they contribute to scientific knowledge in psychology. For phenomenological psychologists the crucial challenge is, as expressed by Edmund Husserl (quoted above), to show how phenomenology provides a " concrete grounding " and " fertile significance " to the development of psychology as a science. Historically, it is well known that psychology, by and large, has imitated the methodology of the natural sciences. As expressed by Amedeo Giorgi (quoted above), by emulating physical science, psychology gave up studying human beings "as persons ." In response to this critical flaw at the heart of modern psychology, phenomenological psychologists endeavor to redirect psychology toward a more phenomenologically based direction. The centerpiece of this project has been the development of a qualitative research methodology that would make a phenomenological psychological science possible. What follows is an outline of the original research method, where we also offer an example of data analysis as carried out by the researcher.
2 Historical context: the project of a human science psychology
Before we launch into our main presentation, we believe that it is important to offer a brief historical review to illustrate the unique way in which this method developed in close collaboration with phenomenological philosophy. The following section is a synthesis that draws from historical accounts by Smith ( 2002 ), ( 2010 ), Cloonan ( 1995 ), and Churchill and Wertz’s ( 2015 ), as well as from the past experience of the authors.
In the early 1960’s Giorgi found phenomenology to be practiced in an ambivalent and often methodologically contradictory manner in European academic psychology. Similarly, American humanistic psychologists, sympathetic to phenomenology, were active critics of the deterministic approaches of mainstream psychology. But they, nonetheless, like their European counterparts, also defaulted to non-phenomenological measurement techniques when it came to their own research designs. It was as a response to this situation that the first systematically phenomenological psychology program was founded at Duquesne University in the early 1960’s. In this context Giorgi and his colleagues articulated this distinctly phenomenological way of doing psychological research—a methodology consistent with its phenomenological foundations. While Giorgi took the lead role in the development of this methodology, it needs to be stressed that this a was also an interdisciplinary community endeavor that took place between the philosophy and psychology departments at Duquesne University spanning the 1960’s to the late 1980’s. John Scanlon, the translator of Husserl’s phenomenological psychology lectures, was particularly supportive as a consultant to Giorgi and his colleagues during this period—as was Richard Rojcewicz, Al Lingis, Lester Embree, and several non-Duquesne but sympathetic scholars such as Martin Dillon, William Richardson and many others whom, records show, were often invited as guest speakers and consultants. Also, the psychology curriculum required students to take a minimum of two courses in modern philosophy, whereas the psychology faculty consistently audited philosophy courses.
In 1970 Giorgi launched the Journal of Phenomenological Psychology , which was at the outset a joint venture with European phenomenologically oriented psychologists and psychiatrists, as well as phenomenological philosophers. The journal was initially co-edited by Georges Thines and Carl F. Graumann. Serving on the first editorial board were Europeans such as Blankenburg, Buytendijk, Gurwitsch, van den Berg, van Breda, and Straus. The key point here is that the work being done on the development of the research methodology was part of a radically interdisciplinary and international project from the very beginning. As part of the overall project, Giorgi also founded the Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center . This research center also carries a copy of Husserl’s unpublished papers from the archives in Leuven, as well as the archives of Gurwitsch, Straus, Strasser, Bouman, Heidegger’s Marburg lectures, Buytendijk’s Pensée Repensée , and over 20,000 volumes, making it the largest collection of existential-phenomenological literature in the world. At the official inception of the center, Giorgi invited John Salis as his co-director.
Giorgi's seminal work, Psychology as a Human Science: A Phenomenology-Based Approach ( 1970 ) expressed a phenomenological response to the historical situation of psychology as a natural science. This also served as a foundational text for the psychology curriculum at Duquesne. Here, as a psychologist, he first proposed the necessity of a rigorously procedural, qualitative research method for a human scientific psychology. It made the appeal for an overall paradigmatic unity of “approach, method, and content” as the basis for a non-naturalistic psychology—an authentic Geisteswissenschaft or ‘human scientific’ psychology. Giorgi insisted that if psychology is to be true to its own subject matter, the scientific study of humans as persons, then the meaning of term 'empirical' in psychology must by necessity be 'broadened' beyond empiricism’s restriction to the sensory (see also, Giorgi, 1971 , 2009 ). A phenomenologically empirical science would be inclusive of all experience. This would include (in Husserl’s terms) the ir-real, or the more than sensory aspects of experience, not just the real or sense-based measurables of classical empiricism. The vision was to employ the overall phenomenological paradigm to ground a human scientific psychology, a scientific enterprise autonomous from the naturalistic juggernaut of mainstream psychology.
Over this 50-year history this methodological approach has been known by various names: the phenomenological psychological method, the existential-phenomenological psychological method, the qualitative phenomenological method, human science psychology and even “the Duquesne method.” The founding Duquesne faculty mostly preferred the term “ Existential-Phenomenological Psychology ” to highlight the influence of all main continental thinkers: Heidegger, Sartre and Merleau-Ponty—as well as Husserl and many others. The term “existential” also expressed their emphasis on concrete psychological situatedness in contrast to transcendental phenomenological philosophy. Phenomenological psychologists who received their graduate training from within the Duquesne research tradition, such as, Frederick Wertz (Wertz et al., 2011 ) used the term “Phenomenological Psychological Method,” whereas Scott Churchill ( 2022 ) maintains the original Duquesne term “Existential Phenomenological Research.” As we will see ahead, it was only in 2009 that Giorgi committed to the nomenclature of “the descriptive phenomenological method in psychology.” The emphasis on description was done to offer a counterpoint to the penchant among qualitative researchers, often influenced by cultural postmodernism, to take the extreme position that 'everything is an interpretation'—something rejected by Giorgi as the imposition of a hermeneutic universalism (Giorgi, 1992 ). Footnote 3 However, while generally based on Husserl’s approach, it is very important to highlight how in his 2009 text he never claimed his method to be identical to Husserl's. It was instead it was a modification of Husserlian philosophical methodology to adapt to the human scientific context of the discipline of psychology (Giorgi, 2014 , 2021 ). Footnote 4 In addition, Giorgi ( 2006 , 2010 , 2018 ) has also made several critical comparisons with other qualitative phenomenological methods as well as replies to philosophers (Giorgi, 2017 , 2020 , 2021 ). Several of his psychology colleagues and ex-students have developed variations of the method. Davidson ( 1988 , 2003 , 2021 ), for example, offers such a variation, to which both Giorgi ( 2020 , 2021 ) and Wertz ( 2016 ) are sympathetic. Churchill ( 2022 ) maintains the core Husserlian elements while complimenting them with Heideggerian insights. But all such variations maintain most of the key components of the overall method—as shall be outlined ahead.
Across the development of this research tradition, there have been innumerable studies published in various psychology journals and books based on this overall approach. This research tradition is cited as a significant development within the history of modern psychology (see Brennan & Houde, 2017 ). Important theoretical and original qualitative research findings were published in the four volume, Duquesne Studies in Phenomenological Psychology (Giorgi et al., 1971 , 1975 , 1979 , 1983 ), as well as the edited volume Phenomenology and Psychological Research (Giorgi, 1985 ). The latter contains paradigmatic empirical studies on learning (by Giorgi) criminal victimization (by Wertz), thinking while playing chess (by Aanstoos), and self-deception (by Fischer). A brief representative sampling that illustrates the range of recent research outputs is as follows: Living through positive experiences of psychotherapy (Giorgi & Gallegos, 2005 ), Lived persistent meaning of early emotional memories (Englander, 2007 ), Art appreciation (Roald, 2008 ), Pivotal moments in therapy (B. Giorgi, 2011 ), Postpartum depression (Røseth et al., 2011 ), Autism and culture (Desai et al., 2012 ), Leading a police vehicle pursuit (Broomé, 2013 ), Social anxiety (Beck, 2013 ), The suffering of older adults (Morrissey, 2015 ), The beginning of an extra-marital affair (Zapien, 2016 ), Mental health and the workplace (Tangvald-Pedersen and Bongaardt, 2017 ) Disturbances in maternal affection (Røseth and Bongaardt, 2019 ) Cross cultural learning (DeRobertis, 2017 , 2020 ), and Black men’s experience of police harassment (Vogel, 2021 ).
3 Data collection
Since this research tradition is oriented toward data analysis, this section on data collection will be brief and limited to some basic principles. Because psychologists are usually already well trained in interview techniques (Englander, 2020 ; Giorgi, 2020 ), it is natural that interviews will be commonly used to collect descriptive material. However, we stress that the method is not, by itself, an interview method. Footnote 5 Instead, each data collection strategy is developed in an idiosyncratic way by first understanding how each phenomenon best reveals itself in its own unique mode of appearance (Englander, 2020 ). For instance, when studying ‘thinking while playing chess’ Aanstoos ( 1985 ), found interviewing, by itself, to be insufficient for accessing the subtle psychological nuances of playing chess. To accommodate this phenomenon, Aanstoos ( 1983 ), developed a 'think aloud method' where one player freely spoke his thoughts into a recorder during a chess game while the opponent had his ears covered. In other words, the principle here was to design the data collection process by attending closely to the particularity of the phenomenon. Typically, the phenomenon is carefully circumscribed in advance through pilot studies, field work and clinical contexts from which the researcher can uncover the ways to best solicit descriptions and expressions that can most successfully reveal deeper psychological meanings.
Our main point here is that there should be a ‘custom fit’ between the phenomenon and the data collection design to solicit maximally good descriptions of the phenomenon within the context of everyday life. Strategies for collecting such descriptions should not be presumed beforehand and imposed on the phenomenon. The data collection design should fit the phenomenon instead of the phenomenon being forced to fit the design . Concretely, the phenomenon or related phenomena should be carefully studied through the trial-and-error process of pilot studies before any final decisions are made regarding data collection strategies.
Having made these points, some general recommendations have been laid out for data collection procedures. Drawing from existential-phenomenological philosophers such as Sartre ( 1962 , 28–29) and Merleau-Ponty ( 1962 ), phenomenological psychologists acknowledge that a person is always in a situation. At the start of any data collection, the research focus is on a concrete situation in which the participant has directly experienced the phenomenon under investigation. A concrete situation is not an idea, an attitude or anything abstract and conceptual—it is an experience that is directly lived. This acknowledgement of the situated concrete nature of psychological phenomena is another reason why data collection designs, again, need to be unique to the phenomenon and independently ‘custom-designed’ by the researcher. Or put another way, each study seeks the mode of investigation that allows the phenomenon to best express itself in its own distinctive way.
4 Data analysis
For a chronological development of the methodology, see Giorgi ( 1975a , 1975b , 1985 , 1997 , 2009 , 2018 ).
This is a ‘whole-part-whole’ qualitative method that includes steps where the researcher adopts the phenomenological psychological attitude and applies the technique of eidetic variation. Again, in contrast to philosophical analysis, phenomenological psychology begins and ends with meanings as lived and contextualized within the mundane, everyday lifeworld.
4.1 Concrete 5 step method of data analysis
The data analysis has five steps. Over the course of nearly five decades of experience we have learned that success with this method is best achieved by applying each step in a generally sequential relation to the other steps. In this way, all five steps work as an integral whole. The steps that follow where adopted from a recent publication by Giorgi et al. ( 2017 ). Having said this, it is important to also point out that these steps have both a linier and non-linier dimension to them. The linear sequential ‘steps’ offers an initial structure and organization that can also liberate the researcher to move back and forth, reviewing previous steps and revising them in relation to new discoveries and intuitions. In actual concrete practice, the process becomes more like a working draft or scaffold to work from. Ahead, in our discussion of the case analysis, this non-linier dimension will be more fully addressed.
4.2 Step 1. Initial reading for a sense of the whole
As this is a whole-part-whole method, the procedure begins with the ‘sense of the whole,’ proceeds with an analysis of the parts, and concludes with a newly elucidated ‘sense of the whole.’ Thus, the preliminary ‘appreciation’ of the entire description is important because it prepares and assists the researcher for the next steps where one studies its parts. This ‘sense of a whole’ should not be confused with hypothesis, conclusions or theorizations. Instead, it should be seen as a tentative understanding that is only an opening prelude to a relationship with the descriptive material. Importantly, it is this ‘sense of the whole,’ provided by the participant’s full descriptive account, that will act as the background to the diacritical figure-ground analysis carried out during the latter steps. In concrete practical terms, the researcher reviews the transcription (or audio or video) several times before starting Step 2. Again, this first step establishes the figure-ground framework that will drive the part-whole analysis of the entire method as every part, or meaning unit, will usually be explicated in terms of its relationship with the whole of the description.
4.3 Step 2. Adopting the phenomenological psychological attitude
Adopting the overall phenomenological attitude or ‘way of seeing’ is what distinguishes this method from other forms of non-phenomenological qualitative research. Importantly, and this can’t be stressed enough from the onset, in our work as social scientists doing life-world qualitative research, the epoché and the reduction function in a different context then in philosophy. Footnote 7 So, modified to accommodate the psychological sphere of interest, this attitude is essential to the next steps of the data analysis. Most would agree that time needs to be dedicated to the study authoritative primary sources in phenomenology to fully understand the nature of this phenomenological approach to research. This involves, (1) the epoché (or suspension) of the natural attitude, and (2) an assumption of the phenomenological psychological reduction.
With the practice of the epoché we try to just let the experience of something arise in its “givenness.” Footnote 8 In Husserl’s terms this is a ‘putting out of play’ or ‘parenthesizing’ of any positions of belief or doubt toward the world as independent of our consciousness of the world. This ordinary everyday position towards reality is what phenomenologists call the ‘natural attitude.’ A corollary of the natural attitude is the naturalistic attitude which is the commonsense belief that all things are ultimately explained by the physical causes of natural science. So, the psychologist appropriates the epoché for several reasons, (1) it clears the way for us to better understand how the participants are experiencing the world, self and others, and (2) it liberates us to better describe other people’s experiences without falling back on physical explanations, rationalizations, stereotypes or explaining them away with hypothetical models and concepts. (3). It allows researchers to become more aware of how, as Merleau-Ponty ( 1962 , p xiii) put it, one’s own ‘intentional threads’ are themselves influencing the phenomenon. (4). It invites researchers to overcome prejudices and doubts with regard to their own aptitudes for intuitive imagination. Put another way, the epoché opens us to see how the world is profusely intertwined with both the researchers and the research participant's experience of it, characterizing a radically non-dogmatic and open-minded perspective towards psychological research.
We will next go into some detail on the nature of the reduction in phenomenological psychology because it is here that phenomenological psychologists make significant and necessary modifications to the reduction, and in turn the epoché , as originally expressed by Husserl and philosophical phenomenologists. The phenomenological psychological reduction is what one does after first understanding the perspective of the epoché. Here we ‘reduce’ or restrict our frame of reference to a particular region of meaning. The psychological, in this sense, can be viewed as a particular region of science that is a psychological reduction. In the human scientific context of a qualitative psychology, a psychological reduction takes on a different meaning than Husserl’s original incomplete depiction of the psychological reduction. Husserl saw the psychological reduction as both a propaedeutic steppingstone towards the transcendental (or philosophical) reduction, Footnote 9 as much as he also saw it as the basis for new kind of psychological science—as we are applying it here. However, not being a psychologist, Husserl was not able to offer detail on how to apply the psychological reduction in an applied human science context. It is here where Giorgi's modification of the psychological reduction incorporates the doings of science to qualitative psychological research. The psychological region pertains to a particular domain of lived experience—an experience that is neither abstractly conceptual, nor objectively physical; it is concretely and personally lived, by a particular person, always socially engaged, in a particular situation in everyday social life, in space, time and history.
In this sense, the psychological reduction maintains an intimate but distinctively delicate, even tricky, relationship with the natural attitude. While philosophers may be disinterested in the natural attitude in order to pursue other matters, the phenomenological psychologist is studying exactly the natural attitude itself. This mundane world of everyday common-sense beliefs is precisely the subject matter of the phenomenological psychologist—and any other phenomenologically identified social scientists. In this sense, the psychological position transforms the nature of the epoché. Instead of the philosopher’s full suspension of the world of the natural attitude, the psychologist takes strong interest in exactly this world of the natural attitude. This means that the psychologist performs an epoché that is both in and out of the natural attitude. Within the psychological reduction we ‘step back’ from the natural attitude in order to study its structures. Again, the phenomenological psychologist is cognizant of the faith of the assumed world of the natural attitude but still studies this worldview not unlike the empathic manner of an anthropologist, doing field work, who both spontaneously participates in village life, like a fellow villager, while also maintaining his social scientific perspective. So, unlike the faith of the participant, the researcher’s is a faith that regularly, and methodically, steps back and questions itself. These points will be further developed in our reflection on how this attitude, particular to the phenomenological psychologists, was applied to the data analysis process performed on our sample case description.
Another aspect of this circumscribed 'psychological' region is that it pertains to the domain of relevance that is, itself, the ‘discipline’ of psychology Footnote 10 and what Giorgi ( 2009 ) has referred to as the 'disciplinary perspective'. Giorgi suggests that this ‘disciplinary’ reduction to the domain of the psychological (2009) should be most accurately depicted as a human scientific reduction. Footnote 11 In stark contrast to the empirical theory of science that drives mainstream psychology, the approach provided here allows researchers to explicate psychological meanings in their morphological, provisional, phenomenological sense.
4.4 Step 3. Dividing data into meaning units
This next step is motivated by practicality. Attempting to analyze, for example, 30–40 pages of transcribed interview material all at once is a daunting task. This is precisely why a data analysis method is helpful. Nevertheless, to stay consistent with a phenomenological theory of science, Step 3 is carried out from within the phenomenological attitude. For example, while reading through the recorded material, the researcher breaks down the material into smaller manageable parts to allow for a closer and more detailed focus in the upcoming Step 4. By phenomenologically elucidating the parts, the researcher is also able to begin distinguishing the participants’ meanings from how these appear in the natural attitude. This allows the expression by the participants to later (i.e., in Step 4) be explicated into phenomenologically psychologically sensitive description. The material is thus broken into manageable sections referred to as “meaning units.” The length of a meaning unit can vary from one sentence to an entire paragraph or (on rare occasions) a whole page of material. The length of meaning units can also vary from researcher to researcher, and such variation does not necessarily have any bearing on the general findings at the end of the analysis. Often the material can be easily differentiated. The main point is that too large a meaning unit can be unwieldy to analysis. It is also important to point out that not all meaning units are essential to the general structure of the phenomenon. However, all meaning units need to be analyzed (in Step 4). This last point is important, because sometimes when the researcher relaxes the epoché and returns to the natural attitude, some meaning units might mistakenly appear redundant. Nevertheless, when analyzed carefully, there is always the possibility of discovery.
Typically, researchers break this into two side-by-side columns that are written out in text form, referred to as Column 1 and Column 2 . This two-column transcription procedure serves several purposes. It conveniently organizes the process for the researcher and, importantly, it makes the data analysis process transparent and thus open for critique by other phenomenological researchers. As an additional procedure to this step, Giorgi also suggests that one modifies the participants’ expression into third person expressions. However, this is only a suggestion intended for researchers who are having difficulty in seeing the difference between the individual (or the idiographic level) and the phenomenon (the nomothetic level). Another discretionary modification is to extend columns, beyond the usual two, into three or even four columns. This was employed in the daydream analysis ahead where the researcher found a third column to be of value as it allowed him to visually check his more generalized transformations with the original meaning units—right before his eyes.
4.5 Step 4. Transformation of everyday expression to psychological meaning
The relationship between Column 1 (i.e., everyday expression, or naive description, of the participant) and Column 2 (i.e., phenomenological description of psychological meaning) is distinctive to this method. Here one carefully elucidates the participants’ essential meanings into generalizable terms within the domain of psychological relevance—as expressed above. We grasp and draw out the fuller psychological meanings embedded within the everyday description. Now, it is in this particular step that the phenomenological attitude takes center stage and is explicitly put into practice for the purpose of a phenomenological psychological analysis. In addition, in order to seek the general meanings within the lived experience this step also includes the tool of eidetic variation . This means that the researcher needs to maintain a general focus on the phenomenon under investigation while carrying out this detailed analysis. In this context, phenomenological elucidation is not a matter of mere notetaking, summarizing, annotating or just condensing meanings. It is more about how the researcher adjusts one’s mindset so as to allow the psychologically relevant meanings to emerge to one’s consciousness. In a certain sense, one opens oneself, or renders oneself a vehicle to the fuller meanings of the participant’s naive description, but always with a focus on the phenomenon. This is a receptive or ‘discovery’ mode of consciousness—not one of actively applying ideas, theories or concepts. One can understand this position as a contemplative openness to the givens of the other’s experience as it emerges through the participants’ expressions. There is an imaginative participation in the subjects’ descriptions not unlike the engagement one experiences when reading a novel, a poem, or any act of expressive art. There is here an ironically 'focused openness' or put another way: a resolute receptiveness. One converts the participant’s expressions (as conveyed within the natural attitude) into phenomenologically clarified psychological meanings by carefully following the intentionality in the participants' expression. The watchwords here are: elucidation, illumination, and explication. Here, we do not add to what our participants say, instead we bring forth the fuller meanings.
In addition, one does not need to restrict oneself to only one column during the analysis. It is perfectly feasible for the researcher to extend the analysis of the initial meaning unit into several levels of elucidation—such as a column 3 or 4. As noted in the previous section on Step 3, this 4th step is also about the spirit of transparency in science (similar to how one shows one's work when doing mathematics). By extending the analysis into stages or levels of analysis, one is showing colleagues exactly how one has reached these extended levels of generalization.
4.6 Step 5. Returning to the whole and moving toward the general structure
It is at this phase that the researcher moves from a part-whole eidetic analysis to a new focus on the whole again. But now we have a new whole, a whole that is the end result of this entire procedure. Remaining within the phenomenological psychological attitude, as described above, the researcher’s intimate engagement with the meaning unit analysis now becomes an act of synthesis of the parts together into what is usually a temporally sequential narrative. The watchword here is structure. A structure is understood in gestalt terms as a whole, but a whole composed only of essential parts. The idea here is that if one where to hypothetically remove one of the parts, then the rest of the structure would fall apart. Therefore, the researcher wants to be prudent to not overstuff a structure. A good structure should follow the elegance of simplicity—as much as reasonable. Furthermore, the features or constituent parts should be invariant. By invariant we do not mean universal or absolute. We are fully aware that human phenomena are contingent to history and culture. We only mean that an invariant psychological structure should “hold together” within this culture at this point in history. Within these parameters we think it reasonable that generalized psychological claims can be made. Footnote 12
It is important to note that most other qualitative research methods present their conclusions in terms of ‘themes.’ But because this approach emphasizes phenomena as totalities, i.e. as structures, we avoid any overemphasis on themes and prefer to comment on the structure of the phenomenon as a totality as much as possible. When we do discuss parts, we prefer the term ‘constituents’ to stress their relatedness to the whole of the structure. It is conventional for many other methods to present to readers curated direct quotes from their participants. But because we have already performed a very close analysis of the direct expressions of the participants in the earlier steps of the data analysis, we prefer to offer readers the more structural, or general, levels of meaning in any discussion of our results as will be seen ahead when we discuss the results of our analysis of an experience of daydreaming. In short, our inclination is to offer readers prepared or explicated data instead of curated raw data.
4.7 Situated structures
As an optional procedure one can add an extra step between the meaning unit analysis (step 4) and the General Structure (step 5). While Giorgi stressed the general structure, most advanced researchers find it effective to add this intermediary step—as demonstrated in the analysis offered ahead. Footnote 13 This can support the eventual goal of generality and can be an extremely helpful ‘bridge step’ toward the general structural description. But it must be stressed that to remain only on the level of situated individual experience would miss the key purpose of the method—which is to achieve a general (inter-subjective) structural description of the phenomenon. Having said this, a situated structure can be very rich in life world details and remarkably illuminative in its own right. One could depict this as a structure on the idiographic or individual level. This is often popular with clinical psychologists who prefer an individual ‘case-study’ level of understanding. But unlike ‘clinical’ case-studies, this is a research phenomenon which is different from a diagnostic, or therapeutic relationship. Here the research intention is paramount—not the clinical intention. Again, this is the elucidation of an individual participant’s experience performed as a step before moving to the general structure. This would be an essential structure of the invariant aspects of an individual person’s experience of the phenomenon. In more simple language this is a basic summary of the psychologically relevant aspects of this particular person’s experience of the phenomenon. Developing situated structures from three or more research participants can be a very helpful way to eidetically scrutinize the phenomenon as experienced by all of the participants. But when it comes to groups, it is important to emphasize that within the phenomenological approach to science, eidetic comparison (Wertz, 2010 ) should not be confused with statistical comparison. Though more challenging (especially for newcomers), in phenomenological psychology an eidetic analysis could just as well be performed on a single participant as on a group. But having made this qualification, a group of any number of situated structures is always a great support to one’s eidetic analysis towards generalizability. Footnote 14
4.8 The general structure
At this point, these phenomenologically elucidated ‘parts’ of the data analysis (including the situated structures) are brought back together into a new whole . Phenomenological psychology is definitively a search for psychological essences or what we prefer to call general invariant structures. Husserl called this ‘eidetic analysis’ and the primary technique he used for this level of analysis he called eidetic or ‘imaginary variation.’ In this analysis, one imaginatively reviews the phenomenologically clarified parts of the previous analysis as achieved in step 4, with an eye for intuiting a new whole. Again, this is a discovery frame of mind where I render myself open to the continually emerging intuitions and patterns in the elucidated data as they give themselves to my awareness. In other words, it is not an empirical summary or the common denominator of facts across the cases, but another level of the analysis. Specific to this level of the analysis is the technique of imagining the phenomenon in its various profiles, angles or possibilities. For example, as a researcher I can ask myself if the structure of this phenomenon is possible without any of the particular constituent parts that I have discovered during my analysis in Step 4? I may even imagine adding new parts that were not explicitly expressed in the data but ‘apperceptively’ or intuitively suggested by the data. To reiterate, in contrast to most other qualitative approaches, the general structure is an integral whole and is never just a series of separate themes. The key idea here is that a structure is a full gestalt , a whole, or a totality that dissipates when a part is removed. Therefore, it is important to edit a general structure with rigor and integrity and to delete all that is unessential to the systemic pattern that makes the phenomenon what it is. The general structure is typically narrated in the present tense—though not always. Sometimes a phenomenon may split off into types or variants. In such cases one could have two or three general structures, representing different ‘types.’ Therefore, forcing a closure by applying a psychological theory is not an option. The findings, as supported by the analysis, can at a later stage in the discussion section (of the research report) be presented in dialogue with established psychological theories (‘backloading’ in current nomenclature) and other research results (See Fig. 1 ).
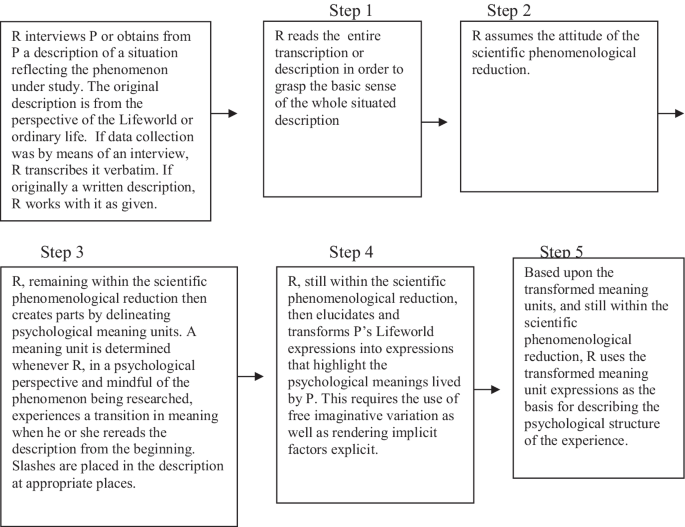
Overview—flowchart of data analysis process (from Giorgi et al., 2017 ). R researcher, P participant
5 Case example
What follows is a brief case example of a phenomenological psychological data analysis. Again, unlike philosophy where the research is done in a solitary first person manner, in phenomenological psychology we take a second person position. We see ourselves as participants —not mere observers—as we try to grasp the fuller meaning of other people’s concrete descriptions as expressed within the natural attitude of everyday life (Englander, 2020 ; Giorgi, 2009 ). We make no demands on our participants to take the reflective attitude of the practicing phenomenologist. Instead, only the researcher is responsible for taking the phenomenological stance as he or she reads the expressions of the participant. Here the data analysis is conducted within the tension of two intertwined goals: to be faithful to the intentional meanings as expressed while also deepening their meaning through their re-expression within the phenomenological psychological attitude—as performed in meaning unit analysis (step 4) and the development of structures (step 5). This, again, is what we call elucidation or explication . This is a fidelity that also takes us into a deeper understanding of the expressed intentions our participants. This is exactly the power of the epoché (within the psychological standpoint) as applied to the grasping or bringing-forth of psychological meaning. Like the way certain artists can transform the taken-for-granted experience of an ordinary object, such as an apple in a still-life painting, into an apple seen afresh ‘as if for the first time,’ so does the phenomenological psychologist strive to bring out the psychological meaning of the participant’s experience of the phenomenon.
The sample presented here is taken from the context of an ongoing research project on daydreaming that is currently replicating and updating a previously published study (Morley, 1998 , 1999 , 2003 ) through fresh interview material. As explained above, the data collection process was customized to suit the unique nature of the phenomenon. Here, in this particular research context, the procedure for collecting daydream reports has been to first request a self-written protocol from persons who are not themselves directly involved with psychology. A formal protocol question prompt (see below) was given to the participant to help guide the written description. As mentioned above, the reason for beginning with a written description is that, as an imaginary phenomenon, daydreaming can become unwieldy and difficult to articulate during an interview. Through pilot trials we have learned that written descriptions help the participant to ground or anchor their memory of the daydream. It then serves as an organizing point of reference for the interview—without imposing any leading external influences. Then, the researcher and participant begin the interview itself by re-reading the written protocol together to refresh their memories of the event. The researcher initiates the interview by asking the participant to take the initiative to express what, in the written description, he or she feels is most in need of elaboration or expansion. After the participants have offered further elaborations on what stands out as most important to them, the researcher will then pose questions from an informal semi-structured check-list of points of special phenomenological interest to the researcher. Specifically, the researcher asks for fuller descriptions of existential constants such as space, time, embodiment, social relations, sense of reality, and sense of self as experienced during the various temporal phases of the daydream. The actual interview approach, for this particular phenomenon, will vary across a spectrum from a gentle reiterative style to intensive and challenging inquiries Footnote 15 —depending on circumstances. As described above, this data collection method was developed through the researcher’s intimate relationship with the phenomenon over time.
A full data analysis of an entire interview would surfeit the space of this presentation. So it is for this reason that we chose to offer a concise sample of the analysis process drawn from material that was recently collected in the form of an initial written protocol. While not as detailed and spontaneous as the interview that followed, the written protocol still offers the reader a rich “sense of the whole’ that allows for a faithful sample the data analysis process. So, though brief, this was still a reasonably good description that offers a worthy example of the whole-part-whole dynamic central to the analysis process of this method. Choosing a brief sample also expresses the authors’ confidence that even the smallest fragment of an everyday type of description will explode in meaning when approached from within the phenomenological psychological attitude. Not unlike how the sensory empirical world burst open with the introduction of telescopes and microscopes, so does the human life world open up before us when beheld from within the openness provided by the lens of the overall phenomenological perspective as expressed above.
Having said this, we again caution that as a sample data analysis it does not benefit from the detail offered by the follow-up interview. This small sample is offered for strictly didactic reasons. More importantly, it also stands alone without the fuller dimensionality offered by the intersubjective eidetic analysis at least two other individual case examples to which it’s whole and constituent parts could be eidetically compared. It was for this reason that we restricted the title of the phenomenon from “daydreaming” to “an anxiety daydream” to reflect the particularity of the one sample. But even without the intersubjective corroboration of at least two other daydream descriptions, we hope readers will agree that it can be surprising to see what can emerge when using only one case example.
To reiterate, in brief, we begin with the whole daydream description as depicted in the written protocol. After reading for the whole we then break it into parts—or meaning units. Then, we phenomenologically elucidate each of the parts, or meaning units, though the technique of using columns—in this case we used 3 columns (most researchers only use two). Finally, we return to a renewed sense of the whole in both of the situated and general structures. The situated structure, like a case study, is idiographic to the particular description while the general structure is an attempt to achieve a nomothetic statement on the phenomenon of anxious daydreaming. In this instance, the general structure will be restricted to the meanings elicited from this single, and very brief, case example and will therefore be somewhat limited and tentative. It’s very important to note that in most research instances the general structure will be an eidetic analysis based on the various other individual situated structures. The general structure corresponds to what one could call the results of the research process. While the constituent parts of the whole structure will be discussed in most research reports, unlike most other qualitative methods that discuss themes , typically supported with selected quotes, we prefer to keep the whole structure of the experience as the primary reference point.
Ahead, within the analysis we will refer to the participant as ‘P.’ Later, in the discussion, we will address the participant through the pseudonym of Ashling.
5.1 Written daydream protocol—initial protocol prompt to the participant (P)
Please concretely describe a situation in which you experienced a daydream. Please describe what was happening when the daydream began, what the daydream was about, what it was like while having the daydream, and how the daydream came to an end. Please try to be as concrete and detailed in your description as possible.
5.2 Ashling’s written protocol description—including step 3, marking the meaning units
On March 14, 2020, I was in Tepoztlán, Mexico. Trump had recently announced he would be suspending travel from Europe to the US due to COVID-19. I had just moved to Mexico a few months prior. I feared if the closure was happening with Europe it would most likely be happening with Mexico very soon, a golden moment for Trump to assert his plan for the border with Mexico to be even more impenetrable. As we drove back from Tepoztlán to Mexico City and night was falling, I started to gaze out the window, daydreaming, as we passed the silhouetted Popocatépetl volcano in the distance.
I started thinking about how I would get back to my family in the US if flights were suspended with Mexico. As we continued to drive I thought about if we didn’t stop in Mexico city but just continued all the way to the border (about a 15 h drive). In my daydream I imagined arriving at the border and that there would be mayhem, cars piled up for miles and the border patrol not allowing anyone across. The border agents were armed and aggressive and unreachable. I imagined the reasons I would give, that my family needed me etc., but reasoning with them was not working. And I envisioned somehow managing to get past them as they were distracted by the chaos, and the relief felt by speeding into the US away from the border and onward towards home.
I felt anxious imagining the border patrol and their dominance, their potential to shoot us when we sped past, defying their rules of closure. But I then felt relief at the outcome of getting past, of fighting our way in and across and making it to a place of safety.
When my partner and I later got to the apartment in Mexico City that night I looked into flights to get to Boston where we would be in a familiar place during this most intensive and uncertain time. My good friend called me from Rennes in France and told me how bad it was, that death rates were rising, and how she wasn't leaving the house at all. She advised me to leave quickly and that to have a garden was a saving grace for her, and that at least in Boston I would have a garden. I booked my flight and packed a small case. I daydreamed again as I looked around the apartment, that 10 or so years would pass, and I would finally be able to come back and all my things would be here but between and around old weeds and crumbled walls and cobwebs, a scene left untouched and abandoned.
5.3 Meaning unit analysis
5.4 situated structure of an anxiety daydream.
Daydreaming for this person was an imaginary manifestation of her feelings of anxiety. By manifesting this anxiety as a dramatically staged scenario, she was able to live-out or play-out the enactment of her anxiety and its eventual resolution. This particular daydream occurred as a person’s affective response to the threat of having her freedom of movement, across international borders, curtailed or restricted by political forces beyond her control. In particular she feared being cut-off and separated from her home and family during a time of great uncertainty. These strongly felt emotions around the experience of constraint or restriction had no means of expression within the context of a long road trip in a car. Turning her gaze, away from the car interior, out the window towards the twilight horizon of the landscape, P entered into an imagined scenario where she is in the same car but has arrived at the international border between her foreign country of residence and her desired home country. The daydream manifests the person’s own momentary existential situation as a scene of chaos and mayhem enforced by the imposing, threatening and impersonal agents of power i.e. the border guards who refuse to allow her to cross the border into her home country. P imagines trying to reason or negotiate with the guards but realizes that dialogue is futile in this situation. Again, these are circumstances out of her control. As a staged enactment or ‘metaphorization’ of her actual existential situation, the daydream is both the expression and revelation of her life situation. It allows her to “express” her immersion in the situation which also, in a reversible way, offers her a reflective distance to “see” the feeling of restriction that has occupied her. As both the expression and revelation of her present life situation the daydream is, in this sense, lived ambiguously as both an active and passive experience. These ambiguously dual, yet interwoven, perspectives are implicit to her daydreaming experience. Next, within the imaginary narrative of the daydream, the daydreaming/daydreamed person commits an act of defiant transgression. P shifts the narrative from that of passive casualty of powers beyond her control, to one where she takes charge, or assumes agency, by choosing the extreme risk of speeding past the distracted guards and thus flouting their overbearing authority by driving across the border without their sanctioned permission. By taking matters into her own hands and transgressing the rules, P escapes confinement and experiences the satisfaction that comes with the security of having returned to her home country. The daydream concludes with feelings of relief. The experience of this daydream allowed P to articulate her desire to return home to her native country during this time of uncertainty—a desire that was converted into an actual concrete decision to eventually book an airline flight home to family and friends.
5.5 Tentative general structure of an anxiety daydream
Daydreaming emerges in a situation of unfulfilling circumstances. In the case of anxiety, it appears in the form on an ominous and yet opaque threat to one’s well-being. This feeling presents itself as a demand for action—to seek the source of the threat and to overcome it. However, this demand for action cannot be achieved in the current situation as it is impeded by circumstances where no real behavioral action is possible. This becomes a tension between the feeling’s demand for action, regarding the ominous threat, and its restraining context. The person turns attention away from the immediately restraining situation by seeking out and shifting attention to another horizonal field of focus. It is here that the emotion takes the course of expressing itself through the medium of an imaginary scenario that opens up an opportunity for the fulfillment of the emotion. The emotion transforms into a world scenario where it is expressed in the form of an enacted narrative drama. The person assumes a dual intentional role as both the author/narrator of the dramatic scenario and well as the actor immersed within the dramatic action. The emotion is now lived in a narrative context that allows the possibility of its fulfilment. As a staged enactment the daydream can become a living metaphor of the person’s actual existential situation. The daydream scenario can be both the expression and revelation of one’s emotional situation. Its expression makes it possible to “see” one’s immersion in the emotional dramatic scenario. It can offer the opportunity for a reflective distance from the feeling of restriction that had previously occupied the person. As both expression and revelation of the person’s present life situation daydreaming reveals an ambiguous interplay between both active and passive aspects of experience. These ambiguously interwoven perspectives vary between being implicit or explicit to the daydreamer. Though daydreaming takes place within an imaginary region of experience, this region is always also interfused within one’s life historical horizons—always expressing one’s life projects and goals.
6 Commentary on the analysis
In any phenomenological psychological research report, there is an extensive theoretical discussion of the results (i.e. the constituent parts of general and situated structures) with the phenomenological and natural scientific literature. We have much to say here, especially with regard to such constituents as ‘dual intentionality’ ‘multiple realities, the ‘affective-imaginary dynamic,’ the “linkage of expression with revelation’ and, of course, the comparison of these findings with current studies in cognitive science (such as the default mode network). But alas, as the purpose of this essay is didactic with regard to the method, and due to the limits of space, we must defer this full dialogue to a future publication.
Due to the brevity of the written description, and the very fact of there being only a single participant, the researcher can only modestly offer a highly tentative sample general structure. However, despite its brevity, the participant, whom we will here call ‘Ashling,’ offered a rich and full description and the researcher feels confident that the situated structure was faithful to the participants experience.
6.1 The non-linier dimension of data analysis
While the researcher initially worked with fidelity to the 5 step method, it is also important to note that there was a significantly non-linier dimension to this process. This was especially the case when it came to the composition of the situated and general structures. Once the meaning units were demarcated, the process towards the situated and eventual general structures took on a life of its own. In other words, while the meaning units established a framework for data analysis, once the 3 column framework was established, and the participant’s expressions were laid out before his eyes , the researcher began a back-and-forth process of checking, rechecking, reflecting and intuitively linking the meanings into fuller wholes and patterns. To use an imperfect metaphor, we can compare this explication process to what is called a detective’s “crazy wall” that is used to help interpret and understand a crime case. From detective stories and movies, we are familiar with how the investigator will post pieces of data and information across a wallboard, or sometimes a city map. The detective can then use this to meaningfully link the information and datapoints with connecting strings. Seeing the constituent parts ‘before his eyes’ helps the investigator to make the ‘meaningfully intuitive connections’ that lead to better understanding of the case. Obviously, this helps the investigator to step back and see the dynamic relation between the parts and the whole and it is from this perspective that insights and discoveries can arise. This is exactly the benefit of meaning unit analysis.
6.2 The diacritical aspect of data analysis
To reiterate, the psychological phenomenological attitude is focused on understanding the particular experience of a particular person. Obviously, as evidenced by the general structure, we do not stop a the particular—but this is where we begin. While this attitude undoubtedly suspends the naturalistic attitude of physical science, its disposition towards the more global natural attitude, as discussed above, contains a strategic ambiguity. Very importantly, unlike phenomenological philosophy, phenomenological psychology directly takes up the naively believed world of the natural attitude as a subject of inquiry. Ours is, as Maurice Natanson, citing Alfred Schutz, calls it: “a phenomenology of the natural attitude” ( 1973 , p107). In other words, while we ourselves as researchers are trained to be aware of our own natural attitude, and ‘step back’ from it as best we can, it is also true that we do not entirely put it aside. So, for example, when reading Ashling’s description of her daydream, the researcher imaginatively participated with the description of her daydream and, for that moment, may have been empathically engrossed within the world of her natural attitude. In a recent publication this is well described by Scott Churchill as a ‘disciplined fascination’ (Churchill, 2022 ). Also, as a denizen of the natural attitude oneself, the researcher may well have applied his background stock of knowledge of daydreaming, garnered from personal experiences as well as professional readings on the subject; all of this in order to better understand Ashling’s experience and intentional structures. Hence, as discussed above, this is not a pure epoché or a pure reduction as practiced by the philosopher. On the other hand, unlike Ashling, or any research participant, the researcher continually practices a ‘stepping back’ from that believed world, again, in order to better understand her world. There is, in this way, a weaving process that is unique to the phenomenological psychological attitude.
The figure-ground metaphors used by Merleau-Ponty are very helpful here. Throughout his works he explicitly describes what we are calling the phenomenological psychological attitude, as a ‘ diacritical ’ process (Kearney, 2011 ) that is, like the act of breathing—both inhaling and exhaling as one whole act. This is precisely what we mean by the strategic ambiguity of the phenomenological psychological position. In his well-known discussion on methodology Merleau-Ponty describes the attitude of the researcher as follows: “Reflection does not withdraw us from the world…’ “…it steps back to watch the forms of transcendence fly up like sparks from a fire; it slackens the intentional threads which attach us to the world and thus brings them to our notice…” ( 1962 , p xiii). As psychologists these threads or tethers to the natural attitude are never cut, they are “loosened or slackened” to enable us to see the intentions of others—as well as one’s own. Seeing my own intentional threads can reveal fore-understandings that could either inhibit or enhance my analysis.
In this case, a young woman is learning about the encroaching covid pandemic, wants to return to the security of her home and family, and becomes upset about the closing international borders that could restrict, and become an obstacle, to her desire to return home. This was the big picture to which the researcher returned, in a circular manner, throughout the analysis.
The researcher came to see how Ashling was originally overcome with a desire to go home while simultaneously experiencing a feeling of being impeded from that intention. Though she did not explicitly say this, one could easily imagine how, as more borders closed, Ashling’s desire to return home would only intensify. The beginning part of the daydream narrative reflected this distressing and overwhelming devils circle where she is impeded by powers beyond her control. But in meaning unit 7 we see a turn.
Another diacritical element is the weaving between the whole of the description and its parts. As a reader one could say that I am “zooming-in” on the unique and minute details of the participants expressions as much as I am continually “zooming-out” to use the whole as the context for understanding these details. For example, Ashling’s use of key expressions in Meaning Unit 7 (MU7) such as “envisioned,” “getting past” and “the relief felt” all offered a basis for enhanced eidetic exploration and fuller illumination. They allowed the researcher to come to the insight of Ashling’s shift in position, from that of passive victim of overpowering circumstances to that of an active agent of an imaginary act of courageous transgression—driving past the armed and aggressive border guards to cross the border. Understanding the “whole” of her situation is what brought to light the essential meaning of the daydream.
6.3 Spelling out tacit meanings
By explication, or elucidation, we mean the process of spelling-out latent or tacit meanings. To offer an example, Ashling, of course, never explicitly said that she experienced a ‘dual intentional structure.’ It was the task of the researcher to cull out this structural component that was implicit to the description and likely lived-out in a pre-thematic way by Ashling. The researcher’s recognition of this constituent happened during the researcher’s transition from the meaning unit analysis to the whole of the situated structure. It was in this process of “putting the whole story back together again” that the researcher saw how this double intentionality was experienced by Ashling. Here, there were two distinct but related intentions, (1). the intention to deal with the practical frustrations of booking a flight home during an uncertain period of international crisis (the actual world), and (2). the daydreamed intention of getting past imaginary border guards (the daydreamed world scenario). The researcher came to see Ashling as experiencing both intentions and both corresponding world relations—the actual car scenario and the other being the daydreamed car scenario. Hence, the dual intentional structure. One could call this a “generalizing process” but, in actual practice, it was a much fuzzier and more unclear event than any such nominalizations can portray. Once again, we can understand this as a diacritical process: (1). The insight came ‘as given’ in the discovery manner of a direct phenomenological intuition, and (2). This pattern was ‘recognized’ from the researcher’s background stock of knowledge (or fore-understanding) as a daydream researcher and reader of phenomenological literature. Because this elucidation process is itself somewhat pre-reflective, one can never have absolute certainty over whether it was an intuitive given or a pre-understanding.
Again, Merleau-Ponty’s diacritical approach helps to illuminate this elucidation process. In describing Merleau-Ponty’s ( 1968 ) diacritical approach to grasping meaning, Kearney cites James Joyce’s statement that it is possible to have “two thinks at a time.” ( 2011 , p 1). Directly addressing psychological research, Merleau-Ponty says: “One may say indeed that psychological knowledge is reflection but that it is at the same time an experience. According to the phenomenologist (Husserl) it is a material apriori . Psychological reflection is a “constatation” (a finding). Its task is to discover the meaning of behavior through an effective contact with my own behavior and that of others. Phenomenological psychology is therefore a search for the essence, or meaning, but not apart from the facts.” (Merleau-Ponty, 1964 , p.95).
With the term “constatation’ Merleau-Ponty is suggesting that both observing , (receiving the intuitive givens) and asserting (actively applying one’s stock of knowledge) can be at play in the same act of psychological understanding. Both are one whole movement within the same act—in the chiasmatic, reversable manner of a figure-ground dynamic. While space does not allow us to develop this issue in the detail it deserves, we raise this matter to try to bring some light to the act of elucidation that is so central to this method. The take home point here is that, while the method highlights the significance of description, this does not mean that one needs to choose between stark antinomies such as description and interpretation, or phenomenology and hermeneutics as within this elucidation process of ‘disciplined fascination’ both movements come together.
7 Conclusion
7.1 towards dual disciplinary citizenship.
This method was designed to give psychological researchers an organized and structured framework for doing second person research. The whole-part-whole process, in itself, is not complicated or difficult to understand and learn. What is difficult for those who are beginning this style of research, is the assumption of the phenomenological psychological attitude. This attitude, which distinguishes this method from non-phenomenological qualitative research methods, can’t be taken for granted and requires training, study, and the support of a like-minded research community. Because it is founded in phenomenological epistemology, phenomenological psychology is a hybrid discipline. The practice of phenomenological psychology requires a kind of ‘dual citizenship’ in both psychology and phenomenological philosophy. Those trained solely in philosophy’s orthodox emphasis on textual exegesis may often lack experience in practical professional life-world applications as well as an overall knowledge of the literature and scientific history psychology. On the other hand, those trained solely in psychology, with little to no exposure to philosophy, coupled with the field’s strictly naturalist experimental orientation—which underscores the natural/naturalistic attitude—come to phenomenology with this resilient attitudinal disadvantage that can take effort to overcome. What we have here, in the current academic world, is a set-up for mutual misunderstanding between these disciplines. While the sharp disciplinary divides of the current academic world make such ‘dual citizenship’ training difficult and rare, this is possible, but only with special effort and unique pedagogical interventions. There are institutionalized training programs, usually schools of psychotherapy, that are open to such interdisciplinary training. Yet, these programs are few and far-ranging in their offerings. Most independent researchers entering this field need to supplement their training in naturalistic psychology with an intense period of philosophical study of primary sources and guidance in this study is too often lacking. Then, on the other hand, it is encouraging to see the increasing number of philosophers who are taking an interest in “applied phenomenology.” Yet, we currently see little cognizance, in much of this recent literature, of the 50-year phenomenological psychological research tradition. We mention this, as a friendly invitation to psychologically interested philosophical researchers to acquaint themselves with their predecessors to avoid re-inventing the wheel and duplicating research results and techniques that have already been developed within the phenomenological psychological research tradition. In the same breath, we would just as strongly urge our colleagues in the social sciences to give more serious study to the phenomenological philosophical tradition.
Change history
20 february 2022.
Springer Nature's version of this paper was updated to present the corrected funding note.
From Husserl’s inaugural lecture in Freiburg given 1917 and published in Husserl—Shorter Works ( 1981 , 17).
This quote is from a talk that Giorgi gave at the Symposium on science and scientism: the human sciences Trinity College, May 15–16, 1970 and documented by Maurice Friedman ( 1984 ) Contemporary Psychology: revealing and obscuring the human . Pittsburgh: Duquesne University Press. (p.30).
To Giorgi, relativism is as much a dogmatism to be avoided in psychology as is reductionism. Giorgi's ( 2009 ) method, hence, became known as the descriptive phenomenological psychological research method. With the emphasis on description Giorgi intended to apply the phenomenological attitude by staying true to discoveries from the everyday lifeworld. So even though discoveries may sometimes be incomplete, he preferred that they were described in their incompleteness rather than forced into unnecessary closure for aesthetic or ideological reasons (ibid.). Hence, both psychologically relevant aspects of Husserl's phenomenology as well as the discovery-oriented spirit of science became essential influences on Giorgi's approach to the project of a qualitative research method in psychology.
Initially influenced by Merleau-Ponty’s psychologically oriented thought, Giorgi turned more to Husserl’s methodological emphasis in his pursuit of a phenomenological theory of science to support a qualitative psychological research method (see Giorgi, 2009 ). As Giorgi ( 2014 , 236) recently stated "…I use Husserl because he confronts the issue directly and he contrasts his position with that of the empiricists." In the late 90’s, several other qualitative methods using a phenomenological approach started to emerge, most had a stronger emphasis on postmodernism or hermeneutics. Giorgi differentiated his method from the newer ones by stressing that his was a more descriptive emphasis as opposed to an interpretative one (Giorgi, 1992 , see also, Giorgi 2006 , 2010 , 2018 ). Of course, the distinction should not be understood too literally, because in certain settings the use of the word ‘interpretation’ could synonymously refer to the act of ‘description.’ However, with the term ‘description’ Giorgi ( 1992 ) simply meant to stay true, or rooted, to what appeared in the data . This is similar to what is called a “close reading of the text” in literary studies. The intention was to avoid the kind of intrusive and overly imposing 'interpretations' where gaps in the qualitative data would be 'filled' with theoretical explanations, abstractions or even speculations.
Developing phenomenological interviewing skills requires practice and training that is often already present in the education of most clinical psychologists and health care workers. However, phenomenological psychologists have been recently applying the insights of philosophical phenomenology to better articulate the role of empathic reflection in participant observation (Englander, 2020 ; Churchill 2010 ) and designing phenomenologically inspired teaching methods (Englander 2014 ; Churchill, 2018 ) for improving quality of psychological interviewing and qualitative phenomenological research generally.
Referring to Schutz, Michal Barber points out how these terms are “analogous to the phenomenological prototype.” In other words, again, as social scientists we apply them with a different purpose than that of the philosopher. See: Barber, Michael, "Alfred Schutz", The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Summer 2021 Edition, Edward N. Zalta (ed.),
URL = < https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/sum2021/entries/schutz/ > .
The history of phenomenology could be considered one big ongoing deliberation about the meaning and possibility of the epoché. We hope readers will forgive us for sidestepping these discussions for the purposes of this presentation where space only permits us to present the epoché as practically applied to the research process in phenomenological psychology. But we will make this one brief point. All major phenomenological themes such as embodiment, temporality, intersubjectivity and even the hermeneutic circle were developed by philosophers thorough their initial employment of the epoché —or awareness of the natural attitude. It is therefore important, we believe, for one to understand the practice of the epoché to, in turn, fully grasp these phenomenological concepts. We find it inconceivable that one could proficiently comprehend basic phenomenological concepts such as the lived body or intersubjectivity while remaining unreflectively within the influence of the natural attitude. Similarly, we have learned through experience that success with the method we are presenting here is often in direct proportion to one’s awareness of their natural attitude.
The relation between the transcendental and the psychological reduction is another long-deliberated issue in the history of phenomenology which we can’t develop here. In brief, because the transcendental “philosophical” reduction is a non-personal and non-situated level of reflection it is simply not appropriate for performing qualitative psychological research—at the moment that we are doing it. To our knowledge, no phenomenological psychologist would claim to be doing both standpoints at once. But this does not mean that psychologists must, or should, ignore the insights of transcendentally derived philosophical concepts when we design our research or reflect on the results of our psychological analysis. Phenomenological philosophy can be a perfectly compatible basis from which to deepen our understandings of the results of our descriptive analysis. In short, psychologists may visit the transcendental position, but we do not unpack our bags, and we always remember our return ticket.
This is very similar to the relevance structure of a world as suggested by Schutz ( 1962 ).
As Giorgi ( 2009 , 99–100) writes, “The researcher does, of course, assume the human scientific (psychological) reduction. Everything in the raw data is taken to be how the objects were experienced by the describer, and no claim is made that the events described really happened as they were described. The personal past experiences of the researcher and all his or her past knowledge about the phenomenon are also bracketed. This bracketing results in a fresh approach to the raw data and the refusal to posit the existential claim allows the noetic-noematic relation to come to the fore so that the substratum of the psychologist's reality can be focused upon. That is, the particular way in which the describer's personal acts of consciousness were enacted to allow the phenomenal intentional objects to appear from the basis of the sense determination that the psychologist is interested in uncovering.”.
For a more elaborate discussion on general knowledge claims in qualitative research and its relation to a phenomenological theory of science, see for example, Englander ( 2019 ).
Giorgi originally included situated structures but later dropped them to emphasize the nomothetic (or generalized knowledge) aspect of the method. But most Giorgi’s colleagues and ex-students prefer to include situated structures as a transition to the general. As teachers we have learned that this psychologically rich transitional step is of great pedagogical value. For most newcomers to the method, it is intuitively much easier to construct situated structures before moving on to develop general structures. We also find situated structures to be of great psychological value in their own right—as we hope is demonstrated in our case example ahead.
It is important to note that research participants are not considered from the stance of an empirical theory of science. Any qualitative methodology, grounded in a phenomenological theory of science, cannot naively adopt the concept of the population (and sampling methods ) as its ground for making general knowledge claims (see for example, Englander, 2019 ).
At points in the interview when a more active questioning is called for, evocation techniques like those from the explication interview, or the micro phenomenological interview method, can be very effective. (see Petitmengin et al., 2018 ) Here, we invoke the daydream so that both the interviewer and the participant can, in an almost trance-like way, imaginatively re-live the daydream together. These techniques can provoke profoundly rich description. Here is another example of how we approach data collection as always contingent to the manner in which the phenomenon best expresses itself. Again, this is why we endorse an adaptable approach to data collection.
Aanstoos, C. M. (1983). The think aloud method in descriptive research. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 14 , 243–266.
Article Google Scholar
Aanstoos, C. (1985). The structure of thinking in chess. In A. Giorgi (Ed.), Phenomenology and psychological research (pp. 23–85). Duquesne University Press.
Google Scholar
Beck, T. J. (2013). A phenomenological analysis of anxiety as experienced in social situations. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 44 (2), 179–219.
Brennan, J. F., & Houde, K. A. (2017). History and systems of psychology . Cambridge University Press.
Book Google Scholar
Broomé, R. (2013). The lived-experience of leading a successful police vehicle pursuit: A descriptive phenomenological psychological inquiry. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 44 (2), 220–243.
Churchill, S. D. (2010). “Second person” perspectivity in observing and understanding emotional expression. In L. Embree, M. Barber, & T. Nenon (Eds.), Phenomenology: Selected essays from North America. Part 2: Phenomenology beyond philosophy (Vol. 5, pp. 81–106). Zeta Books.
Churchill, S. D. (2018). Explorations in teaching the phenomenological method: Challenging psychology students to “grasp at meaning” in human science research. Qualitative Psychology, 5 , 207–227.
Churchill, S. D. (2022). Essentials of existential phenomenological research . American Psychological Association.
Churchill, S. D., & Wertz, F. (2015). An introduction to phenomenological research in psychology: Historical, conceptual, and methodological foundations. In K. J. Schneider & J. F. Pierson (Eds.), The handbook of humanistic psychology: Leading edges in theory, research, and practice (2nd ed., pp. 275–295). Sage.
Cloonan, T. (1995). The early history of phenomenological psychological research methods in America. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 26 , 46–126.
Davidson, L. (1988). Husserl’s refutation of psychologism and the possibility of a phenomenological psychology. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 19 (1), 1–17.
Davidson, L. (2003). Living outside mental illness: Qualitative studies of recovery in schizophrenia . New York University Press.
Davidson, L. (2021). Overcoming psychologism: Husserl and the transcendental reform of psychology . Springer International Publishing.
DeRobertis, E. (2020). From personal threat to cross cultural learning: An eidetic investigation. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 51 (1), 1–15.
DeRobertis, E. M. (2017). The phenomenology of learning and becoming . Palgrave McMillan.
Desai, M. U., Divan, G., Wertz, F. J., & Patel, V. (2012). The discovery of autism: Indian parents’ experience of caring for their child with an autism spectrum disorder. Transcultural Psychiatry, 49 , 613–637.
Englander, M. (2007). Persistent psychological meaning of early emotional memories. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 38 (2), 181–216.
Englander, M. (2014). Empathy training from a phenomenological perspective. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology., 45 (1), 5–26.
Englander, M. (2019). General knowledge claims in qualitative research. The Humanistic Psychologist, 47 (1), 1–14.
Englander, M. (2020). Phenomenological psychological interviewing. The Humanistic Psychologist, 48 (1), 54–73.
Friedman, M. (1984). Contemporary psychology: Revealing and obscuring the human . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (1970). Psychology as a human science: A phenomenologically based approach . Harper & Row.
Giorgi, A. (1971). Phenomenology and experimental psychology II. In A. Giorgi, W. Fischer, & R. von Eckartsberg (Eds.), Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology I (pp. 17–19). Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (1975). An application of phenomenological method in psychology. In A. Giorgi, C. Fischer, & E. Murray (Eds.), Duquesne studies in phenomenological Psychology II (pp. 82–103). Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (1975). Divergence of qualitative and quantitative methods in psychology. In A. C. F. Giorgi & E. Murray (Eds.), Duquesne studies in phenomenological Psychology II (pp. 72–79). Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (Ed.). (1985). Phenomenology and psychological research . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (1992). Description versus interpretation: Competing alternative strategies for qualitative research. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 23 (2), 119–135.
Giorgi, A. (1997). The theory, practice, and evaluation of the phenomenological method as a qualitative research procedure. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 28 , 235–260.
Giorgi, A. (2006). Concerning variations in the application of the phenomenological method. The Humanistic Psychologist, 34 , 305–319.
Giorgi, A. (2009). The descriptive phenomenological method in psychology: A modified Husserlian approach . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A. (2010). Phenomenology and the practice of science. Existential Analysis, 21 , 3–22.
Giorgi, A. (2014). Phenomenological philosophy as the basis for a human scientific psychology. The Humanistic Psychologist, 42 (3), 233–248.
Giorgi, A. (2017). A response to the attempted critique of the scientific phenomenological method. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 48 (1), 83–144.
Giorgi, A. (2018). Reflections on certain qualitative and phenomenological psychological methods . University Professor’s Press.
Giorgi, A. (2020). In defense of scientific phenomenologies. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 51 (2), 135–161.
Giorgi, A. (2021). The necessity of the epochē and reduction for a Husserlian phenomenological science of psychology. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 52 (1), 1–18.
Giorgi, B. (2011). A phenomenological analysis of the experience of pivotal moments in therapy as defined by clients. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 42 (1), 61–106.
Giorgi, A., & Gallegos, N. (2005). Living through some positive experiences of psychotherapy. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 36 (2), 195–218.
Giorgi, A., Barton, A., & Maes, C. (Eds.). (1983). Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology IV . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A., Fischer, C., & Murray, E. (Eds.). (1975). Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology II . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A., Fischer, W., & von Eckartsberg, R. (Eds.). (1971). Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology I . Duquesne University Press.
Giorgi, A., Giorgi, B., & Morley, J. (2017). The descriptive phenomenological psychological method. In C. Willig & W. Staiton-Rogers (Eds.), The SAGE handbook of qualitative research in psychology (pp. 176–192). Sage.
Chapter Google Scholar
Giorgi, A., Knowles, R., & Smith, D. L. (Eds.). (1979). Duquesne studies in phenomenological psychology III . Duquesne University Press.
Husserl, E. (1981). Pure phenomenology, its method, and its field of investigation. In: P. McCormick & F. Elliston (Eds.) Husserl Shorter Works (R.W. Jordan, Trans.) University of Notre Dame Press/Harvester Press.
Husserl, E. (1991). On the phenomenology of the consciousness of internal time (1893–1917). (J.B. Brough Trans.) Kluwer Academic Publishers. (German original, 1966).
Kearney, R. (2011). What is diacritical hermeneutics? Journal of Applied Hermeneutics . https://doi.org/10.11575/jah.v0i0.53187
Merleau-Ponty, M. (1962). Phenomenology of perception . Routledge.
Merleau-Ponty, M. (1964). The primacy of perception. In: J. Eddie (eds.) (J. Wild Trans.). Northwestern University Press.
Merleau-Ponty, M. (1968). The visible and the invisible C. Lefort (Eds.) (A. Lingus Trans.). Northwestern University Press.
Morley, J. (1998). The private theatre: A phenomenological investigation of daydreaming. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 29, 116–134.
Morley, J. (1999). The sleeping subject: Merleau-Ponty on dreaming. Theory and Psychology, 9 (1), 89–101.
Morley, J. (2003). The texture of the real: Merleau-Ponty, imagination, and psychopathology. In J. Morley & J. Phillips (Eds.), Imagination and its pathologies (pp. 93–108). Cambridge: M.I.T. Press.
Morrissey, M. B. (2015). Suffering narratives of older adults: A phenomenological approach to serious illness, chronic pain, recovery and maternal care . Routledge.
Natanson, M. (1973). Edmund Husserl: Philosopher of infinite tasks . Northwestern University Press.
Petitmengin, C., Van Beek, M., Bitbol, M., Nissou, J.-M., & Roepstorff, A. (2018). Studying the experience of meditation through micro-phenomenology. Current Opinions in Psychology, 28 , 54–59.
Roald, T. (2008). Toward a phenomenological psychology of art appreciation. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 39 (2), 189–212.
Røseth, I., & Bongaardt, R. (2019). I don’t love my baby?!: A descriptive phenomenological analysis of disturbances in maternal affection. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 50 (1), 90–111.
Røseth, I., Binder, P.-E., & Malt, U. F. (2011). Two ways of living through postpartum depression. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 42 (2), 174–194.
Sartre, J.-P. (1962). A sketch for a theory of the emotions . Methuen.
Schutz, A. (1962). Collected papers I: The problem of social reality . Martinus Nijhoff.
Smith, D. (2002). Fearfully and wonderfully made: The history of Duquesne University’s graduate psychology programs . Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center, Duquesne University.
Smith, D. L. (2010). A history of Amedeo P. Giorgi’s contribution to the psychology department and phenomenology center of Duquesne University in his twenty-five years there. In T. F. Cloonan & C. Thiboutot (Eds.), The redirection of psychology: Essays in honor of Amedeo P. Giorgi (pp. 329–351). CIRP.
Tangvald-Pedersen, O., & Bongaardt, R. (2017). The interconnection between mental health, work and belonging: A phenomenological investigation. Indo-Pacific Journal of Phenomenology., 17 (2), 1–11.
Vogel, E. B. (2021). Black men’s experience of police harassment a descriptive phenomenological study. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 52 (1), 96–117.
Wertz, F. J. (2010). The method of eidetic analysis for psychology. In T. F. Cloonan & C. Thiboutot (Eds.), The redirection of psychology: Essays in honor of Amedeo P. Giorgi (pp. 371–398). CIRP.
Wertz, F. J. (2016). Outline of the relationship among transcendental phenomenology, phenomenological psychology, and the sciences of persons. Schutzian Research, 8 , 139–162.
Wertz, F. J., Charmaz, K., McMullen, L. M., Josslson, R., Anderson, R., & McSpadden, E. (2011). Five ways of doing qualitative analysis: Phenomenological psychology, grounded theory, discourse analysis, narrative research, and intuitive inquiry . The Guilford Press.
Zapien, N. (2016). The beginning of an extra-marital affair: A descriptive phenomenological study and clinical implications. Journal of Phenomenological Psychology, 47 (2), 134–155.
Download references
Open access funding provided by Malmö University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Social Work, Faculty of Health & Society, Malmö University, Malmö, Sweden
Magnus Englander
Department of Psychology, Ramapo College of New Jersey, Mahwah, NJ, USA
James Morley
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Magnus Englander .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Englander, M., Morley, J. Phenomenological psychology and qualitative research. Phenom Cogn Sci 22 , 25–53 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11097-021-09781-8
Download citation
Accepted : 23 September 2021
Published : 30 October 2021
Issue Date : February 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11097-021-09781-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Phenomenology
- Qualitative research
Advertisement
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide
Phenomenology – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

Phenomenology
Definition:
Phenomenology is a branch of philosophy that is concerned with the study of subjective experience and consciousness. It is based on the idea that the essence of things can only be understood through the way they appear to us in experience, rather than by analyzing their objective properties or functions.
Phenomenology is often associated with the work of philosopher Edmund Husserl, who developed a method of phenomenological inquiry that involves suspending one’s preconceptions and assumptions about the world and focusing on the pure experience of phenomena as they present themselves to us. This involves bracketing out any judgments, beliefs, or theories about the phenomena, and instead attending closely to the subjective qualities of the experience itself.
Phenomenology has been influential not only in philosophy but also in other fields such as psychology, sociology, and anthropology, where it has been used to explore questions of perception, meaning, and human experience.
History of Phenomenology
Phenomenology is a philosophical movement that began in the early 20th century, primarily in Germany. It was founded by Edmund Husserl, a German philosopher who is often considered the father of phenomenology.
Husserl’s work was deeply influenced by the philosophy of Immanuel Kant, particularly his emphasis on the importance of subjective experience. However, Husserl sought to go beyond Kant’s transcendental idealism by developing a rigorous method of inquiry that would allow him to examine the structures of consciousness and the nature of experience in a systematic way.
Husserl’s first major work, Logical Investigations (1900-1901), laid the groundwork for phenomenology by introducing the idea of intentional consciousness, or the notion that all consciousness is directed towards objects in the world. He went on to develop a method of “bracketing” or “epoche,” which involved setting aside one’s preconceptions and assumptions about the world in order to focus on the pure experience of phenomena as they present themselves.
Other philosophers, such as Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre, built on Husserl’s work and developed their own versions of phenomenology. Heidegger, in particular, emphasized the importance of language and the role it plays in shaping our understanding of the world, while Sartre focused on the relationship between consciousness and freedom.
Today, phenomenology continues to be an active area of philosophical inquiry, with many contemporary philosophers drawing on its insights to explore questions of perception, meaning, and human experience.
Types of Phenomenology
There are several types of phenomenology that have emerged over time, each with its own focus and approach. Here are some of the most prominent types of phenomenology:
Transcendental Phenomenology
This is the type of phenomenology developed by Edmund Husserl, which aims to investigate the structures of consciousness and experience in a systematic way by using the method of epoche or bracketing.
Existential Phenomenology
This type of phenomenology, developed by philosophers such as Martin Heidegger and Jean-Paul Sartre, focuses on the subjective experience of individual existence, emphasizing the role of freedom, authenticity, and the search for meaning in human life.
Hermeneutic Phenomenology
This type of phenomenology, developed by philosophers such as Hans-Georg Gadamer and Paul Ricoeur, emphasizes the role of interpretation and understanding in human experience, particularly in the context of language and culture.
Phenomenology of Perception
This type of phenomenology, developed by Maurice Merleau-Ponty, emphasizes the embodied and lived nature of perception, arguing that perception is not simply a matter of passive reception but is instead an active and dynamic process of engagement with the world.
Phenomenology of Sociality
This type of phenomenology, developed by philosophers such as Alfred Schutz and Emmanuel Levinas, focuses on the social dimension of human experience, exploring how we relate to others and how our understanding of the world is shaped by our interactions with others.
Methods of Phenomenology
Here are some of the key methods that phenomenologists use to investigate human experience:
Epoche (Bracketing)
This is a key method in phenomenology, which involves setting aside one’s preconceptions and assumptions about the world in order to focus on the pure experience of phenomena as they present themselves. By bracketing out any judgments, beliefs, or theories about the phenomena, one can attend more closely to the subjective qualities of the experience itself.
Introspection
Phenomenologists often rely on introspection, or a careful examination of one’s own mental states and experiences, as a way of gaining insight into the nature of consciousness and subjective experience.
Descriptive Analysis
Phenomenology also involves a careful description and analysis of subjective experiences, paying close attention to the way things appear to us in experience, rather than analyzing their objective properties or functions.
Another method used in phenomenology is the variation technique, in which one systematically varies different aspects of an experience in order to gain a deeper understanding of its structure and meaning.
Phenomenological Reduction
This method involves reducing a phenomenon to its essential features or structures, in order to gain a deeper understanding of its nature and significance.
Epoché Variations
This method involves examining different aspects of an experience through the process of epoché or bracketing, to gain a more nuanced understanding of its subjective qualities and significance.
Applications of Phenomenology
Phenomenology has a wide range of applications across many fields, including philosophy, psychology, sociology, education, and healthcare. Here are some of the key applications of phenomenology:
- Philosophy : Phenomenology is primarily a philosophical approach, and has been used to explore a wide range of philosophical issues related to consciousness, perception, identity, and the nature of reality.
- Psychology : Phenomenology has been used in psychology to study human experience and consciousness, particularly in the areas of perception, emotion, and cognition. It has also been used to develop new forms of psychotherapy, such as existential and humanistic psychotherapy.
- Sociology : Phenomenology has been used in sociology to study the subjective experience of individuals within social contexts, particularly in the areas of culture, identity, and social change.
- Education : Phenomenology has been used in education to explore the subjective experience of students and teachers, and to develop new approaches to teaching and learning that take into account the individual experiences of learners.
- Healthcare : Phenomenology has been used in healthcare to explore the subjective experience of patients and healthcare providers, and to develop new approaches to patient care that are more patient-centered and focused on the individual’s experience of illness.
- Design : Phenomenology has been used in design to better understand the subjective experience of users and to create more user-centered products and experiences.
- Business : Phenomenology has been used in business to better understand the subjective experience of consumers and to develop more effective marketing strategies and user experiences.
Purpose of Phenomenology
The purpose of phenomenology is to understand the subjective experience of human beings. Phenomenology is concerned with the way things appear to us in experience, rather than their objective properties or functions. The goal of phenomenology is to describe and analyze the essential features of subjective experience, and to gain a deeper understanding of the nature of consciousness, perception, and human existence.
Phenomenology is particularly concerned with the ways in which subjective experience is structured, and with the underlying meanings and significance of these structures. Phenomenologists seek to identify the essential features of subjective experience, such as intentionality, embodiment, and lived time, and to explore the ways in which these features give rise to meaning and significance in human life.
Phenomenology has a wide range of applications across many fields, including philosophy, psychology, sociology, education, healthcare, and design. In each of these fields, phenomenology is used to gain a deeper understanding of human experience, and to develop new approaches and strategies that are more focused on the subjective experiences of individuals.
Overall, the purpose of phenomenology is to deepen our understanding of human experience and to provide insights into the nature of consciousness, perception, and human existence. Phenomenology offers a unique perspective on the subjective aspects of human life, and its insights have the potential to transform our understanding of ourselves and the world around us.
Examples of Phenomenology
Phenomenology has many real-life examples across different fields. Here are some examples of phenomenology in action:
- Psychology : In psychology, phenomenology is used to study the subjective experience of individuals with mental health conditions. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of anxiety in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder, or the experience of depression in individuals with major depressive disorder.
- Healthcare : In healthcare, phenomenology is used to explore the subjective experience of patients and to develop more patient-centered approaches to care. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of chronic pain in patients, in order to develop more effective pain management strategies that are based on the patient’s individual experience of pain.
- Education : In education, phenomenology is used to study the subjective experience of students and to develop more effective teaching and learning strategies. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of learning in students, in order to develop teaching methods that are more focused on the individual needs and experiences of learners.
- Business : In business, phenomenology is used to better understand the subjective experience of consumers, and to develop more effective marketing strategies and user experiences. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of using a particular product or service, in order to identify areas for improvement and to create a more user-centered experience.
- Design : In design, phenomenology is used to better understand the subjective experience of users, and to create more user-centered products and experiences. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of using a particular app or website, in order to identify ways to improve the user interface and user experience.
When to use Phenomenological Research
Here are some situations where phenomenological research might be appropriate:
- When you want to explore the meaning and significance of an experience : Phenomenological research is particularly useful when you want to gain a deeper understanding of the subjective experience of individuals and the meanings and significance that they attach to their experiences. For example, if you want to understand the experience of being a first-time parent, phenomenological research can help you explore the various emotions, challenges, and joys that are associated with this experience.
- When you want to develop more patient-centered healthcare: Phenomenological research can be useful in healthcare settings where there is a need to develop more patient-centered approaches to care. For example, if you want to improve pain management strategies for patients with chronic pain, phenomenological research can help you gain a better understanding of the individual experiences of pain and the different ways in which patients cope with this experience.
- When you want to develop more effective teaching and learning strategies : Phenomenological research can be used in education settings to explore the subjective experience of students and to develop more effective teaching and learning strategies that are based on the individual needs and experiences of learners.
- When you want to improve the user experience of a product or service: Phenomenological research can be used in design settings to gain a deeper understanding of the subjective experience of users and to develop more user-centered products and experiences.
Characteristics of Phenomenology
Here are some of the key characteristics of phenomenology:
- Focus on subjective experience: Phenomenology is concerned with the subjective experience of individuals, rather than objective facts or data. Phenomenologists seek to understand how individuals experience and interpret the world around them.
- Emphasis on lived experience: Phenomenology emphasizes the importance of lived experience, or the way in which individuals experience the world through their own unique perspectives and histories.
- Reduction to essence: Phenomenology seeks to reduce the complexities of subjective experience to their essential features or structures, in order to gain a deeper understanding of the nature of consciousness, perception, and human existence.
- Emphasis on description: Phenomenology is primarily concerned with describing the features and structures of subjective experience, rather than explaining them in terms of underlying causes or mechanisms.
- Bracketing of preconceptions: Phenomenology involves bracketing or suspending preconceptions and assumptions about the world, in order to approach subjective experience with an open and unbiased perspective.
- Methodological approach: Phenomenology is both a philosophical and methodological approach, which involves a specific set of techniques and procedures for studying subjective experience.
- Multiple approaches: Phenomenology encompasses a wide range of approaches and variations, including transcendental phenomenology, hermeneutic phenomenology, and existential phenomenology, among others.
Advantages of Phenomenology
Phenomenology offers several advantages as a research approach, including:
- Provides rich, in-depth insights: Phenomenology is focused on understanding the subjective experiences of individuals in a particular context, which allows for a rich and in-depth exploration of their experiences, emotions, and perceptions.
- Allows for participant-centered research: Phenomenological research prioritizes the experiences and perspectives of the participants, which makes it a participant-centered approach. This can help to ensure that the research is relevant and meaningful to the participants.
- Provides a flexible approach: Phenomenological research offers a flexible approach that can be adapted to different research questions and contexts. This makes it suitable for use in a wide range of fields and research areas.
- Can uncover new insights : Phenomenological research can uncover new insights into subjective experience and can challenge existing assumptions and beliefs about a particular phenomenon or experience.
- Can inform practice and policy: Phenomenological research can provide insights that can be used to inform practice and policy decisions in fields such as healthcare, education, and design.
- Can be used in combination with other research approaches : Phenomenological research can be used in combination with other research approaches, such as quantitative methods, to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular phenomenon or experience.
Limitations of Phenomenology
Despite the many advantages of phenomenology, there are also several limitations that should be taken into account, including:
- Subjective nature: Phenomenology is focused on subjective experience, which means that it can be difficult to generalize findings to a larger population or to other contexts.
- Limited external validity: Because phenomenological research is focused on a specific context or experience, the findings may have limited external validity or generalizability.
- Potential for researcher bias: Phenomenological research relies heavily on the researcher’s interpretations and analyses of the data, which can introduce potential for bias and subjectivity.
- Time-consuming and resource-intensive: Phenomenological research is often time-consuming and resource-intensive, as it involves in-depth data collection and analysis.
- Difficulty with data analysis: Phenomenological research involves a complex process of data analysis, which can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Lack of standardized procedures: Phenomenology encompasses a range of approaches and variations, which can make it difficult to compare findings across studies or to establish standardized procedures.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Focus Groups – Steps, Examples and Guide

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Histogram – Types, Examples and Making Guide

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...

Qualitative Research Methods
- Gumberg Library and CIQR
- Qualitative Methods Overview
Phenomenology
- Case Studies
- Grounded Theory
- Narrative Inquiry
- Oral History
- Feminist Approaches
- Action Research
- Finding Books
- Getting Help
Phenomenology helps us to understand the meaning of people's lived experience. A phenomenological study explores what people experienced and focuses on their experience of a phenomenon. As phenomenology has a strong foundation in philosophy, it is recommended that you explore the writings of key thinkers such as Husserl, Heidegger, Sartre and Merleau-Ponty before embarking on your research. Duquesne's Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center maintains a collection of resources connected to phenomenology as well as hosting lectures, and is a good place to start your exploration.
- Simon Silverman Phenomenology Center
- Husserl, Edmund, 1859–1938
- Heidegger, Martin, 1889–1976
- Sartre, Jean Paul, 1905–1980
- Merleau-Ponty, Maurice, 1908–1961
Books and eBooks
Online Resources
- Phenomenology Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy entry.
- << Previous: Qualitative Methods Overview
- Next: Case Studies >>
- Last Updated: Aug 18, 2023 11:56 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.duq.edu/qualitative_research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
What is Phenomenology?. Here is a brief overview from The SAGE encyclopedia of qualitative research methods:. Phenomenology is the reflective study of prereflective or lived experience. To say it somewhat differently, a main characteristic of the phenomenological tradition is that it is the study of the lifeworld as we immediately experience it, prereflectively, rather than as we conceptualize ...
Phenomenology is a branch of philosophy dedicated to the description and analysis of phenomena, that is, the way things, in the broadest sense of the word, appear (Husserl, 1911, 1913; see e.g., Hintikka, 1995).In recent decades, phenomenological concepts and methodological ideals have been adopted by qualitative researchers.
Phenomenology is both a philosophical movement and a family of qualitative research methodologies. The term 'phenomenology' refers to the study of phenomena, where a phenomenon is anything ...
Phenomenology is a type of qualitative research as it requires an in-depth understanding of the audience's thoughts and perceptions of the phenomenon you're researching. It goes deep rather than broad, unlike quantitative research. Finding the lived experience of the phenomenon in question depends on your interpretation and analysis.
interviews in phenomenology, multiple forms in case study research to provide the in-depth case picture). At the data analysis stage, the differences are most pronounced. Not only is the distinction one of specificity of the analysis phase (e.g., grounded the-ory most specific, narrative research less defined) but the number of steps to be under-
Focus on Experience: Phenomenology is concerned with the "phenomena," which refers to anything that appears in the way that it appears to consciousness. This includes experiences, perceptions, thoughts, feelings, and meanings. First-Person Perspective: Phenomenology emphasizes the importance of the first-person, subjective experience. It ...
Now called Descriptive Phenomenology, this study design is one of the most commonly used methodologies in qualitative research within the social and health sciences. ... Phenomenology as a healthcare research method. Journal of Evidence Based Nursing, 21(4), 96-98. doi: 10.1136/eb-2018-102990 << Previous: Methodologies;
Abstract. This article distills the core principles of a phenomenological research design and, by means of a specific study, illustrates the phenomenological methodology. After a brief overview of the developments of phenomenology, the research paradigm of the specific study follows. Thereafter the location of the data, the data-gathering the ...
Qual Data Analysis & Phenomenology. Data Analysis. Oct 6, 2023. by Janet Salmons, PhD, Research Community Manager for SAGE Methodspace. Qualitative data analysis varies by methodology. This post introduces approaches for phenomenological studies and offers a collection of open access articles. Phenomenology is the reflective study of lived ...
What is difficult for those who are beginning this style of research, is the assumption of the phenomenological psychological attitude. This attitude, which distinguishes this method from non-phenomenological qualitative research methods, can't be taken for granted and requires training, study, and the support of a like-minded research community.
According to Padilla-Díaz (), three types of phenomenological methods are used in qualitative research designs.They include: (a) Descriptive or hermeneutical phenomenology—which refers to the study of personal experience and requires a description or interpretation of the meanings of phenomena experienced by participants in an investigation; (b) Eidetic (essence) or transcendental ...
Qualitative research is an advanced field of study. The key aim of this chapter was to discuss the three major types of qualitative research—narrative inquiry, phenomenology, and grounded theory. This chapter firstly provided a brief discussion on qualitative research, its philosophical foundations, and types. Secondly, it provided a ...
The methods of new phenomenology, or American phenomenology, should be applied if the researcher seeks to understand a person's experience(s) of the phenomenon. 1. See Table 6.1. for two different examples of phenomenological research. Advantages and disadvantages of phenomenological research
Qualitative, Multimethod, and Mixed Methods Research. Paul Mihas, in International Encyclopedia of Education(Fourth Edition), 2023. Phenomenologies. Phenomenology is a philosophy, a perspective, and a qualitative research tradition (Farrell, 2020).As a research tradition, it is aimed at "opening up" our understanding of complex experiential accounts, moving beyond a simple description of ...
This article presents the tradition of phenomenologically founded psychological research that was originally initiated by Amedeo Giorgi. This data analysis method is inseparable from the broader project of establishing an autonomous phenomenologically based human scientific psychology. After recounting the history of the method from the 1960's to the present, we explain the rationale for why ...
Second, methodological considerations, drawn from this phenomenological basis, will be explicated and illustrated through a research study of pediatric intensive care unit (PICU) nurses' lived experience of a major hospital transformation project in Canada—thus offering guidance on how to align qualitative research methods and process with ...
Phenomenology has many real-life examples across different fields. Here are some examples of phenomenology in action: Psychology: In psychology, phenomenology is used to study the subjective experience of individuals with mental health conditions. For example, a phenomenological study might explore the experience of anxiety in individuals with ...
Phenomenology as qualitative methodology The complete reference for the finalised and published version of this book chapter is : Gill, M.J. (2020) Phenomenological approaches to research, in Mik ...
Phenomenological Research Methods by Clark Moustakas In this volume, Clark Moustakas clearly discusses the theoretical underpinnings of phenomenology, based on the work of Husserl and others, and takes the reader step-by-step through the process of conducting a phenomenological study. His concise guide provides numerous examples of successful phenomenological studies from a variety of fields ...
Introduction. The phenomenological approach to research emerges as a response to the radicalism of what is objectifiable. It is based on the study of life experiences, regarding an event, from the subject's perspective. This approach is based on the analysis of the most complex aspects of human life, of what is beyond the quantifiable aspects.
Recently, phenomenological philosophy itself has branched out into performing systematic qualitative research, resulting in a heterogeneous field of qualitative phenomenological philosophy.
Qualitative research is useful for gaining deep insight into a topic or generating new ideas and theories. Qualitative research can be conducted on its own or in combination with quantitative research methods (which use numerical data). The combination of qualitative and quantitative approaches is called mixed methods research.
This chapter reflects on the use of qualitative research methodology in the studies described in this volume. Although all studies were concerned with the ways in which meaning is negotiated, modified or reproduced when people engage with phenomena that are relevant to mental health, they deployed a wide range of research designs including textual analysis (including various types of discourse ...