- New QB365-SLMS
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Probability Case Study Questions 2021
By QB365 on 22 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
10th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Case Study Questions

(ii) a monkey
(iii) a teddy bear
(iv) not a monkey
(v) not a pokemon
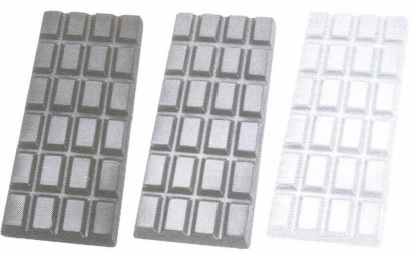
(ii) If the probability of distributing dark chocolates is 4/9, then the number of dark chocolates Rohit has, is
(iii) The probability of distributing white chocolates is
(iv) The probability of distributing both milk and white chocolates is
(v) The probability of distributing all the chocolates is
In a party, some children decided to play musical chair game. In the game the person playing the music has been advised to stop the music at any time in the interval of 3 mins after he start the music in each turn. On the basis of the given information, answer the following questions. (i) What is the probability that the music will stop within first 30 sees after starting?
(ii) The probability that the music will stop within 45 sees after starting is
(iii) The probability that the music will stop after 2 mins after starting is
(iv) The probability that the music will not stop within first 60 sees after starting is
(v) The probability that the music will stop within first 82 sees after starting is

(ii) The probability of getting exactly 1 head is
(iii) The probability of getting exactly 3 tails is
(iv) The probability of getting atmost 3 heads is
(v) The probability of getting atleast two heads is
(ii) not of yellow colour
(iii) of green colour
(iv) of yellow colour
(v) not of blue colour
*****************************************
Cbse 10th standard maths subject probability case study questions 2021 answer keys.
Total number of puppets in claw crane = 58 + 42 + 36 + 64 = 200 (i) (b): P(picking a tiger) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{36}{200}=\frac{9}{50} \end{equation}\) (ii) (a): P(picking a monkey) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{64}{200}=\frac{8}{25} \end{equation}\) (iii) (c) : P(picking a teddy bear) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{58}{200}=\frac{29}{100} \end{equation}\) (iv) (d) : P(not picking a monkey) = 1 - P(picking a monkey) \(\begin{equation} =1-\frac{8}{25}=\frac{17}{25} \end{equation}\) (v) (d): P(picking a pokemon) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{42}{200}=\frac{21}{100} \end{equation}\) P(not picking a pokemon) = 1 - P(picking a pokemon) \(\begin{equation} =1-\frac{21}{100}=\frac{79}{100} \end{equation}\)
Since, every student get one chocolate. So, number of chocolates Rohit has is equal to the number of students in the class. (i) (a): Let number of milk chocolates Rohit has = x Probability of distributing milk chocolates = \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{3} \end{equation}\) \(\begin{equation} \Rightarrow \frac{x}{54}=\frac{1}{3} \Rightarrow x=\frac{54}{3}=18 \end{equation}\) (ii) (c): Let number of dark chocolates Rohit has = y Probability of distributing dark chocolates = \(\begin{equation} \frac{4}{9} \end{equation}\) \(\begin{equation} \Rightarrow \frac{y}{54}=\frac{4}{9} \Rightarrow y=\frac{4 \times 54}{9}=24 \end{equation}\) (iii) (d) : Number of white chocolates Rohit has = 54 -(18 + 24) = 12 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{12}{54}=\frac{2}{9} \end{equation}\) (iv) (b) : Total number of milk and white chocolates = 18 + 12 = 30 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{30}{54}=\frac{5}{9} \end{equation}\) (v) (b): Since all students gets one chocolate. So, total number of chocolates distributed = 54 \(\begin{equation} \text { Required probability }=\frac{54}{54}=1 \end{equation}\)
Total time = 3 mins = 3 x 60 sees = 180 secs (i) (a): Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{30}{180}=\frac{1}{6} \end{equation}\) (ii) (a): Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{45}{180}=\frac{1}{4} \end{equation}\) (iii) (d) : P(music will stop within 2 mins) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{120}{180}=\frac{2}{3} \end{equation}\) P(music will stop after 2 mins) = \(\begin{equation} 1-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{1}{3} \end{equation}\) (iv) (b) : Required probability = 1 - P(music will stop within first 60 secs) \(\begin{equation} =1-\frac{60}{180}=1-\frac{1}{3}=\frac{2}{3} \end{equation}\) (v) (b): Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{82}{180}=\frac{41}{90} \end{equation}\)
Sample space (5) = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT} \(\Rightarrow\) n(5) = 8 (i) (c): Let A be the event of getting atmost one tail. A = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH} \(\Rightarrow\) n(A) = 4 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2} \end{equation}\) (ii) (d ): Let B be the event of getting exactly 1 head. B = {HTT, THT, TTH} \(\Rightarrow\) n(B) = 3 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{3}{8} \end{equation}\) (iii) (d) : Let C be the event of getting exactly 3 tails. C = {TTT} \(\Rightarrow\) n( C) = 1 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{8} \end{equation}\) \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{8} \end{equation}\) \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{8} \end{equation}\) \(\begin{equation} \frac{1}{8} \end{equation}\) (iv) (b) : Let D be the event of getting atmost 3 heads. D = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT} \(\Rightarrow\) n(D) = 8 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{8}{8}=1 \end{equation}\) (v) (c): Let E be the event of getting atleast two heads. E = {HHT, HTH, THH, HHH} \(\Rightarrow\) n(E) = 4 Required probability = \(\begin{equation} \frac{n(E)}{n(S)}=\frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2} \end{equation}\)
Total number of blocks in the kit = 120 Number of red blocks = 40 Number of blue blocks = 25 Number of green blocks = 30 Number of yellow blocks = 120 - (40 + 25 + 30) = 120 - 95 = 25 (i) (d): P(block is red) \(\begin{equation} =\frac{40}{120}=\frac{1}{3} \end{equation}\) (ii) (c): P(block is not yellow) = 1 - P(block is yellow) \(\begin{equation} =1-\frac{25}{120}=1-\frac{5}{24}=\frac{19}{24} \end{equation}\) (iii) (c) : P(block is green) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{30}{120}=\frac{1}{4} \end{equation}\) (iv) (b) : P(block is yellow) = \(\begin{equation} \frac{5}{24} \end{equation}\) (v) (b): P(block is not blue) = 1 - P(block is blue) \(\begin{equation} =1-\frac{25}{120}=1-\frac{5}{24}=\frac{19}{24} \end{equation}\)
Related 10th Standard CBSE Maths Materials
10th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 10th social science the making of a global world chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science nationalism in india chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th social science the rise of nationalism in europe chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science metals and non metals chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science acids, bases and salts chapter case study question with answers, cbse 10th science chemical reactions and equations chapter case study question with answers, class 10th science - our environment case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - magnetic effects of electric current case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - electricity case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - human eye and the colourful world case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - light reflection and refraction case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - heredity and evolution case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - how do organisms reproduce case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - life processes case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023, class 10th science - periodic classification of elements case study questions and answers 2022 - 2023.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.

10th Standard CBSE Study Materials

10th Standard CBSE Subjects
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 10 Maths: Case Study Questions of Chapter 15 Probability PDF Download
Case study Questions in the Class 10 Mathematics Chapter 15 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability

In CBSE Class 10 Maths Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Probability Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
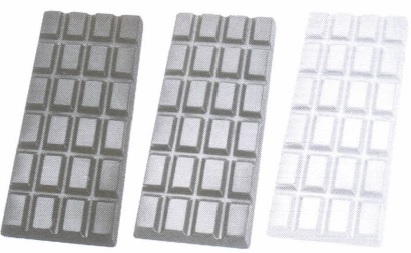
Answer: (a) 18
(ii) If the probability of distributing dark chocolates is 4/9, then the number of dark chocolates Rohit has, is
Answer: (c) 24
(iii) The probability of distributing white chocolates is
Answer: (d) 2/9
(iv) The probability of distributing both milk and white chocolates is
Answer: (b) 5/9
(v) The probability of distributing all the chocolates is
Answer: (b) 1
Question 2:
Rahul and Ravi planned to play Business ( board game) in which they were supposed to use two dice.

1. Ravi got first chance to roll the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 8?
Answer: b) 5/36
2. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 13?
Answer: d) 0
3. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is less than or equal to 12?
Answer: a) 1
4. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is equal to 7?
Answer: c) 1/6
5. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is greater than 8?
Answer: d) 5/18
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Maths Probability Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 15 Probability PDF Download
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 15 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions Chapter 15 Probability
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

These case study questions challenge students to apply their knowledge of quadrilaterals in practical scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving abilities. This article provides the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 15 Probability, enabling students to practice and excel in their examinations.
Probability Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: A jeweler has different types of bracelets in his shop. Sunita wants to purchase a bracelet for her sister’s birthday gift. When Sunita goes to the shop, she founds the following data which represents the number of bracelets of different types in the shop.

Find the probability that Sunita chooses Chain Bracelet. (a) 23/180 (b) 37/180 (c) 37/90 (d) 23/90
Answer: (b) 37/180
Find the probability that she chooses Pearl bracelet. (a) 23/180 (b) 37/180 (c) 37/90 (d) 23/90
Answer: (d) 23/90
What is the probability of a sure event? (a) 1 (b) 0 (c) 1/2 (d) 2/3
Answer: (a) 1
What is the probability that she chooses neither Bangle bracelet nor Pearl bracelet? (a) 23/180 (b) 45/180 (c) 109/180 (d) 23/45
Answer: (c) 109/180
What is the probability that Sunita purchased a Cuff bracelet? (a) 6/17(b)2/13 (c) 1 (d) 2/15
Answer: (d) 2/15
Case Study 2: In a factory, the workers are paid on a daily basis. The new manager wants to know the salary slab of the workers and finds the data given below.

Now, if a worker is chosen at random, then :
The probability that the worker is getting at most ₹ 500 is (a) 3/80 (b) 9/80 (c) 1/80 (d) 4/25
Answer: (b) 9/80
The probability that the worker is getting at least ₹ 701 is (a) 23/80 (b) 43/80 (c) 41/80 (d) 61/80
Answer: (b) 43/80
Probability that the worker is getting at most ₹ 900 is (a)7/40 (b) 3/31 (c) 31/40 (d) 4/31
Answer: (c) 31/40
Case Study 3: A group of students is studying probability in their math class. They encountered the following scenario:
Rajesh and Aisha decided to conduct an experiment with a deck of playing cards to understand the concept of probability. They made the following observations:
- Rajesh drew a card from a standard deck of 52 playing cards and found that it was a spade.
- Aisha drew a card from the same deck and found that it was a face card (king, queen, or jack).
Based on this information, the students were asked to analyze the probabilities of their respective outcomes. Let’s see if you can answer the questions correctly:
MCQ Questions:
Q1. The probability of drawing a spade card, as observed by Rajesh, is: (a) 1/4 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) Cannot be determined
Answer: (a) 1/4
Q2. The probability of drawing a face card, as observed by Aisha, is: (a) 3/13 (b) 4/13 (c) 1/13 (d) Cannot be determined
Answer: (a) 3/13
Q3. In a standard deck of playing cards, the probability of drawing a spade card is: (a) 1/4 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/2
Q4. In a standard deck of playing cards, the probability of drawing a face card is: (a) 3/13 (b) 4/13 (c) 1/13 (d) 1/4
Answer: (b) 4/13
Q5. If Rajesh drew a card and found that it was a spade, what is the probability that it is also a face card? (a) 1/13 (b) 3/13 (c) 1/4 (d) 1/2
Answer: (c) 1/4
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Mathematics Chapter 15 Probability with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Maths Probability Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Class 9 science case study questions chapter 3 atoms and molecules, class 9 mcq questions for chapter 8 motion with answers, सामाजिक विज्ञान ncert books class 9 pdf download | सामाजिक विज्ञान की पुस्तक कक्षा 9 हिंदी, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 3 Minutes
Case Study Questions:
Question 1:
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card.
(i) Find the probability of getting a king of red colour. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
(ii) Find the probability of getting a face card. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 2/13 (d) 3/13
(iii) Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/52 (c) 3/52 (d) 3/26
(iv) Find the probability of getting a red face card. (a) 3/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
(v) Find the probability of getting a spade. (a) 1/26 (b) 1/13 (c) 1/52 (d) 1/4
✨ Free Quizzes, Test Series and Learning Videos for CBSE Class 10 Maths
You may also like:
Chapter 1 Real Numbers Chapter 2 Polynomials Chapter 3 Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables C hapter 4 Quadratic Equations Chapter 5 Arithmetic Progressions Chapter 6 Triangles Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry Chapter 8 Introduction to Trigonometry Chapter 9 Some Applications of Trigonometry Chapter 10 Circles Chapter 11 Constructions Chapter 12 Areas Related to Circles Chapter 13 Surface Areas and Volumes Chapter 14 Statistics Chapter 15 Probability
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- CBSE Class 10 Study Material
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 - Probability (Published by CBSE)
Cbse class 10 maths case study questions for chapter 15 - probability are published by the cbse board itself to help students understand the new format of questions. these questions are important for the cbse class 10 maths 2022 board exam preparations..

CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 - Probability are provided here. These questions are quite useful to understand how real-life problems can be put in the form of questions. These case study questions are published by the CBSE board. Solve all these questions to prepare for your exams and score the desired marks.
Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - Probability:
CASE STUDY 1:
On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card.

1. Find the probability of getting a king of red colour.
Answer: a) 1/26
2. Find the probability of getting a face card.
Answer: d) 3/13
3. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
4. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
Answer: a) 3/13
5. Find the probability of getting a jack of hearts.
Answer: d) 1/4
CASE STUDY 2:
Rahul and Ravi planned to play Business ( board game) in which they were supposed to use two dice.

1. Ravi got first chance to roll the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 8?
Answer: b) 5/36
2. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is 13?
Answer: d) 0
3. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is less than or equal to 12?
Answer: a) 1
4. Rahul got next chance. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is equal to 7?
Answer: c) 1/6
5. Now it was Ravi’s turn. He rolled the dice. What is the probability that he got the sum of the two numbers appearing on the top face of the dice is greater than 8?
Answer: d) 5/18
Also Check:
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths - All Chapters
Tips to Solve Case Study Based Questions Accurately
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification and articles in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari , Sarkari Result and Exam Preparation . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App .
- Territorial Army Recruitment 2024
- RSMSSB Rajasthan CET Answer Key 2024
- ADRE Grade 4 Admit Card 2024
- MLSU Result 2024
- RSMSSB CET Admit Card 2024
- RSMSSB CET Exam Analysis 2024
- Rajasthan CET Question Paper 2024
- OSSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- RSMSSB Exam Calendar 2024
- Star Sighting Time Today
- Education News
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
The Rise of Education Industry 5.0: Integrating Human and AI Collaboration in Higher Education
Top 5 Words Of the Day For Morning School Assembly: 28th October, 2024
Diwali 2024 Holiday: यूपी, बिहार और राजस्थान में दिवाली की कितनी छुट्टी? यहां देखें लिस्ट
RPSC EO RO Exam Date 2024 OUT at rpsc.rajasthan.gov.in: Check Dates Here
SSC CGL Result 2024 Date: Check Expected Date and Other Details
APSSB CSLE Admit Card 2024 OUT at apssb.nic.in: Download Call Letter Here
Dreaming of Working in Germany? New Visa Increase for Indians Makes It Easier
Top 5 Current Affairs of the Day for Govt. Jobs: 25 October 2024-IN-SPACe, Railway projects, Kittur Vijayotsava, Chushul And Others
BRICS Summit 2024: 16th Edition Key Highlights, Major Outcomes and Relevance
Today Current Affairs One Liners 25 October 2024: Indian Ambassador to Sweden
Brain Teaser IQ Test: Can You Spot The Poor Family In This Dining Scene In 5 Seconds?
Current Affairs Quiz 25 October 2024: Next Chief Justice of India
CG SI Syllabus 2024: सब इंस्पेक्टर और सूबेदार के लिए CGPSC सिलेबस पीडीएफ डाउनलोड करें
Tamil Nadu NEET UG Counselling 2024 Stray Vacancy Round Schedule Out at tnmedicalselection.net
[OUT] RSCIT Result 2024: 06 अक्टूबर वीएमओयू आरकेसीएल परीक्षा का रिजल्ट rkcl.vmou.ac.in पर जारी, यहां से डाउनलोड करें सर्टिफिकेट
राजस्थान CET 12th लेवल आंसर की 2024: 22, 23, 24 अक्टूबर शिफ्ट 1, 2 की अनौपचारिक उत्तर कुंजी PDF करें डाउनलोड
Magadh University Result 2024 OUT: यहां देखें BA, MA, MSc, MCom, BSc,और BCom सहित अन्य मगध यूनिवर्सिटी UG, PG सेमेस्टर मार्कशीट PDF
Punjab Police Jail Warder Admit Card 2024 Out at sssb.gov.in, ये रहा Download Link
Flower Rangoli for Diwali: 10+ Easy Rangoli Ideas for School Students
इंडिया पोस्ट जीडीएस 4th मेरिट लिस्ट 2024: indiapostgdsonline.gov.in पर जारी होगा होगा जीडीएस रिजल्ट, ऐसे डाउनलोड कर सकेंगे सर्कल वाइज PDF
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability Free PDF

Mere Bacchon, you must practice the CBSE Case Study Questions Class 10 Maths Probability in order to fully complete your preparation . They are very very important from exam point of view. These tricky Case Study Based Questions can act as a villain in your heroic exams!
I have made sure the questions (along with the solutions) prepare you fully for the upcoming exams. To download the latest CBSE Case Study Questions , just click ‘ Download PDF ’.
CBSE Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability PDF
Checkout our case study questions for other chapters.
- Chapter 11: Construction Case Study Questions
- Chapter 12: Area Related to Circles Case Study Questions
- Chapter 13: Surface Area and Volumes Case Study Questions
- Chapter 14: Statistics Case Study Questions
How should I study for my upcoming exams?
First, learn to sit for at least 2 hours at a stretch
Solve every question of NCERT by hand, without looking at the solution.
Solve NCERT Exemplar (if available)
Sit through chapter wise FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS
Practice MCQ Questions (Very Important)
Practice Assertion Reason & Case Study Based Questions
Sit through FULLY INVIGILATED TESTS involving MCQs. Assertion reason & Case Study Based Questions
After Completing everything mentioned above, Sit for atleast 6 full syllabus TESTS.
Contact Form
Privacy Policy

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- JEE Toppers Notes
- JEE Formula
- JEE Important Question
- JEE Mind Map
- JEE Integer-Numerical Type Question
- JEE Study Planner
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths PDF
The passage-based questions are commonly known as case study questions. Students looking for Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths can use this page to download the PDF file.
The case study questions on Probability are based on the CBSE Class 12 Maths Syllabus, and therefore, referring to the Probability case study questions enable students to gain the appropriate knowledge and prepare better for the Class 12 Maths board examination. Continue reading to know how should students answer it and why it is essential to solve it, etc.
Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths with Solutions in PDF
Our experts have also kept in mind the challenges students may face while solving the case study on Probability, therefore, they prepared a set of solutions along with the case study questions on Probability.
The case study on Probability Class 12 Maths with solutions in PDF helps students tackle questions that appear confusing or difficult to answer. The answers to the Probability case study questions are very easy to grasp from the PDF - download links are given on this page.
Why Solve Probability Case Study Questions on Class 12 Maths?
There are three major reasons why one should solve Probability case study questions on Class 12 Maths - all those major reasons are discussed below:
- To Prepare for the Board Examination: For many years CBSE board is asking case-based questions to the Class 12 Maths students, therefore, it is important to solve Probability Case study questions as it will help better prepare for the Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Develop Problem-Solving Skills: Class 12 Maths Probability case study questions require students to analyze a given situation, identify the key issues, and apply relevant concepts to find out a solution. This can help CBSE Class 12 students develop their problem-solving skills, which are essential for success in any profession rather than Class 12 board exam preparation.
- Understand Real-Life Applications: Several Probability Class 12 Maths Case Study questions are linked with real-life applications, therefore, solving them enables students to gain the theoretical knowledge of Probability as well as real-life implications of those learnings too.
How to Answer Case Study Questions on Probability?
Students can choose their own way to answer Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths, however, we believe following these three steps would help a lot in answering Class 12 Maths Probability Case Study questions.
- Read Question Properly: Many make mistakes in the first step which is not reading the questions properly, therefore, it is important to read the question properly and answer questions accordingly.
- Highlight Important Points Discussed in the Clause: While reading the paragraph, highlight the important points discussed as it will help you save your time and answer Probability questions quickly.
- Go Through Each Question One-By-One: Ideally, going through each question gradually is advised so, that a sync between each question and the answer can be maintained. When you are solving Probability Class 12 Maths case study questions make sure you are approaching each question in a step-wise manner.

What to Know to Solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Probability?
A few essential things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Probability are -
- Basic Formulas of Probability: One of the most important things to know to solve Case Study Questions on Class 12 Probability is to learn about the basic formulas or revise them before solving the case-based questions on Probability.
- To Think Analytically: Analytical thinkers have the ability to detect patterns and that is why it is an essential skill to learn to solve the CBSE Class 12 Maths Probability case study questions.
- Strong Command of Calculations: Another important thing to do is to build a strong command of calculations especially, mental Maths calculations.
Where to Find Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths?
Use Selfstudys.com to find Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths. For ease, here is a step-wise procedure to download the Probability Case Study for Class 12 Maths in PDF for free of cost.
Since you are already on this page, you can scroll to the top section of this page to get access to the Case Study on Probability. To help others reach this page let them know these steps:
- Open Selfstudys.com on your computer/laptop or Smartphone
- Once the website gets loaded, click on the navigation button
- Find CBSE from the given menu
- Click on Case Study
- Choose Class 12
- Search Maths and then navigate to the Probability Class 12 Maths Case Study
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

One Last Step...

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

myCBSEguide
- Mathematics
- Case Study Class 10...
Case Study Class 10 Maths Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
Now, CBSE will ask only subjective questions in class 10 Maths case studies. But if you search over the internet or even check many books, you will get only MCQs in the class 10 Maths case study in the session 2022-23. It is not the correct pattern. Just beware of such misleading websites and books.
We advise you to visit CBSE official website ( cbseacademic.nic.in ) and go through class 10 model question papers . You will find that CBSE is asking only subjective questions under case study in class 10 Maths. We at myCBSEguide helping CBSE students for the past 15 years and are committed to providing the most authentic study material to our students.
Here, myCBSEguide is the only application that has the most relevant and updated study material for CBSE students as per the official curriculum document 2022 – 2023. You can download updated sample papers for class 10 maths .
First of all, we would like to clarify that class 10 maths case study questions are subjective and CBSE will not ask multiple-choice questions in case studies. So, you must download the myCBSEguide app to get updated model question papers having new pattern subjective case study questions for class 10 the mathematics year 2022-23.
Class 10 Maths has the following chapters.
- Real Numbers Case Study Question
- Polynomials Case Study Question
- Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables Case Study Question
- Quadratic Equations Case Study Question
- Arithmetic Progressions Case Study Question
- Triangles Case Study Question
- Coordinate Geometry Case Study Question
- Introduction to Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Some Applications of Trigonometry Case Study Question
- Circles Case Study Question
- Area Related to Circles Case Study Question
- Surface Areas and Volumes Case Study Question
- Statistics Case Study Question
- Probability Case Study Question
Format of Maths Case-Based Questions
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions will have one passage and four questions. As you know, CBSE has introduced Case Study Questions in class 10 and class 12 this year, the annual examination will have case-based questions in almost all major subjects. This article will help you to find sample questions based on case studies and model question papers for CBSE class 10 Board Exams.
Maths Case Study Question Paper 2023
Here is the marks distribution of the CBSE class 10 maths board exam question paper. CBSE may ask case study questions from any of the following chapters. However, Mensuration, statistics, probability and Algebra are some important chapters in this regard.
Case Study Question in Mathematics
Here are some examples of case study-based questions for class 10 Mathematics. To get more questions and model question papers for the 2021 examination, download myCBSEguide Mobile App .
Case Study Question – 1
In the month of April to June 2022, the exports of passenger cars from India increased by 26% in the corresponding quarter of 2021–22, as per a report. A car manufacturing company planned to produce 1800 cars in 4th year and 2600 cars in 8th year. Assuming that the production increases uniformly by a fixed number every year.
- Find the production in the 1 st year.
- Find the production in the 12 th year.
- Find the total production in first 10 years. OR In which year the total production will reach to 15000 cars?
Case Study Question – 2
In a GPS, The lines that run east-west are known as lines of latitude, and the lines running north-south are known as lines of longitude. The latitude and the longitude of a place are its coordinates and the distance formula is used to find the distance between two places. The distance between two parallel lines is approximately 150 km. A family from Uttar Pradesh planned a round trip from Lucknow (L) to Puri (P) via Bhuj (B) and Nashik (N) as shown in the given figure below.
- Find the distance between Lucknow (L) to Bhuj(B).
- If Kota (K), internally divide the line segment joining Lucknow (L) to Bhuj (B) into 3 : 2 then find the coordinate of Kota (K).
- Name the type of triangle formed by the places Lucknow (L), Nashik (N) and Puri (P) OR Find a place (point) on the longitude (y-axis) which is equidistant from the points Lucknow (L) and Puri (P).
Case Study Question – 3
- Find the distance PA.
- Find the distance PB
- Find the width AB of the river. OR Find the height BQ if the angle of the elevation from P to Q be 30 o .
Case Study Question – 4
- What is the length of the line segment joining points B and F?
- The centre ‘Z’ of the figure will be the point of intersection of the diagonals of quadrilateral WXOP. Then what are the coordinates of Z?
- What are the coordinates of the point on y axis equidistant from A and G? OR What is the area of area of Trapezium AFGH?
Case Study Question – 5
The school auditorium was to be constructed to accommodate at least 1500 people. The chairs are to be placed in concentric circular arrangement in such a way that each succeeding circular row has 10 seats more than the previous one.
- If the first circular row has 30 seats, how many seats will be there in the 10th row?
- For 1500 seats in the auditorium, how many rows need to be there? OR If 1500 seats are to be arranged in the auditorium, how many seats are still left to be put after 10 th row?
- If there were 17 rows in the auditorium, how many seats will be there in the middle row?
Case Study Question – 6
- Draw a neat labelled figure to show the above situation diagrammatically.
- What is the speed of the plane in km/hr.
More Case Study Questions
We have class 10 maths case study questions in every chapter. You can download them as PDFs from the myCBSEguide App or from our free student dashboard .
As you know CBSE has reduced the syllabus this year, you should be careful while downloading these case study questions from the internet. You may get outdated or irrelevant questions there. It will not only be a waste of time but also lead to confusion.
Here, myCBSEguide is the most authentic learning app for CBSE students that is providing you up to date study material. You can download the myCBSEguide app and get access to 100+ case study questions for class 10 Maths.
How to Solve Case-Based Questions?
Questions based on a given case study are normally taken from real-life situations. These are certainly related to the concepts provided in the textbook but the plot of the question is always based on a day-to-day life problem. There will be all subjective-type questions in the case study. You should answer the case-based questions to the point.
What are Class 10 competency-based questions?
Competency-based questions are questions that are based on real-life situations. Case study questions are a type of competency-based questions. There may be multiple ways to assess the competencies. The case study is assumed to be one of the best methods to evaluate competencies. In class 10 maths, you will find 1-2 case study questions. We advise you to read the passage carefully before answering the questions.
Case Study Questions in Maths Question Paper
CBSE has released new model question papers for annual examinations. myCBSEguide App has also created many model papers based on the new format (reduced syllabus) for the current session and uploaded them to myCBSEguide App. We advise all the students to download the myCBSEguide app and practice case study questions for class 10 maths as much as possible.
Case Studies on CBSE’s Official Website
CBSE has uploaded many case study questions on class 10 maths. You can download them from CBSE Official Website for free. Here you will find around 40-50 case study questions in PDF format for CBSE 10th class.
10 Maths Case Studies in myCBSEguide App
You can also download chapter-wise case study questions for class 10 maths from the myCBSEguide app. These class 10 case-based questions are prepared by our team of expert teachers. We have kept the new reduced syllabus in mind while creating these case-based questions. So, you will get the updated questions only.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper 2020-21
- Class 12 Maths Case Study Questions
- CBSE Reduced Syllabus Class 10 (2020-21)
- Class 10 Maths Basic Sample Paper 2024
- How to Revise CBSE Class 10 Maths in 3 Days
- CBSE Practice Papers 2023
- Class 10 Maths Sample Papers 2024
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Class 10 Maths Chapter 14 Case Based Questions - Probability
Study case - 1.

Q2: The probability of drawing a ball of colour other than green colour is: (a) 0 (b) 4/25 (c) 21/25 (d) 17/25 Ans: (c) Explanation: From part (A), number of green balls = 4. ∴ Number of balls of colour other than = 25 − 4 = 21. ∴ Probability of drawing a ball of colour other than green colour = 21/25.
Q3: The probability of drawing either a green or white ball is: (a) 0 (b) 12/25 (c) 13/25 (d) 17/25 Ans: (b) Explanation: The number of green balls = 4 and number of white balls =8. Therefore, total number of green balls + white balls = 4 + 8 = 12.. ∴ Probability of drawing either a or a white ball = 12/25.
Study Case - 2

Q1: The probability of getting almost one tail is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/4 Ans: (c) Explanation: Sample space (S) = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTH, TTT} ⇒ n(S) = 8 Let A be the event of getting at most one tail. ∴ A = {HHH, HHT, HTH, THH} ⇒ n(A) = 4 ∴ Required probability = 4/8 = 1/2
Q2: The probability of getting exactly 1 head is: (a) 1/2 (b) 1/4 (c) 1/8 (d) 3/8 Ans: (d) Explanation: Let B be the event of getting exactly 1 head. ∴B = {HTT, THT, TTH} ⇒ n(B) = 3 ∴ Required probability = 3/8 Q3: The probability of getting exactly 3 tails is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/4 (d) 1/8 Ans: (d) Explanation: Let C be the event of getting exactly 3 tails. ∴ C = {TTT} ⇒ n(C) = 1 ∴ Required probability = 1/8 Q4: The probability of getting at most 3 heads is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/8 Ans: (b) Explanation: Let D be the event of getting atmost 3 heads. ∴ D = {HHH, HHT, HTH, HTT, THH, THT, TTT} ⇒ n(D) = 8 ∴ Required probability = 8/8 = 1.
Q5: The probability of getting at least two heads is: (a) 0 (b) 1 (c) 1/2 (d) 1/4 Ans: (c) Explanation: Let E be the event of getting at least two heads. ∴E = {HHT, HTH, THH, HHH} ⇒ n(E) = 4 ∴ Required probability = n(E)/n(S) = 4/8 = 1/2.
Top Courses for Class 10
Mock tests for examination, past year papers, study material, objective type questions, video lectures, sample paper, practice quizzes, viva questions, extra questions, important questions, previous year questions with solutions, semester notes, shortcuts and tricks.

Case Based Questions: Probability Free PDF Download
Importance of case based questions: probability, case based questions: probability notes, case based questions: probability class 10, study case based questions: probability on the app, welcome back, create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Change country.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Check Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 - Probability. These questions are published by the CBSE Board and are important for the Class 10 Maths Exam 2021-22. By...
CBSE 10th Standard Maths Subject Probability Case Study Questions 2021. By QB365 on 22 May, 2021. QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 10 Maths, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions .
You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 15 Probability. In CBSE Class 10 Maths Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well.
These case study questions challenge students to apply their knowledge of quadrilaterals in practical scenarios, enhancing their problem-solving abilities. This article provides the Class 9 Maths Case Study Questions of Chapter 15 Probability, enabling students to practice and excel in their examinations.
Case Study Questions: Question 1: On a weekend Rani was playing cards with her family. The deck has 52 cards. If her brother drew one card. (i) Find the probability of getting a king of red colour. (a) 1/26. (b) 1/13. (c) 1/52. (d) 1/4. Show Answer. (ii) Find the probability of getting a face card. (a) 1/26. (b) 1/13. (c) 2/13. (d) 3/13.
CBSE Class 10 Maths Case Study Questions for Chapter 15 - Probability are provided here. These questions are quite useful to understand how real-life problems can be put in the form of...
These Case Study Questions for Class 10 Maths Probability are latest, comprehensive, confidence inspiring, with easy to understand explanation.
Case Study on Probability Class 12 Maths: Here, you will get Case Study Questions on Class 12 Probability PDF at free of cost. Along with you can also download Probability case study questions for class 12 exercise wise for getting higher marks in board exams.
Maths Case Study Question Paper 2023. Here is the marks distribution of the CBSE class 10 maths board exam question paper. CBSE may ask case study questions from any of the following chapters. However, Mensuration, statistics, probability and Algebra are some important chapters in this regard. Units.
The notes and questions for Case Based Questions: Probability have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about Case Based Questions: Probability covers topics like Study Case - 1, Study Case - 2 and Case Based Questions: Probability Example, for Class 10 2024 Exam.