- Find a Course
- For Business
- For Educators
- Product News

Analytical thinking: what it is and why it matters more than ever
January 30, 2024

Welcome back to our high-impact workplace skills series. We really enjoyed the conversations happening in the comments section of last week’s top skills of 2023 issue, so be sure to check those out for perspectives and insights from fellow members of our Career Chat community.
One comment that’s been on our mind came from Kendra Vivian Lewis , who asked some thoughtful questions about the comparative importance of workplace and technical skills and if there’s a way to forecast which skills will be important in the coming years. This week’s topic—analytical thinking, the number one skill on the list—is a great example as we explore both questions. Be sure to read to the end to discover a special offer that we’re running on Coursera Plus subscriptions through September 21.
What it means to think analytically
Analytical thinking involves using data to understand problems, identify potential solutions, and suggest the solution that’s most likely to have the desired impact. It’s similar to critical thinking skills , which are the skills you use to interpret information and make decisions.
In order to succeed as a strong analytical thinker, you also need to have strong technical skills in your field. Remember: technical skills describe the things you do, while workplace skills describe how you do them. So your workplace skills, used effectively, enhance your technical skills. That’s why we consider them to be high-impact—they stand to make your work more impactful than it would have been had you only used your technical skills.
To illustrate, suppose you just started a job as a data analyst for a think tank focused on climate change, and you’ve been tasked with raising community engagement in future climate action efforts.
You might start with your technical data analysis skills as you gather data from a few sources. Then, you’ll use your analytical thinking skills to determine the validity of each data source. Perhaps you’ll discard one source when you learn the research was funded by a firm with a financial stake in fossil fuel consumption. Your technical skills lead again as you clean data, and then you’ll return to your analytical thinking skills to analyze and interpret your findings, ultimately leading to your recommendation to start a transparency campaign to display water and energy use in the community.
Tell us in the comments: How do you use your analytical skills alongside your technical skills in your day-to-day work?
Why analytical skills top the list
To develop the skills list, the World Economic Forum surveyed 800+ global employers on their views of skills and jobs over the next five years, so this list is forward-looking. According to the Future of Jobs Report , employers believe analytical thinking skills will grow in importance by 72 percent in this timeframe.
The reason employers are keen to hire employees with strong analytical thinking skills is informed by trends in automation and technological advancements. While technical data analysis becomes easier with automation, reasoning and decision-making automation is advancing at a much slower pace—meaning employers anticipate that, within the next five years, we’ll have a wealth of data at our fingertips and too few people to interpret what that data means.
Where to begin
For a crash course in critical thinking, try the University of California, Davis’s Critical Thinking Skills for the Professional course. You can finish this beginner-level course in about 7 hours.
For a more comprehensive exploration into analytical thinking , try Duke University’s Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking Specialization . Over four courses, you’ll learn how to effectively argue and reason using logic.
For a technical process to guide your analytical thinking, try Google’s Data Analytics Professional Certificate . Ground your analytical thinking skills in technical know-how in this eight-course series.
Interested in multiple programs? Don’t miss this special offer!
Through September 21, we’re offering $100 off annual Coursera Plus subscriptions for new subscribers. With this offer, you’ll pay less than $25 per month for one year of access to 6,100 courses, Specializations, and Professional Certificates with flexibility to start new courses and move between programs at your pace.
This offer is a great choice if you are frequently tempted to enroll in multiple courses at once or plan to complete a Specialization or Professional Certificate within the next year. If that sounds like you, take a closer look at the offer and the Coursera Plus course catalog.
That’s all for this week! Join us next week to talk about motivation and self-awareness skills.
Keep reading
- How to answer interview questions with the STAR method
- Coursera Receives Industry-first Authorized Instructional Platform Designation from the American Council on Education
- How to answer “what are your strengths and weaknesses?” in interviews

A Handbook for Analytical Writing
Keys to Strategic Thinking
- © 2013
- William E. Winner 0
Department of Forestry and Environmental Resources, North Carolina State University, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Part of the book series: Synthesis Lectures on Professionalism and Career Advancement for Scientists and Engineers (SLPCASE)
1444 Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this book
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Other ways to access
Licence this eBook for your library
Institutional subscriptions
Table of contents (13 chapters)
Front matter, introduction.
William E. Winner
Descriptive and Analytical Writing
Guidelines for students and teachers, choosing topics, writing teams, organization, the writing process, construction, top ten writing tips, ethics: bias and plagiarism, final products, evaluating analytical writing, classroom excercises for teachers and students, back matter, about this book, authors and affiliations, about the author, bibliographic information.
Book Title : A Handbook for Analytical Writing
Book Subtitle : Keys to Strategic Thinking
Authors : William E. Winner
Series Title : Synthesis Lectures on Professionalism and Career Advancement for Scientists and Engineers
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-02507-5
Publisher : Springer Cham
eBook Packages : Synthesis Collection of Technology (R0) , eBColl Synthesis Collection 5
Copyright Information : Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2013
Softcover ISBN : 978-3-031-01379-9 Published: 12 April 2013
eBook ISBN : 978-3-031-02507-5 Published: 31 May 2022
Series ISSN : 2329-5058
Series E-ISSN : 2329-5066
Edition Number : 1
Number of Pages : XV, 123
Topics : Mathematics, general , Engineering, general , Professional & Vocational Education
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.5 Critical Thinking and Research Applications
Learning objectives.
- Analyze source materials to determine how they support or refute the working thesis.
- Identify connections between source materials and eliminate redundant or irrelevant source materials.
- Identify instances when it is appropriate to use human sources, such as interviews or eyewitness testimony.
- Select information from sources to begin answering the research questions.
- Determine an appropriate organizational structure for the research paper that uses critical analysis to connect the writer’s ideas and information taken from sources.
At this point in your project, you are preparing to move from the research phase to the writing phase. You have gathered much of the information you will use, and soon you will be ready to begin writing your draft. This section helps you transition smoothly from one phase to the next.
Beginning writers sometimes attempt to transform a pile of note cards into a formal research paper without any intermediary step. This approach presents problems. The writer’s original question and thesis may be buried in a flood of disconnected details taken from research sources. The first draft may present redundant or contradictory information. Worst of all, the writer’s ideas and voice may be lost.
An effective research paper focuses on the writer’s ideas—from the question that sparked the research process to how the writer answers that question based on the research findings. Before beginning a draft, or even an outline, good writers pause and reflect. They ask themselves questions such as the following:
- How has my thinking changed based on my research? What have I learned?
- Was my working thesis on target? Do I need to rework my thesis based on what I have learned?
- How does the information in my sources mesh with my research questions and help me answer those questions? Have any additional important questions or subtopics come up that I will need to address in my paper?
- How do my sources complement each other? What ideas or facts recur in multiple sources?
- Where do my sources disagree with each other, and why?
In this section, you will reflect on your research and review the information you have gathered. You will determine what you now think about your topic. You will synthesize , or put together, different pieces of information that help you answer your research questions. Finally, you will determine the organizational structure that works best for your paper and begin planning your outline.
Review the research questions and working thesis you developed in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” . Set a timer for ten minutes and write about your topic, using your questions and thesis to guide your writing. Complete this exercise without looking over your notes or sources. Base your writing on the overall impressions and concepts you have absorbed while conducting research. If additional, related questions come to mind, jot them down.
Selecting Useful Information
At this point in the research process, you have gathered information from a wide variety of sources. Now it is time to think about how you will use this information as a writer.
When you conduct research, you keep an open mind and seek out many promising sources. You take notes on any information that looks like it might help you answer your research questions. Often, new ideas and terms come up in your reading, and these, too, find their way into your notes. You may record facts or quotations that catch your attention even if they did not seem immediately relevant to your research question. By now, you have probably amassed an impressively detailed collection of notes.
You will not use all of your notes in your paper.
Good researchers are thorough. They look at multiple perspectives, facts, and ideas related to their topic, and they gather a great deal of information. Effective writers, however, are selective. They determine which information is most relevant and appropriate for their purpose. They include details that develop or explain their ideas—and they leave out details that do not. The writer, not the pile of notes, is the controlling force. The writer shapes the content of the research paper.
While working through Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.4 “Strategies for Gathering Reliable Information” , you used strategies to filter out unreliable or irrelevant sources and details. Now you will apply your critical-thinking skills to the information you recorded—analyzing how it is relevant, determining how it meshes with your ideas, and finding how it forms connections and patterns.
Writing at Work
When you create workplace documents based on research, selectivity remains important. A project team may spend months conducting market surveys to prepare for rolling out a new product, but few managers have time to read the research in its entirety. Most employees want the research distilled into a few well-supported points. Focused, concise writing is highly valued in the workplace.
Identify Information That Supports Your Thesis
In Note 11.81 “Exercise 1” , you revisited your research questions and working thesis. The process of writing informally helped you see how you might begin to pull together what you have learned from your research. Do not feel anxious, however, if you still have trouble seeing the big picture. Systematically looking through your notes will help you.
Begin by identifying the notes that clearly support your thesis. Mark or group these, either physically or using the cut-and-paste function in your word-processing program. As you identify the crucial details that support your thesis, make sure you analyze them critically. Ask the following questions to focus your thinking:
- Is this detail from a reliable, high-quality source? Is it appropriate for me to cite this source in an academic paper? The bulk of the support for your thesis should come from reliable, reputable sources. If most of the details that support your thesis are from less-reliable sources, you may need to do additional research or modify your thesis.
- Is the link between this information and my thesis obvious—or will I need to explain it to my readers? Remember, you have spent more time thinking and reading about this topic than your audience. Some connections might be obvious to both you and your readers. More often, however, you will need to provide the analysis or explanation that shows how the information supports your thesis. As you read through your notes, jot down ideas you have for making those connections clear.
- What personal biases or experiences might affect the way I interpret this information? No researcher is 100 percent objective. We all have personal opinions and experiences that influence our reactions to what we read and learn. Good researchers are aware of this human tendency. They keep an open mind when they read opinions or facts that contradict their beliefs.
It can be tempting to ignore information that does not support your thesis or that contradicts it outright. However, such information is important. At the very least, it gives you a sense of what has been written about the issue. More importantly, it can help you question and refine your own thinking so that writing your research paper is a true learning process.
Find Connections between Your Sources
As you find connections between your ideas and information in your sources, also look for information that connects your sources. Do most sources seem to agree on a particular idea? Are some facts mentioned repeatedly in many different sources? What key terms or major concepts come up in most of your sources regardless of whether the sources agree on the finer points? Identifying these connections will help you identify important ideas to discuss in your paper.
Look for subtler ways your sources complement one another, too. Does one author refer to another’s book or article? How do sources that are more recent build upon the ideas developed in earlier sources?
Be aware of any redundancies in your sources. If you have amassed solid support from a reputable source, such as a scholarly journal, there is no need to cite the same facts from an online encyclopedia article that is many steps removed from any primary research. If a given source adds nothing new to your discussion and you can cite a stronger source for the same information, use the stronger source.
Determine how you will address any contradictions found among different sources. For instance, if one source cites a startling fact that you cannot confirm anywhere else, it is safe to dismiss the information as unreliable. However, if you find significant disagreements among reliable sources, you will need to review them and evaluate each source. Which source presents a sounder argument or more solid evidence? It is up to you to determine which source is the most credible and why.
Finally, do not ignore any information simply because it does not support your thesis. Carefully consider how that information fits into the big picture of your research. You may decide that the source is unreliable or the information is not relevant, or you may decide that it is an important point you need to bring up. What matters is that you give it careful consideration.
As Jorge reviewed his research, he realized that some of the information was not especially useful for his purpose. His notes included several statements about the relationship between soft drinks that are high in sugar and childhood obesity—a subtopic that was too far outside of the main focus of the paper. Jorge decided to cut this material.
Reevaluate Your Working Thesis
A careful analysis of your notes will help you reevaluate your working thesis and determine whether you need to revise it. Remember that your working thesis was the starting point—not necessarily the end point—of your research. You should revise your working thesis if your ideas changed based on what you read. Even if your sources generally confirmed your preliminary thinking on the topic, it is still a good idea to tweak the wording of your thesis to incorporate the specific details you learned from research.
Jorge realized that his working thesis oversimplified the issues. He still believed that the media was exaggerating the benefits of low-carb diets. However, his research led him to conclude that these diets did have some advantages. Read Jorge’s revised thesis.
Although following a low-carbohydrate diet can benefit some people, these diets are not necessarily the best option for everyone who wants to lose weight or improve their health.
Synthesizing and Organizing Information
By now your thinking on your topic is taking shape. You have a sense of what major ideas to address in your paper, what points you can easily support, and what questions or subtopics might need a little more thought. In short, you have begun the process of synthesizing information—that is, of putting the pieces together into a coherent whole.
It is normal to find this part of the process a little difficult. Some questions or concepts may still be unclear to you. You may not yet know how you will tie all of your research together. Synthesizing information is a complex, demanding mental task, and even experienced researchers struggle with it at times. A little uncertainty is often a good sign! It means you are challenging yourself to work thoughtfully with your topic instead of simply restating the same information.
Use Your Research Questions to Synthesize Information
You have already considered how your notes fit with your working thesis. Now, take your synthesis a step further. Analyze how your notes relate to your major research question and the subquestions you identified in Chapter 11 “Writing from Research: What Will I Learn?” , Section 11.2 “Steps in Developing a Research Proposal” . Organize your notes with headings that correspond to those questions. As you proceed, you might identify some important subtopics that were not part of your original plan, or you might decide that some questions are not relevant to your paper.
Categorize information carefully and continue to think critically about the material. Ask yourself whether the sources are reliable and whether the connections between ideas are clear.
Remember, your ideas and conclusions will shape the paper. They are the glue that holds the rest of the content together. As you work, begin jotting down the big ideas you will use to connect the dots for your reader. (If you are not sure where to begin, try answering your major research question and subquestions. Add and answer new questions as appropriate.) You might record these big ideas on sticky notes or type and highlight them within an electronic document.
Jorge looked back on the list of research questions that he had written down earlier. He changed a few to match his new thesis, and he began a rough outline for his paper.

Review your research questions and working thesis again. This time, keep them nearby as you review your research notes.
- Identify information that supports your working thesis.
- Identify details that call your thesis into question. Determine whether you need to modify your thesis.
- Use your research questions to identify key ideas in your paper. Begin categorizing your notes according to which topics are addressed. (You may find yourself adding important topics or deleting unimportant ones as you proceed.)
- Write out your revised thesis and at least two or three big ideas.
You may be wondering how your ideas are supposed to shape the paper, especially since you are writing a research paper based on your research. Integrating your ideas and your information from research is a complex process, and sometimes it can be difficult to separate the two.
Some paragraphs in your paper will consist mostly of details from your research. That is fine, as long as you explain what those details mean or how they are linked. You should also include sentences and transitions that show the relationship between different facts from your research by grouping related ideas or pointing out connections or contrasts. The result is that you are not simply presenting information; you are synthesizing, analyzing, and interpreting it.
Plan How to Organize Your Paper
The final step to complete before beginning your draft is to choose an organizational structure. For some assignments, this may be determined by the instructor’s requirements. For instance, if you are asked to explore the impact of a new communications device, a cause-and-effect structure is obviously appropriate. In other cases, you will need to determine the structure based on what suits your topic and purpose. For more information about the structures used in writing, see Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” .
The purpose of Jorge’s paper was primarily to persuade. With that in mind, he planned the following outline.

Review the organizational structures discussed in this section and Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” . Working with the notes you organized earlier, follow these steps to begin planning how to organize your paper.
- Create an outline that includes your thesis, major subtopics, and supporting points.
- The major headings in your outline will become sections or paragraphs in your paper. Remember that your ideas should form the backbone of the paper. For each major section of your outline, write out a topic sentence stating the main point you will make in that section.
- As you complete step 2, you may find that some points are too complex to explain in a sentence. Consider whether any major sections of your outline need to be broken up and jot down additional topic sentences as needed.
- Review your notes and determine how the different pieces of information fit into your outline as supporting points.
Collaboration
Please share the outline you created with a classmate. Examine your classmate’s outline and see if any questions come to mind or if you see any area that would benefit from an additional point or clarification. Return the outlines to each other and compare observations.
The structures described in this section and Chapter 10 “Rhetorical Modes” can also help you organize information in different types of workplace documents. For instance, medical incident reports and police reports follow a chronological structure. If the company must choose between two vendors to provide a service, you might write an e-mail to your supervisor comparing and contrasting the choices. Understanding when and how to use each organizational structure can help you write workplace documents efficiently and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- An effective research paper focuses on presenting the writer’s ideas using information from research as support.
- Effective writers spend time reviewing, synthesizing, and organizing their research notes before they begin drafting a research paper.
- It is important for writers to revisit their research questions and working thesis as they transition from the research phase to the writing phrase of a project. Usually, the working thesis will need at least minor adjustments.
- To organize a research paper, writers choose a structure that is appropriate for the topic and purpose. Longer papers may make use of more than one structure.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

10 Analytical Writing Skills and How To Improve Them
Discover 10 Analytical Writing skills along with some of the best tips to help you improve these abilities.

Analytical writing is a type of writing that requires you to analyze a text or situation and form an argument based on your findings. Many people find analytical writing to be challenging, but with practice, it can be a valuable skill to have. In this guide, we’ll discuss what analytical writing is, why it’s important, and how you can improve your analytical writing skills.
Critical Thinking
Problem solving, rhetorical analysis, persuasive writing, argumentation.
Critical thinking is the ability to examine ideas or arguments and evaluate them based on reason. It’s a way of thinking that questions assumptions, looks at the evidence and draws conclusions. When you critically think about something, you’re not just accepting what you’re being told. You’re thinking critically about the information you’re being given and coming to your own conclusions.
Critical thinking is an important skill for both personal and professional reasons. In your personal life, critical thinking can help you make better decisions and avoid making decisions based on emotion. In your professional life, critical thinking can help you solve problems, think creatively and make better decisions.
Problem solving is a key analytical writing skill because it allows you to identify and solve problems. When you can effectively solve problems, you can improve efficiency and productivity. Additionally, problem solving can help you identify and avoid future problems.
To solve a problem, you need to first identify the problem. Once you’ve identified the problem, you can brainstorm potential solutions. Then, you can evaluate the solutions and choose the best one. Finally, you can implement the solution and monitor its effectiveness.
Research is an important analytical writing skill because it allows you to gather information and data to support your argument. When you are able to find relevant information, you can make a stronger case for your argument. Additionally, research can help you identify flaws in your opponent’s argument and find ways to counter their arguments.
To do effective research, you need to be able to find and use sources effectively. You also need to be able to critically evaluate the information you find to determine if it is reliable and relevant. Additionally, you need to be able to organize your research and present it in a clear and concise way.
Analytical writing is a process of examining and evaluating information, and then making conclusions based on that analysis. In other words, analytical writing is the process of breaking down information into its component parts, and then putting the pieces back together in a way that makes sense.
This process of analysis is important in a variety of different fields, from business to science to law. In each of these fields, analytical writing is used to make decisions, solve problems and reach conclusions. In order to be an effective analytical writer, you need to be able to break down information into its component parts, and then put the pieces back together in a way that makes sense.
Synthesis is the ability to put together different ideas, concepts or pieces of information to form a new idea, concept or piece of information. In the context of analytical writing, synthesis is the ability to take different ideas and concepts and put them together to form a new idea, concept or piece of information. This new idea, concept or piece of information is often called a synthesis.
Synthesis is an important analytical writing skill because it allows you to take different ideas and concepts and put them together to form a new idea, concept or piece of information. This new idea, concept or piece of information can then be used to support your argument or position.
Evaluation is the process of making a judgment about the value, worth or quality of something. In the context of writing, evaluation often means making a judgment about the merits of an argument or piece of writing. When you’re evaluating something, you’re making a subjective judgment based on your own personal standards.
Evaluation is an important skill for writers because it allows you to make judgments about the arguments you’re presenting. When you’re evaluating an argument, you’re looking at the evidence the writer is providing and deciding whether or not you think the argument is valid. You’re also looking at the writing itself and deciding whether or not the argument is well-made.
Logic is the process of reasoning from one proposition to another. It’s the foundation of all arguments, and it’s important to be able to see the logical connections between different ideas. When you’re writing an analytical essay, you need to be able to make a case for your position by supporting it with evidence. To do this, you need to be able to see the relationships between different ideas and make logical connections between them.
Being able to see the logical connections between ideas is a sign of good critical thinking skills. Being able to make logical connections between ideas is also important for being able to solve problems. When you’re able to see the relationships between different ideas, you can often find creative solutions to problems.
Rhetorical analysis is the process of examining the elements of a text to determine the author’s purpose and the ways in which the author attempts to persuade the audience. This process of analysis can be applied to any type of text, from a newspaper article to a speech to a blog post.
Rhetorical analysis is an important skill for writers because it allows them to better understand the ways in which authors use language to persuade their audience. This understanding can help writers craft their own persuasive arguments and choose the most effective language to use.
Persuasive writing is an important analytical writing skill because it allows you to convince your audience to agree with your point of view. You can do this by using effective arguments, supporting your claims with evidence and using language that appeals to your audience.
To be a successful persuasive writer, you need to understand your audience and what will convince them. You also need to be able to organize your thoughts and arguments in a clear and concise way. Finally, you need to be able to use language that appeals to your audience and that will convince them to agree with you.
Argumentation is a form of analytical writing that involves presenting a case for or against a particular idea, concept or position. The goal of argumentation is to convince your audience that your position is correct by providing evidence and reasoning.
In order to effectively argue a position, you need to be able to understand and analyze the arguments of others. You also need to be able to craft a clear, concise argument of your own. This requires good critical thinking and research skills.
How to Improve Your Analytical Writing Skills
1. Take a class One of the best ways to improve analytical writing skills is to take a class. There are many online and in-person classes available that can help you hone your skills.
2. Use workbooks Workbooks can be a great way to practice analytical writing. Many workbooks provide instructions and advice on how to complete the exercises as well as answers so you can check your work.
3. Hire a tutor If you need more personalized attention, you may want to consider hiring a tutor. A tutor can help you with specific areas that you find challenging and answer any specific questions you may have.
4. Practice The best way to improve analytical writing skills is to practice. Use your skills regularly to ensure you maintain your proficiency. Try to avoid using a template or formula for every piece you write and instead allow your analytical skills to shine through.
5. Read One of the best ways to improve analytical writing skills is to read. Reading can help improve your writing by exposing you to different styles and formats. As you read, pay attention to the way the author uses language to make their point and try to incorporate some of those techniques into your own writing.
10 Discipline Skills and How To Improve Them
10 farming skills and how to improve them, you may also be interested in..., 16 sap basis administrator skills for your career and resume, what does a channel manager do, what does a walgreens pharmacy technician do, what does a behavioral health assistant do.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
Critical thinking refers to deliberately scrutinizing and evaluating theories, concepts, or ideas using reasoned reflection and analysis. The act of thinking critically involves moving beyond simply understanding information, but also questioning its source, its production, and its presentation in order to expose potential bias or researcher subjectivity [i.e., evidence of being influenced by personal opinions and feelings rather than by external determinants ] . Applying critical thinking to investigating a research problem involves actively challenging basic assumptions and questioning the choices and potential motives underpinning how a study was designed and executed and how the author arrived at particular conclusions or recommended courses of action.
Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design . New York: Routledge, 2017.
Thinking Critically
Applying Critical Thinking to Research and Writing
Professors like to use the term critical thinking; in fact, the idea of being a critical thinker permeates much of higher education writ large. In the classroom, the idea of thinking critically is often mentioned by professors when students ask how they should approach writing a research paper [other approaches your professor might mention include interdisciplinarity, compare and contrast, gendered perspective, global, etc.]. However, critical thinking is more than just an approach to research and writing. It is an acquired skill associated with becoming a complex learner capable of discerning important relationships among the elements of, as well as integrating multiple ways of understanding applied to, the research problem. Critical thinking is a lens through which you holistically interrogate a topic.
Given this, critical thinking encompasses a variety of inter-related connotations applied to writing a college-level research paper:
- Integrated and Multi-Dimensional . Critical thinking is not focused on any one element of research, but instead, is applied holistically throughout the process of identifying the research problem, reviewing the literature, applying methods of analysis, describing the results, discussing their implications, and, if appropriate, offering recommendations for further research. It permeates the entire research endeavor from contemplating what to write about to proofreading the final product.
- Humanizes the Research . Thinking critically can help humanize what is being studied by extending the scope of your analysis beyond the traditional boundaries of prior research. The scope of prior research, for example, could have involved only sampling homogeneous populations, only considering certain factors related to the investigation of a phenomenon, or was limited by the way the study was framed or contextualized. Critical thinking supports opportunities to think about incorporating the experiences of others into the research, leading to a more inclusive and representative examination of the topic.
- Non-Linear . This refers to analyzing a research problem in ways that do not rely on sequential decision-making or rational forms of reasoning. Creative thinking relies on intuitive judgement, flexibility, and unconventional approaches to investigating complex phenomena in order to discover new insights, connections, and potential solutions . Thinking critically involves going back and modifying your thinking as new evidence emerges , perhaps multiple times throughout the research process, and then drawing conclusions from multiple perspectives.
- Normative . This refers to the idea that critical thinking can be used to challenge prior assumptions in ways that advocate for social justice, equity, and resilience that can lead to research having a more transformative and expansive impact. In this respect, critical thinking can be viewed as a method for breaking away from dominant culture norms so as to produce research outcomes that illuminate previously hidden aspects of exploitation and injustice.
- Power Dynamics . Research in the social sciences often includes examining aspects of power, focusing on how it operates, how it can be acquired, and how it can be maintained, thereby shaping social relations, organizations, institutions, and the production and maintenance of knowledge. Thinking critically can reveal how societal structures perpetuate power and influence in ways that marginalizes and oppresses specific groups or communities within the contexts of history , politics, economics, culture, and other factors.
- Reflection . A key component of critical thinking is practicing reflexivity; the act of turning ideas and concepts back onto yourself in order to reveal and clarify your own beliefs, assumptions, and perspectives. Being critically reflexive is important because it can reveal hidden biases you may have that could unintentionally influence how you interpret and validate information. The more reflexive you are, the better able and more comfortable you are in opening yourself up to new modes of understanding.
- Rigorous Questioning . Thinking critically is guided by asking questions that lead to addressing complex concepts, principles, theories, or problems more effectively, and in so doing, help distinguish what is known from from what is not known [or that may be hidden]. Critical thinking involves deliberately framing inquiries not only as hypotheses, but as a way to apply systematic, disciplined, in-depth forms of questioning concerning the research problem and in relation to your positionality as a researcher.
- Social Change . An overarching goal of critical thinking applied to research and writing is to seek to identify and challenge sources of inequality, exploitation, oppression, and marinalization that contribute to maintaining the status quo within institutions of society. This can include, for example, schools, court system, businesses, government agencies, or religious organizations that have been created and maintained through certain ways of thinking within the dominant culture.
Critical thinking permeates the entire research and writing process. However, it applies in particular to the literature review and discussion sections of your paper . These two sections of a research paper reflect the dual external and internal reasoning skills of critical thinking.
In reviewing the literature, it is important to reflect upon specific aspects of a study, such as, determining if the research design effectively establishes cause and effect relationships or provides insight into explaining why certain phenomena do or do not occur, assessing whether the method of gathering data or information supports the objectives of your study, and evaluating if the assumptions used t o arrive at a specific conclusion are evidence-based and relevant to addressing the topic. Critically thinking applies to these elements of reviewing prior research by evaluating how each source might perpetuate inequalities or hides the voices of others, thereby, limiting its applicability in understanding the research problem.
Critical thinking applies to the discussion section of your paper because this is where you contemplate the results of your study and explain its value and significance in relation to the research problem. Discussion involves more than just summarizing findings and describing outcomes. It includes deliberately considering their importance and providing reasoned explanations why your paper helps to fill a gap in the literature or expand knowledge and understanding in ways that inform practice. Critical thinking uses reflection to examine your own beliefs concerning the significance of the results in ways that avoid using biased judgment and decision making.
U sing Questions to Enable Critical Thinking
[CONTENT COMING SOON]
Behar-Horenstein, Linda S., and Lian Niu. “Teaching Critical Thinking Skills in Higher Education: A Review of the Literature.” Journal of College Teaching and Learning 8 (February 2011): 25-41; Bayou, Yemeserach and Tamene Kitila. "Exploring Instructors’ Beliefs about and Practices in Promoting Students’ Critical Thinking Skills in Writing Classes." GIST–Education and Learning Research Journal 26 (2023): 123-154; Butcher, Charity. "Using In-class Writing to Promote Critical Thinking and Application of Course Concepts." Journal of Political Science Education 18 (2022): 3-21; Loseke, Donileen R. Methodological Thinking: Basic Principles of Social Research Design. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2012; Mintz, Steven. "How the Word "Critical" Came to Signify the Leading Edge of Cultural Analysis." Higher Ed Gamma Blog , Inside Higher Ed, February 13, 2024; Hart, Claire et al. “Exploring Higher Education Students’ Critical Thinking Skills through Content Analysis.” Thinking Skills and Creativity 41 (September 2021): 100877; Lewis, Arthur and David Smith. "Defining Higher Order Thinking." Theory into Practice 32 (Summer 1993): 131-137; Sabrina, R., Emilda Sulasmi, and Mandra Saragih. "Student Critical Thinking Skills and Student Writing Ability: The Role of Teachers' Intellectual Skills and Student Learning." Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences 17 (2022): 2493-2510. Suter, W. Newton. Introduction to Educational Research: A Critical Thinking Approach. 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2012; Van Merriënboer, Jeroen JG and Paul A. Kirschner. Ten Steps to Complex Learning: A Systematic Approach to Four-component Instructional Design. New York: Routledge, 2017; Vance, Charles M., et al. "Understanding and Measuring Linear–Nonlinear Thinking Style for Enhanced Management Education and Professional Practice." Academy of Management Learning and Education 6 (2007): 167-185; Yeh, Hui-Chin, Shih-hsien Yang, Jo Shan Fu, and Yen-Chen Shih. "Developing College Students’ Critical Thinking through Reflective Writing." Higher Education Research & Development 42 (2023): 244-259.
- << Previous: Academic Writing Style
- Next: Choosing a Title >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 10:51 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Critical Thinking in Academic Research - Second Edition
(4 reviews)
Cindy Gruwell, University of West Florida
Robin Ewing, St. Cloud State University
Copyright Year: 2022
Last Update: 2023
Publisher: Minnesota State Colleges and Universities
Language: English
Formats Available
Conditions of use.
Learn more about reviews.
Reviewed by Julie Jaszkowiak, Community Faculty, Metropolitan State University on 12/22/23
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III –... read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 5 see less
Organized in 11 parts, this his textbook includes introductory information about critical thinking and details about the academic research process. The basics of critical thinking related to doing academic research in Parts I and II. Parts III – XI provide specifics on various steps in doing academic research including details on finding and citing source material. There is a linked table of contents so the reader is able to jump to a specific section as needed. There is also a works cited page with information and links to works used for this textbook.
Content Accuracy rating: 5
The content of this textbook is accurate and error free. It contains examples that demonstrate concepts from a variety of disciplines such as “hard science” or “popular culture” that assist in eliminating bias. The authors are librarians so it is clear that their experience as such leads to clear and unbiased content.
Relevance/Longevity rating: 5
General concepts about critical thinking and academic research methodology is well defined and should not become obsolete. Specific content regarding use of citation tools and attribution structure may change but the links to various research sites allow for simple updates.
Clarity rating: 5
This textbook is written in a conversational manner that allows for a more personal interaction with the textbook. It is like the reader is having a conversation with a librarian. Each part has an introduction section that fully defines concepts and terms used for that part.
Consistency rating: 5
In addition to the written content, this textbook contains links to short quizzes at the end of each section. This is consistent throughout each part. Embedded links to additional information are included as necessary.
Modularity rating: 4
This textbook is arranged in 11 modular parts with each part having multiple sections. All of these are linked so a reader can go to a distinct part or section to find specific information. There are some links that refer back to previous sections in the document. It can be challenging to return to where you were once you have jumped to a different section.
Organization/Structure/Flow rating: 5
There is clear definition as to what information is contained within each of the parts and subsequent sections. The textbook follows the logical flow of the process of researching and writing a research paper.
Interface rating: 4
The pictures have alternative text that appears when you hover over the text. There is one picture on page 102 that is a link to where the downloaded picture is from. The pictures are clear and supportive of the text for a visual learner. All the links work and go to either the correct area of the textbook or to a valid website. If you are going to use the embedded links to go to other sections of the textbook you need to keep track of where you are as it can sometimes get confusing as to where you went based on clicking links.
Grammatical Errors rating: 4
This is not really a grammatical error but I did notice on some of the quizzes if you misspelled a work for fill in the blank it was incorrect. It was also sometimes challenging to come up with the correct word for the fill in the blanks.
Cultural Relevance rating: 5
There are no examples or text that are culturally insensitive or offensive. The examples are general and would be applicable to a variety of students study many different academic subjects. There are references and information to many research tools from traditional such as checking out books and articles from the library to more current such as blogs and other electronic sources. This information appeals to a wide expanse of student populations.
I really enjoyed the quizzes at the end of each section. It is very beneficial to test your knowledge and comprehension of what you just read. Often I had to return and reread the content more critically based on my quiz results! They are just the right length to not disrupt the overall reading of the textbook and cover the important content and learning objectives.
Reviewed by Sara Stigberg, Adjunct Reference Librarian, Truman College, City Colleges of Chicago on 3/15/23
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices... read more
Critical Thinking in Academic Research thoroughly covers the basics of academic research for undergraduates, including well-guided deeper dives into relevant areas. The authors root their introduction to academic research principles and practices in the Western philosophical tradition, focused on developing students' critical thinking skills and habits around inquiry, rationales, and frameworks for research.
This text conforms to the principles and frames of the Framework for Information Literacy for Higher Education, published by the Association of College and Research Libraries. It includes excellent, clear, step-by-step guides to help students understand rationales and techniques for academic research.
Essential for our current information climate, the authors present relevant information for students who may be new to academic research, in ways and with content that is not too broad or too narrow, or likely to change drastically in the near future.
The authors use clear and well-considered language and explanations of ideas and terms, contextualizing the scholarly research process and tools in a relatable manner. As mentioned earlier, this text includes excellent step-by-step guides, as well as illustrations, visualizations, and videos to instruct students in conducting academic research.
(4.75) The terminology and framework of this text are consistent. Early discussions of critical thinking skills are tied in to content in later chapters, with regard to selecting different types of sources and search tools, as well as rationales for choosing various formats of source references. Consciously making the theme of critical thinking as applied to the stages of academic research more explicit and frequent within the text would further strengthen it, however.
Modularity rating: 5
Chapters are divided in a logical, progressive manner throughout the text. The use of embedded links to further readings and some other relevant sections of the text are an excellent way of providing references and further online information, without overwhelming or side-tracking the reader.
Topics in the text are organized in logical, progressive order, transitioning cleanly from one focus to the next. Each chapter begins with a helpful outline of topics that will be covered within it.
There are no technical issues with the interface for this text. Interactive learning tools such as the many self-checks and short quizzes that are included throughout the text are a great bonus for reinforcing student learning, and the easily-accessible table of contents was very helpful. There are some slight inconsistencies across chapters, however, relative to formatting images and text and spacing, and an image was missing in the section on Narrowing a Topic. Justifying copy rather than aligning-left would prevent hyphenation, making the text more streamlined.
Grammatical Errors rating: 5
(4.75) A few minor punctuation errors are present.
The authors of this text use culturally-relevant examples and inclusive language. The chapter on Barriers to Critical Thinking works directly to break down bias and preconceived notions.
Overall, Critical Thinking in Academic Research is an excellent general textbook for teaching the whys and hows of academic research to undergraduates. A discussion of annotated bibliographies would be a great addition for future editions of the text. ---- (As an aside for the authors, I am curious if the anonymous data from the self-checks and quizzes is being collected and analyzed for assessment purposes. I'm sure it would be interesting!)
Reviewed by Ann Bell-Pfeifer, Program Director/ Instructor, Minnesota State Community and Technical College on 2/15/23
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included. read more
Comprehensiveness rating: 4 see less
The book has in depth coverage of academic research. A formal glossary and index were not included.
The book appears error free and factual.
The content is current and would support students who are pursuing writing academic research papers.
Excellent explanations for specific terms were included throughout the text.
The text is easy to follow with a standardized format and structure.
The text contains headings and topics in each section.
It is easy to follow the format and review each section.
Interface rating: 5
The associated links were useful and not distracting.
No evidence of grammatical errors were found in the book.
The book is inclusive.
The book was informative, easy to follow, and sequential allowing the reader to digest each section before moving into another.
Reviewed by Jenny Inker, Assistant Professor, Virginia Commonwealth University on 8/23/22
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and... read more
This book provides a comprehensive yet easily comprehensible introduction to critical thinking in academic research. The author lays a foundation with an introduction to the concepts of critical thinking and analyzing and making arguments, and then moves into the details of developing research questions and identifying and appropriately using research sources. There are many wonderful links to other open access publications for those who wish to read more or go deeper.
The content of the book appears to be accurate and free of bias.
The examples used throughout the book are relevant and up-to-date, making it easy to see how to apply the concepts in real life.
The text is very accessibly written and the content is presented in a simple, yet powerful way that helps the reader grasp the concepts easily. There are many short, interactive exercises scattered throughout each chapter of the book so that the reader can test their own knowledge as they go along. It would be even better if the author had provided some simple feedback explaining why quiz answers are correct or incorrect in order to bolster learning, but this is a very minor point and the interactive exercises still work well without this.
The book appears consistent throughout with regard to use of terminology and tone of writing. The basic concepts introduced in the early chapters are used consistently throughout the later chapters.
This book has been wonderfully designed into bite sized chunks that do not overwhelm the reader. This is perhaps its best feature, as this encourages the reader to take in a bit of information, digest it, check their understanding of it, and then move on to the next concept. I loved this!
The book is organized in a manner that introduces the basic architecture of critical thinking first, and then moves on to apply it to the subject of academic research. While the entire book would be helpful for college students (undergraduates particularly), the earlier chapters on critical thinking and argumentation also stand well on their own and would be of great utility to students in general.
This book was extremely easy to navigate with a clear, drop down list of chapters and subheadings on the left side of the screen. When the reader clicks on links to additional material, these open up in a new tab which keeps things clear and organized. Images and charts were clear and the overall organization is very easy to follow.
I came across no grammatical errors in the text.
Cultural Relevance rating: 4
This is perhaps an area where the book could do a little more. I did not come across anything that seemed culturally insensitive or offensive but on the other hand, the book might have taken more opportunities to represent a greater diversity of races, ethnicities, and backgrounds.
This book seems tailor made for undergraduate college students and I would highly recommend it. I think it has some use for graduate students as well, although some of the examples are perhaps little basic for this purpose. As well as using this book to guide students on doing academic research, I think it could also be used as a very helpful introduction to the concept of critical thinking by focusing solely on chapters 1-4.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Part I. What is Critical Thinking?
- Part II. Barriers to Critical Thinking
- Part III. Analyzing Arguments
- Part IV. Making an Argument
- Part V. Research Questions
- Part VI. Sources and Information Needs
- Part VII. Types of Sources
- Part VIII. Precision Searching
- Part IX. Evaluating Sources
- Part X. Ethical Use and Citing Sources
- Part XI. Copyright Basics
- Works Cited
- About the Authors
Ancillary Material
About the book.
Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as well as additional interactive elements throughout the text.
About the Contributors
Cindy Gruwell is an Assistant Librarian/Coordinator of Scholarly Communication at the University of West Florida. She is the library liaison to the department of biology and the College of Health which has extensive nursing programs, public health, health administration, movement, and medical laboratory sciences. In addition to supporting health sciences faculty, she oversees the Argo IRCommons (Institutional Repository) and provides scholarly communication services to faculty across campus. Cindy graduated with her BA (history) and MLS from the University of California, Los Angeles and has a Masters in Education from Bemidji State University. Cindy’s research interests include academic research support, publishing, and teaching.
Robin Ewing is a Professor/Collections Librarian at St. Cloud State University. Robin is the liaison to the College of Education and Learning Design. She oversees content selection for the Library’s collections. Robin graduated with her BBA (Management) and MLIS from the University of Oklahoma. She also has a Masters of Arts in Teaching from Bemidji State University. Robin’s research interests include collection analysis, assessment, and online teaching.
Contribute to this Page

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What is Analytical Thinking: An Introduction
Get introduced to "Analytical Thinking" with this comprehensive blog. Delve into the core concept of analytical thinking, exploring its characteristics such as curiosity, systematic approach, problem-solving aptitude and open-mindedness. By the end of this exploration, you'll have a clear understanding of what analytical thinking is and why it's a crucial skill.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Leadership Skills Training
- Instructional Design Training
- Design Thinking Course
- Business Development Training
- Leadership and Management Course

Table of Contents
1) What is Analytical Thinking?
2) Why is Analytical Thinking important?
3) Important elements of Analytical Thinking
4) How to master Analytical Thinking?
5) Conclusion
What is Analytical Thinking ?
Analytical Thinking is the cognitive process of dissecting intricate problems, data, or situations into smaller components to discern patterns, relationships, and underlying principles. It involves critical observation, logical reasoning, and systematic analysis to arrive at informed conclusions or solutions.

Why is Analytical Thinking important?
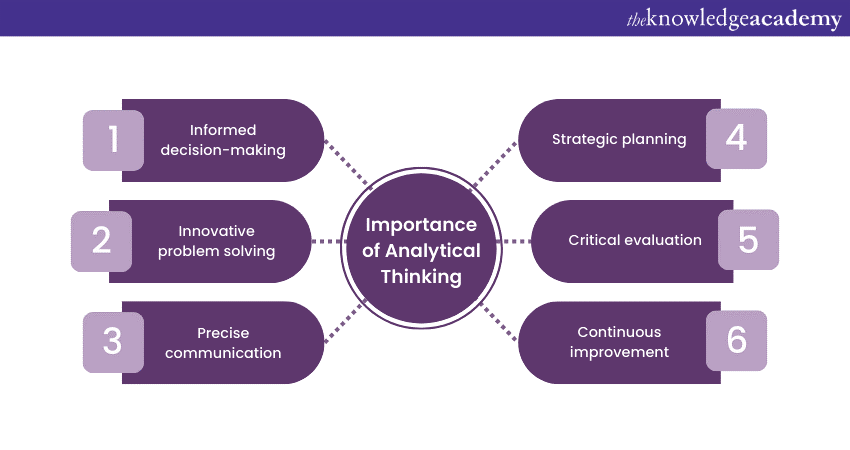
Informed decision-making
At its core, Analytical Thinking equips individuals with the tools to dissect intricate scenarios, distil pertinent information, and make informed decisions. From someone pondering a career move, considering a significant investment to someone deciding on a course of action, Analytical Thinking allows you to assess the pros and cons, identify potential pitfalls, and forecast outcomes.
Innovative problem solving
Innovation often springs from the ability to connect disparate dots and unearth hidden solutions. Analytical thinkers possess the capability for dissecting complex problems, breaking them into manageable components, and reassembling them in novel ways. This cognitive dexterity breeds innovation, as it enables individuals to envision alternative paths and approaches that might otherwise remain concealed.
Precise communication
Clear and effective communication is essential in all walks of life. Analytical Thinking fosters the capacity to organise thoughts logically, structure arguments coherently, and present ideas with precision. Regardless of whether you're explaining a concept to a colleague, delivering a persuasive pitch, or writing a research paper, the analytical thinker's ability to present complex ideas succinctly and comprehensibly is an invaluable asset.
Strategic planning
From business strategies to personal goals, strategic planning hinges on the ability to anticipate outcomes, devise contingencies, and adapt to changing circumstances. Analytical Thinking lends itself to strategic prowess by enabling individuals to assess multiple variables, foresee potential roadblocks, and chart a course that maximises the likelihood of success.
Critical evaluation
In a world rife with misinformation and biased narratives, the skill of critical evaluation is more crucial than ever. Analytical Thinking empowers individuals to sift through a barrage of information, discern credible sources, and separate fact from fiction. This aptitude for discernment is a bulwark against being swayed by superficial allure or baseless assertions.
Continuous improvement
Analytical thinkers possess an innate curiosity that propels them towards constant learning and growth. They see challenges not as insurmountable obstacles but as opportunities for enhancement. This drive for self-improvement extends beyond their capabilities; analytical thinkers often seek to refine processes, systems, and products, contributing to advancing their fields and industries.
Unlock your creative potential and enhance your Analytical Thinking skills with our comprehensive Creative and Analytical Thinking Training !
Important Elements of Analytical Thinking
Now that you know the meaning of Analytical Thinking, let's explore its characteristics. Analytical Thinking is more than a mere mental exercise; it's a unique cognitive approach that involves a specific set of traits and habits. Those with these characteristics are adept at dissecting complexities, drawing insights from data, and arriving at well-reasoned conclusions. Here are the key attributes that define Analytical thinkers:
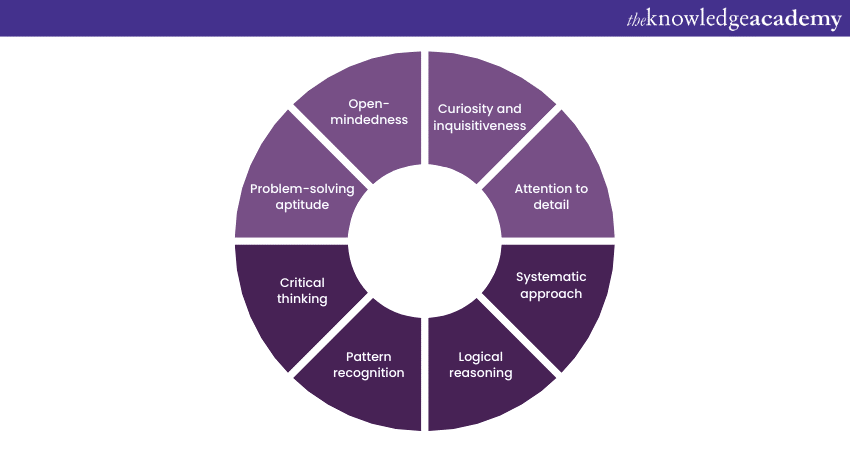
Curiosity and inquisitiveness
Analytical Thinkers exhibit a natural curiosity about the world around them. They possess an insatiable desire to understand how things work and why they are the way they are. This curiosity fuels their exploration of concepts, data, and problems, leading them to uncover hidden connections and unexpected insights.
Attention to detail
One of the hallmarks of Analytical Thinking is an unwavering attention to detail. Analytical individuals have a knack for spotting even the minutest discrepancies, anomalies, or patterns within data or scenarios that might go unnoticed by others. This acute attention to detail is instrumental in identifying potential issues and crafting precise solutions.
Systematic approach
Analytical Thinkers approach problems methodically. They break down complex issues into manageable parts, which allows them to analyse each component individually before synthesising a comprehensive understanding. This systematic approach enables them to unravel intricate challenges and address them step by logically.
Logical reasoning
Logical reasoning is the bedrock of Analytical Thinking . Those who possess this trait are skilled at constructing and deconstructing arguments, identifying flaws in reasoning, and evaluating the validity of information. This ability helps them sift through the noise and reach well-founded conclusions based on evidence and logic.
Pattern recognition
Analytical Thinkers excel at recognising patterns and trends across various data sets or scenarios. They have an innate ability to identify similarities and differences, allowing them to generalise principles from specific instances and apply them to broader contexts.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is a cornerstone of Analytical Thinking . Individuals with this characteristic are not content with accepting information at face value; they question assumptions, challenge norms, and seek underlying reasons. This intellectual rigour ensures that their conclusions are well-substantiated and comprehensive.
Problem-solving aptitude
Analytical Thinkers thrive on solving complex problems. They approach challenges with a blend of creativity and logic, devising innovative solutions that address the root causes rather than merely treating symptoms. Their ability to dissect problems and explore multiple angles empowers them to tackle even the most daunting issues.
Open-mindedness
While Analytical Thinkers possess strong reasoning skills, they also embrace open-mindedness. They acknowledge that not all problems have linear solutions and are willing to explore unconventional ideas and viewpoints. This adaptability allows them to adapt their approach when encountering new and unexpected scenarios.
Unlock your potential with our Decision-Making Skills Training - empower your choices and lead with confidence!
How to master Analytical Thinking?
In order to master your Analytical Thinking skills, you can adapt the following skills:
1) Analysing information involves thoroughly examining data or a situation to identify crucial elements, assess their strengths and weaknesses, and leverage this understanding to construct a compelling argument, offer recommendations, or address a problem effectively.
2) Breaking down problems simplifies significant challenges by dividing them into more minor, manageable issues that are easier to solve individually.
3) Gathering information requires asking pertinent questions of oneself and others to gain valuable insights, facilitating more informed decision-making when tackling problems.
4) Identifying issues and problems involves honing the skill of recognising underlying issues or challenges through analysing trends, associations, and cause-effect relationships within datasets.
5) Identifying the root cause is conducting a thorough analysis to pinpoint the fundamental cause of a problem, ensuring that efforts are focused on addressing the actual issue rather than just its symptoms.
6) Organising information entails systematically arranging and integrating all collected data to derive insights and generate ideas, laying the groundwork for potential solutions to the problems at hand.
Conclusion
Analytical Thinking emerges as an invaluable beacon in a world demanding ever-greater insight and adaptability. Its ability to unravel complexity, innovate solutions, and foster critical evaluation empowers individuals across diverse domains. By cultivating a curious mind, attention to detail and logic, we can get started on a journey of continuous improvement. Hope we could answer all your queries about “What is Analytical Thinking”!
Unlock your l eadership potential with our comprehensive Leadership Training - J oin now for a transformative learning journey!
Frequently Asked Questions
Here's how you can enhance Analytical Thinking skills:
a) Practice regularly: Solve puzzles and engage in analytical games.
b) Read widely: Explore diverse topics for a broader perspective.
c) Critical reflection: Reflect on experiences and decisions critically.
d) Ask questions: Challenge information and seek underlying reasons.
e) Break down issues: Analyse complex problems by breaking them into parts.
f) Seek feedback: Discuss analyses with peers for valuable insights.
g) Learn from mistakes: Analyse failures for continuous improvement.
h) Data literacy: Understand and interpret data for informed decisions.
i) Stay curious: Cultivate curiosity to explore various problem angles.
j) Take on projects: Apply analytical skills in practical scenarios for hands-on experience.
Analytical Thinking is vital for career growth, enabling strategic decision-making and effective problem-solving. It empowers professionals to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and drive innovation. Those skilled in Analytical Thinking excel in strategic planning, problem-solving, and efficient decision-making. They contribute to organisational success by optimising operations, fostering innovation, and exhibiting leadership qualities. This skill enhances adaptability in dynamic environments, encourages continuous learning, and improves communication with diverse stakeholders.
Individuals with strong analytical skills can create detailed plans, identify critical milestones, and allocate resources efficiently by breaking down complex projects into manageable components. This approach allows setting of precise timelines and realistic goal-setting. Analytical thinkers excel at anticipating potential challenges, enabling proactive problem-solving and risk mitigation. They prioritise tasks based on strategic importance and resource availability, ensuring optimal time utilisation. Additionally, Analytical Thinking aids in assessing project progress through data analysis, facilitating informed adjustments when necessary.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide. Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue , encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA . The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses , including Leadership Skills, Creative Leader Thinking and Creative and Analytical Thinking. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Leadership Qualities Our Leadership Training blogs covers a range of topics related to leadership and analytical thinking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Leadership skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 7th Jun 2024
Fri 2nd Aug 2024
Fri 4th Oct 2024
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Writing to Think: Critical Thinking and the Writing Process
“Writing is thinking on paper.” (Zinsser, 1976, p. vii)
Google the term “critical thinking.” How many hits are there? On the day this tutorial was completed, Google found about 65,100,000 results in 0.56 seconds. That’s an impressive number, and it grows more impressively large every day. That’s because the nation’s educators, business leaders, and political representatives worry about the level of critical thinking skills among today’s students and workers.
What is Critical Thinking?
Simply put, critical thinking is sound thinking. Critical thinkers work to delve beneath the surface of sweeping generalizations, biases, clichés, and other quick observations that characterize ineffective thinking. They are willing to consider points of view different from their own, seek and study evidence and examples, root out sloppy and illogical argument, discern fact from opinion, embrace reason over emotion or preference, and change their minds when confronted with compelling reasons to do so. In sum, critical thinkers are flexible thinkers equipped to become active and effective spouses, parents, friends, consumers, employees, citizens, and leaders. Every area of life, in other words, can be positively affected by strong critical thinking.
Released in January 2011, an important study of college students over four years concluded that by graduation “large numbers [of American undergraduates] didn’t learn the critical thinking, complex reasoning and written communication skills that are widely assumed to be at the core of a college education” (Rimer, 2011, para. 1). The University designs curriculum, creates support programs, and hires faculty to help ensure you won’t be one of the students “[showing]no significant gains in . . . ‘higher order’ thinking skills” (Rimer, 2011, para. 4). One way the University works to help you build those skills is through writing projects.
Writing and Critical Thinking
Say the word “writing” and most people think of a completed publication. But say the word “writing” to writers, and they will likely think of the process of composing. Most writers would agree with novelist E. M. Forster, who wrote, “How can I know what I think until I see what I say?” (Forster, 1927, p. 99). Experienced writers know that the act of writing stimulates thinking.
Inexperienced and experienced writers have very different understandings of composition. Novice writers often make the mistake of believing they have to know what they’re going to write before they can begin writing. They often compose a thesis statement before asking questions or conducting research. In the course of their reading, they might even disregard material that counters their pre-formed ideas. This is not writing; it is recording.
In contrast, experienced writers begin with questions and work to discover many different answers before settling on those that are most convincing. They know that the act of putting words on paper or a computer screen helps them invent thought and content. Rather than trying to express what they already think, they express what the act of writing leads them to think as they put down words. More often than not, in other words, experienced writers write their way into ideas, which they then develop, revise, and refine as they go.
What has this notion of writing to do with critical thinking? Everything.
Consider the steps of the writing process: prewriting, outlining, drafting, revising, editing, seeking feedback, and publishing. These steps are not followed in a determined or strict order; instead, the effective writer knows that as they write, it may be necessary to return to an earlier step. In other words, in the process of revision, a writer may realize that the order of ideas is unclear. A new outline may help that writer re-order details. As they write, the writer considers and reconsiders the effectiveness of the work.
The writing process, then, is not just a mirror image of the thinking process: it is the thinking process. Confronted with a topic, an effective critical thinker/writer
- asks questions
- seeks answers
- evaluates evidence
- questions assumptions
- tests hypotheses
- makes inferences
- employs logic
- draws conclusions
- predicts readers’ responses
- creates order
- drafts content
- seeks others’ responses
- weighs feedback
- criticizes their own work
- revises content and structure
- seeks clarity and coherence
Example of Composition as Critical Thinking
“Good writing is fueled by unanswerable questions” (Lane, 1993, p. 15).
Imagine that you have been asked to write about a hero or heroine from history. You must explain what challenges that individual faced and how they conquered them. Now imagine that you decide to write about Rosa Parks and her role in the modern Civil Rights movement. Take a moment and survey what you already know. She refused to get up out of her seat on a bus so a White man could sit in it. She was arrested. As a result, Blacks in Montgomery protested, influencing the Montgomery Bus Boycott. Martin Luther King, Jr. took up leadership of the cause, and ultimately a movement was born.
Is that really all there is to Rosa Parks’s story? What questions might a thoughtful writer ask? Here a few:
- Why did Rosa Parks refuse to get up on that particular day?
- Was hers a spontaneous or planned act of defiance?
- Did she work? Where? Doing what?
- Had any other Black person refused to get up for a White person?
- What happened to that individual or those individuals?
- Why hadn’t that person or those persons received the publicity Parks did?
- Was Parks active in Civil Rights before that day?
- How did she learn about civil disobedience?
Even just these few questions could lead to potentially rich information.
Factual information would not be enough, however, to satisfy an assignment that asks for an interpretation of that information. The writer’s job for the assignment is to convince the reader that Parks was a heroine; in this way the writer must make an argument and support it. The writer must establish standards of heroic behavior. More questions arise:
- What is heroic action?
- What are the characteristics of someone who is heroic?
- What do heroes value and believe?
- What are the consequences of a hero’s actions?
- Why do they matter?
Now the writer has even more research and more thinking to do.
By the time they have raised questions and answered them, raised more questions and answered them, and so on, they are ready to begin writing. But even then, new ideas will arise in the course of planning and drafting, inevitably leading the writer to more research and thought, to more composition and refinement.
Ultimately, every step of the way over the course of composing a project, the writer is engaged in critical thinking because the effective writer examines the work as they develop it.
Why Writing to Think Matters
Writing practice builds critical thinking, which empowers people to “take charge of [their] own minds” so they “can take charge of [their] own lives . . . and improve them, bringing them under [their] self command and direction” (Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2020, para. 12). Writing is a way of coming to know and understand the self and the changing world, enabling individuals to make decisions that benefit themselves, others, and society at large. Your knowledge alone – of law, medicine, business, or education, for example – will not be enough to meet future challenges. You will be tested by new unexpected circumstances, and when they arise, the open-mindedness, flexibility, reasoning, discipline, and discernment you have learned through writing practice will help you meet those challenges successfully.
Forster, E.M. (1927). Aspects of the novel . Harcourt, Brace & Company.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking. (2020, June 17). Our concept and definition of critical thinking . https://www.criticalthinking.org/pages/our-concept-of-critical-thinking/411
Lane, B. (1993). After the end: Teaching and learning creative revision . Heinemann.
Rimer, S. (2011, January 18). Study: Many college students not learning to think critically . The Hechinger Report. https://www.mcclatchydc.com/news/nation-world/national/article24608056.html
Zinsser, W. (1976). On writing well: The classic guide to writing nonfiction . HarperCollins.
Share this:
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
Follow Blog via Email
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive email notifications of new posts.
Email Address
- RSS - Posts
- RSS - Comments
- COLLEGE WRITING
- USING SOURCES & APA STYLE
- EFFECTIVE WRITING PODCASTS
- LEARNING FOR SUCCESS
- PLAGIARISM INFORMATION
- FACULTY RESOURCES
- Student Webinar Calendar
- Academic Success Center
- Writing Center
- About the ASC Tutors
- DIVERSITY TRAINING
- PG Peer Tutors
- PG Student Access
Subscribe to Blog via Email
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
- College Writing
- Using Sources & APA Style
- Learning for Success
- Effective Writing Podcasts
- Plagiarism Information
- Faculty Resources
- Tutor Training
Twitter feed
Academic Writing: Critical Thinking & Writing
- Academic Writing
- Planning your writing
- Structuring your assignment
- Critical Thinking & Writing
- Building an argument
- Reflective Writing
- Summarising, paraphrasing and quoting
Critical Thinking
One of the most important features of studying at university is the expectation that you will engage in thinking critically about your subject area.
Critical thinking involves asking meaningful questions concerning the information, ideas, beliefs, and arguments that you will encounter. It requires you to approach your studies with a curious, open mind, discard preconceptions, and interrogate received knowledge and established practices.
Critical thinking is key to successfully expressing your individuality as an independent learner and thinker in an academic context. It is also a valuable life skill.
Critical thinking enables you to:
- Evaluate information, its validity and significance in a particular context.
- Analyse and interpret evidence and data in response to a line of enquiry.
- Weigh-up alternative explanations and arguments.
- Develop your own evidence-based and well-reasoned arguments.
- Develop well-informed viewpoints.
- Formulate your own independent, justifiable ideas.
- Actively engage with the wider scholarship of your academic community.
Writing Critically
Being able to demonstrate and communicate critical thinking in your written assignments through critical writing is key to achieving academic success.
Critical writing can be distinguished from descriptive writing which is concerned with conveying information rather than interrogating information. Understanding the difference between these two styles of academic writing and when to use them is important.
The balance between descriptive writing and critical writing will vary depending on the nature of the assignment and the level of your studies. Some level of descriptive writing is generally necessary to support critical writing. More sophisticated criticality is generally required at higher levels of study with less descriptive content. You will continue to develop your critical writing skills as you progress through your course.
Descriptive Writing and Critical Writing
- Descriptive Writing
- Critical Writing
- Examples of Critical Writing
Descriptive writing demonstrates the knowledge you have of a subject, and your knowledge of what other people say about that subject. Descriptive writing often responds to questions framed as ‘what’ , ‘where’ , ‘who’ and ‘when’ .
Descriptive writing might include the following:
- Description of what something is or what it is about (an account, facts, observable features, details): a topic, problem, situation, or context of the subject under discussion.
- Description of where it takes place (setting and context), who is involved and when it occurs.
- Re-statement or summary of what others say about the topic.
- Background facts and information for a discussion.
Description usually comes before critical content so that the reader can understand the topic you are critically engaging with.
Critical writing requires you to apply interpretation, analysis, and evaluation to the descriptions you have provided. Critical writing often responds to questions framed as ‘how’ or ‘why’ . Often, critical writing will require you to build an argument which is supported by evidence.
Some indicators of critical writing are:
- Investigation of positive and negative perspectives on ideas
- Supporting ideas and arguments with evidence, which might include authoritative sources, data, statistics, research, theories, and quotations
- Balanced, unbiased appraisal of arguments and counterarguments/alternative viewpoints
- Honest recognition of the limitations of an argument and supporting evidence
- Plausible, rational, convincing, and well-reasoned conclusions
Critical writing might include the following:
- Applying an idea or theory to different situations or relate theory to practice. Does the idea work/not work in practice? Is there a factor that makes it work/not work? For example: 'Smith's (2008) theory on teamwork is effective in the workplace because it allows a diverse group of people with different skills to work effectively'.
- Justifying why a process or policy exists. For example: 'It was necessary for the nurse to check the patient's handover notes because...'
- Proposing an alternative approach to view and act on situations. For example: 'By adopting a Freirian approach, we could view the student as a collaborator in our teaching and learning'. Or: 'If we had followed the NMC guidelines we could have made the patient feel calm and relaxed during the consultation'.
- Discussion of the strengths and weaknesses of an idea/theory/policy. Why does this idea/theory/policy work? Or why does this idea not work? For example: 'Although Smith's (2008) theory on teamwork is useful for large teams, there are challenges in applying this theory to teams who work remotely'.
- Discussion of how the idea links to other ideas in the field (synthesis). For example: 'the user experience of parks can be greatly enhanced by examining Donnelly's (2009) customer service model used in retail’.
- Discussion of how the idea compares and contrasts with other ideas/theories. For example: ‘The approach advocated by the NMC differs in comparison because of factor A and factor C’.
- Discussion of the ‘’up-to-datedness” and relevance of an idea/theory/policy (its currency). For example: 'although this approach was successful in supporting the local community, Smith's model does not accommodate the needs of a modern global economy'.
- Evaluating an idea/theory/policy by providing evidence-informed judgment. For example: 'Therefore, May's delivery model should be discontinued as it has created significant issues for both customers and staff (Ransom, 2018)'.
- Creating new perspectives or arguments based on knowledge. For example: 'to create strong and efficient buildings, we will look to the designs provided by nature. The designs of the Sydney Opera House are based on the segments of an orange (Cook, 2019)'.
Further Reading
- << Previous: Structuring your assignment
- Next: Building an argument >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 3:27 PM
- URL: https://libguides.uos.ac.uk/academic-writing
➔ About the Library
➔ Meet the Team
➔ Customer Service Charter
➔ Library Policies & Regulations
➔ Privacy & Data Protection
Essential Links
➔ A-Z of eResources
➔ Frequently Asked Questions
➔Discover the Library
➔Referencing Help
➔ Print & Copy Services
➔ Service Updates
Library & Learning Services, University of Suffolk, Library Building, Long Street, Ipswich, IP4 1QJ
✉ Email Us: [email protected]
✆ Call Us: +44 (0)1473 3 38700
- About us
Analytical thinking skills: definition, examples & ways to improve
Analytical skills are required in every industry. They help employees investigate a problem and find an efficient solution for companies’ success. In this article, we’ll explore why analytical skills matter, how to highlight them in various scenarios, and improve.
What’s analytical thinking?
Analytical thinking involves the research and analysis of complex issues for developing new ideas or finding solutions. Analytical skills are critical for work and listed as required in many job descriptions.
When do we use our analytical skills at work?
We need analytical skills for working with data and brainstorming ideas, solutions, and making decisions based on factors and options.
When we use critical thinking at work, we follow several steps before we create an idea or find a solution. The result of analytical thinking is usually followed by gathering and analyzing information.
Why are analytical thinking skills important?
Analytical skills are crucial because they allow you to solve problems and make decisions. These abilities are in demand by many employers in various industries.
Nowadays job applicants are measured both by hard and soft skills. Analytical skills are soft skills you can use in any industry. They show the level of professionalism, so you can highlight them if you want to get a job.
Companies value employees’ analytical skills because they help them achieve corporate goals and stay competitive on the market. Understanding problems and analyzing the situation are vital for every business.
Many jobs require using analytical thinking, including programming, customer service, teaching, marketing, and others. Some positions may require industry-specific hard skills, too. Still, analytical skills can be transferred to every industry. If you have strong analytical skills, you can apply for many vacancies.
5 must-have analytical skills
Many valuable analytical skills are worth including on your resume. Here are five must-have skills.
Creative thinking
Creative thinking relates to problem-solving and is a key skill for many jobs. To analyze information you need to be creative to notice hidden spots or trends not everyone can see. Creative thinkers can find a non-trivial solution that is more valuable than the obvious one. Creative people think outside the box to work out an effective solution or brainstorm ideas.
If you are a creative thinker, you will be able to:
- Optimize processes and operations.
- Collaborate for brainstorming with others.
- Solve complex problems in a non-trivial way.
- Think strategically.
- Integrate massive volumes of information into existing solutions.
Conducting an in-depth research is an integral part of analytical thinking. To solve a problem, you need to learn more about it. In simple words, you need to gather information before analyzing it.
This part of the analytical thinking process can involve various types of research and depends on the source of data. You can do online research, gathering information by comparing competitives, reviewing official documents, or interviewing experts, etc. It’s also valuable to know what kind of data is required for problem-solving.
To conduct a research, you need to be able to:
- Investigate the topic based on different data sources.
- Work with metrics.
- Prioritize data sources.
- Pay attention to the accuracy of the collected data.
Data analysis
Data analysis is one of the most crucial parts of analytical thinking. To solve a problem, you need to be able to analyze the information for identifying trends in a large volume of raw data. It is not enough to just read the information; you need to understand which information is worth highlighting for decision-making.
Using analytical thinking, you may need to be able to conduct some of the types of data analysis below:
- Quantitative/qualitative analysis
- Business analysis
- Industry or competitor analysis
- ROI analysis
- Process/Operational analysis
- Financial analysis
Problem-solving
After you collect and analyze the information, you need to identify the problem. Once it’s identified, you can find a reasonable solution. How? With your problem-solving skills, you need to be able to sort the data to find a rational and effective solution.
Sometimes you may need to identify small problems that cause a more significant way. Problem-solving skills will help you detect them and prevent a bigger one.
Communication
It’s useful to be able to research, analyze, and solve problems, but it means nothing if you lack compelling communication skills. Working with a team, you need to express your idea as clearly as you can. An effective communicator will not only solve the problem but will also save time.
How to show analytical skills?
Now you understand which of the analytical skills you possess, you need to know how to highlight them to do your best at getting a job or growing your career.
Mention on your resume
Including analytical skills on your resume, you will make it more attractive for employers. You can include them in the following sections:
- Professional history
Tell in the job interview
When telling about your working experience, be as specific as you can. Give detailed responses and show how analytical skills improved or solved your former employer’s issues. You may also be offered to do a pre-employment test to show your analytical skills.
Use at the workplace
Once you get a job, don’t stop using analytical skills. Be proactive in solving problems. Don’t be afraid of being a volunteer to participate in problem-solving and decision-making. It will be a great opportunity to highlight the analytical skills you possess.
7 ways to improve analytical skills
Like other skills, analytical thinking skills are natural but not inborn. To land a job you want or succeed in professional growth, you need to improve analytical skills. Use these tips we’ve worked out for students and employees who are interested in developing analytical skills.
1. Play brain games
If you want to improve analytical skills, you play brain games like chess, Sudoku, puzzles, and others. They can help you train thinking critically. Playing 15-20 minutes a day can stimulate your brain function and strengthen analytical skills.
Brain games are fun and make your pastime more productive. Instead of watching TV all evening, play a brain game alone or with your family. The best part is that you can play them online wherever you are.
LogicLike is an excellent brain training app with access to 3500 tasks in your smartphone for free. This is a unique platform with a systematized complex that makes up the best collection of brain games up to date. At any point, you can run a memory test or IQ quiz to check the progress and focus on improving your thinking skills.
LogicLike’s games include:
- Logic games
- 3D-thinking: spatial games
- True or false
- Smart counting
- Scaling and transfusion
- Chess problems for rookies
- Games in tables: honeycombs, Sudoku, kakuro

- Flexible mind and confidence Training on LogicLike, you develop logical reasoning, savvy and self-confidence!
- Good foundation for career growth We teach to deal with information efficiently and develop logic!
- Great for any age LogicLike is fun and helpful activity for kids and adults!
2. Take an online course on a new topic
After graduating from university, we may become passive about learning new things. Once we get a job and know what we are good at, we stop learning and may relax for some time.
Indeed, education plays an important part in professional growth. You should try to expand your knowledge to stay competitive in the job market.
You can take up an online course on the topic you are not good at. For example, not many employers are advanced users of MS Word. If you have time for education, it’s time to challenge yourself with a new topic. You will not only get new knowledge but also improve your analytical skills, including data research and analysis.
3. Solve math problems
Mathematics involves logic and solving a problem step-by-step. Since all math problems are based on logic, solving them will sharpen your analytical skills.
Practice various forms of math problems that will build your problem-solving abilities. You can visit additional math classes at college or university. Reasoning with others will also develop your communication skills. If you prefer doing it online, you can download an app with math games on your smartphone.
More than 150,000 users all over the world keep their brain toned thanks to Logiclike.
4. Participate in debates
Debates are one of the best activities that improve analytical skills, ranging from research to communication. If you are unfamiliar with this activity, you should try it. You can join your local debate club or organize a debate evening with your friends.
Why is it useful for analytical skills?
Taking part in a debate, you become more sociable because you meet new people and discuss various topics. To be well-prepared for debates, you need to research the topic, ask questions, and be ready with substantial arguments.
Debates are an efficient way to challenge yourself and improve your analytical skills.
5. Join online communities
Online communities are a good place to find like-minded people to discuss any issue you are interested in. Researching and reasoning together with other community members will encourage your analytical skills.
Don’t be shy when you need to ask or express your point of view. Anyway, you are there for getting new knowledge or sharing your ideas with others.
6. Develop curiosity by asking questions
Asking questions is the inborn talent we use from childhood. Indeed, questions are a good tool for developing curiosity. Curious people are more motivated and creative.
When you are interested in any topic, don’t be afraid of asking questions. Ask anyone who is an expert in the field of knowledge are you are interested in. Finally, the more questions you ask, the more answers and information you get.
After all, curiosity encourages us to ask questions. Don’t leave them unanswered!
7. Never make quick and crash decisions
To be an efficient problem-solver, you need to take time to think about the problem. Thinking about things and considering multiple factors and options are good habits if you want to develop analytical things.
Useful tips to have at hand:
- Analyze different scenarios of the solution you find to solve the problem. Think of their pros and cons.
- Consider the solution from multiple sides before you choose the best option.
- Don’t choose the easiest solution that lays on the surface. If you think more, you may find another solution that is more efficient.
Key takeaways:
- Analytical skills are soft skills required in many industry fields.
- Among the must-have analytical skills are creative thinking, research, data analysis, problem-solving, and communication.
- You can highlight your analytical skills on your resume, on the job, and at the workplace.
- You need to improve your analytical skills. You can play brain games, take an online course on a new topic, solve math problems, join a debate club, or online communities.
More than 550,000 parents from all over the world are already improving thinking skills with their kids.
8.5 Writing Process: Creating an Analytical Report
Learning outcomes.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify the elements of the rhetorical situation for your report.
- Find and focus a topic to write about.
- Gather and analyze information from appropriate sources.
- Distinguish among different kinds of evidence.
- Draft a thesis and create an organizational plan.
- Compose a report that develops ideas and integrates evidence from sources.
- Give and act on productive feedback to works in progress.
You might think that writing comes easily to experienced writers—that they draft stories and college papers all at once, sitting down at the computer and having sentences flow from their fingers like water from a faucet. In reality, most writers engage in a recursive process, pushing forward, stepping back, and repeating steps multiple times as their ideas develop and change. In broad strokes, the steps most writers go through are these:
- Planning and Organization . You will have an easier time drafting if you devote time at the beginning to consider the rhetorical situation for your report, understand your assignment, gather ideas and information, draft a thesis statement, and create an organizational plan.
- Drafting . When you have an idea of what you want to say and the order in which you want to say it, you’re ready to draft. As much as possible, keep going until you have a complete first draft of your report, resisting the urge to go back and rewrite. Save that for after you have completed a first draft.
- Review . Now is the time to get feedback from others, whether from your instructor, your classmates, a tutor in the writing center, your roommate, someone in your family, or someone else you trust to read your writing critically and give you honest feedback.
- Revising . With feedback on your draft, you are ready to revise. You may need to return to an earlier step and make large-scale revisions that involve planning, organizing, and rewriting, or you may need to work mostly on ensuring that your sentences are clear and correct.
Considering the Rhetorical Situation
Like other kinds of writing projects, a report starts with assessing the rhetorical situation —the circumstance in which a writer communicates with an audience of readers about a subject. As the writer of a report, you make choices based on the purpose of your writing, the audience who will read it, the genre of the report, and the expectations of the community and culture in which you are working. A graphic organizer like Table 8.1 can help you begin.
Summary of Assignment
Write an analytical report on a topic that interests you and that you want to know more about. The topic can be contemporary or historical, but it must be one that you can analyze and support with evidence from sources.
The following questions can help you think about a topic suitable for analysis:
- Why or how did ________ happen?
- What are the results or effects of ________?
- Is ________ a problem? If so, why?
- What are examples of ________ or reasons for ________?
- How does ________ compare to or contrast with other issues, concerns, or things?
Consult and cite three to five reliable sources. The sources do not have to be scholarly for this assignment, but they must be credible, trustworthy, and unbiased. Possible sources include academic journals, newspapers, magazines, reputable websites, government publications or agency websites, and visual sources such as TED Talks. You may also use the results of an experiment or survey, and you may want to conduct interviews.
Consider whether visuals and media will enhance your report. Can you present data you collect visually? Would a map, photograph, chart, or other graphic provide interesting and relevant support? Would video or audio allow you to present evidence that you would otherwise need to describe in words?
Another Lens. To gain another analytic view on the topic of your report, consider different people affected by it. Say, for example, that you have decided to report on recent high school graduates and the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the final months of their senior year. If you are a recent high school graduate, you might naturally gravitate toward writing about yourself and your peers. But you might also consider the adults in the lives of recent high school graduates—for example, teachers, parents, or grandparents—and how they view the same period. Or you might consider the same topic from the perspective of a college admissions department looking at their incoming freshman class.
Quick Launch: Finding and Focusing a Topic
Coming up with a topic for a report can be daunting because you can report on nearly anything. The topic can easily get too broad, trapping you in the realm of generalizations. The trick is to find a topic that interests you and focus on an angle you can analyze in order to say something significant about it. You can use a graphic organizer to generate ideas, or you can use a concept map similar to the one featured in Writing Process: Thinking Critically About a “Text.”
Asking the Journalist’s Questions
One way to generate ideas about a topic is to ask the five W (and one H) questions, also called the journalist’s questions : Who? What? When? Where? Why? How? Try answering the following questions to explore a topic:
Who was or is involved in ________?
What happened/is happening with ________? What were/are the results of ________?
When did ________ happen? Is ________ happening now?
Where did ________ happen, or where is ________ happening?
Why did ________ happen, or why is ________ happening now?
How did ________ happen?
For example, imagine that you have decided to write your analytical report on the effect of the COVID-19 shutdown on high-school students by interviewing students on your college campus. Your questions and answers might look something like those in Table 8.2 :
Asking Focused Questions
Another way to find a topic is to ask focused questions about it. For example, you might ask the following questions about the effect of the 2020 pandemic shutdown on recent high school graduates:
- How did the shutdown change students’ feelings about their senior year?
- How did the shutdown affect their decisions about post-graduation plans, such as work or going to college?
- How did the shutdown affect their academic performance in high school or in college?
- How did/do they feel about continuing their education?
- How did the shutdown affect their social relationships?
Any of these questions might be developed into a thesis for an analytical report. Table 8.3 shows more examples of broad topics and focusing questions.
Gathering Information
Because they are based on information and evidence, most analytical reports require you to do at least some research. Depending on your assignment, you may be able to find reliable information online, or you may need to do primary research by conducting an experiment, a survey, or interviews. For example, if you live among students in their late teens and early twenties, consider what they can tell you about their lives that you might be able to analyze. Returning to or graduating from high school, starting college, or returning to college in the midst of a global pandemic has provided them, for better or worse, with educational and social experiences that are shared widely by people their age and very different from the experiences older adults had at the same age.
Some report assignments will require you to do formal research, an activity that involves finding sources and evaluating them for reliability, reading them carefully, taking notes, and citing all words you quote and ideas you borrow. See Research Process: Accessing and Recording Information and Annotated Bibliography: Gathering, Evaluating, and Documenting Sources for detailed instruction on conducting research.
Whether you conduct in-depth research or not, keep track of the ideas that come to you and the information you learn. You can write or dictate notes using an app on your phone or computer, or you can jot notes in a journal if you prefer pen and paper. Then, when you are ready to begin organizing your report, you will have a record of your thoughts and information. Always track the sources of information you gather, whether from printed or digital material or from a person you interviewed, so that you can return to the sources if you need more information. And always credit the sources in your report.
Kinds of Evidence
Depending on your assignment and the topic of your report, certain kinds of evidence may be more effective than others. Other kinds of evidence may even be required. As a general rule, choose evidence that is rooted in verifiable facts and experience. In addition, select the evidence that best supports the topic and your approach to the topic, be sure the evidence meets your instructor’s requirements, and cite any evidence you use that comes from a source. The following list contains different kinds of frequently used evidence and an example of each.
Definition : An explanation of a key word, idea, or concept.
The U.S. Census Bureau refers to a “young adult” as a person between 18 and 34 years old.
Example : An illustration of an idea or concept.
The college experience in the fall of 2020 was starkly different from that of previous years. Students who lived in residence halls were assigned to small pods. On-campus dining services were limited. Classes were small and physically distanced or conducted online. Parties were banned.
Expert opinion : A statement by a professional in the field whose opinion is respected.
According to Louise Aronson, MD, geriatrician and author of Elderhood , people over the age of 65 are the happiest of any age group, reporting “less stress, depression, worry, and anger, and more enjoyment, happiness, and satisfaction” (255).
Fact : Information that can be proven correct or accurate.
According to data collected by the NCAA, the academic success of Division I college athletes between 2015 and 2019 was consistently high (Hosick).
Interview : An in-person, phone, or remote conversation that involves an interviewer posing questions to another person or people.
During our interview, I asked Betty about living without a cell phone during the pandemic. She said that before the pandemic, she hadn’t needed a cell phone in her daily activities, but she soon realized that she, and people like her, were increasingly at a disadvantage.
Quotation : The exact words of an author or a speaker.
In response to whether she thought she needed a cell phone, Betty said, “I got along just fine without a cell phone when I could go everywhere in person. The shift to needing a phone came suddenly, and I don’t have extra money in my budget to get one.”
Statistics : A numerical fact or item of data.
The Pew Research Center reported that approximately 25 percent of Hispanic Americans and 17 percent of Black Americans relied on smartphones for online access, compared with 12 percent of White people.
Survey : A structured interview in which respondents (the people who answer the survey questions) are all asked the same questions, either in person or through print or electronic means, and their answers tabulated and interpreted. Surveys discover attitudes, beliefs, or habits of the general public or segments of the population.
A survey of 3,000 mobile phone users in October 2020 showed that 54 percent of respondents used their phones for messaging, while 40 percent used their phones for calls (Steele).
- Visuals : Graphs, figures, tables, photographs and other images, diagrams, charts, maps, videos, and audio recordings, among others.
Thesis and Organization
Drafting a thesis.
When you have a grasp of your topic, move on to the next phase: drafting a thesis. The thesis is the central idea that you will explore and support in your report; all paragraphs in your report should relate to it. In an essay-style analytical report, you will likely express this main idea in a thesis statement of one or two sentences toward the end of the introduction.
For example, if you found that the academic performance of student athletes was higher than that of non-athletes, you might write the following thesis statement:
student sample text Although a common stereotype is that college athletes barely pass their classes, an analysis of athletes’ academic performance indicates that athletes drop fewer classes, earn higher grades, and are more likely to be on track to graduate in four years when compared with their non-athlete peers. end student sample text
The thesis statement often previews the organization of your writing. For example, in his report on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, Trevor Garcia wrote the following thesis statement, which detailed the central idea of his report:
student sample text An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths. end student sample text
After you draft a thesis statement, ask these questions, and examine your thesis as you answer them. Revise your draft as needed.
- Is it interesting? A thesis for a report should answer a question that is worth asking and piques curiosity.
- Is it precise and specific? If you are interested in reducing pollution in a nearby lake, explain how to stop the zebra mussel infestation or reduce the frequent algae blooms.
- Is it manageable? Try to split the difference between having too much information and not having enough.
Organizing Your Ideas
As a next step, organize the points you want to make in your report and the evidence to support them. Use an outline, a diagram, or another organizational tool, such as Table 8.4 .
Drafting an Analytical Report
With a tentative thesis, an organization plan, and evidence, you are ready to begin drafting. For this assignment, you will report information, analyze it, and draw conclusions about the cause of something, the effect of something, or the similarities and differences between two different things.
Introduction
Some students write the introduction first; others save it for last. Whenever you choose to write the introduction, use it to draw readers into your report. Make the topic of your report clear, and be concise and sincere. End the introduction with your thesis statement. Depending on your topic and the type of report, you can write an effective introduction in several ways. Opening a report with an overview is a tried-and-true strategy, as shown in the following example on the U.S. response to COVID-19 by Trevor Garcia. Notice how he opens the introduction with statistics and a comparison and follows it with a question that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text With more than 83 million cases and 1.8 million deaths at the end of 2020, COVID-19 has turned the world upside down. By the end of 2020, the United States led the world in the number of cases, at more than 20 million infections and nearly 350,000 deaths. In comparison, the second-highest number of cases was in India, which at the end of 2020 had less than half the number of COVID-19 cases despite having a population four times greater than the U.S. (“COVID-19 Coronavirus Pandemic,” 2021). How did the United States come to have the world’s worst record in this pandemic? underline An examination of the U.S. response shows that a reduction of experts in key positions and programs, inaction that led to equipment shortages, and inconsistent policies were three major causes of the spread of the virus and the resulting deaths end underline . end student sample text
For a less formal report, you might want to open with a question, quotation, or brief story. The following example opens with an anecdote that leads to the thesis statement (underlined).
student sample text Betty stood outside the salon, wondering how to get in. It was June of 2020, and the door was locked. A sign posted on the door provided a phone number for her to call to be let in, but at 81, Betty had lived her life without a cell phone. Betty’s day-to-day life had been hard during the pandemic, but she had planned for this haircut and was looking forward to it; she had a mask on and hand sanitizer in her car. Now she couldn’t get in the door, and she was discouraged. In that moment, Betty realized how much Americans’ dependence on cell phones had grown in the months since the pandemic began. underline Betty and thousands of other senior citizens who could not afford cell phones or did not have the technological skills and support they needed were being left behind in a society that was increasingly reliant on technology end underline . end student sample text
Body Paragraphs: Point, Evidence, Analysis
Use the body paragraphs of your report to present evidence that supports your thesis. A reliable pattern to keep in mind for developing the body paragraphs of a report is point , evidence , and analysis :
- The point is the central idea of the paragraph, usually given in a topic sentence stated in your own words at or toward the beginning of the paragraph. Each topic sentence should relate to the thesis.
- The evidence you provide develops the paragraph and supports the point made in the topic sentence. Include details, examples, quotations, paraphrases, and summaries from sources if you conducted formal research. Synthesize the evidence you include by showing in your sentences the connections between sources.
- The analysis comes at the end of the paragraph. In your own words, draw a conclusion about the evidence you have provided and how it relates to the topic sentence.
The paragraph below illustrates the point, evidence, and analysis pattern. Drawn from a report about concussions among football players, the paragraph opens with a topic sentence about the NCAA and NFL and their responses to studies about concussions. The paragraph is developed with evidence from three sources. It concludes with a statement about helmets and players’ safety.
student sample text The NCAA and NFL have taken steps forward and backward to respond to studies about the danger of concussions among players. Responding to the deaths of athletes, documented brain damage, lawsuits, and public outcry (Buckley et al., 2017), the NCAA instituted protocols to reduce potentially dangerous hits during football games and to diagnose traumatic head injuries more quickly and effectively. Still, it has allowed players to wear more than one style of helmet during a season, raising the risk of injury because of imperfect fit. At the professional level, the NFL developed a helmet-rating system in 2011 in an effort to reduce concussions, but it continued to allow players to wear helmets with a wide range of safety ratings. The NFL’s decision created an opportunity for researchers to look at the relationship between helmet safety ratings and concussions. Cocello et al. (2016) reported that players who wore helmets with a lower safety rating had more concussions than players who wore helmets with a higher safety rating, and they concluded that safer helmets are a key factor in reducing concussions. end student sample text
Developing Paragraph Content
In the body paragraphs of your report, you will likely use examples, draw comparisons, show contrasts, or analyze causes and effects to develop your topic.
Paragraphs developed with Example are common in reports. The paragraph below, adapted from a report by student John Zwick on the mental health of soldiers deployed during wartime, draws examples from three sources.
student sample text Throughout the Vietnam War, military leaders claimed that the mental health of soldiers was stable and that men who suffered from combat fatigue, now known as PTSD, were getting the help they needed. For example, the New York Times (1966) quoted military leaders who claimed that mental fatigue among enlisted men had “virtually ceased to be a problem,” occurring at a rate far below that of World War II. Ayres (1969) reported that Brigadier General Spurgeon Neel, chief American medical officer in Vietnam, explained that soldiers experiencing combat fatigue were admitted to the psychiatric ward, sedated for up to 36 hours, and given a counseling session with a doctor who reassured them that the rest was well deserved and that they were ready to return to their units. Although experts outside the military saw profound damage to soldiers’ psyches when they returned home (Halloran, 1970), the military stayed the course, treating acute cases expediently and showing little concern for the cumulative effect of combat stress on individual soldiers. end student sample text
When you analyze causes and effects , you explain the reasons that certain things happened and/or their results. The report by Trevor Garcia on the U.S. response to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 is an example: his report examines the reasons the United States failed to control the coronavirus. The paragraph below, adapted from another student’s report written for an environmental policy course, explains the effect of white settlers’ views of forest management on New England.
student sample text The early colonists’ European ideas about forest management dramatically changed the New England landscape. White settlers saw the New World as virgin, unused land, even though indigenous people had been drawing on its resources for generations by using fire subtly to improve hunting, employing construction techniques that left ancient trees intact, and farming small, efficient fields that left the surrounding landscape largely unaltered. White settlers’ desire to develop wood-built and wood-burning homesteads surrounded by large farm fields led to forestry practices and techniques that resulted in the removal of old-growth trees. These practices defined the way the forests look today. end student sample text
Compare and contrast paragraphs are useful when you wish to examine similarities and differences. You can use both comparison and contrast in a single paragraph, or you can use one or the other. The paragraph below, adapted from a student report on the rise of populist politicians, compares the rhetorical styles of populist politicians Huey Long and Donald Trump.
student sample text A key similarity among populist politicians is their rejection of carefully crafted sound bites and erudite vocabulary typically associated with candidates for high office. Huey Long and Donald Trump are two examples. When he ran for president, Long captured attention through his wild gesticulations on almost every word, dramatically varying volume, and heavily accented, folksy expressions, such as “The only way to be able to feed the balance of the people is to make that man come back and bring back some of that grub that he ain’t got no business with!” In addition, Long’s down-home persona made him a credible voice to represent the common people against the country’s rich, and his buffoonish style allowed him to express his radical ideas without sounding anti-communist alarm bells. Similarly, Donald Trump chose to speak informally in his campaign appearances, but the persona he projected was that of a fast-talking, domineering salesman. His frequent use of personal anecdotes, rhetorical questions, brief asides, jokes, personal attacks, and false claims made his speeches disjointed, but they gave the feeling of a running conversation between him and his audience. For example, in a 2015 speech, Trump said, “They just built a hotel in Syria. Can you believe this? They built a hotel. When I have to build a hotel, I pay interest. They don’t have to pay interest, because they took the oil that, when we left Iraq, I said we should’ve taken” (“Our Country Needs” 2020). While very different in substance, Long and Trump adopted similar styles that positioned them as the antithesis of typical politicians and their worldviews. end student sample text
The conclusion should draw the threads of your report together and make its significance clear to readers. You may wish to review the introduction, restate the thesis, recommend a course of action, point to the future, or use some combination of these. Whichever way you approach it, the conclusion should not head in a new direction. The following example is the conclusion from a student’s report on the effect of a book about environmental movements in the United States.
student sample text Since its publication in 1949, environmental activists of various movements have found wisdom and inspiration in Aldo Leopold’s A Sand County Almanac . These audiences included Leopold’s conservationist contemporaries, environmentalists of the 1960s and 1970s, and the environmental justice activists who rose in the 1980s and continue to make their voices heard today. These audiences have read the work differently: conservationists looked to the author as a leader, environmentalists applied his wisdom to their movement, and environmental justice advocates have pointed out the flaws in Leopold’s thinking. Even so, like those before them, environmental justice activists recognize the book’s value as a testament to taking the long view and eliminating biases that may cloud an objective assessment of humanity’s interdependent relationship with the environment. end student sample text
Citing Sources
You must cite the sources of information and data included in your report. Citations must appear in both the text and a bibliography at the end of the report.
The sample paragraphs in the previous section include examples of in-text citation using APA documentation style. Trevor Garcia’s report on the U.S. response to COVID-19 in 2020 also uses APA documentation style for citations in the text of the report and the list of references at the end. Your instructor may require another documentation style, such as MLA or Chicago.
Peer Review: Getting Feedback from Readers
You will likely engage in peer review with other students in your class by sharing drafts and providing feedback to help spot strengths and weaknesses in your reports. For peer review within a class, your instructor may provide assignment-specific questions or a form for you to complete as you work together.
If you have a writing center on your campus, it is well worth your time to make an online or in-person appointment with a tutor. You’ll receive valuable feedback and improve your ability to review not only your report but your overall writing.
Another way to receive feedback on your report is to ask a friend or family member to read your draft. Provide a list of questions or a form such as the one in Table 8.5 for them to complete as they read.
Revising: Using Reviewers’ Responses to Revise your Work
When you receive comments from readers, including your instructor, read each comment carefully to understand what is being asked. Try not to get defensive, even though this response is completely natural. Remember that readers are like coaches who want you to succeed. They are looking at your writing from outside your own head, and they can identify strengths and weaknesses that you may not have noticed. Keep track of the strengths and weaknesses your readers point out. Pay special attention to those that more than one reader identifies, and use this information to improve your report and later assignments.
As you analyze each response, be open to suggestions for improvement, and be willing to make significant revisions to improve your writing. Perhaps you need to revise your thesis statement to better reflect the content of your draft. Maybe you need to return to your sources to better understand a point you’re trying to make in order to develop a paragraph more fully. Perhaps you need to rethink the organization, move paragraphs around, and add transition sentences.
Below is an early draft of part of Trevor Garcia’s report with comments from a peer reviewer:
student sample text To truly understand what happened, it’s important first to look back to the years leading up to the pandemic. Epidemiologists and public health officials had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the U.S. National Security Council (NSC) published a 69-page document with the intimidating title Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents . The document’s two sections address responses to “emerging disease threats that start or are circulating in another country but not yet confirmed within U.S. territorial borders” and to “emerging disease threats within our nation’s borders.” On 13 January 2017, the joint Obama-Trump transition teams performed a pandemic preparedness exercise; however, the playbook was never adopted by the incoming administration. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Do the words in quotation marks need to be a direct quotation? It seems like a paraphrase would work here. end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: I’m getting lost in the details about the playbook. What’s the Obama-Trump transition team? end annotated text
student sample text In February 2018, the administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; cuts to other health agencies continued throughout 2018, with funds diverted to unrelated projects such as housing for detained immigrant children. end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph has only one sentence, and it’s more like an example. It needs a topic sentence and more development. end annotated text
student sample text Three months later, Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic. “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no.” end student sample text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: This paragraph is very short and a lot like the previous paragraph in that it’s a single example. It needs a topic sentence. Maybe you can combine them? end annotated text
annotated text Peer Review Comment: Be sure to cite the quotation. end annotated text
Reading these comments and those of others, Trevor decided to combine the three short paragraphs into one paragraph focusing on the fact that the United States knew a pandemic was possible but was unprepared for it. He developed the paragraph, using the short paragraphs as evidence and connecting the sentences and evidence with transitional words and phrases. Finally, he added in-text citations in APA documentation style to credit his sources. The revised paragraph is below:
student sample text Epidemiologists and public health officials in the United States had long known that a global pandemic was possible. In 2016, the National Security Council (NSC) published Playbook for Early Response to High-Consequence Emerging Infectious Disease Threats and Biological Incidents , a 69-page document on responding to diseases spreading within and outside of the United States. On January 13, 2017, the joint transition teams of outgoing president Barack Obama and then president-elect Donald Trump performed a pandemic preparedness exercise based on the playbook; however, it was never adopted by the incoming administration (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). A year later, in February 2018, the Trump administration began to cut funding for the Prevention and Public Health Fund at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, leaving key positions unfilled. Other individuals who were fired or resigned in 2018 were the homeland security adviser, whose portfolio included global pandemics; the director for medical and biodefense preparedness; and the top official in charge of a pandemic response. None of them were replaced, leaving the White House with no senior person who had experience in public health (Goodman & Schulkin, 2020). Experts voiced concerns, among them Luciana Borio, director of medical and biodefense preparedness at the NSC, who spoke at a symposium marking the centennial of the 1918 influenza pandemic in May 2018: “The threat of pandemic flu is the number one health security concern,” she said. “Are we ready to respond? I fear the answer is no” (Sun, 2018, final para.). end student sample text
A final word on working with reviewers’ comments: as you consider your readers’ suggestions, remember, too, that you remain the author. You are free to disregard suggestions that you think will not improve your writing. If you choose to disregard comments from your instructor, consider submitting a note explaining your reasons with the final draft of your report.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Authors: Michelle Bachelor Robinson, Maria Jerskey, featuring Toby Fulwiler
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Writing Guide with Handbook
- Publication date: Dec 21, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/1-unit-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/writing-guide/pages/8-5-writing-process-creating-an-analytical-report
© Dec 19, 2023 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
EN-121 - Resources for Analytical Thinking, Writing, and Research: Gathering Sources and Conducting Research
- Gathering Sources and Conducting Research
- Choosing and Narrowing Your Topic and Formulating a Thesis Statement
- Annotated Bibliography
- In-Text Citations
- Writing the Rough Draft / Writing the Final Revision
- Making Presentations
EN-121 Research Instruction Video Playlist
Visual learner , visit the en-121 youtube playlist.

This frequently-updated playlist includes instructional videos on research, writing, and critical thinking from many colleges and universities.
Citation Generators
How do citation generators work, according to purdue owl, citation generators are programs that turn information about a source into a citation that the writer can use in a project..
Here is a list of recommended citation generators
MyBib MyBib citation generator provides complete APA Citations, pre-formatted In-text Citations, and a Reference page.
- BibMe - APA Citation Generator and Plagiarism Checker from Chegg
- CiteFast - APA Citation Generator
- CiteThisForMe - APA Citation Generator from Harvard University
- KnightCite Citation Service - provided by the Hekman Library of Calvin College.
- Scribber - APA Citation Generator
Fact-Checking Websites
Reputable sources help fact-check reliability of information you find questionable.
Fact Checking Websites :
- Opensecrets.org
- American Press Institute Guide to Fact-Checking Resources
What is a Primary Source?
WHAT IS A PRIMARY SOURCE? DEFINITIONS FROM THE SMITHSONIAN INSTITUTION ARCHIVES
Primary sources -
First-person testimony: the account of a person who actually was present at or participated in an event. Examples are oral history interviews, diaries, letters, photographs and drawings of events, and court testimony of an eyewitness; a document or object that was created by an individual or group as part of their daily lives. These documents are written or spoken using "I" statements, to indicate direct observation of or participation in an event.
Primary source documents: including birth certificates, photographs, diaries, letters, embroidered samplers, clothing, household implements, and newspapers.
Secondary sources - summaries, second-hand accounts, and analyses of events created by someone who did not witness the event , but may have read or heard about it. Examples may include: books or articles written on a topic, artworks depicting an event, letters or diaries recounting a version of events told to the author by another source.
Second person or hearsay testimony - an account repeated by someone who did not actually participate in the event. Examples are newspaper accounts from interviews of observers, letters that repeat a story told to the writer, drawings based on other people’s observations, or a book written about a topic.
Mixed sources - A document that is a primary source may contain both first person testimony and second hand testimony. An example would be a diary entry that records a person’s eyewitness observations of an event (first person testimony) but also contains additional stories told to the writer by a family member (second hand testimony). Newspapers often contain a mixture of first and second hand accounts.
It may depend on the question you are asking – The same document can be a primary and secondary source, depending upon the question you ask. For example, a Baltimore newspaper’s account of Lincoln’s death that includes unattributed accounts of what happened at Ford’s Theater contains second hand testimony, if your question is what exactly happened at Ford’s Theater that night. But if your question is how people in Baltimore heard about Lincoln’s assassination and what did they hear, then the newspaper is a primary sources for answering that question.
CRAAP Website Evaluation: Is the website trustworthy?
- CRAAP Evaluation Flyer DOES YOUR WEB RESOURCE PASS THE CRAAP TEST?
Do You Need a Newspaper Article or a Database Article?
Do you need an article from a newspaper or website , be careful to evaluate any websites for the quality of the information they offer. always run the craap test ..
Newspaper articles:
- are published for a general public audience (but are not " scholarly" research articles).
- must pass editorial review (The editorial board of a news provider is not the same as a scholarly peer-review panel.)
- are usually (but not always) subject to the journalistic code of ethics .
- at the national level, can be reasonably expected to have been fact-checked prior to publication
When you use the Internet, you should always try to find out who posted the information and how much they know about the topic .
Are they experts in their field?
Are they giving facts or are they giving their own opinion? You might want to check their media bias score !
For more help, (and to learn about the CRAAP test) see the Website Evaluation & Citation LibGuide
Need both sides of the story? Try starting here:
Finding Newspaper and Website Articles on the Internet
Go to the best source for the type of information that you want.
Some suggested websites:
- AP Top News
- Google News Top Stories
- Twitter #News
- FINANCE : Bloomberg or Forbes or the Minority Business Development Agency
- POLITICS : The Hill or C-SPAN
- TECH : The Verge or C|Net
- Vice News Tonight
- LoHud News (Westchester County)
- Queens Gazette
- Bronx Times
- BBC News World
- Freedom Forum World News
- United Press International
Why and How to Search for Peer-Reviewed Articles
Don't forget: In order to search for academic and scholarly articles, you'll need to log in to the Library Databases .
1.) Login to MyMonroe .
Your professor may require that you use peer-reviewed journal articles as sources for your research.
WHY USE PEER-REVIEWED JOURNAL ARTICLES?
Because these articles generally contain the best (and often the most current) information available on a given subject.
Academic and scholarly journal articles must be:
- written by scholars conducting and reporting on research on their particular topic and then
- reviewed by a panel of the author's peers (i.e. peer-reviewed by other experts in the field) before the article is published.
The review process means the article must meet high standards of:
- Currency (meaning the information is current at the time of publication) ,
- Relevance (meaning the article is highly relevant to the subject it addresses, without commercial subtext or other issues distracting from the topic) ,
- Accuracy (meaning the article has been checked for any bias or missing/misleading information) ,
- Authenticity (meaning the author's credentials have been verified and their cited sources confirmed) , and
- Purpose (meaning the author must be free of commercial motivation for their writing; it must be informational and/or educational in its purpose) .
This process is meant to ensure the integrity of the journal, as well as the quality of the article .
For best results, you should start your search in a database that specializes in academic and scholarly/peer-reviewed articles . See a list of specialized databases in the column to the right: →
Best Databases for Peer-Reviewed, Scholarly Journal Articles
Three databases that specialize in peer-reviewed articles are:
Academic OneFile (Gale)
Research Library (ProQuest)
(Check the box marked Peer reviewed .)

Academic Search Premier (Ebsco)

ALL Databases offer the ability to Download Full-Text Articles and APA Citations .
Be sure to download the full text of all articles you wish to use for your paper, and be sure to download and save the APA 7 citation for all articles you download.

Video: Is This Article Scholarly?
Selected Primary-Source History Websites (Listed Alphabetically)
Africana age.
American Historical Association
Biographical Dictionary of the United States Congress

ProQuest Black Freedom Struggle in the United States
- ProQuest Black Freedom Struggle in the United States (No Login Required) This website presents primary source documents from several time periods in American History... [with a focus on] the fierce, often violent opposition that Black people have faced on the road to freedom. This website contains more... less... over 3,000 documents focused on six different phases of Black Freedom: Slavery and the Abolitionist Movement (1790-1860) The Civil War and the Reconstruction Era (1861-1877) Jim Crow Era from 1878 to the Great Depression (1878-1932) The New Deal and World War II (1933-1945) The Civil Rights and Black Power Movements (1946-1975) The Contemporary Era (1976-2000)
Digital Collections in American History - Library of Congress

- Ansel Adams's Photographs of Japanese-American Internment at Manzanar
- Civil Rights History Project
- Frederick Douglass Papers at the Library of Congress and many more.
Discovering American Women's History Online
Caribbean histories revealed.

Castle Garden Immigration Center

Chronicling America: Historic American Newspapers


Digital Library of the Caribbean

Digital Schomburg

Historical Documents in Foreign Relations

New-York Historical Society

New York City Municipal Archives Online Gallery

New York State Historical Literature Collection

New York State Historic Newspapers
New York State Military Museum and Veterans Research Center

NYPD & CRIMINAL PROSECUTION

Primary Source Sets from the Digital Public Library of America

The Pulitzer Prizes

Slavery in America

Transatlantic Slave Trade Database

Westchester County Archives

- Information Literacy, Critical Thinking, and Website Evaluation
How to Use the Databases
- How to Use the Databases - (Click to open presentation in a new tab)
The presentation below is also available as a PDF document. View or download by clicking on the icon above.
- Next: Choosing and Narrowing Your Topic and Formulating a Thesis Statement >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 1:14 PM
- URL: https://monroecollege.libguides.com/EN-121
- Research Guides |
- Databases |
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- CBE Life Sci Educ
- v.17(1); Spring 2018
Understanding the Complex Relationship between Critical Thinking and Science Reasoning among Undergraduate Thesis Writers
Jason e. dowd.
† Department of Biology, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708
Robert J. Thompson, Jr.
‡ Department of Psychology and Neuroscience, Duke University, Durham, NC 27708
Leslie A. Schiff
§ Department of Microbiology and Immunology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455
Julie A. Reynolds
Associated data.
This study empirically examines the relationship between students’ critical-thinking skills and scientific reasoning as reflected in undergraduate thesis writing in biology. Writing offers a unique window into studying this relationship, and the findings raise potential implications for instruction.
Developing critical-thinking and scientific reasoning skills are core learning objectives of science education, but little empirical evidence exists regarding the interrelationships between these constructs. Writing effectively fosters students’ development of these constructs, and it offers a unique window into studying how they relate. In this study of undergraduate thesis writing in biology at two universities, we examine how scientific reasoning exhibited in writing (assessed using the Biology Thesis Assessment Protocol) relates to general and specific critical-thinking skills (assessed using the California Critical Thinking Skills Test), and we consider implications for instruction. We find that scientific reasoning in writing is strongly related to inference , while other aspects of science reasoning that emerge in writing (epistemological considerations, writing conventions, etc.) are not significantly related to critical-thinking skills. Science reasoning in writing is not merely a proxy for critical thinking. In linking features of students’ writing to their critical-thinking skills, this study 1) provides a bridge to prior work suggesting that engagement in science writing enhances critical thinking and 2) serves as a foundational step for subsequently determining whether instruction focused explicitly on developing critical-thinking skills (particularly inference ) can actually improve students’ scientific reasoning in their writing.
INTRODUCTION
Critical-thinking and scientific reasoning skills are core learning objectives of science education for all students, regardless of whether or not they intend to pursue a career in science or engineering. Consistent with the view of learning as construction of understanding and meaning ( National Research Council, 2000 ), the pedagogical practice of writing has been found to be effective not only in fostering the development of students’ conceptual and procedural knowledge ( Gerdeman et al. , 2007 ) and communication skills ( Clase et al. , 2010 ), but also scientific reasoning ( Reynolds et al. , 2012 ) and critical-thinking skills ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ).
Critical thinking and scientific reasoning are similar but different constructs that include various types of higher-order cognitive processes, metacognitive strategies, and dispositions involved in making meaning of information. Critical thinking is generally understood as the broader construct ( Holyoak and Morrison, 2005 ), comprising an array of cognitive processes and dispostions that are drawn upon differentially in everyday life and across domains of inquiry such as the natural sciences, social sciences, and humanities. Scientific reasoning, then, may be interpreted as the subset of critical-thinking skills (cognitive and metacognitive processes and dispositions) that 1) are involved in making meaning of information in scientific domains and 2) support the epistemological commitment to scientific methodology and paradigm(s).
Although there has been an enduring focus in higher education on promoting critical thinking and reasoning as general or “transferable” skills, research evidence provides increasing support for the view that reasoning and critical thinking are also situational or domain specific ( Beyer et al. , 2013 ). Some researchers, such as Lawson (2010) , present frameworks in which science reasoning is characterized explicitly in terms of critical-thinking skills. There are, however, limited coherent frameworks and empirical evidence regarding either the general or domain-specific interrelationships of scientific reasoning, as it is most broadly defined, and critical-thinking skills.
The Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education Initiative provides a framework for thinking about these constructs and their interrelationship in the context of the core competencies and disciplinary practice they describe ( American Association for the Advancement of Science, 2011 ). These learning objectives aim for undergraduates to “understand the process of science, the interdisciplinary nature of the new biology and how science is closely integrated within society; be competent in communication and collaboration; have quantitative competency and a basic ability to interpret data; and have some experience with modeling, simulation and computational and systems level approaches as well as with using large databases” ( Woodin et al. , 2010 , pp. 71–72). This framework makes clear that science reasoning and critical-thinking skills play key roles in major learning outcomes; for example, “understanding the process of science” requires students to engage in (and be metacognitive about) scientific reasoning, and having the “ability to interpret data” requires critical-thinking skills. To help students better achieve these core competencies, we must better understand the interrelationships of their composite parts. Thus, the next step is to determine which specific critical-thinking skills are drawn upon when students engage in science reasoning in general and with regard to the particular scientific domain being studied. Such a determination could be applied to improve science education for both majors and nonmajors through pedagogical approaches that foster critical-thinking skills that are most relevant to science reasoning.
Writing affords one of the most effective means for making thinking visible ( Reynolds et al. , 2012 ) and learning how to “think like” and “write like” disciplinary experts ( Meizlish et al. , 2013 ). As a result, student writing affords the opportunities to both foster and examine the interrelationship of scientific reasoning and critical-thinking skills within and across disciplinary contexts. The purpose of this study was to better understand the relationship between students’ critical-thinking skills and scientific reasoning skills as reflected in the genre of undergraduate thesis writing in biology departments at two research universities, the University of Minnesota and Duke University.
In the following subsections, we discuss in greater detail the constructs of scientific reasoning and critical thinking, as well as the assessment of scientific reasoning in students’ thesis writing. In subsequent sections, we discuss our study design, findings, and the implications for enhancing educational practices.
Critical Thinking
The advances in cognitive science in the 21st century have increased our understanding of the mental processes involved in thinking and reasoning, as well as memory, learning, and problem solving. Critical thinking is understood to include both a cognitive dimension and a disposition dimension (e.g., reflective thinking) and is defined as “purposeful, self-regulatory judgment which results in interpretation, analysis, evaluation, and inference, as well as explanation of the evidential, conceptual, methodological, criteriological, or contextual considerations upon which that judgment is based” ( Facione, 1990, p. 3 ). Although various other definitions of critical thinking have been proposed, researchers have generally coalesced on this consensus: expert view ( Blattner and Frazier, 2002 ; Condon and Kelly-Riley, 2004 ; Bissell and Lemons, 2006 ; Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ) and the corresponding measures of critical-thinking skills ( August, 2016 ; Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ).
Both the cognitive skills and dispositional components of critical thinking have been recognized as important to science education ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ). Empirical research demonstrates that specific pedagogical practices in science courses are effective in fostering students’ critical-thinking skills. Quitadamo and Kurtz (2007) found that students who engaged in a laboratory writing component in the context of a general education biology course significantly improved their overall critical-thinking skills (and their analytical and inference skills, in particular), whereas students engaged in a traditional quiz-based laboratory did not improve their critical-thinking skills. In related work, Quitadamo et al. (2008) found that a community-based inquiry experience, involving inquiry, writing, research, and analysis, was associated with improved critical thinking in a biology course for nonmajors, compared with traditionally taught sections. In both studies, students who exhibited stronger presemester critical-thinking skills exhibited stronger gains, suggesting that “students who have not been explicitly taught how to think critically may not reach the same potential as peers who have been taught these skills” ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 , p. 151).
Recently, Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight (2016) found that first-year general chemistry students who engaged in a science writing heuristic laboratory, which is an inquiry-based, writing-to-learn approach to instruction ( Hand and Keys, 1999 ), had significantly greater gains in total critical-thinking scores than students who received traditional laboratory instruction. Each of the four components—inquiry, writing, collaboration, and reflection—have been linked to critical thinking ( Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ). Like the other studies, this work highlights the value of targeting critical-thinking skills and the effectiveness of an inquiry-based, writing-to-learn approach to enhance critical thinking. Across studies, authors advocate adopting critical thinking as the course framework ( Pukkila, 2004 ) and developing explicit examples of how critical thinking relates to the scientific method ( Miri et al. , 2007 ).
In these examples, the important connection between writing and critical thinking is highlighted by the fact that each intervention involves the incorporation of writing into science, technology, engineering, and mathematics education (either alone or in combination with other pedagogical practices). However, critical-thinking skills are not always the primary learning outcome; in some contexts, scientific reasoning is the primary outcome that is assessed.
Scientific Reasoning
Scientific reasoning is a complex process that is broadly defined as “the skills involved in inquiry, experimentation, evidence evaluation, and inference that are done in the service of conceptual change or scientific understanding” ( Zimmerman, 2007 , p. 172). Scientific reasoning is understood to include both conceptual knowledge and the cognitive processes involved with generation of hypotheses (i.e., inductive processes involved in the generation of hypotheses and the deductive processes used in the testing of hypotheses), experimentation strategies, and evidence evaluation strategies. These dimensions are interrelated, in that “experimentation and inference strategies are selected based on prior conceptual knowledge of the domain” ( Zimmerman, 2000 , p. 139). Furthermore, conceptual and procedural knowledge and cognitive process dimensions can be general and domain specific (or discipline specific).
With regard to conceptual knowledge, attention has been focused on the acquisition of core methodological concepts fundamental to scientists’ causal reasoning and metacognitive distancing (or decontextualized thinking), which is the ability to reason independently of prior knowledge or beliefs ( Greenhoot et al. , 2004 ). The latter involves what Kuhn and Dean (2004) refer to as the coordination of theory and evidence, which requires that one question existing theories (i.e., prior knowledge and beliefs), seek contradictory evidence, eliminate alternative explanations, and revise one’s prior beliefs in the face of contradictory evidence. Kuhn and colleagues (2008) further elaborate that scientific thinking requires “a mature understanding of the epistemological foundations of science, recognizing scientific knowledge as constructed by humans rather than simply discovered in the world,” and “the ability to engage in skilled argumentation in the scientific domain, with an appreciation of argumentation as entailing the coordination of theory and evidence” ( Kuhn et al. , 2008 , p. 435). “This approach to scientific reasoning not only highlights the skills of generating and evaluating evidence-based inferences, but also encompasses epistemological appreciation of the functions of evidence and theory” ( Ding et al. , 2016 , p. 616). Evaluating evidence-based inferences involves epistemic cognition, which Moshman (2015) defines as the subset of metacognition that is concerned with justification, truth, and associated forms of reasoning. Epistemic cognition is both general and domain specific (or discipline specific; Moshman, 2015 ).
There is empirical support for the contributions of both prior knowledge and an understanding of the epistemological foundations of science to scientific reasoning. In a study of undergraduate science students, advanced scientific reasoning was most often accompanied by accurate prior knowledge as well as sophisticated epistemological commitments; additionally, for students who had comparable levels of prior knowledge, skillful reasoning was associated with a strong epistemological commitment to the consistency of theory with evidence ( Zeineddin and Abd-El-Khalick, 2010 ). These findings highlight the importance of the need for instructional activities that intentionally help learners develop sophisticated epistemological commitments focused on the nature of knowledge and the role of evidence in supporting knowledge claims ( Zeineddin and Abd-El-Khalick, 2010 ).
Scientific Reasoning in Students’ Thesis Writing
Pedagogical approaches that incorporate writing have also focused on enhancing scientific reasoning. Many rubrics have been developed to assess aspects of scientific reasoning in written artifacts. For example, Timmerman and colleagues (2011) , in the course of describing their own rubric for assessing scientific reasoning, highlight several examples of scientific reasoning assessment criteria ( Haaga, 1993 ; Tariq et al. , 1998 ; Topping et al. , 2000 ; Kelly and Takao, 2002 ; Halonen et al. , 2003 ; Willison and O’Regan, 2007 ).
At both the University of Minnesota and Duke University, we have focused on the genre of the undergraduate honors thesis as the rhetorical context in which to study and improve students’ scientific reasoning and writing. We view the process of writing an undergraduate honors thesis as a form of professional development in the sciences (i.e., a way of engaging students in the practices of a community of discourse). We have found that structured courses designed to scaffold the thesis-writing process and promote metacognition can improve writing and reasoning skills in biology, chemistry, and economics ( Reynolds and Thompson, 2011 ; Dowd et al. , 2015a , b ). In the context of this prior work, we have defined scientific reasoning in writing as the emergent, underlying construct measured across distinct aspects of students’ written discussion of independent research in their undergraduate theses.
The Biology Thesis Assessment Protocol (BioTAP) was developed at Duke University as a tool for systematically guiding students and faculty through a “draft–feedback–revision” writing process, modeled after professional scientific peer-review processes ( Reynolds et al. , 2009 ). BioTAP includes activities and worksheets that allow students to engage in critical peer review and provides detailed descriptions, presented as rubrics, of the questions (i.e., dimensions, shown in Table 1 ) upon which such review should focus. Nine rubric dimensions focus on communication to the broader scientific community, and four rubric dimensions focus on the accuracy and appropriateness of the research. These rubric dimensions provide criteria by which the thesis is assessed, and therefore allow BioTAP to be used as an assessment tool as well as a teaching resource ( Reynolds et al. , 2009 ). Full details are available at www.science-writing.org/biotap.html .
Theses assessment protocol dimensions
In previous work, we have used BioTAP to quantitatively assess students’ undergraduate honors theses and explore the relationship between thesis-writing courses (or specific interventions within the courses) and the strength of students’ science reasoning in writing across different science disciplines: biology ( Reynolds and Thompson, 2011 ); chemistry ( Dowd et al. , 2015b ); and economics ( Dowd et al. , 2015a ). We have focused exclusively on the nine dimensions related to reasoning and writing (questions 1–9), as the other four dimensions (questions 10–13) require topic-specific expertise and are intended to be used by the student’s thesis supervisor.
Beyond considering individual dimensions, we have investigated whether meaningful constructs underlie students’ thesis scores. We conducted exploratory factor analysis of students’ theses in biology, economics, and chemistry and found one dominant underlying factor in each discipline; we termed the factor “scientific reasoning in writing” ( Dowd et al. , 2015a , b , 2016 ). That is, each of the nine dimensions could be understood as reflecting, in different ways and to different degrees, the construct of scientific reasoning in writing. The findings indicated evidence of both general and discipline-specific components to scientific reasoning in writing that relate to epistemic beliefs and paradigms, in keeping with broader ideas about science reasoning discussed earlier. Specifically, scientific reasoning in writing is more strongly associated with formulating a compelling argument for the significance of the research in the context of current literature in biology, making meaning regarding the implications of the findings in chemistry, and providing an organizational framework for interpreting the thesis in economics. We suggested that instruction, whether occurring in writing studios or in writing courses to facilitate thesis preparation, should attend to both components.
Research Question and Study Design
The genre of thesis writing combines the pedagogies of writing and inquiry found to foster scientific reasoning ( Reynolds et al. , 2012 ) and critical thinking ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ; Quitadamo et al. , 2008 ; Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ). However, there is no empirical evidence regarding the general or domain-specific interrelationships of scientific reasoning and critical-thinking skills, particularly in the rhetorical context of the undergraduate thesis. The BioTAP studies discussed earlier indicate that the rubric-based assessment produces evidence of scientific reasoning in the undergraduate thesis, but it was not designed to foster or measure critical thinking. The current study was undertaken to address the research question: How are students’ critical-thinking skills related to scientific reasoning as reflected in the genre of undergraduate thesis writing in biology? Determining these interrelationships could guide efforts to enhance students’ scientific reasoning and writing skills through focusing instruction on specific critical-thinking skills as well as disciplinary conventions.
To address this research question, we focused on undergraduate thesis writers in biology courses at two institutions, Duke University and the University of Minnesota, and examined the extent to which students’ scientific reasoning in writing, assessed in the undergraduate thesis using BioTAP, corresponds to students’ critical-thinking skills, assessed using the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (CCTST; August, 2016 ).
Study Sample
The study sample was composed of students enrolled in courses designed to scaffold the thesis-writing process in the Department of Biology at Duke University and the College of Biological Sciences at the University of Minnesota. Both courses complement students’ individual work with research advisors. The course is required for thesis writers at the University of Minnesota and optional for writers at Duke University. Not all students are required to complete a thesis, though it is required for students to graduate with honors; at the University of Minnesota, such students are enrolled in an honors program within the college. In total, 28 students were enrolled in the course at Duke University and 44 students were enrolled in the course at the University of Minnesota. Of those students, two students did not consent to participate in the study; additionally, five students did not validly complete the CCTST (i.e., attempted fewer than 60% of items or completed the test in less than 15 minutes). Thus, our overall rate of valid participation is 90%, with 27 students from Duke University and 38 students from the University of Minnesota. We found no statistically significant differences in thesis assessment between students with valid CCTST scores and invalid CCTST scores. Therefore, we focus on the 65 students who consented to participate and for whom we have complete and valid data in most of this study. Additionally, in asking students for their consent to participate, we allowed them to choose whether to provide or decline access to academic and demographic background data. Of the 65 students who consented to participate, 52 students granted access to such data. Therefore, for additional analyses involving academic and background data, we focus on the 52 students who consented. We note that the 13 students who participated but declined to share additional data performed slightly lower on the CCTST than the 52 others (perhaps suggesting that they differ by other measures, but we cannot determine this with certainty). Among the 52 students, 60% identified as female and 10% identified as being from underrepresented ethnicities.
In both courses, students completed the CCTST online, either in class or on their own, late in the Spring 2016 semester. This is the same assessment that was used in prior studies of critical thinking ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ; Quitadamo et al. , 2008 ; Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ). It is “an objective measure of the core reasoning skills needed for reflective decision making concerning what to believe or what to do” ( Insight Assessment, 2016a ). In the test, students are asked to read and consider information as they answer multiple-choice questions. The questions are intended to be appropriate for all users, so there is no expectation of prior disciplinary knowledge in biology (or any other subject). Although actual test items are protected, sample items are available on the Insight Assessment website ( Insight Assessment, 2016b ). We have included one sample item in the Supplemental Material.
The CCTST is based on a consensus definition of critical thinking, measures cognitive and metacognitive skills associated with critical thinking, and has been evaluated for validity and reliability at the college level ( August, 2016 ; Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ). In addition to providing overall critical-thinking score, the CCTST assesses seven dimensions of critical thinking: analysis, interpretation, inference, evaluation, explanation, induction, and deduction. Scores on each dimension are calculated based on students’ performance on items related to that dimension. Analysis focuses on identifying assumptions, reasons, and claims and examining how they interact to form arguments. Interpretation, related to analysis, focuses on determining the precise meaning and significance of information. Inference focuses on drawing conclusions from reasons and evidence. Evaluation focuses on assessing the credibility of sources of information and claims they make. Explanation, related to evaluation, focuses on describing the evidence, assumptions, or rationale for beliefs and conclusions. Induction focuses on drawing inferences about what is probably true based on evidence. Deduction focuses on drawing conclusions about what must be true when the context completely determines the outcome. These are not independent dimensions; the fact that they are related supports their collective interpretation as critical thinking. Together, the CCTST dimensions provide a basis for evaluating students’ overall strength in using reasoning to form reflective judgments about what to believe or what to do ( August, 2016 ). Each of the seven dimensions and the overall CCTST score are measured on a scale of 0–100, where higher scores indicate superior performance. Scores correspond to superior (86–100), strong (79–85), moderate (70–78), weak (63–69), or not manifested (62 and below) skills.
Scientific Reasoning in Writing
At the end of the semester, students’ final, submitted undergraduate theses were assessed using BioTAP, which consists of nine rubric dimensions that focus on communication to the broader scientific community and four additional dimensions that focus on the exhibition of topic-specific expertise ( Reynolds et al. , 2009 ). These dimensions, framed as questions, are displayed in Table 1 .
Student theses were assessed on questions 1–9 of BioTAP using the same procedures described in previous studies ( Reynolds and Thompson, 2011 ; Dowd et al. , 2015a , b ). In this study, six raters were trained in the valid, reliable use of BioTAP rubrics. Each dimension was rated on a five-point scale: 1 indicates the dimension is missing, incomplete, or below acceptable standards; 3 indicates that the dimension is adequate but not exhibiting mastery; and 5 indicates that the dimension is excellent and exhibits mastery (intermediate ratings of 2 and 4 are appropriate when different parts of the thesis make a single category challenging). After training, two raters independently assessed each thesis and then discussed their independent ratings with one another to form a consensus rating. The consensus score is not an average score, but rather an agreed-upon, discussion-based score. On a five-point scale, raters independently assessed dimensions to be within 1 point of each other 82.4% of the time before discussion and formed consensus ratings 100% of the time after discussion.
In this study, we consider both categorical (mastery/nonmastery, where a score of 5 corresponds to mastery) and numerical treatments of individual BioTAP scores to better relate the manifestation of critical thinking in BioTAP assessment to all of the prior studies. For comprehensive/cumulative measures of BioTAP, we focus on the partial sum of questions 1–5, as these questions relate to higher-order scientific reasoning (whereas questions 6–9 relate to mid- and lower-order writing mechanics [ Reynolds et al. , 2009 ]), and the factor scores (i.e., numerical representations of the extent to which each student exhibits the underlying factor), which are calculated from the factor loadings published by Dowd et al. (2016) . We do not focus on questions 6–9 individually in statistical analyses, because we do not expect critical-thinking skills to relate to mid- and lower-order writing skills.
The final, submitted thesis reflects the student’s writing, the student’s scientific reasoning, the quality of feedback provided to the student by peers and mentors, and the student’s ability to incorporate that feedback into his or her work. Therefore, our assessment is not the same as an assessment of unpolished, unrevised samples of students’ written work. While one might imagine that such an unpolished sample may be more strongly correlated with critical-thinking skills measured by the CCTST, we argue that the complete, submitted thesis, assessed using BioTAP, is ultimately a more appropriate reflection of how students exhibit science reasoning in the scientific community.
Statistical Analyses
We took several steps to analyze the collected data. First, to provide context for subsequent interpretations, we generated descriptive statistics for the CCTST scores of the participants based on the norms for undergraduate CCTST test takers. To determine the strength of relationships among CCTST dimensions (including overall score) and the BioTAP dimensions, partial-sum score (questions 1–5), and factor score, we calculated Pearson’s correlations for each pair of measures. To examine whether falling on one side of the nonmastery/mastery threshold (as opposed to a linear scale of performance) was related to critical thinking, we grouped BioTAP dimensions into categories (mastery/nonmastery) and conducted Student’s t tests to compare the means scores of the two groups on each of the seven dimensions and overall score of the CCTST. Finally, for the strongest relationship that emerged, we included additional academic and background variables as covariates in multiple linear-regression analysis to explore questions about how much observed relationships between critical-thinking skills and science reasoning in writing might be explained by variation in these other factors.
Although BioTAP scores represent discreet, ordinal bins, the five-point scale is intended to capture an underlying continuous construct (from inadequate to exhibiting mastery). It has been argued that five categories is an appropriate cutoff for treating ordinal variables as pseudo-continuous ( Rhemtulla et al. , 2012 )—and therefore using continuous-variable statistical methods (e.g., Pearson’s correlations)—as long as the underlying assumption that ordinal scores are linearly distributed is valid. Although we have no way to statistically test this assumption, we interpret adequate scores to be approximately halfway between inadequate and mastery scores, resulting in a linear scale. In part because this assumption is subject to disagreement, we also consider and interpret a categorical (mastery/nonmastery) treatment of BioTAP variables.
We corrected for multiple comparisons using the Holm-Bonferroni method ( Holm, 1979 ). At the most general level, where we consider the single, comprehensive measures for BioTAP (partial-sum and factor score) and the CCTST (overall score), there is no need to correct for multiple comparisons, because the multiple, individual dimensions are collapsed into single dimensions. When we considered individual CCTST dimensions in relation to comprehensive measures for BioTAP, we accounted for seven comparisons; similarly, when we considered individual dimensions of BioTAP in relation to overall CCTST score, we accounted for five comparisons. When all seven CCTST and five BioTAP dimensions were examined individually and without prior knowledge, we accounted for 35 comparisons; such a rigorous threshold is likely to reject weak and moderate relationships, but it is appropriate if there are no specific pre-existing hypotheses. All p values are presented in tables for complete transparency, and we carefully consider the implications of our interpretation of these data in the Discussion section.
CCTST scores for students in this sample ranged from the 39th to 99th percentile of the general population of undergraduate CCTST test takers (mean percentile = 84.3, median = 85th percentile; Table 2 ); these percentiles reflect overall scores that range from moderate to superior. Scores on individual dimensions and overall scores were sufficiently normal and far enough from the ceiling of the scale to justify subsequent statistical analyses.
Descriptive statistics of CCTST dimensions a
a Scores correspond to superior (86–100), strong (79–85), moderate (70–78), weak (63–69), or not manifested (62 and lower) skills.
The Pearson’s correlations between students’ cumulative scores on BioTAP (the factor score based on loadings published by Dowd et al. , 2016 , and the partial sum of scores on questions 1–5) and students’ overall scores on the CCTST are presented in Table 3 . We found that the partial-sum measure of BioTAP was significantly related to the overall measure of critical thinking ( r = 0.27, p = 0.03), while the BioTAP factor score was marginally related to overall CCTST ( r = 0.24, p = 0.05). When we looked at relationships between comprehensive BioTAP measures and scores for individual dimensions of the CCTST ( Table 3 ), we found significant positive correlations between the both BioTAP partial-sum and factor scores and CCTST inference ( r = 0.45, p < 0.001, and r = 0.41, p < 0.001, respectively). Although some other relationships have p values below 0.05 (e.g., the correlations between BioTAP partial-sum scores and CCTST induction and interpretation scores), they are not significant when we correct for multiple comparisons.
Correlations between dimensions of CCTST and dimensions of BioTAP a
a In each cell, the top number is the correlation, and the bottom, italicized number is the associated p value. Correlations that are statistically significant after correcting for multiple comparisons are shown in bold.
b This is the partial sum of BioTAP scores on questions 1–5.
c This is the factor score calculated from factor loadings published by Dowd et al. (2016) .
When we expanded comparisons to include all 35 potential correlations among individual BioTAP and CCTST dimensions—and, accordingly, corrected for 35 comparisons—we did not find any additional statistically significant relationships. The Pearson’s correlations between students’ scores on each dimension of BioTAP and students’ scores on each dimension of the CCTST range from −0.11 to 0.35 ( Table 3 ); although the relationship between discussion of implications (BioTAP question 5) and inference appears to be relatively large ( r = 0.35), it is not significant ( p = 0.005; the Holm-Bonferroni cutoff is 0.00143). We found no statistically significant relationships between BioTAP questions 6–9 and CCTST dimensions (unpublished data), regardless of whether we correct for multiple comparisons.
The results of Student’s t tests comparing scores on each dimension of the CCTST of students who exhibit mastery with those of students who do not exhibit mastery on each dimension of BioTAP are presented in Table 4 . Focusing first on the overall CCTST scores, we found that the difference between those who exhibit mastery and those who do not in discussing implications of results (BioTAP question 5) is statistically significant ( t = 2.73, p = 0.008, d = 0.71). When we expanded t tests to include all 35 comparisons—and, like above, corrected for 35 comparisons—we found a significant difference in inference scores between students who exhibit mastery on question 5 and students who do not ( t = 3.41, p = 0.0012, d = 0.88), as well as a marginally significant difference in these students’ induction scores ( t = 3.26, p = 0.0018, d = 0.84; the Holm-Bonferroni cutoff is p = 0.00147). Cohen’s d effect sizes, which reveal the strength of the differences for statistically significant relationships, range from 0.71 to 0.88.
The t statistics and effect sizes of differences in dimensions of CCTST across dimensions of BioTAP a
a In each cell, the top number is the t statistic for each comparison, and the middle, italicized number is the associated p value. The bottom number is the effect size. Correlations that are statistically significant after correcting for multiple comparisons are shown in bold.
Finally, we more closely examined the strongest relationship that we observed, which was between the CCTST dimension of inference and the BioTAP partial-sum composite score (shown in Table 3 ), using multiple regression analysis ( Table 5 ). Focusing on the 52 students for whom we have background information, we looked at the simple relationship between BioTAP and inference (model 1), a robust background model including multiple covariates that one might expect to explain some part of the variation in BioTAP (model 2), and a combined model including all variables (model 3). As model 3 shows, the covariates explain very little variation in BioTAP scores, and the relationship between inference and BioTAP persists even in the presence of all of the covariates.
Partial sum (questions 1–5) of BioTAP scores ( n = 52)
** p < 0.01.
*** p < 0.001.
The aim of this study was to examine the extent to which the various components of scientific reasoning—manifested in writing in the genre of undergraduate thesis and assessed using BioTAP—draw on general and specific critical-thinking skills (assessed using CCTST) and to consider the implications for educational practices. Although science reasoning involves critical-thinking skills, it also relates to conceptual knowledge and the epistemological foundations of science disciplines ( Kuhn et al. , 2008 ). Moreover, science reasoning in writing , captured in students’ undergraduate theses, reflects habits, conventions, and the incorporation of feedback that may alter evidence of individuals’ critical-thinking skills. Our findings, however, provide empirical evidence that cumulative measures of science reasoning in writing are nonetheless related to students’ overall critical-thinking skills ( Table 3 ). The particularly significant roles of inference skills ( Table 3 ) and the discussion of implications of results (BioTAP question 5; Table 4 ) provide a basis for more specific ideas about how these constructs relate to one another and what educational interventions may have the most success in fostering these skills.
Our results build on previous findings. The genre of thesis writing combines pedagogies of writing and inquiry found to foster scientific reasoning ( Reynolds et al. , 2012 ) and critical thinking ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ; Quitadamo et al. , 2008 ; Stephenson and Sadler-McKnight, 2016 ). Quitadamo and Kurtz (2007) reported that students who engaged in a laboratory writing component in a general education biology course significantly improved their inference and analysis skills, and Quitadamo and colleagues (2008) found that participation in a community-based inquiry biology course (that included a writing component) was associated with significant gains in students’ inference and evaluation skills. The shared focus on inference is noteworthy, because these prior studies actually differ from the current study; the former considered critical-thinking skills as the primary learning outcome of writing-focused interventions, whereas the latter focused on emergent links between two learning outcomes (science reasoning in writing and critical thinking). In other words, inference skills are impacted by writing as well as manifested in writing.
Inference focuses on drawing conclusions from argument and evidence. According to the consensus definition of critical thinking, the specific skill of inference includes several processes: querying evidence, conjecturing alternatives, and drawing conclusions. All of these activities are central to the independent research at the core of writing an undergraduate thesis. Indeed, a critical part of what we call “science reasoning in writing” might be characterized as a measure of students’ ability to infer and make meaning of information and findings. Because the cumulative BioTAP measures distill underlying similarities and, to an extent, suppress unique aspects of individual dimensions, we argue that it is appropriate to relate inference to scientific reasoning in writing . Even when we control for other potentially relevant background characteristics, the relationship is strong ( Table 5 ).
In taking the complementary view and focusing on BioTAP, when we compared students who exhibit mastery with those who do not, we found that the specific dimension of “discussing the implications of results” (question 5) differentiates students’ performance on several critical-thinking skills. To achieve mastery on this dimension, students must make connections between their results and other published studies and discuss the future directions of the research; in short, they must demonstrate an understanding of the bigger picture. The specific relationship between question 5 and inference is the strongest observed among all individual comparisons. Altogether, perhaps more than any other BioTAP dimension, this aspect of students’ writing provides a clear view of the role of students’ critical-thinking skills (particularly inference and, marginally, induction) in science reasoning.
While inference and discussion of implications emerge as particularly strongly related dimensions in this work, we note that the strongest contribution to “science reasoning in writing in biology,” as determined through exploratory factor analysis, is “argument for the significance of research” (BioTAP question 2, not question 5; Dowd et al. , 2016 ). Question 2 is not clearly related to critical-thinking skills. These findings are not contradictory, but rather suggest that the epistemological and disciplinary-specific aspects of science reasoning that emerge in writing through BioTAP are not completely aligned with aspects related to critical thinking. In other words, science reasoning in writing is not simply a proxy for those critical-thinking skills that play a role in science reasoning.
In a similar vein, the content-related, epistemological aspects of science reasoning, as well as the conventions associated with writing the undergraduate thesis (including feedback from peers and revision), may explain the lack of significant relationships between some science reasoning dimensions and some critical-thinking skills that might otherwise seem counterintuitive (e.g., BioTAP question 2, which relates to making an argument, and the critical-thinking skill of argument). It is possible that an individual’s critical-thinking skills may explain some variation in a particular BioTAP dimension, but other aspects of science reasoning and practice exert much stronger influence. Although these relationships do not emerge in our analyses, the lack of significant correlation does not mean that there is definitively no correlation. Correcting for multiple comparisons suppresses type 1 error at the expense of exacerbating type 2 error, which, combined with the limited sample size, constrains statistical power and makes weak relationships more difficult to detect. Ultimately, though, the relationships that do emerge highlight places where individuals’ distinct critical-thinking skills emerge most coherently in thesis assessment, which is why we are particularly interested in unpacking those relationships.
We recognize that, because only honors students submit theses at these institutions, this study sample is composed of a selective subset of the larger population of biology majors. Although this is an inherent limitation of focusing on thesis writing, links between our findings and results of other studies (with different populations) suggest that observed relationships may occur more broadly. The goal of improved science reasoning and critical thinking is shared among all biology majors, particularly those engaged in capstone research experiences. So while the implications of this work most directly apply to honors thesis writers, we provisionally suggest that all students could benefit from further study of them.
There are several important implications of this study for science education practices. Students’ inference skills relate to the understanding and effective application of scientific content. The fact that we find no statistically significant relationships between BioTAP questions 6–9 and CCTST dimensions suggests that such mid- to lower-order elements of BioTAP ( Reynolds et al. , 2009 ), which tend to be more structural in nature, do not focus on aspects of the finished thesis that draw strongly on critical thinking. In keeping with prior analyses ( Reynolds and Thompson, 2011 ; Dowd et al. , 2016 ), these findings further reinforce the notion that disciplinary instructors, who are most capable of teaching and assessing scientific reasoning and perhaps least interested in the more mechanical aspects of writing, may nonetheless be best suited to effectively model and assess students’ writing.
The goal of the thesis writing course at both Duke University and the University of Minnesota is not merely to improve thesis scores but to move students’ writing into the category of mastery across BioTAP dimensions. Recognizing that students with differing critical-thinking skills (particularly inference) are more or less likely to achieve mastery in the undergraduate thesis (particularly in discussing implications [question 5]) is important for developing and testing targeted pedagogical interventions to improve learning outcomes for all students.
The competencies characterized by the Vision and Change in Undergraduate Biology Education Initiative provide a general framework for recognizing that science reasoning and critical-thinking skills play key roles in major learning outcomes of science education. Our findings highlight places where science reasoning–related competencies (like “understanding the process of science”) connect to critical-thinking skills and places where critical thinking–related competencies might be manifested in scientific products (such as the ability to discuss implications in scientific writing). We encourage broader efforts to build empirical connections between competencies and pedagogical practices to further improve science education.
One specific implication of this work for science education is to focus on providing opportunities for students to develop their critical-thinking skills (particularly inference). Of course, as this correlational study is not designed to test causality, we do not claim that enhancing students’ inference skills will improve science reasoning in writing. However, as prior work shows that science writing activities influence students’ inference skills ( Quitadamo and Kurtz, 2007 ; Quitadamo et al. , 2008 ), there is reason to test such a hypothesis. Nevertheless, the focus must extend beyond inference as an isolated skill; rather, it is important to relate inference to the foundations of the scientific method ( Miri et al. , 2007 ) in terms of the epistemological appreciation of the functions and coordination of evidence ( Kuhn and Dean, 2004 ; Zeineddin and Abd-El-Khalick, 2010 ; Ding et al. , 2016 ) and disciplinary paradigms of truth and justification ( Moshman, 2015 ).
Although this study is limited to the domain of biology at two institutions with a relatively small number of students, the findings represent a foundational step in the direction of achieving success with more integrated learning outcomes. Hopefully, it will spur greater interest in empirically grounding discussions of the constructs of scientific reasoning and critical-thinking skills.
This study contributes to the efforts to improve science education, for both majors and nonmajors, through an empirically driven analysis of the relationships between scientific reasoning reflected in the genre of thesis writing and critical-thinking skills. This work is rooted in the usefulness of BioTAP as a method 1) to facilitate communication and learning and 2) to assess disciplinary-specific and general dimensions of science reasoning. The findings support the important role of the critical-thinking skill of inference in scientific reasoning in writing, while also highlighting ways in which other aspects of science reasoning (epistemological considerations, writing conventions, etc.) are not significantly related to critical thinking. Future research into the impact of interventions focused on specific critical-thinking skills (i.e., inference) for improved science reasoning in writing will build on this work and its implications for science education.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments.
We acknowledge the contributions of Kelaine Haas and Alexander Motten to the implementation and collection of data. We also thank Mine Çetinkaya-Rundel for her insights regarding our statistical analyses. This research was funded by National Science Foundation award DUE-1525602.
- American Association for the Advancement of Science. (2011). Vision and change in undergraduate biology education: A call to action . Washington, DC: Retrieved September 26, 2017, from https://visionandchange.org/files/2013/11/aaas-VISchange-web1113.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- August D. (2016). California Critical Thinking Skills Test user manual and resource guide . San Jose: Insight Assessment/California Academic Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Beyer C. H., Taylor E., Gillmore G. M. (2013). Inside the undergraduate teaching experience: The University of Washington’s growth in faculty teaching study . Albany, NY: SUNY Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bissell A. N., Lemons P. P. (2006). A new method for assessing critical thinking in the classroom . BioScience , ( 1 ), 66–72. https://doi.org/10.1641/0006-3568(2006)056[0066:ANMFAC]2.0.CO;2 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Blattner N. H., Frazier C. L. (2002). Developing a performance-based assessment of students’ critical thinking skills . Assessing Writing , ( 1 ), 47–64. [ Google Scholar ]
- Clase K. L., Gundlach E., Pelaez N. J. (2010). Calibrated peer review for computer-assisted learning of biological research competencies . Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Education , ( 5 ), 290–295. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Condon W., Kelly-Riley D. (2004). Assessing and teaching what we value: The relationship between college-level writing and critical thinking abilities . Assessing Writing , ( 1 ), 56–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asw.2004.01.003 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Ding L., Wei X., Liu X. (2016). Variations in university students’ scientific reasoning skills across majors, years, and types of institutions . Research in Science Education , ( 5 ), 613–632. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-015-9473-y . [ Google Scholar ]
- Dowd J. E., Connolly M. P., Thompson R. J., Jr., Reynolds J. A. (2015a). Improved reasoning in undergraduate writing through structured workshops . Journal of Economic Education , ( 1 ), 14–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220485.2014.978924 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Dowd J. E., Roy C. P., Thompson R. J., Jr., Reynolds J. A. (2015b). “On course” for supporting expanded participation and improving scientific reasoning in undergraduate thesis writing . Journal of Chemical Education , ( 1 ), 39–45. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed500298r . [ Google Scholar ]
- Dowd J. E., Thompson R. J., Jr., Reynolds J. A. (2016). Quantitative genre analysis of undergraduate theses: Uncovering different ways of writing and thinking in science disciplines . WAC Journal , , 36–51. [ Google Scholar ]
- Facione P. A. (1990). Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations . Newark, DE: American Philosophical Association; Retrieved September 26, 2017, from https://philpapers.org/archive/FACCTA.pdf . [ Google Scholar ]
- Gerdeman R. D., Russell A. A., Worden K. J., Gerdeman R. D., Russell A. A., Worden K. J. (2007). Web-based student writing and reviewing in a large biology lecture course . Journal of College Science Teaching , ( 5 ), 46–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Greenhoot A. F., Semb G., Colombo J., Schreiber T. (2004). Prior beliefs and methodological concepts in scientific reasoning . Applied Cognitive Psychology , ( 2 ), 203–221. https://doi.org/10.1002/acp.959 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Haaga D. A. F. (1993). Peer review of term papers in graduate psychology courses . Teaching of Psychology , ( 1 ), 28–32. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15328023top2001_5 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Halonen J. S., Bosack T., Clay S., McCarthy M., Dunn D. S., Hill G. W., Whitlock K. (2003). A rubric for learning, teaching, and assessing scientific inquiry in psychology . Teaching of Psychology , ( 3 ), 196–208. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15328023TOP3003_01 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Hand B., Keys C. W. (1999). Inquiry investigation . Science Teacher , ( 4 ), 27–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Holm S. (1979). A simple sequentially rejective multiple test procedure . Scandinavian Journal of Statistics , ( 2 ), 65–70. [ Google Scholar ]
- Holyoak K. J., Morrison R. G. (2005). The Cambridge handbook of thinking and reasoning . New York: Cambridge University Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Insight Assessment. (2016a). California Critical Thinking Skills Test (CCTST) Retrieved September 26, 2017, from www.insightassessment.com/Products/Products-Summary/Critical-Thinking-Skills-Tests/California-Critical-Thinking-Skills-Test-CCTST .
- Insight Assessment. (2016b). Sample thinking skills questions. Retrieved September 26, 2017, from www.insightassessment.com/Resources/Teaching-Training-and-Learning-Tools/node_1487 .
- Kelly G. J., Takao A. (2002). Epistemic levels in argument: An analysis of university oceanography students’ use of evidence in writing . Science Education , ( 3 ), 314–342. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.10024 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn D., Dean D., Jr. (2004). Connecting scientific reasoning and causal inference . Journal of Cognition and Development , ( 2 ), 261–288. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327647jcd0502_5 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhn D., Iordanou K., Pease M., Wirkala C. (2008). Beyond control of variables: What needs to develop to achieve skilled scientific thinking? . Cognitive Development , ( 4 ), 435–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogdev.2008.09.006 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Lawson A. E. (2010). Basic inferences of scientific reasoning, argumentation, and discovery . Science Education , ( 2 ), 336–364. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.20357 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Meizlish D., LaVaque-Manty D., Silver N., Kaplan M. (2013). Think like/write like: Metacognitive strategies to foster students’ development as disciplinary thinkers and writers . In Thompson R. J. (Ed.), Changing the conversation about higher education (pp. 53–73). Lanham, MD: Rowman & Littlefield. [ Google Scholar ]
- Miri B., David B.-C., Uri Z. (2007). Purposely teaching for the promotion of higher-order thinking skills: A case of critical thinking . Research in Science Education , ( 4 ), 353–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11165-006-9029-2 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Moshman D. (2015). Epistemic cognition and development: The psychology of justification and truth . New York: Psychology Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- National Research Council. (2000). How people learn: Brain, mind, experience, and school . Expanded ed. Washington, DC: National Academies Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Pukkila P. J. (2004). Introducing student inquiry in large introductory genetics classes . Genetics , ( 1 ), 11–18. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.166.1.11 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Quitadamo I. J., Faiola C. L., Johnson J. E., Kurtz M. J. (2008). Community-based inquiry improves critical thinking in general education biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 3 ), 327–337. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.07-11-0097 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Quitadamo I. J., Kurtz M. J. (2007). Learning to improve: Using writing to increase critical thinking performance in general education biology . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 2 ), 140–154. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.06-11-0203 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds J. A., Smith R., Moskovitz C., Sayle A. (2009). BioTAP: A systematic approach to teaching scientific writing and evaluating undergraduate theses . BioScience , ( 10 ), 896–903. https://doi.org/10.1525/bio.2009.59.10.11 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds J. A., Thaiss C., Katkin W., Thompson R. J. (2012). Writing-to-learn in undergraduate science education: A community-based, conceptually driven approach . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 1 ), 17–25. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.11-08-0064 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reynolds J. A., Thompson R. J. (2011). Want to improve undergraduate thesis writing? Engage students and their faculty readers in scientific peer review . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 2 ), 209–215. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.10-10-0127 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rhemtulla M., Brosseau-Liard P. E., Savalei V. (2012). When can categorical variables be treated as continuous? A comparison of robust continuous and categorical SEM estimation methods under suboptimal conditions . Psychological Methods , ( 3 ), 354–373. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029315 . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Stephenson N. S., Sadler-McKnight N. P. (2016). Developing critical thinking skills using the science writing heuristic in the chemistry laboratory . Chemistry Education Research and Practice , ( 1 ), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RP00102A . [ Google Scholar ]
- Tariq V. N., Stefani L. A. J., Butcher A. C., Heylings D. J. A. (1998). Developing a new approach to the assessment of project work . Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 3 ), 221–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/0260293980230301 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Timmerman B. E. C., Strickland D. C., Johnson R. L., Payne J. R. (2011). Development of a “universal” rubric for assessing undergraduates’ scientific reasoning skills using scientific writing . Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 5 ), 509–547. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602930903540991 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Topping K. J., Smith E. F., Swanson I., Elliot A. (2000). Formative peer assessment of academic writing between postgraduate students . Assessment and Evaluation in Higher Education , ( 2 ), 149–169. https://doi.org/10.1080/713611428 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Willison J., O’Regan K. (2007). Commonly known, commonly not known, totally unknown: A framework for students becoming researchers . Higher Education Research and Development , ( 4 ), 393–409. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360701658609 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Woodin T., Carter V. C., Fletcher L. (2010). Vision and Change in Biology Undergraduate Education: A Call for Action—Initial responses . CBE—Life Sciences Education , ( 2 ), 71–73. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.10-03-0044 . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Zeineddin A., Abd-El-Khalick F. (2010). Scientific reasoning and epistemological commitments: Coordination of theory and evidence among college science students . Journal of Research in Science Teaching , ( 9 ), 1064–1093. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.20368 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman C. (2000). The development of scientific reasoning skills . Developmental Review , ( 1 ), 99–149. https://doi.org/10.1006/drev.1999.0497 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Zimmerman C. (2007). The development of scientific thinking skills in elementary and middle school . Developmental Review , ( 2 ), 172–223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dr.2006.12.001 . [ Google Scholar ]
- Archives & Special Collections home
- Art Library home
- Ekstrom Library home
- Kornhauser Health Sciences Library home
- Law Library home
- Music Library home
- University of Louisville Hospital home
- Interlibrary Loan
- Off-Campus Login
- Renew Books
- Cardinal Card
- My Print Center
- Business Ops
- Cards Career Connection
Search Site
Search catalog, critical thinking and academic research: intro.
- Information
- Point of View
- Assumptions
- Implications
Critical Thinking and Academic Research
Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers.
The research process is not simply collecting data, evidence, or "facts," then piecing together this preexisting information into a paper. Instead, the research process is about inquiry—asking questions and developing answers through serious critical thinking and thoughtful reflection.
As a result, the research process is recursive, meaning that the researcher regularly revisits ideas, seeks new information when necessary, and reconsiders and refines the research question, topic, or approach. In other words, research almost always involves constant reflection and revision.
This guide is designed to help you think through various aspects of the research process. The steps are not sequential, nor are they prescriptive about what steps you should take at particular points in the research process. Instead, the guide should help you consider the larger, interrelated elements of thinking involved in research.
Research Anxiety?
Research is not often easy or straightforward, so it's completely normal to feel anxious, frustrated, or confused. In fact, if you feel anxious, it can be a good sign that you're engaging in the type of critical thinking necessary to research and write a high-quality paper.
Think of the research process not as one giant, impossibly complicated task, but as a series of smaller, interconnected steps. These steps can be messy, and there is not one correct sequence of steps that will work for every researcher. However, thinking about research in small steps can help you be more productive and alleviate anxiety.
Paul-Elder Framework
This guide is based on the "Elements of Reasoning" from the Paul-Elder framework for critical thinking. For more information about the Paul-Elder framework, click the link below.
Some of the content in this guide has been adapted from The Aspiring Thinker's Guide to Critical Thinking (2009) by Linda Elder and Richard Paul.
- Next: Purpose >>
- Last Updated: Jul 10, 2023 11:50 AM
- Librarian Login
Critical Writing 101
Descriptive vs analytical vs critical writing.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | April 2017
Across the thousands of students we work with , descriptive writing (as opposed to critical or analytical writing) is an incredibly pervasive problem . In fact, it’s probably the biggest killer of marks in dissertations, theses and research papers . So, in this post, we’ll explain the difference between descriptive and analytical writing in straightforward terms, along with plenty of practical examples.
Descriptive vs Analytical Writing
Writing critically is one of the most important skills you’ll need to master for your academic journey, but what exactly does this mean?
Well, when it comes to writing, at least for academic purposes, there are two main types – descriptive writing and critical writing. Critical writing is also sometimes referred to as analytical writing, so we’ll use these two terms interchangeably.
To understand what constitutes critical (or analytical) writing, it’s useful to compare it against its opposite, descriptive writing. At the most basic level, descriptive writing merely communicates the “ what ”, “ where ”, “ when ” or “ who ”. In other words, it describes a thing, place, time or person. It doesn’t consider anything beyond that or explore the situation’s impact, importance or meaning. Here’s an example of a descriptive sentence:
“Yesterday, the president unexpectedly fired the minister of finance.”
As you can see, this sentence just states what happened, when it happened and who was involved. Classic descriptive writing.
Contrasted to this, critical writing takes things a step further and unveils the “ so what? ” – in other words, it explains the impact or consequence of a given situation. Let’s stick with the same event and look at an example of analytical writing:
“The president’s unexpected firing of the well-respected finance minister had an immediate negative impact on investor confidence. This led to a sharp decrease in the value of the local currency, especially against the US dollar. This devaluation means that all dollar-based imports are now expected to rise in cost, thereby raising the cost of living for citizens, and reducing disposable income.”
As you can see in this example, the descriptive version only tells us what happened (the president fired the finance minister), whereas the critical version goes on to discuss some of the impacts of the president’s actions.

Ideally, critical writing should always link back to the broader objectives of the paper or project, explaining what each thing or event means in relation to those objectives. In a dissertation or thesis, this would involve linking the discussion back to the research aims, objectives and research questions – in other words, the golden thread .
Sounds a bit fluffy and conceptual? Let’s look at an example:
If your research aims involved understanding how the local environment impacts demand for specialty imported vegetables, you would need to explain how the devaluation of the local currency means that the imported vegetables would become more expensive relative to locally farmed options. This in turn would likely have a negative impact on sales, as consumers would turn to cheaper local alternatives.
As you can see, critical (or analytical) writing goes beyond just describing (that’s what descriptive writing covers) and instead focuses on the meaning of things, events or situations, especially in relation to the core research aims and questions.
Need a helping hand?
But wait, there’s more.
This “ what vs so what” distinction is important in understanding the difference between description and analysis, but it is not the only difference – the differences go deeper than this. The table below explains some other key differences between descriptive and analytical writing.
Should I avoid descriptive writing altogether?
Not quite. For the most part, you’ll need some descriptive writing to lay the foundation for the critical, analytical writing. In other words, you’ll usually need to state the “what” before you can discuss the “so what”. Therefore, description is simply unavoidable and in fact quite essential , but you do want to keep it to a minimum and focus your word count on the analytical side of things.
As you write, a good rule of thumb is to identify every what (in other words, every descriptive point you make) and then check whether it is accompanied by a so what (in other words, a critical conclusion regarding its meaning or impact).
Of course, this won’t always be necessary as some conclusions are fairly obvious and go without saying. But, this basic practice should help you minimise description, maximise analysis, and most importantly, earn you marks!
Let’s recap.
So, the key takeaways for this post are as follows:
- Descriptive writing focuses on the what , while critical/analytical writing focuses on the so what .
- Analytical writing should link the discussion back to the research aims, objectives or research questions (the golden thread).
- Some amount of description will always be needed, but aim to minimise description and maximise analysis to earn higher marks.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

19 Comments
Thank you so much. This was helpful and a switch from the bad writing habits to the good habits.
Great to hear that, Sarah. Glad you found it useful!
I am currently working on my Masters Thesis and found this extremely informative and helpful. Thank you kindly.
I’m currently a University student and this is so helpful. Thank you.
It really helped me to get the exact meaning of analytical writing. Differences between the two explains it well
Thank you! this was very useful
With much appreciation, I say thank you. Your explanations are down to earth. It has been helpful.
Very helpful towards my theses journey! Many thanks 👍
very helpful
very helpful indeed
Thanks Derek for the useful coaching
Thank you for sharing this. I was stuck on descriptive now I can do my corrections. Thank you.
I was struggling to differentiate between descriptive and analytical writing. I googled and found this as it is so helpful. Thank you for sharing.
I am glad to see this differences of descriptive against analytical writing. This is going to improve my masters dissertation
Thanks in deed. It was helpful
Thank you so much. I’m now better informed
Busy with MBA in South Africa, this is very helpful as most of the writing requires one to expound on the topics. thanks for this, it’s a salvation from watching the blinking cursor for hours while figuring out what to write to hit the 5000 word target 😂
It’s been fantastic and enriching. Thanks a lot, GRAD COACH.
Wonderful explanation of descriptive vs analytic writing with examples. This is going to be greatly helpful for me as I am writing my thesis at the moment. Thank you Grad Coach. I follow your YouTube videos and subscribed and liked every time I watch one.
Very useful piece. thanks
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Reading & Writing Purposes
Introduction: critical thinking, reading, & writing, critical thinking.
The phrase “critical thinking” is often misunderstood. “Critical” in this case does not mean finding fault with an action or idea. Instead, it refers to the ability to understand an action or idea through reasoning. According to the website SkillsYouNeed [1]:
Critical thinking might be described as the ability to engage in reflective and independent thinking.
In essence, critical thinking requires you to use your ability to reason. It is about being an active learner rather than a passive recipient of information.
Critical thinkers rigorously question ideas and assumptions rather than accepting them at face value. They will always seek to determine whether the ideas, arguments, and findings represent the entire picture and are open to finding that they do not.
Critical thinkers will identify, analyze, and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct.
Someone with critical thinking skills can:
- Understand the links between ideas.
- Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas.
- Recognize, build, and appraise arguments.
- Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
- Approach problems in a consistent and systematic way.
- Reflect on the justification of their own assumptions, beliefs and values.
Read more at: https://www.skillsyouneed.com/learn/critical-thinking.html

Critical thinking—the ability to develop your own insights and meaning—is a basic college learning goal. Critical reading and writing strategies foster critical thinking, and critical thinking underlies critical reading and writing.
Critical Reading
Critical reading builds on the basic reading skills expected for college.
College Readers’ Characteristics
- College readers are willing to spend time reflecting on the ideas presented in their reading assignments. They know the time is well-spent to enhance their understanding.
- College readers are able to raise questions while reading. They evaluate and solve problems rather than merely compile a set of facts to be memorized.
- College readers can think logically. They are fact-oriented and can review the facts dispassionately. They base their judgments on ideas and evidence.
- College readers can recognize error in thought and persuasion as well as recognize good arguments.
- College readers are skeptical. They understand that not everything in print is correct. They are diligent in seeking out the truth.
Critical Readers’ Characteristics
- Critical readers are open-minded. They seek alternative views and are open to new ideas that may not necessarily agree with their previous thoughts on a topic. They are willing to reassess their views when new or discordant evidence is introduced and evaluated.
- Critical readers are in touch with their own personal thoughts and ideas about a topic. Excited about learning, they are eager to express their thoughts and opinions.
- Critical readers are able to identify arguments and issues. They are able to ask penetrating and thought-provoking questions to evaluate ideas.
- Critical readers are creative. They see connections between topics and use knowledge from other disciplines to enhance their reading and learning experiences.
- Critical readers develop their own ideas on issues, based on careful analysis and response to others’ ideas.
The video below, although geared toward students studying for the SAT exam (Scholastic Aptitude Test used for many colleges’ admissions), offers a good, quick overview of the concept and practice of critical reading.
Critical Reading & Writing
College reading and writing assignments often ask you to react to, apply, analyze, and synthesize information. In other words, your own informed and reasoned ideas about a subject take on more importance than someone else’s ideas, since the purpose of college reading and writing is to think critically about information.
Critical thinking involves questioning. You ask and answer questions to pursue the “careful and exact evaluation and judgment” that the word “critical” invokes (definition from The American Heritage Dictionary ). The questions simply change depending on your critical purpose. Different critical purposes are detailed in the next pages of this text.
However, here’s a brief preview of the different types of questions you’ll ask and answer in relation to different critical reading and writing purposes.
When you react to a text you ask:
- “What do I think?” and
- “Why do I think this way?”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “reaction” questions about the topic assimilation of immigrants to the U.S. , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: I think that assimilation has both positive and negative effects because, while it makes life easier within the dominant culture, it also implies that the original culture is of lesser value.
When you apply text information you ask:
- “How does this information relate to the real world?”
e.g., If I asked and answered this “application” question about the topic assimilation , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: During the past ten years, a group of recent emigrants has assimilated into the local culture; the process of their assimilation followed certain specific stages.
When you analyze text information you ask:
- “What is the main idea?”
- “What do I want to ‘test’ in the text to see if the main idea is justified?” (supporting ideas, type of information, language), and
- “What pieces of the text relate to my ‘test?'”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “analysis” questions about the topic immigrants to the United States , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop in an essay: Although Lee (2009) states that “segmented assimilation theory asserts that immigrant groups may assimilate into one of many social sectors available in American society, instead of restricting all immigrant groups to adapting into one uniform host society,” other theorists have shown this not to be the case with recent immigrants in certain geographic areas.
When you synthesize information from many texts you ask:
- “What information is similar and different in these texts?,” and
- “What pieces of information fit together to create or support a main idea?”
e.g., If I asked and answered these “synthesis” questions about the topic immigrants to the U.S. , I might create the following main idea statement, which I could then develop by using examples and information from many text articles as evidence to support my idea: Immigrants who came to the United States during the immigration waves in the early to mid 20th century traditionally learned English as the first step toward assimilation, a process that was supported by educators. Now, both immigrant groups and educators are more focused on cultural pluralism than assimilation, as can be seen in educators’ support of bilingual education. However, although bilingual education heightens the child’s reasoning and ability to learn, it may ultimately hinder the child’s sense of security within the dominant culture if that culture does not value cultural pluralism as a whole.

Critical reading involves asking and answering these types of questions in order to find out how the information “works” as opposed to just accepting and presenting the information that you read in a text. Critical writing involves recording your insights into these questions and offering your own interpretation of a concept or issue, based on the meaning you create from those insights.
- Crtical Thinking, Reading, & Writing. Authored by : Susan Oaks, includes material adapted from TheSkillsYouNeed and Reading 100; attributions below. Project : Introduction to College Reading & Writing. License : CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- Critical Thinking. Provided by : TheSkillsYouNeed. Located at : https://www.skillsyouneed.com/ . License : Public Domain: No Known Copyright . License Terms : Quoted from website: The use of material found at skillsyouneed.com is free provided that copyright is acknowledged and a reference or link is included to the page/s where the information was found. Read more at: https://www.skillsyouneed.com/
- The Reading Process. Authored by : Scottsdale Community College Reading Faculty. Provided by : Maricopa Community College. Located at : https://learn.maricopa.edu/courses/904536/files/32966438?module_item_id=7198326 . Project : Reading 100. License : CC BY: Attribution
- image of person thinking with light bulbs saying -idea- around her head. Authored by : Gerd Altmann. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/light-bulb-idea-think-education-3704027/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved
- video What is Critical Reading? SAT Critical Reading Bootcamp #4. Provided by : Reason Prep. Located at : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5Hc3hmwnymw . License : Other . License Terms : YouTube video
- image of man smiling and holding a lightbulb. Authored by : africaniscool. Provided by : Pixabay. Located at : https://pixabay.com/photos/man-african-laughing-idea-319282/ . License : CC0: No Rights Reserved

Privacy Policy
- How it works
What is Critical Thinking in Academics – Guide With Examples
Published by Grace Graffin at October 17th, 2023 , Revised On October 17, 2023
In an era dominated by vast amounts of information, the ability to discern, evaluate, and form independent conclusions is more crucial than ever. Enter the realm of “critical thinking.” But what does this term truly mean?
What is Critical Thinking?
Critical thinking is the disciplined art of analysing and evaluating information or situations by applying a range of intellectual skills. It goes beyond mere memorisation or blind acceptance of information, demanding a deeper understanding and assessment of evidence, context, and implications.
Moreover, paraphrasing in sources is an essential skill in critical thinking, as it allows for representing another’s ideas in one’s own words, ensuring comprehension.
Critical thinking is not just an academic buzzword but an essential tool. In academic settings, it serves as the backbone of genuine understanding and the springboard for innovation. When students embrace critical thinking, they move from being passive recipients of information to active participants in their own learning journey.
They question, evaluate, and synthesise information from various sources, fostering an intellectual curiosity that extends beyond the classroom. Part of this involves understanding how to integrate sources into their work, which means not only including information from various places, but also doing so in a cohesive and logical way.
The importance of critical thinking in academics cannot be overstated. It equips students with the skills to discern credible sources from unreliable ones, develop well-informed arguments, and approach problems with a solution-oriented mindset.
The Origins and Evolution of Critical Thinking
The idea of critical thinking isn’t a new-age concept. Its roots reach back into ancient civilisations, moulding the foundations of philosophy, science, and education. To appreciate its evolution, it’s vital to delve into its historical context and the influential thinkers who have championed it.
Historical Perspective on the Concept of Critical Thinking
The seeds of critical thinking can be traced back to Ancient Greece, particularly in the city-state of Athens. Here, the practice of debate, dialogue, and philosophical inquiry was valued and was seen as a route to knowledge and wisdom. This era prized the art of questioning, investigating, and exploring diverse viewpoints to reach enlightened conclusions.
In medieval Islamic civilisation, scholars in centres of learning, such as the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, played a pivotal role in advancing critical thought. Their works encompassed vast areas, including philosophy, mathematics, and medicine, often intertwining rigorous empirical observations with analytical reasoning.
The Renaissance period further nurtured critical thinking as it was a time of revival in art, culture, and intellect. This era championed humanistic values, focusing on human potential and achievements. It saw the rebirth of scientific inquiry, scepticism about religious dogma, and an emphasis on empirical evidence.
Philosophers and Educators Who Championed Critical Thinking
Several philosophers and educators stand out for their remarkable contributions to the sphere of critical thinking:
Known for the Socratic method, a form of cooperative argumentative dialogue, Socrates would ask probing questions, forcing his pupils to think deeply about their beliefs and assumptions. His methodology still influences modern education, emphasising the answer and the path of reasoning that leads to it.
A student of Socrates, Plato believed in the importance of reason and inquiry. His allegory of the cave highlights the difference between blindly accepting information and seeking true knowledge.
He placed great emphasis on empirical evidence and logic. His works on syllogism and deductive reasoning laid the foundation for systematic critical thought.
Al-Farabi And Ibn Rushd (Averroes)
Islamic philosophers, who harmonised Greek philosophy with Islamic thought, emphasised the importance of rationality and critical inquiry.
Sir Francis Bacon
An advocate for the scientific method, Bacon believed that knowledge should be based on empirical evidence, observation, and experimentation rather than mere reliance on accepted truths.
A modern proponent of critical thinking, Dewey viewed it as an active, persistent, and careful consideration of a belief or supposed form of knowledge. He emphasised that students should be taught to think for themselves rather than just memorise facts.
Paulo Freire
Recognised for his ideas on “problem-posing education,” Freire believed that students should be encouraged to question, reflect upon, and respond to societal issues, fostering critical consciousness.
Characteristics of Critical Thinkers
Critical thinkers are not defined merely by the knowledge they possess, but by the manner in which they process, analyse, and use that knowledge. While the profile of a critical thinker can be multifaceted, certain core traits distinguish them. Let’s delve into these characteristics:
1. Open-mindedness
Open-mindedness refers to the willingness to consider different ideas, opinions, and perspectives, even if they challenge one’s existing beliefs. It allows critical thinkers to avoid being trapped in their own biases or preconceived notions. By being open to diverse viewpoints, they can make more informed and holistic decisions.
- Listening to a debate without immediately taking sides.
- Reading literature from different cultures to understand various world views.
2. Analytical Nature
An analytical nature entails the ability to break down complex problems or information into smaller, manageable parts to understand the whole better. Being analytical enables individuals to see patterns, relationships, and inconsistencies, allowing for deeper comprehension and better problem-solving.
- Evaluating a research paper by examining its methodology, results, and conclusions separately.
- Breaking down the components of a business strategy to assess its viability.
3. Scepticism
Scepticism is the tendency to question and doubt claims or assertions until sufficient evidence is presented. Skepticism ensures that critical thinkers do not accept information at face value. They seek evidence and are cautious about jumping to conclusions without verification.
- Questioning the results of a study that lacks a control group.
- Doubting a sensational news headline and researching further before believing or sharing it.
4. Intellectual Humility
Intellectual humility involves recognising and accepting the limitations of one’s knowledge and understanding. It is about being aware that one does not have all the answers. This trait prevents arrogance and overconfidence. Critical thinkers with intellectual humility are open to learning and receptive to constructive criticism.
- Admitting when one is wrong in a discussion.
- Actively seeking feedback on a project or idea to enhance it.
5. Logical Reasoning
Logical reasoning is the ability to think sequentially and make connections between concepts in a coherent manner. It involves drawing conclusions that logically follow from the available information. Logical reasoning ensures that decisions and conclusions are sound and based on valid premises. It helps avoid fallacies and cognitive biases.
- Using deductive reasoning to derive a specific conclusion from a general statement.
- Evaluating an argument for potential logical fallacies like “slippery slope” or “ad hominem.”
The Difference Between Critical Thinking and Memorisation
In today’s rapidly changing educational landscape, there is an ongoing debate about the importance of rote memorisation versus the significance of cultivating critical thinking skills. Both have their place in learning, but they serve very different purposes.
Nature Of Learning
- Rote Learning: Involves memorising information exactly as it is, without necessarily understanding its context or underlying meaning. It’s akin to storing data as-is, without processing.
- Analytical Processing (Critical Thinking): Involves understanding, questioning, and connecting new information with existing knowledge. It’s less about storage and more about comprehension and application.
Depth of Engagement
- Rote Learning: Often remains at the surface level. Students might remember facts for a test, but might forget them shortly after.
- Analytical Processing: Engages deeper cognitive skills. When students think critically, they’re more likely to retain information because they’ve processed it deeper.
Application in New Situations
- Rote Learning: Information memorised through rote often does not easily apply to new or unfamiliar situations, since it is detached from understanding.
- Analytical Processing: Promotes adaptability. Critical thinkers can transfer knowledge and skills to different contexts because they understand underlying concepts and principles.
Why Critical Thinking Produces Long-Term Academic Benefits
Here are the benefits of critical thinking in academics.
Enhanced Retention
Critical thinking often involves active learning—discussions, problem-solving, and debates—which promotes better retention than passive memorisation.
Skill Development
Beyond content knowledge, critical thinking develops skills like analysis, synthesis, source evaluation , and problem-solving. These are invaluable in higher education and professional settings.
Adaptability
In an ever-evolving world, the ability to adapt is crucial. Critical thinkers are better equipped to learn and adapt because they don’t just know facts; they understand concepts.
Lifelong Learning
Critical thinkers are naturally curious. They seek to understand, question, and explore, turning them into lifelong learners who continually seek knowledge and personal growth.
Improved Decision-Making
Analytical processing allows students to evaluate various perspectives, weigh evidence, and make well-informed decisions, a skill far beyond academics.
Preparation for Real-World Challenges
The real world does not come with a textbook. Critical thinkers can navigate unexpected challenges, connect disparate pieces of information, and innovate solutions.
Steps in the Critical Thinking Process
Critical thinking is more than just a skill—it is a structured process. By following a systematic approach, critical thinkers can navigate complex issues and ensure their conclusions are well-informed and reasoned. Here’s a breakdown of the steps involved:
Step 1. Identification and Clarification of the Problem or Question
Recognizing that a problem or question exists and understanding its nature. It’s about defining the issue clearly, without ambiguity. A well-defined problem serves as the foundation for the subsequent steps. The entire process may become misguided without a clear understanding of what’s being addressed.
Example: Instead of a vague problem like “improving the environment,” a more specific question could be “How can urban areas reduce air pollution?”
Step 2. Gathering Information and Evidence
Actively seeking relevant data, facts, and evidence. This might involve research, observations, experiments, or discussions. Reliable decisions are based on solid evidence. The quality and relevance of the information gathered can heavily influence the final conclusion.
Example: To address urban air pollution, one might gather data on current pollution levels, sources of pollutants, existing policies, and strategies employed by other cities.
Step 3. Analysing the Information
Breaking down the gathered information, scrutinising its validity, and identifying patterns, contradictions, and relationships. This step ensures that the information is not just accepted at face value. Critical thinkers can differentiate between relevant and irrelevant information and detect biases or inaccuracies by analysing data.
Example: When examining data on pollution, one might notice that certain industries are major contributors or that pollution levels rise significantly at specific times of the year.
Step 4. Drawing Conclusions and Making Decisions
After thorough analysis, formulating an informed perspective, solution, or decision-based on the evidence. This is the culmination of the previous steps. Here, the critical thinker synthesises the information and applies logic to arrive at a reasoned conclusion.
Example: Based on the analysis, one might conclude that regulating specific industries and promoting public transportation during peak pollution periods can help reduce urban air pollution.
Step 5. Reflecting on the Process And The Conclusions Reached
Take a step back to assess the entire process, considering any potential biases, errors, or alternative perspectives. It is also about evaluating the feasibility and implications of the conclusions. Reflection ensures continuous learning and improvement. Individuals can refine their approach to future problems by evaluating their thinking process.
Example: Reflecting on the proposed solution to reduce pollution, one might consider its economic implications, potential industry resistance, and the need for public awareness campaigns.
The research done by our experts have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- Authentic Sources

The Role of Critical Thinking in Different Academic Subjects
Critical thinking is a universal skill applicable across disciplines. Its methodologies might differ based on the subject, but its core principles remain consistent. Let us explore how critical thinking manifests in various academic domains:
1. Sciences
- Hypothesis Testing: Science often begins with a hypothesis—a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. Critical thinking is essential in formulating a testable hypothesis and determining its validity based on experimental results.
- Experimental Design: Designing experiments requires careful planning to ensure valid and reliable results. Critical thinking aids in identifying variables, ensuring controls, and determining the best methodologies to obtain accurate data.
- Example: In a biology experiment to test the effect of light on plant growth, critical thinking helps ensure variables like water and soil quality are consistent, allowing for a fair assessment of the light’s impact.
2. Humanities
- Analysing Texts: Humanities often involve studying texts—literature, historical documents, or philosophical treatises. Critical thinking lets students decode themes, discern authorial intent, and recognise underlying assumptions or biases.
- Understanding Contexts: Recognizing a text or artwork’s cultural, historical, or social contexts is pivotal. Critical thinking allows for a deeper appreciation of these contexts, providing a holistic understanding of the subject.
- Example: When studying Shakespeare’s “Othello,” critical thinking aids in understanding the play’s exploration of jealousy, race, and betrayal, while also appreciating its historical context in Elizabethan England.
3. Social Sciences
- Evaluating Arguments: Social sciences, such as sociology or political science, often present various theories or arguments about societal structures and behaviours. Critical thinking aids in assessing the merits of these arguments and recognising their implications.
- Understanding Biases: Since social sciences study human societies, they’re susceptible to biases. Critical thinking helps identify potential biases in research or theories, ensuring a more objective understanding.
- Example: In studying economic policies, critical thinking helps weigh the benefits and drawbacks of different economic models, considering both empirical data and theoretical arguments.
4. Mathematics
- Problem-Solving: Mathematics is more than just numbers; it is about solving problems. Critical thinking enables students to identify the best strategies to tackle problems, ensuring efficient and accurate solutions.
- Logical Deduction: Mathematical proofs and theorems rely on logical steps. Critical thinking ensures that each step is valid and the conclusions sound.
- Example: In geometry, when proving that two triangles are congruent, critical thinking helps ensure that each criterion (like side lengths or angles) is met and the logic of the proof is coherent.
Examples of Critical Thinking in Academics
Some of the critical thinking examples in academics are discussed below.
Case Study 1: Evaluating A Scientific Research Paper
Scenario: A research paper claims that a new herbal supplement significantly improves memory in elderly individuals.
Critical Thinking Application:
Scrutinising Methodology:
- Was the study double-blind and placebo-controlled?
- How large was the sample size?
- Were the groups randomised?
- Were there any potential confounding variables?
Assessing Conclusions:
- Do the results conclusively support the claim, or are there other potential explanations?
- Are the statistical analyses robust, and do they show a significant difference?
- Is the effect size clinically relevant or just statistically significant?
Considering Broader Context:
- How does this study compare with existing literature on the subject?
- Were there any conflicts of interest, such as funding from the supplement company?
Critical analysis determined that while the study showed statistical significance, the effect size was minimal. Additionally, the sample size was small, and there was potential bias as the supplement manufacturer funded the study.
Case Study 2: Analysing a Literary Text
Scenario: A reading of F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby.”
Understanding Symbolism:
- What does the green light represent for Gatsby and in the broader context of the American Dream?
- How does the Valley of Ashes symbolise societal decay?
Recognising Authorial Intent:
- Why might Fitzgerald depict the characters’ lavish lifestyles amid underlying dissatisfaction?
- What critiques of American society is Fitzgerald potentially making?
Contextual Analysis:
- How does the era in which the novel was written (Roaring Twenties) influence its themes and characters?
Through critical analysis, the reader recognises that while “The Great Gatsby” is a tale of love and ambition, it’s also a poignant critique of the hollowness of the American Dream and the societal excesses of the 1920s.
Case Study 3: Decoding Historical Events
Scenario: The events leading up to the American Revolution.
Considering Multiple Perspectives:
- How did the British government view the colonies and their demands?
- What were the diverse perspectives within the American colonies, considering loyalists and patriots?
Assessing Validity of Sources:
- Which accounts are primary sources, and which are secondary?
- Are there potential biases in these accounts, based on their origins?
Analysing Causation and Correlation:
- Were taxes and representation the sole reasons for the revolution, or were there deeper economic and philosophical reasons?
Through critical analysis, the student understands that while taxation without representation was a significant catalyst, the American Revolution was also influenced by Enlightenment ideas, economic interests, and long-standing grievances against colonial policies.
Challenges to Developing Critical Thinking Skills
In our complex and rapidly changing world, the importance of critical thinking cannot be overstated. However, various challenges can impede the cultivation of these vital skills.
1. Common Misconceptions and Cognitive Biases
Human brains often take shortcuts in processing information, leading to cognitive biases. Additionally, certain misconceptions about what constitutes critical thinking can hinder its development.
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to search for, interpret, and recall information that confirms one’s pre-existing beliefs.
- Anchoring Bias: Relying too heavily on the first piece of information encountered when making decisions.
- Misconception: Believing that critical thinking merely means being critical or negative about ideas, rather than evaluating them objectively.
These biases can skew perception and decision-making, making it challenging to objectively approach issues.
2. The Influence of Technology and Social Media
While providing unprecedented access to information, the digital age also presents unique challenges. The barrage of information, the immediacy of social media reactions, and algorithms that cater to user preferences can hinder critical thought.
- Information Overload: The sheer volume of online data can make it difficult to discern credible sources from unreliable ones.
- Clickbait and Misinformation: Articles with sensational titles designed to generate clicks might lack depth or accuracy.
- Algorithmic Bias: Platforms showing users content based on past preferences can limit exposure to diverse viewpoints.
Relying too heavily on technology and social media can lead to superficial understanding, reduced attention spans, and a narrow worldview.
3. The Danger of Echo Chambers and Confirmation Bias
An echo chamber is a situation in which beliefs are amplified or reinforced by communication and repetition inside a closed system, cutting off differing viewpoints.
- Social Media Groups: Joining groups or following pages that only align with one’s beliefs can create a feedback loop, reinforcing existing opinions without challenge.
- Selective Media Consumption: Only watching news channels or reading websites that align with one’s political or social views.
Echo chambers reinforce confirmation bias, limit exposure to diverse perspectives, and can polarise opinions, making objective, critical evaluation of issues challenging.
Benefits of Promoting Critical Thinking in Education
When cultivated and promoted in educational settings, critical thinking can have transformative effects on students, equipping them with vital skills to navigate their academic journey and beyond. Here’s an exploration of the manifold benefits of emphasising critical thinking in education:
Improved Problem-Solving Skills
Critical thinking enables students to approach problems methodically, breaking them down into manageable parts, analysing each aspect, and synthesising solutions.
- Academic: Enhances students’ ability to tackle complex assignments, research projects, and unfamiliar topics.
- Beyond School: Prepares students for real-world challenges where they might encounter problems without predefined solutions.
Enhanced Creativity and Innovation
Critical thinking is not just analytical but also involves lateral thinking, helping students see connections between disparate ideas and encouraging imaginative solutions.
- Academic: Promotes richer discussions, more creative projects, and the ability to view topics from multiple angles.
- Beyond School: Equips students for careers and situations where innovative solutions can lead to advancements in fields like technology, arts, or social entrepreneurship.
Better Decision-Making Abilities
Critical thinkers evaluate information thoroughly, weigh potential outcomes, and make decisions based on evidence and reason rather than impulse or peer pressure.
- Academic: Helps students make informed choices about their studies, research directions, or group projects.
- Beyond School: Prepares students to make sound decisions in personal and professional spheres, from financial choices to ethical dilemmas.
Greater Resilience in the Face of Complex Challenges
Critical thinking nurtures a growth mindset. When students think critically, they are more likely to view challenges as opportunities for learning rather than insurmountable obstacles.
- Academic: Increases perseverance in difficult subjects, promoting a deeper understanding rather than superficial learning. Students become more resilient in handling academic pressures and setbacks.
- Beyond School: Cultivates individuals who can navigate the complexities of modern life, from career challenges to societal changes, with resilience and adaptability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is critical thinking.
Critical thinking is the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue to form a judgment. It involves gathering relevant information, discerning potential biases, logically connecting ideas, and questioning assumptions. Essential for informed decision-making, it promotes scepticism and requires the ability to think independently and rationally.
What makes critical thinking?
Critical thinking arises from questioning assumptions, evaluating evidence, discerning fact from opinion, recognising biases, and logically connecting ideas. It demands curiosity, scepticism, and an open mind. By continuously challenging one’s beliefs and considering alternative viewpoints, one cultivates the ability to think clearly, rationally, and independently.
What is the purpose of critical thinking?
The purpose of critical thinking is to enable informed decisions by analysing and evaluating information objectively. It fosters understanding, problem-solving, and clarity, reducing the influence of biases and misconceptions. Through critical thinking, individuals discern truth, make reasoned judgments, and engage more effectively in discussions and debates.
How to improve critical thinking?
- Cultivate curiosity by asking questions.
- Practice active listening.
- Read widely and diversely.
- Engage in discussions and debates.
- Reflect on your thought processes.
- Identify biases and challenge assumptions.
- Solve problems systematically.
What are some critical thinking skills?
- Analysis: breaking concepts into parts.
- Evaluation: judging information’s validity.
- Inference: drawing logical conclusions.
- Explanation: articulating reasons.
- Interpretation: understanding meaning.
- Problem-solving: devising effective solutions.
- Decision-making: choosing the best options.
What is information literacy?
Information literacy is the ability to find, evaluate, and use information effectively. It encompasses understanding where to locate information, determining its credibility, distinguishing between facts and opinions, and using it responsibly. Essential in the digital age, it equips individuals to navigate the vast sea of data and make informed decisions.
What makes a credible source?
- Authorship by experts or professionals.
- Reliable publisher or institution backing.
- Transparent sourcing and references.
- Absence of bias or clear disclosure of it.
- Recent publications or timely updates.
- Peer review or editorial oversight.
- Clear, logical arguments.
- Reputability in its field or domain.
How do I analyse information critically?
- Determine the source’s credibility.
- Identify the main arguments or points.
- Examine the evidence provided.
- Spot inconsistencies or fallacies.
- Detect biases or unspoken assumptions.
- Cross-check facts with other sources.
- Evaluate the relevance to your context.
- Reflect on your own biases or beliefs.
You May Also Like
A secondary source refers to any material that interprets, analyses, or reviews information originally presented elsewhere. Unlike primary sources, which offer direct evidence or first-hand testimony, secondary sources work on those original materials, offering commentary, critiques, and perspectives.
When researching or exploring a new topic, the distinction between primary and secondary sources is paramount. The validity, reliability, and relevance of the information you gather will heavily depend on the type of source you consult.
In today’s information age, where vast amounts of knowledge are easily accessible, it is crucial to know how to use and represent that knowledge correctly and how to cite sources properly.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
- Make a Gift
- Directories
Search form
You are here.
- Autumn 2024
ENGL 103 A: Writing from Sources
- Newsletter
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
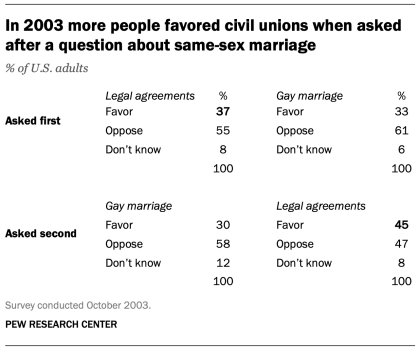
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
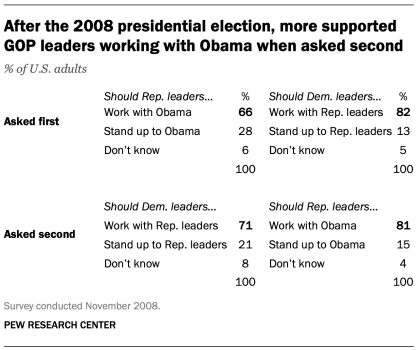
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- Boise State News
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share through Email
- Faculty and Staff in Action
- Health, Science and Technology
- News for the Campus Community
Kinesiology students tackle questions and build skills through research
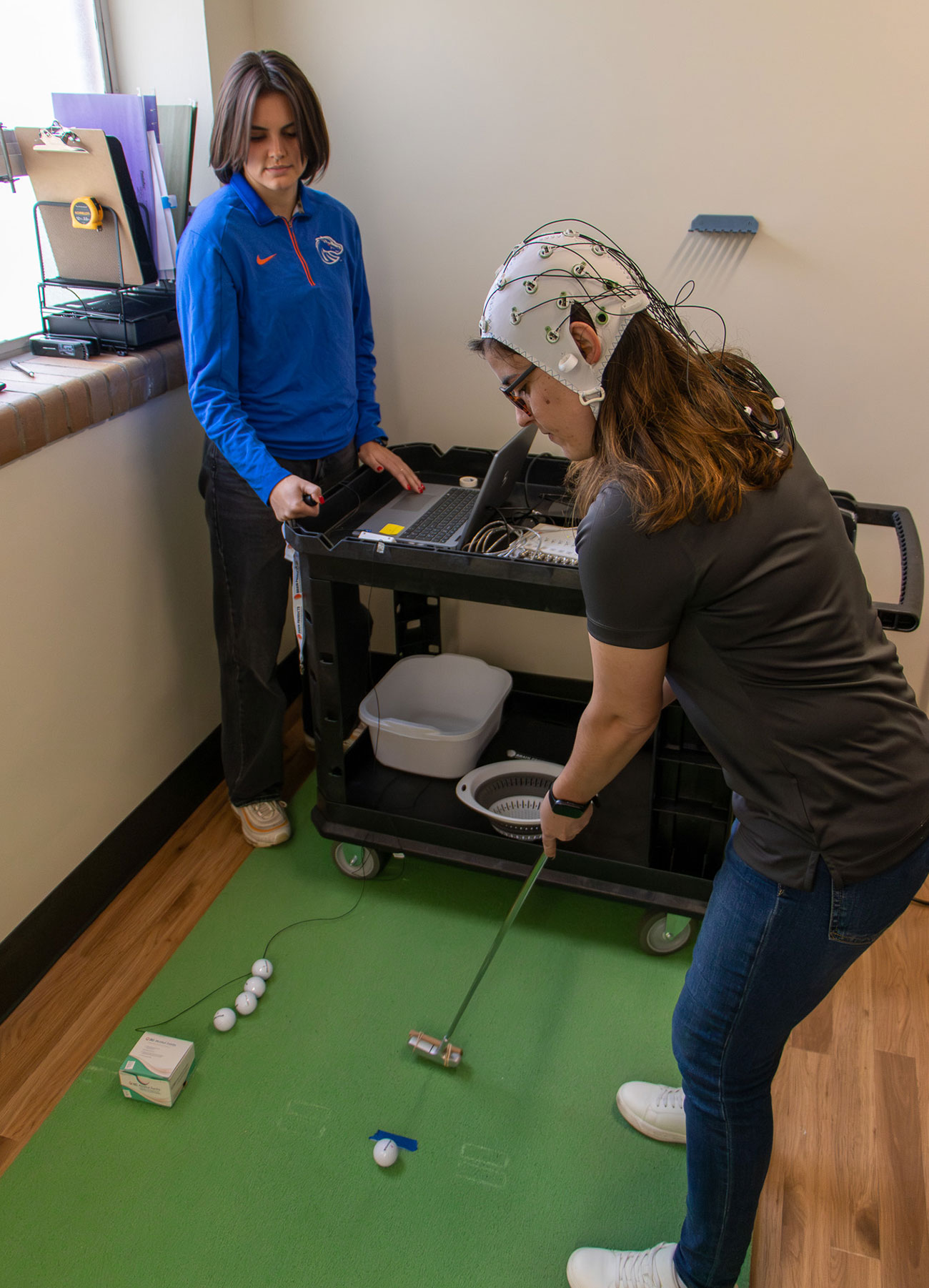

Critical questions, like how the benefits of physical activity can be observed at the brain level, are the core of Mariane Bacelar’s Skill Acquisition and Psychophysiology Lab . Bacelar, an assistant professor of kinesiology, helps her students get to the bottom of questions such as:
If you say you want to exercise and don’t, why is that? And what would change the situation for you?
How have you acquired a certain motor skill? Has motivation played a part?
How do rewards of various types shape your behavior?
How do you apply feedback to learn a certain skill? How do you translate that information into action?
Bacelar’s lab was built when Bacelar joined Boise State in the fall of 2022 after completing her doctoral program at Auburn University. She serves as the lab’s director. The lab’s physical space opened this spring.
Joined by six undergraduate students and one graduate student, she investigates questions related to motor skill acquisition and physical activity. They mostly focus on young adults, however, and as a result of a new grant, older adults will be the focus of study in the future.
Because the team examines motor learning and physical activity using neuropsychological measures to uncover the neural mechanisms underlying these phenomena, the lab is housed in Department of Kinesiology. But because human movement – and its hows and whys – is universal, the research and findings are important and applicable to most human endeavors.
Engaging student researchers

Along with groundbreaking research, students who sign up for the lab experience also embark on other meaningful work. They’re learning practical skills and helping to rebuild the credibility of the scientific community at the same time.
The student researchers learn how to apply behavioral and neurophysiological methods, such as electroencephalography (commonly referred to as EEG) to record brain activity and metascience techniques into research. They’re also learning how to collect and analyze data, design experiments, present research findings, think critically and work as part of a research team. Every other week, student teams present on scientific articles with group discussions to follow.
“It has a broader impact,” Bacelar said.
“Some students may not know how important research is. Some people may associate this experience with wanting to become a researcher, but this helps develop a lot of skills. It’s not necessarily ‘for’ research. It’s ‘through’ research.” –Mariane Bacelar, assistant professor of kinesiology
And while it’s early days for the lab and lab findings, the lab is succeeding in the ways its director has envisioned.
“We’re still collecting data, but we have a couple of predictions,” Bacelar said, adding that it has become apparent that a fundamental premise underpinning these parts of science is still, in fact, an open question.
“We often assume that motivation is associated with learning, but we’re learning that it has not been established,” she said.
The lab is built on the concept of “open science,” the idea that science should be transparent, accessible and collaborative. Bacelar and many others are hopeful that these principles roll back some of the criticism and skepticism the sciences have faced in recent years, what she describes as a “replication crisis.”
“Our goal is to enhance reliability in our research findings,” she said. “We need to be able to verify our findings, and we need to be transparent, and we need to have rigor.”
Bacelar encourages students from across the university’s disciplines to get involved – but there’s a catch. Because she wants to ensure a quality experience, she’s able to accept only a handful of student researchers. And this year’s lab team will likely be next year’s as well.
“We welcome all types of researchers,” she said. “I think having research experience as an undergrad is valuable. It should be a meaningful experience.”
Office of Communications and Marketing
UGC NET 2024 Paper 1: List of topics you must prepare for
Apr 26, 2024
Teaching Aptitude
Teaching methods encompass various strategies such as lectures, discussions, and demonstrations, each suited to different learning objectives and audiences. A good teacher possesses qualities like patience, effective communication skills, and adaptability to engage and inspire learners.
Image Source: Canva
Classroom Management
Effective classroom management techniques are essential for maintaining a productive learning environment. This includes establishing clear expectations, managing behavior, and fostering positive relationships among students.
Evaluation Methods
Assessment methods such as assignments and tests are crucial for measuring students' understanding and progress. Choosing appropriate evaluation techniques aligned with learning objectives ensures fair and accurate assessment.
Learner's Characteristics
Understanding Piaget's stages of cognitive development helps educators tailor instruction to meet students' cognitive abilities. Recognizing diverse learning styles, including auditory, visual, and kinesthetic, allows for differentiated instruction to cater to individual needs.
Individual Differences
Every learner is unique, with varying abilities, backgrounds, and motivations. Acknowledging and addressing these differences is vital for creating inclusive learning environments and fostering student success.
Factors Affecting Teaching
Effective curriculum design is fundamental to facilitating meaningful learning experiences. Integrating teaching aids and technology enhances engagement and understanding, while the learning environment and external influences like parental involvement play significant roles in shaping learning outcomes.
You may also like
Infrastructure & learning environment.
The physical and social environment in which learning occurs significantly impacts student engagement and achievement. Providing adequate infrastructure and cultivating a supportive learning atmosphere are essential for maximizing learning potential
Teaching Methods
Utilising e-learning platforms like SWAYAM and MOOCs expands access to educational resources and promotes self-directed learning. Group discussions and collaborative learning activities foster critical thinking, communication skills, and peer interaction.
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking
Encouraging problem-solving methods and critical thinking skills development empowers learners to analyze situations, explore alternatives, and make informed decisions. Balancing learner-centered and teacher-centered approaches fosters active engagement and deep understanding.
Research Aptitude
Differentiating between quantitative and qualitative research methodologies informs effective research design and data collection techniques. Upholding research ethics and avoiding plagiarism ensures the integrity and credibility of scholarly inquiry.
Thanks For Reading!
Next: Meet Nilkrishna Gajare: A Farmer's Son Who Topped JEE Main 2024

University of Northern Iowa to offer fully online MBA degree with updated curriculum

CEDAR FALLS, Iowa – Following unanimous approval by the Iowa Board of Regents, working professionals will now be able to earn their Masters of Business Administration (MBA) degree from the University of Northern Iowa fully online. The move comes with a revamped curriculum to meet the demands of modern business professionals. The top-ranked MBA program offered by the Wilson College of Business highlights the university’s dedication to academic excellence and meeting student needs, making it easier and more flexible for professionals to advance their careers.
“I am thrilled about the opportunity to extend our top-tier education to a broader audience through our new online offering," said Leslie Wilson, dean of the Wilson College of Business. The program will begin offering courses online starting in the summer of 2024, with the entire course lineup available by the fall of 2025. "UNI has consistently been ranked as a 'Best Business School' by The Princeton Review for over a decade reflects our commitment to academic excellence, personal development, and career advancement within the Wilson MBA program”
The MBA program features a redesigned curriculum that includes three stackable graduate certificates tailored to the needs of today's business professionals: Business Fundamentals, Managerial Analytics, and Strategic Leadership and Innovation. Each certificate requires the completion of four courses.
"UNI alumni want to earn a Wilson MBA. They value the coursework, experiences and relationships they have developed during their undergraduate program,” said Mary Connerley, associate dean of the Wilson College of Business. “I'm excited to deliver the same level of excellence and support to all professionals across Iowa and beyond. Our focus is on meeting the needs of employers who are looking for professionals with strong written and oral communication skills and critical thinking abilities."
Participants in the program with a desire to earn their MBA have the option of a flexible pathway to achieving their goal by completing all three certificate programs. The program aims to enhance the skills of degree holders, responding to employers' growing demand for professionals with strong communication and critical thinking skills.
“These new stackable certificates, along with the online MBA program, are designed to offer unparalleled convenience,” said Stephanie Huffman, dean of the College of Graduate, Research and Online Education . “This allows students to tailor their education to their career goals while studying from anywhere.”
The Wilson MBA program is comprised of 10 courses, totaling 30 credits. Those in the program can attend these courses online from any location.
"Our decision to add an online MBA program is a direct response to the evolving needs of today's business professionals," said Alicia Rosburg, MBA program coordinator. "By adding an online format, we prioritize convenience and flexibility, reflecting our dedication to student success. This approach guarantees that all students can access our top-tier education from anywhere, creating opportunities to advance their education, especially for those living outside of the Cedar Valley or those balancing work and family commitments."
Prospective students interested in earning their MBA through the Wilson College of Business can find more information about the program and admissions process at business.uni.edu/mba .
Media Contact: Adam Amdor
[email protected], uni introduces online pathway for special education endorsements.

Brewing for a better tomorrow

Global accounting firm finds its future professionals at UNI


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Analytical thinking involves using a systemic approach to make decisions or solve problems. Analytical thinkers can better understand information and come to a sensible conclusion by breaking it into parts. For instance, once analytical thinkers identify a problem, they typically gather more information, develop possible solutions, test them ...
Analytical thinking involves using data to understand problems, identify potential solutions, and suggest the solution that's most likely to have the desired impact. It's similar to critical thinking skills, which are the skills you use to interpret information and make decisions. In order to succeed as a strong analytical thinker, you also ...
This handbook accelerates the development of analytical writing skills for high school students, students in higher education, and working professionals in a broad range of careers. This handbook builds on the idea that writing clarifies thought, and that through analytical writing comes improved insight and understanding for making decisions ...
Critical thinking is important in all disciplines and throughout all stages of the research process. The types of evidence used in the sciences and in the humanities may differ, but critical thinking skills are relevant to both. In academic writing, critical thinking can help you to determine whether a source: Is free from research bias ...
The Link between Critical Reading, Thinking and Writing. Communicating Research. Nov 13, 2023. By Alex Baratta, PhD Senior Lecturer, Manchester Institute of Education. Dr. Baratta is the author of How to Read and Write Critically (2022) and Read Critically (2020). Use the code MSPACEQ423 for a 20% discount on his books.
Select information from sources to begin answering the research questions. Determine an appropriate organizational structure for the research paper that uses critical analysis to connect the writer's ideas and information taken from sources. At this point in your project, you are preparing to move from the research phase to the writing phase.
Analytical thinking is essential for effective problem-solving, decision-making, and equitable leadership. And yet, more research reveals only 38% of employees demonstrate the necessary balance of ...
5. Read. One of the best ways to improve analytical writing skills is to read. Reading can help improve your writing by exposing you to different styles and formats. As you read, pay attention to the way the author uses language to make their point and try to incorporate some of those techniques into your own writing.
Applying Critical Thinking to Research and Writing. Professors like to use the term critical thinking; in fact, the idea of being a critical thinker permeates much of higher education writ large. In the classroom, the idea of thinking critically is often mentioned by professors when students ask how they should approach a research and writing ...
Critical Thinking in Academic Research - 2nd Edition provides examples and easy-to-understand explanations to equip students with the skills to develop research questions, evaluate and choose the right sources, search for information, and understand arguments. This 2nd Edition includes new content based on student feedback as well as additional interactive elements throughout the text.
The skill of Analytical Thinking empowers individuals to make well-judged decisions, innovate creatively, and communicate complex ideas. Analytical Thinking is a bedrock of effective problem-solving, enabling individuals to navigate challenges with precision and adaptability, whether in daily life, business, or academic pursuits.
"Writing is thinking on paper." (Zinsser, 1976, p. vii) Google the term "critical thinking." How many hits are there? On the day this tutorial was completed, Google found about 65,100,000 results in 0.56 seconds. That's an impressive number, and it grows more impressively large every day. That's because the nation's educators, business leaders, and political…
Critical writing requires you to apply interpretation, analysis, and evaluation to the descriptions you have provided. Critical writing often responds to questions framed as 'how' or 'why'.Often, critical writing will require you to build an argument which is supported by evidence.. Some indicators of critical writing are:. Investigation of positive and negative perspectives on ideas
If you want to improve analytical skills, you play brain games like chess, Sudoku, puzzles, and others. They can help you train thinking critically. Playing 15-20 minutes a day can stimulate your brain function and strengthen analytical skills. Brain games are fun and make your pastime more productive.
between research and information. Critical writing shares some features of analytical writing, but it will have a different structure. Evaluation Evaluation is when you review the given texts and evaluate how efficient and effective the argument is. This can be done by including phrases like "the author adequately," "the author
1.3 Glance at Critical Response: Rhetoric and Critical Thinking; ... 12.5 Writing Process: Integrating Research; 12.6 Editing Focus: Integrating Sources and Quotations; 12.7 Evaluation: ... Write an analytical report on a topic that interests you and that you want to know more about. The topic can be contemporary or historical, but it must be ...
EN-121 - Resources for Analytical Thinking, Writing, and Research: Gathering Sources and Conducting Research. ... (DPLA) Primary Source Sets are designed to help students develop critical thinking skills by exploring topics in history, literature, and culture through primary sources. Drawing online materials from libraries, archives, and ...
The findings support the important role of the critical-thinking skill of inference in scientific reasoning in writing, while also highlighting ways in which other aspects of science reasoning (epistemological considerations, writing conventions, etc.) are not significantly related to critical thinking. Future research into the impact of ...
Critical Thinking and Academic Research. Academic research focuses on the creation of new ideas, perspectives, and arguments. The researcher seeks relevant information in articles, books, and other sources, then develops an informed point of view within this ongoing "conversation" among researchers. The research process is not simply collecting ...
40355. Heather Ringo & Athena Kashyap. City College of San Francisco via ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative. This text offers instruction in analytical, critical, and argumentative writing, critical thinking, research strategies, information literacy, and proper documentation through the study of literary works from major genres, while ...
Descriptive writing focuses on the what, while critical/analytical writing focuses on the so what. Analytical writing should link the discussion back to the research aims, objectives or research questions (the golden thread). Some amount of description will always be needed, but aim to minimise description and maximise analysis to earn higher ...
Critical thinkers will identify, analyze, and solve problems systematically rather than by intuition or instinct. Someone with critical thinking skills can: Understand the links between ideas. Determine the importance and relevance of arguments and ideas. Recognize, build, and appraise arguments. Identify inconsistencies and errors in reasoning.
Critical thinking helps identify potential biases in research or theories, ensuring a more objective understanding. Example: In studying economic policies, critical thinking helps weigh the benefits and drawbacks of different economic models, considering both empirical data and theoretical arguments. 4. Mathematics.
This study explores the connection between critical thinking skills and academic writing. It looks into how writing process mirrors critical thinking skills. This quantitative study is done on 207 ...
Developmental and practice of reading, writing, and critical thinking strategies needed to create organized and correctly documented papers using academic sources. Practices critical reading of academic texts, developing research questions, making claims, determining credibility of sources, and appropriately citing sources in writing.
[View more Methods 101 Videos]. An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would "favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein's rule," 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action.
At the heart of her course, Sociology of the Environment (SOC/ENSS 244), Amanda McMillan Lequieu, PhD, assigns students a multi-stage case study and guides them through a process that exposes them to the skills needed to analyze research and use that information to make a persuasive case for a potential policy measure.
Kinesiology faculty Mariane Bacelar putts a golf ball while wearing an EEG hat, master's student Jet Taylor records the data on a laptop. Critical questions, like how the benefits of physical activity can be observed at the brain level, are the core of Mariane Bacelar's Skill Acquisition and Psychophysiology Lab.Bacelar, an assistant professor of kinesiology, helps her students get to the ...
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking. Encouraging problem-solving methods and critical thinking skills development empowers learners to analyze situations, explore alternatives, and make informed ...
The program aims to enhance the skills of degree holders, responding to employers' growing demand for professionals with strong communication and critical thinking skills."These new stackable certificates, along with the online MBA program, are designed to offer unparalleled convenience," said Stephanie Huffman, dean of the College of ...