The Sheridan Libraries
- Write a Literature Review
- Sheridan Libraries
- Find This link opens in a new window
- Evaluate This link opens in a new window

Get Organized
- Lit Review Prep Use this template to help you evaluate your sources, create article summaries for an annotated bibliography, and a synthesis matrix for your lit review outline.
Synthesize your Information
Synthesize: combine separate elements to form a whole.
Synthesis Matrix
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other.
After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables.
By arranging your sources by theme or variable, you can see how your sources relate to each other, and can start thinking about how you weave them together to create a narrative.
- Step-by-Step Approach
- Example Matrix from NSCU
- Matrix Template
- << Previous: Summarize
- Next: Integrate >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 10:25 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.jhu.edu/lit-review
- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Literature Syntheis 101
How To Synthesise The Existing Research (With Examples)
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Eunice Rautenbach (DTech) | August 2023
One of the most common mistakes that students make when writing a literature review is that they err on the side of describing the existing literature rather than providing a critical synthesis of it. In this post, we’ll unpack what exactly synthesis means and show you how to craft a strong literature synthesis using practical examples.
This post is based on our popular online course, Literature Review Bootcamp . In the course, we walk you through the full process of developing a literature review, step by step. If it’s your first time writing a literature review, you definitely want to use this link to get 50% off the course (limited-time offer).
Overview: Literature Synthesis
- What exactly does “synthesis” mean?
- Aspect 1: Agreement
- Aspect 2: Disagreement
- Aspect 3: Key theories
- Aspect 4: Contexts
- Aspect 5: Methodologies
- Bringing it all together
What does “synthesis” actually mean?
As a starting point, let’s quickly define what exactly we mean when we use the term “synthesis” within the context of a literature review.
Simply put, literature synthesis means going beyond just describing what everyone has said and found. Instead, synthesis is about bringing together all the information from various sources to present a cohesive assessment of the current state of knowledge in relation to your study’s research aims and questions .
Put another way, a good synthesis tells the reader exactly where the current research is “at” in terms of the topic you’re interested in – specifically, what’s known , what’s not , and where there’s a need for more research .
So, how do you go about doing this?
Well, there’s no “one right way” when it comes to literature synthesis, but we’ve found that it’s particularly useful to ask yourself five key questions when you’re working on your literature review. Having done so, you can then address them more articulately within your actual write up. So, let’s take a look at each of these questions.

1. Points Of Agreement
The first question that you need to ask yourself is: “Overall, what things seem to be agreed upon by the vast majority of the literature?”
For example, if your research aim is to identify which factors contribute toward job satisfaction, you’ll need to identify which factors are broadly agreed upon and “settled” within the literature. Naturally, there may at times be some lone contrarian that has a radical viewpoint , but, provided that the vast majority of researchers are in agreement, you can put these random outliers to the side. That is, of course, unless your research aims to explore a contrarian viewpoint and there’s a clear justification for doing so.
Identifying what’s broadly agreed upon is an essential starting point for synthesising the literature, because you generally don’t want (or need) to reinvent the wheel or run down a road investigating something that is already well established . So, addressing this question first lays a foundation of “settled” knowledge.
Need a helping hand?
2. Points Of Disagreement
Related to the previous point, but on the other end of the spectrum, is the equally important question: “Where do the disagreements lie?” .
In other words, which things are not well agreed upon by current researchers? It’s important to clarify here that by disagreement, we don’t mean that researchers are (necessarily) fighting over it – just that there are relatively mixed findings within the empirical research , with no firm consensus amongst researchers.
This is a really important question to address as these “disagreements” will often set the stage for the research gap(s). In other words, they provide clues regarding potential opportunities for further research, which your study can then (hopefully) contribute toward filling. If you’re not familiar with the concept of a research gap, be sure to check out our explainer video covering exactly that .

3. Key Theories
The next question you need to ask yourself is: “Which key theories seem to be coming up repeatedly?” .
Within most research spaces, you’ll find that you keep running into a handful of key theories that are referred to over and over again. Apart from identifying these theories, you’ll also need to think about how they’re connected to each other. Specifically, you need to ask yourself:
- Are they all covering the same ground or do they have different focal points or underlying assumptions ?
- Do some of them feed into each other and if so, is there an opportunity to integrate them into a more cohesive theory?
- Do some of them pull in different directions ? If so, why might this be?
- Do all of the theories define the key concepts and variables in the same way, or is there some disconnect? If so, what’s the impact of this ?
Simply put, you’ll need to pay careful attention to the key theories in your research area, as they will need to feature within your theoretical framework , which will form a critical component within your final literature review. This will set the foundation for your entire study, so it’s essential that you be critical in this area of your literature synthesis.
If this sounds a bit fluffy, don’t worry. We deep dive into the theoretical framework (as well as the conceptual framework) and look at practical examples in Literature Review Bootcamp . If you’d like to learn more, take advantage of our limited-time offer to get 60% off the standard price.

4. Contexts
The next question that you need to address in your literature synthesis is an important one, and that is: “Which contexts have (and have not) been covered by the existing research?” .
For example, sticking with our earlier hypothetical topic (factors that impact job satisfaction), you may find that most of the research has focused on white-collar , management-level staff within a primarily Western context, but little has been done on blue-collar workers in an Eastern context. Given the significant socio-cultural differences between these two groups, this is an important observation, as it could present a contextual research gap .
In practical terms, this means that you’ll need to carefully assess the context of each piece of literature that you’re engaging with, especially the empirical research (i.e., studies that have collected and analysed real-world data). Ideally, you should keep notes regarding the context of each study in some sort of catalogue or sheet, so that you can easily make sense of this before you start the writing phase. If you’d like, our free literature catalogue worksheet is a great tool for this task.
5. Methodological Approaches
Last but certainly not least, you need to ask yourself the question: “What types of research methodologies have (and haven’t) been used?”
For example, you might find that most studies have approached the topic using qualitative methods such as interviews and thematic analysis. Alternatively, you might find that most studies have used quantitative methods such as online surveys and statistical analysis.
But why does this matter?
Well, it can run in one of two potential directions . If you find that the vast majority of studies use a specific methodological approach, this could provide you with a firm foundation on which to base your own study’s methodology . In other words, you can use the methodologies of similar studies to inform (and justify) your own study’s research design .
On the other hand, you might argue that the lack of diverse methodological approaches presents a research gap , and therefore your study could contribute toward filling that gap by taking a different approach. For example, taking a qualitative approach to a research area that is typically approached quantitatively. Of course, if you’re going to go against the methodological grain, you’ll need to provide a strong justification for why your proposed approach makes sense. Nevertheless, it is something worth at least considering.
Regardless of which route you opt for, you need to pay careful attention to the methodologies used in the relevant studies and provide at least some discussion about this in your write-up. Again, it’s useful to keep track of this on some sort of spreadsheet or catalogue as you digest each article, so consider grabbing a copy of our free literature catalogue if you don’t have anything in place.

Bringing It All Together
Alright, so we’ve looked at five important questions that you need to ask (and answer) to help you develop a strong synthesis within your literature review. To recap, these are:
- Which things are broadly agreed upon within the current research?
- Which things are the subject of disagreement (or at least, present mixed findings)?
- Which theories seem to be central to your research topic and how do they relate or compare to each other?
- Which contexts have (and haven’t) been covered?
- Which methodological approaches are most common?
Importantly, you’re not just asking yourself these questions for the sake of asking them – they’re not just a reflection exercise. You need to weave your answers to them into your actual literature review when you write it up. How exactly you do this will vary from project to project depending on the structure you opt for, but you’ll still need to address them within your literature review, whichever route you go.
The best approach is to spend some time actually writing out your answers to these questions, as opposed to just thinking about them in your head. Putting your thoughts onto paper really helps you flesh out your thinking . As you do this, don’t just write down the answers – instead, think about what they mean in terms of the research gap you’ll present , as well as the methodological approach you’ll take . Your literature synthesis needs to lay the groundwork for these two things, so it’s essential that you link all of it together in your mind, and of course, on paper.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Literature Review Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
You Might Also Like:

excellent , thank you
Thank you for this significant piece of information.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

Library Guides
Literature reviews: synthesis.
- Criticality
Synthesise Information
So, how can you create paragraphs within your literature review that demonstrates your knowledge of the scholarship that has been done in your field of study?
You will need to present a synthesis of the texts you read.
Doug Specht, Senior Lecturer at the Westminster School of Media and Communication, explains synthesis for us in the following video:
Synthesising Texts
What is synthesis?
Synthesis is an important element of academic writing, demonstrating comprehension, analysis, evaluation and original creation.
With synthesis you extract content from different sources to create an original text. While paraphrase and summary maintain the structure of the given source(s), with synthesis you create a new structure.
The sources will provide different perspectives and evidence on a topic. They will be put together when agreeing, contrasted when disagreeing. The sources must be referenced.
Perfect your synthesis by showing the flow of your reasoning, expressing critical evaluation of the sources and drawing conclusions.
When you synthesise think of "using strategic thinking to resolve a problem requiring the integration of diverse pieces of information around a structuring theme" (Mateos and Sole 2009, p448).
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise.
How to synthesise in a literature review:
Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an outline.
Read the literature and identify these themes/issues.
Critically analyse the texts asking: how does the text I'm reading relate to the other texts I've read on the same topic? Is it in agreement? Does it differ in its perspective? Is it stronger or weaker? How does it differ (could be scope, methods, year of publication etc.). Draw your conclusions on the state of the literature on the topic.
Start writing your literature review, structuring it according to the outline you planned.
Put together sources stating the same point; contrast sources presenting counter-arguments or different points.
Present your critical analysis.
Always provide the references.
The best synthesis requires a "recursive process" whereby you read the source texts, identify relevant parts, take notes, produce drafts, re-read the source texts, revise your text, re-write... (Mateos and Sole, 2009).
What is good synthesis?
The quality of your synthesis can be assessed considering the following (Mateos and Sole, 2009, p439):
Integration and connection of the information from the source texts around a structuring theme.
Selection of ideas necessary for producing the synthesis.
Appropriateness of the interpretation.
Elaboration of the content.
Example of Synthesis
Original texts (fictitious):
Synthesis:
Animal experimentation is a subject of heated debate. Some argue that painful experiments should be banned. Indeed it has been demonstrated that such experiments make animals suffer physically and psychologically (Chowdhury 2012; Panatta and Hudson 2016). On the other hand, it has been argued that animal experimentation can save human lives and reduce harm on humans (Smith 2008). This argument is only valid for toxicological testing, not for tests that, for example, merely improve the efficacy of a cosmetic (Turner 2015). It can be suggested that animal experimentation should be regulated to only allow toxicological risk assessment, and the suffering to the animals should be minimised.
Bibliography
Mateos, M. and Sole, I. (2009). Synthesising Information from various texts: A Study of Procedures and Products at Different Educational Levels. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 24 (4), 435-451. Available from https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03178760 [Accessed 29 June 2021].
- << Previous: Structure
- Next: Criticality >>
- Last Updated: Nov 18, 2023 10:56 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/literature-reviews
CONNECT WITH US

Literature Review How To
- Things To Consider
- Synthesizing Sources
- Video Tutorials
- Books On Literature Reviews
What is Synthesis
What is Synthesis? Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. In synthesis, you search for the links between various materials in order to make your point. Most advanced academic writing, including literature reviews, relies heavily on synthesis. (Temple University Writing Center)
How To Synthesize Sources in a Literature Review
Literature reviews synthesize large amounts of information and present it in a coherent, organized fashion. In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text – your literature review.
You will use common points among the sources you have gathered to help you synthesize the material. This will help ensure that your literature review is organized by subtopic, not by source. This means various authors' names can appear and reappear throughout the literature review, and each paragraph will mention several different authors.
When you shift from writing summaries of the content of a source to synthesizing content from sources, there is a number things you must keep in mind:
- Look for specific connections and or links between your sources and how those relate to your thesis or question.
- When writing and organizing your literature review be aware that your readers need to understand how and why the information from the different sources overlap.
- Organize your literature review by the themes you find within your sources or themes you have identified.
- << Previous: Things To Consider
- Next: Video Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: Nov 30, 2018 4:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.csun.edu/literature-review
Report ADA Problems with Library Services and Resources

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Systematic reviews & evidence synthesis methods.
- Schedule a Consultation / Meet our Team
- What is Evidence Synthesis?
- Types of Evidence Synthesis
- Evidence Synthesis Across Disciplines
- Finding and Appraising Existing Systematic Reviews
- 0. Preliminary Searching
- 1. Develop a Protocol
- 2. Draft your Research Question
- 3. Select Databases
- 4. Select Grey Literature Sources
- 5. Write a Search Strategy
- 6. Register a Protocol
- 7. Translate Search Strategies
- 8. Citation Management
- 9. Article Screening
- 10. Risk of Bias Assessment
- 11. Data Extraction
- 12. Synthesize, Map, or Describe the Results
- Open Access Evidence Synthesis Resources
About This Guide
This research guide provides an overview of the evidence synthesis process, guidance documents for conducting evidence synthesis projects, and links to resources to help you conduct a comprehensive and systematic search of the scholarly literature. Navigate the guide using the tabs on the left.
"Evidence synthesis" refers to rigorous, well-documented methods of identifying, selecting, and combining results from multiple studies. These projects are conducted by teams and follow specific methodologies to minimize bias and maximize reproducibility. A systematic review is a type of evidence synthesis. We use the term evidence synthesis to better reflect the breadth of methodologies that we support, including systematic reviews, scoping reviews , evidence gap maps, umbrella reviews, meta-analyses and others.
Note: Librarians at UC Irvine Libraries have supported systematic reviews and related methodologies in STEM fields for several years. As our service has evolved, we have added capacity to support these reviews in the Social Sciences as well.
Systematic Review OR Literature Review Conducted Systematically?
There are many types of literature reviews. Before beginning a systematic review, consider whether it is the best type of review for your question, goals, and resources. The table below compares systematic reviews, scoping reviews, and systematized reviews (narrative literature reviews employing some, but not all elements of a systematic review) to help you decide which is best for you. See the Types of Evidence Synthesis page for a more in-depth overview at types of reviews.
- Next: UCI Libraries Evidence Synthesis Service >>
- Last Updated: May 25, 2024 10:49 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/evidence-synthesis
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
How to Synthesize Written Information from Multiple Sources
Shona McCombes
Content Manager
B.A., English Literature, University of Glasgow
Shona McCombes is the content manager at Scribbr, Netherlands.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
On This Page:
When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you’ve read – you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own research fits in).
Synthesizing simply means combining. Instead of summarizing the main points of each source in turn, you put together the ideas and findings of multiple sources in order to make an overall point.
At the most basic level, this involves looking for similarities and differences between your sources. Your synthesis should show the reader where the sources overlap and where they diverge.
Unsynthesized Example
Franz (2008) studied undergraduate online students. He looked at 17 females and 18 males and found that none of them liked APA. According to Franz, the evidence suggested that all students are reluctant to learn citations style. Perez (2010) also studies undergraduate students. She looked at 42 females and 50 males and found that males were significantly more inclined to use citation software ( p < .05). Findings suggest that females might graduate sooner. Goldstein (2012) looked at British undergraduates. Among a sample of 50, all females, all confident in their abilities to cite and were eager to write their dissertations.
Synthesized Example
Studies of undergraduate students reveal conflicting conclusions regarding relationships between advanced scholarly study and citation efficacy. Although Franz (2008) found that no participants enjoyed learning citation style, Goldstein (2012) determined in a larger study that all participants watched felt comfortable citing sources, suggesting that variables among participant and control group populations must be examined more closely. Although Perez (2010) expanded on Franz’s original study with a larger, more diverse sample…
Step 1: Organize your sources
After collecting the relevant literature, you’ve got a lot of information to work through, and no clear idea of how it all fits together.
Before you can start writing, you need to organize your notes in a way that allows you to see the relationships between sources.
One way to begin synthesizing the literature is to put your notes into a table. Depending on your topic and the type of literature you’re dealing with, there are a couple of different ways you can organize this.
Summary table
A summary table collates the key points of each source under consistent headings. This is a good approach if your sources tend to have a similar structure – for instance, if they’re all empirical papers.
Each row in the table lists one source, and each column identifies a specific part of the source. You can decide which headings to include based on what’s most relevant to the literature you’re dealing with.
For example, you might include columns for things like aims, methods, variables, population, sample size, and conclusion.
For each study, you briefly summarize each of these aspects. You can also include columns for your own evaluation and analysis.
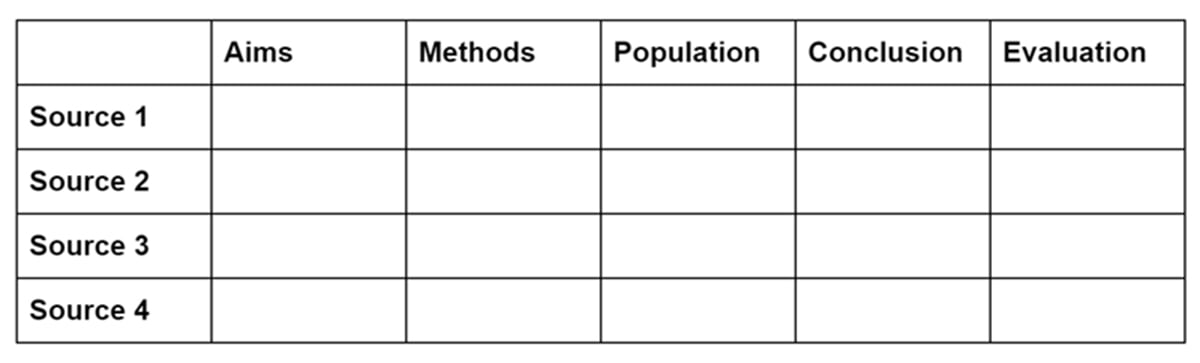
The summary table gives you a quick overview of the key points of each source. This allows you to group sources by relevant similarities, as well as noticing important differences or contradictions in their findings.
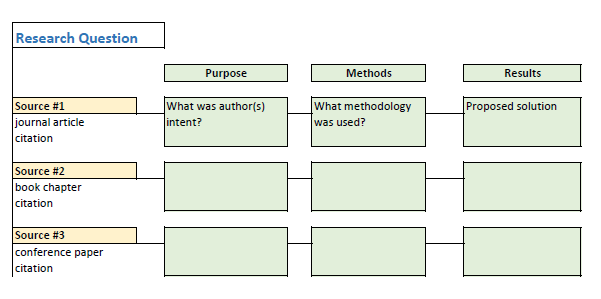
Synthesis matrix
A synthesis matrix is useful when your sources are more varied in their purpose and structure – for example, when you’re dealing with books and essays making various different arguments about a topic.
Each column in the table lists one source. Each row is labeled with a specific concept, topic or theme that recurs across all or most of the sources.
Then, for each source, you summarize the main points or arguments related to the theme.
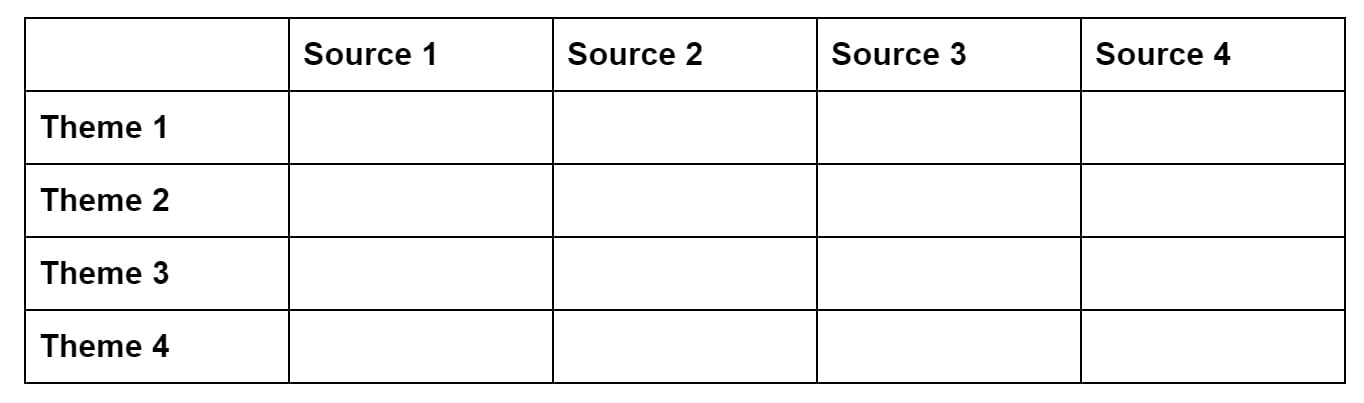
The purposes of the table is to identify the common points that connect the sources, as well as identifying points where they diverge or disagree.
Step 2: Outline your structure
Now you should have a clear overview of the main connections and differences between the sources you’ve read. Next, you need to decide how you’ll group them together and the order in which you’ll discuss them.
For shorter papers, your outline can just identify the focus of each paragraph; for longer papers, you might want to divide it into sections with headings.
There are a few different approaches you can take to help you structure your synthesis.
If your sources cover a broad time period, and you found patterns in how researchers approached the topic over time, you can organize your discussion chronologically .
That doesn’t mean you just summarize each paper in chronological order; instead, you should group articles into time periods and identify what they have in common, as well as signalling important turning points or developments in the literature.
If the literature covers various different topics, you can organize it thematically .
That means that each paragraph or section focuses on a specific theme and explains how that theme is approached in the literature.
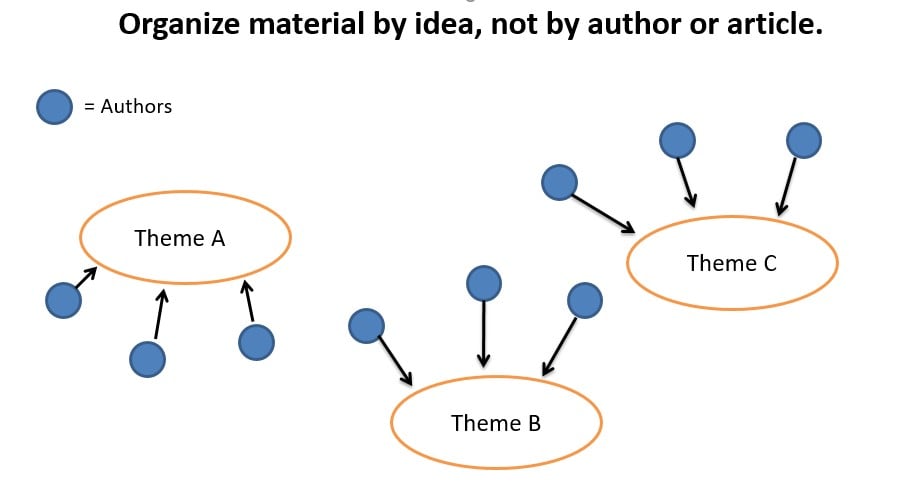
Source Used with Permission: The Chicago School
If you’re drawing on literature from various different fields or they use a wide variety of research methods, you can organize your sources methodologically .
That means grouping together studies based on the type of research they did and discussing the findings that emerged from each method.
If your topic involves a debate between different schools of thought, you can organize it theoretically .
That means comparing the different theories that have been developed and grouping together papers based on the position or perspective they take on the topic, as well as evaluating which arguments are most convincing.
Step 3: Write paragraphs with topic sentences
What sets a synthesis apart from a summary is that it combines various sources. The easiest way to think about this is that each paragraph should discuss a few different sources, and you should be able to condense the overall point of the paragraph into one sentence.
This is called a topic sentence , and it usually appears at the start of the paragraph. The topic sentence signals what the whole paragraph is about; every sentence in the paragraph should be clearly related to it.
A topic sentence can be a simple summary of the paragraph’s content:
“Early research on [x] focused heavily on [y].”
For an effective synthesis, you can use topic sentences to link back to the previous paragraph, highlighting a point of debate or critique:
“Several scholars have pointed out the flaws in this approach.” “While recent research has attempted to address the problem, many of these studies have methodological flaws that limit their validity.”
By using topic sentences, you can ensure that your paragraphs are coherent and clearly show the connections between the articles you are discussing.
As you write your paragraphs, avoid quoting directly from sources: use your own words to explain the commonalities and differences that you found in the literature.
Don’t try to cover every single point from every single source – the key to synthesizing is to extract the most important and relevant information and combine it to give your reader an overall picture of the state of knowledge on your topic.
Step 4: Revise, edit and proofread
Like any other piece of academic writing, synthesizing literature doesn’t happen all in one go – it involves redrafting, revising, editing and proofreading your work.
Checklist for Synthesis
- Do I introduce the paragraph with a clear, focused topic sentence?
- Do I discuss more than one source in the paragraph?
- Do I mention only the most relevant findings, rather than describing every part of the studies?
- Do I discuss the similarities or differences between the sources, rather than summarizing each source in turn?
- Do I put the findings or arguments of the sources in my own words?
- Is the paragraph organized around a single idea?
- Is the paragraph directly relevant to my research question or topic?
- Is there a logical transition from this paragraph to the next one?
Further Information
How to Synthesise: a Step-by-Step Approach
Help…I”ve Been Asked to Synthesize!
Learn how to Synthesise (combine information from sources)
How to write a Psychology Essay
Related Articles

Student Resources
How To Cite A YouTube Video In APA Style – With Examples

How to Write an Abstract APA Format

APA References Page Formatting and Example

APA Title Page (Cover Page) Format, Example, & Templates

How do I Cite a Source with Multiple Authors in APA Style?
How to Write a Psychology Essay
Research to Action
The Global Guide to Research Impact
Social Media
Framing challenges
Synthetic literature reviews: An introduction
By Steve Wallis and Bernadette Wright 26/05/2020
Whether you are writing a funding proposal or an academic paper, you will most likely be required to start with a literature review of some kind. Despite (or because of) the work involved, a literature review is a great opportunity to showcase your knowledge on a topic. In this post, we’re going to take it one step further. We’re going to tell you a very practical approach to conducting literature reviews that allows you to show that you are advancing scientific knowledge before your project even begins. Also – and this is no small bonus – this approach lets you show how your literature review will lead to a more successful project.
Literature review – start with the basics
A literature review helps you shape effective solutions to the problems you (and your organisation) are facing. A literature review also helps you demonstrate the value of your activities. You can show how much you add to the process before you spend any money collecting new data. Finally, your literature review helps you avoid reinventing the wheel by showing you what relevant research already exists, so that you can target your new research more efficiently and more effectively.
We all want to conduct good research and have a meaningful impact on people’s lives. To do this, a literature review is a critical step. For funders, a literature review is especially important because it shows how much useful knowledge the writer already has.
Past methods of literature reviews tend to be focused on ‘muscle power’, that is spending more time and more effort to review more papers and adhering more closely to accepted standards. Examples of standards for conducting literature reviews include the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions and the guidelines for assessing the quality and applicability of systematic reviews developed by the Task Force on Systematic Review and Guidelines . Given the untold millions of papers in many disciplines, even a large literature review that adheres to the best guidelines does little to move us toward integrated knowledge in and across disciplines.
In short, we need we need to work smarter, not harder!
Synthetic literature reviews
One approach that can provide more benefit is the synthetic literature review. Synthetic meaning synthesised or integrated, not artificial. Rather than explaining and reflecting on the results of previous studies (as is typically done in literature reviews), a synthetic literature review strives to create a new and more useful theoretical perspective by rigorously integrating the results of previous studies.
Many people find the process of synthesis difficult, elusive, or mysterious. When presenting their views and making recommendations for research, they tend to fall back on intuition (which is neither harder nor smarter).
After defining your research topic (‘poverty’ for example), the next step is to search the literature for existing theories or models of poverty that have been developed from research. You can use Google Scholar or your institutional database, or the assistance of a research librarian. A broad topic such as ‘poverty’, however, will lead you to millions of articles. You’ll narrow that field by focusing more closely on your topic and adding search terms. For example, you might be more interested in poverty among Latino communities in central California. You might also focus your search according to the date of the study (often, but not always, more recent results are preferred), or by geographic location. Continue refining and focusing your search until you have a workable number of papers (depending on your available time and resources). You might also take this time to throw out the papers that seem to be less relevant.
Skim those papers to be sure that they are really relevant to your topic. Once you have chosen a workable number of relevant papers, it is time to start integrating them.
Next, sort them according to the quality of their data.
Next, read the theory presented in each paper and create a diagram of the theory. The theory may be found in a section called ‘theory’ or sometimes in the ‘introduction’. For research papers, that presented theory may have changed during the research process, so you should look for the theory in the ‘findings’, ‘results’, or ‘discussion’ sections.
That diagram should include all relevant concepts from the theory and show the causal connections between the concepts that have been supported by research (some papers will present two theories, one before and one after the research – use the second one – only the hypotheses that have been supported by the research).
For a couple of brief and partial example from a recent interdisciplinary research paper, one theory of poverty might say ‘Having more education will help people to stay out of poverty’, while another might say ‘The more that the economy develops, the less poverty there will be’.
We then use those statements to create a diagram as we have in Figure 1.

Figure 1. Two (simple, partial) theories of poverty. (We like to use dashed lines to indicate ’causes less’, and solid lines to indicate ’causes more’)
When you have completed a diagram for each theory, the next step is to synthesise (integrate) them where the concepts are the same (or substantively similar) between two or more theories. With causal diagrams such as these, the process of synthesis becomes pretty direct. We simply combine the two (or more) theories to create a synthesised theory, such as in Figure 2.

Figure 2. Two theories synthesised where they overlap (in this case theories of poverty)
Much like a road map, a causal diagram of a theory with more concepts and more connecting arrows is more useful for navigation. You can show that your literature review is better than previous reviews by showing that you have taken a number of fragmented theories (as in Figure 1) and synthesised them to create a more coherent theory (as in Figure 2).
To go a step further, you may use Integrative Propositional Analysis (IPA) to quantify the extent to which your research has improved the structure and potential usefulness of your knowledge through the synthesis. Another source is our new book from Practical Mapping for Applied Research and Program Evaluation (see especially Chapter 5). (For the basics, you can look at Chapter One for free on the publisher’s site by clicking on the ‘Preview’ tab here. )
Once you become comfortable with the process, you will certainly be working ‘smarter’ and showcasing your knowledge to funders!
Contribute Write a blog post, post a job or event, recommend a resource
Partner with Us Are you an institution looking to increase your impact?
Most Recent Posts
- How to design a research uptake plan
- Development and Outreach Officer: Girls not Brides
- Using the PPE approach to improve advocacy evaluation processes
- AEN African Evidence Ecosystem Podcast – Season 1
- Making knowledge systems more equitable: lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic
This Week's Most Read
- AEN Evidence 23 – Online Access Registration now open!
- How to write actionable policy recommendations
- What do we mean by ‘impact’?
- Outcome Mapping: A Basic Introduction
- Gap analysis for literature reviews and advancing useful knowledge
- 12ft Ladder: Making research accessible
- How to develop input, activity, output, outcome and impact indicators
- Policymaker, policy maker, or policy-maker?
- AI in Research: Its Uses and Limitations
- Stakeholder Engagement a Tool to Measure Public Policy
Research To Action (R2A) is a learning platform for anyone interested in maximising the impact of research and capturing evidence of impact.
The site publishes practical resources on a range of topics including research uptake, communications, policy influence and monitoring and evaluation. It captures the experiences of practitioners and researchers working on these topics and facilitates conversations between this global community through a range of social media platforms.
R2A is produced by a small editorial team, led by CommsConsult . We welcome suggestions for and contributions to the site.
Subscribe to our newsletter!
Our contributors
Browse all authors
Friends and partners
- Global Development Network (GDN)
- Institute of Development Studies (IDS)
- International Initiative for Impact Evaluation (3ie)
- On Think Tanks
- Politics & Ideas
- Research for Development (R4D)
- Research Impact

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 7: Synthesizing Sources
Learning objectives.
At the conclusion of this chapter, you will be able to:
- synthesize key sources connecting them with the research question and topic area.
7.1 Overview of synthesizing
7.1.1 putting the pieces together.
Combining separate elements into a whole is the dictionary definition of synthesis. It is a way to make connections among and between numerous and varied source materials. A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question.

Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the results of your analysis into your own literature review. Each paper collected should be critically evaluated and weighed for “adequacy, appropriateness, and thoroughness” ( Garrard, 2017 ) before inclusion in your own review. Papers that do not meet this criteria likely should not be included in your literature review.
Begin the synthesis process by creating a grid, table, or an outline where you will summarize, using common themes you have identified and the sources you have found. The summary grid or outline will help you compare and contrast the themes so you can see the relationships among them as well as areas where you may need to do more searching. Whichever method you choose, this type of organization will help you to both understand the information you find and structure the writing of your review. Remember, although “the means of summarizing can vary, the key at this point is to make sure you understand what you’ve found and how it relates to your topic and research question” ( Bennard et al., 2014 ).
As you read through the material you gather, look for common themes as they may provide the structure for your literature review. And, remember, research is an iterative process: it is not unusual to go back and search information sources for more material.
At one extreme, if you are claiming, ‘There are no prior publications on this topic,’ it is more likely that you have not found them yet and may need to broaden your search. At another extreme, writing a complete literature review can be difficult with a well-trod topic. Do not cite it all; instead cite what is most relevant. If that still leaves too much to include, be sure to reference influential sources…as well as high-quality work that clearly connects to the points you make. ( Klingner, Scanlon, & Pressley, 2005 ).
7.2 Creating a summary table
Literature reviews can be organized sequentially or by topic, theme, method, results, theory, or argument. It’s important to develop categories that are meaningful and relevant to your research question. Take detailed notes on each article and use a consistent format for capturing all the information each article provides. These notes and the summary table can be done manually, using note cards. However, given the amount of information you will be recording, an electronic file created in a word processing or spreadsheet is more manageable. Examples of fields you may want to capture in your notes include:
- Authors’ names
- Article title
- Publication year
- Main purpose of the article
- Methodology or research design
- Participants
- Measurement
- Conclusions
Other fields that will be useful when you begin to synthesize the sum total of your research:
- Specific details of the article or research that are especially relevant to your study
- Key terms and definitions
- Strengths or weaknesses in research design
- Relationships to other studies
- Possible gaps in the research or literature (for example, many research articles conclude with the statement “more research is needed in this area”)
- Finally, note how closely each article relates to your topic. You may want to rank these as high, medium, or low relevance. For papers that you decide not to include, you may want to note your reasoning for exclusion, such as ‘small sample size’, ‘local case study,’ or ‘lacks evidence to support assertion.’
This short video demonstrates how a nursing researcher might create a summary table.
7.2.1 Creating a Summary Table

Summary tables can be organized by author or by theme, for example:
For a summary table template, see http://blogs.monm.edu/writingatmc/files/2013/04/Synthesis-Matrix-Template.pdf
7.3 Creating a summary outline
An alternate way to organize your articles for synthesis it to create an outline. After you have collected the articles you intend to use (and have put aside the ones you won’t be using), it’s time to identify the conclusions that can be drawn from the articles as a group.
Based on your review of the collected articles, group them by categories. You may wish to further organize them by topic and then chronologically or alphabetically by author. For each topic or subtopic you identified during your critical analysis of the paper, determine what those papers have in common. Likewise, determine which ones in the group differ. If there are contradictory findings, you may be able to identify methodological or theoretical differences that could account for the contradiction (for example, differences in population demographics). Determine what general conclusions you can report about the topic or subtopic as the entire group of studies relate to it. For example, you may have several studies that agree on outcome, such as ‘hands on learning is best for science in elementary school’ or that ‘continuing education is the best method for updating nursing certification.’ In that case, you may want to organize by methodology used in the studies rather than by outcome.
Organize your outline in a logical order and prepare to write the first draft of your literature review. That order might be from broad to more specific, or it may be sequential or chronological, going from foundational literature to more current. Remember, “an effective literature review need not denote the entire historical record, but rather establish the raison d’etre for the current study and in doing so cite that literature distinctly pertinent for theoretical, methodological, or empirical reasons.” ( Milardo, 2015, p. 22 ).
As you organize the summarized documents into a logical structure, you are also appraising and synthesizing complex information from multiple sources. Your literature review is the result of your research that synthesizes new and old information and creates new knowledge.
7.4 Additional resources:
Literature Reviews: Using a Matrix to Organize Research / Saint Mary’s University of Minnesota
Literature Review: Synthesizing Multiple Sources / Indiana University
Writing a Literature Review and Using a Synthesis Matrix / Florida International University
Sample Literature Reviews Grid / Complied by Lindsay Roberts
Select three or four articles on a single topic of interest to you. Then enter them into an outline or table in the categories you feel are important to a research question. Try both the grid and the outline if you can to see which suits you better. The attached grid contains the fields suggested in the video .
Literature Review Table
Test yourself.
- Select two articles from your own summary table or outline and write a paragraph explaining how and why the sources relate to each other and your review of the literature.
- In your literature review, under what topic or subtopic will you place the paragraph you just wrote?
Image attribution
Literature Reviews for Education and Nursing Graduate Students Copyright © by Linda Frederiksen is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Synthesising the literature as part of a literature review
Affiliation.
- 1 University of Manchester, England.
- PMID: 25783281
- DOI: 10.7748/ns.29.29.44.e8957
This article examines how to synthesise and critique research literature. To place the process of synthesising the research literature into context, the article explores the critiquing process by breaking it down into seven sequential steps. The article explains how and why these steps need to be kept in mind if a robust comprehensive literature search and analysis are to be achieved. The article outlines how to engage in the critiquing process and explains how the literature review needs to be assembled to generate a logical and reasoned debate to examine a topic of interest or research in more detail.
Keywords: Critical analysis; critique; evaluation; integrative review; literature review; literature search; research; research question; search strategy; synthesis.
- Research / standards*
- Research Design*
- Review Literature as Topic*

Synthesis and Literature Reviews
Why do we seek to understand the ways that authors or sources “converse” with one another?
So that we can synthesize various perspectives on a topic to more deeply understand it .
In academic writing, this understanding of the “conversation” may become the content of an explanatory synthesis paper – a paper in which you, the writer, point out various various themes or key points from a conversation on a particular topic.
Or, another assignment that you may complete in college is a literature review , which applies your synthesis skills. Literature reviews are often found in the beginning of scholarly journal articles. Literature reviews synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic.
- Literature reviews can be arranged by topic or theme , much like a traditional explanatory synthesis paper.
- Literature reviews can also be arranged chronologically , according to various time periods of research on a topic (i.e., what was published ten years ago, five years ago, and within the last year, for example).
- Finally, literature reviews can be arranged by discipline or field (i.e., what is the current research being done by biologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by psychologists on this topic? What is the current research being done by [insert academic discipline] on this topic?).
Just like in an explanatory synthesis paper, a Literature Review offers only a report on what others have already written about. The Literature Review does not reflect the author’s own argument or contributions to the field of research. Instead, it indicates that the author has read others’ important contributions and understands what has come before him or her.
The Literature Review provides context for the author’s own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author’s research grows. Context = credibility in academic writing. When authors have broad Literature Review, they demonstrate their credibility as researchers.
English 102: Reading, Research, and Writing by Emilie Zickel is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- AIMS Public Health
- v.3(1); 2016

What Synthesis Methodology Should I Use? A Review and Analysis of Approaches to Research Synthesis
Kara schick-makaroff.
1 Faculty of Nursing, University of Alberta, Edmonton, AB, Canada
Marjorie MacDonald
2 School of Nursing, University of Victoria, Victoria, BC, Canada
Marilyn Plummer
3 College of Nursing, Camosun College, Victoria, BC, Canada
Judy Burgess
4 Student Services, University Health Services, Victoria, BC, Canada
Wendy Neander
Associated data, additional file 1.
When we began this process, we were doctoral students and a faculty member in a research methods course. As students, we were facing a review of the literature for our dissertations. We encountered several different ways of conducting a review but were unable to locate any resources that synthesized all of the various synthesis methodologies. Our purpose is to present a comprehensive overview and assessment of the main approaches to research synthesis. We use ‘research synthesis’ as a broad overarching term to describe various approaches to combining, integrating, and synthesizing research findings.
We conducted an integrative review of the literature to explore the historical, contextual, and evolving nature of research synthesis. We searched five databases, reviewed websites of key organizations, hand-searched several journals, and examined relevant texts from the reference lists of the documents we had already obtained.
We identified four broad categories of research synthesis methodology including conventional, quantitative, qualitative, and emerging syntheses. Each of the broad categories was compared to the others on the following: key characteristics, purpose, method, product, context, underlying assumptions, unit of analysis, strengths and limitations, and when to use each approach.
Conclusions
The current state of research synthesis reflects significant advancements in emerging synthesis studies that integrate diverse data types and sources. New approaches to research synthesis provide a much broader range of review alternatives available to health and social science students and researchers.
1. Introduction
Since the turn of the century, public health emergencies have been identified worldwide, particularly related to infectious diseases. For example, the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) epidemic in Canada in 2002-2003, the recent Ebola epidemic in Africa, and the ongoing HIV/AIDs pandemic are global health concerns. There have also been dramatic increases in the prevalence of chronic diseases around the world [1] – [3] . These epidemiological challenges have raised concerns about the ability of health systems worldwide to address these crises. As a result, public health systems reform has been initiated in a number of countries. In Canada, as in other countries, the role of evidence to support public health reform and improve population health has been given high priority. Yet, there continues to be a significant gap between the production of evidence through research and its application in practice [4] – [5] . One strategy to address this gap has been the development of new research synthesis methodologies to deal with the time-sensitive and wide ranging evidence needs of policy makers and practitioners in all areas of health care, including public health.
As doctoral nursing students facing a review of the literature for our dissertations, and as a faculty member teaching a research methods course, we encountered several ways of conducting a research synthesis but found no comprehensive resources that discussed, compared, and contrasted various synthesis methodologies on their purposes, processes, strengths and limitations. To complicate matters, writers use terms interchangeably or use different terms to mean the same thing, and the literature is often contradictory about various approaches. Some texts [6] , [7] – [9] did provide a preliminary understanding about how research synthesis had been taken up in nursing, but these did not meet our requirements. Thus, in this article we address the need for a comprehensive overview of research synthesis methodologies to guide public health, health care, and social science researchers and practitioners.
Research synthesis is relatively new in public health but has a long history in other fields dating back to the late 1800s. Research synthesis, a research process in its own right [10] , has become more prominent in the wake of the evidence-based movement of the 1990s. Research syntheses have found their advocates and detractors in all disciplines, with challenges to the processes of systematic review and meta-analysis, in particular, being raised by critics of evidence-based healthcare [11] – [13] .
Our purpose was to conduct an integrative review of the literature to explore the historical, contextual, and evolving nature of research synthesis [14] – [15] . We synthesize and critique the main approaches to research synthesis that are relevant for public health, health care, and social scientists. Research synthesis is the overarching term we use to describe approaches to combining, aggregating, integrating, and synthesizing primary research findings. Each synthesis methodology draws on different types of findings depending on the purpose and product of the chosen synthesis (see Additional File 1 ).
3. Method of Review
Based on our current knowledge of the literature, we identified these approaches to include in our review: systematic review, meta-analysis, qualitative meta-synthesis, meta-narrative synthesis, scoping review, rapid review, realist synthesis, concept analysis, literature review, and integrative review. Our first step was to divide the synthesis types among the research team. Each member did a preliminary search to identify key texts. The team then met to develop search terms and a framework to guide the review.
Over the period of 2008 to 2012 we extensively searched the literature, updating our search at several time points, not restricting our search by date. The dates of texts reviewed range from 1967 to 2015. We used the terms above combined with the term “method* (e.g., “realist synthesis” and “method*) in the database Health Source: Academic Edition (includes Medline and CINAHL). This search yielded very few texts on some methodologies and many on others. We realized that many documents on research synthesis had not been picked up in the search. Therefore, we also searched Google Scholar, PubMed, ERIC, and Social Science Index, as well as the websites of key organizations such as the Joanna Briggs Institute, the University of York Centre for Evidence-Based Nursing, and the Cochrane Collaboration database. We hand searched several nursing, social science, public health and health policy journals. Finally, we traced relevant documents from the references in obtained texts.
We included works that met the following inclusion criteria: (1) published in English; (2) discussed the history of research synthesis; (3) explicitly described the approach and specific methods; or (4) identified issues, challenges, strengths and limitations of the particular methodology. We excluded research reports that resulted from the use of particular synthesis methodologies unless they also included criteria 2, 3, or 4 above.
Based on our search, we identified additional types of research synthesis (e.g., meta-interpretation, best evidence synthesis, critical interpretive synthesis, meta-summary, grounded formal theory). Still, we missed some important developments in meta-analysis, for example, identified by the journal's reviewers that have now been discussed briefly in the paper. The final set of 197 texts included in our review comprised theoretical, empirical, and conceptual papers, books, editorials and commentaries, and policy documents.
In our preliminary review of key texts, the team inductively developed a framework of the important elements of each method for comparison. In the next phase, each text was read carefully, and data for these elements were extracted into a table for comparison on the points of: key characteristics, purpose, methods, and product; see Additional File 1 ). Once the data were grouped and extracted, we synthesized across categories based on the following additional points of comparison: complexity of the process, degree of systematization, consideration of context, underlying assumptions, unit of analysis, and when to use each approach. In our results, we discuss our comparison of the various synthesis approaches on the elements above. Drawing only on documents for the review, ethics approval was not required.
We identified four broad categories of research synthesis methodology: Conventional, quantitative, qualitative, and emerging syntheses. From our dataset of 197 texts, we had 14 texts on conventional synthesis, 64 on quantitative synthesis, 78 on qualitative synthesis, and 41 on emerging syntheses. Table 1 provides an overview of the four types of research synthesis, definitions, types of data used, products, and examples of the methodology.
Although we group these types of synthesis into four broad categories on the basis of similarities, each type within a category has unique characteristics, which may differ from the overall group similarities. Each could be explored in greater depth to tease out their unique characteristics, but detailed comparison is beyond the scope of this article.
Additional File 1 presents one or more selected types of synthesis that represent the broad category but is not an exhaustive presentation of all types within each category. It provides more depth for specific examples from each category of synthesis on the characteristics, purpose, methods, and products than is found in Table 1 .
4.1. Key Characteristics
4.1.1. what is it.
Here we draw on two types of categorization. First, we utilize Dixon Woods et al.'s [49] classification of research syntheses as being either integrative or interpretive . (Please note that integrative syntheses are not the same as an integrative review as defined in Additional File 1 .) Second, we use Popay's [80] enhancement and epistemological models .
The defining characteristics of integrative syntheses are that they involve summarizing the data achieved by pooling data [49] . Integrative syntheses include systematic reviews, meta-analyses, as well as scoping and rapid reviews because each of these focus on summarizing data. They also define concepts from the outset (although this may not always be true in scoping or rapid reviews) and deal with a well-specified phenomenon of interest.
Interpretive syntheses are primarily concerned with the development of concepts and theories that integrate concepts [49] . The analysis in interpretive synthesis is conceptual both in process and outcome, and “the product is not aggregations of data, but theory” [49] , [p.12]. Interpretive syntheses involve induction and interpretation, and are primarily conceptual in process and outcome. Examples include integrative reviews, some systematic reviews, all of the qualitative syntheses, meta-narrative, realist and critical interpretive syntheses. Of note, both quantitative and qualitative studies can be either integrative or interpretive
The second categorization, enhancement versus epistemological , applies to those approaches that use multiple data types and sources [80] . Popay's [80] classification reflects the ways that qualitative data are valued in relation to quantitative data.
In the enhancement model , qualitative data adds something to quantitative analysis. The enhancement model is reflected in systematic reviews and meta-analyses that use some qualitative data to enhance interpretation and explanation. It may also be reflected in some rapid reviews that draw on quantitative data but use some qualitative data.
The epistemological model assumes that quantitative and qualitative data are equal and each has something unique to contribute. All of the other review approaches, except pure quantitative or qualitative syntheses, reflect the epistemological model because they value all data types equally but see them as contributing different understandings.
4.1.2. Data type
By and large, the quantitative approaches (quantitative systematic review and meta-analysis) have typically used purely quantitative data (i.e., expressed in numeric form). More recently, both Cochrane [81] and Campbell [82] collaborations are grappling with the need to, and the process of, integrating qualitative research into a systematic review. The qualitative approaches use qualitative data (i.e., expressed in words). All of the emerging synthesis types, as well as the conventional integrative review, incorporate qualitative and quantitative study designs and data.
4.1.3. Research question
Four types of research questions direct inquiry across the different types of syntheses. The first is a well-developed research question that gives direction to the synthesis (e.g., meta-analysis, systematic review, meta-study, concept analysis, rapid review, realist synthesis). The second begins as a broad general question that evolves and becomes more refined over the course of the synthesis (e.g., meta-ethnography, scoping review, meta-narrative, critical interpretive synthesis). In the third type, the synthesis begins with a phenomenon of interest and the question emerges in the analytic process (e.g., grounded formal theory). Lastly, there is no clear question, but rather a general review purpose (e.g., integrative review). Thus, the requirement for a well-defined question cuts across at least three of the synthesis types (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, and emerging).
4.1.4. Quality appraisal
This is a contested issue within and between the four synthesis categories. There are strong proponents of quality appraisal in the quantitative traditions of systematic review and meta-analysis based on the need for strong studies that will not jeopardize validity of the overall findings. Nonetheless, there is no consensus on pre-defined criteria; many scales exist that vary dramatically in composition. This has methodological implications for the credibility of findings [83] .
Specific methodologies from the conventional, qualitative, and emerging categories support quality appraisal but do so with caveats. In conventional integrative reviews appraisal is recommended, but depends on the sampling frame used in the study [18] . In meta-study, appraisal criteria are explicit but quality criteria are used in different ways depending on the specific requirements of the inquiry [54] . Among the emerging syntheses, meta-narrative review developers support appraisal of a study based on criteria from the research tradition of the primary study [67] , [84] – [85] . Realist synthesis similarly supports the use of high quality evidence, but appraisal checklists are viewed with scepticism and evidence is judged based on relevance to the research question and whether a credible inference may be drawn [69] . Like realist, critical interpretive syntheses do not judge quality using standardized appraisal instruments. They will exclude fatally flawed studies, but there is no consensus on what ‘fatally flawed’ means [49] , [71] . Appraisal is based on relevance to the inquiry, not rigor of the study.
There is no agreement on quality appraisal among qualitative meta-ethnographers with some supporting and others refuting the need for appraisal. [60] , [62] . Opponents of quality appraisal are found among authors of qualitative (grounded formal theory and concept analysis) and emerging syntheses (scoping and rapid reviews) because quality is not deemed relevant to the intention of the synthesis; the studies being reviewed are not effectiveness studies where quality is extremely important. These qualitative synthesis are often reviews of theoretical developments where the concept itself is what is important, or reviews that provide quotations from the raw data so readers can make their own judgements about the relevance and utility of the data. For example, in formal grounded theory, the purpose of theory generation and authenticity of data used to generate the theory is not as important as the conceptual category. Inaccuracies may be corrected in other ways, such as using the constant comparative method, which facilitates development of theoretical concepts that are repeatedly found in the data [86] – [87] . For pragmatic reasons, evidence is not assessed in rapid and scoping reviews, in part to produce a timely product. The issue of quality appraisal is unresolved across the terrain of research synthesis and we consider this further in our discussion.
4.2. Purpose
All research syntheses share a common purpose -- to summarize, synthesize, or integrate research findings from diverse studies. This helps readers stay abreast of the burgeoning literature in a field. Our discussion here is at the level of the four categories of synthesis. Beginning with conventional literature syntheses, the overall purpose is to attend to mature topics for the purpose of re-conceptualization or to new topics requiring preliminary conceptualization [14] . Such syntheses may be helpful to consider contradictory evidence, map shifting trends in the study of a phenomenon, and describe the emergence of research in diverse fields [14] . The purpose here is to set the stage for a study by identifying what has been done, gaps in the literature, important research questions, or to develop a conceptual framework to guide data collection and analysis.
The purpose of quantitative systematic reviews is to combine, aggregate, or integrate empirical research to be able to generalize from a group of studies and determine the limits of generalization [27] . The focus of quantitative systematic reviews has been primarily on aggregating the results of studies evaluating the effectiveness of interventions using experimental, quasi-experimental, and more recently, observational designs. Systematic reviews can be done with or without quantitative meta-analysis but a meta-analysis always takes place within the context of a systematic review. Researchers must consider the review's purpose and the nature of their data in undertaking a quantitative synthesis; this will assist in determining the approach.
The purpose of qualitative syntheses is broadly to synthesize complex health experiences, practices, or concepts arising in healthcare environments. There may be various purposes depending on the qualitative methodology. For example, in hermeneutic studies the aim may be holistic explanation or understanding of a phenomenon [42] , which is deepened by integrating the findings from multiple studies. In grounded formal theory, the aim is to produce a conceptual framework or theory expected to be applicable beyond the original study. Although not able to generalize from qualitative research in the statistical sense [88] , qualitative researchers usually do want to say something about the applicability of their synthesis to other settings or phenomena. This notion of ‘theoretical generalization’ has been referred to as ‘transferability’ [89] – [90] and is an important criterion of rigour in qualitative research. It applies equally to the products of a qualitative synthesis in which the synthesis of multiple studies on the same phenomenon strengthens the ability to draw transferable conclusions.
The overarching purpose of emerging syntheses is challenging the more traditional types of syntheses, in part by using data from both quantitative and qualitative studies with diverse designs for analysis. Beyond this, however, each emerging synthesis methodology has a unique purpose. In meta-narrative review, the purpose is to identify different research traditions in the area, synthesize a complex and diverse body of research. Critical interpretive synthesis shares this characteristic. Although a distinctive approach, critical interpretive synthesis utilizes a modification of the analytic strategies of meta-ethnography [61] (e.g., reciprocal translational analysis, refutational synthesis, and lines of argument synthesis) but goes beyond the use of these to bring a critical perspective to bear in challenging the normative or epistemological assumptions in the primary literature [72] – [73] . The unique purpose of a realist synthesis is to amalgamate complex empirical evidence and theoretical understandings within a diverse body of literature to uncover the operative mechanisms and contexts that affect the outcomes of social interventions. In a scoping review, the intention is to find key concepts, examine the range of research in an area, and identify gaps in the literature. The purpose of a rapid review is comparable to that of a scoping review, but done quickly to meet the time-sensitive information needs of policy makers.

4.3. Method
4.3.1. degree of systematization.
There are varying degrees of systematization across the categories of research synthesis. The most systematized are quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses. There are clear processes in each with judgments to be made at each step, although there are no agreed upon guidelines for this. The process is inherently subjective despite attempts to develop objective and systematic processes [91] – [92] . Mullen and Ramirez [27] suggest that there is often a false sense of rigour implied by the terms ‘systematic review’ and ‘meta-analysis’ because of their clearly defined procedures.
In comparison with some types of qualitative synthesis, concept analysis is quite procedural. Qualitative meta-synthesis also has defined procedures and is systematic, yet perhaps less so than concept analysis. Qualitative meta-synthesis starts in an unsystematic way but becomes more systematic as it unfolds. Procedures and frameworks exist for some of the emerging types of synthesis [e.g., [50] , [63] , [71] , [93] ] but are not linear, have considerable flexibility, and are often messy with emergent processes [85] . Conventional literature reviews tend not to be as systematic as the other three types. In fact, the lack of systematization in conventional literature synthesis was the reason for the development of more systematic quantitative [17] , [20] and qualitative [45] – [46] , [61] approaches. Some authors in the field [18] have clarified processes for integrative reviews making them more systematic and rigorous, but most conventional syntheses remain relatively unsystematic in comparison with other types.
4.3.2. Complexity of the process
Some synthesis processes are considerably more complex than others. Methodologies with clearly defined steps are arguably less complex than the more flexible and emergent ones. We know that any study encounters challenges and it is rare that a pre-determined research protocol can be followed exactly as intended. Not even the rigorous methods associated with Cochrane [81] systematic reviews and meta-analyses are always implemented exactly as intended. Even when dealing with numbers rather than words, interpretation is always part of the process. Our collective experience suggests that new methodologies (e.g., meta-narrative synthesis and realist synthesis) that integrate different data types and methods are more complex than conventional reviews or the rapid and scoping reviews.
4.4. Product
The products of research syntheses usually take three distinct formats (see Table 1 and Additional File 1 for further details). The first representation is in tables, charts, graphical displays, diagrams and maps as seen in integrative, scoping and rapid reviews, meta-analyses, and critical interpretive syntheses. The second type of synthesis product is the use of mathematical scores. Summary statements of effectiveness are mathematically displayed in meta-analyses (as an effect size), systematic reviews, and rapid reviews (statistical significance).
The third synthesis product may be a theory or theoretical framework. A mid-range theory can be produced from formal grounded theory, meta-study, meta-ethnography, and realist synthesis. Theoretical/conceptual frameworks or conceptual maps may be created in meta-narrative and critical interpretive syntheses, and integrative reviews. Concepts for use within theories are produced in concept analysis. While these three product types span the categories of research synthesis, narrative description and summary is used to present the products resulting from all methodologies.
4.5. Consideration of context
There are diverse ways that context is considered in the four broad categories of synthesis. Context may be considered to the extent that it features within primary studies for the purpose of the review. Context may also be understood as an integral aspect of both the phenomenon under study and the synthesis methodology (e.g., realist synthesis). Quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have typically been conducted on studies using experimental and quasi-experimental designs and more recently observational studies, which control for contextual features to allow for understanding of the ‘true’ effect of the intervention [94] .
More recently, systematic reviews have included covariates or mediating variables (i.e., contextual factors) to help explain variability in the results across studies [27] . Context, however, is usually handled in the narrative discussion of findings rather than in the synthesis itself. This lack of attention to context has been one criticism leveled against systematic reviews and meta-analyses, which restrict the types of research designs that are considered [e.g., [95] ].
When conventional literature reviews incorporate studies that deal with context, there is a place for considering contextual influences on the intervention or phenomenon. Reviews of quantitative experimental studies tend to be devoid of contextual considerations since the original studies are similarly devoid, but context might figure prominently in a literature review that incorporates both quantitative and qualitative studies.
Qualitative syntheses have been conducted on the contextual features of a particular phenomenon [33] . Paterson et al. [54] advise researchers to attend to how context may have influenced the findings of particular primary studies. In qualitative analysis, contextual features may form categories by which the data can be compared and contrasted to facilitate interpretation. Because qualitative research is often conducted to understand a phenomenon as a whole, context may be a focus, although this varies with the qualitative methodology. At the same time, the findings in a qualitative synthesis are abstracted from the original reports and taken to a higher level of conceptualization, thus removing them from the original context.
Meta-narrative synthesis [67] , [84] , because it draws on diverse research traditions and methodologies, may incorporate context into the analysis and findings. There is not, however, an explicit step in the process that directs the analyst to consider context. Generally, the research question guiding the synthesis is an important factor in whether context will be a focus.
More recent iterations of concept analysis [47] , [96] – [97] explicitly consider context reflecting the assumption that a concept's meaning is determined by its context. Morse [47] points out, however, that Wilson's [98] approach to concept analysis, and those based on Wilson [e.g., [45] ], identify attributes that are devoid of context, while Rodgers' [96] , [99] evolutionary method considers context (e.g., antecedents, consequences, and relationships to other concepts) in concept development.
Realist synthesis [69] considers context as integral to the study. It draws on a critical realist logic of inquiry grounded in the work of Bhaskar [100] , who argues that empirical co-occurrence of events is insufficient for inferring causation. One must identify generative mechanisms whose properties are causal and, depending on the situation, may nor may not be activated [94] . Context interacts with program/intervention elements and thus cannot be differentiated from the phenomenon [69] . This approach synthesizes evidence on generative mechanisms and analyzes contextual features that activate them; the result feeds back into the context. The focus is on what works, for whom, under what conditions, why and how [68] .
4.6. Underlying Philosophical and Theoretical Assumptions
When we began our review, we ‘assumed’ that the assumptions underlying synthesis methodologies would be a distinguishing characteristic of synthesis types, and that we could compare the various types on their assumptions, explicit or implicit. We found, however, that many authors did not explicate the underlying assumptions of their methodologies, and it was difficult to infer them. Kirkevold [101] has argued that integrative reviews need to be carried out from an explicit philosophical or theoretical perspective. We argue this should be true for all types of synthesis.
Authors of some emerging synthesis approaches have been very explicit about their assumptions and philosophical underpinnings. An implicit assumption of most emerging synthesis methodologies is that quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have limited utility in some fields [e.g., in public health – [13] , [102] ] and for some kinds of review questions like those about feasibility and appropriateness versus effectiveness [103] – [104] . They also assume that ontologically and epistemologically, both kinds of data can be combined. This is a significant debate in the literature because it is about the commensurability of overarching paradigms [105] but this is beyond the scope of this review.
Realist synthesis is philosophically grounded in critical realism or, as noted above, a realist logic of inquiry [93] , [99] , [106] – [107] . Key assumptions regarding the nature of interventions that inform critical realism have been described above in the section on context. See Pawson et al. [106] for more information on critical realism, the philosophical basis of realist synthesis.
Meta-narrative synthesis is explicitly rooted in a constructivist philosophy of science [108] in which knowledge is socially constructed rather than discovered, and what we take to be ‘truth’ is a matter of perspective. Reality has a pluralistic and plastic character, and there is no pre-existing ‘real world’ independent of human construction and language [109] . See Greenhalgh et al. [67] , [85] and Greenhalgh & Wong [97] for more discussion of the constructivist basis of meta-narrative synthesis.
In the case of purely quantitative or qualitative syntheses, it may be an easier matter to uncover unstated assumptions because they are likely to be shared with those of the primary studies in the genre. For example, grounded formal theory shares the philosophical and theoretical underpinnings of grounded theory, rooted in the theoretical perspective of symbolic interactionism [110] – [111] and the philosophy of pragmatism [87] , [112] – [114] .
As with meta-narrative synthesis, meta-study developers identify constructivism as their interpretive philosophical foundation [54] , [88] . Epistemologically, constructivism focuses on how people construct and re-construct knowledge about a specific phenomenon, and has three main assumptions: (1) reality is seen as multiple, at times even incompatible with the phenomenon under consideration; (2) just as primary researchers construct interpretations from participants' data, meta-study researchers also construct understandings about the primary researchers' original findings. Thus, meta-synthesis is a construction of a construction, or a meta-construction; and (3) all constructions are shaped by the historical, social and ideological context in which they originated [54] . The key message here is that reports of any synthesis would benefit from an explicit identification of the underlying philosophical perspectives to facilitate a better understanding of the results, how they were derived, and how they are being interpreted.
4.7. Unit of Analysis
The unit of analysis for each category of review is generally distinct. For the emerging synthesis approaches, the unit of analysis is specific to the intention. In meta-narrative synthesis it is the storyline in diverse research traditions; in rapid review or scoping review, it depends on the focus but could be a concept; and in realist synthesis, it is the theories rather than programs that are the units of analysis. The elements of theory that are important in the analysis are mechanisms of action, the context, and the outcome [107] .
For qualitative synthesis, the units of analysis are generally themes, concepts or theories, although in meta-study, the units of analysis can be research findings (“meta-data-analysis”), research methods (“meta-method”) or philosophical/theoretical perspectives (“meta-theory”) [54] . In quantitative synthesis, the units of analysis range from specific statistics for systematic reviews to effect size of the intervention for meta-analysis. More recently, some systematic reviews focus on theories [115] – [116] , therefore it depends on the research question. Similarly, within conventional literature synthesis the units of analysis also depend on the research purpose, focus and question as well as on the type of research methods incorporated into the review. What is important in all research syntheses, however, is that the unit of analysis needs to be made explicit. Unfortunately, this is not always the case.
4.8. Strengths and Limitations
In this section, we discuss the overarching strengths and limitations of synthesis methodologies as a whole and then highlight strengths and weaknesses across each of our four categories of synthesis.
4.8.1. Strengths of Research Syntheses in General
With the vast proliferation of research reports and the increased ease of retrieval, research synthesis has become more accessible providing a way of looking broadly at the current state of research. The availability of syntheses helps researchers, practitioners, and policy makers keep up with the burgeoning literature in their fields without which evidence-informed policy or practice would be difficult. Syntheses explain variation and difference in the data helping us identify the relevance for our own situations; they identify gaps in the literature leading to new research questions and study designs. They help us to know when to replicate a study and when to avoid excessively duplicating research. Syntheses can inform policy and practice in a way that well-designed single studies cannot; they provide building blocks for theory that helps us to understand and explain our phenomena of interest.
4.8.2. Limitations of Research Syntheses in General
The process of selecting, combining, integrating, and synthesizing across diverse study designs and data types can be complex and potentially rife with bias, even with those methodologies that have clearly defined steps. Just because a rigorous and standardized approach has been used does not mean that implicit judgements will not influence the interpretations and choices made at different stages.
In all types of synthesis, the quantity of data can be considerable, requiring difficult decisions about scope, which may affect relevance. The quantity of available data also has implications for the size of the research team. Few reviews these days can be done independently, in particular because decisions about inclusion and exclusion may require the involvement of more than one person to ensure reliability.
For all types of synthesis, it is likely that in areas with large, amorphous, and diverse bodies of literature, even the most sophisticated search strategies will not turn up all the relevant and important texts. This may be more important in some synthesis methodologies than in others, but the omission of key documents can influence the results of all syntheses. This issue can be addressed, at least in part, by including a library scientist on the research team as required by some funding agencies. Even then, it is possible to miss key texts. In this review, for example, because none of us are trained in or conduct meta-analyses, we were not even aware that we had missed some new developments in this field such as meta-regression [117] – [118] , network meta-analysis [119] – [121] , and the use of individual patient data in meta-analyses [122] – [123] .
One limitation of systematic reviews and meta-analyses is that they rapidly go out of date. We thought this might be true for all types of synthesis, although we wondered if those that produce theory might not be somewhat more enduring. We have not answered this question but it is open for debate. For all types of synthesis, the analytic skills and the time required are considerable so it is clear that training is important before embarking on a review, and some types of review may not be appropriate for students or busy practitioners.
Finally, the quality of reporting in primary studies of all genres is variable so it is sometimes difficult to identify aspects of the study essential for the synthesis, or to determine whether the study meets quality criteria. There may be flaws in the original study, or journal page limitations may necessitate omitting important details. Reporting standards have been developed for some types of reviews (e.g., systematic review, meta-analysis, meta-narrative synthesis, realist synthesis); but there are no agreed upon standards for qualitative reviews. This is an important area for development in advancing the science of research synthesis.
4.8.3. Strengths and Limitations of the Four Synthesis Types
The conventional literature review and now the increasingly common integrative review remain important and accessible approaches for students, practitioners, and experienced researchers who want to summarize literature in an area but do not have the expertise to use one of the more complex methodologies. Carefully executed, such reviews are very useful for synthesizing literature in preparation for research grants and practice projects. They can determine the state of knowledge in an area and identify important gaps in the literature to provide a clear rationale or theoretical framework for a study [14] , [18] . There is a demand, however, for more rigour, with more attention to developing comprehensive search strategies and more systematic approaches to combining, integrating, and synthesizing the findings.
Generally, conventional reviews include diverse study designs and data types that facilitate comprehensiveness, which may be a strength on the one hand, but can also present challenges on the other. The complexity inherent in combining results from studies with diverse methodologies can result in bias and inaccuracies. The absence of clear guidelines about how to synthesize across diverse study types and data [18] has been a challenge for novice reviewers.
Quantitative systematic reviews and meta-analyses have been important in launching the field of evidence-based healthcare. They provide a systematic, orderly and auditable process for conducting a review and drawing conclusions [25] . They are arguably the most powerful approaches to understanding the effectiveness of healthcare interventions, especially when intervention studies on the same topic show very different results. When areas of research are dogged by controversy [25] or when study results go against strongly held beliefs, such approaches can reduce the uncertainty and bring strong evidence to bear on the controversy.
Despite their strengths, they also have limitations. Systematic reviews and meta-analyses do not provide a way of including complex literature comprising various types of evidence including qualitative studies, theoretical work, and epidemiological studies. Only certain types of design are considered and qualitative data are used in a limited way. This exclusion limits what can be learned in a topic area.
Meta-analyses are often not possible because of wide variability in study design, population, and interventions so they may have a narrow range of utility. New developments in meta-analysis, however, can be used to address some of these limitations. Network meta-analysis is used to explore relative efficacy of multiple interventions, even those that have never been compared in more conventional pairwise meta-analyses [121] , allowing for improved clinical decision making [120] . The limitation is that network meta-analysis has only been used in medical/clinical applications [119] and not in public health. It has not yet been widely accepted and many methodological challenges remain [120] – [121] . Meta-regression is another development that combines meta-analytic and linear regression principles to address the fact that heterogeneity of results may compromise a meta-analysis [117] – [118] . The disadvantage is that many clinicians are unfamiliar with it and may incorrectly interpret results [117] .
Some have accused meta-analysis of combining apples and oranges [124] raising questions in the field about their meaningfulness [25] , [28] . More recently, the use of individual rather than aggregate data has been useful in facilitating greater comparability among studies [122] . In fact, Tomas et al. [123] argue that meta-analysis using individual data is now the gold standard although access to the raw data from other studies may be a challenge to obtain.
The usefulness of systematic reviews in synthesizing complex health and social interventions has also been challenged [102] . It is often difficult to synthesize their findings because such studies are “epistemologically diverse and methodologically complex” [ [69] , p.21]. Rigid inclusion/exclusion criteria may allow only experimental or quasi-experimental designs into consideration resulting in lost information that may well be useful to policy makers for tailoring an intervention to the context or understanding its acceptance by recipients.
Qualitative syntheses may be the type of review most fraught with controversy and challenge, while also bringing distinct strengths to the enterprise. Although these methodologies provide a comprehensive and systematic review approach, they do not generally provide definitive statements about intervention effectiveness. They do, however, address important questions about the development of theoretical concepts, patient experiences, acceptability of interventions, and an understanding about why interventions might work.
Most qualitative syntheses aim to produce a theoretically generalizable mid-range theory that explains variation across studies. This makes them more useful than single primary studies, which may not be applicable beyond the immediate setting or population. All provide a contextual richness that enhances relevance and understanding. Another benefit of some types of qualitative synthesis (e.g., grounded formal theory) is that the concept of saturation provides a sound rationale for limiting the number of texts to be included thus making reviews potentially more manageable. This contrasts with the requirements of systematic reviews and meta-analyses that require an exhaustive search.
Qualitative researchers debate about whether the findings of ontologically and epistemological diverse qualitative studies can actually be combined or synthesized [125] because methodological diversity raises many challenges for synthesizing findings. The products of different types of qualitative syntheses range from theory and conceptual frameworks, to themes and rich descriptive narratives. Can one combine the findings from a phenomenological study with the theory produced in a grounded theory study? Many argue yes, but many also argue no.
Emerging synthesis methodologies were developed to address some limitations inherent in other types of synthesis but also have their own issues. Because each type is so unique, it is difficult to identify overarching strengths of the entire category. An important strength, however, is that these newer forms of synthesis provide a systematic and rigorous approach to synthesizing a diverse literature base in a topic area that includes a range of data types such as: both quantitative and qualitative studies, theoretical work, case studies, evaluations, epidemiological studies, trials, and policy documents. More than conventional literature reviews and systematic reviews, these approaches provide explicit guidance on analytic methods for integrating different types of data. The assumption is that all forms of data have something to contribute to knowledge and theory in a topic area. All have a defined but flexible process in recognition that the methods may need to shift as knowledge develops through the process.
Many emerging synthesis types are helpful to policy makers and practitioners because they are usually involved as team members in the process to define the research questions, and interpret and disseminate the findings. In fact, engagement of stakeholders is built into the procedures of the methods. This is true for rapid reviews, meta-narrative syntheses, and realist syntheses. It is less likely to be the case for critical interpretive syntheses.
Another strength of some approaches (realist and meta-narrative syntheses) is that quality and publication standards have been developed to guide researchers, reviewers, and funders in judging the quality of the products [108] , [126] – [127] . Training materials and online communities of practice have also been developed to guide users of realist and meta-narrative review methods [107] , [128] . A unique strength of critical interpretive synthesis is that it takes a critical perspective on the process that may help reconceptualize the data in a way not considered by the primary researchers [72] .
There are also challenges of these new approaches. The methods are new and there may be few published applications by researchers other than the developers of the methods, so new users often struggle with the application. The newness of the approaches means that there may not be mentors available to guide those unfamiliar with the methods. This is changing, however, and the number of applications in the literature is growing with publications by new users helping to develop the science of synthesis [e.g., [129] ]. However, the evolving nature of the approaches and their developmental stage present challenges for novice researchers.
4.9. When to Use Each Approach
Choosing an appropriate approach to synthesis will depend on the question you are asking, the purpose of the review, and the outcome or product you want to achieve. In Additional File 1 , we discuss each of these to provide guidance to readers on making a choice about review type. If researchers want to know whether a particular type of intervention is effective in achieving its intended outcomes, then they might choose a quantitative systemic review with or without meta-analysis, possibly buttressed with qualitative studies to provide depth and explanation of the results. Alternately, if the concern is about whether an intervention is effective with different populations under diverse conditions in varying contexts, then a realist synthesis might be the most appropriate.
If researchers' concern is to develop theory, they might consider qualitative syntheses or some of the emerging syntheses that produce theory (e.g., critical interpretive synthesis, realist review, grounded formal theory, qualitative meta-synthesis). If the aim is to track the development and evolution of concepts, theories or ideas, or to determine how an issue or question is addressed across diverse research traditions, then meta-narrative synthesis would be most appropriate.
When the purpose is to review the literature in advance of undertaking a new project, particularly by graduate students, then perhaps an integrative review would be appropriate. Such efforts contribute towards the expansion of theory, identify gaps in the research, establish the rationale for studying particular phenomena, and provide a framework for interpreting results in ways that might be useful for influencing policy and practice.
For researchers keen to bring new insights, interpretations, and critical re-conceptualizations to a body of research, then qualitative or critical interpretive syntheses will provide an inductive product that may offer new understandings or challenges to the status quo. These can inform future theory development, or provide guidance for policy and practice.
5. Discussion
What is the current state of science regarding research synthesis? Public health, health care, and social science researchers or clinicians have previously used all four categories of research synthesis, and all offer a suitable array of approaches for inquiries. New developments in systematic reviews and meta-analysis are providing ways of addressing methodological challenges [117] – [123] . There has also been significant advancement in emerging synthesis methodologies and they are quickly gaining popularity. Qualitative meta-synthesis is still evolving, particularly given how new it is within the terrain of research synthesis. In the midst of this evolution, outstanding issues persist such as grappling with: the quantity of data, quality appraisal, and integration with knowledge translation. These topics have not been thoroughly addressed and need further debate.
5.1. Quantity of Data
We raise the question of whether it is possible or desirable to find all available studies for a synthesis that has this requirement (e.g., meta-analysis, systematic review, scoping, meta-narrative synthesis [25] , [27] , [63] , [67] , [84] – [85] ). Is the synthesis of all available studies a realistic goal in light of the burgeoning literature? And how can this be sustained in the future, particularly as the emerging methodologies continue to develop and as the internet facilitates endless access? There has been surprisingly little discussion on this topic and the answers will have far-reaching implications for searching, sampling, and team formation.
Researchers and graduate students can no longer rely on their own independent literature search. They will likely need to ask librarians for assistance as they navigate multiple sources of literature and learn new search strategies. Although teams now collaborate with library scientists, syntheses are limited in that researchers must make decisions on the boundaries of the review, in turn influencing the study's significance. The size of a team may also be pragmatically determined to manage the search, extraction, and synthesis of the burgeoning data. There is no single answer to our question about the possibility or necessity of finding all available articles for a review. Multiple strategies that are situation specific are likely to be needed.
5.2. Quality Appraisal
While the issue of quality appraisal has received much attention in the synthesis literature, scholars are far from resolution. There may be no agreement about appraisal criteria in a given tradition. For example, the debate rages over the appropriateness of quality appraisal in qualitative synthesis where there are over 100 different sets of criteria and many do not overlap [49] . These differences may reflect disciplinary and methodological orientations, but diverse quality appraisal criteria may privilege particular types of research [49] . The decision to appraise is often grounded in ontological and epistemological assumptions. Nonetheless, diversity within and between categories of synthesis is likely to continue unless debate on the topic of quality appraisal continues and evolves toward consensus.
5.3. Integration with Knowledge Translation
If research syntheses are to make a difference to practice and ultimately to improve health outcomes, then we need to do a better job of knowledge translation. In the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) definition of knowledge translation (KT), research or knowledge synthesis is an integral component [130] . Yet, with few exceptions [131] – [132] , very little of the research synthesis literature even mentions the relationship of synthesis to KT nor does it discuss strategies to facilitate the integration of synthesis findings into policy and practice. The exception is in the emerging synthesis methodologies, some of which (e.g., realist and meta-narrative syntheses, scoping reviews) explicitly involve stakeholders or knowledge users. The argument is that engaging them in this way increases the likelihood that the knowledge generated will be translated into policy and practice. We suggest that a more explicit engagement with knowledge users in all types of synthesis would benefit the uptake of the research findings.
Research synthesis neither makes research more applicable to practice nor ensures implementation. Focus must now turn seriously towards translation of synthesis findings into knowledge products that are useful for health care practitioners in multiple areas of practice and develop appropriate strategies to facilitate their use. The burgeoning field of knowledge translation has, to some extent, taken up this challenge; however, the research-practice gap continues to plague us [133] – [134] . It is a particular problem for qualitative syntheses [131] . Although such syntheses have an important place in evidence-informed practice, little effort has gone into the challenge of translating the findings into useful products to guide practice [131] .
5.4. Limitations
Our study took longer than would normally be expected for an integrative review. Each of us were primarily involved in our own dissertations or teaching/research positions, and so this study was conducted ‘off the sides of our desks.’ A limitation was that we searched the literature over the course of 4 years (from 2008–2012), necessitating multiple search updates. Further, we did not do a comprehensive search of the literature after 2012, thus the more recent synthesis literature was not systematically explored. We did, however, perform limited database searches from 2012–2015 to keep abreast of the latest methodological developments. Although we missed some new approaches to meta-analysis in our search, we did not find any new features of the synthesis methodologies covered in our review that would change the analysis or findings of this article. Lastly, we struggled with the labels used for the broad categories of research synthesis methodology because of our hesitancy to reinforce the divide between quantitative and qualitative approaches. However, it was very difficult to find alternative language that represented the types of data used in these methodologies. Despite our hesitancy in creating such an obvious divide, we were left with the challenge of trying to find a way of characterizing these broad types of syntheses.
6. Conclusion
Our findings offer methodological clarity for those wishing to learn about the broad terrain of research synthesis. We believe that our review makes transparent the issues and considerations in choosing from among the four broad categories of research synthesis. In summary, research synthesis has taken its place as a form of research in its own right. The methodological terrain has deep historical roots reaching back over the past 200 years, yet research synthesis remains relatively new to public health, health care, and social sciences in general. This is rapidly changing. New developments in systematic reviews and meta-analysis, and the emergence of new synthesis methodologies provide a vast array of options to review the literature for diverse purposes. New approaches to research synthesis and new analytic methods within existing approaches provide a much broader range of review alternatives for public health, health care, and social science students and researchers.
Acknowledgments
KSM is an assistant professor in the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta. Her work on this article was largely conducted as a Postdoctoral Fellow, funded by KRESCENT (Kidney Research Scientist Core Education and National Training Program, reference #KRES110011R1) and the Faculty of Nursing at the University of Alberta.
MM's work on this study over the period of 2008-2014 was supported by a Canadian Institutes of Health Research Applied Public Health Research Chair Award (grant #92365).
We thank Rachel Spanier who provided support with reference formatting.
List of Abbreviations (in Additional File 1 )
Conflict of interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest in this article.
Authors' contributions: KSM co-designed the study, collected data, analyzed the data, drafted/revised the manuscript, and managed the project.
MP contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
JB contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
WN contributed to searching the literature, developing the analytic framework, and extracting data for the Additional File.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Additional Files: Additional File 1 – Selected Types of Research Synthesis
This Additional File is our dataset created to organize, analyze and critique the literature that we synthesized in our integrative review. Our results were created based on analysis of this Additional File.
Writing in the Health and Social Sciences: Literature Reviews and Synthesis Tools
- Journal Publishing
- Style and Writing Guides
- Readings about Writing
- Citing in APA Style This link opens in a new window
- Resources for Dissertation Authors
- Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- What are Literature Reviews?
- Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Tutorials & Tools for Literature Reviews
Systematic Literature Reviews: Steps & Resources
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below .
Also see subpages for more information about:
- The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods
- Tools & Tutorials
Literature Review & Systematic Review Steps
- Develop a Focused Question
- Scope the Literature (Initial Search)
- Refine & Expand the Search
- Limit the Results
- Download Citations
- Abstract & Analyze
- Create Flow Diagram
- Synthesize & Report Results
1. Develop a Focused Question
Consider the PICO Format: Population/Problem, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome
Focus on defining the Population or Problem and Intervention (don't narrow by Comparison or Outcome just yet!)
"What are the effects of the Pilates method for patients with low back pain?"
Tools & Additional Resources:
- PICO Question Help
- Stillwell, Susan B., DNP, RN, CNE; Fineout-Overholt, Ellen, PhD, RN, FNAP, FAAN; Melnyk, Bernadette Mazurek, PhD, RN, CPNP/PMHNP, FNAP, FAAN; Williamson, Kathleen M., PhD, RN Evidence-Based Practice, Step by Step: Asking the Clinical Question, AJN The American Journal of Nursing : March 2010 - Volume 110 - Issue 3 - p 58-61 doi: 10.1097/01.NAJ.0000368959.11129.79
2. Scope the Literature
A "scoping search" investigates the breadth and/or depth of the initial question or may identify a gap in the literature.
Eligible studies may be located by searching in:
- Background sources (books, point-of-care tools)
- Article databases
- Trial registries
- Grey literature
- Cited references
- Reference lists
When searching, if possible, translate terms to controlled vocabulary of the database. Use text word searching when necessary.
Use Boolean operators to connect search terms:
- Combine separate concepts with AND (resulting in a narrower search)
- Connecting synonyms with OR (resulting in an expanded search)
Search: pilates AND ("low back pain" OR backache )
Video Tutorials - Translating PICO Questions into Search Queries
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in PubMed (YouTube, Carrie Price, 5:11)
- Translate Your PICO Into a Search in CINAHL (YouTube, Carrie Price, 4:56)
3. Refine & Expand Your Search
Expand your search strategy with synonymous search terms harvested from:
- database thesauri
- reference lists
- relevant studies
Example:
(pilates OR exercise movement techniques) AND ("low back pain" OR backache* OR sciatica OR lumbago OR spondylosis)
As you develop a final, reproducible strategy for each database, save your strategies in a:
- a personal database account (e.g., MyNCBI for PubMed)
- Log in with your NYU credentials
- Open and "Make a Copy" to create your own tracker for your literature search strategies
4. Limit Your Results
Use database filters to limit your results based on your defined inclusion/exclusion criteria. In addition to relying on the databases' categorical filters, you may also need to manually screen results.
- Limit to Article type, e.g.,: "randomized controlled trial" OR multicenter study
- Limit by publication years, age groups, language, etc.
NOTE: Many databases allow you to filter to "Full Text Only". This filter is not recommended . It excludes articles if their full text is not available in that particular database (CINAHL, PubMed, etc), but if the article is relevant, it is important that you are able to read its title and abstract, regardless of 'full text' status. The full text is likely to be accessible through another source (a different database, or Interlibrary Loan).
- Filters in PubMed
- CINAHL Advanced Searching Tutorial
5. Download Citations
Selected citations and/or entire sets of search results can be downloaded from the database into a citation management tool. If you are conducting a systematic review that will require reporting according to PRISMA standards, a citation manager can help you keep track of the number of articles that came from each database, as well as the number of duplicate records.
In Zotero, you can create a Collection for the combined results set, and sub-collections for the results from each database you search. You can then use Zotero's 'Duplicate Items" function to find and merge duplicate records.

- Citation Managers - General Guide
6. Abstract and Analyze
- Migrate citations to data collection/extraction tool
- Screen Title/Abstracts for inclusion/exclusion
- Screen and appraise full text for relevance, methods,
- Resolve disagreements by consensus
Covidence is a web-based tool that enables you to work with a team to screen titles/abstracts and full text for inclusion in your review, as well as extract data from the included studies.

- Covidence Support
- Critical Appraisal Tools
- Data Extraction Tools
7. Create Flow Diagram
The PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses) flow diagram is a visual representation of the flow of records through different phases of a systematic review. It depicts the number of records identified, included and excluded. It is best used in conjunction with the PRISMA checklist .

Example from: Stotz, S. A., McNealy, K., Begay, R. L., DeSanto, K., Manson, S. M., & Moore, K. R. (2021). Multi-level diabetes prevention and treatment interventions for Native people in the USA and Canada: A scoping review. Current Diabetes Reports, 2 (11), 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-021-01414-3
- PRISMA Flow Diagram Generator (ShinyApp.io, Haddaway et al. )
- PRISMA Diagram Templates (Word and PDF)
- Make a copy of the file to fill out the template
- Image can be downloaded as PDF, PNG, JPG, or SVG
- Covidence generates a PRISMA diagram that is automatically updated as records move through the review phases
8. Synthesize & Report Results
There are a number of reporting guideline available to guide the synthesis and reporting of results in systematic literature reviews.
It is common to organize findings in a matrix, also known as a Table of Evidence (ToE).

- Reporting Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Download a sample template of a health sciences review matrix (GoogleSheets)
Steps modified from:
Cook, D. A., & West, C. P. (2012). Conducting systematic reviews in medical education: a stepwise approach. Medical Education , 46 (10), 943–952.
- << Previous: Citation Management and Formatting Tools
- Next: What are Literature Reviews? >>
- Last Updated: May 15, 2024 11:19 AM
- URL: https://guides.nyu.edu/healthwriting

- Research Guides
Literature Review: A Self-Guided Tutorial
Using a synthesis matrix.
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Peer Review
- Reading the Literature
- Using Concept Maps
- Developing Research Questions
- Considering Strong Opinions
- 2. Review discipline styles
- Super Searching
- Finding the Full Text
- Citation Searching This link opens in a new window
- When to stop searching
- Citation Management
- Annotating Articles Tip
- 5. Critically analyze and evaluate
- How to Review the Literature
- 7. Write literature review
A synthesis matrix visually represents your research by organizing your sources by themes:
- Sample Synthesis Matrix Example provided by Ashford University Writing Center .
- << Previous: How to Review the Literature
- Next: 7. Write literature review >>
- Last Updated: Feb 22, 2024 10:53 AM
- URL: https://libguides.williams.edu/literature-review
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

About the Research and Synthesis Tables
Research Tables and Synthesis Tables are useful tools for organizing and analyzing your research as you assemble your literature review. They represent two different parts of the review process: assembling relevant information and synthesizing it. Use a Research table to compile the main info you need about the items you find in your research -- it's a great thing to have on hand as you take notes on what you read! Then, once you've assembled your research, use the Synthesis table to start charting the similarities/differences and major themes among your collected items.
We've included an Excel file with templates for you to use below; the examples pictured on this page are snapshots from that file.
- Research and Synthesis Table Templates This Excel workbook includes simple templates for creating research tables and synthesis tables. Feel free to download and use!
Using the Research Table

This is an example of a research table, in which you provide a basic description of the most important features of the studies, articles, and other items you discover in your research. The table identifies each item according to its author/date of publication, its purpose or thesis, what type of work it is (systematic review, clinical trial, etc.), the level of evidence it represents (which tells you a lot about its impact on the field of study), and its major findings. Your job, when you assemble this information, is to develop a snapshot of what the research shows about the topic of your research question and assess its value (both for the purpose of your work and for general knowledge in the field).
Think of your work on the research table as the foundational step for your analysis of the literature, in which you assemble the information you'll be analyzing and lay the groundwork for thinking about what it means and how it can be used.
Using the Synthesis Table

This is an example of a synthesis table or synthesis matrix , in which you organize and analyze your research by listing each source and indicating whether a given finding or result occurred in a particular study or article ( each row lists an individual source, and each finding has its own column, in which X = yes, blank = no). You can also add or alter the columns to look for shared study populations, sort by level of evidence or source type, etc. The key here is to use the table to provide a simple representation of what the research has found (or not found, as the case may be). Think of a synthesis table as a tool for making comparisons, identifying trends, and locating gaps in the literature.
How do I know which findings to use, or how many to include? Your research question tells you which findings are of interest in your research, so work from your research question to decide what needs to go in each Finding header, and how many findings are necessary. The number is up to you; again, you can alter this table by adding or deleting columns to match what you're actually looking for in your analysis. You should also, of course, be guided by what's actually present in the material your research turns up!
- << Previous: Synthesizing Research
- Next: Additional Resources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals More You are viewing from: Google Indexer
You are here
- Volume 29, Issue 3
- Rapid reviews methods series: guidance on rapid qualitative evidence synthesis
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4808-3880 Andrew Booth 1 , 2 ,
- Isolde Sommer 3 , 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4238-5984 Jane Noyes 2 , 5 ,
- Catherine Houghton 2 , 6 ,
- Fiona Campbell 1 , 7
- The Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group and Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group (CQIMG)
- 1 EnSyGN Sheffield Evidence Synthesis Group , University of Sheffield , Sheffield , UK
- 2 Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group (CQIMG) , London , UK
- 3 Department for Evidence-based Medicine and Evaluation , University for Continuing Education Krems , Krems , Austria
- 4 Cochrane Rapid Reviews Group & Cochrane Austria , Krems , Austria
- 5 Bangor University , Bangor , UK
- 6 University of Galway , Galway , Ireland
- 7 University of Newcastle upon Tyne , Newcastle upon Tyne , UK
- Correspondence to Professor Andrew Booth, Univ Sheffield, Sheffield, UK; a.booth{at}sheffield.ac.uk
This paper forms part of a series of methodological guidance from the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group and addresses rapid qualitative evidence syntheses (QESs), which use modified systematic, transparent and reproducible methodsu to accelerate the synthesis of qualitative evidence when faced with resource constraints. This guidance covers the review process as it relates to synthesis of qualitative research. ‘Rapid’ or ‘resource-constrained’ QES require use of templates and targeted knowledge user involvement. Clear definition of perspectives and decisions on indirect evidence, sampling and use of existing QES help in targeting eligibility criteria. Involvement of an information specialist, especially in prioritising databases, targeting grey literature and planning supplemental searches, can prove invaluable. Use of templates and frameworks in study selection and data extraction can be accompanied by quality assurance procedures targeting areas of likely weakness. Current Cochrane guidance informs selection of tools for quality assessment and of synthesis method. Thematic and framework synthesis facilitate efficient synthesis of large numbers of studies or plentiful data. Finally, judicious use of Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach for assessing the Confidence of Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research assessments and of software as appropriate help to achieve a timely and useful review product.
- Systematic Reviews as Topic
- Patient Care
Data availability statement
No data are available. Not applicable. All data is from published articles.
This is an open access article distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited, appropriate credit is given, any changes made indicated, and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/ .
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2023-112620
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
WHAT IS ALREADY KNOWN ON THIS TOPIC
Rapid Qualitative Evidence Synthesis (QES) is a relatively recent innovation in evidence synthesis and few published examples currently exists.
Guidance for authoring a rapid QES is scattered and requires compilation and summary.
WHAT THIS STUDY ADDS
This paper represents the first attempt to compile current guidance, illustrated by the experience of several international review teams.
We identify features of rapid QES methods that could be accelerated or abbreviated and where methods resemble those for conventional QESs.
HOW THIS STUDY MIGHT AFFECT RESEARCH, PRACTICE OR POLICY
This paper offers guidance for researchers when conducting a rapid QES and informs commissioners of research and policy-makers what to expect when commissioning such a review.
Introduction
This paper forms part of a series from the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group providing methodological guidance for rapid reviews. While other papers in the series 1–4 focus on generic considerations, we aim to provide in-depth recommendations specific to a resource-constrained (or rapid) qualitative evidence synthesis (rQES). 5 This paper is accompanied by recommended resources ( online supplemental appendix A ) and an elaboration with practical considerations ( online supplemental appendix B ).
Supplemental material
The role of qualitative evidence in decision-making is increasingly recognised. 6 This, in turn, has led to appreciation of the value of qualitative evidence syntheses (QESs) that summarise findings across multiple contexts. 7 Recognition of the need for such syntheses to be available at the time most useful to decision-making has, in turn, driven demand for rapid qualitative evidence syntheses. 8 The breadth of potential rQES mirrors the versatility of QES in general (from focused questions to broad overviews) and outputs range from descriptive thematic maps through to theory-informed syntheses (see table 1 ).
- View inline
Glossary of important terms (alphabetically)
As with other resource-constrained reviews, no one size fits all. A team should start by specifying the phenomenon of interest, the review question, 9 the perspectives to be included 9 and the sample to be determined and selected. 10 Subsequently, the team must finalise the appropriate choice of synthesis. 11 Above all, the review team should consider the intended knowledge users, 3 including requirements of the funder.
An rQES team, in particular, cannot afford any extra time or resource requirements that might arise from either a misunderstanding of the review question, an unclear picture of user requirements or an inappropriate choice of methods. The team seeks to align the review question and the requirements of the knowledge user with available time and resources. They also need to ensure that the choice of data and choice of synthesis are appropriate to the intended ‘knowledge claims’ (epistemology) made by the rQES. 11 This involves the team asking ‘what types of data are meaningful for this review question?’, ‘what types of data are trustworthy?’ and ‘is the favoured synthesis method appropriate for this type of data?’. 12 This paper aims to help rQES teams to choose methods that best fit their project while understanding the limitations of those choices. Our recommendations derive from current QES guidance, 5 evidence on modified QES methods, 8 13 and practical experience. 14 15
This paper presents an overview of considerations and recommendations as described in table 2 . Supplemental materials including additional resources details of our recommendations and practical examples are provided in online supplemental appendices A and B .
Recommendations for resource-constrained qualitative evidence synthesis (rQES)
Setting the review question and topic refinement
Rapid reviews summarise information from multiple research studies to produce evidence for ‘the public, researchers, policymakers and funders in a systematic, resource-efficient manner’. 16 Involvement of knowledge users is critical. 3 Given time constraints, individual knowledge users could be asked only to feedback on very specific decisions and tasks or on selective sections of the protocol. Specifically, whenever a QES is abbreviated or accelerated, a team should ensure that the review question is agreed by a minimum number of knowledge users with expertise or experience that reflects all the important review perspectives and with authority to approve the final version 2 5 11 ( table 2 , item R1).
Involvement of topic experts can ensure that the rQES is responsive to need. 14 17 One Cochrane rQES saved considerable time by agreeing the review topic within a single meeting and one-phase iteration. 9 Decisions on topics to be omitted are also informed by a knowledge of existing QESs. 17
An information specialist can help to manage the quantity and quality of available evidence by setting conceptual boundaries and logistic limits. A structured question format, such as Setting-Perspective-Interest, phenomenon of-Comparison-Evaluation or Population-Interest, phenomenon of-Context helps in communicating the scope and, subsequently, in operationalising study selection. 9 18
Scoping (of review parameters) and mapping (of key types of evidence and likely richness of data) helps when planning the review. 5 19 The option to choose purposive sampling over comprehensive sampling approaches, as offered by standard QES, may be particularly helpful in the context of a rapid QES. 8 Once a team knows the approximate number and distribution of studies, perhaps mapping them against country, age, ethnicity, etc), they can decide whether or not to use purposive sampling. 12 An rQES for the WHO combined purposive with variation sampling. Sampling in two stages started by reducing the initial number of studies to a more manageable sampling frame and then sampling approximately a third of the remaining studies from within the sampling frame. 20
Sampling may target richer studies and/or privilege diversity. 8 21 A rich qualitative study typically illustrates findings with verbatim extracts from transcripts from interviews or textual responses from questionnaires. Rich studies are often found in specialist qualitative research or social science journals. In contrast, less rich studies may itemise themes with an occasional indicative text extract and tend to summarise findings. In clinical or biomedical journals less rich findings may be placed within a single table or box.
No rule exists on an optimal number of studies; too many studies makes it challenging to ‘maintain insight’, 22 too few does not sustain rigorous analysis. 23 Guidance on sampling is available from the forthcoming Cochrane-Campbell QES Handbook.
A review team can use templates to fast-track writing of a protocol. The protocol should always be publicly available ( table 2 , item R2). 24 25 Formal registration may require that the team has not commenced data extraction but should be considered if it does not compromise the rQES timeframe. Time pressures may require that methods are left suitably flexible to allow well-justified changes to be made as a detailed picture of the studies and data emerge. 26 The first Cochrane rQES drew heavily on text from a joint protocol/review template previously produced within Cochrane. 24
Setting eligibility criteria
An rQES team may need to limit the number of perspectives, focusing on those most important for decision-making 5 9 27 ( table 2 , item R3). Beyond the patients/clients each additional perspective (eg, family members, health professionals, other professionals, etc) multiplies the additional effort involved.
A rapid QES may require strict date and setting restrictions 17 and language restrictions that accommodate the specific requirements of the review. Specifically, the team should consider whether changes in context over time or substantive differences between geographical regions could be used to justify a narrower date range or a limited coverage of countries and/or languages. The team should also decide if ‘indirect evidence’ is to substitute for the absence of direct evidence. An rQES typically focuses on direct evidence, except when only indirect evidence is available 28 ( table 2 , item R4). Decisions on relevance are challenging—precautions for swine influenza may inform precautions for bird influenza. 28 A smoking ban may operate similarly to seat belt legislation, etc. A review team should identify where such shared mechanisms might operate. 28 An rQES team must also decide whether to use frameworks or models to focus the review. Theories may be unearthed within the topic search or be already known to team members, fro example, Theory of Planned Behaviour. 29
Options for managing the quantity and quality of studies and data emerge during the scoping (see above). In summary, the review team should consider privileging rich qualitative studies 2 ; consider a stepwise approach to inclusion of qualitative data and explore the possibility of sampling ( table 2 , item R5). For example, where data is plentiful an rQES may be limited to qualitative research and/or to mixed methods studies. Where data is less plentiful then surveys or other qualitative data sources may need to be included. Where plentiful reviews already exist, a team may decide to conduct a review of reviews 5 by including multiple QES within a mega-synthesis 28 29 ( table 2 , item R6).
Searching for QES merits its own guidance, 21–23 30 this section reinforces important considerations from guidance specific to qualitative research. Generic guidance for rapid reviews in this series broadly applies to rapid QESs. 1
In addition to journal articles, by far the most plentiful source, qualitative research is found in book chapters, theses and in published and unpublished reports. 21 Searches to support an rQES can (a) limit the number of databases searched, deliberately selecting databases from diverse disciplines, (b) use abbreviated study filters to retrieve qualitative designs and (c) employ high yield complementary methods (eg, reference checking, citation searching and Related Articles features). An information specialist (eg, librarian) should be involved in prioritising sources and search methods ( table 2 , item R7). 11 14
According to empirical evidence optimal database combinations include Scopus plus CINAHL or Scopus plus ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global (two-database combinations) and Scopus plus CINAHL plus ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global (three-database combination) with both choices retrieving between 89% and 92% of relevant studies. 30
If resources allow, searches should include one or two specialised databases ( table 2 , item R8) from different disciplines or contexts 21 (eg, social science databases, specialist discipline databases or regional or institutional repositories). Even when resources are limited, the information specialist should factor in time for peer review of at least one search strategy ( table 2 , item R9). 31 Searches for ‘grey literature’ should selectively target appropriate types of grey literature (such as theses or process evaluations) and supplemental searches, including citation chaining or Related Articles features ( table 2 , item R10). 32 The first Cochrane rQES reported that searching reference lists of key papers yielded an extra 30 candidate papers for review. However, the team documented exclusion of grey literature as a limitation of their review. 15
Study selection
Consistency in study selection is achieved by using templates, by gaining a shared team understanding of the audience and purpose, and by ongoing communication within, and beyond, the team. 2 33 Individuals may work in parallel on the same task, as in the first Cochrane rQES, or follow a ‘segmented’ approach where each reviewer is allocated a different task. 14 The use of machine learning in the specific context of rQES remains experimental. However, the possibility of developing qualitative study classifiers comparable to those for randomised controlled trials offers an achievable aspiration. 34
Title and abstract screening
The entire screening team should use pre-prepared, pretested title and abstract templates to limit the scale of piloting, calibration and testing ( table 2 , item R11). 1 14 The first Cochrane rQES team double-screened titles and abstracts within Covidence review software. 14 Disagreements were resolved with reference to a third reviewer achieving a shared understanding of the eligibility criteria and enhancing familiarity with target studies and insight from data. 14 The team should target and prioritise identified risks of either over-zealous inclusion or over-exclusion specific to each rQES ( table 2 , item R12). 14 The team should maximise opportunities to capture divergent views and perspectives within study findings. 35
Full-text screening
Full-text screening similarly benefits from using a pre-prepared pretested standardised template where possible 1 14 ( table 2 , item R11). If a single reviewer undertakes full-text screening, 8 the team should identify likely risks to trustworthiness of findings and focus quality control procedures (eg, use of additional reviewers and percentages for double screening) on specific threats 14 ( table 2 , item R13). The Cochrane rQES team opted for double screening to assist their immersion within the topic. 14
Data extraction
Data extraction of descriptive/contextual data may be facilitated by review management software (eg, EPPI-Reviewer) or home-made approaches using Google Forms, or other survey software. 36 Where extraction of qualitative findings requires line-by-line coding with multiple iterations of the data then a qualitative data management analysis package, such as QSR NVivo, reaps dividends. 36 The team must decide if, collectively, they favour extracting data to a template or coding direct within an electronic version of an article.
Quality control must be fit for purpose but not excessive. Published examples typically use a single reviewer for data extraction 8 with use of two independent reviewers being the exception. The team could limit data extraction to minimal essential items. They may also consider re-using descriptive details and findings previously extracted within previous well-conducted QES ( table 2 , item R14). A pre-existing framework, where readily identified, may help to structure the data extraction template. 15 37 The same framework may be used to present the findings. Some organisations may specify a preferred framework, such as an evidence-to-decision-making framework. 38
Assessment of methodological limitations
The QES community assess ‘methodological limitations’ rather than use ‘risk of bias’ terminology. An rQES team should pick an approach appropriate to their specific review. For example, a thematic map may not require assessment of individual studies—a brief statement of the generic limitations of the set of studies may be sufficient. However, for any synthesis that underpins practice recommendations 39 assessment of included studies is integral to the credibility of findings. In any decision-making context that involves recommendations or guidelines, an assessment of methodological limitations is mandatory. 40 41
Each review team should work with knowledge users to determine a review-specific approach to quality assessment. 27 While ‘traffic lights’, similar to the outputs from the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool, may facilitate rapid interpretation, accompanying textual notes are invaluable in highlighting specific areas for concern. In particular, the rQES team should demonstrate that they are aware (a) that research designs for qualitative research seek to elicit divergent views, rather than control for variation; (b) that, for qualitative research, the selection of the sample is far more informative than the size of the sample; and (c) that researchers from primary research, and equally reviewers for the qualitative synthesis, need to be thoughtful and reflexive about their possible influences on interpretation of either the primary data or the synthesised findings.
Selection of checklist
Numerous scales and checklists exist for assessing the quality of qualitative studies. In the absence of validated risk of bias tools for qualitative studies, the team should choose a tool according to Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group (CQIMG) guidance together with expediency (according to ease of use, prior familiarity, etc) ( table 2 , item R15). 41 In comparison to the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme checklist which was never designed for use in synthesis, 42 the Cochrane qualitative tool is similarly easy to use and was designed for QES use. Work is underway to identify an assessment process that is compatible with QESs that support decision-making. 41 For now the choice of a checklist remains determined by interim Cochrane guidance and, beyond this, by personal preference and experience. For an rQES a team could use a single reviewer to assess methodological limitations, with verification of judgements (and support statements) by a second reviewer ( table 2 , item R16).
The CQIMG endorses three types of synthesis; thematic synthesis, framework synthesis and meta-ethnography ( box 1 ). 43 44 Rapid QES favour descriptive thematic synthesis 45 or framework synthesis, 46 47 except when theory generation (meta-ethnography 48 49 or analytical thematic synthesis) is a priority ( table 2 , item R17).
Choosing a method for rapid qualitative synthesis
Thematic synthesis: first choice method for rQES. 45 For example, in their rapid QES Crooks and colleagues 44 used a thematic synthesis to understand the experiences of both academic and lived experience coresearchers within palliative and end of life research. 45
Framework synthesis: alternative where a suitable framework can be speedily identified. 46 For example, Bright and colleagues 46 considered ‘best-fit framework synthesis’ as appropriate for mapping study findings to an ‘a priori framework of dimensions measured by prenatal maternal anxiety tools’ within their ‘streamlined and time-limited evidence review’. 47
Less commonly, an adapted meta-ethnographical approach was used for an implementation model of social distancing where supportive data (29 studies) was plentiful. 48 However, this QES demonstrates several features that subsequently challenge its original identification as ‘rapid’. 49
Abbrevations: QES, qualitative evidence synthesis; rQES, resource-constrained qualitative evidence synthesis.
The team should consider whether a conceptual model, theory or framework offers a rapid way for organising, coding, interpreting and presenting findings ( table 2 , item R18). If the extracted data appears rich enough to sustain further interpretation, data from a thematic or framework synthesis can subsequently be explored within a subsequent meta-ethnography. 43 However, this requires a team with substantial interpretative expertise. 11
Assessments of confidence in the evidence 4 are central to any rQES that seeks to support decision-making and the QES-specific Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation approach for assessing the Confidence of Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative research (GRADE-CERQual) approach is designed to assess confidence in qualitative evidence. 50 This can be performed by a single reviewer, confirmed by a second reviewer. 26 Additional reviewers could verify all, or a sample of, assessments. For a rapid assessment a team must prioritise findings, using objective criteria; a WHO rQES focused only on the three ‘highly synthesised findings’. 20 The team could consider reusing GRADE-CERQual assessments from published QESs if findings are relevant and of demonstrable high quality ( table 2 , item R19). 50 No rapid approach to full application of GRADE-CERQual currently exists.
Reporting and record management
Little is written on optimal use of technology. 8 A rapid review is not a good time to learn review management software or qualitative analysis management software. Using such software for all general QES processes ( table 2 , item R20), and then harnessing these skills and tools when specifically under resource pressures, is a sounder strategy. Good file labelling and folder management and a ‘develop once, re-use multi-times’ approach facilitates resource savings.
Reporting requirements include the meta-ethnography reporting guidance (eMERGe) 51 and the Enhancing transparency in reporting the synthesis of qualitative research (ENTREQ) statement. 52 An rQES should describe limitations and their implications for confidence in the evidence even more thoroughly than a regular QES; detailing the consequences of fast-tracking, streamlining or of omitting processes all together. 8 Time spent documenting reflexivity is similarly important. 27 If QES methodology is to remain credible rapid approaches must be applied with insight and documented with circumspection. 53 54 (56)
Ethics statements
Patient consent for publication.
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
- Klerings I ,
- Robalino S ,
- Booth A , et al
- Nussbaumer-Streit B ,
- Hamel C , et al
- Garritty C ,
- Tricco AC ,
- Smith M , et al
- Gartlehner G ,
- Devane D , et al
- NHS Scotland
- Campbell F ,
- Flemming K , et al
- Glenton C ,
- Lubarsky S ,
- Varpio L , et al
- Meskell P ,
- Glenton C , et al
- Houghton C ,
- Delaney H , et al
- Beecher C ,
- Maeso B , et al
- McKenzie JE , et al
- Harris JL ,
- Cargo M , et al
- Varley-Campbell J , et al
- Downe S , et al
- Shamseer L ,
- Clarke M , et al
- Nussbaumer-Streit B , et al
- Finlayson KW ,
- Lawrie TA , et al
- Lewin S , et al
- Frandsen TF ,
- Gildberg FA ,
- Tingleff EB
- Mshelia S ,
- Analo CV , et al
- Husk K , et al
- Carmona C ,
- Carroll C ,
- Ilott I , et al
- Meehan B , et al
- Munthe-Kaas H ,
- Bohren MA ,
- Munthe-Kaas HM ,
- French DP ,
- Flemming K ,
- Garside R , et al
- Shulman C , et al
- Dixon-Woods M
- Bright KS ,
- Norris JM ,
- Letourneau NL , et al
- Sadjadi M ,
- Mörschel KS ,
- Petticrew M
- France EF ,
- Cunningham M ,
- Ring N , et al
- McInnes E , et al
- Britten N ,
- Garside R ,
- Pope C , et al
Supplementary materials
Supplementary data.
This web only file has been produced by the BMJ Publishing Group from an electronic file supplied by the author(s) and has not been edited for content.
- Data supplement 1
Correction notice Since this paper first published, updates have been made to the left hand column of table 2.
Contributors All authors (AB, IS, JN, CH, FC) have made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the guidance document. AB led on drafting the work and revising it critically for important intellectual content. All other authors (IS, JN, CH, FC) contributed to revisions of the document. All authors (AB, IS, JN, CH, FC) have given final approval of the version to be published. As members of the Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group and/or the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group all authors (AB, IS, JN, CH, FC) agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests AB is co-convenor of the Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group. In the last 36 months, he received royalties from Systematic Approaches To a Successful Literature Review (Sage 3rd edition), honoraria from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and travel support from the WHO. JN is lead convenor of the Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group. In the last 36 months, she has received honoraria from the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality and travel support from the WHO. CH is co-convenor of the Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group.
Patient and public involvement Patients and/or the public were not involved in the design, or conduct, or reporting, or dissemination plans of this research.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; internally peer reviewed.
Supplemental material This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Read the full text or download the PDF:
- Open access
- Published: 23 May 2024
Interventions to reduce inequalities for pregnant women living with disadvantage in high-income countries: an umbrella review protocol
- N. Vousden ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5216-8268 1 ,
- D. Geddes-Barton 1 ,
- N. Roberts 2 &
- M. Knight 1
Systematic Reviews volume 13 , Article number: 139 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Women who live with disadvantages such as socioeconomic deprivation, substance misuse, poor mental health, or domestic abuse face inequalities in health before, during, and after pregnancy and for their infants through to childhood. Women do not experience these factors alone; they accumulate and interact. Therefore, there is a need for an overview of interventions that work across health and social care and target women at risk of inequalities in maternal or child health.
Systematic review methodology will be used to identify systematic reviews from high-income countries that describe interventions aiming to reduce inequalities for women who experience social disadvantage during pregnancy. We will describe the range of interventions and their effectiveness in reducing inequalities in maternal or child health. Any individual, hospital, or community-level activity specific to women during the pre-conception, antenatal, or postpartum period up to 1 year after birth will be included, regardless of the setting in which they are delivered. We will search eight electronic databases with the pre-determined search strategy and supplement them with extensive grey literature searches. We will present a narrative synthesis, taking into account the quality assessment and coverage of included studies.
Inequalities in maternal and child health are a key priority area for national policymakers. Understanding the range and effectiveness of interventions across the perinatal period will inform policy and practice. Identifying gaps in the evidence will inform future research.
Systematic review registration
PROSPERO CRD42023455502.
Peer Review reports
Women who live in the most deprived areas of England are more than twice as likely to die in pregnancy [ 1 ] or experience poor outcomes such as stillbirth [ 2 ], preterm birth, and fetal growth restriction [ 3 ] compared to women in the most affluent areas. This evidence is based on neighborhood deprivation measures therefore inadequately describes the extent of health inequity experienced by individuals who live at the extreme margins of social disadvantage or have multiple intersecting risk factors. For example, low socioeconomic status is often associated with increased social risks such as housing instability and poor mental health. Confidential inquiries into the care of women who die during pregnancy and the postnatal period in the United Kingdom have identified that 12% experienced severe and multiple disadvantages [ 1 ], most commonly mental health diagnosis, substance use, and domestic abuse [ 1 ]. In addition, the negative health and educational impacts on offspring of growing up in poverty [ 4 ] or being exposed to adverse experiences in childhood [ 5 ] are widely documented. This highlights the need for interventions to effectively prevent and address multiple complex needs as a whole, rather than for discrete populations with a single risk factor.
Reducing socio-economic inequalities in maternal and perinatal health has been a key priority for the government in the UK [ 6 , 7 , 8 ] and internationally [ 9 ]. Current National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) guidance on complex social factors in pregnancy, written in 2010, focuses on four key areas, women with alcohol or drug misuse, recent migrant or asylum seeker status, young mothers, and women experiencing domestic abuse [ 10 ]. However, it was written in 2010 and the lack of high-quality evidence to inform personalized care for women with social complexity, meant the guidance heavily relied on expert opinion. Later reviews of this guidance in 2012 and 2018 recommended a wider range of social complexity was covered including mental health and homelessness [ 11 ].
There are conflicting opinions on the persisting focus on health systems to mitigate social determinants of health. While structural change, for example, reduction of family poverty through improved welfare systems and employment opportunities is undoubtedly vital [ 12 ], pregnancy and the postnatal period have been proposed to be a unique opportunity when nearly all women access health services and potentially can be engaged in health-promoting activities with long-term intergenerational impacts [ 13 ]. Existing reviews have explored interventions to reduce inequalities focusing on the model of antenatal care [ 14 , 15 ] or specific short-term pregnancy outcomes such as preterm birth [ 16 ]. But, given that socioeconomic disadvantage is present before pregnancy, and has far-reaching implications for the next generation, there is a need to identify and understand interventions that utilize a cross-disciplinary approach, beyond maternity care [ 17 ].
Confidential inquiries into maternal mortality in the UK consistently report the need for improved integration of health and social care services to create seamless pathways [ 17 ]. This is echoed in an analysis of the Lancet series on midwifery, which highlighted that future research should prioritize care “tailored to individuals, (which) weighs benefits and harms, is person-centered, (and) works across the whole continuum of care” [ 7 ]. Therefore, there is a need for an overview of interventions across health and social care targeting women at risk of inequalities in maternal or child health as a result of social disadvantage before, during, and after pregnancy.
This review is informed by perspectives on social exclusion [ 18 ], intersectionality [ 19 ], and life-course epidemiology [ 20 ] which examine how factors accumulate and intersect over time and affect health. With a recent policy that prioritizes person-centered care [ 7 ] and equity of health outcomes [ 7 , 21 ], we anticipate that the findings will be beneficial to policymakers, service providers, and commissioners.
Registration and protocol adherence
This research question has been developed by a multidisciplinary team of clinicians, researchers, and methodologists. It was designed in accordance with Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA) [ 22 ] and registered on the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews on 22/08/2023 (PROSPERO, no: CRD42023455502). We started developing this protocol in May 2023 and the review is expected to be completed in January 2024. The terms ‘pregnant women’ and ‘mothers’ will be used throughout this paper [ 23 ], but the authors recognize not everyone who is pregnant or giving birth will identify as a woman or a mother.
This systematic review aims to synthesize the quantitative literature in order to identify what interventions exist, and how effective they are, at reducing inequalities in maternal and child health for pregnant women living with disadvantages in high-income countries.
Eligibility Criteria and Population, Intervention, Comparison, and Outcome (PICO) framework
There is no clear definition for risks that define disadvantage. Therefore, the eligibility criteria for this study were defined as exposures or factors that are associated with deprivation and with adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (or a strong hypothesis for this, in the absence of data). Women with one or more of the following exposures prior to or during pregnancy: substance or alcohol misuse (excluding tobacco), involvement in the judicial system/prison, victim of modern slavery, homelessness or insecure housing, socioeconomic deprivation (measured for individual), domestic abuse or intimate partner violence, experience of sex work, young mothers (age < 20) [ 24 , 25 , 26 ], underserved migrant women, women with a mental health diagnosis [ 27 ] and women from minoritized ethnic groups including Gypsy, Roma and Travelling communities [ 28 ].
Interventions
Any individual, hospital, or community-level activity will be included, regardless of the setting in which they are delivered. Interventions must be specific to women during the pre-conception, antenatal, or postpartum period up to 1 year after birth. For the purposes of this paper, we defined pre-conception as interventions that targeted preparing for a healthy pregnancy. Therefore, interventions in women of reproductive age who experienced disadvantages that were not targeting any part of the pregnancy journey (preparing, pregnancy, or postnatal period) will not be eligible for inclusion. We will also evaluate the suitability of any effective interventions to the UK health and social care setting and perform a sub-analysis if appropriate.
Studies with any comparison or control group will be included.
The main outcomes of interest will be maternal morbidity and mortality, preterm birth, birth weight, and attendance at care, reflecting the existing literature on important inequalities in maternal and child health. However, we will include all outcomes related to inequalities in maternal and child health up to 5 years of age from all retrieved studies. For example, mode of birth, mental well-being as assessed by validated screening scales, breastfeeding initiation and duration, family planning, immunization, and indicators of adverse childhood experience (e.g., emergency hospital attendances).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
This umbrella review will include only systematic reviews and meta-analyses as defined by the Cochrane Collaboration’s Handbook definition of systematic reviews of interventions (i.e., “reviews of clearly formulated questions that use systematic and explicit methods to identify, select and critically appraise relevant research”). Therefore, the reviews must use a comprehensive literature search strategy and a satisfactory technique for assessing the risk of bias in individual studies that were included in the review. This has been chosen as the aim is to assess the effectiveness of interventions, not just identify or map interventions, and therefore assessment of methodological limitations and bias is the key in the interpretation of the evidence. The umbrella review will enable a summation of a broad literature base of disadvantages in pregnancy which would be unfeasible if primary studies were included.
Studies undertaken in high-income countries, as defined by the World Bank GNI (2019), published in any language from 2013 to 2023 will be included. This 10-year period was selected as per the Joanna Briggs Institute guidance as they are considered to represent the contemporaneous evidence base over the previous 30 years [ 29 ]. Included studies will either specifically target the defined population or present disaggregated data for a defined subgroup. Abstracts, comments, editorials, letters, or non-systematic reviews will be excluded. Solely qualitative studies will be excluded. We will include systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials and non-randomized studies of health care interventions. This method has been selected as we aspire to identify the range of interventions available across the spectrum of disadvantage, but also be able to report definitive effectiveness data with a feasible number of results.
Data collection and appraisal
The search strategy has been developed with assistance from an expert information specialist and adapted for each database (Additional file 1). The following electronic databases will be searched: EMBASE (OvidSP), MEDLINE (OvidSP), Science Citation Index & Social Science Citation Index via Web of Science Core Collection, CINAHL (EBSCOHost), PsycINFO (OvidSP) and ASSIA (Proquest), and systematic review repositories: Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Cochrane Library, Wiley) and Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects ( https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/CRDWeb/ ). Grey literature sources will include backward and forward citation searches for all included articles and reference lists of related systematic reviews. Relevant third-sector organizations such as Birth Rights, Birth Companions, Maternity Action, and Sands will also be searched for evidence summaries, alongside the first 150 results of Google Scholar and clinicaltrials.gov.
The titles and abstracts of the studies retrieved during the searches will be independently assessed by two reviewers for relevance. The full texts of potentially eligible studies will then be retrieved and reviewed independently using a checklist of the inclusion and exclusion criteria by two reviewers. Any disagreements will be resolved by consensus and, if necessary, a third review researcher will be consulted, and will resolve issues. A table of excluded studies is found in Additional file 2.
A data extraction form will be designed in Excel and initially piloted on a small sample of papers by two review authors. Data extraction for the first 20% of the studies will be undertaken independently by two authors, if there is good agreement then a single author will complete data extraction for the remaining studies. This will include (1) author and publication year, (2) methodology (aim, type of review, location), (3) population characteristics (number of participants, demographics), (4) search methods (number of databases searched, date range of searching, publication date range of studies included in the review that inform each outcome of interest, (5) number of studies, type of studies, country of origin of studies included in each review, (6) instrument used to appraise the primary studies and their risk of bias, (7) included intervention details including timing, duration, setting (e.g., community or hospital) and mode of delivery, (8) outcomes related to this question, (9) method of synthesis and (10) quality of the included primary studies as assessed by review authors, (11) conflict of interest. In line with PRISMA guidelines, a flowchart will summarize the selection process. EndNote™ will be used to collect and manage the studies retrieved [ 30 ]. Covidence™ will be used for deduplication and study selection [ 31 ]. We will extract data from the systematic review (and any supplementary material), not from original primary studies. If there is data missing or inadequately described in reviews, we will note the gap in coverage but will not routinely refer back to the primary studies due to the additional burden on time and resources [ 29 , 32 ].
The AMSTAR 2 appraisal tool will be used to assess the quality of included reviews [ 33 ]. This will enable an overall rating of confidence in the results of the review (high, moderate, low, or critically low). Quality appraisal results will be summarized in a table, including the rating for each question of the tool for each review, the rationale behind assessments, and the overall rating for each review. All reviews meeting the inclusion criteria will be presented, irrespective of AMSTAR findings [ 33 ]. Two authors will assess the quality of each text for 20% of studies with discrepancies resolved by consensus. If there is good agreement then a single author will assess the quality of the remaining texts.
Data synthesis
This data synthesis plan is informed by Cochrane guidance for undertaking an overview of reviews [ 32 ]. Due to the broad topic being studied and the expected heterogeneity of the exposure group and interventions, we will present a narrative synthesis of the systematic reviews and not meta-analysis.
We will present an overlap of primary studies using a pairwise intersection heat map [ 34 ]. This has been chosen to visually and simply demonstrate patterns of high or low overlap given the anticipated large number of primary studies that will be included. Where meta-analysis from separate reviews contains overlapping primary studies, we will prioritize the summary result from the highest quality review according to the AMSTAR rating.
We will map the available evidence and explore the patterns in the data. For example, we will describe the findings according to the target population, for example, whether a specific social exposure (e.g., domestic abuse and intimate partner violence) was the focus or broader inclusion criteria were used and categorize interventions by the timing of delivery (pre-pregnancy, pregnancy or postnatal) and the level of change that was intended, for example individual, organizational or community interventions. Where there is sufficient homogeneity in the population, intervention type, and outcome, we will describe similarities and differences between the findings, taking into account the strength of evidence and risk of bias of the reviews and the included studies.
Since the purpose of the review is to identify the breadth and effectiveness of interventions, where relevant reviews entirely meet our inclusion criteria, we will summarize the narrative or meta-analysis results, reporting the summary result, 95% confidence intervals, and measures of heterogeneity [ 32 ]. In this case, we will extract and report GRADE assessments, where available, to describe the certainty of evidence. If relevant reviews include only some primary studies conducted in the target population/setting/study design, then the findings of these primary studies will be presented, where there is a specific subgroup reported or at least three primary studies meet our inclusion criteria. In this case, we will narratively re-synthesize the outcome data from primary studies that meet the inclusion criteria of this review (e.g., primary studies of pregnant women with social disadvantage in a review that included all pregnant women). Where GRADE assessments are available for these subgroups these will also be extracted and reported. Overall, we will then narratively describe interventions according to whether they are effective, promising, ineffective, or probably ineffective or unable to conclude effectiveness.
Stakeholder engagement
To enhance the usefulness of the review we will actively involve stakeholders (families, midwives, doctors, health visitors, third sector, health decision-makers, and funders). We will create a lived experience team of women with social disadvantages around pregnancy and use a series of discussions to explore the acceptability and relevance of the identified interventions. We will carry out two stakeholder workshops to explore how the findings fit with current guidance, practice, and need, in the context of the UK health and social care system, in order to identify the implications for services, policy, and research.
The design of this umbrella review has been chosen to provide an overview of the range and efficacy of interventions aiming to mitigate social disadvantages around pregnancy. This design is beneficial in giving an overview of the types of interventions and quality of research in this field to date [ 35 ]. This is specifically useful given the aim of evaluating interventions that may work across health and social care systems before, during, and after pregnancy. However, there are limitations in this approach in that the heterogeneity in studies increases the burden for decision-makers [ 36 ] and promising interventions that have not been examined in systematic reviews will not be included.
This study is also limited to exploring the quantitative effect of interventions on health outcomes. This simple perspective was selected to provide a clear resource for clinicians and policymakers. However, it leaves many questions about the components of multifaceted interventions, and how they work and interact in different settings, unanswered [ 37 , 38 ].
The findings of this umbrella review will enable recommendations for future research where there are gaps for women known to be at increased risk. We also hope to identify potential effective interventions that warrant further investigation, or that can inform policy and practice to reduce inequalities in maternal and child health.
Availability of data and materials
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
Knight M, Bunch K, Felker A, Patel R, Kotnis R, Kenyon S, Kurinczuk JJ, on behalf of MBRRACE-UK, editors. Saving lives, improving mothers’ care core report - lessons learned to inform maternity care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2019–21. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit: University of Oxford; 2023. https://www.npeu.ox.ac.uk/assets/downloads/mbrrace-uk/reports/maternal-report-2023/MBRRACE-UK_Maternal_Compiled_Report_2023.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Draper ES GI, Smith LK, Matthews RJ, Fenton AC, Kurinczuk JJ, Smith PW, Manktelow BN, on behalf of the MBRRACE-UK Collaboration. MBRRACE-UK perinatal mortality surveillance: UK perinatal deaths for births from January to December 2021: The State of the Nation Report Leicester: The Infant Mortality and Morbidity Studies: Department of Population Health Sciences, University of Leicester; 2023. https://timms.le.ac.uk/mbrrace-uk-perinatal-mortality/surveillance/ . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Jardine J, Walker K, Gurol-Urganci I, Webster K, Muller P, Hawdon J, et al. Adverse pregnancy outcomes attributable to socioeconomic and ethnic inequalities in England: a national cohort study. Lancet. 2021;398(10314):1905–12.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Jutte DP, Brownell M, Roos NP, Schippers C, Boyce WT, Syme SL. Rethinking what is important: biologic versus social predictors of childhood health and educational outcomes. Epidemiology. 2010;21(3):314–23.
Houtepen LC, Heron J, Suderman MJ, Fraser A, Chittleborough CR, Howe LD. Associations of adverse childhood experiences with educational attainment and adolescent health and the role of family and socioeconomic factors: a prospective cohort study in the UK. PLoS Med. 2020;17(3):e1003031.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Department of Health & Social Care. Maternity Disparities Taskforce: terms of reference. 2022. https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/maternity-disparities-taskforce-terms-of-reference/maternity-disparities-taskforce-terms-of-reference . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Alderwick H, Dixon J. The NHS long term plan. BMJ. 2019;364:l84.
NHS England. Equity and equality guidance for local maternity systems. NHS England; 2021. https://www.england.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/C0734-equity-and-equality-guidance-for-local-maternity-systems.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Ki-Moon B. Global Strategy for Women's and Children's Health. New York: World Health Organisation: United Nations; 2010. https://www.ohchr.org/sites/default/files/Documents/Issues/Women/WRGS/Health/GlobalStrategy.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2024.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Pregnancy and complex social factors: a model for service provision for pregnant women with complex social factors. NICE guidelines CG110: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2010. Available from: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg110 . Accessed 15 May 2024.
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Surveillance proposal consultation document: 2018 surveillance of pregnancy and complex social factors NICE: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; 2018. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg110/resources/2018-surveillance-of-pregnancy-and-complex-social-factors-a-model-for-service-provision-for-pregnant-women-with-complex-social-factors-nice-guideline-cg110-6532362253/chapter/Overview-of-2018-surveillance-methods?tab=evidence . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Stewart E, Pearce A, Given J, Gilbert R, Brophy S, Cookson R, et al. Identifying opportunities for upstream evaluations relevant to child and maternal health: a UK policy-mapping review. Arch Dis Child. 2023;108(7):556–62.
Conry JA. Women’s health across the life course and opportunities for improvement: Every woman, every time, everywhere. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2023;160(S1):7.
Article Google Scholar
Khan Z, Vowles Z, Fernandez Turienzo C, Barry Z, Brigante L, Downe S, et al. Targeted health and social care interventions for women and infants who are disproportionately impacted by health inequalities in high-income countries: a systematic review. Int J Equity Health. 2023;22(1):131.
Hollowell J, Oakley L, Kurinczuk JJ, Brocklehurst P, Gray R. The effectiveness of antenatal care programmes to reduce infant mortality and preterm birth in socially disadvantaged and vulnerable women in high-income countries: a systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2011;11:13.
Pedersen JF, Kallesoe SB, Langergaard S, Overgaard C. Interventions to reduce preterm birth in pregnant women with psychosocial vulnerability factors-A systematic review. Midwifery. 2021;100:103018.
Knight MBK, Patel R, Shakespeare J, Kotnis R, Kenyon S, Kurinczuk JJ, on behalf of MBRRACE-UK, editors. Lessons leaned to inform maternity care from the UK and Ireland Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths and Morbidity 2018–20. Oxford: National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit: University of Oxford; 2022. https://www.npeu.ox.ac.uk/assets/downloads/mbrrace-uk/reports/maternal-report-2022/MBRRACE-UK_Maternal_MAIN_Report_2022_UPDATE.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Peace R. Social exclusion: a concept in need of definition. Soc Policy J N Z. 2001;16:17–36. https://www.msd.govt.nz/documents/about-msd-and-our-work/publications-resources/journals-and-magazines/social-policy-journal/spj16/16-pages17-36.pdf . Accessed 17 May 2024.
Fitzpatrick S, Bramley G, Johnsen S. Pathways into multiple exclusion homelessness in seven UK cities. Urban Studies. 2013;50(1):148–68.
Kuh D, Ben-Shlomo Y, Lynch J, Hallqvist J, Power C. Life course epidemiology. J Epidemiol Community Health. 2003;57(10):778–83.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
NHS England. Core20PLUS5 (adults) - an approach to reducing healthcare inequalities. 2023 [cited 2023 August ]. Available from: https://www.england.nhs.uk/about/equality/equality-hub/national-healthcare-inequalities-improvement-programme/core20plus5/ .
Shamseer L, Moher D, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ. 2015;350:g7647.
Gribble KD, Bewley S, Bartick MC, Mathisen R, Walker S, Gamble J, et al. Effective communication about pregnancy, birth, lactation, breastfeeding and newborn care: the importance of sexed language. Front Glob Women’s Health. 2022;3:818856.
Sangsawang B, Wacharasin C, Sangsawang N. Interventions for the prevention of postpartum depression in adolescent mothers: a systematic review. Arch Womens Ment Health. 2019;22(2):215–28.
Harden A, Brunton G, Fletcher A, Oakley A. Teenage pregnancy and social disadvantage: systematic review integrating controlled trials and qualitative studies. BMJ. 2009;339:b4254.
Bottorff JL, Poole N, Kelly MT, Greaves L, Marcellus L, Jung M. Tobacco and alcohol use in the context of adolescent pregnancy and postpartum: a scoping review of the literature. Health Soc Care Community. 2014;22(6):561–74.
Chow R, Huang E, Li A, Li S, Fu SY, Son JS, et al. Appraisal of systematic reviews on interventions for postpartum depression: systematic review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2021;21(1):18.
Esan OBAN, Saberian S, Christianson L, McHale P, Pennington A, Geary R, Ayorinde A. Mapping existing policy interventions to tackle ethnic health inequalities in maternal and neonatal health in England: a systematic scoping review with stakeholder engagement. NHS Race & Health Observatory; 2022. https://www.nhsrho.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/RHO-Mapping-existing-policy-interventions_December-2022.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Aromataris E, Fernandez R, Godfrey CM, Holly C, Khalil H, Tungpunkom P. Summarizing systematic reviews: methodological development, conduct and reporting of an umbrella review approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13(3):132–40.
Endnote. EndNote. 20th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Clarivate; 2013.
Google Scholar
Veritas. Covidence Systematic Review Software. Melbourne: Veritas Health Innovation; 2021.
Pollock M, Fernandes RM, Becker LA, Pieper D, Hartling L. Chapter V: Overviews of Reviews. In Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane; 2023. Accessed https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-v . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Shea BJ, Reeves BC, Wells G, Thuku M, Hamel C, Moran J, et al. AMSTAR 2: a critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ. 2017;358:j4008.
Bougioukas KI, Vounzoulaki E, Mantsiou CD, Savvides ED, Karakosta C, Diakonidis T, et al. Methods for depicting overlap in overviews of systematic reviews: An introduction to static tabular and graphical displays. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;132:34–45.
Lazaros B, Vanesa B, John PAI. Conducting umbrella reviews BMJ Medicine. 2022;1(1):e000071.
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, editor. John Wiley & Sons; 2011. https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current . Accessed 15 May 2024.
Petticrew M, Anderson L, Elder R, Grimshaw J, Hopkins D, Hahn R, et al. Complex interventions and their implications for systematic reviews: a pragmatic approach. J Clin Epidemiol. 2013;66(11):1209–14.
Julian PTH, José AL-L, Betsy JB, Sarah RD, Sarah D, Jeremy MG, et al. Synthesising quantitative evidence in systematic reviews of complex health interventions. BMJ Global Health. 2019;4(Suppl 1):e000858.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
MK is an NIHR Senior Investigator. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR, or the Department of Health and Social Care. There are no other funding/sponsors to declare.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Population Health, National Perinatal Epidemiology Unit, University of Oxford, Old Road Campus, NuffieldHeadington, Oxford, OX3 7LF, UK
N. Vousden, D. Geddes-Barton & M. Knight
Nuffield Department of Population Health, Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences and Department of Oncology, Bodleian Health Care Libraries, Oxford, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
NV wrote the first draft of this manuscript with input from DG, NR, and MK. MK is the guarantor for this paper and accepts responsibility for the overall integrity of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to M. Knight .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. medline search strategy., additional file 2. prisma-p 2015 checklist., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Vousden, N., Geddes-Barton, D., Roberts, N. et al. Interventions to reduce inequalities for pregnant women living with disadvantage in high-income countries: an umbrella review protocol. Syst Rev 13 , 139 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02556-7
Download citation
Received : 31 October 2023
Accepted : 03 May 2024
Published : 23 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-024-02556-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Inequalities
- Disadvantage
- Deprivation
- Social risk
- Umbrella review
- Effectiveness
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

COMMENTS
A synthesis matrix helps you record the main points of each source and document how sources relate to each other. After summarizing and evaluating your sources, arrange them in a matrix or use a citation manager to help you see how they relate to each other and apply to each of your themes or variables. By arranging your sources by theme or ...
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image. For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.
Learn how to synthesise the existing research for your literature review using five key questions: agreement, disagreement, key theories, contexts and methodologies. See practical examples and get 50% off the online course Literature Review Bootcamp.
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question. It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation, or research paper, in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
Analyze what you learn in (4) using a tool like a Synthesis Table. Your goal is to identify relevant themes, trends, gaps, and issues in the research. Your literature review will collect the results of this analysis and explain them in relation to your research question. Analysis tips
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays).
Synthesis is a complex activity, which requires a high degree of comprehension and active engagement with the subject. As you progress in higher education, so increase the expectations on your abilities to synthesise. How to synthesise in a literature review: Identify themes/issues you'd like to discuss in the literature review. Think of an ...
Synthesis writing is a form of analysis related to comparison and contrast, classification and division. On a basic level, synthesis requires the writer to pull together two or more summaries, looking for themes in each text. ... In a literature review you will be combining material from several texts to create a new text - your literature ...
Review the information in the Resources box to learn about using a synthesis matrix. Create your own literature review synthesis matrix using the Word or Excel files available in the Activity box. Organize and synthesize literature related to your topic using your synthesis matrix
Before beginning a systematic review, consider whether it is the best type of review for your question, goals, and resources. The table below compares systematic reviews, scoping reviews, and systematized reviews (narrative literature reviews employing some, but not all elements of a systematic review) to help you decide which is best for you.
Step 1 Organize your sources. Step 2 Outline your structure. Step 3 Write paragraphs with topic sentences. Step 4 Revise, edit and proofread. When you write a literature review or essay, you have to go beyond just summarizing the articles you've read - you need to synthesize the literature to show how it all fits together (and how your own ...
Rather than explaining and reflecting on the results of previous studies (as is typically done in literature reviews), a synthetic literature review strives to create a new and more useful theoretical perspective by rigorously integrating the results of previous studies. Many people find the process of synthesis difficult, elusive, or mysterious.
A literature review is not an annotated bibliography, organized by title, author, or date of publication. Rather, it is grouped by topic to create a whole view of the literature relevant to your research question. Figure 7.1. Your synthesis must demonstrate a critical analysis of the papers you collected as well as your ability to integrate the ...
The different literature review typologies discussed earlier and the type of literature being synthesized will guide the reviewer to appropriate synthesis methods. The synthesis methods, in turn, will guide the data extraction process—for example, if one is doing a meta-analysis, data extraction will be centered on what's needed for a meta ...
Literature reviews (sometimes shortened to "lit reviews") synthesize previous research that has been done on a particular topic, summarizing important works in the history of research on that topic. The literature review provides context for the author's own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author's research ...
One way that seems particularly helpful in organizing literature reviews is the synthesis matrix. The synthesis matrix is a chart that allows a researcher to sort and categorize the different arguments presented on an issue. Across the top of the chart are the spaces to record sources, and along the side of the chart are the spaces to record ...
This article is a practical guide to conducting data analysis in general literature reviews. The general literature review is a synthesis and analysis of published research on a relevant clinical issue, and is a common format for academic theses at the bachelor's and master's levels in nursing, physiotherapy, occupational therapy, public health and other related fields.
Learn how to synthesise the existing literature for your literature review by addressing five key questions. In this video, we explain exactly how you can en...
Review Literature as Topic*. This article examines how to synthesise and critique research literature. To place the process of synthesising the research literature into context, the article explores the critiquing process by breaking it down into seven sequential steps. The article explains how and why these steps need to be ke ….
The Literature Review provides context for the author's own new research. It is the basis and background out of which the author's research grows. Context = credibility in academic writing. When authors have broad Literature Review, they demonstrate their credibility as researchers. Previous: Synthesis as a Conversation.
Types of Research Synthesis: Key Characteristics: Purpose: Methods: Product: CONVENTIONAL Integrative Review: What is it? "The integrative literature review is a form of research that reviews, critiques, and synthesizes representative literature on a topic in an integrated way such that new frameworks and perspectives on the topic are generated" [, p.356]. ...
These steps for conducting a systematic literature review are listed below. Also see subpages for more information about: What are Literature Reviews? The different types of literature reviews, including systematic reviews and other evidence synthesis methods; Conducting & Reporting Systematic Reviews; Finding Systematic Reviews; Tools & Tutorials
Using a Synthesis Matrix ; 7. Write literature review; Using a Synthesis Matrix. A synthesis matrix visually represents your research by organizing your sources by themes: Theme #1 Theme #2 Theme #3; Source #1 : Source #2 : Source #3 : Sample Synthesis Matrix. Example provided by Ashford University Writing Center.
Research Tables and Synthesis Tables are useful tools for organizing and analyzing your research as you assemble your literature review. They represent two different parts of the review process: assembling relevant information and synthesizing it. Use a Research table to compile the main info you need about the items you find in your research ...
This paper forms part of a series of methodological guidance from the Cochrane Rapid Reviews Methods Group and addresses rapid qualitative evidence syntheses (QESs), which use modified systematic, transparent and reproducible methodsu to accelerate the synthesis of qualitative evidence when faced with resource constraints. This guidance covers the review process as it relates to synthesis of ...
The review's strengths lie in its thematic focus, which allowed an analysis of the various ways therapists use themselves in therapy and identified gaps in current literature. Adopting a qualitative systematic review also allowed for an in-depth analysis of the narratives of therapists and their personal experiences in the use of their self.
We will search eight electronic databases with the pre-determined search strategy and supplement them with extensive grey literature searches. We will present a narrative synthesis, taking into account the quality assessment and coverage of included studies. Inequalities in maternal and child health are a key priority area for national ...
A systematic literature review was conducted to broaden research panorama and identify spatial, temporal, and thematic trends and challenges present in wastewater assessments of Latin American urban peripheries, this using the SALSA (search, appraisal, synthesis, and analysis) protocol in a search through international databases Scopus and Web ...