20+ SAMPLE University Business Plan in PDF
University business plan, 20+ sample university business plan, what is a university business plan, common marketing strategies used by universities, creating a university business plan, what are some of the benefits of a business plan, what are some of the different types of planning, what are college grants.


University Business Plan Competition

University Business Plan Importance

University Small Business Development Plan

Developing Business Plan for the University

University Business Plan for Expansion

University Academic Business Plan

State University Business Plan

University Business Plan Summit

Successful Business Plan of University

University Small Business Development Center Plan

University Transnational Program Business Plan

University Library Business Plan

5 Year Business Plan University

University Basic Business Plan

University Business Plan Implementation

University Business Plan Development for Online Learning

University Standard Business Plan

University Business Plan Program

University Park Community Center Business Plan

University College Strategy and Business Plan
What is a university business plan , common marketing strategies used by universities , 1. executive summary, 2. market analysis, 3. university offerings, 4. marketing strategy, 5. financial planning, share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 5+ sample investment company business plan in pdf.

What do you do when you have tons of spare cash lying around your home or burning a hole in your wallet or expensive jeans pocket? For some people, the…
41+ SAMPLE Unit Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
As a teacher, you might know about every school policy, the steps to keep classrooms safe for intellectual development, how to set up an organized classroom, and the proposed…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
How to Start a University: Everything You Need to Know
When wondering how to start a university, you should be motivated to share your knowledge with students and possess an educational philosophy about which you feel strongly. 3 min read updated on February 01, 2023
Updated October 29, 2020:
Starting a University/College: Introduction
When wondering how to start a university, you should be motivated to share your knowledge with students and possess an educational philosophy about which you feel strongly.
Starting a university can be very difficult, particularly because you will need to meet a variety of regulations intended to ensure you are providing your students with a quality education.
Before you start your university, you will need to decide whether you will run a physical or virtual school. Starting a virtual university can be much less expensive in terms of overhead costs, but you will likely need advanced technical knowledge to set up and run your university. The biggest obstacle to starting a university will be securing funding .
Starting a University/College
The first step of starting your university is determining your area of education and then developing your mission statement .
You should research universities similar to your own to find out what they offer and to decide if you want to provide the same courses and services. It's also important to develop a strategy for outselling other colleges in your area. Students spending money on your school will want to know that you'll provide them with the best educational experience possible.
Attempting to undercut the prices of other universities is a common mistake, as running a college is much more expensive than you might imagine. Universities that do not have a large amount of capital should refrain from listing low-cost as their purpose.
In your mission statement, you should include information about:
- Why your university exists.
- Your university's educational philosophy.
- The curriculum you will offer.
- The personal goals you wish to achieve.
To make sure you've written a strong mission statement, you should let your family and friends read your statement and then ask them for feedback. In particular, you should ask the people that read your mission statement if it would make them likely to send their children to your university or to attend themselves. By using the feedback from your family and friends, you can clarify your mission statement and develop a pitch that you can use to attract investors.
Think about whether your university will have a physical location or if you will run a virtual school. It is also possible for you to combine these two options. If you want to open a physical university, you should be aware that your costs , particularly your startup costs , will be much higher. The facilities that you choose will need to be able to accommodate your projected number of students. You will also need to comply with health, insurance, and safety regulations.
You will also need to choose the right location for your university. To attract students, you will need to choose a safe location that students can easily reach by foot or bike. Finding such a location will usually require you to spend more money. Before choosing your location, it's important to do a lot of research.
When you're first starting your university, only offering virtual courses is a great choice, as this will drastically lower your costs. If you want to offer online courses, you will either need to possess technical expertise or will need to invest in an IT staff. You will also need strong security and privacy strategy, adequate server space, and support staff that your students can contact whenever they need to resolve connection issues. People expect that technology will work immediately, so you should be very careful when planning your courses and starting your virtual school.
It's always a good idea to get advice and guidance from those who possess experience in the educational field, as well as finance and business . Try to schedule a meeting with the founders of universities in your area and ask them for suggestions on how best to overcome obstacles when starting your school.
You should research options for funding your university before you move forward with the process of opening your school. If you plan to establish a non-profit university, you should look for people that are interested in supporting this type of educational institution. Depending on the area where you are starting your university, you may have access to grants. When searching for investors, you should look for people that share your educational philosophy and believe in the stated mission of your university.
To get the help you need to start a university, you can post your legal needs on UpCounsel's marketplace. UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers to its site. Lawyers on UpCounsel come from law schools such as Harvard Law and Yale Law and average 14 years of legal experience, including work with or on behalf of companies like Google, Menlo Ventures, and Airbnb.
Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees
Content Approved by UpCounsel
- Bayh-Dole Act
- Using a Virtual Office as a Registered Business Address
- What Is a Company Statement
- How to Start a Virtual Office Business
- Intellectual Property Policy Example
- What Is a Business Lawyer
- Business Philosophy Definition
- How to Start a Furniture Business
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide for Entrepreneurs
- Unionization

How To Open a Private University or College in the US

What Do I Need to Know Before I start?
Starting a university is a complex and multi-faceted process that requires careful planning and execution. Before embarking on this journey, it's crucial to understand the key elements that form the foundation of a successful educational institution. In this article, we'll explore the essential considerations you need to address before opening a university.
1. Defining Your University's Purpose and Goals
The first step in establishing a university is to clearly define its purpose and goals. This involves answering questions such as: What kind of institution do you want to create? What values and principles will guide its operations? What impact do you hope to make on students, the community, and society at large? For example, your university might aim to foster innovation, promote diversity, and prepare students for the challenges of the 21st century.
2. Understanding Legal and Regulatory Requirements
To become an accredited college or university, there are 3 steps that you have to take:
Step 1: Business Formation
When starting a university, one of the first crucial steps is to establish a legal entity. The type of entity you choose will depend on various factors, such as ownership structure, liability protection, and tax considerations. Here are some common options:
Sole Proprietorship:
If you are the sole owner of the university, you can start with a sole proprietorship. This is the simplest and most straightforward business structure, allowing you to operate under your own name or a fictitious business name. However, it's important to note that a sole proprietorship does not provide personal asset protection, meaning your personal assets could be at risk in case of legal issues or debts related to the university.
Limited Liability Company (LLC):
If you want to protect your personal assets, consider establishing an LLC. This structure provides limited liability protection, separating your personal assets from the university's liabilities. An LLC can be owned by one or more individuals and offers flexibility in management and taxation.
S-Corporation (S-Corp) or C-Corporation (C-Corp):
If you have partners in your university venture, an S-Corp or C-Corp may be more suitable. These structures provide limited liability protection and allow for multiple shareholders. The main difference between the two is taxation: an S-Corp is a pass-through entity, meaning the company's income and losses are passed through to the shareholders' personal tax returns, while a C-Corp is taxed as a separate entity.
For non-US residents, a C-Corp is the best option available when establishing a university in the United States.
Once you have chosen your business entity, the next step is to obtain a business license. This process can typically be completed online through the Secretary of State's website in the state where your university will be located. The application process may vary by state but generally involves providing information about your business, such as its name, purpose, and ownership structure.
The time it takes to obtain a business license can range from one to six weeks, depending on the state and the complexity of your application. It's essential to allow sufficient time for this process and to ensure that all required documents and fees are submitted accurately.
Step 2: State Authorization and Licensing
One of the most critical steps in establishing a university is obtaining state authorization and licensing. This process involves securing the necessary approvals from state agencies to operate as a higher education institution. However, the requirements and regulations vary significantly from state to state, making it a complex and potentially time-consuming endeavor.
Researching State Requirements:
Before beginning the state authorization process, it's crucial to thoroughly research each state's specific requirements. Failing to do so could result in wasted time and resources. The type of programs you plan to offer will also impact the applicable regulations and timeframes.
States Prohibiting Non-Accredited Universities:
It's important to note that 29 states do not allow non-accredited universities to obtain a license to operate. These states are: Alabama, Arkansas, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Kentucky, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Mississippi, Montana, Nebraska, New Mexico, North Dakota, Ohio, Oklahoma, Oregon, Rhode Island, South Carolina, South Dakota, Utah, West Virginia, and Wyoming.
If you plan to establish your university in one of these states, you will need to secure accreditation before applying for state authorization.
States with Lengthy and Expensive Processes:
Among the remaining 21 states, some have particularly long, expensive, and complex processes for obtaining a license to operate. For example, states like New York, California, Virginia, Colorado, and Nevada can take up to 2-3 years to grant a license to a degree-granting institution.
States with Faster Authorization Processes:
As of March 2024, the fastest states to obtain a license to operate a degree-granting institution in the United States are:
- Tennessee
- Wisconsin
These states have streamlined processes and may be more attractive options for those looking to establish a university quickly.
States with Unique Requirements:
Some states have specific nuances in their authorization processes. For example, in Texas, if you plan to offer degree programs, you must submit two separate applications to two different agencies: the Texas Workforce Commission (TWC) and the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board (THECB). This dual-application process can make the overall timeline longer and more expensive compared to other states.
Understanding Timelines
Obtaining state authorization and licensing is a crucial step in establishing a university, but the process can be complex and time-consuming. The requirements and regulations vary significantly from state to state, and the timeline for approval depends on the type of programs you plan to offer.
Degree Programs:
If your university intends to offer degree programs, you should expect the approval process to take between 12 and 24 months, sometimes even longer. During this period, you are not permitted to begin marketing or enrolling students. However, you are expected to have a full curriculum, a campus, faculty, and administrative staff in place. This means that you must invest significant time and resources into developing your university's infrastructure and academic offerings before you can even begin the state authorization process.
Non-Degree Programs:
If your university plans to offer non-degree programs, such as certificates or diplomas, the approval process can be shorter. In some cases, you can obtain approval in as little as six to nine months. This shorter timeline can be advantageous if you want to start offering programs and enrolling students more quickly.
Exemptions:
In some cases, your university may qualify for exemptions from certain state authorization requirements. If you meet the criteria for an exemption, you can obtain verification of that exemption in 3-6 months or less. It's essential to research the specific exemptions available in your chosen state and determine whether your university qualifies.
Step 3: Getting Accredited
Accreditation is a crucial aspect of establishing a university, as it serves as a stamp of approval that demonstrates the quality and legitimacy of your institution and its programs. When a college or university becomes accredited, it signals to government officials, students, and the public that the education provided meets high standards and is worthy of recognition.
What is Accreditation?
Accreditation is a process by which an independent, external body evaluates an institution's programs, faculty, facilities, and policies to ensure they meet established standards of quality. When a university is accredited, it means that it has undergone a rigorous review process and has been deemed to provide a high-quality education.
Importance of Accreditation :
- Accreditation is often a condition for obtaining and maintaining a license to operate a degree or non-degree-granting institution. Non-accredited colleges or universities are typically given provisional licenses with the requirement that they become fully accredited within a specified timeframe. Failure to meet this condition can result in the suspension or revocation of the institution's license.
- Accreditation is essential for students to access government and state financial aid. Without accreditation, your institution's enrollment rates may be significantly affected, as students will have limited access to funding options.
Types of Accreditation :
1. Regional Accreditation: This type of accreditation serves specific regions in the U.S. There are six regional accreditors, each covering a different educational region: Middle States Commission on Higher Education, Western Association of Schools and Colleges, Higher Learning Commission, Southern Association of Colleges and Schools, Northwest Commission on Colleges and Universities, and New England Association of Schools and Colleges. Regional accreditation is often considered more prestigious due to its rigorous application process but can take longer and be more expensive than other types of accreditation.
2. National Accreditation: National accreditation is given by bodies that are not limited by region, such as those that accredit distance learning or faith-based institutions. The application process for national accreditation is generally faster and more affordable compared to regional accreditation.
3. Programmatic Accreditation: Also known as specialized accreditation, this type of accreditation is awarded to specific programs within a university, such as nursing or business. Programmatic accreditation demonstrates that a particular program meets the standards set by the relevant professional field. Typically, an institution must first be regionally or nationally accredited before seeking programmatic accreditation.
Timeline for Accreditation:
Accreditation is a lengthy process, and the timeline varies depending on the type of accreditation and the programs offered.
- For degree programs, institutions are required by law (in some states) to become fully accredited within 3-5 years of obtaining their license. Failure to meet this deadline can result in the revocation of the institution's license.
- National and programmatic accreditation can take 2-3 years to complete.
- Regional accreditation is the most time-consuming, often taking 3-5 years.
It is crucial to keep these timeframes in mind when planning the establishment of your university and to work diligently to meet all accreditation requirements within the specified deadlines.
Seeking accreditation from recognized accrediting bodies is essential for ensuring the quality and credibility of your university's programs. By understanding the different types of accreditation and their associated timelines, you can make informed decisions and take the necessary steps to secure the appropriate accreditation for your institution.
3. Developing a Comprehensive Business Plan
A solid business plan is the roadmap for your university's success. It should include:
- Financial Projections: Detailed estimates of startup costs, operating expenses, revenue streams, and long-term financial sustainability.
- Market Analysis: An assessment of the demand for your programs, target student demographics, and competitive landscape.
- Operational Plan: An outline of your university's organizational structure, facilities, technology infrastructure, and staffing requirements.
- Marketing Strategy: A plan for promoting your university, recruiting students, and building brand awareness.
A well-crafted business plan will not only guide your decision-making but also help you secure funding from investors, donors, or financial institutions.
4. Assembling a Strong Leadership and Academic Team
The success of your university largely depends on the quality and expertise of its leadership and academic team. This includes:
- Board of Trustees: A group of experienced individuals who provide strategic guidance and oversight for the university.
- President and Senior Administrators: Experienced leaders who can manage the university's operations, finances, and external relations.
- Academic Leadership: Deans, department chairs, and program directors who can develop and implement high-quality academic programs.
- Faculty : Qualified and passionate educators who can deliver engaging instruction and conduct research in their fields.
Building a strong team requires careful recruitment, competitive compensation, and a commitment to professional development and support.
5. Developing High-Quality Academic Programs
The heart of any university lies in its academic programs. To attract and retain students, your university must offer relevant, rigorous, and innovative programs that meet the needs of today's learners. This involves:
- Curriculum Development: Designing curricula that are aligned with industry standards, accreditation requirements, and student learning outcomes.
- Faculty Recruitment and Development: Hiring qualified faculty members and providing ongoing professional development opportunities.
- Assessment and Continuous Improvement: Regularly evaluating the effectiveness of your programs and making data-driven improvements.
By focusing on academic quality and student success, your university can establish a strong reputation and attract a diverse student body.
6. Investing in Technology and Infrastructure
In today's digital age, technology plays a crucial role in the delivery and management of education. To support your university's operations and enhance the student experience, you'll need to invest in:
- Learning Management Systems (LMS): Platforms that facilitate online course delivery, student collaboration, and assessment.
- Student Information Systems (SIS): Databases that manage student records, registration, and financial aid.
- Campus Infrastructure: Modern facilities, classrooms, laboratories, and study spaces that support student learning and engagement.
Careful planning and budgeting for technology and infrastructure investments will ensure that your university can meet the evolving needs of students and faculty.
7. Building Partnerships and Community Engagement
No university exists in isolation. To thrive, your institution must build strong partnerships and engage with the broader community. This can involve:
- Industry Collaborations: Partnering with businesses and organizations to provide internships, research opportunities, and career pathways for students.
- Community Outreach: Engaging with local schools, non-profits, and community groups to address social issues and promote civic engagement.
- Alumni Relations: Cultivating a strong network of alumni who can serve as mentors, donors, and advocates for your university.
By fostering meaningful connections beyond campus, your university can enhance its impact and sustainability.
Starting a university is a complex and rewarding endeavor that requires careful planning, strategic thinking, and a commitment to student success. By addressing these essential considerations, you can lay the foundation for an institution that will make a lasting impact on students, communities, and the world.
For a free consultation, call +1(925)208-9037 or email me [email protected] today. I have been helping clients open and run their institutions for the last two decades and I look forward to helping you too.
Unlock the potential of your university vision with our expert guidance. Schedule a free consultation.

SCHEDULE A CALL


- Arts & Culture
- Civic Engagement
- Economic Development
- Environment
- Human Rights
- Social Services
- Water & Sanitation
- Foundations
- Nonprofits & NGOs
- Social Enterprise
- Collaboration
- Design Thinking
- Impact Investing
- Measurement & Evaluation
- Organizational Development
- Philanthropy & Funding
- Current Issue
- Sponsored Supplements
- Global Editions
- In-Depth Series
- Stanford PACS
- Submission Guidelines
Creating a University From Scratch
How Minerva is reimagining higher education now and partnering to scale for impact in the future.
- order reprints
- related stories
By Ben Nelson, Diana El Azar & Ayo Seligman May 11, 2020

Imagine building a university from the ground up, and doing it specifically with 21st-century students in mind. It would mean no baggage, no legacy systems, and no outdated curricula. It would also mean attracting a completely new faculty and student body, and raising the funding needed to operate.
This was our challenge. Born in 2012 to address the problems inherent in the centuries-old system of higher education, Minerva’s ambition is to establish a model for the next generation university: intentionally designed to equip future leaders and innovators to solve complex challenges, to make decisions of consequence, and to work collaboratively to improve the world. We’ll not only outline how we began an innovative university from scratch, but how we are will scale our impact through strategic partnerships across educational levels, sectors, and geographies.

Minerva’s model addresses four core systemic concerns:
- How to admit students based entirely on merit, not wealth, relationships, or athletic ability
- How to provide an exceptional, outcomes-driven education
- How to engage students at the lowest possible cost
- How to produce purpose-driven global citizens, ready to contribute to society
An Unconventional Admissions Process
Because Minerva sought to admit students with the highest potential—regardless of family background, wealth, or geographic location—we needed a new approach to admissions. In addition to high school grades, Minerva considers applicant accomplishments outside of class, their performance on a series of cognitive challenges, and their conduct during a video interview. Standardized test scores and standard application essays have all been shown to produce bias toward wealthy applicants. Focusing on high school transcripts, extracurricular accomplishments, and cognitive tests allows Minerva to better predict future success.
While Minerva values diversity, there are no quotas or protocols to balance gender, religion, or ethnicity. But focusing on merit alone has attracted a student body that’s almost equally male and female, with a globally diverse student body: roughly a quarter of our students come from North America, a quarter from Asia, a quarter from Europe, and the remaining quarter coming from Africa, Latin America, and the Middle East. This organic diversity helps to validate our belief hypothesis that talent is equally distributed around the world.
Our commitment to student access extends to the overall cost to attend, which is kept as low as possible by eliminating superfluous campus infrastructure and amenities (Minerva owns no real estate and only leases student housing). Minerva grants financial aid to every admitted student that demonstrates need: much of it supplied through a robust work-study program, in which students gain professional experience, with the remainder provided by low-interest loans and grants.
An Intentional Curriculum
Every aspect of the Minerva curriculum is intentionally designed, rather than students picking-and-choosing from a vast array of courses chosen by the subject matter and expertise of research faculty. Our goal is not only to shape a mindset but to impart a universal skill set: in addition to a distinctive way of looking at the world, our students acquire the range of tools necessary to make meaningful, positive change within it.
The educational model is structured by three interconnected features: 1. cross-contextual curricular scaffolding, in which concepts are repeated with increasing complexity, across diverse contexts; 2. fully active learning, where students are engaged in every class session; and 3. systematic, formative feedback and assessment, all facilitated through an advanced virtual learning environment, called Forum™. For example, after students learn the concept of “heuristics” during their first year, they will continuously apply the concept in different subjects and new contexts, demonstrating their command in the classroom through live discussions, polling, and breakouts (while their instructors continuously assess their engagement and understanding using Forum, which registers all interactions).
During the first year, all students take the same four foundational courses— Complex Systems, Empirical Analyses, Formal Analyses, and Multimodal Communications —which are explicitly structured to impart universal cognitive tools and frameworks that can be applied across different domains. In the second year, Minerva students select a major field of study—arts and humanities, business, computational sciences, natural sciences, or social sciences—where they continue to explore their interests before committing to a more focused concentration (for example, data science and statistics, within the computational sciences major). As Minerva students progress, their studies become increasingly individualized and self-directed, including co-design of their fourth-year coursework and an independent project that incorporates both intensive research and creative problem solving. These capstone projects, chosen from within their fields of study, must present novel concepts, just as a graduate thesis would.
This cross-contextual curricular scaffolding continually reinforces pre-established learning outcomes in each class, throughout courses, across domains, and over time. The learning outcomes comprise a set of approximately eighty Habits of Mind (cognitive skills that come to be triggered automatically) and Foundational Concepts (fundamental knowledge that is broadly applicable) . These act as the building blocks of four core competencies: critical thinking, creative thinking, effective communication, and effective interaction. The Habits and Concepts (HCs) are introduced early, reinforced often, and consistently assessed. Through deliberate, spaced practice and prompted application, students learn to use them for more effective decision-making, devise inventive solutions to complex challenges, manage ambiguity and navigate uncertainty, and, ultimately, to transfer them to novel situations.
The 80 HCs were identified by Minerva as part of an iterative process to find the paramount skills for the next generation of leaders, innovators, and engaged global citizens . Importantly, though derived from the universal skills employers consistently seek , the HCs used in Minerva’s academic programs need not be identical for other academic institutions.
Flexible and Engaged Pedagogy
When hearing the words “online classes,” many people envision pre-recorded lectures, pre-programmed activities, and other content-driven educational approaches. But simply taking traditional classroom instruction and putting it online has been shown, time and again, to be ineffective, leading to low course completion rates , and result in minimal understanding, retention, or recall of the information being taught.
The Minerva platform was purpose-built to facilitate the learning outcomes of our curriculum. It utilizes live, multi-stream video, integrated course development and management tools, and rich data collection and analysis features. Most importantly, the pedagogy emphasizes fully active learning, in which students are kept engaged during every class session, through guided Socratic discussion, collaborative work, role play, simulations, polling, and other means. This methodology has been repeatedly demonstrated to improve understanding, retention, and recall when compared to traditional lecture-based instruction. All Minerva instructors are trained with an emphasis on tracking learner engagement, progress, and specific educational outcomes.
When students enter class, they are met with a series of activities and discussions that reference reading and other work assigned prior to joining. Imagine being asked, immediately upon arrival, to not only recall, but comment on a scholarly article you read the previous night. Then, as the instructor selects the most interesting answer—not necessarily the most correct—you are asked to opine on your classmate’s comment. Because instructors are directed to speak less than 15 percent of the time in any class session, students are continually called on, keeping them focused so as not to be caught unprepared. Classes often also incorporate a series of small breakout group activities in which students collaborate on problems related to pre-readings or exhibits introduced in class, and the sessions typically end with a synthesis activity, such as a poll. All classes are recorded and student engagement is also tracked throughout each session, enabling instructors to evaluate in-class contributions and measure progress by comparing student understanding from class to class. This performance is a major component of each student’s final grade.
Lastly, Minerva courses are grounded in salient global concerns, from food and water scarcity to scientific advances and complex social and geopolitical dynamics. For example, in the first year, students grapple with big, multifaceted questions, such as “How can we feed the world?” or “Who should own information?” The students engage with these questions using the aforementioned Habits and Concepts: searching for the right problem, breaking it down, conducting a gap analysis, understanding constraints and analogies, and applying heuristics. These are practical concepts that will be used again and again, throughout their courses and across domains.
Beyond Classroom Walls
To augment this rigorous academic programming, Minerva devised a modern approach to experiential learning. Instead of a sequestered life on campus, students are immersed in the world, living and learning in seven diverse cultural contexts: After the first year in San Francisco, students spend the next six semesters rotating through Seoul, Hyderabad, Berlin, Buenos Aires, London, and Taipei. In each of these cities, students engage in a variety of experiential programs, including community projects, working with local businesses and government agencies, and student-centric activities like communal meals, club meetings, and hackathons. These programs incorporate individual coaching and are closely integrated with academics, so students receive formative feedback across multiple dimensions, including professionalism, self-management, cultural dexterity, personal responsibility, and interpersonal engagement.
Such global programming is only possible because classes take place in a digital environment: Because faculty are based anywhere, students can live around the globe while still attending their online seminars every day. Moving students seven times over the course of four years is expensive and logistically complex, but we keep costs down by leasing reasonably priced residence halls, and employing nimble teams in each city (and students manage many of these initiatives themselves, with minimal institutional support).
This approach teaches the skills sought by a variety of organizations, which typically take years of experience to acquire. The global, integrated learning accelerates their development of these universal skills, while fostering a dedication to societal participation. By being continually challenged, students learn to approach problems in a comprehensive, interdisciplinary manner, with an intellectual maturity rarely found at the undergraduate level.
Scaling for Impact
Seven years after its founding, Minerva saw its first graduating class emerge, nearly 150 strong. While most have already begun making an impact in a broad range of categories—from the sciences, technology, and business to government and social sectors—their numbers remain relatively small. Minerva set out to build the best university, not the biggest, so to have a much greater effect, the model needed to be adopted and adapted by others.
In 2018, Minerva, through its for-profit arm, began offering partners the core elements of the model: the curricular design, the pedagogical approach, the systematic assessment, and the virtual learning environment. Coupled with the deep expertise of the Minerva team, the model enables high schools, colleges and universities, organizations, and governments to help transform learning at every stage and in any part of the world. Partnerships include a top STEM university in Hong Kong, a leading US law school, and the honors students in an all-virtual college preparatory high school. Like students, as faculty and administrators are exposed to the transformative power of the Minerva model, many undergo a shift in perspective: They want more of their colleagues and peers to adopt the approach, so more learners can benefit.
While the spread of COVID-19 has disrupted most academic institutions and pushed them to seek digital solutions for remote teaching, the partnerships that Minerva establishes go far beyond that, helping transform institutions that have a genuine desire to improve the educational outcomes for their students. Like most organizations, Minerva seeks to partner with institutions that share its mission and vision about rethinking what they are teaching and how they are teaching it, whether digitally or physically. Where a digital platform enables the continuous delivery of education in a crisis, as the future of education includes increasingly virtual platforms, academic institutions will need to invest not just in technology, but also in curriculum and teaching methodologies.
What We've Learned Along the Way
While building a university from scratch meant we did not have to grapple with entrenched beliefs or legacy systems, there have been many challenges.
- Gaining accreditation is crucial for establishing the credibility of academic programs, but is typically a painstaking process. New institutions are normally required to operate for a minimum of five years before being accredited, a timespan which would have made it nearly inconceivable to attract the caliber of students we sought from the outset. Minerva therefore adopted an “incubation model,” beginning our programs as part of the already-accredited Keck Graduate Institute (KGI), enabling our students to be confident their degrees would be trusted by employers.
- The admissions process rigorously screens for cultural adaptability and resilience, essential character traits for success at Minerva, and we do not admit students we think will be unable to navigate the intellectual and emotional challenges the program includes. These are highly subjective measures, unfortunately, so we try to minimize built-in bias with automated video interviews (as live interviewers can have unconscious influences on candidate performance), distributed reviews which evaluate each piece of the process independently from the results of other components, and a consistent set of evaluation criteria used to generate scores.
- One of our biggest challenges has been supplying financial aid for nearly 80 percent of our students. In pursuing needs-blind admissions, we underestimated how many students would be reliant on aid. This has meant a continuous effort to secure funds from philanthropic organizations, as well as to identify work-study opportunities for our students. It has also meant maintaining a relatively small student body and collaborating with partners to achieve financial viability through scale.
Hundreds of years from now, if the Minerva vision takes root, the entire educational system will be reformed. Universities everywhere, even those that are centuries-old today, will have changed their approaches, to incorporate deliberate, outcomes-driven instruction and produce legions of more informed and engaged global citizens, more creative and collaborative problem solvers, and wiser decision makers. Only then would we have accomplished our mission to nurture critical wisdom for the sake of the world.
Support SSIR ’s coverage of cross-sector solutions to global challenges. Help us further the reach of innovative ideas. Donate today .
Read more stories by Ben Nelson , Diana El Azar & Ayo Seligman .
SSIR.org and/or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and to our better understanding of user needs. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to otherwise browse this site, you agree to the use of cookies.
How to start a business while at university: tips from the students who did it
Three entrepreneurs share the resources and advice that any university student planning to start a business will find valuable.

The Covid-19 pandemic has vastly altered the traditional nine-to-five office job. With many new industries emerging, graduates around the world are beginning to make the most of the changing landscape to develop their own business ideas.
Building your own business as a university student requires huge amounts of creativity, resilience and vision, but it can be an extremely rewarding path.

Want to know more about the University of Dundee School of Business?
Below, three successful entrepreneurs share their top tips and guidance for starting a business at university.
1. Make the most of your university’s resources to develop your idea
Many universities have their own entrepreneurship centre or venture studios, which can help students develop their ideas and access resources and mentoring.
For example, Hadeel Ayoub came to the UK from the Middle East as a mature international student to do a postgraduate degree in computational arts at Goldsmiths, University of London . While there, she founded BrightSign, a company that develops assistive technology such as the BrightSign Glove, which translates the wearer’s sign language into texted speech.
For Hadeel, the support available for entrepreneurial students at Goldsmiths made all the difference.
“Goldsmiths supported me in learning the fundamentals of becoming an entrepreneur, like how to register your company, how to do your taxes, and how to create projections and use them to build a business model,” says Hadeel, speaking at the THE Student Festival: UK in October 2021. “I was also matched with a mentor, who gave me invaluable advice and guidance,” she adds.
Hadeel was later selected to represent her university at the annual Santander Universities Entrepreneurship Awards, where she won the People’s Choice Award for her work on the BrightSign Glove.
Amar Mehta, an international student from New Zealand studied for a master’s in neuroscience at King’s College London before joining the university’s King’s20 Accelerator programme. Through this scheme, he has been working on the development of Advicely, which uses artificial intelligence in digital advertising for small businesses.
“I have been really impressed by the level of support at my university, all of which has tangibly helped my business,” he says. “I was offered monthly catch-ups to check my progress, access to office space and time with experts associated with King’s, to name a few examples. I even found my current developer through contacts at the King’s Entrepreneurship Institute.”
Accelerator programmes such as King’s20 can also provide funding and visa sponsorship to international students like Amar. After finishing his neuroscience course, Amar was able to get sponsorship for a year-long start-up visa from King’s College London as a member of the King’s20 project. When a new cohort began on the programme the following year, the university offered Amar the chance to remain as a start-up-in-residence to coach the incoming group of entrepreneurs, and it supported him through a new visa application to extend his stay.
Tanuvi Ethunandan, another student entrepreneur, completed her undergraduate degree at the Falmouth University .
While there, Tanuvi joined Falmouth’s Launchpad, a venture studio, where she co-founded Data Duopoly to solve visitor congestion and lack of data insights at venues such as theme parks and museums.
Entrepreneurship is a new career choice for university students How to network as an international student The one skill all students should acquire to boost employability How to boost your career prospects as a university student
2. Know your market
If you want your business idea to succeed, you need a deep understanding of the sector you want to go into, including what’s missing from it, what problems your product or service would solve and what potential competition you might face.
Many students who pursue a subject other than entrepreneurship and business will go on to found companies based on innovations specifically needed in their field.
For Hadeel, studying computing was pivotal to becoming an entrepreneur, as it was during her degree course that she first encountered the machine learning technology that she later applied to create the BrightSign Glove.
“Once I found a new application for the technology and realised people wanted to buy it, my business grew organically out of that,” she says.
“Don’t discount universities as a market in themselves. If you’re a student, you’ll already know about the sector and have contacts within it,” advises Tanuvi. During the Covid-19 pandemic, she shifted gears to apply the technology she developed with her business to help Falmouth University students return safely to campus.
“Focus on building a business and not coming up with an idea to get a visa,” advises Amar. “You need to have a strong business idea that can genuinely provide value to the UK or wherever you want to be located. Make sure you really understand your market and what your audience actually wants, and test and learn as much as possible. Expect your first assumptions about your business to change quickly as you get feedback from your target audience,” he adds.
3. Play the student card outside your university
As well as finding mentors and networking opportunities through your university, you can use your student status to your advantage to seek external advice.
Making inroads into external networks and support systems will also help to ease the transition into the business world once you graduate.
Even if your idea is still in development, there’s no harm in getting in touch with potential mentors, or any incubators and accelerator opportunities early in the process.
“You really can use the student card anywhere,” says Hadeel. “From mentorship, promoting you to their network or even offering you free office space, people want to support you to get your idea out there.”
“If you are booking tickets for trade shows, say that you are a student. You can often get reduced price tickets,” advises Tanuvi.
“Also, take advantage of your long summer holidays,” she adds. “Get to work on your idea or look for a relevant internship or work experience that will complement your business.”
4. Don’t try to do it all alone
The portrayal of successful entrepreneurs as totally self-made and self-reliant can be misleading. Even the most visionary businesspeople will have had a strong support team behind them and will be wise enough to listen to advice from others.
“If you have an idea already, university is a great place to test it,” according to Tanuvi. “Higher education institutions can provide you a safe space to try and fail, while surrounding you with people who are willing you to succeed.
“I would recommend co-founding your business with a partner,” she adds. “You’ll need that person by your side to help you commiserate the lows as well as celebrate the highs.”
Hadeel says: “At the beginning of my journey developing BrightSign, I thought I could do it all on my own. I quickly discovered the very hard way that I couldn’t.”
She points out that as a student at Goldsmiths, she was able to get access to alumni across all University of London institutions, which was a great step up when it came to networking and finding support.
“Once I had the right help, things accelerated fast,” Hadeel says. “I know I lost time from not seeking advice earlier in my journey.”
5. Prepare for long hours
If you want to start your own business, you need to be ready to commit your time.
“Be prepared for long hours,” says Tanuvi. “Working well over 40 hours is not unusual in the beginning.”
“In the early years of building a business, putting in a lot of your time is pretty unavoidable,” adds Amar. “If you’re balancing your business with your studies, this can be really difficult – you’ll need a supportive team you can rely on, and I’d recommend setting strong boundaries of how you’re going to allocate your time.”
Making realistic work plans are key to avoiding burnout. If you’re planning to put in a lot of hours over a certain period, make sure you allot some time for rest and relaxation to recover.

You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Studying in Canada gave me the opportunities to start my own business
Meti Basiri

Digital Leaders: top universities for digital entrepreneurship

Your student experience is on hold; career development doesn’t have to be
Miguel Rodriguez
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
- UConn Library
- Topic: Entrepreneurship & Business Plan Guide
- Business Plan (How to & Samples)
Topic: Entrepreneurship & Business Plan Guide — Business Plan (How to & Samples)
- Idea Generation
- Industry Information
- Competitors
- Market Research
- Financial Data
- Advertising & Promotion
- Small Business Advisors
- Products, R&D, Strategy
- Patents and Trademarks
- Grants, Loans, and Financing
- Franchises & Franchising
- Celebrating Connecticut
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is "a guide—a roadmap for your business that outlines goals and details how you plan to achieve those goals."--Tim Berry from Bplans site.
- An Introduction to Business Plans Introduction to a tutorial on business plans written by the staff at Entrepreneur magazine.
- Business Planning Guide Step-by-Step guide to write a Business Plan by Bplans site.
- Create Your Business Plan, from the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) The SBA has delivered millions of loans, loan guarantees, contracts, counseling sessions and other forms of assistance to small businesses.
What is included in a Business Plan?
The following components make up a business plan:
Table of Contents
Executive Summary : Appears first, written last. Provides a snapshot of your company explaining who you are, what you do, and why.
Mission & Vision: Here you define the purpose of your business (Mission) and a statement about your perception of the company's growth and potential (Vision). Include specific goals and objectives of the business
Business Description: Provide background information about the company including brief history of the business and list of key company principals.
Define Your Market: Describe the industry within which your business will operate, identify your target market, provide a general profile of your targeted clients, and describe what share of the market your currently have and/or anticipate. For this section of the business plan, your will undertake following types of research:
Industry Analysis : how is the industry structured, trends and statistics, key players, segmentation, sales and distribution channels etc.
Competitive Analysis : major competitors, strengths and weaknesses, how would you position yourself against the competition, market niche, product/service comparison
Customers: who are the customers (demographic data), what do they want, customer buying habits, market share/market size, consumer preferences
Advertising and Promotion : How will you reach out to potential customers? Where do they currently shop for product/service? Where will you advertise and how will you measure the effectiveness of your advertising and promotion efforts?
Pricing : strategy, policies, price list, break-even analysis
Location : Where is your business located? (home-based; retail; commercial, etc….), is the location of your business important? Any special zoning, land or building improvements needed to accommodate your operation? If location is important, what are the features of your location?
Products & Services: Describe all your products and services; explain how your products and services are competitive including unique features, benefits of the product or service, niche served, stage of product/service development, production, future growth.
Organization & Management: Describe how your company is organized including legal structure(sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation etc); identify any special licenses and/or permists your business operates with; provide brief bio of key managers within the company; include an organization chart if available.
Marketing & Sales Strategy: Identify and describe your maket -- who are your customers and what's the demand for your products and services; channels of dsitribution you will use; your sales strategy specific to pricing, promotion, products, and place.
Financial Management:
For new business include: estimate of start-up costs (all one-time expenses such as equipment, deposits, fees, etc.); projected balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement (1 year forward)
For existing business include: balance sheets (last 3 years), income statements (last 3 years), cash flow statements (12 months)
If applying for a loan: current personal financial statement on each principal; federal tax return for prior year
Appendices: This section may include company brochures, resumes of key employees, list of business equipment, copies of press articles and advertisements (if available), pictures of your business location and products, any applicable information about your industry and /or products, key business agreements such as lease, contracts etc.
(Adapted from: SBA's Business Plan Template )
Finding Sample Business Plans
- Business Plans Handbook/ Lynn M. Pearce, ed. Vol 13. Includes sample plans on numerous topics such as advertising, fitness center, landscaping, and technology solutions provider and more.
- Business Plans Handbook/ Lynn M. Pearce, ed. Vol. 19. Includes business plans for assisted living facility, auto dealing, bowling alley, commodities trading firm, digital presentations, farm, furniture store, gas station, laundry mat, web design, and more.
- Business Plans Handbook (via Reference for Business) Earlier volumes of the Business Plans Handbook are available at the above sites for free.
- BPlans.com Includes samples of business plans as well as advice and tips on writing a business plan, starting and running a business.
Why You Need a Business Plan?
You need a business plan:
- To see if you have a viable business idea
- To identify your (and your company's) strengths and weaknesses
- To assess the market for your product or service
- To size up the competition
- To determine your financial needs
- To attract investors
- To set up milestones and monitor your business
- << Previous: Idea Generation
- Next: Industry Information >>
- Last Updated: Apr 15, 2024 1:46 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uconn.edu/entrepreneurship

Start-Up Resources: Write a Winning Business Plan
Click on each heading to learn more about writing a business plan.
Business Plan Basics
Buerk Center Advisory Board members’ presentations on writing a business plan.
Marc Barros , Entrepreneur, co-founder and former CEO of Contour “Start your company! . . . Did you start your company yet? . . . Seriously, you’re already behind!” Marc emphasizes the business plan as a tool to organize thoughts for a business you’ve already started. View slides
T.A. McCann , Gist T.A. is the founder and CEO of Gist, which was acquired by RIM in 2011. His past experience includes Vulcan Capital and Polaris Venture Partners, where he was an entrepreneur-in-residence. View slides
Writing Resources
Resources for writing a stellar business plan.
How to Write a Great Business Plan Harvard Business Review Thorough article that covers the essential elements that belong in a business plan. A must read for anyone about to write a business plan.
How to Structure a Business Plan Inc. Magazine Magazine Extensive resource that covers everything from idea feasibility to presentation.
How to Write a Great Business Plan Inc. Magazine Advice for small businesses on what it takes to create a solid business plan, including forming an outline, integrating financial specifics, and spelling out your marketing strategy.
Business Plan Basics MIT Excellent slide deck from the MIT Course, The Nuts and Bolts of Business Plans . Covers why you write a plan, what you should cover in it, and who should write it. Content starts on slide 13.
Writing a Business Plan Sequoia Capital Includes elements of sustainable companies and a straightforward business plan outline.
Presentations on marketing your start-up. Who are your customers? What drives them to make a purchase? How do you segment the market? How do you market your business on a shoestring budget?
Marketing in a Competitive Environment Sharelle Klaus , CEO of DRY Soda Sharelle brings more than a decade of entrepreneurial, financial and technology experience to DRY Soda. Her presentation provides the tools you need to overcome marketing challenges commonly faced by start-ups. View slides
How to Market Consumer Products Presentation Jason Stoffer , Maveron Jason is a principal at Maveron, a local VC firm that is focused solely on consumer businesses. His presentation covers the key elements of a consumer products pitch, as well as the questions you should be able to answer about your product and the market it exists in. View slides
Presentations on the fundamentals of financial projections–What are they? How do you create them? How do you avoid the common pitfalls that drive investors crazy?
SEC Filings and Forms All publicly traded companies must disclose financial information to the SEC. Research companies that have similar cost structure, distribution channels, customers, etc. to help you estimate costs for your start-up.
Financials and Funding for Start-Ups Presentations Alan Dishlip, CFO of Billing Revolution Alan joined Billing Revolution as CFO in 2009, after holding that position at WildTangent Games for five years. He has both operational and venture capital experience and has been involved in helping build and grow early-stage companies for more than 30 years. View slides

College Business Plan

When you think of a college business plan , what is often the first thing you think about? The majority may say a business idea of setting up a college or a university for local and international students. Another may see it as a school that offers business as part of their academic course. What reason may it be or what idea you may have, it is always best to have and match it with a business plan. Making a college business plan will also matter and help you in the long run. With that, here are example templates you can download to start now.
10+ College Business Plan Examples
1. college business plan template.

- Google Docs
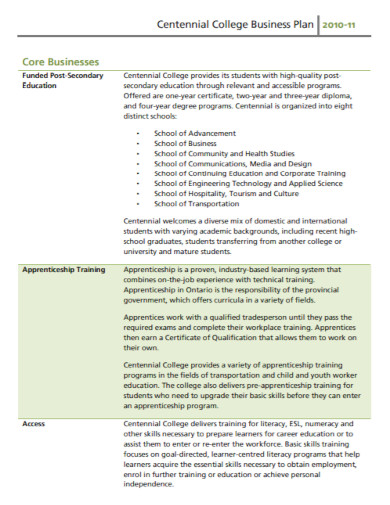
2. Centennial College Business Plan
Size: 586 KB
3. Professional College Business Plan

Size: 895 KB
4. College Business Plan in PDF

Size: 122 KB
5. Developed College Business Plan

6. College Leadership Business Plan

Size: 167 KB
7. National College Business Plan

Size: 181 KB
8. Secondary College Business Plan

Size: 314 KB
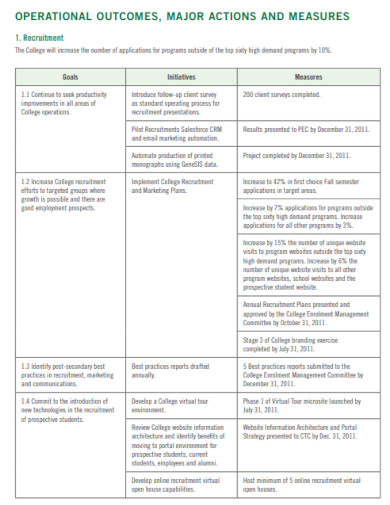
9. Operational College Business Plan
10. College Business Operation Plan

11. Community College Business Plan

Size: 235 KB
What Is a College Business Plan?
A college business plan is a handy tool used in order to guide the user to better success and better roads. When you think of starting up a college, or adding a business course to a college, you will also need a business plan with it. A college business plan is seen as a means of gathering steps to making it work. May it be through a simple business plan or a complex one. Regardless, the main purpose of a college business plan is to gather steps or strategies to reach the main goal.
How to Create a College Business Plan
When you plan to make a college business plan, you think carefully about the steps that go with it. The most basic thing to see in a college business plan is the summary of your business and of course the marketing strategies. But these are not enough to make your business plan. To get a good idea, here are simple steps to create your college business plan.
Step 1: Always Plan Ahead
This may sound cliché but the most important thing to remember and to get started is to plan ahead . Do some brainstorming and get to know what you want in your business. This helps by making your college business plan better and can reap a better and positive result. Part of planning ahead is to plan for a title page, a title, or a goal you want to achieve. This can sometimes come off as the most difficult part of the entire business plan.
Step 2: Create Your Executive Summary
The next will be to create your executive summary . In this section of your business plan, you will be talking about your business, the timeline of your business, and any information that will help you explain about your business. Basically the executive summary gives you the opportunity to expound on your business and the description and nature of your college business.
Step 3: Discuss Marketing Strategies
Third step to your college business plan is to discuss marketing strategies . Marketing strategies help in maintaining your business goals. If you are not sure where to begin with your marketing strategies, you can always make a marketing strategies checklist . As this also creates ways in helping you figure out how to attract customers or clients to your business. They must also be practical for your business and your management team to do, or the whole marketing plan and strategies will be pointless.
Step 4: Check on Your Business Plan
From the first three steps to creating your college business plan, you may think that everything will be enough. You must be open to checking, updating, and reviewing your college business plan. The whole point of it is to make sure you are open to the ideas of updating progress reports you are going to be getting through the business plan milestones.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a lengthy document that has a complete detail of how a business you plan to set up is recorded. The business plan is also seen as a tool or a roadmap to help you find out the best roads to setting up a successful business.
Why do you need to update your business plan?
The main purpose for updating your business plan is because every progress is important. Every single detail that may show positive or negative changes have to be reported in order to keep your business plan updated as well.
What factors are in a business plan?
The factors you need in order to complete a business plan are the most simple and basic things like:
- executive summary
- practical strategies and steps
- a practical timeline and milestones
When you think of a college business plan, you know for a fact that you will need to make the business plan in a practical manner. Your business plan must have everything that you need to make this a success. With that, download any of the examples to start your college business plan now.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a study plan for final exams in high school
Develop a project timeline for a middle school science fair.
Business Plan Template for College Students
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds

Starting a business as a college student can be both exciting and challenging. You have big dreams and innovative ideas, but how do you turn them into a successful reality? ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way!
With this template, you can:
- Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success
- Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans
- Effectively communicate your business ideas to stakeholders and secure funding or resources
Don't let your entrepreneurial dreams fade away. Use ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students to bring your vision to life and make a lasting impact in the business world. Start planning and building your future today!
Business Plan Template for College Students Benefits
Starting a business as a college student is an exciting and challenging endeavor. With a Business Plan Template for College Students, you can:
- Clearly articulate your business goals and strategies, giving potential investors and partners a comprehensive understanding of your vision
- Create a solid financial forecast that demonstrates the potential profitability of your venture, increasing your chances of securing funding or resources
- Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans to mitigate risks, ensuring your business is well-prepared for any challenges that may arise
- Effectively communicate your business idea to others, including professors, mentors, and potential customers, gaining valuable feedback and support for your startup.
Main Elements of College Students Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students provides a comprehensive framework for college students to develop and present their business ideas effectively:
- Custom Statuses: Easily track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Use custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add important details to your business plan, such as references, approval status, and specific sections.
- Custom Views: Access different views like Topics, Status, Timeline, Business Plan, and Getting Started Guide to organize your business plan information, track progress, create a timeline, and refer to a guide to get started.
- Collaboration Tools: Collaborate with team members, mentors, or advisors by assigning tasks, adding comments, and attaching files directly within the template.
- Goal Tracking: Set goals within your business plan and use ClickUp's Goals feature to track their progress and measure success.
- Document Management: Store important documents, financial projections, and market research within ClickUp's Docs feature for easy access and reference.
How To Use Business Plan Template for College Students
If you're a college student looking to start your own business, using ClickUp's Business Plan Template can help you get organized and create a solid plan for success. Just follow these six steps:
1. Define your business idea and goals
Start by clearly defining your business idea and the goals you want to achieve. What problem does your business solve? Who is your target audience? What are your short-term and long-term goals? Take the time to brainstorm and outline these key details.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to document your business idea and goals.
2. Conduct market research
Next, conduct thorough market research to understand your industry, competition, and target market. Identify trends, customer needs, and potential challenges. This research will help you refine your business idea, identify opportunities, and develop strategies to stand out in the market.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Plan your products or services
Based on your market research, plan out the products or services you will offer. Determine their unique selling points, pricing strategy, and how they will meet the needs of your target market. Consider any additional features or benefits that will set you apart from competitors.
Create tasks in ClickUp to outline and organize your product or service plans.
4. Develop a marketing strategy
Now it's time to develop a comprehensive marketing strategy to promote your business and attract customers. Identify the most effective channels to reach your target audience, such as social media, content marketing, or email campaigns. Outline your branding, messaging, and promotional tactics.
Use the Board view in ClickUp to visually plan and track your marketing initiatives.
5. Create a financial plan
A solid financial plan is crucial for any business. Determine your startup costs, revenue projections, and expenses. Create a budget that includes marketing, operations, and any other necessary expenses. Consider different funding options and outline your financial goals for the first year and beyond.
Use custom fields in ClickUp to track and analyze your financial projections.
6. Review and revise
Once you have completed your business plan using ClickUp's template, review it thoroughly and make any necessary revisions. Share it with trusted mentors, advisors, or teammates for feedback. Continuously update and refine your plan as your business evolves.
Set recurring tasks in ClickUp to regularly review and update your business plan.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for College Students
College students who are starting their own businesses or pursuing entrepreneurial ventures can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template to effectively communicate their business ideas and secure funding or resources for their startups.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a comprehensive business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize different sections of your business plan, such as Executive Summary, Market Analysis, Marketing Strategy, Financial Projections, etc.
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- The Timeline View will allow you to set deadlines and visualize the timeline for completing each section of your business plan
- The Business Plan View will provide a holistic overview of your entire business plan, allowing you to see how different sections fit together
- The Getting Started Guide View will provide step-by-step instructions and resources to help you navigate through the business planning process
- Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add additional information and categorize different aspects of your business plan
- Regularly update and revise your business plan as you progress, ensuring that it reflects the most accurate and up-to-date information.
- Business Plan Template for Lululemon
- Business Plan Template for Hotel Industry
- Business Plan Template for Packaging Manufacturers
- Business Plan Template for Sales Teams
- Business Plan Template for Photography Business
Template details
Free forever with 100mb storage.
Free training & 24-hours support
Serious about security & privacy
Highest levels of uptime the last 12 months
- Product Roadmap
- Affiliate & Referrals
- On-Demand Demo
- Integrations
- Consultants
- Gantt Chart
- Native Time Tracking
- Automations
- Kanban Board
- vs Airtable
- vs Basecamp
- vs MS Project
- vs Smartsheet
- Software Team Hub
- PM Software Guide

- Starting a Business
- Free Online Education to Start Your Own Business
- Our Courses

The popular original course is designed for the aspiring entrepreneur who wants to learn how to start a business . Comprised of 15 sessions that you can pursue at your own pace, Starting a Business provides step-by-step information and the essentials you need to know to start your business. The content is clearly explained and has an emphasis on learning how to write a business plan, including an introduction to MOBI's free Business Plan Template .
We welcome you to take some time to explore and learn about the Starting a Business course and great resources offered in our curriculum. All of the sessions of the course are available to preview. Once you decide you are ready to learn more and pursue your certificate, please click here to register for the entire online course.
Preview the sessions included in the Starting a Business course:
- Session 1: Choosing the Right Business
- Session 2: The Business Plan
- Session 3: Freelance, Independent, and Home-Based Business
- Session 4: Financing the Business
- Session 5: Business Organization
- Session 6: Licenses and Permits
- Session 7: Business Risk and Insurance
- Session 8: Communication Tools
- Session 9: Buying a Business or Franchise
- Session 10: Choosing a Business Location
- Session 11: Accounting and Cash Flow
- Session 12: Ecommerce
- Session 13: Marketing
- Session 14: Managing Employees
- Session 15: Expanding and Handling Problems
FOLLOW MOBI ON SOCIAL MEDIA
Certificate Courses Login

I refuse to pay my daughter's college tuition even though I made over $500,000 last year
- Andrea Mac, a business owner who made $550,000 last year, refuses to pay her daughter's tuition.
- Mac questions the value of investing such a significant amount of money into a college education.
- She and her husband want to instill independence, responsibility, and success in their children.

This as-told-to essay is based on a conversation with Andrea Mac , a growth strategist at Prequal from the Greater Chicago area. It's been edited for length and clarity.
For the last seven years I've built a business that made just under $550,000 in 2023. I'm projecting that I'll make seven figures in 2024.
Despite this income, my husband and I have not agreed to — nor do we plan to — pay for the college tuition of our oldest daughter, a sophomore at the University of Iowa.
Stating that feels vulnerable and unpopular because, within our network, this is an uncommon or less commonly talked-about choice. But we didn't make this decision lightly, and we considered many factors.
Seven key considerations went into our decision.
1. Fostering autonomy and independence in our children
When everything — including school choice, scholarships, performance, and even access to grades — is dictated or overseen by parents, students can become passive participants in their education. By not paying for college , we want our children to own their academic journey fully. This means they'll need to make crucial decisions, seek scholarships, and manage their finances, which will help them truly understand the value of their education.
To be fair, we've decided that we, as parents, don't get to choose which college our children attend. If they spent our money on tuition, we'd need a say in that decision. Instead, we've told our college-age daughter: You can choose to attend a college that costs $5,000 or $100,000 a year, but we're not writing a blank check.
2. Making sure they understand the privilege of attending college
My husband and I feel that pursuing a college degree is not a rite of passage but a choice and commitment to higher education.
As a young adult transitioning from high school, it's the perfect opportunity to evaluate the opportunity cost critically, the investment of both time and money, and the projected return on investment from such a commitment.
If they choose college, this sense of ownership can drive them to perform better and take their studies more seriously. Knowing they've worked hard to contribute to their education can instill pride and accomplishment.
3. Keeping our financial future secure
We've worked very hard to achieve economic mobility and to live in a neighborhood that offers the best educational opportunities we can afford. I've worked, and continue to work, diligently to provide for our family of six.
Related stories
Committing about $800,000 — an average of $200,000 per child for a four-year university degree — could jeopardize our future financial security . Paying for college for four children would stretch our finances beyond what we're willing to risk.
For example, investing $200,000 over four years into scaling my consultancy firm could produce more revenue and provide more significant long-term benefits for our family. Likewise, with an average annual return for stock-market investments at about 10%, that same $200,000 could yield almost an additional $100,000 in return over that same four-year time period.
4. Living within our means
Financial prudence is a core value for us. We're not willing to take on debt to pay for college . We believe in financial stability and the importance of living within our means.
This decision aligns with our commitment to avoid debt and maintain a healthy financial position, which benefits our entire family.
5. Considering the return on investment
Education is an investment, and we consider the potential return like any investment. With rising tuition costs, my husband and I think it's essential to evaluate whether the outcomes in terms of ROI justify the financial outlay for college.
We question the value of investing such a significant amount of money into a college education , especially when there are alternative paths to success that don't involve incurring massive debt.
6. Maintaining equality between siblings
We have four children aged 5 to 19, and we care about equality among siblings. Committing to paying for one child's college education means we must do the same for all of them to maintain fairness.
This long-term financial commitment could span many years, potentially affecting our ability to support our younger children in other meaningful ways. We want to ensure our financial decisions don't create inequality among our children.
7. Avoid fostering a sense of entitlement in our children
By making them responsible for their college expenses, we hope to instill a strong work ethic and a sense of responsibility in our kids. We also hope our choice will help them understand the value of hard work and the importance of making prudent financial decisions.
We're encouraging our children to take responsibility for their education and financial choices
Our children must evaluate cost-effective options, seek scholarships, and consider alternative education paths like community college, vocational training, or starting their careers earlier. This approach teaches them to be pragmatic and resourceful, skills that will serve them well throughout their lives.
Evaluating whether to pay for our kids' college tuition was a challenging decision, but it's rooted in our desire to foster autonomy, responsibility, and financial prudence.
Ultimately, by empowering our children to take charge of their education and finances, we feel we're helping to set them up for a lifetime of independence, responsibility, and success.
If you are teaching your children a unique financial lesson and would like to share your story, email Manseen Logan at [email protected] .
Watch: Supreme Court strikes down Biden's student-debt relief plan
- Main content
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Market Research
Business planning, website development, product or service selection, marketing and promotion, is it a good idea to start an online business, can i start an online business with $100, what are different types of online marketing strategies, the bottom line.
- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
How to Start an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting a Winning Business Plan: Setting Goals and Strategies
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53823-1434118722-5bfc2a8c46e0fb005119858e.jpg)
Katie Miller is a consumer financial services expert. She worked for almost two decades as an executive, leading multi-billion dollar mortgage, credit card, and savings portfolios with operations worldwide and a unique focus on the consumer. Her mortgage expertise was honed post-2008 crisis as she implemented the significant changes resulting from Dodd-Frank required regulations.
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide CURRENT ARTICLE
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Oscar Wong / Getty Images
If you want to get into the online business game, it’s a good time to start. The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped online consumer spending, including how people shop online and how they research products.
Today, 76% of Americans buy products online. Furthermore, roughly a third of people purchase items online weekly. From setting up an ecommerce business to offering web design services, there are countless avenues to explore as an entrepreneur.
Below, we’ll walk through each step to building an online business.
Key Takeaways
- When starting an online business, comprehensive market research is critical for identifying your target audience and learning how to resonate with your customers and understand their needs.
- Creating a business plan is an important step for outlining your business goals. It also includes your product description, target market, and financial projections, among other core components.
- Building your website involves setting up a domain name, finding a hosting company, and designing a strong website with consistent branding that allows your customers to navigate it intuitively.
- Choosing the right product or service to sell is essential. It’s important to think about how you’re addressing an unmet need.
- Several digital marketing strategies can be utilized, from content marketing to paid advertising, to help your business grow.
Successful online entrepreneurs study hard in order to have a thorough understanding of their market. This is important for knowing exactly how to reach your target market , because these are the people who will buy your products and drive your business growth.
At its core, market research is about understanding your customers’ needs, pain points, and solutions. It is designed to help your business better meet these needs.
Steps to Conduct Market Research
Market research involves understanding key aspects of your current and future customers. To get a clear sense of your target market, outline the characteristics of your audience—for example, age, location, gender, income, job title, and key pain points.
Once you have identified your target audience, conduct research on the following topics, which will tell you about how they make decisions and how you can better position your business:
- What are the challenges that your target market faces?
- Where do they research a given product or service?
- What are their views on pricing for this product or service?
- What factors influence their decision to make a purchase?
- Who are your competitors?
To put this market research into action, there are a number of different avenues you can take:
- Focus groups
- Competitive analysis
- Brand awareness research
- Market segmentation research
Consider the following questions that may be asked in an interview or focus group to learn more about your audience:
- “How do you search for that product?”
- “How useful was it?”
- “What words do you use when you search on Google?”
When you have completed your market research, identify what you have learned as well as your next steps based on these insights.
Creating a business plan is a key first step for all business owners . It is important for companies looking to secure funding resources. It also serves as a blueprint to summarize your key business objectives and goals.
To write a business plan , incorporate these eight main sections, which are often found in traditional templates:
- Executive summary : This is typically a one-page section that explains your objectives and includes your mission statement, core team, and why your company is positioned for success.
- Company description : This describes what you offer, your competitive advantages, and your business goals.
- Market analysis : This is where you explain your target market, market size, market trends, and competitive landscape.
- Organization and management : Explain who is working on your team and their professional background and experience.
- Service or product line : Describe the product or service you are offering, including any copyright or plans for patenting.
- Marketing and sales : Discuss your marketing and sales strategy. Discuss your pricing, key metrics, and sales plan.
- Funding request : If you are a company looking for funding, here is where you outline the capital you are requesting and where it will be allocated.
- Financial projections : Include projections for your company’s revenue and expenses. Consider including an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in this section.
A business plan is important because it helps clarify your action points, who you are, and what you offer, all in a coherent template.
Getting your business online is the next key step. In an ever-changing environment, it is important to know the tools, trends, and strategies for building a strong online presence to allow your business to grow.
Registering Your Domain
The first step is registering your name, or your website address. This can be in the form of your business name “.com.” To purchase your domain name, you can go to sites like GoDaddy or Namecheap . If you decide to build your website using WordPress, you will need to use a site such as these to host your website.
Web Hosting Companies
Alternatively, you can buy your domain name at a hosting company. These are companies like Shopify , Wix , or Amazon Web Services , that may also offer tools to build your website and release content on them.
Website Design
A well-designed website is important for many reasons. Using a website builder, such as Mailchimp or Squarespace , can allow you to choose a theme, customize your pages, create relevant content, and set up a payment page.
Other key aspects of your website design include its functionality, simplicity, and ease of use. Allowing your potential customers to navigate the site intuitively will be key to their experience. Brand consistency—in your logo, colors, and typeface, for example—is also key to creating a unified brand.
Another essential part of website design is its mobile application. You’ll want to ensure that your website runs smoothly on mobile, that images load properly, that the text is legible, and that buttons are intuitive to click.
This step focuses on how to choose the right product or service to sell. At the heart of this choice is the goal of solving a customer’s problem. But there are a number of strategies you can use to identify your product idea.
For example, you might consider analyzing companies with high-profit margins, products that align with your passion, burgeoning trends, items trending on online marketplaces, and/or customer reviews.
With this in mind, analyze how this product will get to your customers. Additionally, you may consider products that are not available in stores in your local market but are offered in communities such as Europe or Japan, for example.
Marketing strategy and promotion is an essential driver of business growth. As the digital landscape evolves, it’s important to have an effective marketing plan that resonates with changing consumer preferences and needs.
Here are questions that companies can consider as they create their marketing strategy, navigating today’s environment:
- Impact, value, and growth : What are the goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success for your business? How will you explain the value that the business provides to its customers and/or society? Create an “elevator speech”—a 30-second description of what you offer and why it’s special.
- Customer need and brand promise : How does the brand meet a customer’s need through its products and services?
- Customer experience : How will the business deliver the best experiences at each stage of the customer journey?
- Organizational model : How will the business operate to serve the customer with the most impact?
These will help you understand what types of strategies can have real impact.
Types of Marketing Strategies
Consider the following digital marketing strategies that can be used for your online business:
- Email marketing
- Social media marketing
- Paid advertising
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Content marketing
- Influencer marketing
Each of these presents a different way to reach your target audience, drive conversions, or build brand awareness, depending on your marketing goals.
You need to determine that for yourself. But before starting an online business, it’s important to assess the time, investment, and resources you’ll need to get it off the ground. While the barrier to entry can be quite low, it’s worth considering your goals and strategies for making it a reality.
However, compared with starting up a traditional brick-and-mortar business, the risks of launching an online business may be reduced due to lower upfront costs such as rent, staff, and materials, among others.
The short answer: yes. While it depends on the type of business you hope to pursue, there are many ways to set up an online business at very little cost. For example, you could offer your services doing freelance work, photography, bookkeeping, or personal training. The primary costs involved include setting up your business website, which can cost as little as $2 to $20 each year with companies such as GoDaddy.
There are a number of digital marketing strategies that online businesses can use, such as content marketing, email marketing, paid advertising, SEO, and influencer marketing. Each of these strategies can be useful, depending on your product and goals.
Starting an online business can be a powerful way to launch a new product or service while reaching a wider audience. With market research, a solid business plan, a strong website, and a digital marketing strategy, you can get started in growing your company effectively. As customers increasingly make decisions virtually, building an online business is vital to any business owner’s success.
Pew Research Center. “ For Shopping, Phones Are Common and Influencers Have Become a Factor—Especially for Young Adults .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
Ogilvy. “ Getting Future Ready with Marketing Transformation ,” Page 15.
GoDaddy. “ How Much Does a Domain Name Cost? Find Out! ”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/shutterstock_222400081-5bfc47c7c9e77c00587d6bbf.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

How Teens Can Start a Lawn Care Business: 4 Important Steps
B esides being one of the most industrious things you can do to kickstart your financial freedom journey, starting a business as a teenager is a good way to get ahead in life financially.
Think about it.
If your business generates an income, you can handle your college fees and financial needs without accruing student loans or getting into debt.
However, as you probably already know, running a business is not a walk in the park for anyone, let alone a teenager like yourself. But it’s not impossible if you take the right approach.
So, if you’re a teenager looking to start a lawn care business, here are four important steps that address the requirements, business planning, and essential tips to help set you up for success.
1. Understand Your Market and Target Audience
The first and perhaps most important thing you should understand is that success in any business, including lawn care, boils down to finding and serving the right customers.
So, to whom do you want to offer your lawn care services? Do you want to target multi-family residential communities, strip centers, malls, restaurants, commercial office buildings, etc.?
After identifying your target market, your next goal is creating a list of prospective lawn care leads and then determining the best way to approach these prospective clients because, let’s face it, if you don’t approach clients, you won’t land your first, second, or fiftieth client.
2. Plan Your Business
Every successful business achieved success because the proprietor had a plan. Creating a business plan ensures your business has a strong foundation. As you can imagine, the planning stage will involve a lot of research, fact-finding, and decision-making.
In this stage, you will also lay out your strategic approach, decide on your business financing , the scale of your business, favorable location, choose your partners, if any, and make other such decisions.
It is impossible to run a successful lawn care business if you don’t have an operations plan. So, determine all the resources and skills you will need in the field while executing your lawn care duties. For example, will you handle all the jobs, hire some people to help, or outsource some services?
3. Set Up Shop
Setting up your shop will be a process, not an event. Generally, setting up shop will consist of registering your business, getting licensed, getting insured, and setting up business banking and accounts.
It is essential to have all the legal requirements handled. In that regard, you must choose a legal business structure . Once you have all the official requirements handled, it’s time to secure a location and set up your physical shop address if you need one.
4. Understand the Cost of Running the Business
What will it take to run your lawn care business? The most basic things you need are equipment, finance, human resources, and personal sacrifice.
The upside of opening a business as a teen is that you learn early, and not having too many responsibilities gives the business a better chance to grow. The downside is that you might not have the financial muscle for it.
The best thing is that you can leverage community and family support to start your business. For example, you can ask your clients to let you use their equipment if they have any, and then you can work for them at a discount. Or, you can start with your family’s lawn care equipment if they have any.
Additionally, you can learn primary lawn care skills, such as different lawn mowing techniques , and other advanced skills, such as installing artificial grass . Hands-on skills are vital at the beginning of the business to help you save money on human resources.
There you have it: simple steps to help you start a lawn care business as a teen. As you start, remember that, like any other business, success in the lawn care industry will take time. Be patient and keep implementing strategic plans to grow your business.
The post How Teens Can Start a Lawn Care Business: 4 Important Steps appeared first on Sunny Sweet Days .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There is no strict format when it comes to making a university business plan. A business plan has to be flexible enough to be able to meet the needs or demands of a university. To make the planning successful, the following elements should be included in a university business plan. 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary provides an ...
Starting a University/College. The first step of starting your university is determining your area of education and then developing your mission statement. You should research universities similar to your own to find out what they offer and to decide if you want to provide the same courses and services. It's also important to develop a strategy ...
Capital Budget-Worksheet Template #5: An important part of any business plan, the capital equipment needs must be budgeted in detail for each semester of the first three years of program implementation of its operating expenses plus pre-inception (start-up).
Step 1: Business Formation. When starting a university, one of the first crucial steps is to establish a legal entity. The type of entity you choose will depend on various factors, such as ownership structure, liability protection, and tax considerations. Here are some common options:
Golden rules for starting a business. Keep your best start-up business ideas on track with some common sense: Don't do anything illegal. Don't compromise anyone's safety to make a buck. Don't slack on your studies in favour of making some cash. Check any rules your uni or student insurance provider might have about running a business.
Creating a University From Scratch. How Minerva is reimagining higher education now and partnering to scale for impact in the future. Imagine building a university from the ground up, and doing it specifically with 21st-century students in mind. It would mean no baggage, no legacy systems, and no outdated curricula.
2008-2009: The Academic Business Plan Format. To facilitate the operation of a non academic unit as well as to determine its feasibility, benefit, cost, and ongoing viability, it is essential that a business plan be developed to support the goals of the University and Academic Agenda. While the general form of a business plan as used in the ...
Creating a business plan is a critical part of starting your own company, and this guide offers everything you need to get started. Follow along and get started today! ... The University of Arizona Global Campus is accredited by WASC Senior College and University Commission (WSCUC), 1080 Marina Village Parkway, Suite 500, Alameda, CA 94501, 510 ...
This MOBI Business Plan Template consists of sections that relate to the content included in the MOBI Starting a Business course. You can also use this template as a guide independently. We have created this template with the input of key stakeholders such as economic development agencies, lenders, mentors and successful entrepreneurs.
Make sure you really understand your market and what your audience actually wants, and test and learn as much as possible. Expect your first assumptions about your business to change quickly as you get feedback from your target audience," he adds. 3. Play the student card outside your university.
A business plan is "a guide—a roadmap for your business that outlines goals and details how you plan to achieve those goals."--Tim Berry from Bplans site. An Introduction to Business Plans Introduction to a tutorial on business plans written by the staff at Entrepreneur magazine.
learning and real-world problem solving as soon as students begin their university experience. For businesses that recognize the value of having an innovative university in an easily accessible location, Florida Polytechnic will be a powerful resource and research . partner. The University will work to build partnerships with these businesses, and
Buerk Center Advisory Board members' presentations on writing a business plan. Marc Barros, Entrepreneur, co-founder and former CEO of Contour ... Financials and Funding for Start-Ups Presentations ... Michael G. Foster School of Business. Box 353200. University of Washington. Seattle, WA 98195-3200. Enter search text: Campus; Contact ...
A business plan describes the venture that you will create to exploit a concept. It has traditionally three primary functions: Action Plan A business plan can help to move you to action. You may have been thinking for years about starting a business or engaging in some venture, but the process may seem too daunting, too large and too ...
Provide projections for two to four years in the future, including: 1. Forecasted income (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 2. Forecasted cash flows by month (monthly for first two years, then by quarter or year thereafter), 3. Forecasted balance sheet for all years (year-end), and. 4.
What Is a College Business Plan? A college business plan is a handy tool used in order to guide the user to better success and better roads. When you think of starting up a college, or adding a business course to a college, you will also need a business plan with it. A college business plan is seen as a means of gathering steps to making it work.
If you're a university student looking to start your own business venture, using the Business Plan Template in ClickUp can help you get started. Follow these four steps to create a comprehensive business plan: 1. Define your business concept. Begin by clearly defining your business concept.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for College Students is here to guide you every step of the way! With this template, you can: Clearly define your business goals and strategies for success. Create a comprehensive financial plan and projections to attract investors. Identify potential obstacles and develop contingency plans.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
The popular original course is designed for the aspiring entrepreneur who wants to learn how to start a business.Comprised of 15 sessions that you can pursue at your own pace, Starting a Business provides step-by-step information and the essentials you need to know to start your business. The content is clearly explained and has an emphasis on learning how to write a business plan, including ...
2. Start a tutoring business. Help high school students with summer studies or younger students prep for the college classes you aced last semester. You can advertise your services on campus and across other marketing channels. Use a simple ecommerce website to sell time slots and showcase your skills and offerings. 3.
The first step is to calculate the start-up costs. Identify a list of expenses and put a dollar amount to each of them through research and requesting quotes. The SBA has a start-up costs ...
Okay, so is time management, but you can have two. Start by mapping out your week in advance, noting down your classes, study sessions, business meetings, and any other commitments you might have ...
Andrea Mac, a business owner who made $550,000 last year, refuses to pay her daughter's tuition. Mac questions the value of investing such a significant amount of money into a college education ...
4. Pet Care Services. A dog walking business is an excellent opportunity for someone who loves dogs and is good with other people's dogs. You get out every day and enjoy fresh air with grateful ...
Starting an online business can be a powerful way to launch a new product or service while reaching a wider audience. With market research, a solid business plan, a strong website, and a digital ...
So, if you're a teenager looking to start a lawn care business, here are four important steps that address the requirements, business planning, and essential tips to help set you up for success ...
According to the National Center for Education Statistics, students pursuing a bachelor's degree at a public four-year school paid an average in-state tuition of $9,596 in 2021-2022. Out-of-state students paid around $27,500, while students at private colleges paid an average of $34,041. The total cost of college varies by institution, so it's ...