When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Your Methods


Ensure understanding, reproducibility and replicability
What should you include in your methods section, and how much detail is appropriate?
Why Methods Matter
The methods section was once the most likely part of a paper to be unfairly abbreviated, overly summarized, or even relegated to hard-to-find sections of a publisher’s website. While some journals may responsibly include more detailed elements of methods in supplementary sections, the movement for increased reproducibility and rigor in science has reinstated the importance of the methods section. Methods are now viewed as a key element in establishing the credibility of the research being reported, alongside the open availability of data and results.
A clear methods section impacts editorial evaluation and readers’ understanding, and is also the backbone of transparency and replicability.
For example, the Reproducibility Project: Cancer Biology project set out in 2013 to replicate experiments from 50 high profile cancer papers, but revised their target to 18 papers once they understood how much methodological detail was not contained in the original papers.
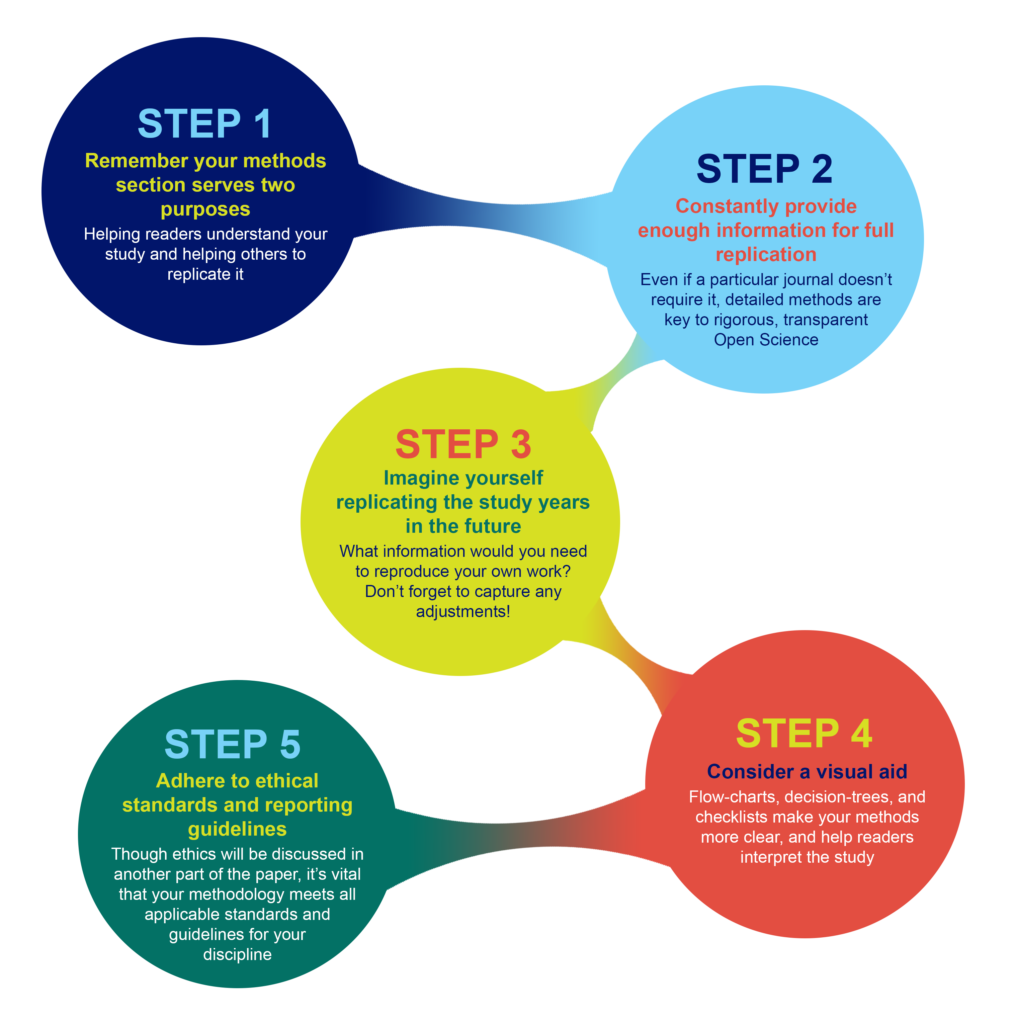
What to include in your methods section
What you include in your methods sections depends on what field you are in and what experiments you are performing. However, the general principle in place at the majority of journals is summarized well by the guidelines at PLOS ONE : “The Materials and Methods section should provide enough detail to allow suitably skilled investigators to fully replicate your study. ” The emphases here are deliberate: the methods should enable readers to understand your paper, and replicate your study. However, there is no need to go into the level of detail that a lay-person would require—the focus is on the reader who is also trained in your field, with the suitable skills and knowledge to attempt a replication.
A constant principle of rigorous science
A methods section that enables other researchers to understand and replicate your results is a constant principle of rigorous, transparent, and Open Science. Aim to be thorough, even if a particular journal doesn’t require the same level of detail . Reproducibility is all of our responsibility. You cannot create any problems by exceeding a minimum standard of information. If a journal still has word-limits—either for the overall article or specific sections—and requires some methodological details to be in a supplemental section, that is OK as long as the extra details are searchable and findable .
Imagine replicating your own work, years in the future
As part of PLOS’ presentation on Reproducibility and Open Publishing (part of UCSF’s Reproducibility Series ) we recommend planning the level of detail in your methods section by imagining you are writing for your future self, replicating your own work. When you consider that you might be at a different institution, with different account logins, applications, resources, and access levels—you can help yourself imagine the level of specificity that you yourself would require to redo the exact experiment. Consider:
- Which details would you need to be reminded of?
- Which cell line, or antibody, or software, or reagent did you use, and does it have a Research Resource ID (RRID) that you can cite?
- Which version of a questionnaire did you use in your survey?
- Exactly which visual stimulus did you show participants, and is it publicly available?
- What participants did you decide to exclude?
- What process did you adjust, during your work?
Tip: Be sure to capture any changes to your protocols
You yourself would want to know about any adjustments, if you ever replicate the work, so you can surmise that anyone else would want to as well. Even if a necessary adjustment you made was not ideal, transparency is the key to ensuring this is not regarded as an issue in the future. It is far better to transparently convey any non-optimal methods, or methodological constraints, than to conceal them, which could result in reproducibility or ethical issues downstream.
Visual aids for methods help when reading the whole paper
Consider whether a visual representation of your methods could be appropriate or aid understanding your process. A visual reference readers can easily return to, like a flow-diagram, decision-tree, or checklist, can help readers to better understand the complete article, not just the methods section.
Ethical Considerations
In addition to describing what you did, it is just as important to assure readers that you also followed all relevant ethical guidelines when conducting your research. While ethical standards and reporting guidelines are often presented in a separate section of a paper, ensure that your methods and protocols actually follow these guidelines. Read more about ethics .
Existing standards, checklists, guidelines, partners
While the level of detail contained in a methods section should be guided by the universal principles of rigorous science outlined above, various disciplines, fields, and projects have worked hard to design and develop consistent standards, guidelines, and tools to help with reporting all types of experiment. Below, you’ll find some of the key initiatives. Ensure you read the submission guidelines for the specific journal you are submitting to, in order to discover any further journal- or field-specific policies to follow, or initiatives/tools to utilize.
Tip: Keep your paper moving forward by providing the proper paperwork up front
Be sure to check the journal guidelines and provide the necessary documents with your manuscript submission. Collecting the necessary documentation can greatly slow the first round of peer review, or cause delays when you submit your revision.
Randomized Controlled Trials – CONSORT The Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) project covers various initiatives intended to prevent the problems of inadequate reporting of randomized controlled trials. The primary initiative is an evidence-based minimum set of recommendations for reporting randomized trials known as the CONSORT Statement .
Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses – PRISMA The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses ( PRISMA ) is an evidence-based minimum set of items focusing on the reporting of reviews evaluating randomized trials and other types of research.
Research using Animals – ARRIVE The Animal Research: Reporting of In Vivo Experiments ( ARRIVE ) guidelines encourage maximizing the information reported in research using animals thereby minimizing unnecessary studies. (Original study and proposal , and updated guidelines , in PLOS Biology .)
Laboratory Protocols Protocols.io has developed a platform specifically for the sharing and updating of laboratory protocols , which are assigned their own DOI and can be linked from methods sections of papers to enhance reproducibility. Contextualize your protocol and improve discovery with an accompanying Lab Protocol article in PLOS ONE .
Consistent reporting of Materials, Design, and Analysis – the MDAR checklist A cross-publisher group of editors and experts have developed, tested, and rolled out a checklist to help establish and harmonize reporting standards in the Life Sciences . The checklist , which is available for use by authors to compile their methods, and editors/reviewers to check methods, establishes a minimum set of requirements in transparent reporting and is adaptable to any discipline within the Life Sciences, by covering a breadth of potentially relevant methodological items and considerations. If you are in the Life Sciences and writing up your methods section, try working through the MDAR checklist and see whether it helps you include all relevant details into your methods, and whether it reminded you of anything you might have missed otherwise.
Summary Writing tips
The main challenge you may find when writing your methods is keeping it readable AND covering all the details needed for reproducibility and replicability. While this is difficult, do not compromise on rigorous standards for credibility!

- Keep in mind future replicability, alongside understanding and readability.
- Follow checklists, and field- and journal-specific guidelines.
- Consider a commitment to rigorous and transparent science a personal responsibility, and not just adhering to journal guidelines.
- Establish whether there are persistent identifiers for any research resources you use that can be specifically cited in your methods section.
- Deposit your laboratory protocols in Protocols.io, establishing a permanent link to them. You can update your protocols later if you improve on them, as can future scientists who follow your protocols.
- Consider visual aids like flow-diagrams, lists, to help with reading other sections of the paper.
- Be specific about all decisions made during the experiments that someone reproducing your work would need to know.

Don’t
- Summarize or abbreviate methods without giving full details in a discoverable supplemental section.
- Presume you will always be able to remember how you performed the experiments, or have access to private or institutional notebooks and resources.
- Attempt to hide constraints or non-optimal decisions you had to make–transparency is the key to ensuring the credibility of your research.
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Staff Directory
- Library Policies
- Hege Research Award
- Quaker Archives
- Art Gallery
- Student Support
- Teaching & Learning
- Reserving spaces
- Technology Lending
- Interlibrary Loan
- Course Reserves
- Copyright & Fair Use
- Poster Printing
- Virtual Reference
- Research Guides
- Off-campus access
- Digital Scholarship
- Guilford Sources
- Open Educational Resources
- Quaker Collections
- Digital Collections
- College Archives
- Underground Railroad
- Universities Studying Slavery
- Images & Exhibitions
Service Alert

Hege Library & Learning Technologies
Guide for Thesis Research
- Introduction to the Thesis Process
- Project Planning
- Literature Review
- Theoretical Frameworks
- Research Methodology
- GC Honors Program Theses
- Thesis Submission Instructions This link opens in a new window
- Accessing Guilford Theses from 1898 to 2020 This link opens in a new window
Basics of Methodology
Research is a process of inquiry that is carried out in a pondered, organized, and strategic manner. In order to obtain high quality results, it is important to understand methodology.
Research methodology refers to how your project will be designed, what you will observe or measure, and how you will collect and analyze data. The methods you choose must be appropriate for your field and for the specific research questions you are setting out to answer.
A strong understanding of methodology will help you:
- apply appropriate research techniques
- design effective data collection instruments
- analyze and interpret your data
- develop well-founded conclusions
Below, you will find resources that mostly cover general aspects of research methodology. In the left column, you will find resources that specifically cover qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research.
General Works on Methodology
Qualitative Research
Quantitative Research
Mixed Methods Research
- << Previous: Theoretical Frameworks
- Next: Citation >>
- Last Updated: Jan 23, 2024 4:31 PM
- URL: https://library.guilford.edu/thesis-guide
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
Research Methods | Definition, Types, Examples
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analysing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design . When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make.
First, decide how you will collect data . Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question :
- Qualitative vs quantitative : Will your data take the form of words or numbers?
- Primary vs secondary : Will you collect original data yourself, or will you use data that have already been collected by someone else?
- Descriptive vs experimental : Will you take measurements of something as it is, or will you perform an experiment?
Second, decide how you will analyse the data .
- For quantitative data, you can use statistical analysis methods to test relationships between variables.
- For qualitative data, you can use methods such as thematic analysis to interpret patterns and meanings in the data.
Table of contents
Methods for collecting data, examples of data collection methods, methods for analysing data, examples of data analysis methods, frequently asked questions about methodology.
Data are the information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question . The type of data you need depends on the aims of your research.
Qualitative vs quantitative data
Your choice of qualitative or quantitative data collection depends on the type of knowledge you want to develop.
For questions about ideas, experiences and meanings, or to study something that can’t be described numerically, collect qualitative data .
If you want to develop a more mechanistic understanding of a topic, or your research involves hypothesis testing , collect quantitative data .
You can also take a mixed methods approach, where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Primary vs secondary data
Primary data are any original information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys , observations and experiments ). Secondary data are information that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in a government census or previous scientific studies).
If you are exploring a novel research question, you’ll probably need to collect primary data. But if you want to synthesise existing knowledge, analyse historical trends, or identify patterns on a large scale, secondary data might be a better choice.
Descriptive vs experimental data
In descriptive research , you collect data about your study subject without intervening. The validity of your research will depend on your sampling method .
In experimental research , you systematically intervene in a process and measure the outcome. The validity of your research will depend on your experimental design .
To conduct an experiment, you need to be able to vary your independent variable , precisely measure your dependent variable, and control for confounding variables . If it’s practically and ethically possible, this method is the best choice for answering questions about cause and effect.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Your data analysis methods will depend on the type of data you collect and how you prepare them for analysis.
Data can often be analysed both quantitatively and qualitatively. For example, survey responses could be analysed qualitatively by studying the meanings of responses or quantitatively by studying the frequencies of responses.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative analysis is used to understand words, ideas, and experiences. You can use it to interpret data that were collected:
- From open-ended survey and interview questions, literature reviews, case studies, and other sources that use text rather than numbers.
- Using non-probability sampling methods .
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions.
Quantitative analysis methods
Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive studies) or cause-and-effect relationships (in experiments).
You can use quantitative analysis to interpret data that were collected either:
- During an experiment.
- Using probability sampling methods .
Because the data are collected and analysed in a statistically valid way, the results of quantitative analysis can be easily standardised and shared among researchers.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population. Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research.
For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
Statistical sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population. There are various sampling methods you can use to ensure that your sample is representative of the population as a whole.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyse data (e.g. experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
Is this article helpful?
More interesting articles.
- A Quick Guide to Experimental Design | 5 Steps & Examples
- Between-Subjects Design | Examples, Pros & Cons
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
- Cluster Sampling | A Simple Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Confounding Variables | Definition, Examples & Controls
- Construct Validity | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Content Analysis | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Control Groups and Treatment Groups | Uses & Examples
- Controlled Experiments | Methods & Examples of Control
- Correlation vs Causation | Differences, Designs & Examples
- Correlational Research | Guide, Design & Examples
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Cross-Sectional Study | Definitions, Uses & Examples
- Data Cleaning | A Guide with Examples & Steps
- Data Collection Methods | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Descriptive Research Design | Definition, Methods & Examples
- Doing Survey Research | A Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
- Explanatory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Explanatory vs Response Variables | Definitions & Examples
- Exploratory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- External Validity | Types, Threats & Examples
- Extraneous Variables | Examples, Types, Controls
- Face Validity | Guide with Definition & Examples
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Guide & Examples
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | Examples & Definition
- Independent vs Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
- Inductive Reasoning | Types, Examples, Explanation
- Inductive vs Deductive Research Approach (with Examples)
- Internal Validity | Definition, Threats & Examples
- Internal vs External Validity | Understanding Differences & Examples
- Longitudinal Study | Definition, Approaches & Examples
- Mediator vs Moderator Variables | Differences & Examples
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Multistage Sampling | An Introductory Guide with Examples
- Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Population vs Sample | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods
- Quasi-Experimental Design | Definition, Types & Examples
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
- Reliability vs Validity in Research | Differences, Types & Examples
- Reproducibility vs Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Research Design | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques, & Examples
- Semi-Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Simple Random Sampling | Definition, Steps & Examples
- Stratified Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Systematic Review | Definition, Examples & Guide
- Systematic Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
- The 4 Types of Reliability in Research | Definitions & Examples
- The 4 Types of Validity | Types, Definitions & Examples
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
- Triangulation in Research | Guide, Types, Examples
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Examples
- Types of Variables in Research | Definitions & Examples
- Unstructured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Are Control Variables | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Case-Control Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
- What Is a Double-Barrelled Question?
- What Is a Double-Blind Study? | Introduction & Examples
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- What Is a Prospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Retrospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
- What Is Concurrent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Content Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convergent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Criterion Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Deductive Reasoning? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Discriminant Validity? | Definition & Example
- What Is Ecological Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Ethnography? | Meaning, Guide & Examples
- What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
- What Is Predictive Validity? | Examples & Definition
- What Is Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Purposive Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition & Methods
- What Is Quota Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What is Secondary Research? | Definition, Types, & Examples
- What Is Snowball Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- Within-Subjects Design | Explanation, Approaches, Examples

How to Write a Research Paper
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Research Paper Fundamentals
How to choose a topic or question, how to create a working hypothesis or thesis, common research paper methodologies, how to gather and organize evidence , how to write an outline for your research paper, how to write a rough draft, how to revise your draft, how to produce a final draft, resources for teachers .
It is not fair to say that no one writes anymore. Just about everyone writes text messages, brief emails, or social media posts every single day. Yet, most people don't have a lot of practice with the formal, organized writing required for a good academic research paper. This guide contains links to a variety of resources that can help demystify the process. Some of these resources are intended for teachers; they contain exercises, activities, and teaching strategies. Other resources are intended for direct use by students who are struggling to write papers, or are looking for tips to make the process go more smoothly.
The resources in this section are designed to help students understand the different types of research papers, the general research process, and how to manage their time. Below, you'll find links from university writing centers, the trusted Purdue Online Writing Lab, and more.
What is an Academic Research Paper?
"Genre and the Research Paper" (Purdue OWL)
There are different types of research papers. Different types of scholarly questions will lend themselves to one format or another. This is a brief introduction to the two main genres of research paper: analytic and argumentative.
"7 Most Popular Types of Research Papers" (Personal-writer.com)
This resource discusses formats that high school students commonly encounter, such as the compare and contrast essay and the definitional essay. Please note that the inclusion of this link is not an endorsement of this company's paid service.
How to Prepare and Plan Out Writing a Research Paper
Teachers can give their students a step-by-step guide like these to help them understand the different steps of the research paper process. These guides can be combined with the time management tools in the next subsection to help students come up with customized calendars for completing their papers.
"Ten Steps for Writing Research Papers" (American University)
This resource from American University is a comprehensive guide to the research paper writing process, and includes examples of proper research questions and thesis topics.
"Steps in Writing a Research Paper" (SUNY Empire State College)
This guide breaks the research paper process into 11 steps. Each "step" links to a separate page, which describes the work entailed in completing it.
How to Manage Time Effectively
The links below will help students determine how much time is necessary to complete a paper. If your sources are not available online or at your local library, you'll need to leave extra time for the Interlibrary Loan process. Remember that, even if you do not need to consult secondary sources, you'll still need to leave yourself ample time to organize your thoughts.
"Research Paper Planner: Timeline" (Baylor University)
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment.
"Research Paper Planner" (UCLA)
UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
There's a reason teachers spend a long time talking about choosing a good topic. Without a good topic and a well-formulated research question, it is almost impossible to write a clear and organized paper. The resources below will help you generate ideas and formulate precise questions.
"How to Select a Research Topic" (Univ. of Michigan-Flint)
This resource is designed for college students who are struggling to come up with an appropriate topic. A student who uses this resource and still feels unsure about his or her topic should consult the course instructor for further personalized assistance.
"25 Interesting Research Paper Topics to Get You Started" (Kibin)
This resource, which is probably most appropriate for high school students, provides a list of specific topics to help get students started. It is broken into subsections, such as "paper topics on local issues."
"Writing a Good Research Question" (Grand Canyon University)
This introduction to research questions includes some embedded videos, as well as links to scholarly articles on research questions. This resource would be most appropriate for teachers who are planning lessons on research paper fundamentals.
"How to Write a Research Question the Right Way" (Kibin)
This student-focused resource provides more detail on writing research questions. The language is accessible, and there are embedded videos and examples of good and bad questions.
It is important to have a rough hypothesis or thesis in mind at the beginning of the research process. People who have a sense of what they want to say will have an easier time sorting through scholarly sources and other information. The key, of course, is not to become too wedded to the draft hypothesis or thesis. Just about every working thesis gets changed during the research process.
CrashCourse Video: "Sociology Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is tailored to sociology students, it is applicable to students in a variety of social science disciplines. This video does a good job demonstrating the connection between the brainstorming that goes into selecting a research question and the formulation of a working hypothesis.
"How to Write a Thesis Statement for an Analytical Essay" (YouTube)
Students writing analytical essays will not develop the same type of working hypothesis as students who are writing research papers in other disciplines. For these students, developing the working thesis may happen as a part of the rough draft (see the relevant section below).
"Research Hypothesis" (Oakland Univ.)
This resource provides some examples of hypotheses in social science disciplines like Political Science and Criminal Justice. These sample hypotheses may also be useful for students in other soft social sciences and humanities disciplines like History.
When grading a research paper, instructors look for a consistent methodology. This section will help you understand different methodological approaches used in research papers. Students will get the most out of these resources if they use them to help prepare for conversations with teachers or discussions in class.
"Types of Research Designs" (USC)
A "research design," used for complex papers, is related to the paper's method. This resource contains introductions to a variety of popular research designs in the social sciences. Although it is not the most intuitive site to read, the information here is very valuable.
"Major Research Methods" (YouTube)
Although this video is a bit on the dry side, it provides a comprehensive overview of the major research methodologies in a format that might be more accessible to students who have struggled with textbooks or other written resources.
"Humanities Research Strategies" (USC)
This is a portal where students can learn about four methodological approaches for humanities papers: Historical Methodologies, Textual Criticism, Conceptual Analysis, and the Synoptic method.
"Selected Major Social Science Research Methods: Overview" (National Academies Press)
This appendix from the book Using Science as Evidence in Public Policy , printed by National Academies Press, introduces some methods used in social science papers.
"Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: 6. The Methodology" (USC)
This resource from the University of Southern California's library contains tips for writing a methodology section in a research paper.
How to Determine the Best Methodology for You
Anyone who is new to writing research papers should be sure to select a method in consultation with their instructor. These resources can be used to help prepare for that discussion. They may also be used on their own by more advanced students.
"Choosing Appropriate Research Methodologies" (Palgrave Study Skills)
This friendly and approachable resource from Palgrave Macmillan can be used by students who are just starting to think about appropriate methodologies.
"How to Choose Your Research Methods" (NFER (UK))
This is another approachable resource students can use to help narrow down the most appropriate methods for their research projects.
The resources in this section introduce the process of gathering scholarly sources and collecting evidence. You'll find a range of material here, from introductory guides to advanced explications best suited to college students. Please consult the LitCharts How to Do Academic Research guide for a more comprehensive list of resources devoted to finding scholarly literature.
Google Scholar
Students who have access to library websites with detailed research guides should start there, but people who do not have access to those resources can begin their search for secondary literature here.
"Gathering Appropriate Information" (Texas Gateway)
This resource from the Texas Gateway for online resources introduces students to the research process, and contains interactive exercises. The level of complexity is suitable for middle school, high school, and introductory college classrooms.
"An Overview of Quantitative and Qualitative Data Collection Methods" (NSF)
This PDF from the National Science Foundation goes into detail about best practices and pitfalls in data collection across multiple types of methodologies.
"Social Science Methods for Data Collection and Analysis" (Swiss FIT)
This resource is appropriate for advanced undergraduates or teachers looking to create lessons on research design and data collection. It covers techniques for gathering data via interviews, observations, and other methods.
"Collecting Data by In-depth Interviewing" (Leeds Univ.)
This resource contains enough information about conducting interviews to make it useful for teachers who want to create a lesson plan, but is also accessible enough for college juniors or seniors to make use of it on their own.
There is no "one size fits all" outlining technique. Some students might devote all their energy and attention to the outline in order to avoid the paper. Other students may benefit from being made to sit down and organize their thoughts into a lengthy sentence outline. The resources in this section include strategies and templates for multiple types of outlines.
"Topic vs. Sentence Outlines" (UC Berkeley)
This resource introduces two basic approaches to outlining: the shorter topic-based approach, and the longer, more detailed sentence-based approach. This resource also contains videos on how to develop paper paragraphs from the sentence-based outline.
"Types of Outlines and Samples" (Purdue OWL)
The Purdue Online Writing Lab's guide is a slightly less detailed discussion of different types of outlines. It contains several sample outlines.
"Writing An Outline" (Austin C.C.)
This resource from a community college contains sample outlines from an American history class that students can use as models.
"How to Structure an Outline for a College Paper" (YouTube)
This brief (sub-2 minute) video from the ExpertVillage YouTube channel provides a model of outline writing for students who are struggling with the idea.
"Outlining" (Harvard)
This is a good resource to consult after completing a draft outline. It offers suggestions for making sure your outline avoids things like unnecessary repetition.
As with outlines, rough drafts can take on many different forms. These resources introduce teachers and students to the various approaches to writing a rough draft. This section also includes resources that will help you cite your sources appropriately according to the MLA, Chicago, and APA style manuals.
"Creating a Rough Draft for a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
This resource is useful for teachers in particular, as it provides some suggested exercises to help students with writing a basic rough draft.
Rough Draft Assignment (Duke of Definition)
This sample assignment, with a brief list of tips, was developed by a high school teacher who runs a very successful and well-reviewed page of educational resources.
"Creating the First Draft of Your Research Paper" (Concordia Univ.)
This resource will be helpful for perfectionists or procrastinators, as it opens by discussing the problem of avoiding writing. It also provides a short list of suggestions meant to get students writing.
Using Proper Citations
There is no such thing as a rough draft of a scholarly citation. These links to the three major citation guides will ensure that your citations follow the correct format. Please consult the LitCharts How to Cite Your Sources guide for more resources.
Chicago Manual of Style Citation Guide
Some call The Chicago Manual of Style , which was first published in 1906, "the editors' Bible." The manual is now in its 17th edition, and is popular in the social sciences, historical journals, and some other fields in the humanities.
APA Citation Guide
According to the American Psychological Association, this guide was developed to aid reading comprehension, clarity of communication, and to reduce bias in language in the social and behavioral sciences. Its first full edition was published in 1952, and it is now in its sixth edition.
MLA Citation Guide
The Modern Language Association style is used most commonly within the liberal arts and humanities. The MLA Style Manual and Guide to Scholarly Publishing was first published in 1985 and (as of 2008) is in its third edition.
Any professional scholar will tell you that the best research papers are made in the revision stage. No matter how strong your research question or working thesis, it is not possible to write a truly outstanding paper without devoting energy to revision. These resources provide examples of revision exercises for the classroom, as well as tips for students working independently.
"The Art of Revision" (Univ. of Arizona)
This resource provides a wealth of information and suggestions for both students and teachers. There is a list of suggested exercises that teachers might use in class, along with a revision checklist that is useful for teachers and students alike.
"Script for Workshop on Revision" (Vanderbilt University)
Vanderbilt's guide for leading a 50-minute revision workshop can serve as a model for teachers who wish to guide students through the revision process during classtime.
"Revising Your Paper" (Univ. of Washington)
This detailed handout was designed for students who are beginning the revision process. It discusses different approaches and methods for revision, and also includes a detailed list of things students should look for while they revise.
"Revising Drafts" (UNC Writing Center)
This resource is designed for students and suggests things to look for during the revision process. It provides steps for the process and has a FAQ for students who have questions about why it is important to revise.
Conferencing with Writing Tutors and Instructors
No writer is so good that he or she can't benefit from meeting with instructors or peer tutors. These resources from university writing, learning, and communication centers provide suggestions for how to get the most out of these one-on-one meetings.
"Getting Feedback" (UNC Writing Center)
This very helpful resource talks about how to ask for feedback during the entire writing process. It contains possible questions that students might ask when developing an outline, during the revision process, and after the final draft has been graded.
"Prepare for Your Tutoring Session" (Otis College of Art and Design)
This guide from a university's student learning center contains a lot of helpful tips for getting the most out of working with a writing tutor.
"The Importance of Asking Your Professor" (Univ. of Waterloo)
This article from the university's Writing and Communication Centre's blog contains some suggestions for how and when to get help from professors and Teaching Assistants.
Once you've revised your first draft, you're well on your way to handing in a polished paper. These resources—each of them produced by writing professionals at colleges and universities—outline the steps required in order to produce a final draft. You'll find proofreading tips and checklists in text and video form.
"Developing a Final Draft of a Research Paper" (Univ. of Minnesota)
While this resource contains suggestions for revision, it also features a couple of helpful checklists for the last stages of completing a final draft.
Basic Final Draft Tips and Checklist (Univ. of Maryland-University College)
This short and accessible resource, part of UMUC's very thorough online guide to writing and research, contains a very basic checklist for students who are getting ready to turn in their final drafts.
Final Draft Checklist (Everett C.C.)
This is another accessible final draft checklist, appropriate for both high school and college students. It suggests reading your essay aloud at least once.
"How to Proofread Your Final Draft" (YouTube)
This video (approximately 5 minutes), produced by Eastern Washington University, gives students tips on proofreading final drafts.
"Proofreading Tips" (Georgia Southern-Armstrong)
This guide will help students learn how to spot common errors in their papers. It suggests focusing on content and editing for grammar and mechanics.
This final set of resources is intended specifically for high school and college instructors. It provides links to unit plans and classroom exercises that can help improve students' research and writing skills. You'll find resources that give an overview of the process, along with activities that focus on how to begin and how to carry out research.
"Research Paper Complete Resources Pack" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, rubrics, and other resources is designed for high school students. The resources in this packet are aligned to Common Core standards.
"Research Paper—Complete Unit" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This packet of assignments, notes, PowerPoints, and other resources has a 4/4 rating with over 700 ratings. It is designed for high school teachers, but might also be useful to college instructors who work with freshmen.
"Teaching Students to Write Good Papers" (Yale)
This resource from Yale's Center for Teaching and Learning is designed for college instructors, and it includes links to appropriate activities and exercises.
"Research Paper Writing: An Overview" (CUNY Brooklyn)
CUNY Brooklyn offers this complete lesson plan for introducing students to research papers. It includes an accompanying set of PowerPoint slides.
"Lesson Plan: How to Begin Writing a Research Paper" (San Jose State Univ.)
This lesson plan is designed for students in the health sciences, so teachers will have to modify it for their own needs. It includes a breakdown of the brainstorming, topic selection, and research question process.
"Quantitative Techniques for Social Science Research" (Univ. of Pittsburgh)
This is a set of PowerPoint slides that can be used to introduce students to a variety of quantitative methods used in the social sciences.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 1929 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 40,694 quotes across 1929 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .
Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 6. The Methodology
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The methods section describes actions taken to investigate a research problem and the rationale for the application of specific procedures or techniques used to identify, select, process, and analyze information applied to understanding the problem, thereby, allowing the reader to critically evaluate a study’s overall validity and reliability. The methodology section of a research paper answers two main questions: How was the data collected or generated? And, how was it analyzed? The writing should be direct and precise and always written in the past tense.
Kallet, Richard H. "How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper." Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004): 1229-1232.
Importance of a Good Methodology Section
You must explain how you obtained and analyzed your results for the following reasons:
- Readers need to know how the data was obtained because the method you chose affects the results and, by extension, how you interpreted their significance in the discussion section of your paper.
- Methodology is crucial for any branch of scholarship because an unreliable method produces unreliable results and, as a consequence, undermines the value of your analysis of the findings.
- In most cases, there are a variety of different methods you can choose to investigate a research problem. The methodology section of your paper should clearly articulate the reasons why you have chosen a particular procedure or technique.
- The reader wants to know that the data was collected or generated in a way that is consistent with accepted practice in the field of study. For example, if you are using a multiple choice questionnaire, readers need to know that it offered your respondents a reasonable range of answers to choose from.
- The method must be appropriate to fulfilling the overall aims of the study. For example, you need to ensure that you have a large enough sample size to be able to generalize and make recommendations based upon the findings.
- The methodology should discuss the problems that were anticipated and the steps you took to prevent them from occurring. For any problems that do arise, you must describe the ways in which they were minimized or why these problems do not impact in any meaningful way your interpretation of the findings.
- In the social and behavioral sciences, it is important to always provide sufficient information to allow other researchers to adopt or replicate your methodology. This information is particularly important when a new method has been developed or an innovative use of an existing method is utilized.
Bem, Daryl J. Writing the Empirical Journal Article. Psychology Writing Center. University of Washington; Denscombe, Martyn. The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects . 5th edition. Buckingham, UK: Open University Press, 2014; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Groups of Research Methods
There are two main groups of research methods in the social sciences:
- The e mpirical-analytical group approaches the study of social sciences in a similar manner that researchers study the natural sciences . This type of research focuses on objective knowledge, research questions that can be answered yes or no, and operational definitions of variables to be measured. The empirical-analytical group employs deductive reasoning that uses existing theory as a foundation for formulating hypotheses that need to be tested. This approach is focused on explanation.
- The i nterpretative group of methods is focused on understanding phenomenon in a comprehensive, holistic way . Interpretive methods focus on analytically disclosing the meaning-making practices of human subjects [the why, how, or by what means people do what they do], while showing how those practices arrange so that it can be used to generate observable outcomes. Interpretive methods allow you to recognize your connection to the phenomena under investigation. However, the interpretative group requires careful examination of variables because it focuses more on subjective knowledge.
II. Content
The introduction to your methodology section should begin by restating the research problem and underlying assumptions underpinning your study. This is followed by situating the methods you used to gather, analyze, and process information within the overall “tradition” of your field of study and within the particular research design you have chosen to study the problem. If the method you choose lies outside of the tradition of your field [i.e., your review of the literature demonstrates that the method is not commonly used], provide a justification for how your choice of methods specifically addresses the research problem in ways that have not been utilized in prior studies.
The remainder of your methodology section should describe the following:
- Decisions made in selecting the data you have analyzed or, in the case of qualitative research, the subjects and research setting you have examined,
- Tools and methods used to identify and collect information, and how you identified relevant variables,
- The ways in which you processed the data and the procedures you used to analyze that data, and
- The specific research tools or strategies that you utilized to study the underlying hypothesis and research questions.
In addition, an effectively written methodology section should:
- Introduce the overall methodological approach for investigating your research problem . Is your study qualitative or quantitative or a combination of both (mixed method)? Are you going to take a special approach, such as action research, or a more neutral stance?
- Indicate how the approach fits the overall research design . Your methods for gathering data should have a clear connection to your research problem. In other words, make sure that your methods will actually address the problem. One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper.
- Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use , such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data, such as a data set or archival documents, describe how it was originally created or gathered and by whom. Also be sure to explain how older data is still relevant to investigating the current research problem.
- Explain how you intend to analyze your results . Will you use statistical analysis? Will you use specific theoretical perspectives to help you analyze a text or explain observed behaviors? Describe how you plan to obtain an accurate assessment of relationships, patterns, trends, distributions, and possible contradictions found in the data.
- Provide background and a rationale for methodologies that are unfamiliar for your readers . Very often in the social sciences, research problems and the methods for investigating them require more explanation/rationale than widely accepted rules governing the natural and physical sciences. Be clear and concise in your explanation.
- Provide a justification for subject selection and sampling procedure . For instance, if you propose to conduct interviews, how do you intend to select the sample population? If you are analyzing texts, which texts have you chosen, and why? If you are using statistics, why is this set of data being used? If other data sources exist, explain why the data you chose is most appropriate to addressing the research problem.
- Provide a justification for case study selection . A common method of analyzing research problems in the social sciences is to analyze specific cases. These can be a person, place, event, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis that are either examined as a singular topic of in-depth investigation or multiple topics of investigation studied for the purpose of comparing or contrasting findings. In either method, you should explain why a case or cases were chosen and how they specifically relate to the research problem.
- Describe potential limitations . Are there any practical limitations that could affect your data collection? How will you attempt to control for potential confounding variables and errors? If your methodology may lead to problems you can anticipate, state this openly and show why pursuing this methodology outweighs the risk of these problems cropping up.
NOTE : Once you have written all of the elements of the methods section, subsequent revisions should focus on how to present those elements as clearly and as logically as possibly. The description of how you prepared to study the research problem, how you gathered the data, and the protocol for analyzing the data should be organized chronologically. For clarity, when a large amount of detail must be presented, information should be presented in sub-sections according to topic. If necessary, consider using appendices for raw data.
ANOTHER NOTE : If you are conducting a qualitative analysis of a research problem , the methodology section generally requires a more elaborate description of the methods used as well as an explanation of the processes applied to gathering and analyzing of data than is generally required for studies using quantitative methods. Because you are the primary instrument for generating the data [e.g., through interviews or observations], the process for collecting that data has a significantly greater impact on producing the findings. Therefore, qualitative research requires a more detailed description of the methods used.
YET ANOTHER NOTE : If your study involves interviews, observations, or other qualitative techniques involving human subjects , you may be required to obtain approval from the university's Office for the Protection of Research Subjects before beginning your research. This is not a common procedure for most undergraduate level student research assignments. However, i f your professor states you need approval, you must include a statement in your methods section that you received official endorsement and adequate informed consent from the office and that there was a clear assessment and minimization of risks to participants and to the university. This statement informs the reader that your study was conducted in an ethical and responsible manner. In some cases, the approval notice is included as an appendix to your paper.
III. Problems to Avoid
Irrelevant Detail The methodology section of your paper should be thorough but concise. Do not provide any background information that does not directly help the reader understand why a particular method was chosen, how the data was gathered or obtained, and how the data was analyzed in relation to the research problem [note: analyzed, not interpreted! Save how you interpreted the findings for the discussion section]. With this in mind, the page length of your methods section will generally be less than any other section of your paper except the conclusion.
Unnecessary Explanation of Basic Procedures Remember that you are not writing a how-to guide about a particular method. You should make the assumption that readers possess a basic understanding of how to investigate the research problem on their own and, therefore, you do not have to go into great detail about specific methodological procedures. The focus should be on how you applied a method , not on the mechanics of doing a method. An exception to this rule is if you select an unconventional methodological approach; if this is the case, be sure to explain why this approach was chosen and how it enhances the overall process of discovery.
Problem Blindness It is almost a given that you will encounter problems when collecting or generating your data, or, gaps will exist in existing data or archival materials. Do not ignore these problems or pretend they did not occur. Often, documenting how you overcame obstacles can form an interesting part of the methodology. It demonstrates to the reader that you can provide a cogent rationale for the decisions you made to minimize the impact of any problems that arose.
Literature Review Just as the literature review section of your paper provides an overview of sources you have examined while researching a particular topic, the methodology section should cite any sources that informed your choice and application of a particular method [i.e., the choice of a survey should include any citations to the works you used to help construct the survey].
It’s More than Sources of Information! A description of a research study's method should not be confused with a description of the sources of information. Such a list of sources is useful in and of itself, especially if it is accompanied by an explanation about the selection and use of the sources. The description of the project's methodology complements a list of sources in that it sets forth the organization and interpretation of information emanating from those sources.
Azevedo, L.F. et al. "How to Write a Scientific Paper: Writing the Methods Section." Revista Portuguesa de Pneumologia 17 (2011): 232-238; Blair Lorrie. “Choosing a Methodology.” In Writing a Graduate Thesis or Dissertation , Teaching Writing Series. (Rotterdam: Sense Publishers 2016), pp. 49-72; Butin, Dan W. The Education Dissertation A Guide for Practitioner Scholars . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin, 2010; Carter, Susan. Structuring Your Research Thesis . New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2012; Kallet, Richard H. “How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper.” Respiratory Care 49 (October 2004):1229-1232; Lunenburg, Frederick C. Writing a Successful Thesis or Dissertation: Tips and Strategies for Students in the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2008. Methods Section. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin, Madison; Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. “The Method Chapter: Describing Your Research Plan.” In Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . (Thousand Oaks, Sage Publications, 2015), pp. 87-115; What is Interpretive Research. Institute of Public and International Affairs, University of Utah; Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Methods and Materials. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Writing Tip
Statistical Designs and Tests? Do Not Fear Them!
Don't avoid using a quantitative approach to analyzing your research problem just because you fear the idea of applying statistical designs and tests. A qualitative approach, such as conducting interviews or content analysis of archival texts, can yield exciting new insights about a research problem, but it should not be undertaken simply because you have a disdain for running a simple regression. A well designed quantitative research study can often be accomplished in very clear and direct ways, whereas, a similar study of a qualitative nature usually requires considerable time to analyze large volumes of data and a tremendous burden to create new paths for analysis where previously no path associated with your research problem had existed.
To locate data and statistics, GO HERE .
Another Writing Tip
Knowing the Relationship Between Theories and Methods
There can be multiple meaning associated with the term "theories" and the term "methods" in social sciences research. A helpful way to delineate between them is to understand "theories" as representing different ways of characterizing the social world when you research it and "methods" as representing different ways of generating and analyzing data about that social world. Framed in this way, all empirical social sciences research involves theories and methods, whether they are stated explicitly or not. However, while theories and methods are often related, it is important that, as a researcher, you deliberately separate them in order to avoid your theories playing a disproportionate role in shaping what outcomes your chosen methods produce.
Introspectively engage in an ongoing dialectic between the application of theories and methods to help enable you to use the outcomes from your methods to interrogate and develop new theories, or ways of framing conceptually the research problem. This is how scholarship grows and branches out into new intellectual territory.
Reynolds, R. Larry. Ways of Knowing. Alternative Microeconomics . Part 1, Chapter 3. Boise State University; The Theory-Method Relationship. S-Cool Revision. United Kingdom.
Yet Another Writing Tip
Methods and the Methodology
Do not confuse the terms "methods" and "methodology." As Schneider notes, a method refers to the technical steps taken to do research . Descriptions of methods usually include defining and stating why you have chosen specific techniques to investigate a research problem, followed by an outline of the procedures you used to systematically select, gather, and process the data [remember to always save the interpretation of data for the discussion section of your paper].
The methodology refers to a discussion of the underlying reasoning why particular methods were used . This discussion includes describing the theoretical concepts that inform the choice of methods to be applied, placing the choice of methods within the more general nature of academic work, and reviewing its relevance to examining the research problem. The methodology section also includes a thorough review of the methods other scholars have used to study the topic.
Bryman, Alan. "Of Methods and Methodology." Qualitative Research in Organizations and Management: An International Journal 3 (2008): 159-168; Schneider, Florian. “What's in a Methodology: The Difference between Method, Methodology, and Theory…and How to Get the Balance Right?” PoliticsEastAsia.com. Chinese Department, University of Leiden, Netherlands.
- << Previous: Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Next: Qualitative Methods >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 9:47 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
What is Research Methodology? Definition, Types, and Examples

Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of the research. Several aspects must be considered before selecting an appropriate research methodology, such as research limitations and ethical concerns that may affect your research.
The research methodology section in a scientific paper describes the different methodological choices made, such as the data collection and analysis methods, and why these choices were selected. The reasons should explain why the methods chosen are the most appropriate to answer the research question. A good research methodology also helps ensure the reliability and validity of the research findings. There are three types of research methodology—quantitative, qualitative, and mixed-method, which can be chosen based on the research objectives.
What is research methodology ?
A research methodology describes the techniques and procedures used to identify and analyze information regarding a specific research topic. It is a process by which researchers design their study so that they can achieve their objectives using the selected research instruments. It includes all the important aspects of research, including research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and the overall framework within which the research is conducted. While these points can help you understand what is research methodology, you also need to know why it is important to pick the right methodology.
Why is research methodology important?
Having a good research methodology in place has the following advantages: 3
- Helps other researchers who may want to replicate your research; the explanations will be of benefit to them.
- You can easily answer any questions about your research if they arise at a later stage.
- A research methodology provides a framework and guidelines for researchers to clearly define research questions, hypotheses, and objectives.
- It helps researchers identify the most appropriate research design, sampling technique, and data collection and analysis methods.
- A sound research methodology helps researchers ensure that their findings are valid and reliable and free from biases and errors.
- It also helps ensure that ethical guidelines are followed while conducting research.
- A good research methodology helps researchers in planning their research efficiently, by ensuring optimum usage of their time and resources.
Writing the methods section of a research paper? Let Paperpal help you achieve perfection
Types of research methodology.
There are three types of research methodology based on the type of research and the data required. 1
- Quantitative research methodology focuses on measuring and testing numerical data. This approach is good for reaching a large number of people in a short amount of time. This type of research helps in testing the causal relationships between variables, making predictions, and generalizing results to wider populations.
- Qualitative research methodology examines the opinions, behaviors, and experiences of people. It collects and analyzes words and textual data. This research methodology requires fewer participants but is still more time consuming because the time spent per participant is quite large. This method is used in exploratory research where the research problem being investigated is not clearly defined.
- Mixed-method research methodology uses the characteristics of both quantitative and qualitative research methodologies in the same study. This method allows researchers to validate their findings, verify if the results observed using both methods are complementary, and explain any unexpected results obtained from one method by using the other method.
What are the types of sampling designs in research methodology?
Sampling 4 is an important part of a research methodology and involves selecting a representative sample of the population to conduct the study, making statistical inferences about them, and estimating the characteristics of the whole population based on these inferences. There are two types of sampling designs in research methodology—probability and nonprobability.
- Probability sampling
In this type of sampling design, a sample is chosen from a larger population using some form of random selection, that is, every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected. The different types of probability sampling are:
- Systematic —sample members are chosen at regular intervals. It requires selecting a starting point for the sample and sample size determination that can be repeated at regular intervals. This type of sampling method has a predefined range; hence, it is the least time consuming.
- Stratified —researchers divide the population into smaller groups that don’t overlap but represent the entire population. While sampling, these groups can be organized, and then a sample can be drawn from each group separately.
- Cluster —the population is divided into clusters based on demographic parameters like age, sex, location, etc.
- Convenience —selects participants who are most easily accessible to researchers due to geographical proximity, availability at a particular time, etc.
- Purposive —participants are selected at the researcher’s discretion. Researchers consider the purpose of the study and the understanding of the target audience.
- Snowball —already selected participants use their social networks to refer the researcher to other potential participants.
- Quota —while designing the study, the researchers decide how many people with which characteristics to include as participants. The characteristics help in choosing people most likely to provide insights into the subject.
What are data collection methods?
During research, data are collected using various methods depending on the research methodology being followed and the research methods being undertaken. Both qualitative and quantitative research have different data collection methods, as listed below.
Qualitative research 5
- One-on-one interviews: Helps the interviewers understand a respondent’s subjective opinion and experience pertaining to a specific topic or event
- Document study/literature review/record keeping: Researchers’ review of already existing written materials such as archives, annual reports, research articles, guidelines, policy documents, etc.
- Focus groups: Constructive discussions that usually include a small sample of about 6-10 people and a moderator, to understand the participants’ opinion on a given topic.
- Qualitative observation : Researchers collect data using their five senses (sight, smell, touch, taste, and hearing).
Quantitative research 6
- Sampling: The most common type is probability sampling.
- Interviews: Commonly telephonic or done in-person.
- Observations: Structured observations are most commonly used in quantitative research. In this method, researchers make observations about specific behaviors of individuals in a structured setting.
- Document review: Reviewing existing research or documents to collect evidence for supporting the research.
- Surveys and questionnaires. Surveys can be administered both online and offline depending on the requirement and sample size.
Let Paperpal help you write the perfect research methods section. Start now!
What are data analysis methods.
The data collected using the various methods for qualitative and quantitative research need to be analyzed to generate meaningful conclusions. These data analysis methods 7 also differ between quantitative and qualitative research.
Quantitative research involves a deductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed at the beginning of the research and precise measurement is required. The methods include statistical analysis applications to analyze numerical data and are grouped into two categories—descriptive and inferential.
Descriptive analysis is used to describe the basic features of different types of data to present it in a way that ensures the patterns become meaningful. The different types of descriptive analysis methods are:
- Measures of frequency (count, percent, frequency)
- Measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode)
- Measures of dispersion or variation (range, variance, standard deviation)
- Measure of position (percentile ranks, quartile ranks)
Inferential analysis is used to make predictions about a larger population based on the analysis of the data collected from a smaller population. This analysis is used to study the relationships between different variables. Some commonly used inferential data analysis methods are:
- Correlation: To understand the relationship between two or more variables.
- Cross-tabulation: Analyze the relationship between multiple variables.
- Regression analysis: Study the impact of independent variables on the dependent variable.
- Frequency tables: To understand the frequency of data.
- Analysis of variance: To test the degree to which two or more variables differ in an experiment.
Qualitative research involves an inductive method for data analysis where hypotheses are developed after data collection. The methods include:
- Content analysis: For analyzing documented information from text and images by determining the presence of certain words or concepts in texts.
- Narrative analysis: For analyzing content obtained from sources such as interviews, field observations, and surveys. The stories and opinions shared by people are used to answer research questions.
- Discourse analysis: For analyzing interactions with people considering the social context, that is, the lifestyle and environment, under which the interaction occurs.
- Grounded theory: Involves hypothesis creation by data collection and analysis to explain why a phenomenon occurred.
- Thematic analysis: To identify important themes or patterns in data and use these to address an issue.
How to choose a research methodology?
Here are some important factors to consider when choosing a research methodology: 8
- Research objectives, aims, and questions —these would help structure the research design.
- Review existing literature to identify any gaps in knowledge.
- Check the statistical requirements —if data-driven or statistical results are needed then quantitative research is the best. If the research questions can be answered based on people’s opinions and perceptions, then qualitative research is most suitable.
- Sample size —sample size can often determine the feasibility of a research methodology. For a large sample, less effort- and time-intensive methods are appropriate.
- Constraints —constraints of time, geography, and resources can help define the appropriate methodology.
Got writer’s block? Kickstart your research paper writing with Paperpal now!
How to write a research methodology .
A research methodology should include the following components: 3,9
- Research design —should be selected based on the research question and the data required. Common research designs include experimental, quasi-experimental, correlational, descriptive, and exploratory.
- Research method —this can be quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method.
- Reason for selecting a specific methodology —explain why this methodology is the most suitable to answer your research problem.
- Research instruments —explain the research instruments you plan to use, mainly referring to the data collection methods such as interviews, surveys, etc. Here as well, a reason should be mentioned for selecting the particular instrument.
- Sampling —this involves selecting a representative subset of the population being studied.
- Data collection —involves gathering data using several data collection methods, such as surveys, interviews, etc.
- Data analysis —describe the data analysis methods you will use once you’ve collected the data.
- Research limitations —mention any limitations you foresee while conducting your research.
- Validity and reliability —validity helps identify the accuracy and truthfulness of the findings; reliability refers to the consistency and stability of the results over time and across different conditions.
- Ethical considerations —research should be conducted ethically. The considerations include obtaining consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, and addressing conflicts of interest.
Streamline Your Research Paper Writing Process with Paperpal
The methods section is a critical part of the research papers, allowing researchers to use this to understand your findings and replicate your work when pursuing their own research. However, it is usually also the most difficult section to write. This is where Paperpal can help you overcome the writer’s block and create the first draft in minutes with Paperpal Copilot, its secure generative AI feature suite.
With Paperpal you can get research advice, write and refine your work, rephrase and verify the writing, and ensure submission readiness, all in one place. Here’s how you can use Paperpal to develop the first draft of your methods section.
- Generate an outline: Input some details about your research to instantly generate an outline for your methods section
- Develop the section: Use the outline and suggested sentence templates to expand your ideas and develop the first draft.
- P araph ras e and trim : Get clear, concise academic text with paraphrasing that conveys your work effectively and word reduction to fix redundancies.
- Choose the right words: Enhance text by choosing contextual synonyms based on how the words have been used in previously published work.
- Check and verify text : Make sure the generated text showcases your methods correctly, has all the right citations, and is original and authentic. .
You can repeat this process to develop each section of your research manuscript, including the title, abstract and keywords. Ready to write your research papers faster, better, and without the stress? Sign up for Paperpal and start writing today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What are the key components of research methodology?
A1. A good research methodology has the following key components:
- Research design
- Data collection procedures
- Data analysis methods
- Ethical considerations
Q2. Why is ethical consideration important in research methodology?
A2. Ethical consideration is important in research methodology to ensure the readers of the reliability and validity of the study. Researchers must clearly mention the ethical norms and standards followed during the conduct of the research and also mention if the research has been cleared by any institutional board. The following 10 points are the important principles related to ethical considerations: 10
- Participants should not be subjected to harm.
- Respect for the dignity of participants should be prioritized.
- Full consent should be obtained from participants before the study.
- Participants’ privacy should be ensured.
- Confidentiality of the research data should be ensured.
- Anonymity of individuals and organizations participating in the research should be maintained.
- The aims and objectives of the research should not be exaggerated.
- Affiliations, sources of funding, and any possible conflicts of interest should be declared.
- Communication in relation to the research should be honest and transparent.
- Misleading information and biased representation of primary data findings should be avoided.
Q3. What is the difference between methodology and method?
A3. Research methodology is different from a research method, although both terms are often confused. Research methods are the tools used to gather data, while the research methodology provides a framework for how research is planned, conducted, and analyzed. The latter guides researchers in making decisions about the most appropriate methods for their research. Research methods refer to the specific techniques, procedures, and tools used by researchers to collect, analyze, and interpret data, for instance surveys, questionnaires, interviews, etc.
Research methodology is, thus, an integral part of a research study. It helps ensure that you stay on track to meet your research objectives and answer your research questions using the most appropriate data collection and analysis tools based on your research design.
Accelerate your research paper writing with Paperpal. Try for free now!
- Research methodologies. Pfeiffer Library website. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://library.tiffin.edu/researchmethodologies/whatareresearchmethodologies
- Types of research methodology. Eduvoice website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://eduvoice.in/types-research-methodology/
- The basics of research methodology: A key to quality research. Voxco. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.voxco.com/blog/what-is-research-methodology/
- Sampling methods: Types with examples. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/types-of-sampling-for-social-research/
- What is qualitative research? Methods, types, approaches, examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-qualitative-research-methods-types-examples/
- What is quantitative research? Definition, methods, types, and examples. Researcher.Life blog. Accessed August 15, 2023. https://researcher.life/blog/article/what-is-quantitative-research-types-and-examples/
- Data analysis in research: Types & methods. QuestionPro website. Accessed August 16, 2023. https://www.questionpro.com/blog/data-analysis-in-research/#Data_analysis_in_qualitative_research
- Factors to consider while choosing the right research methodology. PhD Monster website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://www.phdmonster.com/factors-to-consider-while-choosing-the-right-research-methodology/
- What is research methodology? Research and writing guides. Accessed August 14, 2023. https://paperpile.com/g/what-is-research-methodology/
- Ethical considerations. Business research methodology website. Accessed August 17, 2023. https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/ethical-considerations/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Dangling Modifiers and How to Avoid Them in Your Writing
- Webinar: How to Use Generative AI Tools Ethically in Your Academic Writing
- Research Outlines: How to Write An Introduction Section in Minutes with Paperpal Copilot
- How to Paraphrase Research Papers Effectively
Language and Grammar Rules for Academic Writing
Climatic vs. climactic: difference and examples, you may also like, how to write a high-quality conference paper, how paperpal is enhancing academic productivity and accelerating..., academic editing: how to self-edit academic text with..., 4 ways paperpal encourages responsible writing with ai, what are scholarly sources and where can you..., how to write a hypothesis types and examples , what is academic writing: tips for students, what is hedging in academic writing , how to use ai to enhance your college..., how to use paperpal to generate emails &....
Table of Contents
Ai, ethics & human agency, collaboration, information literacy, writing process, research methods.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
Understand how to identify appropriate research methods for particular methodological communities , rhetorical situations , and research questions .
Research Methods are the tools and techniques (aka protocols , processes , strategies ) that investigators and methodological communities use to conduct research .
Research methods may be empirical (aka the scientific method), informal , or textual .
Key Terms: Methodological Community ; Research Methodology
If you are doing more than writing an essay that relies on sources, then you can benefit from understanding why there are different research methods. Learn more about how academic and professional researchers employ diverse research methods. Understand the philosophical assumptions that inform researchers in different disciplines.
Academic disciplines—for example, mathematics, psychology, physics, engineering, or business—have different ways of conducting and evaluating research. An anthropologist’s account of kinship patterns in a tribe of Native Americans bears almost no resemblance to a cognitive psychologist’s investigation of sensory responses to light stimuli. Even within a particular academic discipline, researchers may disagree over what makes good research. Different researchers employ different research methodologies because they have opposing, sometimes contradictory ideas, about what constitutes a valid knowledge claim. Not only do people disagree about appropriate methods of research, but their ideas may change over time. Conceptions about knowledge, available technologies, and research practices influence each other and change constantly. For example, capturing gorillas and studying them in cages might have been considered good research in the 1920s. The work of later researchers like Dian Fossey, however, demonstrated how animals might be better understood in their natural environment. Today, research based on observations of wild animals in captivity would gain little support or interest.
Research methods are a social, rhetorical construct . Different academic and professional communities —e.g., mathematics, psychology, physics, engineering, or business—employ unique research methods. A primary focus of training in academic and professional disciplines concerns learning how to use disciplinary-specific methods, tools, protocols, and processes for gathering and assessing information. For instance, an anthropologist’s account of kinship patterns in a tribe of Native Americans bears almost no resemblance to a cognitive psychologist’s investigation of sensory responses to light stimuli.
Whether research results, truth claims , are understood or judged to be valid or convincing depends to a great extent on whether the investigator follows the tacit and explicit guidelines a discourse community considers appropriate for a particular research question and rhetorical situation . This is why rhetorical reasoning (especially audience awareness ) plays such a formative role in the selection of research methods.
Research methods are not necessarily paired with particular methodologies , epistemological values , such as the rejection of positivism . Rather, methodological communities may employ the same methods yet hold contrary assumptions about the sort of knowledge those methods produce. For instance, a researcher could argue a case study creates universal knowledge —insights that transcend individuals, cultures, and historical periods. For instance, based on his therapy notes, Freud theorized we all have an id, ego, and superego. Jung suggested we all play archetypal roles including the hero, the shadow, the anima and animus. In contrast, another researcher could conduct a case study with similar subjects and yet argue the insights gleaned from the research do not illustrate universal knowledge—i.e., the results are stories, narratives, that provide robust details about the subjects interviewed . . . and nothing more.
Research Methods are constantly changing in response to new technologies. Eager to develop new knowledge or test knowledge claims , investigators experiment with new methods as technologies evolve. For example, the internet enables investigators to conduct worldwide research with online survey tools and video conferencing tools. Businesses are working with big data and analytics to commercialize data about consumers habits as they traverse the internet or purchase items in the world. Machine learning theorists are looking at how people write to develop artificial intelligence so technologies like Amazon’s Alexa can speak with humans.
Research Methods are evolving in response to new cultural mores. Communities of practice reconsider ethical principles and engage in dialectics regarding best practices. For example, capturing gorillas and studying them in cages might have been considered good research in the 1920s. The work of later researchers like Dian Fossey, however, demonstrated how animals might be better understood in their natural environment. Today, research based on observations of wild animals in captivity would gain little support or interest.
Consumers of research studies are wise to evaluate research methods. As a consumer of research, you are wise to critically evaluate a researcher’s methods. You would, for example, take your doctor’s diagnosis of a life-threatening disease more seriously than a fortune teller’s prediction of an early death. What distinguishes a physician’s prognosis from a fortune teller’s prophecy are research methods: the doctor may be looking at the results of your physical, blood work, x rays, CT Scans, MRI, or family history, whereas the fortune teller may be gazing into a crystal ball, pendulum, Tarot cars, or astrological charts.
[ The CRAAP Test (Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, Purpose) ]
Taxonomy of Research Methods
Research methods & mindset.
How deeply we engage in Informal Research, Textual Research, or Primary Research is tied to our mindset as an investigator, the importance of the occasion and exigency, and our judgment as to whether it’s the best possible kairotic moment.
Our engagement with research methods is also tied to our training. In high schools and colleges in the U.S., students learn about information literacy perspectives & practices and write with sources . Additionally, some fortunate students learn to conduct lab experiments in high schools. But it really isn’t until college — and, for some, graduate school — that students receive training from experts in empirical research methods.
Our information seeking behaviors are also shaped by the seriousness of the occasion to ourselves and others. For instance, when COVID-19 virus became a pandemic in the spring of 2020, many scientists from throughout the world dropped what they had been working on and turned to finding a vaccine or medications to ameliorate the virus.
Related Articles:

Empirical Research Methods
Informal research methods, mixed research methods, qualitative research methods, quantitative research methods.

Textual Research Methods
Suggested edits.
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

Inspire yourself and strengthen your cognive competencies by being reflective, by engaging in informal research to solve problems or inspire more formal research methods.

Create more agency in your life. Sharpen your critical reading and thinking competencies by engaging in critical analysis of texts. Understand disparities in textual interpretations. Learn different ways to interpret...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World


Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- How to Do Research for an Excellent Essay: The Complete Guide

One of the biggest secrets to writing a good essay is the Boy Scouts’ motto: ‘be prepared’. Preparing for an essay – by conducting effective research – lays the foundations for a brilliant piece of writing, and it’s every bit as important as the actual writing part. Many students skimp on this crucial stage, or sit in the library not really sure where to start; and it shows in the quality of their essays. This just makes it easier for you to get ahead of your peers, and we’re going to show you how. In this article, we take you through what you need to do in order to conduct effective research and use your research time to best effect.
Allow enough time
First and foremost, it’s vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don’t leave your essay until the last minute . If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay’s lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to whether you’re at Sixth Form or university, and according to how well you know the topic and what teaching you’ve had on it, but make sure you factor in more time than you think you’ll need. You may come across a concept that takes you longer to understand than you’d expected, so it’s better to allow too much time than too little.
Read the essay question and thoroughly understand it
If you don’t have a thorough understanding of what the essay question is asking you to do, you put yourself at risk of going in the wrong direction with your research. So take the question, read it several times and pull out the key things it’s asking you to do. The instructions in the question are likely to have some bearing on the nature of your research. If the question says “Compare”, for example, this will set you up for a particular kind of research, during which you’ll be looking specifically for points of comparison; if the question asks you to “Discuss”, your research focus may be more on finding different points of view and formulating your own.
Begin with a brainstorm
Start your research time by brainstorming what you already know. Doing this means that you can be clear about exactly what you’re already aware of, and you can identify the gaps in your knowledge so that you don’t end up wasting time by reading books that will tell you what you already know. This gives your research more of a direction and allows you to be more specific in your efforts to find out certain things. It’s also a gentle way of introducing yourself to the task and putting yourself in the right frame of mind for learning about the topic at hand.
Achieve a basic understanding before delving deeper
If the topic is new to you and your brainstorm has yielded few ideas, you’ll need to acquire a basic understanding of the topic before you begin delving deeper into your research. If you don’t, and you start by your research by jumping straight in at the deep end, as it were, you’ll struggle to grasp the topic. This also means that you may end up being too swayed by a certain source, as you haven’t the knowledge to question it properly. You need sufficient background knowledge to be able to take a critical approach to each of the sources you read. So, start from the very beginning. It’s ok to use Wikipedia or other online resources to give you an introduction to a topic, though bear in mind that these can’t be wholly relied upon. If you’ve covered the topic in class already, re-read the notes you made so that you can refresh your mind before you start further investigation.
Working through your reading list
If you’ve been given a reading list to work from, be organised in how you work through each of the items on it. Try to get hold of as many of the books on it as you can before you start, so that you have them all easily to hand, and can refer back to things you’ve read and compare them with other perspectives. Plan the order in which you’re going to work through them and try to allocate a specific amount of time to each of them; this ensures that you allow enough time to do each of them justice and that focus yourself on making the most of your time with each one. It’s a good idea to go for the more general resources before honing in on the finer points mentioned in more specialised literature. Think of an upside-down pyramid and how it starts off wide at the top and becomes gradually narrower; this is the sort of framework you should apply to your research.
Ask a librarian
Library computer databases can be confusing things, and can add an extra layer of stress and complexity to your research if you’re not used to using them. The librarian is there for a reason, so don’t be afraid to go and ask if you’re not sure where to find a particular book on your reading list. If you’re in need of somewhere to start, they should be able to point you in the direction of the relevant section of the library so that you can also browse for books that may yield useful information.
Use the index
If you haven’t been given specific pages to read in the books on your reading list, make use of the index (and/or table of contents) of each book to help you find relevant material. It sounds obvious, but some students don’t think to do this and battle their way through heaps of irrelevant chapters before finding something that will be useful for their essay.
Taking notes
As you work through your reading, take notes as you go along rather than hoping you’ll remember everything you’ve read. Don’t indiscriminately write down everything – only the bits that will be useful in answering the essay question you’ve been set. If you write down too much, you risk writing an essay that’s full of irrelevant material and getting lower grades as a result. Be concise, and summarise arguments in your own words when you make notes (this helps you learn it better, too, because you actually have to think about how best to summarise it). You may want to make use of small index cards to force you to be brief with what you write about each point or topic. We’ve covered effective note-taking extensively in another article, which you can read here . Note-taking is a major part of the research process, so don’t neglect it. Your notes don’t just come in useful in the short-term, for completing your essay, but they should also be helpful when it comes to revision time, so try to keep them organised.
Research every side of the argument
Never rely too heavily on one resource without referring to other possible opinions; it’s bad academic practice. You need to be able to give a balanced argument in an essay, and that means researching a range of perspectives on whatever problem you’re tackling. Keep a note of the different arguments, along with the evidence in support of or against each one, ready to be deployed into an essay structure that works logically through each one. If you see a scholar’s name cropping up again and again in what you read, it’s worth investigating more about them even if you haven’t specifically been told to do so. Context is vital in academia at any level, so influential figures are always worth knowing about.
Keep a dictionary by your side
You could completely misunderstand a point you read if you don’t know what one important word in the sentence means. For that reason, it’s a good idea to keep a dictionary by your side at all times as you conduct your research. Not only does this help you fully understand what you’re reading, but you also learn new words that you might be able to use in your forthcoming essay or a future one . Growing your vocabulary is never a waste of time!
Start formulating your own opinion
As you work through reading these different points of view, think carefully about what you’ve read and note your own response to different opinions. Get into the habit of questioning sources and make sure you’re not just repeating someone else’s opinion without challenging it. Does an opinion make sense? Does it have plenty of evidence to back it up? What are the counter-arguments, and on balance, which sways you more? Demonstrating your own intelligent thinking will set your essay apart from those of your peers, so think about these things as you conduct your research.
Be careful with web-based research
Although, as we’ve said already, it’s fine to use Wikipedia and other online resources to give you a bit of an introduction to a topic you haven’t covered before, be very careful when using the internet for researching an essay. Don’t take Wikipedia as gospel; don’t forget, anybody can edit it! We wouldn’t advise using the internet as the basis of your essay research – it’s simply not academically rigorous enough, and you don’t know how out of date a particular resource might be. Even if your Sixth Form teachers may not question where you picked up an idea you’ve discussed in your essays, it’s still not a good habit to get into and you’re unlikely to get away with it at a good university. That said, there are still reliable academic resources available via the internet; these can be found in dedicated sites that are essentially online libraries, such as JSTOR. These are likely to be a little too advanced if you’re still in Sixth Form, but you’ll almost certainly come across them once you get to university.
Look out for footnotes
In an academic publication, whether that’s a book or a journal article, footnotes are a great place to look for further ideas for publications that might yield useful information. Plenty can be hidden away in footnotes, and if a writer is disparaging or supporting the ideas of another academic, you could look up the text in question so that you can include their opinion too, and whether or not you agree with them, for extra brownie points.
Don’t save doing all your own references until last
If you’re still in Sixth Form, you might not yet be required to include academic references in your essays, but for the sake of a thorough guide to essay research that will be useful to you in the future, we’re going to include this point anyway (it will definitely come in useful when you get to university, so you may as well start thinking about it now!). As you read through various books and find points you think you’re going to want to make in your essays, make sure you note down where you found these points as you go along (author’s first and last name, the publication title, publisher, publication date and page number). When you get to university you will be expected to identify your sources very precisely, so it’s a good habit to get into. Unfortunately, many students forget to do this and then have a difficult time of going back through their essay adding footnotes and trying to remember where they found a particular point. You’ll save yourself a great deal of time and effort if you simply note down your academic references as you go along. If you are including footnotes, don’t forget to add each publication to a main bibliography, to be included at the end of your essay, at the same time.
Putting in the background work required to write a good essay can seem an arduous task at times, but it’s a fundamental step that can’t simply be skipped. The more effort you put in at this stage, the better your essay will be and the easier it will be to write. Use the tips in this article and you’ll be well on your way to an essay that impresses!
To get even more prepared for essay writing you might also want to consider attending an Oxford Summer School .
Image credits: banner
15 Types of Research Methods

Research methods refer to the strategies, tools, and techniques used to gather and analyze data in a structured way in order to answer a research question or investigate a hypothesis (Hammond & Wellington, 2020).
Generally, we place research methods into two categories: quantitative and qualitative. Each has its own strengths and weaknesses, which we can summarize as:
- Quantitative research can achieve generalizability through scrupulous statistical analysis applied to large sample sizes.
- Qualitative research achieves deep, detailed, and nuance accounts of specific case studies, which are not generalizable.
Some researchers, with the aim of making the most of both quantitative and qualitative research, employ mixed methods, whereby they will apply both types of research methods in the one study, such as by conducting a statistical survey alongside in-depth interviews to add context to the quantitative findings.
Below, I’ll outline 15 common research methods, and include pros, cons, and examples of each .
Types of Research Methods
Research methods can be broadly categorized into two types: quantitative and qualitative.
- Quantitative methods involve systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques, providing an in-depth understanding of a specific concept or phenomenon (Schweigert, 2021). The strengths of this approach include its ability to produce reliable results that can be generalized to a larger population, although it can lack depth and detail.
- Qualitative methods encompass techniques that are designed to provide a deep understanding of a complex issue, often in a specific context, through collection of non-numerical data (Tracy, 2019). This approach often provides rich, detailed insights but can be time-consuming and its findings may not be generalizable.
These can be further broken down into a range of specific research methods and designs:
Combining the two methods above, mixed methods research mixes elements of both qualitative and quantitative research methods, providing a comprehensive understanding of the research problem . We can further break these down into:
- Sequential Explanatory Design (QUAN→QUAL): This methodology involves conducting quantitative analysis first, then supplementing it with a qualitative study.
- Sequential Exploratory Design (QUAL→QUAN): This methodology goes in the other direction, starting with qualitative analysis and ending with quantitative analysis.
Let’s explore some methods and designs from both quantitative and qualitative traditions, starting with qualitative research methods.
Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research methods allow for the exploration of phenomena in their natural settings, providing detailed, descriptive responses and insights into individuals’ experiences and perceptions (Howitt, 2019).
These methods are useful when a detailed understanding of a phenomenon is sought.
1. Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research emerged out of anthropological research, where anthropologists would enter into a setting for a sustained period of time, getting to know a cultural group and taking detailed observations.
Ethnographers would sometimes even act as participants in the group or culture, which many scholars argue is a weakness because it is a step away from achieving objectivity (Stokes & Wall, 2017).
In fact, at its most extreme version, ethnographers even conduct research on themselves, in a fascinating methodology call autoethnography .
The purpose is to understand the culture, social structure, and the behaviors of the group under study. It is often useful when researchers seek to understand shared cultural meanings and practices in their natural settings.
However, it can be time-consuming and may reflect researcher biases due to the immersion approach.
Example of Ethnography
Liquidated: An Ethnography of Wall Street by Karen Ho involves an anthropologist who embeds herself with Wall Street firms to study the culture of Wall Street bankers and how this culture affects the broader economy and world.
2. Phenomenological Research
Phenomenological research is a qualitative method focused on the study of individual experiences from the participant’s perspective (Tracy, 2019).
It focuses specifically on people’s experiences in relation to a specific social phenomenon ( see here for examples of social phenomena ).
This method is valuable when the goal is to understand how individuals perceive, experience, and make meaning of particular phenomena. However, because it is subjective and dependent on participants’ self-reports, findings may not be generalizable, and are highly reliant on self-reported ‘thoughts and feelings’.
Example of Phenomenological Research
A phenomenological approach to experiences with technology by Sebnem Cilesiz represents a good starting-point for formulating a phenomenological study. With its focus on the ‘essence of experience’, this piece presents methodological, reliability, validity, and data analysis techniques that phenomenologists use to explain how people experience technology in their everyday lives.
3. Historical Research
Historical research is a qualitative method involving the examination of past events to draw conclusions about the present or make predictions about the future (Stokes & Wall, 2017).
As you might expect, it’s common in the research branches of history departments in universities.
This approach is useful in studies that seek to understand the past to interpret present events or trends. However, it relies heavily on the availability and reliability of source materials, which may be limited.
Common data sources include cultural artifacts from both material and non-material culture , which are then examined, compared, contrasted, and contextualized to test hypotheses and generate theories.
Example of Historical Research
A historical research example might be a study examining the evolution of gender roles over the last century. This research might involve the analysis of historical newspapers, advertisements, letters, and company documents, as well as sociocultural contexts.
4. Content Analysis
Content analysis is a research method that involves systematic and objective coding and interpreting of text or media to identify patterns, themes, ideologies, or biases (Schweigert, 2021).
A content analysis is useful in analyzing communication patterns, helping to reveal how texts such as newspapers, movies, films, political speeches, and other types of ‘content’ contain narratives and biases.
However, interpretations can be very subjective, which often requires scholars to engage in practices such as cross-comparing their coding with peers or external researchers.
Content analysis can be further broken down in to other specific methodologies such as semiotic analysis, multimodal analysis , and discourse analysis .
Example of Content Analysis
How is Islam Portrayed in Western Media? by Poorebrahim and Zarei (2013) employs a type of content analysis called critical discourse analysis (common in poststructuralist and critical theory research ). This study by Poorebrahum and Zarei combs through a corpus of western media texts to explore the language forms that are used in relation to Islam and Muslims, finding that they are overly stereotyped, which may represent anti-Islam bias or failure to understand the Islamic world.
5. Grounded Theory Research
Grounded theory involves developing a theory during and after data collection rather than beforehand.
This is in contrast to most academic research studies, which start with a hypothesis or theory and then testing of it through a study, where we might have a null hypothesis (disproving the theory) and an alternative hypothesis (supporting the theory).
Grounded Theory is useful because it keeps an open mind to what the data might reveal out of the research. It can be time-consuming and requires rigorous data analysis (Tracy, 2019).
Grounded Theory Example
Developing a Leadership Identity by Komives et al (2005) employs a grounded theory approach to develop a thesis based on the data rather than testing a hypothesis. The researchers studied the leadership identity of 13 college students taking on leadership roles. Based on their interviews, the researchers theorized that the students’ leadership identities shifted from a hierarchical view of leadership to one that embraced leadership as a collaborative concept.
6. Action Research
Action research is an approach which aims to solve real-world problems and bring about change within a setting. The study is designed to solve a specific problem – or in other words, to take action (Patten, 2017).
This approach can involve mixed methods, but is generally qualitative because it usually involves the study of a specific case study wherein the researcher works, e.g. a teacher studying their own classroom practice to seek ways they can improve.
Action research is very common in fields like education and nursing where practitioners identify areas for improvement then implement a study in order to find paths forward.
Action Research Example
Using Digital Sandbox Gaming to Improve Creativity Within Boys’ Writing by Ellison and Drew was a research study one of my research students completed in his own classroom under my supervision. He implemented a digital game-based approach to literacy teaching with boys and interviewed his students to see if the use of games as stimuli for storytelling helped draw them into the learning experience.
7. Natural Observational Research
Observational research can also be quantitative (see: experimental research), but in naturalistic settings for the social sciences, researchers tend to employ qualitative data collection methods like interviews and field notes to observe people in their day-to-day environments.
This approach involves the observation and detailed recording of behaviors in their natural settings (Howitt, 2019). It can provide rich, in-depth information, but the researcher’s presence might influence behavior.
While observational research has some overlaps with ethnography (especially in regard to data collection techniques), it tends not to be as sustained as ethnography, e.g. a researcher might do 5 observations, every second Monday, as opposed to being embedded in an environment.
Observational Research Example
A researcher might use qualitative observational research to study the behaviors and interactions of children at a playground. The researcher would document the behaviors observed, such as the types of games played, levels of cooperation , and instances of conflict.
8. Case Study Research
Case study research is a qualitative method that involves a deep and thorough investigation of a single individual, group, or event in order to explore facets of that phenomenon that cannot be captured using other methods (Stokes & Wall, 2017).
Case study research is especially valuable in providing contextualized insights into specific issues, facilitating the application of abstract theories to real-world situations (Patten, 2017).
However, findings from a case study may not be generalizable due to the specific context and the limited number of cases studied (Walliman, 2021).
See More: Case Study Advantages and Disadvantages
Example of a Case Study
Scholars conduct a detailed exploration of the implementation of a new teaching method within a classroom setting. The study focuses on how the teacher and students adapt to the new method, the challenges encountered, and the outcomes on student performance and engagement. While the study provides specific and detailed insights of the teaching method in that classroom, it cannot be generalized to other classrooms, as statistical significance has not been established through this qualitative approach.
Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods involve the systematic empirical investigation of observable phenomena via statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques (Pajo, 2022). The focus is on gathering numerical data and generalizing it across groups of people or to explain a particular phenomenon.
9. Experimental Research
Experimental research is a quantitative method where researchers manipulate one variable to determine its effect on another (Walliman, 2021).
This is common, for example, in high-school science labs, where students are asked to introduce a variable into a setting in order to examine its effect.
This type of research is useful in situations where researchers want to determine causal relationships between variables. However, experimental conditions may not reflect real-world conditions.
Example of Experimental Research
A researcher may conduct an experiment to determine the effects of a new educational approach on student learning outcomes. Students would be randomly assigned to either the control group (traditional teaching method) or the experimental group (new educational approach).
10. Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are quantitative methods that involve asking research participants structured and predefined questions to collect data about their attitudes, beliefs, behaviors, or characteristics (Patten, 2017).
Surveys are beneficial for collecting data from large samples, but they depend heavily on the honesty and accuracy of respondents.
They tend to be seen as more authoritative than their qualitative counterparts, semi-structured interviews, because the data is quantifiable (e.g. a questionnaire where information is presented on a scale from 1 to 10 can allow researchers to determine and compare statistical means, averages, and variations across sub-populations in the study).
Example of a Survey Study
A company might use a survey to gather data about employee job satisfaction across its offices worldwide. Employees would be asked to rate various aspects of their job satisfaction on a Likert scale. While this method provides a broad overview, it may lack the depth of understanding possible with other methods (Stokes & Wall, 2017).
11. Longitudinal Studies
Longitudinal studies involve repeated observations of the same variables over extended periods (Howitt, 2019). These studies are valuable for tracking development and change but can be costly and time-consuming.
With multiple data points collected over extended periods, it’s possible to examine continuous changes within things like population dynamics or consumer behavior. This makes a detailed analysis of change possible.
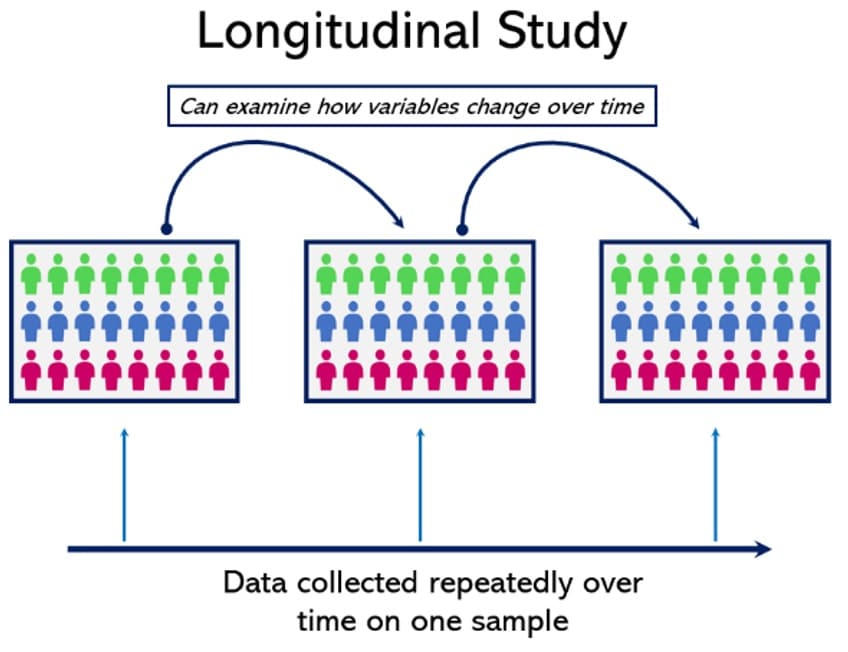
Perhaps the most relatable example of a longitudinal study is a national census, which is taken on the same day every few years, to gather comparative demographic data that can show how a nation is changing over time.
While longitudinal studies are commonly quantitative, there are also instances of qualitative ones as well, such as the famous 7 Up study from the UK, which studies 14 individuals every 7 years to explore their development over their lives.
Example of a Longitudinal Study
A national census, taken every few years, uses surveys to develop longitudinal data, which is then compared and analyzed to present accurate trends over time. Trends a census can reveal include changes in religiosity, values and attitudes on social issues, and much more.
12. Cross-Sectional Studies
Cross-sectional studies are a quantitative research method that involves analyzing data from a population at a specific point in time (Patten, 2017). They provide a snapshot of a situation but cannot determine causality.
This design is used to measure and compare the prevalence of certain characteristics or outcomes in different groups within the sampled population.
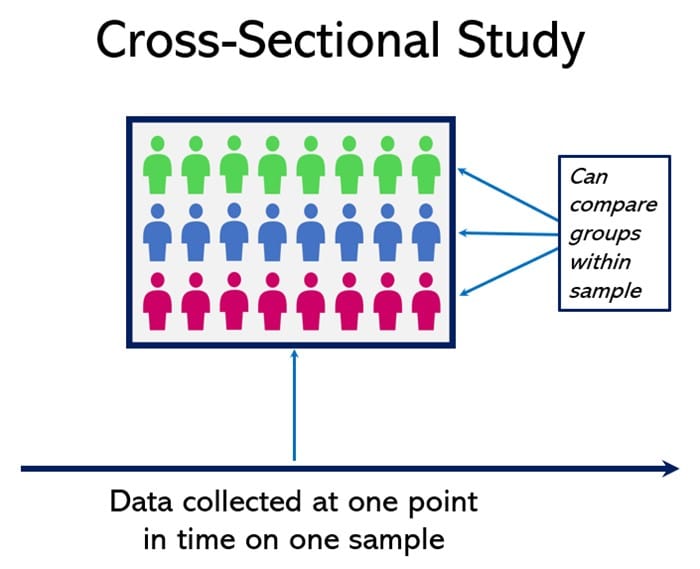
The major advantage of cross-sectional design is its ability to measure a wide range of variables simultaneously without needing to follow up with participants over time.
However, cross-sectional studies do have limitations . This design can only show if there are associations or correlations between different variables, but cannot prove cause and effect relationships, temporal sequence, changes, and trends over time.
Example of a Cross-Sectional Study
Our longitudinal study example of a national census also happens to contain cross-sectional design. One census is cross-sectional, displaying only data from one point in time. But when a census is taken once every few years, it becomes longitudinal, and so long as the data collection technique remains unchanged, identification of changes will be achievable, adding another time dimension on top of a basic cross-sectional study.
13. Correlational Research
Correlational research is a quantitative method that seeks to determine if and to what degree a relationship exists between two or more quantifiable variables (Schweigert, 2021).
This approach provides a fast and easy way to make initial hypotheses based on either positive or negative correlation trends that can be observed within dataset.
While correlational research can reveal relationships between variables, it cannot establish causality.
Methods used for data analysis may include statistical correlations such as Pearson’s or Spearman’s.
Example of Correlational Research
A team of researchers is interested in studying the relationship between the amount of time students spend studying and their academic performance. They gather data from a high school, measuring the number of hours each student studies per week and their grade point averages (GPAs) at the end of the semester. Upon analyzing the data, they find a positive correlation, suggesting that students who spend more time studying tend to have higher GPAs.
14. Quasi-Experimental Design Research
Quasi-experimental design research is a quantitative research method that is similar to experimental design but lacks the element of random assignment to treatment or control.
Instead, quasi-experimental designs typically rely on certain other methods to control for extraneous variables.
The term ‘quasi-experimental’ implies that the experiment resembles a true experiment, but it is not exactly the same because it doesn’t meet all the criteria for a ‘true’ experiment, specifically in terms of control and random assignment.
Quasi-experimental design is useful when researchers want to study a causal hypothesis or relationship, but practical or ethical considerations prevent them from manipulating variables and randomly assigning participants to conditions.
Example of Quasi-Experimental Design
A researcher wants to study the impact of a new math tutoring program on student performance. However, ethical and practical constraints prevent random assignment to the “tutoring” and “no tutoring” groups. Instead, the researcher compares students who chose to receive tutoring (experimental group) to similar students who did not choose to receive tutoring (control group), controlling for other variables like grade level and previous math performance.
Related: Examples and Types of Random Assignment in Research
15. Meta-Analysis Research
Meta-analysis statistically combines the results of multiple studies on a specific topic to yield a more precise estimate of the effect size. It’s the gold standard of secondary research .
Meta-analysis is particularly useful when there are numerous studies on a topic, and there is a need to integrate the findings to draw more reliable conclusions.
Some meta-analyses can identify flaws or gaps in a corpus of research, when can be highly influential in academic research, despite lack of primary data collection.
However, they tend only to be feasible when there is a sizable corpus of high-quality and reliable studies into a phenomenon.
Example of a Meta-Analysis
The power of feedback revisited (Wisniewski, Zierer & Hattie, 2020) is a meta-analysis that examines 435 empirical studies research on the effects of feedback on student learning. They use a random-effects model to ascertain whether there is a clear effect size across the literature. The authors find that feedback tends to impact cognitive and motor skill outcomes but has less of an effect on motivational and behavioral outcomes.
Choosing a research method requires a lot of consideration regarding what you want to achieve, your research paradigm, and the methodology that is most valuable for what you are studying. There are multiple types of research methods, many of which I haven’t been able to present here. Generally, it’s recommended that you work with an experienced researcher or research supervisor to identify a suitable research method for your study at hand.
Hammond, M., & Wellington, J. (2020). Research methods: The key concepts . New York: Routledge.
Howitt, D. (2019). Introduction to qualitative research methods in psychology . London: Pearson UK.
Pajo, B. (2022). Introduction to research methods: A hands-on approach . New York: Sage Publications.
Patten, M. L. (2017). Understanding research methods: An overview of the essentials . New York: Sage
Schweigert, W. A. (2021). Research methods in psychology: A handbook . Los Angeles: Waveland Press.
Stokes, P., & Wall, T. (2017). Research methods . New York: Bloomsbury Publishing.
Tracy, S. J. (2019). Qualitative research methods: Collecting evidence, crafting analysis, communicating impact . London: John Wiley & Sons.
Walliman, N. (2021). Research methods: The basics. London: Routledge.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Animism Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Magical Thinking Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Social-Emotional Learning (Definition, Examples, Pros & Cons)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ What is Educational Psychology?
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
ReviseSociology
A level sociology revision – education, families, research methods, crime and deviance and more!
Research Methods Essays – How to Write Them
Last Updated on April 17, 2017 by
Essay planning and writing for the AS and A Level sociology exams – hints and tips
The research methods section of the AS sociology 7191 (2) exam (research methods and topics in sociology) consists of one short answer question (out of 4 marks) and one essay question (out of 16 marks).
You should aim to spend approximately 20-25 minutes answering this essay question
This longer methods question will nearly always ask you to evaluate either the strengths or limitations of a particular method, for example ‘Evaluate the strengths of using social surveys in Social Research’.
This means that you will need to evaluate either the strengths or the limitations of the particular method as directed in the question.
You should always use the following structure whether talking about strengths or limitations of the method. Remember that you will need to emphasis the relevant sections depending on whether you are asked to evaluate strengths or limitations.
Define the method
Explain why Positivists like or dislike the method
Explain why Interpretivists like or dislike the method
Validity – explain why the method has good or bad validity
Reliability – explain why the method has good or bad reliability
Representativeness – explain how easy it is to get a large, representative sample
Practical factors – explain what practical strengths or limitations the method has
Ethical issues – explain any ethical problems associated with the method, or talk about the ethical strengths as appropriate
Say what kind of topics this method is useful for researching and why
Say when you wouldn’t use this method and why
Compare the relative strengths and weaknesses of different types of the method.
It is good practice to use examples of actual examples of research studies that have used the method under examination, preferably woven into the body of the essay.
It is also good practice to distinguish between different ways of doing the method throughout, as you are asked to do in number 11.
You can remember the above 11 point plan by memorizing the handy acronym DPIVRRPETTC
If you like this sort of thing, then you might like to purchase more of the same…

Related Posts
Methods in Context Essay Template
Assessment Objectives and Key Skills in A Level Sociology – for an explanation of what ‘evaluation’ means
AQA Assessment Resources – AS paper 2 has an example of a pure research methods question.
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr
One thought on “Research Methods Essays – How to Write Them”
- Pingback: AS and First Year A Level Sociology – Whole Course Overview | ReviseSociology
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Discover more from ReviseSociology
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading


The One Method That Changes Your—and All Students’—Writing
Science-based writing methods can achieve dramatic results..
Posted May 14, 2024 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- Why Education Is Important
- Find a Child Therapist
- A systematic writing framework offers a method for dramatically improving the teaching of writing.
- This method received only limited uptake, despite high-profile research publications and textbooks.
- A focus on writing style might have limited the method's impacts.

I remember spending hours commenting painstakingly on my students’ papers when I was a graduate student teaching in the Expository Writing Program at New York University. My students loved our classes, and they filled my sections and gave me terrific course evaluations. Yet I could see that their writing failed to change significantly over the course of the semester. I ended up feeling as if I should refund their money, haunted by the blunt instruments we had to teach writing.
As I’ve learned from directing five writing programs at three different universities, methods matter. When I reviewed comments on papers from instructors who taught in my programs, I discovered that the quantity and quality of comments on students’ papers made only a slight impact on writing outcomes. For instance, one notoriously lazy instructor took several weeks to return assignments and only used spelling and grammar checkers to automate comments. But his conscientious colleague made dozens of sharp observations about students’ arguments, paragraphs, and sentences. However, Mr. Conscientious’ students improved perhaps only 10% over Mr. Minimalist’s students. Even then, the differences stemmed from basic guidelines Mr. Conscientious insisted his students write to, which included providing context sentences at the outset of their essay introductions.
Educators have also poured resources into teaching writing, with increasing numbers of hours dedicated to teaching writing across primary, secondary, and higher education . Yet studies continue to find writing skills inadequate . In higher education, most universities require at least a year of writing-intensive courses, with many universities also requiring writing across the curriculum or writing in the disciplines to help preserve students’ writing skills. However, writing outcomes have remained mostly unchanged .
While pursuing my doctorate, I dedicated my research to figuring out how writing worked. As a graduate student also teaching part-time, I was an early convert to process writing. I also taught those ancient principles of logos, ethos, and pathos, as well as grammar and punctuation. Nevertheless, these frameworks only created a canvas for students’ writing. What was missing: how writers should handle words, sentence structure, and relationships between sentences.
Yet researchers published the beginnings of a science-based writing method over 30 years ago. George Gopen, Gregory Colomb, and Joseph Williams created a framework for identifying how to maximize the clarity, coherence, and continuity of writing. In particular, Gopen and Swan (1990) created a methodology for making scientific writing readable . This work should have been a revelation to anyone teaching in or directing a writing program. But, weirdly, comparatively few writing programs or faculty embraced this work, despite Williams, Colomb, and Gopen publishing both research and textbooks outlining the method and process.
Peculiarly, this framework—represented by Williams’ Style series of textbooks and Gopen’s reader expectation approach—failed to become standard in writing courses, likely because of two limitations. First, both Gopen and Williams hewed to a relativistic stance on writing methods, noting that rule-flouting often creates a memorable style. This stance created a raft of often-contradictory principles for writing. For example, Williams demonstrated that beginning sentences with There is or There are openings hijacked the clarity of sentences, then argued writers should use There is or There are to shunt important content into sentence emphasis positions, where readers recall content best. Second, these researchers failed to tie this writing framework to the wealth of data in psycholinguistics, cognitive neuroscience , or cognitive psychology on how our reading brains process written English. For instance, textbooks written by these three principal researchers avoid any mention of why emphasis positions exist at the ends of sentences and paragraphs—despite the concept clearly originating in the recency effect. This limitation may stem from the humanities’ long-held antipathy to the idea that writing is a product, rather than a process. Or even that science-based methods can help teachers and programs measure the effectiveness of writing, one reason why university First-Year Writing programs have failed to improve students’ writing in any measurable way.
Nevertheless, when you teach students how our reading brains work, you create a powerful method for rapidly improving their writing—in any course that requires writing and at all levels of education. Students can grasp how writing works as a system and assess the costs and benefits of decisions writers face, even as they choose their first words. This method also works powerfully to help students immediately understand how, for instance, paragraph heads leverage priming effects to shape readers’ understanding of paragraph content.
Using this method, I and my colleagues have helped students use a single writing assignment to secure hundreds of jobs, win millions in grant funding, and advance through the ranks in academia. However, we’ve also used the same method without modifications in elementary and secondary classrooms to bolster students’ writing by as much as three grade levels in a single year.
Perhaps the time has arrived for this well-kept secret to revolutionizing student writing outcomes to begin making inroads into more writing classrooms.
Gopen, G. D. and J. A. Swan (1990). "The Science of Scientific Writing." American Scientist 78(6): 550-558.
Gopen, George. The Sense of Structure: Writing from the Reader’s Perspective . Pearson, 2004.
Gopen, George. Expectations: Teaching Writing from the Reader’s Perspective . Pearson, 2004.
Williams, Joseph. Style: Toward Clarity and Grace . University of Chicago Press, 1995.
Williams, Joseph. Style: Ten Lessons in Clarity and Grace . Harper Collins, 1994.
Williams, Joseph. Style: The Basics of Clarity and Grace . Longman, 2002.

Jane Yellowlees Douglas, Ph.D. , is a consultant on writing and organizations. She is also the author, with Maria B. Grant, MD, of The Biomedical Writer: What You Need to Succeed in Academic Medicine .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
- Open access
- Published: 16 May 2024
Promoting equality, diversity and inclusion in research and funding: reflections from a digital manufacturing research network
- Oliver J. Fisher 1 ,
- Debra Fearnshaw ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6498-9888 2 ,
- Nicholas J. Watson 3 ,
- Peter Green 4 ,
- Fiona Charnley 5 ,
- Duncan McFarlane 6 &
- Sarah Sharples 2
Research Integrity and Peer Review volume 9 , Article number: 5 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
146 Accesses
Metrics details
Equal, diverse, and inclusive teams lead to higher productivity, creativity, and greater problem-solving ability resulting in more impactful research. However, there is a gap between equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) research and practices to create an inclusive research culture. Research networks are vital to the research ecosystem, creating valuable opportunities for researchers to develop their partnerships with both academics and industrialists, progress their careers, and enable new areas of scientific discovery. A feature of a network is the provision of funding to support feasibility studies – an opportunity to develop new concepts or ideas, as well as to ‘fail fast’ in a supportive environment. The work of networks can address inequalities through equitable allocation of funding and proactive consideration of inclusion in all of their activities.
This study proposes a strategy to embed EDI within research network activities and funding review processes. This paper evaluates 21 planned mitigations introduced to address known inequalities within research events and how funding is awarded. EDI data were collected from researchers engaging in a digital manufacturing network activities and funding calls to measure the impact of the proposed method.
Quantitative analysis indicates that the network’s approach was successful in creating a more ethnically diverse network, engaging with early career researchers, and supporting researchers with care responsibilities. However, more work is required to create a gender balance across the network activities and ensure the representation of academics who declare a disability. Preliminary findings suggest the network’s anonymous funding review process has helped address inequalities in funding award rates for women and those with care responsibilities, more data are required to validate these observations and understand the impact of different interventions individually and in combination.
Conclusions
In summary, this study offers compelling evidence regarding the efficacy of a research network's approach in advancing EDI within research and funding. The network hopes that these findings will inform broader efforts to promote EDI in research and funding and that researchers, funders, and other stakeholders will be encouraged to adopt evidence-based strategies for advancing this important goal.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Achieving equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) is an underpinning contributor to human rights, civilisation and society-wide responsibility [ 1 ]. Furthermore, promoting and embedding EDI within research environments is essential to make the advancements required to meet today’s research challenges [ 2 ]. This is evidenced by equal, diverse and inclusive teams leading to higher productivity, creativity and greater problem-solving ability [ 3 ], which increases the scientific impact of research outputs and researchers [ 4 ]. However, there remains a gap between EDI research and the everyday implementation of inclusive practices to achieve change [ 5 ]. This paper presents and reflects on the EDI measures trialled by the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) funded digital manufacturing research network, Connected Everything (grant number: EP/S036113/1) [ 6 ]. The EPSRC is a UK research council that funds engineering and physical sciences research. By sharing these reflections, this work aims to contribute to the wider effort of creating an inclusive research culture. The perceptions of equality, diversity, and inclusion may vary among individuals. For the scope of this study, the following definitions are adopted:
Equality: Equality is about ensuring that every individual has an equal opportunity to make the most of their lives and talents. No one should have poorer life chances because of the way they were born, where they come from, what they believe, or whether they have a disability.
Diversity: Diversity concerns understanding that each individual is unique, recognising our differences, and exploring these differences in a safe, positive, and nurturing way to value each other as individuals.
Inclusion: Inclusion is an effort and practice in which groups or individuals with different backgrounds are culturally and socially accepted, welcomed and treated equally. This concerns treating each person as an individual, making them feel valued, and supported and being respectful of who they are.
Research networks have varied goals, but a common purpose is to create new interdisciplinary research communities, by fostering interactions between researchers and appropriate scientific, technological and industrial groups. These networks aim to offer valuable career progression opportunities for researchers, through access to research funding, forming academic and industrial collaborations at network events, personal and professional development, and research dissemination. However, feedback from a 2021 survey of 19 UK research networks, suggests that these research networks are not always diverse, and whilst on the face of it they seem inclusive, they are perceived as less inclusive by minority groups (including non-males, those with disabilities, and ethnic minority respondents) [ 7 ]. The exclusivity of these networks further exacerbates the inequality within the academic community as it prevents certain groups from being able to engage with all aspects of network activities.
Research investigating the causes of inequality and exclusivity has identified several suggestions to make research culture more inclusive, including improving diverse representation within event programmes and panels [ 8 , 9 ]; ensuring events are accessible to all [ 10 ]; providing personalised resources and training to build capacity and increase engagement [ 11 ]; educating institutions and funders to understand and address the barriers to research [ 12 ]; and increasing diversity in peer review and funding panels [ 13 ]. Universities, research institutions and research funding bodies are increasingly taking responsibility to ensure the health of the research and innovation system and to foster inclusion. For example, the EPSRC has set out their own ‘Expectation for EDI’ to promote the formation of a diverse and inclusive research culture [ 14 ]. To drive change, there is an emphasis on the importance of measuring diversity and links to measured outcomes to benchmark future studies on how interventions affect diversity [ 5 ]. Further, collecting and sharing EDI data can also drive aspirations, provide a target for actions, and allow institutions to consider common issues. However, there is a lack of available data regarding the impact of EDI practices on diversity that presents an obstacle, impeding the realisation of these benefits and hampering progress in addressing common issues and fostering diversity and inclusion [ 5 ].
Funding acquisition is important to an academic’s career progression, yet funding may often be awarded in ways that feel unequal and/or non-transparent. The importance of funding in academic career progression means that, if credit for obtaining funding is not recognised appropriately, careers can be damaged, and, as a result of the lack of recognition for those who have been involved in successful research, funding bodies may not have a complete picture of the research community, and are unable to deliver the best value for money [ 15 ]. Awarding funding is often a key research network activity and an area where networks can have a positive impact on the wider research community. It is therefore important that practices are established to embed EDI consideration within the funding process and to ensure that network funding is awarded without bias. Recommendations from the literature to make the funding award process fairer include: ensuring a diverse funding panel; funders instituting reviewer anti-bias training; anonymous review; and/or automatic adjustments to correct for known biases [ 16 ]. In the UK, the government organisation UK Research and Innovation (UKRI), tasked with overseeing research and innovation funding, has pledged to publish data to enhance transparency. This initiative aims to furnish an evidence base for designing interventions and evaluating their efficacy. While the data show some positive signs (e.g., the award rates for male and female PI applicants were equal at 29% in 2020–21), Ottoline Leyser (UKRI Chief Executive) highlights the ‘persistent pernicious disparities for under-represented groups in applying for and winning research funding’ [ 17 ]. This suggests that a more radical approach to rethinking the traditional funding review process may be required.
This paper describes the approach taken by the ‘Connected Everything’ EPSRC-funded Network to embed EDI in all aspects of its research funding process, and evaluates the impact of this ambition, leading to recommendations for embedding EDI in research funding allocation.
Connected everything’s equality diversity and inclusion strategy
Connected Everything aims to create a multidisciplinary community of researchers and industrialists to address key challenges associated with the future of digital manufacturing. The network is managed by an investigator team who are responsible for the strategic planning and, working with the network manager, to oversee the delivery of key activities. The network was first funded between 2016–2019 (grant number: EP/P001246/1) and was awarded a second grant (grant number: EP/S036113/1). The network activities are based around three goals: building partnerships, developing leadership and accelerating impact.
The Connected Everything network represents a broad range of disciplines, including manufacturing, computer science, cybersecurity, engineering, human factors, business, sociology, innovation and design. Some of the subject areas, such as Computer Science and Engineering, tend to be male-dominated (e.g., in 2021/22, a total of 185,42 higher education student enrolments in engineering & technology subjects was broken down as 20.5% Female and 79.5% Male [ 18 ]). The networks also face challenges in terms of accessibility for people with care responsibilities and disabilities. In 2019, Connected Everything committed to embedding EDI in all its network activities and published a guiding principle and goals for improving EDI (see Additional file 1 ). When designing the processes to deliver the second iteration of Connected Everything, the team identified several sources of potential bias/exclusion which have the potential to impact engagement with the network. Based on these identified factors, a series of mitigation interventions were implemented and are outlined in Table 1 .
Connected everything anonymous review process
A key Connected Everything activity is the funding of feasibility studies to enable cross-disciplinary, foresight, speculative and risky early-stage research, with a focus on low technology-readiness levels. Awards are made via a short, written application followed by a pitch to a multidisciplinary diverse panel including representatives from industry. Six- to twelve-month-long projects are funded to a maximum value of £60,000.
The current peer-review process used by funders may reveal the applicants’ identities to the reviewer. This can introduce dilemmas to the reviewer regarding (a) deciding whether to rely exclusively on information present within the application or search for additional information about the applicants and (b) whether or not to account for institutional prestige [ 34 ]. Knowing an applicant’s identity can bias the assessment of the proposal, but by focusing the assessment on the science rather than the researcher, equality is more frequently achieved between award rates (i.e., the proportion of successful applications) [ 15 ]. To progress Connected Everything’s commitment to EDI, the project team created a 2-stage review process, where the applicants’ identity was kept anonymous during the peer review stage. This anonymous process, which is outlined in Fig. 1 , was created for the feasibility study funding calls in 2019 and used for subsequent funding calls.
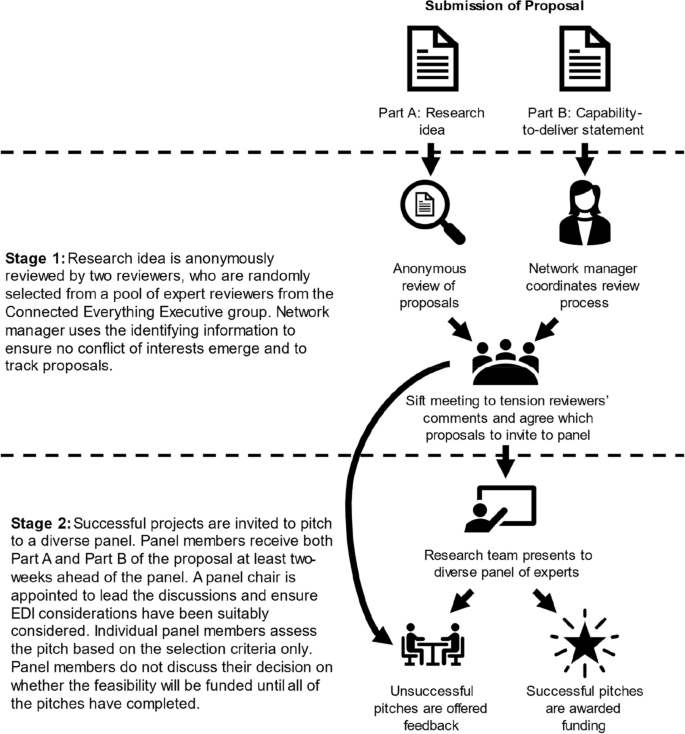
Connected Everything’s anonymous review process [EDI: Equality, diversity, and inclusion]
To facilitate the anonymous review process, the proposal was submitted in two parts: part A the research idea and part B the capability-to-deliver statement. All proposals were first anonymously reviewed by a random selection of two members from the Connected Everything executive group, which is a diverse group of digital manufacturing experts and peers from academia, industry and research institutions that provide guidance and leadership on Connected Everything activities. The reviewers rated the proposals against the selection criteria (see Additional file 1 , Table 1) and provided overall comments alongside a recommendation on whether or not the applicant should be invited to the panel pitch. This information was summarised and shared with a moderation sift panel, made up of a minimum of two Connected Everything investigators and a minimum of one member of the executive group, that tensioned the reviewers’ comments (i.e. comments and evaluations provided by the peer reviewers are carefully considered and weighed against each other) and ultimately decided which proposals to invite to the panel. This tension process included using the identifying information to ensure the applicants did have the capability to deliver the project. If this remained unclear, the applicants were asked to confirm expertise in an area the moderation sift panel thought was key or asked to bring in additional expertise to the project team during the panel pitch.
During stage two the applicants were invited to pitch their research idea to a panel of experts who were selected to reflect the diversity of the community. The proposals, including applicants’ identities, were shared with the panel at least two weeks ahead of the panel. Individual panel members completed a summary sheet at the end of the pitch session to record how well the proposal met the selection criteria (see Additional file 1 , Table 1). Panel members did not discuss their funding decision until all the pitches had been completed. A panel chair oversaw the process but did not declare their opinion on a specific feasibility study unless the panel could not agree on an outcome. The panel and panel chair were reminded to consider ways to manage their unconscious bias during the selection process.
Due to the positive response received regarding the anonymous review process, Connected Everything extended its use when reviewing other funded activities. As these awards were for smaller grant values (~ £5,000), it was decided that no panel pitch was required, and the researcher’s identity was kept anonymous for the entire process.
Data collection and analysis methods
Data collection.
Equality, diversity and inclusion data were voluntarily collected from applicants for Connected Everything research funding and from participants who won scholarships to attend Connected Everything funded activities. Responses to the EDI data requests were collected from nine Connected Everything coordinated activities between 2019 and 2022. Data requests were sent after the applicant had applied for Connected Everything funding or had attended a Connected Everything funded activity. All data requests were completed voluntarily, with reassurance given that completion of the data requested in no way affected their application. In total 260 responses were received, of which the three feasibility study calls comprised 56.2% of the total responses received. Overall, there was a 73.8% response rate.
To understand the diversity of participants engaging with Connected Everything activities and funding, the data requests asked for details of specific diversity characteristics: gender, transgender, disability, ethnicity, age, and care responsibilities. Although sex and gender are terms that are often used interchangeably, they are two different concepts. To clarify, the definitions used by the UK government describe sex as a set of biological attributes that is generally limited to male or female, and typically attributed to individuals at birth. In contrast, gender identity is a social construction related to behaviours and attributes, and is self-determined based on a person’s internal perception, identification and experience. Transgender is a term used to describe people whose gender identity is not the same as the sex they were registered at birth. Respondents were first asked to identify their gender and then whether their gender was different from their birth sex.
For this study, respondents were asked to (voluntarily) self-declare whether they consider themselves to be disabled or not. Ethnicity within the data requests was based on the 2011 census classification system. When reporting ethnicity data, this study followed the AdvanceHE example to aggregate the census categories into six groups to enable benchmarking against the available academic ethnicity data. AdvanceHE is a UK charity that works to improve the higher education system for staff, students and society. However, it was acknowledged that there were limitations with this grouping, including the assumption that minority ethnic staff or students are a homogenous group [ 16 ]. Therefore, this study made sure to breakdown these groups during the discussion of the results. The six groups are:
Asian: Asian/Asian British: Indian, Pakistani, Bangladeshi, and any other Asian background;
Black: Black/African/Caribbean/Black British: African, Caribbean, and any other Black/African/Caribbean background;
Other ethnic backgrounds, including Arab.
White: all white ethnic groups.
Benchmarking data
Published data from the Higher Education Statistics Agency [ 26 ] (a UK organisation responsible for collecting, analysing, and disseminating data related to higher education institutions and students), UKRI funding data [ 19 , 35 ] and 2011 census data [ 36 ] were used to benchmark the EDI data collected within this study. The responses to the data collected were compared to the engineering and technology cluster of academic disciplines, as this is most represented by Connected Everything’s main funded EPSRC. The Higher Education Statistics Agency defines the engineering and technology cluster as including the following subject areas: general engineering; chemical engineering; mineral, metallurgy & materials engineering; civil engineering; electrical, electronic & computer engineering; mechanical, aero & production engineering and; IT, systems sciences & computer software engineering [ 37 ].
When assessing the equality in funding award rates, previous studies have focused on analysing the success rates of only the principal investigators [ 15 , 16 , 38 ]; however, Connected Everything recognised that writing research proposals is a collaborative task, so requested diversity data from the whole research team. The average of the last six years of published principal investigator and co-investigator diversity data for UKRI and EPSRC funding awards (2015–2021) was used to benchmark the Connected Everything funding data [ 35 ]. The UKRI and EPSRC funding review process includes a peer review stage followed by panel pitch and assessment stage; however, the applicant's track record is assessed during the peer review stage, unlike the Connected Everything review process.
The data collected have been used to evaluate the success of the planned migrations to address EDI factors affecting the higher education research ecosystem, as outlined in Table 1 (" Connected Everything’s Equality Diversity and Inclusion Strategy " Section).
Dominance of small number of research-intensive universities receiving funding from network
The dominance of a small number of research-intensive universities receiving funding from a network can have implications for the field of research, including: the unequal distribution of resources; a lack of diversity of research, limited collaboration opportunities; and impact on innovation and progress. Analysis of published EPSRC funding data between 2015 and 2021 [ 19 ], shows that the funding has been predominately (74.1%, 95% CI [71.%, 76.9%] out of £3.98 billion) awarded to Russell Group universities. The Russell Group is a self-selected association of 24 research-intensive universities (out of the 174 universities) in the UK, established in 1994. Evaluation of the universities that received Connected Everything feasibility study funding between 2016–2019, shows that Connected Everything awarded just over half (54.6%, 95% CI [25.1%, 84.0%] out of 11 awards) to Russell Group universities. Figure 2 shows that the Connected Everything funding awarded to Russell Group universities reduced to 44.4%, 95% CI [12.0%, 76.9%] of 9 awards between 2019–2022.
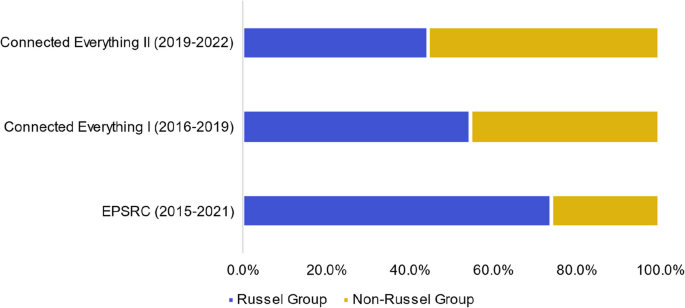
A comparison of funding awarded by EPSRC (total = £3.98 billion) across Russell Group universities and non-Russell Group universities, alongside the allocations for Connected Everything I (total = £660 k) and Connected Everything II (total = £540 k)
Dominance of successful applications from men
The percentage point difference between the award rates of researchers who identified as female, those who declare a disability, or identified as ethnic minority applicants and carers and their respective counterparts have been plotted in Fig. 3 . Bars to the right of the axis mean that the award rate of the female/declared-disability/ethnic-minority/carer applicants is greater than that of male/non- disability/white/not carer applicants.
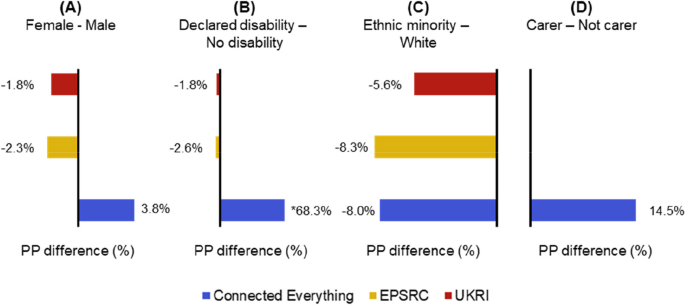
Percentage point (PP) differences in award rate by funding provider for gender, disability status, ethnicity and care responsibilities (data not collected by UKRI and EPSRC [ 35 ]). The total number of applicants for each funder are as follows: Connected Everything = 146, EPSRC = 37,960, and UKRI = 140,135. *The numbers of applicants were too small (< 5) to enable a meaningful discussion
Figure 3 (A) shows that between 2015 and 2021 research team applicants who identified as male had a higher award rate than those who identified as female when applying for EPSRC and wider UKRI research council funding. Connected Everything funding applicants who identified as female achieved a higher award rate (19.4%, 95% CI [6.5%, 32.4%] out of 146) compared to male applicants (15.6%, 95% CI [8.8%, 22.4%] out of 146). These data suggest that biases have been reduced by the Connected Everything review process and other mitigation strategies (e.g., visible gender diversity in panel pitch members and publishing CE principal and goals to demonstrate commitment to equality and fairness). This finding aligns with an earlier study that found gender bias during the peer review process, resulting in female investigators receiving less favourable evaluations than their male counterparts [ 15 ].
Over-representation of people identifying as male in engineering and technology academic community
Figure 4 shows the response to the gender question, with 24.2%, 95% CI [19.0%, 29.4%] of 260 responses identifying as female. This aligns with the average for the engineering and technology cluster (21.4%, 95% CI [20.9%, 21.9%] female of 27,740 academic staff), which includes subject areas representative of our main funder, EPSRC [ 22 ]. We also sought to understand the representation of transgender researchers within the network. However, following the rounding policy outlined by UK Government statistics policies and procedures [ 39 ], the number of responses that identified as a different sex to birth was too low (< 5) to enable a meaningful discussion.
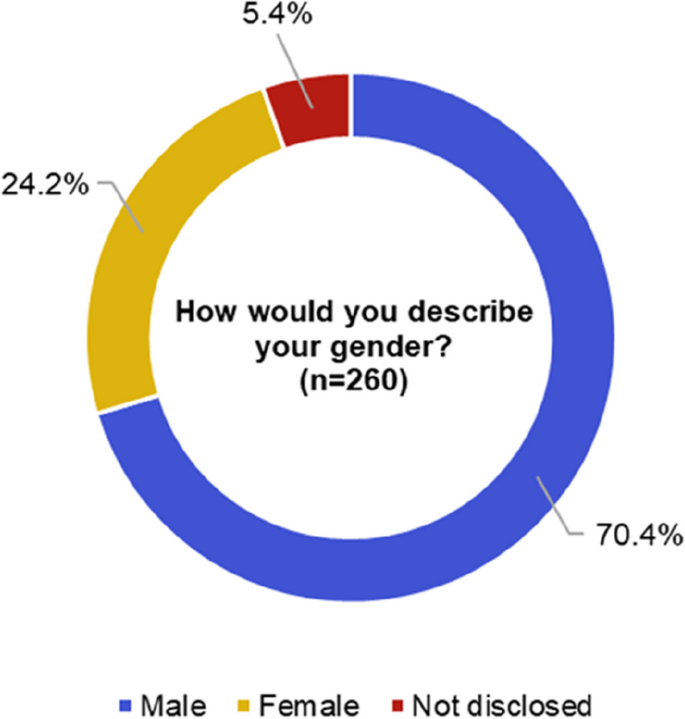
Gender question responses from a total of 260 respondents
Dominance of successful applications from white academics
Figure 3 (C) shows that researchers with a minority ethnicity consistently have a lower award rate than white researchers when applying for EPSRC and UKRI funding. Similarly, the results in Fig. 3 (C) indicate that white researchers are more successful (8.0% percentage point, 95% CI [-8.6%, 24.6%]) when applying for Connected Everything funding. These results indicate that more measures should be implemented to support the ethnic minority researchers applying for Connected Everything funding, as well as sense checking there is no unconscious bias in any of the Connected Everything funding processes. The breakdown of the ethnicity diversity of applicants at different stages of the Connected Everything review process (i.e. all applications, applicants invited to panel pitch and awarded feasibility studies) has been plotted in Fig. 5 to help identify where more support is needed. Figure 5 shows an increase in the proportion of white researchers from 54%, 95% CI [45.4%, 61.8%] of all 146 applicants to 66%, 95% CI [52.8%, 79.1%] of the 50 researchers invited to the panel pitch. This suggests that stage 1 of the Connected Everything review process (anonymous review of written applications) may favour white applicants and/or introduce unconscious bias into the process.
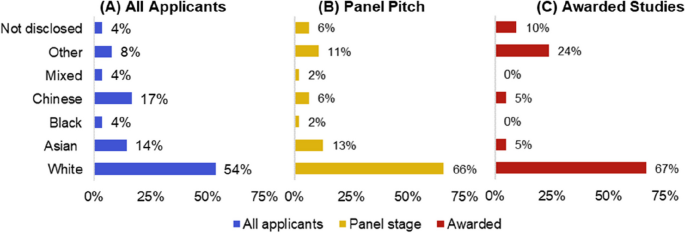
Ethnicity questions responses from different stages during the Connected Everything anonymous review process. The total number of applicants is 146, with 50 at the panel stage and 23 ultimately awarded
Under-representation of those from black or minority ethnic backgrounds
Connected Everything appears to have a wide range of ethnic diversity, as shown in Fig. 6 . The ethnicities Asian (18.3%, 95% CI [13.6%, 23.0%]), Black (5.1%, 95% CI [2.4%, 7.7%]), Chinese (12.5%, 95% CI [8.4%, 16.5%]), mixed (3.5%, 95% CI [1.3%, 5.7%]) and other (7.8%, 95% CI [4.5%, 11.1%]) have a higher representation among the 260 individuals engaging with network’s activities, in contrast to both the engineering and technology academic community and the wider UK population. When separating these groups into the original ethnic diversity answers, it becomes apparent that there is no engagement with ‘Black or Black British: Caribbean’, ‘Mixed: White and Black Caribbean’ or ‘Mixed: White and Asian’ researchers within Connected Everything activities. The lack of engagement with researchers from a Caribbean heritage is systemic of a lack of representation within the UK research landscape [ 25 ].
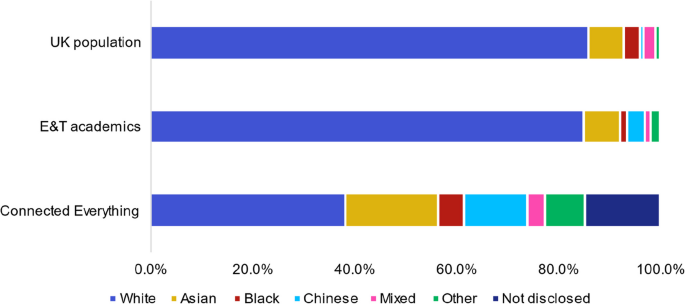
Ethnicity question responses from a total of 260 respondents compared to distribution of the 13,085 UK engineering and technology (E&T) academic staff [ 22 ] and 56 million people recorded in the UK 2011 census data [ 36 ]
Under-representation of disabilities, chronic conditions, invisible illnesses and neurodiversity in funded activities and events.
Figure 7 (A) shows that 5.7%, 95% CI [2.4%, 8.9%] of 194 responses declared a disability. This is higher than the average of engineering and technology academics that identify as disabled (3.4%, 95% CI [3.2%, 3.7%] of 27,730 academics). Between Jan-March 2022, 9.0 million people of working age (16–64) within the UK were identified as disabled by the Office for National Statistics [ 40 ], which is 21% of the working age population [ 27 ]. Considering these statistics, there is a stark under-representation of disabilities, chronic conditions, invisible illnesses and neurodiversity amongst engineering and technology academic staff and those engaging in Connected Everything activities.
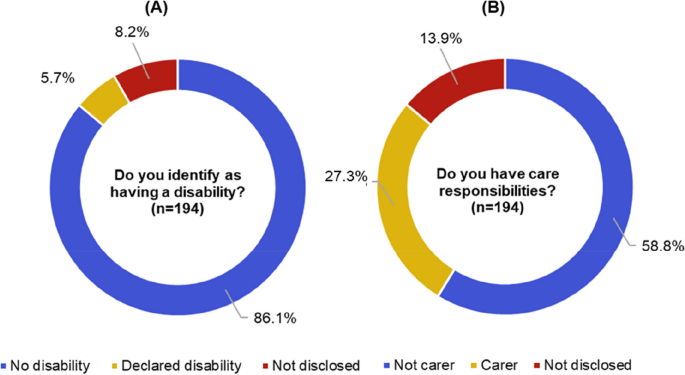
Responses to A Disability and B Care responsibilities questions colected from a total of 194 respondents
Between 2015 and 2020 academics that declared a disability have been less successful than academics without a disability in attracting UKRI and EPSRC funding, as shown in Fig. 3 (B). While Fig. 3 (B) shows that those who declare a disability have a higher Connected Everything funding award rate, the number of applicants who declared a disability was too small (< 5) to enable a meaningful discussion regarding this result.
Under-representation of those with care responsibilities in funded activities and events
In response to the care responsibilities question, Fig. 7 (B) shows that 27.3%, 95% CI [21.1%, 33.6%] of 194 respondents identified as carers, which is higher than the 6% of adults estimated to be providing informal care across the UK in a UK Government survey of the 2020/2021 financial year [ 41 ]. However, the ‘informal care’ definition used by the 2021 survey includes unpaid care to a friend or family member needing support, perhaps due to illness, older age, disability, a mental health condition or addiction [ 41 ]. The Connected Everything survey included care responsibilities across the spectrum of care that includes partners, children, other relatives, pets, friends and kin. It is important to consider a wide spectrum of care responsibilities, as key academic events, such as conferences, have previously been demonstrably exclusionary sites for academics with care responsibilities [ 42 ]. Breakdown analysis of the responses to care responsibilities by gender in Fig. 8 reveals that 37.8%, 95% CI [25.3%, 50.3%] of 58 women respondents reported care responsibilities, compared to 22.6%, 95% CI [61.1%, 76.7%] of 136 men respondents. Our findings reinforce similar studies that conclude the burden of care falls disproportionately on female academics [ 43 ].
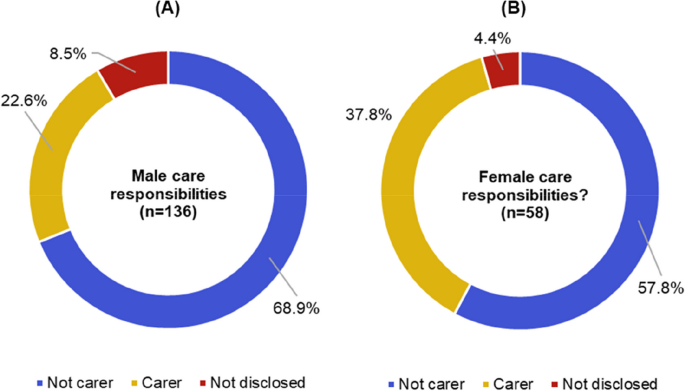
Responses to care responsibilities when grouped by A 136 males and B 58 females
Figure 3 (D) shows that researchers with careering responsibilities applying for Connected Everything funding have a higher award rate than those researchers applying without care responsibilities. These results suggest that the Connected Everything review process is supportive of researchers with care responsibilities, who have faced barriers in other areas of academia.
Reduced opportunities for ECRs
Early-career researchers (ECRs) represent the transition stage between starting a PhD and senior academic positions. EPSRC defines an ECR as someone who is either within eight years of their PhD award, or equivalent professional training or within six years of their first academic appointment [ 44 ]. These periods exclude any career break, for example, due to family care; health reasons; and reasons related to COVID-19 such as home schooling or increased teaching load. The median age for starting a PhD in the UK is 24 to 25, while PhDs usually last between three and four years [ 45 ]. Therefore, these data would imply that the EPSRC median age of ECRs is between 27 and 37 years. It should be noted, however, that this definition is not ideal and excludes ECRs who may have started their research career later in life.
Connected Everything aims to support ECRs via measures that include mentoring support, workshops, summer schools and podcasts. Figure 9 shows a greater representation of researchers engaging with Connected Everything activities that are aged between 30–44 (62.4%, 95% CI [55.6%, 69.2%] of 194 respondents) when compared to the wider engineering and technology academic community (43.7%, 95% CI [43.1%, 44.3%] of 27,780 academics) and UK population (26.9%, 95% CI [26.9%, 26.9%]).
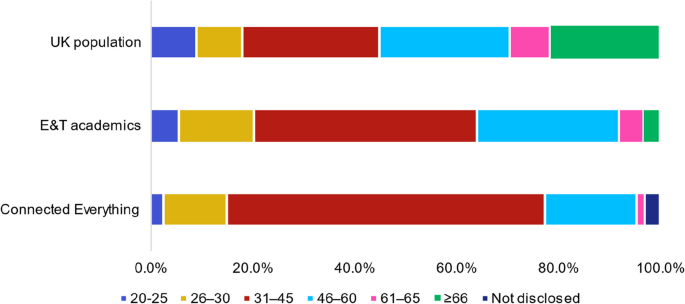
Age question responses from a total of 194 respondents compared to distribution of the 27,780 UK engineering and technology (E&T) academic staff [ 22 ] and 56 million people recorded in the UK 2011 census data [ 36 ]
High competition for funding has a greater impact on ECRs
Figure 10 shows that the largest age bracket applying for and winning Connected Everything funding is 31–45, whereas 72%, CI 95% [70.1%, 74.5%] of 12,075 researchers awarded EPSRC grants between 2015 and 2021 were 40 years or older. These results suggest that measures introduced by Connected Everything has been successful at providing funding opportunities for researchers who are likely to be early-mid career stage.
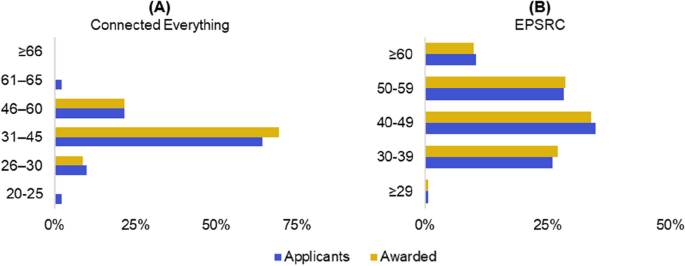
Age of researchers at applicant and awarded funding stages for A Connected Everything between 2019–2022 (total of 146 applicants and 23 awarded) and B EPSRC funding between 2015–2021 [ 35 ] (total of 35,780 applicants and 12,075 awarded)
The results of this paper provide insights into the impact that Connected Everything’s planned mitigations have had on promoting equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) in research and funding. Collecting EDI data from individuals who engage with network activities and apply for research funding enabled an evaluation of whether these mitigations have been successful in achieving the intended outcomes outlined at the start of the study, as summarised in Table 2 .
The results in Table 2 indicate that Connected Everything’s approach to EDI has helped achieve the intended outcome to improve representation of women, ECRs, those with a declared disability and black/minority ethnic backgrounds engaging with network events when compared to the engineering and technology academic community. In addition, the network has helped raise awareness of the high presence of researchers with care responsibilities at network events, which can help to track progress towards making future events inclusive and accessible towards these carers. The data highlights two areas for improvement: (1) ensuring a gender balance; and (2) increasing representation of those with declared disabilities. Both these discrepancies are indicative of the wider imbalances and underrepresentation of these groups in the engineering and technology academic community [ 26 ], yet represent areas where networks can strive to make a difference. Possible strategies include: using targeted outreach; promoting greater representation of these groups in event speakers; and going further to create a welcoming and inclusive environment. One barrier that can disproportionately affect women researchers is the need to balance care responsibilities with attending network events [ 46 ]. This was reflected in the Connected Everything data that reported 37.8%, 95% CI [25.3%, 50.3%] of women engaging with network activities had care responsibilities, compared to 22.6%, 95% CI [61.1%, 76.7%] of men. Providing accommodations such as on-site childcare, flexible scheduling, or virtual attendance options can therefore help to promote inclusivity and allow more women researchers to attend.
Only 5.7%, 95% CI [2.4%, 8.9%] of responses engaging with Connected Everything declared a disability, which is higher than the engineering and technology academic community (3.4%, 95% CI [3.2%, 3.7%]) [ 26 ], but unrepresentative of the wider UK population. It has been suggested that academics can be uncomfortable when declaring disabilities because scholarly contributions and institutional citizenship are so prized that they feel they cannot be honest about their issues or health concerns and keep them secret [ 47 ]. In research networks, it is important to be mindful of this hidden group within higher education and ensure that measures are put in place to make the network’s activities inclusive to all. Future considerations for accommodations to improve research events inclusivity include: improving physical accessibility of events; providing assistive technology such as screen readers, audio descriptions, and captioning can help individuals with visual or hearing impairments to access and participate; providing sign language interpreters; offering flexible scheduling options; and the provision of quiet rooms, written materials in accessible formats, and support staff trained to work with individuals with cognitive disabilities.
Connected Everything introduced measures (e.g., anonymised reviewing process, Q&A sessions before funding calls, inclusive design of panel pitch) to help address inequalities in how funding is awarded. Table 2 shows success in reducing the dominance of researchers who identify as male and research-intensive universities in winning research funding and that researchers with care responsibilities were more successful at winning funding than those without care responsibilities. The data revealed that the proposed measures were unable to address the inequality in award rates between white and ethnic minority researchers, which is an area to look to improve. The inequality appears to occur during the anonymous review stage, with a greater proportion of white researchers being invited to panel. Recommendations to make the review process fairer include: ensuring greater diversity of reviewers; reviewer anti-bias training; and automatic adjustments to correct for known biases in writing style [ 16 , 32 ].
When reflecting on the development of a strategy to embed EDI throughout the network, Connected Everything has learned several key lessons that may benefit other networks undergoing a similar activity. These include:
EDI is never ‘done’: There is a constant need to review approaches to EDI to ensure they remain relevant to the network community. Connected Everything could review its principles to include the concept of justice in its approach to diversity and inclusion. The concept of justice concerning EDI refers to the removal of systematic barriers that stop fair and equitable distribution of resources and opportunities among all members of society, regardless of their individual characteristics or backgrounds. The principles and subsequent actions could be reviewed against the EDI expectations [ 14 ], paying particular attention to areas where barriers may still be present. For example, shifting from welcoming people into existing structures and culture to creating new structures and culture together, with specific emphasis on decision or advisory mechanisms within the network. This activity could lend itself to focusing more on tailored support to overcome barriers, thus achieving equity, if it is not within the control of the network to remove the barrier itself (justice).
Widen diversity categories: By collecting data on a broad range of characteristics, we can identify and address disparities and biases that might otherwise be overlooked. A weakness of this dataset is that ignores the experience of those with intersectional identities, across race, ethnicity, gender, class, disability and/ or LGBTQI. The Wellcome Trust noted how little was known about the socio-economic background of scientists and researchers [ 48 ].
Collect data on whole research teams: For the first two calls for feasibility study funding, Connected Everything only asked the Principal Investigator to voluntarily provide their data. We realised that this was a limited approach and, in the third call, asked for the data regarding the whole research team to be shared anonymously. Furthermore, we do not currently measure the diversity of our event speakers, panellists or reviewers. Collecting these data in the future will help to ensure the network is accountable and will ensure that all groups are represented during our activities and in the funding decision-making process.
High response rate: Previous surveys measuring network diversity (e.g., [ 7 ]) have struggled to get responses when surveying their memberships; whereas, this study achieved a response rate of 73.8%. We attribute this high response rate to sending EDI data requests on the point of contact with the network (e.g., on submitting funding proposals or after attending network events), rather than trying to survey the entire network membership at anyone point in time.
Improve administration: The administration associated with collecting EDI data requires a commitment to transparency, inclusivity, and continuous improvement. For example, during the first feasibility funding call, Connected Everything made it clear that the review process would be anonymous, but the application form was not in separate documents. This made anonymising the application forms extremely time-consuming. For the subsequent calls, separate documents were created – Part A for identifying information (Principal Investigator contact details, Project Team and Industry collaborators) and Part B for the research idea.
Accepting that this can be uncomfortable: Trying to improve EDI can be uncomfortable because it often requires challenging our assumptions, biases, and existing systems and structures. However, it is essential if we want to make real progress towards equity and inclusivity. Creating processes to support embedding EDI takes time and Connected Everything has found it is rare to get it right the first time. Connected Everything is sharing its learning as widely as possible both to support others in their approaches and continue our learning as we reflect on how to continually improve, even when it is challenging.
Enabling individual engagement with EDI: During this work, Connected Everything recognised that methods for engaging with such EDI issues in research design and delivery are lacking. Connected Everything, with support from the Future Food Beacon of Excellence at the University of Nottingham, set out to develop a card-based tool [ 49 ] to help researchers and stakeholders identify questions around how their work may promote equity and increase inclusion or have a negative impact towards one or more protected groups and how this can be overcome. The results of this have been shared at conference presentations [ 50 ] and will be published later.
While this study provides insights into how EDI can be improved in research network activities and funding processes, it is essential to acknowledge several limitations that may impact the interpretation of the findings.
Sample size and generalisability: A total of 260 responses were received, which may not be representative of our overall network of 500 + members. Nevertheless, this data provides a sense of the current diversity engaging in Connected Everything activities and funding opportunities, which we can compare with other available data to steer action to further diversify the network.
Handling of missing data: Out of the 260 responses, 66 data points were missing for questions regarding age, disability, and caring responsibilities. These questions were mistakenly omitted from a Connected Everything summer school survey, contributing to 62 missing data points. While we assumed the remainer of missing data to be at random during analysis, it's important to acknowledge it could be related to other factors, potentially introducing bias into our results.
Emphasis on quantitative data: The study relies on using quantitative data to evaluate the impact of the EDI measures introduced by Connected Everything. However, relying solely on quantitative metrics may overlook nuanced aspects of EDI that cannot be easily quantified. For example, EDI encompasses multifaceted issues influenced by historical, cultural, and contextual factors. These nuances may not be fully captured by numbers alone. In addition, some EDI efforts may not yield immediate measurable outcomes but still contribute to a more inclusive environment.
Diversity and inclusion are not synonymous: The study proposes 21 measures to contribute towards creating an equal, diverse and inclusive research culture and collects diversity data to measure the impact of these measures. However, while diversity is simpler to monitor, increasing diversity alone does not guarantee equality or inclusion. Even with diverse research groups, individuals from underrepresented groups may still face barriers, microaggressions, or exclusion.
Balancing anonymity and rigour in grant reviews:The proposed anonymous review process proposed by Connected Everything removes personal and organisational details from the research ideas under reviewer evaluation. However, there exists a possibility that a reviewer could discern the identity of the grant applicant based on the research idea. Reviewers are expected to be subject matter experts in the field relevant to the grant proposal they are evaluating. Given the specialised nature of scientific research, it is conceivable that a well-known applicant could be identified through the specifics of the work, the methodologies employed, and even the writing style.
Expanding gender identity options: A limitation of this study emerged from the restricted gender options (male, female, other, prefer not to say) provided to respondents when answering the gender identity question. This limitation reflects the context of data collection in 2018, a time when diversity monitoring guidance was still limited. As our understanding of gender identity evolves beyond binary definitions, future data collection efforts should embrace a more expansive and inclusive approach, recognising the diverse spectrum of gender identities.
In conclusion, this study provides evidence of the effectiveness of a research network's approach to promoting equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) in research and funding. By collecting EDI data from individuals who engage with network activities and apply for research funding, this study has shown that the network's initiatives have had a positive impact on representation and fairness in the funding process. Specifically, the analysis reveals that the network is successful at engaging with ECRs, and those with care responsibilities and has a diverse range of ethnicities represented at Connected Everything events. Additionally, the network activities have a more equal gender balance and greater representation of researchers with disabilities when compared to the engineering and technology academic community, though there is still an underrepresentation of these groups compared to the national population.
Connected Everything introduced measures to help address inequalities in how funding is awarded. The measures introduced helped reduce the dominance of researchers who identified as male and research-intensive universities in winning research funding. Additionally, researchers with care responsibilities were more successful at winning funding than those without care responsibilities. However, inequality persisted with white researchers achieving higher award rates than those from ethnic minority backgrounds. Recommendations to make the review process fairer include: ensuring greater diversity of reviewers; reviewer anti-bias training; and automatic adjustments to correct for known biases in writing style.
Connected Everything’s approach to embedding EDI in network activities has already been shared widely with other EPSRC-funded networks and Hubs (e.g. the UKRI Circular Economy Hub and the UK Acoustics Network Plus). The network hopes that these findings will inform broader efforts to promote EDI in research and funding and that researchers, funders, and other stakeholders will be encouraged to adopt evidence-based strategies for advancing this important goal.
Availability of data and materials
The data collected was anonymously, however, it may be possible to identify an individual by combining specific records of the data request form data. Therefore, the study data has been presented in aggregate form to protect the confidential of individuals and the data utilised in this study cannot be made openly accessible due to ethical obligations to protect the privacy and confidentiality of the data providers.
Abbreviations
Early career researcher
Equality, diversity and inclusion
Engineering physical sciences research council
UK research and innovation
Xuan J, Ocone R. The equality, diversity and inclusion in energy and AI: call for actions. Energy AI. 2022;8:100152.
Article Google Scholar
Guyan K, Oloyede FD. Equality, diversity and inclusion in research and innovation: UK review. Advance HE; 2019. https://www.ukri.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/UKRI-020920-EDI-EvidenceReviewUK.pdf .
Cooke A, Kemeny T. Cities, immigrant diversity, and complex problem solving. Res Policy. 2017;46:1175–85.
AlShebli BK, Rahwan T, Woon WL. The preeminence of ethnic diversity in scientific collaboration. Nat Commun. 2018;9:5163.
Gagnon S, Augustin T, Cukier W. Interplay for change in equality, diversity and inclusion studies: Hum Relations. Epub ahead of print 23 April 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/00187267211002239 .
Everything C. https://connectedeverything.ac.uk/ . Accessed 27 Feb (2023).
Chandler-Wilde S, Kanza S, Fisher O, Fearnshaw D, Jones E. Reflections on an EDI Survey of UK-Government-Funded Research Networks in the UK. In: The 51st International Congress and Exposition on Noise Control Engineering. St. Albans: Institute of Acoustics; 2022. p. 9.0–940.
Google Scholar
Prathivadi Bhayankaram K, Prathivadi Bhayankaram N. Conference panels: do they reflect the diversity of the NHS workforce? BMJ Lead 2022;6:57 LP – 59.
Goodman SW, Pepinsky TB. Gender representation and strategies for panel diversity: Lessons from the APSA Annual Meeting. PS Polit Sci Polit 2019;52:669–676.
Olsen J, Griffiths M, Soorenian A, et al. Reporting from the margins: disabled academics reflections on higher education. Scand J Disabil Res. 2020;22:265–74.
Baldie D, Dickson CAW, Sixsmith J. Building an Inclusive Research Culture. In: Knowledge, Innovation, and Impact. 2021, pp. 149–157.
Sato S, Gygax PM, Randall J, et al. The leaky pipeline in research grant peer review and funding decisions: challenges and future directions. High Educ 2020 821. 2020;82:145–62.
Recio-Saucedo A, Crane K, Meadmore K, et al. What works for peer review and decision-making in research funding: a realist synthesis. Res Integr Peer Rev. 2022;2022 71:7: 1–28.
EPSRC. Expectations for equality, diversity and inclusion – UKRI, https://www.ukri.org/about-us/epsrc/our-policies-and-standards/equality-diversity-and-inclusion/expectations-for-equality-diversity-and-inclusion/ (2022, Accessed 26 Apr 2022).
Witteman HO, Hendricks M, Straus S, et al. Are gender gaps due to evaluations of the applicant or the science? A natural experiment at a national funding agency. Lancet. 2019;393:531–40.
Li YL, Bretscher H, Oliver R, et al. Racism, equity and inclusion in research funding. Sci Parliam. 2020;76:17–9.
UKRI publishes latest diversity. data for research funding – UKRI, https://www.ukri.org/news/ukri-publishes-latest-diversity-data-for-research-funding/ (Accessed 28 July 2022).
Higher Education Statistics Agency. What do HE students study? https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis/students/what-study (2023, Accessed 25 March 2023).
UKRI. Competitive funding decisions, https://www.ukri.org/what-we-offer/what-we-have-funded/competitive-funding-decisions / (2023, Accessed 2 April 2023).
Santos G, Van Phu SD. Gender and academic rank in the UK. Sustain. 2019;11:3171.
Jebsen JM, Nicoll Baines K, Oliver RA, et al. Dismantling barriers faced by women in STEM. Nat Chem. 2022;14:1203–6.
Advance HE. Equality in higher education: staff statistical report 2021 | Advance HE, https://www.advance-he.ac.uk/knowledge-hub/equality-higher-education-statistical-report-2021 (28 October 2021, Accessed 26 April 2022).
EngineeringUK. Engineering in Higher Education, https://www.engineeringuk.com/media/318874/engineering-in-higher-education_report_engineeringuk_march23_fv.pdf (2023, Accessed 25 March 2023).
Bhopal K. Academics of colour in elite universities in the UK and the USA: the ‘unspoken system of exclusion’. Stud High Educ. 2022;47:2127–37.
Williams P, Bath S, Arday J et al. The Broken Pieline: Barriers to Black PhD Students Accessing Research Council Funding . 2019.
HESA. Who’s working in HE? Personal characteristics, https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis/staff/working-in-he/characteristics (2023, Accessed 1 April 2023).
Office for National Statistics. Principal projection - UK population in age groups, https://www.ons.gov.uk/peoplepopulationandcommunity/populationandmigration/populationprojections/datasets/tablea21principalprojectionukpopulationinagegroups (2022, Accessed 3 August 2022).
HESA. Who’s studying in HE? Personal characteristics, https://www.hesa.ac.uk/data-and-analysis/students/whos-in-he/characteristics (2023, Accessed 1 April 2023).
Herman E, Nicholas D, Watkinson A et al. The impact of the pandemic on early career researchers: what we already know from the internationally published literature. Prof la Inf ; 30. Epub ahead of print 11 March 2021. https://doi.org/10.3145/epi.2021.mar.08 .
Moreau M-P, Robertson M. ‘Care-free at the top’? Exploring the experiences of senior academic staff who are caregivers, https://srhe.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Moreau-Robertson-SRHE-Research-Report.pdf (2019).
Shillington AM, Gehlert S, Nurius PS, et al. COVID-19 and long-term impacts on tenure-line careers. J Soc Social Work Res. 2020;11:499–507.
de Winde CM, Sarabipour S, Carignano H et al. Towards inclusive funding practices for early career researchers. J Sci Policy Gov; 18. Epub ahead of print 24 March 2021. https://doi.org/10.38126/JSPG180105 .
Trust W. Grant funding data report 2018/19, https://wellcome.org/sites/default/files/grant-funding-data-2018-2019.pdf (2020).
Vallée-Tourangeau G, Wheelock A, Vandrevala T, et al. Peer reviewers’ dilemmas: a qualitative exploration of decisional conflict in the evaluation of grant applications in the medical humanities and social sciences. Humanit Soc Sci Commun. 2022;2022 91:9: 1–11.
Diversity data – UKRI. https://www.ukri.org/what-we-offer/supporting-healthy-research-and-innovation-culture/equality-diversity-and-inclusion/diversity-data/ (accessed 30 September 2022).
2011 Census - Office for National Statistics. https://www.ons.gov.uk/census/2011census (Accessed 2 August 2022).
Cost centres. (2012/13 onwards) | HESA, https://www.hesa.ac.uk/support/documentation/cost-centres/2012-13-onwards (Accessed 28 July 2022).
Viner N, Powell P, Green R. Institutionalized biases in the award of research grants: a preliminary analysis revisiting the principle of accumulative advantage. Res Policy. 2004;33:443–54.
ofqual. Rounding policy - GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/ofquals-statistics-policies-and-procedures/rounding-policy (2023, Accessed 2 April 2023).
Office for National Statistics. Labour market status of disabled people, https://www.ons.gov.uk/employmentandlabourmarket/peopleinwork/employmentandemployeetypes/datasets/labourmarketstatusofdisabledpeoplea08 (2022, Accessed 3 August 2022).
Family Resources Survey. financial year 2020 to 2021 - GOV.UK, https://www.gov.uk/government/statistics/family-resources-survey-financial-year-2020-to-2021 (Accessed 10 Aug 2022).
Henderson E. Academics in two places at once: (not) managing caring responsibilities at conferences. 2018, p. 218.
Jolly S, Griffith KA, DeCastro R, et al. Gender differences in time spent on parenting and domestic responsibilities by high-achieving young physician-researchers. Ann Intern Med. 2014;160:344–53.
UKRI. Early career researchers, https://www.ukri.org/what-we-offer/developing-people-and-skills/esrc/early-career-researchers/ (2022, Accessed 2 April 2023).
Cornell B. PhD Life: The UK student experience , www.hepi.ac.uk (2019, Accessed 2 April 2023).
Kibbe MR, Kapadia MR. Underrepresentation of women at academic medical conferences—manels must stop. JAMA Netw Open 2020; 3:e2018676–e2018676.
Brown N, Leigh J. Ableism in academia: where are the disabled and ill academics? 2018; 33: 985–989. https://doi.org/10.1080/0968759920181455627
Bridge Group. Diversity in Grant Awarding and Recruitment at Wellcome Summary Report. 2017.
Peter Craigon O, Fisher D, Fearnshaw et al. VERSION 1 - The Equality Diversity and Inclusion cards. Epub ahead of print 2022. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.21222212.v3 .
Connected Everything II. EDI ideation cards for research - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GdJjL6AaBbc&ab_channel=ConnectedEverythingII (2022, Accessed 7 June 2023).
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) [grant number EP/S036113/1], Connected Everything II: Accelerating Digital Manufacturing Research Collaboration and Innovation. The authors would also like to gratefully acknowledge the Connected Everything Executive Group for their contribution towards developing Connected Everything’s equality, diversity and inclusion strategy.
This work was supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) [grant number EP/S036113/1].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Food, Water, Waste Research Group, Faculty of Engineering, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, UK
Oliver J. Fisher
Human Factors Research Group, Faculty of Engineering, University of Nottingham, University Park, Nottingham, UK
Debra Fearnshaw & Sarah Sharples
School of Food Science and Nutrition, University of Leeds, Leeds, UK
Nicholas J. Watson
School of Engineering, University of Liverpool, Liverpool, UK
Peter Green
Centre for Circular Economy, University of Exeter, Exeter, UK
Fiona Charnley
Institute for Manufacturing, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK
Duncan McFarlane
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
OJF analysed and interpreted the data, and was the lead author in writing and revising the manuscript. DF led the data acquisition and supported the interpretation of the data. DF was also a major contributor to the design of the equality diversity and inclusion (EDI) strategy proposed in this work. NJW supported the design of the EDI strategy and was a major contributor in reviewing and revising the manuscript. PG supported the design of the EDI strategy, and was a major contributor in reviewing and revising the manuscript. FC supported the design of the EDI strategy and the interpretation of the data. DM supported the design of the EDI strategy. SS led the development EDI strategy proposed in this work, and was a major contributor in data interpretation and reviewing and revising the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Debra Fearnshaw .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Research was considered exempt from requiring ethical approval as is uses completely anonymous surveys results that are routinely collected as part of the administration of the network plus and informed consent was obtained at the time of original data collection.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fisher, O.J., Fearnshaw, D., Watson, N.J. et al. Promoting equality, diversity and inclusion in research and funding: reflections from a digital manufacturing research network. Res Integr Peer Rev 9 , 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-024-00144-w
Download citation
Received : 12 October 2023
Accepted : 09 April 2024
Published : 16 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41073-024-00144-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Research integrity
- Network policy
- Funding reviewing
- EDI interventions
Research Integrity and Peer Review
ISSN: 2058-8615
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT
- 17 May 2024
Reading between the lines: application essays predict university success
Analysis of more than 40,000 university application essays found that gradual transitions between chunks of text correlated with higher marks. Credit: Dusan Stankovic/Getty
Aspiring students who wrote content-rich university admission essays were more likely to end up with higher grades in their classes 1 .
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-01396-8
Berger, J. & Toubia, O. PNAS Nexus 3 , pgae163 (2024).
Article Google Scholar
Download references
How to stop students cramming for exams? Send them to sea
News & Views 30 APR 24

How young people benefit from Swiss apprenticeships
Spotlight 17 APR 24

Ready or not, AI is coming to science education — and students have opinions
Career Feature 08 APR 24
Senior Postdoctoral Research Fellow
Senior Postdoctoral Research Fellow required to lead exciting projects in Cancer Cell Cycle Biology and Cancer Epigenetics.
Melbourne University, Melbourne (AU)
University of Melbourne & Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre
Overseas Talent, Embarking on a New Journey Together at Tianjin University
We cordially invite outstanding young individuals from overseas to apply for the Excellent Young Scientists Fund Program (Overseas).
Tianjin, China
Tianjin University (TJU)
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology
SPST seeks top Faculty scholars in Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Precision Instruments and Optoelectronic Engineering
We are committed to accomplishing the mission of achieving a world-top-class engineering school.
Chair Professor Positions in the School of Mechanical Engineering
Aims to cultivate top talents, train a top-ranking faculty team, construct first-class disciplines and foster a favorable academic environment.
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
The research methodology is an important section of any research paper or thesis, as it describes the methods and procedures that will be used to conduct the research. It should include details about the research design, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
provide when you are writing a paper. Here are some useful guidelines: o If you're writing a research paper, do not assume that your reader has read all the sources that you are writing about. You'll need to offer context about what those sources say so that your reader can understand why you have brought them into the conversation.
Your Methods Section contextualizes the results of your study, giving editors, reviewers and readers alike the information they need to understand and interpret your work. Your methods are key to establishing the credibility of your study, along with your data and the results themselves. A complete methods section should provide enough detail ...
Research Methods: the Basics by Nicholas Walliman Research Methods: The Basicsis an accessible, user-friendly introduction to the different aspects of research theory, methods and practice. Structured in two parts, the first covering the nature of knowledge and the reasons for research, and the second the specific methods used to carry out effective research, this book covers: Structuring and ...
You can also take a mixed methods approach, where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods. Primary vs secondary data. Primary data are any original information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys, observations and experiments). Secondary data are information that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in ...
This interactive resource from Baylor University creates a suggested writing schedule based on how much time a student has to work on the assignment. "Research Paper Planner" (UCLA) UCLA's library offers this step-by-step guide to the research paper writing process, which also includes a suggested planning calendar.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
One of the most common deficiencies found in research papers is that the proposed methodology is not suitable to achieving the stated objective of your paper. Describe the specific methods of data collection you are going to use, such as, surveys, interviews, questionnaires, observation, archival research. If you are analyzing existing data ...
Definition, Types, and Examples. Research methodology 1,2 is a structured and scientific approach used to collect, analyze, and interpret quantitative or qualitative data to answer research questions or test hypotheses. A research methodology is like a plan for carrying out research and helps keep researchers on track by limiting the scope of ...
Research Methods vs. Research Methodologies Researchers distinguish between research methods and methodologies: (1) research methods are tools and techniques used to collect and analyze data. For example, an Interview or Survey is a tool. (2) Research Methodologies are the justification a researcher provides for using particular methods. A researcher's methodology is the rationale for using ...
In research methods essays, however, it's a little different. Many students make the mistake of explaining what the results show about behaviour, whereas in research methods essays you need to explain how the study shows the use of the method. For example, if using a study that's a true experiment you explain how the manipulation of the IV ...
Allow enough time. First and foremost, it's vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don't leave your essay until the last minute. If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay's lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to ...
These methods are useful when a detailed understanding of a phenomenon is sought. 1. Ethnographic Research. Ethnographic research emerged out of anthropological research, where anthropologists would enter into a setting for a sustained period of time, getting to know a cultural group and taking detailed observations.
Quantitative research methods are used to collect and analyze numerical data. This type of research is useful when the objective is to test a hypothesis, determine cause-and-effect relationships, and measure the prevalence of certain phenomena. Quantitative research methods include surveys, experiments, and secondary data analysis.
This is why the literature review as a research method is more relevant than ever. Traditional literature reviews often lack thoroughness and rigor and are conducted ad hoc, rather than following a specific methodology. Therefore, questions can be raised about the quality and trustworthiness of these types of reviews.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Definition: Research Paper is a written document that presents the author's original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue. It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new ...
The research methods section of the AS sociology 7191 (2) exam (research methods and topics in sociology) consists of one short answer question (out of 4 marks) and one essay question (out of 16 marks). You should aim to spend approximately 20-25 minutes answering this essay question. This longer methods question will nearly always ask you to ...
The Link between Critical Reading, Thinking and Writing. Communicating Research. Nov 13, 2023. By Alex Baratta, PhD Senior Lecturer, Manchester Institute of Education. Dr. Baratta is the author of How to Read and Write Critically (2022) and Read Critically (2020). Use the code MSPACEQ423 for a 20% discount on his books.
Methods. In order to assess the efficacy of reflective essays for social research methods education and training, undergraduate students enrolled on the social research methods module described above were invited to complete a short, qualitative survey (see online Appendix A).As well as offering the potential for rich data on student experiences of completing the assignment (Braun et al ...
A systematic writing framework offers a method for dramatically improving the teaching of writing. This method received only limited uptake, despite high-profile research publications and ...
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK's leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service. ... Mixed methods research is particularly advantageous when a multifaceted understanding of a phenomenon is required. This approach is widely used in education, public health, and social sciences, where combining qualitative depth with ...
Introduction. This systematic review contributes to the field of research into the development of academic literacy through learning discipline-specific knowledge, often referred to as an embedded approach (e.g. Wingate Citation 2018).Proponents of embedded approaches argue for teaching academic literacy within disciplinary contexts because it is tailored to specific assessments (i.e. it is ...
Equal, diverse, and inclusive teams lead to higher productivity, creativity, and greater problem-solving ability resulting in more impactful research. However, there is a gap between equality, diversity, and inclusion (EDI) research and practices to create an inclusive research culture. Research networks are vital to the research ecosystem, creating valuable opportunities for researchers to ...
Analysis of more than 40,000 university application essays found that gradual transitions between chunks of text correlated with higher marks. Credit: Dusan Stankovic/Getty. Aspiring students who ...