ClassRoomNotes
Week 4 – start may 13th and end may 17th, 2024.
Third Term Lessons Notes | Third Term Exam Questions | How I spent my Last Holiday | 2023/2024 School Academic Calendar | Join Us @ 080WhatsApp | 080TeleGram and WhatsApp Channel

Expository or Explanatory Composition (Primary 6)
ENGLISH STUDIES
SECOND TERM
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY OR EXPLANATORY COMPOSITION
PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES
By the end of the lesson, the pupils should have attained the following objectives (cognitive, affective and psychomotor) and should be able to:
1. Write composition on expository or explanatory types. 2. Make a clear logical presentation of point.
ENTRY BEHAVIOR
INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
The teacher will teach the lesson with the aid of pictures of marriage, celebration, road accidents or similar events extract from books, newspapers or magazines.
METHOD OF TEACHING – Choose a suitable and appropriate methods for the lessons.
Note – Irrespective of choosing methods of teaching, always introduce an activities that will arouse pupil’s interest or lead them to the lessons.
REFERENCE MATERIALS
Scheme of Work 9 – Years Basic Education Curriculum Course Book All Relevant Material Online Information
CONTENT OF THE LESSON
WRITING A COMPOSITION ON EXPOSITION/EXPLANATION
Writing a composition one exposition/explanation requires logical sequencing i.e. one thing thing happens before the next thing and so on.
Explanation of an event, e.g. causes of road accidents, marriage custom and traditional, etc.
Compositions
1. A traditional marriage I have witnessed. MacMillan Brilliant Primary English 6 Module 2, Page 6. 2. Causes of road accidents 3. How I sent my holiday
PRESENTATION
- To deliver the lesson, the teacher adopts the following steps:
1. To introduce the lesson, the teacher revises the previous lesson. Based on this, he/she asks the pupils some questions; 2. Explains how to present ideas in a logical order. Pupil’s Activities – Listen attentively to the teacher. 3. Let’s the pupils discuss either ‘a traditional marriage I witness or causes of road accidents’ in an informal way so that everybody will be interested in contributing ideas. Pupil’s Activities – Discuss the given topic in an informal way. 4. Lets the pupils put down their ideas in writing. Pupil’s Activities – Put down ideas in a clear and logical way.
- To conclude the lesson for the week, the teacher revises the entire lesson and links it to the following week’s lesson – narrative essay.
LESSON EVALUATION
Pupils to write an expository essay in a logical order.
Share this:
Related posts.

Production of Mosaics II (Primary 5)

Jesus the Good Shepherd Primary 3 (Basic 3) – Christian Religious Studies (CRS)

Introduction to Ratio | Simplifying a Ratio in its Lowest Form | Word Problems on Ratio | Application of Ratio to Everyday Life Primary 5 (Basic 5)
About the author.
Alabi M. S.
Welcome! We believe teachers inspire our future. CRN (ClassRoomNotes) is a website FOR TEACHERS BY TEACHERS, and we aim to continuously inform and encourage teaching! All materials are subject to TERMLY review.
English Language Primary 6
On this page, get all English Primary 6 topics from First Term to Third Term. Find them below, study them, and excel in your examination!
Course Information
Categories: Primary 6
Course Instructor
Student Enrollment
Second term, speech pronunciation and practice – tongue twister, new words and meaning , writing: letters of invitation, nouns from adjectives, explanatory composition, speech work: tone and voice, reading comprehension, teaching of new words and meaning, structure: construction with clauses, adjectives from noun, composition: a day i will never forget, new words and meaning, newspaper reading, reading comprehension democratic v military rule, reading comprehension: democratic or military rule, letters and speech sounds, types of vowels, conversation and dialogue, safe and clean water, verbs from adjectives, information and description passage, words and opposite, intonation practice, idiomatic expression, formation of verbs, quarrels and exchanges of instructions, words of similar meaning, simile and metaphor, grammar: writing dialogue, speech work: conversation between a teacher and a student, writing of sentences, composition: my favorite place in the world, structure: clauses, speech work: call and responses, writing: tenses, preposition, revision of last term’s work, sentence building primary 6, report making, pronouns and types of pronouns, features of formal letter, features of informal letter, grammar: verbs, types of verbs, structure: passive voice conversation, writing: argumentative essay, introductory paragraph: role of religion, types of adjectives, writing: concluding paragraph, speech work: telephone conversation , new words and meaning, types of adverbs, guide to good essay writing, structure: instructions, preposition and usage, direct and indirect speech, new words and their meaning, sentence building ii, conjuctions, simple future questions, simple past tense, intonation ii, exclamation and interjection, speech work: conversation on dental issues, prefix and suffix, sentence building iii, business letters, writing business letters, writing emails and text messages, biographies, giving formal speech, structure: main clauses, writing: features of informal letters, features of formal letters, autobiographies, speaking at interviews, differences between pair of sentences, dictation of suitable passage, valedictory speeches, functional words, expressing wishes, indefinite pronouns, indefinite adverbs, singular and plural, composition: my favorite sport, speech pronunciation and practice, new words and meaning, punctuation marks, composition: how i will spend my coming holidays, share this lesson with your friend.
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Telegram (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
2 thoughts on “English Language Primary 6”
Very good work
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
ClassNotes.ng is an Afrilearn brand.
- 08051544949
- [email protected]
- Teach for CN
- Testimonials
- Terms of use
- Privacy Policy
Weekly Newsletter
WhatsApp us
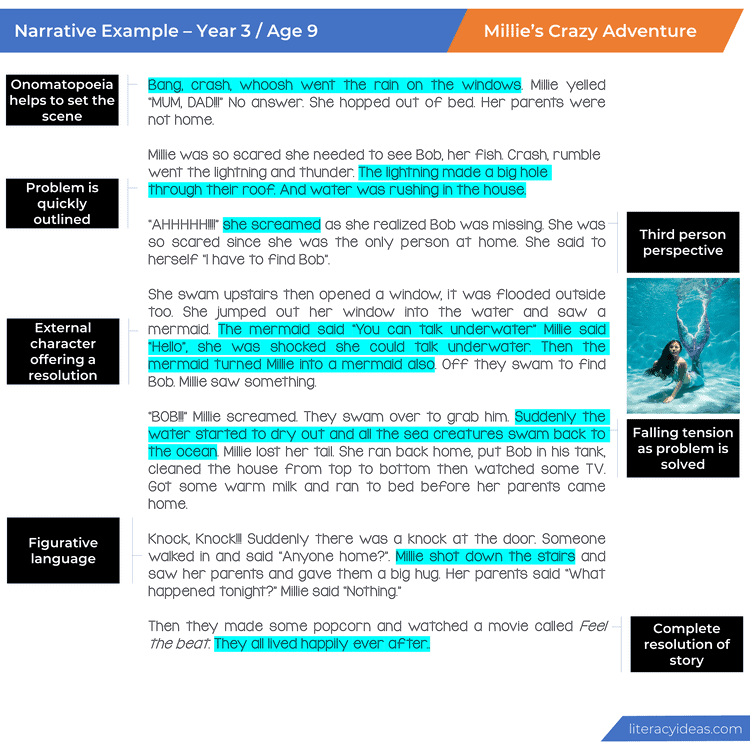
A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Narrative Writing
July 29, 2018
Can't find what you are looking for? Contact Us

Listen to this post as a podcast:
Sponsored by Peergrade and Microsoft Class Notebook
This post contains Amazon Affiliate links. When you make a purchase through these links, Cult of Pedagogy gets a small percentage of the sale at no extra cost to you.
“Those who tell the stories rule the world.” This proverb, attributed to the Hopi Indians, is one I wish I’d known a long time ago, because I would have used it when teaching my students the craft of storytelling. With a well-told story we can help a person see things in an entirely new way. We can forge new relationships and strengthen the ones we already have. We can change a law, inspire a movement, make people care fiercely about things they’d never given a passing thought.
But when we study storytelling with our students, we forget all that. Or at least I did. When my students asked why we read novels and stories, and why we wrote personal narratives and fiction, my defense was pretty lame: I probably said something about the importance of having a shared body of knowledge, or about the enjoyment of losing yourself in a book, or about the benefits of having writing skills in general.
I forgot to talk about the power of story. I didn’t bother to tell them that the ability to tell a captivating story is one of the things that makes human beings extraordinary. It’s how we connect to each other. It’s something to celebrate, to study, to perfect. If we’re going to talk about how to teach students to write stories, we should start by thinking about why we tell stories at all . If we can pass that on to our students, then we will be going beyond a school assignment; we will be doing something transcendent.
Now. How do we get them to write those stories? I’m going to share the process I used for teaching narrative writing. I used this process with middle school students, but it would work with most age groups.
A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?
When teaching narrative writing, many teachers separate personal narratives from short stories. In my own classroom, I tended to avoid having my students write short stories because personal narratives were more accessible. I could usually get students to write about something that really happened, while it was more challenging to get them to make something up from scratch.
In the “real” world of writers, though, the main thing that separates memoir from fiction is labeling: A writer might base a novel heavily on personal experiences, but write it all in third person and change the names of characters to protect the identities of people in real life. Another writer might create a short story in first person that reads like a personal narrative, but is entirely fictional. Just last weekend my husband and I watched the movie Lion and were glued to the screen the whole time, knowing it was based on a true story. James Frey’s book A Million Little Pieces sold millions of copies as a memoir but was later found to contain more than a little bit of fiction. Then there are unique books like Curtis Sittenfeld’s brilliant novel American Wife , based heavily on the early life of Laura Bush but written in first person, with fictional names and settings, and labeled as a work of fiction. The line between fact and fiction has always been really, really blurry, but the common thread running through all of it is good storytelling.
With that in mind, the process for teaching narrative writing can be exactly the same for writing personal narratives or short stories; it’s the same skill set. So if you think your students can handle the freedom, you might decide to let them choose personal narrative or fiction for a narrative writing assignment, or simply tell them that whether the story is true doesn’t matter, as long as they are telling a good story and they are not trying to pass off a fictional story as fact.
Here are some examples of what that kind of flexibility could allow:
- A student might tell a true story from their own experience, but write it as if it were a fiction piece, with fictional characters, in third person.
- A student might create a completely fictional story, but tell it in first person, which would give it the same feel as a personal narrative.
- A student might tell a true story that happened to someone else, but write it in first person, as if they were that person. For example, I could write about my grandmother’s experience of getting lost as a child, but I might write it in her voice.
If we aren’t too restrictive about what we call these pieces, and we talk about different possibilities with our students, we can end up with lots of interesting outcomes. Meanwhile, we’re still teaching students the craft of narrative writing.
A Note About Process: Write With Your Students
One of the most powerful techniques I used as a writing teacher was to do my students’ writing assignments with them. I would start my own draft at the same time as they did, composing “live” on the classroom projector, and doing a lot of thinking out loud so they could see all the decisions a writer has to make.
The most helpful parts for them to observe were the early drafting stage, where I just scratched out whatever came to me in messy, run-on sentences, and the revision stage, where I crossed things out, rearranged, and made tons of notes on my writing. I have seen over and over again how witnessing that process can really help to unlock a student’s understanding of how writing actually gets made.
A Narrative Writing Unit Plan
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me.
Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere
Getting our students to tell stories should be easy. They hear and tell stories all the time. But when they actually have to put words on paper, they forget their storytelling abilities: They can’t think of a topic. They omit relevant details, but go on and on about irrelevant ones. Their dialogue is bland. They can’t figure out how to start. They can’t figure out how to end.
So the first step in getting good narrative writing from students is to help them see that they are already telling stories every day . They gather at lockers to talk about that thing that happened over the weekend. They sit at lunch and describe an argument they had with a sibling. Without even thinking about it, they begin sentences with “This one time…” and launch into stories about their earlier childhood experiences. Students are natural storytellers; learning how to do it well on paper is simply a matter of studying good models, then imitating what those writers do.
So start off the unit by getting students to tell their stories. In journal quick-writes, think-pair-shares, or by playing a game like Concentric Circles , prompt them to tell some of their own brief stories: A time they were embarrassed. A time they lost something. A time they didn’t get to do something they really wanted to do. By telling their own short anecdotes, they will grow more comfortable and confident in their storytelling abilities. They will also be generating a list of topic ideas. And by listening to the stories of their classmates, they will be adding onto that list and remembering more of their own stories.
And remember to tell some of your own. Besides being a good way to bond with students, sharing your stories will help them see more possibilities for the ones they can tell.
Step 2: Study the Structure of a Story
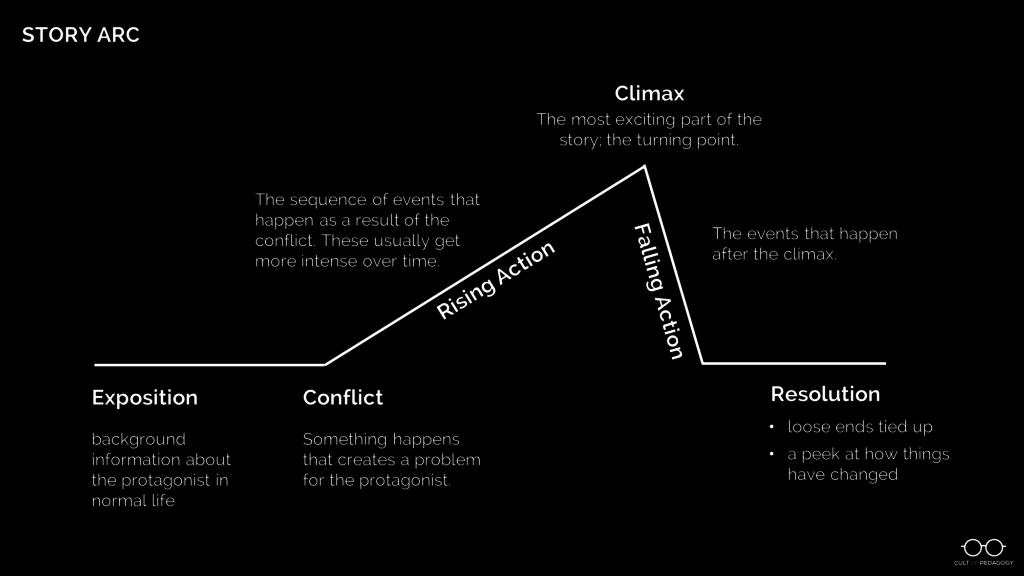
Now that students have a good library of their own personal stories pulled into short-term memory, shift your focus to a more formal study of what a story looks like.
Use a diagram to show students a typical story arc like the one below. Then, using a simple story (try a video like The Present or Room ), fill out the story arc with the components from that story. Once students have seen this story mapped out, have them try it with another one, like a story you’ve read in class, a whole novel, or another short video.
Step 3: Introduce the Assignment
Up to this point, students have been immersed in storytelling. Now give them specific instructions for what they are going to do. Share your assignment rubric so they understand the criteria that will be used to evaluate them; it should be ready and transparent right from the beginning of the unit. As always, I recommend using a single point rubric for this.
Step 4: Read Models
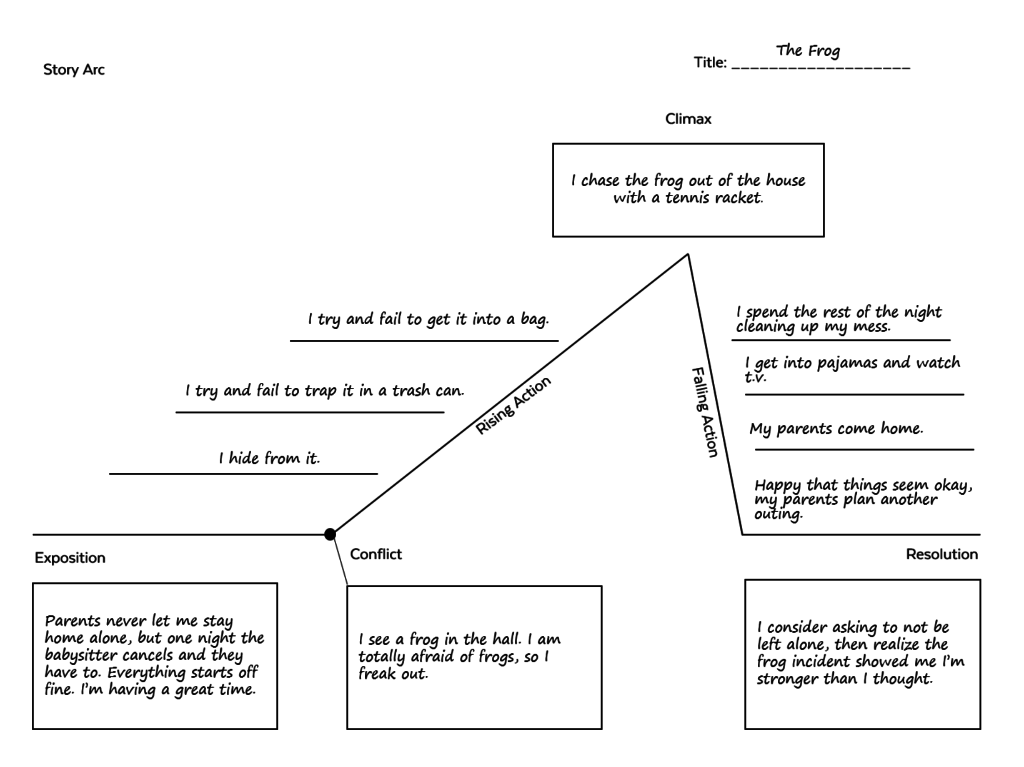
Once the parameters of the assignment have been explained, have students read at least one model story, a mentor text that exemplifies the qualities you’re looking for. This should be a story on a topic your students can kind of relate to, something they could see themselves writing. For my narrative writing unit (see the end of this post), I wrote a story called “Frog” about a 13-year-old girl who finally gets to stay home alone, then finds a frog in her house and gets completely freaked out, which basically ruins the fun she was planning for the night.
They will be reading this model as writers, looking at how the author shaped the text for a purpose, so that they can use those same strategies in their own writing. Have them look at your rubric and find places in the model that illustrate the qualities listed in the rubric. Then have them complete a story arc for the model so they can see the underlying structure.
Ideally, your students will have already read lots of different stories to look to as models. If that isn’t the case, this list of narrative texts recommended by Cult of Pedagogy followers on Twitter would be a good place to browse for titles that might be right for your students. Keep in mind that we have not read most of these stories, so be sure to read them first before adopting them for classroom use.
Step 5: Story Mapping
At this point, students will need to decide what they are going to write about. If they are stuck for a topic, have them just pick something they can write about, even if it’s not the most captivating story in the world. A skilled writer could tell a great story about deciding what to have for lunch. If they are using the skills of narrative writing, the topic isn’t as important as the execution.
Have students complete a basic story arc for their chosen topic using a diagram like the one below. This will help them make sure that they actually have a story to tell, with an identifiable problem, a sequence of events that build to a climax, and some kind of resolution, where something is different by the end. Again, if you are writing with your students, this would be an important step to model for them with your own story-in-progress.
Step 6: Quick Drafts
Now, have students get their chosen story down on paper as quickly as possible: This could be basically a long paragraph that would read almost like a summary, but it would contain all the major parts of the story. Model this step with your own story, so they can see that you are not shooting for perfection in any way. What you want is a working draft, a starting point, something to build on for later, rather than a blank page (or screen) to stare at.
Step 7: Plan the Pacing
Now that the story has been born in raw form, students can begin to shape it. This would be a good time for a lesson on pacing, where students look at how writers expand some moments to create drama and shrink other moments so that the story doesn’t drag. Creating a diagram like the one below forces a writer to decide how much space to devote to all of the events in the story.

Step 8: Long Drafts
With a good plan in hand, students can now slow down and write a proper draft, expanding the sections of their story that they plan to really draw out and adding in more of the details that they left out in the quick draft.
Step 9: Workshop
Once students have a decent rough draft—something that has a basic beginning, middle, and end, with some discernible rising action, a climax of some kind, and a resolution, you’re ready to shift into full-on workshop mode. I would do this for at least a week: Start class with a short mini-lesson on some aspect of narrative writing craft, then give students the rest of the period to write, conference with you, and collaborate with their peers. During that time, they should focus some of their attention on applying the skill they learned in the mini-lesson to their drafts, so they will improve a little bit every day.
Topics for mini-lessons can include:
- How to weave exposition into your story so you don’t give readers an “information dump”
- How to carefully select dialogue to create good scenes, rather than quoting everything in a conversation
- How to punctuate and format dialogue so that it imitates the natural flow of a conversation
- How to describe things using sensory details and figurative language; also, what to describe…students too often give lots of irrelevant detail
- How to choose precise nouns and vivid verbs, use a variety of sentence lengths and structures, and add transitional words, phrases, and features to help the reader follow along
- How to start, end, and title a story
Step 10: Final Revisions and Edits
As the unit nears its end, students should be shifting away from revision , in which they alter the content of a piece, toward editing , where they make smaller changes to the mechanics of the writing. Make sure students understand the difference between the two: They should not be correcting each other’s spelling and punctuation in the early stages of this process, when the focus should be on shaping a better story.
One of the most effective strategies for revision and editing is to have students read their stories out loud. In the early stages, this will reveal places where information is missing or things get confusing. Later, more read-alouds will help them immediately find missing words, unintentional repetitions, and sentences that just “sound weird.” So get your students to read their work out loud frequently. It also helps to print stories on paper: For some reason, seeing the words in print helps us notice things we didn’t see on the screen.
To get the most from peer review, where students read and comment on each other’s work, more modeling from you is essential: Pull up a sample piece of writing and show students how to give specific feedback that helps, rather than simply writing “good detail” or “needs more detail,” the two comments I saw exchanged most often on students’ peer-reviewed papers.
Step 11: Final Copies and Publication
Once revision and peer review are done, students will hand in their final copies. If you don’t want to get stuck with 100-plus papers to grade, consider using Catlin Tucker’s station rotation model , which keeps all the grading in class. And when you do return stories with your own feedback, try using Kristy Louden’s delayed grade strategy , where students don’t see their final grade until they have read your written feedback.
Beyond the standard hand-in-for-a-grade, consider other ways to have students publish their stories. Here are some options:
- Stories could be published as individual pages on a collaborative website or blog.
- Students could create illustrated e-books out of their stories.
- Students could create a slideshow to accompany their stories and record them as digital storytelling videos. This could be done with a tool like Screencastify or Screencast-O-Matic .
So this is what worked for me. If you’ve struggled to get good stories from your students, try some or all of these techniques next time. I think you’ll find that all of your students have some pretty interesting stories to tell. Helping them tell their stories well is a gift that will serve them for many years after they leave your classroom. ♦
Want this unit ready-made?
If you’re a writing teacher in grades 7-12 and you’d like a classroom-ready unit like the one described above, including slideshow mini-lessons on 14 areas of narrative craft, a sample narrative piece, editable rubrics, and other supplemental materials to guide students through every stage of the process, take a look at my Narrative Writing unit . Just click on the image below and you’ll be taken to a page where you can read more and see a detailed preview of what’s included.

What to Read Next

Categories: Instruction , Podcast
Tags: English language arts , Grades 6-8 , Grades 9-12 , teaching strategies
52 Comments
Wow, this is a wonderful guide! If my English teachers had taught this way, I’m sure I would have enjoyed narrative writing instead of dreading it. I’ll be able to use many of these suggestions when writing my blog! BrP
Lst year I was so discouraged because the short stories looked like the quick drafts described in this article. I thought I had totally failed until I read this and realized I did not fai,l I just needed to complete the process. Thank you!
I feel like you jumped in my head and connected my thoughts. I appreciate the time you took to stop and look closely at form. I really believe that student-writers should see all dimensions of narrative writing and be able to live in whichever style and voice they want for their work.
Can’t thank you enough for this. So well curated that one can just follow it blindly and ace at teaching it. Thanks again!
Great post! I especially liked your comments about reminding kids about the power of storytelling. My favourite podcasts and posts from you are always about how to do things in the classroom and I appreciate the research you do.
On a side note, the ice breakers are really handy. My kids know each other really well (rural community), and can tune out pretty quickly if there is nothing new to learn about their peers, but they like the games (and can remember where we stopped last time weeks later). I’ve started changing them up with ‘life questions’, so the editable version is great!
I love writing with my students and loved this podcast! A fun extension to this narrative is to challenge students to write another story about the same event, but use the perspective of another “character” from the story. Books like Wonder (R.J. Palacio) and Wanderer (Sharon Creech) can model the concept for students.
Thank you for your great efforts to reveal the practical writing strategies in layered details. As English is not my first language, I need listen to your podcast and read the text repeatedly so to fully understand. It’s worthy of the time for some great post like yours. I love sharing so I send the link to my English practice group that it can benefit more. I hope I could be able to give you some feedback later on.
Thank you for helping me get to know better especially the techniques in writing narrative text. Im an English teacher for 5years but have little knowledge on writing. I hope you could feature techniques in writing news and fearute story. God bless and more power!
Thank you for this! I am very interested in teaching a unit on personal narrative and this was an extremely helpful breakdown. As a current student teacher I am still unsure how to approach breaking down the structures of different genres of writing in a way that is helpful for me students but not too restrictive. The story mapping tools you provided really allowed me to think about this in a new way. Writing is such a powerful way to experience the world and more than anything I want my students to realize its power. Stories are how we make sense of the world and as an English teacher I feel obligated to give my students access to this particular skill.
The power of story is unfathomable. There’s this NGO in India doing some great work in harnessing the power of storytelling and plots to brighten children’s lives and enlighten them with true knowledge. Check out Katha India here: http://bit.ly/KathaIndia
Thank you so much for this. I did not go to college to become a writing professor, but due to restructuring in my department, I indeed am! This is a wonderful guide that I will use when teaching the narrative essay. I wonder if you have a similar guide for other modes such as descriptive, process, argument, etc.?
Hey Melanie, Jenn does have another guide on writing! Check out A Step-by-Step Plan for Teaching Argumentative Writing .
Hi, I am also wondering if there is a similar guide for descriptive writing in particular?
Hey Melanie, unfortunately Jenn doesn’t currently have a guide for descriptive writing. She’s always working on projects though, so she may get around to writing a unit like this in the future. You can always check her Teachers Pay Teachers page for an up-to-date list of materials she has available. Thanks!
I want to write about the new character in my area
That’s great! Let us know if you need any supports during your writing process!
I absolutely adore this unit plan. I teach freshmen English at a low-income high school and wanted to find something to help my students find their voice. It is not often that I borrow material, but I borrowed and adapted all of it in the order that it is presented! It is cohesive, understandable, and fun. Thank you!!
So glad to hear this, Nicole!
Thanks sharing this post. My students often get confused between personal narratives and short stories. Whenever I ask them to write a short story, she share their own experiences and add a bit of fiction in it to make it interesting.
Thank you! My students have loved this so far. I do have a question as to where the “Frog” story mentioned in Step 4 is. I could really use it! Thanks again.
This is great to hear, Emily! In Step 4, Jenn mentions that she wrote the “Frog” story for her narrative writing unit . Just scroll down the bottom of the post and you’ll see a link to the unit.
I also cannot find the link to the short story “Frog”– any chance someone can send it or we can repost it?
This story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. You can find a link to this unit in Step 4 or at the bottom of the article. Hope this helps.
I cannot find the frog story mentioned. Could you please send the link.? Thank you
Hi Michelle,
The Frog story was written for Jenn’s narrative writing unit. There’s a link to this unit in Step 4 and at the bottom of the article.
Debbie- thanks for you reply… but there is no link to the story in step 4 or at the bottom of the page….
Hey Shawn, the frog story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link Debbie is referring to at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit and you would have to purchase that to gain access to the frog story. I hope this clears things up.
Thank you so much for this resource! I’m a high school English teacher, and am currently teaching creative writing for the first time. I really do value your blog, podcast, and other resources, so I’m excited to use this unit. I’m a cyber school teacher, so clear, organized layout is important; and I spend a lot of time making sure my content is visually accessible for my students to process. Thanks for creating resources that are easy for us teachers to process and use.
Do you have a lesson for Informative writing?
Hey Cari, Jenn has another unit on argumentative writing , but doesn’t have one yet on informative writing. She may develop one in the future so check back in sometime.
I had the same question. Informational writing is so difficult to have a good strong unit in when you have so many different text structures to meet and need text-dependent writing tasks.
Creating an informational writing unit is still on Jenn’s long list of projects to get to, but in the meantime, if you haven’t already, check out When We All Teach Text Structures, Everyone Wins . It might help you out!
This is a great lesson! It would be helpful to see a finished draft of the frog narrative arc. Students’ greatest challenge is transferring their ideas from the planner to a full draft. To see a full sample of how this arc was transformed into a complete narrative draft would be a powerful learning tool.
Hi Stacey! Jenn goes into more depth with the “Frog” lesson in her narrative writing unit – this is where you can find a sample of what a completed story arc might look. Also included is a draft of the narrative. If interested in checking out the unit and seeing a preview, just scroll down to the bottom of the post and click on the image. Hope this helps!
Helped me learn for an entrance exam thanks very much
Is the narrative writing lesson you talk about in https://www.cultofpedagogy.com/narrative-writing/
Also doable for elementary students you think, and if to what levels?
Love your work, Sincerely, Zanyar
Hey Zanyar,
It’s possible the unit would work with 4th and 5th graders, but Jenn definitely wouldn’t recommend going any younger. The main reason for this is that some of the mini-lessons in the unit could be challenging for students who are still concrete thinkers. You’d likely need to do some adjusting and scaffolding which could extend the unit beyond the 3 weeks. Having said that, I taught 1st grade and found the steps of the writing process, as described in the post, to be very similar. Of course learning targets/standards were different, but the process itself can be applied to any grade level (modeling writing, using mentor texts to study how stories work, planning the structure of the story, drafting, elaborating, etc.) Hope this helps!
This has made my life so much easier. After teaching in different schools systems, from the American, to British to IB, one needs to identify the anchor standards and concepts, that are common between all these systems, to build well balanced thematic units. Just reading these steps gave me the guidance I needed to satisfy both the conceptual framework the schools ask for and the standards-based practice. Thank you Thank you.
Would this work for teaching a first grader about narrative writing? I am also looking for a great book to use as a model for narrative writing. Veggie Monster is being used by his teacher and he isn’t connecting with this book in the least bit, so it isn’t having a positive impact. My fear is he will associate this with writing and I don’t want a negative association connected to such a beautiful process and experience. Any suggestions would be helpful.
Thank you for any information you can provide!
Although I think the materials in the actual narrative writing unit are really too advanced for a first grader, the general process that’s described in the blog post can still work really well.
I’m sorry your child isn’t connecting with The Night of the Veggie Monster. Try to keep in mind that the main reason this is used as a mentor text is because it models how a small moment story can be told in a big way. It’s filled with all kinds of wonderful text features that impact the meaning of the story – dialogue, description, bold text, speech bubbles, changes in text size, ellipses, zoomed in images, text placement, text shape, etc. All of these things will become mini-lessons throughout the unit. But there are lots of other wonderful mentor texts that your child might enjoy. My suggestion for an early writer, is to look for a small moment text, similar in structure, that zooms in on a problem that a first grader can relate to. In addition to the mentor texts that I found in this article , you might also want to check out Knuffle Bunny, Kitten’s First Full Moon, When Sophie Gets Angry Really Really Angry, and Whistle for Willie. Hope this helps!
I saw this on Pinterest the other day while searching for examples of narritives units/lessons. I clicked on it because I always click on C.o.P stuff 🙂 And I wasn’t disapointed. I was intrigued by the connection of narratives to humanity–even if a student doesn’t identify as a writer, he/she certainly is human, right? I really liked this. THIS clicked with me.
A few days after I read the P.o.C post, I ventured on to YouTube for more ideas to help guide me with my 8th graders’ narrative writing this coming spring. And there was a TEDx video titled, “The Power of Personal Narrative” by J. Christan Jensen. I immediately remembered the line from the article above that associated storytelling with “power” and how it sets humans apart and if introduced and taught as such, it can be “extraordinary.”
I watched the video and to the suprise of my expectations, it was FANTASTIC. Between Jennifer’s post and the TEDx video ignited within me some major motivation and excitement to begin this unit.
Thanks for sharing this with us! So glad that Jenn’s post paired with another text gave you some motivation and excitement. I’ll be sure to pass this on to Jenn!
Thank you very much for this really helpful post! I really love the idea of helping our students understand that storytelling is powerful and then go on to teach them how to harness that power. That is the essence of teaching literature or writing at any level. However, I’m a little worried about telling students that whether a piece of writing is fact or fiction does not matter. It in fact matters a lot precisely because storytelling is powerful. Narratives can shape people’s views and get their emotions involved which would, in turn, motivate them to act on a certain matter, whether for good or for bad. A fictional narrative that is passed as factual could cause a lot of damage in the real world. I believe we should. I can see how helping students focus on writing the story rather than the truth of it all could help refine the needed skills without distractions. Nevertheless, would it not be prudent to teach our students to not just harness the power of storytelling but refrain from misusing it by pushing false narratives as factual? It is true that in reality, memoirs pass as factual while novels do as fictional while the opposite may be true for both cases. I am not too worried about novels passing as fictional. On the other hand, fictional narratives masquerading as factual are disconcerting and part of a phenomenon that needs to be fought against, not enhanced or condoned in education. This is especially true because memoirs are often used by powerful people to write/re-write history. I would really like to hear your opinion on this. Thanks a lot for a great post and a lot of helpful resources!
Thank you so much for this. Jenn and I had a chance to chat and we can see where you’re coming from. Jenn never meant to suggest that a person should pass off a piece of fictional writing as a true story. Good stories can be true, completely fictional, or based on a true story that’s mixed with some fiction – that part doesn’t really matter. However, what does matter is how a student labels their story. We think that could have been stated more clearly in the post , so Jenn decided to add a bit about this at the end of the 3rd paragraph in the section “A Note About Form: Personal Narrative or Short Story?” Thanks again for bringing this to our attention!
You have no idea how much your page has helped me in so many ways. I am currently in my teaching credential program and there are times that I feel lost due to a lack of experience in the classroom. I’m so glad I came across your page! Thank you for sharing!
Thanks so much for letting us know-this means a whole lot!
No, we’re sorry. Jenn actually gets this question fairly often. It’s something she considered doing at one point, but because she has so many other projects she’s working on, she’s just not gotten to it.
I couldn’t find the story
Hi, Duraiya. The “Frog” story is part of Jenn’s narrative writing unit, which is available on her Teachers Pay Teachers site. The link at the bottom of this post will take you to her narrative writing unit, which you can purchase to gain access to the story. I hope this helps!
I am using this step-by-step plan to help me teach personal narrative story writing. I wanted to show the Coca-Cola story, but the link says the video is not available. Do you have a new link or can you tell me the name of the story so I can find it?
Thank you for putting this together.
Hi Corri, sorry about that. The Coca-Cola commercial disappeared, so Jenn just updated the post with links to two videos with good stories. Hope this helps!
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.
K-12 Resources By Teachers, For Teachers Provided by the K-12 Teachers Alliance
- Teaching Strategies
- Classroom Activities
- Classroom Management
- Technology in the Classroom
- Professional Development
- Lesson Plans
- Writing Prompts
- Graduate Programs
Narrative Writing
- Subject Language Arts

Introduction
This is an engaging sixth grade lesson on narrative writing that includes several different activities that provide scaffolding and opportunity for differentiation. This lesson is very involved and may need to be spread out over more than one day depending on time constraints.
Learning Objectives
CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.6.3
- Write narratives to develop real or imagined experiences or events using effective technique, relevant descriptive details, and well-structured event sequences.
For the full lesson plan, download the PDF.
Download Full Lesson Plan: Narrative Writing

Related Lesson Plans

“The Rose That Grew From Concrete” Poem Exploration
Students explore and learn to identify theme in poetry by Tupac Shakur.

“Eleven” – Analyzing Emotions
Students create their own narrative essays about their worst birthday ever.

“The Lottery” Reading Comprehension Activity
Students employ their reading comprehension skills analyzing a short story.

“The Scholarship Jacket”
Students explore the theme of “The Scholarship Jacket” and develop argumentative essays.

FIRST TERM COMPUTER STUDIES SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6)
Lagos State Scheme of work, Scheme of work for Primary School Nigeria - Edudelight.com, COMPUTER SYSTEM, Computer network

FIRST TERM PHYSICAL AND HEALTH SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6)/ BASIC SIX (6)
Lagos State Scheme of work for Physical and Health Education TOPICS Creative rhythmic activities: meaning and types Of rhythmic…
SECOND TERM MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6)/ BASIC SIX (6)
1. REVISION OF 1ST TERM’S WORK 2. MONEY (RATES, TAXES, SHARES AND DIVIDENDS) 3. LENGTH 4. PERIMETER (REGULAR & IRREGULAR…
FIRST TERM MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6)/ BASIC SIX (6)
1.READING AND WRITING NUMBERS TO ONE BILLION IN WORDS AND FIGURE. 2. BINARY 3. A. PLACE VALUE OF WHOLE NUMBERS.…
SECOND TERM MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY FIVE (5)/ BASIC FIVE (5)
1. RATIO AND PERCENTAGE 2. SIMPLE PROBLEMS ON PERCENTAGES. 3. OPEN SENTENCE. 4. MONEY 5. MONEY SIMPLE INTEREST 6.MONEY (CONTD)…
FIRST TERM CULTURAL AND CREATIVE ART SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6) /BASIC SIX (6)
WEEK 1 and 2 TOPIC: STILL LIFE DRAWING Units: Meaning of Still Life DrawingStill life objects as in Pot, a…
Types and Importance of Apprenticeship System
TITLE: NOTE OF LESSON ON CULTURAL AND CREATIVE SUBJECT: CULTURAL AND CREATIVE ARTS THEME: CUSTOMS AND TRADITION NAME OF TEACHER:…

SYNTHETIC AND NATURALLY OCCURING DRUGS
TITLE: NOTE OF LESSON ON SOCIAL STUDIES SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES THEME: CITIZENSHIP TERM: SECOND TERM WEEK: WEEK 10 CLASS: PRIMARY…

BASIC CONCEPT OF DRUG AND DRUG ABUSE, NATURE OF DRUG ABUSE.

PEACE EDUCATION
TITLE: NOTE OF LESSON ON SOCIAL STUDIES SUBJECT: SOCIAL STUDIES THEME: CITIZENSHIP TERM: SECOND TERM WEEK: WEEK 9 CLASS: PRIMARY…
Privacy Overview

Narrative Writing: A Complete Guide for Teachers and Students
MASTERING THE CRAFT OF NARRATIVE WRITING
Narratives build on and encourage the development of the fundamentals of writing. They also require developing an additional skill set: the ability to tell a good yarn, and storytelling is as old as humanity.
We see and hear stories everywhere and daily, from having good gossip on the doorstep with a neighbor in the morning to the dramas that fill our screens in the evening.
Good narrative writing skills are hard-won by students even though it is an area of writing that most enjoy due to the creativity and freedom it offers.
Here we will explore some of the main elements of a good story: plot, setting, characters, conflict, climax, and resolution . And we will look too at how best we can help our students understand these elements, both in isolation and how they mesh together as a whole.

WHAT IS A NARRATIVE?

A narrative is a story that shares a sequence of events , characters, and themes. It expresses experiences, ideas, and perspectives that should aspire to engage and inspire an audience.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well.
Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as ‘creative writing’ or story writing.
The purpose of a narrative is simple, to tell the audience a story. It can be written to motivate, educate, or entertain and can be fact or fiction.
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING NARRATIVE WRITING

Teach your students to become skilled story writers with this HUGE NARRATIVE & CREATIVE STORY WRITING UNIT . Offering a COMPLETE SOLUTION to teaching students how to craft CREATIVE CHARACTERS, SUPERB SETTINGS, and PERFECT PLOTS .
Over 192 PAGES of materials, including:

TYPES OF NARRATIVE WRITING
There are many narrative writing genres and sub-genres such as these.
We have a complete guide to writing a personal narrative that differs from the traditional story-based narrative covered in this guide. It includes personal narrative writing prompts, resources, and examples and can be found here.

As we can see, narratives are an open-ended form of writing that allows you to showcase creativity in many directions. However, all narratives share a common set of features and structure known as “Story Elements”, which are briefly covered in this guide.
Don’t overlook the importance of understanding story elements and the value this adds to you as a writer who can dissect and create grand narratives. We also have an in-depth guide to understanding story elements here .
CHARACTERISTICS OF NARRATIVE WRITING
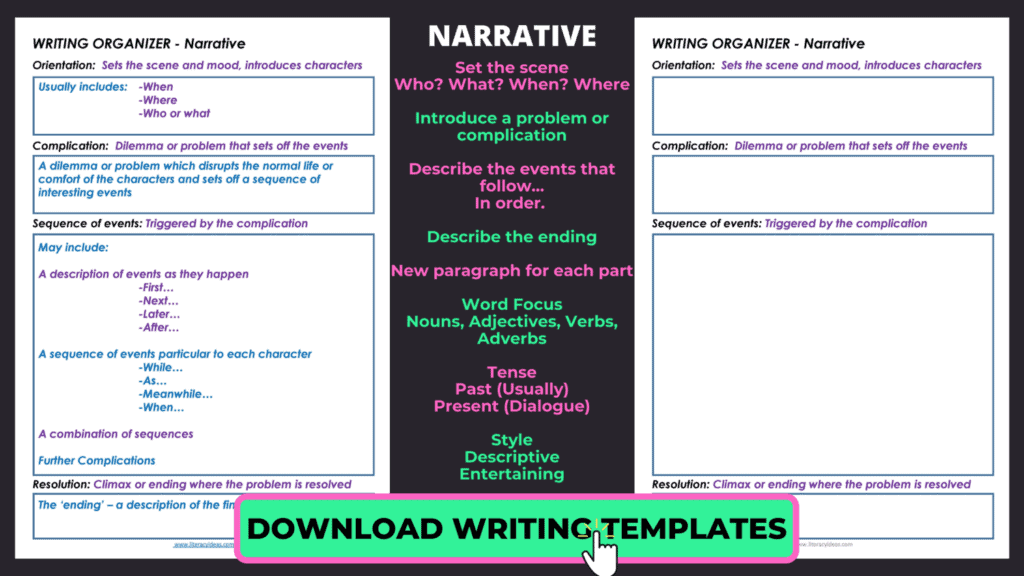
Narrative structure.
ORIENTATION (BEGINNING) Set the scene by introducing your characters, setting and time of the story. Establish your who, when and where in this part of your narrative
COMPLICATION AND EVENTS (MIDDLE) In this section activities and events involving your main characters are expanded upon. These events are written in a cohesive and fluent sequence.
RESOLUTION (ENDING) Your complication is resolved in this section. It does not have to be a happy outcome, however.
EXTRAS: Whilst orientation, complication and resolution are the agreed norms for a narrative, there are numerous examples of popular texts that did not explicitly follow this path exactly.
NARRATIVE FEATURES
LANGUAGE: Use descriptive and figurative language to paint images inside your audience’s minds as they read.
PERSPECTIVE Narratives can be written from any perspective but are most commonly written in first or third person.
DIALOGUE Narratives frequently switch from narrator to first-person dialogue. Always use speech marks when writing dialogue.
TENSE If you change tense, make it perfectly clear to your audience what is happening. Flashbacks might work well in your mind but make sure they translate to your audience.
THE PLOT MAP
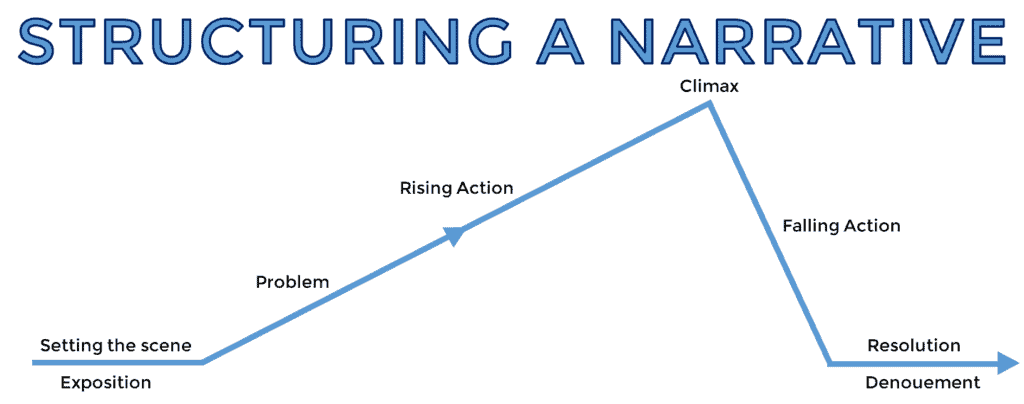
This graphic is known as a plot map, and nearly all narratives fit this structure in one way or another, whether romance novels, science fiction or otherwise.
It is a simple tool that helps you understand and organise a story’s events. Think of it as a roadmap that outlines the journey of your characters and the events that unfold. It outlines the different stops along the way, such as the introduction, rising action, climax, falling action, and resolution, that help you to see how the story builds and develops.
Using a plot map, you can see how each event fits into the larger picture and how the different parts of the story work together to create meaning. It’s a great way to visualize and analyze a story.
Be sure to refer to a plot map when planning a story, as it has all the essential elements of a great story.
THE 5 KEY STORY ELEMENTS OF A GREAT NARRATIVE (6-MINUTE TUTORIAL VIDEO)
This video we created provides an excellent overview of these elements and demonstrates them in action in stories we all know and love.

HOW TO WRITE A NARRATIVE

Now that we understand the story elements and how they come together to form stories, it’s time to start planning and writing your narrative.
In many cases, the template and guide below will provide enough details on how to craft a great story. However, if you still need assistance with the fundamentals of writing, such as sentence structure, paragraphs and using correct grammar, we have some excellent guides on those here.
USE YOUR WRITING TIME EFFECTIVELY: Maximize your narrative writing sessions by spending approximately 20 per cent of your time planning and preparing. This ensures greater productivity during your writing time and keeps you focused and on task.
Use tools such as graphic organizers to logically sequence your narrative if you are not a confident story writer. If you are working with reluctant writers, try using narrative writing prompts to get their creative juices flowing.
Spend most of your writing hour on the task at hand, don’t get too side-tracked editing during this time and leave some time for editing. When editing a narrative, examine it for these three elements.
- Spelling and grammar ( Is it readable?)
- Story structure and continuity ( Does it make sense, and does it flow? )
- Character and plot analysis. (Are your characters engaging? Does your problem/resolution work? )
1. SETTING THE SCENE: THE WHERE AND THE WHEN

The story’s setting often answers two of the central questions in the story, namely, the where and the when. The answers to these two crucial questions will often be informed by the type of story the student is writing.
The story’s setting can be chosen to quickly orient the reader to the type of story they are reading. For example, a fictional narrative writing piece such as a horror story will often begin with a description of a haunted house on a hill or an abandoned asylum in the middle of the woods. If we start our story on a rocket ship hurtling through the cosmos on its space voyage to the Alpha Centauri star system, we can be reasonably sure that the story we are embarking on is a work of science fiction.
Such conventions are well-worn clichés true, but they can be helpful starting points for our novice novelists to make a start.
Having students choose an appropriate setting for the type of story they wish to write is an excellent exercise for our younger students. It leads naturally onto the next stage of story writing, which is creating suitable characters to populate this fictional world they have created. However, older or more advanced students may wish to play with the expectations of appropriate settings for their story. They may wish to do this for comic effect or in the interest of creating a more original story. For example, opening a story with a children’s birthday party does not usually set up the expectation of a horror story. Indeed, it may even lure the reader into a happy reverie as they remember their own happy birthday parties. This leaves them more vulnerable to the surprise element of the shocking action that lies ahead.
Once the students have chosen a setting for their story, they need to start writing. Little can be more terrifying to English students than the blank page and its bare whiteness stretching before them on the table like a merciless desert they must cross. Give them the kick-start they need by offering support through word banks or writing prompts. If the class is all writing a story based on the same theme, you may wish to compile a common word bank on the whiteboard as a prewriting activity. Write the central theme or genre in the middle of the board. Have students suggest words or phrases related to the theme and list them on the board.
You may wish to provide students with a copy of various writing prompts to get them started. While this may mean that many students’ stories will have the same beginning, they will most likely arrive at dramatically different endings via dramatically different routes.

A bargain is at the centre of the relationship between the writer and the reader. That bargain is that the reader promises to suspend their disbelief as long as the writer creates a consistent and convincing fictional reality. Creating a believable world for the fictional characters to inhabit requires the student to draw on convincing details. The best way of doing this is through writing that appeals to the senses. Have your student reflect deeply on the world that they are creating. What does it look like? Sound like? What does the food taste like there? How does it feel like to walk those imaginary streets, and what aromas beguile the nose as the main character winds their way through that conjured market?
Also, Consider the when; or the time period. Is it a future world where things are cleaner and more antiseptic? Or is it an overcrowded 16th-century London with human waste stinking up the streets? If students can create a multi-sensory installation in the reader’s mind, then they have done this part of their job well.
Popular Settings from Children’s Literature and Storytelling
- Fairytale Kingdom
- Magical Forest
- Village/town
- Underwater world
- Space/Alien planet
2. CASTING THE CHARACTERS: THE WHO
Now that your student has created a believable world, it is time to populate it with believable characters.
In short stories, these worlds mustn’t be overpopulated beyond what the student’s skill level can manage. Short stories usually only require one main character and a few secondary ones. Think of the short story more as a small-scale dramatic production in an intimate local theater than a Hollywood blockbuster on a grand scale. Too many characters will only confuse and become unwieldy with a canvas this size. Keep it simple!
Creating believable characters is often one of the most challenging aspects of narrative writing for students. Fortunately, we can do a few things to help students here. Sometimes it is helpful for students to model their characters on actual people they know. This can make things a little less daunting and taxing on the imagination. However, whether or not this is the case, writing brief background bios or descriptions of characters’ physical personality characteristics can be a beneficial prewriting activity. Students should give some in-depth consideration to the details of who their character is: How do they walk? What do they look like? Do they have any distinguishing features? A crooked nose? A limp? Bad breath? Small details such as these bring life and, therefore, believability to characters. Students can even cut pictures from magazines to put a face to their character and allow their imaginations to fill in the rest of the details.
Younger students will often dictate to the reader the nature of their characters. To improve their writing craft, students must know when to switch from story-telling mode to story-showing mode. This is particularly true when it comes to character. Encourage students to reveal their character’s personality through what they do rather than merely by lecturing the reader on the faults and virtues of the character’s personality. It might be a small relayed detail in the way they walk that reveals a core characteristic. For example, a character who walks with their head hanging low and shoulders hunched while avoiding eye contact has been revealed to be timid without the word once being mentioned. This is a much more artistic and well-crafted way of doing things and is less irritating for the reader. A character who sits down at the family dinner table immediately snatches up his fork and starts stuffing roast potatoes into his mouth before anyone else has even managed to sit down has revealed a tendency towards greed or gluttony.
Understanding Character Traits
Again, there is room here for some fun and profitable prewriting activities. Give students a list of character traits and have them describe a character doing something that reveals that trait without ever employing the word itself.
It is also essential to avoid adjective stuffing here. When looking at students’ early drafts, adjective stuffing is often apparent. To train the student out of this habit, choose an adjective and have the student rewrite the sentence to express this adjective through action rather than telling.
When writing a story, it is vital to consider the character’s traits and how they will impact the story’s events. For example, a character with a strong trait of determination may be more likely to overcome obstacles and persevere. In contrast, a character with a tendency towards laziness may struggle to achieve their goals. In short, character traits add realism, depth, and meaning to a story, making it more engaging and memorable for the reader.
Popular Character Traits in Children’s Stories
- Determination
- Imagination
- Perseverance
- Responsibility
We have an in-depth guide to creating great characters here , but most students should be fine to move on to planning their conflict and resolution.
3. NO PROBLEM? NO STORY! HOW CONFLICT DRIVES A NARRATIVE

This is often the area apprentice writers have the most difficulty with. Students must understand that without a problem or conflict, there is no story. The problem is the driving force of the action. Usually, in a short story, the problem will center around what the primary character wants to happen or, indeed, wants not to happen. It is the hurdle that must be overcome. It is in the struggle to overcome this hurdle that events happen.
Often when a student understands the need for a problem in a story, their completed work will still not be successful. This is because, often in life, problems remain unsolved. Hurdles are not always successfully overcome. Students pick up on this.
We often discuss problems with friends that will never be satisfactorily resolved one way or the other, and we accept this as a part of life. This is not usually the case with writing a story. Whether a character successfully overcomes his or her problem or is decidedly crushed in the process of trying is not as important as the fact that it will finally be resolved one way or the other.
A good practical exercise for students to get to grips with this is to provide copies of stories and have them identify the central problem or conflict in each through discussion. Familiar fables or fairy tales such as Three Little Pigs, The Boy Who Cried Wolf, Cinderella, etc., are great for this.
While it is true that stories often have more than one problem or that the hero or heroine is unsuccessful in their first attempt to solve a central problem, for beginning students and intermediate students, it is best to focus on a single problem, especially given the scope of story writing at this level. Over time students will develop their abilities to handle more complex plots and write accordingly.
Popular Conflicts found in Children’s Storytelling.
- Good vs evil
- Individual vs society
- Nature vs nurture
- Self vs others
- Man vs self
- Man vs nature
- Man vs technology
- Individual vs fate
- Self vs destiny
Conflict is the heart and soul of any good story. It’s what makes a story compelling and drives the plot forward. Without conflict, there is no story. Every great story has a struggle or a problem that needs to be solved, and that’s where conflict comes in. Conflict is what makes a story exciting and keeps the reader engaged. It creates tension and suspense and makes the reader care about the outcome.
Like in real life, conflict in a story is an opportunity for a character’s growth and transformation. It’s a chance for them to learn and evolve, making a story great. So next time stories are written in the classroom, remember that conflict is an essential ingredient, and without it, your story will lack the energy, excitement, and meaning that makes it truly memorable.
4. THE NARRATIVE CLIMAX: HOW THINGS COME TO A HEAD!

The climax of the story is the dramatic high point of the action. It is also when the struggles kicked off by the problem come to a head. The climax will ultimately decide whether the story will have a happy or tragic ending. In the climax, two opposing forces duke things out until the bitter (or sweet!) end. One force ultimately emerges triumphant. As the action builds throughout the story, suspense increases as the reader wonders which of these forces will win out. The climax is the release of this suspense.
Much of the success of the climax depends on how well the other elements of the story have been achieved. If the student has created a well-drawn and believable character that the reader can identify with and feel for, then the climax will be more powerful.
The nature of the problem is also essential as it determines what’s at stake in the climax. The problem must matter dearly to the main character if it matters at all to the reader.
Have students engage in discussions about their favorite movies and books. Have them think about the storyline and decide the most exciting parts. What was at stake at these moments? What happened in your body as you read or watched? Did you breathe faster? Or grip the cushion hard? Did your heart rate increase, or did you start to sweat? This is what a good climax does and what our students should strive to do in their stories.
The climax puts it all on the line and rolls the dice. Let the chips fall where the writer may…
Popular Climax themes in Children’s Stories
- A battle between good and evil
- The character’s bravery saves the day
- Character faces their fears and overcomes them
- The character solves a mystery or puzzle.
- The character stands up for what is right.
- Character reaches their goal or dream.
- The character learns a valuable lesson.
- The character makes a selfless sacrifice.
- The character makes a difficult decision.
- The character reunites with loved ones or finds true friendship.
5. RESOLUTION: TYING UP LOOSE ENDS
After the climactic action, a few questions will often remain unresolved for the reader, even if all the conflict has been resolved. The resolution is where those lingering questions will be answered. The resolution in a short story may only be a brief paragraph or two. But, in most cases, it will still be necessary to include an ending immediately after the climax can feel too abrupt and leave the reader feeling unfulfilled.
An easy way to explain resolution to students struggling to grasp the concept is to point to the traditional resolution of fairy tales, the “And they all lived happily ever after” ending. This weather forecast for the future allows the reader to take their leave. Have the student consider the emotions they want to leave the reader with when crafting their resolution.
While the action is usually complete by the end of the climax, it is in the resolution that if there is a twist to be found, it will appear – think of movies such as The Usual Suspects. Pulling this off convincingly usually requires considerable skill from a student writer. Still, it may well form a challenging extension exercise for those more gifted storytellers among your students.
Popular Resolutions in Children’s Stories
- Our hero achieves their goal
- The character learns a valuable lesson
- A character finds happiness or inner peace.
- The character reunites with loved ones.
- Character restores balance to the world.
- The character discovers their true identity.
- Character changes for the better.
- The character gains wisdom or understanding.
- Character makes amends with others.
- The character learns to appreciate what they have.
Once students have completed their story, they can edit for grammar, vocabulary choice, spelling, etc., but not before!
As mentioned, there is a craft to storytelling, as well as an art. When accurate grammar, perfect spelling, and immaculate sentence structures are pushed at the outset, they can cause storytelling paralysis. For this reason, it is essential that when we encourage the students to write a story, we give them license to make mechanical mistakes in their use of language that they can work on and fix later.
Good narrative writing is a very complex skill to develop and will take the student years to become competent. It challenges not only the student’s technical abilities with language but also her creative faculties. Writing frames, word banks, mind maps, and visual prompts can all give valuable support as students develop the wide-ranging and challenging skills required to produce a successful narrative writing piece. But, at the end of it all, as with any craft, practice and more practice is at the heart of the matter.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT NARRATIVE
- Start your story with a clear purpose: If you can determine the theme or message you want to convey in your narrative before starting it will make the writing process so much simpler.
- Choose a compelling storyline and sell it through great characters, setting and plot: Consider a unique or interesting story that captures the reader’s attention, then build the world and characters around it.
- Develop vivid characters that are not all the same: Make your characters relatable and memorable by giving them distinct personalities and traits you can draw upon in the plot.
- Use descriptive language to hook your audience into your story: Use sensory language to paint vivid images and sequences in the reader’s mind.
- Show, don’t tell your audience: Use actions, thoughts, and dialogue to reveal character motivations and emotions through storytelling.
- Create a vivid setting that is clear to your audience before getting too far into the plot: Describe the time and place of your story to immerse the reader fully.
- Build tension: Refer to the story map earlier in this article and use conflict, obstacles, and suspense to keep the audience engaged and invested in your narrative.
- Use figurative language such as metaphors, similes, and other literary devices to add depth and meaning to your narrative.
- Edit, revise, and refine: Take the time to refine and polish your writing for clarity and impact.
- Stay true to your voice: Maintain your unique perspective and style in your writing to make it your own.
NARRATIVE WRITING EXAMPLES (Student Writing Samples)
Below are a collection of student writing samples of narratives. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to read these creative stories in detail and the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of narratives to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of story writing.
We recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type.
NARRATIVE WRITING PROMPTS (Journal Prompts)
When students have a great journal prompt, it can help them focus on the task at hand, so be sure to view our vast collection of visual writing prompts for various text types here or use some of these.
- On a recent European trip, you find your travel group booked into the stunning and mysterious Castle Frankenfurter for a single night… As night falls, the massive castle of over one hundred rooms seems to creak and groan as a series of unexplained events begin to make you wonder who or what else is spending the evening with you. Write a narrative that tells the story of your evening.
- You are a famous adventurer who has discovered new lands; keep a travel log over a period of time in which you encounter new and exciting adventures and challenges to overcome. Ensure your travel journal tells a story and has a definite introduction, conflict and resolution.
- You create an incredible piece of technology that has the capacity to change the world. As you sit back and marvel at your innovation and the endless possibilities ahead of you, it becomes apparent there are a few problems you didn’t really consider. You might not even be able to control them. Write a narrative in which you ride the highs and lows of your world-changing creation with a clear introduction, conflict and resolution.
- As the final door shuts on the Megamall, you realise you have done it… You and your best friend have managed to sneak into the largest shopping centre in town and have the entire place to yourselves until 7 am tomorrow. There is literally everything and anything a child would dream of entertaining themselves for the next 12 hours. What amazing adventures await you? What might go wrong? And how will you get out of there scot-free?
- A stranger walks into town… Whilst appearing similar to almost all those around you, you get a sense that this person is from another time, space or dimension… Are they friends or foes? What makes you sense something very strange is going on? Suddenly they stand up and walk toward you with purpose extending their hand… It’s almost as if they were reading your mind.
NARRATIVE WRITING VIDEO TUTORIAL

Teaching Resources
Use our resources and tools to improve your student’s writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
When teaching narrative writing, it is essential that you have a range of tools, strategies and resources at your disposal to ensure you get the most out of your writing time. You can find some examples below, which are free and paid premium resources you can use instantly without any preparation.
FREE Narrative Graphic Organizer
THE STORY TELLERS BUNDLE OF TEACHING RESOURCES

A MASSIVE COLLECTION of resources for narratives and story writing in the classroom covering all elements of crafting amazing stories. MONTHS WORTH OF WRITING LESSONS AND RESOURCES, including:
NARRATIVE WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
OTHER GREAT ARTICLES ABOUT NARRATIVE WRITING

Narrative Writing for Kids: Essential Skills and Strategies

7 Great Narrative Lesson Plans Students and Teachers Love

Top 7 Narrative Writing Exercises for Students

How to Write a Scary Story

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.1 Narration
Learning objectives.
- Determine the purpose and structure of narrative writing.
- Understand how to write a narrative essay.
Rhetorical modes simply mean the ways in which we can effectively communicate through language. This chapter covers nine common rhetorical modes. As you read about these nine modes, keep in mind that the rhetorical mode a writer chooses depends on his or her purpose for writing. Sometimes writers incorporate a variety of modes in any one essay. In covering the nine modes, this chapter also emphasizes the rhetorical modes as a set of tools that will allow you greater flexibility and effectiveness in communicating with your audience and expressing your ideas.
The Purpose of Narrative Writing
Narration means the art of storytelling, and the purpose of narrative writing is to tell stories. Any time you tell a story to a friend or family member about an event or incident in your day, you engage in a form of narration. In addition, a narrative can be factual or fictional. A factual story is one that is based on, and tries to be faithful to, actual events as they unfolded in real life. A fictional story is a made-up, or imagined, story; the writer of a fictional story can create characters and events as he or she sees fit.
The big distinction between factual and fictional narratives is based on a writer’s purpose. The writers of factual stories try to recount events as they actually happened, but writers of fictional stories can depart from real people and events because the writers’ intents are not to retell a real-life event. Biographies and memoirs are examples of factual stories, whereas novels and short stories are examples of fictional stories.
Because the line between fact and fiction can often blur, it is helpful to understand what your purpose is from the beginning. Is it important that you recount history, either your own or someone else’s? Or does your interest lie in reshaping the world in your own image—either how you would like to see it or how you imagine it could be? Your answers will go a long way in shaping the stories you tell.
Ultimately, whether the story is fact or fiction, narrative writing tries to relay a series of events in an emotionally engaging way. You want your audience to be moved by your story, which could mean through laughter, sympathy, fear, anger, and so on. The more clearly you tell your story, the more emotionally engaged your audience is likely to be.
On a separate sheet of paper, start brainstorming ideas for a narrative. First, decide whether you want to write a factual or fictional story. Then, freewrite for five minutes. Be sure to use all five minutes, and keep writing the entire time. Do not stop and think about what to write.
The following are some topics to consider as you get going:
The Structure of a Narrative Essay
Major narrative events are most often conveyed in chronological order , the order in which events unfold from first to last. Stories typically have a beginning, a middle, and an end, and these events are typically organized by time. Certain transitional words and phrases aid in keeping the reader oriented in the sequencing of a story. Some of these phrases are listed in Table 10.1 “Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time” . For more information about chronological order, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” and Chapter 9 “Writing Essays: From Start to Finish” .
Table 10.1 Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time
The following are the other basic components of a narrative:
- Plot . The events as they unfold in sequence.
- Characters . The people who inhabit the story and move it forward. Typically, there are minor characters and main characters. The minor characters generally play supporting roles to the main character, or the protagonist .
- Conflict . The primary problem or obstacle that unfolds in the plot that the protagonist must solve or overcome by the end of the narrative. The way in which the protagonist resolves the conflict of the plot results in the theme of the narrative.
- Theme . The ultimate message the narrative is trying to express; it can be either explicit or implicit.
Writing at Work
When interviewing candidates for jobs, employers often ask about conflicts or problems a potential employee has had to overcome. They are asking for a compelling personal narrative. To prepare for this question in a job interview, write out a scenario using the narrative mode structure. This will allow you to troubleshoot rough spots, as well as better understand your own personal history. Both processes will make your story better and your self-presentation better, too.
Take your freewriting exercise from the last section and start crafting it chronologically into a rough plot summary. To read more about a summary, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” . Be sure to use the time transition words and phrases listed in Table 10.1 “Transition Words and Phrases for Expressing Time” to sequence the events.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your rough plot summary.
Writing a Narrative Essay
When writing a narrative essay, start by asking yourself if you want to write a factual or fictional story. Then freewrite about topics that are of general interest to you. For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .
Once you have a general idea of what you will be writing about, you should sketch out the major events of the story that will compose your plot. Typically, these events will be revealed chronologically and climax at a central conflict that must be resolved by the end of the story. The use of strong details is crucial as you describe the events and characters in your narrative. You want the reader to emotionally engage with the world that you create in writing.
To create strong details, keep the human senses in mind. You want your reader to be immersed in the world that you create, so focus on details related to sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch as you describe people, places, and events in your narrative.
As always, it is important to start with a strong introduction to hook your reader into wanting to read more. Try opening the essay with an event that is interesting to introduce the story and get it going. Finally, your conclusion should help resolve the central conflict of the story and impress upon your reader the ultimate theme of the piece. See Chapter 15 “Readings: Examples of Essays” to read a sample narrative essay.
On a separate sheet of paper, add two or three paragraphs to the plot summary you started in the last section. Describe in detail the main character and the setting of the first scene. Try to use all five senses in your descriptions.
Key Takeaways
- Narration is the art of storytelling.
- Narratives can be either factual or fictional. In either case, narratives should emotionally engage the reader.
- Most narratives are composed of major events sequenced in chronological order.
- Time transition words and phrases are used to orient the reader in the sequence of a narrative.
- The four basic components to all narratives are plot, character, conflict, and theme.
- The use of sensory details is crucial to emotionally engaging the reader.
- A strong introduction is important to hook the reader. A strong conclusion should add resolution to the conflict and evoke the narrative’s theme.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
By registering, you agree to our Terms & Conditions .
- +2348180191933
- Login or Register
- $ US DOLLAR
- How It Works
English Language Primary 6 (Basic Six) Second Term
Price ₦ 300.00
Need a discount? See Current Offers
- Chapters 10
- Category Primary 6
- Author ClassNotes Edu
For Schools & Teachers
For Schools and Teacher who want to subscribe to all of the subjects, a class or term at a discounted price.

Create Your Bundle
Need many subjects? Waste no time. Select many subjects together in one subscription at a discounted price.

Recent News.
5 tips to improve your note-taking skills, boost your academic performance with classnotes.com.ng, featured subject., english language sss1 second term.
Please check through the topics down and be sure it conform with the scheme you are using.
Subject Reviews:
No reviews yet., also available in bundles, primary 6 second term all subjects, primary 6 all subjects.
Narrative Essay
A narration is simply the telling of a story. Whenever someone recounts an event or tells a story, he or she is using narration. A narration essay recounts an event or tells a story to illustrate an idea. A narration essay may be entertaining or informative.
Five Basic Steps to Writing a Narrative Essay
- Purpose: Why are you telling the story? Every narration must have a point or purpose, usually to entertain or to inform.
- Context: You should establish the context of your narrative early in the essay. You can follow these basic guidelines: who, what, where, when.
- Point of View: A narrative essay may be written in the first-person (I) or third-person (he, she, it) point of view; do not use second person (you). If you were part of the action, the first-person provides the best perspective. If you are relating an event based upon other sources, use the third-person point of view. In some circumstances, you may be forced to choose the point of view (if, for example, you were a witness, but not a participant). Once you have decided upon a point of view, stay consistent with it.
- Details: Include enough details for clarity; however, select only the facts that are relevant.
- Organization: A narrative usually follows a chronological time line; however, you may find flashbacks a creative option as long as the narrative can be clearly followed by the reader. Most narratives are told in the past tense. You should keep tenses consistent.
Thesis Statements for Narrative Essays
To create a thesis statement, combine the claim and the supporting details in one sentence. The direction of your essay can change depending on the pattern in which you organize the supporting details.
Once you have drafted a narrative, it’s always a good idea to ask someone else to read it. And, of course, you yourself will want to review what you have written from the standpoint of a critical reader.
Questions to Keep in Mind When Checking a Narrative
PURPOSE AND AUDIENCE. Does the narrative serve the purpose it is intended to serve? Is it appropriate for its intended audience? Does it need any additional background information or definitions?
THE STORY. Does it consist mainly of actions and events? Do they constitute a plot, with a clear beginning, middle, and end? Is every action in the narrative necessary to the plot? Have any essential actions been left out?
THE POINT. Does the narrative have a clear point to make? What is it? Is it stated explicitly in a thesis? If not, should it be?
ORGANIZATION. Is the storyline easy to follow? Are the events in chronological order? Are there any unintentional lapses in chronology or verb tense? Are intentional deviations from chronology, such as flashbacks, clearly indicated?
TRANSITIONS. Are there clear transitions to help readers follow the sequence of events? Have you checked over each transition to see that it logically connects the adjoining parts of the narrative?
DIALOGUE AND POINT OF VIEW. If there is no dialogue in the narrative, would some direct speech help bring it to life? If there is dialogue, does it sound like real people talking? Is the narrative told from a consistent, plausible point of view?
DETAILS. Does the narrative include lots of concrete details, especially sensory details (visual, olfactory, tactile, and auditory)? Does it show as well as tell? Can your reader imagine themselves there?
THE BEGINNING. Will the beginning of the narrative get the reader’s attention? How? How well does it set up what follows? How else might the narrative begin?
THE ENDING. How satisfying is it? What does it leave the reader thinking or feeling? How else might the narrative end?
Michael| 2018
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

6.3: Writing a Narrative Essay
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 6256

- Amber Kinonen, Jennifer McCann, Todd McCann, & Erica Mead
- Bay College Library
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
When writing a narrative essay, you may want to start by freewriting about topics that are of general interest to you.
Once you have a general idea of what you will be writing about, you should sketch out the major events of the story that will compose your plot. Often, these events will be revealed chronologically and climax at a central conflict that must be resolved by the end of the story. The use of strong details is crucial as you describe the events and characters in your narrative. You want the reader to emotionally engage with the world that you create in writing.
To create strong details, keep the five senses in mind. You want your reader to be immersed in the world that you create, so focus on details related to sight, sound, smell, taste, and touch as you describe people, places, and events in your narrative.
key takeaways
- Narration is the art of storytelling.
- Narratives can be either factual or fictional. In either case, narratives should emotionally engage the reader.
- Most narratives are composed of major events sequenced in chronological order.
- Time transition words and phrases are used to orient the reader in the sequence of a narrative.
- The four basic components to all narratives are plot, character, conflict, and theme.
- The use of sensory details is crucial to emotionally engaging the reader.
- A strong introduction is important to hook the reader. A strong conclusion should discuss the conflict and evoke the narrative theme.
Examples of Narrative Essays
- “Indian Education,” by Sherman Alexie
- “Us and Them,” by David Sedaris
- “Sixty-Nine Cents,” by Gary Shteyngart
- “Only Daughter,” by Sandra Cisneros
MUST-HAVE END-OF-THE-YEAR RESOURCES

English Language Arts
Classroom Management

Building Community

Freebie Vault

Free Vocabulary Activities!
Writing narrative endings.
I have to be honest. Teaching writing is tough. Each year, I set out to build a community of writers, and it is no easy task. One of the toughest things for my students is writing endings. They always start out with catchy beginnings only to get bogged down and just stop at the end.
How many writing pieces have you read with the words THE END scribbled at the bottom? Yes, I know it’s the end. I always tell my students that they don’t have to tell me it’s the end. I should know it’s the end if they’re writing a good ending! The first time I see this in a student’s writing, I write THE END on a piece of paper, crumble it up, and throw it in the trash. It’s like a mini ceremony to say goodbye to THE END, and it sends a strong message!
Barry Lane said it best in his book Reviser’s Toolbox: “ Don’t write endings, find them… Endings grow from beginnings and reveal themselves through clues within the story, characters, or ideas.”
I typically follow the Writers Workshop model in my classroom, as I have found the most success with this management style. We always spend quite a bit of time writing narratives, as I believe this genre is the most fun for students. It allows them to be creative, and it helps me to identify their voice as a writer.
To start our mini-unit on writing endings, I gave my students a pre-assessment of the substandard to figure out where their knowledge is with writing endings.

These substandard writing assessments are from my English Language Arts Assessments and Teaching Notes for grades 3-6 . I call them writing partial completes in each of my assessments. For each writing substandard, I include writing passages that are not complete. Students must complete the writing to show their knowledge of the standard. You can see for this substandard assessment above, the ending is left out for students to complete.
Once I pre-assess students, I can then quickly check their work to figure out what I need to modify or differentiate in my teaching. Once I hand back their pre-assessments, they document their scores in their Student Data Tracking Binders , rate their levels of understanding of the standard, and we begin!
We start our lesson by addressing the standard so students know where they are headed with their learning.

The great thing about this substandard is that it is extremely open ended. As long as students provide some type of closure or conclusion that follows from the narrated experiences or events, they will meet the standard. The way in which a student can get there is endless.
The main thing I focus on when teaching endings is to notice different endings in all of the literature that we read. Most of the time, students just finish a book without any reflection on the different strategies the author used to end the story.
On day 1, I brought out mentor texts that my students were already familiar with, and we “noticed” different endings the author used.
I modeled for students by re-reading different endings and talking to them about what I noticed about certain endings. I said things like, “I noticed that the ending was just a picture.” Or, “This ending left me wondering about what might happen next.”
Once I modeled this with one or two mentor texts, I then turned it over to students for their active involvement. I read a book (or just the ending of a familiar book), had students turn to a neighbor and share what they noticed, and then we came back together as a class to discuss.
We then worked together to compile an anchor chart of what we noticed about the endings of these mentor texts.

After our mini-lesson, we linked what we learned to students’ work time. On this first day, I had students work in small groups to notice different things about endings from more mentor texts. I put out a basket of books on each table for students to read through. Then, they used sticky notes to write down what they noticed.

After students had been given enough time, we came back together and shared more of what we noticed.
This ended our lesson for the day. But if there was time, I would have encouraged students to go back to their writing notebooks to revise their stories based on what they’ve learned so far.
Note: If you feel like your students need an extra day with any of the mini-lessons, give them that time in order to make sure they understand the content. Each class is different. Some students may need more time, and some may need less time.
On day 1, we noticed different ways in which authors end their stories. On day 2, we focused in on the specific strategies those authors used to end their stories.
We revisited a few more picture books as mentor texts. I specifically chose mentor texts with endings that I knew my students needed a bit more help with. For example, I knew they were extremely familiar with the question, dialogue, and funny endings, so I chose to grab mentor texts that had cliffhanger and reflection endings to give my students the extra practice.
Together, my students and I created this anchor chart to identify different endings authors use (you may use more than just these endings, but these are the endings we focused on). We gathered this information from all of the different picture books we looked through the day before.

I created a printable version of this anchor chart for students to reference.

You can click HERE to grab it as a freebie to use with your students.
If you need more mentor text ideas for each ending, check out the list I’ve created for you! You can download this page HERE , and click each book cover to check out each book!

After our lesson, students went back to their seats to sit and explore even more picture books. Now that students can name each ending, they can have a different focus when they are sifting through these picture books. With any writing lesson, the more students are exposed to examples of real writing in picture books, they better chance they have to use those specific strategies in their own writing.

After students had been given enough time to explore more endings, we came back together as a class and shared our findings. Since students had two days of exposure to different types of endings in numerous picture books, I gave them the opportunity to go back to their own narrative writing and work to revise their endings using the strategies we’ve learned over the last few days. Since this mini-lesson was a bit longer, students only had a few moments to go back to their writing. I told my students that this was a great time to start brainstorming what type of ending would fit best with the writing they had already done on their personal narratives. When conferencing with students, I noticed that some students had jotted down a list of certain ideas or an ending types they wanted to include in their writing so they could come back during our next writing lesson and get right to work!
Students have now had at least two days worth of exposure to many different types of endings. We’ve read many different picture books as mentor texts for these endings, and we have worked together to create an anchor chart of different endings authors use.
On day 3, I did a quick re-visit of the anchor chart, and we recapped what we had learned over the last few days. I answered any questions students had and reminded them of the focus of the standard. (Remember to also have your students rate and date their understanding of the standard if you are using my Student Data Tracking Binders. )
In addition to this, I reminded students that the main focus for day 3 was for them to really get into their own writing, and they were eager to do this by day 3!
Note: You can decide whether or not it’s worth it to pull your students to the carpet for your recap mini-lesson, or if you’d rather just keep them at their seats for this. I typically keep my kids at their seats and remind them that today’s focus is just to WRITE using the strategies they have learned about writing endings over the last few days.

While my students worked to revise their endings, I pulled small groups for re-teachings, conferenced one-on-one with a few students, and walked the room peeking over the shoulders of as many writers as possible. I especially kept my eye out for students who had done a great job revising their endings with the strategies they learned. It’s always best to use your students’ examples in front of the class.
After having the chance to write for some time, I stopped my students and pulled them back together to quickly discuss their progress. I asked for volunteers to share what they did to revise their ending, and I noticed a particular student’s piece that was great, so I asked him if I could share it with the class.
I always find that when I share a student’s example, many students are really tuned in, and often go back and start writing even more! To share their work, I put it under the document camera for the entire class to see.
After this quick interruption, I invited my students to think about the examples they saw in their peers’ writing and get back to it!
This day depends on your students and their progress with the standard. I typically gauge my students’ understanding with their work to make a decision as to whether or not they need more time to work on their endings and if students need more time for interventions and reteaching. If they do need more time, I make sure to continue conferencing with students. I pair students up to revise each other’s work and give constructive criticism. In addition to this, I may pull a small group of students to review even more mentor texts with them. Again, it depends on your students.
If you feel that your students have had enough time, and are successful with revising their endings, you can complete the post-assessment of the standard and have them graph their scores in their Student Data Tracking Binders .
33 Comments
This is fantastic! My problem with my students is not “The End”, but an abrupt ending with no closure and the words “To Be Continued.” So a lesson on endings is just what I need.
Thanks so much, Deena! I’m so glad to hear this lesson will be helpful for your students!
I read this blog post last week and thought it was great because my class is currently working on narrative writing. One of my author chairs shared a story on Tuesday and ended it with The End. I pointed out that though her story was wonderful I was a little disappointed to hear The End at the end because I have noticed that authors usually end their books in a way that I know it is the end without them ever uttering those words. We are having a funeral for The End today, followed by your lessons on ending! Thank you for this great resource. You are an awesome teacher!!
I love that! Thank you so much for your kind words! I hope your lesson went well!
Love this idea this will help me in the future when I become a teacher , and with picking a good ending my narrative essay !
Thanks so much for your kind words, Mel! I’m so glad to hear it will help you!
This looks fabulous and thorough! You’re right, we do tend to focus more on starting off strong. A strong finish is important too!
Thanks so much for your comments, Alicia!
I’m a parent of a 4th grader, teaching my kid to write. I’m impressed with the amount of research you have done to categorize different types of ending and to back it up with the wonderful book collections, to read them as examples for kids. Thanks a lot for sharing. :)
Thanks so much for your comments! I’m so glad to hear this helped you and your kiddo! :)
Thank-you so much for this resource! I was racking my brains for a good resource for supporting kids with endings (there are so many for beginnings) when I came across your website. I got so much more out of it than I expected.
I am very excited for the sixth grade version to come out!! All of your products look amazing, and it’s rare to find quality assessments for sixth graders :)
Thank you so much, Brittany! I appreciate your kind words!
I love this, too. I teach 8th grade, though. We tend to read longer texts. How do I amass a set of stories for the students to use to examine endings without having to wait until we are far into the year? We do personal narratives during first marking period.
So does the ending have to be resolved? Like I mean the problem isn’t resolved, the ending of my narrative is someone getting killed and finding out who the killer is
You sound like a very dedicated teacher and very resourceful. I echo the praise above. However, please do not call this Narrative writing. As a Middle and High School teacher, I also teach writing, and Narrative writing is a different animal altogether. When a student writes a Narrative, the ending needs to be conclusive… leave the reader feeling satisfied. I tell my students not to end a Narrative with a cliff hanger or a … to be continued… because it does not follow the instructions for the writing. What you have presented are great ways to end other types of stories, so perhaps you can just adjust your lesson to “Story Endings” to be more all encompassing. I really do appreciate the hard work you put into the lesson and I know your students are lucky to have you as a teacher. Thanks for sharing. I hope my comments are taken in the same collegial tone that I intend. Teach on! :)
I agree… I don’t want that either and may leave that off when I share with my third graders… Want a resolution to the small moments that we teach…
Where can I get the copy of your post page?
Hi Mary- Are you asking about the post-assessment for writing? If yes, you can find your grade level’s version here: https://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Kristine-Nannini/Category/ELA-Assessments-and-Teaching-Notes-123484
Love workshop too! The third grade lesson for endings was just a midworkshop interruption or share! It deserved its own lesson! THANK YOU! Renee
Why now I can’t do the questions w/o reading thanks thanks a lot ?
Thanks, Kristine! This definitely will be helpful for the students. Great workshop! Joem | http://www.paraphrasingtool.info/
Thank you so much for the tips on “endings”! I can’t wait to get my hands on these mentor text and allow my kiddos to explore different endings!
Thanks so much, Erica!
I teach beginning reporting and writing at the college level as an adjunct and your example of narrative endings just rocks it! Endings are hard and endings are usually the reason there’s a line at the front of the room when class is over with half a dozen laptops held up for advice. Thanks!
Thanks so much, Freda!
Loved your tips about writing essays.
This is awesome. It’s so hard to come up with activities during the narrative unit because the whole objective is for students to spend time just writing. This helps diversify the unit. Gracias!
Hi there. I was trying to download the link with the books on it that you share and mention that we should be able to click on the books and see them. Can you let me know how I can do this. Thank you in advance for this great resource;
Hi Kim- Thanks for your message! Here is the link: https://kristinenannini.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/01/MentorTextsClickable.pdf . I hope that helps!
Do you have any posters for your endings like you do your leads?
Thank you so much for sharing. I learnt so much to help me with the grade 5 students drama class.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Review Cart
No products in the cart.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Guide to Good Essay Writing (Primary 6) Utter coherent. Distinguished between narrative descriptive and argumentative writing. Write short narrative, descriptive and argumentative compositions. The teacher will teach the lesson with the aid of suitable reading materials to serve as models. METHOD OF TEACHING - Choose a suitable and ...
A narrative essay is an essay in which a candidate is expected to relate an event or incident just as an eye witness would do. It can also be conceived as an essay in which a candidate performs an act or a process of storytelling. Features of a Narrative Essay. It must have a title. It must be very interesting, convincing and attractive.
Note: - Your essay must be very interesting and convincing. - The narrative should follow the order in which the events took place. - State the facts as they were. - The dominant tense used in the narrative essay is the past simple tense. Evaluation: Write an essay of about 250 words on the topic "My Most Memorable Day".
TOPIC: EXPOSITORY OR EXPLANATORY COMPOSITION PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVESBy the end of the lesson, the pupils should have attained the following objectives (cognitive, affective and psychomotor) and should be able to:1. Write composition on expository or explanatory types.2. Make a clear logical presentation of point.
A narrative is a story that is narrated verbally or in writing. A narrative essay tells a story in essay format. It is about a personal experience and told from the author's perspective. It has a ...
2 Comments / By ClassPrefect / September 2, 2020. On this page, get all English Primary 6 topics from First Term to Third Term. Find them below, study them, and excel in your examination! For more class notes, homework help, exam practice, download our App HERE. Join ClassNotes.ng Telegram Community for exclusive content and support HERE.
Before I get into these steps, I should note that there is no one right way to teach narrative writing, and plenty of accomplished teachers are doing it differently and getting great results. This just happens to be a process that has worked for me. Step 1: Show Students That Stories Are Everywhere. Getting our students to tell stories should ...
Narrative Essay Example. Mark wrote: The alley where my friends and I used to play kick-the-can always smelled like garbage and flowers. There were dumpsters on one side of the alley, but Mrs ...
Writing. Grade 6, Standard 3: W.6.3.a. Engage and orient the reader by establishing a context and introducing a narrator and/or characters; organize an appropriate narrative sequence. A1 Examples: 1. The writer introduces the main character in the first sentence of the narrative (Vanessa woke up with a yawn.).
When applying for college, you might be asked to write a narrative essay that expresses something about your personal qualities. For example, this application prompt from Common App requires you to respond with a narrative essay. College application prompt. Recount a time when you faced a challenge, setback, or failure.
This is an engaging sixth grade lesson on narrative writing that includes several different activities that provide scaffolding and opportunity for differentiation. This lesson is very involved and may need to be spread out over more than one day depending on time constraints. Learning Objectives. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.W.6.3
FIRST TERM MATHEMATICS SCHEME OF WORK FOR PRIMARY SIX (6)/ BASIC SIX (6) 1.READING AND WRITING NUMBERS TO ONE BILLION IN WORDS AND FIGURE. 2. BINARY 3. A. PLACE VALUE OF WHOLE NUMBERS.…. Read More ». Lessonplan.
A narrative can spark emotion, encourage reflection, and convey meaning when done well. Narratives are a popular genre for students and teachers as they allow the writer to share their imagination, creativity, skill, and understanding of nearly all elements of writing. We occasionally refer to a narrative as 'creative writing' or story writing.
Register now to start learning your favourite subjects, Get access to our rich library of lessons in different formats (videos, ebooks, audiobooks, etc.) without any limit.
Exercise 1. On a separate sheet of paper, start brainstorming ideas for a narrative. First, decide whether you want to write a factual or fictional story. Then, freewrite for five minutes. Be sure to use all five minutes, and keep writing the entire time. Do not stop and think about what to write.
Writing skills need to be practised constantly so you can improve the standard of your essays. The link below is a helpful guide on writing narrative essays. Watch the video carefully and answer one of the essay topics I have provided. When you are done planning and writing the final copy, ask an adult to grade your essay.
For the latest catalogue Fax 01772 01772 863158 866153 email: [email protected] Visit our Website at: www.topical-resources.co.uk. Year 6 - Independent Writing Activities. Introduction.
Narration means the art of storytelling, and the purpose of narrative writing is to tell stories. Any time you tell a story to a friend or family member about an event or incident in your day, you engage in a form of narration. In addition, a narrative can be factual or fictional. A factual story is one that is based on, and tries to be ...
English Language Primary 6 (Basic Six) Second Term. Week:- 3Topic: Speech Work Pronunciation practice: Put stress on the right SyllablesReading: Teaching of new words, meanings and ComprehensionStructure: More constructions with clauses Using, 'when' 'who' 'which' 'where'Grammar: Word formation adjective formed from NounWriting: Narrative essay: A day I will not forgetVerbal ...
You can follow these basic guidelines: who, what, where, when. Point of View: A narrative essay may be written in the first-person (I) or third-person (he, she, it) point of view; do not use second person (you). If you were part of the action, the first-person provides the best perspective. If you are relating an event based upon other sources ...
Narration is the art of storytelling. Narratives can be either factual or fictional. In either case, narratives should emotionally engage the reader. Most narratives are composed of major events sequenced in chronological order. Time transition words and phrases are used to orient the reader in the sequence of a narrative.
To start our mini-unit on writing endings, I gave my students a pre-assessment of the substandard to figure out where their knowledge is with writing endings. These substandard writing assessments are from my English Language Arts Assessments and Teaching Notes for grades 3-6. I call them writing partial completes in each of my assessments.
1. Narrative 2. Personal Recount 3. Descriptive 4. Discursive 1. Narrative Narrative What How A fictional but realistic story driven by a clear plot with an interesting ending Select appropriate vocabulary to convey different depths of feelings or emotions. A personal recount of an incident, involving conflict, success, emotion, etc, that includes