Top Science News
Latest top headlines.
- Diet and Weight Loss
- Children's Health
- Prostate Cancer
- Lung Cancer
- Neuroscience
- Intelligence
- Virtual Reality
- Computer Graphics
- Energy and the Environment
- Energy Technology
- Electricity
- Nature of Water
- Black Holes
- Evolutionary Biology
- Frogs and Reptiles
- Paleontology
- New Species
- Mating and Breeding
- Oceanography
- Global Warming
- Fussy Eater? Most Parents Play Short Order Cook
- Affordable and Targeted Anticancer Agent
- How Working Memory Reallly Works
- Exercise Cuts Stress-Related Brain Activity

Top Physical/Tech
- Holographic Displays: An Immersive Future
- Harvesting Energy Where River Meets Sea
- Making Diamonds at Ambient Pressure
- Eruption of Mega-Magnetic Star
Top Environment
- Bioluminescence in Animals 540 Million Years Ago
- Fossil Frogs Share Their Skincare Secrets
- Two Species Interbreeding Created New Butterfly
- Warming Antarctic Deep-Sea and Sea Level Rise
Health News
Latest health headlines.
- Immune System
- Brain Tumor
- Staying Healthy
- Mental Health
- Mental Health Research
- Crohn's Disease
- Environmental Awareness
- Medical Devices
- Medical Technology
- Social Psychology
- Relationships
- STEM Education
- Educational Policy
- Educational Technology
- Brain-Computer Interfaces
Health & Medicine
- Significantly Improving Cancer Immunotherapies
- Getting Kids to Eat Fruits and Veggies
- Low Intensity Exercise: Less Depression
- Family of Proteins and Inflammatory Diseases
Mind & Brain
- 'Disaster Subculture' In Extreme Events
- Beta Rhythms Implement Cognitive Control
- Magnetic Microcoils Unlock Therapies
- Rekindling Friendships as Scary as Making Them
Living Well
- World's Chocolate Supply Threatened by Virus
- Infected: Understanding Spread of Behavior
- Can AI Simulate Multidisciplinary Workshops?
- Brain Synchronization Patterns and Social Ties
Physical/Tech News
Latest physical/tech headlines.
- Wind Energy
- Geomagnetic Storms
- Astrophysics
- Solar Energy
- Environmental Issues
- Biochemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Solar System
- Extrasolar Planets
- Sleep Disorders
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Veterinary Medicine
- Pests and Parasites
- Materials Science
- Civil Engineering
- Spintronics Research
- Spintronics
- Information Technology
Matter & Energy
- Toward Unification of Turbulence Framework
- Positive Perceptions of Solar Projects
- Light Without Heat Can Vaporize Water
- Biophysics: Testing How Well Biomarkers Work
Space & Time
- Oldest Evidence of Earth's Magnetic Field
- To Find Life in the Universe, View Deadly Venus
- Giant Galactic Explosion: Galaxy Pollution
- Simulated Microgravity Affects Sleep Rhythms
Computers & Math
- AI Diagnoses Moon Blindness from Horse Photos
- Control of Valley Polarization in Bulk Materials
- Clean Fuel Generation With Simple Twist
- Tiny Chip Can Safeguard User Data On Smartphone
Environment News
Latest environment headlines.
- Hurricanes and Cyclones
- Microbes and More
- Ecology Research
- Air Pollution
- Hazardous Waste
- Recycling and Waste
- Ozone Holes
- Air Quality
- Resource Shortage
- Severe Weather
- Ancient Civilizations
- Lost Treasures
- Anthropology
- Biochemistry Research
- Cell Biology
Plants & Animals
- Hurricanes Jeopardize Carbon-Storing in Forests
- Giant Viruses Infect Deadly Parasite
- How Parasites Shape Complex Food Webs
- Broader Effects of Wildfires in Siberia
Earth & Climate
- Remote Monitoring of Cloud Properties
- Sustainable Recovery of Minerals from E-Waste
- Ozone Layer: Pollution and Climate
- Storm Protection and Sea-Level Rise
Fossils & Ruins
- Everest Mountaineer's Letters Digitized
- 'Forgotten City'
- RNA's Hidden Potential: Future Bioengineering
- Worst-Case Warming Less Likely, Analysis Shows
Society/Education News
Latest society/education headlines.
- Diseases and Conditions
- Public Health
- Breast Cancer
- Security and Defense
- Weapons Technology
- Surveillance
- Mathematics
- Computer Modeling
- Child Psychology
- Child Development
- K-12 Education
- Infant and Preschool Learning
- Language Acquisition
- Sustainability
- Environmental Policies
- Land Management
- Energy Issues
Science & Society
- Financial Hardships With Cancer Diagnosis
- Fecal Contamination of Coastal Waters
- Modernizing the U.S. Nuclear Deterrent
- New Sensing Checks Overhaul Manufacturing
Education & Learning
- Pupils Enlarge When People Focus On Tasks
- Synchrony Between Parents and Children
- Evolving Attitudes of Gen X Toward Evolution
- Talk to Your Baby: It Matters
Business & Industry
- Sustainability in Agricultural Trade
- Active Workstations and Cognitive Performance
- Suppressing Boredom at Work Hurts Productivity
- Pairing Crypto Mining With Green Hydrogen
- Precise Time Measurement: Superradiant Atoms
- Artificial Cells That Act Like Living Cells
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat, about this site.
ScienceDaily features breaking news about the latest discoveries in science, health, the environment, technology, and more -- from leading universities, scientific journals, and research organizations.
Visitors can browse more than 500 individual topics, grouped into 12 main sections (listed under the top navigational menu), covering: the medical sciences and health; physical sciences and technology; biological sciences and the environment; and social sciences, business and education. Headlines and summaries of relevant news stories are provided on each topic page.
Stories are posted daily, selected from press materials provided by hundreds of sources from around the world. Links to sources and relevant journal citations (where available) are included at the end of each post.
For more information about ScienceDaily, please consult the links listed at the bottom of each page.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
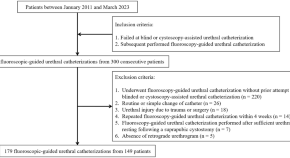
Safety and efficacy of fluoroscopy-guided urethral catheterization in case of failed blind or cystoscopy-assisted urethral catheterization
- Sang Woo Kim
- In Chul Nam
- Sung Eun Park
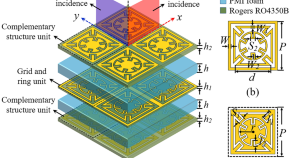
Design and analysis of a complementary structure-based high selectivity tri-band frequency selective surface
- Xiaolong Weng
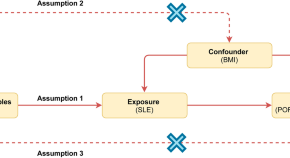
The genetic relationship between systemic lupus erythematosus and risk of primary ovarian failure from a mendelian randomization study
- Xiangfei Wang
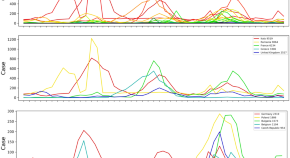
Assessment of using Google Trends for real-time monitoring of infectious disease outbreaks: a measles case study
- John Cameron Lang
- Yao-Hsuan Chen
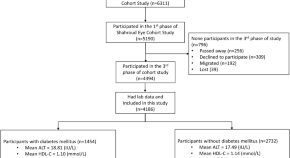
The association of ALT to HDL-C ratio with type 2 diabetes in 50–74 years old adults: a population-based study
- Abolfazl Emamian
- Mohammad Hassan Emamian
- Akbar Fotouhi
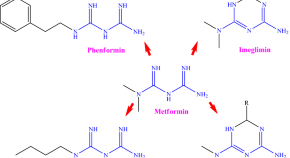
Synthesis and molecular docking studies of new aryl imeglimin derivatives as a potent antidiabetic agent in a diabetic zebrafish model
- Aylin Khodakhah
- Hassan Mohammadi
- Massoud Amanlou

Management of pediatric vanishing testes syndrome based on pathological diagnosis: a single-center retrospective study
- Chang-Kun Mao
- Yong-Sheng Cao
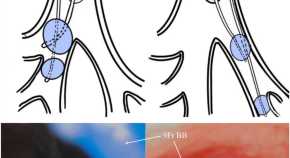
Protecting the non-operative lobe/s of the operative lung can reduce the pneumonia incidence after thoracoscopic lobectomy: a randomised controlled trial

Comprehensive quantitative determination of aquifer confinement based on tidal response of well water level and its application in North China
- Luming Zhang
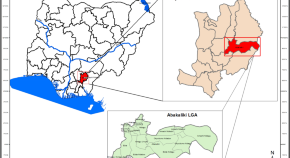
Employing post classification comparison to detect land use cover change patterns and quantify conversions in Abakaliki LGA Nigeria from 2000 to 2022
- Francis E. Onuegbu
- Anthony U. Egbu
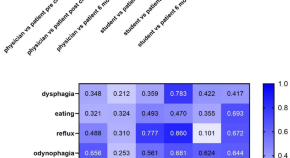
Students and physicians differ in perception of quality of life in patients with tumors of the upper gastrointestinal tract
- Lena Schooren
- Grace Oberhoff
- Sophia M. Schmitz
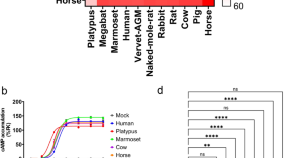
A cAMP-biosensor-based assay for measuring plasma arginine–vasopressin levels
- Kouki Kawakami
- Asuka Inoue
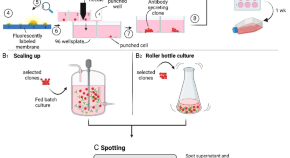
A nanowell platform to identify, sort and expand high antibody-producing cells
- Fikri Abali
- Richard Schasfoort
- Leon W. M. M. Terstappen
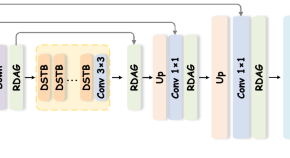
Uncertainty-driven mixture convolution and transformer network for remote sensing image super-resolution
- Xiaomin Zhang
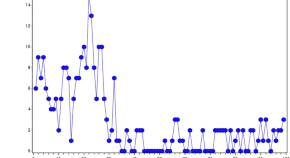
Mobile monitoring system detects the disease activity pattern and shows the association with clinical outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease
- Yoo Jin Lee
- Sang Gyu Kwak
- Eun Young Kim
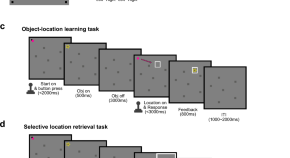
Gaze patterns reflect the retrieval and selection of memories in a context-dependent object location retrieval task
- Somang Paeng
- Hyoung F. Kim
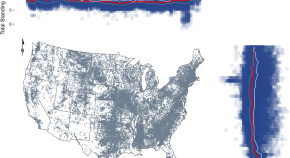
Reservoir ecosystems support large pools of fish biomass
- Christine A. Parisek
- Francine A. De Castro
- Andrew L. Rypel
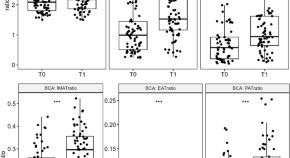
Elexacaftor/tezacaftor/ivacaftor influences body composition in adults with cystic fibrosis: a fully automated CT-based analysis
- Dirk Westhölter
- Johannes Haubold
- Marcel Opitz
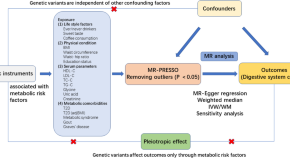
The effect of metabolism-related lifestyle and clinical risk factors on digestive system cancers in East Asian populations: a two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
- Xianlei Cai
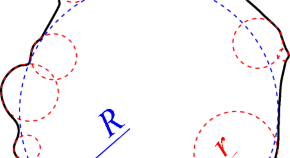
An improved corner dealiasing and recognition algorithm for 2D Wadell roundness computation
- Jianhuang Chen
- Zhongjian Zhang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
PubMed Central (PMC) Home Page
PubMed Central ® (PMC) is a free full-text archive of biomedical and life sciences journal literature at the U.S. National Institutes of Health's National Library of Medicine (NIH/NLM)
Discover a digital archive of scholarly articles, spanning centuries of scientific research.
Learn how to find and read articles of interest to you.
Collections
Browse the PMC Journal List or learn about some of PMC's unique collections.
For Authors
Navigate the PMC submission methods to comply with a funder mandate, expand access, and ensure preservation.
For Publishers
Learn about deposit options for journals and publishers and the PMC selection process.
For Developers
Find tools for bulk download, text mining, and other machine analysis.
9.8 MILLION articles are archived in PMC.
Content provided in part by:, full participation journals.
Journals deposit the complete contents of each issue or volume.
NIH Portfolio Journals
Journals deposit all NIH-funded articles as defined by the NIH Public Access Policy.
Selective Deposit Programs
Publisher deposits a subset of articles from a collection of journals.
March 21, 2024
Preview upcoming improvements to pmc.
We are pleased to announce the availability of a preview of improvements planned for the PMC website. These…
Dec. 15, 2023
Update on pubreader format.
The PubReader format was added to PMC in 2012 to make it easier to read full text articles on tablet, mobile, and oth…

We are pleased to announce the availability of a preview of improvements planned for the PMC website. These improvements will become the default in October 2024.
Subscribe or renew today
Every print subscription comes with full digital access
Science News

A new method of making diamonds doesn’t require extreme pressure
Lab-grown diamonds can form at atmospheric pressure in a liquid of gallium, iron, nickel and silicon.
How a sugar acid crucial for life could have formed in interstellar clouds
Protein whisperer oluwatoyin asojo fights neglected diseases.

A rapid shift in ocean currents could imperil the world’s largest ice shelf
Roughly the size of Spain, the Ross Ice Shelf stabilizes major glaciers along Antarctica’s coast — and is at risk of retreating, a new study finds.
A new U.S. tool maps where heat will be dangerous for your health
Polar forests may have just solved a solar storm mystery.

Pelvic exams at hospitals require written consent, new U.S. guidelines say
Hospitals must now get written consent to perform pelvic, breast, prostate and rectal exams on sedated patients or risk losing federal funding.
Language models may miss signs of depression in Black people’s Facebook posts

A vaccine for bees has an unexpected effect
Honeybees vaccinated against a bacterial disease were also protected from a viral disease.
Glowing octocorals have been around for at least 540 million years
Plant ‘time bombs’ highlight how sneaky invasive species can be.

Scientists find a naturally occurring molecule that forms a fractal
The protein assembles itself into a repeating triangle pattern. The fractal seems to be an accident of evolution, scientists say.

How two outsiders tackled the mystery of arithmetic progressions
A predicted quasicrystal is based on the ‘einstein’ tile known as the hat.

Separating science fact from fiction in Netflix’s ‘3 Body Problem’
Real science underpins much of the action in the show — along with a hefty dose of artistic liberty.
Physicists take a major step toward making a nuclear clock
During a total solar eclipse, some colors really pop. here’s why, science & society, aimee grant investigates the needs of autistic people, pluto’s heart-shaped basin might not hide an ocean after all, our picture of habitability on europa, a top contender for hosting life, is changing.

This robot can tell when you’re about to smile — and smile back
Using machine learning, researchers trained Emo to make facial expressions in sync with humans.
AI learned how to sway humans by watching a cooperative cooking game
Why large language models aren’t headed toward humanlike understanding.

Trustworthy journalism comes at a price.
Scientists and journalists share a core belief in questioning, observing and verifying to reach the truth. Science News reports on crucial research and discovery across science disciplines. We need your financial support to make it happen – every contribution makes a difference.
Subscribers, enter your e-mail address for full access to the Science News archives and digital editions.
Not a subscriber? Become one now .

Explore millions of high-quality primary sources and images from around the world, including artworks, maps, photographs, and more.
Explore migration issues through a variety of media types
- Part of The Streets are Talking: Public Forms of Creative Expression from Around the World
- Part of The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Vol. 34, No. 1 (Winter 2020)
- Part of Cato Institute (Aug. 3, 2021)
- Part of University of California Press
- Part of Open: Smithsonian National Museum of African American History & Culture
- Part of Indiana Journal of Global Legal Studies, Vol. 19, No. 1 (Winter 2012)
- Part of R Street Institute (Nov. 1, 2020)
- Part of Leuven University Press
- Part of UN Secretary-General Papers: Ban Ki-moon (2007-2016)
- Part of Perspectives on Terrorism, Vol. 12, No. 4 (August 2018)
- Part of Leveraging Lives: Serbia and Illegal Tunisian Migration to Europe, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (Mar. 1, 2023)
- Part of UCL Press
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR.
Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world’s leading museums, archives, and scholars.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Trending Articles
- Efficacy and safety of eco-friendly inhalers: focus on combination ipratropium bromide and albuterol in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Panos RJ. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2013. PMID: 23658481 Free PMC article. Review.
- Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990-2021: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Lancet. 2024. PMID: 38642570
- Labour promotes systemic mobilisation of monocytes, T cell activation and local secretion of chemotactic factors in the intervillous space of the placenta. Vikberg S, et al. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36969250 Free PMC article.
- QDPR deficiency drives immune suppression in pancreatic cancer. Liu J, et al. Cell Metab. 2024. PMID: 38642552
- Dual-role transcription factors stabilize intermediate expression levels. He J, et al. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38631355
Latest Literature
- Crit Care Med (2)
- J Clin Endocrinol Metab (3)
- J Immunol (1)
- Methods Mol Biol (46)
- Nature (16)
- PLoS One (1)
- Pediatrics (1)
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Scientists push new paradigm of animal consciousness, saying even insects may be sentient
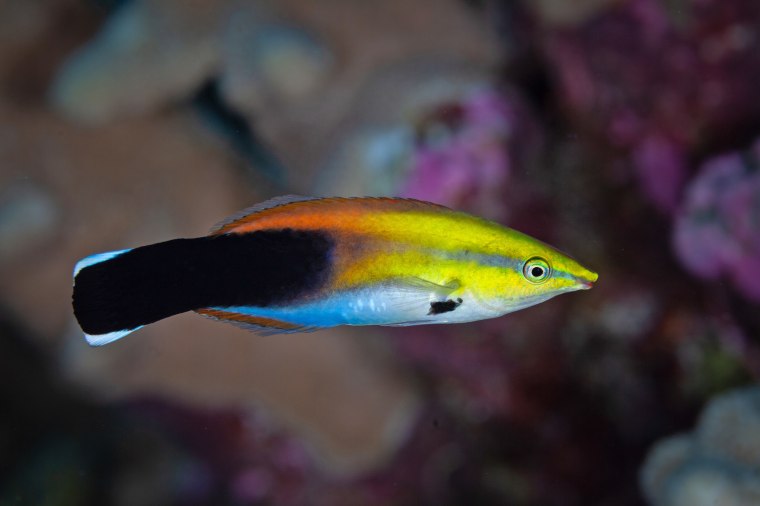

Bees play by rolling wooden balls — apparently for fun . The cleaner wrasse fish appears to recognize its own visage in an underwater mirror . Octopuses seem to react to anesthetic drugs and will avoid settings where they likely experienced past pain.
All three of these discoveries came in the last five years — indications that the more scientists test animals, the more they find that many species may have inner lives and be sentient. A surprising range of creatures have shown evidence of conscious thought or experience, including insects, fish and some crustaceans.
That has prompted a group of top researchers on animal cognition to publish a new pronouncement that they hope will transform how scientists and society view — and care — for animals.
Nearly 40 researchers signed “ The New York Declaration on Animal Consciousness ,” which was first presented at a conference at New York University on Friday morning. It marks a pivotal moment, as a flood of research on animal cognition collides with debates over how various species ought to be treated.
The declaration says there is “strong scientific support” that birds and mammals have conscious experience, and a “realistic possibility” of consciousness for all vertebrates — including reptiles, amphibians and fish. That possibility extends to many creatures without backbones, it adds, such as insects, decapod crustaceans (including crabs and lobsters) and cephalopod mollusks, like squid, octopus and cuttlefish.
“When there is a realistic possibility of conscious experience in an animal, it is irresponsible to ignore that possibility in decisions affecting that animal,” the declaration says. “We should consider welfare risks and use the evidence to inform our responses to these risks.”
Jonathan Birch, a professor of philosophy at the London School of Economics and a principal investigator on the Foundations of Animal Sentience project, is among the declaration’s signatories. Whereas many scientists in the past assumed that questions about animal consciousness were unanswerable, he said, the declaration shows his field is moving in a new direction.
“This has been a very exciting 10 years for the study of animal minds,” Birch said. “People are daring to go there in a way they didn’t before and to entertain the possibility that animals like bees and octopuses and cuttlefish might have some form of conscious experience.”
From 'automata' to sentient
There is not a standard definition for animal sentience or consciousness, but generally the terms denote an ability to have subjective experiences: to sense and map the outside world, to have capacity for feelings like joy or pain. In some cases, it can mean that animals possess a level of self-awareness.
In that sense, the new declaration bucks years of historical science orthodoxy. In the 17th century, the French philosopher René Descartes argued that animals were merely “material automata” — lacking souls or consciousness.
Descartes believed that animals “can’t feel or can’t suffer,” said Rajesh Reddy, an assistant professor and director of the animal law program at Lewis & Clark College. “To feel compassion for them, or empathy for them, was somewhat silly or anthropomorphizing.”
In the early 20th century, prominent behavioral psychologists promoted the idea that science should only study observable behavior in animals, rather than emotions or subjective experiences . But beginning in the 1960s, scientists started to reconsider. Research began to focus on animal cognition, primarily among other primates.
Birch said the new declaration attempts to “crystallize a new emerging consensus that rejects the view of 100 years ago that we have no way of studying these questions scientifically.”
Indeed, a surge of recent findings underpin the new declaration. Scientists are developing new cognition tests and trying pre-existing tests on a wider range of species, with some surprises.
Take, for example, the mirror-mark test, which scientists sometimes use to see if an animal recognizes itself.
In a series of studies, the cleaner wrasse fish seemed to pass the test .
The fish were placed in a tank with a covered mirror, to which they exhibited no unusual reaction. But after the cover was lifted, seven of 10 fish launched attacks toward the mirror, signaling they likely interpreted the image as a rival fish.
After several days, the fish settled down and tried odd behaviors in front of the mirror, like swimming upside down, which had not been observed in the species before. Later, some appeared to spend an unusual amount of time in front of the mirror, examining their bodies. Researchers then marked the fish with a brown splotch under the skin, intended to resemble a parasite. Some fish tried to rub the mark off.
“The sequence of steps that you would only ever have imagined seeing with an incredibly intelligent animal like a chimpanzee or a dolphin, they see in the cleaner wrasse,” Birch said. “No one in a million years would have expected tiny fish to pass this test.”
In other studies, researchers found that zebrafish showed signs of curiosity when new objects were introduced into their tanks and that cuttlefish could remember things they saw or smelled . One experiment created stress for crayfish by electrically shocking them , then gave them anti-anxiety drugs used in humans. The drugs appeared to restore their usual behavior.
Birch said these experiments are part of an expansion of animal consciousness research over the past 10 to 15 years. “We can have this much broader canvas where we’re studying it in a very wide range of animals and not just mammals and birds, but also invertebrates like octopuses, cuttlefish,” he said. “And even increasingly, people are talking about this idea in relation to insects.”
As more and more species show these types of signs, Reddy said, researchers might soon need to reframe their line of inquiry altogether: “Scientists are being forced to reckon with this larger question — not which animals are sentient, but which animals aren’t?”
New legal horizons
Scientists’ changing understanding of animal sentience could have implications for U.S. law, which does not classify animals as sentient on a federal level, according to Reddy. Instead, laws pertaining to animals focus primarily on conservation, agriculture or their treatment by zoos, research laboratories and pet retailers.
“The law is a very slow moving vehicle and it really follows societal views on a lot of these issues,” Reddy said. “This declaration, and other means of getting the public to appreciate that animals are not just biological automatons, can create a groundswell of support for raising protections.”
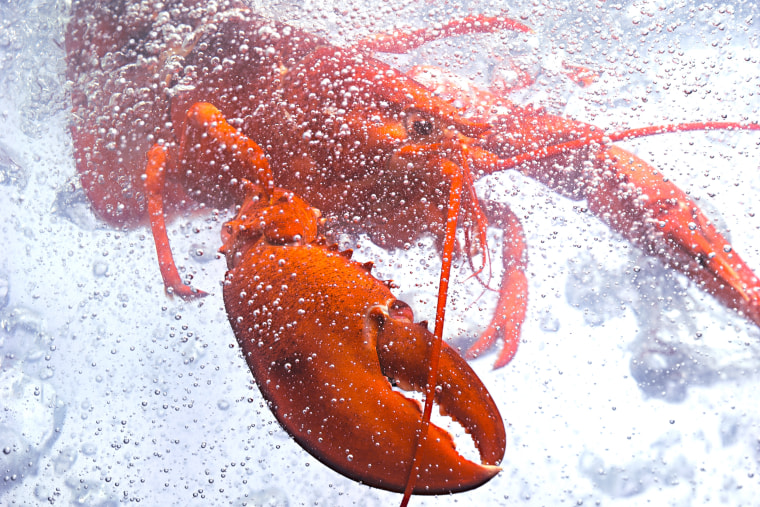

State laws vary widely. A decade ago, Oregon passed a law recognizing animals as sentient and capable of feeling pain, stress and fear, which Reddy said has formed the bedrock of progressive judicial opinions in the state.
Meanwhile, Washington and California are among several states where lawmakers this year have considered bans on octopus farming, a species for which scientists have found strong evidence of sentience.
British law was recently amended to consider octopuses sentient beings — along with crabs and lobsters .
“Once you recognize animals as sentient, the concept of humane slaughter starts to matter, and you need to make sure that the sort of methods you’re using on them are humane,” Birch said. “In the case of crabs and lobsters, there are pretty inhumane methods, like dropping them into pans of boiling water, that are very commonly used.”
Evan Bush is a science reporter for NBC News. He can be reached at [email protected].

Students Will Perform Research at National Laboratories
WASHINGTON, D.C . – The Department of Energy’s (DOE’s) Office of Science has selected 86 graduate students representing 31 states and Puerto Rico for the Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program’s 2023 Solicitation 2 cycle. Through world-class training and access to state-of-the-art facilities and resources at DOE national laboratories, SCGSR prepares graduate students to enter jobs of critical importance to the DOE mission and secures our national position at the forefront of discovery and innovation.
“The Graduate Student Research program is a unique opportunity for graduate students to complete their PhD training with teams of world-class experts aiming to answer some of the most challenging problems in fundamental science,” said Harriet Kung, Acting Director of the DOE Office of Science . “Gaining access to cutting edge tools for scientific discovery at DOE national laboratories will be instrumental in preparing the next generation of scientific leaders.”
Awardees were selected from a diverse pool of graduate applicants from institutions around the country. Selection was based on merit review by external scientific experts. Since 2014, the SCGSR program has provided more than 1150 U.S. graduate awardees from 165 universities with supplemental funds to conduct part of their thesis research at a host DOE laboratory in collaboration with a DOE laboratory scientist. In this cohort, more than 31% of SCGSR awardees are women, about 16% of the awardees attend Minority Serving Institutions (MSIs), and 13% are from institutions in jurisdictions that are part of the Established Program to Stimulate Competitive Research (EPSCoR).
SCGSR awardees work on research projects of significant importance to the Office of Science mission that address critical energy, environmental, and nuclear challenges at national and international scales. Projects in this cohort span seven Office of Science research programs. Awards were made through the SCGSR program’s first of two annual solicitation cycles for FY 2023.
Applications for the ongoing 2024 Solicitation 1 cycle are due 5:00pm EST, May 1, 2024. Graduate students currently pursuing Ph.D. degrees in areas of physics, chemistry, material sciences, biology (non-medical), geology, planetary sciences, mathematics, engineering, computer or computational sciences, or specific areas of environmental sciences that are aligned with the mission of the Office of Science are eligible to apply to the SCGSR program. The research projects are expected to advance the graduate awardees’ overall doctoral research and training while providing access to the expertise, resources, and capabilities available at the DOE national laboratories. The award cohort from the 2024 Solicitation 1 cycle is expected to be announced around September 2024.
A list of the 86 awardees, their institutions, host DOE laboratory/facility, and priority research areas of projects can be found at the SCGSR Awards and Publications page.
For more information on SCGSR, please go to the Office of Science Graduate Student Research program page .
Princeton University
Princeton engineering, holographic displays offer a glimpse into an immersive future.
By Julia Schwarz
April 22, 2024

Researchers at Princeton and Meta have created a tiny optical device that makes holographic images larger and clearer. Small enough to fit on a pair of eyeglasses, the device could enable a new kind of immersive virtual reality display. Illustration by Liz Sabol, photo by Nathan Matsuda
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
Holographic images have real depth because they are three dimensional, whereas monitors merely simulate depth on a 2D screen. Because we see in three dimensions, holographic images could be integrated seamlessly into our normal view of the everyday world.
The result is a virtual and augmented reality display that has the potential to be truly immersive, the kind where you can move your head normally and never lose the holographic images from view. “To get a similar experience using a monitor, you would need to sit right in front of a cinema screen,” said Felix Heide , assistant professor of computer science and senior author on a paper published April 22 in Nature Communications.
And you wouldn’t need to wear a screen in front of your eyes to get this immersive experience. Optical elements required to create these images are tiny and could potentially fit on a regular pair of glasses. Virtual reality displays that use a monitor, as current displays do, require a full headset. And they tend to be bulky because they need to accommodate a screen and the hardware necessary to operate it.
“Holography could make virtual and augmented reality displays easily usable, wearable, and ultrathin,” said Heide. They could transform how we interact with our environments, everything from getting directions while driving, to monitoring a patient during surgery, to accessing plumbing instructions while doing a home repair.
One of the most important challenges is quality. Holographic images are created by a small chip-like device called a spatial light modulator. Until now, these modulators could only create images that are either small and clear or large and fuzzy. This tradeoff between image size and clarity results in a narrow field of view, too narrow to give the user an immersive experience. “If you look towards the corners of the display, the whole image may disappear,” said Nathan Matsuda, research scientist at Meta and co-author on the paper.

Heide, Matsuda and Ethan Tseng , doctoral student in computer science, have created a device to improve image quality and potentially solve this problem. Along with their collaborators, they built a second optical element to work in tandem with the spatial light modulator. Their device filters the light from the spatial light modulator to expand the field of view while preserving the stability and fidelity of the image. It creates a larger image with only a minimal drop in quality.
Image quality has been a core challenge preventing the practical applications of holographic displays, said Matsuda. “The research brings us one step closer to resolving this challenge,” he said.
The new optical element is like a very small custom-built piece of frosted glass, said Heide. The pattern etched into the frosted glass is the key. Designed using AI and optical techniques, the etched surface scatters light created by the spatial light modulator in a very precise way, pushing some elements of an image into frequency bands that are not easily perceived by the human eye. This improves the quality of the holographic image and expands the field of view.
Still, hurdles to making a working holographic display remain. The image quality isn’t yet perfect, said Heide, and the fabrication process for the optical elements needs to be improved. “A lot of technology has to come together to make this feasible,” said Heide. “But this research shows a path forward.”
The paper, “Neural Etendue Expander for Ultra-Wide-Angle High-Fidelity Holographic Display” was published April 22 in Nature Communications. In addition to Heide and Tseng, co-authors from Princeton include Seung-Hwan Baek and Praneeth Chakravarthula. In addition to Matsuda, co-authors from Meta Research are Grace Kuo, Andrew Maimone, Florian Schiffers, and Douglas Lanman. Qiang Fu and Wolfgang Heidrich from the Visual Computing Center at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology in Saudi Arabia also contributed. The work was supported by Princeton University’s Imaging and Analysis Center and the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology’s Nanofabrication Core Lab.
Related News

Retro-reflectors could help future cities keep their cool

A good way to cool a sweltering urban canyon? Put a lid on it.

Engineers use moisture to pull carbon dioxide out of the air

Climate change likely to drive more floods in some parts of the U.S., fewer in others

Princeton researchers, industry leaders drive new era of innovation in wireless and networking technologies

Transforming microbes into factories for the future

Felix Heide

Computing and Network Systems
Related department.

Computer Science
April 19, 2024
How Anti-Trans Efforts Misuse and Distort Science
Three types of misinformation are being used against transgender people: oversimplifying scientific knowledge, fabricating and misinterpreting research and promoting false equivalences
By Corey S. Powell & OpenMind Magazine

Falsehoods and half-truths obscure the actual science around trans rights.
Jorg Greuel/Getty Images
In 2023 alone, more than 500 anti-trans bills were proposed or adopted in nearly every state in the United States, targeting everything from drag performances to gender-affirming medical care to school inclusion policies for trans people. Support for these measures has been enabled and propelled by scientific misinformation, which has proven to be a distressingly effective tool in outraging a public that might otherwise be broadly empathetic, or at least uncertain about where to stand. In the following Q&A, law professor Florence Ashley and scientist Simón(e) Sun describe to OpenMind co-editor Corey S. Powell how deceptions in science have been used to disenfranchise trans people and other marginalized groups. (This conversation has been edited for length and clarity.)
Anti-trans sentiment has existed for a long time, but it seems like we're at a moment of particularly intense attacks. Why is that?
Florence Ashley : It’s definitely been getting worse. A lot of people who have been out since the '70s and '80s are saying that this is an unprecedented level of public hate. Even if there's been progress around rights for a lot of people, there's a whole lot more hostility. I am located in Canada, where we're starting to have anti-trans bills that would have been mostly unheard of just five years ago. In the U.S., the fact that the courts are so stacked by Trump appointees at the federal level has been particularly daunting. We are seeing alliances between the anti-reproductive justice and anti-trans movements, which is really concerning.
On supporting science journalism
If you're enjoying this article, consider supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing . By purchasing a subscription you are helping to ensure the future of impactful stories about the discoveries and ideas shaping our world today.
Trans culture is more visible today than it has been in the past. Does that help, or is increased visibility stirring up the anti-trans movement?
Florence Ashley : Visibility is very much a double-edged sword. There are good sides to visibility, of course. It helps people realize that they're trans. You have more access to trans narratives, which gives you more space to understand yourself, and that's very positive. But at the social and political level, it has been quite negative. We're seeing a lot more people who vehemently hate trans people, who are even willing to harm trans people. Whereas people who are favorable to trans people largely just leave us alone. And a lot of reforms that we were able to achieve with relative ease, in a less visible manner, are now being rolled back.
Listen to the Podcast
Simón(e) Sun and Florence Ashley on anti-trans myths
Both of you work within academia, which is regarded, from the outside, as largely progressive. From your inside perspective, has the academic community been helpful and supportive?
Simón(e) Sun : It’s easy to assume, broadly, that academics tend to lean left, or lean progressive, but it’s much more nuanced in terms of what specific issues you're talking about. Often scientists have a false view of themselves as existing outside of social or political issues. Especially in the basic sciences, a lot of scientists feel like they don't have to think about any kind of political question.
Many of the arguments against trans rights center on the idea that transness itself is not legitimate—that there are just two sexes, period. You describe this idea as “sex essentialism.” Can you explain that term, and talk about how it shapes the debate
Simón(e) Sun : Essentialism is the idea that you can take any phenomenon that is complex and distill it down to a particular set of traits. In the case of sex essentialism, the idea is that you can sufficiently describe sex by a few particular characteristics. In this debate, it used to be chromosomes, now it’s gametes (egg and sperm cells). The target is always moving, because if you want to make something binary, then you need to find the most binary characteristic. Today, sex essentialism boils all of sex down to the gametes that a person produces. Then you draw a line from gametes to all of these other characteristics—to sex roles, even to the personality of an entire individual. But biology is just not that simple. The sex essentialist perspective is completely wrong about the biology of how sex characteristics arise.
What is the error at the center of sex essentialism and this attempt at a simple, binary definition of sex?
Simón(e) Sun : The error is simply that the gametes are a determining factor of sex—that once you know what gametes a person produces, that’s their sex and nothing about it can change. But biology is a dynamic system where an organism starts in a particular state and grows through life and through development with multiple systems interacting. That is, more precisely, how sex works. Sex essentialism boils all that down to one, immutable characteristic to preclude transness as a biological phenomenon. If you start with a model of sex that is binary, you'll always produce a binary result. And if you insist that it is true, then it is the only answer that you get.
Florence Ashley : There's something to be said about the rhetorical tricks here. The people who use ideas about biological sex against trans people are first appealing to the idea of biology as a description of difference, but then they do a jump and use that conception of biology as a form of meaning. The thing is, we organize society around meaning, not difference. Biology at its core can't tell you what matters to human organizations. So there is a fallacy here of looking at the human difference at the biological level, oversimplifying it, and then saying, “That's what we should organize people around.” We should really be asking what we care about, and then look to see if biology has anything to say about it. If you go through that exercise, then you realize that biology really has very little, if not virtually nothing, to say about things like trans rights.
You use the term “epistemological violence” to describe how people can apply ostensibly neutral scientific ideas in harmful ways. Can you explain that concept
Florence Ashley : Epistemological violence occurs when a researcher or somebody else interprets empirical results in a way that devalues, pathologizes or harms a marginalized group, even though there are equally good or better explanations for the same data. Science is always “under-determined,” a technical term that basically means there are always multiple possible ways to interpret a set of data. That’s where a lot of misinformation and oversimplification comes from, in that gap that's left. The idea of epistemological violence is that it's wrong to interpret data in a way that punches down on marginalized people. We should try to interpret the data in a way that's compatible with their inclusion and well-being, if that's an equally good interpretation. We shouldn't be cherry-picking the data to support prejudice and biased points.
You have written about three broad misinformation techniques in the trans debates: oversimplifying scientific knowledge, fabricating and misinterpreting research and promoting false equivalences. Are these the same techniques that have been used in science-based arguments about race and other human traits?
Simón(e) Sun : Absolutely. Even in climate change. Perhaps the most salient example is race science. There’s an entire history of asking about the science of racial differences, and how can we describe them in a biological way. That kind of research has been used in the past, and still is to some extent today, to bolster racist arguments. It’s an oversimplification to say that one population exhibits a lower average IQ than another population. That’s just biology, but there’s also social environment, socioeconomic status and other factors that come into play.
Here's a huge question: How do you help the general public recognize legitimate information from BS?
Florence Ashley : We need to get out of the idea that correcting misinformation by itself will convince people. But once you’ve appealed to people's emotions, once you've appealed to people's values and desire to be on your side, then correcting misinformation can make their commitment to equality sustainable. And there’s another gap, which is people who don't really have an opinion. If you already don't have an opinion on the topic, then being exposed to actual, scientifically grounded information can be very helpful. That's often what we see in courts, where even judges who were appointed by Donald Trump will sometimes rule in favor of trans rights when they're presented with information and they don’t have much preconceptions. They realize, oh, there’s so much evidence in favor of trans rights, we’ve got to do something about that. That's possible because we are talking about people who didn't have strong political attachments yet.
OK, so how can we help the general public identify the falsehoods?
Florence Ashley : There's no foolproof way. There is so much noise and misinformation that it's just hard to know even the most basic of facts. And because the problem of epistemological violence, it's not only difficult to find what the science says in terms of data, it’s difficult to interpret it on your own. We need journalists to do a better job and probe some of the basics of what people are saying. They’re legitimating a lot of anti-trans voice without really questioning the basis of their opinions, notably around claims that youth are being fast-tracked through medical transition. There's the other implied claim that if we take things slower, it's going to prevent potential regrets . We just published a review article in Psychology of Sexual Orientation and Gender Diversity where we find that there's no empirical or theoretical basis for that claim. The New York Times has been a particularly bad offender in that regard. For individuals, try to get information from a trans person who actually knows these issues.
What about ordinary people who want to help but don't know where to start—what can they do?
Florence Ashley : Shut down misinformation and hate when you see it crop up around you. Oftentimes we don't like confrontation, so we just let misinformation go. We need people to start speaking up whenever it comes up. And be loud. We’re in an ecosystem where the anti-trans voices are trying to portray themselves as speaking for a silent majority. We need people to be loud enough to counter any impression of a silent majority. You can also help trans people materially. Give them a job, help them get housing, help them pay for transition-related medical care. Share your power with trans people, giving them opportunities to write, opportunities to share with audiences and opportunities to have a say in policy-making. And share your skills.
This Q&A is part of a series of OpenMind essays, podcasts and videos supported by a generous grant from the Pulitzer Center 's Truth Decay initiative.
This story originally appeared on OpenMind , a digital magazine tackling science controversies and deceptions.
Argonne National Laboratory
Keane wins 2024 gopal k. shenoy excellence in beamline science award, award recognizes beamline scientists for significant contributions to research or instrumentation at the advanced photon source.

Physicist Denis T. Keane is the 2024 recipient of the Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award. He is a beamline scientist and director of the Dupont-Northwestern-Dow Collaborative Access Team ( DND-CAT ) at the U.S. Department of Energy’s ( DOE ) Advanced Photon Source ( APS ) at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory. He is also a research professor in the Materials Science and Engineering Department at Northwestern University.
The annual award recognizes active beamline scientists at the APS , a DOE Office of Science user facility, for significant contributions to research or instrumentation and support of the beamline user community. The APS Users Office, which grants the award, renamed it in 2017 in honor of the late Gopal K. Shenoy. Shenoy was an accomplished materials scientist closely involved in the inception of the APS as well as an enthusiastic supporter of scientists who conducted research there.
“ It is a special honor to receive the Gopal K. Shenoy award,” said Keane. “ Thirty years ago, Gopal welcomed us to the APS as we began building the DND beamlines, and his leadership was vital in enabling us and the APS to succeed. I am grateful to my scientific collaborators and the DND staff for our partnership, and to DuPont, Northwestern, Dow and the APS for their support.”
Keane has served as director of DND-CAT since 2005. Located in sector five of the APS , the state-of-the-art X-ray facility is unique in that it combines industrial scale testing and product development with academic vigor, meaning Keane has the challenging task of balancing the needs and expectations of both industry and academic partners. He is also taking on the job of upgrading the DND-CAT facility concurrently with the APS Upgrade.
“ It is a special honor to receive the Gopal K. Shenoy award. Thirty years ago, Gopal welcomed us to the APS as we began building the DND beamlines, and his leadership was vital in enabling us and the APS to succeed. I am grateful to my scientific collaborators and the DND staff for our partnership, and to DuPont, Northwestern, Dow and the APS for their support.” — Denis T. Keane, physicist and director of DND-CAT
During Keane’s time as director, DND-CAT has been an important contributor to the productivity of the APS , producing more than 1,200 papers. Nominators mentioned that only under truly extraordinary leadership can a beamline achieve, year after year, such a scientific impact.
Keane has also made significant direct contributions to science through his own research. He has been successful in developing and demonstrating new advanced synchrotron X-ray methods and has made an impact on the field of microtomography.
Those who nominated him commented on his patience, his problem solving ability and his dedication. They mentioned his commitment to teaching students and postdocs how to operate the beamline, and how to adapt their experiments to make the measurements possible.
Known for supporting the APS user community, Keane has served as a member of and was elected chair of the APS Partner User Council. He has also served as appointed chair of the Beamtime Allocation Committee, which is responsible for allocating general user beamtime.
Keane received his doctorate in physics from Princeton University and his undergraduate degree in physics from Harvard University.
About the Advanced Photon Source
The U. S. Department of Energy Office of Science’s Advanced Photon Source ( APS ) at Argonne National Laboratory is one of the world’s most productive X-ray light source facilities. The APS provides high-brightness X-ray beams to a diverse community of researchers in materials science, chemistry, condensed matter physics, the life and environmental sciences, and applied research. These X-rays are ideally suited for explorations of materials and biological structures; elemental distribution; chemical, magnetic, electronic states; and a wide range of technologically important engineering systems from batteries to fuel injector sprays, all of which are the foundations of our nation’s economic, technological, and physical well-being. Each year, more than 5,000 researchers use the APS to produce over 2,000 publications detailing impactful discoveries, and solve more vital biological protein structures than users of any other X-ray light source research facility. APS scientists and engineers innovate technology that is at the heart of advancing accelerator and light-source operations. This includes the insertion devices that produce extreme-brightness X-rays prized by researchers, lenses that focus the X-rays down to a few nanometers, instrumentation that maximizes the way the X-rays interact with samples being studied, and software that gathers and manages the massive quantity of data resulting from discovery research at the APS .
This research used resources of the Advanced Photon Source, a U.S. DOE Office of Science User Facility operated for the DOE Office of Science by Argonne National Laboratory under Contract No. DE-AC02-06CH11357 .
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology. The nation’s first national laboratory, Argonne conducts leading-edge basic and applied scientific research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne researchers work closely with researchers from hundreds of companies, universities, and federal, state and municipal agencies to help them solve their specific problems, advance America’s scientific leadership and prepare the nation for a better future. With employees from more than 60 nations, Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science .
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science .
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Social justice
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
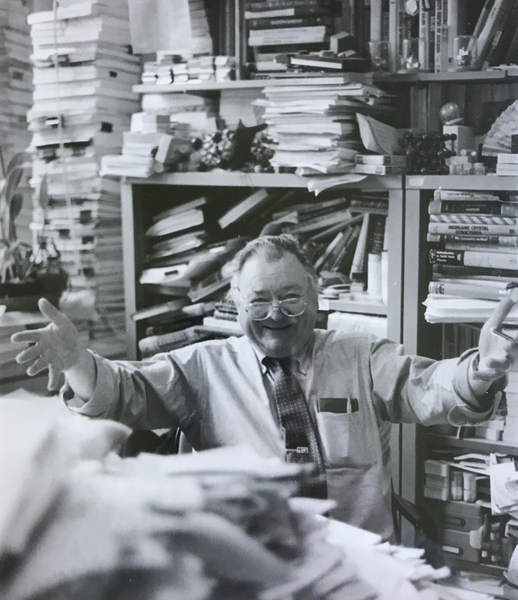
Professor Emeritus Bernhardt Wuensch, crystallographer and esteemed educator, dies at 90
Press contact :.

Previous image Next image
MIT Professor Emeritus Bernhardt Wuensch ’55, SM ’57, PhD ’63, a crystallographer and beloved teacher whose warmth and dedication to ensuring his students mastered the complexities of a precise science matched the analytical rigor he applied to the study of crystals, died this month in Concord, Massachusetts. He was 90.
Remembered fondly for his fastidious attention to detail and his office stuffed with potted orchids and towers of papers, Wuensch was an expert in X-ray crystallography, which involves shooting X-ray beams at crystalline materials to determine their underlying structure. He did pioneering work in solid-state ionics, investigating the movement of charged particles in solids that underpins technologies critical for batteries, fuel cells, and sensors. In education, he carried out a major overhaul of the curriculum in what is today MIT’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE).
Despite his wide-ranging research and teaching interests, colleagues and students said, he was a perfectionist who favored quality over quantity.
“All the work he did, he wasn’t in a hurry to get a lot of stuff done,” says DMSE’s Professor Harry Tuller. “But what he did, he wanted to ensure was correct and proper, and that was characteristic of his research.”
Born in Paterson, New Jersey, in 1933, Wuensch first arrived at MIT as a first-year undergraduate in the 1950s. He earned bachelor’s and master’s degrees in physics before switching to crystallography and earning a PhD from what was then the Department of Geology (now Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences). He joined the faculty of the Department of Metallurgy in 1964 and saw its name change twice over his 46 years, retiring from DMSE in 2011.
As a professor of ceramics, Wuensch was a part of the 20th-century shift from a traditional focus on metals and mining to a broader class of materials that included polymers, ceramics, semiconductors, and biomaterials. In a 1973 letter supporting his promotion to full professor, then-department head Walter Owen credits Wuensch for contributing to “a completely new approach to the teaching of the structure of materials.”
His research led to major advancements in understanding how atomic-level structures affect magnetic and electrical properties of materials. For example, Tuller says, he was one of the first to detail how the arrangement of atoms in fast-ion conductors — materials used in batteries, fuel cells, and other devices — influences their ability to swiftly conduct ions.
Wuensch was a leading light in other areas, including diffusion, the movement of ions in materials such as liquids or gases, and neutron diffraction, aiming neutrons at materials to collect information about their atomic and magnetic structure.
Tuller, a DMSE faculty member for 49 years, tapped Wuensch’s expertise to study zinc oxide, a material used to make varistors, semiconducting components that protect circuits from high-voltage surges of electricity. Together, Tuller and Wuensch found that in such materials ions move much more rapidly along the grain boundaries — the interfaces between the crystallites that make up these polycrystalline ceramic materials.
“It’s what happens at those grain boundaries that actually limits the power that would go through your computer during a voltage surge by instead short-circuiting the current through these devices,” Tuller says. He credited the partnership with Wuensch for the knowledge. “He was instrumental in helping us confirm that we could engineer those grain boundaries by taking advantage of the very rapid diffusivity of impurity elements along those boundaries.”
In recognition of his accomplishments, Wuensch was elected a fellow of the American Ceramics Society and the Mineralogical Society of America and belonged to other professional associations, including The Electrochemical Society and Materials Research Society. In 2003 he was awarded an honorary doctorate from South Korea’s Hanyang University for his work in crystallography and diffusion-related phenomena in ceramic materials.
“A great, great teacher”
Known as “Bernie” to friends and colleagues, Wuensch was equally at home in the laboratory and the classroom. “He instilled in several generations of young scientists this ability to think deeply, be very careful about their research, and be able to stand behind it,” Tuller says.
One of those scientists is Sossina Haile ’86, PhD ’92, the Walter P. Murphy Professor of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University, a researcher of solid-state ionic materials who develops new types of fuel cells, devices that convert fuel into electricity.
Her introduction to Wuensch, in the 1980s, was his class 3.13 (Symmetry Theory). Haile was at first puzzled by the subject, the study of the symmetrical properties of crystals and their effects on material properties. The arrangements of atoms and molecules in a material is crucial for predicting how materials behave in different situations — whether they will be strong enough for certain uses, for example, or can conduct electricity — but to an undergraduate it was “a little esoteric.”
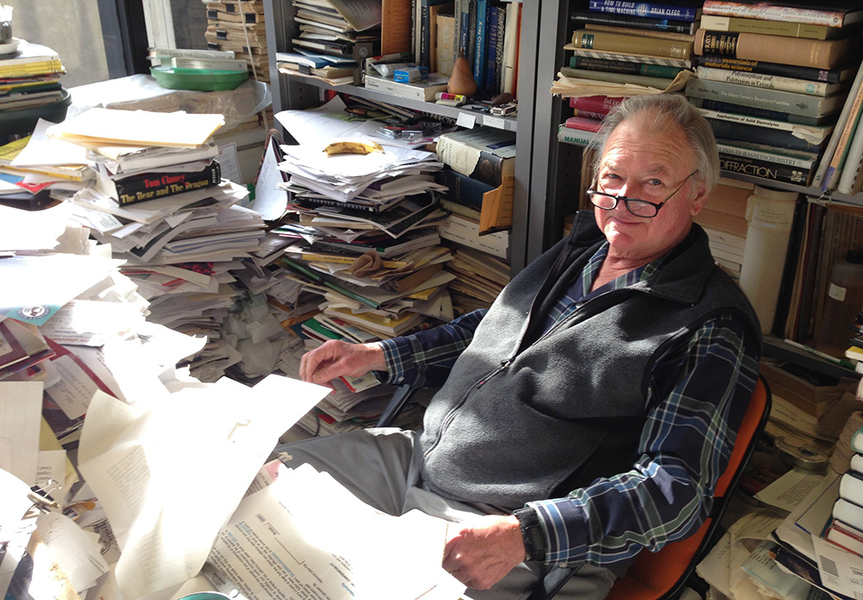
“I certainly remember thinking to myself, ‘What is this good for?’” Haile says with a laugh. She would later return to MIT as a PhD student working alongside Wuensch in his laboratory with a renewed perspective.

Previous item Next item
“He just made seemingly esoteric topics really interesting and was very astute in knowing whether or not a student understood.” Haile describes Wuensch’s articulate speech, “immaculate” handwriting, and detailed drawings of three-dimensional objects on the chalkboard. Haile notes that his sketches were so skillful that students felt disappointed when they looked at a figure they tried to copy in their notebooks.
“They couldn’t tell what it was,” Haile says. “It felt really clear during lecture, and it wasn’t clear afterwards because no one had a drawing as good as his.”
Carl Thompson, the Stavros V. Salapatas Professor in Materials Science and Engineering at DMSE, was another student of Wuensch’s who came away with a broadened outlook. In 3.13, Thompson recalls Wuensch asking students to look for symmetry outside of class, patterns in a brick wall or in subway station tiles. “He said, ‘This course will change the way you see the world,’ and it did. He was a great, great teacher.”
In a 2005 videorecorded session of 3.60 (Symmetry, Structure, and Tensor Properties of Materials), a graduate class that he taught for three decades, Wuensch writes his name on the board along with his telephone extension number, 6889, pointing out its rotational symmetry.
“You can pick it up, turn it head-over-heels by 180 degrees, and it’s mapped into coincidence with itself,” Wuensch said. “You might think I would have had to have fought for years to get it, an extension number like that, but no. It just happened to come my way.”
(The class can be watched in its entirety on MIT OpenCourseWare .)
Wuensch also had a whimsical sense of humor, which he often exercised in the margins of his students’ papers, Haile says. In a LinkedIn tribute to him, she recalled a time she sent him a research manuscript with figures that was missing Figure 5 but referred to it in the text, writing that it plotted conductivity versus temperature.
“Bernie noted that figures don’t plot; people do, and evidently Figure 5 was missing because ‘it was off plotting somewhere,’” Haile wrote.
Reflecting on Wuensch’s legacy in materials science and engineering, Haile says his knowledge of crystallography and the manual analysis and interpretation he did in his time was critical. Today, materials science students use crystallographic software that automates the algorithms and calculations.
“The current students don’t know that analysis but benefit from it because people like Bernie made sure it got into the common vernacular at the time when code was being put together,” Haile said.
A multifaceted tenure
Wuensch served DMSE and MIT in innumerable other ways, serving on departmental committees on curriculum development, graduate students, and policy, and on School of Engineering and Institute-level committees on education and foreign scholarships, among others. “He was always involved in any committee work he was asked to do,” Thompson says.
He was acting department head for six months starting in 1980, and in 1988-93 he was the director of the Center for Materials Science and Engineering, an earlier iteration of today’s Materials Research Center.
For all his contributions, there are few things Wuensch was better known for at MIT than his office in Building 13, which had shelves lined with multicolored crystal lattice models, representing the arrangements of atoms in materials, and orchids he took meticulous care of. And then there was the cityscape of papers, piled in heaps on the floor, on his desk, on pullout extensions. Thompson says walking into his office was like navigating a canyon.
“He had so many stacks of paper that he had no place to actually work at his desk, so he would put things on his lap — he would start writing on his lap,” Haile says. “I remember calling him at one point in time and talking to him, and I said, ‘Bernie, you’re writing this down on your lap, aren’t you?’ And he said, ‘In fact, yes, I am.’”
Wuensch was also known for his kindness and decency. Angelita Mireles, graduate academic administrator at DMSE, says he was a popular pick for graduate students assembling committees for their thesis area examinations, which test how prepared students are to conduct doctoral research, “because he was so nice.”
That said, he had exacting standards. “He expected near perfection from his students, and that made them a lot deeper,” Tuller says.

Outside of MIT, Wuensch enjoyed tending his garden; collecting minerals, gemstones, and rare coins; and reading spy novels. Other pastimes included fishing and clamming in Maine, splitting his own firewood, and traveling with his wife, Mary Jane.
Wuensch is survived by his wife; son Stefan Wuensch and wife Wendy Joseph; daughter Katrina Wuensch and partner Jason Staly; and grandchildren Noemi and Jack.
Friends and family are invited to a memorial service Sunday, April 28, at 1:30 p.m. at Duvall Chapel at 80 Deaconess Road in Concord, Massachusetts. Memories or condolences can be posted at obits.concordfuneral.com/bernhardt-wuensch .
Share this news article on:
Related links.
- Materials Research Laboratory
- Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Related Topics
- Education, teaching, academics
- Energy storage
- Materials science and engineering
Related Articles
A green hydrogen innovation for clean energy

Harry Tuller honored for career advancing solid-state chemistry and electrochemistry

Harry Tuller wins Egleston Medal for his electroceramics work
More mit news.

Study demonstrates efficacy of MIT-led Brave Behind Bars program
Read full story →

Bringing an investigator’s eye to complex social challenges

MIT announces 2024 Bose Grants

Circadian rhythms can influence drugs’ effectiveness

Ian Waitz named vice president for research
A closed-loop drug-delivery system could improve chemotherapy
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Research articles
Structures of human γδ t cell receptor–cd3 complex.
- Bangdong Huang
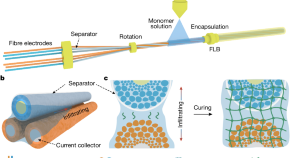
High-performance fibre battery with polymer gel electrolyte
A fibre lithium-ion battery that can potentially be woven into textiles shows enhanced battery performance and safety compared with liquid electrolytes.
- Haibo Jiang
- Huisheng Peng
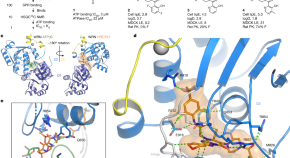
Discovery of WRN inhibitor HRO761 with synthetic lethality in MSI cancers
HRO761 is a potent, selective, allosteric WRN inhibitor that binds at the interface of the D1 and D2 helicase domains, locking WRN in an inactive conformation.
- Stephane Ferretti
- Jacques Hamon
- Marta Cortés-Cros
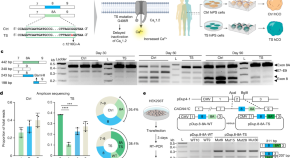
Antisense oligonucleotide therapeutic approach for Timothy syndrome
Antisense oligonucleotides effectively decrease the inclusion of exon 8A of CACNA1C in human cells both in vitro and in rodents transplanted with human brain organoids, and a single intrathecal administration rescued both calcium changes and in vivo dendrite morphology of patient neurons.
- Xiaoyu Chen
- Fikri Birey
- Sergiu P. Pașca
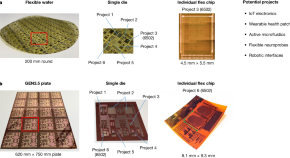
Multi-project wafers for flexible thin-film electronics by independent foundries
The iconic 6502 microprocessor designed in two key thin-film transistor technologies by independent foundries is used to demonstrate and expand the multi-project wafer approach for flexible electronics.
- Hikmet Çeliker
- Wim Dehaene
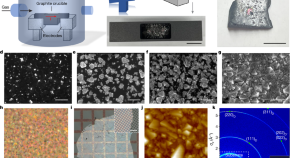
Growth of diamond in liquid metal at 1 atm pressure
Diamond crystals and polycrystalline diamond films can be grown using liquid metal at standard pressure and high temperature instead of conventional high pressure and high temperature.
- Rodney S. Ruoff
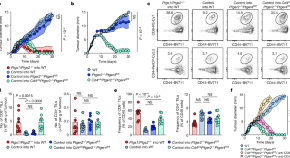
PGE 2 limits effector expansion of tumour-infiltrating stem-like CD8 + T cells
Tumour-derived prostaglandin E 2 , signaling through its receptors EP 2 and EP 4 , is shown to restrain the responses of tumour-infiltrating stem-like TCF1 + CD8 + T lymphocytes, and modulation of T cell EP 2 and EP 4 can restore anticancer immunity.
- Sebastian B. Lacher
- Janina Dörr
- Jan P. Böttcher
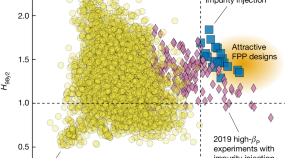
A high-density and high-confinement tokamak plasma regime for fusion energy
A stable tokamak plasma has been demonstrated with a high plasma density and a high energy confinement quality, both of which are simultaneously important for fusion reactors.
- A. M. Garofalo
- J. M. Hanson
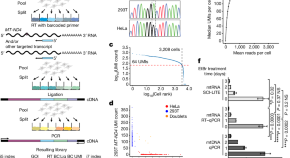
Single-cell analysis reveals context-dependent, cell-level selection of mtDNA
A new method for tracking single-cell heteroplasmy, called SCI-LITE, is combined with mitochondrial DNA base editing to reveal principles of heteroplasmy dynamics in dividing cells.
- Anna V. Kotrys
- Timothy J. Durham
- Vamsi K. Mootha
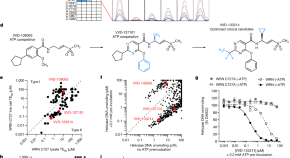
Chemoproteomic discovery of a covalent allosteric inhibitor of WRN helicase
VVD-133214, a clinical-stage, covalent allosteric inhibitor of the helicase WRN, was well tolerated in mice and led to robust tumour regression in multiple microsatellite-instability-high colorectal cancer cell lines and patient-derived xenograft models.
- Kristen A. Baltgalvis
- Kelsey N. Lamb
- Todd M. Kinsella

A magnetar giant flare in the nearby starburst galaxy M82
We report observations of GRB 231115A, positionally coincident with the starburst galaxy M82, that unambiguously qualify this burst as a giant flare from a magnetar, which is a rare explosive event releasing gamma rays.
- Sandro Mereghetti
- Michela Rigoselli
- Pietro Ubertini
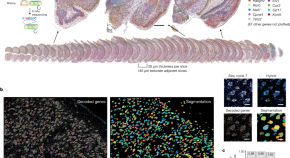
Whole-cortex in situ sequencing reveals input-dependent area identity
BARseq interrogates the expression of 104 cell-type marker genes in 10.3 million cells over nine mouse forebrain hemispheres to reveal the role of peripheral inputs on cortical area development.
- Xiaoyin Chen
- Stephan Fischer
- Anthony M. Zador
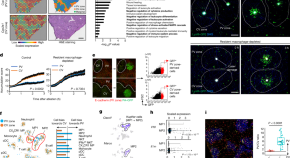
Periportal macrophages protect against commensal-driven liver inflammation
A subset of Macro-positive macrophages is identified to have immunosuppressive functions in the periportal vein zones of the liver to mediate excessive inflammation, and their effects depend on commensal gut bacteria.
- Yu Miyamoto
- Junichi Kikuta
- Masaru Ishii
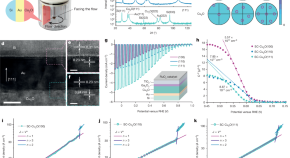
High carrier mobility along the [111] orientation in Cu 2 O photoelectrodes
A study introduces a novel method to grow single-crystal Cu 2 O thin films with selected crystal orientations, highlighting enhanced bulk carrier mobility and carrier diffusion length along the [111] direction that yields Cu 2 O photocathodes with improved performance.
- Linfeng Pan
- Samuel D. Stranks
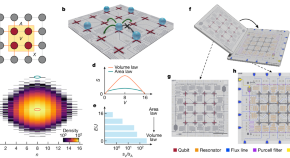
Probing entanglement in a 2D hard-core Bose–Hubbard lattice
By emulating a 2D hard-core Bose–Hubbard lattice using a controllable 4 × 4 array of superconducting qubits, volume-law entanglement scaling as well as area-law scaling at different locations in the energy spectrum are observed.
- Amir H. Karamlou
- Ilan T. Rosen
- William D. Oliver
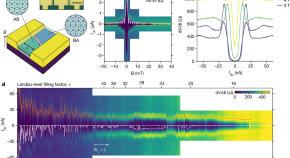
One-dimensional proximity superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime
We show that domain walls in minimally twisted bilayer graphene support exceptionally robust proximity superconductivity in the quantum Hall regime.
- Julien Barrier
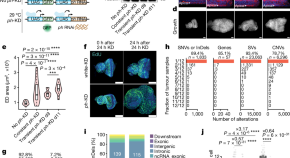
Transient loss of Polycomb components induces an epigenetic cancer fate
A transient perturbation of transcriptional silencing mediated by Polycomb proteins is sufficient to induce an epigenetic cancer cell fate in Drosophila in the absence of driver mutations.
- V. Loubiere
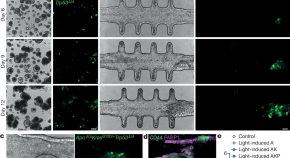
Spatiotemporally resolved colorectal oncogenesis in mini-colons ex vivo
Topobiologically complex mini-colons—which enable the faithful in vitro recapitulation of colorectal cancer tumorigenesis and its environmental determinants—offer the possibility to reduce animal use in a wide range of experimental applications.
- L. Francisco Lorenzo-Martín
- Tania Hübscher
- Matthias P. Lutolf
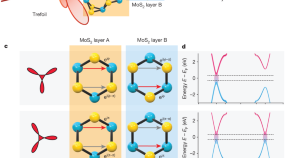
Valleytronics in bulk MoS 2 with a topologic optical field
We develop an optical method that can set and read the state of electrons in the valley polarization of bulk transition metal dichalcogenide semiconductors, with potential utility as digital storage at quantum coherent timescales and application in quantum computing.
- Igor Tyulnev
- Álvaro Jiménez-Galán
- Jens Biegert
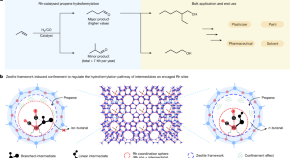
Regioselective hydroformylation of propene catalysed by rhodium-zeolite
Rhodium catalysts confined in zeolite pores exhibit high regioselectivity in the hydroformylation process of propene to high-value n -butanal, surpassing the performance of all heterogeneous and most homogeneous catalysts developed so far.
- Xiangjie Zhang
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
About ScholarSearch help. Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions.
Read the latest Research articles from Scientific Reports. ... Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Article (197836) Conference Proceeding (56) Matters Arising (48)
Browse the archive of articles on Nature. Skip to main content. ... Research Highlights (4493) Scientific Correspondence (4028) Supplement to Nature (1556) Year. All. All; 2024 (1320) 2023 (4320)
3.3 million articles on ScienceDirect are open access. Articles published open access are peer-reviewed and made freely available for everyone to read, download and reuse in line with the user license displayed on the article. ScienceDirect is the world's leading source for scientific, technical, and medical research.
Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Appointments Vacant (974) ... Research Article (564) Science in Europe (54) Scientific Correspondence (4028) Supplement to Nature (1556)
ScienceDaily features breaking news about the latest discoveries in science, health, the environment, technology, and more -- from leading universities, scientific journals, and research ...
Read the latest Research articles from Scientific Reports. Skip to main content. ... research articles. Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Article (197721) Conference Proceeding (56) Matters Arising (48) Registered Report (18) Year. All. All; 2024 (8767) 2023 (22198) 2022 (21835)
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
Science News features news articles, videos and more about the latest scientific advances. ... membership organization dedicated to public engagement in scientific research and education (EIN 53 ...
Discover a digital archive of scholarly articles, spanning centuries of scientific research. ... Journals deposit all NIH-funded articles as defined by the NIH Public Access Policy. 44 Selective Deposit Programs. Publisher deposits a subset of articles from a collection of journals.
Science is a leading outlet for scientific news, commentary, and cutting-edge research. Through its print and online incarnations, Science reaches an estimated worldwide readership of more than one million. Science 's authorship is global too, and its articles consistently rank among the world's most cited research. mission & scope.
It is published by the Society for Science, a nonprofit 501(c)(3) membership organization dedicated to public engagement in scientific research and education (EIN 53-0196483). Science News ...
Science; Research Article or Resource; clear all. Article Type. Research And Reviews 3585; Peer Reviewed. Yes 3585; Publication Date. 1986. 2024. Apply. Last Year 648; Last 6 Months 347; ... Research Article. Two inhibitory neuronal classes govern acquisition and recall of spinal sensorimotor adaptation. Add to reading list. by. Simon Lavaud ...
Harness the power of visual materials—explore more than 3 million images now on JSTOR. Enhance your scholarly research with underground newspapers, magazines, and journals. Explore collections in the arts, sciences, and literature from the world's leading museums, archives, and scholars. JSTOR is a digital library of academic journals ...
One of the largest and most authoritative collections of online journals, books, and research resources, covering life, health, social, and physical sciences. Wiley Online Library | Scientific research articles, journals, books, and reference works
Find breaking science news and analysis from the world's leading research journal.
Support Science Journalism. Discover world-changing science. Explore our digital archive back to 1845, including articles by more than 150 Nobel Prize winners. Subscribe Now!
Find the research you need | With 160+ million publications, 1+ million questions, and 25+ million researchers, this is where everyone can access science. Discover the world's scientific knowledge
New advances in science, medicine, health, and technology.Stem cell research, drug research, and new treatments for disease.
Moved Permanently. The document has moved here.
Far more animals than previously thought likely have consciousness, top scientists say in a new declaration — including fish, lobsters and octopus. Recent research backs them up.
Students Will Perform Research at National Laboratories. WASHINGTON, D.C.. - The Department of Energy's (DOE's) Office of Science has selected 86 graduate students representing 31 states and Puerto Rico for the Office of Science Graduate Student Research (SCGSR) program's 2023 Solicitation 2 cycle. Through world-class training and access to state-of-the-art facilities and resources at ...
Setting the stage for a new era of immersive displays, researchers are one step closer to mixing the real and virtual worlds in an ordinary pair of eyeglasses using high-definition 3D holographic images, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers. Holographic images have real depth because they are three dimensional, whereas ...
Three types of misinformation are being used against transgender people: oversimplifying scientific knowledge, fabricating and misinterpreting research and promoting false equivalences
Physicist Denis T. Keane is the 2024 recipient of the Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award. He is a beamline scientist and director of the Dupont-Northwestern-Dow Collaborative Access Team (DND-CAT) at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Advanced Photon Source (APS) at DOE's Argonne National Laboratory.He is also a research professor in the Materials Science and ...
Top articles. Explore the most downloaded* papers from Scientific Reports in 2023. Featuring authors from around the world, these collections highlight valuable research from an international ...
MIT Professor Emeritus Bernhardt Wuensch '55, SM '57, PhD '63, a crystallographer and beloved teacher whose warmth and dedication to ensuring his students mastered the complexities of a precise science matched the analytical rigor he applied to the study of crystals, died this month in Concord, Massachusetts.
Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community. Browse all Top 50 subject area collections here .
University of Maryland Department of Computer Science Professor Hal Daumé III was honored for his leadership in artificial intelligence at the 2024 Maryland Research Excellence Celebration on April 16 at The Hotel. UMD recognized the achievements of more than 200 faculty members and researchers at the event. The event honored the distinct and notable accomplishments of UMD researchers and ...
Research articles. Filter By: Article Type. All. All; Appointments Vacant (974) ... Research Article (564) Science in Europe (54) Scientific Correspondence (4028) Supplement to Nature (1556)