

Essay on Inflation in Pakistan for Students
by Pakiology | May 21, 2024 | Essay | 0 comments
In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, we will look at the causes, effects, and solutions to this issue that has been affecting the country for decades. The term ‘inflation’ refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching a peak in 2023. We will explore the various factors that have contributed to inflation in Pakistan, its economic effects, and what can be done to address the issue.
Page Contents
Essay on Inflation Outlines
Causes of inflation in pakistan, effects of inflation, solution to control inflation.
- Introduction
Inflation in Pakistan is caused by several factors, which can be divided into two main categories: domestic and external. The main domestic causes of inflation are an increase in money supply, an increase in government spending, an increase in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The most significant contributor to inflation in Pakistan is an increase in the money supply. When there is too much money chasing after too few goods, prices rise, creating a situation known as demand-pull inflation. An increase in the money supply can be caused by the central bank printing more money or by the government borrowing more money from the public.
In addition, higher government spending can lead to inflation. This occurs when the government prints more money to finance its expenditure or borrows from the public and transfers the cost of this additional spending to businesses and consumers. This leads to higher prices for goods and services. Indirect taxes are another major factor that contributes to inflation in Pakistan. When indirect taxes are increased, prices of goods and services also increase, leading to an overall rise in prices.
Finally, low economic growth can also cause inflation in Pakistan. A weak economy reduces people’s purchasing power, forcing them to buy less, which reduces demand and leads to lower prices. However, when economic growth stalls, businesses are unable to sell their products at the same price as before, leading to a rise in prices.
Overall, inflation in Pakistan is caused by a combination of domestic and external factors. These include an increase in money supply, higher government spending, increases in indirect taxes, and a decrease in economic growth.
The effects of inflation on the economy can be both positive and negative. Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, meaning that each unit of currency is worth less than it was before. This means that, as the cost of living increases, people can purchase fewer goods and services for the same amount of money. As a result, their standard of living decreases.
Inflation also reduces the real return on investments and savings, which can have a detrimental effect on economic growth. When inflation is high, people prefer to save their money rather than invest in a business or other activities. This reduces the availability of capital and results in slower economic growth.
In addition to decreasing standards of living, inflation can lead to unemployment if companies are not able to increase wages at the same rate as prices rise. This can lead to an increase in poverty, as people struggle to afford necessities. Furthermore, when prices rise faster than wages, it puts pressure on government budgets and can increase public debt.
Inflation can also cause the value of the local currency to depreciate against foreign currencies. This has a direct impact on the cost of imports and makes domestic goods less competitive in international markets. It can also have an indirect impact on exports, as it reduces the competitiveness of local producers in foreign markets.
Inflation is a serious issue in Pakistan, and it needs to be addressed to improve the country’s economic conditions. The following are some of the measures that can be taken to control inflation in Pakistan:
1. Fiscal policy: A strong fiscal policy is necessary for controlling inflation. The government should increase its revenue by implementing taxes on the wealthy and reducing public spending. This will help reduce budget deficits, which will result in lower inflation.
2. Monetary policy: The State Bank of Pakistan should adopt a tighter monetary policy to control inflation. It should raise interest rates so that investors have an incentive to save rather than spend, thus curbing demand-pull inflation.
3. Supply-side measures: There should be an increase in the production of essential commodities and products to meet the demand of consumers. This will help reduce prices and inflation in the long run.
4. Subsidies: The government should provide subsidies to those who are suffering due to the high prices of essential items. This will help them cope with the rising cost of living and ensure that they have access to essential goods and services.
5. Stabilizing exchange rate: A stable exchange rate between foreign currencies and the rupee is necessary for controlling inflation. The State Bank of Pakistan should strive to keep the rupee’s value stable by using currency swaps and other methods.
These measures can go a long way in controlling inflation in Pakistan. By taking these measures, the government can help improve the country’s economic condition and create an environment conducive to investment and growth.
What is inflation in simple words?
Inflation is a sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
What are the 4 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: Demand-pull inflation: when there is an increase in demand for goods and services that outstrip the economy’s ability to produce them. Cost-push inflation: when the cost of production increases, causing companies to raise prices to maintain their profit margins. Built-in inflation: when businesses expect prices to rise and build that expectation into their prices, causing a self-fulfilling cycle of inflation. Imported inflation: when the cost of imported goods increases, leading to higher prices for consumers.
What are the 5 main causes of inflation?
The 4 main causes of inflation are: 1. Demand-pull inflation 2. Cost-push inflation 3. Built-in inflation 4. Imported inflation 5. Monetary inflation
What is inflation introduction?
Inflation is a phenomenon that has been observed throughout history. It refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time.
Find more Essays on the following Topics
Ask Your Questions
You might like, health is wealth essay for students.
In this essay, we explore why health is wealth and why it is crucial to prioritize our physical and mental well-being...
An Essay on My Mother: A Tribute to Mothers
Mothers are the backbone of a family and a crucial influence in the lives of their children. From an early age,...
Women Empowerment Essay For Students
This women empowerment essay highlights the importance of empowering women for the growth and development of society....
Essay On How to Control Inflation in Pakistan
Inflation is a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services in an economy over a period of time....
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- class-9-notes
- Friendship quotes
- Scholarships
- Science News
- Study Abroad
- Study in Australia
- SZABMU MDCAT
- UHS Past MCQs
- Universities
- Privacy Policy

Essay on inflation/Rising prices in Pakistan with quotations
Rising prices / inflation essay 300 - 400 words.

Inflation essay for 2nd year, class 12 PDF download
Inflation is taxation without legislation - Milton Friedman
Inflation is the crabgrass in your savings - Robert Orben
Inflation is the parent of unemployment and the unseen robber of those who have saved - Margret Thatcher
Production is the only answer to inflation - Anonymous
8 comments:
Just better butnit good
Nice Good effort
It's short a little bit but the content is good
Post a Comment
Trending Topics
Latest posts.
- 1st year Tarjuma tul Quran book pdf download
- 1st year Islamiat Elective notes pdf download
- 1st year biology guess 2024 pdf download
- 1st year math chapterwise mcqs with answers pdf download
- 1st year Past papers solved and unsolved all Punjab Boards
- 1st year guess paper 2024 Punjab Board pdf
- 1st Year Computer Science Guess paper 2024
- 1st year Islamiat Elective Guess paper 2024 pdf download
- 1st year Math guess paper 2024 Punjab boards
- 1st year all subjects notes for FBISE and Punjab Boards pdf
- 1st year English guess paper 2024 Punjab board
- 1st year English MCQs Objective Solved Notes
- 1st year English complete notes pdf download
- 2nd year guess paper 2024 Punjab board
- 2nd year tarjuma tul Quran book pdf download
- 2nd year pak study short questions notes pdf download
- BISE Hyderabad
- BISE Lahore
- bise rawalpindi
- BISE Sargodha
- career-counseling
- how to pass
- Punjab Board
- Sindh-Board
- Solved mcqs
- Student-Guide
Famous Personalities
- Economic Challenges
- Environmental Issues
- Educational System and Corruption
- Founding Fathers
- Historical Figures
- Corruption and Greed
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
Select Page
- Essay on Inflation in Pakistan: Revealing Causes and Consequences
Posted by wisemindsphere.com | Aug 15, 2023 | Economic Challenges | 0 |

Inflation , a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, is a pressing economic concern that has cast its shadow over Pakistan’s economy for years. In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, exploring the root causes and the far-reaching impact of inflation on the nation’s economy and its people will be explored.
Reasons behind Inflation in Pakistan
The reasons behind inflation in Pakistan are as diverse as they are complex. One of the primary drivers is the demand-pull inflation, where excessive demand for goods and services outpaces supply. Government spending, often financed through borrowing from the central bank, adds fuel to this fire. Moreover, supply-side factors, such as energy shortages, agricultural production constraints, and inefficiencies in distribution networks, contribute to price hikes. External factors, like global oil price fluctuations, can also send ripples through the economy, impacting inflation rates.
Monetary Policy and Inflation
The role of monetary policy in exacerbating or mitigating inflation cannot be understated. Pakistan’s central bank, the State Bank of Pakistan, plays a pivotal role in managing the money supply and interest rates. If monetary policy is loose – characterized by excessive money supply and low interest rates – it can spur demand but also contribute to inflationary pressures. Conversely, a tight monetary policy can help curb inflation but may also slow down economic growth.
Impact of Inflation in Pakistan
The impact of inflation in Pakistan is felt on various fronts, affecting both individuals and the broader economy. On a personal level, rising prices erode purchasing power, leading to reduced standards of living. The cost of essential goods like food and fuel takes a larger share of household budgets, leaving less room for discretionary spending. For the poorest segments of society, this can push them further into poverty.
Inflation’s Ripple Effect on the Economy
Inflation’s effects reverberate throughout the economy, impacting businesses and industries alike. Entrepreneurs face uncertainty in production costs, which can disrupt investment and expansion plans. Businesses may also struggle to afford higher wages for their employees, leading to labor disputes. Moreover, inflation distorts economic planning and decision-making, making long-term investments riskier due to unpredictable future costs.
Challenges to Fiscal Policy
Fiscal policy, which involves government spending and taxation, can either mitigate or exacerbate inflation. High levels of government borrowing to finance budget deficits can contribute to money supply growth, driving inflation upwards. Similarly, inefficient tax collection systems limit government revenue, forcing it to rely on borrowing. Achieving a balance between necessary public spending and responsible fiscal management is crucial to combating inflation.
Inflation’s Impact on Savings and Investment
Inflation’s corrosive impact extends to savings and investment. High inflation erodes the real value of savings, discouraging people from putting money aside for the future. This can have dire consequences for retirement planning and financial stability. Moreover, investment decisions become riskier in an inflationary environment, as the uncertainty about future returns complicates business strategies.
Tackling Inflation: The Way Forward
Addressing inflation in Pakistan requires a multi-pronged approach that involves coordination between various economic policy levers. Fiscal discipline is paramount, necessitating prudent management of government expenditure and revenue. Monetary policy should strike a delicate balance between stimulating economic growth and containing inflation. Structural reforms, such as improving energy production, enhancing agricultural productivity, and investing in infrastructure, can mitigate supply-side constraints that fuel inflation.
Inflation in Pakistan remains a formidable challenge that demands strategic and coordinated efforts. Understanding the reasons behind inflation, comprehending its impact on the economy and individuals, and implementing effective policies are crucial steps toward achieving price stability and fostering sustainable economic growth. As the nation strives to navigate these economic waters, the careful calibration of policies and the commitment to reform hold the promise of a more stable and prosperous future for Pakistan.
About The Author
wisemindsphere.com
Related posts.

Essay on Inflation Unveiled: Causes, Consequences, and Economic Realities
July 30, 2023
- Essay on Energy Crisis in Pakistan: Unraveling Causes and Charting Solutions
August 15, 2023
Recent Posts
- Essay on Floods in Pakistan
- Essay on Education: Education’s Empowering Capacity for Transformation
- Essay on Allama Iqbal: The Awesome Poet of the East and Enlightened Visionary of Pakistan
Recent Comments
- August 2023
- [No need to type Codes] [360 Primogems] Version 3.9 Redemption Codes | Genshin Impact
- [No need to type Codes] 4 New Redemption Codes | 360 Primogems | Genshin Impact V. 3.8
- [FREE] Get 400 Steller Jades NOW | 4 New Redemption Codes | Star Rail 1.1
- [No need to type Codes] 4 New Redemption Codes | 360 Primogems | Genshin Impact V. 3.6
- [No need to type Codes] 4 New Redemption Codes | 360 Primogems | Genshin Impact V. 3.5

Let's Tech it!

Inflation in Pakistan – Its Effects & Drivers | Complete FREE Essay with Outline
Inflation is again high in Pakistan, having risen further to 8.2 per cent.
- What is Inflation?
- Moderate Inflation
- Erosion of Currency
- Moderate Inflation in Pakistan
- Poor Vs. Rich
- Inflation Discourages Investment
- Inflation Erodes Trust in National Currency
- Money Growth
- Global Oil Price Movements
- Domestic Supply Shocks
Inflation is a situation of a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy. In othe words, it means an increase in the cost of living as the price of goods and services rise. Importantly, inflation is a tax that erodes the purchasing power of the currency.
If all inflation is bad and whether it should be zero? The answer is no. Most economists today only consider inflation above high single digits to be bad.
Moderate inflation, in the 3pc to 6pc range is generally considered desirable, and inflation below 3pc can actually be risky. Why? Moderate inflation can serve as a useful signal of demand pressures in normal times, and also lends flexibility to an economy adjusting to adverse shocks: if inflation is near zero, disinflation must involve nominal wage cuts, which are politically difficult.
In Pakistan, this erosion of currency has been significant: by the mid-1970s, the Pakistani rupee had lost half of the purchasing power it had in 1956; and by the early 1990s, it had lost 90pc.

Large as it seems, it is a much less dramatic decline than witnessed by Turkey, Egypt and Morocco. And a comparison starting in 1980, and excluding rich countries, suggests Pakistan has done no worse than its South Asian neighbours.
For much of Pakistan’s history, inflation has been moderate, with two noticeable exceptions: 1972-76 and 2008-14, both of which coincided with record-high international oil prices; and followed/ accompanied public or private spending booms.
Although inflation has picked up in the past few months and is now in the upper single digits, its level is still low by recent historical standards.
Inflation is again high in Pakistan, having risen further to 8.2 per cent in February 2019. Increase in Inflation rates comes with its own costs.
For the poor, a rise in the prices of essential items (if it exceeds income growth) can be a death knell, both literally (for subsistence households), and indirectly, due to the inability to afford needed medical and health spending. It can also force parents to choose between whether their child goes to school or works.
Thus, the poor, who hold much of their assets in cash, bear this tax disproportionately, while the rich can partly evade it by holding assets that are return-bearing (like bonds), increasing in value (like land), or in a stable foreign currency (like the dollar).
By raising uncertainty about the future, inflation discourages investment in projects that raise the economy’s productive capacity. Businesses start focusing on projects with short-term returns, or transactions in foreign currency.

Inflation erodes trust in the national currency as a store of value, it also erodes the associated national pride, and this is felt by all citizens.
Given this, the key policy issues for inflation management are: avoiding the big spikes (that take inflation above the desirable range), and ensuring that the poor are well protected against inflation. On the former, we note that there are several (not one) drivers of inflation:
The first is money growth. For a fixed supply of goods, more money in circulation means higher prices. Monetary loosening can happen due to structural factors like fiscal dominance, where the central bank is forced to print money to finance fiscal deficits; and/ or cyclical surges in capital inflows, and the accompanying credit/ real estate booms.
Fiscal dominance has been a perennial problem in Pakistan, as evinced by the strong co-movement of inflation and State Bank credit to the government over the past 15 years (only Egypt is worse in this regard).
Two things can help fix it: a rise in the tax-to-GDP ratio so that there is a buffer in public finances; and greater de jure and de facto independence for the State Bank (progression on this has been quite uneven).

Capital inflow booms have been rarer but equally impactful, eg the mid-2000s real estate boom financed by Gulf money, which ended badly for the economy. With the government trying to lure investments from China and the Gulf, care would have to be taken to ensure the resource inflow expands the productive capacity of the economy and does not just fuel prices.
The second is factors that affect import prices. As a heavily oil-reliant importer, and with no real foreign exchange or fiscal buffers to limit pass-through to domestic prices, a part of Pakistani inflation is simply determined by global oil price movements.
At one level, a government neither deserves credit for lower inflation when oil prices fall (as they did from 2014-16) nor the blame for higher inflation when they rise (as they sporadically did in 2017-18). However, to be constantly at the mercy of a known exogenous quantity is not pardonable:
Pakistan must make a concerted effort to diversify its energy reliance away from oil and towards hydro, solar, nuclear, clean coal.

Currency depreciation affects inflation similarly, except that they raise the domestic price of all imported goods, not just oil.
Depreciations are needed to fix balance-of-payments problems which can arise due to unsustainable spending booms (as in the aftermath of the mid-2000s, as well as 2014-17); adverse terms of trade shocks (like oil price rises); or weakening global demand for Pakistani goods and services (as occurred during the 2008 global financial crisis).
Governments cannot do much to avoid depreciation when they are needed, but they can make them less dramatic by allowing a more flexible exchange rate regime.
The third is the domestic supply shocks. Floods, droughts, crop pests can all raise the price of domestic goods, and often goods that are essential to the poor. While governments cannot wish these shocks away, it can and must invest in resilience mechanisms, as these are likely to benefit the poor most.
In sum, inflation is a multi-source problem. It has been high, but manageable, in Pakistan. But because it affects the poor disproportionately, the government must continue to take structural measures to keep it low and to compensate the poor via lifeline tariffs and cash transfers for any temporary surges.
By Nadir Cheema
The writer teaches economics at SOAS University of London, and is a senior research fellow at Bloomsbury Pakistan.
@NadirCheema
The essays included here are from numerous sources or authors (sources mentioned in each essay). The most important question is ‘how to write an essay?’ The answer varies from person to person. Yet, the main purpose of Essaypspedia/Tech Urdu is to give you an idea of the essays. It is now up to you, being an aspirant of the competitive examinations, to edit/update/improve/add in it. You can also submit your essays at [email protected]
Top#10 Essays Worth Your Time
- Digital Revolution in Pakistan | Complete Essay with Outline
- The Crises of Urban Housing | Complete Essay with Outline
- Climate Change – A Ticking Bomb | Complete Essay with Outline
- Reading Culture | Complete Essay with Outline
- Population Peril | Complete Essay with Outline
- Regional Risks for Doing Business – The Case of Pakistan | Complete Essay with Outline
- Top#5 Essays on Social/Society Issues Related Matters
- Pollution – Impacts, Types, History and Control | Complete Essay with Outline
- Human Development – The Status of Pakistan | Complete Essay with Outline
- Top #5 Water Scarcity Issues in Pakistan Essays
Naeem Javid
Naeem Javid Muhammad Hassani is working as Deputy Conservator of Forests in Balochistan Forest & Wildlife Department (BFWD). He is the CEO of Tech Urdu (techurdu.net) Forestrypedia (forestrypedia.com), All Pak Notifications (allpaknotifications.com), Essayspedia, etc & their YouTube Channels). He is an Environmentalist, Blogger, YouTuber, Developer & Vlogger.
See author's posts
- White Holes Vs. Black Holes
- #8: Your Weekly Vocabulary List
You May Also Like

The Menace of Inflation | Complete Essay with Outline
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
More you share more you learn
Inflation English Essay with Quotations in Pakistan

Table of Contents
Inflation English Essay with Quotations pdf Download: The PDF version of the second-year English smart syllabus essays is now available for students to access. Those who are searching for individual essays on specific topics can refer to the list of essays designed for class 12. In particular, I have shared an exceptional essay on the issue of inflation or rising prices in Pakistan that you may find helpful.
Inflation English Essay Headings
I. introduction.
- Definition of inflation and its impact
- Overview of inflation in Pakistan
Inflation is a significant economic issue that affects individuals, businesses, and the country as a whole. Pakistan, like many developing countries, has struggled with inflation in recent years. In this essay, we will explore the causes and consequences of inflation in Pakistan, as well as some potential solutions to the problem.
II. Causes of Inflation in Pakistan
- Rising oil prices
- Government policies
- Currency devaluation
- Global economic factors
Firstly, the main causes of inflation in Pakistan are rising oil prices, government policies, currency devaluation, and global economic factors. Rising oil prices have a direct impact on the prices of goods and services, which leads to higher inflation rates. Government policies such as excessive money printing and high taxation can also lead to inflation, as they increase the cost of production and decrease the purchasing power of individuals. Currency devaluation can also cause inflation as it increases the cost of imported goods and services. Finally, global economic factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic have contributed to inflation in Pakistan due to supply chain disruptions and higher demand for certain goods and services.
III. Consequences of Inflation in Pakistan
- Decreased purchasing power
- Higher production costs
- Political instability
The consequences of inflation in Pakistan are severe and far-reaching. High inflation rates reduce the purchasing power of individuals, leading to a decrease in their standard of living. It also makes it more difficult for businesses to operate, as they have to contend with higher production costs. In addition, inflation can lead to political instability, as citizens become dissatisfied with the government’s inability to control prices.
IV. Solutions to Combat Inflation in Pakistan
- Increasing interest rates
- Reducing government spending
- Policies promoting economic growth
To combat inflation, the government can take various measures, including increasing interest rates, reducing government spending, and implementing policies that promote economic growth. As the famous economist John Maynard Keynes said, “Inflation is unjust, deflation is inexpedient. Of the two, deflation is worse.” This implies that it is better to tackle inflation through monetary and fiscal policy rather than deflation.
V. Quotations on Inflation in Pakistan
- “Inflation is taxation without legislation” – Milton Friedman
- “Inflation is the crabgrass in your savings” – Robert Orben
VI. Conclusion
- Summary of the main points
- Call to action to address inflation in Pakistan.
In conclusion, inflation is a significant issue in Pakistan that affects the country’s economic stability and citizens’ standard of living. The government must take steps to address inflation and implement policies that promote economic growth and stability. As the former Prime Minister of Pakistan, Shaukat Aziz, said, “Inflation is the enemy of progress and the friend of ignorance.” It is imperative that Pakistan takes this issue seriously and works to combat it.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Publish Your Blog
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
Inflation in Pakistan: unpacking the factors and finding fixes
The causes of inflation in pakistan are complex and multifaceted, but there are a number of potential solutions that could help to alleviate its adverse effects..
Inflation is an economic phenomenon that affects nations worldwide, and Pakistan is no exception. Over the past few years, the country has experienced high levels of inflation, burdening its citizens and impacting their purchasing power. In this blog, we delve into the primary factors behind Pakistan’s high inflation and explore potential solutions to alleviate its adverse effects.
The Causes of High Inflation in Pakistan
There are a number of factors that have contributed to high inflation in Pakistan. These include:
An energy crisis: Pakistan faces a persistent energy crisis, marked by frequent power outages and an over-reliance on imported energy. This energy deficit drives up production costs, leading to higher prices for essential goods and services.
Currency devaluation:
The depreciating value of the Pakistani rupee against major international currencies, such as the US dollar, contributes significantly to inflation. As the value of the rupee decreases, the cost of imported goods and raw materials rises, leading to higher prices for consumers across various sectors.
Fiscal mismanagement and excessive borrowing:
Pakistan’s fiscal mismanagement has played a crucial role in exacerbating inflationary pressures. The government’s reckless borrowing to finance budget deficits crowds out private sector investments, increases reliance on the central bank for funding, and elevates inflationary risks.
Supply and demand imbalances:
Supply-chain disruptions and distribution inefficiencies contribute to inflation by creating a mismatch between supply and demand. Factors such as poor infrastructure, inadequate storage facilities, and a lack of investment in agriculture lead to food shortages and price hikes. Similarly, the limited availability of affordable housing, coupled with increasing urbanization, contributes to rising property prices.
Uncontrolled money supply:
A rapid increase in the money supply without corresponding growth in the real economy fuels inflation. The excessive printing of money adds more currency into circulation, driving up aggregate demand without a commensurate increase in the supply of goods and services. Until measures are taken to curtail money supply growth and address structural issues within the economy, inflationary pressures are likely to persist.
Solutions to High Inflation in Pakistan
The high inflation in Pakistan is a multifaceted challenge requiring a comprehensive and coordinated approach to address its underlying causes. Some potential solutions include:
Implementing long-term energy solutions
One of the most important steps that Pakistan can take to address inflation is to implement long-term energy solutions. This would help reduce the country’s reliance on imported energy and stabilize energy prices.
There are a number of different energy solutions that Pakistan could pursue, such as developing renewable energy sources, improving energy efficiency, and promoting energy conservation. Each of these solutions has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best approach will depend on the specific circumstances of Pakistan.
Stabilizing the currency
Another important step that Pakistan can take to address inflation is to stabilize the currency. This would help reduce the cost of imported goods and raw materials, which would in turn help lower inflation.
The Pakistani rupee has been depreciating against major international currencies in recent years, which has contributed to inflation. There are a number of factors that have contributed to the depreciation of the rupee, such as the current account deficit, political instability, and uncertainty about the future of the economy.
The government of Pakistan has taken some steps to stabilize the currency, such as raising interest rates and imposing capital controls. However, these measures have had limited success so far.

Prioritizing fiscal discipline
The government of Pakistan also needs to prioritize fiscal discipline in order to address inflation. This means reducing the government’s budget deficits and reliance on debt financing.
The government’s budget deficits have been widening in recent years, which has put pressure on the currency and contributed to inflation. The government needs to take steps to reduce its spending and increase its revenue in order to balance the budget.
Improving agricultural practices
Pakistan is a major agricultural country, and the agricultural sector plays a vital role in the economy. However, the agricultural sector is also one of the most inefficient sectors in the economy.
The government of Pakistan needs to take steps to improve agricultural practices in order to increase the supply of food and reduce food prices. This could be done by providing farmers with access to better seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation systems.
Adopting prudent monetary policies
The central bank of Pakistan also needs to adopt prudent monetary policies in order to address inflation. This means controlling the growth of the money supply and preventing inflation from spiralling out of control.
The central bank has raised interest rates in recent months in an effort to control inflation. However, it is important to note that interest rate hikes can have a negative impact on economic growth.
The government and the central bank of Pakistan need to work together to address the underlying causes of inflation and implement solutions that will help alleviate its adverse effects.
High inflation in Pakistan is a serious problem that has a significant impact on the lives of ordinary citizens. The government and other stakeholders need to take urgent action to address the underlying causes of inflation and implement solutions that will help alleviate its adverse effects.
The views expressed in all articles and blogs are solely those of the authors and do not represent the official stance of Aware Pakistan or its editorial staff!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Essay on Inflation: Types, Causes and Effects
Essay on Inflation!
Essay on the Meaning of Inflation:
Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously.
Inflation is often defined in terms of its supposed causes. Inflation exists when money supply exceeds available goods and services. Or inflation is attributed to budget deficit financing. A deficit budget may be financed by additional money creation. But the situation of monetary expansion or budget deficit may not cause price level to rise. Hence the difficulty of defining ‘inflation’ .
Inflation may be defined as ‘a sustained upward trend in the general level of prices’ and not the price of only one or two goods. G. Ackley defined inflation as ‘a persistent and appreciable rise in the general level or average of prices’ . In other words, inflation is a state of rising price level, but not rise in the price level. It is not high prices but rising prices that constitute inflation.
ADVERTISEMENTS:
It is an increase in the overall price level. A small rise in prices or a sudden rise in prices is not inflation since these may reflect the short term workings of the market. It is to be pointed out here that inflation is a state of disequilibrium when there occurs a sustained rise in price level.
It is inflation if the prices of most goods go up. However, it is difficult to detect whether there is an upward trend in prices and whether this trend is sustained. That is why inflation is difficult to define in an unambiguous sense.
Let’s measure inflation rate. Suppose, in December 2007, the consumer price index was 193.6 and, in December 2008 it was 223.8. Thus the inflation rate during the last one year was 223.8 – 193.6/193.6 × 100 = 15.6%.
As inflation is a state of rising prices, deflation may be defined as a state of falling prices but not fall in prices. Deflation is, thus, the opposite of inflation, i.e., rise in the value or purchasing power of money. Disinflation is a slowing down of the rate of inflation.
Essay on the Types of Inflation :
As the nature of inflation is not uniform in an economy for all the time, it is wise to distinguish between different types of inflation. Such analysis is useful to study the distributional and other effects of inflation as well as to recommend anti-inflationary policies.
Inflation may be caused by a variety of factors. Its intensity or pace may be different at different times. It may also be classified in accordance with the reactions of the government toward inflation.
Thus, one may observe different types of inflation in the contemporary society:
(a) According to Causes:
i. Currency Inflation:
This type of inflation is caused by the printing of currency notes.
ii. Credit Inflation:
Being profit-making institutions, commercial banks sanction more loans and advances to the public than what the economy needs. Such credit expansion leads to a rise in price level.
iii. Deficit-Induced Inflation:
The budget of the government reflects a deficit when expenditure exceeds revenue. To meet this gap, the government may ask the central bank to print additional money. Since pumping of additional money is required to meet the budget deficit, any price rise may be called deficit-induced inflation.
iv. Demand-Pull Inflation:
An increase in aggregate demand over the available output leads to a rise in the price level. Such inflation is called demand-pull inflation (henceforth DPI). But why does aggregate demand rise? Classical economists attribute this rise in aggregate demand to money supply.
If the supply of money in an economy exceeds the available goods and services, DPI appears. It has been described by Coulborn as a situation of “too much money chasing too few goods” .
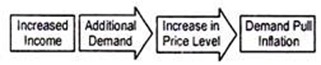
Note that, in this region, price level begins to rise. Ultimately, the economy reaches full employment situation, i.e., Range 3, where output does not rise but price level is pulled upward. This is demand-pull inflation. The essence of this type of inflation is “too much spending chasing too few goods.”
v. Cost-Push Inflation:
Inflation in an economy may arise from the overall increase in the cost of production. This type of inflation is known as cost-push inflation (henceforth CPI). Cost of production may rise due to increase in the price of raw materials, wages, etc. Often trade unions are blamed for wage rise since wage rate is not market-determined. Higher wage means higher cost of production.
Prices of commodities are thereby increased. A wage-price spiral comes into operation. But, at the same time, firms are to be blamed also for the price rise since they simply raise prices to expand their profit margins. Thus we have two important variants of CPI: wage-push inflation and profit-push inflation. Anyway, CPI stems from the leftward shift of the aggregate supply curve.

The price level thus determined is OP 1 . As aggregate demand curve shifts to AD 2 , price level rises to OP 2 . Thus, an increase in aggregate demand at the full employment stage leads to an increase in price level only, rather than the level of output. However, how much price level will rise following an increase in aggregate demand depends on the slope of the AS curve.
Causes of Demand-Pull Inflation :
DPI originates in the monetary sector. Monetarists’ argument that “only money matters” is based on the assumption that at or near full employment, excessive money supply will increase aggregate demand and will thus cause inflation.
An increase in nominal money supply shifts aggregate demand curve rightward. This enables people to hold excess cash balances. Spending of excess cash balances by them causes price level to rise. Price level will continue to rise until aggregate demand equals aggregate supply.
Keynesians argue that inflation originates in the non-monetary sector or the real sector. Aggregate demand may rise if there is an increase in consumption expenditure following a tax cut. There may be an autonomous increase in business investment or government expenditure. Governmental expenditure is inflationary if the needed money is procured by the government by printing additional money.
In brief, an increase in aggregate demand i.e., increase in (C + I + G + X – M) causes price level to rise. However, aggregate demand may rise following an increase in money supply generated by the printing of additional money (classical argument) which drives prices upward. Thus, money plays a vital role. That is why Milton Friedman believes that inflation is always and everywhere a monetary phenomenon.
There are other reasons that may push aggregate demand and, hence, price level upwards. For instance, growth of population stimulates aggregate demand. Higher export earnings increase the purchasing power of the exporting countries.
Additional purchasing power means additional aggregate demand. Purchasing power and, hence, aggregate demand, may also go up if government repays public debt. Again, there is a tendency on the part of the holders of black money to spend on conspicuous consumption goods. Such tendency fuels inflationary fire. Thus, DPI is caused by a variety of factors.
Cost-Push Inflation Theory :
In addition to aggregate demand, aggregate supply also generates inflationary process. As inflation is caused by a leftward shift of the aggregate supply, we call it CPI. CPI is usually associated with the non-monetary factors. CPI arises due to the increase in cost of production. Cost of production may rise due to a rise in the cost of raw materials or increase in wages.
Such increases in costs are passed on to consumers by firms by raising the prices of the products. Rising wages lead to rising costs. Rising costs lead to rising prices. And rising prices, again, prompt trade unions to demand higher wages. Thus, an inflationary wage-price spiral starts.
This causes aggregate supply curve to shift leftward. This can be demonstrated graphically (Fig. 11.4) where AS 1 is the initial aggregate supply curve. Below the full employment stage this AS curve is positive sloping and at full employment stage it becomes perfectly inelastic. Intersection point (E 1 ) of AD 1 and AS 1 curves determines the price level.
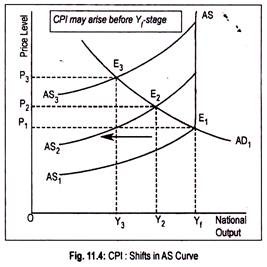
Now, there is a leftward shift of aggregate supply curve to AS 2 . With no change in aggregate demand, this causes price level to rise to OP 2 and output to fall to OY 2 .
With the reduction in output, employment in the economy declines or unemployment rises. Further shift in the AS curve to AS 2 results in higher price level (OP 3 ) and a lower volume of aggregate output (OY 3 ). Thus, CPI may arise even below the full employment (Y f ) stage.
Causes of CPI :
It is the cost factors that pull the prices upward. One of the important causes of price rise is the rise in price of raw materials. For instance, by an administrative order the government may hike the price of petrol or diesel or freight rate. Firms buy these inputs now at a higher price. This leads to an upward pressure on cost of production.
Not only this, CPI is often imported from outside the economy. Increase in the price of petrol by OPEC compels the government to increase the price of petrol and diesel. These two important raw materials are needed by every sector, especially the transport sector. As a result, transport costs go up resulting in higher general price level.
Again, CPI may be induced by wage-push inflation or profit-push inflation. Trade unions demand higher money wages as a compensation against inflationary price rise. If increase in money wages exceeds labour productivity, aggregate supply will shift upward and leftward. Firms often exercise power by pushing up prices independently of consumer demand to expand their profit margins.
Fiscal policy changes, such as an increase in tax rates leads to an upward pressure in cost of production. For instance, an overall increase in excise tax of mass consumption goods is definitely inflationary. That is why government is then accused of causing inflation.
Finally, production setbacks may result in decreases in output. Natural disaster, exhaustion of natural resources, work stoppages, electric power cuts, etc., may cause aggregate output to decline.
In the midst of this output reduction, artificial scarcity of any goods by traders and hoarders just simply ignite the situation.
Inefficiency, corruption, mismanagement of the economy may also be the other reasons. Thus, inflation is caused by the interplay of various factors. A particular factor cannot be held responsible for inflationary price rise.
Essay on the Effects of Inflation :
People’s desires are inconsistent. When they act as buyers they want prices of goods and services to remain stable but as sellers they expect the prices of goods and services should go up. Such a happy outcome may arise for some individuals; “but, when this happens, others will be getting the worst of both worlds.” Since inflation reduces purchasing power it is bad.
The old people are in the habit of recalling the days when the price of say, meat per kilogram cost just 10 rupees. Today it is Rs. 250 per kilogram. This is true for all other commodities. When they enjoyed a better living standard. Imagine today, how worse we are! But meanwhile, wages and salaries of people have risen to a great height, compared to the ‘good old days’. This goes unusually untold.
When price level goes up, there is both a gainer and a loser. To evaluate the consequence of inflation, one must identify the nature of inflation which may be anticipated and unanticipated. If inflation is anticipated, people can adjust with the new situation and costs of inflation to the society will be smaller.
In reality, people cannot predict accurately future events or people often make mistakes in predicting the course of inflation. In other words, inflation may be unanticipated when people fail to adjust completely. This creates various problems.
One can study the effects of unanticipated inflation under two broad headings:
(i) Effect on distribution of income and wealth
(ii) Effect on economic growth.
(a) Effects of Inflation on Income and Wealth Distribution :
During inflation, usually people experience rise in incomes. But some people gain during inflation at the expense of others. Some individuals gain because their money incomes rise more rapidly than the prices and some lose because prices rise more rapidly than their incomes during inflation. Thus, it redistributes income and wealth.
Though no conclusive evidence can be cited, it can be asserted that following categories of people are affected by inflation differently:
i. Creditors and Debtors:
Borrowers gain and lenders lose during inflation because debts are fixed in rupee terms. When debts are repaid their real value declines by the price level increase and, hence, creditors lose. An individual may be interested in buying a house by taking a loan of Rs. 7 lakh from an institution for 7 years.
The borrower now welcomes inflation since he will have to pay less in real terms than when it was borrowed. Lender, in the process, loses since the rate of interest payable remains unaltered as per agreement. Because of inflation, the borrower is given ‘dear’ rupees, but pays back ‘cheap’ rupees.
However, if in an inflation-ridden economy creditors chronically loose, it is wise not to advance loans or to shut down business. Never does it happen. Rather, the loan- giving institution makes adequate safeguard against the erosion of real value.
ii. Bond and Debenture-Holders:
In an economy, there are some people who live on interest income—they suffer most.
Bondholders earn fixed interest income:
These people suffer a reduction in real income when prices rise. In other words, the value of one’s savings decline if the interest rate falls short of inflation rate. Similarly, beneficiaries from life insurance programmes are also hit badly by inflation since real value of savings deteriorate.
iii. Investors:
People who put their money in shares during inflation are expected to gain since the possibility of earning business profit brightens. Higher profit induces owners of firms to distribute profit among investors or shareholders.
iv. Salaried People and Wage-Earners:
Anyone earning a fixed income is damaged by inflation. Sometimes, unionized worker succeeds in raising wage rates of white-collar workers as a compensation against price rise. But wage rate changes with a long time lag. In other words, wage rate increases always lag behind price increases.
Naturally, inflation results in a reduction in real purchasing power of fixed income earners. On the other hand, people earning flexible incomes may gain during inflation. The nominal incomes of such people outstrip the general price rise. As a result, real incomes of this income group increase.
v. Profit-Earners, Speculators and Black Marketeers:
It is argued that profit-earners gain from inflation. Profit tends to rise during inflation. Seeing inflation, businessmen raise the prices of their products. This results in a bigger profit. Profit margin, however, may not be high when the rate of inflation climbs to a high level.
However, speculators dealing in business in essential commodities usually stand to gain by inflation. Black marketeers are also benefited by inflation.
Thus, there occurs a redistribution of income and wealth. It is said that rich becomes richer and poor becomes poorer during inflation. However, no such hard and fast generalizations can be made. It is clear that someone wins and someone loses from inflation.
These effects of inflation may persist if inflation is unanticipated. However, the redistributive burdens of inflation on income and wealth are most likely to be minimal if inflation is anticipated by the people.
With anticipated inflation, people can build up their strategies to cope with inflation. If the annual rate of inflation in an economy is anticipated correctly people will try to protect them against losses resulting from inflation.
Workers will demand 10 p.c. wage increase if inflation is expected to rise by 10 p.c. Similarly, a percentage of inflation premium will be demanded by creditors from debtors. Business firms will also fix prices of their products in accordance with the anticipated price rise. Now if the entire society “learns to live with inflation” , the redistributive effect of inflation will be minimal.
However, it is difficult to anticipate properly every episode of inflation. Further, even if it is anticipated it cannot be perfect. In addition, adjustment with the new expected inflationary conditions may not be possible for all categories of people. Thus, adverse redistributive effects are likely to occur.
Finally, anticipated inflation may also be costly to the society. If people’s expectation regarding future price rise become stronger they will hold less liquid money. Mere holding of cash balances during inflation is unwise since its real value declines. That is why people use their money balances in buying real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Such investment is referred to as unproductive investment. Thus, during inflation of anticipated variety, there occurs a diversion of resources from priority to non-priority or unproductive sectors.
b. Effect on Production and Economic Growth :
Inflation may or may not result in higher output. Below the full employment stage, inflation has a favourable effect on production. In general, profit is a rising function of the price level. An inflationary situation gives an incentive to businessmen to raise prices of their products so as to earn higher doses of profit.
Rising price and rising profit encourage firms to make larger investments. As a result, the multiplier effect of investment will come into operation resulting in higher national output. However, such a favourable effect of inflation will be temporary if wages and production costs rise very rapidly.
Further, inflationary situation may be associated with the fall in output, particularly if inflation is of the cost-push variety. Thus, there is no strict relationship between prices and output. An increase in aggregate demand will increase both prices and output, but a supply shock will raise prices and lower output.
Inflation may also lower down further production levels. It is commonly assumed that if inflationary tendencies nurtured by experienced inflation persist in future, people will now save less and consume more. Rising saving propensities will result in lower further outputs.
One may also argue that inflation creates an air of uncertainty in the minds of business community, particularly when the rate of inflation fluctuates. In the midst of rising inflationary trend, firms cannot accurately estimate their costs and revenues. Under the circumstance, business firms may be deterred in investing. This will adversely affect the growth performance of the economy.
However, slight dose of inflation is necessary for economic growth. Mild inflation has an encouraging effect on national output. But it is difficult to make the price rise of a creeping variety. High rate of inflation acts as a disincentive to long run economic growth. The way the hyperinflation affects economic growth is summed up here.
We know that hyperinflation discourages savings. A fall in savings means a lower rate of capital formation. A low rate of capital formation hinders economic growth. Further, during excessive price rise, there occurs an increase in unproductive investment in real estate, gold, jewellery, etc.
Above all, speculative businesses flourish during inflation resulting in artificial scarcities and, hence, further rise in prices. Again, following hyperinflation, export earnings decline resulting in a wide imbalance in the balance of payments account.
Often, galloping inflation results in a ‘flight’ of capital to foreign countries since people lose confidence and faith over the monetary arrangements of the country, thereby resulting in a scarcity of resources. Finally, real value of tax revenue also declines under the impact of hyperinflation. Government then experiences a shortfall in investible resources.
Thus, economists and policy makers are unanimous regarding the dangers of high price rise. But the consequence of hyperinflation is disastrous. In the past, some of the world economies (e.g., Germany after the First World War (1914-1918), Latin American countries in the 1980s) had been greatly ravaged by hyperinflation.
The German Inflation of 1920s was also Catastrophic:
During 1922, the German price level went up 5,470 per cent, in 1923, the situation worsened; the German price level rose 1,300,000,000 times. By October of 1923, the postage of the lightest letter sent from Germany to the United States was 200,000 marks.
Butter cost 1.5 million marks per pound, meat 2 million marks, a loaf of bread 200,000 marks, and an egg 60,000 marks Prices increased so rapidly that waiters changed the prices on the menu several times during the course of a lunch!! Sometimes, customers had to pay double the price listed on the menu when they observed it first!!!
During October 2008, Zimbabwe, under the President-ship of Robert G. Mugabe, experienced 231,000,000 p.c. (2.31 million p.c.) as against 1.2 million p.c. price rise in September 2008—a record after 1923. It is an unbelievable rate. In May 2008, the cost of price of a toilet paper itself and not the costs of the roll of the toilet paper came to 417 Zimbabwean dollars.
Anyway, people are harassed ultimately by the high rate of inflation. That is why it is said that ‘inflation is our public enemy number one’. Rising inflation rate is a sign of failure on the part of the government.
Related Articles:
- Essay on the Causes of Inflation (473 Words)
- Cost-Push Inflation and Demand-Pull or Mixed Inflation
- Demand Pull Inflation and Cost Push Inflation | Money
- Essay on Inflation: Meaning, Measurement and Causes
- Beginner's Guide
- Past Papers
- CSP Members
- Members List
- Social Groups
- Mark Forums Read
- Erosion of Currency
- Moderate Inflation in Pakistan
- Effects of Inflation
- Poor Vs. Rich
- Inflation Discourages Investment
- Inflation Erodes Trust in National Currency
- Money Growth
- Global Oil Price Movements
- Domestic Supply Shocks
- Study Abroad Guide
- Study Abroad Visa
- Study in Australia
- Study in Canada
- Study In china
- Study In Ireland
- Study in UK
- Study in USA
- Sample Papers
- Universities
- Accountancy
- Introduction
- Courses After 10th
- courses after 12th
- Engineering
- Mass Communication
- O/A Level Courses
- Research Thesis
- Short Courses
- Spoken English
- Islamic banks In Pakistan
- Educational Institutes
- Research Institutes in Pakistan
- Admission Fee
- Training & workshops
- Merit Lists
- Roll No Slip
- Technology News
- English Tests
- Amazing Tips
- Girls Fashion
- Latest technology Blog
- Student experience's
- Student jokes
- Ramzan ul Mubarak Special
- Career in Pakistan
- CV & RESUME
- Jobs in Karachi
- jobs in Lahore
- Sample Interview Questions
- Learning articles
- Learning English
- Pakistan Information
- Pakistan Issues
- B.A/BSC Past Papers
- Balochistan and AJK Board
- CSS Past Papers
- Punjab Board
- Sindh Board
- Great Personalities
- Inter Model Papers
- Matric Model Papers
- Scholarships
- Uncategorized
- Book Reviews
- Foreign Universities
- Pakistan Universities
- student stories
- Top Universities
- University Reviews

Inflation in Pakistan Essay
Do you know what the Inflation in Pakistan Essay Pakistan is considered to be one of those unfortunate countries in the world which have the highest Inflation rate in the world? Basically, inflation is known as the term in which the prices of commodities are changed on the regular basis. The inflation rate basically identifies the change of prices in a particular area, and it is also being observed that once the inflation rate is made high the buying power of the people just gets reduced which means that the basic necessities of life get beyond their buying power and beyond their reach and access. The Inflation in Pakistan Essay is being calculated and reported by the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics known as PBS. For the month of November-December 2022, the inflation rate which is being recorded for Pakistan is 10.90 percent.
The Inflation in Pakistan Essay was recorded at 10.90 percent in November 2022. Pakistan has a history of the most unpredictable and most varying inflation rates in the world and there are so many internal and external factors that contribute to the sudden change and decline of Inflation in Pakistan Essay. Amongst these factors the most crucial factor is the political instability in the state, as the weak government and administration are the main cause of the increased inflation rate in any state, secondly, the Pakistan currency is declining day by day which is increasing the international debt on the state day by day because the debt has to be paid in Dollars and the decline in Pakistani rupee is increasing the worth of dollars as this is another very important and core factor due to which the Inflation in Pakistan Essay is not getting stabilize and fluctuations in it are being observed on regular basis.
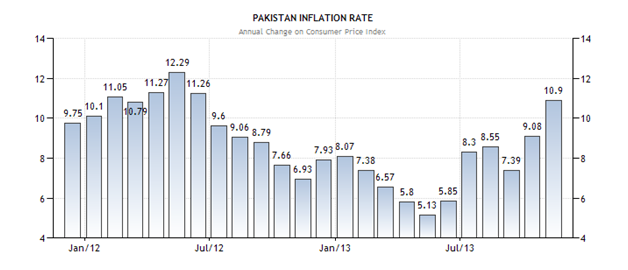
Let us have an overview of the inflation Rates in Pakistan in the various tenures and time durations. From the time duration and time span of 1957 to 2013, the average rate in Pakistan is 8.02 percent. There are various time periods when the inflation rate is either abnormally raised or declined. The real-time example of this is when the rate in Pakistan was raised to a massive height of 37.81 Percent in December of 1973 and at the same time, there is a record low ratio calculated which was just -10.32 Percent in February 1959. In Pakistan, the most important categories in the consumer price index are food and non-alcoholic beverages, housing, water, electricity, gas, and fuels (29 percent); clothing and footwear (8 percent), and transport (7 percent). The index also includes furnishings and household equipment (4 percent), education (4 percent), communication (3 percent), and health (2 percent). The remaining 8 percent is composed of recreation and culture, restaurants and hotels, alcoholic beverages and tobacco, and other goods and services.
Moin akhtar
I am committed to helping Pakistani students craft successful career paths by merging their individual passions with market trends. As a career counselor, we'll explore both well-established fields and modern industries to find the best fit for you. With personalized counseling and strategic planning, we aim to transform your educational journey into a thriving professional future.
Post Comment Cancel reply

Essay on Inflation
Students are often asked to write an essay on Inflation in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Inflation
Understanding inflation.
Inflation is when prices of goods and services rise over time. This means you need more money to buy the same things. It’s like a slow-motion robbery!
Causes of Inflation
Inflation is often due to increased production costs or increased demand for goods and services. When people want more of something, and it’s scarce, prices go up.
Impact of Inflation
Inflation affects everyone. If your income doesn’t increase as fast as inflation, you’ll have less buying power. But, if you’re a business owner, you might be able to raise prices and make more money.
Controlling Inflation
Governments try to control inflation by adjusting interest rates, taxes, and government spending. It’s a tricky balancing act to keep inflation low but not too low.
Also check:
- Paragraph on Inflation
250 Words Essay on Inflation
Inflation, a crucial economic concept, refers to the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently eroding purchasing power. It’s an indicator of the economic health of a nation, with moderate inflation signifying a growing economy.
The Causes of Inflation
Inflation generally occurs due to two primary factors: demand-pull and cost-push inflation. Demand-pull inflation transpires when demand for goods and services surpasses their supply. On the other hand, cost-push inflation arises when the costs of production escalate, causing producers to increase prices to maintain profit margins.
Effects of Inflation
Inflation impacts various aspects of the economy. It erodes the purchasing power of money, causing consumers to spend more for the same goods or services. Inflation can also create uncertainty in the economy, affecting investment and saving decisions. However, moderate inflation can stimulate spending and investment, driving economic growth.
Managing Inflation
Central banks attempt to control inflation through monetary policy. By adjusting interest rates, they influence the level of spending and investment in the economy. Higher interest rates typically reduce spending, curbing inflation. Conversely, lower interest rates stimulate spending, potentially leading to inflation.
Inflation is a complex and multifaceted subject. Understanding its causes, effects, and the measures to control it is essential for both macroeconomic stability and individual financial well-being. As future leaders, it’s crucial for us as students to grasp these concepts to make informed decisions in our professional and personal lives.
500 Words Essay on Inflation
Introduction to inflation.
Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives, from the cost of living to the value of money. It is defined as the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently, purchasing power is falling. Central banks attempt to limit inflation, and avoid deflation, in order to keep the economy running smoothly.
Inflation is primarily caused by an increase in the money supply that outpaces economic growth. Ever since the end of the gold standard, governments have had the ability to create money at will. If a nation’s money supply grows too rapidly compared to its production of goods and services, prices will increase, leading to inflation.
Additionally, inflation can be spurred by demand-pull conditions, where demand for goods and services exceeds their supply. Cost-push inflation, on the other hand, occurs when the costs of production increase, causing producers to raise prices to maintain their profit margins.
Impacts of Inflation
Inflation affects economies in various ways. While mild inflation is viewed as a sign of a healthy economy, hyperinflation can lead to economic instability. It erodes purchasing power as the same amount of money can buy fewer goods and services. This can lead to uncertainty and a decrease in spending and investment, which can slow economic growth.
Moreover, inflation can harm savers if the inflation rate surpasses the interest rate on their savings. It also favors borrowers, as the real value of their debt diminishes over time. This redistribution of wealth from savers to borrowers can lead to social and economic inequalities.
Central banks use monetary policy to control inflation. They adjust the money supply by setting interest rates and through open market operations. By raising interest rates, central banks can decrease the money supply, making borrowing more expensive and slowing economic activity, thereby reducing inflation.
Furthermore, governments can use fiscal policy to control inflation. This involves changing tax rates and levels of government spending to influence the level of demand in the economy. By reducing demand, governments can put downward pressure on prices and reduce inflation.
Inflation is an intricate part of our economic systems. It is a double-edged sword that can stimulate economic growth when mild, but can also lead to economic instability when it becomes too high. Understanding inflation is crucial for policymakers, investors, and consumers alike as it influences our decisions and shapes our economic reality. By effectively managing inflation, governments can promote economic stability and growth, thereby improving the standard of living for their citizens.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
- Essay on Indian Culture
- Essay on Importance of Education
- Essay on Immigration
Apart from these, you can look at all the essays by clicking here .
Happy studying!
Nice Very Nice
It is helpful …thanks alot
EXCELLENT AND ALSO VERY BENIFICAL FOR US AND ALSO FOR BEGINEERS
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Ground Reports
- 50-Word Edit
- National Interest
- Campus Voice
- Security Code
- Off The Cuff
- Democracy Wall
- Around Town
- PastForward
- In Pictures
- Last Laughs
- ThePrint Essential

Islamabad [Pakistan], May 20 (ANI): The salaried class in Pakistan has been struggling to make ends meet as inflation is now the biggest issue faced by the general public, there is no choice but to compromise and sometimes cheat to ensure survival.
Amjad Iqbal, a resident of Lahore and an expert on the matter, said, “There is no doubt that the income of an individual in Pakistan has not increased. Notably, the business class of the country in the case of inflation is not that affected, as they can adjust their earnings by increasing and decreasing their profit margins. These people increase their profit margins when inflation increases and decrease their margins when inflation rates are controlled. But the ones most affected are the people who have a fixed monthly income.”
“These salaried employees are the most important part of Pakistan’s economy, and it continues to suffer. If they have some money left with them they only boost the economy, these are the ones who spend during the festival season enabling the production cycle to continue. But this part of Pakistan’s economy remains at risk now. And if they continue to remain in such a miserable condition then, who will be spent during the festive season,” he added.

Also, while highlighting the issue of tax fraud, Iqbal mentioned, “Our tax to GDP ratio currently is not that much. But, because we have never paid our taxes with honesty, that is why we find paying taxes difficult. Everyone in Pakistan tries to save their taxes, once there was a fixed tax declared based on income levels in Pakistan, they then came out on roads for protesting at that time.”
“Both big and small business owners keep their money in hard cash, and not in banks it is because they intend to hide their incomes and commit tax frauds, as there is no other option,” he added.
Blue-collared and white-collared employees in Pakistan’s Karachi face several difficulties as the administration has made no clear labour laws, defining the set norms of the employee class in Pakistan.
Hence, people face employment-related issues and are forced to work on the terms decided by the employer, willingly or unwillingly, as they have no other option due to unemployment. (ANI)
This report is auto-generated from ANI news service. ThePrint holds no responsibility for its content.
Subscribe to our channels on YouTube , Telegram & WhatsApp
Support Our Journalism
India needs fair, non-hyphenated and questioning journalism, packed with on-ground reporting. ThePrint – with exceptional reporters, columnists and editors – is doing just that.
Sustaining this needs support from wonderful readers like you.
Whether you live in India or overseas, you can take a paid subscription by clicking here .
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Most Popular
Modi’s global stature nowhere close to that of nehru, indira or vajpayee, says yashwant sinha, social stock exchange brings new dawn for ngos. it will link india’s social sector to markets, deepa mehta is back with a film on transwoman sirat taneja. ‘all good art is political’.
Required fields are marked *
Copyright © 2024 Printline Media Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Free Essays
- Citation Generator

Inflation in Pakistan
You May Also Find These Documents Helpful
Eco 372 week 1 dq 3 different types of unemployment.
Any type of unemployment is important to the labor force and economic growth. A person who is actively searching work, but unable to find work is classified as unemployed. The size of the labor force is used to determine the unemployment rate.…
Unemployment. Only one man is unemployed in a city of 100,000 is his personal trouble, and for its relief we properly look to the character of the man, his skill, and his immediate opportunities. But when in a nation of 50 million employees, 15 million men are unemployed, that is an issue, and we may not hope to find its solution within the range of opportunities open to any one individual.…
Unemloyment Rate in the United States
Unemployment is one of the principal macroeconomic problems facing the United States economy. This implies that the economy is not operating under full employment. United States has been experiencing a high level of unemployment in the past. However, in the recent past the United States unemployment has fallen down to 7.7 percent as per statistics this year in the month of November. This is the lowest unemployment rate United States labor department has recorded in the past four years. According to a report by the labor department, about 146000 jobs were added in the economy. This resulted to the unemployment rate falling from 7.8 to 7.7 percent. The fall is largely attributed to the fact that most households stopped looking for employment opportunities in the economy (Zhang, 1).…
Current Event
When the economy declines, jobs will tend to decline. In today’s society unemployment is one of the greatest challenge that is facing many people around the world. Because of the low unemployment is seen in countries like Greece and North America, the people cannot live to their potential. Unemployment brings uncertainty and fear.…
Sociological Perspectives on Unemployment
One sociological perspective on unemployment can be taken from the famous Functionalist Theory. Functionalists believe everything serves a specific function in our society and these functions need to be understood (Kendall 23). The theorist behind functionalism is Durkheim. Durkheim’s concern was how to preserve society. The basis for social order was not economic, but rather moral. In a functionalist society, everyone has a role and a purpose. In order for this theory to be successful, the individuals in a…
Unemployment in America
The unemployment rate is important to us because it is one of the ways in which we measure economic health and gauge the economy’s growth rate. The effects of unemployment do spill over into other areas of the economy. When people are jobless, they have less disposable income causing a lower demand for nonessential goods and services. With lower spending by consumers, firms may be forced to look at ways to cut costs in order to stay afloat. One way to reduce expenses is to lay off more workers, resulting in a seemingly endless cycle as even fewer families are able to spend money to rejuvenate the companies’ business levels.…
Unemployment Rate In The United States
Comparing to the unemployment rate (10%) after 2008’s recession, US is now reaching a relatively low unemployment rate. A low unemployment rate is one of the four macroeconomic objectives that economists always want their nations to achieve. Unemployment is simply defined as the state of being out of work, seeking for a job but unable to find a job. The author stated that US employers added more work opportunities to their payrolls. The job growth in the last year reduces the unemployed people and “maintain low unemployment once the labor market…
The Problem Of Unemployment In Canada
The topic of unemployment has always been a subject that sparks interest in a conversation. Being unemployed can lead to a life of misery, like the snowball rolling down a mountain only to grow with every roll. From unemployment, people live in poverty and sleep on the streets, starve and may even develop health issues, purely because they were never able to provide a living for themselves. Being without a job is a gateway to a variety of terrible living situations.…
Unemployment from a functionalist and conflict perspective
education, government and health) are affected by unemployment. It will also look at Karl Marx and Emile Durkheim and their contribution to sociology and the theory of functionalism and conflict. Unemployment affects almost everyone to some degree during their lives, the need to understand how we can deal with the issue is becoming critically important to society as a whole.…
Unemployment a Major Challenge
The subject of unemployment a major challenge is a controversial issue. In depth analysis of unemployment a major challenge can be an enriching experience. Indispensable to homosapians today, it is impossible to overestimate its impact on modern thought. It still has the power to shock global commercial enterprises, who are yet to grow accustomed to its disombobulating nature. With the primary aim of demonstrating my considerable intellect I will now demonstrate the complexity of the many faceted issue that is unemployment a major challenge.…
The Sociological Imagination and Understanding Personal Troubles as Social Issues
With unemployment we need to see the “bigger picture”, past our own perspective, why there are so many people without work. An unemployed person may think that because he or she can’t find work that it is his or her problem alone. Instead it can be seen as a social issue if many thousands of people in society are also unemployed and struggling to find work. The approach which should also be taken when dealing with a complex issue such as unemployment is that the stereotypes about the issue should be discarded because…
Importance of the Macroeconomics Objectives Towards the Malaysia Economic Performance.
Unemployment is an important measure of the economy's strength. The low rate of unemployment shows the economic is in good condition. It means most of the people are able and willing to work. In contrast, the higher rate of unemployment means most of the labour force that is without jobs. It might affect the condition of national economy. The most worrisome is the rise in the share of the long-term unemployed.…
Are Education Systems Modern as Well as Practical Enough to Eliminate Unemployment, and Thus Poverty?
With the annual population growth being 1.8% during the last four years, nearly a million workers are being added to the workforce every year. However despite such vast potential at hand, the employment rates are creating an unfavorable environment. Nearly 60% of the population is in the 'economically productive' age group and with the alarming fact that the rate of youth unemployment in Pakistan is 8%, higher than the overall unemployment rate of 6% this year. Almost half of the Pakistani workforce is unemployed according to the figures released by the Pakistan Economy Watch. The low growth in labour productivity has not matched the rising labour force and due to the low literacy rate coupled with ongoing economic depression, poverty is constantly growing.…
Problem of Unmployment in Pakistan
(A Case Study of Khyber PakhtunKhwa Province) Abstract The Pakistan’s economy has covered a long distance from backward to developing stage and has now attaining the stage of take off. During the period it has confronted a number of hurdles and difficulties. The major problem related to absorbing ever growing population through providing them job opportunities. The economy being basically agriculture had surplus labour. The process of mechanization of agriculture added fuel to the fire and subsequently aggravated the problem because of additional labour rendered surplus by the agriculture sector. The slow process of industrialization amid the population explosion worsened the situation. This paper focuses on the basic issues and as an objective will suggest practicable measures for increasing the rate of employment or for that matter reducing the level of unemployment. Research Methodology To make an enquiry into the problem, find out the reasons for suggesting solution, secondary data available on official record will be used. First hand information where deem necessary will be collected through local inquiries with the use of questionnaire and face to face interview from a selected segment of the population. Variable: Unemployment rate. Objective of the study This paper primarily is meant to create awareness about the unemployment rate in the country and causes of unemployment in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. As such it aims at creating an understanding among the readers on the issues relating to low rate of employment and its…
Political Economy of Pakistan
Economic and social outcomes in Pakistan have been a mixture of paradoxes since the country came into being. Pakistan, once a regional economic power in 1960’s could not realize its potential and fell behind its East Asian fellow countries. Politically, religious fundamentalism, sectarian violence, ethnic differences, terrorism and regional economic disparities have made country unstable which contributed toward the unsatisfactory economic condition.…
Related Topics
- Unemployment

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The term 'inflation' refers to a sustained rise in the prices of goods and services in an economy. In Pakistan, inflation has been a major concern since the late 1990s, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reaching a peak in 2023. We will explore the various factors that have contributed to inflation in Pakistan, its economic effects, and ...
Rising Prices / Inflation Essay 300 - 400 words. This essay is suitable for class 10 and class 12, 2nd year. The essay covers details about the recent inflation and rising prices in Pakistan. The essay topics has been given in 2nd year smart syllabus 2020.
Inflation, a persistent rise in the general price level of goods and services, is a pressing economic concern that has cast its shadow over Pakistan's economy for years.In this essay on inflation in Pakistan, exploring the root causes and the far-reaching impact of inflation on the nation's economy and its people will be explored.
Inflation is again high in Pakistan, having risen further to 8.2 per cent in February 2019. Increase in Inflation rates comes with its own costs. For the poor, a rise in the prices of essential items (if it exceeds income growth) can be a death knell, both literally (for subsistence households), and indirectly, due to the inability to afford ...
Graphical Analysis of Inflation from 2008 to 2012 Using CPI. The inflation rate in Pakistan was last reported at 10.8 percent in March of 2012. From 2003 until 2010, the average inflation rate in Pakistan was 10.15 percent reaching an historical high of 25.33 percent in August of 2008 and a record low of 1.41 percent in July of 2003.
Inflation is a significant economic issue that affects individuals, businesses, and the country as a whole. Pakistan, like many developing countries, has struggled with inflation in recent years. In this essay, we will explore the causes and consequences of inflation in Pakistan, as well as some potential solutions to the problem. II.
This study explored the effect of money supply, GDP, oil prices, and exchange rate on the rate of inflation in Pakistan. The sample period of study ranges from the year 1989 to 2019.
The Causes of High Inflation in Pakistan. There are a number of factors that have contributed to high inflation in Pakistan. These include: An energy crisis: Pakistan faces a persistent energy crisis, marked by frequent power outages and an over-reliance on imported energy. This energy deficit drives up production costs, leading to higher ...
1. Introduction of inflation and growth. The economy of Pakistan presented a sobering picture at the end of FY09. Inflation reached an unprecedented level of 25.3% in August 2008 and rested at 17.2% (year-on-year) as of April 2009. GDP growth had slowed to 3.7% for 2008 and 1.2% for 2009.
2008 and lowest inflation rate of 1.41% in July 2003 whi ch is a r ecord in Pakistan history. In Pakis tan, 2003-2010, the average inflation is recorded as 10.15%. According to FBS, 2010 ...
Essay on Inflation! Essay on the Meaning of Inflation: Inflation and unemployment are the two most talked-about words in the contemporary society. These two are the big problems that plague all the economies. Almost everyone is sure that he knows what inflation exactly is, but it remains a source of great deal of confusion because it is difficult to define it unambiguously. Inflation is often ...
Domestic Supply Shocks. Conclusion. Inflation is a situation of a sustained increase in the general price level in an economy. In other words, it means an increase in the cost of living as the price of goods and services rise. Importantly, inflation is a tax that erodes the purchasing power of the currency. If all inflation is bad and whether ...
The document is an essay on inflation in Pakistan that is 560 words long. It discusses several leading causes of inflation in Pakistan, including fragile economic policies, hoarding and dishonest practices by traders. It also notes that deficit budgeting and wrong taxation policies have contributed to rising prices. The essay outlines steps the government has taken to curb inflation, such as ...
MONETARY POLICY: Monetary policy is termed as the regulation of interest rate and the availability of money to maintain steady growth and prevent hard market crashes. An institution in charge of the monetary policy usually does it in two ways. One of the ways is by buying back securities from banks.
With monetary growth picking up, inflation followed. and increased sharply in late 2003, peaking at 11 percent year- on-year in April 2005. Average annual. inflation stabilised around 8 to 9 ...
Essay Inflation in Pakistan - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Inflation in Pakistan 187 II. BASIC ELEMENTS OF THE MODEL Several studies highlight the role of monetary factors for inflation in Pakistan.3 For example, Khan and Qasim (1996) find that overall inflation is only determined by money supply, import prices, and real GDP. The empirical evidence is inconclusive regarding the role of the exchange rate.
The Inflation in Pakistan Essay was recorded at 10.90 percent in November 2022. Pakistan has a history of the most unpredictable and most varying inflation rates in the world and there are so many internal and external factors that contribute to the sudden change and decline of Inflation in Pakistan Essay. Amongst these factors the most crucial ...
The first essay is a long essay on Inflation of 400-500 words. This long essay about Inflation is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on Inflation of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
500 Words Essay on Inflation Introduction to Inflation. Inflation is a complex economic phenomenon that affects every aspect of our lives, from the cost of living to the value of money. It is defined as the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising, subsequently, purchasing power is falling. Central banks ...
Essay Inflation in Pakistan-1 - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Essay Inflation in Pakistan-1
A-. A+. Islamabad [Pakistan], May 20 (ANI): The salaried class in Pakistan has been struggling to make ends meet as inflation is now the biggest issue faced by the general public, there is no choice but to compromise and sometimes cheat to ensure survival. Amjad Iqbal, a resident of Lahore and an expert on the matter, said, "There is no doubt ...
The unemployment rate (10 years and over) in Pakistan was last reported at 5.7 percent in the second quarter of 2011. Historically, from 1990 until 2011, Pakistan Unemployment Rate averaged 5.8% reaching an all-time high of 7.8% in June of 2002 and a record low of 3.13% in December of 1990.