- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Corporate Finance
- Financial Analysis

What Is Business Forecasting? Definition, Methods, and Model
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/andy__andrew_beattie-5bfc262946e0fb005143d642.jpg)
What Is Business Forecasting?
Business forecasting involves making informed guesses about certain business metrics, regardless of whether they reflect the specifics of a business, such as sales growth, or predictions for the economy as a whole. Financial and operational decisions are made based on economic conditions and how the future looks, albeit uncertain.
Key Takeaways:
- Forecasting is valuable to businesses so that they can make informed business decisions.
- Financial forecasts are fundamentally informed guesses, and there are risks involved in relying on past data and methods that cannot include certain variables.
- Forecasting approaches include qualitative models and quantitative models.
Understanding Business Forecasting
Companies use forecasting to help them develop business strategies. Past data is collected and analyzed so that patterns can be found. Today, big data and artificial intelligence has transformed business forecasting methods. There are several different methods by which a business forecast is made. All the methods fall into one of two overarching approaches: qualitative and quantitative .
While there might be large variations on a practical level when it comes to business forecasting, on a conceptual level, most forecasts follow the same process:
- A problem or data point is chosen. This can be something like "will people buy a high-end coffee maker?" or "what will our sales be in March next year?"
- Theoretical variables and an ideal data set are chosen. This is where the forecaster identifies the relevant variables that need to be considered and decides how to collect the data.
- Assumption time. To cut down the time and data needed to make a forecast, the forecaster makes some explicit assumptions to simplify the process.
- A model is chosen. The forecaster picks the model that fits the dataset, selected variables, and assumptions.
- Analysis. Using the model, the data is analyzed, and a forecast is made from the analysis.
- Verification. The forecast is compared to what actually happens to identify problems, tweak some variables, or, in the rare case of an accurate forecast, pat themselves on the back.
Once the analysis has been verified, it must be condensed into an appropriate format to easily convey the results to stakeholders or decision-makers. Data visualization and presentation skills are helpful here.
Types of Business Forecasting
There are two key types of models used in business forecasting—qualitative and quantitative models.
Qualitative Models
Qualitative models have typically been successful with short-term predictions, where the scope of the forecast was limited. Qualitative forecasts can be thought of as expert-driven, in that they depend on market mavens or the market as a whole to weigh in with an informed consensus.
Qualitative models can be useful in predicting the short-term success of companies, products, and services, but they have limitations due to their reliance on opinion over measurable data. Qualitative models include:
- Market research : Polling a large number of people on a specific product or service to predict how many people will buy or use it once launched.
- Delphi method : Asking field experts for general opinions and then compiling them into a forecast.
Quantitative Models
Quantitative models discount the expert factor and try to remove the human element from the analysis. These approaches are concerned solely with data and avoid the fickleness of the people underlying the numbers. These approaches also try to predict where variables such as sales, gross domestic product , housing prices, and so on, will be in the long term, measured in months or years. Quantitative models include:
- The indicator approach : The indicator approach depends on the relationship between certain indicators, for example, GDP and the unemployment rate remaining relatively unchanged over time. By following the relationships and then following leading indicators, you can estimate the performance of the lagging indicators by using the leading indicator data.
- Econometric modeling : This is a more mathematically rigorous version of the indicator approach. Instead of assuming that relationships stay the same, econometric modeling tests the internal consistency of datasets over time and the significance or strength of the relationship between datasets. Econometric modeling is applied to create custom indicators for a more targeted approach. However, econometric models are more often used in academic fields to evaluate economic policies.
- Time series methods : Time series use past data to predict future events. The difference between the time series methodologies lies in the fine details, for example, giving more recent data more weight or discounting certain outlier points. By tracking what happened in the past, the forecaster hopes to get at least a better than average view of the future. This is one of the most common types of business forecasting because it is inexpensive and no better or worse than other methods.
Criticism of Forecasting
Forecasting can be dangerous. Forecasts become a focus for companies and governments mentally limiting their range of actions by presenting the short to long-term future as pre-determined. Moreover, forecasts can easily break down due to random elements that cannot be incorporated into a model, or they can be just plain wrong from the start.
But business forecasting is vital for businesses because it allows them to plan production, financing, and other strategies. However, there are three problems with relying on forecasts:
- The data is always going to be old. Historical data is all we have to go on, and there is no guarantee that the conditions in the past will continue in the future.
- It is impossible to factor in unique or unexpected events, or externalities . Assumptions are dangerous, such as the assumption that banks were properly screening borrowers prior to the subprime meltdown . Black swan events have become more common as our reliance on forecasts has grown.
- Forecasts cannot integrate their own impact. By having forecasts, accurate or inaccurate, the actions of businesses are influenced by a factor that cannot be included as a variable. This is a conceptual knot. In a worst-case scenario, management becomes a slave to historical data and trends rather than worrying about what the business is doing now.
Negatives aside, business forecasting is here to stay. Appropriately used, forecasting allows businesses to plan ahead for their needs, raising their chances of staying competitive in the markets. That's one function of business forecasting that all investors can appreciate.
Kesh, Someswar and Raja, M.K. "Development of a Qualitative Reasoning Model for Financial Forecasting." Information Management & Computer Security, vol. 13, no. 2, 2005, pp. 167-179.
Infiniti Research. " Business Forecasting: The Challenges in Knowing the Unknown ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-699097865-5914251597ff43a1b2e59a0c3cecc660.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Business Forecasting: Why You Need It & How to Do It

Table of Contents
What is business forecasting, the importance of business forecasting, business forecasting process, business forecasting methods, elements of business forecasting, sources of data for forecasting, business forecasting only goes so far, how projectmanager helps business forecasting.
Well-run organizations don’t fly by the seat of their pants; they’re constantly working on business forecasting and business planning. Every decision and every process is based on data obtained from business forecasting, business intelligence tools, market research and scenario planning. Companies focus their energies on ways to predict market trends to help them set successful long-term strategies.
Some business forecasts are based on highly sophisticated statistical methods while others are based on experience and past data. Others simply follow a gut feeling. One thing remains constant: all industries rely on business forecasting.
Business forecasting refers to the process of predicting future market conditions by using business intelligence tools and forecasting methods to analyze historical data.
Business forecasting can be either qualitative or quantitative. Quantitative business forecasting relies on subject matter experts and market research while quantitative business forecasting focuses only on data analysis.
You can access historical data with project management tools such as ProjectManager , project management software that delivers real-time data for more insightful business forecasting. Our live dashboard requires no setup and automatically captures six project metrics which are displayed in easy-to-read graphs and charts. Get a high-level view of your project for better business planning. Get started with ProjectManager for free today.
Quantitative Forecasting
Quantitative forecasting is applicable when there is accurate past data available to predict the probability of future events. This method pulls patterns from the data that allow for more probable outcomes. The data used in quantitative forecasting can include in-house data such as sales numbers and professionally gathered data such as census statistics. Generally, quantitative forecasting seeks to connect different variables in order to establish cause and effect relationships that can be exploited to benefit the business.
Qualitative Forecasting
Qualitative forecasting is based on the opinion and judgment of consumers and experts. This business forecasting method is useful if you have insufficient historical data to make any statistically relevant conclusions. In such cases, an expert can help piece together the known bits of data you do have to try to make a qualitative prediction from that known information.
Qualitative business forecasting is also useful when little is known about the future in your industry. Relying on historical data is useless if that data is not relevant to the uncharted future you are approaching. This can be the case in innovative industries, or if there’s a new constraint entering the market that has never occurred before such as new tax law.
Business forecasting is critical for businesses whenever the future is uncertain or whenever an important strategic business decision is being made. The more the business can focus on the probable outcome, the more success the organization has as it moves forward.
Here are the steps that a business forecaster should typically follow:
- Define the question or problem you need to solve with your business forecasting efforts. For example, you might be interested in estimating whether your organization will be able to meet product demand for the next quarter.
- Identify the datasets and variables that need to be taken into consideration. In this case, datasets such as the sales records from the previous year and variables related to capacity, production and demand planning .
- Choose a business forecasting method that adjusts to your dataset and forecasting goals. That depends on whether your problem or question can be solved using a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach.
- Based on the analysis of historical data, you can proceed to estimate future business performance. Keep in mind that the accuracy of your business forecasting depends on the quality of your data.
- Determine the discrepancy between your business forecast and actual business performance. Document your findings and improve your business forecasting process.
As stated above, there are two main types of business forecasting methods, qualitative and quantitative. We’ve compiled some of the more common forecasting models from both sides below.
Delphi Method
This qualitative business forecasting method consists in gathering a panel of subject matter experts and getting their opinions on the same topic in a manner in which they can’t know each other’s thoughts. This is done to prevent bias , which makes it possible for a manager to objectively compare their opinions and see if there are patterns, consensus or division.
Market Research
There are many market research techniques that evaluate the behavior of customers and their response to a certain product or service. Some of those market research methods collect and analyze quantitative data, such as digital marketing metrics and others qualitative data, such as product testing, or customer interviews.
Time Series Analysis
Also referred to as “trend analysis method,” this business forecasting technique simply requires the forecaster to analyze historical data to identify trends. This data analysis process requires statistical analysis as outliers need to be removed. More recent data should be given more weight to better reflect the current state of the business.
The Average Approach
The average approach says that the predictions of all future values are equal to the mean of the past data. Past data is required to use this method, so it can be considered a type of quantitative forecasting. This approach is often used when you need to predict unknown values as it allows you to make calculations based on past averages, where one assumes that the future will closely resemble the past.
The Naïve Approach
The naïve approach is the most cost-effective and is often used as a benchmark to compare against more sophisticated methods. It’s only used for time series data where forecasts are made equal to the last observed value. This approach is useful in industries and sectors where past patterns are unlikely to be reproduced in the future. In such cases, the most recent observed value may prove to be the most informative.
- Develop the Basis: Before you can start forecasting, you must develop a system to investigate the current economic situation around you. That includes your industry and its present position as well as its popular products to better estimate sales and general business operations.
- Estimating Future Business Operations: Now comes the estimation of future conditions, such as the course that future events are likely to take in your industry. Again, this is based on collected data to help with quantitative estimates for the scale of operations in the future.
- Regulating Forecasts: Whatever your forecast is, it must be compared to actual results. This is the only way to find deviations from the norm. Then the reasons for those deviations must be figured out, so action can be taken to correct those deviations in the future.
- Reviewing Forecasting Process: By reviewing the deviations between forecasts and actual performance data, improvements are made in the process, allowing you to refine and review the information for accuracy.
Your forecast will only be as good as the data you put into it. Before collecting data, ask yourself these questions:
- Why collect data?
- What kind of data?
- When to collect it?
- Where to collect it?
- Who will collect it?
- How will it be collected?
These are the questions that will shape your plan for the collection of data, a crucial facet of business forecasting. Once you have your plan, you can collect data from a variety of sources.
Primary Sources
Primary sources contain first-hand data, often collected with reporting tools . These are the ones that you or the person assigned this task to collect personally. If primary data is not available, you must go out and source it through interviews, questionnaires or observations.
Secondary Sources
Secondary sources contain published data or data that has been collected by others. This includes official reports from governments, publications, financial statements from banks or other financial institutions, annual reports of companies, journals, newspapers, magazines and other periodicals.
If business forecasting were a crystal ball, then everyone would be reaping the rewards of their foresight. While business forecasting is a tool to get a better view of what the future might have in store, there’s the argument that it’s wasting valuable time and resources on little return.
It’s true; you can follow the steps, use a variety of methodologies and still get it wrong. It is, after all, the future. There’s no way to ever manage all the variables that can impact future events. There are errors in calculations and the innate prejudices of the people managing the process, all of which add to the unpredictability of the results.
While you’re not going to have a clear, unobscured vision of the future by using business forecasting, it can provide you with insight into probable future trends to give your organization an advantage. Even a small step can be a great leap forward in the highly competitive world of business. By combining statistical and econometric models with experience, skill and objectivity, business forecasting is a formidable tool for any organization looking for a competitive advantage.
Clearly, business forecasting is a project unto itself. To manage a project and collect the data in a way that’s useful in the future, you need a project management tool that can help you plan your process and select the data that helps you decide on a way forward.
ProjectManager is award-winning software that organizes projects with features that address every phase. The first thing in forecasting is choosing how you’ll take action and make a plan. For example, if you’re going to interview customers to see where the market is likely headed, you’ll need to schedule those interviews. Our online Gantt chart places those interviews as tasks on a timeline so you can get everyone interviewed before your deadline.
Store All of Your Data in One Place
Those interviews will produce a lot of paperwork, and your data needs to be collected and stored somewhere easily accessible. You can attach notes to each task so the paperwork for each interviewee is saved with the notes that you took. You can also tag those tasks to make it easier to filter the project and locate the interview subjects for which you’re looking. If you’re worried that there’ll be too many documents and images attached to one task, don’t worry as we have unlimited file storage.
ProjectManager can’t predict the future, but it does provide you with the tools you need to take advantage of business forecasting. Our project management software collects data in real-time, and stores past data, allowing you to filter information and pull up the metrics you need to make the right decision. Try it today with this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and under budget
Start planning your projects.
How to write a sales forecast for a business plan
Table of Contents
What is a sales forecast?
Why do you need a sales forecast, how do you write a sales forecast, top-down or bottom-up, writing your sales forecast, calculating a sales forecast, how can countingup help manage your forecasting.
Sales forecasts are an important part of your business plan . If done correctly, they can give accurate projections of your business’ cash flow, and let you better prepare for the year ahead. They can also make it easier to find the right investors . While it’s easier for existing businesses with plenty of data, you can still calculate a sales forecast for a new business .
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- How can you manage your forecasting?
A sales forecast is a prediction of your business’ future revenue. In order to be an accurate prediction, the forecast is based on previous sales, current economic trends, and industry performance. Having a sales forecast is a useful tool, because it gives you a better idea of how to manage your business.
Having a sales forecast is like using the past to have a peek into the future of your company. It might not be 100% accurate, but it can help you plan any future spending, or prevent any cash flow issues from occurring.
You can also use your sales forecast to monitor your business’ progress. For instance, if your business regularly performs better than your forecast, it could be a sign that your business is continuing to grow. On the other hand, if your actual sales are frequently less than expected, this could be a sign that your business is struggling and needs adjustment.
It’s important to remember that any projections you make aren’t guaranteed, there can be advantages and disadvantages of financial forecasting .
Now we’ve run through why having a sales forecast can help you run your business, let’s look at how to write one.
While there are two types of sales forecasting (top-down and bottom-up), one is a lot more accurate for small businesses than the other. A top-down forecast looks at the market as a whole and attributes a portion of the market to your business.
A top-down approach may work for large businesses that already own a significant chunk of the market. When forecasting for a small business, it’s easy to overestimate your market share. For example, a 1% market share may not seem like a lot, but a small restaurant owning 1% of the £89.5 billion UK market is extremely unrealistic.
The alternative to top-down is bottom-up. A bottom-up sales forecast starts with existing company data (like customer or product information) and works up to revenue. Since this starts with the company, it’s easier to
Your sales forecast is ultimately a prediction of your revenue over a set period. It considers the amount you think you’ll sell, and the cost of those sales. We’ve included how to calculate a sales forecast below.
A sales forecast consists of three separate values: revenue, cost of goods sold, and gross profit. For estimating values in the calculations below, it’s best to use any existing business data to be as accurate as possible.
To calculate your predicted revenue:
- Make a list of your available goods and services
- Note the price of each of your goods and services
- Estimate the expected sales of each good or service
- Multiply the price by the estimated sales to get your estimated revenue
- Add them all together to get your total revenue
For example, if your food truck business sold pizzas at £10 and burgers at £5, you would multiply these values by how much you expected to sell. For calculating a weekly sales forecast, you might estimate selling 60 pizzas and 80 burgers. Your predicted revenue for that week would be £600 for pizzas and £400 for burgers — giving £1,000 total.
In order to figure out how much profit you’ll make, you also need to calculate your costs for those predicted sales. To calculate your predicted costs:
- Figure out how much each good or service will cost per unit
- Multiply each cost by the projected sales
Using the same example as above, assume a single pizza cost £3.50 to make and a burger cost £2. Using the estimated sales, the total cost for your pizzas (3.5 x 60) would be £210, and £160 for your burgers (2 x 80). Combining these two figures gives you a total cost of £370.
The last step is to work out your gross profit , and it’s a relatively simple calculation.
- Subtract the total predicted cost from your total predicted revenue
Continuing with the example above, your revenue (£1,000) minus your costs (£370), leaves you with a projected gross profit of £630 for the week. Using this estimate, you can then plan how much working capital your business should have access to. It’s important to remember that these are only estimates, and your actual values can be higher or lower than your forecast.
If you want your forecasts to be as accurate as possible, you need to refer to all of your business’ financial data. Since collecting and collating this data can be challenging, you may want to use financial management software like the Countingup app.
When trying to calculate your sales forecasts, having an up-to-date log of your current sales can be hugely beneficial. By combining a business current account with accounting software, Countingup is the only software that provides real-time cash flow tracking.
The Countingup app also provides business owners with access to automatically generated profit and loss statements. These can prove invaluable when trying to stay aware of all your business’ costs.
Start your three-month free trial today. Find out more here .

- Counting Up on Facebook
- Counting Up on Twitter
- Counting Up on LinkedIn
Related Resources
How to throw a launch party for a new business.
So your business is all set up and you’re ready to launch in
How to set up a TikTok shop (2024)
TikTok can be an excellent platform for growing a business, big or small.
Best side hustle ideas to start in 2024 (UK Edition)
Looking to start a new career? Or maybe you’re looking to embrace your
10 key tips to starting a business in the UK
10 things you need to know before starting a business in the UK
How to Register A Company in the UK
There are over four million companies registered in the UK – could your
How to set up your business: Sole trader or limited company
If you’ve just started a business, you’ll likely be faced with the early
How to register as a sole trader
Running a small business and considering whether to register as a sole trader?
How to open a Barclays business account
When starting a new business, one of the first things you need to
6 examples of objectives for a small business plan
Your new company’s business plan is a crucial part of your success, as
How to start a successful business during a recession
Starting a business during a recession may sound like madness, but some big
What is a mission statement (and how to write one)
When starting a small business, you’ll need a plan to get things up
How does self-employment work?
The decision to become self-employed is not one to take lightly, and you
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books.
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Run » finance, how to create a financial forecast for a startup business plan.
Financial forecasting allows you to measure the progress of your new business by benchmarking performance against anticipated sales and costs.

When starting a new business, a financial forecast is an important tool for recruiting investors as well as for budgeting for your first months of operating. A financial forecast is used to predict the cash flow necessary to operate the company day-to-day and cover financial liabilities.
Many lenders and investors ask for a financial forecast as part of a business plan; however, with no sales under your belt, it can be tricky to estimate how much money you will need to cover your expenses. Here’s how to begin creating a financial forecast for a new business.
[Read more: Startup 2021: Business Plan Financials ]
Start with a sales forecast
A sales forecast attempts to predict what your monthly sales will be for up to 18 months after launching your business. Creating a sales forecast without any past results is a little difficult. In this case, many entrepreneurs make their predictions using industry trends, market analysis demonstrating the population of potential customers and consumer trends. A sales forecast shows investors and lenders that you have a solid understanding of your target market and a clear vision of who will buy your product or service.
A sales forecast typically breaks down monthly sales by unit and price point. Beyond year two of being in business, the sales forecast can be shown quarterly, instead of monthly. Most financial lenders and investors like to see a three-year sales forecast as part of your startup business plan.
Lower fixed costs mean less risk, which might be theoretical in business schools but are very concrete when you have rent and payroll checks to sign.
Tim Berry, president and founder of Palo Alto Software
Create an expenses budget
An expenses budget forecasts how much you anticipate spending during the first years of operating. This includes both your overhead costs and operating expenses — any financial spending that you anticipate during the course of running your business.
Most experts recommend breaking down your expenses forecast by fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs are things such as rent and payroll, while variable costs change depending on demand and sales — advertising and promotional expenses, for instance. Breaking down costs into these two categories can help you better budget and improve your profitability.
"Lower fixed costs mean less risk, which might be theoretical in business schools but are very concrete when you have rent and payroll checks to sign," Tim Berry, president and founder of Palo Alto Software, told Inc . "Most of your variable costs are in those direct costs that belong in your sales forecast, but there are also some variable expenses, like ads and rebates and such."
Project your break-even point
Together, your expenses budget and sales forecast paints a picture of your profitability. Your break-even projection is the date at which you believe your business will become profitable — when more money is earned than spent. Very few businesses are profitable overnight or even in their first year. Most businesses take two to three years to be profitable, but others take far longer: Tesla , for instance, took 18 years to see its first full-year profit.
Lenders and investors will be interested in your break-even point as a projection of when they can begin to recoup their investment. Likewise, your CFO or operations manager can make better decisions after measuring the company’s results against its forecasts.
[Read more: Startup 2021: Writing a Business Plan? Here’s How to Do It, Step by Step ]
Develop a cash flow projection
A cash flow statement (or projection, for a new business) shows the flow of dollars moving in and out of the business. This is based on the sales forecast, your balance sheet and other assumptions you’ve used to create your expenses projection.
“If you are starting a new business and do not have these historical financial statements, you start by projecting a cash-flow statement broken down into 12 months,” wrote Inc . The cash flow statement will include projected cash flows from operating, investing and financing your business activities.
Keep in mind that most business plans involve developing specific financial documents: income statements, pro formas and a balance sheet, for instance. These documents may be required by investors or lenders; financial projections can help inform the development of those statements and guide your business as it grows.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .

Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more finance tips
What is enterprise resource planning, choosing an enterprise resource planning tool for your small business, 10 benefits of erp systems for small businesses.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
- Professional Services
- Creative & Design
- See all teams
- Project Management
- Workflow Management
- Task Management
- Resource Management
- See all use cases
Apps & Integrations
- Microsoft Teams
- See all integrations
Explore Wrike
- Book a Demo
- Take a Product Tour
- Start With Templates
- Customer Stories
- ROI Calculator
- Find a Reseller
- Mobile & Desktop Apps
- Cross-Tagging
- Kanban Boards
- Project Resource Planning
- Gantt Charts
- Custom Item Types
- Dynamic Request Forms
- Integrations
- See all features
Learn and connect
- Resource Hub
- Educational Guides
Become Wrike Pro
- Submit A Ticket
- Help Center
- Premium Support
- Community Topics
- Training Courses
- Facilitated Services
What Is Business Forecasting? Why It Matters
April 25, 2021 - 10 min read
Companies conduct business forecasts to determine their goals, targets, and project plans for each new period, whether quarterly, annually, or even 2–5 year planning.
Forecasting helps managers guide strategy and make informed decisions about critical business operations such as sales, expenses, revenue, and resource allocation . When done right, forecasting adds a competitive advantage and can be the difference between successful and unsuccessful companies.
In this guide to business forecasting, we'll cover:
- What is business forecasting?
- What are the best forecasting techniques?
- Why forecasting in management is important
- How to conduct business forecasts
- A few forecasting examples for businesses
An introduction to business forecasting
What is business forecasting? Business forecasting is a projection of future developments of a business or industry based on trends and patterns of past and present data.
This business practice helps determine how to allocate resources and plan strategically for upcoming projects, activities, and costs. Forecasting enables organizations to manage resources , align their goals with present trends, and increase their chances of surviving and staying competitive.
The purpose of forecasts is to develop better strategies and project plans using available, relevant data from the past and present to secure your business's future . Good business forecasting allows organizations to gain unique, proprietary insights into likely future events, leverage their resources, set product team OKR , and become market leaders.
Managers conduct careful and detailed business forecasts to guarantee sound decision-making based on data and logic, not emotions or gut feelings.
What are important business forecasting methods?
There are several business forecasting methods. They fall into two main approaches:
- Quantitative forecasting
Qualitative forecasting
Quantitative and qualitative forecasting techniques use and provide different sets of data and are needed at different stages of a product's life cycle.
Note that significant changes in a company, such as new product focus, new competitors or competitive strategies, or changing compliance requirements diminish the connection between past and future trends. This makes choosing the right forecasting method even more important.
Quantitative business forecasting
Use quantitative forecasting when there is accurate past data available to analyze patterns and predict the probability of future events in your business or industry.
Quantitative forecasting extracts trends from existing data to determine the more probable results. It connects and analyzes different variables to establish cause and effect between events, elements, and outcomes. An example of data used in quantitative forecasting is past sales numbers.
Quantitative models work with data, numbers, and formulas. There is little human interference in quantitative analysis. Examples of quantitative models in business forecasting include:
- The indicator approach : This approach depends on the relationship between specific indicators being stable over time, e.g., GDP and the unemployment rate. By following the relationship between these two factors, forecasters can estimate a business's performance.
- The average approach : This approach infers that the predictions of future values are equal to the average of the past data. It is best to use this approach only when assuming that the future will resemble the past.
- Econometric modeling : Econometric modeling is a mathematically rigorous approach to forecasting. Forecasters assume the relationships between indicators stay the same and test the consistency and strength of the relationship between datasets.
- Time-series methods : Time-series methods use historical data to predict future outcomes. By tracking what happened in the past, forecasters expect to get a near-accurate view of the future.
Qualitative business forecasting is predictions and projections based on experts' and customers' opinions. This method is best when there is insufficient past data to analyze to reach a quantitative forecast. In these cases, industry experts and forecasters piece together available data to make qualitative predictions.
Qualitative models are most successful with short-term projections. They are expert-driven, bringing up contrasting opinions and reliance on judgment over calculable data. Examples of qualitative models in business forecasting include:
- Market research : This involves polling people – experts, customers, employees – to get their preferences, opinions, and feedback on a product or service.
- Delphi method : The Delphi method relies on asking a panel of experts for their opinions and recommendations and compiling them into a forecast.
How do you choose the right business forecasting technique?
- Choosing the right business forecasting technique depends on many factors. Some of these are:
- Context of the forecast
- Availability and relevance of past data
- Degree of accuracy required
- Allocated time to conduct the forecast
- Period to be forecast
- Costs and benefits of the forecast
- Stage of the product or business needing the forecast
Managers and forecasters must consider the stage of the product or business as this influences the availability of data and how you establish relationships between variables. A new startup with no previous revenue data would be unable to use quantitative methods in its forecast.
The more you understand the use, capabilities, and impact of different forecasting techniques, the more likely you will succeed in business forecasting.
Why is business forecasting important?
Any insight into the future puts your organization at an advantage. Forecasting helps you predict potential issues, make better decisions, and measure the impact of those decisions.
By combining quantitative and qualitative techniques, statistical and econometric models , and objectivity, forecasting becomes a formidable tool for your company.
Business forecasting helps managers develop the best strategies for current and future trends and events. Today, artificial intelligence, forecasting software, and big data make business forecasting easier, more accurate, and personalized to each organization.
Forecasting does not promise an accurate picture of the future or how your business will evolve, but it points in a direction informed by data, logic, and experiential reasoning.
What are the integral elements of business forecasting?
While there are different forecasting techniques and methods, all forecasts follow the same process on a conceptual level. Standard elements of business forecasting include:
- Prepare the stage : Before you begin, develop a system to investigate the current state of business.
- Choose a data point : An example for any business could be "What is our sales projection for next quarter?"
- Choose indicators and data sets : Identify the relevant indicators and data sets you need and decide how to collect the data.
- Make initial assumptions : To kickstart the forecasting process, forecasters may make some assumptions to measure against variables and indicators.
- Select forecasting technique : Pick the technique that fits your forecast best.
- Analyze data : Analyze available data using your selected forecasting technique.
- Estimate forecasts : Estimate future conditions based on data you've gathered to reach data-backed estimates.
- Verify forecasts : Compare your forecast to the eventual results. This helps you identify any problems, tweak errant variables, correct deviations, and continue to improve your forecasting technique.
- Review forecasting process : Review any deviations between your forecasts and actual performance data.
How do you do business forecasting?
Successful business forecasting begins with a collaboration between the manager and forecaster. They work together to answer the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the forecast? How will it be used?
- What are the components and dynamics of the system the forecast is focused on?
- How relevant is past data in estimating the future?
Once these answers are clear, choose the best forecasting methods based on the stage of the product or business life cycle, availability of past data, and skills of the forecasters and managers leading the project.
With the right forecasting method, you can develop your process using the integral elements of business forecasting mentioned above.
How do you get data for business forecasting?
A forecast is only as good as the data supplied. Before collecting data, ask:
- Why do you need it?
- What kind of data do you need?
- When will you collect it?
- Where will you gather it?
- Who is in charge of collecting it?
- How will you collect it?
- How will you analyze it?
When you have these answers, you can start collecting data from two main sources:
- Primary sources : These sources are gathered first-hand using reporting tools — you or members of your team source data through interviews, surveys, research, or observations.
- Secondary sources : Secondary sources are second-hand information or data that others have collected. Examples include government reports, publications, financial statements, competitors' annual reports, journals, and other periodicals.
Business forecasting examples
Some forecasting examples for business include:
- Calculating cash flow forecasts, i.e., predicting your financial needs within a timeframe
- Estimating the threat of new entrants into your market
- Measuring the opportunity of developing a new product or service
- Estimating the costs of recurring bills
- Predicting future sales growth based on past sales performance
- Analyzing relationships between variables, e.g., Facebook ads and potential revenue
- Budgeting contingencies and efficient allocation of resources
- Comparing customer acquisition costs and customer lifetime value over time
What are the limits of business forecasting?
You can follow the rules, use the right methods, and still get your business forecast wrong. It is, after all, an attempt to predict the future. Some limits to business forecasting include:
- Biases and errors by the forecasters or managers
- Incorrect information from employees, experts, or customers
- Inaccurate past numbers
- Sudden change in market conditions
- New industry regulations
How Wrike helps with business forecasting
The more accurate your business forecasting, the more effective your strategies and plans can be. While many things in business are out of your control, having an informed forecast of what lies ahead makes you prepared and confident about the future.
Wrike helps gather data in one central platform, extract insights, and communicate findings with forecasters and managers. Other benefits of Wrike include real-time data, integrations with other forecasting software, streamlined collaboration, and visibility into every business forecasting project.
Are you ready to make projections for your business, allocate your resources for the best results, and improve your business forecasting process? Get started with a two-week free trial of Wrike today.
Kelechi Udoagwu
Kelechi is a freelance writer and founder of Week of Saturdays, a platform for digital freelancers and remote workers living in Africa.
Related articles

Strengthen and Optimize Agency Resource Management
Improve your agency’s resource management processes and learn how Wrike boosts performance across the board with our robust project management software.

Release Management: Definition, Phases, and Benefits
What is release management and how can it improve software development strategy? In this guide, we talk about release management processes and their benefits.

The Definitive Guide to Data-Driven Marketing
Wondering what data-driven marketing is and how to reap its benefits for your business? Find out how to create your own data-driven strategy with our guide.

Get weekly updates in your inbox!
You are now subscribed to wrike news and updates.
Let us know what marketing emails you are interested in by updating your email preferences here .
Sorry, this content is unavailable due to your privacy settings. To view this content, click the “Cookie Preferences” button and accept Advertising Cookies there.
The Last Guide to Sales Forecasting You’ll Ever Need: How-To Guides and Examples
By Kate Eby | January 26, 2020 (updated August 26, 2021)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
Sales forecasts are a critical part of your business planning. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn how to do them correctly, including explanations of different forecasting methods, step-by-step tutorials, and advice from experienced finance and sales leaders.
Included on this page, you'll find details on more than 20 sales forecasting techniques , information regarding how to forecast sales for new businesses and products , a step-by-step guide on how to forecast sales , and a free sales forecast template .
What Is Sales Forecasting?
When you produce a sales forecast , you are predicting what your sales or revenue will be in the future. An accurate sales forecast helps your firm make better decisions and is arguably the most important piece of your business plan.
A sales forecast contrasts with a sales goal . The former is the realistic representation of what you believe will occur, while the latter is what you want to occur. Forecasts are never perfectly accurate, but you should be as objective as possible when creating a sales forecast. Goals, on the other hand, can be based on optimistic or motivational targets.
Because the sales forecast is critical to business planning, many different stakeholders in a company (beyond sales managers and representatives) rely on these estimates, including human resources planners, finance directors, and C-level executives.
In this article, you’ll learn about different sales forecasting methods with varying levels of sophistication. The most basic method is called naive forecasting , which uses the prior period’s actual sales for the new period’s forecast and does not apply any adjustments for growth or inflation. Naive forecasts are used as comparative figures for more robust methods.
What Is Sales Planning?
A sales plan describes the goals, strategies, target customers, and likely hurdles for your sales effort. The sales plan defines your sales strategy and the method of execution you will use to achieve the numbers in your sales forecast.
Overview of Sales Forecasting Steps
Your sales forecasting model can ultimately become very sophisticated, but to grasp the basics, you should first gain a high-level understanding of what is involved. There are three primary steps to getting started:
- Decide which forecasting method or technique you will use. Also, determine the time period for your forecast. Later in this guide, we will review different methods of forecasting sales, including how to know which is best for your business.
- Gather the data to plug into your forecast model. The data points will vary by method, but will almost always include your actual past sales and current growth rate.
- Pick a tool to support your forecasting effort. For learning purposes, you can start with pencil and paper, but soon after, you’ll want to take advantage of digital solutions. Common tools include spreadsheets, accounting software, and customer relationship management (CRM) or sales management solutions.
As you get going, remember not to be overly focused on complex formulas. Do regular reality checks to make sure your sales forecasts accord with common sense. Bounce forecasts off sales reps to get realistic feedback, and revise.
You will likely achieve greater accuracy if you build your forecasts based on unit sales wherever possible, because pricing can move independently from unit sales. Use data if you have it.
Benefits and Importance of Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting helps your business by giving you data to make decisions concerning allocating resources, assigning staff, and managing cash flow and overhead. Using this data reduces your risk and supports your growth.
Your sales forecast enables you to predict both short and long-term performance and customer demand for your product. In the short term, having a sales forecast makes it easy for you to spot when actual sales are not meeting estimates and gives you an opportunity to make corrections early in the period.
The forecast guides how much you spend on marketing and administration, and the projections generate your sales reps’ objectives. In this way, sales forecasts are an important benchmark for gauging the performance of your sales reps.
Sales forecasts also lead to better management of inventory levels. With a good idea of how much product you will sell, you can stock enough to meet customer demand without missing any sales and without carrying more than you need. Excess inventory ties up capital and reduces profit margins.
In the long term, sales forecasts can help you prepare for changes in your business. For example, you might see that within a few years, your company will require more manufacturing capacity to meet growing sales. To expand capacity, you may need to build a new factory, so now you can start planning how you will pay for it. Predictive sales forecasting is a critical part of your presentation if you are seeking equity capital from investors or commercial loans for expansion.
In short, sales forecasting helps your business avoid surprises, so you aren’t making decisions in a crisis environment. Companies with trustworthy sales forecasts see a 10 percentage point greater increase in annual revenues compared to counterparts without, according to research from the Aberdeen Group .
What Makes a Good Sales Forecast?
The most important quality for a sales forecast is accuracy. But, the benefits of accuracy must be weighed against the time, effort, and expense of the forecasting technique.
Useful sales forecasts are also easily understood and often include visual elements, such as charts, graphs, and tables, to make important trends visible.
Ideally, you can quickly build a highly reliable sales forecast with simple, economical methods. The ultimate forecast method would automatically (i.e., without manual intervention) fetch the relevant data and make predictions using an algorithm finely tuned to your business.
In reality, the forecasting process is more time consuming and subjective. Sales forecasts often depend on reps’ assessments of how likely their prospects are to close, and perceptions vary widely. (A conservative rep’s 60 percent probability may be understated, while another rep’s 60 percent may be overly optimistic.)
Sales managers, who are usually responsible for forecasting, spend a lot of time factoring in these nuances and other market factors when calculating forecasts.
Surprisingly, spending more time on forecasting does not always improve accuracy. According to research from CSO Insights, sales managers who spend 15 to 20 percent of their time producing their forecast had win rates for approximately 46.5 percent of deals. But, when they spend more than 20 percent of their time on forecasting, the win rate declined by more than two percentage points.
An axiom of forecasting is that accuracy is highest during time periods that are close at hand and lowest during those that are far into the future. Short-term forecasts draw upon the following: deals that are already in the sales pipeline, the current economic environment, and actual market trends. So, the data underlying short-term forecasts is more reliable.
Forecasting for distant time periods requires bigger guesses about opportunities, demand, competitor activity, and product trends, so it makes sense that the forecast becomes less accurate the further into the future you go. (This concept applies to many companies, especially those that are young and growing; the concept becomes more relevant for all businesses at three years and beyond.) Bear this thought in mind when you look at your sales forecast in order to make long-term decisions.
Sales Forecasting Methods: Qualitative and Quantitative
Sales forecasting methods break down broadly into qualitative and quantitative techniques. Qualitative forecasts depend on opinions and subjective judgment, while quantitative methods use historical data and statistical modeling.
Qualitative Methods for Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting often uses five qualitative methods. These are based on different ways of generating informed opinions about sales prospects. Creating and conducting these kinds of surveys is often expensive and time intensive. These five qualitative methods include the following:
- Jury of Executive Opinion or Panel Method: In this method, an executive group meets, discusses sales predictions, and reaches a consensus. The advantage of this method is that the result represents the collective wisdom of your most informed people. The disadvantage is that the result may be skewed by dominant personalities or the group may spend less time reflecting.
- Delphi Method: Here, you question or survey each expert separately, then analyze and compile the results. The output is then returned to the experts, who can reconsider their responses in light of others’ views and answers. You may repeat this process multiple times to reach a consensus or a narrow range of forecasts. This process avoids the influence of groupthink and may generate a helpful diversity of viewpoints. Unfortunately, it can be time consuming.
- Sales Force Composite Method: With this technique, you ask sales representatives to forecast sales for their territory or accounts. Sales managers and the head of sales then review these forecasts, along with the product owners. This method progressively refines the views of those closest to the customers and market, but may be distorted by any overly optimistic forecasts by sales reps. The composite method also does not take into account larger trends, such as the political or regulatory climate and product innovation.
- Customer Surveys: With this approach, you survey your customers (or a representative sample of your customers) about their purchase plans. For mass-market consumer products, you may use market research techniques to get an idea about demand trends for your product.
- Scenario Planning: Sales forecasters use this technique most often when they face a lot of uncertainty, such as when they are estimating sales for more than three years in the future or when a market or industry is in great flux. Under scenario planning, you brainstorm different circumstances and how they impact sales. For example, these scenarios might include what would happen to your sales if there were a recession or if new duties on your subcomponents increased prices dramatically. The goal of scenario planning is not to arrive at a single accepted forecast, but to give you the opportunity to counter-plan for the worst-case scenarios.
Quantitative Methods for Sales Forecasting
Quantitative sales forecasting methods use data and statistical formulas or models to project future sales. Here are some of the most popular quantitative methods:
- Time Series: This method uses historical data and assumes history will repeat itself, including seasonality or sales cycles. To arrive at future sales, you multiply historical sales by the growth rate. This method requires chronologically ordered data. Popular time-series techniques include moving average, exponential smoothing, ARIMA, and X11.
- Causal: This method looks at the historical cause and effect between different variables and sales. Causal techniques allow you to factor in multiple influences, while time series models look only at past results. With causal methods, you usually try to take account of all the possible factors that could impact your sales, so the data may include internal sales results, consumer sentiment, macroeconomic trends, third-party surveys, and more. Some popular causal models are linear or multiple regression, econometric, and leading indicators.
Sales Forecasting Techniques with Examples
In reality, most businesses use a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods to produce sales forecasts. Let’s look at the common ways that companies put sales forecasting into action with examples.
Intuitive Method
This forecasting method draws on sales reps’ and sales managers’ opinions about how likely an opportunity is to close, so the technique is highly subjective. Estimates from reps with a lot of experience are likely to be more accurate, and the reliability of the forecast requires reps and managers to be realistic and honest.
This method can be especially helpful if you do not have historical data or if you are assessing new prospects early in your funnel. In these cases, a rep’s gut feeling after initial contact can be a good indicator. If you are a manager, you will review reps’ estimates with an eye for any outliers and work with those reps to make any necessary adjustments.
Here is an example of the intuitive method in action: You manage a team of four sales reps. You go to each one and inquire about the leads they are nurturing. You ask each rep which opportunities they believe they will win in the next quarter and how much those sales will be worth. John, your strongest rep, tells you $175,000. Alice, another strong performer, says $115,000. Bob, who is in his second year at your company, reports $85,000. Jennifer, a recent college graduate, projects $100,000. You calculate the total of those forecasts and arrive at an intuitive forecast of $450,000. However, you suspect Jennifer’s forecast is unrealistic, because she is inexperienced, so you ask her more questions. Based on what you learn, you decide that only half of Jennifer’s deals are likely to close, so you reduce her contribution to $50,000 and revise your total quarterly forecast to $400,000.
Scenarios Method
Scenario forecasts are qualitative and involve you projecting sales outcomes based on a variety of assumptions. This process can also be a helpful business planning exercise, because once you identify major risks or uncertainty for your company, you can develop action plans to deal with these circumstances if they arise.
Scenario forecasts require an in-depth knowledge of your business and industry, and the quality of the forecast will vary with the expertise of the person or group who prepares the estimate.
To create a scenario forecast, think about the key factors that affect sales, external forces that could influence the outcome, and major uncertainties. Then, write a narrative and numerical description of how the scenario would play out under various combinations of these key factors, external forces, and uncertainties.
Here is an example of the scenarios method in action: Your company sells components for military vehicles. You notice that the most impactful things your sales reps do are meeting with procurement officers in the defense departments of major nations and holding factory tours and product demonstrations for them. These are your key factors.
The external forces are the number of tenders or requests for proposals that military procurement departments announce, and the value of those items. The risk of conflict in various parts of the world, scarcity of your raw materials, and trends in budget authorizations for defense by major countries are your critical uncertainties.
You look at how your key factors, external factors, and major uncertainties might combine. One scenario might entail the outcome if your reps increased the number of meetings and product events by 20 percent, the value of U.S. tenders launched rose by six percent, and France decreased defense spending by two percent.
Under this scenario, you might forecast a six percent increase in unit sales resulting from the following:
- Having more in-person sales contacts should boost sales by five percent based on past performance.
- You can increase revenue by three percent due to greater U.S. tender opportunities and your current market share.
- Major customer France will not purchase anything, reducing sales by two percent.
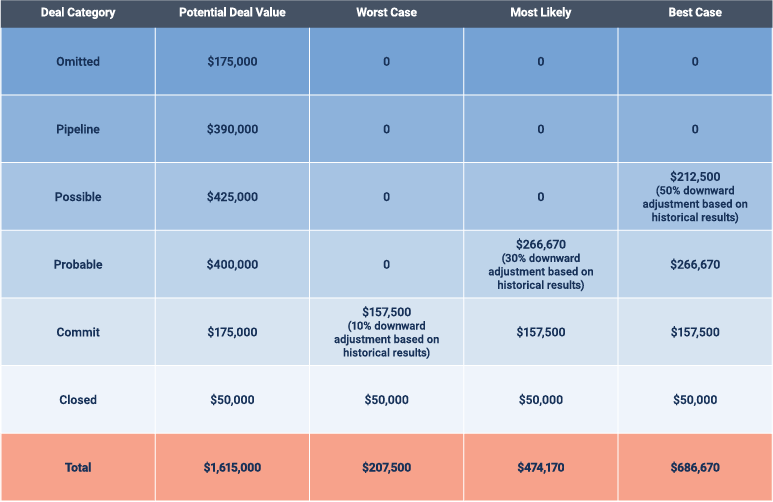
Sales Category Method
The category forecasting method looks at the probability that an opportunity will close and divides opportunities into groups based on this probability. The technique relies somewhat on intuition, as does the intuitive method, but the sales category method brings more structure and discipline to the process.
The categories that each company uses vary widely, but they correspond broadly to stages in the sales pipeline. These are some typical labels and definitions:
- Omitted: The deal has been lost or the prospect is no longer engaging.
- Pipeline: The opportunity will not realistically close during the quarter.
- Possible, Best Case, Upside, or Longshot: There is a realistic possibility that the deal could close at the projected value in the quarter if everything falls into place, but this is not certain. Overall, fewer than half of the opportunities in this group end up closing in the quarter at the planned value.
- Probable or Forecast: The sales rep is confident that the deal will close at the planned value in the quarter. Most of these opportunities will come to fruition as expected.
- Commit or Confident: The salesperson is highly confident that the deal will close as expected in this quarter, and only something extraordinary and unpredictable could derail it. The probability in this category is 80 to 90 percent. Any deal that does not close as forecast should generally experience only a short, unanticipated delay, rather than a total loss.
- Closed: The deal has been completed; payment and delivery have been processed; and the sale is already counted in the quarter’s revenue.
To compile your forecast, look at the combined value of the potential deals in the categories under three scenarios:
- Worst Case: This is the minimum value you can anticipate, based on the closed and committed deals. If you have very good historical data for your sales reps and categories and feel confident making adjustments, such as counting a portion of probable deals, you may do so, but it is important to be consistent and objective.
- Most Likely: This scenario is your most realistic forecast and looks at closed, committed, and probable deal values, again with possible adjustments based on historical results. For example, if you have tracked that only 60 percent of your probable deals tend to close in the quarter, adjust their contribution downward by 40 percent.
- Best Case: This is your most optimistic forecast and hinges on executing your sales process perfectly. You count deals in the closed, commit, probable, and possible categories, with adjustments based on past performance. The possible category, in particular, requires a downward adjustment.
As the quarter or period progresses, you revise the forecast based on updated information. This method can quickly get cumbersome and time consuming without an analytics solution.
Here is an example of the sales category method in action: You interview your sales team and get details from the reps on each deal they are working on. You assign the opportunities to a category, then make adjustments for each scenario based on past results. For example, you see that over the past three years, only half the deals in the possible category each quarter came to fruition. Here’s what the forecast looks like:
Top-Down Sales Forecasting
In top-down sales forecasting, you start by looking at the size of your entire market, called the total addressable market (TAM), and then estimate what percentage of the market you can capture.
This method requires access to industry and geographic market data, and sales experts say top-down forecasting is vulnerable to unrealistic objectives, because expectations of future market share are often largely conjecture.
Here is an example of top-down sales forecasting in action: You operate a new car dealership in San Diego County, California. From industry and government statistics, you learn that in 2018, 112 dealers sold approximately 36,000 new cars and light trucks in the county. You represent the top-selling brand in the market, you have a large sales force, and your dealership is located in the most populous part of the county. You estimate that you can capture eight percent of the market (2,880 vehicles). The average selling price per vehicle in the county last year was $36,000, so you forecast gross annual sales of $103.7 million. From there, you determine how many vehicles each rep must sell each month to meet that mark.
Bottom-Up Sales Forecasting
Bottom-up sales forecasting works the opposite way, by starting with your individual business and its attributes and then moving outward. This method takes account of your production capacity, the potential sales for specific products, and actual trends in your customer base. Staff throughout your business participates in this kind of forecasting, and it tends to be more realistic and accurate.
Begin by estimating how many potential customers you could have contact with in the period. This potential quantity of customers is called your share of market (SOM) or your target market . Then, think about how many of those potential customers will interact with you. Then, make an actual purchase.
Of those who do purchase, factor in how many units of your product they will buy on average and then how much revenue that represents. If you aren’t sure how much your customers will spend, you can interview a few.
Here is an example of bottom-up sales forecasting in action: Your firm sells IT implementation services to mid-sized manufacturers in the Midwest. You have a booth at a regional trade show, and 3,000 potential customers stop by and give you their contact information. You estimate that you can engage 10 percent of those people in a sales call after the trade show and convert 10 percent of those calls into deals. That represents 30 sales. Your service packages cost an average of $250,000. So, you forecast sales of $7.5 million.
Market Build-Up Method
In the market build-up method, based on data about the industry, you estimate how many buyers there are for your product in each market or territory and how much they could potentially purchase.
Here is an example of the market build-up method in action: Your company makes safety devices for subways and other rail transit systems. You divide the United States into markets and look at how many cities in each region have subways or rail. In the West Coast territory, you count nine. To implement your product, you need a device for each mile of rail track, so you tally how many miles of track each of those cities have. In the West Coast market, there are a total of 454 miles of track. Each device sells for $25,000, so the West Coast market would be worth a total $11.4 million. From there, you would estimate how much of that total you could realistically capture.
Historical Method
The historical sales forecasting technique is a classic example of the time-series forecasting that we discussed under quantitative methods.
With historical models, you use past sales to forecast the future. To account for growth, inflation, or a drop in demand, you multiply past sales by your average growth rate in order to compile your forecast.
This method has the advantage of being simple and quick, but it doesn’t account for common variables, such as an increase in the number of products you sell, growth in your sales force, or the hot, new product your competitor has introduced that is drawing away your customers.
Here is an example of the historical method in action: You are forecasting sales for March, and you see that last year your sales for the month were $48,000. Your growth rate runs about eight percent year over year. So, you arrive at a forecast of $51,840 for this March.
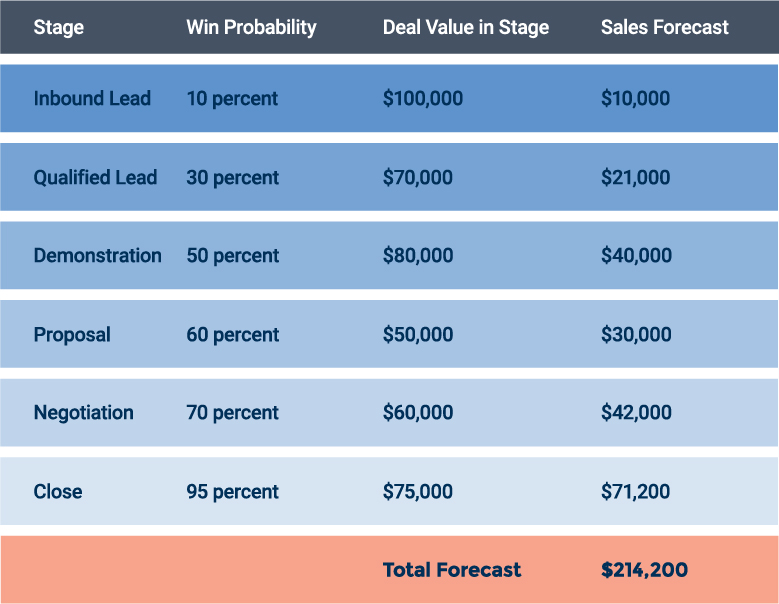
Opportunity Stage Method
The opportunity stage technique is popular, especially for high-value enterprise sales that require a lot of nurturing. This method entails looking at deals in your pipeline and multiplying the value of each potential sale by its probability of closing.
To estimate the probability of closing, you look at your sales funnel and historical conversion rates from top to bottom. The further a deal progresses through the stages in your funnel or pipeline, the higher likelihood it has of closing.
The strong points of this method are that it is straightforward to calculate and easy to do with most CRM systems.
But, opportunity-stage forecasting can be time consuming.
Moreover, this method doesn’t account for the unique characteristics of each deal (such as a longtime repeat customer vs. a new prospect). In addition, the deal value, stage, and projected close date have to be accurate and updated. And, the age of the potential deal is not reflected. This method treats a deal progressing quickly through the stages of your pipeline the same as one that has stalled for months.
If your sales process, products, or marketing have changed, the use of historical data may make this method unreliable.
Here is an example of the opportunity stage method in action: Say your sales pipeline comprises six stages. Based on historical data, you calculate the close probability at each stage. Then, to arrive at a forecast, you look at the potential value of the deals at each stage and multiply them by the probability.
Length-of-Sales-Cycle Method
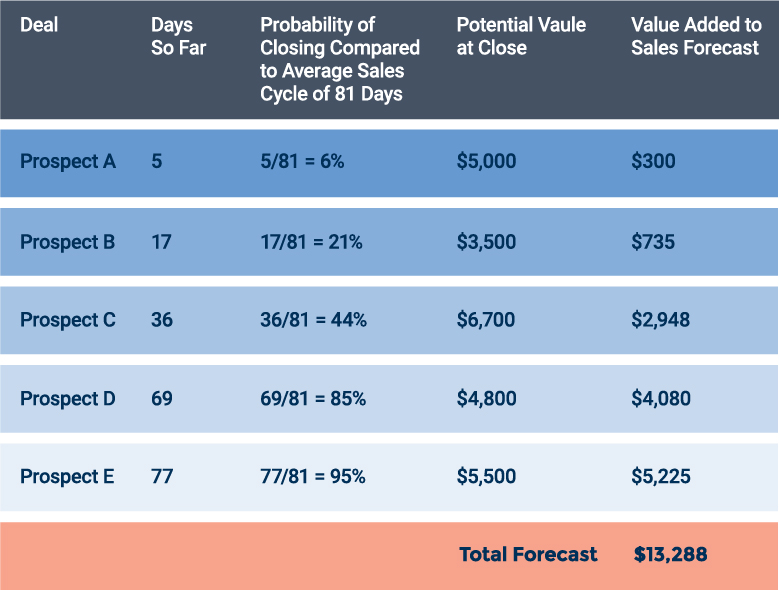
This is another quantitative method that shares some similarities with the deal stage method. However, this model looks at the length of your average sales cycle.
First, determine the average length in days of your sales process. This figure is also known as time to purchase or sales velocity . Add the total number of days it took to close all of the past year’s deals and divide by the number of deals. Then, calculate the probability of new deals closing in a certain period of time as a percentage of the average sales cycle length.
With this method, the biases of individual reps are less of a factor than with the deal stage model. Also, with this technique, you can fine-tune the probabilities for different lead types. (For example, prospects referred by current customers may close in an average of 27 days, while prospects who make contact after an online search need an average of 62 days.) But, this technique requires you to know and record how and when prospects enter your pipeline, which can be time intensive.
Here is an example of the length-of-sales-cycle method in action: You review the 37 deals your company won last year and see that they took a total of 2,997 days to close. To calculate the average length of the sales cycle, you divide 2,997 by 37 and see that the average sales cycle lasted 81 days. You then look at the five deals currently in your pipeline.
Lead Scoring Method
This technique requires you to have lead scoring in place. With lead scoring, you profile your ideal customers based on attributes (like industry, size, and location) as well as behavior (such as whether they have recently raised capital or whether the contact person has requested a demonstration of your product).
You then classify future leads based on how closely they match your ideal customer. You can label the categories with distinctions such as A, B, or C or hot, warm, or cold, or you can assign numbers up to one hundred using formulas that add and subtract points for different attributes and behaviors. (For example, “They requested a demo, which adds 15 points, but they are not in your ideal industry, which subtracts 10 points.”)
To create your forecast, you then look at the historical close rate for leads in each category and multiply that by the value of the opportunities currently in the group.
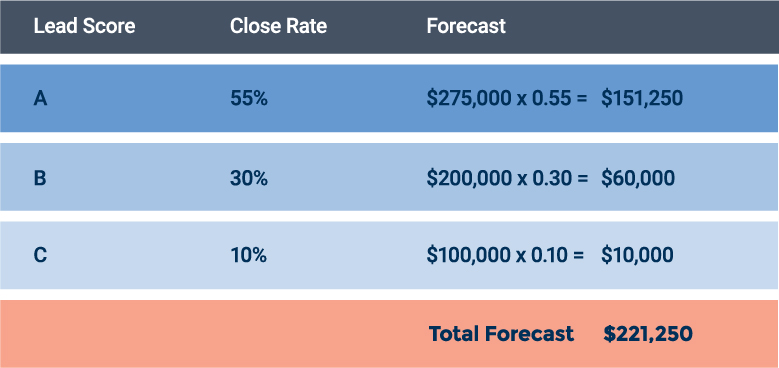
Here is an example of the lead scoring method in action: Your company sells textbooks for advanced math and science. Your ideal customer is a university with at least 25,0000 students that has an engineering school and is located on the east coast. These are your A prospects. B prospects have at least 10,000 students. C prospects have at least 10,000 students, but are located elsewhere in the country.
You then look at the close rates and potential deal values for each lead score. Finally, you multiply the close rate by the potential value of the deals in the category or by your average sales value.
Lead Source Method
This model forecasts future sales based on how you acquired the lead, using the behavior of previous leads as a benchmark.
For example, say your company sells a software application. Some leads come from search traffic to your website; some originate with demonstration requests at conferences, and some are referrals from existing customers.
Look at your historical data to track the percentage of leads who converted to sales for each lead source. In addition, calculate the average value of a sale for each source. Then, by using the conversion probability and sales values, you can forecast the sales that the leads at the top of your funnel are likely to generate.
Here is an example of the lead source method in action: Based on source, you compile your historical data and discover the following conversion rates and sales value for leads.
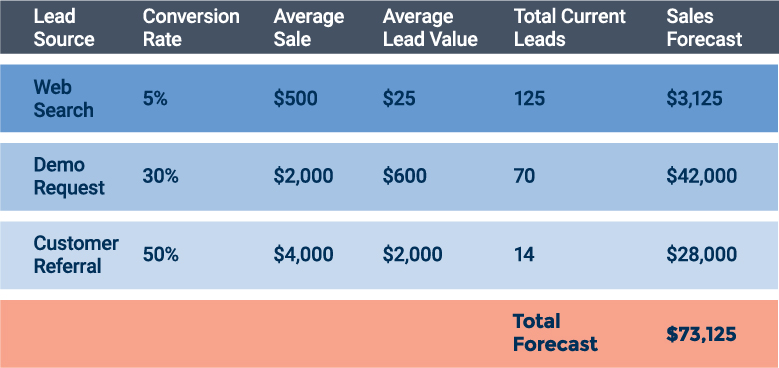
One advantage of this sales forecasting method is that you can project how many leads of each type you would need to generate in order to hit a target. Suppose you have a conference coming up where participants will be able to request demonstrations of your product, and you would like to win an additional $30,000 in sales from the demo leads. Based on the average lead value of $600, you know you will want to generate 50 leads who request demos at the conference.
One drawback to lead source forecasting is that the method does not account for potential differences in the length of the sales cycle for the lead types. That makes it difficult to pinpoint the period in which the revenue will occur. Therefore, you should do a separate analysis of time to purchase in order to allocate sales to the right period.
Another challenge is that sometimes you may not be sure of the lead source. For example, suppose that another customer has recommended your product to a contact and that that contact decides to first check you out on your website. You might very well assign a lower lead value to this prospect, assuming they will behave like our web-originated leads, when, in reality, they will probably behave more like the customer referral leads.
Lastly, remember that this method won’t account for changes in your marketing or pricing that influence conversion rates and customer behavior.
Sales by Row Method
This method is a good fit for small businesses that sell different products or services. Rather than forecasting sales for each individual product type, you project sales for categories.
Each row in your forecast will cover different physical products (such as pick-up trucks, heavy trucks, and delivery vans) and service units (such as hours of labor or service types like replacing a faucet, unclogging a drain, or installing a toilet).
You can employ this method to forecast units and then factor them by average prices to arrive at revenue. Or, you can look exclusively at revenue. If you sell a subscription service, you can calculate recurring revenue for each product type.
For each row, you would look at how much you sold in the same period a year earlier and then adjust for factors such as inflation, organic growth, new products, increased workforce, or special circumstances.
Here is an example of the sales by row method: You operate a combination fuel station and mini-market. Your forecast would cover the broad categories of your business, such as sales of gasoline, diesel, food, beverages, and sundries.
For March’s forecast, you take into account that the new housing development near your business, which was under construction last year, is now almost completely sold and that there are many more commuters filling up. Your gas sales have been growing by almost 15 percent year over year. Also, in March, there will be a special event at the nearby fairgrounds that could draw thousands of additional vehicles to your area.
On the downside, a new retail complex with a full-service grocery store has opened nearby, so your sales of food and drinks have slipped. Also, increased congestion in the neighborhood has caused some long-haul truckers who used to stop for fuel to reroute.
Regression or Multivariable Analysis Method
Regression or multivariable analysis is one of the most sophisticated forecasting methods, and allows you to build a custom model combining any factors that you feel are relevant to your sales.
For regression analysis, you need accurate historical data on all the variables under consideration, expertise in statistics, and, for practical purposes, an analytics solution or application that can perform the analysis.
Because this method incorporates a multitude of influences on your sales, the resulting forecast is the most accurate. But, the costs tend to be high because of the data collection, expertise, and technology requirements.
Regression analysis looks at the dependent variable (the factor that you are trying to predict, in this case, the amount of future sales) and independent variables (the factors that you believe affect sales results, such as opportunity stage or lead score).
In a simple example, you would create a chart, plotting the sales results on the Y axis and the independent variable on the X axis. This chart will reveal correlations. If you draw a line through the middle of the data points, you can calculate the degree to which the independent variable affects sales.
This line is called the regression line , and, by calculating the slope of the line, you can use numbers to represent the relationship between the variable and sales. The equation for this is Y = a + bX. Excel and other software will perform this analysis and calculate a and b for you. In more sophisticated applications, the formula will also include a factor for error to account for the reality that other variables are also at work.
Going further, you can look at how multiple variables interplay, such as individual rep close rate, customer size, and deal stage. Making these kinds of calculations becomes increasingly difficult with simple charts and demands more advanced math knowledge.
Remember that correlation is not the same as causation. Bear in mind that while two variables may seem closely related to each other, the reality may be more subtle.
Here is an example of the regression method in action: You want to look at the relationship between the amount of time a prospect has progressed in your sales cycle and the probability of the deal closing.
So, plot on a chart the probability of close for past deals when they were at various stages of your sales cycle, which lasts an average of 100 days. Deals early in the sales cycle have a low probability of closing compared to those that occur in the later stages of negotiation and contract signing on day 85 and up. (Be sure to eliminate any prospects that stall or disengage at any stage.)
By drawing a line through those points (i.e., the intersection between the sales close probability and the percentage of the average sales cycle), you can see that there is a nearly one-to-one relationship between percentage point increases in time elapsed relative to the average sales cycle and percentage point increases in the probability of closing.
This calculation becomes more complex when you consider multiple variables. Let’s say you have two sales reps working with prospects. Gloria, your best closer, is giving a product demonstration to a new Fortune 500 account. Leonard, a strong performer, whose close rate is a little lower than Gloria’s, is negotiating with a repeat customer, a mid-sized company.
Your multivariable analysis of these situations could take into account each rep’s average close rate for an opportunity, given the following factors: the specific stage; deal size; time left in the period; probability of close for a repeat customer versus a new customer; and time to close for an enterprise customer with more than 10 people involved in decision making versus a mid-sized business with a single decision maker.
Time Horizons in Sales Forecasting
Choosing the time period for your sales forecast is an important step. Depending on your business, the purpose of your forecast, and the resources you can devote to making forecasts, the time frame you target will vary.
A short-term forecast will help set sales rep bonus levels for next quarter, but you need a long-term forecast to decide whether you should plan to build a new factory. A startup that has been doubling revenue every year will have more difficulty making a 20-year forecast than a century-old concern in a mature industry. Here are the three time frames for forecasts:
- Short-Term Forecasts: These cover up to a year and can include monthly or quarterly forecasts. They help set production levels, sales targets, and overhead costs.
- Medium-Term Forecasts: These range from one to four years and guide product development, workforce planning, and real estate needs.
- Long-Term Forecasts: These extend from five to 20 years and inform capital investment, capacity planning, long-range financing programs, succession planning, and workforce skill and training requirements.
Getting Started with Sales Forecasting: What You Need to Know
Regardless of the sales forecast method you use, you generally need to have certain pieces of information and conditions in place. These include the following:
- Well-Documented and Defined Sales Process: You need to understand your customer journey and have an established sequence for nurturing each prospect. Without this, you cannot predict which opportunities are getting closer to purchasing. This structure creates accountability.
- Consensus on Pipeline Stages: Your sales team needs to have a clear and shared understanding of what you mean by lead, prospect, qualified, possible, probable, committed, and other relevant terms.
- Definition of Success: Communicate clearly what your sales team is striving for in terms of sales quotas or goals; include these quotas and goals for each individual rep, for the team as a whole, and for conversion through each stage of your pipeline.
- Historical Data: You require benchmarks for data points, such as average time to close, conversion rates, average deal size, lifetime customer value, win-loss ratio, and seasonal sales trends. These sales metrics and KPIs are often critical pieces of your forecast.
- Current Status: Up-to-date knowledge of your pipeline is essential, including how many opportunities are at each stage and the potential value of these sales.
- Forecasting Tools: This will almost always include a CRM application and may also include financial management or accounting software, analytics solutions, and spreadsheets.
Influences and Assumptions in Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting should not happen in a vacuum. Take into account changes in the business environment and question assumptions, such as that past growth will continue. Also, be sure to factor in your ideas about global economic trends and competitor behavior.
Here are some common factors to consider regarding your sales forecast. Many of these can have either a positive or negative influence on sales. For example, changing reps’ account assignments may reduce sales, because members of your team will have to familiarize themselves with customers that are new to them. However, sales could increase if your new hotshot gets your biggest opportunity.
- Economic Trends: Inflation, growth, consumer sentiment, risk appetite, and purchasing power
- Regulation: Trade policies such as tariffs, duties, and quotas; health, safety, and environmental rulings on products or processes; court decisions; intellectual property disputes; and competition policy
- Seasonal Trends: Cyclical demand fluctuation, production patterns, and variation in raw material availability
- Competitor Behavior: New product innovations, pricing changes, and market entries and exits
- Business Economics: Selling prices, direct prices, unit costs, gross margins, and the impact of accrual versus cash accounting on when you can book a sale
- Staffing and Compensation: Hiring or firing new reps, changes in leadership, policies on commissions and bonuses, and training
- Territory Management: Redrawing of territories and changes in account assignments
- Products and Services: Product lifecycle, new products and services, user experience, defects, ticket resolution, changes in distribution, and market entries and exits
- Marketing: Demand generation, advertising, pricing, special campaigns, social media activity, and prospecting
Sales Forecasting for New Businesses and Products
If you are starting a new business or launching a new product, your sales forecasts are crucial because they will determine how much you can spend in order to break even. However, when dealing with a new entity, you lack the advantage of historical data, which you need for almost every forecasting technique.
If you don’t have historical data, you can use industry benchmarks from trade publications, industry associations, and consultants. For example, if you are launching a new recipe app, look at market research on how other cooking apps have performed.
Dining establishments can look at number of tables, hours of service, and menu prices to estimate average order amounts and table turnover. Retail outlets use square feet, foot traffic, and average selling prices to forecast sales.
If you are adding a new product to your line, you can forecast sales by looking at how your most similar existing product performed at launch. Then, you can make tweaks based on other relevant information, such as that the new product is harder to master than its predecessor, that it is a later entrant into a crowded space, or that it already has a backlog of orders before launch.
New service businesses can base forecasts on capacity, such as number of staff and service hours and how much to charge for the most popular services. Once you have this data, you can make adjustments accordingly.

Michael Barbarita, President of Next Step CFO , works as a contracted CFO to produce sales forecasts for companies. He likes to tie the sales forecast for service businesses to a metric called sales per direct labor hour , which you can calculate this by dividing sales by the working hours of people in the field performing customer work. For example, an electrical contractor would calculate the sales per direct labor hour of its electricians and multiply that figure by the number of electricians and the hours they work.
For instance, you may decide that operating at half capacity is a good estimate for your first six months in business. Then, you may operate at three-quarters capacity for the second six months. Therefore, you would multiply maximum capacity by average revenue and then multiply that resulting figure by 0.50 and 0.75, respectively.
Quick-Start: Sales Forecasting Formulas
If you are eager to dive in and want to generate some simple sales forecasts, you can make use of basic equations. Here are a few easy ones:
- Simple Forecast with No Organic Growth: This formula assumes that this period will duplicate the prior period, except for the impact of inflation. Revenue Prior Period) + (Revenue Prior Period x Inflation Rate) = Sales Forecast
- Historical Plus Growth: This formula helps you reflect current trends.You look at the prior year and then factor it by your recent growth rate. (Last Year Revenue x Percentage Growth Rate) + Last Year Revenue = Sales Forecast
- Partial Year: In this method, you project the rest of the year based on historical patterns and early results. Imagine that you know your sales for the first two months of the year and that last year these months represented seven and nine percent of your sales respectively and totaled $100,000. Using the formula below, you would forecast sales of $625,00 for the year: ($100,000 x 100) ÷ 16 = $625,000. (Current Period Revenue x 100) ÷ Percent That Equivalent Period Represented Last Year = Forecast Sales
- Pipeline Formula: This formula replicates the opportunity stage method that we discussed earlier. You calculate the value of deals at each stage of your pipeline by multiplying the potential deal value by the close probability and adding up the result for each stage. (Deal Amount x Close Probability) + (Deal Amount x Close Probability) etc. = Sales Forecast
How to Make a Basic Sales Forecast Step by Step
Here are step-by-step instructions for a manually generated sales forecast:
- Pick Your Time Period: The way in which you will use your forecast determines the most appropriate time interval, whether that be monthly, quarterly, annually, or on an even longer timeline. If you are making your first forecast, estimating on a monthly or quarterly basis for the upcoming year is a good starting point. Experts suggest doing monthly estimates for the first year and then doing annual forecasts for years two through five.
- List Products or Services: Write down the items or services that you sell. If you have a lot of them, group them into categories. For example, if you sell clothing, your rows might include shirts, pants, and shoes. Match these revenue streams to the way you organize your accounting. So, if your books look at women’s and men’s clothing separately, do the same for your sales forecast. That way, you can pair your sales forecast with information on your cost of goods sold and overhead to project profit.
- Estimate Unit Sales: Predict how many units you will sell in the selected time period. If you have historical data, use that and then factor in assumptions about demand for the upcoming period. For example, is your business growing? Is the economy in recession? Did you launch a big promotion? Use the answers to these questions to make downward or upward adjustments to the historical figure. You can also interview some customers to get insights into their likely purchasing plans. Lastly, don’t forget to factor in seasonal fluctuations.
- Multiply by the Selling Price: Multiply the unit sales numbers by the average selling price (ASP). Determine the ASP by analyzing historical sales and adjusting for inflation and other factors. To obtain this figure, you also need to consider discounts, free trials, and unsold inventory.
- Repeat for Each Forecast Period: Go through the same calculation for each category and time interval. As you forecast more distant periods, your estimates are likely to be less accurate, so you may want to make a range of forecasts, such as for best, worst, and average scenarios. As time passes, add the actual values and fine-tune your forecast. For instance, you may see that for the first few months of the year, you underestimated sales by 12 percent. Therefore, you decide to increase your forecasted sales amounts in the upcoming months.
How to Forecast Sales in Excel
Here is a step-by-step guide to building your own sales forecast in Excel:
- Enter Historical Data: Open a worksheet and enter your past date data in the first column. Then, in the second column, enter the corresponding sales values. If possible, make sure you space the dates consistently (e.g., the first day of every month).
- Create Forecast: In the date column, fill out the next date cell with the future date you are forecasting. Select the corresponding sales value cell and in the function field, type: =(FORECAST( A10, B2:B9, A2:A9)), where A10 is the future date cell, B2 to B9 are the historical sales amounts, and A2 to A9 are the historical dates. Hit enter and the forecast sales amount will appear.
- Repeat: Continue the pattern for your remaining future dates. Remember that the formula uses only known variables, so do not add forecasted amounts to the cell ranges. This function is a linear forecasting method.
- Power Up: If you have Excel 2016, you can use the forecast sheet function, which automates forecasting and adds a chart. To use this function, select both data columns, and, on the data tab, click the forecast sheet. In the create forecast worksheet box, select whether you want a line or bar chart. In the forecast end field, choose an ending date and then click create. Excel will create a new worksheet that contains both historical and forecast sales data as well as a visual representation.
For a pre-made basic sales forecast, download this template that projects product sales with both units and sales amount.
Basic Sales Forecast Sample Template
Excel | Google Sheets | Smartsheet
For a wide range of pre-built sales forecast templates in a variety of formats, see this comprehensive collection .
How to Choose the Right Sales Forecasting Methodology
Your goal is to build the most reliable forecast possible, with the minimum amount of resources you need to be effective. To choose the method that fits best, consider these seven questions:

- Is the Time Frame Short, Medium, or Long Term? Qualitative methods are a good choice for short-term horizons, but they generally underperform quantitative methods for periods beyond a few months. Similarly, consider where you are in your business or product lifecycle. If you are ramping up or in a high-growth phase, you may be making costly investment decisions, so you need a method with a high degree of accuracy, but also relatively quick production time. When you are in a mature phase of your business, decisions about production and marketing are more routine.
- How Much Data Do You Have? The less data you have, the more likely you will be to select a qualitative technique. If you have limited data, you will turn toward more simplistic models. A company that has collected a lot of data and has great confidence in its reliability can choose sophisticated quantitative models.
- How Relevant Will History Be in Predicting the Future? If your business has undergone big changes, such as launching major new products, experiencing large growth in the sales force, or introducing a different pricing structure, your past results will have less value as a guide to future performance. So, methods that diminish the weight put on historical data and qualitative techniques are a better choice.
- In Terms of Time and Money, How Much Does It Cost to Produce the Forecast? How Does This Cost Compare to the Value of the Potential Benefits?You will need to make tradeoffs between the time and cost to build your forecast and the potential benefits, such as cost savings. Also, consider the potential cost of error. For example, suppose you are contemplating a high-cost sales-forecasting technique (one that takes a lot of data gathering, the creation of a custom model, and expensive staff and technology to produce). The forecast could allow your company to reduce the amount of inventory it holds. Weigh the value of inventory savings against the forecasting cost. If you reduce inventory and the forecast proves inaccurate, what are the potential costs of lost sales — because you did not stock adequately or because you did not cut back enough?
- What Degree of Accuracy Do You Need? Forecast accuracy rises with the cost and complexity of the methodology. Depending on how you will use the forecast, the size of your company, and the variability of your business, you may feel that it’s not cost effective to produce a maximum-accuracy forecast. If you are a giant global company, a fraction of a percentage point error in your sales forecast could represent many millions. So, the bigger the dollar values, the more meaningful every degree of enhanced accuracy becomes.
- How Complex Are the Factors That Will Drive the Forecast? If your sales dynamic is straightforward — the more sunny days there are, the more beach umbrellas you sell at your beach kiosk — then building a sophisticated, AI-driven forecasting model will be overkill. “It's important not to spend time and energy developing a complex model, when a much simpler one will do the job,” says Nicholas. But when you are facing a subtle and complex interplay of variables, you need a technique that accounts for them. Suppose you have new products, changes in your marketing, and additional sales reps. A sophisticated model would allow you to forecast the net effects and also try out different scenarios in which the variables fluctuated.
Why Accuracy Is Important in Sales Forecasts
According to CSO Insights, 60 percent of forecasted deals do not close and 25 percent of sales managers are unhappy with the accuracy of their forecasts. Inaccuracy in sales forecasts causes problems for businesses and impacts performance.
People throughout your company depend on your forecasts to make a multitude of decisions — from pay raises to real estate acquisitions. Let’s look at some of the important reasons to strive for accuracy:
- Early Warning: Your sales forecast helps you spot trouble early, like when revenues are not materializing as expected; the forecast also allows you to intervene and problem solve before this underperformance becomes a crisis.
- Decision Making: The forecast gives leaders confidence and a sound basis for deciding how much and where to spend or invest. Production planners, HR, and others will use the forecast.
- Goal Setting: You set achievable targets for sales reps when you have an accurate forecast. Goal setting prevents sales reps from getting discouraged by unrealistic expectations. Following this strategy also ensures that your commission and bonus scale are calibrated appropriately.
- Customer Satisfaction: When you are prepared for the right level of demand, your company can improve its record of fulfilling orders on time and in full.
- Inventory Management: You will be more likely to have the right level of inventory if your sales forecasts are accurate. Making accurate predictions allows you to better manage your supply chain and order raw materials or parts in a timely fashion. You also gain more control over your pricing if you have the right amount of inventory. When you have to resort to discounting to get rid of excess inventory, your profitability suffers.
How to Improve Sales Forecast Accuracy and More Best Practices from Experts
Producing high-quality forecasts takes organizational commitment and long-term effort, and best practices will help improve accuracy.

”Sales forecasting is both an art and a science. Where companies tend to go wrong is relying too heavily on one or the other. You need a consistent process and reliable data,” says Charlene DeCesare, CEO of sales training and advisory firm Charlene Ignites .
She emphasizes five best practices:
- Ensure that the pipeline feeding the forecast is accurate. You don't need historical data to predict the future when you have a well-defined sales process.
- Everyone must use the CRM, and should enter notes and coding opportunities in a clear, consistent way.
- Buyer behavior is a much more reliable predictor of future sales than gut feel. Challenge optimism that doesn't align with the applicable stage in the sales cycle or isn't supported by clear, mutually agreed-upon next steps.
- In general, buyer/seller behavior is the leading indicator to rely upon. Too many companies rely on results, which is actually the lagging indicator.
- Sales leadership can have a huge impact. Sales reps must be rewarded for both honesty and accuracy. Sales forecasting must be an individual, team, and company priority.

Rob Stephens, a CPA whose firm CFO Perspective advises businesses on forecasts, adds: “A big planning mistake is spending too much of your precious time trying to find the one right scenario… Start with a range of reasonable forecasts based on solid fundamentals. For example, you may project from historical growth rates, customer indications of future sales, or projections of market growth. A company with a new product may need to extrapolate from existing products or early indications from potential customers. Use a higher-probability scenario as a beginning base scenario, but identify why the future may deviate from it.”
Common Mistakes and Pitfalls in Sales Forecasts
Sales pros say they see the same sales forecasting errors on a regular basis and that these often relate to letting the discipline of the forecasting process lapse.

“The most common operational mistakes are basing forecasts on hope rather than evidence, ignoring repeated close date slippage, failing to take into account the historic forecast accuracy (or inaccuracy) of the salesperson concerned, and failing to hold salespeople accountable for the relative accuracy of their forecasts,” notes Bob Apollo, Founder of Inflexion-Point Strategy Partners, a sales training firm.
“The most common cultural mistake is when sales leaders press salespeople to forecast a target number without any evidence or confidence that it will actually be achieved," he notes.

Evan Lorendo , Director of Revenue Accelerator, which advises service companies on revenue strategies, says he sees companies with monthly recurring revenue (MRR), such as software as a service (SaaS), frequently make mistakes in sales forecasting.
He gives the example of a company with an MRR product that wants to generate $120,000 in revenue a year. How much in new sales do they need each month? “Most of my clients say $10,000/month, but that is wrong. Because a client is paying on a monthly basis, a client that signs up in January is actually paying 12 times during the year. On the flip side, a client signing up in July will make six payments during the year,” he explains.
That means there are a total of 78 potential payment configurations per year, not 12. The customer who buys in January will make 12 payments, but November’s buyer will make two. (12 + 11 + 10 + 9 + 8 + 7+ 6 + 5 + 4 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 78.)
“If you want to know how much you need to sell in new sales each month to hit that $120,000 goal, the answer is $1,539 ($120,000/78). That actually seems much more manageable, doesn't it? Based on poor forecasting, a miscalculation can turn off good salespeople who can't hit their quota,” he says.
KPIs for Sales Forecasting
As your sales forecasting improves, you reap bigger benefits, such as better planning and higher profits. So, you will want to assess and monitor your forecasting effort by using key performance indicators (KPIs).
Below are the main KPIs for sales forecasting. Some of them draw from statistics concepts, such as standard deviation, and computer applications and statistics guides can help you calculate them.
- Bias or Variance: This KPI tells how much the actual results deviated from the forecast over a given period of time. Calculate bias as an absolute number of dollars or units or as a percent of sales. A positive number means sales exceeded projections and a negative number indicates underperformance. Actual Units - Forecast Units = Bias
- Mean Absolute Deviation (MAD): This metric describes the size of your forecast error in total units or dollars. You calculate how much the actual results deviated from the forecast average, add the deviations, and divide the result by the total number of data points.
- Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE): This is similar to MAD, but gives the forecast error as a percent of sales volume.
- Tracking Signal: This is another expression of forecast error and looks at how the error rate varies among forecast values. Normally, you expect all forecast amounts to be wrong by about the same degree. If, from one data point to another, there is a large variation in the error rate, you need to rework your model. Tracking Signal = Accumulated Forecast Errors ÷ Mean Absolute Deviation
- Forecast Value Added: This metric measures how much better the forecast was than simply using unadjusted historical data. If your forecasting effort got you closer to actual than the so-called naive forecast (i.e., using historical figures as your forecast), you have added positive value. You calculate this metric by comparing the MAPE of your forecast to the naive forecast.
- Linearity: This looks at how sales are paced over the course of the period. As your reps seek to meet quota, you might see a flurry of deals at the end of the quarter. Or, deals might be spread evenly across the time period. The most stable situation is a deal cadence or velocity that is constant. If expressed as a trend line, this stable situation would appear visually as a flat line. This pattern is called highly linear .
Application of Sales Forecasting
Your sales forecast obviously gives you an idea of how much you will sell in the future, but sales forecasting has other important use cases. Here are five ways you can apply your forecast to business questions:
- Sales Planning: As noted earlier, your sales plan encompasses your goals, tactics, and processes for achieving your sales forecast. As part of this plan, your sales forecast helps you decide if you need to hire more sales reps to achieve your forecast and if you need to put more energy and resources into marketing.
- Demand Planning: Demand planning is the process of forecasting how much product your customers will want to buy and making sure inventory aligns with that forecast. In ideal conditions, forecast demand and sales would be virtually the same. But, consider a scenario in which your new product becomes the hot gift of the holiday season. You forecast demand of 100,000 units (the number consumers will want to buy). A large shipment turns out to be defective, and the product is unsellable. So, you forecast sales of just 75,000 units (how much you will actually sell.)
- Financial Planning: Your sales forecast is vital to the work of your finance department. The finance team will rely on the forecast to build a budget, manage overhead, and figure out long-term capital needs.
- Operations Planning: The unit-sales numbers in your forecast are also important for operations planners. They will look at the production required to meet those sales and confirm that manufacturing capacity can accommodate them. They will want to know when sales are likely to rise or fall, so they can avoid excess inventory. A big increase in sales will also require operations managers to make changes in warehousing and distribution. Retailers may change the product mix at individual stores based on your sales forecast.
- Product Planning: The trends you foresee in sales will have big implications for product managers too. They will look at products that you forecast as top sellers for ideas about new products or product modifications they should introduce. A forecast of declining sales may signal it is time to discontinue or revamp a product.
Levels of Maturity in Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasts can be simply scribbled-down estimates, or they can be statistical masterpieces produced with the aid of the most sophisticated technology. The style you pursue relates in large part to your level of forecasting maturity (as well as the size and history of your business).
Below is a description of the four levels of the sales forecasting maturity model:
- Level One: In the beginning stages of sales forecasting, the estimates are usually not very accurate and take a lot of time to produce. The forecasting process depends on reps’ best guesses, and sales managers spend a lot of time gathering these guesses by interviewing each rep. Then, they roll them up into a consolidated forecast. Inconsistent data collection and personal bias can skew the results. Sales managers use spreadsheets, which quickly become outdated, and the forecasts often reflect little more than intuition.
- Level Two: As your forecasting culture grows, you are probably still inputting data by hand, and the forecast is often inaccurate or outdated. But, a CRM solution is enabling your team to have a shared repository for contacts, sales activity, and deal status. Reps don’t see value in spending time contributing to the forecast, and quality is weak. Your CRM automatically aggregates those results, so you can start to examine trends and anomalies. But, your system is not very flexible, and forecasting remains unwieldy and resource intensive.
- Level Three: At this point, automation starts to offer radical improvements in sales forecasting. Solutions backed by artificial intelligence automatically bring together data from a multitude of sources, including email, CRM, marketing platforms, chat logs, and calendars. There is no more manual data entry, and sales managers gain increased visibility into the sales pipeline. KPIs become reliable and an important tool for monitoring performance.
- Level Four: Technology ensures sales that data is accurate and timely. AI and machine learning find patterns and correlations in your historical data, and predictive analytics offer robust forecasting. The forecasting model is continually refined. Forecast accuracy rises, and sales managers can focus more of their time on supporting reps and developing opportunities. These tools make it apparent when reps are sandbagging or being too optimistic, and accountability increases.
Advances in Sales Forecasting Methodologies
While sales forecasting has been around as long as private enterprise, the field continues to evolve, and researchers are looking at ways to improve sales forecasting methodologies.
Indiana University Professor Douglas J. Dalrymple performed an influential study in 1987 that surveyed how businesses prepared sales forecasts. He found that qualitative and naive techniques predominated, but that early adopters were reducing errors by using computer analysis. At this time, PCs were starting to proliferate and come down in price.
By 2008, Zhan-Li Sun and his researchers at the Institute of Textiles and Clothing at Hong Kong Polytechnic University were experimenting with an advanced AI-driven technique called extreme learning machine to see if they could improve forecasts for the volatile retail fashion industry by quantifying the influence of factors such as design on sales.
Scholars F.L. Chen and T.Y. Ou at the National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan took this further with a 2011 study. The study documented sales forecasting advances when combining extreme learning-machine, so-called Taguchi statistical methods for manufacturing quality with novel analysis theories that work on variables with imperfect information.
Features to Look for in a Sales Forecasting Tool
Paper forecasts and Excel spreadsheets quickly become cumbersome. Sales forecasting capability is available in CRM software, sales analytics and automation platforms, and AI-driven sales technology. These capabilities often overlap among these applications.
Here are some of the features to look for when evaluating a sales forecasting tool:
- Integrations with other software, such as ERP, CRM, marketing suites, contact management, calendars, and more
- Automated collection of data and sales rep activity
- Real-time reporting
- Robust data security
- Analytics and automated scoring of deals
- Insights on most promising deals
- Scenario modeling
- Lead scoring
- Automated forecast roll-ups or summaries by category and team
- Dashboards and graphic displays of KPIs
- Benchmarking
- Customizable forecasting algorithms
- Forecast auditing and error analysis
Improve Sales Forecasting with Smartsheet for Sales
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- *New* Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
7 Financial Forecasting Methods to Predict Business Performance

- 21 Jun 2022
Much of accounting involves evaluating past performance. Financial results demonstrate business success to both shareholders and the public. Planning and preparing for the future, however, is just as important.
Shareholders must be reassured that a business has been, and will continue to be, successful. This requires financial forecasting.
Here's an overview of how to use pro forma statements to conduct financial forecasting, along with seven methods you can leverage to predict a business's future performance.
What Is Financial Forecasting?
Financial forecasting is predicting a company’s financial future by examining historical performance data, such as revenue, cash flow, expenses, or sales. This involves guesswork and assumptions, as many unforeseen factors can influence business performance.
Financial forecasting is important because it informs business decision-making regarding hiring, budgeting, predicting revenue, and strategic planning . It also helps you maintain a forward-focused mindset.
Each financial forecast plays a major role in determining how much attention is given to individual expense items. For example, if you forecast high-level trends for general planning purposes, you can rely more on broad assumptions than specific details. However, if your forecast is concerned with a business’s future, such as a pending merger or acquisition, it's important to be thorough and detailed.
Access your free e-book today.
Forecasting with Pro Forma Statements
A common type of forecasting in financial accounting involves using pro forma statements . Pro forma statements focus on a business's future reports, which are highly dependent on assumptions made during preparation, such as expected market conditions.
Because the term "pro forma" refers to projections or forecasts, pro forma statements apply to any financial document, including:
- Income statements
- Balance sheets
- Cash flow statements
These statements serve both internal and external purposes. Internally, you can use them for strategic planning. Identifying future revenues and expenses can greatly impact business decisions related to hiring and budgeting. Pro forma statements can also inform endeavors by creating multiple statements and interchanging variables to conduct side-by-side comparisons of potential outcomes.
Externally, pro forma statements can demonstrate the risk of investing in a business. While this is an effective form of forecasting, investors should know that pro forma statements don't typically comply with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) . This is because pro forma statements don't include one-time expenses—such as equipment purchases or company relocations—which allows for greater accuracy because those expenses don't reflect a company’s ongoing operations.
7 Financial Forecasting Methods
Pro forma statements are incredibly valuable when forecasting revenue, expenses, and sales. These findings are often further supported by one of seven financial forecasting methods that determine future income and growth rates.
There are two primary categories of forecasting: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative Methods
When producing accurate forecasts, business leaders typically turn to quantitative forecasts , or assumptions about the future based on historical data.
1. Percent of Sales
Internal pro forma statements are often created using percent of sales forecasting . This method calculates future metrics of financial line items as a percentage of sales. For example, the cost of goods sold is likely to increase proportionally with sales; therefore, it’s logical to apply the same growth rate estimate to each.
To forecast the percent of sales, examine the percentage of each account’s historical profits related to sales. To calculate this, divide each account by its sales, assuming the numbers will remain steady. For example, if the cost of goods sold has historically been 30 percent of sales, assume that trend will continue.
2. Straight Line
The straight-line method assumes a company's historical growth rate will remain constant. Forecasting future revenue involves multiplying a company’s previous year's revenue by its growth rate. For example, if the previous year's growth rate was 12 percent, straight-line forecasting assumes it'll continue to grow by 12 percent next year.
Although straight-line forecasting is an excellent starting point, it doesn't account for market fluctuations or supply chain issues.
3. Moving Average
Moving average involves taking the average—or weighted average—of previous periods to forecast the future. This method involves more closely examining a business’s high or low demands, so it’s often beneficial for short-term forecasting. For example, you can use it to forecast next month’s sales by averaging the previous quarter.
Moving average forecasting can help estimate several metrics. While it’s most commonly applied to future stock prices, it’s also used to estimate future revenue.
To calculate a moving average, use the following formula:
A1 + A2 + A3 … / N
Formula breakdown:
A = Average for a period
N = Total number of periods
Using weighted averages to emphasize recent periods can increase the accuracy of moving average forecasts.
4. Simple Linear Regression
Simple linear regression forecasts metrics based on a relationship between two variables: dependent and independent. The dependent variable represents the forecasted amount, while the independent variable is the factor that influences the dependent variable.
The equation for simple linear regression is:
Y = Dependent variable (the forecasted number)
B = Regression line's slope
X = Independent variable
A = Y-intercept
5. Multiple Linear Regression
If two or more variables directly impact a company's performance, business leaders might turn to multiple linear regression . This allows for a more accurate forecast, as it accounts for several variables that ultimately influence performance.
To forecast using multiple linear regression, a linear relationship must exist between the dependent and independent variables. Additionally, the independent variables can’t be so closely correlated that it’s impossible to tell which impacts the dependent variable.

Qualitative Methods
When it comes to forecasting, numbers don't always tell the whole story. There are additional factors that influence performance and can't be quantified. Qualitative forecasting relies on experts’ knowledge and experience to predict performance rather than historical numerical data.
These forecasting methods are often called into question, as they're more subjective than quantitative methods. Yet, they can provide valuable insight into forecasts and account for factors that can’t be predicted using historical data.
6. Delphi Method
The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance.
A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge. The facilitator then compiles their analyses and sends them to other experts for comments. The goal is to continue circulating them until a consensus is reached.
7. Market Research
Market research is essential for organizational planning. It helps business leaders obtain a holistic market view based on competition, fluctuating conditions, and consumer patterns. It’s also critical for startups when historical data isn’t available. New businesses can benefit from financial forecasting because it’s essential for recruiting investors and budgeting during the first few months of operation.
When conducting market research, begin with a hypothesis and determine what methods are needed. Sending out consumer surveys is an excellent way to better understand consumer behavior when you don’t have numerical data to inform decisions.

Improve Your Forecasting Skills
Financial forecasting is never a guarantee, but it’s critical for decision-making. Regardless of your business’s industry or stage, it’s important to maintain a forward-thinking mindset—learning from past patterns is an excellent way to plan for the future.
If you’re interested in further exploring financial forecasting and its role in business, consider taking an online course, such as Financial Accounting , to discover how to use it alongside other financial tools to shape your business.
Do you want to take your financial accounting skills to the next level? Consider enrolling in Financial Accounting —one of three courses comprising our Credential of Readiness (CORe) program —to learn how to use financial principles to inform business decisions. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
- Company management
Navigating the future with business forecasting

In today's dynamic and ever-changing business environment, organisations must make accurate future predictions to stay competitive and thrive. Business forecasting is one tool that enables companies to make informed decisions about their future.
What is business forecasting?
Business forecasting is predicting future outcomes based on past and present data. This involves analysing historical trends, market conditions, customer behaviour, and other relevant factors to determine prospects and threats.
The main goal of business forecasting is to develop an informed estimate of future events and circumstances . This enables businesses to make strategic decisions and prepare for future expansion.
Why is business forecasting important?
Forecasting is important for businesses as :
- It helps organisations to make strategic plans for the future.
- Helps organisations to allocate resources effectively and efficiently.
- Plays a crucial role in financial planning by helping businesses estimate future revenues, expenses, and profits.
- Helps organisations to identify problems, potential risks and uncertainties and develop risk management strategies to mitigate them.
- Provides decision-makers with valuable insights and data, which can help them make better-informed decisions and develop short & long term success strategies .
Related article: The best cash flow forecasting software in 2023
Business forecasting process
Effective business forecasting requires careful planning and execution. The following steps provide a comprehensive guide on how to develop a successful forecasting plan:
Define the objective : The first step in the business forecasting process is to define the objective of the forecast by identifying the key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales, revenue, or market share.
Gather data : Next, gather relevant data, including historical data on the KPIs, market trends, and other variables that may impact the forecast.
Analyse the data : Once the data has been gathered, it must be analysed to identify patterns, trends, and other factors that may impact the forecast. This can be done using statistical models, machine learning algorithms, or other analytical tools.
Develop the forecast : Based on the analysis of the data, a forecast can be developed using the insights gained from the data analysis to generate a prediction of future performance on the KPIs.
Validate the forecast : Now, it should be validated to ensure its accuracy. This can be done by comparing the forecast to actual performance data from past periods.
Implement the forecast : Finally, the forecast can be used to make informed decisions about business operations. This involves adjusting resource allocation, pricing strategies, or other aspects of the business based on the predicted future performance.
As business forecasting is an iterative process, it's important to monitor actual performance against the forecast and adjust the forecast as required to ensure its accuracy over time.
👉 Watch our video on cash flow forecasting
What are 2 basic methods of forecasting in business?
Two main methods of forecasting are:
Qualitative forecasting : This approach uses expert opinions, market research, surveys, and other subjective data to predict future trends. Qualitative forecasting is useful when historical data is limited, and the future is uncertain.
Quantitative forecasting : This method relies on historical data and statistical analysis to predict future trends. Quantitative forecasting is suitable for industries with a lot of historical data and stable market conditions.
4 Basic forecasting techniques
The four basic forecasting techniques are:
Trend analysis : This method identifies patterns and trends in historical data to predict future values. Trend analysis helps forecast long-term trends.
Regression analysis : Regression analysis is helpful for forecasting in complex environments where multiple variables are involved. This approach identifies the relationship between two or more variables to predict future values.
Moving average : This method calculates the average of past data points to identify trends and predict future values. Moving averages are helpful for forecasting in stable and predictable environments.
Exponential smoothing : Exponential smoothing is helpful for forecasting in rapidly changing environments. This technique assigns more weight to recent data points than older ones to predict future values.
A few other business forecasting techniques are:
- Scenario analysis
- Judgmental forecasting
- Causal forecasting
- Econometric forecasting
- Delphi method
- Simulation modelling
See also: Improving liquidity in your business in 5 easy ways
5 Forecast models:
Forecast models in business forecasting are mathematical or statistical tools used to predict future trends and outcomes based on historical data and various influencing factors. These models are designed to analyse patterns, relationships, and dependencies within the data to generate reliable forecasts.
The forecast models serve as valuable tools for businesses to anticipate demand, sales, market trends, financial performance, and other crucial factors, enabling them to make informed decisions and develop effective strategies. By leveraging these forecast models, businesses can make data-driven decisions, improve resource allocation, optimise inventory levels, and enhance operational efficiency.
There are several types of forecast models commonly used in business forecasting, such as:
1. Time Series Models: These models analyse historical data to identify patterns and make predictions based on the assumption that future trends will continue in a similar pattern. Time series models, such as moving averages and exponential smoothing, are commonly used in businesses to forecast demand, sales, and financial metrics. These models can predict future trends by analysing historical patterns and seasonality and help businesses optimise inventory management, production planning, and resource allocation.
2. Regression Models: Regression analysis uses historical data to establish relationships between variables, allowing for the prediction of one variable based on the values of other related variables. It is widely applied in business forecasting to understand the relationships between variables. For example, businesses may use regression models to forecast sales based on factors like marketing expenditure, pricing, and macroeconomic indicators. These models provide insights into the impact of different variables on business performance and inform strategic decision-making.
3. Exponential Smoothing Models: Exponential smoothing models place greater emphasis on recent data points, giving them more weight in the forecast calculation while gradually decreasing the impact of older data. Exponential smoothing models are helpful for short-term forecasting and are commonly employed in inventory management and sales forecasting. By assigning different weights to recent and older data points, these models give more significance to recent trends, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changes in demand.
4. Econometric Models: These models incorporate economic theory and statistical techniques to forecast business outcomes by considering factors such as GDP, inflation, interest rates, and other macroeconomic indicators. These models are applied in areas such as financial forecasting, market analysis, and pricing strategies. By considering macroeconomic factors and their impact on specific industries, businesses can predict market conditions and adjust their strategy accordingly.
5. Machine Learning Models: Machine learning algorithms can analyse large volumes of data, identify complex patterns, and make forecasts based on the identified patterns. Machine learning algorithms, including neural networks, decision trees, and random forests, can be utilised to forecast various business metrics. These models can analyse large datasets, identify complex patterns, and make accurate predictions. Businesses apply machine learning models for demand forecasting, customer behaviour analysis, fraud detection, and personalised marketing campaigns.

What are examples of business forecasts?
Let's take the example of business forecasting for a company that manufactures and sells organic skincare products. Based on the assumptions, that the company has been in business for a few years and has historical sales data, it could use that data to forecast its sales using trend analysis for the next year.
They might consider such cases and scenarios, as mentioned under:
- Past sales trends : If sales have steadily increased by 10% each year, they might assume they will see similar growth in the coming year.
- Market trends : They would also look at broader trends - Whether more people are becoming interested in organic products. Is there a new ingredient that is gaining popularity? These factors could influence the company's sales.
- Marketing initiatives: If the company plans to launch a new product line or run a major advertising campaign, it might expect a boost in sales.
Using this information, the company could create a sales forecast for the following year. They might forecast a 10% increase in sales based on historical trends, plus an additional 5% increase based on market trends and marketing initiatives.
Business Forecasting Software
Business forecasting software uses cutting-edge algorithms and statistical approaches to analyse historical data and current market conditions to generate accurate forecasts about future outcomes. It helps organisations to predict future trends, patterns, and behaviours related to their business operations.
Business forecasting software is used by companies in various industries. Its key features include data visualisation tools, predictive analytics, scenario planning, and automated reporting.
Using a business forecasting software:
- Businesses can make more informed decisions about resource allocation, budgeting, and strategic planning.
- Businesses can identify potential risks and opportunities and adjust their operations to stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Wrapping Up
Business forecasting emerges as a vital tool for organisations aiming to make well-informed decisions regarding the future.
By following a comprehensive process that includes defining the objective, gathering data, selecting the methodology, developing the forecast, and monitoring and reviewing, companies can develop accurate and reliable predictions that inform strategic decisions and drive growth.
Subscribe to our newsletter
You may also like.

201 Borough High Street London SE1 1JA
- Manage your cash flow
- Cash flow monitoring
- Cash flow forecast
- Consolidation
- Custom dashboards
- Debt management
- Late payment reminders
- Supplier Invoice Management
- Terms of Use
- General Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- We're hiring

Close more deals with the latest sales trends and tips from Salesblazers.
The Complete Guide to Building a Sales Forecast

Set your company up for predictable revenue growth with the right forecasting processes and tools.

Paul Bookstaber
Share article.
- Link Copied
Building a sales forecast is both an art and a science. Accurate sales forecasts keep your leaders happy and your business healthy. In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about sales forecasting — so you can get a clear picture of your company’s projected sales and keep everyone’s expectations on track.
We’ve organized this reference guide by the top questions sales teams have about the sales forecasting process, based on our internal conversations and more than 20 years of experience developing sales solutions .
Build sales forecasts with accuracy
Use the real-time data updates and insights of Sales Cloud to keep your forecasts accurate and your teams on track to hit targets.

What you’ll learn:
What is a sales forecast, why is sales forecasting important, who is responsible for sales forecasts, who uses sales forecasts, what are the objectives of sales forecasting, how do i design a sales forecasting plan.
- What happens to sales forecasting in unpredictable times?
How accurate are sales forecasts?
What tools do you use to forecast sales revenue and how do crm systems forecast revenue, how is forecasting better with crm vs. other methods.
If you’re a sales leader who’s already well-versed in the who and what of sales forecasts, skip to the sections on designing a sales forecasting plan and tools to improve sales forecasts for more relevant knowledge. Sales forecasting can become especially tough when we face an unexpected turn of events, so head to the section on what happens to sales forecasts in unpredictable times for more on that.
A sales forecast is an expression of expected sales revenue. A sales forecast estimates how much your company plans to sell within a certain time period (like quarter or year). The best sales forecasts do this with a high degree of accuracy, and they’re only as accurate as the data that fuels them.
A strong data culture is at the heart of an accurate sales forecast. This means all sales data is available to everyone at the company, and all teams do their part in keeping it updated, leaning on AI and automation to help. More on that in the section on tools used to forecast sales revenue .
All sales forecasts answer two key questions:
- How much: Each sales opportunity has its own projected amount it’ll bring into the business. Whether that’s $500 or $5 million, sales teams have to come up with one number representing that new business. To create the number, they take everything they know about the prospect into account.
- When: Sales forecasts pinpoint a month, quarter, or year when the sales team expects the revenue to hit.
Coming up with those two sales projections is no easy feat. So sales teams factor in the important ingredients of who, what, where, why, and how to make their forecasts:
- Who: Sales teams are responsible for sales forecasting.
- What: Forecasts should be based on the exact solutions you plan to sell. In turn, that should be based on problems your prospects have voiced, which your company can uniquely solve .
- Where: Where is the buying decision made, and where will the actual products be used? Sales teams see better accuracy when they get closer (at least for a visit) to the center of the action.
- Why: Why is the prospect or existing customer considering new services from your company in the first place? Is there a compelling event making them consider it now? Without a forcing function and a clear why, the deal may stall inevitably.
- How: How does this prospect tend to make purchasing decisions? If you’re not accounting for how they do it now and how they’ve done it in the past in your forecast, it may be fuzzy math.
Forecasting lets leaders set realistic sales targets, create attainable and motivating quotas for sales reps, and gauge expected revenue, aiding in budgeting and spending decisions for the whole company. If forecasts are inaccurate, businesses may overspend (putting themselves in a risky spot), and set unreachable quotas (which is demoralizing for reps).
To understand why sales forecasting is so important to business health, think about two example scenarios: one with a car manufacturer and another with an e-commerce shop.
In the case of a car manufacturer, cars take a long time to build. The manufacturer has a complex supply chain to ensure every car part is available exactly when they need to build cars, so the number of cars available to purchase will meet demand.
When you buy something online, whether that’s from a large marketplace or a small boutique, you get a delivery estimate. If your delivery comes a day or a week after it’s promised, that’ll affect your satisfaction with the company — and decrease your willingness to want to do business with them again.
Sales forecasting is similar in both cases. Sales forecasts help the entire business plan resources to ship products, pay for marketing, hire employees, and beyond. Accurate sales forecasting yields a well-oiled machine that meets customer demand, both today and in the future. And internally on sales teams, sales revenue that delivers in its estimated time period keeps leaders and collaborators happy, just like a shipment that arrives on time.
If forecasts are off, the company faces challenges that affect everything from pricing to product delivery to the end user. Meanwhile, if forecasts are on point and sales quotas are met, the company can make better investments, perhaps hiring 20 new developers instead of 10, or building a much-needed new sales office in a prime new territory.
Get articles selected just for you, in your inbox
Each organization has its own sales forecast owners. These are some of the teams who are usually responsible:
- Product leaders: They put a stake in the ground for what products will be available to sell when.
- Sales leaders: They promise the numbers that their teams will deliver. Depending on the seniority of the leader, how they forecast varies. For example, first-line managers forecast collections of opportunities, where third-line managers consider a wide set of numbers and traditional close rates to come up with an overall forecast.
- Sales reps: They report their own numbers to their managers.
No matter how a company calculates its sales forecasts, the process should be transparent. And at the end of the day, sales leadership has to be responsible to call a number. Whether met, exceeded, or missed, the forecast responsibility falls on them.
Sales forecasts touch virtually all departments in a business. For example, the finance department uses sales forecasts to decide how to make annual and quarterly investments. Product leaders use them to plan demand for new products. And the HR department uses forecasts to align recruiting needs to where the business is going.
At some level, sales forecasting affects everyone in the company.
The main objective of sales forecasting is to paint an accurate picture of expected sales. Leaders are looking to these numbers when they’re building out their operational roadmap and budget. If they’re confident in the projected growth, they can get to planning.
They could decide to staff more customer service touchpoints, fund more external marketing events, or invest more in the community. They could get ahead of purchasing new equipment or upgrades that get more expensive the longer they wait. Without a sales forecast, leaders are making critical spending decisions in the dark. If sales don’t go as planned, it could lead to cutting workforce, reducing support, or halting product development.
Sales forecasting is a muscle, not an item to check off your to-do list. While you should absolutely design a framework for your sales forecasting plan each year, you should also change up your strategies from time to time so new muscles develop.
Craft a sales forecasting plan with your team by focusing on three primary activities:
- Calculating number and time period: Your plan should explain how you’ll calculate the estimated monetary amount and what the timeframes will be. See the section on how a CRM can help with forecasting later in this guide for more on the sales forecasting tools you can use to do this.
- Reviewing and revising: You should also plan to review the forecast at key milestones and revise it if necessary. Most sales leaders track progress against their forecast daily! But you’ll also want to schedule designated check-ins throughout the quarter. Make sure you’re reviewing the latest numbers with sales automation tools that sync your CRM’s forecast data.
- Breaking the patterns: Even the best sales organizations need to shake up their sales process once in a while. Breaking your patterns can help you find new ways of crafting even more accurate forecasting. Try skip-level forecasting, ask different questions, have executive sponsorship reviews, and take different angles of the data.
Trending Articles

3 Ways Generative AI Will Help Marketers Connect With Customers

Learn AI Skills on Trailhead
What happens to sales forecasts in unpredictable times.
Unpredictable events have an enormous impact on your sales forecast. Extreme weather or economic crises all dramatically change your forecast. What you thought you knew about expected revenue growth can be suddenly flipped on its head.
As soon as an extraordinary event hits, sales and finance leaders at your company will quickly want to know:
- How’s our sales pipeline looking today?
- What are the best- and worst-case scenarios?
- How has the forecast changed from a week or a month ago?
Your forecast implicates resourcing, headcount, and more (see the section on sales forecasting objectives ). So although things may be changing quickly, you don’t want to give up on your forecast.
Rather than attempt to recalculate your forecast based on dubious estimates or conjecture, your best bet is to rely on a CRM solution to get an accurate view of deal status and pipeline in real time.
During a crisis, reps need to feed their CRM with data as events unfold so leaders have clear visibility into the rapidly evolving pipe. That data enables those leaders to support their reps with corporate-level decisions about where they should be focusing their time — and craft the new forecasts. Your forecast is only as good as the data coming into it from your sales teams.
In uncertain times, quick access to sales data and the ability to pivot sales territory and resource deployment accordingly can make the difference between business continuity and dissolution. There’s no silver bullet to forecast perfectly in a crisis or unforeseen scenario. But vigilantly updating what’s in the pipeline and analyzing sales data more frequently than usual will help you see trends and retool your forecast accordingly.
Empathy and care are always fundamental, but this is especially true in these situations. Empathizing with your customers’ challenges and caring for your own sales reps should come before anything else. Build trust with internal and external partners. That trust will help you grow again in the future. Learn more about maintaining customer relationships as a sales leader .
Only 45% of sales leaders are confident in their organization’s sales forecasts, according to Gartner . While it’s natural for sales reps to bring in some intuition to their sales forecasts, that’s where room for error can creep in.
This brings us back to embracing a strong data culture . To get a more accurate forecast, everyone in the sales cycle — from reps to managers to execs — should have a stake in making sure those numbers reflect the latest reality. Reps can keep all prospect info up to date, managers can track pipeline progress, and leaders can review how all teams are tracking toward those forecast numbers, with AI playing backup to spot any inaccuracies or chances to adjust along the way.
A CRM gives sales leaders a real-time view into their entire team’s forecast. The tool forecasts revenue by giving you:
- An accurate view of your entire business. Comprehensive forecasts in a CRM come with a complete view of your pipeline.
- Tracking of your top performers. See which reps are on track to beat their targets with up-to-the-minute leaderboards.
- Forecasting for complex sales teams. Overlay splits allows you to credit the right amounts to sales overlays, by revenue, contract value, and more.
A forecast is based on the gross rollup of a set of opportunities. You can think of a forecast as a rollup of currency or quantity against a set of dimensions: owner, time, forecast categories, product family, and territory. You can collaborate on forecasts with all the necessary people to see how opportunities are stacking up. Drill down into opportunities by sales leader, operating unit, manager, and individuals.
We also love a CRM with reports and dashboards . These highlight where the business challenges are, in plain and simple terms. It could be that four of five selling teams are at the right growth rate, and we just need to focus on another one. It could be that a certain product is challenged. The data opens up new doors to grow sales and see what could be working more effectively.
Another thing that’s great about a CRM is the guidance from AI. An AI for sales tool offers a neutral perspective on what’s actually happening in sales. For example, AI might note that an opportunity has been pushed out three quarters in a row — a finding that would’ve taken an individual reviewing the data longer to discover. Think of AI as your personal data scientist, taking your forecasting and entire sales operations to a new level.
Predictive AI tools take a look at historical sales data to give you a glimpse of what you might expect in the future. The AI will analyze factors like win rate or number of customer meetings. It takes some of the guesswork out of sales forecasting and helps you get to more accurate numbers. Try to analyze sales data for at least 12 months. Otherwise, there may not be enough data to get accurate sales predictions.
Sales forecasting is significantly more accurate when using a CRM instead of a spreadsheet. When a company is just starting out, sales teams usually rely on spreadsheets or back-of-the-napkin ways to calculate their sales forecasts. This may work for a while, but eventually, you’ll find this doesn’t scale.
The reality is, selling is more complex than ever. It involves everything from how demand generation campaigns are performing to how your phone calls to prospects are landing. The more you want to sell, the more you’ll want to rely on a CRM .
See how Salesforce manages forecasts with confidence
The secret to an accurate forecast? Reliable, well-maintained pipelines. See how we manage both efficiently (with the help of the right technology), and use our best practices in your business.

Just For You

A Close Look at At-Risk Pay and the Purpose Behind Performance-Based Compensation

How Presales Sets the Stage for Your Team’s Next Big Deal


Explore related content by topic
- Experience Cloud
- Sales Cloud
- Revenue Cloud
- Service Cloud
- Customer Experience
- Salesblazer
- Forecasting
- Sales Management

Paul Bookstaber is a writer at Salesforce. He has a decade of experience in content marketing in B2B tech. Before that, he published a magazine and ran a tabloid blog. Today, he splits his time between Florida and the Mountain West, and loves to hike, ski, and watch Bravo. He is in a polyamorous relationship with Luke and Roger, who are cats.
Get the latest articles in your inbox.

The Sales Team’s Guide to Using Mutual Action Plans

Why Are Commission Caps So Rare in Modern-Day Sales?

What Is Sales Performance Management? Examples and Tips

How to Calculate Your Sales Growth Rate (with Examples)

Why Incentive Compensation Matters – and How to Build the Program that Suits Your Business

Why Sales and Marketing Have to Work Together if You Want to Win

27 Top Sales Influencers You Should Follow in 2024

22 Sales Training Programs and Courses to Level Up Your Game

New to Salesforce?
- What is Salesforce?
- Best CRM software
- Explore all products
- What is cloud computing
- Customer success
- Product pricing
About Salesforce
- Salesforce.org
- Sustainability
Popular Links
- Salesforce Mobile
- AppExchange
- CRM software
- Salesforce LIVE
- Salesforce for startups
- América Latina (Español)
- Brasil (Português)
- Canada (English)
- Canada (Français)
- United States (English)
Europe, Middle East, and Africa
- España (Español)
- Deutschland (Deutsch)
- France (Français)
- Italia (Italiano)
- Nederland (Nederlands)
- Sverige (Svenska)
- United Kingdom (English)
- All other countries (English)
Asia Pacific
- Australia (English)
- India (English)
- Malaysia (English)
- ประเทศไทย (ไทย)
© Copyright 2024 Salesforce, Inc. All rights reserved. Various trademarks held by their respective owners. Salesforce, Inc. Salesforce Tower, 415 Mission Street, 3rd Floor, San Francisco, CA 94105, United States
Bringing a real-world edge to forecasting
CFOs know what a “good” forecasting process should look like: it should be accurate and comprehensive but flexible enough to inform a range of critical business decisions—capital reallocation, hiring, strategy, sales, production, and more.
But CFOs also recognize that there is no “typical” forecasting process: it will look different in different organizations based on sector-specific factors, feedback cycles, and, most critically, how the forecast is being used. A maker of packaged foods that is releasing new products every quarter will rely on the forecast to keep a close watch on inventory, while a mining company that is considering new plant construction over the next three years will use the forecast to predict capacity and pricing.
How do your forecasts roll?
The best predictor of satisfaction among the CFOs we surveyed was whether or not they used a “rolling” forecast—one that provides frequent updates and adjusts inputs in a predictable way as conditions change. These types of forecasts are common in a retail or software setting, where customers provide near-real-time feedback through usage, traffic, and purchasing patterns. Rolling forecasts can be used to great effect in other situations as well. An organization that maintained industrial equipment built a simple model to update its forecasts as equipment came into the shop, rather than waiting until end-of-year estimates to adjust financial figures. This helped the company avoid sudden swings in recognized revenue in a percent-complete contract model. It also put the management team on the offensive as certain contracts over- or underperformed during the year.
Data availability is typically a major inhibitor of rolling forecasts. But it doesn’t have to be. Many companies have reams of data at their fingertips but don’t know where to get started. In our survey, we found that less than half of companies use any given form of nonfinancial internal data in creating their forecasts. Only 35 percent use external market data, and only 18 percent use additional types of data like weather, traffic, and other external factors as leading indicators of the business (exhibit). With such scant inputs, it’s no surprise that forecast outputs are often underwhelming.
Of course, there is still an important place for one-time forecasting to make major decisions. When it comes to drug development, the initiation of capital projects, or the decision to enter new markets, for instance, senior leaders’ overoptimism about projects, concerns about sunk costs, and other biases can get in the way of their review of the full range of potential outcomes. In these cases, conducting an assessment against a carefully selected reference class of similar business scenarios can produce valuable insights.
What’s more, companies’ access to ever-larger data sets continues to complicate the forecasting process as much as it enlightens it, leading to even more variety in how forecasts are built. Many of the 130 CFOs we surveyed in a recent study 1 We polled 130 CFOs—90 from small and medium-size companies (less than $200 million in revenue) and 40 from large companies (greater than $1 billion in revenue). Half of them were members of the CFO Leadership Council, a North American professional association of finance executives. The research base included companies from a range of sectors, including technology, healthcare, and industrials. say they now run more than one type of forecasting process in their organizations—rolling forecasts to manage the business, and ad hoc processes to make specific decisions (see sidebar, “How do your forecasts roll?”).
But while many of the CFOs we surveyed expressed general satisfaction with the results of their forecasting efforts (exhibit), some 40 percent also told us that their forecasts are not particularly accurate and that the process takes far too much time.
That’s likely because they use financial measures rather than operational outcomes as indicators of forecasting effectiveness—if they review the success of their forecasting efforts at all. A focus only on financial inputs can mask big issues with companies’ forecasting processes. By contrast, incorporating real-world operations insights into the financial-forecasting process can help CFOs and finance teams predict bottom-line issues early, based on a careful assessment of quality, operations, and customer-retention measurements. Senior leaders can then address performance issues before they become big problems, and the incentives of even the smallest subunit of the business would be targeted toward long-term value creation.
Integrating operations data within forecasts won’t be easy, of course. Finance and business leaders will need to let go of traditional budgeting mindsets and explore new ways of working together. The good news? Automation and other digital technologies now make that easier. And four criteria show promise for injecting more accuracy and reliability into forecasting models, regardless of industry: build a momentum case separate from the business plan, use a variety of operational and external inputs, automate the forecast, and measure effectiveness with a fine-grained level of detail.
Building a better forecast
The typical forecasting process follows a pattern that contributes to inaccurate projections and a defeating, self-reinforcing cycle.
At one large industrial manufacturing and services company, for instance, managers in the business units and subunits are held to earnings targets that are rolled up into the overarching forecast. Over the years, these managers have become adept at finding the one or two things that will help them make their number, often at the expense of longer-term investment in quality, customer retention, and operational efficiency. Under the typical finance-focused forecasting exercise, no one checks operational metrics so long as the bottom line comes in strong, which it had for a while. Now the company’s performance is stuck in low gear: the most successful business units keep committing to higher numbers that eventually lead to a deterioration in quality, while the least successful businesses get scrutinized, adjusted, and fixed. The winners and losers flip, and the cycle repeats itself.
Some companies have worked at breaking this disappointing pattern. They’ve begun rethinking how they measure the success of their forecasting processes—focusing on the following four questions:
Have we built a momentum case? Many financial-planning and analysis (FP&A) teams spend most of their time looking at historical data to explain current outcomes. When they do get to look forward, they are likely focused on the budget, or on rolling up commitments from different business units into the overall business plan. Sometimes the business plan itself passes for the forecast. This, of course, just creates an echo chamber. No one is explicitly discussing how external factors and impending market shifts could affect forecasts. A better approach is to create a market-momentum case that relies on internal and external data as well as end-market trends to build the forecast. Once this unbiased momentum case is in place, senior managers can layer new and additional market information on top. Then any initiatives, investments, and strategic moves can be assessed relative to the base case.
In one industrial company that makes construction products, for instance, initiatives proposed across different lines of business were being valued in a vacuum. The teams charged with managing grouts and concrete, for instance, had no line of sight into what was going on with the frame-protection or frame-reinforcement business units. It was hard for senior leaders, then, to understand how to react to market shifts throughout the year and what actions the company should take. The FP&A team built a momentum case that set targets based on market dynamics in individual lines of business rather than allocating a single rate of improvement to all products. These targets much more closely reflected the full potential of the individual business lines, and, when compared with base-case and other scenarios, allowed the company to allocate resources and take on initiatives to address market changes with much more agility than before.
The CFO’s role in this process is to work with business-unit leaders to set realistic but aggressive targets in light of the market environment in which they operate. That means providing clear direction to all the business-unit finance leaders about which basic assumptions to use in the forecasts—for instance, market-growth rates—even if the process of forecasting sales and profit for each business remains distributed.
Are we using a variety of operational indicators and external inputs? Operational inputs are important leading indicators of performance; often, line leaders know how the company is faring months before the financial reports appear. Many times, however, operating data sit in disparate systems that don’t work well with financial enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. And rather than adhere to a standard set of key performance indicators (KPIs) for use throughout the organization, managers at different levels use different indicators. Some track the business, some manage individual performance, and some review indicators of financial performance.
One aerospace company had collected thousands of data points on every aircraft in its fleet. However, when the time came to create the annual forecast, it used only a small fraction of the data because much of the information was inaccessible. Operational and financial data were siloed, spread across many different IT systems. Recognizing a lost opportunity, the company created a thin analytics layer—a simple rules-based SQL program in a data lake—on top of its existing IT infrastructure. This program automatically gathered data from the multiple systems, allowing business-unit leaders to see information about the entire fleet on a single screen. They finally had operational KPIs integrated into the financial picture. If one site went overbudget on a repair, that information would get immediately recorded in the master model. Leaders at the company are now more confident about setting targets and stretch goals based on a distinct set of operational issues.
Surprisingly, the technical changes required were not difficult; in most cases, it takes no more than a few weeks or months (depending on product complexity) to rebuild forecasting models and link them to the company’s financial-management systems.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy and Corporate Finance Practice ?
Have we explored automation? Once business leaders have identified the most critical inputs to include in the forecast model, they should consider ways to automate the process and make it easier for business and operations teams to work together on forecasts.
In some cases, the company will need to explore new technologies and modeling techniques. Leadership at a multinational pharmaceutical company, for instance, used machine learning and advanced analytics to understand the variables affecting the performance of its clinical trials. The operations team worked with the business side to aggregate five years of data from more than 300 separate clinical trials (involving more than 100,000 patients) and to evaluate factors such as the clinical trials’ time and costs across multiple geographies. They saw correlations between the rate of enrollment in certain sites and the success of the trials, and they used the data to introduce improvements.
In other instances, the whole forecasting model may be run automatically using macro commands in an Excel spreadsheet, with only a handful of manual inputs from the operations team, the CFO, and the finance team.
Whichever method is chosen, companies can use data that already exist in the company’s ERP or other functional databases and, with simple transformations, spit out a real-time dashboard.
Once the CFO or another senior finance leader decides that automation is a high priority for FP&A, he or she should convene a small team (no more than three to five people from IT and finance) to “connect the pipes.” The team should tackle this challenge incrementally—automating some elements of the forecasting process initially and adding others once the value of the effort is proved.
Are we measuring effectiveness at a fine-grained level? Once the forecast incorporates a range of internal and external inputs, CFOs can test the accuracy of each input, as well as the accuracy of aggregate estimates. By monitoring detailed measures, such as labor productivity, on-time delivery, and other metrics associated with costs and revenues, business leaders will be able to spot the “softer” KPIs that are being overlooked in light of temporarily strong bottom-line performance. They can then react accordingly.
When the CFO and operations leader at one consumer-goods company reviewed underlying performance metrics for each of the business lines, they saw that a major business unit was being propped up by one rapidly growing product. Based on this insight, senior leadership decided to sell the underperforming parts of that business and double-down where they saw profitable growth. The team had until that point not looked past the simple financial performance of the business unit to the product-level sales and profitability.
If finance and operations leaders can maintain the forecast as a living model, with a clear feed-back loop, they can ensure that any forecasting failures (and there will be failures) lead to real improvements.

The right role for multiples in valuation
Getting started.
Making these changes to the forecasting processes can seem like a monumental shift—“rebuilding the plane while it is flying” is a common complaint among finance teams. With that in mind, the most effective move is to start small. For instance, the CFO should task the FP&A team in a single business unit or region to come up with a model and pressure test it both in the finance function and with nonfinancial leaders. Once there is agreement that the model is unearthing valuable insights, it can be automated, and a similar process can be scaled to the rest of the business.
It’s important that the forecast be pulled out of the politics of budgeting, and that inputs are streamlined, automated, and pressure tested. Even if the business units each manage their own forecast, there is a role for central FP&A to debias the process. The FP&A team at one fashion company, for instance, built a simple regression analysis to understand which business units were forecasting statistically significant changes in their performance or growth trajectory. The outliers were required to provide a detailed buildup of initiatives to prove the forecast was achievable.
Once the hard work of process reengineering is done, finance teams will see a dramatic change in the value of forecasts to the business. They can use time previously spent justifying assumptions to focus on delivering new ideas for improving the performance of the business—and serving as proactive business partners.
Ankur Agrawal is a partner in McKinsey’s New York office, and Jonathan Slonim is a consultant in the New Jersey office. Mark Khavkin is the chief financial officer of Pantheon Platform in San Francisco.
The authors wish to thank the CFO Leadership Council for its contributions to this article.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Is your budget process stuck on last year’s numbers?

Bias Busters: Being objective about budgets

How Business Forecasting Works and Why You Should Use It

As you grow your small business, you need to plan and develop your long-term strategy. Well-run companies don’t just address things as they come up, they plan ahead. As a small business owner, it’s important to keep sight of the bigger picture through business forecasting.
With business forecasting, companies use different methods and data to predict market trends to help determine their short-term and long-term business outlook. This data is a vital part of helping companies grow, start new initiatives, and plan their finances for the quarter and year. It can also help you plan for potential seasonal dips in your cash flow or plan for future expansions.
Keep reading to find out more about the different types of and elements that make up business forecasting as well as why every small business should consider using forecasting methods.
What Is Business Forecasting?
Business forecasting is making informed predictions about business metrics. That can include specific aspects of a business, such as launching a new product, or cover the company as a whole. Often, financial, operational, and business decisions will be based on these forecasting techniques.
While no one can predict the future, business forecasting methods can help even small businesses develop strategies. With business forecasting, historical data is collected and analyzed to find potential patterns. Today, most forecasting includes some form of technology, such as artificial intelligence, to help develop models.
Why Should You Use Business Forecasting?
Business forecasts can be used for budgeting, expanding your business , figuring out where to allocate funding, making decisions about cash flow, and helping create timelines for business operations, such as new initiatives. It helps companies make decisions based on data rather than on intuition and opinion.
For example, forecasting can be used to figure out how much pressure competition will put on your business, measure the demand for a product, help allocate resources, and forecast earnings.
Small business owners can use business forecasting to identify weaknesses in their long-term plans, come up with a plan of action for the future growth of the company, and adapt to changes in the economy.
Types of Business Forecasting
There are a few methods to conduct business forecasting and planning. Most are either qualitative (which uses non-numerical data such as market reports and surveys) or quantitative (meaning they use mathematical and statistical modeling).
Qualitative Models
Qualitative forecasting models are usually used for short-term forecasting. They tend to rely more on opinions and trends rather than measurable data. This type of analysis is more expert-driven but can be limited to longer-term projections.
Some of the common qualitative models for business forecasting include:
Market research: Market research is a business forecasting technique that uses polling and surveying large numbers of prospective customers to collect information. This might be on the specific brand or product or about the company as a whole. Market research can be used to predict if customers will buy more or less of a specific product in the foreseeable future.
Delphi method: With the delphi method of analysis, experts are polled about specific topics. This usually includes a panel where the experts are presented with a questionnaire in a few rounds. After each round, the experts can adjust their responses based on the aggregate answers of all respondents. The opinions are then compiled to help forecast future trends.
Quantitative Models
Quantitative methods use hard data and avoid opinions or polls from people. Instead, these techniques focus solely on numbers. Quantitative models are used to predict long-term trends and variables, such as sales forecasts.
Some of the most common quantitative forecasting include:
Time series methods: This forecasting model, also called a time series analysis, uses past data points to predict the future, excluding deviations. It’s also the most common method used by companies. To use a time series method though, you need to have access to a lot of historical data that shows clear and stable trends, otherwise, your forecasting models will be inaccurate.
Indicator approach: This methodology uses the relations between different types of indicators — for example, looking at gross domestic product and the unemployment rate. It will look at the performance of the lagging indicators to try to measure the impact of business strategies.
Econometric modeling: With econometric modeling, you make several mathematical equations to test the consistency of datasets over time and measure the relationship between the different sets of data. This method is very math-heavy and can be used to predict changes in the economy and market conditions and the potential impact those changes could have on a company.
5 Steps of Business Forecasting
To get accurate forecasts in your business forecasting, you need to make sure the information you get is accurate. While each method uses different strategies, they generally each follow the same steps:
Identify your question or problem: First, you need to figure out what it is you want to know. What problem in your business are you trying to solve? For example, you might want to know if you can meet demand next quarter or calculate how much of a product you will sell over the year.
Gather data: Next, you need to figure out the data you have available to you. That can be anything from sales data, how long it takes you to produce products, demand forecasts, customer satisfaction forms, and more.
Choose your forecasting method: Once you have your data, you can decide which type of business forecasting analysis you want to use. The type of method you will choose will depend on what it is you’re trying to find out.
Make an estimate: Using the forecasting method chosen, you can start to make business predictions. This can help you estimate future business performance. Keep in mind that your forecasts are only as good as your data, so make sure you have the most accurate, updated data points.
Figure out any discrepancies: Look back at your predictions to determine if they were accurate. Keep track of your findings to help improve your forecasting models in the future. You can also consider using third-party business forecasting models and data to help create business predictions.
Grow Your Company With Accurate and Reliable Data
Business forecasting can help companies with their business planning and decision-making. Forecasting models help predict future trends and assist you in figuring out your operations and budgeting forecasts for the next year.
While there’s no crystal ball that can tell you exactly what will happen in the future, forecasting is the closest you can get to understanding the future. Of course, the more data you have, the easier it is to make accurate business forecasts.
If your financial models show that you might have a dip in your cash flow, make sure to plan ahead. With Backd, you can get access to a working capital advance of up to $2 million that can be used to bridge a seasonality gap or invest in equipment to expand your business.
You can also get a business line of credit so you have access to funds whenever you need them. Plus, you can apply in just minutes and your credit score won’t be affected.
Apply today and find out if you qualify in just 24 hours.
What would you do with the right amount of capital?
Working capital advance.
Easy payment structures offer amounts with fast turnaround, Simple and easy process to access working capital.
- Flexible - no collateral required
- Terms up to 16 months
- Automatic daily or weekly, or semi-monthly payments
Learn more...
Business Line of Credit
Get instant access to revolving credit with unlimited terms, and the best rates for your business.
- Draw funds anytime
- $10K - $750K
- Unlimited terms, incredible rates
- Soft credit pull that doesn't affect your credit score
More Articles
Working capital.
What is working capital? How do you ensure you’ve got the right amount? What do you do if you need an influx of it, fast?
Working Capital Ratio
Working capital ratios are delicate things. How do you determine the sweet spot for your business?
Working Capital Management
A breakdown of the components of working capital and the approaches to working capital management, as well as short-term business funding.
Working Capital Financing: What Are the Different Options?
Working capital financing helps you keep your business running when you need to cover a cash flow gap. Discover the funding available to you and how to choose.

1949 S I-35 Frontage Rd Austin, Texas 78741, USA
Business Plan
- Our Services
- Our Process
WhatsApp: +92 345 5384026
E-mail: [email protected]
A Comprehensive Guide: How to Forecast Revenues for Your Business Plan
Introduction:.
Forecasting revenues is a crucial aspect of developing a business plan. Accurate revenue projections not only attract investors but also provide a roadmap for sustainable growth and financial success. This article will provide you with a step-by-step guide to help you forecast revenues effectively. By following these strategies and best practices, you can make informed decisions, set realistic goals, and build a solid foundation for your business.
I. Understand Your Market and Customers:
Before you can forecast revenues, it's essential to gain a deep understanding of your target market and customers. Conduct market research to analyze trends, demand, and competition. Identify your target audience's needs, preferences, and purchasing behavior. This information will help you estimate the potential market size and assess the revenue potential for your products or services.
II. Break Down Revenue Streams:
Next, break down your revenue streams into specific categories. For example, if you have multiple products or services, create separate revenue streams for each. Consider the pricing structure, sales volume, and average transaction value for each category. This breakdown enables you to analyze and forecast revenues with greater accuracy.
III. Utilize Historical Data:
If you have been in business for some time, historical data can serve as a valuable resource for revenue forecasting. Analyze past financial records, sales data, and customer trends. Identify patterns, seasonal variations, and growth rates. Use this information as a baseline to project future revenues, accounting for any market changes or new product launches.
IV. Determine Key Assumptions:
Forecasting revenues involves making certain assumptions about your business and the market. Identify the key factors that will impact your revenue projections, such as market growth rates, pricing changes, or shifts in consumer behavior. Document these assumptions clearly, ensuring they are realistic and supported by data and market trends.
V. Use Multiple Forecasting Methods:
To enhance the accuracy of your revenue projections, employ various forecasting methods. Here are a few commonly used techniques:
a) Top-Down Approach:
Start with the overall market size, estimate your market share, and calculate revenues based on this share.
b) Bottom-Up Approach:
Begin with individual product or service sales projections and aggregate them to obtain total revenue estimates.
c) Time-Series Analysis:
Analyze historical sales data to identify patterns, trends, and seasonality. Apply statistical methods like moving averages or exponential smoothing to project future revenues.
d) Market Research and Surveys:
Conduct market surveys or customer interviews to gather insights on demand, price sensitivity, and purchasing behavior. Use this data to estimate market size and forecast revenues.
VI. Account for External Factors:
Consider external factors that could impact your revenue forecast, such as economic conditions, industry trends, regulatory changes, or technological advancements. Conduct a thorough analysis of these factors and assess their potential influence on your business. Adjust your revenue projections accordingly to reflect any anticipated challenges or opportunities.
VII. Monitor and Review:
Once you have developed your revenue forecast, it is crucial to continuously monitor and review its accuracy. Regularly compare your projections with actual revenue performance and adjust your forecast as needed. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to track your progress and make informed decisions to drive revenue growth.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can enhance the accuracy and reliability of your revenue forecast for your business plan.
Here are a few additional tips to keep in mind:
Sensitivity Analysis:
Perform a sensitivity analysis by testing your revenue projections against various scenarios. This will help you understand the potential impact of changes in key variables such as pricing, market share, or economic conditions. It provides a more comprehensive view of the range of possible outcomes.
Seek Expert Advice:
If you're unsure about certain aspects of revenue forecasting or lack expertise in financial analysis, consider consulting with us. At businessplanprovider.com , we have professionals such as accountants, financial advisors, and industry experts. Their insights and guidance can add credibility to your revenue forecast.
Regularly Update Your Forecast:
Revenue forecasting is not a one-time exercise. As your business grows and market conditions evolve, it's crucial to update your forecast regularly. Review and revise your projections quarterly or annually, taking into account any new information or changes in your business environment.
Validate with Market Feedback:
Don't rely solely on internal data or assumptions. Seek feedback from potential customers, industry experts, or mentors to validate your revenue projections. Incorporate their insights into your forecast, as they can provide valuable perspectives and highlight blind spots.
Be Realistic and Conservative:
While it's important to set ambitious goals, it's equally crucial to be realistic and conservative in your revenue forecast. Investors and stakeholders appreciate a forecast that demonstrates a clear understanding of potential challenges and uncertainties. Avoid overestimating revenues, as it may lead to unrealistic expectations and undermine your credibility.
Remember that revenue forecasting is both an art and a science. It requires a blend of data analysis, market understanding, and informed decision-making. Be prepared to adjust your forecast as new information becomes available or market dynamics change.
Conclusion:
Forecasting revenues for your business plan requires a systematic and data-driven approach. By understanding your market and customers, utilizing historical data, making key assumptions, employing multiple forecasting methods, accounting for external factors, and continuously monitoring and reviewing your forecast, you can develop realistic revenue projections. Remember, revenue forecasting is an ongoing process that should be regularly updated to align with market changes and business growth. By accurately forecasting revenues, you can make informed strategies, allocate resources effectively, and attract investors and stakeholders who are confident in the potential of your business.
A well-structured and thoughtfully prepared revenue forecast will not only guide your business planning and decision-making but also demonstrate your professionalism and strategic thinking to potential investors. By following the steps and best practices outlined in this guide, you can develop a robust revenue forecast that will support the growth and success of your business.
Transforming Your Vision into a Winning Business Plan
Get in touch, got some ideas have questions we're ready for them..
©2023 businessplanprovider.com. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy
How to Create a Cash Flow Forecast

10 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023
A good cash flow forecast might be the most important single piece of a business plan . All the strategy, tactics, and ongoing business activities mean nothing if there isn’t enough money to pay the bills.
That’s what a cash flow forecast is about—predicting your money needs in advance.
By cash, we mean money you can spend. Cash includes your checking account, savings, and liquid securities like money market funds. It is not just coins and bills.
Profits aren’t the same as cash
Profitable companies can run out of cash if they don’t know their numbers and manage their cash as well as their profits.
For example, your business can spend money that does not show up as an expense on your profit and loss statement . Normal expenses reduce your profitability. But, certain spending, such as spending on inventory, debt repayment, new equipment, and purchasing assets reduces your cash but does not reduce your profitability. Because of this, your business can spend money and still look profitable.
On the sales side of things, your business can make a sale to a customer and send out an invoice, but not get paid right away. That sale adds to the revenue in your profit and loss statement but doesn’t show up in your bank account until the customer pays you.
That’s why a cash flow forecast is so important. It helps you predict how much money you’ll have in the bank at the end of every month, regardless of how profitable your business is.
Learn more about the differences between cash and profits .
- Two ways to create a cash flow forecast
There are several legitimate ways to do a cash flow forecast. The first method is called the “Direct Method” and the second is called the “Indirect Method.” Both methods are accurate and valid – you can choose the method that works best for you and is easiest for you to understand.
Unfortunately, experts can be annoying. Sometimes it seems like as soon as you use one method, somebody who is supposed to know business financials tells you you’ve done it wrong. Often that means that the expert doesn’t know enough to realize there is more than one way to do it.
- The direct method for forecasting cash flow
The direct method for forecasting cash flow is less popular than the indirect method but it can be much easier to use.
The reason it’s less popular is that it can’t be easily created using standard reports from your business’s accounting software. But, if you’re creating a forecast – looking forward into the future – you aren’t relying on reports from your accounting system so it may be a better choice for you.
That downside of choosing the direct method is that some bankers, accountants, and investors may prefer to see the indirect method of a cash flow forecast. Don’t worry, though, the direct method is just as accurate. After we explain the direct method, we’ll explain the indirect method as well.
The direct method of forecasting cash flow relies on this simple overall formula:
Cash Flow = Cash Received – Cash Spent
And here’s what that cash flow forecast actually looks like:
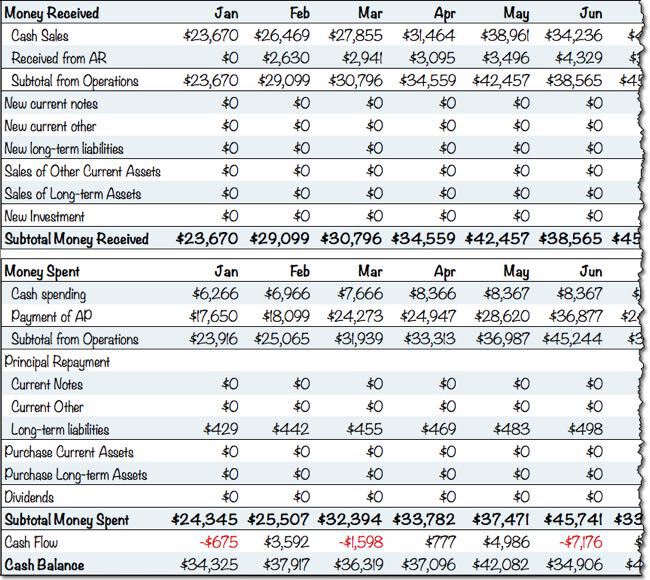
Let’s start by estimating your cash received and then we’ll move on to the other sections of the cash flow forecast.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Forecasting cash received
You receive cash from four primary sources:
1. Sales of your products and services
In your cash flow forecast, this is the “Cash from Operations” section. When you sell your products and services, some customers will pay you immediately in cash – that’s the “cash sales” row in your spreadsheet. You get that money right away and can deposit it in your bank account. You might also send invoices to customers and then have to collect payment. When you do that, you keep track of the money you are owed in Accounts Receivable . When customers pay those invoices, that cash shows up on your cash flow forecast in the “Cash from Accounts Receivable” row. The easiest way to think about forecasting this row is to think about what invoices will be paid by your customers and when.
2. New loans and investments in your business
You can also receive cash by getting a new loan from a bank or an investment. When you receive this kind of cash, you’ll track it in the rows for loans and investments. It’s worth keeping these two different types of cash in-flows separate from each other, mostly because loans need to be repaid while investments do not need to be repaid.
3. Sales of assets
Assets are things that your business owns, such as vehicles, equipment, or property. When you sell an asset, you’ll usually receive cash from that sale and you track that cash in the “Sales of Assets” section of your cash flow forecast. For example, if you sell a truck that your company no longer needs, the proceeds from that sale would show up in your cash flow statement.
4. Other income and sales tax
Businesses can bring in money from other sources besides sales. For example, your business may make interest income from the money that it has in a savings account. Many businesses also collect taxes from their customers in the form of sales tax, VAT, HST/GST, and other tax mechanisms. Ideally, businesses record the collection of this money not in sales but in the cash flow forecast in a specific row. You want to do this because the tax money collected isn’t yours – it’s the government’s money and you’ll eventually end up paying it to them.
Forecasting cash spent
Similar to how you forecast the cash that you plan on receiving, you’ll forecast the cash that you plan on spending in a few categories:
1. Cash spending and paying your bills
You’ll want to forecast two types of cash spending related to your business’s operations: Cash Spending and Payment of Accounts Payable. Cash spending is money that you spend when you use petty cash or pay a bill immediately. But, there are also bills that you get and then pay later. You track these bills in Accounts Payable . When you pay bills that you’ve been tracking in accounts payable, that cash payment will show up in your cash flow forecast as “payment of accounts payable”. When you’re forecasting this row, think about what bills you’ll pay and when you’ll pay them. In this section of your cash flow forecast, you exclude a few things: loan payments, asset purchases, dividends, and sales taxes.
2. Loan Payments
When you make forecast loan repayments, you’ll forecast the repayment of the principal in your cash flow forecast. The interest on the loan is tracked in the “non-operating expense” that we’ll discuss below.
3. Purchasing Assets
Similar to how you track sales of assets, you’ll forecast asset purchases in your cash flow forecast. Asset purchases are purchases of long-lasting, tangible things. Typically, vehicles, equipment, buildings, and other things that you could potentially re-sell in the future. Inventory is an asset that your business might purchase if you keep inventory on hand.
4. Other non-operating expenses and sales tax
Your business may have other expenses that are considered “non-operating” expenses. These are expenses that are not associated with running your business, such as investments that your business may make and interest that you pay on loans. In addition, you’ll forecast when you make tax payments and include those cash outflows in this section.
Forecasting cash flow and cash balance
In the direct cash flow forecasting method, calculating cash flow is simple. Just subtract the amount of cash you plan on spending in a month from the amount of cash you plan on receiving. This will be your “net cash flow”. If the number is positive, you receive more cash than you spend. If the number is negative, you will be spending more cash than you receive. You can predict your cash balance by adding your net cash flow to your cash balance.
- The indirect method
The indirect method of cash flow forecasting is as valid as the direct and reaches the same results.
Where the direct method looks at sources and uses of cash, the indirect method starts with net income and adds back items like depreciation that affect your profitability but don’t affect the cash balance.
The indirect method is more popular for creating cash flow statements about the past because you can easily get the data for the report from your accounting system.
You create the indirect cash flow statement by getting your Net Income (your profits) and then adding back in things that impact profit, but not cash. You also remove things like sales that have been booked, but not paid for yet.
Here’s what an indirect cash flow statement looks like:
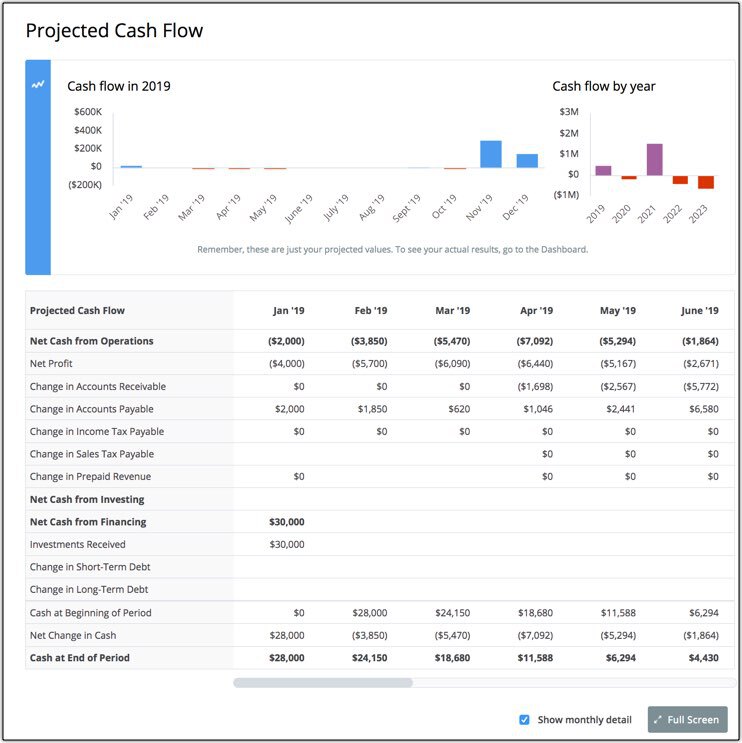
There are five primary categories of adjustments that you’ll make to your profit number to figure out your actual cash flow:
1. Adjust for the change in accounts receivable
Not all of your sales arrive as cash immediately. In the indirect cash flow forecast, you need to adjust your net profit to account for the fact that some of your sales didn’t end up as cash in the bank but instead increased your accounts receivable.
2. Adjust for the change in accounts payable
Very similar to how you make an adjustment for accounts receivable, you’ll need to account for expenses that you may have booked on your income statement but not actually paid yet. You’ll need to add these expenses back because you still have that cash on hand and haven’t paid the bills yet.
3. Taxes & Depreciation
On your income statement, taxes and depreciation work to reduce your profitability. On the cash flow statement, you’ll need to add back in depreciation because that number doesn’t actually impact your cash. Taxes are may have been calculated as an expense, but you may still have that money in your bank account. If that’s the case, you’ll need to add that back in as well to get an accurate forecast of your cash flow.
4. Loans and Investments
Similar to the direct method of cash flow, you’ll want to add in any additional cash you’ve received in the form of loans and investments. Make sure to also subtract any loan payments in this row.
5. Assets Purchased and Sold
If you bought or sold assets, you’ll need to add that into your cash flow calculations. This is, again, similar to the direct method of forecasting cash flow.
- Cash flow is about management
Remember: You should be able to project cash flow using competently educated guesses based on an understanding of the flow in your business of sales, sales on credit, receivables, inventory, and payables.
These are useful projections. But, real management is minding the projections every month with plan versus actual analysis so you can catch changes in time to manage them.
A good cash flow forecast will show you exactly when cash might run low in the future so you can prepare. It’s always better to plan ahead so you can set up a line of credit or secure additional investment so your business can survive periods of negative cash flow.
- Cash Flow Forecasting Tools
Forecasting cash flow is unfortunately not a simple task to accomplish on your own. You can do it with spreadsheets, but the process can be complicated and it’s easy to make mistakes.
Fortunately, there are affordable options that can make the process much easier – no spreadsheets or in-depth accounting knowledge required.
If you’re interested in checking out a cash flow forecasting tool, take a look at LivePlan for cash flow forecasting. It’s affordable and makes cash flow forecasting simple.
One of the key views in LivePlan is the cash flow assumptions view, as shown below, which highlights key cash flow assumptions in an interactive view that you can use to test the results of key assumptions:

With simple tools like this, you can explore different scenarios quickly to see how they will impact your future cash.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Profits aren’t the same as cash
Related Articles

8 Min. Read
How to Plan Your Exit Strategy

1 Min. Read
How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI)

4 Min. Read
How to Create an Expense Budget

2 Min. Read
How to Use These Common Business Ratios
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
7-step guide to financial forecasting & planning for any business
What is financial forecasting, why is it important, and how to properly conduct financial planning and forecasting
- What is financial forecasting?
- Why is it important?
- 4 common types of financial forecasting
- How to do financial forecasting in 7 steps
- Financial forecasting FAQs
Join our newsletter for the latest in SaaS
By subscribing you agree to receive the Paddle newsletter. Unsubscribe at any time.
Uncertainty is one of the constant aspects of doing business. Many factors beyond your control can potentially influence the market in ways you didn't expect. For example, new technologies are constantly changing operations across almost all industries at a fundamental level.
It pays to know what to expect in the near future and plan ahead, hence the need for financial forecasting. Every business (including monopolies) could benefit incredibly from regular financial forecasting . Here is a comprehensive guide on the importance of financial forecasting for your business model and how to do it.
Failure to conduct regular financial forecasting leaves you flying blind.
What is financial forecasting?
Financial forecasting refers to financial projections performed to facilitate any decision-making relevant for determining future business performance. The financial forecasting process includes the analysis of past business performance, current business trends , and other relevant factors.
However, some aspects of financial forecasting may change depending on the type and purpose of the forecast, as will be discussed later.
Importance of financial forecasting
Hypothetically speaking, failure to conduct regular financial forecasting leaves you flying blind. Regular forecasting has extensive benefits for some of your business' fundamental operations, including:
Annual budget planning
A budget represents your business' cash flow, financial positions, and future goals and expectations for a set fiscal period. Financial forecasting and planning work in tandem, as forecasting essentially offers an insight into your business' future—these insights help make budgeting accurate.
Establishing realistic business goals
Accurate forecasting will help predict whether (and by how much) your business will grow or decline. As such, you can set realistic and achievable goals—and manage your expectations.
Identifying problem areas
Financial forecasting can help you identify ongoing problems by analyzing the business' past performance. Additionally, you can identify potential problems by getting an insight into what the future holds.
Reduction of financial risk
You risk overspending by creating a budget without financial forecasting. In fact, most of your financial decisions would be ill-informed without the input of a financial forecast's results.
Greater company appeal to attract investors
Investors use a company's financial forecast to predict its future performance—and the potential ROIs on their investments. Additionally, regular forecasting shows your investors that you are in control and have a solid business plan prepared for the future.
4 common types of financial forecasting
Businesses conduct financial forecasting for varying purposes. Consequently, forecasting practices are categorized into four types:
1. Sales forecasting
Sales forecasting entails predicting the amounts of products/services you expect to sell within a projected fiscal period. There are two sales forecasting methodologies: top-down forecasting and bottom-up forecasting.
Sales forecasting has many uses and benefits, including budgeting and planning production cycles. It also helps companies manage and allocate resources more efficiently.
2. Cash flow forecasting
Cash flow forecasting entails estimating the flow of cash in and out of the company over a set fiscal period. It's based on factors such as income and expenses. It has many uses and benefits, including identifying immediate funding needs and budgeting. However, it is worth noting that cash flow financial forecasting is more accurate over a short term.
3. Budget forecasting
As a financial guide for your business' future, a budget creates certain expectations about your company's performance. Budget forecasting aims to determine the ideal outcome of the budget, assuming that everything proceeds as planned. It relies on the budget's data, which relies on financial forecasting data.
4. Income forecasting
Income forecasting entails analyzing the company's past revenue performance and current growth rate to estimate future income. It is integral to doing cash flow and balance sheet forecasting. Additionally, the company's investors, suppliers, and other concerned third parties use this data to make crucial decisions. For example, suppliers use it when determining how much to credit the company in supplies.
How to do financial forecasting in 7 steps
Many integral aspects of your company's current and future operations hinge on the results of your financial forecasts. For example, forecasting results will influence investors' decisions, determine how much your company can get in credit, and more.
As such, accuracy cannot be overemphasized. Here is a step-by-step guide to ensure that you do it right:
1. Define the purpose of a financial forecast
What do you hope to learn from the financial forecast? Do you hope to estimate how many units of your products or services you will sell? Or perhaps you wish to see how the company's current budget will shape its future? Defining your financial forecast's purpose is essential to determining which metrics and factors to consider when doing it.
2. Gather past financial statements and historical data
One of the components of financial forecasting involves analyzing past financial data, as explained. As such, it is important to gather all relevant historical data and records , including:
- Liabilities
- Investments
- Expenditures
- Comprehensive income
- Earnings per share
- Fixed costs
It's important to ensure that you gather all required information as your financial forecast's results will be inaccurate if you exclude relevant data.
3. Choose a time frame for your forecast
Financial forecasts are designed to give business owners an insight into the company's future. You get to decide how far into the future to look, and it can range from several weeks to several years. However, most companies do forecasts for one fiscal year.
Financial forecasts change over time as factors such as business and market trends change. Consequently, it is worth noting that financial forecasting is more accurate in the short term than in the long term.
4. Choose a financial forecast method
There are two financial forecasting methods:
- Quantitative forecasting uses historical information and data to identify trends, reliable patterns, and trends.
- Qualitative forecasting analyzes experts' opinions and sentiments about the company and market as a whole.
Each method is suitable for different uses and has its strengths and shortcomings. However, qualitative forecasting is more suitable for startups without past data to which they can refer.
5. Document and monitor results
Financial forecasts are never 100% accurate and tend to change over time. As such, it is important to document and monitor your forecast's results over time, especially after major internal and external developments. It is also important to update your forecasts to reflect the latest developments. Using forecasting software to automate related tasks may help too.
6. Analyze financial data
Regularly analyzing financial data is the best way to tell whether your financial forecasts are accurate. Additionally, continuous financial management and analysis helps you prepare better for the next financial forecast and gives you crucial insights into the company's current financial performance.
7. Repeat based on the previously defined time frame
Smart companies conduct regular financial forecasting to stay in the know and in control. As such, it is advisable to repeat the process once the time period set for the current financial forecast elapses. It's also prudent to keep collecting, recording, and analyzing data to improve your financial forecasts' accuracy.
Get accurate metrics for financial forecasting—absolutely free
An efficient system of collecting, storing, and analyzing data is necessary for accurate financial forecasting. ProfitWell Metrics is a subscription analytics software designed to do all of this on one platform. Some of the metrics that you can get using this program include:
- Monthly and annual recurring revenues
- Market and customer segments
- Customer acquisition and retention
- Customer lifetime value
- Churn rate
- The average revenue per user
ProfitWell Metrics collects and records all important metrics , giving you enough data to work with when conducting a financial forecast. Additionally, the data collected in real-time offers crucial insights to help you update your forecasts and other projects accordingly.
ProfitWell Metrics also integrates seamlessly with other popular data analytics programs, including Google Sheets and Stripe. More importantly, it's 100% free and secure.

Take the headache out of growing your software business
We handle your payments, tax, subscription management and more, so you can focus on growing your software and subscription business.
Financial forecasting FAQs
Some of the most frequently asked questions regarding financial forecasting include:
What is the role of forecasting in financial planning?
Financial forecasting estimates important financial metrics such as sales, income, and future revenue. These metrics are crucial for finance-related operations such as budgeting and financial planning as a whole. Consequently, forecasting functions as a guiding tool (or marking scheme) for financial planning.
What is the difference between financial forecasting and modeling?
On the one hand, financial forecasting entails predicting the business' future performance. On the other hand, financial modeling entails simulating how financial forecasts and other data may affect the company's future if everything goes according to plan. Financial modeling is done for very specific and often discrete purposes.
What is the difference between financial forecasting and budgeting?
Financial forecasting and budgeting work in tandem and are often misinterpreted as meaning the same thing. However, financial forecasting entails estimating and predicting the company's future performance (financially and in other aspects). On the other hand, budgeting is the company's financial expectations for the future (expectations based on financial forecasts and other data).
What are the three pro forma statements needed for financial forecasting?
Pro forma statements are financial reports designed to give insights into how different scenarios would play out based on hypothetical circumstances. There are three pro forma statements:
- Pro forma statements of income
- Pro forma cash flow statements
- Pro forma balance sheets
Pro forma statements may be hypothetical, but they help companies prepare for an uncertain future. Consequently, they're useful when conducting financial forecasts.
Related reading

Financial forecast example for new businesses and startups
The financial forecast is an essential step when creating a business plan. The financial forecast allows you to anticipate the revenues and expenses of your new business over a given period.
Even if the exercise is sometimes delicate to carry out, it is nevertheless essential for any entrepreneur. Indeed, it allows you to define quantified objectives, which, if meticulously tracked, will allow you to grow your business in good conditions.
To help you, here's a financial forecast example as well as tools you can use to create yours.

Financial forecast examples for new businesses
Example of a sales forecast.
The sales forecast is used to estimate the company's turnover. It is generally presented by category of products and services, types of customers, or time slots.
In our financial forecast example, we have included below a sales forecast for a hostel, organised by categories of services with the bed's occupancy forecast broken down based on seasonality:
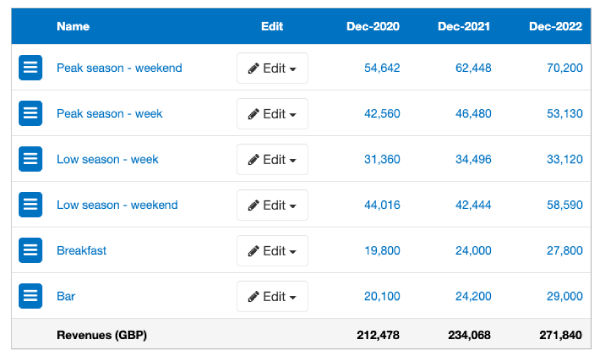
To ensure a fair and realistic evaluation of your company's revenues, You will need to base your forecast on thorough and reliable market analysis, including an analysis of what your competition offers. You will also need to think carefully about your pricing policy and distribution strategy beforehand.
Examples of financial statements to include in your forecast
Your forecast will need to include 3 financial statements:
- The P&L statement
- The cash flow statement
- The balance sheet
P&L statement
The profit and loss statement enables you to assess:
- the growth of the company by analyzing the evolution of the turnover over several years;
- the profitability of the company by looking at the difference between the expected revenues and the costs which will need to be incurred to generate these sales.
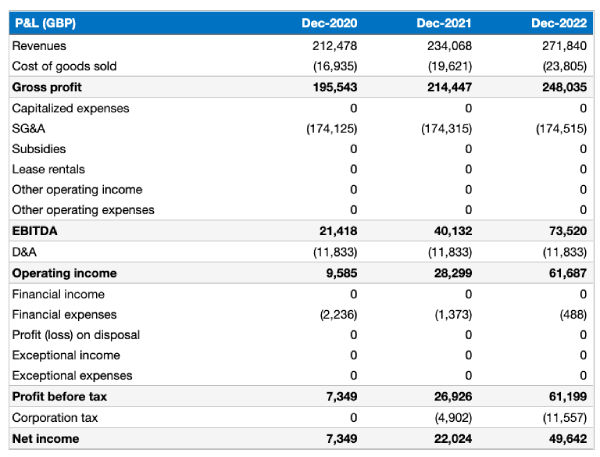
The main shortcoming of the projected income statement is that it does not take into account cash flows. Your profits should turn into cash at some point, but based on when your clients pay you, how much inventory you keep, or when you pay your suppliers, the cash flow could be very different from your profit.
To overcome this shortcoming, we need to look at the forecasted cash flow statement included in our financial forecast example.
Cash flow statement
The cash flow statement shows all anticipated cash movements for a given year.
It enables you to evaluate:
- the ability to generate operating cash flow;
- the company's investment and financing policies.
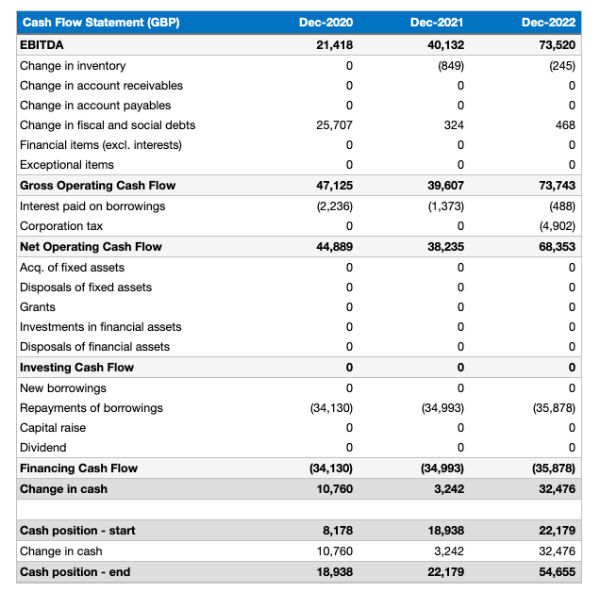
The cash flow statement is highly complementary to the P&L statement. Together they provide a clear view of the company's profitability, the cash generated by the operations, the investments made and the financing flows.
Balance sheet
The forecasted balance sheet, the last link in the chain, provides an overview of the company's net worth at a given moment in time and is part of our financial forecast example. It enables you to evaluate:
- the value of the company's assets;
- the weight of its working capital;
- the level of financial indebtedness;
- the book value of shareholders' equity.
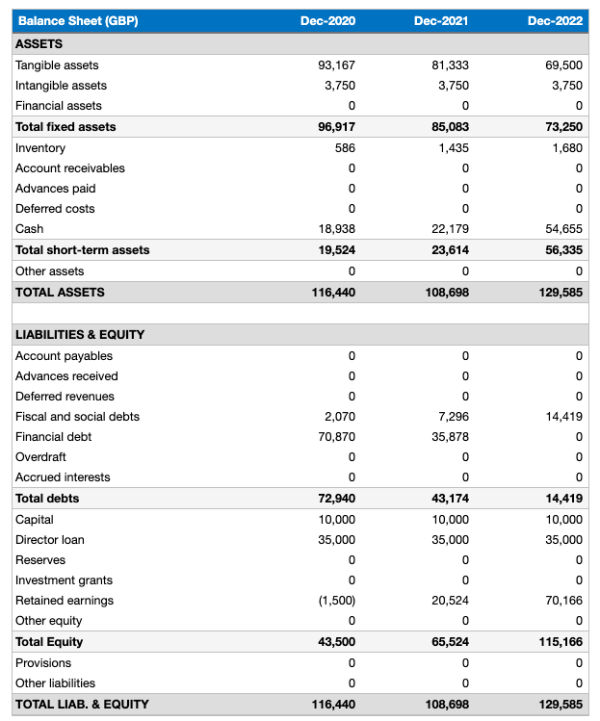
The forecasted balance sheet complements the other two tables. Nevertheless, it has two weak points:
- It provides a snapshot of the company's net worth at a specific moment in time - giving a very static view of the company. Especially given the balance sheet is usually produced several months after the end of the financial year (and therefore the information it contains is already stale!)
- It gives an accounting vision of the company, based on historical cost, and not a financial vision, based on market value.
Where can I find other financial forecast examples?
At The Business Plan Shop, we offer an online software that includes a financial forecasting tool and helps you throughout the drafting of the business plan on top of financial forecast examples included in our business plan templates .
Using a software like ours to realize your business plan has several advantages:
- You can easily create your financial forecast by letting the software take care of the calculations and financial aspects for you.
- You are guided in the drafting process by detailed instructions and examples for each part of the plan.
- You get a professional document, formatted and ready to be sent to your bank or investors.
If you are interested in our solution, you can try our software for free here .
Our article is coming to an end. We hope that our financial forecast example has given you a better understanding of what this exercise is all about.
The forecast is a crucial element of a business plan that will be of particular interest to your financial partners if you are looking for financing; but don't forget that it is also a mean for you, as an entrepreneur, to evaluate the viability of your new business idea.
Also on The Business Plan Shop
- How to do financial projections for a new business?
- How to establish a Profit & Loss forecast in your business plan?
- How to do a financial forecast for a restaurant?

Founder & CEO at The Business Plan Shop Ltd
Guillaume Le Brouster is a seasoned entrepreneur and financier.
Guillaume has been an entrepreneur for more than a decade and has first-hand experience of starting, running, and growing a successful business.
Prior to being a business owner, Guillaume worked in investment banking and private equity, where he spent most of his time creating complex financial forecasts, writing business plans, and analysing financial statements to make financing and investment decisions.
Guillaume holds a Master's Degree in Finance from ESCP Business School and a Bachelor of Science in Business & Management from Paris Dauphine University.
Create a convincing business plan
Assess the profitability of your business idea and create a persuasive business plan to pitch to investors
500,000+ entrepreneurs have already tried our solution - why not join them?
Not ready to try our on-line tool ? Learn more about our solution here
Need some inspiration for your business plan?
Subscribe to The Business Plan Shop and gain access to our business plan template library.

Need a professional business plan? Discover our solution
Write your business plan with ease!

It's easy to create a professional business plan with The Business Plan Shop
Want to find out more before you try? Learn more about our solution here
- Wholesale & Distribution
- Other Industries
Intact Xline
Agile development, implementation, technical support, digital transformation, training academy.
- Careers HIRING
Graduate Programme
Partnership program, customer stories, customer hub, news & events.
Discover how our Merchant customers operate at their best with Intact iQ.
- Builders Merchants
- Plumbing & Heating Merchants
- Timber Merchants
- Tiles, Bathrooms & Kitchens
- Electrical & Lighting
Discover how our Wholesale & Distribution customers operate at their best with Intact iQ.
- Office Supplies
- Pharma & Medical Supplies
- Flooring & Timber
- Food, Beverage & Cash and Carry
- Work Wear & Safety Wear
- Janitorial & Cleaning
- Tools, Fixtrues & Equipment Supplies
- Paper & Packaging
- Giftware, Homeware, Furniture
Discover how our Retail customers operate at their best with Intact iQ.
- DIY & Agri Stores
- Central Distribution
- Furniture & Fittings
- Agri Co-operatives
- Homewares & Value Stores
Discover how businesses from a wide range of sectors operate at their best with Intact iQ Design Suite.
Our flagship product, Intact iQ, is next-generation ERP software designed for today’s digital economy.
By Industry
Intact Xline is a powerful business management software solution designed for small to medium-sized companies.
Valued additions
- Intact Cliqx - eCommerce Solution
- Intact Access - Enterprise Mobililty Solution
Intact Cliqx
Our range of online options make it easier for your customers to do business with you.
Online Options
- NEW - Online Account Management
Intact Access
Boost the productivity of your remote teams with access to the key business information and controls they need 24/7.
- Enterprise Mobility
Our agile development framework enables us to quickly develop and regularly deliver new features that provide the most business value.
Our consultants work directly with our project team to future-proof your business, facilitate your long-term goals and accelerate growth.
Our local, dedicated technical support specialists are on hand to ensure your system is always operating at its best.
Our qualified and experienced team of professionals will advise and help you on all your digital transformation needs.
We offer a range of courses to help you get the most out of your software and further deliver on your overall business objectives.
Implementing and supporting our leading ERP and business management software solutions since 1992
We are instigators. Change makers. Future thinkers. Determined to take your business to the next level.
Hear what our team of Intacters have to say about life inside Intact
If you are looking to make a significant impact, support meaningful change and help transform businesses across the globe, then come join us and ignite your career at Intact, beginning September 2022.
Provides a unique range of benefits to enable partners to differentiate themselves in the marketplace and add exceptional customer value.
Our local, expert team are on hand to answer any queries you may have. Get started and elevate your business with Intact.
Find out how our software solutions enable our customers to elevate their businesses
We’re here to partner, collaborate and innovate with you. Our mission is to ensure your perfect fit software solution continuously enables you to elevate your business.
Explore our range of ebooks, white-papers, videos and product brochures
Keep up to date with the latest Intact news and events
Our technology and industry experts keep you informed of the latest trends, expert advice and best practice applications impacting your business
How to Create a Sales Forecast Business Plan

Sales forecasting is a powerful way to improve decision-making and make smarter choices as a business. But the reality is, many organisations don’t get it right.
Accurate sales forecasts rely on astute insights driven from robust, holistic data. If your business has struggled to accurately predict future sales revenue in the past, our guide could help you get it right in the future.
Ready to get started? Use the links below to navigate or read on for our full guide to accurate sales forecasting.
Quick Links
What is a Sales Forecast?
Why is sales forecasting important, what factors can affect sales forecasting, how to create a sales forecast, tools to help with sales forecasting.
A sales forecast is an estimate of what a company will sell in a week, month, quarter or year. It’s used to predict future revenue, accounting for the number of units an individual, team or company is likely to sell over a set period.
Sales forecasting offers many benefits when leveraged as part of a broader business strategy. At all levels and across all functions within a business, forecasting can facilitate shrewd decision-making, whether that’s setting goals and budgets, prospecting for new leads, deciding on the best time to hire new staff, or effective stock management to help maximise cashflow.
Accurate sales forecasting is a projection of where a company will stand in the future. And that’s important, not only for business continuity and growth, but for cultivating credibility, trust and advocacy with key stakeholders – be it partners, investors, clients or customers.

Let’s take a look at some of the reasons why sales forecasting matters:
- Bolsters decision-making – accurate predictions about future revenue can facilitate improved decision-making across all business functions, from hiring managers tasked with recruiting new talent, to procurement teams discerning when and how much stock to source.
- Adds value to all business functions – sales forecasting defines the value brought by different departments across the business. It highlights how different functions and channels contribute to revenue generation, helping businesses manage their resources.
- Accurate sales and buying for reduced costs – a sales forecast simplifies inventory management, with accurate stock predictions reducing costs and freeing up valuable resources, like warehouse space.
- Allocation of sales and marketing budget – Forecasting helps account for peaks and troughs in sales, so you can assign marketing budgets and determine which products and services need attention.
- Guarantees timely recruitment and outsourcing to drive business growth – understanding the areas of your business that drive the most revenue can make for seamless recruitment. Reinvesting revenue in personnel is a seismic driver of business growth, and sales forecasting can help you decide where to make hires and when. Not only that, but it can help companies decide whether they should look at outsourcing or whether to bring outsourced activities back in-house, e.g., the use of courier companies versus investing in your own delivery fleet.
- Provides valuable revenue expectations to outside stakeholders, like investors – sales forecasting quantifies your revenue predictions, making it easier and less risky to attain outside support from investors and stakeholders.
- Allows for simple company benchmarking against competitors – where your business ranks against competitors is important, and sales forecasting highlights how your trajectory compares to your closest rivals.
- Offers a powerful means of motivating sales personnel – a sales forecast is the best way of benchmarking the performance of salespeople within your business. It’s also a great motivator, particularly for staff incentivised by the promise of commission.

Many internal and external factors can impact the accuracy of your sales forecasts. You’ll need to account for all sorts of influences when predicting sales activity, including:
- Economic uncertainty and conditions
- Competitor changes
- Market trends and seasonality
- Product changes and future innovations
- Internal pricing or policy changes
- Available marketing spend and budgets
- Staff levels (more or fewer sales personnel will affect figures, for example)
- Future business plans e.g., expansion or diversification plans
This isn’t an exhaustive list of factors that can affect sales forecasting, but it does provide a steer for the types of influences that you’ll need to factor into your predictions.
Sales forecasting isn’t rocket science, but it does require a methodical approach to guarantee accuracy. Here, we’ll demonstrate how to make accurate sales predictions in five easy-to-follow steps.
Step 1: Consider Sales History
The first step to accurate sales forecasting is to look not to the future, but the past. By examining sales data over the past 12 months, you’ll glean insights that you can use as the basis of your future sales predictions, noting things like volumes, trends, and seasonality changes that caused peaks and troughs in demand.
When exploring historic sales data, be mindful of your ‘sales run rate’ – the number of projected sales for a particular period. For example, sales data may reveal a large disparity between quarterly sales figures, affecting the overall run rate; you’ll need to factor this into your forecasts for the future.

Step 2: Anticipate Changes and External Influences
While historic sales data provides a clear view of when and where sales typically happen over a year, it doesn’t guarantee the same sales figures for the future. Depending on a plethora of external and internal influences, next year’s sales could be up or down – so how do you accurately predict future revenue?
Start by taking each influence in turn and assess how such a force would have impacted last year’s sales figures. For example, do you plan to increase prices over the next 12 months? If so, how might this affect sales in relation to previous figures?
Here are some of the factors you should consider when predicting future sales performance:
- Pricing changes – will your prices change? How might this affect custom?
- Customer changes and trends – are consumer trends turning in your favour, or going the other way? Market awareness is crucial for accurate sales forecasting.
- Promotions – do you have any sales or promotions lined up to increase demand? How might these affect sales targets?
- Product alterations – are you improving your products and services?
- Sales channels – do you plan to expand into additional sales channels in the near future or acquire new branches?
Step 3: Lean on the Right Systems for Accurate Data Capture and Analysis
Sales forecasting becomes much simpler and more accurate when the right tools are used to capture and analyse data. Integrated ERP software, for example, collates sales data from every channel of your business – including trade counter or EPOS sales, telesales, sales rep orders, ecommerce etc. – so you can make data-backed predictions with confidence.
A great example of the types of tools you can use for accurate sales forecasting is predictive stock management. Automating the forecasting process, it presents the user with a forecast prediction aligned to their stock preferences, e.g., how much buffer stock you want to carry, as well as stock lead times.

Presented with this data, the procurement team can then use their insight and knowledge to tweak this forecast where necessary. It’s a great example of the marriage of automation to reduce manual work, whilst still allowing people to have input on the end result.
Elsewhere, utilising customised dashboards or control desks, instead of static reports, to differentiate pipeline value by rep, branch, prospect customer etc., can give businesses dynamic information to adjust their forecasts and be agile around expectations and demand.
What’s more, clever use of the CRM in conjunction with opportunity probability management enables you to allocate an estimated percentage chance that you think you will win a sales deal. By giving each sales opportunity/quotation a probability, you can produce a sales weighting forecast that will give you a fairly accurate idea of what your sales will be.
This will give you a better chance of forecasting the revenue and stock position of months and years ahead.
Step 4: Align Sales Predictions with Your Business Strategy
Many businesses have a five-year plan, a strategy that looks to drive business growth and profitability. But remember, such a plan will impact sales in one way or another, so it’s important that you align your sales forecasts with your short and long-term business objectives.
Say, for example, your business plan sets out a period of growth in the form of new hires or the creation of a whole new department. How will this affect sales? And to what extent should it be factored into your revenue forecasts?
Aligning your business strategy and sales forecasts is a crucial step. It helps prioritise business activity, ensuring that the right decisions are made to drive the business forward.

Step 5: Set Out Your Sales Forecasts in the Right Way
Charts, graphs and annotations can all be used to set out your sales forecasts for the year ahead. These should be included in your business plan, providing an accessible means of sharing forecasts with key stakeholders, personnel and investors.
As well as charting forecasts in number terms, you should set out your sales strategy, including how you arrived at the quoted figures. This not only quantifies your reasoning, but serves as a reminder of the market position at the time of writing – something that could prove useful if you need to refer back to where the figures came from at a later date.
Sales forecasting can be a laborious process, particularly if you want to guarantee accuracy. There are, however, a range of tools and software which can be leveraged to automate some elements of the process, removing some of the legwork associated with sales forecasting.
At Intact, we’re well aware of the importance of sales forecasting – and the arduous nature of it. That’s why we offer specialist expertise and solutions to help automate and simplify the process, from ERP software and predictive stock management to data analytics tools designed to improve data-driven decision-making.
We hope this guide helps you take stock of sales forecasting. If you’d like to optimise this area of your business, the Intact team can help. For more information or to speak to a member of our specialist team, visit the homepage . Alternatively, for more help and advice on ways to manage your inventory, take a look at our free guide to effective stock management .

Thinking of upgrading your business management software?
This e ssential step-by-step guide will help you make your software implementation journey as seamless and effective as possible.
Other posts you might also like

WTH (What the heck) is IFTTT: How codeless customisation tools like Nexus work

Intact attending the NMBS Exhibition 2024
Sign me up for intact news and updates.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Client management
Predicting business expenses: How to forecast accounts payable
“Entrepreneurs believe that profit is what matters most in a new enterprise. But profit is secondary. Cash flow matters most.” ~Peter Drucker, management consultant, educator, and a leading voice in modern project management theory
No matter what type of business you run, you can’t do it successfully without having a handle on your cash flow.
At least not for very long.
One of the troublesome parts of dealing with balance sheets and working capital is that expenses are unpredictable, especially if your organization is in a growth phase. Your day-to-day expenses don’t occur evenly, and even if they did, bills don’t come in or come due at even increments.
Not to mention, you’re facing the same issue on the other end, with clients that pay with varying degrees of timeliness.
Accounts payable forecasting is the practice of predicting at least one side of that equation: the money you’ll owe in the coming months.
Here’s what you need to know about getting started with forecasting accounts payable.
What are accounts payable?
)
Accounts payable (AP) is a term for all the money a company owes to others for goods and services the company has already received. These are debts that must be repaid relatively quickly, usually within 90 days. Bills from vendors, freelancers, and suppliers are all part of AP.
Businesses use AP to understand their expenses (specifically what money is already promised to go out the door) more clearly, enhancing decision-making and financial planning. It’s an oversimplification to say, “you can’t spend money you don’t have.” But at some level, it’s true — spend money you owe vendors on your own office renovation, and you’ll find yourself in an uncomfortable position.
Think of AP like a more complex version of a personal credit card. Each month you receive a statement showing how much you owe and a due date that tells you when to pay to avoid penalties (interest and fees).
With AP, the challenge is that no one else is collecting the “credit card charges” — your business has to do that on its own. As an added layer of complexity, you’ll often have to deal with varying due dates, too.
Just like keeping on top of your credit card payments helps your overall financial health and keeps you from getting into financial hot water, accurately tracking your agency’s AP is essential for managing cash flow, avoiding disruptions, and maintaining vendor relationships.
- The basics of forecasting
Accounts payable forecasting is a financial planning process that predicts and plans for near-term expenses. This financial modeling tool measures your current liabilities and paints a part of the picture of your future cash flows.
It’s similar to budgeting for future needs at home. For example, if you know your car needs new tires, you can plan for the expense by making budget adjustments for a couple of months prior. If you wait until you get in an accident because your worn-out tire blows out on the interstate, your expenses will be much higher — and unplanned.
AP forecasting is the business equivalent of planning for that tire replacement (and the rest of your month-to-month and one-time expenses).
To forecast project expenses well, a business needs linear, scheduled, and repeatable processes. Include at least the following steps in your process:
Collect historical data
Most business expenses are cyclical. Even if they don’t come due every month, they aren’t completely random. For example, you might not know exactly when you’ll need to pull in a specialist freelancer, but you already have a pretty good idea that you’ll do so three or four times in the coming year.
If you’re collecting and using historical data, that is.
Some AP forecasting trends might not be front of mind and might not show up in consistent or identical patterns, but they’re still predictable if you look more closely at historical data.
Where do you get this data? If your organization uses accounting software or works with an external accounting partner, that’s a great place to start! If you’re tracking AP and accounts receivable (AR) in another location or document, dive into the data there.
Analyze spending patterns
Take a closer look at your current spending patterns. If you aren’t categorizing expenses, it’s wise to start doing so.
Refer back to that specialist freelancer. Maybe you use quite a few of them for various specialties or verticals, and it’s a little daunting to pull individual invoices and receipts. If you’re categorizing those expenses properly, you’ll be able to quickly isolate all freelancer expenses.
)
Take Google Ads as another example. Some businesses buy these for their customers, but it’s not a real “expense” in the sense the customer pays for them as part of their broader contract. Being able to quickly identify all such expenses via categorization helps maintain clear thinking about expenses and income.
Consider external factors
Does the industry you serve experience heavy seasonality? If so, your clients may pay a flat monthly rate while your actual expenses ebb and flow with their seasonality. Market conditions can also factor into cash flow forecasting: inflation, changes in an industry, and so on.
Implement a review process
Don’t assume your AP forecasting process is perfect. (Because it will never be perfect!)
Make sure to create and implement a review process that evaluates your AP forecasting against actual AP. Where it’s not lining up, identify what adjustments you need to make to your formulas.
One more note: A conservative estimate is better than a hopeful one. AP and AR forecasting shouldn’t be what you’re hoping to be paid and what you’re hoping to owe. Instead, use a conservative, realistic estimate of what is most likely to happen.
- Accounts payable vs. accounts receivable: What’s the difference?
Businesses rarely track AP alone. They track it alongside accounts receivable (AR), which is the amount of money that others owe to the company. AP is your outflows, money that will be going out . AR is money that will be coming in (inflow).
Both of these elements (among many others, like current assets, liabilities, and liquidity) will be included in an organization’s financial statements. Keep the two terms straight by remembering this:
P/Pay/Payable = Bills to pay
R/Receive/Receivable = Money you’ll receive
Let’s examine these concepts in more detail.
Accounts payable
Accounts payable refers to any outstanding bills for goods or services already delivered that will be due in the near term. It’s money you’ve already committed to spend, which is why businesses use accounts payable as they forecast resource costs .
)
Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable refers to any outstanding source of income for goods or services you’ve already delivered to others (such as invoices that you’ve sent to clients for completed work, but that clients haven’t paid yet). It’s money your customers or clients have already committed to pay you, but hasn’t hit your bank account yet.
- Accounts payable formulas
There are already several established accounts payable formulas out there. Businesses use one or more of them to forecast AP. Which one is right for you depends on the types of clients you serve and the specifics of your financial situation.
Historical trend analysis
The formula for historical trend analysis looks like this:
Current amount - base/previous amount = change in amount
To turn that into a percentage, divide the answer by the base year/previous amount.
Using this formula, you can track changes over time, either by percentage or in real numbers. You might use this to compare AP and AR over time to project future trajectory or identify past seasonality.
Regression analysis
Regression analysis compares a dependent variable and an independent one and can be used in AP forecasting to identify what a specific change is likely to do to another aspect of the business.
A simple linear regression looks like this:
Y = a + bX + ϵ
And a typical regression analysis extends out to this:
Y = a + bX + cX + dX + ϵ
(Courtesy of the Corporate Finance Institute )
Cash conversion cycles (CCC)
CCC is calculated by adding days inventory outstanding (DIO) and days sales outstanding (DSO), then subtracting days payable outstanding (DPO). In a formula:
CCC = DIO + DSO - DPO
This formula measures how long it takes for goods (or services) to turn into income, minus how long it takes you to pay your AP. A low figure is usually considered healthy, and if your CCC score starts to rise, it’s wise to investigate why.
Of course, it requires knowing how to calculate the average number of days in your DPO, DSO, and DIO metrics. Here’s a detailed guide.
Simple moving average
The formula for simple moving average (SMA) looks like this:
)
This formula averages every instance of a figure over a fixed set of periods, such as a 50-day moving average, showing what the average price is during that stretch. It’s useful for comparing volatile figures over time, such as if your AP or payment patterns are spiky, you could measure this element in a three- or four-month rolling average.
Vendor payment policies (2/10 and Net 30)
2/10 Net 30 is a popular policy where payers get a 2% discount if they pay an invoice within 10 days but otherwise have up to 30 days to pay without penalty. Here’s the formula for the 2/10 part of the policy:
x - .02x = y
Where x is the agreed-upon price and y is the discounted price for early payment (within 10 days).
- Best practices for accurate forecasting
Accounts payable forecasting isn’t easy, and it will never be precise. But when you follow best practices for accurate forecasting, you’ll have a much easier time with resource management and understanding your cash flow.
1. Mine historical data
Your historical data should be a gold mine for forecasting, especially once you have data both on what happened (actual) and on your forecasts for that period. (This is one reason to start forecasting today, not next quarter!)
Look back at periods with sudden expenses. How well did you forecast them? Did your model withstand the spike, or did it punch right through your predictions?
Where you see large variances, look for the “why,” which will often point to what you need to change for next time.
2. Identify patterns
Many unexpected or sudden expenses don’t actually need to be unexpected or sudden.
They’re things that you can plan for. You might not know when you’ll need a new laptop, but you know it will happen sometime between now and the turn of the decade.
Look at those “sudden” expenses in your historical data and see how many of them were predictable or falling into a pattern. Then, incorporate those elements into your forecasting.
3. Understand the ramifications
Not all late payment penalties are the same. But some will cost you financially. Others will cost you reputationally. As you continue honing your forecasting, start identifying these elements as well, especially if money is tight. Should you need to delay on a line item in your AP, it’s advantageous to know which one will have the least amount of impact (whether financial, relational, or both).
Get a stronger, more robust financial forecast for your business with Teamwork.com
Consistently predicting your business expenses accurately is liberating for businesses: you can operate confidently and spend less time worrying about cash flow, freeing you up to focus on your business’s unique selling proposition and delighting your clients.
Teamwork.com is the ideal platform to run every aspect of client work. With budgeting and forecasting tools, you’ll be able to plan and budget for projects with ease and clarity.
)
The only all-in-one platform for client work
Trusted by 20,000 businesses and 6,000 agencies, Teamwork.com lets you easily manage, track, and customize multiple complex projects. Get started with a free 30-day trial.
Try Teamwork.com for free
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- What are accounts payable?
)
Ben is a Senior Content Marketing Specialist at Teamwork.com. Having held content roles at agencies and SaaS companies for the past 8 years, Ben loves writing about the latest tech trends and work hacks in the agency space.
)
How to forecast accounts receivable
)
Unlocking efficiency: Proven tips for professional services billing
)
The comprehensive guide to professional services agreements
)
Understanding cost overrun + prevention techniques
)
The request for quote (RFQ) process: A comprehensive guide
Mastering change request management: Understanding its essentials, tips, and best practices
Stay updated by subscribing to the Teamwork.com newsletter. We’ll keep you in the loop with news and updates regularly.
Advertisement
Supported by
Inflation Was Hotter Than Expected in March, Unwelcome News for the Fed
The surprisingly stubborn reading raised doubts about when — and even whether — the Federal Reserve will be able to start cutting interest rates this year.
- Share full article

+3.8% excluding
food and energy
+3.5% in March

By Jeanna Smialek
A closely watched measure of inflation remained stronger than expected in March, worrying news for Federal Reserve officials who have become increasingly concerned that their progress on lowering price increases might be stalling.
The surprisingly stubborn inflation reading raised doubts among economists about when — and even whether — the Fed will be able to start cutting interest rates this year.
The Consumer Price Index climbed 3.8 percent on an annual basis after stripping out food and fuel prices, which economists do in order to get a better sense of the underlying inflation trend. That “core” index was stronger than the 3.7 percent increase economists had expected, and unchanged from 3.8 percent in February. The monthly reading was also stronger than what economists had forecast.
Counting in food and fuel, the inflation measure climbed 3.5 percent in March from a year earlier, up from 3.2 percent in February and faster than what economists anticipated. A rise in gas prices contributed to that inflation number.
This week’s inflation figures come at a critical juncture for the Fed. Central bankers have been hoping to confirm that warmer-than-expected inflation figures at the start of the year were just a seasonal quirk, not evidence that inflation is getting stuck well above the 2 percent target. Wednesday’s report offers little comfort that the quick early 2024 readings have not lasted.
“It is what it is: It’s a stronger-than-expected number, and it’s showing that those price pressures are strong across goods and services,” said Blerina Uruci, chief U.S. economist at T. Rowe Price. “It’s problematic for the Fed. I don’t see how they can justify a June cut with this strong data.”
Policymakers have made it clear in recent months that they want to see further evidence that inflation is cooling before they cut interest rates. Fed officials raised borrowing costs to 5.3 percent in 2022 and mid-2023, which they think is high enough to meaningfully weigh on the economy. Central bankers forecast in March that they would cut interest rates three times this year.
But Fed officials do not want to cut rates before they are confident inflation is on track to return to normal. Lowering borrowing costs too early or too much would risk allowing price increases to pick back up. And if households and businesses come to expect inflation to remain slightly higher, officials worry that could make it even harder to stamp out down the road.
That threat of lingering inflation has become a more serious concern for policymakers since the start of the year. Inflation flatlined in January and February after months of steady declines, raising some alarm at the Fed and among forecasters. Going into the year, investors expected the Fed to cut rates sharply in 2024 — perhaps five or six times, to about 4 percent — but have steadily dialed back those expectations .
Stocks dropped sharply after the inflation release as investors further pared back their expectations for lower rates. Following the report, market pricing suggested that many investors now expect just one or two cuts his year.
The S&P 500 and the tech-heavy Nasdaq composite each closed nearly 1 percent lower on Wednesday. The Russell 2000 index, which tracks smaller companies, was down nearly 3 percent.
Investors would like to see lower interest rates, which tend to bolster prices for assets like stocks. But the Fed might struggle to explain why it is cutting rates at the current moment: Not only is inflation showing signs of getting stuck well above the central bank’s target, but the economy is growing at a fairly rapid pace and employers are hiring at a robust clip.
In short, the Fed’s policies do not appear to have pushed America to the brink of a recession — and in fact, there are signs that they may not be having as much of an effect as policymakers had expected when it comes to growth.
While the Fed officially targets Personal Consumption Expenditures inflation , a separate measure, the Consumer Price Index report released on Wednesday comes out earlier and includes data that feeds into the other metric. That makes it a closely watched signal of how price pressures are shaping up.
The inflation report’s details offered little reason to dismiss the gauge’s continued stubbornness as a fluke. They showed that housing inflation remains firm, auto insurance costs picked up at a rapid pace and apparel prices climbed.

Monthly changes in March
Motor vehicle insurance
Gasoline (all types)
Motor vehicle repair
Hospital services
Meats, poultry, fish, eggs
Electricity
All items excl. food and energy
Tobacco products
Rent of primary residence
Nonalcoholic beverages
Food away from home
Medical care commodities
Fruits, vegetables
Alcoholic beverages
Physicians’ services
Piped utility gas service
Dairy products
New vehicles
Airline fares
Cereals, bakery products
Used cars, trucks

Motor vehicle maintenance and repair
Meats, poultry, fish and eggs
All items excluding food and energy
Tobacco and smoking products
Nonalcoholic beverages and materials
Fruits and vegetables
Dairy and related products
Cereals and bakery products
Used cars and trucks
In a development that is likely to be especially notable for Fed officials, a measure of services inflation contributed to the pickup in annual inflation. Policymakers watch those prices closely, because they can reflect the strength of the underlying economy and because they tend to persist over time.
The question, increasingly, is whether Fed officials can cut interest rates at all this year in a world where inflation appears to be flatlining.
Ms. Uruci said that with every month inflation stays stubborn, the Fed may need to see more convincing evidence — and a more sustained return to deceleration — to feel confident that price increases are genuinely coming under control.
Kathy Bostjancic, Nationwide’s chief economist, predicted that rate cuts could now be delayed to this autumn, if they happen in 2024 at all.
“We now think September, if they start to cut rates, is more likely than July,” Ms. Bostjancic said. The new report “shakes the confidence that inflation is on this downward trend.”
If the Fed does not cut rates soon, the election could make the start of reductions more politically fraught. Central bankers are independent of the White House and typically insist that they do not make policy with an eye on the political calendar.
Still, cutting in the months just before the election could put policymakers under a partisan spotlight : Former President Donald J. Trump, the presumptive Republican nominee, has already painted possible rate cuts as a political ploy to help Democrats. Lower rates tend to help incumbents, since they bolster the economy.
But the current economic moment is a politically complicated one.
Consumers dislike rapidly rising prices, and inflation has been dogging President Biden’s approval ratings for months. That said, consumers have become less concerned about them in recent months as the pace of inflation has come down from its peak in 2022.
At the same time, some Americans are chafing against high interest rates, the medicine the Fed uses to cure rapid inflation because they make it more expensive to borrow to buy a house or make other large purchases.
Mr. Biden has struck a concerned tone about high prices and tough housing affordability conditions in recent months, while pinning at least some of the blame for recent rapid inflation on corporations.
He reiterated that message on Wednesday, while saying that he still expects to see rate cuts this year. Mr. Biden’s comments amounted to a forecast rather than a prescription, but they were unusual coming from a White House that usually avoids talking about Fed policy out of respect for the central bank’s independence.
“We have dramatically reduced inflation down from 9 percent to close to 3 percent,” Mr. Biden also noted.
Jeanna Smialek covers the Federal Reserve and the economy for The Times from Washington. More about Jeanna Smialek
- Companies & Markets
- Banking & Finance
- Reits & Property
- Energy & Commodities
- Telcos, Media & Tech
Transport & Logistics
- Consumer & Healthcare
- Capital Markets & Currencies
Lufthansa slashes 2024 earnings forecast after costly strikes
LUFTHANSA slashed its full-year earnings outlook for 2024 on Monday (Apr 15), blaming a series of strikes and a slower than planned ramp up of capacity, in a profit warning that sent its share price 2.4 per cent lower.
The company now expects adjusted earnings before interest and taxes (Ebit) of 2.2 billion euros this year, versus a previous forecast for stable earnings development compared to its 2.682 billion euro adjusted Ebit result in 2023, it said in a statement.
Adjusted free cash flow in 2024 is expected to be at least one billion euros, down from the previous forecast of at least 1.5 billion, it added.
Lufthansa also reported a first-quarter loss of 849 million euros, compared to a 273 million loss the previous year.
“The loss was higher than expected due to various strikes, both by different employee groups within the Group and by employees at system partners, which impacted earnings by around 350 million euros,” the statement said.
The group is set to publish final results for the first quarter on Apr 30. REUTERS
GET BT IN YOUR INBOX DAILY

Start and end each day with the latest news stories and analyses delivered straight to your inbox.
KEYWORDS IN THIS ARTICLE
- Lufthansa agrees to pay rise with flight attendants after strike
- Lufthansa, ground staff reach pay deal after strikes
- Lufthansa, ITA Airways deal may hurt competition: EU watchdog
BT is now on Telegram!
For daily updates on weekdays and specially selected content for the weekend. Subscribe to t.me/BizTimes
Tesla’s value dips below US$500 billion in blow to stock bulls
United reports loss on us$200 million hit from boeing grounding, byd unveils two models in latest luxury sport utility push, dali’s singapore owner seeking share of salvage costs from cargo owners as baltimore takes legal action, japan’s nissan bets on solid-state batteries, gigacasting for next-gen evs, honda to launch next-generation evs in china by 2027, support south-east asia's leading financial daily.
Get the latest coverage and full access to all BT premium content.
Browse corporate subscription here

- International
- Opinion & Features
- Startups & Tech
- Working Life
- Events & Awards
- Breaking News
- Newsletters
- Food & Drink
- Style & Travel
- Arts & Design
- Health & Wellness
- Paid Press Releases
- advertise with us
- privacy policy
- terms & conditions
- cookie policy
- data protection policy
SPH MEDIA DIGITAL NEWS
MCI (P) 064/10/2023 © 2024 SPH MEDIA LIMITED. REGN NO. 202120748H

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Create A Strong Business Plan for Any Industry Without the Wait, For Less Cost. Pitch, Plan, & Track Your Business Plan From Start To Finish. Start Today!
But business forecasting is vital for businesses because it allows them to plan production, financing, and other strategies. However, there are three problems with relying on forecasts: The data ...
Now that you understand the basics of business forecasting, it's time to see how it works in practice. Read the following examples to better understand the different approaches to business forecasting. 1. A company forecasting its sales through the end of the year. Let's suppose a small greeting card company wants to forecast its sales ...
Clearly, business forecasting is a project unto itself. To manage a project and collect the data in a way that's useful in the future, you need a project management tool that can help you plan your process and select the data that helps you decide on a way forward. ProjectManager is award-winning software that organizes projects with features ...
Estimate the expected sales of each good or service. Multiply the price by the estimated sales to get your estimated revenue. Add them all together to get your total revenue. For example, if your food truck business sold pizzas at £10 and burgers at £5, you would multiply these values by how much you expected to sell.
So do airlines. A normal sales forecast includes units, price per unit, sales, direct cost per unit, and direct costs. The math is simple, with the direct costs per unit related to total direct costs the same way price per unit relates to total sales. Multiply the units projected for any time period by the unit direct costs, and that gives you ...
Here's how to begin creating a financial forecast for a new business. [Read more: Startup 2021: Business Plan Financials] Start with a sales forecast. A sales forecast attempts to predict what your monthly sales will be for up to 18 months after launching your business. Creating a sales forecast without any past results is a little difficult ...
Business forecasting is a projection of future developments of a business or industry based on trends and patterns of past and present data. This business practice helps determine how to allocate resources and plan strategically for upcoming projects, activities, and costs. Forecasting enables organizations to manage resources, align their ...
In this article, we discuss business forecasts, common forecasting methods companies use and how to create a forecast that can help you plan for future business development. Key takeaways: Business forecasts help organizations plan for financial and operational success. Businesses use quantitative and qualitative methods when forecasting.
When you produce a sales forecast, you are predicting what your sales or revenue will be in the future. An accurate sales forecast helps your firm make better decisions and is arguably the most important piece of your business plan. A sales forecast contrasts with a sales goal. The former is the realistic representation of what you believe will ...
6. Delphi Method. The Delphi method of forecasting involves consulting experts who analyze market conditions to predict a company's performance. A facilitator reaches out to those experts with questionnaires, requesting forecasts of business performance based on their experience and knowledge.
Effective business forecasting requires careful planning and execution. The followingsteps provide a comprehensive guide on how to develop a successful forecasting plan: Define the objective: The first step in the business forecasting process is to define the objective of the forecast by identifying the key performance indicators (KPIs) such as ...
Accurate sales forecasts keep your leaders happy and your business healthy. In this guide, we'll explain everything you need to know about sales forecasting — so you can get a clear picture of your company's projected sales and keep everyone's expectations on track. We've organized this reference guide by the top questions sales teams ...
The typical forecasting process follows a pattern that contributes to inaccurate projections and a defeating, self-reinforcing cycle. At one large industrial manufacturing and services company, for instance, managers in the business units and subunits are held to earnings targets that are rolled up into the overarching forecast.
With business forecasting, companies use different methods and data to predict market trends to help determine their short-term and long-term business outlook. This data is a vital part of helping companies grow, start new initiatives, and plan their finances for the quarter and year. It can also help you plan for potential seasonal dips in ...
Forecasting revenues for your business plan requires a systematic and data-driven approach. By understanding your market and customers, utilizing historical data, making key assumptions, employing multiple forecasting methods, accounting for external factors, and continuously monitoring and reviewing your forecast, you can develop realistic ...
Sales forecasts are often built using historical data. Businesses analyze previous results to extrapolate and create predictions. If a business starts out and lacks a good body of historical sales data, it will struggle to create an accurate sales forecast. The type of business. Each industry has its own series of unique challenges and quirks.
Here are some steps in the process: 1. Develop the basis of forecasting. The first step in the process is investigating the company's condition and identifying where the business is currently positioned in the market. 2. Estimate the future operations of the business.
Financial forecasting is the process of estimating or predicting how a business will perform in the future. The most common type of financial forecast is an income statement; however, in a complete financial model, all three financial statements are forecasted.
In the direct cash flow forecasting method, calculating cash flow is simple. Just subtract the amount of cash you plan on spending in a month from the amount of cash you plan on receiving. This will be your "net cash flow". If the number is positive, you receive more cash than you spend.
4. Choose a financial forecast method. There are two financial forecasting methods: Quantitative forecasting uses historical information and data to identify trends, reliable patterns, and trends. Qualitative forecasting analyzes experts' opinions and sentiments about the company and market as a whole.
The financial forecast is an essential step when creating a business plan. The financial forecast allows you to anticipate the revenues and expenses of your new business over a given period. Even if the exercise is sometimes delicate to carry out, it is nevertheless essential for any entrepreneur. Indeed, it allows you to define quantified ...
Create a sales forecast for the next three to five years: (No. of units to sell X price for each unit) - (cost per unit X No. of units) = sales forecast. Quantify how much capital you have on hand. ... Remember: Creating a business plan is crucial when starting a business. You can use this document to guide your decisions and actions and even ...
This essential step-by-step guide will help you make your software implementation journey as seamless and effective as possible. Download now. If your business has struggled to accurately predict future sales revenue in the past, our guide could help you get it right in the future.
AP forecasting is the business equivalent of planning for that tire replacement (and the rest of your month-to-month and one-time expenses). To forecast project expenses well, a business needs linear, scheduled, and repeatable processes. Include at least the following steps in your process:
The surprisingly stubborn reading raised doubts about when — and even whether — the Federal Reserve will be able to start cutting interest rates this year.
Thousands of VHI policy holders are facing into having to choose new policies in the months ahead, as the insurer plans to retire a number of its most popular plans. In what has been described as ...
LUFTHANSA slashed its full-year earnings outlook for 2024 on Monday (Apr 15), blaming a series of strikes and a slower than planned ramp up of capacity, in a profit warning that sent its share price 2.4 per cent lower. Read more at The Business Times.