Jump to navigation


Cochrane Training
Chapter 15: interpreting results and drawing conclusions.
Holger J Schünemann, Gunn E Vist, Julian PT Higgins, Nancy Santesso, Jonathan J Deeks, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group
Key Points:
- This chapter provides guidance on interpreting the results of synthesis in order to communicate the conclusions of the review effectively.
- Methods are presented for computing, presenting and interpreting relative and absolute effects for dichotomous outcome data, including the number needed to treat (NNT).
- For continuous outcome measures, review authors can present summary results for studies using natural units of measurement or as minimal important differences when all studies use the same scale. When studies measure the same construct but with different scales, review authors will need to find a way to interpret the standardized mean difference, or to use an alternative effect measure for the meta-analysis such as the ratio of means.
- Review authors should not describe results as ‘statistically significant’, ‘not statistically significant’ or ‘non-significant’ or unduly rely on thresholds for P values, but report the confidence interval together with the exact P value.
- Review authors should not make recommendations about healthcare decisions, but they can – after describing the certainty of evidence and the balance of benefits and harms – highlight different actions that might be consistent with particular patterns of values and preferences and other factors that determine a decision such as cost.
Cite this chapter as: Schünemann HJ, Vist GE, Higgins JPT, Santesso N, Deeks JJ, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Guyatt GH. Chapter 15: Interpreting results and drawing conclusions. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
15.1 Introduction
The purpose of Cochrane Reviews is to facilitate healthcare decisions by patients and the general public, clinicians, guideline developers, administrators and policy makers. They also inform future research. A clear statement of findings, a considered discussion and a clear presentation of the authors’ conclusions are, therefore, important parts of the review. In particular, the following issues can help people make better informed decisions and increase the usability of Cochrane Reviews:
- information on all important outcomes, including adverse outcomes;
- the certainty of the evidence for each of these outcomes, as it applies to specific populations and specific interventions; and
- clarification of the manner in which particular values and preferences may bear on the desirable and undesirable consequences of the intervention.
A ‘Summary of findings’ table, described in Chapter 14 , Section 14.1 , provides key pieces of information about health benefits and harms in a quick and accessible format. It is highly desirable that review authors include a ‘Summary of findings’ table in Cochrane Reviews alongside a sufficient description of the studies and meta-analyses to support its contents. This description includes the rating of the certainty of evidence, also called the quality of the evidence or confidence in the estimates of the effects, which is expected in all Cochrane Reviews.
‘Summary of findings’ tables are usually supported by full evidence profiles which include the detailed ratings of the evidence (Guyatt et al 2011a, Guyatt et al 2013a, Guyatt et al 2013b, Santesso et al 2016). The Discussion section of the text of the review provides space to reflect and consider the implications of these aspects of the review’s findings. Cochrane Reviews include five standard subheadings to ensure the Discussion section places the review in an appropriate context: ‘Summary of main results (benefits and harms)’; ‘Potential biases in the review process’; ‘Overall completeness and applicability of evidence’; ‘Certainty of the evidence’; and ‘Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews’. Following the Discussion, the Authors’ conclusions section is divided into two standard subsections: ‘Implications for practice’ and ‘Implications for research’. The assessment of the certainty of evidence facilitates a structured description of the implications for practice and research.
Because Cochrane Reviews have an international audience, the Discussion and Authors’ conclusions should, so far as possible, assume a broad international perspective and provide guidance for how the results could be applied in different settings, rather than being restricted to specific national or local circumstances. Cultural differences and economic differences may both play an important role in determining the best course of action based on the results of a Cochrane Review. Furthermore, individuals within societies have widely varying values and preferences regarding health states, and use of societal resources to achieve particular health states. For all these reasons, and because information that goes beyond that included in a Cochrane Review is required to make fully informed decisions, different people will often make different decisions based on the same evidence presented in a review.
Thus, review authors should avoid specific recommendations that inevitably depend on assumptions about available resources, values and preferences, and other factors such as equity considerations, feasibility and acceptability of an intervention. The purpose of the review should be to present information and aid interpretation rather than to offer recommendations. The discussion and conclusions should help people understand the implications of the evidence in relation to practical decisions and apply the results to their specific situation. Review authors can aid this understanding of the implications by laying out different scenarios that describe certain value structures.
In this chapter, we address first one of the key aspects of interpreting findings that is also fundamental in completing a ‘Summary of findings’ table: the certainty of evidence related to each of the outcomes. We then provide a more detailed consideration of issues around applicability and around interpretation of numerical results, and provide suggestions for presenting authors’ conclusions.
15.2 Issues of indirectness and applicability
15.2.1 the role of the review author.
“A leap of faith is always required when applying any study findings to the population at large” or to a specific person. “In making that jump, one must always strike a balance between making justifiable broad generalizations and being too conservative in one’s conclusions” (Friedman et al 1985). In addition to issues about risk of bias and other domains determining the certainty of evidence, this leap of faith is related to how well the identified body of evidence matches the posed PICO ( Population, Intervention, Comparator(s) and Outcome ) question. As to the population, no individual can be entirely matched to the population included in research studies. At the time of decision, there will always be differences between the study population and the person or population to whom the evidence is applied; sometimes these differences are slight, sometimes large.
The terms applicability, generalizability, external validity and transferability are related, sometimes used interchangeably and have in common that they lack a clear and consistent definition in the classic epidemiological literature (Schünemann et al 2013). However, all of the terms describe one overarching theme: whether or not available research evidence can be directly used to answer the health and healthcare question at hand, ideally supported by a judgement about the degree of confidence in this use (Schünemann et al 2013). GRADE’s certainty domains include a judgement about ‘indirectness’ to describe all of these aspects including the concept of direct versus indirect comparisons of different interventions (Atkins et al 2004, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011b).
To address adequately the extent to which a review is relevant for the purpose to which it is being put, there are certain things the review author must do, and certain things the user of the review must do to assess the degree of indirectness. Cochrane and the GRADE Working Group suggest using a very structured framework to address indirectness. We discuss here and in Chapter 14 what the review author can do to help the user. Cochrane Review authors must be extremely clear on the population, intervention and outcomes that they intend to address. Chapter 14, Section 14.1.2 , also emphasizes a crucial step: the specification of all patient-important outcomes relevant to the intervention strategies under comparison.
In considering whether the effect of an intervention applies equally to all participants, and whether different variations on the intervention have similar effects, review authors need to make a priori hypotheses about possible effect modifiers, and then examine those hypotheses (see Chapter 10, Section 10.10 and Section 10.11 ). If they find apparent subgroup effects, they must ultimately decide whether or not these effects are credible (Sun et al 2012). Differences between subgroups, particularly those that correspond to differences between studies, should be interpreted cautiously. Some chance variation between subgroups is inevitable so, unless there is good reason to believe that there is an interaction, review authors should not assume that the subgroup effect exists. If, despite due caution, review authors judge subgroup effects in terms of relative effect estimates as credible (i.e. the effects differ credibly), they should conduct separate meta-analyses for the relevant subgroups, and produce separate ‘Summary of findings’ tables for those subgroups.
The user of the review will be challenged with ‘individualization’ of the findings, whether they seek to apply the findings to an individual patient or a policy decision in a specific context. For example, even if relative effects are similar across subgroups, absolute effects will differ according to baseline risk. Review authors can help provide this information by identifying identifiable groups of people with varying baseline risks in the ‘Summary of findings’ tables, as discussed in Chapter 14, Section 14.1.3 . Users can then identify their specific case or population as belonging to a particular risk group, if relevant, and assess their likely magnitude of benefit or harm accordingly. A description of the identifying prognostic or baseline risk factors in a brief scenario (e.g. age or gender) will help users of a review further.
Another decision users must make is whether their individual case or population of interest is so different from those included in the studies that they cannot use the results of the systematic review and meta-analysis at all. Rather than rigidly applying the inclusion and exclusion criteria of studies, it is better to ask whether or not there are compelling reasons why the evidence should not be applied to a particular patient. Review authors can sometimes help decision makers by identifying important variation where divergence might limit the applicability of results (Rothwell 2005, Schünemann et al 2006, Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann et al 2013), including biologic and cultural variation, and variation in adherence to an intervention.
In addressing these issues, review authors cannot be aware of, or address, the myriad of differences in circumstances around the world. They can, however, address differences of known importance to many people and, importantly, they should avoid assuming that other people’s circumstances are the same as their own in discussing the results and drawing conclusions.
15.2.2 Biological variation
Issues of biological variation that may affect the applicability of a result to a reader or population include divergence in pathophysiology (e.g. biological differences between women and men that may affect responsiveness to an intervention) and divergence in a causative agent (e.g. for infectious diseases such as malaria, which may be caused by several different parasites). The discussion of the results in the review should make clear whether the included studies addressed all or only some of these groups, and whether any important subgroup effects were found.
15.2.3 Variation in context
Some interventions, particularly non-pharmacological interventions, may work in some contexts but not in others; the situation has been described as program by context interaction (Hawe et al 2004). Contextual factors might pertain to the host organization in which an intervention is offered, such as the expertise, experience and morale of the staff expected to carry out the intervention, the competing priorities for the clinician’s or staff’s attention, the local resources such as service and facilities made available to the program and the status or importance given to the program by the host organization. Broader context issues might include aspects of the system within which the host organization operates, such as the fee or payment structure for healthcare providers and the local insurance system. Some interventions, in particular complex interventions (see Chapter 17 ), can be only partially implemented in some contexts, and this requires judgements about indirectness of the intervention and its components for readers in that context (Schünemann 2013).
Contextual factors may also pertain to the characteristics of the target group or population, such as cultural and linguistic diversity, socio-economic position, rural/urban setting. These factors may mean that a particular style of care or relationship evolves between service providers and consumers that may or may not match the values and technology of the program.
For many years these aspects have been acknowledged when decision makers have argued that results of evidence reviews from other countries do not apply in their own country or setting. Whilst some programmes/interventions have been successfully transferred from one context to another, others have not (Resnicow et al 1993, Lumley et al 2004, Coleman et al 2015). Review authors should be cautious when making generalizations from one context to another. They should report on the presence (or otherwise) of context-related information in intervention studies, where this information is available.
15.2.4 Variation in adherence
Variation in the adherence of the recipients and providers of care can limit the certainty in the applicability of results. Predictable differences in adherence can be due to divergence in how recipients of care perceive the intervention (e.g. the importance of side effects), economic conditions or attitudes that make some forms of care inaccessible in some settings, such as in low-income countries (Dans et al 2007). It should not be assumed that high levels of adherence in closely monitored randomized trials will translate into similar levels of adherence in normal practice.
15.2.5 Variation in values and preferences
Decisions about healthcare management strategies and options involve trading off health benefits and harms. The right choice may differ for people with different values and preferences (i.e. the importance people place on the outcomes and interventions), and it is important that decision makers ensure that decisions are consistent with a patient or population’s values and preferences. The importance placed on outcomes, together with other factors, will influence whether the recipients of care will or will not accept an option that is offered (Alonso-Coello et al 2016) and, thus, can be one factor influencing adherence. In Section 15.6 , we describe how the review author can help this process and the limits of supporting decision making based on intervention reviews.
15.3 Interpreting results of statistical analyses
15.3.1 confidence intervals.
Results for both individual studies and meta-analyses are reported with a point estimate together with an associated confidence interval. For example, ‘The odds ratio was 0.75 with a 95% confidence interval of 0.70 to 0.80’. The point estimate (0.75) is the best estimate of the magnitude and direction of the experimental intervention’s effect compared with the comparator intervention. The confidence interval describes the uncertainty inherent in any estimate, and describes a range of values within which we can be reasonably sure that the true effect actually lies. If the confidence interval is relatively narrow (e.g. 0.70 to 0.80), the effect size is known precisely. If the interval is wider (e.g. 0.60 to 0.93) the uncertainty is greater, although there may still be enough precision to make decisions about the utility of the intervention. Intervals that are very wide (e.g. 0.50 to 1.10) indicate that we have little knowledge about the effect and this imprecision affects our certainty in the evidence, and that further information would be needed before we could draw a more certain conclusion.
A 95% confidence interval is often interpreted as indicating a range within which we can be 95% certain that the true effect lies. This statement is a loose interpretation, but is useful as a rough guide. The strictly correct interpretation of a confidence interval is based on the hypothetical notion of considering the results that would be obtained if the study were repeated many times. If a study were repeated infinitely often, and on each occasion a 95% confidence interval calculated, then 95% of these intervals would contain the true effect (see Section 15.3.3 for further explanation).
The width of the confidence interval for an individual study depends to a large extent on the sample size. Larger studies tend to give more precise estimates of effects (and hence have narrower confidence intervals) than smaller studies. For continuous outcomes, precision depends also on the variability in the outcome measurements (i.e. how widely individual results vary between people in the study, measured as the standard deviation); for dichotomous outcomes it depends on the risk of the event (more frequent events allow more precision, and narrower confidence intervals), and for time-to-event outcomes it also depends on the number of events observed. All these quantities are used in computation of the standard errors of effect estimates from which the confidence interval is derived.
The width of a confidence interval for a meta-analysis depends on the precision of the individual study estimates and on the number of studies combined. In addition, for random-effects models, precision will decrease with increasing heterogeneity and confidence intervals will widen correspondingly (see Chapter 10, Section 10.10.4 ). As more studies are added to a meta-analysis the width of the confidence interval usually decreases. However, if the additional studies increase the heterogeneity in the meta-analysis and a random-effects model is used, it is possible that the confidence interval width will increase.
Confidence intervals and point estimates have different interpretations in fixed-effect and random-effects models. While the fixed-effect estimate and its confidence interval address the question ‘what is the best (single) estimate of the effect?’, the random-effects estimate assumes there to be a distribution of effects, and the estimate and its confidence interval address the question ‘what is the best estimate of the average effect?’ A confidence interval may be reported for any level of confidence (although they are most commonly reported for 95%, and sometimes 90% or 99%). For example, the odds ratio of 0.80 could be reported with an 80% confidence interval of 0.73 to 0.88; a 90% interval of 0.72 to 0.89; and a 95% interval of 0.70 to 0.92. As the confidence level increases, the confidence interval widens.
There is logical correspondence between the confidence interval and the P value (see Section 15.3.3 ). The 95% confidence interval for an effect will exclude the null value (such as an odds ratio of 1.0 or a risk difference of 0) if and only if the test of significance yields a P value of less than 0.05. If the P value is exactly 0.05, then either the upper or lower limit of the 95% confidence interval will be at the null value. Similarly, the 99% confidence interval will exclude the null if and only if the test of significance yields a P value of less than 0.01.
Together, the point estimate and confidence interval provide information to assess the effects of the intervention on the outcome. For example, suppose that we are evaluating an intervention that reduces the risk of an event and we decide that it would be useful only if it reduced the risk of an event from 30% by at least 5 percentage points to 25% (these values will depend on the specific clinical scenario and outcomes, including the anticipated harms). If the meta-analysis yielded an effect estimate of a reduction of 10 percentage points with a tight 95% confidence interval, say, from 7% to 13%, we would be able to conclude that the intervention was useful since both the point estimate and the entire range of the interval exceed our criterion of a reduction of 5% for net health benefit. However, if the meta-analysis reported the same risk reduction of 10% but with a wider interval, say, from 2% to 18%, although we would still conclude that our best estimate of the intervention effect is that it provides net benefit, we could not be so confident as we still entertain the possibility that the effect could be between 2% and 5%. If the confidence interval was wider still, and included the null value of a difference of 0%, we would still consider the possibility that the intervention has no effect on the outcome whatsoever, and would need to be even more sceptical in our conclusions.
Review authors may use the same general approach to conclude that an intervention is not useful. Continuing with the above example where the criterion for an important difference that should be achieved to provide more benefit than harm is a 5% risk difference, an effect estimate of 2% with a 95% confidence interval of 1% to 4% suggests that the intervention does not provide net health benefit.
15.3.2 P values and statistical significance
A P value is the standard result of a statistical test, and is the probability of obtaining the observed effect (or larger) under a ‘null hypothesis’. In the context of Cochrane Reviews there are two commonly used statistical tests. The first is a test of overall effect (a Z-test), and its null hypothesis is that there is no overall effect of the experimental intervention compared with the comparator on the outcome of interest. The second is the (Chi 2 ) test for heterogeneity, and its null hypothesis is that there are no differences in the intervention effects across studies.
A P value that is very small indicates that the observed effect is very unlikely to have arisen purely by chance, and therefore provides evidence against the null hypothesis. It has been common practice to interpret a P value by examining whether it is smaller than particular threshold values. In particular, P values less than 0.05 are often reported as ‘statistically significant’, and interpreted as being small enough to justify rejection of the null hypothesis. However, the 0.05 threshold is an arbitrary one that became commonly used in medical and psychological research largely because P values were determined by comparing the test statistic against tabulations of specific percentage points of statistical distributions. If review authors decide to present a P value with the results of a meta-analysis, they should report a precise P value (as calculated by most statistical software), together with the 95% confidence interval. Review authors should not describe results as ‘statistically significant’, ‘not statistically significant’ or ‘non-significant’ or unduly rely on thresholds for P values , but report the confidence interval together with the exact P value (see MECIR Box 15.3.a ).
We discuss interpretation of the test for heterogeneity in Chapter 10, Section 10.10.2 ; the remainder of this section refers mainly to tests for an overall effect. For tests of an overall effect, the computation of P involves both the effect estimate and precision of the effect estimate (driven largely by sample size). As precision increases, the range of plausible effects that could occur by chance is reduced. Correspondingly, the statistical significance of an effect of a particular magnitude will usually be greater (the P value will be smaller) in a larger study than in a smaller study.
P values are commonly misinterpreted in two ways. First, a moderate or large P value (e.g. greater than 0.05) may be misinterpreted as evidence that the intervention has no effect on the outcome. There is an important difference between this statement and the correct interpretation that there is a high probability that the observed effect on the outcome is due to chance alone. To avoid such a misinterpretation, review authors should always examine the effect estimate and its 95% confidence interval.
The second misinterpretation is to assume that a result with a small P value for the summary effect estimate implies that an experimental intervention has an important benefit. Such a misinterpretation is more likely to occur in large studies and meta-analyses that accumulate data over dozens of studies and thousands of participants. The P value addresses the question of whether the experimental intervention effect is precisely nil; it does not examine whether the effect is of a magnitude of importance to potential recipients of the intervention. In a large study, a small P value may represent the detection of a trivial effect that may not lead to net health benefit when compared with the potential harms (i.e. harmful effects on other important outcomes). Again, inspection of the point estimate and confidence interval helps correct interpretations (see Section 15.3.1 ).
MECIR Box 15.3.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
15.3.3 Relation between confidence intervals, statistical significance and certainty of evidence
The confidence interval (and imprecision) is only one domain that influences overall uncertainty about effect estimates. Uncertainty resulting from imprecision (i.e. statistical uncertainty) may be no less important than uncertainty from indirectness, or any other GRADE domain, in the context of decision making (Schünemann 2016). Thus, the extent to which interpretations of the confidence interval described in Sections 15.3.1 and 15.3.2 correspond to conclusions about overall certainty of the evidence for the outcome of interest depends on these other domains. If there are no concerns about other domains that determine the certainty of the evidence (i.e. risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness or publication bias), then the interpretation in Sections 15.3.1 and 15.3.2 . about the relation of the confidence interval to the true effect may be carried forward to the overall certainty. However, if there are concerns about the other domains that affect the certainty of the evidence, the interpretation about the true effect needs to be seen in the context of further uncertainty resulting from those concerns.
For example, nine randomized controlled trials in almost 6000 cancer patients indicated that the administration of heparin reduces the risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), with a risk ratio of 43% (95% CI 19% to 60%) (Akl et al 2011a). For patients with a plausible baseline risk of approximately 4.6% per year, this relative effect suggests that heparin leads to an absolute risk reduction of 20 fewer VTEs (95% CI 9 fewer to 27 fewer) per 1000 people per year (Akl et al 2011a). Now consider that the review authors or those applying the evidence in a guideline have lowered the certainty in the evidence as a result of indirectness. While the confidence intervals would remain unchanged, the certainty in that confidence interval and in the point estimate as reflecting the truth for the question of interest will be lowered. In fact, the certainty range will have unknown width so there will be unknown likelihood of a result within that range because of this indirectness. The lower the certainty in the evidence, the less we know about the width of the certainty range, although methods for quantifying risk of bias and understanding potential direction of bias may offer insight when lowered certainty is due to risk of bias. Nevertheless, decision makers must consider this uncertainty, and must do so in relation to the effect measure that is being evaluated (e.g. a relative or absolute measure). We will describe the impact on interpretations for dichotomous outcomes in Section 15.4 .
15.4 Interpreting results from dichotomous outcomes (including numbers needed to treat)
15.4.1 relative and absolute risk reductions.
Clinicians may be more inclined to prescribe an intervention that reduces the relative risk of death by 25% than one that reduces the risk of death by 1 percentage point, although both presentations of the evidence may relate to the same benefit (i.e. a reduction in risk from 4% to 3%). The former refers to the relative reduction in risk and the latter to the absolute reduction in risk. As described in Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1 , there are several measures for comparing dichotomous outcomes in two groups. Meta-analyses are usually undertaken using risk ratios (RR), odds ratios (OR) or risk differences (RD), but there are several alternative ways of expressing results.
Relative risk reduction (RRR) is a convenient way of re-expressing a risk ratio as a percentage reduction:
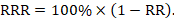
For example, a risk ratio of 0.75 translates to a relative risk reduction of 25%, as in the example above.
The risk difference is often referred to as the absolute risk reduction (ARR) or absolute risk increase (ARI), and may be presented as a percentage (e.g. 1%), as a decimal (e.g. 0.01), or as account (e.g. 10 out of 1000). We consider different choices for presenting absolute effects in Section 15.4.3 . We then describe computations for obtaining these numbers from the results of individual studies and of meta-analyses in Section 15.4.4 .
15.4.2 Number needed to treat (NNT)
The number needed to treat (NNT) is a common alternative way of presenting information on the effect of an intervention. The NNT is defined as the expected number of people who need to receive the experimental rather than the comparator intervention for one additional person to either incur or avoid an event (depending on the direction of the result) in a given time frame. Thus, for example, an NNT of 10 can be interpreted as ‘it is expected that one additional (or less) person will incur an event for every 10 participants receiving the experimental intervention rather than comparator over a given time frame’. It is important to be clear that:
- since the NNT is derived from the risk difference, it is still a comparative measure of effect (experimental versus a specific comparator) and not a general property of a single intervention; and
- the NNT gives an ‘expected value’. For example, NNT = 10 does not imply that one additional event will occur in each and every group of 10 people.
NNTs can be computed for both beneficial and detrimental events, and for interventions that cause both improvements and deteriorations in outcomes. In all instances NNTs are expressed as positive whole numbers. Some authors use the term ‘number needed to harm’ (NNH) when an intervention leads to an adverse outcome, or a decrease in a positive outcome, rather than improvement. However, this phrase can be misleading (most notably, it can easily be read to imply the number of people who will experience a harmful outcome if given the intervention), and it is strongly recommended that ‘number needed to harm’ and ‘NNH’ are avoided. The preferred alternative is to use phrases such as ‘number needed to treat for an additional beneficial outcome’ (NNTB) and ‘number needed to treat for an additional harmful outcome’ (NNTH) to indicate direction of effect.
As NNTs refer to events, their interpretation needs to be worded carefully when the binary outcome is a dichotomization of a scale-based outcome. For example, if the outcome is pain measured on a ‘none, mild, moderate or severe’ scale it may have been dichotomized as ‘none or mild’ versus ‘moderate or severe’. It would be inappropriate for an NNT from these data to be referred to as an ‘NNT for pain’. It is an ‘NNT for moderate or severe pain’.
We consider different choices for presenting absolute effects in Section 15.4.3 . We then describe computations for obtaining these numbers from the results of individual studies and of meta-analyses in Section 15.4.4 .
15.4.3 Expressing risk differences
Users of reviews are liable to be influenced by the choice of statistical presentations of the evidence. Hoffrage and colleagues suggest that physicians’ inferences about statistical outcomes are more appropriate when they deal with ‘natural frequencies’ – whole numbers of people, both treated and untreated (e.g. treatment results in a drop from 20 out of 1000 to 10 out of 1000 women having breast cancer) – than when effects are presented as percentages (e.g. 1% absolute reduction in breast cancer risk) (Hoffrage et al 2000). Probabilities may be more difficult to understand than frequencies, particularly when events are rare. While standardization may be important in improving the presentation of research evidence (and participation in healthcare decisions), current evidence suggests that the presentation of natural frequencies for expressing differences in absolute risk is best understood by consumers of healthcare information (Akl et al 2011b). This evidence provides the rationale for presenting absolute risks in ‘Summary of findings’ tables as numbers of people with events per 1000 people receiving the intervention (see Chapter 14 ).
RRs and RRRs remain crucial because relative effects tend to be substantially more stable across risk groups than absolute effects (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Review authors can use their own data to study this consistency (Cates 1999, Smeeth et al 1999). Risk differences from studies are least likely to be consistent across baseline event rates; thus, they are rarely appropriate for computing numbers needed to treat in systematic reviews. If a relative effect measure (OR or RR) is chosen for meta-analysis, then a comparator group risk needs to be specified as part of the calculation of an RD or NNT. In addition, if there are several different groups of participants with different levels of risk, it is crucial to express absolute benefit for each clinically identifiable risk group, clarifying the time period to which this applies. Studies in patients with differing severity of disease, or studies with different lengths of follow-up will almost certainly have different comparator group risks. In these cases, different comparator group risks lead to different RDs and NNTs (except when the intervention has no effect). A recommended approach is to re-express an odds ratio or a risk ratio as a variety of RD or NNTs across a range of assumed comparator risks (ACRs) (McQuay and Moore 1997, Smeeth et al 1999). Review authors should bear these considerations in mind not only when constructing their ‘Summary of findings’ table, but also in the text of their review.
For example, a review of oral anticoagulants to prevent stroke presented information to users by describing absolute benefits for various baseline risks (Aguilar and Hart 2005, Aguilar et al 2007). They presented their principal findings as “The inherent risk of stroke should be considered in the decision to use oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation patients, selecting those who stand to benefit most for this therapy” (Aguilar and Hart 2005). Among high-risk atrial fibrillation patients with prior stroke or transient ischaemic attack who have stroke rates of about 12% (120 per 1000) per year, warfarin prevents about 70 strokes yearly per 1000 patients, whereas for low-risk atrial fibrillation patients (with a stroke rate of about 2% per year or 20 per 1000), warfarin prevents only 12 strokes. This presentation helps users to understand the important impact that typical baseline risks have on the absolute benefit that they can expect.
15.4.4 Computations
Direct computation of risk difference (RD) or a number needed to treat (NNT) depends on the summary statistic (odds ratio, risk ratio or risk differences) available from the study or meta-analysis. When expressing results of meta-analyses, review authors should use, in the computations, whatever statistic they determined to be the most appropriate summary for meta-analysis (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Here we present calculations to obtain RD as a reduction in the number of participants per 1000. For example, a risk difference of –0.133 corresponds to 133 fewer participants with the event per 1000.
RDs and NNTs should not be computed from the aggregated total numbers of participants and events across the trials. This approach ignores the randomization within studies, and may produce seriously misleading results if there is unbalanced randomization in any of the studies. Using the pooled result of a meta-analysis is more appropriate. When computing NNTs, the values obtained are by convention always rounded up to the next whole number.
15.4.4.1 Computing NNT from a risk difference (RD)
A NNT may be computed from a risk difference as
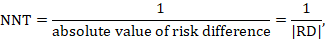
where the vertical bars (‘absolute value of’) in the denominator indicate that any minus sign should be ignored. It is convention to round the NNT up to the nearest whole number. For example, if the risk difference is –0.12 the NNT is 9; if the risk difference is –0.22 the NNT is 5. Cochrane Review authors should qualify the NNT as referring to benefit (improvement) or harm by denoting the NNT as NNTB or NNTH. Note that this approach, although feasible, should be used only for the results of a meta-analysis of risk differences. In most cases meta-analyses will be undertaken using a relative measure of effect (RR or OR), and those statistics should be used to calculate the NNT (see Section 15.4.4.2 and 15.4.4.3 ).
15.4.4.2 Computing risk differences or NNT from a risk ratio
To aid interpretation of the results of a meta-analysis of risk ratios, review authors may compute an absolute risk reduction or NNT. In order to do this, an assumed comparator risk (ACR) (otherwise known as a baseline risk, or risk that the outcome of interest would occur with the comparator intervention) is required. It will usually be appropriate to do this for a range of different ACRs. The computation proceeds as follows:
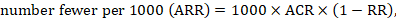
As an example, suppose the risk ratio is RR = 0.92, and an ACR = 0.3 (300 per 1000) is assumed. Then the effect on risk is 24 fewer per 1000:
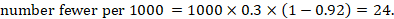
The NNT is 42:
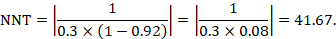
15.4.4.3 Computing risk differences or NNT from an odds ratio
Review authors may wish to compute a risk difference or NNT from the results of a meta-analysis of odds ratios. In order to do this, an ACR is required. It will usually be appropriate to do this for a range of different ACRs. The computation proceeds as follows:
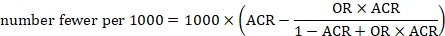
As an example, suppose the odds ratio is OR = 0.73, and a comparator risk of ACR = 0.3 is assumed. Then the effect on risk is 62 fewer per 1000:
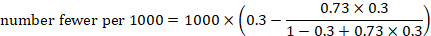
The NNT is 17:
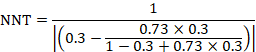
15.4.4.4 Computing risk ratio from an odds ratio
Because risk ratios are easier to interpret than odds ratios, but odds ratios have favourable mathematical properties, a review author may decide to undertake a meta-analysis based on odds ratios, but to express the result as a summary risk ratio (or relative risk reduction). This requires an ACR. Then
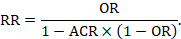
It will often be reasonable to perform this transformation using the median comparator group risk from the studies in the meta-analysis.
15.4.4.5 Computing confidence limits
Confidence limits for RDs and NNTs may be calculated by applying the above formulae to the upper and lower confidence limits for the summary statistic (RD, RR or OR) (Altman 1998). Note that this confidence interval does not incorporate uncertainty around the ACR.
If the 95% confidence interval of OR or RR includes the value 1, one of the confidence limits will indicate benefit and the other harm. Thus, appropriate use of the words ‘fewer’ and ‘more’ is required for each limit when presenting results in terms of events. For NNTs, the two confidence limits should be labelled as NNTB and NNTH to indicate the direction of effect in each case. The confidence interval for the NNT will include a ‘discontinuity’, because increasingly smaller risk differences that approach zero will lead to NNTs approaching infinity. Thus, the confidence interval will include both an infinitely large NNTB and an infinitely large NNTH.
15.5 Interpreting results from continuous outcomes (including standardized mean differences)
15.5.1 meta-analyses with continuous outcomes.
Review authors should describe in the study protocol how they plan to interpret results for continuous outcomes. When outcomes are continuous, review authors have a number of options to present summary results. These options differ if studies report the same measure that is familiar to the target audiences, studies report the same or very similar measures that are less familiar to the target audiences, or studies report different measures.
15.5.2 Meta-analyses with continuous outcomes using the same measure
If all studies have used the same familiar units, for instance, results are expressed as durations of events, such as symptoms for conditions including diarrhoea, sore throat, otitis media, influenza or duration of hospitalization, a meta-analysis may generate a summary estimate in those units, as a difference in mean response (see, for instance, the row summarizing results for duration of diarrhoea in Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.b and the row summarizing oedema in Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.a ). For such outcomes, the ‘Summary of findings’ table should include a difference of means between the two interventions. However, when units of such outcomes may be difficult to interpret, particularly when they relate to rating scales (again, see the oedema row of Chapter 14, Figure 14.1.a ). ‘Summary of findings’ tables should include the minimum and maximum of the scale of measurement, and the direction. Knowledge of the smallest change in instrument score that patients perceive is important – the minimal important difference (MID) – and can greatly facilitate the interpretation of results (Guyatt et al 1998, Schünemann and Guyatt 2005). Knowing the MID allows review authors and users to place results in context. Review authors should state the MID – if known – in the Comments column of their ‘Summary of findings’ table. For example, the chronic respiratory questionnaire has possible scores in health-related quality of life ranging from 1 to 7 and 0.5 represents a well-established MID (Jaeschke et al 1989, Schünemann et al 2005).
15.5.3 Meta-analyses with continuous outcomes using different measures
When studies have used different instruments to measure the same construct, a standardized mean difference (SMD) may be used in meta-analysis for combining continuous data. Without guidance, clinicians and patients may have little idea how to interpret results presented as SMDs. Review authors should therefore consider issues of interpretability when planning their analysis at the protocol stage and should consider whether there will be suitable ways to re-express the SMD or whether alternative effect measures, such as a ratio of means, or possibly as minimal important difference units (Guyatt et al 2013b) should be used. Table 15.5.a and the following sections describe these options.
Table 15.5.a Approaches and their implications to presenting results of continuous variables when primary studies have used different instruments to measure the same construct. Adapted from Guyatt et al (2013b)
15.5.3.1 Presenting and interpreting SMDs using generic effect size estimates
The SMD expresses the intervention effect in standard units rather than the original units of measurement. The SMD is the difference in mean effects between the experimental and comparator groups divided by the pooled standard deviation of participants’ outcomes, or external SDs when studies are very small (see Chapter 6, Section 6.5.1.2 ). The value of a SMD thus depends on both the size of the effect (the difference between means) and the standard deviation of the outcomes (the inherent variability among participants or based on an external SD).
If review authors use the SMD, they might choose to present the results directly as SMDs (row 1a, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). However, absolute values of the intervention and comparison groups are typically not useful because studies have used different measurement instruments with different units. Guiding rules for interpreting SMDs (or ‘Cohen’s effect sizes’) exist, and have arisen mainly from researchers in the social sciences (Cohen 1988). One example is as follows: 0.2 represents a small effect, 0.5 a moderate effect and 0.8 a large effect (Cohen 1988). Variations exist (e.g. <0.40=small, 0.40 to 0.70=moderate, >0.70=large). Review authors might consider including such a guiding rule in interpreting the SMD in the text of the review, and in summary versions such as the Comments column of a ‘Summary of findings’ table. However, some methodologists believe that such interpretations are problematic because patient importance of a finding is context-dependent and not amenable to generic statements.
15.5.3.2 Re-expressing SMDs using a familiar instrument
The second possibility for interpreting the SMD is to express it in the units of one or more of the specific measurement instruments used by the included studies (row 1b, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). The approach is to calculate an absolute difference in means by multiplying the SMD by an estimate of the SD associated with the most familiar instrument. To obtain this SD, a reasonable option is to calculate a weighted average across all intervention groups of all studies that used the selected instrument (preferably a pre-intervention or post-intervention SD as discussed in Chapter 10, Section 10.5.2 ). To better reflect among-person variation in practice, or to use an instrument not represented in the meta-analysis, it may be preferable to use a standard deviation from a representative observational study. The summary effect is thus re-expressed in the original units of that particular instrument and the clinical relevance and impact of the intervention effect can be interpreted using that familiar instrument.
The same approach of re-expressing the results for a familiar instrument can also be used for other standardized effect measures such as when standardizing by MIDs (Guyatt et al 2013b): see Section 15.5.3.5 .
Table 15.5.b Application of approaches when studies have used different measures: effects of dexamethasone for pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy (Karanicolas et al 2008). Reproduced with permission of Wolters Kluwer
1 Certainty rated according to GRADE from very low to high certainty. 2 Substantial unexplained heterogeneity in study results. 3 Imprecision due to wide confidence intervals. 4 The 20% comes from the proportion in the control group requiring rescue analgesia. 5 Crude (arithmetic) means of the post-operative pain mean responses across all five trials when transformed to a 100-point scale.
15.5.3.3 Re-expressing SMDs through dichotomization and transformation to relative and absolute measures
A third approach (row 1c, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ) relies on converting the continuous measure into a dichotomy and thus allows calculation of relative and absolute effects on a binary scale. A transformation of a SMD to a (log) odds ratio is available, based on the assumption that an underlying continuous variable has a logistic distribution with equal standard deviation in the two intervention groups, as discussed in Chapter 10, Section 10.6 (Furukawa 1999, Guyatt et al 2013b). The assumption is unlikely to hold exactly and the results must be regarded as an approximation. The log odds ratio is estimated as
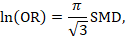
(or approximately 1.81✕SMD). The resulting odds ratio can then be presented as normal, and in a ‘Summary of findings’ table, combined with an assumed comparator group risk to be expressed as an absolute risk difference. The comparator group risk in this case would refer to the proportion of people who have achieved a specific value of the continuous outcome. In randomized trials this can be interpreted as the proportion who have improved by some (specified) amount (responders), for instance by 5 points on a 0 to 100 scale. Table 15.5.c shows some illustrative results from this method. The risk differences can then be converted to NNTs or to people per thousand using methods described in Section 15.4.4 .
Table 15.5.c Risk difference derived for specific SMDs for various given ‘proportions improved’ in the comparator group (Furukawa 1999, Guyatt et al 2013b). Reproduced with permission of Elsevier
15.5.3.4 Ratio of means
A more frequently used approach is based on calculation of a ratio of means between the intervention and comparator groups (Friedrich et al 2008) as discussed in Chapter 6, Section 6.5.1.3 . Interpretational advantages of this approach include the ability to pool studies with outcomes expressed in different units directly, to avoid the vulnerability of heterogeneous populations that limits approaches that rely on SD units, and for ease of clinical interpretation (row 2, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ). This method is currently designed for post-intervention scores only. However, it is possible to calculate a ratio of change scores if both intervention and comparator groups change in the same direction in each relevant study, and this ratio may sometimes be informative.
Limitations to this approach include its limited applicability to change scores (since it is unlikely that both intervention and comparator group changes are in the same direction in all studies) and the possibility of misleading results if the comparator group mean is very small, in which case even a modest difference from the intervention group will yield a large and therefore misleading ratio of means. It also requires that separate ratios of means be calculated for each included study, and then entered into a generic inverse variance meta-analysis (see Chapter 10, Section 10.3 ).
The ratio of means approach illustrated in Table 15.5.b suggests a relative reduction in pain of only 13%, meaning that those receiving steroids have a pain severity 87% of those in the comparator group, an effect that might be considered modest.
15.5.3.5 Presenting continuous results as minimally important difference units
To express results in MID units, review authors have two options. First, they can be combined across studies in the same way as the SMD, but instead of dividing the mean difference of each study by its SD, review authors divide by the MID associated with that outcome (Johnston et al 2010, Guyatt et al 2013b). Instead of SD units, the pooled results represent MID units (row 3, Table 15.5.a and Table 15.5.b ), and may be more easily interpretable. This approach avoids the problem of varying SDs across studies that may distort estimates of effect in approaches that rely on the SMD. The approach, however, relies on having well-established MIDs. The approach is also risky in that a difference less than the MID may be interpreted as trivial when a substantial proportion of patients may have achieved an important benefit.
The other approach makes a simple conversion (not shown in Table 15.5.b ), before undertaking the meta-analysis, of the means and SDs from each study to means and SDs on the scale of a particular familiar instrument whose MID is known. For example, one can rescale the mean and SD of other chronic respiratory disease instruments (e.g. rescaling a 0 to 100 score of an instrument) to a the 1 to 7 score in Chronic Respiratory Disease Questionnaire (CRQ) units (by assuming 0 equals 1 and 100 equals 7 on the CRQ). Given the MID of the CRQ of 0.5, a mean difference in change of 0.71 after rescaling of all studies suggests a substantial effect of the intervention (Guyatt et al 2013b). This approach, presenting in units of the most familiar instrument, may be the most desirable when the target audiences have extensive experience with that instrument, particularly if the MID is well established.
15.6 Drawing conclusions
15.6.1 conclusions sections of a cochrane review.
Authors’ conclusions in a Cochrane Review are divided into implications for practice and implications for research. While Cochrane Reviews about interventions can provide meaningful information and guidance for practice, decisions about the desirable and undesirable consequences of healthcare options require evidence and judgements for criteria that most Cochrane Reviews do not provide (Alonso-Coello et al 2016). In describing the implications for practice and the development of recommendations, however, review authors may consider the certainty of the evidence, the balance of benefits and harms, and assumed values and preferences.
15.6.2 Implications for practice
Drawing conclusions about the practical usefulness of an intervention entails making trade-offs, either implicitly or explicitly, between the estimated benefits, harms and the values and preferences. Making such trade-offs, and thus making specific recommendations for an action in a specific context, goes beyond a Cochrane Review and requires additional evidence and informed judgements that most Cochrane Reviews do not provide (Alonso-Coello et al 2016). Such judgements are typically the domain of clinical practice guideline developers for which Cochrane Reviews will provide crucial information (Graham et al 2011, Schünemann et al 2014, Zhang et al 2018a). Thus, authors of Cochrane Reviews should not make recommendations.
If review authors feel compelled to lay out actions that clinicians and patients could take, they should – after describing the certainty of evidence and the balance of benefits and harms – highlight different actions that might be consistent with particular patterns of values and preferences. Other factors that might influence a decision should also be highlighted, including any known factors that would be expected to modify the effects of the intervention, the baseline risk or status of the patient, costs and who bears those costs, and the availability of resources. Review authors should ensure they consider all patient-important outcomes, including those for which limited data may be available. In the context of public health reviews the focus may be on population-important outcomes as the target may be an entire (non-diseased) population and include outcomes that are not measured in the population receiving an intervention (e.g. a reduction of transmission of infections from those receiving an intervention). This process implies a high level of explicitness in judgements about values or preferences attached to different outcomes and the certainty of the related evidence (Zhang et al 2018b, Zhang et al 2018c); this and a full cost-effectiveness analysis is beyond the scope of most Cochrane Reviews (although they might well be used for such analyses; see Chapter 20 ).
A review on the use of anticoagulation in cancer patients to increase survival (Akl et al 2011a) provides an example for laying out clinical implications for situations where there are important trade-offs between desirable and undesirable effects of the intervention: “The decision for a patient with cancer to start heparin therapy for survival benefit should balance the benefits and downsides and integrate the patient’s values and preferences. Patients with a high preference for a potential survival prolongation, limited aversion to potential bleeding, and who do not consider heparin (both UFH or LMWH) therapy a burden may opt to use heparin, while those with aversion to bleeding may not.”
15.6.3 Implications for research
The second category for authors’ conclusions in a Cochrane Review is implications for research. To help people make well-informed decisions about future healthcare research, the ‘Implications for research’ section should comment on the need for further research, and the nature of the further research that would be most desirable. It is helpful to consider the population, intervention, comparison and outcomes that could be addressed, or addressed more effectively in the future, in the context of the certainty of the evidence in the current review (Brown et al 2006):
- P (Population): diagnosis, disease stage, comorbidity, risk factor, sex, age, ethnic group, specific inclusion or exclusion criteria, clinical setting;
- I (Intervention): type, frequency, dose, duration, prognostic factor;
- C (Comparison): placebo, routine care, alternative treatment/management;
- O (Outcome): which clinical or patient-related outcomes will the researcher need to measure, improve, influence or accomplish? Which methods of measurement should be used?
While Cochrane Review authors will find the PICO domains helpful, the domains of the GRADE certainty framework further support understanding and describing what additional research will improve the certainty in the available evidence. Note that as the certainty of the evidence is likely to vary by outcome, these implications will be specific to certain outcomes in the review. Table 15.6.a shows how review authors may be aided in their interpretation of the body of evidence and drawing conclusions about future research and practice.
Table 15.6.a Implications for research and practice suggested by individual GRADE domains
The review of compression stockings for prevention of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in airline passengers described in Chapter 14 provides an example where there is some convincing evidence of a benefit of the intervention: “This review shows that the question of the effects on symptomless DVT of wearing versus not wearing compression stockings in the types of people studied in these trials should now be regarded as answered. Further research may be justified to investigate the relative effects of different strengths of stockings or of stockings compared to other preventative strategies. Further randomised trials to address the remaining uncertainty about the effects of wearing versus not wearing compression stockings on outcomes such as death, pulmonary embolism and symptomatic DVT would need to be large.” (Clarke et al 2016).
A review of therapeutic touch for anxiety disorder provides an example of the implications for research when no eligible studies had been found: “This review highlights the need for randomized controlled trials to evaluate the effectiveness of therapeutic touch in reducing anxiety symptoms in people diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Future trials need to be rigorous in design and delivery, with subsequent reporting to include high quality descriptions of all aspects of methodology to enable appraisal and interpretation of results.” (Robinson et al 2007).
15.6.4 Reaching conclusions
A common mistake is to confuse ‘no evidence of an effect’ with ‘evidence of no effect’. When the confidence intervals are too wide (e.g. including no effect), it is wrong to claim that the experimental intervention has ‘no effect’ or is ‘no different’ from the comparator intervention. Review authors may also incorrectly ‘positively’ frame results for some effects but not others. For example, when the effect estimate is positive for a beneficial outcome but confidence intervals are wide, review authors may describe the effect as promising. However, when the effect estimate is negative for an outcome that is considered harmful but the confidence intervals include no effect, review authors report no effect. Another mistake is to frame the conclusion in wishful terms. For example, review authors might write, “there were too few people in the analysis to detect a reduction in mortality” when the included studies showed a reduction or even increase in mortality that was not ‘statistically significant’. One way of avoiding errors such as these is to consider the results blinded; that is, consider how the results would be presented and framed in the conclusions if the direction of the results was reversed. If the confidence interval for the estimate of the difference in the effects of the interventions overlaps with no effect, the analysis is compatible with both a true beneficial effect and a true harmful effect. If one of the possibilities is mentioned in the conclusion, the other possibility should be mentioned as well. Table 15.6.b suggests narrative statements for drawing conclusions based on the effect estimate from the meta-analysis and the certainty of the evidence.
Table 15.6.b Suggested narrative statements for phrasing conclusions
Another common mistake is to reach conclusions that go beyond the evidence. Often this is done implicitly, without referring to the additional information or judgements that are used in reaching conclusions about the implications of a review for practice. Even when additional information and explicit judgements support conclusions about the implications of a review for practice, review authors rarely conduct systematic reviews of the additional information. Furthermore, implications for practice are often dependent on specific circumstances and values that must be taken into consideration. As we have noted, review authors should always be cautious when drawing conclusions about implications for practice and they should not make recommendations.
15.7 Chapter information
Authors: Holger J Schünemann, Gunn E Vist, Julian PT Higgins, Nancy Santesso, Jonathan J Deeks, Paul Glasziou, Elie Akl, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group
Acknowledgements: Andrew Oxman, Jonathan Sterne, Michael Borenstein and Rob Scholten contributed text to earlier versions of this chapter.
Funding: This work was in part supported by funding from the Michael G DeGroote Cochrane Canada Centre and the Ontario Ministry of Health. JJD receives support from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Birmingham Biomedical Research Centre at the University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Birmingham. JPTH receives support from the NIHR Biomedical Research Centre at University Hospitals Bristol NHS Foundation Trust and the University of Bristol. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
15.8 References
Aguilar MI, Hart R. Oral anticoagulants for preventing stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and no previous history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005; 3 : CD001927.
Aguilar MI, Hart R, Pearce LA. Oral anticoagulants versus antiplatelet therapy for preventing stroke in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and no history of stroke or transient ischemic attacks. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 3 : CD006186.
Akl EA, Gunukula S, Barba M, Yosuico VE, van Doormaal FF, Kuipers S, Middeldorp S, Dickinson HO, Bryant A, Schünemann H. Parenteral anticoagulation in patients with cancer who have no therapeutic or prophylactic indication for anticoagulation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011a; 1 : CD006652.
Akl EA, Oxman AD, Herrin J, Vist GE, Terrenato I, Sperati F, Costiniuk C, Blank D, Schünemann H. Using alternative statistical formats for presenting risks and risk reductions. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011b; 3 : CD006776.
Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ, Moberg J, Brignardello-Petersen R, Akl EA, Davoli M, Treweek S, Mustafa RA, Rada G, Rosenbaum S, Morelli A, Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Group GW. GRADE Evidence to Decision (EtD) frameworks: a systematic and transparent approach to making well informed healthcare choices. 1: Introduction. BMJ 2016; 353 : i2016.
Altman DG. Confidence intervals for the number needed to treat. BMJ 1998; 317 : 1309-1312.
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Zaza S. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004; 328 : 1490.
Brown P, Brunnhuber K, Chalkidou K, Chalmers I, Clarke M, Fenton M, Forbes C, Glanville J, Hicks NJ, Moody J, Twaddle S, Timimi H, Young P. How to formulate research recommendations. BMJ 2006; 333 : 804-806.
Cates C. Confidence intervals for the number needed to treat: Pooling numbers needed to treat may not be reliable. BMJ 1999; 318 : 1764-1765.
Clarke MJ, Broderick C, Hopewell S, Juszczak E, Eisinga A. Compression stockings for preventing deep vein thrombosis in airline passengers. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016; 9 : CD004002.
Cohen J. Statistical Power Analysis in the Behavioral Sciences . 2nd edition ed. Hillsdale (NJ): Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.; 1988.
Coleman T, Chamberlain C, Davey MA, Cooper SE, Leonardi-Bee J. Pharmacological interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015; 12 : CD010078.
Dans AM, Dans L, Oxman AD, Robinson V, Acuin J, Tugwell P, Dennis R, Kang D. Assessing equity in clinical practice guidelines. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2007; 60 : 540-546.
Friedman LM, Furberg CD, DeMets DL. Fundamentals of Clinical Trials . 2nd edition ed. Littleton (MA): John Wright PSG, Inc.; 1985.
Friedrich JO, Adhikari NK, Beyene J. The ratio of means method as an alternative to mean differences for analyzing continuous outcome variables in meta-analysis: a simulation study. BMC Medical Research Methodology 2008; 8 : 32.
Furukawa T. From effect size into number needed to treat. Lancet 1999; 353 : 1680.
Graham R, Mancher M, Wolman DM, Greenfield S, Steinberg E. Committee on Standards for Developing Trustworthy Clinical Practice Guidelines, Board on Health Care Services: Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust. Washington, DC: National Academies Press; 2011.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011a; 64 : 383-394.
Guyatt GH, Juniper EF, Walter SD, Griffith LE, Goldstein RS. Interpreting treatment effects in randomised trials. BMJ 1998; 316 : 690-693.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Vist GE, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008; 336 : 924-926.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Woodcock J, Brozek J, Helfand M, Alonso-Coello P, Falck-Ytter Y, Jaeschke R, Vist G, Akl EA, Post PN, Norris S, Meerpohl J, Shukla VK, Nasser M, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence--indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011b; 64 : 1303-1310.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Santesso N, Helfand M, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Norris S, Meerpohl J, Djulbegovic B, Alonso-Coello P, Post PN, Busse JW, Glasziou P, Christensen R, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 12. Preparing summary of findings tables-binary outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013a; 66 : 158-172.
Guyatt GH, Thorlund K, Oxman AD, Walter SD, Patrick D, Furukawa TA, Johnston BC, Karanicolas P, Akl EA, Vist G, Kunz R, Brozek J, Kupper LL, Martin SL, Meerpohl JJ, Alonso-Coello P, Christensen R, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 13. Preparing summary of findings tables and evidence profiles-continuous outcomes. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2013b; 66 : 173-183.
Hawe P, Shiell A, Riley T, Gold L. Methods for exploring implementation variation and local context within a cluster randomised community intervention trial. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 2004; 58 : 788-793.
Hoffrage U, Lindsey S, Hertwig R, Gigerenzer G. Medicine. Communicating statistical information. Science 2000; 290 : 2261-2262.
Jaeschke R, Singer J, Guyatt GH. Measurement of health status. Ascertaining the minimal clinically important difference. Controlled Clinical Trials 1989; 10 : 407-415.
Johnston B, Thorlund K, Schünemann H, Xie F, Murad M, Montori V, Guyatt G. Improving the interpretation of health-related quality of life evidence in meta-analysis: The application of minimal important difference units. . Health Outcomes and Qualithy of Life 2010; 11 : 116.
Karanicolas PJ, Smith SE, Kanbur B, Davies E, Guyatt GH. The impact of prophylactic dexamethasone on nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Annals of Surgery 2008; 248 : 751-762.
Lumley J, Oliver SS, Chamberlain C, Oakley L. Interventions for promoting smoking cessation during pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004; 4 : CD001055.
McQuay HJ, Moore RA. Using numerical results from systematic reviews in clinical practice. Annals of Internal Medicine 1997; 126 : 712-720.
Resnicow K, Cross D, Wynder E. The Know Your Body program: a review of evaluation studies. Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine 1993; 70 : 188-207.
Robinson J, Biley FC, Dolk H. Therapeutic touch for anxiety disorders. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 3 : CD006240.
Rothwell PM. External validity of randomised controlled trials: "to whom do the results of this trial apply?". Lancet 2005; 365 : 82-93.
Santesso N, Carrasco-Labra A, Langendam M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Mustafa RA, Heus P, Lasserson T, Opiyo N, Kunnamo I, Sinclair D, Garner P, Treweek S, Tovey D, Akl EA, Tugwell P, Brozek JL, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 3: detailed guidance for explanatory footnotes supports creating and understanding GRADE certainty in the evidence judgments. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 28-39.
Schünemann HJ, Puhan M, Goldstein R, Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH. Measurement properties and interpretability of the Chronic respiratory disease questionnaire (CRQ). COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2005; 2 : 81-89.
Schünemann HJ, Guyatt GH. Commentary--goodbye M(C)ID! Hello MID, where do you come from? Health Services Research 2005; 40 : 593-597.
Schünemann HJ, Fretheim A, Oxman AD. Improving the use of research evidence in guideline development: 13. Applicability, transferability and adaptation. Health Research Policy and Systems 2006; 4 : 25.
Schünemann HJ. Methodological idiosyncracies, frameworks and challenges of non-pharmaceutical and non-technical treatment interventions. Zeitschrift für Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualität im Gesundheitswesen 2013; 107 : 214-220.
Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Reeves BC, Akl EA, Santesso N, Spencer FA, Shea B, Wells G, Helfand M. Non-randomized studies as a source of complementary, sequential or replacement evidence for randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews on the effects of interventions. Research Synthesis Methods 2013; 4 : 49-62.
Schünemann HJ, Wiercioch W, Etxeandia I, Falavigna M, Santesso N, Mustafa R, Ventresca M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Laisaar KT, Kowalski S, Baldeh T, Zhang Y, Raid U, Neumann I, Norris SL, Thornton J, Harbour R, Treweek S, Guyatt G, Alonso-Coello P, Reinap M, Brozek J, Oxman A, Akl EA. Guidelines 2.0: systematic development of a comprehensive checklist for a successful guideline enterprise. CMAJ: Canadian Medical Association Journal 2014; 186 : E123-142.
Schünemann HJ. Interpreting GRADE's levels of certainty or quality of the evidence: GRADE for statisticians, considering review information size or less emphasis on imprecision? Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 75 : 6-15.
Smeeth L, Haines A, Ebrahim S. Numbers needed to treat derived from meta-analyses--sometimes informative, usually misleading. BMJ 1999; 318 : 1548-1551.
Sun X, Briel M, Busse JW, You JJ, Akl EA, Mejza F, Bala MM, Bassler D, Mertz D, Diaz-Granados N, Vandvik PO, Malaga G, Srinathan SK, Dahm P, Johnston BC, Alonso-Coello P, Hassouneh B, Walter SD, Heels-Ansdell D, Bhatnagar N, Altman DG, Guyatt GH. Credibility of claims of subgroup effects in randomised controlled trials: systematic review. BMJ 2012; 344 : e1553.
Zhang Y, Akl EA, Schünemann HJ. Using systematic reviews in guideline development: the GRADE approach. Research Synthesis Methods 2018a: doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1313.
Zhang Y, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt GH, Yepes-Nunez JJ, Akl EA, Hazlewood G, Pardo-Hernandez H, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Qaseem A, Williams JW, Jr., Tugwell P, Flottorp S, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Mustafa RA, Rojas MX, Schünemann HJ. GRADE Guidelines: 19. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences-Risk of bias and indirectness. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018b: doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.1001.1013.
Zhang Y, Alonso Coello P, Guyatt G, Yepes-Nunez JJ, Akl EA, Hazlewood G, Pardo-Hernandez H, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, Qaseem A, Williams JW, Jr., Tugwell P, Flottorp S, Chang Y, Zhang Y, Mustafa RA, Rojas MX, Xie F, Schünemann HJ. GRADE Guidelines: 20. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes or values and preferences - Inconsistency, Imprecision, and other Domains. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018c: doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.1005.1011.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.
How to Present Results in a Research Paper
- First Online: 01 October 2023
Cite this chapter

- Aparna Mukherjee 4 ,
- Gunjan Kumar 4 &
- Rakesh Lodha 5
697 Accesses
The results section is the core of a research manuscript where the study data and analyses are presented in an organized, uncluttered manner such that the reader can easily understand and interpret the findings. This section is completely factual; there is no place for opinions or explanations from the authors. The results should correspond to the objectives of the study in an orderly manner. Self-explanatory tables and figures add value to this section and make data presentation more convenient and appealing. The results presented in this section should have a link with both the preceding methods section and the following discussion section. A well-written, articulate results section lends clarity and credibility to the research paper and the study as a whole. This chapter provides an overview and important pointers to effective drafting of the results section in a research manuscript and also in theses.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Kallestinova ED (2011) How to write your first research paper. Yale J Biol Med 84(3):181–190
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
STROBE. STROBE. [cited 2022 Nov 10]. https://www.strobe-statement.org/
Consort—Welcome to the CONSORT Website. http://www.consort-statement.org/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Korevaar DA, Cohen JF, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP et al (2016) Updating standards for reporting diagnostic accuracy: the development of STARD 2015. Res Integr Peer Rev 1(1):7
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n71
Page MJ, Moher D, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD et al (2021) PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 372:n160
Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups | EQUATOR Network. https://www.equator-network.org/reporting-guidelines/coreq/ . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Aggarwal R, Sahni P (2015) The results section. In: Aggarwal R, Sahni P (eds) Reporting and publishing research in the biomedical sciences, 1st edn. National Medical Journal of India, Delhi, pp 24–44
Google Scholar
Mukherjee A, Lodha R (2016) Writing the results. Indian Pediatr 53(5):409–415
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lodha R, Randev S, Kabra SK (2016) Oral antibiotics for community acquired pneumonia with chest indrawing in children aged below five years: a systematic review. Indian Pediatr 53(6):489–495
Anderson C (2010) Presenting and evaluating qualitative research. Am J Pharm Educ 74(8):141
Roberts C, Kumar K, Finn G (2020) Navigating the qualitative manuscript writing process: some tips for authors and reviewers. BMC Med Educ 20:439
Bigby C (2015) Preparing manuscripts that report qualitative research: avoiding common pitfalls and illegitimate questions. Aust Soc Work 68(3):384–391
Article Google Scholar
Vincent BP, Kumar G, Parameswaran S, Kar SS (2019) Barriers and suggestions towards deceased organ donation in a government tertiary care teaching hospital: qualitative study using socio-ecological model framework. Indian J Transplant 13(3):194
McCormick JB, Hopkins MA (2021) Exploring public concerns for sharing and governance of personal health information: a focus group study. JAMIA Open 4(4):ooab098
Groenland -emeritus professor E. Employing the matrix method as a tool for the analysis of qualitative research data in the business domain. Rochester, NY; 2014. https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=2495330 . Accessed 10 Nov 2022
Download references
Acknowledgments
The book chapter is derived in part from our article “Mukherjee A, Lodha R. Writing the Results. Indian Pediatr. 2016 May 8;53(5):409-15.” We thank the Editor-in-Chief of the journal “Indian Pediatrics” for the permission for the same.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Clinical Studies, Trials and Projection Unit, Indian Council of Medical Research, New Delhi, India
Aparna Mukherjee & Gunjan Kumar
Department of Pediatrics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India
Rakesh Lodha
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Rakesh Lodha .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Retired Senior Expert Pharmacologist at the Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology, and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Gowraganahalli Jagadeesh
Professor & Director, Research Training and Publications, The Office of Research and Development, Periyar Maniammai Institute of Science & Technology (Deemed to be University), Vallam, Tamil Nadu, India
Pitchai Balakumar
Division Cardiology & Nephrology, Office of Cardiology, Hematology, Endocrinology and Nephrology, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, US Food and Drug Administration, Silver Spring, MD, USA
Fortunato Senatore
Ethics declarations
Rights and permissions.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Mukherjee, A., Kumar, G., Lodha, R. (2023). How to Present Results in a Research Paper. In: Jagadeesh, G., Balakumar, P., Senatore, F. (eds) The Quintessence of Basic and Clinical Research and Scientific Publishing. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-1284-1_44
Published : 01 October 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-99-1283-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-99-1284-1
eBook Packages : Biomedical and Life Sciences Biomedical and Life Sciences (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 9. The Conclusion
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research. For most college-level research papers, two or three well-developed paragraphs is sufficient for a conclusion, although in some cases, more paragraphs may be required in describing the key findings and their significance.
Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
Importance of a Good Conclusion
A well-written conclusion provides you with important opportunities to demonstrate to the reader your understanding of the research problem. These include:
- Presenting the last word on the issues you raised in your paper . Just as the introduction gives a first impression to your reader, the conclusion offers a chance to leave a lasting impression. Do this, for example, by highlighting key findings in your analysis that advance new understanding about the research problem, that are unusual or unexpected, or that have important implications applied to practice.
- Summarizing your thoughts and conveying the larger significance of your study . The conclusion is an opportunity to succinctly re-emphasize your answer to the "So What?" question by placing the study within the context of how your research advances past research about the topic.
- Identifying how a gap in the literature has been addressed . The conclusion can be where you describe how a previously identified gap in the literature [first identified in your literature review section] has been addressed by your research and why this contribution is significant.
- Demonstrating the importance of your ideas . Don't be shy. The conclusion offers an opportunity to elaborate on the impact and significance of your findings. This is particularly important if your study approached examining the research problem from an unusual or innovative perspective.
- Introducing possible new or expanded ways of thinking about the research problem . This does not refer to introducing new information [which should be avoided], but to offer new insight and creative approaches for framing or contextualizing the research problem based on the results of your study.
Bunton, David. “The Structure of PhD Conclusion Chapters.” Journal of English for Academic Purposes 4 (July 2005): 207–224; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Structure and Writing Style
I. General Rules
The general function of your paper's conclusion is to restate the main argument . It reminds the reader of the strengths of your main argument(s) and reiterates the most important evidence supporting those argument(s). Do this by clearly summarizing the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem you investigated in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found in the literature. However, make sure that your conclusion is not simply a repetitive summary of the findings. This reduces the impact of the argument(s) you have developed in your paper.
When writing the conclusion to your paper, follow these general rules:
- Present your conclusions in clear, concise language. Re-state the purpose of your study, then describe how your findings differ or support those of other studies and why [i.e., what were the unique, new, or crucial contributions your study made to the overall research about your topic?].
- Do not simply reiterate your findings or the discussion of your results. Provide a synthesis of arguments presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem and the overall objectives of your study.
- Indicate opportunities for future research if you haven't already done so in the discussion section of your paper. Highlighting the need for further research provides the reader with evidence that you have an in-depth awareness of the research problem but that further investigations should take place beyond the scope of your investigation.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is presented well:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize the argument for your reader.
- If, prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the end of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from the data [this is opposite of the introduction, which begins with general discussion of the context and ends with a detailed description of the research problem].
The conclusion also provides a place for you to persuasively and succinctly restate the research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with all the information about the topic . Depending on the discipline you are writing in, the concluding paragraph may contain your reflections on the evidence presented. However, the nature of being introspective about the research you have conducted will depend on the topic and whether your professor wants you to express your observations in this way. If asked to think introspectively about the topics, do not delve into idle speculation. Being introspective means looking within yourself as an author to try and understand an issue more deeply, not to guess at possible outcomes or make up scenarios not supported by the evidence.
II. Developing a Compelling Conclusion
Although an effective conclusion needs to be clear and succinct, it does not need to be written passively or lack a compelling narrative. Strategies to help you move beyond merely summarizing the key points of your research paper may include any of the following:
- If your essay deals with a critical, contemporary problem, warn readers of the possible consequences of not attending to the problem proactively.
- Recommend a specific course or courses of action that, if adopted, could address a specific problem in practice or in the development of new knowledge leading to positive change.
- Cite a relevant quotation or expert opinion already noted in your paper in order to lend authority and support to the conclusion(s) you have reached [a good source would be from your literature review].
- Explain the consequences of your research in a way that elicits action or demonstrates urgency in seeking change.
- Restate a key statistic, fact, or visual image to emphasize the most important finding of your paper.
- If your discipline encourages personal reflection, illustrate your concluding point by drawing from your own life experiences.
- Return to an anecdote, an example, or a quotation that you presented in your introduction, but add further insight derived from the findings of your study; use your interpretation of results from your study to recast it in new or important ways.
- Provide a "take-home" message in the form of a succinct, declarative statement that you want the reader to remember about your study.
III. Problems to Avoid
Failure to be concise Your conclusion section should be concise and to the point. Conclusions that are too lengthy often have unnecessary information in them. The conclusion is not the place for details about your methodology or results. Although you should give a summary of what was learned from your research, this summary should be relatively brief, since the emphasis in the conclusion is on the implications, evaluations, insights, and other forms of analysis that you make. Strategies for writing concisely can be found here .
Failure to comment on larger, more significant issues In the introduction, your task was to move from the general [the field of study] to the specific [the research problem]. However, in the conclusion, your task is to move from a specific discussion [your research problem] back to a general discussion framed around the implications and significance of your findings [i.e., how your research contributes new understanding or fills an important gap in the literature]. In short, the conclusion is where you should place your research within a larger context [visualize your paper as an hourglass--start with a broad introduction and review of the literature, move to the specific analysis and discussion, conclude with a broad summary of the study's implications and significance].
Failure to reveal problems and negative results Negative aspects of the research process should never be ignored. These are problems, deficiencies, or challenges encountered during your study. They should be summarized as a way of qualifying your overall conclusions. If you encountered negative or unintended results [i.e., findings that are validated outside the research context in which they were generated], you must report them in the results section and discuss their implications in the discussion section of your paper. In the conclusion, use negative results as an opportunity to explain their possible significance and/or how they may form the basis for future research.
Failure to provide a clear summary of what was learned In order to be able to discuss how your research fits within your field of study [and possibly the world at large], you need to summarize briefly and succinctly how it contributes to new knowledge or a new understanding about the research problem. This element of your conclusion may be only a few sentences long.
Failure to match the objectives of your research Often research objectives in the social and behavioral sciences change while the research is being carried out. This is not a problem unless you forget to go back and refine the original objectives in your introduction. As these changes emerge they must be documented so that they accurately reflect what you were trying to accomplish in your research [not what you thought you might accomplish when you began].
Resist the urge to apologize If you've immersed yourself in studying the research problem, you presumably should know a good deal about it [perhaps even more than your professor!]. Nevertheless, by the time you have finished writing, you may be having some doubts about what you have produced. Repress those doubts! Don't undermine your authority as a researcher by saying something like, "This is just one approach to examining this problem; there may be other, much better approaches that...." The overall tone of your conclusion should convey confidence to the reader about the study's validity and realiability.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Concluding Paragraphs. College Writing Center at Meramec. St. Louis Community College; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina; Conclusions. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Freedman, Leora and Jerry Plotnick. Introductions and Conclusions. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Leibensperger, Summer. Draft Your Conclusion. Academic Center, the University of Houston-Victoria, 2003; Make Your Last Words Count. The Writer’s Handbook. Writing Center. University of Wisconsin Madison; Miquel, Fuster-Marquez and Carmen Gregori-Signes. “Chapter Six: ‘Last but Not Least:’ Writing the Conclusion of Your Paper.” In Writing an Applied Linguistics Thesis or Dissertation: A Guide to Presenting Empirical Research . John Bitchener, editor. (Basingstoke,UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2010), pp. 93-105; Tips for Writing a Good Conclusion. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Conclusion. San Francisco Edit, 2003-2008; Writing Conclusions. Writing Tutorial Services, Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. Indiana University; Writing: Considering Structure and Organization. Institute for Writing Rhetoric. Dartmouth College.
Writing Tip
Don't Belabor the Obvious!
Avoid phrases like "in conclusion...," "in summary...," or "in closing...." These phrases can be useful, even welcome, in oral presentations. But readers can see by the tell-tale section heading and number of pages remaining that they are reaching the end of your paper. You'll irritate your readers if you belabor the obvious.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8.
Another Writing Tip
New Insight, Not New Information!
Don't surprise the reader with new information in your conclusion that was never referenced anywhere else in the paper. This why the conclusion rarely has citations to sources. If you have new information to present, add it to the discussion or other appropriate section of the paper. Note that, although no new information is introduced, the conclusion, along with the discussion section, is where you offer your most "original" contributions in the paper; the conclusion is where you describe the value of your research, demonstrate that you understand the material that you’ve presented, and position your findings within the larger context of scholarship on the topic, including describing how your research contributes new insights to that scholarship.
Assan, Joseph. "Writing the Conclusion Chapter: The Good, the Bad and the Missing." Liverpool: Development Studies Association (2009): 1-8; Conclusions. The Writing Center. University of North Carolina.
- << Previous: Limitations of the Study
- Next: Appendices >>
- Last Updated: Apr 29, 2024 1:49 PM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
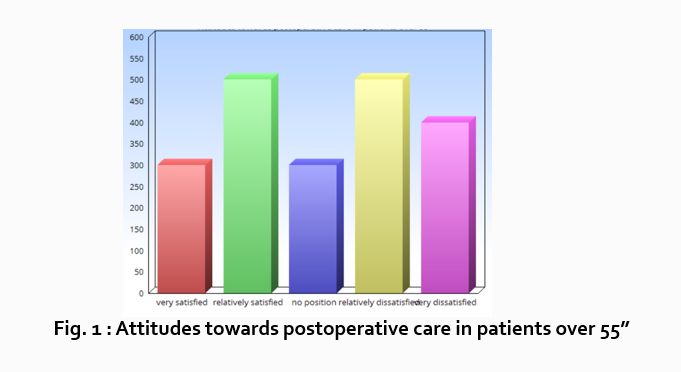
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
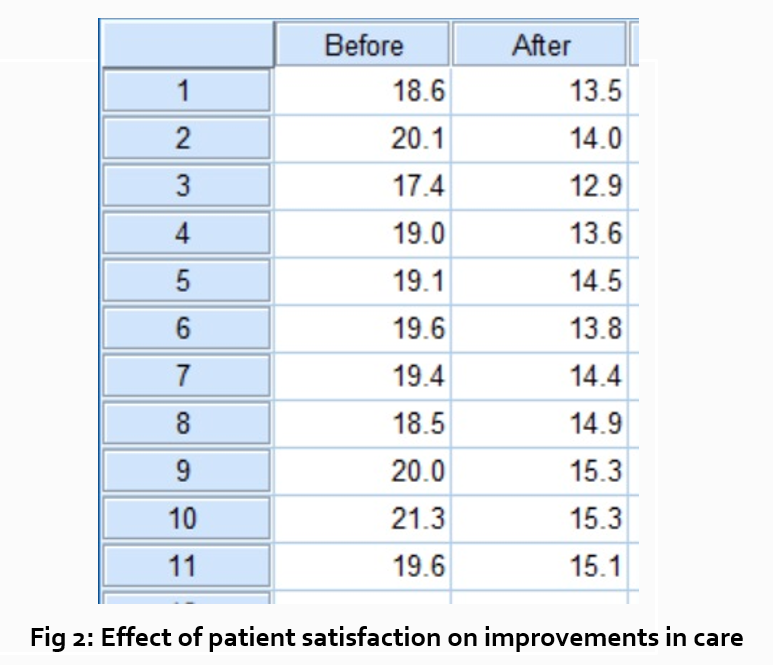
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
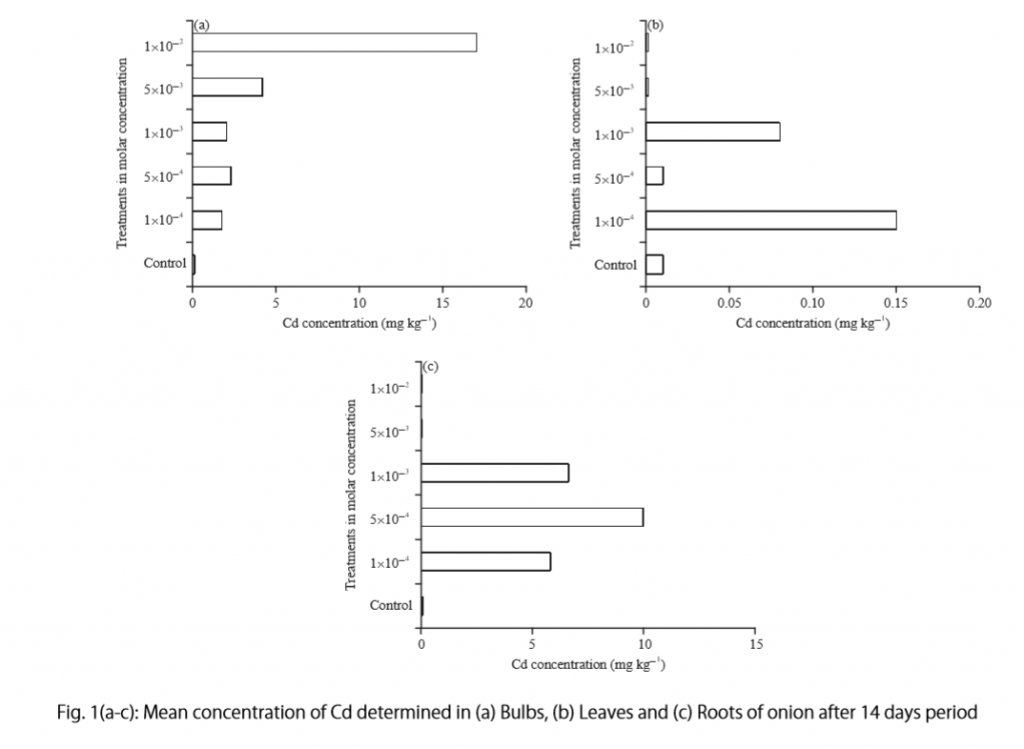
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers


Finding Relevant Scholarly Research for Literature Review: How can we be systematic?
On an average, it takes 15 clicks for a researcher to find an article (which may or may not be related to their research topic) online. This time is not productive because it does not help them gain any knowledge and it could potentially be spent doing something more vital in fostering research and development. Moreover, as most researchers rely on two to three databases to find information for their literature review , the time to find relevant scholarly research data also increases.
Table of Contents
Navigating Through Multiple Scholarly Databases—Is it even necessary?
The Internet has revolutionized the way we access information. Websites and online resources within and outside of academic bibliography are significant resources of literature. However, the challenge in searching and managing the results is undeniable.
Considering the exponential growth in scholarly research data and literature, finding relevant information and reporting your research sooner is imperative. While Open Science has been a positive reform of information access, not all data is available at a click, let alone the relevant one. Researchers fear the possibility of missing out on critical information related to their research topic or accidentally committing plagiarism. Hence, they spend time in toggling through multiple scholarly databases.
In this process of searching for literature on multiple databases, researchers tend to download irrelevant information too. Furthermore, the probability of finding similar resources on multiple databases is higher if the resource is on an Open Access platform. These downloaded papers not only occupy the space in reference managers but also make researchers spend a lot of time deciding whether the paper is worth reading or not.
5 Major Challenges Faced on Multiple Scholarly Databases—How to overcome them?
Finding scholarly research data involves navigating through institutional login pages, subscriptions, and paywalls. Apart from the time, effort, and money spent there are several other challenges that researchers encounter while searching literature on multiple scholarly databases.
Here we discuss 5 major challenges faced by researchers while using multiple scholarly databases:
1. Identifying and Deciding the Resources to Search
The Internet provides information in numerous formats, viz. journal articles, preprints, video recordings, podcasts, infographics, conference proceedings, etc. This wide pool of knowledge gets deeper with advances in scholarly research and literature. Hence, while finding research data on multiple scholarly databases in multiple formats, it becomes difficult to identify and decide the resources to download based on their relevance to the research topic. However, these resources can be easily traced if they all are on a single platform.
2. Search or Navigate Resources Correctly
Researchers use keywords and questions to find scholarly data related to their topic of interest. Databases search for the exact words and phrases. Hence, if researchers use a different word or a synonym that describes the concept, the search results are not relevant. If a single database with optimized keywords is used to access billions of scholarly resources, it not only avoids information overload but also allows navigation of relevant information.
3. Assessing Obtained Search Results
Information overload makes it difficult for researchers to assess every discovered resource. One cannot decide the relevancy of search results based on the research paper ’s title. And reading all sections of all papers—abstract, introduction, results, and/or conclusion—will be extremely time consuming. Furthermore, spending time reading these sections of papers to later find out that it’s not related to your research topic will not help anyone. So, what if there was a tool that could search results beyond keywords using research ideas, questions, etc., and also could summarize the key aspects of each downloaded resource? Definitely something to ponder about.
4. Deciding Which Literature to Select and Cite
Scientists are often overwhelmed with the scholarly research data they find online. It is a never-ending task to decide which literature to select and cite. Thus, it is essential to download only relevant data and assess them based on their relevance to the research topic. Furthermore, citing the literature accurately by following journal-specific guidelines and writing style guides will avoid accidental plagiarism. Such cumbersome tasks can be handled with accuracy using an AI-based tool particularly designed to make academic research and publishing easier.
5. Retrieving Relevant Literature in an Accessible and Editable Format
The inability of some software to save, process, and/or retrieve data in all formats is displeasing in this age of digitization. Hence, scientists prefer software that allows accessing, downloading, managing, and editing research data files in all formats.
How to Find Scholarly Research Data with a Systematic Approach? – 7 simple steps
Given the amount of intelligence on the internet, it is only wise to resort to a reliable system. One which is smart, efficient, precise, accessible, and affordable to integrate the scattered information, help researchers through every step of research reporting and publishing, and save time, effort, and money.
A simple 7-step systematic approach to find relevant scholarly research data
- Search literature based on research ideas, keywords, conference talks, author details, etc.
- Assess the found resources based on their key aspects and findings.
- Search, save, manage, read, and annotate relevant literature on a single platform.
- Use easily accessible and editable formats.
- Cite the literature to avoid plagiarism.
- Follow journal guidelines and format the research paper.
- Connect with co-authors and share your work with them for insights and edits.
An extensive and accurate literature search is the key to performing, reporting, and publishing authentic research. A systematic single-platform search database provides a much better comprehension of insights of the research topic. It helps draw comparisons faster as all results are saved and managed in one place! Moreover, it helps researchers to stimulate the interpretation of ideas, analyze shortcomings, and recognize opportunities of future research.
With advances in technology, this process can be simplified without compromising the quality of the final product. As Artificial Intelligence takes over other realms of society, it’s about time researchers leverage these advances to further streamline research publishing.
What are your ways of literature search? How many databases do you have to use simultaneously? Wouldn’t you want to have all your work on one platform without remembering several login IDs and passwords? This sounds like the future of publishing! What do you think?
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Promoting Research
- Thought Leadership
How Enago Academy Contributes to Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) Through Empowering Researchers
The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a universal call to action to end…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…
- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Using AI for Plagiarism Prevention and AI-Content Detection in Academic Writing
Watch Now In today’s digital age, where information is readily accessible and content creation…
Authenticating AI-Generated Scholarly Outputs: Practical approaches to take
The rapid advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have given rise to a new era of…

- Industry News
ICMJE Updates Guidelines for Medical Journal Publication, Emphasizes on Inclusivity and AI Transparency
The International Committee of Medical Journal Editors (ICMJE) recently updated its recommendations for best practices…
AI for Accuracy in Research and Academic Writing
Upholding Academic Integrity in the Age of AI: Challenges and solutions
AI Assistance in Academia for Searching Credible Scholarly Sources
Call for Responsible Use of Generative AI in Academia: The battle between rising…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
Doctoral students present research findings
Narshini Gunputh and Riley Supple , mathematical modeling Ph.D. students, presented research on mathematical modeling, computation, and data analysis in biological and biomedical applications at the American Mathematical Society 2024 Spring Eastern Sectional Meeting at Howard University. Gunputh presented “Mathematical Modeling of In-Vitro Drug Release from Contact Lenses” and Supple presented “Mathematical Modeling of Ocular Tissue Deformation due to Intraocular Pressure.” Both graduate students are advised by Lucia Carichino , assistant professor, and Kara Maki , associate professor, in the School of Mathematics and Statistics.
Recommended News
April 29, 2024

Students discover research opportunities on the path to graduation
Independent research projects can help cultivate critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. Whether it’s late nights spent in a RIT lab or a field study in the mountains, research experiences can be a cutting-edge way for students to prepare for the future.

RIT and UR partner on fast-track grad degrees in education and counseling
The Rochester Business Journal speaks with John Smithgall, assistant dean in the College of Liberal Arts, about the positive impacts this partnership will bring to students.

RIT and UB School of Law announce 3+3 partnership
The Rochester Business Journal talks to Kelly Norris Martin, interim dean in the College of Liberal Arts, about the unique program. (This content may require a subscription to view.)

Rain Bosworth studies how deaf children experience the world
ScienceNews talks to Rain Bosworth, associate professor in the Department of Liberal Studies, about her research.
- Open access
- Published: 27 April 2024
Assessing fragility of statistically significant findings from randomized controlled trials assessing pharmacological therapies for opioid use disorders: a systematic review
- Leen Naji ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-0994-1109 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Brittany Dennis 4 , 5 ,
- Myanca Rodrigues 2 ,
- Monica Bawor 6 ,
- Alannah Hillmer 7 ,
- Caroul Chawar 8 ,
- Eve Deck 9 ,
- Andrew Worster 2 , 4 ,
- James Paul 10 ,
- Lehana Thabane 11 , 2 &
- Zainab Samaan 12 , 2
Trials volume 25 , Article number: 286 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
22 Accesses
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
The fragility index is a statistical measure of the robustness or “stability” of a statistically significant result. It has been adapted to assess the robustness of statistically significant outcomes from randomized controlled trials. By hypothetically switching some non-responders to responders, for instance, this metric measures how many individuals would need to have responded for a statistically significant finding to become non-statistically significant. The purpose of this study is to assess the fragility index of randomized controlled trials evaluating opioid substitution and antagonist therapies for opioid use disorder. This will provide an indication as to the robustness of trials in the field and the confidence that should be placed in the trials’ outcomes, potentially identifying ways to improve clinical research in the field. This is especially important as opioid use disorder has become a global epidemic, and the incidence of opioid related fatalities have climbed 500% in the past two decades.
Six databases were searched from inception to September 25, 2021, for randomized controlled trials evaluating opioid substitution and antagonist therapies for opioid use disorder, and meeting the necessary requirements for fragility index calculation. Specifically, we included all parallel arm or two-by-two factorial design RCTs that assessed the effectiveness of any opioid substitution and antagonist therapies using a binary primary outcome and reported a statistically significant result. The fragility index of each study was calculated using methods described by Walsh and colleagues. The risk of bias of included studies was assessed using the Revised Cochrane Risk of Bias tool for randomized trials.
Ten studies with a median sample size of 82.5 (interquartile range (IQR) 58, 179, range 52–226) were eligible for inclusion. Overall risk of bias was deemed to be low in seven studies, have some concerns in two studies, and be high in one study. The median fragility index was 7.5 (IQR 4, 12, range 1–26).
Conclusions
Our results suggest that approximately eight participants are needed to overturn the conclusions of the majority of trials in opioid use disorder. Future work should focus on maximizing transparency in reporting of study results, by reporting confidence intervals, fragility indexes, and emphasizing the clinical relevance of findings.
Trial registration
PROSPERO CRD42013006507. Registered on November 25, 2013.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Opioid use disorder (OUD) has become a global epidemic, and the incidence of opioid related fatality is unparalleled to the rates observed in North America, having climbed 500% in the past two decades [ 1 , 2 ]. There is a dire need to identify the most effective treatment modality to maintain patient engagement in treatment, mitigate high risk consumption patterns, as well as eliminate overdose risk. Numerous studies have aimed to identify the most effective treatment modality for OUD [ 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Unfortunately, this multifaceted disease is complicated by the interplay between both neurobiological and social factors, impacting our current body of evidence and clinical decision making. Optimal treatment selection is further challenged by the rising number of pharmacological opioid substitution and antagonist therapies (OSAT) [ 6 ]. Despite this growing body of evidence and available therapies, we have yet to arrive to a consensus regarding the best treatment modality given the substantial variability in research findings and directly conflicting results [ 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 ]. More concerning, international clinical practice guidelines rely on out-of-date systematic review evidence to inform guideline development [ 10 ]. In fact, these guidelines make strong recommendations based on a fraction of the available evidence, employing trials with restrictive eligibility criteria which fail to reflect the common OUD patients seen in clinical practice [ 10 ].
A major factor hindering our ability to advance the field of addiction medicine is our failure to apply the necessary critical lens to the growing body of evidence used to inform clinical practice. While distinct concerns exist regarding the external validity of randomized trials in addiction medicine, the robustness of the universally recognized “well designed” trials remains unknown [ 10 ]. The reliability of the results of clinical trials rests on not only the sample size of the study but also the number of outcome events. In fact, a shift in the results of only a few events could in theory render the findings of the trial null, impacting the traditional hypothesis tests above the standard threshold accepted as “statistical significance.” A metric of this fragility was first introduced in 1990, known formally as the fragility index (FI) [ 11 ]. In 2014, it was adapted for use as a tool to assess the robustness of findings from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) [ 12 ]. Briefly, the FI determines the minimum number of participants whose outcome would have to change from non-event to event in order for a statistically significant result to become non-significant. Larger FIs indicate more robust findings [ 11 , 13 ]. Additionally, when the number of study participants lost to follow-up exceeds the FI of the trial, this implies that the outcome of these participants could have significantly altered the statistical significance and final conclusions of the study. The FI has been applied across multiple fields, often yielding similar results such that the change in a small number of outcome events has been powerful enough to overturn the statistical conclusions of many “well-designed” trials [ 13 ].
The concerning state of the OUD literature has left us with guidelines which neither acknowledge the lack of external validity and actually go so far as to rank the quality of the evidence as good, despite the concerning limitations we have raised [ 10 ]. Such alarming practices necessitate vigilance on behalf of methodologists and practitioners to be critical and open to a thorough review of the evidence in the field of addiction medicine [ 12 ]. Given the complex nature of OUD treatment and the increasing number of available therapies, concentrated efforts are needed to ensure the reliability and internal validity of the results of clinical trials used to inform guidelines. Application of the FI can serve to provide additional insight into the robustness of the evidence in addiction medicine. The purpose of this study is to assess the fragility of findings of RCTs assessing OSAT for OUD.
Systematic review protocol
We conducted a systematic review of the evidence surrounding OSATs for OUD [ 5 ]. The study protocol was registered with PROSPERO a priori (PROSPERO CRD42013006507). We searched Medline, EMBASE, PubMed, PsycINFO, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for relevant studies from inception to September 25, 2021. We included all RCTs evaluating the effectiveness of any OSAT for OUD, which met the criteria required for FI calculation. Specifically, we included all parallel arm or two-by-two factorial design RCTs that allocated patients at a 1:1 ratio, assessed the effectiveness of any OSAT using a binary primary or co-primary outcome, and reported this outcome to be statistically significant ( p < 0.05).
All titles, abstracts, and full texts were screened for eligibility by two reviewers independently and in duplicate. Any discrepancies between the two reviewers were discussed for consensus, and a third reviewer was called upon when needed.
Data extraction and risk of bias assessment (ROB)
Two reviewers extracted the following data from the included studies in duplicate and independently using a pilot-tested excel data extraction sheet: sample size, whether a sample size calculation was conducted, statistical test used, primary outcome, number of responders and non-responders in each arm, number lost to follow-up, and the p -value. The 2021 Thomson Reuters Journal Impact Factor for each included study was also recorded. The ROB of included studies for the dichotomous outcome used in the FI calculation was assessed using the Revised Cochrane ROB tool for randomized trials [ 14 ]. Two reviewers independently assessed the included studies based on the following domains for potential ROB: randomization process, deviations from the intended interventions, missing outcome data, measurement of the outcome, and selection of the reported results.
Statistical analyses
Study characteristics were summarized using descriptive statistics. Means and standard deviations (SD), as well as medians and interquartile ranges (IQR: Q 25 , Q 75 ) were used as measures of central tendency for continuous outcomes with normal and skewed distributions, respectively. Frequencies and percentages were used to summarize categorical variables. The FI was calculated using a publicly available free online calculator, using the methods described by Walsh et al. [ 12 , 15 ] In summary, the number of events and non-events in each treatment arm were entered into a two-by-two contingency table for each trial. An event was added to the treatment arm with the smaller number of events, while subtracting a non-event from the same arm, thus keeping the overall sample size the same. Each time this was done, the two-sided p -value for Fisher’s exact test was recalculated. The FI was defined as the number of non-events that needed to be switched to events for the p -value to reach non-statistical significance (i.e., ≥0.05).
We intended to conduct a linear regression and Spearman’s rank correlations to assess the association between FI and journal impact factor, study sample size, and number events. However, we were not powered to do so given the limited number of eligible studies included in this review and thus refrained from conducting any inferential statistics.
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines for reporting (see Supplementary Material ) [ 16 ].
Study selection
Our search yielded 13,463 unique studies, of which 104 were RCTs evaluating OSAT for OUD. Among these, ten studies met the criteria required for FI calculation and were included in our analyses. Please refer to Fig. 1 for the search results, study inclusion flow diagram, and Table 1 for details on included studies.
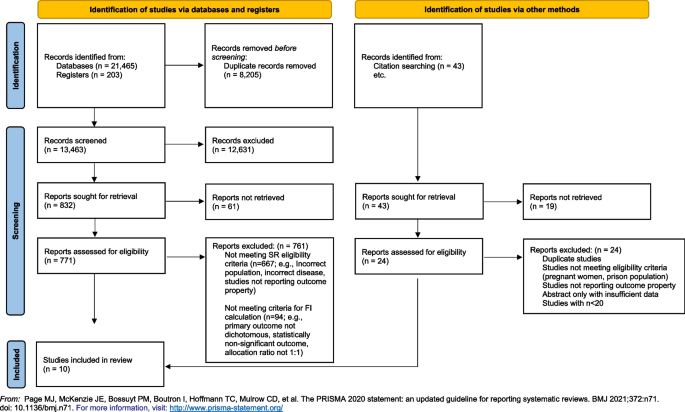
PRISMA flow diagram delineating study selection
Characteristics of included studies
The included studies were published between 1980 and 2018, in eight different journals with a median impact factor of 8.48 (IQR 6.53–56.27, range 3.77–91.25). Four studies reported on a calculated sample size [ 17 , 18 , 19 , 20 ], and only one study specified that reporting guidelines were used [ 21 ]. Treatment retention was the most commonly reported primary outcome ( k = 8). The median sample size of included studies was 82.5 (IQR 58–179, range 52–226).
Overall ROB was deemed to be low in seven studies [ 17 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 ], have some concerns in two studies [ 18 , 25 ], and be high in one study [ 26 ] due to a high proportion of missing outcome data that was not accounted for in the analyses. We present a breakdown of the ROB assessment of the included studies for the dichotomous outcome of interest in Table 2 .
- Fragility index
The median FI of included studies was 7.5 (IQR 4–12; range 1–26). The FI of individual studies is reported in Table 1 . The number of participants lost to follow-up exceeded the FI in two studies [ 23 , 26 ]. We find that there is a relatively positive correlation between the FI and sample size. However, no clear correlation was appreciated between FI and journal impact factor or number of events.
This is the first study to evaluate the FI in the field of addiction medicine, and more specifically in OUD trials. Among the ten RCTs evaluating the OSAT for OUD, we found that, in some cases, changing the outcome of one or two participants could completely alter the study’s conclusions and render the results statistically non-significant.
We compare our findings to those of Holek et al. , wherein they examined the mean FI across all reviews published in PubMed between 2014 and 2019 that assessed the distribution of FI indices, irrespective of discipline (though none were in addiction medicine) [ 13 ]. Among 24 included reviews with a median sample size of 134 (IQR 82, 207), they found a mean FI of 4 (95% CI 3, 5) [ 13 ]. This is slightly lower than our calculated our median FI of 7.5 (IQR 4–12; range 1–26). It is important to note that half of the reviews included in the study by Holek et al. were conducted in surgical disciplines, which are generally subjected to more limitations to internal and external validity, as it is often not possible to conceal allocation, blind participants, or operators, and the intervention is operator dependent. [ 27 ] To date, no study has directly applied FI to the findings of trials in OUD. In the HIV/AIDS literature, however, a population which is commonly shared with addiction medicine due to the prevalence of the comorbidities coexisting, the median fragility across all trials assessing anti-retroviral therapies ( n = 39) was 6 (IQR = 1, 11) [ 28 ], which is more closely related to our calculated FI. Among the included studies, only 3 were deemed to be at high risk of bias, whereas 13 and 20 studies were deemed to be at low and some risk of bias, respectively.
Loss-to-follow-up plays an important role in the interpretation of the FI. For instance, when the number of study participants lost to follow-up exceeds the FI of the trial, this implies that the outcome of these participants could have significantly altered the statistical significance and final conclusions of the study. While only two of the included studies had an FI that was greater than the total number of participants lost to follow-up [ 23 , 26 ], this metric is less important in our case given the primary outcome assessed by the majority of trials was retention in treatment, rendering loss to follow-up an outcome itself. In our report, we considered participants to be lost to follow-up if they left the study for reasons that were known and not necessarily indicative of treatment failure, such as due to factors beyond the participants, control including incarceration or being transferred to another treatment location.
Findings from our analysis of the literature as well as the application of FI to the existing clinical trials in the field of addiction medicine demonstrates significant concerns regarding the robustness of the evidence. This, in conjunction with the large differences between the clinical population and trial participants of opioid-dependent patients inherent in addiction medicine trials, raises larger concerns as to a growing body of evidence with deficiencies in both internal and external validity. The findings from this study raise important clinical concerns regarding the applicability of the current evidence to treating patients in the context of the opioid epidemic. Are we recommending the appropriate treatments for patients with OUD based on robust and applicable evidence? Are we completing our due diligence and ensuring clinicians and researchers alike understand the critical issues rampant in the literature, including the fragility of the data and misconceptions of p -values? Are we possibly putting our patients at risk employing such treatment based on fragile data? These questions cannot be answered until the appropriate re-evaluation of the evidence takes place employing both the use pragmatic trial designs as well as transparent metrics to reflect the reliability and robustness of the findings.
Strengths and limitations
Our study is strengthened by a comprehensive search strategy, rigorous and systematic screening of studies, and the use of an objective measure to gauge the robustness of studies (i.e., FI). The limitations of this study are inherent in the limitations of the FI. Precisely, that it can only be calculated for RCTs with a 1:1 allocation ratio, a parallel arm or two-by-two factorial design, and a dichotomous primary outcome. As a result, 94 RCTs evaluating OSAT for OUD were excluded for not meeting these criteria (Fig. 1 ). Nonetheless, the FI provides a general sense of the robustness of the available studies, and our data reflect studies published across almost four decades in journals of varying impact factor.
Future direction
This study serves as further evidence for the need of a shift away from p -values [ 29 , 30 ]. Although there is increasingly a shift among statisticians to shift away from relying on statistical significance due to its inability to convey clinical importance [ 31 ], this remains the simplest way and most commonly reported metric in manuscripts. p -values provide a simple statistical measure to confirm or refute a null hypothesis, by providing a measure of how likely the observed result would be if the null hypothesis were true. An arbitrary cutoff of 5% is traditionally used as a threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis. However, a major drawback of the p -value is that it does not take into account the effect size of the outcome measure, such that a small incremental change that may not be clinically significant may still be statistically significant in a large enough trial. Contrastingly, a very large effect size that has biological plausibility, for instance, may not reach statistical significance if the trial size is not large enough [ 29 , 30 ]. This is highly problematic given the common misconceptions surrounding the p -value. Increasing emphasis is being placed on the importance of transparency in outcome reporting, and the reporting of confidence intervals to allow the reader to gauge the uncertainty in the evidence, and make a clinically informed decision about whether a finding is clinically significant or not. It has also been recommended that studies report FI where possible to provide readers with a comprehensible way of gauging the robustness of their findings [ 12 , 13 ]. There is a strive to make all data publicly available, allowing for replication of study findings as well as pooling of data among databases for generating more robust analyses using larger pragmatic samples [ 32 ]. Together, these efforts aim to increase transparency of research and facilitate data sharing to allow for stronger and more robust evidence to be produced, allowing for advancements in evidence-based medicine and improvements in the quality of care delivered to patients.
Our results suggest that approximately eight participants are needed to overturn the conclusions of the majority of trials in addiction medicine. Findings from our analysis of the literature and application of FI to the existing clinical trials in the field of addiction medicine demonstrates significant concerns regarding the overall quality and specifically robustness and stability of the evidence and the conclusions of the trials. Findings from this work raises larger concerns as to a growing body of evidence with deficiencies in both internal and external validity. In order to advance the field of addiction medicine, we must re-evaluate the quality of the evidence and consider employing pragmatic trial designs as well as transparent metrics to reflect the reliability and robustness of the findings. Placing emphasis on clinical relevance and reporting the FI along with confidence intervals may provide researchers, clinicians, and guideline developers with a transparent method to assess the outcomes from clinical trials, ensuring vigilance in decisions regarding management and treatment of patients with substance use disorders.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article (and its supplementary information files).
Abbreviations
Interquartile range
- Opioid use disorder
Opioid substitution and antagonist therapies
- Randomized controlled trials
Risk of bias
Standard deviation
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Products - Vital Statistics Rapid Release - Provisional Drug Overdose Data. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nvss/vsrr/drug-overdose-data.htm . Accessed April 26, 2020.
Spencer MR, Miniño AM, Warner M. Drug overdose deaths in the United States, 2001–2021. NCHS Data Brief, no 457. Hyattsville, MD: National Center for Health Statistics. 2022. https://doi.org/10.15620/cdc:122556 .
Mattick RP, Breen C, Kimber J, Davoli M. Methadone maintenance therapy versus no opioid replacement therapy for opioid dependence. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3). https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD002209.PUB2/FULL .
Hedrich D, Alves P, Farrell M, Stöver H, Møller L, Mayet S. The effectiveness of opioid maintenance treatment in prison settings: a systematic review. Addiction. 2012;107(3):501–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1360-0443.2011.03676.X .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Dennis BB, Naji L, Bawor M, et al. The effectiveness of opioid substitution treatments for patients with opioid dependence: a systematic review and multiple treatment comparison protocol. Syst Rev. 2014;3(1):105. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-3-105 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Dennis BB, Sanger N, Bawor M, et al. A call for consensus in defining efficacy in clinical trials for opioid addiction: combined results from a systematic review and qualitative study in patients receiving pharmacological assisted therapy for opioid use disorder. Trials. 2020;21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-019-3995-y .
British Columbia Centre on Substance Use. (2017). A Guideline for the Clinical Management of Opioid Use Disorder . http://www.bccsu.ca/care-guidance-publications/ . Accessed December 4, 2020.
Kampman K, Jarvis M. American Society of Addiction Medicine (ASAM) national practice guideline for the use of medications in the treatment of addiction involving opioid use. J Addict Med. 2015;9(5):358–367.
Srivastava A, Wyman J, Fcfp MD, Mph D. Methadone treatment for people who use fentanyl: recommendations. 2021. www.metaphi.ca . Accessed November 14, 2023.
Dennis BB, Roshanov PS, Naji L, et al. Opioid substitution and antagonist therapy trials exclude the common addiction patient: a systematic review and analysis of eligibility criteria. Trials. 2015;16(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-015-0942-4 .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Feinstein AR. The unit fragility index: an additional appraisal of “statistical significance” for a contrast of two proportions. J Clin Epidemiol. 1990;43(2):201–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-4356(90)90186-S .
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Walsh M, Srinathan SK, McAuley DF, et al. The statistical significance of randomized controlled trial results is frequently fragile: a case for a fragility index. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67(6):622–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.10.019 .
Holek M, Bdair F, Khan M, et al. Fragility of clinical trials across research fields: a synthesis of methodological reviews. Contemp Clin Trials. 2020;97. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cct.2020.106151
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2019;366. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.l4898
Kane SP. Fragility Index Calculator. ClinCalc: https://clincalc.com/Stats/FragilityIndex.aspx . Updated July 19, 2018. Accessed October 17, 2023.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, The PRISMA, et al. statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2020;2021:372. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71 .
Article Google Scholar
Petitjean S, Stohler R, Déglon JJ, et al. Double-blind randomized trial of buprenorphine and methadone in opiate dependence. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2001;62(1):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-8716(00)00163-0 .
Sees KL, Delucchi KL, Masson C, et al. Methadone maintenance vs 180-day psychosocially enriched detoxification for treatment of opioid dependence: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2000;283(10):1303–10. https://doi.org/10.1001/JAMA.283.10.1303 .
Kakko J, Dybrandt Svanborg K, Kreek MJ, Heilig M. 1-year retention and social function after buprenorphine-assisted relapse prevention treatment for heroin dependence in Sweden: a randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet (London, England). 2003;361(9358):662–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)12600-1 .
Oviedo-Joekes E, Brissette S, Marsh DC, et al. Diacetylmorphine versus methadone for the treatment of opioid addiction. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(8):777–86. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0810635 .
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hulse GK, Morris N, Arnold-Reed D, Tait RJ. Improving clinical outcomes in treating heroin dependence: randomized, controlled trial of oral or implant naltrexone. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(10):1108–15. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHGENPSYCHIATRY.2009.130 .
Krupitsky EM, Zvartau EE, Masalov DV, et al. Naltrexone for heroin dependence treatment in St. Petersburg, Russia. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2004;26(4):285–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsat.2004.02.002 .
Krook AL, Brørs O, Dahlberg J, et al. A placebo-controlled study of high dose buprenorphine in opiate dependents waiting for medication-assisted rehabilitation in Oslo. Norway Addiction. 2002;97(5):533–42. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1360-0443.2002.00090.X .
Hartnoll RL, Mitcheson MC, Battersby A, et al. Evaluation of heroin maintenance in controlled trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1980;37(8):877–84. https://doi.org/10.1001/ARCHPSYC.1980.01780210035003 .
Fischer G, Gombas W, Eder H, et al. Buprenorphine versus methadone maintenance for the treatment of opioid dependence. Addiction. 1999;94(9):1337–47. https://doi.org/10.1046/J.1360-0443.1999.94913376.X .
Yancovitz SR, Des Jarlais DC, Peyser NP, et al. A randomized trial of an interim methadone maintenance clinic. Am J Public Health. 1991;81(9):1185–91. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.81.9.1185 .
Demange MK, Fregni F. Limits to clinical trials in surgical areas. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2011;66(1):159–61. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1807-59322011000100027 .
Wayant C, Meyer C, Gupton R, Som M, Baker D, Vassar M. The fragility index in a cohort of HIV/AIDS randomized controlled trials. J Gen Intern Med. 2019;34(7):1236–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11606-019-04928-5 .
Amrhein V, Greenland S, McShane B. Scientists rise up against statistical significance. Nature. 2019;567(7748):305–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/D41586-019-00857-9 .
Ioannidis JPA. Why most published research findings are false. PLoS Med. 2005;2(8):e124. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020124 .
Goodman SN. Toward evidence-based medical statistics. 1: the p value fallacy. Ann Intern Med. 1999;130(12):995–1004. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-130-12-199906150-00008 .
Allison DB, Shiffrin RM, Stodden V. Reproducibility of research: issues and proposed remedies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(11):2561–2. https://doi.org/10.1073/PNAS.1802324115 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors received no funding for this work.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Family Medicine, David Braley Health Sciences Centre, McMaster University, 100 Main St W, 3rdFloor, Hamilton, ON, L8P 1H6, Canada
Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence, and Impact, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Leen Naji, Myanca Rodrigues, Andrew Worster, Lehana Thabane & Zainab Samaan
Department of Medicine, Montefiore Medical Center, New York, NY, USA
Department of Medicine, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Brittany Dennis & Andrew Worster
Department of Medicine, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada
Brittany Dennis
Department of Medicine, Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust, London, UK
Monica Bawor
Department of Psychiatry and Behavaioral Neurosciences, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Alannah Hillmer
Physician Assistant Program, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada
Caroul Chawar
Department of Family Medicine, Western University, London, ON, Canada
Department of Anesthesia, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Biostatistics Unit, Research Institute at St Joseph’s Healthcare, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Lehana Thabane
Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
Zainab Samaan
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
LN, BD, MB, LT, and ZS conceived the research question and protocol. LN, BD, MR, and AH designed the search strategy and ran the literature search. LN, BD, MR, AH, CC, and ED contributed to screening studies for eligibility and data extraction. LN and LT analyzed data. All authors contributed equally to the writing and revision of the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Leen Naji .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Supplementary material 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Naji, L., Dennis, B., Rodrigues, M. et al. Assessing fragility of statistically significant findings from randomized controlled trials assessing pharmacological therapies for opioid use disorders: a systematic review. Trials 25 , 286 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08104-x
Download citation
Received : 11 December 2022
Accepted : 10 April 2024
Published : 27 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13063-024-08104-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Research methods
- Critical appraisal
- Systematic review
ISSN: 1745-6215
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
How can forests be reforested in a climate-friendly way?
Only a few tree species are flexible enough to survive a century of rapid climate change.
Europe's forests have already been severely affected by climate change. Thousands of hectares of trees have already died due to drought and bark beetles. Scientists from the University of Vienna and the Technical University of Munich TUM have now investigated which trees can be used for reforestation. Their findings: only a few tree species are fit for the future, such as English oak in the UK. However, mixed forests are important for the survival of forests, otherwise the forest ecosystem as a whole could be weakened. The results of the study were recently published in the renowned journal Nature Ecology and Evolution .
Although European forests are naturally home to a mix of trees, the number of tree species is lower than in climatically comparable areas of North America or East Asia. In the future, even fewer species will be available to the forestry industry, as scientists led by Johannes Wessely and Stefan Dullinger from the University of Vienna have shown in their new study. Depending on the region, between a third and a half of the tree species found there today will no longer be able to cope with future conditions. "This is an enormous decline," says lead author Johannes Wessely, "especially when you consider that only some of the species are of interest for forestry."
The scientists examined the 69 more common of the just over 100 European tree species with regard to the 21st century in Europe. On average, only nine of these 69 species per location are fit for the future in Europe, compared to four in the UK. "Trees that are planted now for reforestation must survive under both current and future conditions. This is difficult because they have to withstand the cold and frost of the next few years as well as a much warmer climate at the end of the 21st century. There is only a very small overlap," says Wessely. In the UK, these climate-fit species include, for example, the English oak. Which tree species will suit which region of Europe in the future varies greatly overall.
Forest ecosystem at risk due to restriction of species
However, even with the selected set of future-proof trees, a major problem remains: the average of nine species is not enough for a species-rich mixed forest. "Mixed forests consisting of many tree species are an important measure to make forests more robust against disturbances such as bark beetles. In some places in Europe, however, we could run out of tree species to establish such colorful mixed forests," explains last author Rupert Seidl from the Technical University of Munich TUM.
Not all trees offer important properties
Trees store carbon, provide a habitat or food source for animals or can be processed into timber -- these are all important properties of forests. But not all trees fulfill these functions equally; only an average of three of the nine climate-fit tree species can do this.
"Our work clearly shows how severely the vitality of forests is affected by climate change. We cannot rely solely on a new mix of tree species; rapid measures to mitigate climate change are essential for the sustainable protection of our forests," says Wessely.
More information on current research at the University of Vienna can be found in the University of Vienna's science magazine Rudolphina in the section Nature, Climate and the Cosmos.
- Exotic Species
- Environmental Awareness
- Rainforests
- Environmental Policy
- Environmental Issues
- Deforestation
- Old growth forest
- Climate change mitigation
Story Source:
Materials provided by University of Vienna . Note: Content may be edited for style and length.
Journal Reference :
- Johannes Wessely, Franz Essl, Konrad Fiedler, Andreas Gattringer, Bernhard Hülber, Olesia Ignateva, Dietmar Moser, Werner Rammer, Stefan Dullinger, Rupert Seidl. A climate-induced tree species bottleneck for forest management in Europe . Nature Ecology & Evolution , 2024; DOI: 10.1038/s41559-024-02406-8
Cite This Page :
Explore More
- Long Snouts Protect Foxes Diving Into Snow
- Promising Experimental Type 1 Diabetes Drug
- Giant, Prehistoric Salmon Had Tusk-Like Teeth
- Plants On the Menu of Ancient Hunter-Gatherers
- Unexpected Differences in Binary Stars: Origin
- Flexitarian: Invasive Species With Veggies
- T. Rex Not as Smart as Previously Claimed
- Asteroid Ryugu and Interplanetary Space
- Mice Think Like Babies
- Ancient Maya Blessed Their Ballcourts
Trending Topics
Strange & offbeat.
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
In Tight Presidential Race, Voters Are Broadly Critical of Both Biden and Trump
About half of voters say that, if given the chance, they would replace both candidates on the ballot, table of contents.
- The state of the 2024 presidential race
- Other findings: Biden’s job approval ticks up, Trump’s election-related criminal charges
- Educational differences in candidate support
- What are 2020 voters’ preferences today?
- How Biden’s supporters view his personal traits
- How Trump’s supporters view his personal traits
- Views of Biden’s presidency and retrospective evaluations of Trump’s time in office
- Attention to the candidates
- Does it matter who wins?
- What if voters could change the presidential ballot?
- How important is it for the losing candidate to publicly acknowledge the winner?
- 4. Joe Biden’s approval ratings
- Acknowledgments
- The American Trends Panel survey methodology
- Validated voters

Pew Research Center conducted this study to understand voters’ views on the 2024 presidential election, as well how the public views President Joe Biden. For this analysis, we surveyed 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – from April 8 to April 14, 2024. Everyone who took part in this survey is a member of the Center’s American Trends Panel (ATP), an online survey panel that is recruited through national, random sampling of residential addresses. This way nearly all U.S. adults have a chance of selection. The survey is weighted to be representative of the U.S. adult population by gender, race, ethnicity, partisan affiliation, education and other categories. Read more about the ATP’s methodology .
Here are the questions used for this report , along with responses, and the survey methodology .
As the 2024 presidential race heats up, American voters face a similar set of choices as they did four years ago – and many are not happy about it.
With the election still more than six months away, a new Pew Research Center survey finds that the presidential race is virtually tied : 49% of registered voters favor Donald Trump or lean toward voting for him, while 48% support or lean toward Joe Biden.
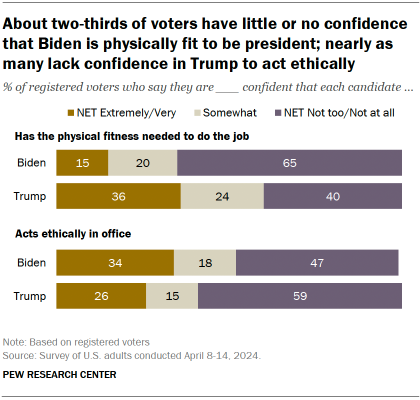
A defining characteristic of the contest is that voters overall have little confidence in either candidate across a range of key traits, including fitness for office, personal ethics and respect for democratic values.
Where Trump has the advantage: More than a third of voters say they are extremely or very confident that Trump has the physical fitness (36%) and mental fitness (38%) needed to do the job of president.
Far fewer say the same of Biden (15% are at least very confident in his physical fitness; 21% are extremely or very confident in his mental fitness). Majorities say they are not too or not at all confident in Biden’s physical and mental fitness.
Where Biden has the advantage: More voters are extremely or very confident in Biden (34%) than in Trump (26%) to act ethically in office. And while 38% say they are at least very confident in Biden to respect the country’s democratic values, fewer (34%) express that level of confidence in Trump. The survey was conducted before the start of Trump’s “hush money” trial in New York City .
( Read more about voters’ views of Biden and Trump in Chapter 2. )
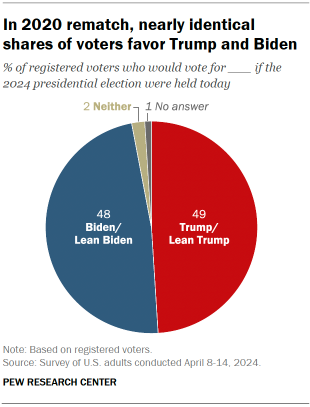
The new Center survey of 8,709 adults – including 7,166 registered voters – conducted April 8-14, 2024, finds large divides in voters’ candidate preference by age, education, and race and ethnicity. As was the case in 2020, younger voters and those with a four-year college degree are more likely to favor Biden than Trump.
Older voters and those with no college degree favor Trump by large margins.
Among racial and ethnic groups:
- White voters favor Trump (56%) over Biden (42%) by a wide margin.
- Roughly three-quarters of Black voters (77%) support Biden, while 18% back Trump.
- Hispanic voters are more evenly divided – 52% favor Biden, while 44% back Trump.
- Asian voters favor Biden (59%) over Trump (36%).
( Read more about voters’ candidate preferences in Chapter 1. )
Most voters who turned out in 2020 favor the same candidate in 2024. Among validated 2020 voters, overwhelming majorities of those who cast ballots for Biden (91%) and Trump (94%) support the same candidate this year. Registered voters who did not vote in 2020 are about evenly divided: 48% back Trump, while 46% support Biden.
A majority of voters say “it really matters who wins” the 2024 race. Today, 69% of voters say it really matters which candidate wins the presidential contest this November. This is somewhat smaller than the share who said this in April 2020 about that year’s election (74%). Nearly identical shares of Biden’s and Trump’s supporters say the outcome of the presidential race really matters.
About half of voters would replace both Biden and Trump on the 2024 ballot
Reflecting their dissatisfaction with the Biden-Trump matchup, nearly half of registered voters (49%) say that, if they had the ability to decide the major party candidates for the 2024 election, they would replace both Biden and Trump on the ballot .
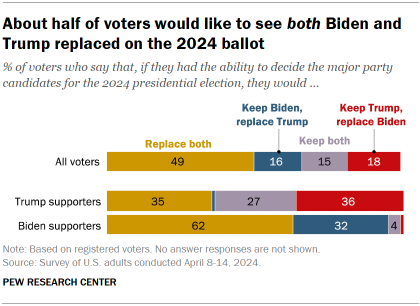
Biden’s supporters are especially likely to say they would replace both candidates if they had the chance. Roughly six-in-ten (62%) express this view, compared with 35% of Trump supporters.
There also are stark age differences in these views: 66% of voters under 30 say they would replace both candidates if they had the chance, compared with 54% of those ages 30 to 49 and fewer than half (43%) of those 50 and older.
( Read more about voters’ feelings toward the upcoming election in Chapter 3. )
Evaluations of the Biden and Trump presidencies
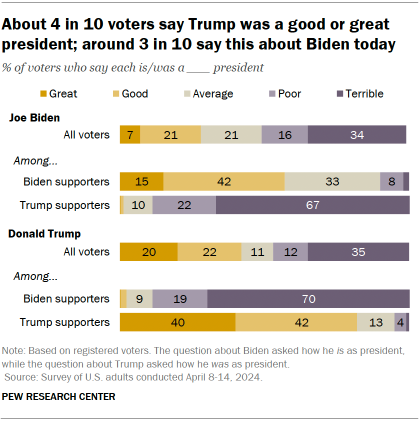
- 42% of voters overall say Trump was a good or great president, while 11% say he was average. This is a modest improvement since March 2021, two months after he left office.
- 28% of voters say Biden is a good or great president, while 21% say he is average. These views are mostly on par with June 2020 assessments of the kind of president Biden would be – but today, a smaller share of voters say he is average.
( Read more about ratings of Biden’s and Trump’s presidencies in Chapter 1. )
- Biden’s approval among the general public: Today, Biden’s approval rating sits at 35% – roughly on par with his rating in January (33%). His job rating has climbed slightly among Democrats over that period, however. Today, 65% of Democrats approve of him – up 4 percentage points since January. ( Read more about Biden’s approval rating in Chapter 4. )
- Conceding the presidential election: A majority of voters say it is important that the losing candidate in November publicly acknowledge the winner as the legitimate president. But Trump’s supporters are far less likely than Biden’s to say it is very important (44% vs. 77%). ( Read more about voters’ views on election concession in Chapter 3. )
Trump’s criminal charges related to the 2020 election
As Trump faces charges that he sought to overturn the outcome of the 2020 election, 45% of Americans say they think Trump’s actions broke the law. This compares with 38% who say his actions did not break the law – including 15% who say his actions were wrong but not illegal, and 23% who say he did nothing wrong. Nearly two-in-ten are not sure.
Democrats mostly say Trump broke the law; Republicans are more divided. An overwhelming majority of Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents (78%) say Trump’s actions in seeking to change the outcome of the 2020 election broke the law.
Among Republicans and Republican leaners:
- 49% say Trump did nothing wrong.
- 21% say he did something wrong but did not break the law.
- 9% say Trump broke the law.
- 20% are not sure.
Sign up for our weekly newsletter
Fresh data delivery Saturday mornings
Sign up for The Briefing
Weekly updates on the world of news & information
- Donald Trump
- Election 2024
- Partisanship & Issues
- Presidential Approval
- Voter Demographics
- Voter Participation
Changing Partisan Coalitions in a Politically Divided Nation
About 1 in 4 americans have unfavorable views of both biden and trump, 2024 presidential primary season was one of the shortest in the modern political era, americans more upbeat on the economy; biden’s job rating remains very low, key facts about hispanic eligible voters in 2024, most popular, report materials.
- April 2024 Biden Job Approval Detailed Tables
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.84(1); 2020 Jan
A Review of the Quality Indicators of Rigor in Qualitative Research
Jessica l. johnson.
a William Carey University School of Pharmacy, Biloxi, Mississippi
Donna Adkins
Sheila chauvin.
b Louisiana State University, School of Medicine, New Orleans, Louisiana
Attributes of rigor and quality and suggested best practices for qualitative research design as they relate to the steps of designing, conducting, and reporting qualitative research in health professions educational scholarship are presented. A research question must be clear and focused and supported by a strong conceptual framework, both of which contribute to the selection of appropriate research methods that enhance trustworthiness and minimize researcher bias inherent in qualitative methodologies. Qualitative data collection and analyses are often modified through an iterative approach to answering the research question. Researcher reflexivity, essentially a researcher’s insight into their own biases and rationale for decision-making as the study progresses, is critical to rigor. This article reviews common standards of rigor, quality scholarship criteria, and best practices for qualitative research from design through dissemination.
INTRODUCTION
Within the past 20 years, qualitative research in health professions education has increased significantly, both in practice and publication. Today, one can pick up most any issue of a wide variety of health professions education journals and find at least one article that includes some type of qualitative research, whether a full study or the inclusion of a qualitative component within a quantitative or mixed methods study. Simultaneously, there have been recurrent calls for enhancing rigor and quality in qualitative research.
As members of the academic community, we share responsibility for ensuring rigor in qualitative research, whether as researchers who design and implement, manuscript reviewers who critique, colleagues who discuss and learn from each other, or scholarly teachers who draw upon results to enhance and innovate education. Therefore, the purpose of this article is to summarize standards of rigor and suggested best practices for designing, conducting, and reporting high-quality qualitative research. To begin, Denzin and Lincoln’s definition of qualitative research, a long-standing cornerstone in the field, provides a useful foundation for summarizing quality standards and best practices:
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study; personal experience; introspection; life story; interview; artifacts; cultural texts and productions; observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe the routine and problematic moments and meanings in individual lives. Accordingly, qualitative researchers deploy a wide range of interconnected interpretative practices, hoping always to get a better understanding of the subject matter at hand. It is understood, however, that each practice makes the world visible in a different way. Hence there is frequently a commitment to using more than one interpretative practice in any study. 1
In recent years, multiple publications have synthesized quality criteria and recommendations for use by researchers and peer reviewers alike, often in the form of checklists. 2-6 Some authors have raised concerns about the use of such checklists and adherence to strict, universal criteria because they do not afford sufficient flexibility to accommodate the diverse approaches and multiple interpretive practices often represented in qualitative studies. 7-11 They argue that a strict focus on using checklists of specific technical criteria may stifle the diversity and multiplicity of practices that are so much a part of achieving quality and rigor within the qualitative paradigm. As an alternative, some of these authors have published best practice guidelines for use by researchers and peer reviewers to achieve and assess methodological rigor and research quality. 12,13
Some journals within the field of health professions education have also established best practice guidance, as opposed to strict criteria or a checklist, for qualitative research. These have been disseminated as guiding questions or evaluation categories. In 2015, Academic Medicine produced an expanded second edition of a researcher/author manual that includes specific criteria with extensive explanations and examples. 14 Still others have disseminated best practice guidelines through a series of methodological articles within journal publications. 2
In this article, attributes of rigor and quality and suggested best practices are presented as they relate to the steps of designing, conducting, and reporting qualitative research in a step-wise approach.
BEST PRACTICES: STEP-WISE APPROACH
Step 1: identifying a research topic.
Identifying and developing a research topic is comprised of two major tasks: formulating a research question, and developing a conceptual framework to support the study. Formulating a research question is often stimulated by real-life observations, experiences, or events in the researcher’s local setting that reflect a perplexing problem begging for systematic inquiry. The research question begins as a problem statement or set of propositions that describe the relationship among certain concepts, behaviors, or experiences. Agee 15 and others 16,17 note that initial questions are usually too broad in focus and too vague regarding the specific context of the study to be answerable and researchable. Creswell reminds us that initial qualitative research questions guide inquiry, but they often change as the author’s understanding of the issue develops throughout the study. 16 Developing and refining a primary research question focused on both the phenomena of interest and the context in which it is situated is essential to research rigor and quality.
Glassick, Huber, and Maeroff identified six criteria applicable to assessing the quality of scholarship. 18,19 Now commonly referred to as the Glassick Criteria ( Table 1 ), these critical attributes outline the essential elements of any scholarly approach and serve as a general research framework for developing research questions and designing studies. The first two criteria, clear purpose and adequate preparation, are directly related to formulating effective research questions and a strong conceptual framework.
Glassick’s Criteria for Assessing the Quality of Scholarship of a Research Study 18

Generating and refining a qualitative research question requires thorough, systematic, and iterative review of the literature, and the use of those results to establish a clear context and foundation for the question and study design. Using an iterative approach, relevant concepts, principles, theories or models, and prior evidence are identified to establish what is known, and more importantly, what is not known. The iterative process contributes to forming a better research question, the criteria for which can be abbreviated by the acronym FINER, ie, f easible, i nteresting, n ovel, e thical, and r elevant, that is answerable and researchable, in terms of research focus, context specificity, and the availability of time, logistics, and resources to carry out the study. Developing a FINER research question is critical to study rigor and quality and should not be rushed, as all other aspects of research design depend on the focus and clarity of the research question(s) guiding the study. 15 Agee provides clear and worthwhile additional guidance for developing qualitative research questions. 15
Reflexivity, the idea that a researcher’s preconceptions and biases can influence decisions and actions throughout qualitative research activities, is a critical aspect of rigor even at the earliest stages of the study. A researcher’s background, beliefs, and experiences may affect any aspect of the research from choosing which specific question to investigate through determining how to present the results. Therefore, even at this early stage, the potential effect of researcher bias and any ethical considerations should be acknowledged and addressed. That is, how will the question’s influence on study design affect participants’ lives, position the researcher in relationship with others, or require specific methods for addressing potential areas of research bias and ethical considerations?
A conceptual framework is then actively constructed to provide a logical and convincing argument for the research. The framework defines and justifies the research question, the methodology selected to answer that question, and the perspectives from which interpretation of results and conclusions will be made. 5,6,20 Developing a well-integrated conceptual framework is essential to establishing a research topic based upon a thorough and integrated review of relevant literature (addressing Glassick criteria #1 and #2: clear purpose and adequate preparation). Key concepts, principles, assumptions, best practices, and theories are identified, defined, and integrated in ways that clearly demonstrate the problem statement and corresponding research question are answerable, researchable, and important to advancing thinking and practice.
Ringsted, Hodges, and Sherpbier describe three essential parts to an effective conceptual framework: theories and/or concepts and principles relevant to the phenomenon of interest; what is known and unknown from prior work, observations, and examples; and the researcher’s observations, ideas, and suppositions regarding the research problem statement and question. 21 Lingard describes four types of unknowns to pursue during literature review: what no one knows; what is not yet well understood; what controversy or conflicting results, understandings, or perspectives exist; and what are unproven assumptions. 22 In qualitative research, these unknowns are critical to achieving a well-developed conceptual framework and a corresponding rigorous study design.
Recent contributions from Ravitch and colleagues present best practices in developing frameworks for conceptual and methodological coherence within a study design, regardless of the research approach. 23,24 Their recommendations and arguments are highly relevant to qualitative research. Figure 1 reflects the primary components of a conceptual framework adapted from Ravitch and Carl 23 and how all components contribute to decisions regarding research design, implementation, and applications of results to future thinking, study, and practice. Notice that each element of the framework interacts with and influences other elements in a dynamic and interactive process from the beginning to the end of a research project. The intersecting bidirectional arrows represent direct relationships between elements as they relate to specific aspects of a qualitative research study.

Adaptation of Ravitch and Carl’s Components of a Conceptual Framework 23
Maxwell also provides useful guidance for developing an effective conceptual framework specific to the qualitative research paradigm. 17 The 2015 second edition of the Review Criteria for Research Manuscripts 14 and work by Ravitch and colleagues 23,24 provide specific guidance for applying the conceptual framework to each stage of the research process to enhance rigor and quality. Quality criteria for assessing a study’s problem statement, conceptual framework, and research question include the following: introduction builds a logical case and provides context for the problem statement; problem statement is clear and well-articulated; conceptual framework is explicit and justified; research purpose and/or question is clearly stated; and constructs being investigated are clearly identified and presented. 14,24,25 As best practice guidelines, these criteria facilitate quality and rigor while providing sufficient flexibility in how each is achieved and demonstrated.
While a conceptual framework is important to rigor in qualitative research, Huberman and Miles caution qualitative researchers about developing and using a framework to the extent that it influences qualitative design deductively because this would violate the very principles of induction that define the qualitative research paradigm. 25 Our profession’s recent emphasis on a holistic admissions process for pharmacy students provides a reasonable example of inductive and deductive reasoning and their respective applications in qualitative and quantitative research studies. Principles of inductive reasoning are applied when a qualitative research study examines a representative group of competent pharmacy professionals to generate a theory about essential cognitive and affective skills for patient-centered care. Deductive reasoning could then be applied to design a hypothesis-driven prospective study that compares the outcomes of two cohorts of students, one group admitted using traditional criteria and one admitted based on a holistic admissions process revised to value the affective skills of applicants. Essentially, the qualitative researcher must carefully generate a conceptual framework that guides the research question and study design without allowing the conceptual framework to become so rigid as to dictate a testable hypothesis, which is the founding principle of deductive reasoning. 26
Step 2: Qualitative Study Design
The development of a strong conceptual framework facilitates selection of appropriate study methods to minimize the bias inherent in qualitative studies and help readers to trust the research and the researcher (see Glassick criteria #3 in Table 1 ). Although researchers can employ great flexibility in the selection of study methods, inclusion of best practice methods for assuring the rigor and trustworthiness of results is critical to study design. Lincoln and Guba outline four criteria for establishing the overall trustworthiness of qualitative research results: credibility, the researcher ensures and imparts to the reader supporting evidence that the results accurately represent what was studied; transferability, the researcher provides detailed contextual information such that readers can determine whether the results are applicable to their or other situations; dependability, the researcher describes the study process in sufficient detail that the work could be repeated; confirmability, the researcher ensures and communicates to the reader that the results are based on and reflective of the information gathered from the participants and not the interpretations or bias of the researcher. 27
Specific best practice methods used in the sampling and data collection processes to increase the rigor and trustworthiness of qualitative research include: clear rationale for sampling design decisions, determination of data saturation, ethics in research design, member checking, prolonged engagement with and persistent observation of study participants, and triangulation of data sources. 28
Qualitative research is focused on making sense of lived, observed phenomenon in a specific context with specifically selected individuals, rather than attempting to generalize from sample to population. Therefore, sampling design in qualitative research is not random but defined purposively to include the most appropriate participants in the most appropriate context for answering the research question. Qualitative researchers recognize that certain participants are more likely to be “rich” with data or insight than others, and therefore, more relevant and useful in achieving the research purpose and answering the question at hand. The conceptual framework contributes directly to determining sample definitions, size, and recruitment of participants. A typical best practice is purposive sampling methods, and when appropriate, convenience sampling may be justified. 29
Purposive sampling reflects intentional selection of research participants to optimize data sources for answering the research question. For example, the research question may be best answered by persons who have particular experience (critical case sampling) or certain expertise (key informant sampling). Similarly, additional participants may be referred for participation by active participants (snowball sampling) or may be selected to represent either similar or opposing viewpoints (confirming or disconfirming samples). Again, the process of developing and using a strong conceptual framework to guide and justify methodological decisions, in this case defining and establishing the study sample, is critical to rigor and quality. 30 Convenience sampling, using the most accessible research participants, is the least rigorous approach to defining a study sample and may result in low accuracy, poor representativeness, low credibility, and lack of transferability of study results.
Qualitative studies typically reflect designs in which data collection and analysis are done concurrently, with results of ongoing analysis informing continuing data collection. Determination of a final sample size is largely based on having sufficient opportunity to collect relevant data until new information is no longer emerging from data collection, new coding is not feasible, and/or no new themes are emerging; that is, reaching data saturation , a common standard of rigor for data collection in qualitative studies . Thus, accurately predicting a sample size during the planning phases of qualitative research can be challenging. 30 Care should be taken that sufficient quantity (think thick description) and quality (think rich description) of data have been collected prior to concluding that data saturation has been achieved. A poor decision regarding sample size is a direct consequence of sampling strategy and quality of data generated, which leaves the researcher unable to fully answer the research question in sufficient depth. 30
Though data saturation is probably the most common terminology used to describe the achievement of sufficient sample size, it does not apply to all study designs. For example, one could argue that in some approaches to qualitative research, data collection could continue infinitely if the event continues infinitely. In education, we often anecdotally observe variations in the personality and structure of a class of students, and as generations of students continue to evolve with time, so too would the data generated from observing each successive class. In such situations, data saturation might never be achieved. Conversely, the number of participants available for inclusion in a sample may be small and some risk of not reaching data saturation may be unavoidable. Thus, the idea of fully achieving data saturation may be unrealistic when applied to some populations or research questions. In other instances, attrition and factors related to time and resources may contribute to not reaching data saturation within the limits of the study. By being transparent in the process and reporting of results when saturation may not have been possible, the resulting data may still contribute to the field and to further inquiry. Replication of the study using other samples and conducting additional types of follow-up studies are other options for better understanding the research phenomenon at hand. 31
In addition to defining the sample and selecting participants, other considerations related to sampling bias may impact the quantity and quality of data generated and therefore the quality of the study result. These include: methods of recruiting, procedures for informed consent, timing of the interviews in relation to experience or emotion, procedures for ensuring participant anonymity/confidentiality, interview setting, and methods of recording/transcribing the data. Any of these factors could potentially change the nature of the relationship between the researcher and the study participants and influence the trustworthiness of data collected or the study result. Thus, ongoing application of previously mentioned researcher reflexivity is critical to the rigor of the study and quality of sampling. 29,30
Common qualitative data collection methods used in health professions education include interview, direct observation methods, and textual/document analysis. Given the unique and often highly sensitive nature of data being collected by the researcher, trustworthiness is an essential component of the researcher-participant relationship. Ethical conduct refers to how moral principles and values are part of the research process. Participants’ perceptions of ethical conduct are fundamental to a relationship likely to generate high quality data. During each step of the research process, care must be taken to protect the confidentiality of participants and shield them from harm relating to issues of respect and dignity. Researchers must be respectful of the participants’ contributions and quotes, and results must be reported truthfully and honestly. 8
Interview methods range from highly structured to increase dependability or completely open-ended to allow for interviewers to clarify a participant’s response for increased credibility and confirmability. Regardless, interview protocols and structure are often modified or refined, based on concurrent data collection and analysis processes to support or refute preliminary interpretations and refine focus and continuing inquiry. Researcher reflexivity, or acknowledgement of researcher bias, is absolutely critical to the credibility and trustworthiness of data collection and analysis in such study designs. 32
Interviews should be recorded and transcribed verbatim prior to coding and analysis. 28 Member checking, a common standard of rigor, is a practice to increase study credibility and confirmability that involves asking a research subject to verify the transcription of an interview. 1,16,28 The research subject is asked to verify the completeness and accuracy of an interview transcript to ensure the transcript truthfully reflects the meaning and intent of the subject’s contribution.
Prolonged engagement involves the researcher gaining familiarity and understanding of the culture and context surrounding the persons or situations being studied. This strategy supports reflexivity, allowing the researcher to determine how they themselves may be a source of bias during the data collection process by altering the nature of how individuals behave or interact with others in the presence of the researcher. Facial expressions, spoken language, body language, style of dress, age, race, gender, social status, culture, and the researcher’s relationship with the participants may potentially influence either participants’ responses or how the researcher interprets those responses. 33 “Fitting in” by demonstrating an appreciation and understanding of the cultural norms of the population being studied potentially allows the researcher to obtain more open and honest responses from participants. However, if the research participants or topic are too familiar or personal, this may also influence data collection or analysis and interpretation of the results. 33 The possible applications of this section to faculty research with student participants in the context of pharmacy education are obvious, and researcher reflexivity is critical to rigor.
Some researchers using observational methods adopt a strategy of direct field observation, while others play partial or full participant roles in the activity being observed. In both observation scenarios, it is impossible to separate the researcher from the environment, and researcher reflexivity is essential. The pros and cons of observation approach, relative to the research question and study purpose, should be evaluated by the researcher, and the justification for the observational strategy selected should be made clear. 34 Regardless of the researcher’s degree of visibility to the study participants, persistent observation of the targeted sample is critical to the confirmability standard and to achieving data saturation. That is, study conclusions must be clearly grounded in persistent phenomena witnessed during the study, rather than on a fluke event. 28
Researchers acknowledge that observational methodologies are limited by the reality that the researcher carries a bias in determining what is observed, what is recorded, how it is recorded, and how it is transcribed for analysis. A study’s conceptual framework is critical to achieving rigor and quality and provides guidance in developing predetermined notions or plans for what to observe, how to record, and how to minimize the influence of potential bias. 34 Researcher notes should be recorded as soon as possible after the observation event to optimize accuracy. The more detailed and complete the notes, the more accurate and useful they can be in data analysis or in auditing processes for enhancing rigor in the interpretation phase of the study. 34
Triangulation is among the common standards of rigor applied within the qualitative research paradigm. Data triangulation is used to identify convergence of data obtained through multiple data sources and methods (eg, observation field notes and interview transcripts) to avoid or minimize error or bias and optimize accuracy in data collection and analysis processes. 33,35,36
Again, researcher practice in reflexivity throughout research processes is integral to rigor in study design and implementation. Researchers must demonstrate attention to appropriate methods and reflective critique, which are represented in both core elements of the conceptual framework ( Figure 1 ) and Glassick criteria ( Table 1 ). In so doing, the researcher will be well-prepared to justify sampling design and data collection decisions to manuscript reviewers and, ultimately, readers.
Step 3: Data Analysis
In many qualitative studies, data collection runs concurrently with data analysis. Specific standards of rigor are commonly used to ensure trustworthiness and integrity within the data analysis process, including use of computer software, peer review, audit trail, triangulation, and negative case analysis.
Management and analyses of qualitative data from written text, observational field notes, and interview transcriptions may be accomplished using manual methods or the assistance of computer software applications for coding and analysis. When managing very large data sets or complex study designs, computer software can be very helpful to assist researchers in coding, sorting, organizing, and weighting data elements. Software applications can facilitate ease in calculating semi-quantitative descriptive statistics, such as counts of specific events, that can be used as evidence that the researcher’s analysis is based on a representative majority of data collected ( inclusivism ) rather than focusing on selected rarities ( anecdotalism ). Using software to code data can also make it easier to identify deviant cases, detect coding errors, and estimate interrater reliability among multiple coders. 37 While such software helps to manage data, the actual analyses and interpretation still reside with the researcher.
Peer review, another common standard of rigor, is a process by which researchers invite an independent third-party researcher to analyze a detailed audit trail maintained by the study author. The audit trail methodically describes the step-by-step processes and decision-making throughout the study. Review of this audit trail occurs prior to manuscript development and enhances study confirmability. 1,16 The peer reviewer offers a critique of the study methods and validation of the conclusions drawn by the author as a thorough check on researcher bias.
Triangulation also plays a role in data analysis, as the term can also be used to describe how multiple sources of data can be used to confirm or refute interpretation, assertions, themes, and study conclusions. If a theme or theory can be arrived at and validated using multiple sources of data, the result of the study has greater credibility and confirmability. 16,33,36 Should any competing or controversial theories emerge during data collection or analysis, it is vital to the credibility and trustworthiness of the study that the author disclose and explore those negative cases. Negative case analysis refers to actively seeking out and scrutinizing data that do not fit or support the researcher’s interpretation of the data. 16
The use of best practices applying to data collection and data analysis facilitates the full examination of data relative to the study purpose and research question and helps to prevent premature closure of the study. Rather than stopping at the initial identification of literal, first-level assertion statements and themes, authors must progress to interpreting how results relate to, revise, or expand the conceptual framework, or offer an improved theory or model for explaining the study phenomenon of interest. Closing the loop on data collection is critical and is achieved when thorough and valid analysis can be linked back to the conceptual framework, as addressed in the next section.
Step 4: Drawing Valid Conclusions
Lingard and Kennedy 38 succinctly state that the purpose of qualitative research is to deepen one’s understanding of specific perspectives, observations, experiences, or events evidenced through the behaviors or products of individuals and groups as they are situated in specific contexts or circumstances. Conclusions generated from study results should enhance the conceptual framework, or contribute to a new theory or model development, and are most often situated within the discussion and conclusion sections of a manuscript.
The discussion section should include interpretation of the results and recommendations for practice. Interpretations should go beyond first-level results or literal description of observed behaviors, patterns, and themes from analysis. The author’s challenge is to provide a complete and thorough examination and explanation of how specific results relate to each other, contribute to answering the research question, and achieve the primary purpose of the research endeavor. The discussion should “close the loop” by integrating study results and analysis with the original conceptual framework. The discussion section should also provide a parsimonious narrative or graphical explanation and interpretation of study results that enhances understanding of the targeted phenomena.
The conclusion section should provide an overall picture or synopsis of the study, including its important and unique contributions to the field from the perspective of both conceptual and practical significance. The conclusion should also include personal and theoretical perspectives and future directions for research. Together, the discussion and conclusion should include responses to the larger questions of the study’s contributions, such as: So what? Why do these results matter? What next?
The strength of conclusions is dependent upon the extent to which standards of rigor and best practices were demonstrated in design, data collection, data analysis, and interpretation, as described in previous sections of this article. 4,12,17,23,24 Quality and rigor expectations for drawing valid conclusions and generating new theories are reflected in the following essential features of rigor and quality, which include: “Close the loop” to clearly link research questions, study design, data collection and analysis, and interpretation of results. Reflect effective integration of the study results with the conceptual framework and explain results in ways that relate, support, elaborate, and/or challenge conclusions of prior scholarship. Descriptions of new or enhanced frameworks or models are clear and effectively grounded in the study results and conclusions. Practical or theoretical implications are effectively discussed, including guidance for future studies. Limitations and issues of reflexivity and ethics are clearly and explicitly described, including references to actions taken to address these areas. 3,4,12,14
Step 5: Reporting Research Results
Key to quality reporting of qualitative research results are clarity, organization, completeness, accuracy, and conciseness in communicating the results to the reader of the research manuscript. O’Brien and others 4 proposed a standardized framework specifically for reporting qualitative studies known as the Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR, Table 2 ). This framework provides detailed explanations of what should be reported in each of 21 sections of a qualitative research manuscript. While the SRQR does not explicitly mention a conceptual framework, the descriptions and table footnote clarification for the introduction and problem statement reflect the essential elements and focus of a conceptual framework. Ultimately, readers of published work determine levels of credibility, trustworthiness, and the like. A manuscript reviewer, the first reader of a study report, has the responsibility and privilege of providing critique and guidance to authors regarding achievement of quality criteria, execution and reporting of standards of rigor, and the extent to which meaningful contributions to thinking and practice in the field are presented. 13,39
An Adaptation of the 21 Elements of O’Brien and Colleagues’ Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR) 4

Authors must avoid language heavy with connotations or adjectives that insert the researcher’s opinion into the database or manuscript. 14,40 The researcher should be as neutral and objective as possible in interpreting data and in presenting results. Thick and rich descriptions, where robust descriptive language is used to provide sufficient contextual information, enable the reader to determine credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability .
The process of demonstrating the credibility of research is rooted in honest and transparent reporting of how biases and other possible confounders were identified and addressed throughout study processes. Such reporting, first described within the study’s conceptual framework, should be revisited in reporting the work. Confounders may include the researcher’s training and previous experiences, personal connections to the background theory, access to the study population, and funding sources. These elements and processes are best represented in Glassick’s criteria for effective presentation and reflective critique ( Table 1 , criteria 5 and 6). Transferability is communicated, in part, through description of sampling factors such as: geographical location of the study, number and characteristics of participants, and the timeframe of data collection and analysis. 40 Such descriptions also contribute to the credibility of the results and readers’ determination of transfer to their and other contexts. To ensure dependability, the research method must be reported in detail such that the reader can determine proper research practices have been followed and that future researchers can repeat the study. 40 The confirmability of the results is influenced by reducing or at a minimum explaining any researcher influence on the result by applying and meeting standards of rigor such as member checking, triangulation, and peer review. 29,33
In qualitative studies, the researcher is often the primary instrument for data collection. Any researcher biases not adequately addressed or errors in judgement can affect the quality of data and subsequent research results. 33 Thus, due to the creative interpretative and contextually bound nature of qualitative studies, the application of standards of rigor and adherence to systematic processes well-documented in an audit trail are essential. The application of rigor and quality criteria extend beyond the researcher and are also important to effective peer review processes within a study and for scholarly dissemination. The goal of rigor in qualitative research can be described as ensuring that the research design, method, and conclusions are explicit, public, replicable, open to critique, and free of bias. 41 Rigor in the research process and results are achieved when each element of study methodology is systematic and transparent through complete, methodical, and accurate reporting. 33 Beginning the study with a well-developed conceptual framework and active use of both researcher reflexivity and rigorous peer review during study implementation can drive both study rigor and quality.
As the number of published qualitative studies in health professions educational research increases, it is important for our community of health care educators to keep in mind the unique aspects of rigor in qualitative studies presented here. Qualitative researchers should select and apply any of the above referenced study methods and research practices, as appropriate to the research question, to achieve rigor and quality. As in any research paradigm, the goal of quality and rigor in qualitative research is to minimize the risk of bias and maximize the accuracy and credibility of research results. Rigor is best achieved through thoughtful and deliberate planning, diligent and ongoing application of researcher reflexivity, and honest communication between the researcher and the audience regarding the study and its results.
Poll: Election interest hits new low in tight Biden-Trump race
The share of voters who say they have high interest in the 2024 election has hit a nearly 20-year low at this point in a presidential race, according to the latest national NBC News poll , with majorities holding negative views of both President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump.
The poll also shows Biden trimming Trump’s previous lead to just 2 points in a head-to-head contest, an improvement within the margin of error compared to the previous survey, as Biden bests Trump on the issues of abortion and uniting the country, while Trump is ahead on competency and dealing with inflation.
And it finds inflation and immigration topping the list of most important issues facing the country, as just one-third of voters give Biden credit for an improving economy.
But what also stands out in the survey is how the low voter interest and the independent candidacy of Robert F. Kennedy Jr. could scramble what has been a stable presidential contest with more than six months until Election Day. While Trump holds a 2-point edge over Biden head to head, Biden leads Trump by 2 points in a five-way ballot test including Kennedy and other third-party candidates.
“I don’t think Biden has done much as a president. And if Trump gets elected, I just feel like it’s going to be the same thing as it was before Biden got elected,” said poll respondent Devin Fletcher, 37, of Wayne, Michigan, a Democrat who said he’s still voting for Biden.
“I just don’t feel like I have a candidate that I’m excited to vote for,” Fletcher added.
Another poll respondent from New Jersey, who declined to provide her name and voted for Biden in 2020, said she wouldn’t be voting in November.
“Our candidates are horrible. I have no interest in voting for Biden. He did nothing. And I absolutely will not vote for Trump,” she said.
Democratic pollster Jeff Horwitt of Hart Research Associates, who conducted the survey with Republican pollster Bill McInturff of Public Opinion Strategies, said, “Americans don’t agree on much these days, but nothing unites the country more than voters’ desire to tune this election out.”
The poll was conducted April 12-16, during yet another turbulent time in American politics, including the beginning of Trump’s criminal trial in New York and new attacks and heightened tensions in the Middle East.
According to the poll, 64% of registered voters say they have high levels of interest in November’s election — registering either a “9” or a 10” on a 10-point scale of interest.
That’s lower than what the NBC News poll showed at this time in the 2008 (74%), 2012 (67%), 2016 (69%) and 2020 (77%) presidential contests.
The question dates to the 2008 election cycle. The lowest level of high election interest in the poll during a presidential cycle was in March 2012 — at 59%. But it quickly ticked up in the next survey.
This election cycle, high interest has been both low and relatively flat for months, according to the poll.
McInturff, the Republican pollster, says the high level of interest in the poll has “always been a signal for the level of turnout” for a presidential contest.
“It makes it very hard for us to predict turnout this far in advance of November, but every signal is turnout will be a lower percentage of eligible voters than in 2020,” he said.
By party, the current poll shows 70% of self-identified Republicans saying they have high interest in the coming election, compared with 65% of Democrats who say so.
Independents are at 48%, while only 36% of voters ages 18 to 34 rate themselves as highly interested in the election.
“They just aren’t low interest,” McInturff said of young voters. “They are off-the-charts low.”
NBC News poll: Frequently asked questions
Professional pollsters at a Democratic polling firm (Hart Research Associates) and a Republican firm (Public Opinion Strategies) have worked together to conduct and operate this poll since 1989. (Coldwater Corporation served as the Republican firm from 1989-2004.)
The polling firms employ a call center, where live interviewers speak by cell phone and telephone with a cross section of (usually) 1,000 respondents. The respondents are randomly selected from national lists of households and cell numbers. Respondents are asked for by name, starting with the youngest male adult or female adult in the household.
One of the common questions that critics ask of polls is, "I wasn't interviewed, so why should this poll matter?” By interviewing 1,000 respondents and applying minimal weights based on race, ethnicity, age, gender, education and the 2020 presidential vote, the poll achieves a representative sample of the nation at large – with a margin of error at a 95% confidence level.
NBC News editors and reporters — along with the pollsters at Hart Research and Public Opinion Strategies — all work to formulate the questions to try to capture the news and current events NBC is trying to gauge. Both Hart Research and Public Opinion Strategies work to ensure the language and placement of the questions are as neutral as possible.
Biden trims Trump’s lead
The poll also finds Trump narrowly ahead of Biden by 2 points among registered voters in a head-to-head matchup, 46% to 44% — down from Trump’s 5-point advantage in January, 47% to 42%.
The movement, which is within the poll’s margin of error of plus or minus 3.1 percentage points, is consistent with what other national polls have found in the Trump-Biden race.
Trump’s biggest advantages are among men (53% to 37%), white voters (54% to 37%) and white voters without college degrees (65% to 25%).
Biden’s top advantages are among Black voters (71% to 13%), women (50% to 39%) and Latinos (49% to 39%).
The poll shows the two candidates are essentially tied among independents (Biden 36%, Trump 34%) and voters ages 18-34 (Biden 44%, Trump 43%). One of the big polling mysteries this cycle is whether young voters have defected from Biden (as the NBC News poll has found over multiple surveys) or whether Democrats have maintained their advantage among that demographic.
When the ballot is expanded to five named candidates, Biden takes a 2-point lead over Trump: Biden 39%, Trump 37%, Kennedy 13%, Jill Stein 3% and Cornel West 2%.
Again, the result between Biden and Trump is within the poll’s margin of error.
Notably, the poll finds a greater share of Trump voters from the head-to-head matchup supporting Kennedy in the expanded ballot compared with Biden voters, different from the results of some other surveys.
(Read more here about how Kennedy's candidacy affe cts the 2024 race, according to the poll.)
The president’s approval rating ticks up to 42%
In addition, the poll found 42% of registered voters approving of Biden’s overall job performance — up 5 points since January’s NBC News poll, which found Biden at the lowest point of his presidency.
Fifty-six percent of voters say they disapprove of the job he has done, which is down 4 points from January.
Biden’s gains over the past few months have come from key parts of his 2020 base, especially among Democrats and Black voters. But he continues to hold low ratings among Latinos (40% approval), young voters (37%) and independents (36%).
“The data across this poll show that Joe Biden has begun to gain some ground in rebuilding his coalition from 2020,” said Horwitt, the Democratic pollster. “The question is whether he can build upon this momentum and make inroads with the groups of voters that still are holding back support.”
But McInturff, the GOP pollster, points out that the only recent presidents who lost re-election had approval ratings higher than Biden’s at this point in the election cycle: George H.W. Bush (43%) and Trump (46%).
“President Biden has a precarious hold on the presidency and is in a difficult position as it relates to his re-election,” McInturff said.
On the issues, 39% of voters say they approve of Biden’s handling of the economy (up from 36% in January), 28% approve of his handling of border security and immigration, and just 27% approve of his handling of the Israel-Hamas war (down from 29% in January).
Voters gave Biden his highest issue rating on addressing student loan debt, with 44% approving of his handling of the issue, compared with 51% who say they disapprove.
Biden leads on abortion and unity; Trump leads on inflation and competency
The NBC News poll asked voters to determine which candidate they thought is better on several different issues and attributes.
Biden holds a 15-point advantage over Trump on dealing with the issue of abortion, and he is ahead by 9 points on having the ability to bring the country together — though that is down from his 24-point advantage on that issue in the September 2020 NBC News poll.
Trump, meanwhile, leads in having the ability to handle a crisis (by 4 points), in having a strong record of accomplishments (by 7 points), in being competent and effective (by 11 points), in having the necessary mental and physical health to be president (by 19 points) and in dealing with inflation and the cost of living (by 22 points).
Inflation, immigration are the top 2024 issues
Inflation and the cost of living top the list of issues in the poll, with 23% of voters saying they’re the most important issue facing the country.
The other top voters is immigration and the situation at the border (22%) — followed by threats to democracy (16%), jobs and the economy (11%), abortion (6%) and health care (6%).
In addition, 63% of voters say their families’ incomes are falling behind the cost of living — essentially unchanged from what the poll found in 2022 and 2023.
And 53% of voters say the country’s economy hasn’t improved, compared with 33% who say that it has improved and that Biden deserves some credit for it and another 8% who agree the economy has improved but don’t give him credit for it.
“If I look back to when I had all three of my children in the house — we only have one child left in the house now, and we’re spending more now than what we did when we had a family of five,” said poll respondent Art Fales, 45, of Florida, who says he’s most likely voting for Trump.
But on a separate question — is there an issue so important that you’ll vote for or against a candidate solely on that basis? — the top responses are protecting democracy and constitutional rights (28%), immigration and border security (20%) and abortion (19%).
Indeed, 30% of Democrats, 29% of young voters and 27% of women say they are single-issue voters on abortion.
“I have a right to what I do with my body,” said poll respondent Amanda Willis, 28, of Louisiana, who said she’s voting for Biden. “And I don’t believe that other people should have the ability to determine that.”
Other poll findings
- With Trump’s first criminal trial underway, 50% of voters say he is being held to the same standard as anyone else when it comes to his multiple legal challenges. That compares with 43% who believe he’s being unfairly targeted in the trials.
- 52% of voters have unfavorable views of Biden, while 53% share the same views of Trump.
- And Democrats and Republicans are essentially tied in congressional preference, with 47% of voters preferring Republicans to control Congress and 46% wanting Democrats in charge. Republicans held a 4-point lead on this question in January.
The NBC News poll of 1,000 registered voters nationwide — 891 contacted via cellphone — was conducted April 12-16, and it has an overall margin of error of plus or minus 3.1 percentage points.
Mark Murray is a senior political editor at NBC News.
Sarah Dean is a 2024 NBC News campaign embed.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Literature Review: This section summarizes previous research studies and findings that are relevant to the current study. Methodology : This section describes the research design, methods, and procedures used in the study, including details on the sample, data collection, and data analysis.
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples. Published on December 21, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on January 17, 2024. The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses.. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields ...
They also inform future research. A clear statement of findings, a considered discussion and a clear presentation of the authors' conclusions are, therefore, important parts of the review. In particular, the following issues can help people make better informed decisions and increase the usability of Cochrane Reviews:
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results. Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach. Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings. This approach can be used to highlight important findings.
The discussion section is often considered the most important part of your research paper because it: Most effectively demonstrates your ability as a researcher to think critically about an issue, to develop creative solutions to problems based upon a logical synthesis of the findings, and to formulate a deeper, more profound understanding of the research problem under investigation;
Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Start this section by reiterating your research problem and concisely summarizing your major findings. To speed up the process you can use a summarizer to quickly get an overview of all important findings. Don't just repeat all the data you have already reported—aim for a clear statement of the overall result that directly answers your main research ...
The use of arrows or other markers may be helpful to highlight important findings. 3.4.2.2 Maps. Maps may be used in some manuscripts to add a crucial demographic context to a research paper, e.g., multi-centre research projects or National level surveys where the country-wise results or participation can be easily illustrated.
Step 1: Choose questions relevant to practice and ground your arguments in their reality. Step 2: Convey your findings to managerial audiences. Unfortunately, there is no "invisible hand" that conveys research findings to managers or policymakers. So we need to do it ourselves.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research.12. CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES. ... In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses.10.
The conclusion is intended to help the reader understand why your research should matter to them after they have finished reading the paper. A conclusion is not merely a summary of the main topics covered or a re-statement of your research problem, but a synthesis of key points derived from the findings of your study and, if applicable, where you recommend new areas for future research.
Look (a) within findings, (b) across findings, and (c) across cases/individuals. State all linkages that can be made to the relevant literature. Instruction:Continue in the same manner for each analytic category, exhausting all possible interpretations. you see emerging from among your findings. After having spent many hours interviewing
Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples ... While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called ...
This article addresses this important gap by positioning "research findings" presentations as a distinctive genre, part of qualitative method, and an expression of scholarly discourse. From the theoretical basis of genre theory, a number of common and damaging mistakes are found to be evident in the manner in which qualitative research ...
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section. "Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M."
Learning to evaluate and use research findings in daily practice is an important and lifelong part of professional development. This requires not only changes in educational programmes, but also a realignment of institutions so that management structures can support changes in knowledge and the implementation of changes in procedures.
Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate; Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic. Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We've written a step-by-step ...
A simple 7-step systematic approach to find relevant scholarly research data. Search literature based on research ideas, keywords, conference talks, author details, etc. Assess the found resources based on their key aspects and findings. Search, save, manage, read, and annotate relevant literature on a single platform.
Altogether, our findings provide important evidence of functional parcellation within the prefrontal cortex and point at mPFC-NA as key for updating Pavlovian S-O associations. Significant statement The ability to update stimulus-outcome (S-O) associations is a key adaptive behavior, essential for surviving and thriving in an ever-changing ...
Narshini Gunputh and Riley Supple, mathematical modeling Ph.D. students, presented research on mathematical modeling, computation, and data analysis in biological and biomedical applications at the American Mathematical Society 2024 Spring Eastern Sectional Meeting at Howard University. Gunputh presented "Mathematical Modeling of In-Vitro Drug Release from Contact Lenses" and Supple ...
Revised on May 31, 2023. A relevant dissertation topic means that your research will contribute something worthwhile to your field in a scientific, social, or practical way. As you plan out your dissertation process, make sure that you're writing something that is important and interesting to you personally, as well as appropriate within your ...
The validity of research findings refers to the extent to which the findings are an accurate representation of the phenomena they are intended to represent. ... the British Medical Journal 9 and Biomedcentral. 10 Medical Education published a useful series of articles on qualitative research. 11 Some of the important issues that should be ...
This is especially important as opioid use disorder has become a global epidemic, and the incidence of opioid related fatalities have climbed 500% in the past two decades. ... we have yet to arrive to a consensus regarding the best treatment modality given the substantial variability in research findings and directly conflicting results [6,7,8,9].
Their findings: only a few tree species are fit for the future, such as English oak in the UK. However, mixed forests are important for the survival of forests, otherwise the forest ecosystem as a ...
Conceding the presidential election: A majority of voters say it is important that the losing candidate in November publicly acknowledge the winner as the legitimate president. But Trump's supporters are far less likely than Biden's to say it is very important (44% vs. 77%). (Read more about voters' views on election concession in Chapter 3.)
The goal of rigor in qualitative research can be described as ensuring that the research design, method, and conclusions are explicit, public, replicable, open to critique, and free of bias. 41 Rigor in the research process and results are achieved when each element of study methodology is systematic and transparent through complete, methodical ...
The study also revealed that the proportion of workers searching for a new job in the past four weeks grew to 25.1%, up from 23.1% in November and the highest share of workers looking since March ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Other poll findings With Trump's first criminal trial underway, 50% of voters say he is being held to the same standard as anyone else when it comes to his multiple legal challenges.