An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Community Med
- v.47(4); Oct-Dec 2022

Juvenile’s Delinquent Behavior, Risk Factors, and Quantitative Assessment Approach: A Systematic Review
Madhu kumari gupta.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
Subrajeet Mohapatra
Prakash kumar mahanta.
1 Department of Clinical Psychology, Ranchi Institute of Neuro-Psychiatry and Allied Science, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
Background:
Not only in India but also worldwide, criminal activity has dramatically increasing day by day among youth, and it must be addressed properly to maintain a healthy society. This review is focused on risk factors and quantitative approach to determine delinquent behaviors of juveniles.
Materials and Methods:
A total of 15 research articles were identified through Google search as per inclusion and exclusion criteria, which were based on machine learning (ML) and statistical models to assess the delinquent behavior and risk factors of juveniles.
The result found ML is a new route for detecting delinquent behavioral patterns. However, statistical methods have used commonly as the quantitative approach for assessing delinquent behaviors and risk factors among juveniles.
Conclusions:
In the current scenario, ML is a new approach of computer-assisted techniques have potentiality to predict values of behavioral, psychological/mental, and associated risk factors for early diagnosis in teenagers in short of times, to prevent unwanted, maladaptive behaviors, and to provide appropriate intervention and build a safe peaceful society.
I NTRODUCTION
Juvenile delinquency is a habit of committing criminal offenses by an adolescent or young person who has not attained 18 years of age and can be held liable for his/her criminal acts. Clinically, it is described as persistent manners of antisocial behavior or conduct by a child/adolescent repeatedly denies following social rules and commits violent aggressive acts against the law and socially unacceptable. The word delinquency is derived from the Latin word “delinquere” which described as “de” means “away” and “linquere” as “to leaveor to abandon.” Minors who are involved in any kind of offense such as violence, gambling, sexual offenses, rape, bullying, stealing, burglary, murder, and other kinds of anti-social behaviors are known as juvenile delinquents. Santrock (2002) defined “an adolescent who breaks the law or engages in any criminal behavior which is considered as illegal is called juvenile delinquent.”[ 1 ] In India, Juvenile Justice (J. J.-Care and protection of Children) Act of 2000 stated that “an individual whether a boy/girl, who is under 18 years of age and has committed an offense, referred or convicted by the juvenile court have considered a juvenile delinquent.”
P REVALENCE R ATE : J UVENILE D ELINQUENCY IN I NDIA
According to the National Crime Records Bureau (India, 2019), statistical data of crimes in India show that overall, 38,685 juveniles were placed under arrest in 32,235 cases, among 35,214 juveniles were taken into custody under cases of IPC and 3471 juveniles were arrested under cases of special and local laws (SLL) during 2019. About 75.2% of the total convicted juveniles (29,084 out of 38,685) were apprehended under both IPC and SLL belonging to the age group 16–18 years. In 2019, 32,235 juvenile cases involving and recorded, indicating a slight increment of 2.0% over 2018 (31,591 cases). The rate of crime also indicates a slight increase from 7.1 (2018) to 7.2 (2019).[ 2 ] The total registered cases against juvenile delinquents are calculated as crime incidence rate per one Lakh population as shown in Figure 1 .

The graphical view of registered cases against Juveniles in conflict with law under Indian penal code and special and local laws crimes during 2014–2019 of all the State (s) and union territories of India Sources: Crime in India National (2014-2019), National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB), Ministry of Home Affairs, 2019
R ISK -F ACTORS A FFECTING D ELINQUENT B EHAVIOR
Studies identify that multiple risk factors are responsible for delinquent behavior categorized as individual, parental, family, community, society, schools/educational, financial, mental as well as psychological factors of the individual and the family shown in Table 1 . Adolescents involve themselves in various anti-social activities to fulfill their basic needs. Basically, “delinquency” is just a recreational activity for earning money. These risk factors differ from person to person during the early childhood period and very crucial because children, who are involved in any kind of deviant activity at an early stage, have a higher chance to adopt delinquent tendencies chronically.[ 33 ]
Developmental phases, risk-factors and developing delinquent behaviours of the child
Juvenile delinquency is caused by a wide range of factors, such as conflicts in the family, lack of proper family control, residential environmental effects, and movie influence, along with other factors are responsible for delinquent behavior.[ 3 ] Family and environmental factors, namely restrictive behaviors, improper supervision, negligence, criminal activities of parents, improper motivation by peers, fear of peer rejection, poverty, illiteracy, poor educational performance at school, lack of moral education may turn the individual personality into delinquents. Moreover, in the environment, deteriorated neighborhood, direct exposure to violence/fighting (or exposure to violence through media), violence-based movies are considered major risk factors.[ 4 ] In India, a higher level of permissive parenting in low-income families had so many family members and due to economic conditions, the adolescents had pressure to search various income sources to sustain the family, and it has affected parental behavior toward adolescents.[ 5 ] The children who belong to the lower middle-socio-economical class and are rejected by society showed more aggressive behavior.[ 6 ]
Juvenile gang members exhibit significantly higher rates of mental health issues such as conduct disorders, attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorders, antisocial personality disorder, posttraumatic-stress-disorders, and anxiety disorders.[ 7 ] As well as the intellectual level of young offenders is significantly different from nonoffenders. Emotional problems on adolescents are related to delinquent behavior and impulsivity directly associated with antisocial behavior among adolescents.[ 8 ] Poor self-control of adolescents involved them in substance use, affected harmfully, and increased involvements in anti-social activities.[ 9 ] Nonviolent people, who not involved in any gang, are less likely to utilize mental-health services, having lower levels of psychiatric morbidity, namely antisocial personality disorders, psychosis, and anxiety disorders, when compared with the group of violent offenders.[ 10 ]
M ACHINE L EARNING : A N EW Q UANTITATIVE E VALUATION A PPROACH
Machine learning (ML) is belonging to the multidisciplinary field that includes programming, math, and statistics, and as a new and dynamic field that necessitates more study. It is a branch of computer science that emerged through pattern recognition and computational learning theory of artificial intelligence. ML is exploring researches and development of algorithms that can learn and genera tea prediction besides a given set of data through the computer. It is a scope for the study that gives computers the capability to learn without being principally programmed.[ 11 ] Tom M. Mitchell explained ML as “a computer-based program to learn from action of “E” concerning any task of ‘T’s, and some performance evaluates “P,” if its performance on “T,” as assessed by “P,” improves with action of E.”[ 12 ] The goal of ML is to mimic human learning in computers.[ 13 ] Humans learn from their experiences and ML methods learn from data. The user provides a portion of a dataset designated to train by the algorithm. The algorithm creates a model based on the relationships among variables in the dataset, and the remaining dataset is used to validate the ML model. In simple words, ML approach is for risk indicator is meant to magnify the potential of current knowledge.[ 15 ] ML sits at the common frontier of many academic fields, including statistics, mathematics, computer science, and engineering.[ 14 , 17 ] ML models principally categorized into three categories, namely supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement based on their task which they are attempting to accomplish. Supervised learning is relying on a training set where some characteristics of data are known, typically labels or classes, and target to find out the universal rule that maps inputs to outputs. Unsupervised learning has no design to give to the learning algorithm, balance itself to find out the patterns through inputs. In reinforcement, interaction with a dynamic environment happens during which a particular target such as driving a vehicle is performed without a driver principally involved in any activities, namely comparison. In numerous studies, pattern classification approaches based on ML algorithms are used to forecast human beings into various categories by maximizing the distance among data groups. ML generally refers to all actions that train a computer algorithm to determine a complicated pattern of data that is conceivable used for forecast category of membership into a new theme (e.g., individual vs. controls).[ 32 ]
R ATIONAL OF THE S TUDY
In the last decade, various researchers have been attracted to the use of quantitative computer-based techniques for analyzing various psychological and clinical aspects, which have greatly contributed to the area of modern psychology. In this analysis, most of the works are devoted to the use of various quantitative analysis techniques, namely ML and statistical methods which has utilized by the researchers for evaluating various risk and protective factors of juveniles. Henceforth, studies on the application of the ML model for risk-assessment of delinquent behavior on juveniles are limited as compared to other techniques, namely logistic regression. Hence, this review paper may explore the utilization of ML to get an easy and quick assessment on juveniles and helpful for future studies. It may help to determine the most significant risk factors and establishment of a successful treatment program that prevents juveniles from delinquent activities and stops them from recidivism.
In this review, all these studies carried out which has used various quantitative techniques to detected juvenile delinquency with specially emphasis on ML and statistical approaches. The review is organized into four sections follows as: Section-I gives an overview of juvenile delinquency, prevalence rates in India, and various behavioral risk factors during the developmental period. It also provides general information about ML as a new approach and their application. Section-II included information about the methodology of the present review. Section-III explores the results and discusses which explore the ML and statistical methods for detecting juvenile behaviors and Section-IV concludes the extant research of the present review and the implications for future work.
M ETHODOLOGY
This review paper aim is to find the various quantitative techniques (computer-assisted techniques) ML and statistical approaches which have been used for assessing/predicting delinquent behaviors, traits, and risk factors among juveniles.
Sources of information
For this review article, a total of 15 research articles were identified and selected through Google-scholar, Web of Science, Academia, PubMed, and Research-Gate, using the keywords, namely juvenile-delinquency, ML, Risk-factors, and delinquent-behavior. All relevant studies were selected for review of the quantitative approaches for identifying delinquent behavior and risk factors of adolescents and the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram for articles search process as shown in Figure 2 .[ 34 ]

Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses flow diagram for search outcomes of quantitative assessment of juvenile delinquent behaviors
Inclusion criteria
Research studies published since 2011–2019, case studies, empirical, quantitative, qualitative, and cross-sectional studies published in English were included, which used ML and statistical models to analyze behaviors, risk and associated factors among juveniles.
Exclusion criteria
Protocol, dissertations, prototype studies, and studies which published in other languages were excluded.
Studies on machine learning and statistical methods among juvenile delinquency
In this review, we performed a rigorous search of the literature to provide a narrative description of the various quantitative computer-based approaches which are applicable to assess and identify the delinquent behaviors and risk factors on juveniles. Initially, the search identified 150 articles through various databases, search outcomes show in the PRISMA flow diagram [ Figure 2 ]. One hundred and thirty-five articles were removed by screening through the title, text, removal of duplicate articles and based on inclusion and exclusion criteria, we identified 15 research articles in full text and these selected articles comprising through expert opinions. The findings of these articles tabulated the diverse approaches on the current state of knowledge about assessment of early diagnosis of delinquent behaviors and risk factors and tried to provide a summary which based on computer-based quantitative analysis [ Table 2 ].
Summary table of relevant studies which used quantitative approach to detect delinquent behaviors and risk factors among juvenile behaviors
GLM: Generalized linear model, ML: Machine learning, PEH: Probabilistic estimation hypothesis, CAPM: Categorization of anxiety predictor model, SES: Socioeconomic status, SEM: Structural equation model
D ISCUSSION
In this systematic review, we performed a rigorous search of the literature to provide a narrative picture of various methods used to identify juveniles’ behaviors. We identified 15 articles, with the objective to analyze the application of ML and other quantitative approaches to assess various delinquent behaviors and risk factors of juveniles. The studies revealed ML is a new quantitative method to identify the risk factors and delinquent behavior henceforth; there very few studies are conducted. In this study, we tried to provide a summary of selected articles on the current state of knowledge about quantitative analysis for assessment of delinquent behaviors of juveniles and there only few articles have used ML as quantitative analysis. The City Social Welfare Development Office of Butuan, Philippines, used a dataset to create predictive models for analyzing the minors at risk and children in conflict with poor financial status. And found children with age range 12–17 years are victims of maltreatment, and adolescents between the ages of 15–17 years commit severe crimes.[ 16 ] Kim et al .[ 18 ] used traditional regression, ML method and certified the predictive validity of the models in numerous ways, along with traditional hold-out validation k-fold cross-validation, and bootstrapping to examine the present practice and policy for assessment, treatment, and management of delinquents who have a history of sexual conviction in multiple jurisdictions from New York, Florida, Oregon, Virginia, and Pennsylvania. Results revealed that important risk factors among juveniles had some criminal history, sexual offending experiences, and delinquent peers. Some dynamic factors viz. performance in school, peer connection, sorrowful feelings, impulsiveness, mental health, and substance abuse are important anticipating factors among sexual offenders for recidivism.
Rokven et al .[ 19 ] used multinomial logistic regression technique to compare four types of delinquent groups: online delinquents, offline delinquents, nondelinquents, and delinquents who belong to both online and offline categories and found juveniles who having both online and offline criminal records are more likely to commit crimes. Delinquency is indirectly linked with sleep deprivation, with poor self-control acting as a catalyst proved by regression models with latent factors.[ 20 ] Violent video games directly associated with anti-social behavior, even though several correlates, such as psychopathologies has present in youth analyzed by negative binomial regression (extended version of Poisson regression).[ 22 ]
Fernández et al . analyzed through multivariate logistic regression and found, school dropouts’ teenagers had a higher level of irresponsibility, substance, and illicit drug abuse compare then nondropouts.[ 23 ] In addition, lack of parental supervision plays a significant role in the prediction of deviant behaviors on school dropouts. School dropout teenagers have multi-dimensional problem that requires proper parental supervision and proactive school policies to reducing drug and alcohol abuse.[ 23 ] Fifty-two percent of juvenile offenders had issues with academic performance, 34% had family history of psychiatric disorders, 60% of juveniles involved in property crime and 54% of offenders involved in drugs and alcohol use-related offenses had some deficiency in academic achievement evaluated by multiple regression techniques.[ 24 ] Wu (2015) created a multidimensional scaling model and found students used a complex cognitive-mechanism measured and compared their position to friends and others.[ 25 ]
Sexually assaulted history has strongly associated and one of the most powerful variables associated with the intensity of psychoactive substances using by juveniles.[ 26 ] Parks[ 28 ] has used binary logistic regression and multivariate models revealed that no major variations in violent juveniles belong to cohabiting families and other families. However, teenagers of cohabiting families have marginally higher risk to involving in nonviolent forms of crime.[ 28 ] Economic conditions of the family has strongly linked to the influences of parents, siblings, and peers at risk and delinquency. Economic stress, having an active sibling aggression, harmful, and more destructive events affected seriously on adolescent delinquent behaviors who belongs to economically poor families.[ 29 ] Coercive parents are directly associated with violent delinquency of adolescents on both ways as explicitly and indirectly and transformed shame on adolescents. As opposed to articulated guilt, shame conversion is the major cause for more violence.[ 30 ]
It is very difficult to evaluate all possible outcomes and explain a single quantitative approach as ML to early identification of delinquent behaviors and risk-factors of juveniles for intervene in the affected factors. Our study has several limitations. First, other studies rather than the English language were we not included in the study. Second, counties like India have very less evidence-based studies in the field of early detection of juveniles and computer-based assessment approaches as ML for quantitative analysis. Third, only 15 articles were considered which fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
I MPLICATION
The modern world is fully based on computers and technology for making works easy and faster. ML model is an emerging future technology in the field of health and mental health. It has the potential to predictive ability to detect health/mental health-related problems as well as for early diagnosis of problems behaviors. This review is acknowledging the use of quantitative analysis focused on ML algorithm as a new research area for early identification of delinquent behaviors of children, to prevent the deviant behaviors and related risk-factors and may be beneficial for future studies and contribute to make a peaceful society and worthful young generation for the nation.
C ONCLUSION
This review showed that available literature based on ML and other quantitative methods to identify the risk factors and delinquent behaviors of juveniles. Young peoples are at a higher risk to learn maladaptive/deviant behaviors as violent, aggressive, hyperactive, and easily involved in criminal activities. According to studies, individual factors, family environment, family structure, size/type of the family, parental status (single/separate/divorces) are highly affected adolescent’s behaviors. In addition, social, environmental, and economic conditions are lead to adapt conductive and delinquent behaviors. There highly need to identify delinquent behaviors in the initial stage to prevent with affected risk factors. It is very crucial for early screening and intervention.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment
Authors acknowledge to Department of Science and Technology- Cognitive Science Research Initiative (DST-CSRI) for sponsored the project in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Birla Institute of Technology, Mesra, India, which explores the technology-based approach in multidisciplinary works. The authors also would like to thank Mr. Abhinash Jenasamanta and Mr. Devesh Upadhyay, Research Scholars, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, BIT, Mesra, Ranchi, for technical and motivational support.
R EFERENCES
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Acquisition
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Religion
- Music and Media
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Strategy
- Business Ethics
- Business History
- Business and Government
- Business and Technology
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic Systems
- Economic History
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

Juvenile Delinquency: Prevention, assessment, and intervention

- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Juvenile offending and anti-social behaviour are enormous societal concerns. This broad-reaching volume summarizes the current evidence on prevention, diversion, causes, and rates of delinquency, as well as assessment of risk and intervention needs. A distinguished cast of contributors from law, psychology, and psychiatry describe what we know about interventions in school, community, and residential contexts, focusing particularly on interventions that are risk reducing and cost effective. Equally important, each chapter comments on what is not well supported through research, distinguishing aspects of current practice that are likely to be effective from those that are not and mapping new directions for research, policy, and practice. Finally, the volume provides a description of a model curriculum for training legal and mental health professionals on conducting relevant assessments of adolescents for the courts.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- Google Scholar Indexing
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
Institutional access
- Sign in with a library card Sign in with username/password Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.

Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Sign in with a library card
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples
🏆 best juvenile delinquency topic ideas & essay examples, 💡 interesting topics to write about juvenile delinquency, 📌 simple & easy juvenile delinquency essay titles, 👍 good essay topics on juvenile delinquency, ❓ research questions on juvenile delinquency.
- The Impact of Media on Juvenile Delinquency Besides, the media have been at the forefront of the fight against juvenile-related crimes. In this view, this document aims at critically evaluating the role of various forms of media in escalating juvenile delinquency, and […]
- Social Learning Theory and juvenile delinquency The empirical studies of the Social Learning Theory on juvenile delinquency helps to provide an insight on the past, present as well as the future of criminology i.e.the study sheds light on the future directions […] We will write a custom essay specifically for you by our professional experts 808 writers online Learn More
- Methodologies Used to Measure Acts of Juvenile Delinquency Before moving into the aspects of measurement of actions of juvenile delinquents, it is necessary to define and know what a juvenile delinquent is, and what actions fall within the ambit of juvenile delinquency.
- Poverty Areas and Effects on Juvenile Delinquency The desire to live a better life contributes to the youths engaging in crimes, thus the increase in cases of juvenile delinquencies amid low-income families. The studies indicate that the fear of poverty is the […]
- The Issue of Juvenile Delinquency At the onset of the industrial revolution, public awareness concerning the fair and ethical treatment of children in workplaces emerged. The role of supervising and guiding children is left to other children, grandparents, or hired […]
- Juvenile Delinquency in Ancient and Modern Times The only policy related to juvenile delinquency existing in ancient Greece was the law that prohibited the youth in ancient Greece from beating their parents.
- The Broken Homes and Juvenile Delinquency The level of measurement in this study will be to assess the frequency of involvement in crime by the children from the broken homes as well as those from the two parent families.
- Juvenile Delinquency: Causes and Intervention The role of the family and parents cannot be discounted in the causes of juvenile delinquency. The courts and the lawyers are involved in the trial and sentencing of juvenile offenders.
- Juvenile Delinquency The defenders of the system on the other hand appreciate the marked role of juvenile justice system in rehabilitating juvenile delinquents and are advocating for the conservation of the system and reforming critical structures that […]
- The Problem of Juvenile Delinquency The addition of family context to the existing perception of adolescent crimes could be used to explore the core reasons for the crimes and to define possible methods for the prevention of juvenile crimes. The […]
- The Cognitive Theory in Juvenile Delinquency At this stage, a child can perform certain actions repeatedly and also be able to differentiate the means of doing actions.
- Problems of Juvenile Delinquency The main aim of writing this paper is to carry out an examination of a juvenile delinquent in order to understand what pushes them into doing the act and applicable solutions which can be applied […]
- The Relationship Between Parental Influence and Juvenile Delinquency Parents that do not allow their children to play with their neighbors, or discourage their children from associating with particular families lead to the children developing a negative attitude towards the families.
- Single Parenthood and Juvenile Delinquency in Modern Society The proposal seeks to establish the relationship between single parenthood and the increase in juvenile delinquency. I propose addressing child delinquency from the perspective of social and family background to understand the risks associated with […]
- Juvenile Delinquency and Affecting Factors The information gathered, synthesized, and analyzed in the research with the help of the proposed question has future value as it identifies factors that can be impacted by the society representatives.
- The Concepts of Nature and Nurture in Modern Psychologist to Explain Juvenile Delinquency Hence any behavior exhibited by a juvenile that is in total contrast with the value demands of the larger society can be termed as Juvenile Delinquency. On the one hand, it is believed that Juvenile […]
- Juvenile Delinquency: Social Disorganization Theory Hence, according to Lopez and Gillespie, tenets of the social disorganization theory have been resourceful in the present-day juvenile delinquency system.
- Developing Solutions to the Juvenile Delinquency Problem These include the creation of a creative activity center, the mandatory introduction of art classes in schools, and the implementation of urban sports programs.
- Juvenile Delinquency is a Product of Nurture These criminals have been exposed to unfavorable conditions in their lives such as violence and poverty and turn to criminal behavior as a coping mechanism.
- The Issue of Juvenile Delinquency: Recent Trends Violence and other criminal actions attract the attention of the government and the general public, as they affect the life of the society adversely.
- Juvenile Delinquency: Impact of Collective Efficacy and Mental Illnesses The perception of collective efficacy can be defined as the consideration that the people in a neighborhood are trustable and can do their part to partake in social control to benefit a specific community.
- Juvenile Delinquency: a Case Analysis The tracking of the juvenile from juvenile court to adult court and then through the system is shown in the outline below: Arrest.
- Implementing an Arts Program to Help Curb Juvenile Delinquency and Reduce Recidivism Therefore, the pieces of art will be customized to rhyme with society needs of the targeted children and the adolescents. Some of the enrollees to this program will be delinquents.
- Role of Family in Reducing Juvenile Delinquency Players in the criminal justice system recognize the contribution of family and familial factors to the development of criminal and delinquent tendencies and their potential to minimize minors’ engagement in illegal and socially unacceptable behaviors.
- Gangs and Juvenile Delinquency Hallsworth and Silverstone argues that although there have been a lot of violence, the main source is not quite clear and people live by speculations that the violence is linked to the emergence of a […]
- Juvenile Delinquency: Three Levels of Prevention It is made up of programs and ideals which are effective in treatment of the offender, reintegrating them in the society and limiting them from committing similar offenses. In conclusion, though most prevention programs are […]
- Day Treatment Centers and Juvenile Delinquency One of the core aspects that should not be disregarded is that such programs may be used as a particular assessment tool that would help to identify needs of a juvenile, and this approach may […]
- Court Unification and Juvenile Delinquency Speaking about the given issue, it is important to give the clear definition of this category and determine who could be judged by the juvenile court.
- Prevent Juvenile Delinquency in the USA Due to this fact, it is possible to describe the existing problem as the increase in the number of crimes that children commit.
- Juvenile Delinquency: Risk Assessment The investigatory processes to know the individual’s character and personality involve the use of complex and simple approaches, and these serve to provide organizations or institutions dealing with child welfare with important information that would […]
- Life Without Parole and Juvenile Delinquency The United States is one of the few countries which recognize the necessity of sentencing juveniles to life without parole. This is the main and only advantage of this approach.
- Juvenile Delinquency and Reasons That Lead to It Irrespective of the cause of juvenile delinquency, juvenile drug abuse is certainly most commonly related directly to either an increase or a decrease in any form of juvenile delinquency. This correlates to the increase in […]
- Drugs Influence on Juvenile Delinquency Additionally, parents are the ones who know the strengths and weaknesses of the children since they spend most of their time together, their suggestions and views towards the crime committed should be handled with a […]
- Theories of Juvenile Delinquency Research showed individuals’ attitudes toward crime may herald their criminal behavior, in agreement with criminological theories such as control theory, learning theory and psychological theories like the theory of reasoned action.
- Criminology Theories and Juvenile Delinquency From the point of view of labeling theory, the initial drinking and the first fight at the party is John’s primary deviance.
- Juvenile Delinquency in the United States According to Pennsylvania laws, children at the age of 10 and above can be trialed as adults for first- and second-degree murders.
- Juvenile Delinquency and the Importance of Socialization At the time of the incident, according to the authors of the article, twenty students out of a total of thirty had arrived for the lecture.
- Theories and Suggestions on Juvenile Delinquency The other factor is that the norms that governed relationships in the different family and societal set-ups such as in the school and the workplace are being challenged.
- The Phenomenon of Juvenile Delinquency They are very important in the proceedings and even have additional authority to propose a waiver of the subject. The judges are the other officials in a juvenile court system.
- The Juvenile Delinquency Rate In order to reduce the rate of crime committed by young people in my community, there is a need to educate the youth in matters of drug and substance abuse.
- Juvenile Delinquency Recidivism Prevention Many studies have been carried out to examine the rates of recidivism among juveniles and the ineffectiveness of the juvenile prison.
- Juvenile Delinquency: The Columbine Shootings This paper seeks to discuss and analyze the casual theory of juvenile delinquency by describing an instance of juvenile delinquency as highlighted in the mass media, by describing the casual theory of juvenile delinquency with […]
- Juvenile Delinquency Theories in the United States School and family are extremely important to juveniles regarding their worldview, and the failure of those communities to guide them may result in turning to questionable ideals and morals.
- Adolescent Diversion Project in Juvenile Delinquency Treatment in Michigan The focus of the program is to prevent future delinquency by creating social attachments to family and other prosocial youth by providing community resources and keeping individuals away from the juvenile justice system which can […]
- Crime Prevention and Juvenile Delinquency As a specific jurisdiction that will serve as the basis for assessing and implementing the provisions of the crime prevention program, the District of Florida will be considered.
- Adolescent Psychology and Juvenile Delinquency I will also promote the idea that when it comes to identifying the factors that contribute to the development of delinquency in youth, one must be willing to consider the effects of the combination of […]
- Juvenile Delinquency, Its Factors and Theories Under the individual risk factors, it is prudent to note that a lack of proper education coupled with lower intelligence might pose a serious risk to a minor in terms of engaging in criminal activities […]
- Factors Associated With Juvenile Delinquency Further, the authors propose that the family should be the main focus of prevention and clinical interventions and that establishment of social policy and programs should be directed to the family.
- Combating Juvenile Delinquency: Projects Management In order to prevent and reduce juvenile violence, the City of Hampton develops and implements various activities that were mentioned above, promoting the importance of moral standards.
- Juvenile Delinquency Investigation The social learning theory that is a part of it suggests that children observe the behavior of others and replicate it.
- Juvenile Delinquency’ Causes and Possible Treatments They investigated the issue in different perspectives but came up to the decision that the best way to treat young offenders is to utilize multisystemic therapy.
- Juvenile Delinquency: Criminological Theories These include the broken windows theory, the culture of the gang theory and the social disorganization theory. Cohen developed the culture of the gang theory to explain the origin of juvenile delinquency.
- Juvenile Delinquency and Criminal Gangs The proliferation of criminal gangs in my area of jurisdiction, as director of the county juvenile court, represents a nationwide problem. In the 1990s, the rate of crime rose in most parts of the world.
- Juvenile Delinquency, Treatment, and Interventions The performance of the child in school is one of the individual factors that are likely to cause the child to get involved in violent behaviors.
- Poverty and Juvenile Delinquency in the United States
- Roles of Family, School, and Church in Juvenile Delinquency
- Understanding Juvenile Delinquency and the Different Ways to Stop the Problem in Our Society
- Juvenile Delinquency and Crime as an Integral Part of the American Society
- Impact of Television Violence In Relation To Juvenile Delinquency
- The Vicious Circle of Child Abuse, Juvenile Delinquency, and Future Abuse
- Juvenile Delinquency, Domestic Violence, and the Effects of Substance Abuse
- The Explorers Program as a Preventative Measure in Juvenile Delinquency
- Juvenile Delinquency, Youth Culture, and Renegade Kids, Suburban Outlaws by Wooden
- The Alarming Rate of Juvenile Delinquency and Cases of Teenage Suicides in the U.S
- The Line Between Juvenile Delinquency And Adult Penalties
- Home Social Environment and Juvenile Delinquency
- The Effects of Neighborhood Crime on the Level of Juvenile Delinquency
- Interpersonal Learning Theory Plus Juvenile Delinquency
- How to Prevent Juvenile Delinquency in the U.S
- Relationship Between Juvenile Delinquency and Learning Disabilities
- The Impact of Television Violence and Its Relation to Juvenile Delinquency
- The Lack of Strong Parental Figures Causes Juvenile Delinquency
- Theories of Juvenile Delinquency: Why Young Individuals Commit Crimes
- Using Drugs and Juvenile Delinquency
- Theory of Social Disorganization and Juvenile Delinquency
- What Is the Best Way to Combat Juvenile Delinquency?
- The Marxist Crime Perspective On Juvenile Delinquency Of African Americans
- The Failures of the Act of Juvenile Delinquency in the United States
- Juvenile Delinquency And Its Effects On The Adult Justice System
- Juvenile Delinquency Contributing Factors Current Research and Intervention
- Impact Of Single Parents On Juvenile Delinquency Rates
- Video Game Violence Leading to Juvenile Delinquency
- Juvenile Delinquency: Exploring Factors of Gender and Family
- The Psychological Aspect of Juvenile Delinquency
- The Antisocial Behavior Leading to Juvenile Delinquency
- Lead and Juvenile Delinquency: New Evidence from Linked Birth, School and Juvenile Detention Records
- The Role of Family in Preventing Juvenile Delinquency and Behavioural Patterns of Children
- The Relationship Between Poverty and Juvenile Delinquency
- The Importance of Family in the Behavior of Children and in Preventing Juvenile Delinquency
- Preventing and Dealing with Juvenile Delinquency
- How Family Structures Can Play a Role in Juvenile Delinquency
- Juvenile Delinquency and A Child’s Emotional Needs
- Family Structural Changes and Juvenile Delinquency
- The Causes of the Problem of Juvenile Delinquency in the United States
- Juvenile Delinquency And The Juvenile Justice System
- The Curfew: Issues On Juvenile Delinquency And Constitutional Rights
- The Socioeconomic Triggers of Juvenile Delinquency: Analysis of “The Outsiders”
- Exploring the Root Causes of the Problem of Juvenile Delinquency
- The Rise of Juvenile Delinquency and the Flaws of the Juvenile Justice System
- The Causes And Possible Solutions Of Juvenile Delinquency
- The History of the Juvenile Delinquency and the Process of the Juvenile Justice System in Malaysia
- The Issue of Juvenile Delinquency Among Girls in the United States
- What Is the Importance of Studying Juvenile Delinquency?
- Does Authoritative Parenting Impact Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Are the Factors of Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Are Juvenile Delinquency Causes and Solutions?
- What Type of Problem Is Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Can Family Structures Play a Role in Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Is the Concept of Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Do You Explain Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Does Poverty and the Environment Cause or Contribute to Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Are the Leading Causes of Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Does Family Contribute to Juvenile Delinquency?
- How the Juvenile Delinquency Impact Society?
- Why Is Juvenile Delinquency a Problem?
- What Factors Cause Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Is the Prevention of Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Are the Types of Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Is an Example of a Juvenile Delinquent?
- How Can We Prevent Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Does Juvenile Delinquency Affect the Community?
- How Does Juvenile Delinquency Affect Education?
- Why Is Juvenile Delinquency a Problem in Our Society?
- How Does Juvenile Delinquency Affect the Individual?
- What Is Another Name for Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Causes Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Does Birth Order Affect Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Is the Main Problem in Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Is the Difference Between Crime and Juvenile Delinquency?
- What Are Some Effects of Juvenile Delinquency?
- How Does Juvenile Delinquency Affect Social Life?
- What Is the Nature of Juvenile Delinquency?
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2023, November 9). 132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/juvenile-delinquency-essay-topics/
"132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." IvyPanda , 9 Nov. 2023, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/juvenile-delinquency-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2023) '132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 9 November.
IvyPanda . 2023. "132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/juvenile-delinquency-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/juvenile-delinquency-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "132 Juvenile Delinquency Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." November 9, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/juvenile-delinquency-essay-topics/.
- Crime Ideas
- Youth Titles
- Criminal Justice Essay Topics
- Youth Violence Research Topics
- CyberCrime Topics
- Adolescence Questions
- Childhood Essay Topics
- Hacking Essay Topics
- Child Development Research Ideas
- Parenting Research Topics
- Crime Prevention Research Topics
- Video Game Topics
- Cyber Bullying Essay Ideas
- Serial Killer Paper Topics
- Criminal Procedure Titles
Juvenile Delinquency Research Paper

This sample juvenile delinquency research paper features: 6300 words (approx. 21 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 76 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
Introduction
Juveniles placed in institutions, creation of the juvenile court, influence of positivism, the emergence of sociological theory, peers and gangs, the use of drugs and its relationship to delinquent behavior, biological explanations of delinquent behavior, psychological explanations of delinquent behavior, sociological explanations of delinquent behavior, is delinquent behavior rational, developmental paths of delinquency, human agency and delinquency across the life course, gender and delinquent behavior, delinquency prevention.
- Bibliography
Juvenile delinquency—crimes committed by young people—constitute, by recent estimates, nearly one fifth of the crimes against people and one-third of the property crimes in the United States. The high incidence of juvenile crime makes the study of juvenile delinquency vital to an understanding of American society. The Uniform Crime Reports, juvenile court statistics, cohort studies, self-report studies, and victimization surveys are the major sources of data used to measure the extent and nature of delinquent behavior. These forms of examination have generally agreed on the following findings:
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
- Juvenile delinquency is widespread in the United States.
- The majority of youths have committed some form of delinquency during their adolescent years.
- Three out of four juvenile arrests are arrests of males.
- Lower-class youths tend to commit more frequent and serious offenses than do higher-class youths.
- Minority youths, especially African American, tend to commit more serious delinquent acts than do white youths.
The number of juvenile homicides has been going down since the mid-1990s. Philip J. Cook and John Laub (1998) found that a changing context, as well as a more limited availability of guns, helped explain the reduced rate of juvenile homicides. Cook and Laub predicted that this changing context would continue to decrease youth homicides in the immediate future. Cook and Jens Ludwig (2004) and Anthony A. Braga (2003) also identified the high correlation between gun ownership and juvenile homicides.
The study of juvenile delinquency is full of conflicting positions. There are those who believe that this area of study should be limited to the theories of why juveniles become involved with crime. Others contend that the study of delinquency also ought to include the environmental influences on juvenile crime, such as the family, school, peer and gang participation, and drug involvements. Still others conclude that the study of delinquency should include the social control of juvenile crime, as well as causation theories and environmental influences.
The study of delinquency has clearly changed over the years. Throughout the twentieth century, delinquency studies became more interdisciplinary, more concerned about the integration with other theories, more methodologically sophisticated, and more focused on long-term follow-up of juveniles, sometimes for several decades. The importance of human agency and delinquency across the life course, both of which rose in theoretical importance during the 1990s, are generating considerable excitement in the early years of the twenty-first century.
The main concerns of this research paper are the origins of the study of delinquency; the emergence of sociological theory; the environmental influences on delinquency; the biological, psychological, and sociological theories that have influenced the field of delinquency; the interdisciplinary theories that are affecting the study of juvenile delinquency; and the prospects for future developments.
Origins of the Study of Juvenile Delinquency
What to do with wayward juveniles has long been a concern of American society. Before the end of the eighteenth century, the family was believed to be the source of cause of deviancy, and therefore, the idea emerged that perhaps the well-adjusted family could provide the model for a correctional institution for children. The house of refuge, the first juvenile institution, reflected the family model wholeheartedly; it was designed to bring the order, discipline, and care of the family into institutional life. The institution was to become the home, the peers, the siblings, the staff, and the parents (Rothman 1971).
The New York House of Refuge, which opened on January 1, 1825, with six girls and three boys, is generally acknowledged as the first house of refuge. Over the next decade, Bangor, Boston, Chicago, Cincinnati, Mobile, Philadelphia, and Richmond followed suit in establishing houses of refuge. Twenty-three schools were chartered in the 1830s and another 30 in the 1840s. Some houses of refuge were established by private agencies, some by state governments or legislatures, and some jointly by public authorities and private organizations (Rothman 1971).
One of the changes in juvenile institutions throughout the remainder of the nineteenth century was the development of the cottage system. Eventually called “training schools” or “industrial schools,” these institutions would house smaller groups of youths in separate buildings, usually no more than 20–40 youths per cottage. House parents, typically a man and his wife, constituted the staff in these cottages. Early cottages were log cabins; later cottages were constructed from brick or stone.
Barbara M. Brenzel’s (1983) study of the State Industrial School for Girls in Lancaster, Massachusetts, the first state reform school for girls in the United States, revealed the growing disillusionment in the mid- to late nineteenth century regarding training schools. Intended as a model reform effort, Lancaster was the first “familystyle” institution in the United States and embodied new theories about the reformation of youths. However, an “examination of a reform institution during the second half of the nineteenth century reveals the evolution from reformist visions and optimistic goals at mid-century to pessimism and ‘scientific’ determinism at the century’s close” (p. 1). Brenzel added that “the mid-century ideal of rehabilitative care changed to the principle of rigid training and custodial care by the 1880s and remained so into the early twentieth century” (pp. 4–5).
During the final decades of the nineteenth century, the Progressive Reformers viewed childhood as a period of dependency and exclusion from the adult world. To institutionalize childhood, they enacted a number of “child saving” laws, including child labor and compulsory school attendance laws. The juvenile court was viewed as another means to achieve unparalleled age segregation of children (Feld 1999). The following are a number of contextual factors that influenced the creation of this court.
Legal Context
The juvenile court was founded in Cook County (Chicago), Illinois, in 1899, when the Illinois legislature passed the Juvenile Court Act, and later that year was established in Denver, Colorado. The parens patriae doctrine provided a legal catalyst for the creation of the juvenile court, furnishing a rationale for use of informal procedures for dealing with juveniles and for expanding state power over the lives of children.
Political Context
In the Child Savers, Anthony Platt (1977) developed the political context of the origin of the juvenile court. He stated that the juvenile court was established in Chicago and later elsewhere because it satisfied several middleclass interest groups. He saw the juvenile court as an expression of middle-class values and of the philosophy of conservative political groups. In denying that the juvenile court was revolutionary, Platt charged that
the child-saving movement was not so much a break with the past as an affirmation of faith in traditional institutions. . . . What seemingly began as a movement to humanize the lives of adolescents soon developed into a program of moral absolutism through which youths were to be saved from movies, pornography, cigarettes, alcohol, and anything else which might possibly rob them of their innocence. (Pp. 98–99)
Economic Context
Platt (1977) argued that the behaviors that the child savers selected to be penalized—such as roaming the streets, drinking, fighting, engaging in sex, frequenting dance halls, and staying out late at night—were found primarily among lower-class children. Accordingly, juvenile justice from it inception, he contended, reflected class favoritism that resulted in the frequent processing of poor children through the system while middle- and upper-class children were more likely to be excused.
Sociocultural Context
The social conditions that were present during the final decades of the nineteenth century were the catalysts that led to the founding of the juvenile court. One social condition was that citizens became increasingly incensed by the treatment of children, especially the policy of jailing children with adults. Another social condition was that the higher status given middle-class women made them interested in exerting their newfound influence to improve the lives of children (Faust and Brantingham 1974).
These pressures for social change took place in the midst of a wave of optimism that swept through the United States during the Progressive Era, the period from 1899 to 1920. The emerging social sciences assured reformers that their problems with delinquents could be solved through positivism. According to positivism, youths were not responsible for their behavior and required treatment rather than punishment.
The concept of the juvenile court spread rapidly across the United States; by 1928, only two states did not have a juvenile court statute. In Cook County, the amendments that followed the original act brought the neglected, the dependent, and the delinquent together under one roof. The “delinquent” category comprised both status offenders and actual violators of criminal law.
Urban juveniles courts, especially, had clinics that provided psychological services for those youths referred to them by the juvenile court. Those who provided such services in the clinics were psychiatrists, clinical psychologists, or psychiatric social workers. The treatment modality that was frequently used was various versions of Freudian psychoanalysis. Typically, in a one-to-one relationship with a therapist, youths in trouble were encouraged to talk about past conflicts that caused them to express emotional problems through aggressive or antisocial behavior. The insights that youths gained from this psychotherapy were intended to help them resolve the conflicts and unconscious needs that drove them to crime. As a final step of psychotherapy, youths would become responsible for their behaviors.
From the second decade of the twentieth century, the Chicago School of Sociology developed a sociological approach to delinquency that differed greatly from that found in psychological positivism. The intellectual movement of social disorganization theory came out of this Chicago school. To William I. Thomas and Florian Znaniecki (1927), social disorganization reflected the influence of an urban, industrial setting on the ability of immigrant subcultures, particularly parents, to socialize and effectively control their children. S. P. Breckinridge and Edith Abbott (1970) contributed the idea of plotting “delinquency maps.” Frederick M. Thrasher (1927) viewed the youth gang as a substitute socializing institution whose function was to provide order, or social organization where there was none, or social disorganization.
Clifford R. Shaw and Henry D. McKay extended social disorganization by focusing specifically on the social characteristics of the community as a cause of delinquency. Their pioneering investigations established that delinquency varied in inverse proportion to the distance from the center of the city, that it varied inversely with socioeconomic status, and that delinquency rates in a residential area persisted regardless of changes in racial and ethic composition of the area (Reiss 1976).
Shaw and McKay viewed juvenile delinquency as resulting from the breakdown of social control among the traditional primary groups, such as the family and the neighborhood, because of the social disorganization of the community. Urbanization, rapid industrialization, and immigration processes contributed to the disorganization of the community. Thus, delinquent behavior became an alternative mode of socialization through which youths who grew up in disorganized communities were attracted to deviant lifestyles (Finestone 1976).
Shaw and McKay turned to ecology to show this relationship between social disorganization and delinquency. Shaw (1929) reported that marked variations of school truancy, juvenile delinquency, and adult criminality existed among different areas in Chicago. Shaw found that the nearer a given locality was to the center of the city, the higher its rates of delinquency and crime. Shaw further found that areas of concentrated crime maintained their high rates over a long period, even when the composition of the population changed markedly. Shaw and McKay (1931), in a study performed for the National Commission on Law Observance and Enforcement, reported that this basic ecological finding was also true for a number of other cities.
In their classic work Juvenile Delinquency and Urban Areas, Shaw and McKay (1942) developed these ecological insights in greater scope and depth. They studied males who were brought into the Cook County juvenile court on delinquency charges in 1900–1906, 1917–1923, and 1927–1933. Over this 33-year period, they discovered that the vast majority of the delinquent boys came from either an area adjacent to the central business and industrial areas or along two forks of the Chicago River. Then, applying Burgess’s concentric zone hypothesis of urban growth, they measured delinquency rates by zone and by areas within the zone. They found that in all three periods, the highest rates of delinquency were in Zone I (the central city), the next highest in Zone II (next to the central city), in progressive steps outward to the lowest in Zone V. Significantly, although the delinquency rates changed from one period to the next, the relationship among the different zones remained constant, even though in some neighborhoods the ethnic compositions of the population changed totally.
Shaw and McKay eventually refocused their analysis from the influence of social disorganization of the community to the importance of economics on high rates of delinquency. They found that the economic and occupational structure of the larger society was more influential in the rise of delinquent behavior than was the social life of the local community. They concluded that the reason members of lower-class groups remained in the inner-city community was less a reflection of their newness of arrival and their lack of acculturation to American institutions than it was a function of their class position in society (Finestone 1976).
Environmental Influences on Juvenile Delinquency
The importance of the Shaw and McKay tradition of the environment and community has long remained in the study of delinquency. An examination of the relationship between the family and delinquency, school performance and delinquency, drug use and delinquency, and participation in gangs and delinquency are generally found in studies of environmental influences on delinquency.
In the midst of conflicting findings about the relationship between delinquency and the family, the following observations have received wide support:
- Family conflict and poor marital adjustment are more likely to lead to delinquency than the structural breakup of the family (Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber 1986).
- Children who have delinquent siblings or criminal parents seem to be more prone to delinquent behavior than those who do not (Lauritsen 1993).
- Rejected children appear to be more prone to delinquent behavior than those who have not been rejected. Children who have experienced severe rejection are more likely to become involved in delinquent behavior than those who have experienced a lesser degree of rejection (Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber 1986).
- Consistency of discipline within the family appears to be important in deterring delinquent behavior (McCord, McCord, and Zola 1959).
- The rate of delinquency seems to increase with the number of unfavorable factors in the home. Thus, multiple handicaps within the family are associated with a higher probability of juvenile delinquency than are single handicaps (Loeber and Stouthamer-Loeber 1986).
Studies have found that the school is a critical context, or arena, of learning delinquent behavior. For example, Eugene Maguin and Rolf Loeber’s (1996) meta-analysis found that “children with lower academic performance offended more frequently, committed more serious and violent offenses, and persisted in their offending” (p. 15).
The extent of delinquency in the school, including vandalism, violence, gangs, and the use of drugs, has received considerable examination (Bartollas 2006). The consequences of dropping out of school have also been investigated (Jarjoura 1993). In addition, there have been a number of efforts to improve the quality of the school experience. The development of alternative schools, the process of designing effective school-based violenceprevention programs, and the process of developing more positive school-community relationships have been three of the most promising intervention strategies in the school setting (Bartollas 2006).
Researchers usually agree that most delinquent behavior, particularly more violent forms, takes place in groups, but they disagree on the quality of relationships within delinquent groups and on the influence of groups on delinquent behavior (Breckinridge and Abbott 1970; Piper 1985). There is still debate on several theoretical questions about groups and delinquency: How do delinquent peers influence each other? What causes the initial attraction to delinquent groups? What do delinquents receive from these friendships that result in continuing them?
Youth gangs represent one of the most serious forms of delinquency groups. Frederick Thrasher’s (1927) definition of gangs is still one of the best definitions:
A gang is an interstitial group originally formed spontaneously and then integrated through conflict. It is characterized by the following types of behavior: meeting face to face, milling, movement through space as a unit, conflict and planning. The result of this collective behavior is the development of tradition, unreflective, internal structure, esprit de corps, solidarity, morale, group awareness, and attachment to local territory. (P. 57)
Juveniles are involved in urban street gangs, where they are typically a minority of the membership. However, they make up nearly the total membership of emerging gangs that spread across the United States in the late 1980s and early 1990s. What has received considerable documentation is that law-violating behaviors increase with gang activities, that core members are involved in more serious delinquent acts than are fringe members, and that gang activities contribute to a pattern of violent behavior (Wolfgang, Thornberry, and Figlio 1987; Battin-Pearson et al. 1998; Miller 2001; Miller and Decker 2001).
Drug and alcohol use and juvenile delinquency have been identified as the most serious problem behaviors of juveniles. The good news is that substance abuse among adolescents has dropped significantly since the late 1970s. The bad news is that drug use has significantly increased among high-risk youths and is becoming commonly linked to juvenile delinquency (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention 2004; Johnston et al. 2004). In addition, more adolescents are selling drugs than ever before in the history of this nation. Moreover, the spread of AIDS within populations of drug users and their sex partners promises to make the problem of substance abuse even more difficult to control.
The Biological, Psychological, and Sociological Theories
A number of theoretical answers have been given to the continually raised question: Why do juveniles commit crime? Early in the twentieth century, biological and psychological causes of delinquent behavior received more attention. In the last two-thirds of the twentieth century, sociological explanations to delinquency behavior received greater support with students of delinquency.
The belief in a biological explanation for criminality has a long history. Early approaches attempted to pinpoint the source of criminality in physical anomalities (Lombroso-Ferrero 1972), genealogical deficiencies (Shah and Roth 1974), and theories of human somatotypes or body types (Glueck and Glueck 1956; Cortes 1972). More recently, research has stressed the interaction between the biological factors within an individual and the influence of the particular environment. Supporters of this form of biological positivism claim that what produces delinquent behavior, like other behaviors, is a combination of genetic traits and social conditions. Recent advances in experimental behavior genetics, human population genetics, knowledge of the biochemistry of the nervous system, experimental and clinical endocrinology and neurophysiology, and other related areas have led to more sophisticated knowledge of the way in which the environment and human genetics interact to affect the growth, development, and functioning of the human organism (Shah and Roth 1974; Fishbein 1990).
Psychological factors have long been popular in the positivist approach to the cause of juvenile delinquency because the very nature of parens patriae philosophy requires treatment of youths who are involved in various forms of delinquency. Psychoanalytic (Freudian) theory was first used with delinquents, but more recently other behavioral and humanistic schools of psychology have been applied to the problem of the illegal behaviors of juveniles. For example, some researchers in the 1980s and 1990s addressed the relationship between sensation seeking and crime (White, Labouvie, and Bates 1985; Fishbein 1990). Jack Katz’s (1988) Seductions of Crime conjectures that when individuals commit crime, they become involved in “an emotional process—seductions and compulsions that have special dynamics” (p. 9). It is this “magical” and “transformative” experience that makes crime “sensible,” even “sensually compelling.” James Q. Wilson and Richard Herrnstein’s (1985) Crime and Human Nature is another example of the influence of psychological factors on criminal or delinquent behaviors. They consider potential causes of crime and noncrime within the context of reinforcement theory, that is, the theory that behavior is governed by its consequent rewards and punishments, as reflected in the history of the individual. The rewards of crime, according to Wilson and Herrnstein (1985), are found in the form of material gain, revenge against an enemy, peer approval, and sexual gratification. The consequences of crime include pangs of conscience, disapproval of peers, revenge by the victim, and, most important, the possibility of punishment.
Sociological theories related to delinquency causation have been grouped in a number of ways; the following sections will group them in structural theories of delinquency causation, process theories of delinquency causation, reaction theories of delinquency causation, and integrated theories of delinquency causation.
Structural Theories of Delinquency Causation
The setting for delinquency, as proposed by social structural theories, is the social and cultural environment in which juveniles grow up or the subcultural groups in which they choose to become involved. Using official statistics as their guide, these analysts claim that such forces as social disorganization, cultural deviance, status frustration, and social mobility are so powerful that they induce youths, especially lower-class ones, to become involved in delinquent behavior. Strain theory is a structural theory that has been widely applied to explaining delinquent behavior. Robert K. Merton’s theory of anomie, Albert K. Cohen’s theory of delinquent subcultures, and Richard A. Cloward and Lloyd E. Ohlin’s opportunity theory are the most widely cited strain theories. Merton (1957) examined how deviant behavior is produced by different social structures. His primary aim was to discover how some social structures exerted pressure upon individuals in the society to engage in nonconforming rather than conforming behavior. Cohen’s (1955) thesis in his book Delinquent Boys: The Culture of the Gang was that lower-class youths are actually protesting against the goals of middle-class culture, but they experience status frustration, or strain, because they are unable to attain these goals. Cloward and Ohlin (1960) conceptualized success and status as separate strivings that can operate independently of each other. They portrayed delinquents who seek an increase in status as striving for membership in the middle class, whereas other delinquent youths try to improve their economic post without changing their class position.
Social Process Theories of Delinquency Causation
Social process theories of delinquency causation examine the interactions between individuals and the environment that influence them to become involved in delinquent behaviors. Differential association, drift, and social control theories became popular in the 1960s because they provided a theoretical mechanism for the translation of environmental factors into individual motivation. Edwin H. Sutherland’s (1947) formulation of differential association theory proposes that delinquents learn crime from others. His basic premise was that delinquency, like any other form of behavior, is a product of social interaction. In developing the theory of differential association, Sutherland contended that individuals are constantly being changed as they take on the expectations and points of view of the people with whom they interact in small, intimate groups. The process of becoming a delinquent, David Matza (1964) says, begins when an adolescent neutralizes himself or herself from the moral bounds of the law and drifts into delinquency. Drift, according to Matza, means that “the delinquent transiently exists in limbo between convention and crime, responding in turn to the demands of each, flirting now with one, now the other, but postponing commitment, evading decision. Thus he drifts between criminal and conventional action” (p. 28). Walter C. Reckless’s (1961) control theory is based on the assumption that strong inner containment and reinforcing external containment provide insulation against deviant behavior. Travis Hirschi’s (1967) Causes of Delinquency linked delinquent behavior to the quality of the bond an individual maintains with society, stating that “delinquent acts result when an individual’s bond to society is weak or broken” (p. 16). He argues that humans’ basic impulses motivate them to become involved in crime and delinquency unless there is reason for them to refrain from such behavior.
Social Reaction Theories of Delinquency Causation
Labeling theory, symbolic interactionst theory of delinquency, and conflict theory can be viewed as social reaction theories of delinquency causation because they focus on the role that social and economic groups and institutions have in producing delinquent behavior. The labeling perspective, whose peak of popularity was in the 1960s and 1970s, is based on the premise that society creates deviance by labeling those who are different from other individuals, when in fact they are different merely because they have been tagged with a deviant label part played by social audiences and their responses to the norm violations of juveniles (Tannenbaum 1938; Lemert 1951; Becker 1963; Triplett and Jarjoura 1994). Ross L. Matsueda (1992) and Karen Heimer (1995) have developed a symbolic interactionist theory of delinquency. This interactionist perspective “presupposes that the social order is the product of an ongoing process of social interaction and communication” (Matsueda 1992:1580). What is “of central importance is the process by which shared meanings, behavioral expectations, and reflected appraisals are built up in interaction and applied to behavior” (p. 1580). The conflict perspective views social control as an outcome of the differential distribution of economic and political power in society; thus, laws are seen as creation by the powerful for their own benefit (Shichor 1980). Conflict criminology has a great deal of variation; some theories emphasize the importance of socioeconomic class, some focus primarily on power and authority relationships, and others emphasize group and cultural conflict.
Integrated Theory
The theoretical development of integrated explanations of delinquency in the 1980s and 1990s has made a significant contribution to the understanding of delinquent behavior. Theory integration usually implies the combination of two or more existing theories on the basis of their perceived commonalities. Three of the better-known integrated theories are Michael R. Gottfredson and Travis Hirschi’s (1990) general theory of crime; Delbert S. Elliot, Suzanne A. Ageton, and Rachelle J. Canter’s (1979) integrated social process theory; and Terence P. Thornberry’s (1987) interactional theory.
In A General Theory of Crime, Gottfredson and Hirschi (1990) define lack of self-control as the common factor underlying problem behaviors. Thus, self-control is the degree to which an individual is “vulnerable to the temptations of the moment.” The other pivotal construct in this theory of crime is crime opportunity, which is a function of the structural or situational circumstances encountered by the individuals (Grasmick et al. 1993).
Elliott et al. (1979) offer “an explanatory model that expands and synthesizes traditional strain, social control, and social learning perspectives into a single paradigm that accounts for delinquent behavior and drug use” (p. 11). They argue that all three theories are flawed in explaining delinquent behavior. Integrating the strongest features of these theories into a single theoretical model, Elliott and colleagues theorize that there is a high probability of involvement in delinquent behavior when bonding to delinquent groups is combined with weak bonding to conventional groups. In Thornberry’s interaction theory of delinquency, the initial impetus toward delinquency comes from a weaning of the person’s bond to conventional society, represented by attachment to parents, commitment to school, and belief in conventional values. Associations with delinquent peers and delinquent values make up the social settling in which delinquency, especially prolonged serious delinquency, is learned and reinforced. These two variables, along with delinquent behavior itself, form a mutually reinforcing casual loop that leads toward increasing delinquency involvement over time (Thornberry 1987, 1989; Thornberry et al. 2003) (Table 1).
Table 1
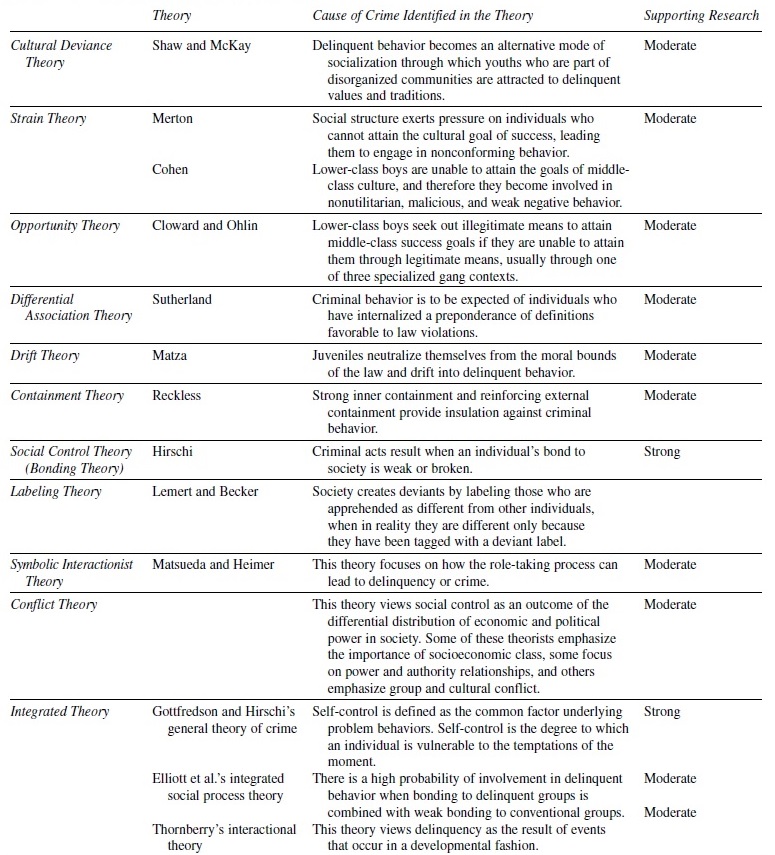
In the 1970s and 1980s, a variety of academic areas, including the sociology of deviance, criminology, economics, and cognitive psychology, began to view crime as the outcome of rational choices and decisions. The ecological tradition in criminology and the economic theory of markets, especially, have applied the notion of rational choice to crime.
Rational choice theory, borrowed primarily from the utility model in economics, was one area of intense interest during the 1980s and 1990s, especially within criminology, sociology, political science, and law. Rational choice theory, an extension of the deterrence doctrine of the classical school, includes incentives as well as deterrents and focuses on the calculation of payoffs and costs before delinquent and criminal acts are committed (Cornish and Clarke 1986; Akers 1990).
An analysis of delinquent behavior leads to the conclusion that antisocial behavior often appears rational and purposeful. Some delinquents clearly engage in delinquent behavior because of the low cost or risk of such behavior. The low risk comes from the parens patriae philosophy that is based on the presumption of innocence for the very young, as well as of reduced responsibility for those up to their midadolescence. Thus, in early adolescence, the potential costs of all but the most serious forms of delinquent behavior are relatively slight.
Conclusion and Prospects for the 21st Century
The development of both sociology and juvenile delinquency was influenced by the rise of the Chicago School of Sociology early in the twentieth century. With this common background, it is not surprising that juvenile delinquency has been so closely related to the discipline of sociology. Juvenile delinquency has been taught in the majority of sociology departments, as well as in many criminology or criminal justice programs in university settings and community colleges. The study of juvenile delinquency is further indebted to sociology because so many of the theories of delinquency causation are sociological theories of crime. Even though the study of juvenile delinquency has become interdisciplinary, sociological principles and theories remain critical in understanding the field of delinquency. Indeed, the new trends in delinquency, such as human agency and delinquency across the life course, are adapted from theoretical and empirical contributions largely taken from the field of sociology.
The prospects for the study of delinquency in the twenty-first century are vibrant and exciting.
Some of the emphases that will guide the study of delinquency are the examination of the development paths of delinquent behavior, a continued examination of human agency and delinquency across the life course, an investigation of the ways in which gender affects the study of delinquency, and a renewed search for more effective means of delinquency prevention.
One of the most exciting aspects about the study of juvenile delinquency today is the increasing number of developmental studies that have followed youth cohorts for a few years or even decades. One of the most widely respected of these studies is the research done by Terrie E. Moffitt and colleagues. For example, Moffitt, Donald R. Lynam, and Phil A. Silva’s (1994) examination of the neuropsychological status of several hundred New Zealand males between the ages of 13 and 18 found that poor neuropsychological scores “were associated with early onset of delinquency” but were “unrelated to delinquency that began in adolescence” (p. 277). Moffitt’s (1993) developmental theory views delinquency as proceeding along two developmental paths. On one path, children develop a lifelong path of delinquency and crime as early as age 3. They may begin to bite and hit shoplift and be truant at age 10, sell drugs and steal cars at age 16, rob and rape at age 22, and commit fraud and child abuse at age 30. These “life-course-persistent” (LCP) delinquents, according to Moffitt, continue their illegal acts throughout the conditions and situations they face. During childhood, they may also exhibit such neuropsychological problems as deficit disorders or hyperactivity and learning problems in schools.
On the other path, the majority of delinquents begin offending during the adolescent years and desist from delinquent behaviors around the 18th birthday. Moffitt refers to these youthful offenders as “adolescent-limited” (AL) delinquents. The early and persistent problems found with members of the LCP group are not found with the AL delinquents. Yet the frequency of offending and even the violence of offending during the adolescent years may be as high as the LCP. Moffitt notes that the AL antisocial behavior is learned from peers and sustained through peerbased rewards and reinforcements. AL delinquents continue in delinquent acts as long as such behaviors appear profitable or rewarding to them, but they have the ability to abandon those behaviors when prosocial styles become more rewarding (Moffitt 1993; Moffitt et al. 2001).
This enormous database of these developmental studies has contributed to the examination of such subjects as the importance of human agency in the lives of youths and later when they become adults and to delinquency or crime across the life course. Human agency refers to the importance given to juveniles who are not only acted upon by social influence and structural constraints but who make choices and decisions based on the alternatives that they see before them. Symbolic interactionism and life history studies have long acknowledged the importance of agency and rationality, and rational choice and routine activities research have more recently placed an importance on rationality in delinquent and criminal behavior. However, it has been the increased attention given to the life course in both sociology and delinquency studies that has sparked a dramatic resurgence of interest in agency in contemporary research.
The various perspectives on the life course relate individuals to their broader social context, but within the constraints of their world, individuals make choices among options that are available to them. It is these decisions that are so important in constructing their life course. Delinquency across the life course has been examined extensively by Robert J. Sampson and James H. Laub’s reanalysis of the Gluecks’ data (Sampson and Laub 1993; Laub and Sampson 2003). This perspective of delinquency and crime across the life course has been employed in studies of the effects of youth gangs, faulty family relationships, poor performance in school, drug use, and gender variations in youth offending (Bartollas 2006).
Moreover, this interactive process develops over the person’s life cycle. During early adolescence, the family is the most influential factor in bonding the youngster to conventional society and reducing delinquency. But as the youth matures and moves through middle adolescence, the world of friends, school, and youth culture becomes the dominant influence over behavior. Finally, as the person enters adulthood, commitment to conventional activities, and to family, especially, offers new avenues to reshape the person’s bond to society and involvement with delinquent behavior (Thornberry 1987; Krohn et al. 2001).
The study of delinquency has been traditionally shaped by male experiences and understanding of the social world (Daly and Chesney-Lind 1988). Carol Smart (1976) and Dorie Klein (1995) were two early criminologists to suggest that a feminist criminology should be formulated because of the neglect of the feminist perspective in classical delinquency theory. Feminist criminologists have been quick to agree that adolescent females have different experiences compared with adolescent males. They generally support that females are more controlled than males, enjoy more social support, are less disposed to crime, and have fewer opportunities for certain types of crimes (Mazerolle 1998).
However, feminist criminologists disagree on how the male-oriented approach to delinquency should be handled. One approach focuses on the question of generalizability. In research on samples that include males and females, a routine strategy for those who emphasize cross-gender similarities is to test whether the given theoretical constructs account for the offending of both groups and to pay little attention to how gender itself might intersect with other factors to create different meanings in the lives of males and females. Those who support this gender-neutral position have generally examined such subjects as the family, social bonding, social learning, delinquent peer relationships, and, to a lesser degree, deterrence and strain (Daly 1995).
In contrast, other feminist theorists argue that new theoretical efforts are needed to help us understand female delinquency and women’s involvement in adult crime. Eileen Leonard (1995), for example, questioned whether anomie, differential association, labeling, and Marist theories can be used to explain the crime patterns of women. She concluded that these traditional theories do not work for explaining female offending. Meda ChesneyLind’s (1989, 1995) application of the male-oriented theories to female delinquency has argued that existing delinquency theories are inadequate to explain female delinquency. She suggested that there is a need for a feminist model of delinquency, because a patriarchal context has shaped the explanations and handling of female delinquents and status offenders. What this means is that adolescent females’ sexual and physical victimizations at home and the relationship between these experiences and their crimes have been systematically ignored.
Delinquency prevention has a long but somewhat disappointing history. The best-known models of delinquency prevention have included the Boston’s Mid-city Project, Cambridge-Somerville Youth Study in Massachusetts, Chicago Area Projects, La Playa de Ponce in Puerto Rico, New York City Youth Board, and Walter C. Reckless and Simon Dinitz’s self-concept studies in Columbus, Ohio. A number of studies have examined the effectiveness of these delinquency-prevention programs and have generally found that few studies showed significant results (Lundman, McFarlane, and Scarpitti 1976; Lundman and Scarpitti 1978).
Beginning in the 1980s and continuing to the present, a number of new delinquency-prevention efforts have been established. The Blueprints for Violence Prevention, developed by the Center for the Study and Prevention of Violence at the University of Colorado–Boulder and supported by the Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, identified 11 model programs, as well as a number of promising violence-prevention and drug abuse programs. The identified model programs were Big Brothers Big Sisters of America; Bully Prevention Program; Functional Family Therapy (FFT); Incredible Years: Parent, Teacher, and Child Training Series; Life Skills Training; Midwestern Prevention Project; Multidimensional Treatment Foster Care (MTFC); Multisystemic Therapy (MST); Nurse-Family Partnership; Project Towards No Drug Abuse; and Promoting Alternative Thinking Strategies (Mihalic et al. 2004).
The popularity of delinquency-prevention programs, of course, is found in the realization that the most desirable strategy is to prevent delinquent behavior before it can occur. Even though delinquency-prevention programs have generally fallen short of controlling youth crime, there is every reason to believe that renewed efforts will be continued throughout the twenty-first century.
Bibliography:
- Akers, Ronald L. 1990. “Rational Choice, Deterrence, and Social Learning Theory in Criminology: The Path Not Taken.” Journal of Criminal Law and Criminology 81:653–76.
- Bartollas, Clemens. 2006. Juvenile Delinquency. 7th ed. Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Battin-Pearson, Sara R., Terence P. Thornberry, J. David Hawkins, and Marvin D. Krohn. 1998. “Gang Membership, Delinquent Peers, and Delinquent Behavior.” Juvenile Justice Bulletin, October .
- Becker, Howard S. 1963. New York: Free Press.
- Braga, Anthony A. 2003. “Serious Youth Gun Offenders and the Epidemic of Youth Violence in Boston.” Journal of Quantitative Criminology 19:33–54.
- Breckinridge, S. P. and Edith Abbott. 1970. The Delinquent Child and the Home. New York: Arno Press.
- Brenzel, Barbara. 1983. Daughters of the State. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2004. Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance-United States. Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
- Chesney-Lind, Meda. 1989. “Girls, Crime and Women’s Place.” Crime and Delinquency 35:5–29.
- Chesney-Lind, Meda. 1995. “Girls, Delinquency and Juvenile Justice: Toward a Feminist Theory of Young Women’s Crime.” Pp. 71–88 in The Criminal Justice System and Women, edited by B. R. Price and N. J. Sokoloff. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Cloward, Richard A. and Lloyd E. Ohlin. 1960. Delinquency and Opportunity: A Theory of Delinquent Gangs. Glencoe, IL: Free Press.
- Cohen, Albert K. 1955. Delinquent Boys: The Culture of the Gang. Glencoe, IL: Free Press.
- Cook, Philip J. and John Laub. 1998. “The Unprecedented Epidemic in Youth Violence.” Pp. 27–64 in Crime and Justice, edited by M. H. Moore and M. Tonry . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Cook, Philip J. and Jens Ludwig. 2004. “Does Gun Prevalence Affect Teen Gun Carrying After All?” Criminology 42:27–54.
- Cornish, Derek and Ronald V. Clarke, eds. 1986. The Reasoning Criminal: Rational Choice Perspectives on Offending. New York: Springer.
- Cortes, Juan B., with Florence M. Gatti. 1972. Delinquency and Crime: A Biopsychosocial Approach; Empirical, Theoretical, and Practical Aspects of Criminal Behavior. New York: Seminar Press.
- Daly, Kathleen. 1995. “Looking Back, Looking Forward: the Promise of Feminist Transformation. Pp. 447–48 in The Criminal Justice System and Women, edited by B. R. Price and N. J. Sokoloff. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Daly, Kathleen and Meda Chesney-Lind. 1988. “Feminism and Criminology?” Justice Quarterly 5:497–538.
- Elliott, Delbert S., Suzanne S. Ageton, and Rachelle J. Canter. 1979. “An Integrated Theoretical Perspective on Delinquent Behavior.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 16:3–27.
- Faust, Frederic and Paul J. Brantingham, eds. 1974. Juvenile Justice Philosophy. Paul, MN: West.
- Feld, Barry. 1999. Bad Kids: Race and the Transformation of the Juvenile Court. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Finestone, Harold. 1976. Victims of Change: Juvenile Delinquents in American Society. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press.
- Fishbein, Diana. H. 1990. “Biological Perspectives in Criminology.” Criminology 28:27–72.
- Glueck, Nelson and Eleanor Glueck. 1956. Physique and Delinquency. New York: Harper & Row.
- Gottfredson, Michael R. and Travis Hirschi. 1990. A General Theory of Crime. Palo Alto, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Grasmick, Harold G., Charles R. Tittle, Robert J. Bursik Jr., and Bruce J. Arneklev. 1993. “Testing the Core Empirical Implications of Gottfredson and Hirschi’s General Theory of Crime.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 30:5–29.
- Heimer, Karen. 1995. “Gender, Race, and the Pathways to Delinquency.” Pp. 140–53 in Crime and Inequality, edited by J. Hagen and R. D. Peterson . Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press.
- Hirschi, Travis. 1967. Causes of Delinquency. Berkeley: California University Press.
- Jarjoura, G. Roger. 1993. “Does Dropping Out of School Enhance Delinquent Involvement? Results from a Large-Scale National Probability Sample.” Criminology 31:149–71.
- Johnston, L. D., P. M. O’Malley, J. G. Bachman, and J. E. Schulenberg. 2004. Monitoring the Future: Monitoring the Future National Results on Adolescent Drug Use: Overview of Key Findings. Bethesda, MD: National Institute of Drug Abuse.
- Katz, Jack. 1988. Seductions of Crime: Moral and Sensual Attractions in Doing Evil. New York: Basic Books.
- Klein, Dorie. 1995. “The Etiology of Female Crime:A Review of the Literature.” Pp. 30–53 in The Criminal Justice System and Women, edited by B. R. Price and N. J. Sokoloff. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Krohn, Marvin D., Terence P. Thornberry, Craig Rivera, and Marc Le Blanc. 2001. “Later Delinquency Careers.” Pp. 67–93 in Child Development, edited by R. Loeber and D. P. Farrington. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Laub, James H. and Robert J. Sampson. 2003. Shared Beginnings, Divergent Lives Delinquent Boys to Age 70. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Lauritsen, Janet L. 1993. “Sibling Resemblance in Juvenile Delinquency: Findings from a National Youth Survey.” Criminology 31:387–409.
- Lemert, Edwin M. 1951. Social Pathology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Leonard, Eileen. 1995. “Theoretical Criminology and Gender.” Pp. 55–70 in The Criminal Justice System and Women, edited by B. R. Price and N. J. Sokoloff. New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Loeber, Rolf and M. Stouthamer-Loeber. 1986. “Family Factors as Correlates and Predictors of Juvenile Conduct Problems and Delinquency.” Pp. 29–149 in Crime and Justice: An Annual Review of Research, edited by M. Tonry and N. Morris. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Lombroso-Ferrero, Gina. 1972. Criminal Man According to Classification of Cesare Lombroso. Montclair, NJ: Patterson Smith.
- Lundman, Richard J., Paul T. McFarlane, and Frank R. Scarpitti. 1976. “Delinquency Prevention: A Description and Assessment of Projects Reported in the Professional Literature.” Crime and Delinquency 22:297–309.
- Lundman, Richard J. and Frank R. Scarpitti. 1978. “Delinquency Prevention: Recommendations for Future Projects.” Crime and Delinquency 24:207–20.
- Maguin, Eugene and Rolf Loeber. 1996. “Academic Performance and Delinquency.” Pp. 145–264 in Crime and Justice: A Review of Research, 20, edited by M. Tonry. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Matsueda, Ross. L. 1992. “Reflected Appraisals: Parental Labeling, and Delinquency: Specifying a Symbolic Interactionist Theory.” American Journal of Sociology 97:1577–611.
- Matza, David. 1964. Delinquency and Drift. New York: John Wiley.
- Mazerolle, Paul. 1998. “Gender, General Strain, and Delinquency:An Empirical Examination.” Justice Quarterly 15:65–91.
- McCord, W. J., J. McCord, and Irvin Zola. 1959. The Origins of Crime. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Robert K. 1957. Social Theory and Social Structure. 2d ed. New York: Free Press.
- Mihalic, Sharon, Katerine Irwin, Abigail Fagan, Diane Ballard, and Delbert Elliott. 2004. Blueprints for Violence Prevention. Washington, DC: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention.
- Miller, Jody. 2001. One of the Guys: Girls, Gangs, and Gender. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Miller, Jody and Scott Decker. 2001. “Young Women and Gang Violence: Gender, Street Offending, and Violent Victimization in Gangs.” Justice Quarterly 18:115–39.
- Moffitt, Terrie. 1993. “Adolescent-Limited and Life-CoursePersistent Antisocial Behavior: A Developmental Taxonomy.” Psychological Review 100:674–701.
- Moffitt, Terrie, Donald R. Lynam, and Phil A. Silva. 1994. “Neuropsychological Tests Predicted Persistent Male Delinquency.” Criminology 32:277–300.
- Moffitt, Terrie E., Avshalom Caspi, Michael Rutter, and Phil A. Silva. 2001. Sex Differences in antisocial behavior. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Piper, Elizabeth S. 1985. “Violent Offenders: Lone Wolf or Wolfpack.” Presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Criminology, San Diego, CA.
- Platt, Anthony. 1977. The Child Savers. 2d ed. Chicago, IL: Chicago University Press.
- Reckless, Walter C. 1961. “A New Theory of Delinquency and Crime.” Federal Probation 24:42–46.
- Reiss, Albert J., Jr. 1976. “Setting the Frontiers of a Pioneer in American Criminology: Henry McKay.” Pp. 64–88 in Delinquency: Crime and Society, edited by J. F. Short . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Rothman, David J. 1971. Discovery of the Asylum. Boston, MA: Little, Brown.
- Sampson, Robert J. and James H. Laub. 1993. Crime in the Making: Pathways and Turning Points through Life. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
- Shah, Saleem A. and Loren H. Roth. 1974. “Biological and Psychophysiological Factors in Criminality.” Pp. 101–73 in Handbook of Criminology, edited by D. Glaser . Chicago, IL: Rand McNally.
- Shaw, Clifford R. 1929. Delinquent Areas. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Shaw, Clifford R. and Henry D. McKay. 1931. Social Factors in Juvenile Delinquency. Washington, DC: National Commission on Law Observance and Enforcement.
- Shaw, Clifford R. and Henry D. McKay. 1942. Juvenile Delinquency and Urban Areas. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Smart, Carol. 1976. Women, Crime and Criminology: A Feminist Critique. Boston, MA: Routledge & Kegan Paul.
- Shichor, David. 1980. “The New Criminology: Some Critical Issues.” British Journal of Criminology 20:1–19.
- Sutherland, Edwin H. 1947. Principles of Criminology. 10th ed . Philadelphia, PA: J. P. Lippincott.
- Frank. 1938. Crime and the Community. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Thomas, William I. and Florian Znaniecki. 1927. The Polish Peasant in Europe and America. 5 vols. New York: Knopf.
- Thornberry, Terence P. 1987. “Toward an Interactional Theory of Delinquency.” Criminology 25:863–91.
- Thornberry, Terence P. 1989. “Reflections on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Theoretical Integration.” Pp. 51–60 in Theoretical Integration in the Study of Deviance and Crime: Problems and Prospects, edited by S. Messner, M. Krohn, and A. Liska . Albany: State University of New York Press.
- Thornberry, Terence P., Marvin D. Krohn, Alan J. Lizotte, Carolyn A. Smith, and Kimberly Tobin. 2003. Gangs and Delinquency in Developmental Perspective. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press.
- Thrasher, Frederick. 1927. The Gang: A Study of 1313 Gangs in Chicago. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Triplett, Ruth Ann and G. Roger Jarjoura. 1994. “Theoretical and Empirical Specification of a Model of Informal Labeling.” Journal of Quantitative Criminology 10:241–76 .
- White, Herlene Raskin, Erich W. Labouvie, and Marsha E. Bates. 1985. “The Relationship between Sensation Seeking and Delinquency: A Longitudinal Analysis.” Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 22:195–211.
- Wilson, James Q. and Richard J. Herrnstein. 1985. Crime and Human Nature. New York: Simon & Schuster.
- Wolfgang, E. Marvin, Terence P. Thornberry, and Robert F. Figlio. 1987. From Boy to Man: From Delinquency to Crime. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


COMMENTS
Leon A. Carley, Questionnaire on Delinquency in Youths and Adults and Its Treatment by the Courts, 6 J. Am. Inst. Crim. L. & Criminology 408 (May 1915 to March 1916) This Article is brought to you for free and open access by Northwestern University School of Law Scholarly Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Journal of Criminal Law ...
Abstract and Figures. The occurrence of juvenile delinquency has become a major societal concern caused by various factors both at the micro and macro levels. This study aims to assess the ...
adequately studied. The research questions focused on identifying which of the city's current programs are perceived as being effective or ineffective in reducing juvenile delinquency and why so. The participants were 15 adults between the ages of 21 years old through 35 years old who were a part of the juvenile justice system as youth.
J-SORRAT-II Juvenile Sexual Offense Recidivism Risk Assessment Tool-II LGBTQ Lesbian, Gay, Bisexual, Transgender, Queer or Questioning MDFT Multidimensional Family Therapy MTF Monitoring the Future NCAR North Carolina Assessment of Risk OJJDP Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention
This study examines trends in juvenile delinquency in the United States in relation. to poverty rates, unemployment rates, adult crime rates, and school dropout rates. Using. secondary data on delinquency and the above mentioned influences, this study addresses. the following four research questions: RQ1.
EXPLORING JUVENILE DELINQUENCY AND THE LINK TO LITERACY by Rachael S. Davis Juvenile delinquency and education are a subject that lacks streamlined research for many reasons. According to a report by Sawyer and Wagner (2020) of the Prison Policy Initiative, each institution and system collects its own data for its own purposes.
juvenile delinquency. Law enforcement agencies have been involved in nearly 1.1 million juvenile delinquency cases (Ryan et al., 2013). Furthermore, reported law enforcement data reflected those juvenile offenders were responsible for 15% of all violent crimes and 24% of all property crimes (Ryan et al., 2013).
Juvenile delinquency is a habit of committing criminal offenses by an adolescent or young person who has not attained 18 years of age and can be held liable for his/her criminal acts. ... A total sample 360 children (177 chidren at risk, or have experience maltreatment and 183 children in conflict with law) To develop a predictive model to ...
The Adolescent Delinquency Questionnaire--Adapted Version (ADQ; Negriff & Trickett, 2010) was developed to measure participants' self-reported delinquent behavior. This questionnaire was adapted from Huizinga and Morse's (1986) measure for a study examining the relationship between pubertal timing and delinquent behavior across two time points in a sample of 303 maltreated and 151 comparison ...
Juvenile offending and anti-social behaviour are enormous societal concerns. This broad-reaching volume summarizes the current evidence on prevention, diversion, causes, and rates of delinquency, as well as assessment of risk and intervention needs. A distinguished cast of contributors from law, psychology, and psychiatry describe what we know ...
Delinquent peer affiliations are one of the. strongest proximal predictors of child delinquency (Ferguson & Meehan, 2011). Rankin and. Quane (2002) also found that neighborhood characteristics were related to peer deviance. Leventhal and Brooks-Gunn's (2004) study was based on social organization theory.
CHILDHOOD TRAUMA AND JUVENILE DELINQUENCY: DOES TIMING OF POSTTRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER MEDIATE THE ASSOCIATION? A Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Arts and Sciences of Georgetown University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Public Policy in Public Policy By Erin Lally Thompson, B.A.
Open Access Library Journal 2019, Volume 6, e5904 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Print: 2333-9705 DOI: 10.4236/oalib.1105904 Dec. 12, 2019 1 Open Access Library Journal
Questionnaire Juvenile Delinquency School Students - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This study seeks to understand students' perceptions of juvenile delinquency among their peers through a questionnaire. Juvenile delinquencies mentioned include robbery, vandalism, rape, weapon possession, and drug/alcohol violations.
To evaluate the central thesis of the TRD Model, ... social and environmental risk factors and juvenile delinquency behavior in a sample of 211 adolescents from the province of Córdoba, Argentina. ... there may be methodological questions about the homogeneity of the sample. In principle, the sampling in the general population tried to resolve ...
The main objective of this study was to explore juvenile delinquent involvement among former young male juvenile delinquents. A phenomenology qualitative research design was utilised to explore ...
2.2 Factors behind delinquency 14 2.3 Perception of fairness 14 2.4 Positive youth development 15-16 2.5 Conclusion 16 Chapter-III Method of the study and results 17-27 3.1 Method of the study 18 3.2 Results 19 3.3 Factors underlying juvenile delinquency 19 3.4 Demographics characteristics of the sample 19-21
Sample Thesis Juvenile Delinquency - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. sample thesis juvenile delinquency
1.3 Robbery. The crime of robbery involves (1) the taking of the property of another (2) from his or her person or in their presence (3) by violence, intimidation or threat (4) with the intent to deprive them of it permanently. According to participants accounts, two (2) of them recalls committing robbery.
The Problem of Juvenile Delinquency. The addition of family context to the existing perception of adolescent crimes could be used to explore the core reasons for the crimes and to define possible methods for the prevention of juvenile crimes. The […] The Cognitive Theory in Juvenile Delinquency.
This study examines social me dia's quantitative effect on juvenile criminality. The researcher intends to quantify how. social media usage affects juvenile delinquency. The research will examine ...
This sample juvenile delinquency research paper features: 6300 words (approx. 21 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 76 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help.
Now downloading t13079_Browne.pdf... Back . Cookie settings