- Key Differences
Know the Differences & Comparisons

Difference between Biography and Autobiography

Both of these two presents the view of, what happened in the past where the author lived. These are non-fiction books, written in chronological order, tells a story about the person who made a significant contribution in a specific field. Many think that the two writing forms are one and the same thing, but there are noticeable difference between the two, that are presented in the given article.
Content: Biography Vs Autobiography
Comparison chart, definition of biography.
A biography also referred as ‘bio’ is a detailed account of a person’s life written or produced by another person. It gives an elaborate information regarding the birthplace, educational background, work, relationships and demise of the person concerned. It presents the subject’s intimate details about life, focusing on the highs and lows and analysing their whole personality.
A biography is usually in the written form but can also be made in other forms of a music composition or literature to film interpretation.
It is the recreation of the life of an individual composed of words by another person. The author collects every single detail about the subject and presents those facts in the biography, which are relevant and interesting, to engross the readers in the story.
Definition of Autobiography
An autobiography is the life sketch of a person written by that person himself or herself. The word auto means ‘self.’ Therefore, autobiography contains all the elements of a biography but composed or narrated by the author himself. He/She may write on their own or may hire ghostwriters to write for them.
An autobiography presents the narrator’s character sketch, the place where he is born and brought up, his education, work, life experiences, challenges, and achievements. This may include events and stories of his childhood, teenage, and adulthood.
Key Differences Between Biography and Autobiography
The difference between biography and autobiography are discussed in detail in the following points:
- Biography is a detailed account of a person’s life written by someone else, while an autobiography is written by the subject themselves.
- Biography can be written with (authorised) or without permission (unauthorised) from the person/heir’s concerned. Therefore, there are chances of factual mistakes in the information. On the other hand, autobiographies are self-written and therefore doesn’t require any authorization.
- Biographies contain information that is collected over a period of time from different sources and thus, it projects a different outlook to the readers. On the other hand, autobiographies are written by the subject themselves, therefore, the writer presents the facts and his thinking in his own way, thus providing an overall narrow and biased perspective to the readers.
- In an Autobiography, the author uses the first narrative like I, me, we, he, she, etc. This, in turn, makes an intimate connection between the author and the reader since the reader experience various aspects as if he/she is in that time period. As opposed a biography is from a third person’s view and is much less intimate.
- The purpose of writing a biography is to introduce and inform the readers about the person and his life whereas an autobiography is written in order to express, the life experiences and achievements of the narrator.
Video: Biography Vs Autobiography
There are several autobiographies which are worth mentioning like ‘The Story of My Life’ by Helen Keller, ‘An Autobiography’ by Jawaharlal Nehru, ‘The Diary of a Young Girl’ by Anne Frank, ‘Memoirs of the Second World War’ by Winston Churchill, ‘Wings of Fire’ by A. P. J. Abdul Kalam and much more.
Examples of some famous biographies are- Tolstoy: A Russian Life by Rosamund Bartlett, His Excellency: George Washington by Joseph J. Ellis, Einstein: The Life and Times by Ronald William Clark, Biography of Walt Disney: The Inspirational Life Story of Walt Disney – The Man Behind “Disneyland” by Steve Walters, Princess Diana- A Biography Of The Princess Of Wales by Drew L. Crichton.
You Might Also Like:

May 4, 2017 at 12:13 am
This website is amazing because my class is reading over it
Joseph says
February 21, 2023 at 8:18 am
I have gotten the answers I really needed at this site
Mukesh Kumar Guar says
February 12, 2019 at 1:52 pm
Little and complete information I was looking for.
Abdul Rahim Muhammad Latif says
February 26, 2019 at 6:09 pm
nice wake well done
Hanady says
October 18, 2019 at 5:51 pm
Amazing! Very helpful and useful. Thank you!
May 7, 2023 at 6:47 am
your article is very well explained
Manish Bhati says
June 21, 2023 at 11:51 am
Great explanation by Surbhi S, it clears confusion between biographies and autobiographies.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Biography vs Autobiography: Similarities and Differences

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A biography is an account of someone’s life story that is written by an author who is not the subject of the nook. An autobiography, on the other hand, involves an individual narrating their own life experiences.
The differences between biographies and autobiographies relate most prominently to the authorhship:
- Autobiography: When you read an autobiography, you’re getting the author’s own interpretation of their life.
- Biography: When you read a biography, you experience the subject’s life through someone else’s lens (Schiffrin & Brockmeier, 2012).
Biography vs Autobiography
1. biography.
A biography is a detailed account of a person’s life, scripted by an author who is not the person who is featured in the text itself.
This type of life story focuses both on factual events in the person’s life, such as birth, education, work, and death, but often also delves into personal aspects like experiences, relationships, and significant achievements.
It may also weave-in cultural and contextual factors that help illuminate the person’s motivations and core values .
Origins of Biographies
The concept of biography as a literary genre dates back to antiquity. Such works were primarily used to capture the lives of dignified individuals, mainly rulers and war heroes.
Suetonius’s Lives of the Caesars and Plutarch’s Parallel Lives are landmark examples from this ancient period (Sweet, 2010).
The popularity of biographical works only grew in the ensuing centuries, and they became a prominent part of many cultures’ literary traditions.
Into the 18th century and during the Enlightenment, biographies began to present a more balanced portrayal of the subject. They would present both their strengths and flaws, providing a holistic perspective on the subject.
Dr. Samuel Johnson’s compilation of English poets biographies, Lives of the Most Eminent English Poets (1779-1781) ushered in a new era of biography writing by focusing on examining human nature (Ditchfield, 2018).
In the modern era, the genre has evolved and broadened, encompassing a diverse range of figures from all walks of life – there’s a biography in every niche imaginable, with each offering readers an in-depth exploration of their lives, their struggles, and their triumphs.
This demonstrates the enduring appeal of biographies and their value in providing snapshots of history through individual lenses.
Key Characteristics of Biographies
Examples of biographies.
Title: The Lives of the Most Eminent English Poets Author: Dr. Samuel Johnson Description: Dr. Johnson’s work profiles the lives of 52 poets from the 17th and 18th centuries, including John Milton and Alexander Pope. He critiques not just the works, but also explores their personal lives and the sociopolitical contexts of their times (Johnson, 1781). Johnson’s study is invaluable for its integrated historic and biographic approach.
Title: The Life of Samuel Johnson Author: James Boswell Description: This work by Boswell explores, in great depth, the life of his friend and mentor, Dr. Samuel Johnson. The biography offers a compelling portrayal of Dr. Johnson’s life, character, eccentricities, and intellectual prowess (Boswell, 1791). Boswell’s vivid account creates a near-physical presence of Johnson to the readers, making it one of the greatest biographies in English literature.
Title: The Rise of Theodore Roosevelt Author: Edmund Morris Description: In this Pulitzer Prize-winning biography, Morris chronicles the early life of Theodore Roosevelt until his ascension to the U.S presidency. The work brilliantly captures Roosevelt’s extraordinary career and his transformation from a frail asthmatic boy into a robust and vigorous leader (Morris, 1979). Morris accurately represents Roosevelt’s indomitable spirit, making it an engaging and educational read.
Title: Steve Jobs Author: Walter Isaacson Description: This comprehensive biography provides a deep-dive into the life and career of Steve Jobs, the co-founder of Apple. Isaacson had unparalleled access to Jobs and those closest to him, thus presenting an intimate and detailed account. He explores Jobs’ professional endeavors as well as his personal life, revealing his ambition, intensity, and visionary mind that revolutionized several high-tech industries (Isaacson, 2011).
Title: Alexander Hamilton Author: Ron Chernow Description: Ron Chernow provides a sweeping narrative of one of America’s most compelling founding fathers, Alexander Hamilton. Chernow combines extensive research with a flair for storytelling, charting Hamilton’s evolution from an orphan into a political genius. The book sheds light on Hamilton’s crucial role in the formation of the United States’ financial system and his political ideologies (Chernow, 2004).
2. Autobiography
An autobiography is a self-written record of someone’s own life. It is a personal narrative in which the author writes about their life from their own perspective.
Autobiographies are usually centered around the author’s personal experiences, including key milestones, challenges, and achievements (Eakin, 2015).
They’re also often a defense of the person’s perspective (especially in political autobiographies) or insight into their thought processes, which can make them very intimate.
Origins of Autobiographies
The term ‘autobiography’ was first used deprecatingly by William Taylor in 1797 in the English periodical The Monthly Review, when he suggested the word as a hybrid but condemned it as ‘pedantic’.
Pioneering examples of the genre form include Thomas De Quincey’s Confessions of an English Opium-Eater (1821) and the memoirs by veterans of the Napoleonic Wars (Lejeune, 2016).
However, apart from these early instances, autobiographies have been composed by a wide array of individuals from history.
In the early 20th century, the genre witnessed major transformations, and autobiographies started to cover a broader spectrum of experiences, including trauma, struggles, and successes.
‘Black Boy’ by Richard Wright, for instance, shares the author’s experiences with racism and his journey towards developing a literary career (Wright, 1945).
This was followed by a host of autobiographies by public figures sharing their diverse stories, such as Ernest Hemingway’s ‘A Moveable Feast’, depicting his days as a struggling young writer in Paris (Hemingway, 1964).
Autobiography as a genre has continued to evolve over the years, and a variety of forms have emerged to communicate individual experiences globally.
As history has progressed, we see more and more people with diverse perspectives sharing their stories, broadening our understanding of the human experience (Smith & Watson, 2010).
Key Characteristics of Autobiographies
Examples of autobiographies.
Title: Long Walk to Freedom Author: Nelson Mandela Description: “Long Walk to Freedom” provides an in-depth exploration of ex-President Nelson Mandela, his political journey, and his stand against apartheid in South Africa. The biography offers a unique perspective into Mandela’s noble character, his indomitable spirit, and his commitment to justice when faced with grave adversities (Mandela, 1995). Mandela serves as one of our times’ great moral and political leaders through this biography.
Title: The Diary of a Young Girl Author: Anne Frank Description: This biography provides a startling firsthand account of a young Jewish girl named Anne Frank, who with her family, hid from the Nazis in Amsterdam during World War II. Her diary entries offer profound insights into the fear, hope, and resilience she demonstrated during her two years in hiding (Frank, 1947). Frank’s posthumous biographical record serves as a reminder of the injustices of the past and as a symbol of endurance in the face of oppression.
Title: I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings Author: Maya Angelou Description: This moving autobiography charts Maya Angelou’s early life, from experiencing racial discrimination in the South to becoming the first black streetcar conductor in San Francisco. Angelou portrays her journey of self-discovery and overcoming traumatic experiences, including racial prejudice and personal trauma, with remarkable strength and grace. Her story is one of resilience, and it speaks powerfully about finding one’s voice (Angelou, 1969).
Title: Night Author: Elie Wiesel Description: “Night” is Wiesel’s personal account of his experiences in Nazi concentration camps during World War II with his father. This heartbreaking narrative describes not only physical hardship and cruel atrocities but also examines the loss of innocence and the struggle to maintain faith in humanity. It stands as a testament to human resilience in the face of unimaginable horror (Wiesel, 1960).
Title: Dreams from My Father Author: Barack Obama Description: In this engaging memoir, the 44th President of the United States narrates the story of his diverse background and early life. The narrative extends from his birth in Hawaii to his first visit to Kenya, from dealing with racial identity to self-discovery. “Dreams from My Father” not only provides personal insights about Obama’s life and values but also discusses issues of race, identity, and purpose (Obama, 1995).
Similarities and Differences Between Biographies and Autobiographies
While both biographies and autobiographies are excellent sources of information and entertainment about significant figures in history (or the present!), they serve different purposes. By knowing the different purposes of each, we can develop stronger media literacy , understanding what the intention of the author is, and how we should approach the text.
Angelou, M. (1969). I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings . Random House.
Baker, J., Davis, E., & Thompson, K. (2013). Reflection and Emotions in Autobiography . Chicago University Press.
Boswell, J. (1791). The Life of Samuel Johnson . J.R. Taylor.
Brown, J., & Brown, S. (2018). Thematic Focus in Autobiography Writing . Princeton University Press.
Chernow, R. (2004). Alexander Hamilton . Penguin Books.
Ditchfield, S. (2018). Extracting the Domestic from the Didactic: Transmission and Translation of the Sacred in The Lives of the Ancient Fathers (1672–1675). Church History and Religious Culture, 98 (1), 28-50.
Eakin, P. J. (2015). How Our Lives Become Stories: Making Selves . Cornell University Press.
Frank, A. (1947). The Diary of a Young Girl . Contact Publishing.
Hemingway, E. (1964). A Moveable Feast . Charles Scribner’s Sons.
Isaacson, W. (2011). Steve Jobs . Simon & Schuster.
Johnson, M., & Johnson, S. (2017). A Comprehensive Guide to Biography Writing . New York: Penguin.
Johnson, S. (1781). The Lives of the Most Eminent English Poets . Printed by C. Bathurst, J. Buckland [and 28 others in London].
Jones, B. (2015). The Art of Writing Biographies: An Objective Approach . Oxford University Press.
Lejeune, P. (2016). On Autobiography . University of Minnesota Press.
Mandela, N. (1995). Long Walk to Freedom: The Autobiography of Nelson Mandela . Macdonald Purnell.
Miller, R. (2014). The Self as the Subject: Autobiography Writing . Stanford University Press.
Morris, E. (1979). The Rise of Theodore Roosevelt . Coward, McCann & Geoghegan.
Obama, B. (1995). Dreams from My Father: A Story of Race and Inheritance . Crown Publishing Group.
Schiffrin D., & Brockmeier J. (2012). Narrative Identity and Autobiographical Recall. Royal Institute of Philosophy Supplements, 70 , 113-144.
Smith, J., Davis, M., & Thompson, S. (2012). Third Party Narratives: An Exploration of Biography Writing . Cambridge University Press.
Smith, S., & Watson, J. (2010). Reading Autobiography: A Guide for Interpreting Life Narratives . University of Minnesota Press.
Sweet, R. (2010). Biographical Dictionaries and Historiography. Bibliothèque d’Humanisme et Renaissance, 72 (2), 355–368.
Wiesel, E. (1960). Night . Hill & Wang.
Williams, T. (2019). The Importance of Facts in Biographies . HarperCollins.
Wright, R. (1945). Black Boy: A Record of Childhood and Youth . Harper & Brothers.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
autobiography
Definition of autobiography
Examples of autobiography in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'autobiography.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
auto- + biography , perhaps after German Autobiographie
1797, in the meaning defined above
Phrases Containing autobiography
- semi - autobiography
Dictionary Entries Near autobiography
autobiographist
Cite this Entry
“Autobiography.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/autobiography. Accessed 29 Oct. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of autobiography, more from merriam-webster on autobiography.
Thesaurus: All synonyms and antonyms for autobiography
Nglish: Translation of autobiography for Spanish Speakers
Britannica English: Translation of autobiography for Arabic Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about autobiography
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
How to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), plural and possessive names: a guide, the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', why is '-ed' sometimes pronounced at the end of a word, what's the difference between 'fascism' and 'socialism', popular in wordplay, weird words for autumn time, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, 10 words from taylor swift songs (merriam's version), 9 superb owl words, 15 words that used to mean something different, games & quizzes.

Autobiography vs Biography: Differences and Similarities

So you want to learn more about your favorite influential figure. Should you read an autobiography or a biography about them?
It depends on what you’re looking for!

Need A Nonfiction Book Outline?
In this guide, we’ll explain autobiography vs biography and help you choose which one you want to read. We’ll also touch on where memoirs fit in with these genres. Let’s dive in!
The similarities between biographies and autobiographies
Both biographies and autobiographies are written accounts of a person’s life. They typically recount the person’s life experiences, challenges, and accomplishments.
Usually, each of these genres is written in a narrative style. In other words, it uses storytelling techniques to convey information about its subject.
Autobiographies and biographies both feature context about the subject’s life by discussing the time in which the subject lived (or is living), the culture and location in which they live(d), and more.
Like any good story, the best biographies and autobiographies often feature narratives about trials that are overcome and lessons that are learned. They may also focus on the influence and impact of the book’s subject.
Difference between biography and autobiography
The biggest difference between an autobiography and a biography is that an autobiography is written by the subject of the book about their own life, while a biography is written by another person.
For example, actress Lucille Ball wrote an autobiography about her life called Love, Lucy . Meanwhile, an author named Kathleen Brady wrote a biography about Lucille Ball called Lucy: The Life of Lucille Ball .

Here are a few other key differences between the two genres:
1. Different perspectives
Naturally, an autobiography is written from the first-person perspective, which means the author is providing a personalized point of view on their own life.
Meanwhile, a biography is written from a third-person perspective , meaning the author is writing from an external point of view, with limited insight into the subject’s personal thoughts or feelings.
2. Control of the narrative
When someone writes their autobiography, they control which parts of their life story they include and which they omit. They can choose which perspective they share and which parts of themselves they want to spotlight.
Meanwhile, a biography relies on research, interviews and sources to construct a complete picture of a subject’s life. A biographer is likely to be more objective in their presentation of a person—perhaps even including unsavory details about their subject that the subject themselves wouldn’t include.
3. Levels of objectivity
Even the best autobiography will be subjective because it’s based on the author’s personal memories and feelings.
On the other hand, many biographers strive to be more objective in their writing. They tend to consult multiple sources, conduct a variety of interviews, and more to make sure they’re writing an accurate portrayal of their subject.
4. Sources used
Because an autobiographer is writing a story about their own life, their sources will primarily be self-generated. Though they may rely on those close to them, like family members, to verify or recount certain memories they hold.
That said, many autobiographers still need to do research to add context and depth to their life stories, whether that’s learning about the town they grew up in, their family history, or something else.
Meanwhile, biographers rely on archival materials, research, interviews, historical documents, and more to help them write the story about their subject .

5. Writing style
Because autobiographies are more personal, they often reflect the author’s unique writing style and personality. You can use an autobiography template to help map out the structure of your book, but ultimately, the flow and details will be dictated by your personal story.
On the other hand, biographies generally strive to be more objective, with a focus on a cohesive, well-researched narrative. (But to be clear: they can still be very engaging!)
Where do memoirs fit in?
We’ve learned about the differences and similarities between autobiographies and biographies, so where do memoirs fit into the puzzle?
Like an autobiography, a memoir is written by the subject of the book. Both genres tend to focus on the author’s personal life, are written in the first person, and can be highly subjective.
However, where autobiography vs memoir differs is partially in the scope of the book. An autobiography often encompasses most of the author’s life, while a memoir is likely to focus on one specific event, theme, or period in the author’s life.
Memoirs also adhere less to chronological storytelling than autobiographies do. They can jump around in time and tend to be centered more on themes, reflection, or specific, impactful moments in the author’s life.
In summary, you can think of memoirs as even more personal than autobiographies, focusing on a selected part of the writer’s life. They’re also more likely than autobiographies to be written by folks who aren’t famous.
Related: Examples of Memoirs
Final thoughts
While biographies, autobiographies and memoirs all tell a subject’s life story, they do it in different ways. The type of genre you’d like to read (or write) will be contingent on what you’d like to learn about your chosen subject.
If you’re interested in writing your own memoir, autobiography or memoir, we can help you do it. Simply schedule a book consultation to get started.
Autobiography
Definition of autobiography.
Autobiography is one type of biography , which tells the life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author’s life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person’s own pen, in his own words. Some autobiographies are written in the form of a fictional tale; as novels or stories that closely mirror events from the author’s real life. Such stories include Charles Dickens ’ David Copperfield and J.D Salinger’s The Catcher in The Rye . In writing about personal experience, one discovers himself. Therefore, it is not merely a collection of anecdotes – it is a revelation to the readers about the author’s self-discovery.
Difference between Autobiography and Memoir
In an autobiography, the author attempts to capture important elements of his life. He not only deals with his career, and growth as a person, he also uses emotions and facts related to family life, relationships, education, travels, sexuality, and any types of inner struggles. A memoir is a record of memories and particular events that have taken place in the author’s life. In fact, it is the telling of a story or an event from his life; an account that does not tell the full record of a life.
Six Types of Autobiography
There are six types of autobiographies:
- Autobiography: A personal account that a person writes himself/herself.
- Memoir : An account of one’s memory.
- Reflective Essay : One’s thoughts about something.
- Confession: An account of one’s wrong or right doings.
- Monologue : An address of one’s thoughts to some audience or interlocuters.
- Biography : An account of the life of other persons written by someone else.
Importance of Autobiography
Autobiography is a significant genre in literature. Its significance or importance lies in authenticity, veracity, and personal testimonies. The reason is that people write about challenges they encounter in their life and the ways to tackle them. This shows the veracity and authenticity that is required of a piece of writing to make it eloquent, persuasive, and convincing.
Examples of Autobiography in Literature
Example #1: the box: tales from the darkroom by gunter grass.
A noble laureate and novelist, Gunter Grass , has shown a new perspective of self-examination by mixing up his quilt of fictionalized approach in his autobiographical book, “The Box: Tales from the Darkroom.” Adopting the individual point of view of each of his children, Grass narrates what his children think about him as their father and a writer. Though it is really an experimental approach, due to Grass’ linguistic creativity and dexterity, it gains an enthralling momentum.
Example #2: The Story of My Life by Helen Keller
In her autobiography, The Story of My Life , Helen Keller recounts her first twenty years, beginning with the events of the childhood illness that left her deaf and blind. In her childhood, a writer sent her a letter and prophesied, “Someday you will write a great story out of your own head that will be a comfort and help to many.”
In this book, Keller mentions prominent historical personalities, such as Alexander Graham Bell, whom she met at the age of six, and with whom she remained friends for several years. Keller paid a visit to John Greenleaf Whittier , a famous American poet, and shared correspondence with other eminent figures, including Oliver Wendell Holmes, and Mrs. Grover Cleveland. Generally, Keller’s autobiography is about overcoming great obstacles through hard work and pain.
Example #3: Self Portraits: Fictions by Frederic Tuten
In his autobiography, “Self Portraits: Fictions ,” Frederic Tuten has combined the fringes of romantic life with reality. Like postmodern writers, such as Jorge Luis Borges, and Italo Calvino, the stories of Tuten skip between truth and imagination, time and place, without warning. He has done the same with his autobiography, where readers are eager to move through fanciful stories about train rides, circus bears, and secrets to a happy marriage; all of which give readers glimpses of the real man.
Example #4: My Prizes by Thomas Bernhard
Reliving the success of his literary career through the lens of the many prizes he has received, Thomas Bernhard presents a sarcastic commentary in his autobiography, “My Prizes.” Bernhard, in fact, has taken a few things too seriously. Rather, he has viewed his life as a farcical theatrical drama unfolding around him. Although Bernhard is happy with the lifestyle and prestige of being an author, his blasé attitude and scathing wit make this recollection more charmingly dissident and hilarious.
Example #5: The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin by Benjamin Franklin
“The Autobiography of Benjamin Franklin ” is written by one of the founding fathers of the United States. This book reveals Franklin’s youth, his ideas, and his days of adversity and prosperity. He is one of the best examples of living the American dream – sharing the idea that one can gain financial independence, and reach a prosperous life through hard work.
Through autobiography, authors can speak directly to their readers, and to their descendants. The function of the autobiography is to leave a legacy for its readers. By writing an autobiography, the individual shares his triumphs and defeats, and lessons learned, allowing readers to relate and feel motivated by inspirational stories. Life stories bridge the gap between peoples of differing ages and backgrounds, forging connections between old and new generations.
Synonyms of Autobiography
The following words are close synonyms of autobiography such as life story, personal account, personal history, diary, journal, biography, or memoir.
Related posts:
- The Autobiography of Malcolm X
Post navigation
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus
Meaning of autobiography in English
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
- multi-volume
You can also find related words, phrases, and synonyms in the topics:
Related words
Autobiography | american dictionary, examples of autobiography, translations of autobiography.
Get a quick, free translation!

Word of the Day
moving images created from drawings, models, etc. that are photographed or created by a computer

Cooking or hitting the books? (Idioms with ‘book’)

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
- English Noun
- American Noun
- Translations
- All translations
To add autobiography to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add autobiography to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
- Literary Terms
- Autobiography
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Write Autobiography
I. What is Autobiography?
An autobiography is a self-written life story.
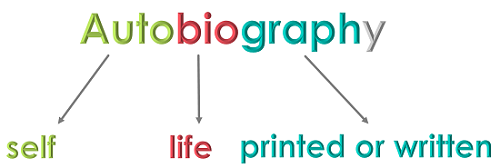
It is different from a biography , which is the life story of a person written by someone else. Some people may have their life story written by another person because they don’t believe they can write well, but they are still considered an author because they are providing the information. Reading autobiographies may be more interesting than biographies because you are reading the thoughts of the person instead of someone else’s interpretation.
II. Examples of Autobiography
One of the United States’ forefathers wrote prolifically (that means a lot!) about news, life, and common sense. His readings, quotes, and advice are still used today, and his face is on the $100 bill. Benjamin Franklin’s good advice is still used through his sayings, such as “We are all born ignorant, but one must work hard to remain stupid.” He’s also the one who penned the saying that’s seen all over many schools: “Tell me and I forget. Teach me and I remember. Involve me and I learn.” His autobiography is full of his adventures , philosophy about life, and his wisdom. His autobiography shows us how much he valued education through his anecdotes (stories) of his constant attempts to learn and improve himself. He also covers his many ideas on his inventions and his thoughts as he worked with others in helping the United States become free from England.
III. Types of Autobiography
There are many types of autobiographies. Authors must decide what purpose they have for writing about their lives, and then they can choose the format that would best tell their story. Most of these types all share common goals: helping themselves face an issue by writing it down, helping others overcome similar events, or simply telling their story.
a. Full autobiography (traditional):
This would be the complete life story, starting from birth through childhood, young adulthood, and up to the present time at which the book is being written. Authors might choose this if their whole lives were very different from others and could be considered interesting.
There are many types of memoirs – place, time, philosophic (their theory on life), occupational, etc. A memoir is a snapshot of a person’s life. It focuses on one specific part that stands out as a learning experience or worth sharing.
c. Psychological illness
People who have suffered mental illness of any kind find it therapeutic to write down their thoughts. Therapists are specialists who listen to people’s problems and help them feel better, but many people find writing down their story is also helpful.
d. Confession
Just as people share a psychological illness, people who have done something very wrong may find it helps to write down and share their story. Sharing the story may make one feel he or she is making amends (making things right), or perhaps hopes that others will learn and avoid the same mistake.
e. Spiritual
Spiritual and religious experiences are very personal . However, many people feel that it’s their duty and honor to share these stories. They may hope to pull others into their beliefs or simply improve others’ lives.
f. Overcoming adversity
Unfortunately, many people do not have happy, shining lives. Terrible events such as robberies, assaults, kidnappings, murders, horrific accidents, and life-threatening illnesses are common in some lives. Sharing the story can inspire others while also helping the person express deep emotions to heal.
IV. The Importance of Autobiography
Autobiographies are an important part of history. Being able to read the person’s own ideas and life stories is getting the first-person story versus the third-person (he-said/she-said) version. In journalism, reporters go to the source to get an accurate account of an event. The same is true when it comes to life stories. Reading the story from a second or third source will not be as reliable. The writer may be incorrectly explaining and describing the person’s life events.
Autobiographies are also important because they allow other people in similar circumstances realize that they are not alone. They can be inspiring for those who are facing problems in their lives. For the author, writing the autobiography allows them to heal as they express their feelings and opinions. Autobiographies are also an important part of history.
V. Examples of Autobiography in Literature
A popular autobiography that has lasted almost 100 years is that of Helen Keller. Her life story has been made into numerous movies and plays. Her teacher, Anne Sullivan, has also had her life story written and televised multiple times. Students today still read and learn about this young girl who went blind and deaf at 19 months of age, causing her to also lose her ability to learn to speak. Sullivan’s entrance into Helen’s life when the girl was seven was the turning point. She learned braille and soon became an activist for helping blind and deaf people across the nation. She died in 1968, but her autobiography is still helping others.
Even in the days before my teacher came, I used to feel along the square stiff boxwood hedges, and, guided by the sense of smell, would find the first violets and lilies. There, too, after a fit of temper, I went to find comfort and to hide my hot face in the cool leaves and grass. What joy it was to lose myself in that garden of flowers, to wander happily from spot to spot, until, coming suddenly upon a beautiful vine, I recognized it by its leaves and blossoms, and knew it was the vine which covered the tumble-down summer-house at the farther end of the garden! (Keller).
An autobiography that many middle and high school students read every year is “Night” by Elie Wiesel. His story is also a memoir, covering his teen years as he and his family went from the comfort of their own home to being forced into a Jewish ghetto with other families, before ending up in a Nazi prison camp. His book is not that long, but the details and description he uses brings to life the horrors of Hitler’s reign of terror in Germany during World War II. Students also read “The Diary of Anne Frank,” another type of autobiography that shows a young Jewish girl’s daily life while hiding from the Nazis to her eventual capture and death in a German camp. Both books are meant to remind us to not be indifferent to the world’s suffering and to not allow hate to take over.
“The people were saying, “The Red Army is advancing with giant strides…Hitler will not be able to harm us, even if he wants to…” Yes, we even doubted his resolve to exterminate us. Annihilate an entire people? Wipe out a population dispersed throughout so many nations? So many millions of people! By what means? In the middle of the twentieth century! And thus my elders concerned themselves with all manner of things—strategy, diplomacy, politics, and Zionism—but not with their own fate. Even Moishe the Beadle had fallen silent. He was weary of talking. He would drift through synagogue or through the streets, hunched over, eyes cast down, avoiding people’s gaze. In those days it was still possible to buy emigration certificates to Palestine. I had asked my father to sell everything, to liquidate everything, and to leave” (Wiesel 8).
VI. Examples of Autobiography in Pop Culture
One example of an autobiography that was a hit in the movie theaters is “American Sniper,” the story of Navy SEAL Chris Kyle. According to an article in the Dallas, Texas, magazine D, Kyle donated all the proceeds from the film to veterans and their families. He had a story to tell, and he used it to help others. His story is a memoir, focusing on a specific time period of his life when he was overseas in the military.
An autobiography by a young Olympian is “Grace, Gold and Glory: My Leap of Faith” by Gabrielle (Gabby) Douglas. She had a writer, Michelle Burford, help her in writing her autobiography. This is common for those who have a story to tell but may not have the words to express it well. Gabby was the darling of the 2012 Olympics, winning gold medals for the U.S. in gymnastics along with being the All-Around Gold Medal winner, the first African-American to do so. Many young athletes see her as an inspiration. Her story also became a television movie, “The Gabby Douglas Story.”
VII. Related Terms
The life story of one person written by another. The purpose may to be highlight an event or person in a way to help the public learn a lesson, feel inspired, or to realize that they are not alone in their circumstance. Biographies are also a way to share history. Historic and famous people may have their biographies written by many authors who research their lives years after they have died.
VIII. Conclusion
Autobiographies are a way for people to share stories that may educate, inform, persuade, or inspire others. Many people find writing their stories to be therapeutic, healing them beyond what any counseling might do or as a part of the counseling. Autobiographies are also a way to keep history alive by allowing people in the present learn about those who lived in the past. In the future, people can learn a lot about our present culture by reading autobiographies by people of today.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Biography is a detailed account of a person’s life written by someone else, while an autobiography is written by the subject themselves. Biography can be written with (authorised) or without permission (unauthorised) from the person/heir’s concerned.
autobiography, the biography of oneself narrated by oneself. Autobiographical works can take many forms, from the intimate writings made during life that were not necessarily intended for publication (including letters, diaries , journals , memoirs , and reminiscences) to a formal book-length autobiography.
While an autobiography and a biography both tell the story of someone’s life, they are not the same thing. When a person writes his or her own life story, the finished work is an autobiography. When an author writes a book about another person’s life, the result is a biography.
Autobiography: When you read an autobiography, you’re getting the author’s own interpretation of their life. Biography: When you read a biography, you experience the subject’s life through someone else’s lens (Schiffrin & Brockmeier, 2012).
The meaning of AUTOBIOGRAPHY is the biography of a person narrated by that person : a usually written account of a person's life in their own words. How to use autobiography in a sentence.
An autobiography, [a] sometimes informally called an autobio, is a self-written biography of one's own life. Definition. The word "autobiography" was first used deprecatingly by William Taylor in 1797 in the English periodical The Monthly Review, when he suggested the word as a hybrid, but condemned it as "pedantic".
The biggest difference between an autobiography and a biography is that an autobiography is written by the subject of the book about their own life, while a biography is written by another person. For example, actress Lucille Ball wrote an autobiography about her life called Love, Lucy.
Definition of Autobiography. Autobiography is one type of biography, which tells the life story of its author, meaning it is a written record of the author’s life. Rather than being written by somebody else, an autobiography comes through the person’s own pen, in his own words.
AUTOBIOGRAPHY definition: 1. a book about a person's life, written by that person: 2. the area of literature relating to…. Learn more.
Definition & Examples. I. What is Autobiography? An autobiography is a self-written life story. It is different from a biography, which is the life story of a person written by someone else.