Community Ecology Study Guide

Outline p. 273-275
Biodiversity
Cooperative Interactions
Ecosystem Changes
Powerpoints:
Community Ecology
Review Questions:
Explain how competition contributes to competitive exclusion, resource partitioning, and character displacement.
Explain how predation contributes to changes in coloration (aposematic and cryptic) and the evolution of mimicry (batesian and mullerian).
Provide examples of mutualism and parasitism, and explain how your examples fit those definitions.
Why are ecologists unsettled on whether or not there are any truly commensal interactions among organisms?
Explain the concept of facilitation. Provide an example facilitator species and why it fits that definition.
What is biodiversity? How is it measured?
How do keystone species contribute to the tropic structure of an ecosystem? Provide examples of the effects of each.
Describe the phenomena of disturbance and succession.
Describe the process of primary succession.
Describe the process of secondary succession.
Describe how ecosystems provide organisms with their energetic and matter requirements.
Explain how changes in climate can influence primary productivity in an ecosystem.
Compare food chains and food webs.
What does it mean by “trophic structure” of a community? Give example
Explain how modeling of the trophic structure of an ecosystem can be used to make predictions about the effects of changes in biotic and abiotic factors on that ecosystem. Describe the strengths and limitations of this approach.
How do “bottom-up” or “top-down” controls on community organization differ?
Provide examples to demonstrate how human activities have impacted ecosystems on local, regional, and global scales. Describe the causes, and effects of these impacts, and discuss possible avenues of mitigating these impacts.
Provide examples of species that have been driven to extinction by human activities.
Explain how interactions among populations affect the pattern of species distribution and abundance.
Explain how competition, parasitism, predation, mutualism, and commensalism can all affect the distribution and abundance of populations. Provide examples of each effect.
Provide examples of how species-specific and environmental catastrophes, geological events, and the sudden influx/depletion of abiotic resources or increased human activities can affect species distribution and abundance.
What properties does a population have that an individual does not?
Explain how introduced species (invasive) can disrupt the structure of an ecosystem. Provide examples
(i.e. Dutch Elm Disease) to support your answer.
Explain how the genetic diversity present in a population is related to the resiliency of the population and its ability to respond to changes in the environment.
Explain why populations with limited genetic diversity are at greater risk of extinction. Provide examples to support your answer.
Describe how keystone species, producers, and limiting abiotic and biotic factors contribute to maintaining the diversity of an ecosystem.
Provide examples of how disruption to keystone species populations can trigger disproportionately largescale changes to the structure of an ecosystem.
Describe two hypotheses that explain why species diversity is greater in tropical regions than in temperate or polar regions.
How does an island’s size and distance from the mainland affect the island’s species diversity?

Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer
Find what you need to study
8.5 Community Ecology
5 min read • january 7, 2023
Caroline Koffke
Jillian Holbrook
Attend a live cram event
Review all units live with expert teachers & students
Species Diversity
A community refers to a group of different populations living in the same area. An example of this would be humans, dogs, and rats living in the city of Chicago. 🐀
Communities can be large or small, and they can be found in a variety of environments, including terrestrial, aquatic, and even the air! In a community , the various species interact with one another through a variety of processes, such as competition for resources , predation , and mutualism , which have differential positive, negative, or neutral effects.
Understanding the dynamics of a community can help scientists and researchers better understand how ecosystems function and how they can be managed and conserved.
When studying a community , scientists often measure the species diversity and species composition in that area, as community dynamics inform ecosystem function, management, and conservation. Species diversity refers to the number of unique species living in the area and the percentage of the population represented by each species.
The structure of a community is described in terms of species composition and species diversity . An environment with a large number of unique species whose populations are also equally distributed is considered highly diverse!
The diversity of a community can be measured using Simpson’s Diversity Index , the following equation:
Diversity Index = 1 - Σ (n / N)^2
n = the total number of organisms of a particular species N = total number of organisms of all species
Interactions between populations in a community determine the health of that community , changes in species and populations over time, and how energy and matter are transferred. These relationships consist of predation , competition, mutualism , commensalism , and parasitism , which we will further explore in terms through the lens of community ecology!
Community Interactions
Predator and Prey (/-)
A predator/prey relationship refers to a relationship in which one organism eats another. The predator in one relationship may be the prey in another relationship. An example of a predator/prey relationship is a snake and a mouse. The snake is the predator and eats the mouse, which is the prey. 🐍
In another scenario, the snake may become the prey. A hawk serves as a potential predator for the snake. This relationship is the most common way of showing the transfer of energy in an ecosystem.
Predation in ecosystems is a top-down control on other species, often making it an ecosystem service. By limiting prey populations, predators create trophic cascades that affect the population sizes or behaviors of species at other levels of an ecosystem.
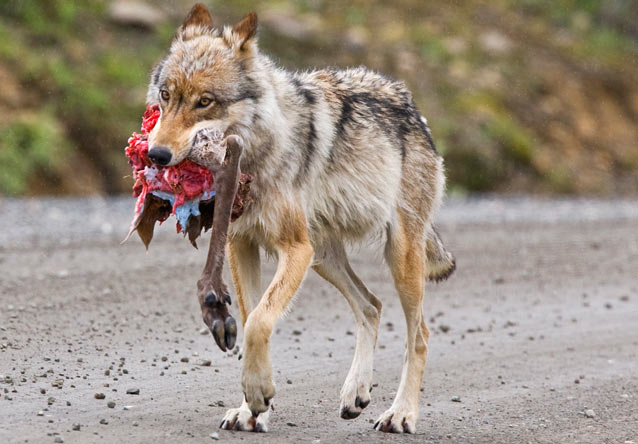

Image courtesy of NPS .
Interspecies competition refers to relationships in which two species are competing for the same limited habitat, food, or water. Any time that two organisms share a common food source in predation , competition might result. As an example, hawks and badgers might be in competition for snakes as a source of food.
Competition can lead to a decrease in one population if another population is more fit to hunt prey. It may also lead to a stabilizing of both populations if both groups are equally fit.
Image courtesy of Giphy .
Niche partitioning is the process by which different species divide up resources and use them in different ways. To avoid interspecies competition , different species utilize different ecological niches .
Mutualism (/)
Mutualism refers to a relationship in which both species involved receive a fitness benefit from the relationship.
A classic example of this is the Acacia tree and the Acacia ant. The tree produces small leaves that possess large quantities of nutrients for the ants to eat. In return, the ants protect the Acacia tree from some predators and reduce the bacterial population on the leaves of the tree. Because both species are equally benefited from the relationship, this is considered an example of mutualism . 🐜
_with_Beltian_bodies%2C_Caves_Branch_Jungle_Lodge%2C_Belmopan%2C_Belize_-_8505045055.jpg?alt=media&token=7580c51a-564b-4aff-822a-677a819ae423)
Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons .
Commensalism (/0)
Commensalism refers to a relationship in which one species benefits and the other species is neither harmed nor helped.
An example of this type of relationship is between a barnacle and a whale. A barnacle is a sea creature that bonds to a surface and waits for the water to carry particles of plankton and other food sources across their mouths.
Barnacles frequently bind to the thick skin of the whale. The barnacle benefits greatly from this because the whale’s frequent movement allows for an increased amount of plankton and other food particles to pass over the barnacle. The whale is neither harmed nor helped by the binding of the barnacle. 🐋
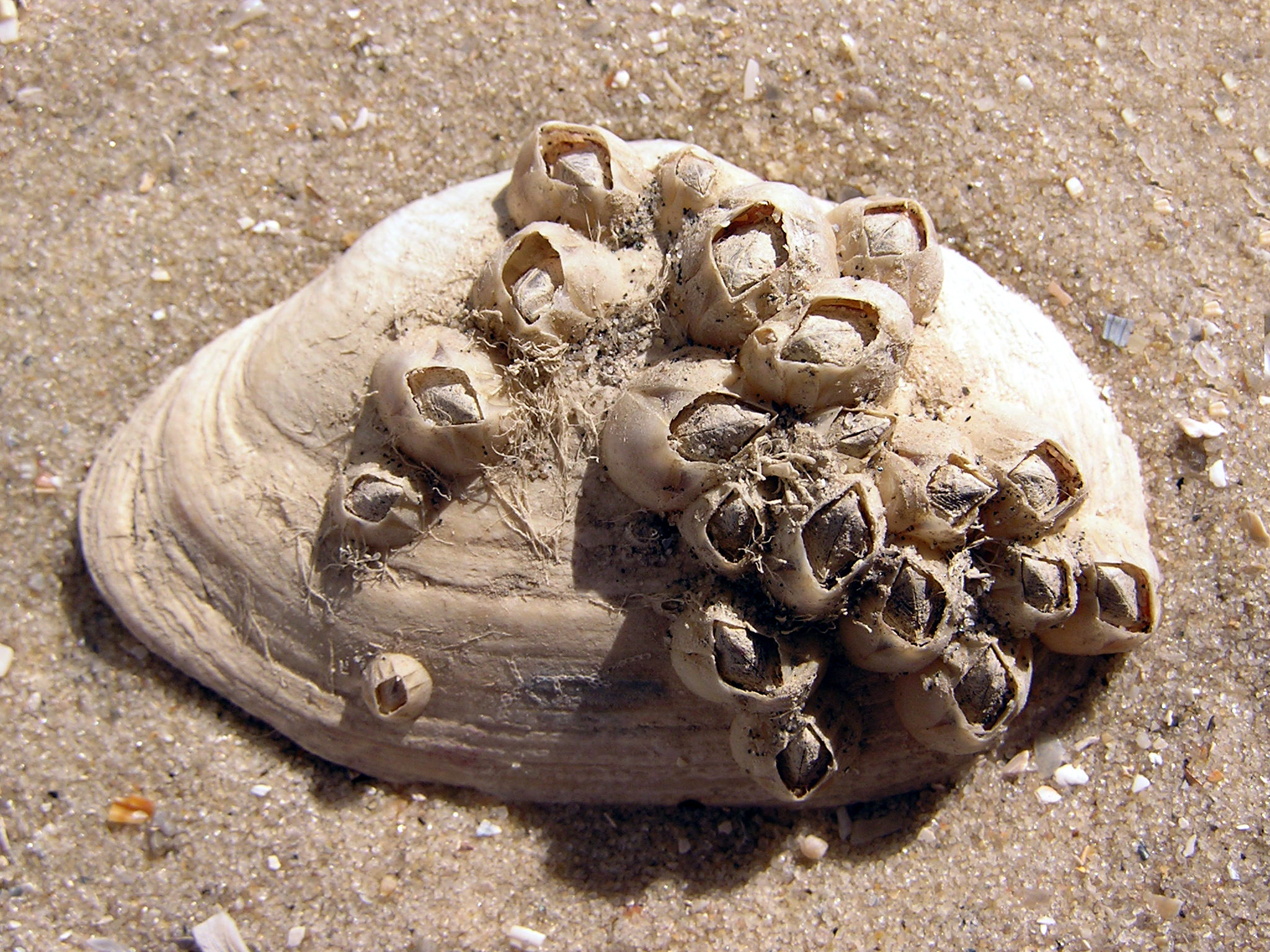

Image courtesy of WikiMedia Commons .
Parasitism (/-)
Parasitism is a type of interaction between species in which one species, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other species, the host.
Parasites can be found in a wide range of species, including plants, animals, and even microorganisms. Many parasites are specialized to infect a particular host species, and they often have complex life cycles that involve multiple hosts. In some cases, the relationship between a parasite and its host can be relatively benign, with the host experiencing only minor effects from the parasite's presence. However, in other cases, the relationship can be much more harmful, with the parasite causing serious illness or even death in the host. Some parasites are able to manipulate the behavior or physiology of their hosts in ways that increase the parasite's chances of survival and reproduction.
Predation and parasitism appear to be similar, as both relationships include one species experiencing a fitness benefit at the expense of the other. However, parasitism can be differentiated, as parasites are relatively small in comparison to the hosts they feed off of, and parasites tend to feed off part of other organisms rather than consume the entire organism, as is common in a predator/prey interaction.
For example, a tick and a dog represent parasitism . Relative to the dog, the tick is small. It bites the dog's skin to feed on nutrients in the dog's blood. In addition to the deprivation of nutrients, ticks carry diseases that may infect the dog. Ultimately, this relationship benefits the tick and harms the dog. 🐕
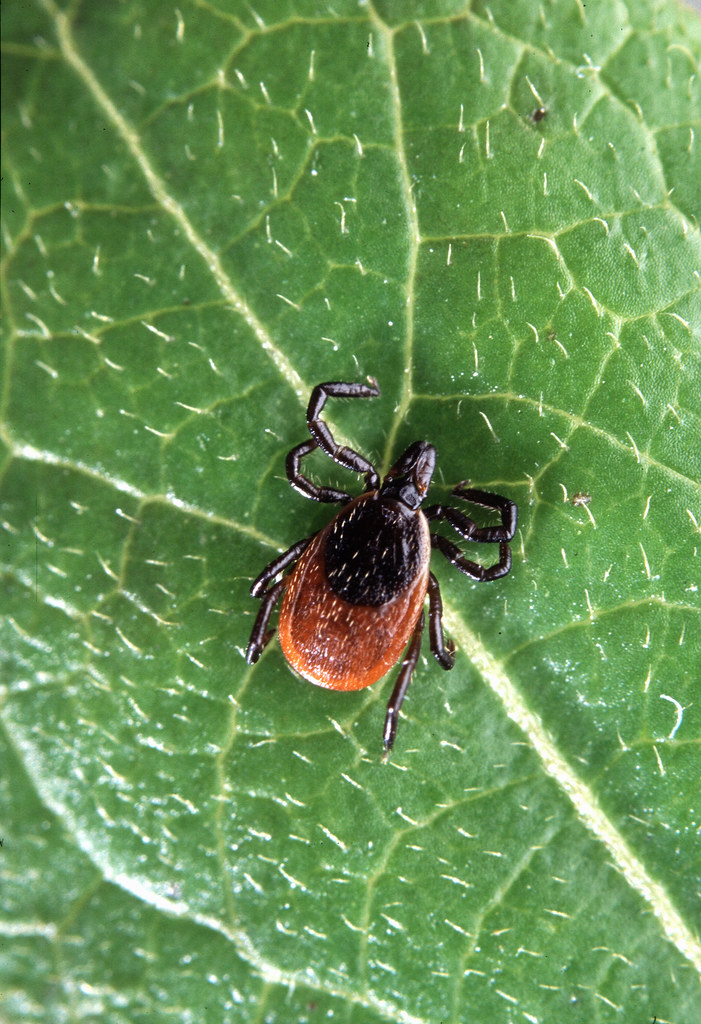

Image courtesy of Flickr .
Key Terms to Review ( 19 )
Acacia Tree and Acacia Ant Mutualism
Aquatic Environment
Barnacle and Whale Commensalism
Commensalism
Competition for Resources
Ecological Niches
Interspecies Competition
Niche Partitioning
Predator and Prey Relationship
Simpson’s Diversity Index
Species Composition
Terrestrial Environment
Trophic Cascades

Stay Connected
© 2024 Fiveable Inc. All rights reserved.
AP® and SAT® are trademarks registered by the College Board, which is not affiliated with, and does not endorse this website.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

5.4: Community Ecology
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 94285

- Matthew R. Fisher
- Oregon Coast Community College via OpenOregon
Populations typically do not live in isolation from other species. Populations that interact within a given habitat form a community . The number of species occupying the same habitat and their relative abundance is known as the diversity of the community. Areas with low species diversity, such as the glaciers of Antarctica, still contain a wide variety of living organisms, whereas the diversity of tropical rainforests is so great that it cannot be accurately assessed. Scientists study ecology at the community level to understand how species interact with each other and compete for the same resources.
Predation and Herbivory
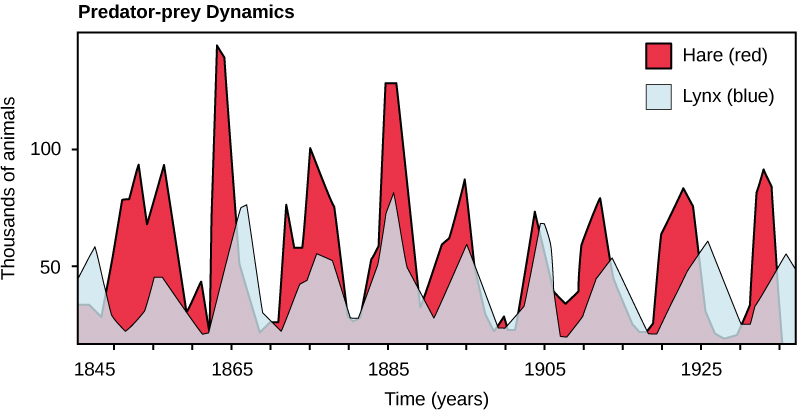
Perhaps the classical example of species interaction is the predator-prey relationship. The narrowest definition of predation describes individuals of one population that kill and then consume the individuals of another population. Population sizes of predators and prey in a community are not constant over time, and they may vary in cycles that appear to be related. The most often cited example of predator-prey population dynamics is seen in the cycling of the lynx (predator) and the snowshoe hare (prey), using 100 years of trapping data from North America (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). This cycling of predator and prey population sizes has a period of approximately ten years, with the predator population lagging one to two years behind the prey population. An apparent explanation for this pattern is that as the hare numbers increase, there is more food available for the lynx, allowing the lynx population to increase as well. When the lynx population grows to a threshold level, however, they kill so many hares that hare numbers begin to decline, followed by a decline in the lynx population because of scarcity of food. When the lynx population is low, the hare population size begins to increase due, in part, to low predation pressure, starting the cycle anew.
Defense Mechanisms against Predation and Herbivory
Predation and predator avoidance are strong influenced by natural selection. Any heritable character that allows an individual of a prey population to better evade its predators will be represented in greater numbers in later generations. Likewise, traits that allow a predator to more efficiently locate and capture its prey will lead to a greater number of offspring and an increase in the commonness of the trait within the population. Such ecological relationships between specific populations lead to adaptations that are driven by reciprocal evolutionary responses in those populations. Species have evolved numerous mechanisms to escape predation (including herbivory , the consumption of plants for food). Defenses may be mechanical, chemical, physical, or behavioral.
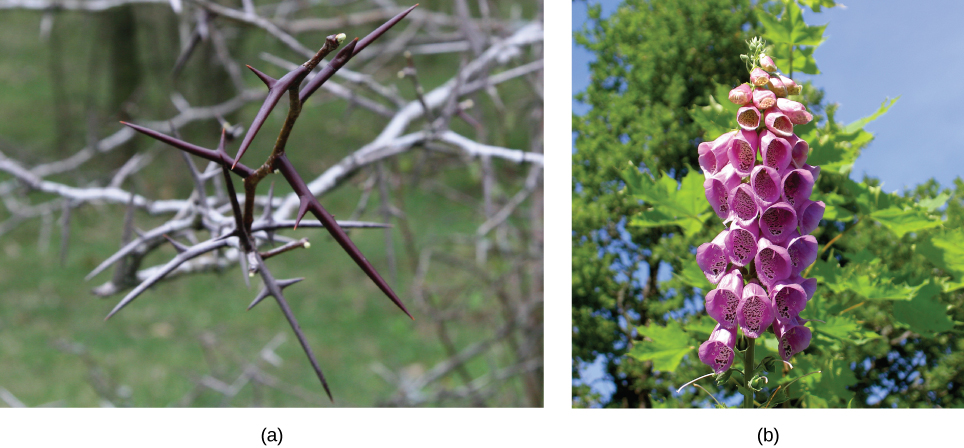

Mechanical defenses, such as the presence of armor in animals or thorns in plants, discourage predation and herbivory by discouraging physical contact (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)a). Many animals produce or obtain chemical defenses from plants and store them to prevent predation. Many plant species produce secondary plant compounds that serve no function for the plant except that they are toxic to animals and discourage consumption. For example, the foxglove produces several compounds, including digitalis, that are extremely toxic when eaten (Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\)b). (Biomedical scientists have repurposed the chemical produced by foxglove as a heart medication, which has saved lives for many decades.)
Many species use their body shape and coloration to avoid being detected by predators. The tropical walking stick is an insect with the coloration and body shape of a twig, which makes it very hard to see when it is stationary against a background of real twigs (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)a). In another example, the chameleon can change its color to match its surroundings (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)b).

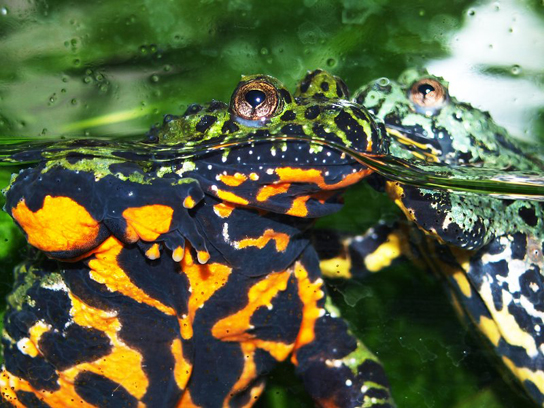
Some species use coloration as a way of warning predators that they are distasteful or poisonous. For example, the monarch butterfly caterpillar sequesters poisons from its food (plants and milkweeds) to make itself poisonous or distasteful to potential predators. The caterpillar is bright yellow and black to advertise its toxicity. The caterpillar is also able to pass the sequestered toxins on to the adult monarch, which is also dramatically colored black and red as a warning to potential predators. Fire-bellied toads produce toxins that make them distasteful to their potential predators (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). They have bright red or orange coloration on their bellies, which they display to a potential predator to advertise their poisonous nature and discourage an attack. Warning coloration only works if a predator uses eyesight to locate prey and can learn—a naïve predator must experience the negative consequences of eating one before it will avoid other similarly colored individuals.

While some predators learn to avoid eating certain potential prey because of their coloration, other species have evolved mechanisms to mimic this coloration to avoid being eaten, even though they themselves may not be unpleasant to eat or contain toxic chemicals. In some cases of mimicry , a harmless species imitates the warning coloration of a harmful species. Assuming they share the same predators, this coloration then protects the harmless ones. Many insect species mimic the coloration of wasps, which are stinging, venomous insects, thereby discouraging predation (Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\)).

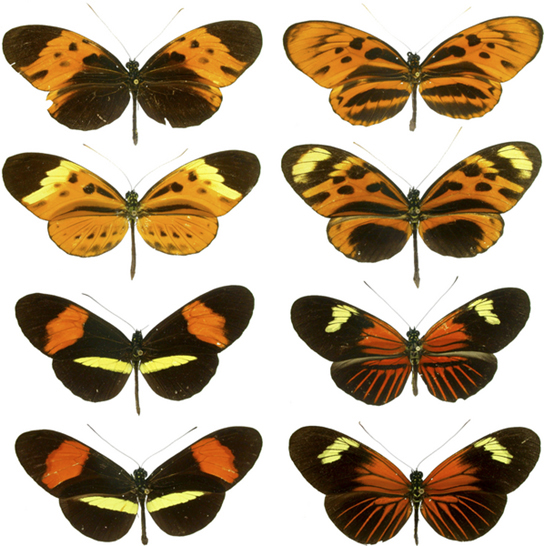
In other cases of mimicry, multiple species share the same warning coloration, but all of them actually have defenses. The commonness of the signal improves the compliance of all the potential predators. Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\) shows a variety of foul-tasting butterflies with similar coloration.

Competitive Exclusion Principle
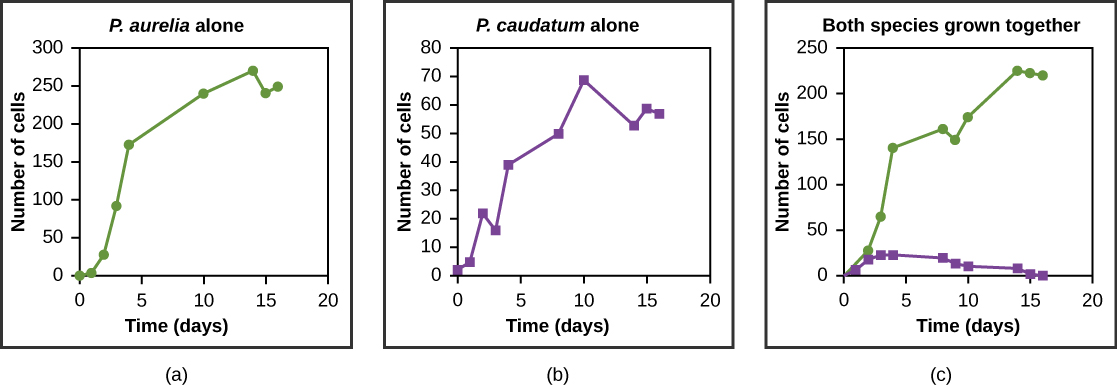
Resources are often limited within a habitat and multiple species may compete to obtain them. Ecologists have come to understand that all species have an ecological niche : the unique set of resources used by a species, which includes its interactions with other species. The competitive exclusion principle states that two species cannot occupy the exact same niche in a habitat. In other words, different species cannot coexist in a community if they are competing for all the same resources. It is important to note that competition is bad for both competitors because it wastes energy. The competitive exclusion principle works because if there is competition between two species for the same resources, then natural selection will favor traits that lessen reliance on the shared resource, thus reducing competition. If either species is unable to evolve to reduce competition, then the species that most efficiently exploits the resource will drive the other species to extinction. An experimental example of this principle is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) with two protozoan species: Paramecium aurelia and Paramecium caudatum . When grown individually in the laboratory, they both thrive. But when they are placed together in the same test tube (habitat), P. aurelia outcompetes P. caudatum for food, leading to the latter’s eventual extinction.
Symbiotic relationships are close, long-term interactions between individuals of different species. Symbioses may be commensal, in which one species benefits while the other is neither harmed nor benefited; mutualistic, in which both species benefit; or parasitic, in which the interaction harms one species and benefits the other.
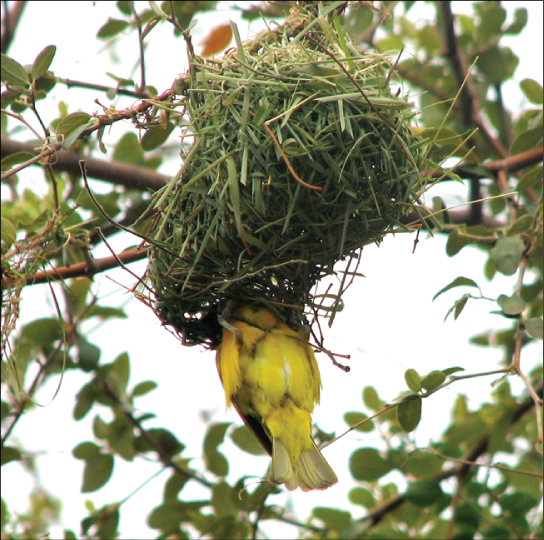

Commensalism occurs when one species benefits from a close prolonged interaction, while the other neither benefits or is harmed. Birds nesting in trees provide an example of a commensal relationship (Figure \(\PageIndex{8}\)). The tree is not harmed by the presence of the nest among its branches. The nests are light and produce little strain on the structural integrity of the branch, and most of the leaves, which the tree uses to get energy by photosynthesis, are above the nest so they are unaffected. The bird, on the other hand, benefits greatly. If the bird had to nest in the open, its eggs and young would be vulnerable to predators. Many potential commensal relationships are difficult to identify because it is difficult to prove that one partner does not derive some benefit from the presence of the other.
A second type of symbiotic relationship is called mutualism , in which two species benefit from their interaction. For example, termites have a mutualistic relationship with protists that live in the insect’s gut (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)a). The termite benefits from the ability of the protists to digest cellulose. However, the protists are able to digest cellulose only because of the presence of symbiotic bacteria within their cells that produce the cellulase enzyme. The termite itself cannot do this; without the protozoa, it would not be able to obtain energy from its food (cellulose from the wood it chews and eats). The protozoa benefit by having a protective environment and a constant supply of food from the wood chewing actions of the termite. In turn, the protists benefit from the enzymes provided by their bacterial endosymbionts, while the bacteria benefit from a doubly protective environment and a constant source of nutrients from two hosts. Lichen are a mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthetic algae or cyanobacteria (Figure \(\PageIndex{9}\)b). The glucose produced by the algae provides nourishment for both organisms, whereas the physical structure of the lichen protects the algae from the elements and makes certain nutrients in the atmosphere more available to the algae. The algae of lichens can live independently given the right environment, but many of the fungal partners are unable to live on their own.

A parasite is an organism that feeds off another without immediately killing the organism it is feeding on. In parasitism , the parasite benefits, but the organism being fed upon, the host, is harmed. The host is usually weakened by the parasite as it siphons resources the host would normally use to maintain itself. Parasites may kill their hosts, but there is usually selection to slow down this process to allow the parasite time to complete its reproductive cycle before it or its offspring are able to spread to another host. Parasitism is a form of predation.
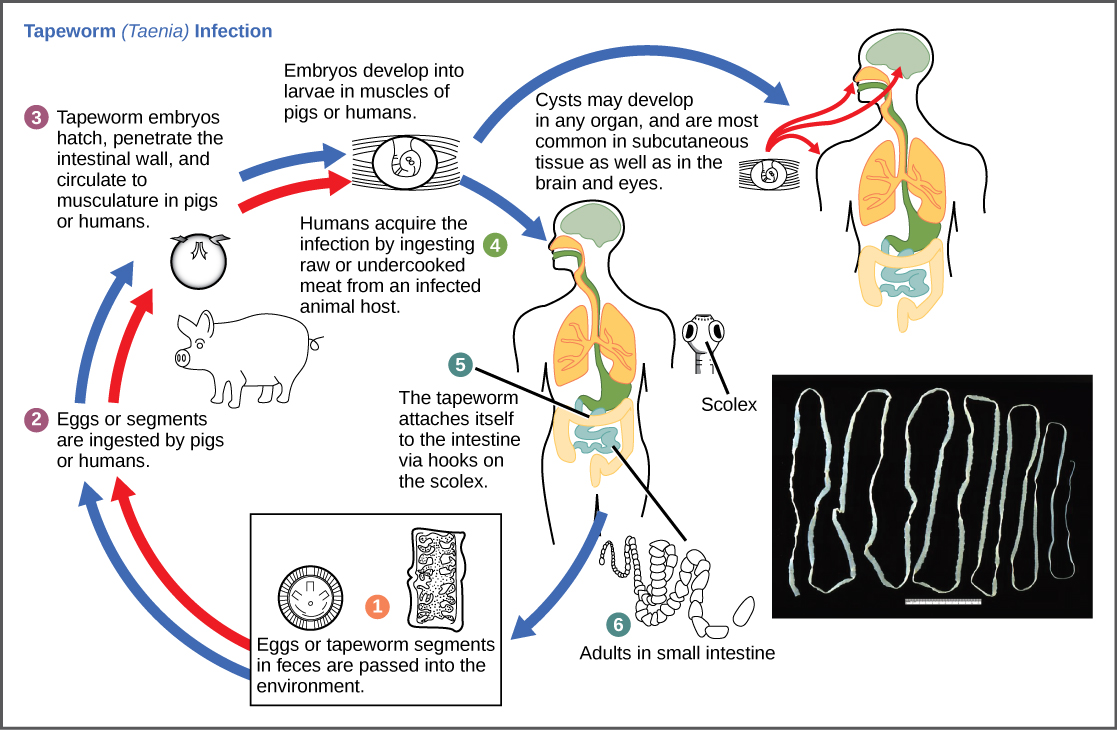
The reproductive cycles of parasites are often very complex, sometimes requiring more than one host species. A tapeworm causes disease in humans when contaminated and under-cooked meat such as pork, fish, or beef is consumed (Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\)). The tapeworm can live inside the intestine of the host for several years, benefiting from the host’s food, and it may grow to be over 50 feet long by adding segments. The parasite moves from one host species to a second host species in order to complete its life cycle.
Characteristics of Communities
Communities are complex systems that can be characterized by their structure (the number and size of populations and their interactions) and dynamics (how the members and their interactions change over time). Understanding community structure and dynamics allows us to minimize impacts on ecosystems and manage ecological communities we benefit from.
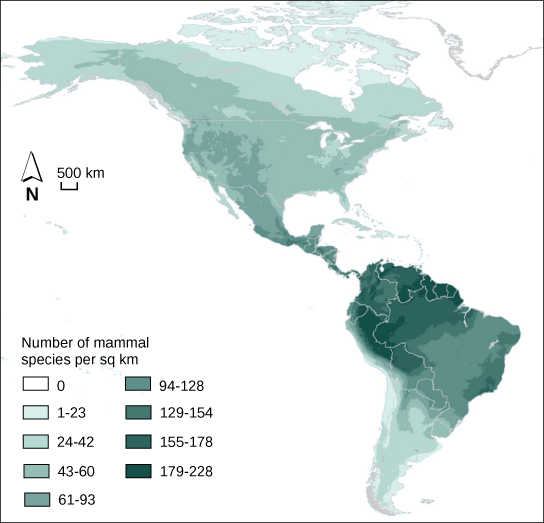
Ecologists have extensively studied one of the fundamental characteristics of communities: biodiversity . One measure of biodiversity used by ecologists is the number of different species in a particular area and their relative abundance. The area in question could be a habitat, a biome, or the entire biosphere. Species richness is the term used to describe the number of species living in a habitat or other unit. Species richness varies across the globe (Figure \(\PageIndex{11}\)). Species richness is related to latitude: the greatest species richness occurs near the equator and the lowest richness occurs near the poles. The exact reasons for this are not clearly understood. Other factors besides latitude influence species richness as well. For example, ecologists studying islands found that biodiversity varies with island size and distance from the mainland.
Relative abundance is the number individuals in a species relative to the total number of individuals in all species within a system. Foundation species, described below, often have the highest relative abundance of species.
Foundation species are considered the “base” or “bedrock” of a community, having the greatest influence on its overall structure. They are often primary producers, and they are typically an abundant organism. For example, kelp, a species of brown algae, is a foundation species that forms the basis of the kelp forests off the coast of California.
Foundation species may physically modify the environment to produce and maintain habitats that benefit the other organisms that use them. Examples include the kelp described above or tree species found in a forest. The photosynthetic corals of the coral reef also provide structure by physically modifying the environment (Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\)). The exoskeletons of living and dead coral make up most of the reef structure, which protects many other species from waves and ocean currents.

A keystone species is one whose presence has inordinate influence in maintaining the prevalence of various species in an ecosystem, the ecological community’s structure, and sometimes its biodiversity. Pisaster ochraceus , the intertidal sea star, is a keystone species in the northwestern portion of the United States (Figure \(\PageIndex{13}\)). Studies have shown that when this organism is removed from communities, mussel populations (their natural prey) increase, which completely alters the species composition and reduces biodiversity. Another keystone species is the banded tetra, a fish in tropical streams, which supplies nearly all of the phosphorus, a necessary inorganic nutrient, to the rest of the community. The banded tetra feeds largely on insects from the terrestrial ecosystem and then excretes phosphorus into the aquatic ecosystem. The relationships between populations in the community, and possibly the biodiversity, would change dramatically if these fish were to become extinct.

BIOLOGY IN ACTION
Invasive species are non-native organisms that, when introduced to an area out of its native range, alter the community they invade. In the United States, invasive species like the purple loosestrife ( Lythrum salicaria ) and the zebra mussel ( Dreissena polymorpha ) have drastically altered the ecosystems they invaded. Some well-known invasive animals include the emerald ash borer ( Agrilus planipennis ) and the European starling ( Sturnus vulgaris ). Whether enjoying a forest hike, taking a summer boat trip, or simply walking down an urban street, you have likely encountered an invasive species.
One of the many recent proliferations of an invasive species concerns the Asian carp in the United States. Asian carp were introduced to the United States in the 1970s by fisheries (commercial catfish ponds) and by sewage treatment facilities that used the fish’s excellent filter feeding abilities to clean their ponds of excess plankton. Some of the fish escaped, and by the 1980s they had colonized many waterways of the Mississippi River basin, including the Illinois and Missouri Rivers.
Voracious feeders and rapid reproducers, Asian carp may outcompete native species for food and could lead to their extinction. One species, the grass carp, feeds on phytoplankton and aquatic plants. It competes with native species for these resources and alters nursery habitats for other fish by removing aquatic plants. In some parts of the Illinois River, Asian carp constitute 95 percent of the community’s biomass. Although edible, the fish is bony and not desired in the United States.
The Great Lakes and their prized salmon and lake trout fisheries are being threatened by Asian carp. The carp are not yet present in the Great Lakes, and attempts are being made to prevent its access to the lakes through the Chicago Ship and Sanitary Canal, which is the only connection between the Mississippi River and Great Lakes basins. To prevent the Asian carp from leaving the canal, a series of electric barriers have been used to discourage their migration; however, the threat is significant enough that several states and Canada have sued to have the Chicago channel permanently cut off from Lake Michigan. Local and national politicians have weighed in on how to solve the problem. In general, governments have been ineffective in preventing or slowing the introduction of invasive species.
Community Dynamics
Community dynamics are the changes in community structure and composition over time, often following environmental disturbances such as volcanoes, earthquakes, storms, fires, and climate change. Communities with a relatively constant number of species are said to be at equilibrium. The equilibrium is dynamic with species identities and relationships changing over time, but maintaining relatively constant numbers. Following a disturbance, the community may or may not return to the equilibrium state.
Succession describes the sequential appearance and disappearance of species in a community over time after a severe disturbance. In primary succession, newly exposed or newly formed rock is colonized by living organisms. In secondary succession , a part of an ecosystem is disturbed and remnants of the previous community remain. In both cases, there is a sequential change in species until a more or less permanent community develops.
Primary Succession and Pioneer Species
Primary succession occurs when new land is formed, or when the soil and all life is removed from pre-existing land. An example of the former is the eruption of volcanoes on the Big Island of Hawaii, which results in lava that flows into the ocean and continually forms new land. From this process, approximately 32 acres of land are added to the Big Island each year. An example of pre-existing soil being removed is through the activity of glaciers. The massive weight of the glacier scours the landscape down to the bedrock as the glacier moves. This removes any original soil and leaves exposed rock once the glacier melts and retreats.

In both cases, the ecosystem starts with bare rock that is devoid of life. New soil is slowly formed as weathering and other natural forces break down the rock and lead to the establishment of hearty organisms, such as lichens and some plants, which are collectively known as pioneer species (Figure \(\PageIndex{14}\)) because they are the first to appear. These species help to further break down the mineral-rich rock into soil where other, less hardy but more competitive species, such as grasses, shrubs, and trees, will grow and eventually replace the pioneer species. Over time the area will reach an equilibrium state, with a set of organisms quite different from the pioneer species.
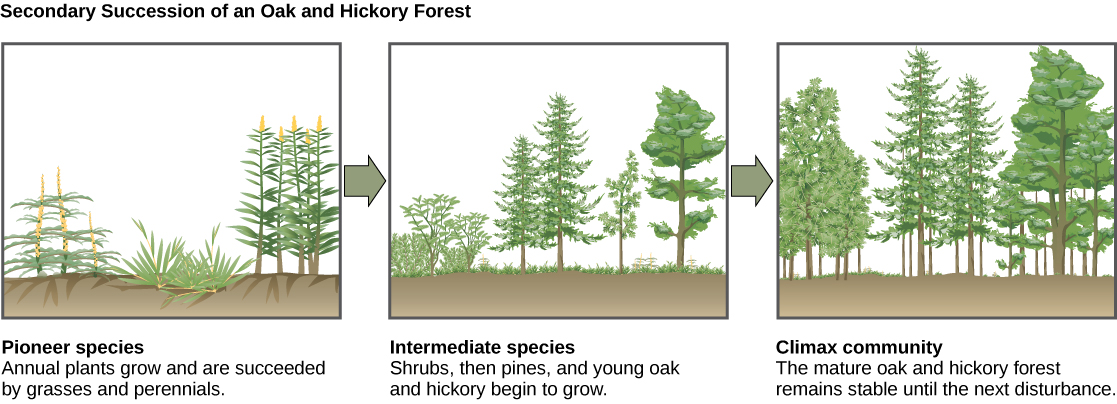
Secondary succession
A classic example of secondary succession occurs in forests cleared by wildfire, or by clearcut logging (Figure \(\PageIndex{15}\)). Wildfires will burn most vegetation, and unless the animals can flee the area, they are killed. Their nutrients, however, are returned to the ground in the form of ash. Thus, although the community has been dramatically altered, there is a soil ecosystem present that provides a foundation for rapid recolonization.
Before the fire, the vegetation was dominated by tall trees with access to the major plant energy resource: sunlight. Their height gave them access to sunlight while also shading the ground and other low-lying species. After the fire, though, these trees are no longer dominant. Thus, the first plants to grow back are usually annual plants followed within a few years by quickly growing and spreading grasses and other pioneer species. Due, at least in part, to changes in the environment brought on by the growth of grasses and forbs, over many years, shrubs emerge along with small trees. These organisms are called intermediate species. Eventually, over 150 years or more, the forest will reach its equilibrium point and resemble the community before the fire. This equilibrium state is referred to as the climax community , which will remain until the next disturbance. The climax community is typically characteristic of a given climate and geology. Although the community in equilibrium looks the same once it is attained, the equilibrium is a dynamic one with constant changes in abundance and sometimes species identities.
Contributors and Attributions
- Community Ecology by OpenStax is licensed under CC BY 4.0. Modified from the original by Matthew R. Fisher.
Community Ecology Homework Worksheets - Ecological Relationships

- Google Apps™
Also included in

Description
This ecology homework resource includes questions on community ecology relationships, symbiosis, mutualism, succession, predation, parasitism, pioneer species, and so much more. This set of printable and digital homework questions is used in my Community Ecology Bundled Unit . Students complete a section of this 5-page document each day during the teaching of the unit. When completed, it is the perfect study guide review for the unit test.
Choose to use the traditional printable version, or one of the paperless, digital Google Apps versions. Both Google Slides and Google Forms versions are included . The student handouts can be printed or used in the paperless digital format in your Google Drive, Google Classroom, Microsoft OneDrive, or similar. This resource is perfect for traditional classroom settings, 1:1 schools, or for distance learning.
What is included in your download folder?
- Printable and Editable Homework Questions (5 student pages with 53 total questions)
- Digital paperless version for use in Google Drive, Google Classroom, and/or Microsoft OneDrive
- Google Slides Version (not editable)
- Google Forms Version (editable)
- Teacher Guide and Answer Key
- Teacher Guide to Google Apps
These homework questions were written to accompany my Powerpoint on this same topic: Community Ecology PowerPoint and Notes .
All answers are included in the additional 4 page teacher guide that is included with this resource.
The questions are of varying difficulty levels. Question types include compare and contrast, fill in the blank, short answer, multiple choice, and true/false. Many of the questions are basic and concrete in nature, but many of the questions involve critical thinking and problem solving skills.
This study guide is appropriate for any biology or life science class with students in grades 8 - 12.
Topics covered in this lesson are:
- Community Interactions: Definition of community, types of community interactions such as competition, predation, symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
- Competition: Definition of competition, definition of resource, the competitive exclusion principle, character displacement, many examples, resource partitioning, the result of organisms having identical niches.
- Predation: Definition, examples, predator, prey, the role of natural selection, adaptations found in predators, adaptations found in prey, mimicry, adaptations found in plants and herbivores.
- Symbiosis: Definition of symbiosis, types of symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism, many examples of each.
- Properties of Communities: Species richness and diversity, definition of species richness, definition of species diversity, the species-area effect, the result of habitat destruction.
- Succession: Disturbances, definition and examples of disturbances, definition of succession, types of succession, primary succession, examples of primary succession, secondary succession, examples of secondary succession, pioneer species, climax communities.
- Succession in a Marine Ecosystem: A Whale-Fall Community.
Related resources include:
- Community Ecology PowerPoint with Notes for Teacher and Student
- Community Ecology Task Cards
- Introduction to Ecology PowerPoint with Notes for Teacher and Student
- Population Ecology PowerPoint with Notes for Teacher and Student
- Ecosystems: Energy Flow and the Recycling of Matter PowerPoint with Notes for Teacher and Student
- Biomes of the World PowerPoint and Notes
- Humans Impact on the Environment PowerPoint and Notes
- FREE Set of Six Ecology Crossword Puzzles
- FREE! Backyard Ecology: An Ecological Assessment of Your Back Yard
- Lab: Soil Communities
- Community Ecology Quiz / Review Worksheet
- Community Ecology REVIEW Powerpoint of 50 Questions/Answers
- Lichens: Informational Text, Critical Reading and Lab Activity
- Community Ecology Unit Test
- Predator Prey Informational Text and Graphing Activity
For updates about sales and new products, please follow my store:
My TpT Store: Amy Brown Science
Questions & Answers
Amy brown science.
- We're hiring
- Help & FAQ
- Privacy policy
- Student privacy
- Terms of service
- Tell us what you think

40 Facts About Elektrostal
Written by Lanette Mayes
Modified & Updated: 02 Mar 2024
Reviewed by Jessica Corbett

Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to captivate you.
This article will provide you with 40 fascinating facts about Elektrostal, giving you a better understanding of why this city is worth exploring. From its origins as an industrial hub to its modern-day charm, we will delve into the various aspects that make Elektrostal a unique and must-visit destination.
So, join us as we uncover the hidden treasures of Elektrostal and discover what makes this city a true gem in the heart of Russia.
Key Takeaways:
- Elektrostal, known as the “Motor City of Russia,” is a vibrant and growing city with a rich industrial history, offering diverse cultural experiences and a strong commitment to environmental sustainability.
- With its convenient location near Moscow, Elektrostal provides a picturesque landscape, vibrant nightlife, and a range of recreational activities, making it an ideal destination for residents and visitors alike.
Known as the “Motor City of Russia.”
Elektrostal, a city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia, earned the nickname “Motor City” due to its significant involvement in the automotive industry.
Home to the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Elektrostal is renowned for its metallurgical plant, which has been producing high-quality steel and alloys since its establishment in 1916.
Boasts a rich industrial heritage.
Elektrostal has a long history of industrial development, contributing to the growth and progress of the region.
Founded in 1916.
The city of Elektrostal was founded in 1916 as a result of the construction of the Elektrostal Metallurgical Plant.
Located approximately 50 kilometers east of Moscow.
Elektrostal is situated in close proximity to the Russian capital, making it easily accessible for both residents and visitors.
Known for its vibrant cultural scene.
Elektrostal is home to several cultural institutions, including museums, theaters, and art galleries that showcase the city’s rich artistic heritage.
A popular destination for nature lovers.
Surrounded by picturesque landscapes and forests, Elektrostal offers ample opportunities for outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, and birdwatching.
Hosts the annual Elektrostal City Day celebrations.
Every year, Elektrostal organizes festive events and activities to celebrate its founding, bringing together residents and visitors in a spirit of unity and joy.
Has a population of approximately 160,000 people.
Elektrostal is home to a diverse and vibrant community of around 160,000 residents, contributing to its dynamic atmosphere.
Boasts excellent education facilities.
The city is known for its well-established educational institutions, providing quality education to students of all ages.
A center for scientific research and innovation.
Elektrostal serves as an important hub for scientific research, particularly in the fields of metallurgy, materials science, and engineering.
Surrounded by picturesque lakes.
The city is blessed with numerous beautiful lakes, offering scenic views and recreational opportunities for locals and visitors alike.
Well-connected transportation system.
Elektrostal benefits from an efficient transportation network, including highways, railways, and public transportation options, ensuring convenient travel within and beyond the city.
Famous for its traditional Russian cuisine.
Food enthusiasts can indulge in authentic Russian dishes at numerous restaurants and cafes scattered throughout Elektrostal.
Home to notable architectural landmarks.
Elektrostal boasts impressive architecture, including the Church of the Transfiguration of the Lord and the Elektrostal Palace of Culture.
Offers a wide range of recreational facilities.
Residents and visitors can enjoy various recreational activities, such as sports complexes, swimming pools, and fitness centers, enhancing the overall quality of life.
Provides a high standard of healthcare.
Elektrostal is equipped with modern medical facilities, ensuring residents have access to quality healthcare services.
Home to the Elektrostal History Museum.
The Elektrostal History Museum showcases the city’s fascinating past through exhibitions and displays.
A hub for sports enthusiasts.
Elektrostal is passionate about sports, with numerous stadiums, arenas, and sports clubs offering opportunities for athletes and spectators.
Celebrates diverse cultural festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal hosts a variety of cultural festivals, celebrating different ethnicities, traditions, and art forms.
Electric power played a significant role in its early development.
Elektrostal owes its name and initial growth to the establishment of electric power stations and the utilization of electricity in the industrial sector.
Boasts a thriving economy.
The city’s strong industrial base, coupled with its strategic location near Moscow, has contributed to Elektrostal’s prosperous economic status.

Houses the Elektrostal Drama Theater.
The Elektrostal Drama Theater is a cultural centerpiece, attracting theater enthusiasts from far and wide.
Popular destination for winter sports.
Elektrostal’s proximity to ski resorts and winter sport facilities makes it a favorite destination for skiing, snowboarding, and other winter activities.
Promotes environmental sustainability.
Elektrostal prioritizes environmental protection and sustainability, implementing initiatives to reduce pollution and preserve natural resources.
Home to renowned educational institutions.
Elektrostal is known for its prestigious schools and universities, offering a wide range of academic programs to students.
Committed to cultural preservation.
The city values its cultural heritage and takes active steps to preserve and promote traditional customs, crafts, and arts.
Hosts an annual International Film Festival.
The Elektrostal International Film Festival attracts filmmakers and cinema enthusiasts from around the world, showcasing a diverse range of films.
Encourages entrepreneurship and innovation.
Elektrostal supports aspiring entrepreneurs and fosters a culture of innovation, providing opportunities for startups and business development.
Offers a range of housing options.
Elektrostal provides diverse housing options, including apartments, houses, and residential complexes, catering to different lifestyles and budgets.
Home to notable sports teams.
Elektrostal is proud of its sports legacy, with several successful sports teams competing at regional and national levels.
Boasts a vibrant nightlife scene.
Residents and visitors can enjoy a lively nightlife in Elektrostal, with numerous bars, clubs, and entertainment venues.
Promotes cultural exchange and international relations.
Elektrostal actively engages in international partnerships, cultural exchanges, and diplomatic collaborations to foster global connections.
Surrounded by beautiful nature reserves.
Nearby nature reserves, such as the Barybino Forest and Luchinskoye Lake, offer opportunities for nature enthusiasts to explore and appreciate the region’s biodiversity.
Commemorates historical events.
The city pays tribute to significant historical events through memorials, monuments, and exhibitions, ensuring the preservation of collective memory.
Promotes sports and youth development.
Elektrostal invests in sports infrastructure and programs to encourage youth participation, health, and physical fitness.
Hosts annual cultural and artistic festivals.
Throughout the year, Elektrostal celebrates its cultural diversity through festivals dedicated to music, dance, art, and theater.
Provides a picturesque landscape for photography enthusiasts.
The city’s scenic beauty, architectural landmarks, and natural surroundings make it a paradise for photographers.
Connects to Moscow via a direct train line.
The convenient train connection between Elektrostal and Moscow makes commuting between the two cities effortless.
A city with a bright future.
Elektrostal continues to grow and develop, aiming to become a model city in terms of infrastructure, sustainability, and quality of life for its residents.
In conclusion, Elektrostal is a fascinating city with a rich history and a vibrant present. From its origins as a center of steel production to its modern-day status as a hub for education and industry, Elektrostal has plenty to offer both residents and visitors. With its beautiful parks, cultural attractions, and proximity to Moscow, there is no shortage of things to see and do in this dynamic city. Whether you’re interested in exploring its historical landmarks, enjoying outdoor activities, or immersing yourself in the local culture, Elektrostal has something for everyone. So, next time you find yourself in the Moscow region, don’t miss the opportunity to discover the hidden gems of Elektrostal.
Q: What is the population of Elektrostal?
A: As of the latest data, the population of Elektrostal is approximately XXXX.
Q: How far is Elektrostal from Moscow?
A: Elektrostal is located approximately XX kilometers away from Moscow.
Q: Are there any famous landmarks in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to several notable landmarks, including XXXX and XXXX.
Q: What industries are prominent in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal is known for its steel production industry and is also a center for engineering and manufacturing.
Q: Are there any universities or educational institutions in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal is home to XXXX University and several other educational institutions.
Q: What are some popular outdoor activities in Elektrostal?
A: Elektrostal offers several outdoor activities, such as hiking, cycling, and picnicking in its beautiful parks.
Q: Is Elektrostal well-connected in terms of transportation?
A: Yes, Elektrostal has good transportation links, including trains and buses, making it easily accessible from nearby cities.
Q: Are there any annual events or festivals in Elektrostal?
A: Yes, Elektrostal hosts various events and festivals throughout the year, including XXXX and XXXX.
Was this page helpful?
Our commitment to delivering trustworthy and engaging content is at the heart of what we do. Each fact on our site is contributed by real users like you, bringing a wealth of diverse insights and information. To ensure the highest standards of accuracy and reliability, our dedicated editors meticulously review each submission. This process guarantees that the facts we share are not only fascinating but also credible. Trust in our commitment to quality and authenticity as you explore and learn with us.
Share this Fact:

Planning a trip? Build a personalized plan with Maya - your AI travel assistant by Live the World
An ultimate guide on Moscow Metro for first-comers

Anastasiya Molchanova
Travel tips for moscow.
Moscow public transport is very convenient and easy for first-comers to get around. Busses , trams , the metro , and the Moscow Central Circle are renovated and not really expensive, but there is a lifehack that tourists don’t usually know about. This ultimate guide will help you out. When you get to a metro station, what is the first thing you do? Correct, you get a ticket. So, you have to go straight to the ticket office and ask for a metro card called “ Troika ”. It costs 50 roubles, and this money is given back to you when you return the card (you can do it at any station you want, not necessarily at the one where you purchased it). Now, each of your rides costs 38 roubles, instead of 55 . Also, when you get a card, you don’t have any credit on it, so you have to top up your card at the ticket office or a ticket machine.

Where can it be used?
1) moscow metro.
Moscow metro is large, and it has more than 200 stations. You will never be late if you take Moscow Metro . Plus some stations are breath-taking, and they look like museums, for example Kievskaya , Park Pobedy , Novoslobodskaya . You can even book an excursion to learn more about the history of Moscow Metro !

2) Busses, trams and trolleys
Public transport in Moscow is the easiest way to get around, and if you don’t feel like spending your time under the ground, you can take a bus, a tram or a trolley. This kind of transport is more interesting as you can do some sightseein g while going to the city centre. The price is still the same, one ride costs 38 roubles.
3) Moscow Central Circle
Moscow Central Circle , an overland encircle line of metro, was opened a couple of years ago, and it helps out a lot of people every day. For tourists, Moscow Central Circle is useful because it’s another way of discovering Moscow . From the train, many places of interest can be observed: Moscow City Skyscrapers , Luzhniki Stadium and many more.

Moscow Transport is not expensive, but we can still save up some money when using it. This guide’s aim is to tell you about the “ Troika ” card that gives a 20 percent discount , and it’s very useful for first-comers who don’t feel like taking a taxi every now and then. Moreover, you can find out more about Russian culture in Moscow Metro, as it is a piece of art. Feel free to book an excursion there. Remember to give the “Troika” card back to the ticket office, so that you can help the environment (it takes about 400 years for plastics to decompose) and get back your 50 roubles .

Kievskaya metro station in Moscow

Park Pobedy metro station in Moscow
Want to plan a trip here? Talk to AI travel assistant Maya.
Interesting towns related to this story
I am Anastasiya from Moscow, a linguistics student who loves hiking, playing the guitar and drawing. On itinari, I will share with you my favorite Moscow’s spots, giving you the opportunity to dive into an amazing Russian way of living.
Plan a trip with Maya - your AI travel assistant

Stories you might also like

Moscow hosts LADYA, the Russian exhibition of national crafts

Save money & experience the culture in Costa Rican Central Markets

See Moscow from a birds-eye perspective

A guide to the public transport in Sofia

A stunning sunset near the Russian Academy of Science in Moscow

Moscow metro kaleidoscope

From horns to mobiles: Museum of Telephone History in Moscow

How to: Vienna Metro

Getting in and out of Minsk by public transport

Garden haute couture at the Moscow Flower Show

A short guide to getting around Warsaw

Tretyakov Gallery in Moscow: the greatest Russian fine art

Take the best photos of Moscow from a boat

Bolshaya Yakimanka Street, Moscow: where past meets modernity

Discovering the marvelous artworks of Almaty Metro

Terem Palace, a hidden gem of the Moscow Kremlin

Moscow's fight: How Russia's capital resists COVID-19

Journey to Christmas, an annual winter festival in Moscow
- Popular Professionals
- Design & Planning
- Construction & Renovation
- Finishes & Fixtures
- Landscaping & Outdoor
- Systems & Appliances
- Interior Designers & Decorators
- Architects & Building Designers
- Design-Build Firms
- Kitchen & Bathroom Designers
- General Contractors
- Kitchen & Bathroom Remodelers
- Home Builders
- Roofing & Gutters
- Cabinets & Cabinetry
- Tile & Stone
- Hardwood Flooring Dealers
- Landscape Contractors
- Landscape Architects & Landscape Designers
- Home Stagers
- Swimming Pool Builders
- Lighting Designers and Suppliers
- 3D Rendering
- Sustainable Design
- Basement Design
- Architectural Design
- Universal Design
- Energy-Efficient Homes
- Multigenerational Homes
- House Plans
- Home Remodeling
- Home Additions
- Green Building
- Garage Building
- New Home Construction
- Basement Remodeling
- Stair & Railing Contractors
- Cabinetry & Cabinet Makers
- Roofing & Gutter Contractors
- Window Contractors
- Exterior & Siding Contractors
- Carpet Contractors
- Carpet Installation
- Flooring Contractors
- Wood Floor Refinishing
- Tile Installation
- Custom Countertops
- Quartz Countertops
- Cabinet Refinishing
- Custom Bathroom Vanities
- Finish Carpentry
- Cabinet Repair
- Custom Windows
- Window Treatment Services
- Window Repair
- Fireplace Contractors
- Paint & Wall Covering Dealers
- Door Contractors
- Glass & Shower Door Contractors
- Landscape Construction
- Land Clearing
- Garden & Landscape Supplies
- Deck & Patio Builders
- Deck Repair
- Patio Design
- Stone, Pavers, & Concrete
- Paver Installation
- Driveway & Paving Contractors
- Driveway Repair
- Asphalt Paving
- Garage Door Repair
- Fence Contractors
- Fence Installation
- Gate Repair
- Pergola Construction
- Spa & Pool Maintenance
- Swimming Pool Contractors
- Hot Tub Installation
- HVAC Contractors
- Electricians
- Appliance Services
- Solar Energy Contractors
- Outdoor Lighting Installation
- Landscape Lighting Installation
- Outdoor Lighting & Audio/Visual Specialists
- Home Theater & Home Automation Services
- Handyman Services
- Closet Designers
- Professional Organizers
- Furniture & Accessories Retailers
- Furniture Repair & Upholstery Services
- Specialty Contractors
- Color Consulting
- Wine Cellar Designers & Builders
- Home Inspection
- Custom Artists
- Columbus, OH Painters
- New York City, NY Landscapers
- San Diego, CA Bathroom Remodelers
- Minneapolis, MN Architects
- Portland, OR Tile Installers
- Kansas City, MO Flooring Contractors
- Denver, CO Countertop Installers
- San Francisco, CA New Home Builders
- Rugs & Decor
- Home Improvement
- Kitchen & Tabletop
- Bathroom Vanities
- Bathroom Vanity Lighting
- Bathroom Mirrors
- Bathroom Fixtures
- Nightstands & Bedside Tables
- Kitchen & Dining
- Bar Stools & Counter Stools
- Dining Chairs
- Dining Tables
- Buffets and Sideboards
- Kitchen Fixtures
- Wall Mirrors
- Living Room
- Armchairs & Accent Chairs
- Coffee & Accent Tables
- Sofas & Sectionals
- Media Storage
- Patio & Outdoor Furniture
- Outdoor Lighting
- Ceiling Lighting
- Chandeliers
- Pendant Lighting
- Wall Sconces
- Desks & Hutches
- Office Chairs
- View All Products
- Designer Picks
- Side & End Tables
- Console Tables
- Living Room Sets
- Chaise Lounges
- Ottomans & Poufs
- Bedroom Furniture
- Nightstands
- Bedroom Sets
- Dining Room Sets
- Sideboards & Buffets
- File Cabinets
- Room Dividers
- Furniture Sale
- Trending in Furniture
- View All Furniture
- Bath Vanities
- Single Vanities
- Double Vanities
- Small Vanities
- Transitional Vanities
- Modern Vanities
- Houzz Curated Vanities
- Best Selling Vanities
- Bathroom Vanity Mirrors
- Medicine Cabinets
- Bathroom Faucets
- Bathroom Sinks
- Shower Doors
- Showerheads & Body Sprays
- Bathroom Accessories
- Bathroom Storage
- Trending in Bath
- View All Bath
- Houzz x Jennifer Kizzee
- Houzz x Motivo Home
- How to Choose a Bathroom Vanity

- Patio Furniture
- Outdoor Dining Furniture
- Outdoor Lounge Furniture
- Outdoor Chairs
- Adirondack Chairs
- Outdoor Bar Furniture
- Outdoor Benches
- Wall Lights & Sconces
- Outdoor Flush-Mounts
- Landscape Lighting
- Outdoor Flood & Spot Lights
- Outdoor Decor
- Outdoor Rugs
- Outdoor Cushions & Pillows
- Patio Umbrellas
- Lawn & Garden
- Garden Statues & Yard Art
- Planters & Pots
- Outdoor Sale
- Trending in Outdoor
- View All Outdoor
- 8 x 10 Rugs
- 9 x 12 Rugs
- Hall & Stair Runners
- Home Decor & Accents
- Pillows & Throws
- Decorative Storage
- Faux Florals
- Wall Panels
- Window Treatments
- Curtain Rods
- Blackout Curtains
- Blinds & Shades
- Rugs & Decor Sale
- Trending in Rugs & Decor
- View All Rugs & Decor
- Pendant Lights
- Flush-Mounts
- Ceiling Fans
- Track Lighting
- Wall Lighting
- Swing Arm Wall Lights
- Display Lighting
- Table Lamps
- Floor Lamps
- Lamp Shades
- Lighting Sale
- Trending in Lighting
- View All Lighting
- Bathroom Remodel
- Kitchen Remodel
- Kitchen Faucets
- Kitchen Sinks
- Major Kitchen Appliances
- Cabinet Hardware
- Backsplash Tile
- Mosaic Tile
- Wall & Floor Tile
- Accent, Trim & Border Tile
- Whole House Remodel
- Heating & Cooling
- Building Materials
- Front Doors
- Interior Doors
- Home Improvement Sale
- Trending in Home Improvement
- View All Home Improvement
- Cups & Glassware
- Kitchen & Table Linens
- Kitchen Storage and Org
- Kitchen Islands & Carts
- Food Containers & Canisters
- Pantry & Cabinet Organizers
- Kitchen Appliances
- Gas & Electric Ranges
- Range Hoods & Vents
- Beer & Wine Refrigerators
- Small Kitchen Appliances
- Cookware & Bakeware
- Tools & Gadgets
- Kitchen & Tabletop Sale
- Trending in Kitchen & Tabletop
- View All Kitchen & Tabletop
- Storage & Organization
- Baby & Kids
- Housekeeping & Laundry
- Pet Supplies

- View all photos
- Dining Room
- Breakfast Nook
- Family Room
- Bed & Bath
- Powder Room
- Storage & Closet
- Outdoor Kitchen
- Bar & Wine
- Wine Cellar
- Home Office
- Popular Design Ideas
- Kitchen Backsplash
- Deck Railing
- Privacy Fence
- Small Closet
- Stories and Guides
- Popular Stories
- Renovation Cost Guides
- Fence Installation Cost Guide
- Window Installation Cost Guide
- Discussions
- Design Dilemmas
- Before & After
- Houzz Research
- View all pros
- View all services
- View all products
- View all sales
- Living Room Chairs
- Dining Room Furniture
- Coffee Tables
- Home Office Furniture
- Join as a Pro
- Interior Design Software
- Project Management
- Custom Website
- Lead Generation
- Invoicing & Billing
- Landscape Contractor Software
- General Contractor Software
- Remodeler Software
- Builder Software
- Roofer Software
- Architect Software
- Takeoff Software
- Lumber & Framing Takeoffs
- Steel Takeoffs
- Concrete Takeoffs
- Drywall Takeoffs
- Insulation Takeoffs
- Stories & Guides
- LATEST FROM HOUZZ
- HOUZZ DISCUSSIONS
- SHOP KITCHEN & DINING
- Kitchen & Dining Furniture
- Sinks & Faucets
- Kitchen Cabinets & Storage
- Knobs & Pulls
- Kitchen Knives
- KITCHEN PHOTOS
- FIND KITCHEN PROS
- Bath Accessories
- Bath Linens
- BATH PHOTOS
- FIND BATH PROS
- SHOP BEDROOM
- Beds & Headboards
- Bedroom Decor
- Closet Storage
- Bedroom Vanities
- BEDROOM PHOTOS
- Kids' Room
- FIND DESIGN PROS
- SHOP LIVING
- Fireplaces & Accessories
- LIVING PHOTOS
- SHOP OUTDOOR
- Pool & Spa
- Backyard Play
- OUTDOOR PHOTOS
- FIND LANDSCAPING PROS
- SHOP LIGHTING
- Bathroom & Vanity
- Flush Mounts
- Kitchen & Cabinet
- Outdoor Wall Lights
- Outdoor Hanging Lights
- Kids' Lighting
- Decorative Accents
- Artificial Flowers & Plants
- Decorative Objects
- Screens & Room Dividers
- Wall Shelves
- About Houzz
- Houzz Credit Cards
- Privacy & Notice
- Cookie Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Mobile Apps
- Copyright & Trademark
- For Professionals
- Houzz vs. Houzz Pro
- Houzz Pro vs. Ivy
- Houzz Pro Advertising Reviews
- Houzz Pro 3D Floor Planner Reviews
- Trade Program
- Buttons & Badges
- Your Orders
- Shipping & Delivery
- Return Policy
- Houzz Canada
- Review Professionals
- Suggested Professionals
- Accessibility
- Houzz Support
- COUNTRY COUNTRY
Home & House Stagers in Elektrostal'
Location (1).
- Use My Current Location
Popular Locations
- Albuquerque
- Cedar Rapids
- Grand Rapids
- Indianapolis
- Jacksonville
- Kansas City
- Little Rock
- Los Angeles
- Minneapolis
- New Orleans
- Oklahoma City
- Orange County
- Philadelphia
- Portland Maine
- Salt Lake City
- San Francisco
- San Luis Obispo
- Santa Barbara
- Washington D.C.
- Elektrostal', Moscow Oblast, Russia
Professional Category (1)
- Accessory Dwelling Units (ADU)
Featured Reviews for Home & House Stagers in Elektrostal'
- Reach out to the pro(s) you want, then share your vision to get the ball rolling.
- Request and compare quotes, then hire the Home Stager that perfectly fits your project and budget limits.
A home stager is a professional who prepares a house for sale, aiming to attract more buyers and potentially secure a higher selling price. They achieve this through the following techniques:
- Rearranging furniture to optimize space and functionality.
- Decluttering to create a clean and spacious look.
- Making repairs to address visible issues.
- Enhancing aesthetics with artwork, accessories, and lighting.
- Introducing new furnishings to update the style.
Their goal is to present the house in the best light. Home stagers in Elektrostal' help buyers envision themselves living there, increasing the chances of a successful sale.
- Decluttering
- Furniture Selection
- Space Planning
- Art Selection
- Accessory Selection
Benefits of the home staging in Elektrostal':
- Attractive and inviting: Staging creates a welcoming atmosphere for potential buyers.
- Faster sale: Homes sell more quickly, reducing time on the market.
- Higher sale price: Staging can lead to higher offers and appeal to a wider range of buyers.
- Showcasing best features: Strategic arrangement highlights positives and minimizes flaws.
- Stand out online: Staged homes capture attention in online listings.
- Emotional connection: Staging creates a positive impression that resonates with buyers.
- Easy visualization: Buyers can easily picture themselves living in a staged home.
- Competitive advantage: Staging sets your home apart from others on the market.
- Affordable investment: Cost-effective way to maximize selling potential and ROI.
- Professional expertise: Experienced stagers ensure optimal presentation for attracting buyers.
What does an Elektrostal' home stager do?
What should i consider before hiring an interior staging company, questions to ask potential real estate staging companies in elektrostal', moscow oblast, russia:, business services, connect with us.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed. secondary succession. is the replacement of species that follows a disturbance in an already existing community. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Community, Competition, Resource and more.
Terms in this set (53) define community. -group of different species within a set space that interact and impart change onto each other. -incorporates a series of different population. define community ecology. study of how the different species within a community interact to create a functional existence. what is tolerance range.
Community Ecology Study Guide . Reading: Outline p. 273-275 . Videos: Niche Biodiversity Cooperative Interactions Ecosystem Changes . Powerpoints: Community Ecology . Review Questions: 1. Explain how competition contributes to competitive exclusion, resource partitioning, and character displacement. 2.
Define ecological niche. The sum of a species' use of the biotic and abiotic resources in its environment is called its ecological niche. 5. Discuss resource partitioning to explain how interspecific competition is reduced. Two species cannot coexist permanently in a community if their niches are identical.
These models will be covered in more detail in the chapter on Antagonistic Interactions. Figure Chapter14.1 C h a p t e r 14. 1: Predation is a short-term interaction in which the predator kills and eats its prey. An osprey (a) uses exceptional eyesight as well as sharp talons and beak to catch prey.
The diversity of a community can be measured using Simpson's Diversity Index, the following equation: Diversity Index = 1 - Σ (n / N)^2. where: n = the total number of organisms of a particular species N = total number of organisms of all species. Interactions between populations in a community determine the health of that community, changes ...
This page titled 4.3: Community Ecology is shared under a CC BY 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Tara Jo Holmberg. Ecosystem ecology is the integrated study of living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components of ecosystems and their interactions within an ecosystem framework. This science examines how ….
When the lynx population is low, the hare population size begins to increase due, in part, to low predation pressure, starting the cycle anew. Figure 5.4.1 5.4. 1. The cycling of snowshoe hare and lynx populations in Northern Ontario is an example of predator-prey dynamics.
A community is composed of all the populations of species that inhabit a specific area. Community ecology studies the interactions between such populations of species. Three important interspecific interactions are predation, competition, and symbiosis. The structure of communities also undergoes change due to abiotic and biotic disturbances ...
An ecological community consists of both biotic and abiotic factors. The biotic factors often interact via a food web. The structure of the community ecology is based on the organisms in the area ...
Teacher Guide and Answer Key; Teacher Guide to Google Apps; These homework questions were written to accompany my Powerpoint on this same topic: Community Ecology PowerPoint and Notes. All answers are included in the additional 4 page teacher guide that is included with this resource. The questions are of varying difficulty levels.
list the three types of symbiosis. parasitism, mutualism, commensalism. competitive exclusion principle. no two species can occupy the same niche in the same habitat at the same time. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like environmental science is the study of, list 5 components of the environment, what is the ...
Biology Roots. Ecology Unit Test and Study Guides contains 1 Unit Test on Ecology and 2 Study Guides. The unit test is 40 multiple choice questions, plus one short-answer which is divided into 4 parts (a,b,c,d). The test is 9 pages long and designed to take 45 minutes. The test is a word document and can be easily modified if need be.
An increase in animal biodiversity. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Khan Academy is a nonprofit with the mission of providing a free, world-class education for anyone, anywhere.
Population Ecology Study Guide. 1. List the three different types of ecology. Population, Community, Ecosystem. 2. Define "population". Group of same species living together in same place. 3. What two types of data do we need to study population ecology.
Teacher Guide and Answer Key; Google Apps Teacher Guide ; This worksheet of homework questions was written to go along with my Powerpoint on this same topic: Community Ecology PowerPoint and Notes. All answers are included in the additional 4 page teacher guide that is included with this resource. The questions are of varying difficulty levels.
40 Facts About Elektrostal. Elektrostal is a vibrant city located in the Moscow Oblast region of Russia. With a rich history, stunning architecture, and a thriving community, Elektrostal is a city that has much to offer. Whether you are a history buff, nature enthusiast, or simply curious about different cultures, Elektrostal is sure to ...
3) Moscow Central Circle. Moscow Central Circle, an overland encircle line of metro, was opened a couple of years ago, and it helps out a lot of people every day. For tourists, Moscow Central Circle is useful because it's another way of discovering Moscow. From the train, many places of interest can be observed: Moscow City Skyscrapers ...
Just answer a few questions to get matched with a local Fireplace professional. Or browse through the list of trusted Fireplace professionals in Elektrostal' on Houzz: See Elektrostal' Fireplace professionals' profiles, dive into their work photos and check out customer reviews.
Just answer a few questions to get matched with a local Home Stager. Or browse through the list of trusted Home Stagers in Elektrostal' on Houzz: See Elektrostal' Home Stagers' profiles, dive into their work photos and check out customer reviews. Reach out to the pro(s) you want, then share your vision to get the ball rolling.