- Scroll to top
- Light Dark Light Dark


Cart review
No products in the cart.
7 Essential Steps: How to Write a Research Brief That Gets Results
- Author Survey Point Team
- Published February 17, 2024

In this blog, we’ll explore seven essential steps to learn how to write a research brief that not only guides your project but also resonates with your audience. Research briefs are the unsung heroes of successful projects. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a newbie, crafting a well-structured brief can significantly impact the quality of your work.
Crafting a research brief that yields results is crucial. Explore the seven essential steps to write an effective research brief, ensuring success in your projects. Learn from experts and avoid common pitfalls.
Embarking on a research journey requires a well-crafted roadmap. A research brief serves as the compass, guiding you through the intricate terrain of data and insights. In this article, we will explore the seven essential steps to create a research brief that not only meets but exceeds expectations, ensuring the desired results.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Research Briefs
Why Research Briefs Matter
Research briefs are the cornerstone of successful projects. They set the tone, define objectives, and guide researchers toward meaningful outcomes. A well-structured brief not only saves time but also ensures the collected data aligns with the project goals.
How to Write a Research Brief: Understanding Your Objective
Defining Clear Research Goals
The first step in creating a research brief is understanding the project’s objective. Clearly define what you aim to achieve, ensuring every subsequent decision aligns with this overarching goal. Clarity at this stage is paramount.
Target Audience Analysis
Identifying and Understanding Your Audience
Knowing your audience is key to effective communication. Dive deep into demographic details, preferences, and behaviors. Tailor your research brief to resonate with the intended audience, enhancing its impact.
Crafting a Clear Research Question
Formulating Effective Research Queries
A well-defined research question is the compass that guides your entire project. Craft a question that is clear, concise, and directly aligns with your objectives. This foundational step ensures focused and purposeful research.
Literature Review
Building a Solid Foundation
Before venturing into uncharted territories, review existing literature. This not only provides valuable insights but also prevents redundancy. Acknowledge the work of others and identify gaps your research can fill.
Research Methodology
Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate research methodology is pivotal. Whether qualitative or quantitative, the chosen approach should align with your objectives. Justify your choice, considering the nature of your research question.
How to Write a Research Brief: Data Collection
Ensuring Quality Information
Collecting data is where the rubber meets the road. Implement a robust data collection strategy, ensuring the information gathered is relevant, accurate, and aligns with your research question. Quality over quantity is the mantra.
Analysis and Interpretation
Extracting Meaningful Insights
Analysis is the heart of research. Interpret the collected data, drawing meaningful conclusions. Your insights should directly contribute to answering your research question and, consequently, achieving your objective.
Crafting a Compelling Title
Making Your Research Brief Stand Out
A captivating title is the first impression your research brief makes. It should be concise, intriguing, and reflective of the study’s essence. Crafting a compelling title sets the stage for your audience’s engagement.
The Power of Effective Communication
Conveying Your Message Clearly
Beyond the data, effective communication is crucial. Present your findings in a clear, concise manner. Utilize visuals, charts, and graphs to enhance understanding. Make your research brief accessible to a broad audience.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes That Can Derail Your Research
Avoiding common pitfalls is as important as following the right steps. Identify and steer clear of potential pitfalls that could compromise the integrity and effectiveness of your research brief. Learn from others’ mistakes to enhance your own success.
Real-life Success Stories
Learnings from Notable Research Briefs
Drawing inspiration from successful research briefs can provide valuable insights. Explore real-life success stories, understand the strategies employed, and apply these lessons to elevate the impact of your own research briefs.
How to Write a Research Brief: FAQ
Can I write multiple research questions? Certainly, but ensure they all align with your main objective. Quality over quantity is crucial in research.
How do I choose between qualitative and quantitative methods? Consider the nature of your research question. Qualitative methods delve into depth, while quantitative methods focus on breadth.
Is a literature review necessary for all research briefs? Yes, a literature review establishes the context for your research and prevents duplication of efforts.
How do I make my title captivating? A captivating title is concise, intriguing, and reflective of your study’s essence. Use language that sparks curiosity.
What are common pitfalls in research briefs? Common pitfalls include unclear objectives, biased data collection, and inadequate analysis. Be vigilant to avoid these pitfalls.
Can I use the same research methodology for every project? Adapt your research methodology to align with each project’s unique objectives. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
Wrapping Up the Research Brief Journey In conclusion, crafting a research brief that gets results requires a strategic approach. By following the seven essential steps outlined in this article, you can navigate the complexities of research with confidence. Remember, a well-prepared brief not only guides your journey but ensures the destination is one of success.
Survey Point Team
Related posts.

- Posted by Survey Point Team
How K12 Data Analytics Can Help You Achieve Your School’s Goals in 2024

Discover Why Data Science is Right for You: 7 Compelling Reasons to Dive In Today

Python vs R for Data Analysis: Which One Should Learn in 2024?

- Business & Enterprise
- Education, Learning & Skills
- Energy & Environment
- Financial Services
- Health & Wellbeing
- Higher Education
- Work & Welfare
- Behavioural insights
- Business Spotlight – IFF’s business omnibus
- Customer experience research
- Customer satisfaction measurement
- National statistics and complex surveys
- Stakeholder research
- Tenant satisfaction measures
- Our approach
- Trusted partner
- Equality, diversity & inclusion at IFF
- Sustainability at IFF
- Charity giving
- Meet the team
- News & resources
- Case studies
How to write an effective research brief
Whether you’re launching a simple survey or planning a large-scale project the quality of your brief will hugely impact on the value you get from the research. While it can take a little time and effort creating a research brief, it will undoubtedly be time well spent – getting you better results and return on your investment and saving you valuable resources on further clarification. At best, a poor brief will be a time drain on you and your team. At worst, the findings will fail to meet your objectives, costing you time and money.
We’ve seen a lot of research briefs over the years. Some of which have been well thought through and clear, helping us prepare a detailed proposal and deliver an effective project and subsequent results. And others which have been not so good, lacking clarity or detail.
Using this experience, we’ve put together a ‘how to’ guide on writing an effective research brief, to help you ensure success on your next project.
1. Preparation is key
As with any project, before you start it’s crucial you think through what you want and need to deliver. Here are some things you should consider:
- Why are you conducting the research? What exactly are you looking to understand?
- Who are you looking to understand better? Who do you need to speak to answer your research questions?
- Who are your internal stakeholders? Have you discussed the project needs with the people in your organisation who will use the findings or who are invested in the research?
- How will the findings be used?
- When do you need the findings?
- Have you agreed a budget with either your procurement team, or the relevant person in your organisation?
2. Be clear on your objectives
This is one of the most important parts of your brief to convey to the reader what you want out of the project and ensure you get results which deliver.
Projects should have around three or four overarching aims which set out what the project ultimately wants to achieve.
These might be things like:
- Assess the impact of……
- Examine views of…..
- Evaluate the effectiveness of….
In addition to project objectives, you should also include the key questions you want the research to answer. These should support you in meeting the aims of the research.
For example, if the project aim is to assess the impact of an intervention, your research questions might include:
- Who did the intervention target?
- What did the project deliver?
- What elements were successful, and why?
- What were the main enablers and barriers?
3. Remember your audience
Research agencies or organisations who will be responding to your brief might not know anything about your business. So, make sure you include enough background information in your brief to enable them to understand your needs and deliver effectively. And avoid use of jargon or acronyms which could lead to errors or confusion.
4. Structure your research brief
Before you start to populate your brief it’s worth considering all the information and sections you need to include, to structure your thinking and ensure you don’t miss anything important.
This might include some, or all, of the following:
- Background info
- Introduction
- Aims and objectives
- Research Question(s)
- Issues / Risks
- Methodology
- Timing and Outputs
- Project Management
5. Make it thorough, yet succinct
While it’s crucial to include all the relevant information to enable bidders to respond effectively, no one wants to read reams and reams of information. To avoid the key information getting lost in the details use annexes to add supplementary information which could be useful.
6. Consider how prescriptive you want to be on the methodology
The extent to which you want to specify the methodology will depend on the project you aim to deliver. There are benefits and risks to being overly prescriptive or offering free reign. If you outline in precise detail how you want the research to be conducted, you will hamper any original ideas from those invited to tender and might limit the impact on the research. Whereas, if you’re less prescriptive, allowing room for creativity, you risk not getting the project or results you want, or receiving proposals on a scale which you can’t resource.
Generally, it is useful to allow those invited to tender some scope to develop the methodology they propose to use. Exceptions might be where previous work has to be very precisely replicated or some other very precise commitment about the nature of findings has been given to stakeholders.
7. Define your timelines
As a minimum, you need to include when you want the project to start and end. But you should also include the timetable for procurement. When planning this, don’t underestimate the time and resource needed to run a procurement exercise. Make sure your evaluators are available when you need them and have enough time blocked out in their diary.
You’ll likely also want to include milestones for when you expect outputs to be delivered, such as deadlines for a draft report (providing opportunity for review and feedback) and the final report; allowing sufficient time between the two to enable your stakeholders to consult, for you to feedback and for the contractor to revise the report.
8. Set expectations on cost
You will most likely have budgetary constraints, with a figure for what you are prepared to spend. To save you and your bidders time, and to set realistic expectations, you should include an indication within your brief. This will prevent you receiving proposals which are way out of the ballpark; enable bidders to plan a project which delivers on (or at least close to) budget; and will prevent any nasty surprises, further down the line.
By following these tips you’ll be well on your way to creating an effective research brief which delivers on time and on budget.
If you’d like more guidance download our “step-by-step” guide, which includes a template and information for what to include in each section to ensure success.
Download the guide now.
- Book a Demo
- Segmentation research
- Shopper Insights
- Customer Experience
- Customer journey mapping
- Brand positioning and differentiation
- Ad and creative testing
- Proposition development
- Product testing
- Concept testing
- Usage and attitude surveys
- Inclusive by design
- Social and consumer research expertise
- All articles
- Online Qual
- Market Research
- Strategic Thinking

How to conduct customer segmentation market research?
Qualitative research enables you to understand your customer base in detail, to explore the feelings and beliefs that lie behind their decisions and behaviour, and to identify the factors that are most likely to differentiate the different customer groups that you would like to target.

Brand research: what, why and how
Regardless of how much time you spend developing a brand strategy and planning your brand identity down to the last detail, all that matters, in the end, is consumer perceptions. In this article we explore different types of brand research, as well as the multiple methods you can choose to accomplish your brand research objectives.
Featured Stories
- Concept Testing: Turning your idea into a valuable asset
- Usage and attitude research: what is it and why do you need it?
- Mapping customer journeys: The role of qualitative market research
- How to build a powerful customer insight strategy
- Using Projective Techniques in Online Qual
- All resources
- How to Guides
- Webinars & Videos
- Together™ Help Centre

- Free Templates
Designed for use with our online qual research platform Together™, our activity templates include a range of activities, from warm-ups and ice-breakers, to deep cultural immersion projects and concept testing.

Conducting research with diverse and multi-cultural consumers
To deeply understand diverse and multi-cultural audiences requires deep expertise and an enabling approach. This guide contains the principles and approaches Further’s award-winning research team use to gather and activate insight and evidence for greater inclusion and equality.
Featured Content
- Understanding the male grooming category
- Using insight to develop a disruptive insurance proposition
- DEMO - An introduction to Further's Online Qual Platform Together™
- Research Briefing Template
- 10 essential tips for analysis and reporting
- Essential Guide to Mobile Ethnography
- Consumer Understanding
- Brand and Communications
- Innovation and NPD
- Case studies
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
How to write a great qualitative research brief
From speaking to researchers across the land, it's clear that it is fast becoming the norm for clients not to have a written brief.
Sure, they know what they want to achieve, what their objectives are, but they don’t always know how to get it down on paper and write a qualitative research brief (or they’ve not got the time!).
I’m always the first to put my hands up and offer to help clients write their briefs. There are three compelling reasons for that
- It takes pressure off the client
- It ensures that all stakeholders are included in the process and that everyone discusses - and agrees - the parameters of the research upfront
- It means we are immersed in the project and the business, deepening our understanding of what you need.
I’m going to share with you my thoughts on what makes a good qualitative research brief outline (for both online qual and face-to-face) and why it’s so necessary to get it right.
Start with the wrong brief, and you’re heading down the wrong path from the get-go. Not only will you set the wrong course, but you’ll probably cost the project incorrectly and even propose the wrong methods.
There's a handy research project brief template you can download along with a number of other useful tools you'll find in the resources section of our website.
.webp?width=635&name=pen-idea-bulb-paper%20(1).webp)
Before I dive into the specifics, here are three key things to consider:
1. Frame and re-frame
First and foremost, the research brief outline frames the client's problem or challenge, and it establishes the fundamental question(s) they want answering. More often than not, research briefs are framed through the lens of the business , when in fact, they should be through the lens of the consumer.
A cautionary tale:
Here's a quick example - naming no names! - of what happens when research is framed through the lens of the business, rather than through the lens of the consumer.
A well-known drinks company was looking to expand its range. An opportunity came up to buy a niche energy drink with a small but dedicated fanbase who loved its distinctive taste.
The company wanted to take the drink mainstream. So, they commissioned research focusing on what would make the drink more palatable to a wider audience.
The results came back saying that the drink should taste sweeter and the design of the packaging should be softened. The changes were made, the drink was relaunched and...
...it flopped. Mainstream consumers didn’t buy it. The original fanbase abandoned it. Why? Because the brief had been framed through the lens of the business, not the consumer. No one asked if the mainstream audience wanted a new energy drink. And as it turned out...they didn’t.
Reframing is perhaps better to be done by the researcher/agency as they can see outside the business more readily than the client. The phrase, ‘wood for the trees’ is poignant.
2. Keep it short and simple
Research project brief templates don’t need to be long and exhaustive. In fact, the the more precise and jargon-free the better. A short brief:
- Ensures clarity. Straightforward language - free from acronyms or industry-specific terms - is easy to understand. It avoids confusion.
- Gets to the point. A concise brief has been thought about and refined: helping to create a tight, accurate focus for your research.
- Encourages buy-in. It’s easy to digest, so it’s easier for stakeholders of all kinds to ‘get it’.
3. Take the right tone
Like any written document that has its readers, a qualitative research brief needs to adopt the appropriate tone, be it a formal business one or a more relaxed consumer-friendly version.
Most businesses are jam-packed with technical jargon , so handle this with care and remove where possible so that everyone can be sure of being (and staying) on the same page.
OK, now to the details...
Here’s what your qualitative research project brief template should include:
1. Some background
Provide a summary of the primary business the client is in. Clearly explain
- Why the business exists
- Its mission and vision
- How its goals have changed over time and its future goals
- The competitive set
- Which markets the study should explore
We sometimes call this a 'research amnesty’. It is vitally important we have sight of any pre-existing research so as not to duplicate any findings that already exist. No matter what form the research/insight is, throw it at us and we’ll read through it to create a detailed picture of the business/ brand .
2. Research objectives
This is where you set about describing what the core research task is. For example, the research objective might be to find out what your customers think of your recently launched product or service.
Set out specific research objectives to:
- Clarify the key questions you need to answer
- Identify the information you need to gather to address the challenge.
Here’s an example of three research objectives we created for a client who wanted to understand the best ways of supporting their employees’ wellbeing:
- To capture people’s attitudes and natural behaviours when it comes to their well-being
- To gather instinctive responses to what they would like to do more of and what is holding them back
- To discover and co-create ways we can help them in the future.
Now you’re starting to motor and get into the details around the questions that need to be answered, or the spaces you’re going to explore.
Remember, qualitative research helps understand why people do what they do, so write the objectives through that lens and think about the behaviours, motivations, thoughts and feelings you want to understand.
3. Business objectives
Your research objective may be driven by a strategic business objective. This is framed differently. Quite simply, it outlines why you are being asked to do this. For example, does the research support modifying a service or product or is it intended to deliver growth?
4. Stakeholder team
Which parties/departments (internal and/or external) will be involved with and have a vested interest in this research study? They might be a sponsor, collaborator or a third-party that needs an actionable outcome. For each stakeholder, detail their requirements and comment on their level and method of involvement. In some instances, different stakeholders will have conflicting expectations or objectives for the research. The focus needs to be agreed and signed-off by everyone before the process goes further.
5. Target audience to research
Who do you need to talk to? Are they current customers, lapsed customers or those of a competitor? Are demographics relevant, such as age, gender, income, occupation, location , company size, etc? Is social profiling relevant, or their personal attributes and proficiencies?
The target audience could include:
- Who you want researched and how many (sample size)?
- Source: Will the client be providing a customer list, or do you need to recommend the best way to source respondents such as panels, free-finding or social media?
6. Methodology
Based on the objectives, which qualitative research methods are best deployed and why. Are you proposing a combination of methods as is usually the case? Should the research be conducted face-to-face, by telephone or even online?
Consider internal milestones such as meetings and decision-making deadlines.
Timescale could include:
- Timescale for the procurement process, the start of the research and when you want the findings
- Whether you want to receive top-line findings in advance of the main findings
- Leaving time to receive a draft set of findings for you to review before receiving the final deliverables.
-1.webp?width=635&name=2021-12-22%20(1)-1.webp)
Do you have a specific research budget in mind, including incentives and recruitment? Can you provide guidance on the available budget, even if it is only a ball-park figure?
The budget might look to include:
- An indication of available budget; stipulate whether or not this includes VAT.
- A breakdown of how recruitment and incentives.
- Payment terms (if standard)
9. Deliverables (what/how/when)
Do you want the findings in a written report format or as a presentation? You may want to have both or to have a meeting with us to discuss the findings.
Deliverables could include:
- Your preferred format for the findings - for example, a report in Word or a presentation in PowerPoint, hardcopy and/or electronic, etc
- Do you want the researcher to present the findings, either in-person or remotely?
- Is there anything else you expect the research team to provide?
10. Hypotheses
If there are any pre-existing hunches, assumptions or hypotheses then now is a good time to share them with us. If they come out part-way through the project they may result in a re-brief and re-costing exercise, which is something to be avoided.
11. Materials the client will provide
Provide a detailed breakdown of the materials, assets and stimulus that the client will provide.
Examples might include:
- Visual brand identity assets
- Market reports/intelligence
- Information about competitors
- Stimulus materials
- Concepts and mock-ups
12. What does success look like?
Cast yourself into the future and imagine you are looking back at the successful project. What made it so successful, what was so good about it. Did it make you ‘famous’, if so why?
13. What does failure look like?
What are the failure factors of this project and what would team it unsuccessful ? Another way to think about this would be to ask the question ‘Why might this project fail?'
14. Client contacts and roles
Who are the immediate client team responsible for running this project, including day-to-day contact details and email addresses. It’s also a good idea to address what time/input the client has to invest in the project as you may find they don’t want to be involved in the way you hope.
There you have it.
There are more things to consider, and more detail to get into, pending the size/scale/risk of the project, but this will get you started.
There are many mistakes you can make in delivering qualitative research (online or in-person) and research community to be mindful of, especially how you see through consumer's half-truths , so beware.
If you have any questions, or have a research brief outline you'd like help with then why not book a demo or discovery call with one of our online qual specialists.
Topics: Online Qual , brief , debrief
ARTICLE CONTENTS
There you have it!
Discover our platform and services
Platform-only.
The insight platform for online qual, research communities, digital diaries, ethnography and more.
Services & Support
A range of expert research services and resources to help you deliver your projects with ease, speed and reach.
Human insight with impact; leveraging our academic and industry experts to uncover insight, create impact and make confident decisions.
You may also like…
Back in the day when online qual was still very much in its infancy, we launched our platform Together™ and we’re extremely proud to have been one of the pioneers of asynchronous online qual. To ...

Published 12 May 2022 4 minutes -->

Are you testing a new website or application? Together™ now includes Screen Recording.
Published 12 May 2022 1 minute -->

Whether you’re an experienced online qual researcher or a more recent convert to online research, it can feel quite daunting to think about everything that needs to get done before you can ...
Published 16 Mar 2022 10 minutes -->

We were amazed at the level of insight we achieved in just a week. Further opened our eyes to new ways of researching and understanding our staff
We helped Conde Nast International define a new global mission and vision statement

Further really understood the brief and were extremely proactive. We are now very confident that we’re taking the right products and proposition to market.
We helped this insuretech startup tailor their customer value proposition for the UK market ahead of a planned launch

Further's expert team pushed us to clarify our assumptions and to think harder about how to communicate the value of our products and services
We helped Keyhouse enter a new market and understand what target users of their case management software needed and how to position their offer

Working with Further was a refreshing and eye-opening experience…...the qualityof their output which was excellent.
We helped Unicef generate insights to support the development of a mass market, sustainable fundraising product.

Strategically, Further’s insights provided clear and directional answers that will guide us through our next phase of growth
We helped Zwift understand users and non-users needs and wants so they could prioritise their innovation pipeline

We helped Chilly’s leadership team consider new ways to understand and co-create with their customers’
%20(1).webp)
We helped disruptive pet insurance company Waggel develop customer personas and map out the current and intended customer journey.
Browse our site, download our resources, request a demo of our platform or speak to one of our experts

@ Copyright Further 2024
Further is a division of Youmeus Limited
© Copyright Further 2024
Ready to level up your insights?
Get ready to streamline, scale and supercharge your research. Fill out this form to request a demo of the InsightHub platform and discover the difference insights empowerment can make. A member of our team will reach out within two working days.
Cost effective insights that scale
Quality insight doesn't need to cost the earth. Our flexible approach helps you make the most of research budgets and build an agile solution that works for you. Fill out this form to request a call back from our team to explore our pricing options.
- What is InsightHub?
- Data Collection
- Data Analysis
- Data Activation
- Research Templates
- Information Security
- Our Expert Services
- Support & Education
- Consultative Services
- Insight Delivery
- Research Methods
- Sectors We Work With
- Meet the team
- Advisory Board
- Press & Media
- Book a Demo
- Request Pricing

Embark on a new adventure. Join Camp InsightHub, our free demo platform, to discover the future of research.

Read a brief overview of the agile research platform enabling brands to inform decisions at speed in this PDF.
InsightHub on the Blog
- Surveys, Video and the Changing Face of Agile Research
- Building a Research Technology Stack for Better Insights
- The Importance of Delegation in Managing Insight Activities
- Common Insight Platform Pitfalls (and How to Avoid Them)
- Support and Education
- Insight Delivery Services

Our services drive operational and strategic success in challenging environments. Find out how.

Close Connections bring stakeholders and customers together for candid, human conversations.
Services on the Blog
- Closing the Client-Agency Divide in Market Research
- How to Speed Up Fieldwork Without Compromising Quality
- Practical Ways to Support Real-Time Decision Making
- Developing a Question Oriented, Not Answer Oriented Culture
- Meet the Team

The FlexMR credentials deck provides a brief introduction to the team, our approach to research and previous work.

We are the insights empowerment company. Our framework addresses the major pressures insight teams face.
Latest News
- Insight as Art Shortlisted for AURA Innovation Award
- FlexMR Launch Video Close Connection Programme
- VideoMR Analysis Tool Added to InsightHub
- FlexMR Makes Shortlist for Quirks Research Supplier Award
- Latest Posts
- Strategic Thinking
- Technology & Trends
- Practical Application
- Insights Empowerment
- View Full Blog Archives

Discover how to build close customer connections to better support real-time decision making.

What is a market research and insights playbook, plus discover why should your team consider building one.
Featured Posts
- Five Strategies for Turning Insight into Action
- How to Design Surveys that Ask the Right Questions
- Scaling Creative Qual for Rich Customer Insight
- How to Measure Brand Awareness: The Complete Guide
- All Resources
- Client Stories
- Whitepapers
- Events & Webinars
- The Open Ideas Panel
- InsightHub Help Centre
- FlexMR Client Network

The insights empowerment readiness calculator measures your progress in building an insight-led culture.

The MRX Lab podcast explores new and novel ideas from the insights industry in 10 minutes or less.
Featured Stories
- Specsavers Informs Key Marketing Decisions with InsightHub
- The Coventry Panel Helps Maintain Award Winning CX
- Isagenix Customer Community Steers New Product Launch
- Curo Engage Residents with InsightHub Community
- Tech & Trends /
- Research Methods /
- Strategic Thinking /
How to Write a Market Research Brief (+ Free Template)
Emily james, 5 design principles to enhance your market researc....
Design is something we all use, whether consciously or unconsciously in the insights industry. Desig...
Sophie Grieve-Williams
- Insights Empowerment (29)
- Practical Application (168)
- Research Methods (283)
- Strategic Thinking (191)
- Survey Templates (7)
- Tech & Trends (386)
A market research brief is a document a client produces detailing important information about their unique situation and research requirements. This information should include (but is not limited to) the context of the situation in which the decision to conduct research was made, the initial objectives, and the resulting actions that hope to be taken after the research has concluded.
This brief would come before the typical market research plan (see our example here ), and so any information that is contained within the brief will be subject to modification once in-depth chats between the client and the research agency have been conducted.
This is one of the most important initiating steps for market research as it provides the necessary information that researchers need to understand your needs as much as you do yourself. There is a lot to be said for being on the same page at this early stage of the research experience. While different agencies will prioritise different aspects of the research project, 90% of the brief will follow the same lines, so a draft should always be made and then it can be easily edited to the agency’s requirements.
Why Create a Market Research Brief?
Writing up a brief is essential for the clear communication of your research requirements. Clear communication from the very start is essential if a positive working relationship is going to bloom between the parties involved. This brief outline of a business’ unique scenario communicates information that researchers need in order to achieve a high level of understanding which they can use to create and further refine a detailed plan the research experience.
Key Components
Just looking at the many template designs out there, we can see that a research brief has a few key aspects that everyone agrees are important:
1. Contextual Information
Now this can be interpreted in two ways, both of which should be included within the market research brief. The first interpretation is contextual information relating to the business hiring the research agency. What does the business do? What are it’s values? How is it run? And then the second interpretation is contextual information relating to how the need for research arose. What are the steps that took place towards the realisation that research was needed? This timeline could span months or just days, but even so, the detail must be included for the researcher to get a full understanding of the situation at hand.
2. Description of Research Purpose
At this point, a description of the product (or service) which is to be researched is needed; whoever is carrying out the research will need to know as much detail as possible about the subject of the study as this will have a big influence on the research method used (more information on that to come).
A description of the target markets will also be needed at this point: covering the geographical territories, the target audience (consumers vs. potential consumers) and any specific demographics that should be included or excluded. If this information is known, an approximate sample size can also be noted down.
If a business is wanting to test adverts, product examples, etc. then example designs or prototypes are going to be needed for both the researcher and the participants to use in the formation of the research tasks and the generation of data.
3. Objectives
Again, this aspect of the brief can be split up into two equally important interpretations. The objectives of the business are incredibly important as they provide another level of contextual understanding for the researcher. The other set of objectives that are needed within the brief, are the research objectives. Now, these are usually formed as questions that the business would like answered, but are subject to modification with the input of the researcher as they will know what is achievable, and what the business needs instead of what they want. Research objectives also cover what the business want to do with the insights generated as that gives an indication of what sort of research needs to be conducted. For the best research experience that ends in fully applicable insights, aligning business and research objectives is imperative.

4. Research Methods
While this will also be subject to modification, an idea of what types of research methods the business might want to employ for this research experience will provide insights on a couple of things to a well-trained researcher. Firstly, it will indicate the business’ level of knowledge on market research, which will allow the researcher to adjust their tone, etc. to accommodate for any knowledge gaps that might be present.
Secondly, it will indicate what type of research that the business is looking to conduct (i.e. qualitative or quantitative, etc.), even if they don’t know it themselves. This section also serves the purpose of sparking a bit of research on the business’ end to see for themselves what options are available to them.
5. Business constraints
This is a relatively simple one. Constraints such as time and budget are imperative to communicate to the researcher, as this will be the main factor in the shaping of your research experience. Depending on whether a business is very constrained or loosely constrained will determine what types of research tasks should be employed, and how extravagant and dedicated a researcher can be in their pursuit of insights for the business.
a. Research Deliverables
Finally, this is an optional category of information that will help shape the research experience in both the formation of the research tasks and the research reports. One important question is, what actions would you want to take after receiving the insights from the research?
If the answer to this question depends on the tone of the insights, then what options do you see for how the results will be used within the business? Different agencies will offer different reporting options and it helps to know which you would like. So, what type of report would you like to receive? The answers to these questions help how the report and project are framed.
Free Template Example
Use this link to download our free market research brief template. This template contains editable sections that complies with the advice above, with brief guidance and tips on how to make the most out of your brief. This template is currently available in .docx format only, and will require a copy of Microsoft Word or an alternative text editor to be used.

About FlexMR
We are The Insights Empowerment Company. We help research, product and marketing teams drive informed decisions with efficient, scalable & impactful insight.
About Emily James
As a professional copywriter, Emily brings our global vision to life through a broad range of industry-leading content.
Stay up to date
You might also like....

Delivering AI Powered Qual at Scale...
It’s safe to say artificial intelligence, and more specifically generative AI, has had a transformative impact on the market research sector. From the contentious emergence of synthetic participants t...

How to Use Digital Ethnography and ...
In one way or another, we’ve all encountered social media spaces. Whether you’ve had a Facebook account since it first landed on the internet, created different accounts to keep up with relatives duri...

5 Ways to Power Up Your Insight Pla...
In case you missed it (which seems unlikely), ChatGPT, the Artificial Intelligence model trained for conversation interactions has been making waves in the last few months. But once you’ve finished as...

- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Resources for Writing Briefs
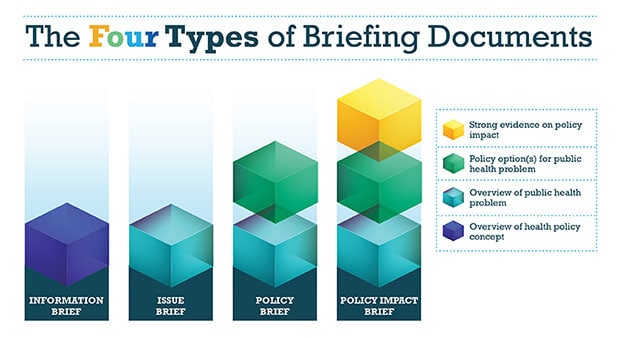
Policy is an important tool for improving population health. Decision makers often look to public health professionals for surveillance data, research findings, and evidence-based interventions and guidelines to help inform policy decisions. CDC has identified four types of briefing documents that can be used to clearly communicate public health evidence. Public health professionals can use the resources below to develop briefs that succinctly inform decision makers and stakeholders of the best available evidence on a public health problem, policy, method, or approach.
Accelerating Science Impact: Four Types of Briefing Documents
The four types of briefing documents can be used to share evidence and inform decisions at every stage of the CDC Policy Process. Selecting the appropriate brief depends on the level of the evidence available and the stage in the policy process. As research evidence grows and more information becomes available, public health professionals can move from an Issue Brief on the public health problem up to a Policy Impact Brief on the potential health, economic, or budgetary impact of a policy. All four brief types are described below.
- An Information Brief provides a summary of the research on a policy method, approach, or other related topic like behavioral economics or the Health in All Policies approach.
- An Issue Brief provides a summary of the best available evidence on a public health problem with policy implications. An issue brief is most appropriate when no policy solutions are known to exist and the issue is still in the problem identification domain of the policy process.
- A Policy Brief builds on an issue brief by providing a summary of evidence-based best practices or policy options for a public health problem. A policy brief is appropriate for issues in domains two, three, four and five of the policy process: policy analysis, strategy and policy development, policy enactment, and policy implementation respectively.
- A Policy Impact Brief is the most in-depth briefing document and provides a summary of the best available evidence on health, economic, or budgetary impact of one or more policies for a public health problem. A policy impact brief is appropriate when evaluations and evidence exist on the health or economic impact of the policy.
Steps for Writing Briefs

Steps for Writing Briefs Infographic Text
When you’re ready to start developing your brief, consider the following steps.
- Identify your key audience. Potential audiences may be those who inform policy at the federal, state, or local level; federal, state, local, or nongovernmental decision makers; or other stakeholders.
- Conduct audience research. In order to translate the evidence in a way that is easy to understand, get to know your audience. Don’t guess or assume. Review data or, when possible, gather new data through formative research.
- Determine your purpose and make sure your material contains one obvious main message.
- Define and explain terms that may be unfamiliar to your audience. Avoid using jargon or technical terms unless absolutely necessary.
- A “chunk” is the amount of words or numbers people can hold in their short-term memory and group with other words or numbers. A chunk should be only one idea that people can connect to other, related ideas.
- Use headings to organize and label chunks.
- Use bulleted or numbered lists to break up text in the body of the material and make information easier to scan and read. Lists with more than seven items should be broken into sub-lists.
- Review the CDC Clear Communication Index for other tips on communicating clearly with your intended audiences.
- Include at least one visual aid that conveys or supports the main message. Photographs, graphs, and infographics are visual aids. Simple, well-designed visual aids help people easily and quickly grasp information. Make sure words and visual aids convey the same message and reinforce each other.
- Include considerations for the key audience. Be clear about what the evidence might mean (as it relates to the issue at hand) but also what it might not mean (if relevant), and frame the evidence in a way that is accurate and easy for the audience to understand.
- Format your brief. Finally, your brief should be concise, compelling, and visually appealing to your audience.
PDF Version – Steps for Writing Briefs Infographic pdf icon [PDF – 479 KB]
Exit Notification / Disclaimer Policy
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) cannot attest to the accuracy of a non-federal website.
- Linking to a non-federal website does not constitute an endorsement by CDC or any of its employees of the sponsors or the information and products presented on the website.
- You will be subject to the destination website's privacy policy when you follow the link.
- CDC is not responsible for Section 508 compliance (accessibility) on other federal or private website.
Popular searches
- How to Get Participants For Your Study
- How to Do Segmentation?
- Conjoint Preference Share Simulator
- MaxDiff Analysis
- Likert Scales
- Reliability & Validity
Request consultation
Do you need support in running a pricing or product study? We can help you with agile consumer research and conjoint analysis.
Looking for an online survey platform?
Conjointly offers a great survey tool with multiple question types, randomisation blocks, and multilingual support. The Basic tier is always free.
Catherine Chipeta
Monthly newsletter.
Get the latest updates about market research, automated tools, product testing and pricing techniques.
A good market research brief helps agencies lead successful projects. Learn what to include and how to write a detailed brief with our template guide.
A market research brief is a client document outlining all the relevant information that a research agency needs to understand the client’s specific research needs to propose the most suitable course of action.
A clear, informed brief will ensure the market researcher can deliver the most effective research possible. It also streamlines the project by reducing the need for back and forth between your company and the researcher. A good brief will leave no confusion and provide a meaningful framework for you and the researcher, maximising the accuracy and reliability of insights collected.
Start your project faster with our market research brief template!
In this article, we’ve broken down the key components of a well-written brief, with examples. Using this template guide, you can confidently equip the researcher with the right information to deliver exemplary research for your next project.
Business Background/ Project Background
This section of the brief introduces your company to the market researcher, giving them a more informed overview of your brand, product/service, and target market. You should provide all available context to ensure you and the researcher are on the same page with the project.
Relevant information to add in this section includes: company details, company mission/vision, industry status and trends, market performance history, competitive context, any existing research.
Business Objectives/ Marketing Objectives
Your business objectives/marketing objectives should answer why you are being asked to conduct the research. The researcher should be able to grasp the existing problems/issues your company is looking to address in the research.
For example, this could involve sales, competition, customer satisfaction, or product innovation, to name a few.
Research Objectives
Research objectives address the specific questions you would like the research to cover, including what insights you wish to gain. This is where you should detail what actions your company is planning to take based on the research you are commissioning.
Your research objective is one of the most important elements of your brief, as it dictates how your study will be conducted and the quality of results.
Target Market
Who will this research focus on? This is where you should state respondents’ demographic and profiling information, along with any pre-existing segments you want to target. Be specific, but also be aware that the more restrictive the criteria are, the higher the sample cost will be. Extensive limitations are also realistically harder to meet.
For example:
- Market: Canada
- Sample size: 200 – 1000
- Demographics: Household income of $150k and above a year
- Markets: Malaysia (priority), Thailand, Singapore
- Sample size: N=200 (Product Variant Selector) + N=500 (Conjoint)
- Demographics: 16 – 50 years old
- National representation: Age, gender and location
- Target definition: Bought electronics online in the past 12 months
- Reads on: 16 – 30-year olds vs. 31 – 50-year olds
- Market: South America
- Sample size: 1800
- Target definition: Main and joint grocery buyers
- 5 target groups: Income, urban/rural, age, family status, shopping frequency (divide each into 3 subgroups, e.g. low, medium, high).
Action Standards/ Decision Rules
Action standards outline which criteria will determine the decisions you make following research. These should detail specific numerical scores and any company benchmarks which need to be met in your research results for decision-making to go ahead. Clear and detailed action standards will allow you to make decisions faster and more confidently following research.
Nestlé’s 60/40 action standard which prioritises preference and nutrition, by aiming “to make products that achieve at least 60% consumer taste preference with the added ‘plus’ of nutritional advantage”.
Pricing is seen as credible by at least 40% of the target market.
Product has at least 50% acceptance from the target market.
Methodology
You should only include methodology if you are certain of the approach you want to take. If you do not know which methodology you should use, leave this section blank for agency recommendations.
Monadic test : Monadic testing introduces survey respondents to individual concepts, products in isolation. It is usually used in studies where independent findings for each stimulus are required, unlike in comparison testing, where several stimuli are tested side-by-side. Each product/concept is displayed and evaluated separately, providing more accurate and meaningful results for specific items.
Discrete choice modelling : Sometimes referred to as choice-based conjoint, discrete choice is a more robust technique consistent with random utility theory and has been proven to simulate customers’ actual behaviour in the marketplace. The output on relative importance of attributes and value by level is aligned to the output from conjoint analysis (partworth analysis).
Qualitative research : Qualitative forms of research focus on non-numerical and unstructured data, such as participant observation, direct observation, unstructured interviews, and case studies.
Quantitative research : Numbers and measurable forms of data make up quantitative research, focusing on ‘how many’, ‘how often’, and ‘how much’, e.g. conjoint analysis , MaxDiff , Gabor-Granger , Van Westendorp .
Deliverables
Deliverables should clearly outline project expectations – both from your company and the agency. This should cover who is responsible for everything required to undertake research, including survey inputs and outputs, materials, reporting, reviewing, and any additional requirements.
- PowerPoint presentation
- Crosstabs of data
- Raw datasets
- Excel simulator
- Online dashboard
- “Typing tool” for future research
Timing and Cost
Timing covers the due dates for key milestones of your research project, most importantly, for your preliminary and final reports. Cost should include your project budget, along with any potential additional costs/constraints.
Contacts and Responsibilities
This section states all stakeholders involved in the project, their role and responsibilities, and their contact details. You should ensure that these are easy to locate on your brief, for quick reference by the agency and easier communication.
Ready-to-use market research brief template with examples
Start your research project faster and get better results. Using this template, you can confidently equip the researcher with the right information to deliver exemplary research for your next project.
Read these articles next:
How to improve your research with time series analysis.
Time series analysis is a powerful tool for analysing data collected throughout an extended period. Here is how you can use it to understand changes in consumer and market trends, and make data-driven decisions.
How to Select Statistics for a Single Variable
What are the different statistics available for a single variable? Selecting statistics for a single variable depends of the type of variable: nominal, ordinal, or interval.
Synthetic respondents are the homoeopathy of market research
This article covers how synthetic responses are generated, their unreliability and invalidity, the allure of synthetic respondents, and the effects of this trend.
Which one are you?
I am new to conjointly, i am already using conjointly, cookie consent.
Conjointly uses essential cookies to make our site work. We also use additional cookies in order to understand the usage of the site, gather audience analytics, and for remarketing purposes.
For more information on Conjointly's use of cookies, please read our Cookie Policy .
Do you want to be updated on new features from Conjointly?
We send an occasional email to keep our users informed about new developments on Conjointly : new types of analysis and features for quality insight.
Subscribe to updates from Conjointly
You can always unsubscribe later. Your email will not be shared with other companies.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Graduate School Applications: Writing a Research Statement

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
What is a Research Statement?
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete.
The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate’s application for post-undergraduate study. This may include applications for graduate programs, post-doctoral fellowships, or faculty positions. The research statement is often the primary way that a committee determines if a candidate’s interests and past experience make them a good fit for their program/institution.
What Should It Look Like?
Research statements are generally one to two single-spaced pages. You should be sure to thoroughly read and follow the length and content requirements for each individual application.
Your research statement should situate your work within the larger context of your field and show how your works contributes to, complicates, or counters other work being done. It should be written for an audience of other professionals in your field.
What Should It Include?
Your statement should start by articulating the broader field that you are working within and the larger question or questions that you are interested in answering. It should then move to articulate your specific interest.
The body of your statement should include a brief history of your past research . What questions did you initially set out to answer in your research project? What did you find? How did it contribute to your field? (i.e. did it lead to academic publications, conferences, or collaborations?). How did your past research propel you forward?
It should also address your present research . What questions are you actively trying to solve? What have you found so far? How are you connecting your research to the larger academic conversation? (i.e. do you have any publications under review, upcoming conferences, or other professional engagements?) What are the larger implications of your work?
Finally, it should describe the future trajectory on which you intend to take your research. What further questions do you want to solve? How do you intend to find answers to these questions? How can the institution to which you are applying help you in that process? What are the broader implications of your potential results?
Note: Make sure that the research project that you propose can be completed at the institution to which you are applying.
Other Considerations:
- What is the primary question that you have tried to address over the course of your academic career? Why is this question important to the field? How has each stage of your work related to that question?
- Include a few specific examples that show your success. What tangible solutions have you found to the question that you were trying to answer? How have your solutions impacted the larger field? Examples can include references to published findings, conference presentations, or other professional involvement.
- Be confident about your skills and abilities. The research statement is your opportunity to sell yourself to an institution. Show that you are self-motivated and passionate about your project.
- Support Center
- System Status

How to write a legal memorandum

- April 16, 2024

Jennifer Anderson
So, you landed your first legal job? Congratulations! If it hasn’t happened already, you should know what’s coming next; a legal memorandum.
Invariably, some high-powered lawyer in your firm will call you into their office and speak words that strike fear into the hearts of many fledgling legal professionals:
“ Can you draft me a memo on [insert arcane legal theory here]?”
The request, while anxiety-producing for many, is a fair one. The legal memorandum is how you earn your chops as a young legal professional. Indeed, few skills are as pivotal as the ability to draft a clear, concise, and persuasive legal memo.
The truth is, a legal memo will always be a critical tool within your practice, both as writer – and years from now – as the seasoned attorney requesting a thorough analysis on one topic or another. At any stage, it’s an important document that provides analysis and advice on key legal issues impacting your clients.
Whether you’re communicating with a senior partner, advising a client, or presenting an argument to a judge, the legal memo is your bridge between legal research and practical application.
Understanding its structure, purpose, and audience is essential for any lawyer aiming to make a significant impact in their job.
Not surprisingly, that is the topic of today’s post.
Understanding the purpose and audience
The cornerstone of any effective professional writing is a deep understanding of both the memo’s purpose and its intended audience . A legal memorandum primarily aims to inform and persuade.
It’s a detailed document that analyzes a particular legal issue or question, outlines the relevant law, applies the law to the facts at hand, and concludes with a recommendation or analysis.
The audience for a legal memo can vary, ranging from senior attorneys within your law firm who are well-versed in legal jargon to clients who may have little to no legal background. This variance in audience necessitates a flexible writing style that can be adapted to be as accessible or as detailed as the situation requires.
Thus, before you ever set out to write a single word of a legal memorandum, it is critical that you understand who you’re writing for and why you’re writing at all. Simple questions, to be sure, but the answers dictate everything else you’ll do in the process.
Components of a legal memorandum
Although the purpose and audience of your memo will certainly inform the final output, each legal memorandum should be made up of the same critical parts . Let’s break down each section:
This section includes the basic information about the memo: who it’s to, who it’s from, the date, and the subject matter.
And, while the information in the heading may seem obvious (and perhaps unnecessary) today, I promise you those details will be critically important for the young attorney in your firm who discovers your memo 10 years from now and is trying to determine if it contains useful information for her topic de jour . Legal memos never die. Hopefully, they just get filed effectively for future use.
Opening statement/issue presented
Begin with a clear and concise statement of the issue at hand. This section should succinctly summarize the legal question or problem your memo is addressing and is often framed as a question. For example, the top of your memo might read: “Issue presented: Does a California landowner have an obligation to disclose dangerous property conditions to a prospective tenant?”
Brief answer
Follow the opening statement with a brief answer . If your “issue presented” was stated as a “yes or no” question, begin your brief answer with one of those two words. Then you can provide a very short explanation of that response. This snapshot of your conclusion allows the reader to understand the memo’s direction from the outset.
The facts section is where you lay out the relevant information that forms the foundation of your legal analysis. It’s critical to be both accurate and objective, presenting the facts in a manner that is unambiguous and straightforward.
This is the heart of the memo, where you provide a detailed legal analysis. Here, you’ll examine the legal precedents, statutes, and principles that are relevant to the issue. It involves critically analyzing how these legal frameworks apply to the facts of your case, and presenting a reasoned argument that supports your conclusions.
In the conclusion , summarize your analysis and reiterate the answer provided in the brief answer section. This part should clearly state your final recommendations or findings based on the preceding discussion and should identify any laws that were critical to your analysis.
Research and analysis
Before drafting a single word of your memorandum, be sure to conduct thorough legal research . The strength of your memo hinges on the validity of your research and the relevance of the legal precedents, statutes, and regulations you identify.
Start by consulting primary sources of law, such as statutes that directly address your legal issue and case law where similar issues have been adjudicated.
Later, secondary sources like law review articles and legal treatises can offer insights into the interpretation and application of the law in various contexts.
Effective legal analysis doesn’t merely recite the law; it involves applying the law to the facts of your case in a manner that supports your conclusions.
Be critical in your research, however. You should look for potential counterarguments and learn those arguments as well as the ones that support your position. This demonstrates not only the depth of your research but also your ability to anticipate and counter opposing viewpoints.
And, as always, don’t forget to make sure the research you’ve relied on is current and remains good law .
Writing style and format
The clarity of your writing is one of the most important aspects of your legal memorandum. The goal is to communicate complex legal analysis in a manner that is both accessible and persuasive.
To achieve this, embrace plain English and strive to be as clear and concise as possible. Avoid unnecessary legal jargon or complex sentence structures that might obscure your message. Instead, use simple, direct language that conveys your analysis effectively.
The format of your memorandum should enhance its readability. Use headings and subheadings to break down the discussion section into manageable parts.
Bullet points or numbered lists can clarify lists of factors or elements. Consistent use of these formatting tools not only makes your memo easier to navigate but also highlights the logical flow of your arguments.
Revising and editing
A well-crafted legal memorandum is often the result of rigorous revising and editing . The first draft is rarely your best work. In fact, you should think of it as a starting point. Begin by reviewing your memo for structural coherence; does the argument flow logically from introduction to conclusion? Are your major points supported by solid evidence and analysis?
Next, scrutinize your language and style. Eliminate any ambiguities, redundancies, or instances of passive voice that can dilute the persuasiveness of your arguments. Pay special attention to legal citations to ensure they comply with the relevant citation manual and accurately support your assertions.
Finally, seek feedback from peers, mentors, or supervisors. A fresh set of eyes can catch errors you might have missed and offer insights to improve the clarity and effectiveness of your memorandum.
In a pinch ( i.e., when you have to work all night to get your memo on the partner’s desk by morning), you’ll have to be your own editor. One effective way to do this is to read your memo aloud to yourself . Somehow, this helps your brain to spot typos and unclear sentences in a way silent reading never does.
Ethical considerations
This tip is crucial, though the practical implications of it can be uncomfortable. Always remember that you have an ethical duty to represent the law accurately and honestly.
This includes presenting a balanced analysis that considers all relevant legal precedents, even those that may not support the outcome your client or your boss want to hear. Misrepresenting the law or selectively citing authorities is not only unethical but can undermine your credibility.
Moreover, ensure that your memorandum adheres to the highest standards of professional integrity by avoiding plagiarism. Properly cite all sources of legal authority, including cases, statutes, and secondary sources. Use quotes accurately and give credit where it is due.
Ultimately, you should think of the legal memorandum as more than just a document. It’s really a manifestation of your ability to analyze, argue, and advise within the confines of the law.
Mastering legal memo writing not only demonstrates your competence in legal analysis but also showcases your ability to communicate effectively – traits that are indispensable in the field you’ve chosen.
Additional resources
If you still feel like your memo-writing skills could use some improvement, consider spending some time with these resources
- Books: Legal Writing in Plain English and The Winning Brief (both by Bryan A. Garner) offer invaluable insights into effective legal writing techniques.
- Online courses: Websites like Coursera , LinkedIn Learning , and edX offer courses on legal writing and research taught by experienced legal professionals.
- Continuing education: You have to do CLE anyway, so why not take a writing course? Companies like Lawline and the National Academy of Continuing Legal Education offer courses on writing. And if you’re in a time crunch, there’s even a crash course in legal writing that will only take a half hour to complete.
Drafting legal memoranda is an essential skill that every lawyer must master early in their career.
A well-constructed legal memo allows you to effectively communicate your analysis, arguments, and recommendations while demonstrating your grasp of legal principles and precedents.
Clarity and precision in writing, thorough research, and an understanding of the audience are all crucial components of an impactful memo. Revising and editing your work ensures that your arguments are well-supported and logically structured.
As you continue to hone your memo-writing skills, you will set yourself apart as a reliable and effective legal professional.
One Legal: Delightfully easy eFiling

Share this article on social media:
More to explore.

Pro bono lawyers: What to know

Preparing for trials: What paralegals and attorneys need to know

A paralegal’s guide on how to do legal research

What is One Legal?
We’re California’s leading litigation services platform, offering eFiling, process serving, and courtesy copy delivery in all 58 California counties. Our simple, dependable platform is trusted by over 20,000 law firms to file and serve over a million cases each year.

All of your litigation support needs at your fingertips
© InfoTrack US, Inc.
- Accessibility statement
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Explore the seven essential steps to write an effective research brief, ensuring success in your projects. Learn from experts and avoid common pitfalls. Embarking on a research journey requires a well-crafted roadmap. A research brief serves as the compass, guiding you through the intricate terrain of data and insights.
2. Be clear on your objectives. This is one of the most important parts of your brief to convey to the reader what you want out of the project and ensure you get results which deliver. Projects should have around three or four overarching aims which set out what the project ultimately wants to achieve.
research within the current policy and practice context and make clear links for them. 3. When should I write a research briefing? Policymakers and practitioners are interested in policy relevant research as it progresses. You can write a briefing at any stage in a project; in fact you may want to plan a number of briefings throughout a project.
Good research briefings should come from good published research study. So for a starter, research briefings should be using peer-reviewed sources (research that has been reviewed by other researchers and experts for accuracy, validity and reliability). Anyone can publish a blog. Anyone can write a self-published book.
This guide contains: nA step-by-step guide to writing a research brief, from idea conception through to brief. nSuggestions on the sections you should include and the information to supply in each. nTop tips to ensure research agencies or other bidders understand your needs and can ivers on time and on budget. www.iffresearch.com.
Introduction (about 50 to 100 words) Write a one-paragraph introduction (50 to 100 words) summarizing the policy problem, the research question, and the key findings. Use the introduction and conclusion to the discussion paper as sources for the introduction (and conclusion) of the brief. This is your homework!
2. Keep it short and simple. Research project brief templates don't need to be long and exhaustive. In fact, the the more precise and jargon-free the better. A short brief: Ensures clarity. Straightforward language - free from acronyms or industry-specific terms - is easy to understand. It avoids confusion.
Here's what your qualitative research brief should include: Background. Provide a summary of the primary business the client is in, and clearly explain why the business exists, what its mission ...
Choose a research paper topic. Conduct preliminary research. Develop a thesis statement. Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft.
Tips for writing an effective brief. Be clear and concise: Use straightforward language and get directly to the point to avoid confusion. Clarity is king in brief writing. Know your audience: Customize the brief to suit the reader's understanding and expectations.
The Structure of a Research Summary typically include: Introduction: This section provides a brief background of the research problem or question, explains the purpose of the study, and outlines the research objectives. Methodology: This section explains the research design, methods, and procedures used to conduct the study.
Free Template Example. Use this link to download our free market research brief template. This template contains editable sections that complies with the advice above, with brief guidance and tips on how to make the most out of your brief. This template is currently available in .docx format only, and will require a copy of Microsoft Word or an ...
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. ... natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and ...
Building Expertise with Brief Writing. Training in doctoral programs, which often encourages lengthy, detail-oriented writing, runs counter to the skills inherent in writing research briefs. While certain programs offer training for writing for non-academic audiences, we advocate for a greater focus on this skill during graduate training.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
A Policy Brief builds on an issue brief by providing a summary of evidence-based best practices or policy options for a public health. problem. A policy brief is appropriate for issues in domains two, three, four and five of the policy process: policy analysis, strategy and policy development, policy enactment, and policy implementation ...
A market research brief is a client document outlining all the relevant information that a research agency needs to understand the client's specific research needs to propose the most suitable course of action. A clear, informed brief will ensure the market researcher can deliver the most effective research possible.
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
While studying in FIU/MAS's Global Strategic Communication Creative Track graduate program you will be weighing your career options upon graduation, from working as a freelancer to working in a digital marketing agency. You will find out that your options will open up as you become exposed to many professionals doing distinct and unique work in
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
A research statement is a short document that provides a brief history of your past research experience, the current state of your research, and the future work you intend to complete. The research statement is a common component of a potential candidate's application for post-undergraduate study.
Books: Legal Writing in Plain English and The Winning Brief (both by Bryan A. Garner) offer invaluable insights into effective legal writing techniques. Online courses: Websites like Coursera, LinkedIn Learning, and edX offer courses on legal writing and research taught by experienced legal professionals.
Example: BODY PARAGRAPH 1. First point. Sub-point. Sub-point of sub-point 1. Essentially the same as the alphanumeric outline, but with the text written in full sentences rather than short points. Example: First body paragraph of the research paper. First point of evidence to support the main argument.