How to master the seven-step problem-solving process
In this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , Simon London speaks with Charles Conn, CEO of venture-capital firm Oxford Sciences Innovation, and McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin about the complexities of different problem-solving strategies.
Podcast transcript
Simon London: Hello, and welcome to this episode of the McKinsey Podcast , with me, Simon London. What’s the number-one skill you need to succeed professionally? Salesmanship, perhaps? Or a facility with statistics? Or maybe the ability to communicate crisply and clearly? Many would argue that at the very top of the list comes problem solving: that is, the ability to think through and come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Looked at this way, it’s no surprise that McKinsey takes problem solving very seriously, testing for it during the recruiting process and then honing it, in McKinsey consultants, through immersion in a structured seven-step method. To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
Charles and Hugo, welcome to the podcast. Thank you for being here.
Hugo Sarrazin: Our pleasure.
Charles Conn: It’s terrific to be here.
Simon London: Problem solving is a really interesting piece of terminology. It could mean so many different things. I have a son who’s a teenage climber. They talk about solving problems. Climbing is problem solving. Charles, when you talk about problem solving, what are you talking about?
Charles Conn: For me, problem solving is the answer to the question “What should I do?” It’s interesting when there’s uncertainty and complexity, and when it’s meaningful because there are consequences. Your son’s climbing is a perfect example. There are consequences, and it’s complicated, and there’s uncertainty—can he make that grab? I think we can apply that same frame almost at any level. You can think about questions like “What town would I like to live in?” or “Should I put solar panels on my roof?”
You might think that’s a funny thing to apply problem solving to, but in my mind it’s not fundamentally different from business problem solving, which answers the question “What should my strategy be?” Or problem solving at the policy level: “How do we combat climate change?” “Should I support the local school bond?” I think these are all part and parcel of the same type of question, “What should I do?”
I’m a big fan of structured problem solving. By following steps, we can more clearly understand what problem it is we’re solving, what are the components of the problem that we’re solving, which components are the most important ones for us to pay attention to, which analytic techniques we should apply to those, and how we can synthesize what we’ve learned back into a compelling story. That’s all it is, at its heart.
I think sometimes when people think about seven steps, they assume that there’s a rigidity to this. That’s not it at all. It’s actually to give you the scope for creativity, which often doesn’t exist when your problem solving is muddled.
Simon London: You were just talking about the seven-step process. That’s what’s written down in the book, but it’s a very McKinsey process as well. Without getting too deep into the weeds, let’s go through the steps, one by one. You were just talking about problem definition as being a particularly important thing to get right first. That’s the first step. Hugo, tell us about that.
Hugo Sarrazin: It is surprising how often people jump past this step and make a bunch of assumptions. The most powerful thing is to step back and ask the basic questions—“What are we trying to solve? What are the constraints that exist? What are the dependencies?” Let’s make those explicit and really push the thinking and defining. At McKinsey, we spend an enormous amount of time in writing that little statement, and the statement, if you’re a logic purist, is great. You debate. “Is it an ‘or’? Is it an ‘and’? What’s the action verb?” Because all these specific words help you get to the heart of what matters.

Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
Simon London: So this is a concise problem statement.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah. It’s not like “Can we grow in Japan?” That’s interesting, but it is “What, specifically, are we trying to uncover in the growth of a product in Japan? Or a segment in Japan? Or a channel in Japan?” When you spend an enormous amount of time, in the first meeting of the different stakeholders, debating this and having different people put forward what they think the problem definition is, you realize that people have completely different views of why they’re here. That, to me, is the most important step.
Charles Conn: I would agree with that. For me, the problem context is critical. When we understand “What are the forces acting upon your decision maker? How quickly is the answer needed? With what precision is the answer needed? Are there areas that are off limits or areas where we would particularly like to find our solution? Is the decision maker open to exploring other areas?” then you not only become more efficient, and move toward what we call the critical path in problem solving, but you also make it so much more likely that you’re not going to waste your time or your decision maker’s time.
How often do especially bright young people run off with half of the idea about what the problem is and start collecting data and start building models—only to discover that they’ve really gone off half-cocked.
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah.
Charles Conn: And in the wrong direction.
Simon London: OK. So step one—and there is a real art and a structure to it—is define the problem. Step two, Charles?
Charles Conn: My favorite step is step two, which is to use logic trees to disaggregate the problem. Every problem we’re solving has some complexity and some uncertainty in it. The only way that we can really get our team working on the problem is to take the problem apart into logical pieces.
What we find, of course, is that the way to disaggregate the problem often gives you an insight into the answer to the problem quite quickly. I love to do two or three different cuts at it, each one giving a bit of a different insight into what might be going wrong. By doing sensible disaggregations, using logic trees, we can figure out which parts of the problem we should be looking at, and we can assign those different parts to team members.
Simon London: What’s a good example of a logic tree on a sort of ratable problem?
Charles Conn: Maybe the easiest one is the classic profit tree. Almost in every business that I would take a look at, I would start with a profit or return-on-assets tree. In its simplest form, you have the components of revenue, which are price and quantity, and the components of cost, which are cost and quantity. Each of those can be broken out. Cost can be broken into variable cost and fixed cost. The components of price can be broken into what your pricing scheme is. That simple tree often provides insight into what’s going on in a business or what the difference is between that business and the competitors.
If we add the leg, which is “What’s the asset base or investment element?”—so profit divided by assets—then we can ask the question “Is the business using its investments sensibly?” whether that’s in stores or in manufacturing or in transportation assets. I hope we can see just how simple this is, even though we’re describing it in words.
When I went to work with Gordon Moore at the Moore Foundation, the problem that he asked us to look at was “How can we save Pacific salmon?” Now, that sounds like an impossible question, but it was amenable to precisely the same type of disaggregation and allowed us to organize what became a 15-year effort to improve the likelihood of good outcomes for Pacific salmon.
Simon London: Now, is there a danger that your logic tree can be impossibly large? This, I think, brings us onto the third step in the process, which is that you have to prioritize.
Charles Conn: Absolutely. The third step, which we also emphasize, along with good problem definition, is rigorous prioritization—we ask the questions “How important is this lever or this branch of the tree in the overall outcome that we seek to achieve? How much can I move that lever?” Obviously, we try and focus our efforts on ones that have a big impact on the problem and the ones that we have the ability to change. With salmon, ocean conditions turned out to be a big lever, but not one that we could adjust. We focused our attention on fish habitats and fish-harvesting practices, which were big levers that we could affect.
People spend a lot of time arguing about branches that are either not important or that none of us can change. We see it in the public square. When we deal with questions at the policy level—“Should you support the death penalty?” “How do we affect climate change?” “How can we uncover the causes and address homelessness?”—it’s even more important that we’re focusing on levers that are big and movable.
Would you like to learn more about our Strategy & Corporate Finance Practice ?
Simon London: Let’s move swiftly on to step four. You’ve defined your problem, you disaggregate it, you prioritize where you want to analyze—what you want to really look at hard. Then you got to the work plan. Now, what does that mean in practice?
Hugo Sarrazin: Depending on what you’ve prioritized, there are many things you could do. It could be breaking the work among the team members so that people have a clear piece of the work to do. It could be defining the specific analyses that need to get done and executed, and being clear on time lines. There’s always a level-one answer, there’s a level-two answer, there’s a level-three answer. Without being too flippant, I can solve any problem during a good dinner with wine. It won’t have a whole lot of backing.
Simon London: Not going to have a lot of depth to it.
Hugo Sarrazin: No, but it may be useful as a starting point. If the stakes are not that high, that could be OK. If it’s really high stakes, you may need level three and have the whole model validated in three different ways. You need to find a work plan that reflects the level of precision, the time frame you have, and the stakeholders you need to bring along in the exercise.
Charles Conn: I love the way you’ve described that, because, again, some people think of problem solving as a linear thing, but of course what’s critical is that it’s iterative. As you say, you can solve the problem in one day or even one hour.
Charles Conn: We encourage our teams everywhere to do that. We call it the one-day answer or the one-hour answer. In work planning, we’re always iterating. Every time you see a 50-page work plan that stretches out to three months, you know it’s wrong. It will be outmoded very quickly by that learning process that you described. Iterative problem solving is a critical part of this. Sometimes, people think work planning sounds dull, but it isn’t. It’s how we know what’s expected of us and when we need to deliver it and how we’re progressing toward the answer. It’s also the place where we can deal with biases. Bias is a feature of every human decision-making process. If we design our team interactions intelligently, we can avoid the worst sort of biases.
Simon London: Here we’re talking about cognitive biases primarily, right? It’s not that I’m biased against you because of your accent or something. These are the cognitive biases that behavioral sciences have shown we all carry around, things like anchoring, overoptimism—these kinds of things.
Both: Yeah.
Charles Conn: Availability bias is the one that I’m always alert to. You think you’ve seen the problem before, and therefore what’s available is your previous conception of it—and we have to be most careful about that. In any human setting, we also have to be careful about biases that are based on hierarchies, sometimes called sunflower bias. I’m sure, Hugo, with your teams, you make sure that the youngest team members speak first. Not the oldest team members, because it’s easy for people to look at who’s senior and alter their own creative approaches.
Hugo Sarrazin: It’s helpful, at that moment—if someone is asserting a point of view—to ask the question “This was true in what context?” You’re trying to apply something that worked in one context to a different one. That can be deadly if the context has changed, and that’s why organizations struggle to change. You promote all these people because they did something that worked well in the past, and then there’s a disruption in the industry, and they keep doing what got them promoted even though the context has changed.
Simon London: Right. Right.
Hugo Sarrazin: So it’s the same thing in problem solving.
Charles Conn: And it’s why diversity in our teams is so important. It’s one of the best things about the world that we’re in now. We’re likely to have people from different socioeconomic, ethnic, and national backgrounds, each of whom sees problems from a slightly different perspective. It is therefore much more likely that the team will uncover a truly creative and clever approach to problem solving.
Simon London: Let’s move on to step five. You’ve done your work plan. Now you’ve actually got to do the analysis. The thing that strikes me here is that the range of tools that we have at our disposal now, of course, is just huge, particularly with advances in computation, advanced analytics. There’s so many things that you can apply here. Just talk about the analysis stage. How do you pick the right tools?
Charles Conn: For me, the most important thing is that we start with simple heuristics and explanatory statistics before we go off and use the big-gun tools. We need to understand the shape and scope of our problem before we start applying these massive and complex analytical approaches.
Simon London: Would you agree with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: I agree. I think there are so many wonderful heuristics. You need to start there before you go deep into the modeling exercise. There’s an interesting dynamic that’s happening, though. In some cases, for some types of problems, it is even better to set yourself up to maximize your learning. Your problem-solving methodology is test and learn, test and learn, test and learn, and iterate. That is a heuristic in itself, the A/B testing that is used in many parts of the world. So that’s a problem-solving methodology. It’s nothing different. It just uses technology and feedback loops in a fast way. The other one is exploratory data analysis. When you’re dealing with a large-scale problem, and there’s so much data, I can get to the heuristics that Charles was talking about through very clever visualization of data.
You test with your data. You need to set up an environment to do so, but don’t get caught up in neural-network modeling immediately. You’re testing, you’re checking—“Is the data right? Is it sound? Does it make sense?”—before you launch too far.
Simon London: You do hear these ideas—that if you have a big enough data set and enough algorithms, they’re going to find things that you just wouldn’t have spotted, find solutions that maybe you wouldn’t have thought of. Does machine learning sort of revolutionize the problem-solving process? Or are these actually just other tools in the toolbox for structured problem solving?
Charles Conn: It can be revolutionary. There are some areas in which the pattern recognition of large data sets and good algorithms can help us see things that we otherwise couldn’t see. But I do think it’s terribly important we don’t think that this particular technique is a substitute for superb problem solving, starting with good problem definition. Many people use machine learning without understanding algorithms that themselves can have biases built into them. Just as 20 years ago, when we were doing statistical analysis, we knew that we needed good model definition, we still need a good understanding of our algorithms and really good problem definition before we launch off into big data sets and unknown algorithms.
Simon London: Step six. You’ve done your analysis.
Charles Conn: I take six and seven together, and this is the place where young problem solvers often make a mistake. They’ve got their analysis, and they assume that’s the answer, and of course it isn’t the answer. The ability to synthesize the pieces that came out of the analysis and begin to weave those into a story that helps people answer the question “What should I do?” This is back to where we started. If we can’t synthesize, and we can’t tell a story, then our decision maker can’t find the answer to “What should I do?”
Simon London: But, again, these final steps are about motivating people to action, right?
Charles Conn: Yeah.
Simon London: I am slightly torn about the nomenclature of problem solving because it’s on paper, right? Until you motivate people to action, you actually haven’t solved anything.
Charles Conn: I love this question because I think decision-making theory, without a bias to action, is a waste of time. Everything in how I approach this is to help people take action that makes the world better.
Simon London: Hence, these are absolutely critical steps. If you don’t do this well, you’ve just got a bunch of analysis.
Charles Conn: We end up in exactly the same place where we started, which is people speaking across each other, past each other in the public square, rather than actually working together, shoulder to shoulder, to crack these important problems.
Simon London: In the real world, we have a lot of uncertainty—arguably, increasing uncertainty. How do good problem solvers deal with that?
Hugo Sarrazin: At every step of the process. In the problem definition, when you’re defining the context, you need to understand those sources of uncertainty and whether they’re important or not important. It becomes important in the definition of the tree.
You need to think carefully about the branches of the tree that are more certain and less certain as you define them. They don’t have equal weight just because they’ve got equal space on the page. Then, when you’re prioritizing, your prioritization approach may put more emphasis on things that have low probability but huge impact—or, vice versa, may put a lot of priority on things that are very likely and, hopefully, have a reasonable impact. You can introduce that along the way. When you come back to the synthesis, you just need to be nuanced about what you’re understanding, the likelihood.
Often, people lack humility in the way they make their recommendations: “This is the answer.” They’re very precise, and I think we would all be well-served to say, “This is a likely answer under the following sets of conditions” and then make the level of uncertainty clearer, if that is appropriate. It doesn’t mean you’re always in the gray zone; it doesn’t mean you don’t have a point of view. It just means that you can be explicit about the certainty of your answer when you make that recommendation.
Simon London: So it sounds like there is an underlying principle: “Acknowledge and embrace the uncertainty. Don’t pretend that it isn’t there. Be very clear about what the uncertainties are up front, and then build that into every step of the process.”
Hugo Sarrazin: Every step of the process.
Simon London: Yeah. We have just walked through a particular structured methodology for problem solving. But, of course, this is not the only structured methodology for problem solving. One that is also very well-known is design thinking, which comes at things very differently. So, Hugo, I know you have worked with a lot of designers. Just give us a very quick summary. Design thinking—what is it, and how does it relate?
Hugo Sarrazin: It starts with an incredible amount of empathy for the user and uses that to define the problem. It does pause and go out in the wild and spend an enormous amount of time seeing how people interact with objects, seeing the experience they’re getting, seeing the pain points or joy—and uses that to infer and define the problem.
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world.
Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There’s a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of the situation. This one almost presupposes that we don’t know the problem until we go see it. The second thing is you need to come up with multiple scenarios or answers or ideas or concepts, and there’s a lot of divergent thinking initially. That’s slightly different, versus the prioritization, but not for long. Eventually, you need to kind of say, “OK, I’m going to converge again.” Then you go and you bring things back to the customer and get feedback and iterate. Then you rinse and repeat, rinse and repeat. There’s a lot of tactile building, along the way, of prototypes and things like that. It’s very iterative.
Simon London: So, Charles, are these complements or are these alternatives?
Charles Conn: I think they’re entirely complementary, and I think Hugo’s description is perfect. When we do problem definition well in classic problem solving, we are demonstrating the kind of empathy, at the very beginning of our problem, that design thinking asks us to approach. When we ideate—and that’s very similar to the disaggregation, prioritization, and work-planning steps—we do precisely the same thing, and often we use contrasting teams, so that we do have divergent thinking. The best teams allow divergent thinking to bump them off whatever their initial biases in problem solving are. For me, design thinking gives us a constant reminder of creativity, empathy, and the tactile nature of problem solving, but it’s absolutely complementary, not alternative.
Simon London: I think, in a world of cross-functional teams, an interesting question is do people with design-thinking backgrounds really work well together with classical problem solvers? How do you make that chemistry happen?
Hugo Sarrazin: Yeah, it is not easy when people have spent an enormous amount of time seeped in design thinking or user-centric design, whichever word you want to use. If the person who’s applying classic problem-solving methodology is very rigid and mechanical in the way they’re doing it, there could be an enormous amount of tension. If there’s not clarity in the role and not clarity in the process, I think having the two together can be, sometimes, problematic.
The second thing that happens often is that the artifacts the two methodologies try to gravitate toward can be different. Classic problem solving often gravitates toward a model; design thinking migrates toward a prototype. Rather than writing a big deck with all my supporting evidence, they’ll bring an example, a thing, and that feels different. Then you spend your time differently to achieve those two end products, so that’s another source of friction.
Now, I still think it can be an incredibly powerful thing to have the two—if there are the right people with the right mind-set, if there is a team that is explicit about the roles, if we’re clear about the kind of outcomes we are attempting to bring forward. There’s an enormous amount of collaborativeness and respect.
Simon London: But they have to respect each other’s methodology and be prepared to flex, maybe, a little bit, in how this process is going to work.
Hugo Sarrazin: Absolutely.
Simon London: The other area where, it strikes me, there could be a little bit of a different sort of friction is this whole concept of the day-one answer, which is what we were just talking about in classical problem solving. Now, you know that this is probably not going to be your final answer, but that’s how you begin to structure the problem. Whereas I would imagine your design thinkers—no, they’re going off to do their ethnographic research and get out into the field, potentially for a long time, before they come back with at least an initial hypothesis.

Want better strategies? Become a bulletproof problem solver
Hugo Sarrazin: That is a great callout, and that’s another difference. Designers typically will like to soak into the situation and avoid converging too quickly. There’s optionality and exploring different options. There’s a strong belief that keeps the solution space wide enough that you can come up with more radical ideas. If there’s a large design team or many designers on the team, and you come on Friday and say, “What’s our week-one answer?” they’re going to struggle. They’re not going to be comfortable, naturally, to give that answer. It doesn’t mean they don’t have an answer; it’s just not where they are in their thinking process.
Simon London: I think we are, sadly, out of time for today. But Charles and Hugo, thank you so much.
Charles Conn: It was a pleasure to be here, Simon.
Hugo Sarrazin: It was a pleasure. Thank you.
Simon London: And thanks, as always, to you, our listeners, for tuning into this episode of the McKinsey Podcast . If you want to learn more about problem solving, you can find the book, Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything , online or order it through your local bookstore. To learn more about McKinsey, you can of course find us at McKinsey.com.
Charles Conn is CEO of Oxford Sciences Innovation and an alumnus of McKinsey’s Sydney office. Hugo Sarrazin is a senior partner in the Silicon Valley office, where Simon London, a member of McKinsey Publishing, is also based.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategy to beat the odds

Five routes to more innovative problem solving
Resources >
Mckinsey approach to problem solving.
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn.
This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process that you can download and customize for your own use.
You can click any section to go directly there:
Overview of the McKinsey Approach to Problem Solving
Problem solving process.
- Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet
Hypothesis trees, issue trees, analyses and workplan, synthesize findings, craft recommendations, distinctiveness practices, harness the power of collaboration, sources and additional reading, download the umbrex toolkit on the mckinsey approach to problem solving.
Problem solving — finding the optimal solution to a given business opportunity or challenge — is the very heart of how consultants create client impact, and considered the most important skill for success at McKinsey.
The characteristic “McKinsey method” of problem solving is a structured, inductive approach that can be used to solve any problem. Using this standardized process saves us from reinventing the problem-solving wheel, and allows for greater focus on distinctiveness in the solution. Every new McKinsey associate must learn this method on his or her first day with the firm.
There are four fundamental disciplines of the McKinsey method:
1. Problem definition
A thorough understanding and crisp definition of the problem.
2. The problem-solving process
Structuring the problem, prioritizing the issues, planning analyses, conducting analyses, synthesizing findings, and developing recommendations.
3. Distinctiveness practices
Constructing alternative perspectives; identifying relationships; distilling the essence of an issue, analysis, or recommendation; and staying ahead of others in the problem-solving process.
4. Collaboratio n
Actively seeking out client, customer, and supplier perspectives, as well as internal and external expert insight and knowledge.
Once the problem has been defined, the problem-solving process proceeds with a series of steps:
- Structure the problem
- Prioritize the issues
- Plan analyses
- Conduct analyses
- Synthesize findings
- Develop recommendations
Not all problems require strict adherence to the process. Some steps may be truncated, such as when specific knowledge or analogies from other industries make it possible to construct hypotheses and associated workplans earlier than their formal place in the process. Nonetheless, it remains important to be capable of executing every step in the basic process.
When confronted with a new and complex problem, this process establishes a path to defining and disaggregating the problem in a way that will allow the team to move to a solution. The process also ensures nothing is missed and concentrates efforts on the highest-impact areas. Adhering to the process gives the client clear steps to follow, building confidence, credibility, and long-term capability.
Problem Definition & Problem Statement Worksheet
The most important step in your entire project is to first carefully define the problem. The problem definition will serve the guide all of the team’s work, so it is critical to ensure that all key stakeholders agree that it is the right problem to be solving.
Problem Statement Worksheet
This is a helpful tool to use to clearly define the problem. There are often dozens of issues that a team could focus on, and it is often not obvious how to define the problem. In any real-life situation, there are many possible problem statements. Your choice of problem statement will serve to constrain the range of possible solutions.
- Use a question . The problem statement should be phrased as a question, such that the answer will be the solution. Make the question SMART: specific, measurable, action-oriented, relevant, and time-bound. Example: “How can XYZ Bank close the $100 million profitability gap in two years?”
- Context . What are the internal and external situations and complications facing the client, such as industry trends, relative position within the industry, capability gaps, financial flexibility, and so on?
- Success criteria . Understand how the client and the team define success and failure. In addition to any quantitative measures identified in the basic question, identify other important quantitative or qualitative measures of success, including timing of impact, visibility of improvement, client capability building required, necessary mindset shifts, and so on.
- Scope and constraints . Scope most commonly covers the markets or segments of interest, whereas constraints govern restrictions on the nature of solutions within those markets or segments.
- Stakeholders . Explore who really makes the decisions — who decides, who can help, and who can block.
- Key sources of insight . What best-practice expertise, knowledge, and engagement approaches already exist? What knowledge from the client, suppliers, and customers needs to be accessed? Be as specific as possible: who, what, when, how, and why.
The problem definition should not be vague, without clear measures of success. Rather, it should be a SMART definition:
- Action-oriented
Example situation – A family on Friday evening
Scenario: A mother, a father, and their two teenage children have all arrived home on a Friday at 6 p.m. The family has not prepared dinner for Friday evening. The daughter has lacrosse practice on Saturday and an essay to write for English class due on Monday. The son has theatre rehearsal on both Saturday and Sunday and will need one parent to drive him to the high school both days, though he can get a ride home with a friend. The family dog, a poodle, must be taken to the groomer on Saturday morning. The mother will need to spend time this weekend working on assignments for her finance class she is taking as part of her Executive MBA. The father plans to go on a 100-mile bike ride, which he can do either Saturday or Sunday. The family has two cars, but one is at the body shop. They are trying to save money to pay for an addition to their house.
What is the problem definition?
A statement of facts does not focus the problem solving:
It is 6 p.m. The family has not made plans for dinner, and they are hungry.
A question guides the team towards a solution:
1. What should the family do for dinner on Friday night?
2. Should the family cook dinner or order delivery?
3. What should the family cook for dinner?
4. What should the family cook for dinner that will not require spending more than $40 on groceries?
5. To cook dinner, what do they need to pick up from the supermarket?
6. How can the family prepare dinner within the next hour using ingredients they already have in the house?
In completing the Problem Statement Worksheet, you are prompted to define the key stakeholders.
As you become involved in the problem-solving process, you should expand the question of key stakeholders to include what the team wants from them and what they want from the team, their values and motivations (helpful and unhelpful), and the communications mechanisms that will be most effective for each of them.
Using the Stakeholder Analysis Worksheet allows you to comprehensively identify:
- Stakeholders
- What you need from them
- Where they are
- What they need from you
The two most helpful techniques for rigorously structuring any problem are hypothesis trees and issue trees. Each of these techniques disaggregates the primary question into a cascade of issues or hypotheses that, when addressed, will together answer the primary question.
A hypothesis tree might break down the same question into two or more hypotheses.
Example: Alpha Manufacturing, Inc.
Problem Statement: How can Alpha increase EBITDA by $13M (to $50M) by 2025?
The hypotheses might be:
- Alpha can add $125M revenues by expanding to new customers, adding $8M of EBITDA
- Alpha can reduce costs to improve EBITDA by $5M
These hypotheses will be further disaggregated into subsidiary hypotheses at the next level of the tree.
The aim at this stage is to structure the problem into discrete, mutually exclusive pieces that are small enough to yield to analysis and that, taken together, are collectively exhaustive.
Articulating the problem as hypotheses, rather than issues, is the preferred approach because it leads to a more focused analysis of the problem. Questions to ask include:
- Is it testable – can you prove or disprove it?
- It is open to debate? If it cannot be wrong, it is simply a statement of fact and unlikely to produce keen insight.
- If you reversed your hypothesis – literally, hypothesized that the exact opposite were true – would you care about the difference it would make to your overall logic?
- If you shared your hypothesis with the CEO, would it sound naive or obvious?
- Does it point directly to an action or actions that the client might take?
Quickly developing a powerful hypothesis tree enables us to develop solutions more rapidly that will have real impact. This can sometimes seem premature to clients, who might find the “solution” reached too quickly and want to see the analysis behind it.
Take care to explain the approach (most important, that a hypothesis is not an answer) and its benefits (that a good hypothesis is the basis of a proven means of successful problem solving and avoids “boiling the ocean”).
Often, the team has insufficient knowledge to build a complete hypothesis tree at the start of an engagement. In these cases, it is best to begin by structuring the problem using an issue tree.
An issue tree is best set out as a series of open questions in sentence form. For example, “How can the client minimize its tax burden?” is more useful than “Tax.” Open questions – those that begin with what, how, or why– produce deeper insights than closed ones. In some cases, an issue tree can be sharpened by toggling between issue and hypothesis – working forward from an issue to identify the hypothesis, and back from the hypothesis to sharpen the relevant open question.
Once the problem has been structured, the next step is to prioritize the issues or hypotheses on which the team will focus its work. When prioritizing, it is common to use a two-by-two matrix – e.g., a matrix featuring “impact” and “ease of impact” as the two axes.
Applying some of these prioritization criteria will knock out portions of the issue tree altogether. Consider testing the issues against them all, albeit quickly, to help drive the prioritization process.
Once the criteria are defined, prioritizing should be straightforward: Simply map the issues to the framework and focus on those that score highest against the criteria.
As the team conducts analysis and learns more about the problem and the potential solution, make sure to revisit the prioritization matrix so as to remain focused on the highest-priority issues.
The issues might be:
- How can Alpha increase revenue?
- How can Alpha reduce cost?
Each of these issues is then further broken down into deeper insights to solutions.
If the prioritization has been carried out effectively, the team will have clarified the key issues or hypotheses that must be subjected to analysis. The aim of these analyses is to prove the hypotheses true or false, or to develop useful perspectives on each key issue. Now the task is to design an effective and efficient workplan for conducting the analyses.
Transforming the prioritized problem structure into a workplan involves two main tasks:
- Define the blocks of work that need to be undertaken. Articulate as clearly as possible the desired end products and the analysis necessary to produce them, and estimate the resources and time required.
- Sequence the work blocks in a way that matches the available resources to the need to deliver against key engagement milestones (e.g., important meetings, progress reviews), as well as to the overall pacing of the engagement (i.e., weekly or twice-weekly meetings, and so on).
A good workplan will detail the following for each issue or hypothesis: analyses, end products, sources, and timing and responsibility. Developing the workplan takes time; doing it well requires working through the definition of each element of the workplan in a rigorous and methodical fashion.
This is the most difficult element of the problem-solving process. After a period of being immersed in the details, it is crucial to step back and distinguish the important from the merely interesting. Distinctive problem solvers seek the essence of the story that will underpin a crisp recommendation for action.
Although synthesis appears, formally speaking, as the penultimate step in the process, it should happen throughout. Ideally, after you have made almost any analytical progress, you should attempt to articulate the “Day 1” or “Week 1” answer. Continue to synthesize as you go along. This will remind the team of the question you are trying to answer, assist prioritization, highlight the logical links of the emerging solution, and ensure that you have a story ready to articulate at all times during the study.
McKinsey’s primary tool for synthesizing is the pyramid principle. Essentially, this principle asserts that every synthesis should explain a single concept, per the “governing thought.” The supporting ideas in the synthesis form a thought hierarchy proceeding in a logical structure from the most detailed facts to the governing thought, ruthlessly excluding the interesting but irrelevant.
While this hierarchy can be laid out as a tree (like with issue and hypothesis trees), the best problem solvers capture it by creating dot-dash storylines — the Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments.
Pyramid Structure for Grouping Arguments
- Focus on action. Articulate the thoughts at each level of the pyramid as declarative sentences, not as topics. For example, “expansion” is a topic; “We need to expand into the European market” is a declarative sentence.
- Use storylines. PowerPoint is poor at highlighting logical connections, therefore is not a good tool for synthesis. A storyline will clarify elements that may be ambiguous in the PowerPoint presentation.
- Keep the emerging storyline visible. Many teams find that posting the storyline or story- board on the team-room wall helps keep the thinking focused. It also helps in bringing the client along.
- Use the situation-complication-resolution structure. The situation is the reason there is action to be taken. The com- plication is why the situation needs thinking through – typically an industry or client challenge. The resolution is the answer.
- Down the pyramid: does each governing thought pose a single question that is answered completely by the group of boxes below it?
- Across: is each level within the pyramid MECE?
- Up: does each group of boxes, taken together, provide one answer – one “so what?” – that is essentially the governing thought above it?
- Test the solution. What would it mean if your hypotheses all came true?
Three Horizons of Engagement Planning
It’s useful to match the workplan to three horizons:
- What is expected at the end of the engagement
- What is expected at key progress reviews
- What is due at daily and/or weekly team meetings
The detail in the workplan will typically be greater for the near term (the next week) than for the long term (the study horizon), especially early in a new engagement when considerable ambiguity about the end state remains.
It is at this point that we address the client’s questions: “What do I do, and how do I do it?” This means not offering actionable recommendations, along with a plan and client commitment for implementation.
The essence of this step is to translate the overall solution into the actions required to deliver sustained impact. A pragmatic action plan should include:
- Relevant initiatives, along with a clear sequence, timing, and mapping of activities required
- Clear owners for each initiative
- Key success factors and the challenges involved in delivering on the initiatives
Crucial questions to ask as you build recommendations for organizational change are:
- Does each person who needs to change (from the CEO to the front line) understand what he or she needs to change and why, and is he or she committed to it?
- Are key leaders and role models throughout the organization personally committed to behaving differently?
- Has the client set in place the necessary formal mechanisms to reinforce the desired change?
- Does the client have the skills and confidence to behave in the desired new way?
Great problem solvers identify unique disruptions and discontinuities, novel insights, and step-out opportunities that lead to truly distinctive impact. This is done by applying a number of practices throughout the problem-solving process to help develop these insights.
Expand: Construct multiple perspectives
Identifying alternative ways of looking at the problem expands the range of possibilities, opens you up to innovative ideas, and allows you to formulate more powerful hypotheses. Questions that help here include:
- What changes if I think from the perspective of a customer, or a supplier, or a frontline employee, or a competitor?
- How have other industries viewed and addressed this same problem?
- What would it mean if the client sought to run the company like a low-cost airline or a cosmetics manufacturer?
Link: Identify relationships
Strong problem solvers discern connections and recognize patterns in two different ways:
- They seek out the ways in which different problem elements – issues, hypotheses, analyses, work elements, findings, answers, and recommendations – relate to one another.
- They use these relationships throughout the basic problem-solving process to identify efficient problem-solving approaches, novel solutions, and more powerful syntheses.
Distill: Find the essence
Cutting through complexity to identify the heart of the problem and its solution is a critical skill.
- Identify the critical problem elements. Are there some issues, approaches, or options that can be eliminated completely because they won’t make a significant difference to the solution?
- Consider how complex the different elements are and how long it will take to complete them. Wherever possible, quickly advance simpler parts of the problem that can inform more complex or time-consuming elements.
Lead: Stay ahead/step back
Without getting ahead of the client, you cannot be distinctive. Paradoxically, to get ahead – and stay ahead – it is often necessary to step back from the problem to validate or revalidate the approach and the solution.
- Spend time thinking one or more steps ahead of the client and team.
- Constantly check and challenge the rigor of the underlying data and analysis.
- Stress-test the whole emerging recommendation
- Challenge the solution against a set of hurdles. Does it satisfy the criteria for success as set out on the Problem Statement Worksheet?
No matter how skilled, knowledgeable, or experienced you are, you will never create the most distinctive solution on your own. The best problem solvers know how to leverage the power of their team, clients, the Firm, and outside parties. Seeking the right expertise at the right time, and leveraging it in the right way, are ultimately how we bring distinctiveness to our work, how we maximize efficiency, and how we learn.
When solving a problem, it is important to ask, “Have I accessed all the sources of insight that are available?” Here are the sources you should consider:
- Your core team
- The client’s suppliers and customers
- Internal experts and knowledge
- External sources of knowledge
- Communications specialists
The key here is to think open, not closed. Opening up to varied sources of data and perspectives furthers our mission to develop truly innovative and distinctive solutions for our clients.
- McKinsey Staff Paper 66 — not published by McKinsey but possibly found through an internet search
- The McKinsey Way , 1999, by Ethan M. Rasiel
For consultants
© Copyright 2023 by Umbrex
Designed by our friends at Filez
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service

Master the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process for Better Decision-Making
Discover the powerful 7-Step Problem-Solving Process to make better decisions and achieve better outcomes. Master the art of problem-solving in this comprehensive guide. Download the Free PowerPoint and PDF Template.

StrategyPunk
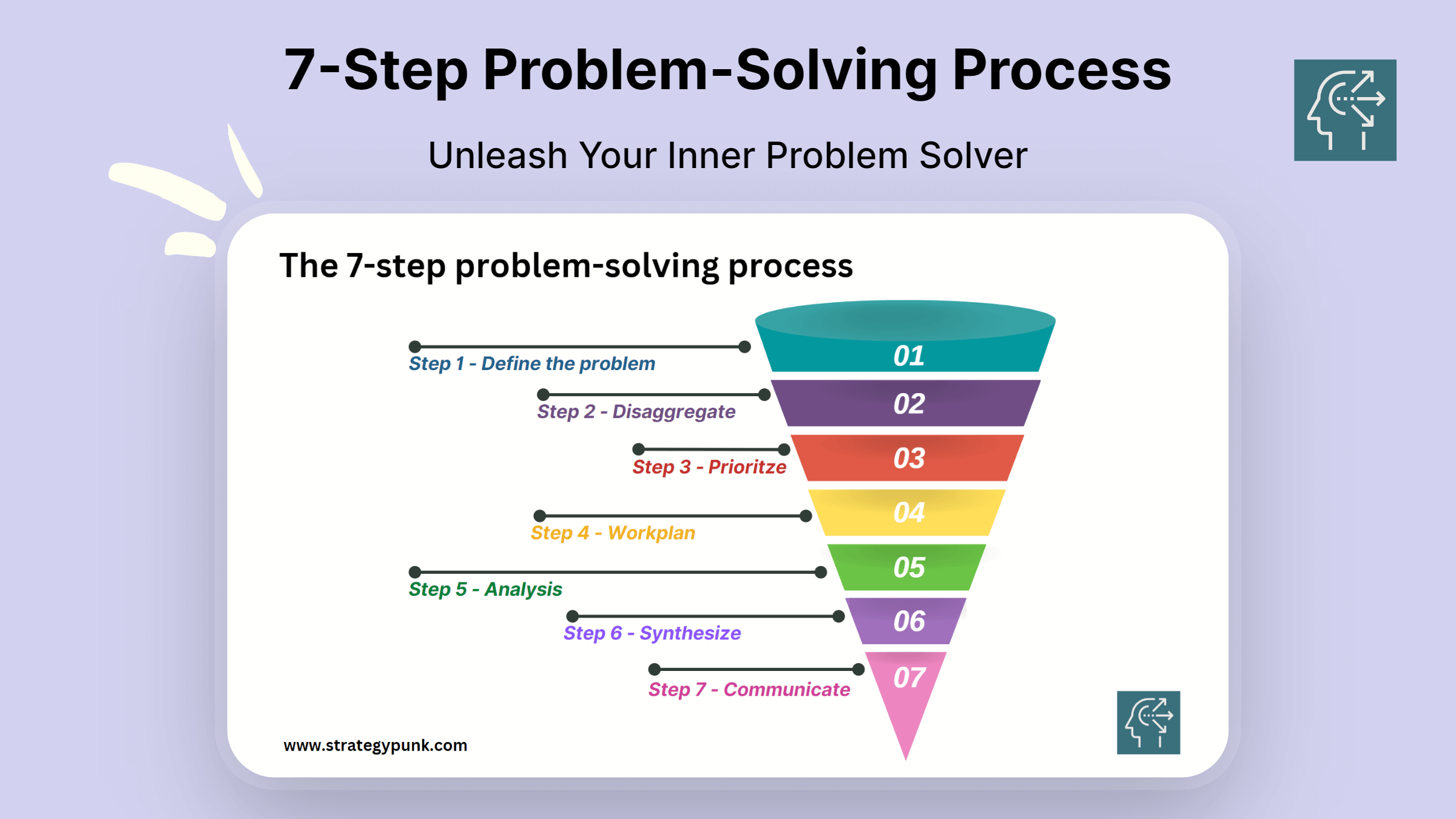
Introduction
Mastering the art of problem-solving is crucial for making better decisions. Whether you're a student, a business owner, or an employee, problem-solving skills can help you tackle complex issues and find practical solutions. The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a proven method that can help you approach problems systematically and efficiently.
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process involves steps that guide you through the problem-solving process. The first step is to define the problem, followed by disaggregating the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Next, you prioritize the features and create a work plan to address each. Then, you analyze each piece, synthesize the information, and communicate your findings to others.
By following this process, you can avoid jumping to conclusions, overlooking important details, or making hasty decisions. Instead, you can approach problems with a clear and structured mindset, which can help you make better decisions and achieve better outcomes.
In this article, we'll explore each step of the 7-Step Problem-Solving Process in detail so you can start mastering this valuable skill. At the end of the blog post, you can download the process's free PowerPoint and PDF templates .
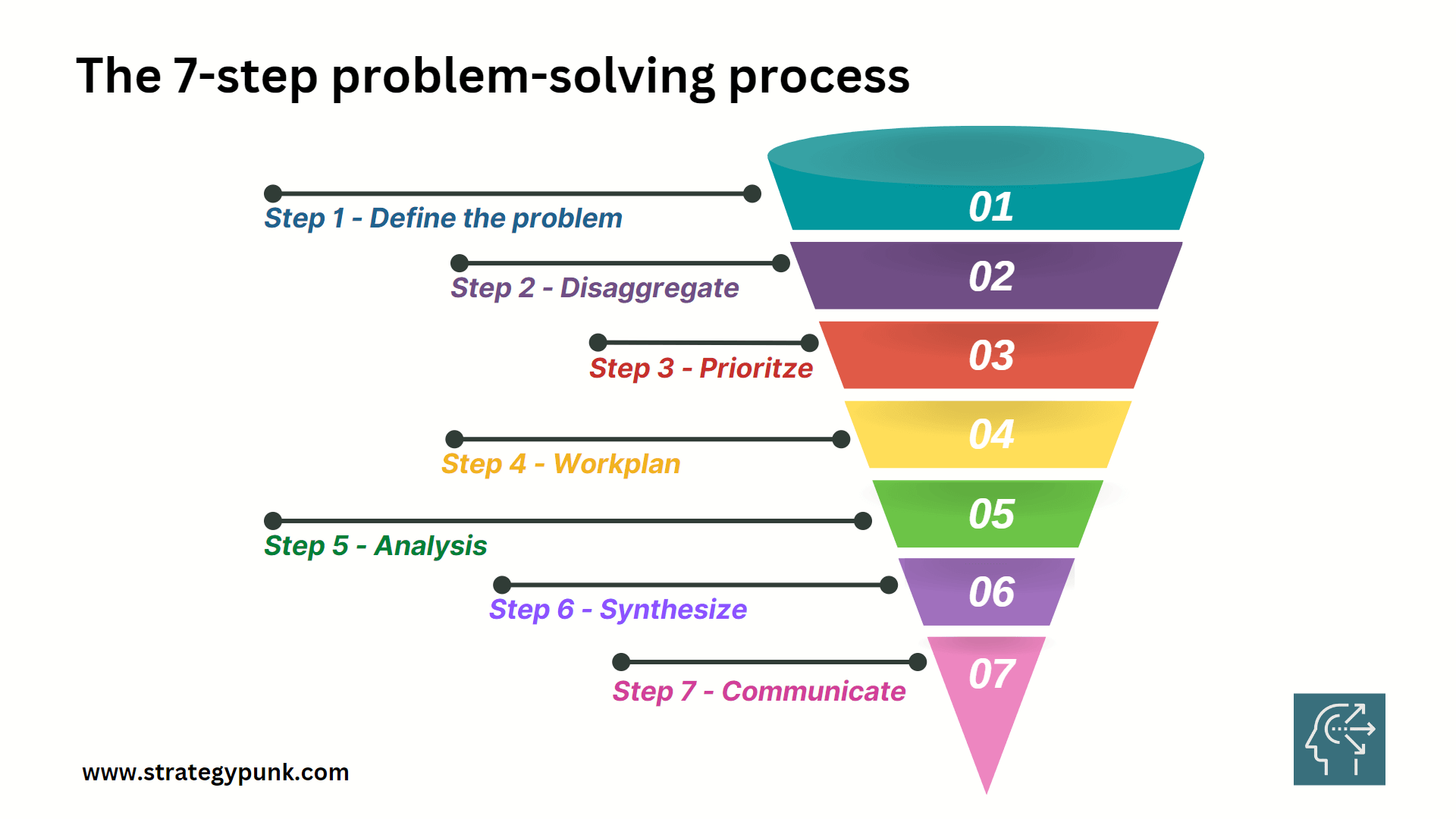
Step 1: Define the Problem
The first step in the problem-solving process is to define the problem. This step is crucial because finding a solution is only accessible if the problem is clearly defined. The problem must be specific, measurable, and achievable.
One way to define the problem is to ask the right questions. Questions like "What is the problem?" and "What are the causes of the problem?" can help. Gathering data and information about the issue to assist in the definition process is also essential.
Another critical aspect of defining the problem is identifying the stakeholders. Who is affected by it? Who has a stake in finding a solution? Identifying the stakeholders can help ensure that the problem is defined in a way that considers the needs and concerns of all those affected.
Once the problem is defined, it is essential to communicate the definition to all stakeholders. This helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that there is a shared understanding of the problem.
Step 2: Disaggregate
After defining the problem, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to disaggregate the problem into smaller, more manageable parts. Disaggregation helps break down the problem into smaller pieces that can be analyzed individually. This step is crucial in understanding the root cause of the problem and identifying the most effective solutions.
Disaggregation can be achieved by breaking down the problem into sub-problems, identifying the contributing factors, and analyzing the relationships between these factors. This step helps identify the most critical factors that must be addressed to solve the problem.
A tree or fishbone diagram is one effective way to disaggregate a problem. These diagrams help identify the different factors contributing to the problem and how they are related. Another way is to use a table to list the other factors contributing to the situation and their corresponding impact on the issue.
Disaggregation helps in breaking down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. It helps understand the relationships between different factors contributing to the problem and identify the most critical factors that must be addressed. By disaggregating the problem, decision-makers can focus on the most vital areas, leading to more effective solutions.
Step 3: Prioritize
After defining the problem and disaggregating it into smaller parts, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is prioritizing the issues that need addressing. Prioritizing helps to focus on the most pressing issues and allocate resources more effectively.
There are several ways to prioritize issues, including:
- Urgency: Prioritize issues based on their urgency. Problems that require immediate attention should be addressed first.
- Impact: Prioritize issues based on their impact on the organization or stakeholders. Problems with a high impact should be given priority.
- Resources: Prioritize issues based on the resources required to address them. Problems that require fewer resources should be dealt with first.
It is important to involve stakeholders in the prioritization process, considering their concerns and needs. This can be done through surveys, focus groups, or other forms of engagement.
Once the issues have been prioritized, developing a plan of action to address them is essential. This involves identifying the resources required, setting timelines, and assigning responsibilities.
Prioritizing issues is a critical step in problem-solving. By focusing on the most pressing problems, organizations can allocate resources more effectively and make better decisions.
Step 4: Workplan
After defining the problem, disaggregating, and prioritizing the issues, the next step in the 7-step problem-solving process is to develop a work plan. This step involves creating a roadmap that outlines the steps needed to solve the problem.
The work plan should include a list of tasks, deadlines, and responsibilities for each team member involved in the problem-solving process. Assigning tasks based on each team member's strengths and expertise ensures the work is completed efficiently and effectively.
Creating a work plan can help keep the team on track and ensure everyone is working towards the same goal. It can also help to identify potential roadblocks or challenges that may arise during the problem-solving process and develop contingency plans to address them.
Several tools and techniques can be used to develop a work plan, including Gantt charts, flowcharts, and mind maps. These tools can help to visualize the steps needed to solve the problem and identify dependencies between tasks.
Developing a work plan is a critical step in the problem-solving process. It provides a clear roadmap for solving the problem and ensures everyone involved is aligned and working towards the same goal.
Step 5: Analysis
Once the problem has been defined and disaggregated, the next step is to analyze the information gathered. This step involves examining the data, identifying patterns, and determining the root cause of the problem.
Several methods can be used during the analysis phase, including:
- Root cause analysis
- Pareto analysis
- SWOT analysis
Root cause analysis is a popular method used to identify the underlying cause of a problem. This method involves asking a series of "why" questions to get to the root cause of the issue.
Pareto analysis is another method that can be used during the analysis phase. This method involves identifying the 20% of causes responsible for 80% of the problems. By focusing on these critical causes, organizations can make significant improvements.
Finally, SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for analyzing the internal and external factors that may impact the problem. This method involves identifying the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to the issue.
Overall, the analysis phase is critical for identifying the root cause of the problem and developing practical solutions. By using a combination of methods, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of the issue and make informed decisions.
Step 6: Synthesize
Once the analysis phase is complete, it is time to synthesize the information gathered to arrive at a solution. During this step, the focus is on identifying the most viable solution that addresses the problem. This involves examining and combining the analysis results for a clear and concise conclusion.
One way to synthesize the information is to use a decision matrix. This involves creating a table that lists the potential solutions and the essential criteria for making a decision. Each answer is then rated against each standard, and the scores are tallied to arrive at a final decision.
Another approach to synthesizing the information is to use a mind map. This involves creating a visual representation of the problem and the potential solutions. The mind map can identify the relationships between the different pieces of information and help prioritize the solutions.
During the synthesis phase, it is vital to remain open-minded and consider all potential solutions. Involving all stakeholders in the decision-making process is essential to ensure everyone's perspectives are considered.
Step 7: Communicate
After synthesizing the information, the next step is communicating the findings to the relevant stakeholders. This is a crucial step because it helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page and that the decision-making process is transparent.
One effective way to communicate the findings is through a well-organized report. The report should include the problem statement, the analysis, the synthesis, and the recommended solution. It should be clear, concise, and easy to understand.
In addition to the report, a presentation explaining the findings is essential. The presentation should be tailored to the audience and highlight the report's key points. Visual aids such as tables, graphs, and charts can make the presentation more engaging.
During the presentation, it is essential to be open to feedback and questions from the audience. This helps ensure everyone agrees with the recommended solution and addresses concerns or objections.
Effective communication is vital to ensuring the decision-making process is successful. Stakeholders can make informed decisions and work towards a common goal by communicating the findings clearly and concisely.
The 7-step problem-solving process is a powerful tool for helping individuals and organizations make better decisions. By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, prioritize potential solutions, and develop a clear plan of action. This process can be applied to various scenarios, from personal challenges to complex business problems.
Through disaggregation, individuals can break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable parts. By prioritizing potential solutions, individuals can focus their efforts on the most impactful actions. The work step allows individuals to develop a clear action plan, while the analysis step provides a framework for evaluating possible solutions.
The synthesis step combines all the information gathered to develop a comprehensive solution. Finally, the communication step allows individuals to share their answers with others and gather feedback.
By mastering the 7-step problem-solving process, individuals can become more effective decision-makers and problem-solvers. This process can help individuals and organizations save time and resources while improving outcomes. With practice, individuals can develop the skills to apply this process to a wide range of scenarios and make better decisions in all areas of life.
7-Step Problem-Solving Process PPT Template
Free powerpoint and pdf template, executive summary: the 7-step problem-solving process.
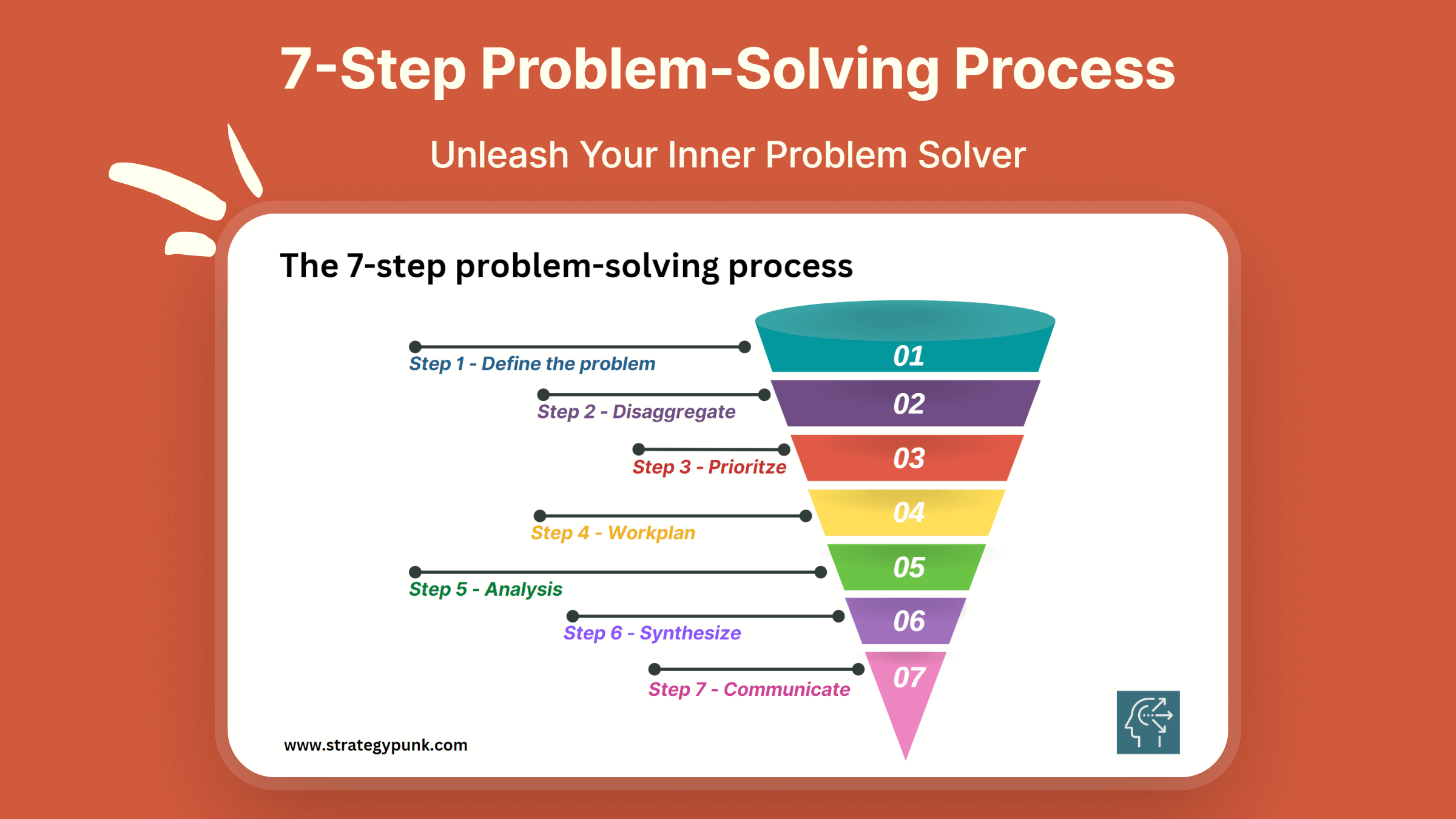
The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts, prioritizing the issues, creating a work plan, analyzing the data, synthesizing the information, and communicating the findings.
By following these steps, individuals can identify the root cause of a problem, break it down into manageable components, and prioritize the most impactful actions. The work plan, analysis, and synthesis steps provide a framework for developing comprehensive solutions, while the communication step ensures transparency and stakeholder engagement.
Mastering this process can improve decision-making and problem-solving capabilities, save time and resources, and improve outcomes in personal and professional contexts.
Please buy me a coffee.
I'd appreciate your support if my templates have saved you time or helped you start a project. Buy Me a Coffee is a simple way to show your appreciation and help me continue creating high-quality templates that meet your needs.

7-Step Problem-Solving Process PDF Template
7-step problem-solving process powerpoint template.

Global Bites: PESTLE Insights into Nestlé (Free PPT)
Download our free PPT template for in-depth PESTLE insights into Nestlé's global strategy. Learn more today!

PESTLE Analysis: Decoding Reddit's Landscape (Free PPT)
Decode Reddit's global influence with our free PowerPoint PESTLE Analysis. Explore the hub of vibrant discussions and ideas.

Navigating the Terrain: A PESTLE Analysis of Lululemon (Free PowerPoint)
Explore Lululemon's business terrain with our free PESTLE analysis PowerPoint. Instant access!

The Art of Strategic Leadership: 5 Keys to Success by Willie Peterson
Explore Willie Peterson's 5 crucial strategies for strategic leadership. Master learning, customer focus, and effective storytelling.


McKinsey Problem Solving: Six steps to solve any problem and tell a persuasive story
The McKinsey problem solving process is a series of mindset shifts and structured approaches to thinking about and solving challenging problems. It is a useful approach for anyone working in the knowledge and information economy and needs to communicate ideas to other people.
Over the past several years of creating StrategyU, advising an undergraduates consulting group and running workshops for clients, I have found over and over again that the principles taught on this site and in this guide are a powerful way to improve the type of work and communication you do in a business setting.
When I first set out to teach these skills to the undergraduate consulting group at my alma mater, I was still working at BCG. I was spending my day building compelling presentations, yet was at a loss for how to teach these principles to the students I would talk with at night.
Through many rounds of iteration, I was able to land on a structured process and way of framing some of these principles such that people could immediately apply them to their work.
While the “official” McKinsey problem solving process is seven steps, I have outline my own spin on things – from experience at McKinsey and Boston Consulting Group. Here are six steps that will help you solve problems like a McKinsey Consultant:
Step #1: School is over, stop worrying about “what” to make and worry about the process, or the “how”
When I reflect back on my first role at McKinsey, I realize that my biggest challenge was unlearning everything I had learned over the previous 23 years. Throughout school you are asked to do specific things. For example, you are asked to write a 5 page paper on Benjamin Franklin — double spaced, 12 font and answering two or three specific questions.
In school, to be successful you follow these rules as close as you can. However, in consulting there are no rules on the “what.” Typically the problem you are asked to solve is ambiguous and complex — exactly why they hire you. In consulting, you are taught the rules around the “how” and have to then fill in the what.
The “how” can be taught and this entire site is founded on that belief. Here are some principles to get started:
Step #2: Thinking like a consultant requires a mindset shift
There are two pre-requisites to thinking like a consultant. Without these two traits you will struggle:
- A healthy obsession looking for a “better way” to do things
- Being open minded to shifting ideas and other approaches
In business school, I was sitting in one class when I noticed that all my classmates were doing the same thing — everyone was coming up with reasons why something should should not be done.
As I’ve spent more time working, I’ve realized this is a common phenomenon. The more you learn, the easier it becomes to come up with reasons to support the current state of affairs — likely driven by the status quo bias — an emotional state that favors not changing things. Even the best consultants will experience this emotion, but they are good at identifying it and pushing forward.
Key point : Creating an effective and persuasive consulting like presentation requires a comfort with uncertainty combined with a slightly delusional belief that you can figure anything out.
Step #3: Define the problem and make sure you are not solving a symptom
Before doing the work, time should be spent on defining the actual problem. Too often, people are solutions focused when they think about fixing something. Let’s say a company is struggling with profitability. Someone might define the problem as “we do not have enough growth.” This is jumping ahead to solutions — the goal may be to drive more growth, but this is not the actual issue. It is a symptom of a deeper problem.
Consider the following information:
- Costs have remained relatively constant and are actually below industry average so revenue must be the issue
- Revenue has been increasing, but at a slowing rate
- This company sells widgets and have had no slowdown on the number of units it has sold over the last five years
- However, the price per widget is actually below where it was five years ago
- There have been new entrants in the market in the last three years that have been backed by Venture Capital money and are aggressively pricing their products below costs
In a real-life project there will definitely be much more information and a team may take a full week coming up with a problem statement . Given the information above, we may come up with the following problem statement:
Problem Statement : The company is struggling to increase profitability due to decreasing prices driven by new entrants in the market. The company does not have a clear strategy to respond to the price pressure from competitors and lacks an overall product strategy to compete in this market.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to “solve” the problem
Now the fun starts!
There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on.
First is top-down . This is what you should start with, especially for a newer “consultant.” This involves taking the problem statement and structuring an approach. This means developing multiple hypotheses — key questions you can either prove or disprove.
Given our problem statement, you may develop the following three hypotheses:
- Company X has room to improve its pricing strategy to increase profitability
- Company X can explore new market opportunities unlocked by new entrants
- Company X can explore new business models or operating models due to advances in technology
As you can see, these three statements identify different areas you can research and either prove or disprove. In a consulting team, you may have a “workstream leader” for each statement.
Once you establish the structure you you may shift to the second type of analysis: a bottom-up approach . This involves doing deep research around your problem statement, testing your hypotheses, running different analysis and continuing to ask more questions. As you do the analysis, you will begin to see different patterns that may unlock new questions, change your thinking or even confirm your existing hypotheses. You may need to tweak your hypotheses and structure as you learn new information.
A project vacillates many times between these two approaches. Here is a hypothetical timeline of a project:

Step 5: Make a slides like a consultant
The next step is taking the structure and research and turning it into a slide. When people see slides from McKinsey and BCG, they see something that is compelling and unique, but don’t really understand all the work that goes into those slides. Both companies have a healthy obsession (maybe not to some people!) with how things look, how things are structured and how they are presented.
They also don’t understand how much work is spent on telling a compelling “story.” The biggest mistake people make in the business world is mistaking showing a lot of information versus telling a compelling story. This is an easy mistake to make — especially if you are the one that did hours of analysis. It may seem important, but when it comes down to making a slide and a presentation, you end up deleting more information rather than adding. You really need to remember the following:
Data matters, but stories change hearts and minds
Here are four quick ways to improve your presentations:
Tip #1 — Format, format, format
Both McKinsey and BCG had style templates that were obsessively followed. Some key rules I like to follow:
- Make sure all text within your slide body is the same font size (harder than you would think)
- Do not go outside of the margins into the white space on the side
- All titles throughout the presentation should be 2 lines or less and stay the same font size
- Each slide should typically only make one strong point
Tip #2 — Titles are the takeaway
The title of the slide should be the key insight or takeaway and the slide area should prove the point. The below slide is an oversimplification of this:

Even in consulting, I found that people struggled with simplifying a message to one key theme per slide. If something is going to be presented live, the simpler the better. In reality, you are often giving someone presentations that they will read in depth and more information may make sense.
To go deeper, check out these 20 presentation and powerpoint tips .
Tip #3 — Have “MECE” Ideas for max persuasion
“MECE” means mutually exclusive, collectively exhaustive — meaning all points listed cover the entire range of ideas while also being unique and differentiated from each other.
An extreme example would be this:
- Slide title: There are seven continents
- Slide content: The seven continents are North America, South America, Europe, Africa Asia, Antarctica, Australia
The list of continents provides seven distinct points that when taken together are mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive . The MECE principle is not perfect — it is more of an ideal to push your logic in the right direction. Use it to continually improve and refine your story.
Applying this to a profitability problem at the highest level would look like this:
Goal: Increase profitability
2nd level: We can increase revenue or decrease costs
3rd level: We can increase revenue by selling more or increasing prices
Each level is MECE. It is almost impossible to argue against any of this (unless you are willing to commit accounting fraud!).
Tip #4 — Leveraging the Pyramid Principle
The pyramid principle is an approach popularized by Barbara Minto and essential to the structured problem solving approach I learned at McKinsey. Learning this approach has changed the way I look at any presentation since.
Here is a rough outline of how you can think about the pyramid principle as a way to structure a presentation:

As you build a presentation, you may have three sections for each hypothesis. As you think about the overall story, the three hypothesis (and the supporting evidence) will build on each other as a “story” to answer the defined problem. There are two ways to think about doing this — using inductive or deductive reasoning:

If we go back to our profitability example from above, you would say that increasing profitability was the core issue we developed. Lets assume that through research we found that our three hypotheses were true. Given this, you may start to build a high level presentation around the following three points:

These three ideas not only are distinct but they also build on each other. Combined, they tell a story of what the company should do and how they should react. Each of these three “points” may be a separate section in the presentation followed by several pages of detailed analysis. There may also be a shorter executive summary version of 5–10 pages that gives the high level story without as much data and analysis.
Step 6: The only way to improve is to get feedback and continue to practice
Ultimately, this process is not something you will master overnight. I’ve been consulting, either working for a firm or on my own for more than 10 years and am still looking for ways to make better presentations, become more persuasive and get feedback on individual slides.
The process never ends.
The best way to improve fast is to be working on a great team . Look for people around you that do this well and ask them for feedback. The more feedback, the more iterations and more presentations you make, the better you will become. Good luck!
If you enjoyed this post, you’ll get a kick out of all the free lessons I’ve shared that go a bit deeper. Check them out here .
Do you have a toolkit for business problem solving? I created Think Like a Strategy Consultant as an online course to make the tools of strategy consultants accessible to driven professionals, executives, and consultants. This course teaches you how to synthesize information into compelling insights, structure your information in ways that help you solve problems, and develop presentations that resonate at the C-Level. Click here to learn more or if you are interested in getting started now, enroll in the self-paced version ($497) or hands-on coaching version ($997). Both versions include lifetime access and all future updates.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

The Leading Source of Insights On Business Model Strategy & Tech Business Models

7 Steps To Problem-Solving
The 7 steps to problem-solving is a disciplined and methodical approach to identifying and then addressing the root cause of problems. Instead, a more robust approach involves working through a problem using the hypothesis-driven framework of the scientific method. Each viable hypothesis is tested using a range of specific diagnostics and then recommendations are made.
Table of Contents

Understanding the 7 steps to problem-solving
The core argument of this approach is that the most obvious solutions to a problem are often not the best solutions.
Good problem-solving in business is a skill that must be learned. Businesses that are adept at problem-solving take responsibility for their own decisions and have courage and confidence in their convictions. Ultimately, this removes doubt which can impede the growth of businesses and indeed employees alike.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving
Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically.
Step 1 – Define the problem
First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified. Actions and behaviors of individuals must be the focus – instead of a focus on the individuals themselves. Whatever the case, the problem must be clearly defined and be universally accepted by all relevant parties.
Step 2 – Disaggregate the problem
In the second step, break down the problem (challenge) into smaller parts using logic trees and develop an early hypothesis. Here, economic and scientific principles can be useful in brainstorming potential solutions. Avoid cognitive biases, such as deciding that a previous solution should be used again because it worked last time.
Step 3 – Prioritize issues
Which constituent parts could be key driving factors of the problem? Prioritize each according to those which have the biggest impact on the problem. Eliminate parts that have negligible impact. This step helps businesses use their resources wisely.
Step 4 – Plan the analyses
Before testing each hypothesis, develop a work and process plan for each. Staff should be assigned to analytical tasks with unique output and completion dates. Hypothesis testing should also be reviewed at regular intervals to measure viability and adjust strategies accordingly.
Step 5 – Conduct the analyses
In step five, gather the critical data required to accept or reject each hypothesis. Data analysis methods will vary according to the nature of the project, but each business must understand the reasons for implementing specific methods. In question-based problem solving, the Five Whys or Fishbone method may be used. More complicated problems may require the use of statistical analysis . In any case, this is often the longest and most complex step of the process.
Step 6 – Synthesise the results
Once the results have been determined, they must be synthesized in such a way that they can be tested for validity and logic. In a business context, assess the implications of the findings for a business moving forward. Does it solve the problem?
Step 7 – Communicate
In the final step, the business must present the solutions in such a way that they link back to the original problem statement. When presenting to clients, this is vital. It shows that the business understands the problem and has a solution supported by facts or hard data. Above all, the data should be woven into a convincing story that ends with recommendations for future action.
Key takeaways
- 7 steps to problem-solving is a methodical approach to problem-solving based on the scientific method.
- Although a somewhat rigorous approach, the strategy can be learned by any business willing to devote the time and resources.
- Fundamentally, the 7 steps to problem-solving method involves formulating and then testing hypotheses. Through the process of elimination, a business can narrow its focus to the likely root cause of a problem.
Key Highlights
- Definition : The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is a structured methodology rooted in the scientific method. It emphasizes systematic hypothesis testing and data analysis to identify and address the root cause of problems, avoiding surface-level solutions.
- Problem-Solving Skill : Effective problem-solving is a learned skill that fosters responsible decision-making, boosts confidence, and supports business growth .
- Define the Problem : Clearly outline the problem’s scope and impact, focusing on actions and behaviors rather than individuals.
- Disaggregate the Problem : Break down the problem into smaller parts using logic trees and form early hypotheses. Avoid biases from past solutions.
- Prioritize Issues : Identify key driving factors of the problem and prioritize them by impact. Eliminate parts with minimal impact to allocate resources efficiently.
- Plan the Analyses : Develop work and process plans for hypothesis testing, assigning staff and setting completion dates. Regularly review and adjust strategies.
- Conduct the Analyses : Gather critical data to accept or reject hypotheses. Use methods like Five Whys, Fishbone diagrams, or statistical analysis .
- Synthesize the Results : Combine and analyze results to determine their validity and implications for the business . Assess if the problem is solved.
- Communicate : Present solutions that link back to the original problem statement, supported by facts. Create a compelling story ending with recommendations.
- The 7 Steps to Problem-Solving is based on the scientific method.
- It requires a structured approach to formulating and testing hypotheses.
- Businesses willing to invest time and resources can learn and apply this method effectively.
Connected Decision-Making Frameworks
Cynefin Framework

SWOT Analysis

Personal SWOT Analysis

Pareto Analysis

Failure Mode And Effects Analysis

Blindspot Analysis

Comparable Company Analysis

Cost-Benefit Analysis

Agile Business Analysis

SOAR Analysis

STEEPLE Analysis

Pestel Analysis

DESTEP Analysis

Paired Comparison Analysis

Related Strategy Concepts: Go-To-Market Strategy , Marketing Strategy , Business Models , Tech Business Models , Jobs-To-Be Done , Design Thinking , Lean Startup Canvas , Value Chain , Value Proposition Canvas , Balanced Scorecard , Business Model Canvas , SWOT Analysis , Growth Hacking , Bundling , Unbundling , Bootstrapping , Venture Capital , Porter’s Five Forces , Porter’s Generic Strategies , Porter’s Five Forces , PESTEL Analysis , SWOT , Porter’s Diamond Model , Ansoff , Technology Adoption Curve , TOWS , SOAR , Balanced
Read Next: Mental Models , Biases , Bounded Rationality , Mandela Effect , Dunning-Kruger Effect , Lindy Effect , Crowding Out Effect , Bandwagon Effect , Decision-Making Matrix .
- Business Models
- Business Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Business Model Innovation
- Platform Business Models
- Network Effects In A Nutshell
- Digital Business Models
More Resources

About The Author
Gennaro Cuofano
Discover more from fourweekmba.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- 70+ Business Models
- Airbnb Business Model
- Amazon Business Model
- Apple Business Model
- Google Business Model
- Facebook [Meta] Business Model
- Microsoft Business Model
- Netflix Business Model
- Uber Business Model
Skip Prichard | Leadership Insights
Ideas, Insight & Inspiration
7 Steps to Problem Solving

Bulletproof Problem Solving
Complex problem solving is the core skill for 21st century teams. It’s the only way to keep up with rapid change. Winning organizations now rely on nimble, iterative problem solving, rather than the traditional planning processes. I had the opportunity to speak with Charles Conn and Robert McLean, two McKinsey alums who share a seven-step systematic approach to creative problem solving that will work in any field or industry. Their new book is BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
New Skills Required
Would you share a little about the evolution of managerial skills and what skills are needed in the current era?
This new era of focus on creative problem solving has been ushered in by massive disruption of the old order in business and society. New business models are rapidly emerging from revolutionary Internet, machine learning, and bioscience technologies that threaten the status quo in every field. Technology change is speeding business up and providing an edge for disruptive innovators.
As a consequence of accelerating change, the old model of managerial skill development and application is no longer effective. It used to be that you could learn the core skills for a career in college and graduate school – think management, accounting, law – and then apply it over forty years. Strategic planning in business assumed an existing playing field and known actors. Today savvy business leaders are prioritizing complex problem solving skills in hiring rather than old domain knowledge, and emphasizing agile team problem solving over traditional planning cycles. This approach rewards the ability to see and quickly respond to new opportunities and threats over the slower traditional big company departmental responses.
We are seeing growing awareness of this. David Brooks of the New York Times said recently, “It doesn’t matter if you are working in the cafeteria or the inspection line of a plant, companies will only hire people who can see problems and organize responses.” And The World Economic Forum in its Future of Jobs Report placed complex problem solving at #1 in its top 10 skills for jobs in 2020.
For those who feel ill-prepared for this era, what are the best ways to acquire the needed skills?
Unfortunately, despite an increasing recognition in the business press that problem solving is the core 21 st century skill, our universities and graduate schools rarely teach systematic problem solving or modern team decision making skills. This is starting to change, and we are seeing that in moves by the OECD and Council for Aid to Education (CAE) which administers the College Learning Assessment plus test.
The OECD Program for International Student Assessment (PISA) started testing individual problem solving skills in 2012 and added collaborative problem solving skills in the 2015 assessments. One of the interesting early findings is that to teach students to become better problem solvers involves other capabilities than simply teaching reading, mathematics, and science literacy well. Capabilities such as creativity, logic, and reasoning are essential contributors to students becoming better problem solvers. That is what this book is about.
You share seven steps in your bulletproof problem solving approach. How did you develop it?
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further for application more broadly to personal, social and environmental problems at all scales in later work with the Nature Conservancy, the Gordon & Betty Moore Foundation, the Rhodes Trust and in start-up companies where we are investors.
1: Define the problem.
2: Disaggregate.
3: Prioritize.
4: Workplan.
5: Analyze.
6: Synthesize.
7. Communicate.
Is there one part of it normally missed or not focused on as much as it should be?

What are some of the best methods for overcoming biases in decision making?
The most important biases to address are confirmation bias, anchoring bias, and loss aversion. These are deep seated in our psyches and often reinforced by traditional hierarchies. We use some simple team approaches to fight bias, including perspective-taking (the act of modeling another team member’s assertion or belief to the point that you can describe it as compellingly as the other), role playing (where you act out one side or the other of difficult choice, sometimes in a red team/blue team structure), team distributive voting on analyses and solution paths (one approach we have used is to assign each team member 10 votes, represented by sticky notes, and have each team member use them to vote on their favorite analysis, allowing cumulative or bullet voting, with the most senior person voting last, so as not to bias the choices of more junior members). The most important team norm to encourage is the obligation to dissent, which means every team member is required to verbally contest decisions when they disagree, regardless of seniority.
What do leadership teams most struggle with in the new environment?
The biggest challenge is the speed of change, which pressures all the management approaches we were taught in business school, particularly around planning cycles. The leadership teams that get good at this typically form and re-form cross-functional teams to deploy on issues as they arise, rather than waiting for conventional departmental responses. And they are comfortable using rapid design cycles to prototype and test products/services in the market, rather than depending on traditional marketing analysis.
How will AI impact the bulletproof approach?
We believe good organization problem solving will increasingly utilize advances in artificial intelligence to predict patterns in consumer behavior, disease, credit risk, and other complex phenomena. Machine learning is getting better at pattern recognition than most humans. But that isn’t the whole story. To meet the challenges of the twenty-first century, mental muscle and machine muscle have to work together. Machine learning frees human problem solvers from computational drudgery and amplifies the pattern recognition required for faster organizational response to external challenges. For this partnership to work, twenty-first century organizations need staff who are quick on their feet, who learn new skills quickly, and who attack emerging problems with confidence.
For more information, see BULLETPROOF PROBLEM SOLVING: The One Skill That Changes Everything .
Continue Reading
Popular posts.

Learn the important power of prioritizing sleep
Subscribe today and receive a free e-book. Get Your Guide to a Solid Night of Sleep free when you sign up to receive blog updates via email.
Thank you! Please check your inbox to confirm your subscription.
Pin it on pinterest.
- Print Friendly
"The McKinsey Way" Book: A Comprehensive Summary
The McKinsey Way is a book by Ethan M. Rasiel , published in 1999, about what McKinsey&Company does, how McKinsey organizes and what working at McKinsey is like.
20 years after publication, the book still holds significant value, offering timeless insights into the world’s most prestigious management consulting firm: McKinsey&Company. In this article, we’ll provide a detailed summary of all the lessons and insights from The McKinsey way . We’ll re-organize the content and occasionally insert supporting insights to make it more friendly to the reader.
The McKinsey Way has 5 Parts (Sections) with 180 pages:
- Part 1: The Problem Solving Methodology of McKinsey
Part 2: Logistics of how a McKinsey project works
Part 3: insights into the actual works of consultants, part 4: how to excel as a junior consultant, part 5: exit opportunities and life after mckinsey.
Table of Contents
Part 1: The McKinsey problem-solving methodology
The McKinsey problem-solving process can be summarized in the 5 steps: define the problems, find the root cause, use “hypothesis-driven” process, analyze with “issue tree” and propose solutions.
1. Define the problem: Every consulting project revolves around a “problem”. But the “problem” is NOT always the problem!
One symptom may have different causes and we as doctors should never rely on the patient to diagnose.
So, always dig deeper. Get facts. Asks questions. Poke around. Challenge the client… until you find the real problem.
2. Find the root cause: Don’t jump straight to the solution, because you might just be fixing the symptoms. The problem will come back if the root cause is not properly dealt with.
3. Use “hypothesis-driven” process: Make educated guesses of possible root-cause A B C and test with data (a.k.a: facts). We’ll sometimes call this a fact-based process.
4. Break down and structure the analysis with the “ issue tree ” framework: A “hypothesis-driven” process may take forever as there are millions of possible root-causes. We need to test hypotheses from the top to the bottom of the issue tree – a top-down fashion. These issue trees need to be MECE.
5. Propose solutions: When the root causes are identified, consultants propose solutions targeting them directly.
A few notes when using this methodology
No.1: Don’t force the facts to say what you want.
When you propose or work extensively with a running hypothesis , it’s easy to get emotionally attached and turn the problem-solving process into a proving exercise. So keep an open mind and listen to what the data have to say.
No.2: Let the hypothesis come to you naturally.
You will not be able to form an initial hypothesis every time. The clients may not even know their problems. The scope of the project is often large and vague. So, dive in, gather facts, conduct analyses, and the hypotheses will show themselves.
No.3: Don’t reinvent the wheel.
Business problems often resemble each other more than they differ. With suitable techniques, you can apply what you and the firm learned from other projects. After all, one of the values consulting firms bring is to provide the “best practice” – what the top players in the game are doing
No.4: Make sure your solution fits your client.
The most brilliant solution is useless without proper implementation. So know your client’s weaknesses, strengths, and capabilities and tailor your solutions accordingly.
No.5: Be mindful of politics.
There are always politics in projects. Many times, McKinsey gets involved in fights between corporate factions. This creates friction that prevents you from doing your job (late data; rejected interviews, etc.).
So think about how your solutions affect the players in an organization and always build a consensus along the way. If consensus requires you to change your solution, try to compromise. It’s no good devising the ideal solution if the client refuses to accept it.
It’s highly recommended that you refer to the following video for a general view on how McKinsey organizes and a better understanding of the insights from this part.
There is a whole system behind how McKinsey solve a business problem. In this part of The McKinsey Way, Ethan Rasiel describes how the company sells their projects, builds a team and manages its hierarchy.
Selling a study/project
McKinsey typically does not sell. The firm does marketing through a constant stream of books, articles, and scholarly journals like the McKinsey Quarterly, etc. The Firm also invites organize press releases and generates quite some coverage by journalists.
These publications help McKinsey Partners build and nurture a vast network of informal contacts with potential clients. And when a problem arises, the client knows who to contact.
Assembling a team
Almost all projects need a full-time team of consultants. Typically, the process goes like this:
- The ED (a.k.a: Project Owner) signs a contract with the client
- The ED hires an EM from within the McKinsey network, from any offices (a.k.a: Project CEO)
- The EM then hires a group of staff, consisting of BAs (a.k.a: Business Analyst) and Associates.
It’s solely the EM’s responsibility to keep the team happy and functional. McKinsey projects have a few common practices to do so:
- A monthly “team-bonding”.
- A “team temperature” (a.k.a: morale) weekly survey.
The hierarchy
The chain of command in McKinsey is very clear and strict. So is the responsibility funnel. In the ED’s eyes, the EM is responsible for everything in the project. In the EM eyes, the BA is responsible for everything within the assigned workstream. Even when a BA messes things up, to the ED, it’s not the BA’s fault, but the EM.
To provide the best solution for the clients, consultants need tons of skills in preparing presentations; conducting researchs and interviews; presenting the final products in a simple structure; communicating with clients; and brainstorming.
Making presentations, a.k.a: the final deliverable documents
Most consultants spend a big portion of their time making presentations (often in PowerPoint). Utilize the support team! Keep it structured, from top to bottom, from end to end.
Note that there are diminishing marginal returns to your effort, meaning that the last miles toward perfection are always much harder than the beginning. So, resist the temptation to tweak your presentation at the last minute. Try to assess its gains vs those of a good night’s sleep for you and the supporting cast.
Visualizing data with charts and exhibits
We subconsciously admire the people who talk in sophisticated language, so we make complex charts. However, simple and easy-to-follow charts go a long way in consulting. Charts are just a means of getting your messages across, not a Ph.D. project.
Also, don’t forget to:
- Write clear chart titles
- List out units of measurement in all axes
- Mark legends and side notes
- Provide data sources
Managing internal communications
- Over-communication is always better. Keep that information flowing. Make sure that your team is up to date with at least the broad outlines of your workstream and your boss up to date with your team’s progress. There are many channels for this: email, voicemail, messaging, small talks during cigarette breaks, meetings, etc.
- Keep your communication brief, yet comprehensive and structured.
- Look over your shoulder – always. You never know who is listening. Remember that your client’s confidentiality is a must.

Working with clients
This is a big one as the true hierarchy at McKinsey is “Client -> Firm -> and then You”. The client is your biggest boss.
There are many tips on client management, but the general principle is to bring the client to your side. You never win by opposing the client. Remind them about mutual benefits. Do it everyday!
Some of the client members can be “liabilities”. There are 2 types of them:
- the merely “useless”.
- the hostile ones.
With both types, the number 1 option is to subtly trade them out of your realm. When that is not possible, the next best option is to play ignorant. Leak out information only with the right “secret audience”.
No matter what, engage the client members in the process. The more they feel everybody is on the same boat, the more they would support you.
You should also get buy-ins throughout the organization along the process. Every important party has to agree with you. Ideally, the final document has already been discussed many times through many rounds with the client before the official presentation.
Doing research
Don’t reinvent the wheel! Whatever you are doing, chances are that someone, somewhere has done something similar. Building upon someone’s work is the best way to save time and energy while achieving the highest standard.
Besides, here are some research tips:
- Start with the annual report. All public companies have them available on their website.
- Look for abnormal patterns (things that are especially good or bad). That’s where all the insights lie.
- Last but not least, look for the best practice. Find out what the best performers in the field are doing and learn from them.
Conducting interviews
This is one of the most effective ways to gather qualitative facts during a project. You will find yourself interviewing multiple industry and function experts as well as key client leaders.
Here are a few tips:
- Be prepared. Know exactly what you want to get out of it. Know as much as you can about the interviewee. Writing an interview brief for yourself is not a bad idea.
- If possible, have the interviewee’s boss set up the meeting.
- Start with some general and open-ended questions then move on to specific ones. Let the content flow naturally.
- Sometimes, it’s useful to use the indirect style. Take time to make the interviewee comfortable with you and the interview process.
- Include some questions you know the answer to. This gives insights into the interviewee’s style, knowledge, and honesty.
- Don’t ask too much. Focus on what you really need (what you prioritize in the interview brief).
- Listen and let the interviewee know you are doing so.
- Paraphrase what you hear in your own words. Confirm whether you understand correctly. This also gives chances for the interviewee to add or amplify important points.
- Near the end, use this last trick to flush out any possible missing insights: “Is there anything else you would like to tell or any question I forgot to ask…?”.
- Adopt the Columbo tactic. Wait until a day or two passes, then drop by the interviewee’s office. “I was just passing by and remembered a question I forgot to ask”. This is a less threatening way to keep the conversation going.
- Lastly, always write a thank-you note. A short and sincerely one always does the work.
Brainstorming at McKinsey
In McKinsey, we often use the word “Problem-Solving” interchangeably with brainstorming sessions. It’s a very topic-focus meeting within the McKinsey team, consisting of the consultant in-charge, the EM, and sometimes even the ED and experts.
Before the session, prepare in advance as much supporting data as possible. It will come handy in the process.Inside the White room: Start with tabula rasa — a clean slate. When you get your team into the room, leave your preconceptions at the door. Bring in only the facts, and find new ways of looking at them.
Management consulting is an interesting yet challenging job. To survive and thrive at McKinsey, here are some advices for you:
Tip 1: Find your own mentor
At McKinsey, every consultant is officially assigned a mentor, who may not be in the same office. How much you benefit from the official mentor is pretty much a matter of luck. If you want great guidance, you have to go out and get your own. Get a few too, don’t stick to just one.
Tip 2: Survive the road
Business travel can be exhausting and difficult, here are some note you can take to deal with it:
- Look at business travel as an adventure.
- Do proper planning. These simple logistics can make a big difference
- Treat everyone with tremendous respect
Tip 3: Have a list of items to bring when traveling
Here is the list:
- Clothing: extra shirts or blouses, spare ties, spare shoes, casual clothes, cashmere sweaters
- Tools: writing pad, copy of whatever you send to the client, calculator
- Personal care Items
- Things to keep you organized and in touch
Tip 4: Treat your assistant well
Having a good assistant is a lifeline. Treat them well. Be clear about what you want. Give them room to grow. Take time to train them well. Answering their questions and showing them the ropes.
Tip 5: Have boundaries to keep your life balance
Since you have a large amount of work to cover as a consultant, there is almost no work-life balance. However, if you want a life, lay down some rules. For example:
- Make one day a week to be completely free of work, both physically and mentally. Tell your boss about it! He/she will respect it. And so should you.
- Don’t take work home. When you are home, you are home!
- Plan long ahead, especially when you travel.

Tip 6: The 80 / 20 Rule
80% of the wealth is owned by just 20% of the population. 80% of the output can be produced by 20% of the effort. 20% of the problems can cause 80% of the trouble.
So if you wanna save time and effort. Always try to find those 20% and act upon them!
Tip 7: Don’t try to analyze everything
If you don’t take shortcuts, there is simply too much to do. Be selective. Find the key drivers. Focus on the core problem, then apply analysis. This helps avoid going down blind alleys and boiling the ocean.
Tip 8: The Elevator Test
Concise communication is crucial in consulting. Anytime the EM asks you for your workstream status, you have to be able to give him a 30 seconds summary. Short yet insightful. This skill takes practice. Try doing it every day in various contexts!
Tip 9: Pluck the Low-Hanging Fruit
Solving only part of the problem can still mean increased profits. Those little wins help you and your customers. Try to see such opportunities and grab them first.
Tip 10: Hit singles
Get your job and only your job done, don’t try to do the work of the whole team.
It’s impossible to do everything yourself all the time. Even if you manage to pull it off once, you raise unrealistic expectations and once you fail, it is difficult to get back credibility.
Tip 11: Look at the big picture
When you are feeling swamped, take a step back, figure out what you are trying to achieve, and then look at what you are doing. “Does this really matter?”
Probably not! All of these troubles will go away!

Tip 12: Just say “I don’t know”
The firm pounds the concept of professional integrity: Honesty. If you don’t know something, just say “I DON’T KNOW” in an empowering fashion. Admitting that is a lot less costly than bluffing.
“Leaving McKinsey is never a question of whether—it’s a question of when”
There are not many people who stay with McKinsey for their whole career life. In the last part of The McKinsey Way , Ethan Rasiel and other ex-McKinsey consultants share their valuable lessons and memories from working at the company.
- “Structure, structure, structure. MECE, MECE, MECE. Hypothesis-driven, Hypothesis-driven, Hypothesis-driven.” – Former associate in Dusseldorf and San Francisco offices
- “The quality of the people. In the corporate world, the average-caliber employee is far below McKinsey’s least intelligent.” – Wesley Sand
- “What stays with me is the rigorous standard of information and analysis, the proving and double-proving of every recommendation, combined with the high standard of communication both to clients and within the Firm.” – Former associate in the Boston and New York offices
- “When faced with an amorphous situation, apply structure to it.” – Kristin Asleson, New York office, 1990-93; now working in Silicon Valley
- “Execution and implementation are the key. A blue book is just a blue book, unless you do something with it. Getting things done is the most important thing.” – Former EM in the New York office
Scoring in the McKinsey PSG/Digital Assessment
The scoring mechanism in the McKinsey Digital Assessment
Related product
/filters:quality(75)//case_thumb/1669802837683_mc_kinsey_comprehensive_bundle.png)
McKinsey Comprehensive Package
Unlock all materials helping you land the next job in McKinsey!
Among MBB firms, people tend to say McKinsey is slightly better than the other two in three factors: prestige, people, practices, and offices
At McKinsey, the salary for entry-level consultants ranges from $90,000 to $110,000/year, while the figure for experienced Associates can go up to $233,000
McKinsey hiring process including 3 phases: resume screening, PST test, and case interview. Each candidate will have to undergo 4-6 interviews during 4-8 weeks
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process The McKinsey Podcast
Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
- Episode Website
- More Episodes
- 2024 McKinsey & Company
More by McKinsey
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

How to master the seven-step problem- solving process

Related Papers
Kevin Spellman, PhD, FRSA
Keywords: collaboration, complexity, creativity, ideation, ideation tools, and practice-led research The focus of this research are ideation tools and their ability to catalyse ideas to address complex design problems. Complex design problems change over time and the interactions among the components of the problem and the interaction between the problem and its environment are of such that the system as a whole cannot be fully understood simply by analyzing its components (Cilliers 1998, pp. I). Ideation for this research is defined as a process of generating, developing and communicating ideas that are critical to the design process (Broadbent, in Fowles 1979, pp. 15). Based on Karni and Arciszewski, who stated that ideation tools should act more like an observer or suggester rather than controller or an expert, I defne design ideation tools as tools or methods that enhance, increase and improve the user's ability to generate ideas with the client (Karni and Arciszewski 1997; Reineg and Briggs 2007). Based on a survey of over 70 ideation tools, protocol analysis of design activities, a web survey and semistructured interviews, I conclude that designers and clients may not have sufcient knowledge of ideation or ideation tools in either testing or practice as a catalyst for generating possibilities and that measuring ideation tools based on how many ideas they generate is misleading because it relates creativity and idea generation but does not adequately refect the participants' experience. Tis research suggests that participants' cultural perceptions of design ideation and the design process actively inhibit idea generation and that a shift from design outcome led ideation tool design to designing ideation tools that engage design contexts are necessary to effectively address complex design problems. Tis research identified a gap in ideation tools for designers to collaborate with their clients during the ideation phase to catalyse possibilities to complex design problems as the contribution to new knowledge.
Philip Schlesinger , Inge Sorensen
This research seeks to review, evaluate and clarify the findings of five reports in relation to the discussion paper Creative Industries in Scotland. Micro-businesses, Access to Finance and the Public Purse by Bob Last for the Cultural Enterprise Office.
Roger Sapsford
• This is the second and final report on a research project commissioned by HMP Kirklevington Grange into how the régime of the prison is experienced by prisoners, how effective it is in preparing them for release and resettlement into the outside world and how its separate elements relate to each other. • In the course of the research we have (a) interviewed 30 prisoners, some of them more than once, including 2 men now released from custody, (b) carried out a survey of all prisoners which yielded an effective sample of 70 completed questionnaires (a 31% response rate), a sample which is reasonably representative of the prison population at the start of the research, (c) interviewed 15 members of staff in a range of occupational positions in the prison, including governor grades, disciplinary staff, the Probation Service and Phoenix House (CARATS), (d) examined the prisoners’ files and (e) benefited from periods of observation of the régime and the prisoners by the researcher who c...
Royal Roads University, Doctor of Social Science (DSocSci) Dissertation
Sharon M McIntyre
This research used a comparative case study methodology to closely examine an emergent phenomenon in the field of entrepreneurship. The literature review examined interconnected shifts in social values, evolving technology, and economic geography systems that have contributed to this emergent phenomenon. The study sought to better understand the qualities, goals, and perceived needs of a purposive sample of entrepreneur business founders in Canada, as well as the drivers guiding the formation and characteristics of their advanced technology enabled organizations, to determine if a distinct model of entrepreneurial innovation existed. The study results affirmed many aspects of the observed phenomenon and provided new details about this distinctive model of entrepreneurship. Given the name GEMINI (an acronym meaning global entrepreneurial micro-niche innovation), this model comprises independent-minded founders with a keen sense of vocation who derive deep meaning from work-life integration, collaborative business building, personal development, and community legacy. Their typically bootstrapped, world-class organizations are formed through an iterative effectuation path to business model refinement, resourceful product design, solid business performance metrics, and a lasting impact on their international industries and communities. Although the stereotype of the young, Silicon Valley–style, high-tech-startup founder and his fast-growth company is still a prevailing discourse in media, political, business, and educational circles, the lived reality in this new model of entrepreneurial innovation is distinctly different from almost all aspects of this construct. Furthermore, public funds continue to be funnelled into a myriad of entrepreneurship strategies and programs—often without significant or sustainable economic community impact. Eighteen recommendations are made to reform related Canadian public policy, programs, and funding to support the development of more GEMINI model founders and businesses.
spapda aspdapd
Aboriginal Stories of Victoria Park: Negotiation, consultation and engagement: Navigating design consultation on colonised and contested urban land
Annie Burgess , Anne M Burgess
In 2008, Col James, a senior lecturer at the University of Sydney, initiated a collaborative design project celebrating Aboriginal culture in Victoria Park, an historic public park on the outskirts of Sydney’s CBD. This project was supported by members of the Aboriginal community, but as the project progressed concerns were raised about the consultation process. A subsequent investigation identified poor consultation as a common trigger for failure in design projects for Aboriginal peoples. A review of the existing literature showed that most consultation guidelines are written for regional or remote areas, and little information is available for urban or contested locations. This research addressed these gaps in the literature by asking whose voices, ways of knowing and conferring authority are given precedent in consultation guidelines for design projects celebrating Aboriginal culture on colonised and urban land, and how might such design projects be best negotiated. Using an ‘outsider researcher’ perspective to address the interface of Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal knowledge systems, the research adopts an outsider’s decolonising and post-colonial critical methodology informed by Linda Tuhiwai-Smith, Michel Foucault and Homi Bhabha. This approach foregrounds previously silenced voices through interviews conducted as guided conversations with Aboriginal Elders and Aboriginal and non-aboriginal design experts. Existing consultation guidelines are critically analysed to identify the different themes, world views, standpoints and agendas which inform them and the findings are then compared to identify correlations and disconnections with the interview findings. The thesis confirms that consultation for Aboriginal design projects in contested locations is a complex issue for designers requiring specialised skills, strategies and competencies to account for and accommodate for historically unequal power relationships between colonised Aboriginal peoples and non-aboriginal people. The thesis re-frames and re-presents the knowledge on consultation in a more fluid, dynamic and flexible form, revealing new understandings about design praxis that move towards the increased inclusion of Aboriginal peoples' voices, perspectives and practices in the design consultation process.
Eric Feeney
Abstract: The purpose of this study was to examine teachers' professional learning situated in a school context in an effort to reveal factors and conditions that both support and hinder how and what teachers learn in the workplace. Workplaces are considered to be unique ...
Kelly Chapman
The Ningaloo Reef is Australia’s largest fringing coral reef and an iconic tourist destination; however tourism development in Ningaloo has been ad hoc and the area is challenged by human pressure on numerous fronts. In response to these challenges a number of research agencies brought together a range of scientists to study the effects of human interaction on the reef. Moving from research to practice has been understood to depend on the adaptive capacity of the institutions responsible for governing human activities, in this case in the Ningaloo area. Knowledge transfer describes the suite of strategies used to try to bridge the gap between research and management. Knowledge transfer efforts, however, seldom have the desired impact of seeing research applied to decision-making. The ubiquity of knowledge transfer difficulties across disciplines suggests a common root to the problem, based in our shared cultural assumptions. This study pairs a multidisciplinary theoretical investigation with action research to shed light on why knowledge transfer efforts so often fall short in terms of seeing research applied to practice. Recent environmental management perspectives on knowledge transfer illustrate the shift towards stakeholder participation as a means of improving knowledge transfer success. As such, the action research study involved the researcher embedding herself in the Ningaloo community for 18 months, adopting the role of a knowledge broker and engaging and collaborating with modelling researchers and local stakeholders on knowledge transfer efforts. However, despite intensive stakeholder engagement, evaluation interviews at the end of the process indicated that although the knowledge transfer process had the effect of catalysing relationships between stakeholder groups in the region, and between regional stakeholders and scientists, it appeared to have relatively little effect on the representational knowledge of local stakeholders or the actual application of research in practice. This led to the question of whether knowledge transfer is itself is part of the research uptake problem, as per the principles of problem formulation, which specify that resolving seemingly intractable problems requires examining the assumptions that underpin our thinking about the problem situation. On this basis, the theoretical component of this study explored the Newtonian assumptions that inform our understanding of knowledge transfer. An alternative complexity-based ontology is proposed, unifying the metaphysics of materialism and idealism, based on a synthesis of process philosophy, mathematical logic, quantum theory, general systems theory and the complexity sciences. The phenomena of cognition, learning, knowledge and organising are compared in relation to how they’ve been understood within the Newtonian paradigm, and how they are now being explained from the perspective of a complexity-based paradigm. By reframing the action research results from a complexity perspective, the Ningaloo knowledge transfer process does not constitute a failure in terms of enhancing the capacity of the Ningaloo system to make more sustainable decisions. Rather, the increased connectivity between stakeholder groups and scientists can be viewed as more importantly enhancing the creative capacity of Ningaloo’s governance system. It is posited that the research uptake problem should be reformulated from the basis of complexity paradigm, and the notions of knowledge transfer and adaptive capacity reconceptualised accordingly. Instead of devising rational objective arguments for someone else to improve the ‘adaptive capacity’ of human systems, scientists should focus instead on improving their own creative capacity in their local interactions.
Fiona Lee , John Vella
The Plimsoll Inquiry (The PI), was the second case study for my PhD, titled 'The Rogue Academy: Conversational Art Events as a Means of Institutional Critique'. It was an event that took place over seven weeks beginning in September 2013 at the University of Tasmania's Plimsoll Gallery at the College of the Arts in Hobart Tasmania. This project report formed part of the second phase of the project.
Electrochimica Acta
Luis Carlos
RELATED PAPERS
Journal of the Saudi Heart Association
A. Al-Masri
Wolfgang Muno
Atmospheric Environment
The International Journal of Narrative Therapy and Community Work
Rhea Almeida
Swapnil Yadre
HUMANITIES OF THE SOUTH OF RUSSIA
Evgeny Dugin
Aurangzeb Khan
SAGE. Arts and Humanities in Higher Education
Olcay Muslu, PhD
Journal of Environmental Management
Serena Gabrielli
Chip Gerfen
Best Practices
Susan Sahertian
Cadernos de Gênero e Tecnologia
Jamil Cabral Sierra
Environmental science & technology
Daniel Tunega
Jurnal Teknik Pengairan
Türkiye’de Zekâtın Kurumsallaşması ve Diyanet Personelinin Bakış Açısı Hakkında Bir Araştırma (Kocaeli Örneği)
Mahmut Bilen
Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society
Paula Tucker
Chi.-Kent L. Rev.
Fred Dallmayr
2007 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory
Marco Chiani
The Italianist
Anna Cento Bull
IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems
Chemical Communications
Linos Lazarides
La Tribuna: Cadernos de Estudos da Casa-Museo Emilia Pardo Bazán
ricardo perez virtanen
Journal of Mathematics and the Arts
Ergun Akleman
Cadernos de História da Educação
Wenceslau Goncalves
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive, and coauthor of the book Bulletproof Problem Solving: The One Skill That Changes Everything [John Wiley & Sons, 2018].
McKinsey and Company is recognized for its rigorous approach to problem solving. They train their consultants on their seven-step process that anyone can learn. This resource guides you through that process, largely informed by the McKinsey Staff Paper 66. It also includes a PowerPoint Toolkit with slide templates of each step of the process ...
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process. The McKinsey Podcast. Management. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges. Episode Website. More Episodes. 2024 McKinsey & Company. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
To discuss the art of problem solving, I sat down in California with McKinsey senior partner Hugo Sarrazin and also with Charles Conn. Charles is a former McKinsey partner, entrepreneur, executive ...
Read more > Listen to the podcast (duration: 25:53) > Structured problem solving can be used to address almost any complex challenge in business or... - Listen to How to master the seven-step problem-solving process by The McKinsey Podcast instantly on your tablet, phone or browser - no downloads needed.
Connecting to Apple Music. If you do not have iTunes, download it for free. If you have iTunes and it does not open automatically, try opening it from your dock or Windows task bar. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
McKinsey 7-Step Problem-Solving Process Step 1: Define the Problem. ... The 7-Step Problem-Solving Process is a robust and systematic method to help individuals and organizations make better decisions by tackling complex issues and finding practical solutions. This process comprises defining the problem, disaggregating it into smaller parts ...
How to master the seven-step problem solving process. Like. Comment. Share. 53 · 2 comments · 1.4K views. McKinsey & Company ... Many would argue that it's problem solving -- that is, the ability to come up with an optimal course of action to address any complex challenge—in business, in public policy, or indeed in life.
Step 4: Dive in, make hypotheses and try to figure out how to "solve" the problem. Now the fun starts! There are generally two approaches to thinking about information in a structured way and going back and forth between the two modes is what the consulting process is founded on. First is top-down.
While it might seem like some people are just born with stronger problem-solving skills, there are strategies that anyone can use to improve them.That's righ...
Problem statements should commence with a question or a firm hypothesis. Be specific, actionable and focus on what the decision maker needs to move forward. Break a problem into component parts so that problems can be divided and allocated. The parts should be MECE. Do it as a team, share with Experts and client to get input and alignment.
Moving through the 7 steps to problem-solving . Although many versions of the 7-step approach exist, the McKinsey approach is the most widely used in business settings. Here is how decision makers can move through each of the steps systematically. Step 1 - Define the problem. First, the scope and extent of the problem must be identified.
The 7-steps approach to problem solving has its roots in the hypothesis-driven structure of the scientific method, but was developed into an approach for business problem solving at McKinsey & Company. Charles wrote one of the early internal documents to systematic problem solving in McKinsey, and both of us have developed the approach further ...
The McKinsey problem-solving process can be summarized in the 5 steps: define the problems, find the root cause, use "hypothesis-driven" process, analyze with "issue tree" and propose solutions. 1. Define the problem: Every consulting project revolves around a "problem". But the "problem" is NOT always the problem!
The important first step is to describe the context and the boundaries of the problem that is agreed upon by those involved in making the decision. A weak problem statement is a common problem. "Rushing into analysis with a vague problem statement is a clear formula for long hours and frustrated clients.". Step Two: Disaggregate the Issues.
How to master the seven-step problem-solving process. The McKinsey Podcast. Management. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges. Episode Website. More Episodes. 2024 McKinsey & Company. Structured problem solving can help address complex business challenges.
McKinsey's 7-Step Problem Solving Approach Consulting Committee Week 7 - Winter 2021. Our client is a teddy bear manufacturer, Fuzzy Factory, ... 7 Step 2 Issue Tree Problem Issue 1 Issue 2 Issue 1a Issue 1b Issue 2a Issue 2b. 8 MECE MUTUALLY EXCLUSIVE, COLLECTIVELY EXHAUSTIVE NO OVERLAPPING NO GAPS MECE. 9
Simon London: Problem definition, but out in the world. Hugo Sarrazin: With an enormous amount of empathy. There's a huge emphasis on empathy. Traditional, more classic problem solving is you define the problem based on an understanding of How to master the seven-step problem-solving process the situation.
Mckinsey Podcast - How to master the seven-step problem-solving process A great podcast on a seven step process to problem solving. For those practicising case studies, you should listen to the emphasis put on understanding the problem before going into solving it and focussing on levers of which you can control.