100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples
Welcome to our list of media analysis essay topics! Here, you will find plenty of content analysis topic ideas. Use them to write a critical paper, a literary analysis, or a mass-media related project. As a bonus, we’ve included media analysis example essays!

🔝 Top 10 Media Analysis Topics for 2024
🏆 best media analysis topic ideas & essay examples, ⭐ interesting topics to write about media analysis, ✅ simple & easy media analysis essay titles, 🔥 content analysis topic ideas.
- Portrayal of Women in Ads
- Media Bias in Political Reporting
- Representation and Diversity on TV
- Social Media’s Impact on Self-Esteem
- Media Coverage of Humanitarian Crises
- How Are News on Climate Change Framed?
- Consequences of Fake News and Misinformation
- How Gender Roles Are portrayed in Children’s Media
- Does Violence in Video Games Lead to Aggressive Behavior?
- The Relationship of Media and Public Opinion in Elections
- Media Analysis of 13 Reasons Why According to the laws of the genre, the atmosphere is intensified, the pace accelerates, and the turns in the plot become more and more abrupt.
- Covering a Pandemic: Critical Media Analysis A lot of work over the past decades has been devoted to the study of media analysis, which has led to the formation of a new area of knowledge, concepts, and categories.
- “Super Bowl LVI Today: Day 1” Media Analysis Hence, it is essential to consider the priorities of the mass communication organization, namely the tone, look and advertising in the show.
- Sociological Media Analysis: “The Bachelor” and “One Day at a Time” The show is misogynistic, with the male protagonist playing the role of the pursuer and the female protagonist assuming the role of the pursued.
- Historical Components of Media Analysis In the case of Mumford and McLuhan, Carey observes that the writing and interpretation of media can result in the reconstruction of wider arguments and even the selection of an antagonistic agent.
- Analysis of Social Media Tools in Business The last item, the detailed analytics of the content and activity, allows for the development of the more efficient business strategy based on the subscribers’ preferences.
- Media Literacy Research: Analysis of the Issue In the process of research, I have significantly expanded my ability to access and analyze media messages as well as to use the power of information to communicate and make a difference in the world.
- Media Influences Learning: Analysis The use of media in learning leads to the achievement of positive outcomes if the medium used is interrelated and confounding.
- Media Analysis: Abuse Over Vaccine Passports The article uses the direct quotations of the restaurant owners, thus making the most of the story based in the first person.
- Media Analysis: Ageism in Advertisement In addition to the idea of saving communicated in E-trade’s ad, the commercial also seems to convey the hope of work among the old population.
- Media Bias Fact Check: Website Analysis For instance, Fact Check relies on the evidence provided by the person or organization making a claim to substantiate the accuracy of the source.
- The Media Economics Analysis In addition, the assessment of the economics of media reveals crucial information about the production, distribution, and consumption patterns of the media services and products.
- Social Media Presence Analysis I think it expresses engagement within my workplace and willingness to learn more to either explore new ideas, be a part of the discussion, and make sure the information I am gathering is accurate and […]
- The HopeLine: Website and Social Media Analysis The organization’s social media and the site contain a body of knowledge that might be also informative or important to revise for the current employees, for instance types and signs of abuse.
- Media Analysis: Gideon’s Trumpet As it has been mentioned above, the purpose of the movie was to show that even a criminal has the right to have someone to represent him in the courtroom.
- Acute Otitis Media Analysis The peak of acute ear infections, which precedes otitis media, is prior to the age of 2 years, and during school entry.
- Modern Mass Media and Tools for Their Analysis A sender is a person who originates the message, a message is the content that is communicated, a channel is a medium used to transmit it, and a recipient is a person to whom the […]
- Analysis of Media Representation Patterns In fact, studies show that the DNA of any given human being is ninety-nine percent identical in comparison to the rest of the population, regardless of their origin.
- News and Media Reliability: Social Analysis At the same time, given the apparent trend to use the Internet as the primary source of news, mobile devices still seem to arouse suspicion among the adult and the older adult population. The most […]
- Analysis Representations of Britishness in Different Media Texts Although it is clear to me that facts of Britishness exist in all three media sources listed above, I understand that it has different sides and is shown as a mixture of cultural peculiarities, breathtaking […]
- On Stereotyping in the Media Viewers watch shows regularly and do not understand the content that is biased while the media is able to attract the attention of the audience by way of drama, comedy and action.
- Media and Injustice: Issues Analysis This paper will high light relations among media and the Injustice, discuss media in it’s past and current perspective and it’s possible role in future challenges by means of special importance on the media management […]
- Media Coverage of Issues Analysis The main arguments that the authors suggest are: Inconsistent use of labels for the alternative plans minimized the likelihood that the public would understand the details of any of them; The conflicts frame narrowed public […]
- Mass Media Communication: Personal Analysis Finally, when I do the same in the kitchen in the morning, I am occupied with preparing and eating my breakfast; therefore, television serves as a background and I cannot be focused on the information […]
- Mass Media Law’s Analysis Indeed, the existing regulations show that the specified action is defined as flag desecration can be interpreted as an affront of the citizen of the United States, as well as the disdain for the law.
- “The New Yorker” and “National Geographic” Media Analysis What finds most interesting about Surowiecki’s article is that he manages to counter the politics of the USA government, whereas, in Alexander’s article, the secret of the buried treasure and the historical events are the […]
- Media Analysis: Jacob’s Cross In the Jacob’s Cross episode that was watched the following scenes that apply to the social justice theme were observed: This episode begins in the morning by Jacob calling his attorney and some other close […]
- Social Media Data Analysis For the company storage purposes, information in wikis is stored in a chronological order and may be used to build the company’s knowledge.
- Fairfax Media Limited Situational Analysis While it has generally taken Fairfax a longer time than expected to identify and adapt to the shift brought about by the rise of technology in market- specifically the internet and social media- the company […]
- Analysis of Media Strategies This is because it uses a reverse marketing strategy which states that the less the advertisement, the higher the pricing and the harder it becomes to find it, the higher the chances that people will […]
- Media Industry News Analysis: Gasland May Take the Oscar To learn more about the world of media, it is better to focus on the news and the main themes of the articles offered to the reader.
- Fairfax Media Industrial Environmental Analysis When the rights are granted, they come with a cost to the company; there has been challenges of print media from free press media in Australia thus Fairfax faces the challenge to handle the situation.
- Content Analysis of Two Different Forms of Media Although the first one uses television and the second uses the Internet and the World-Wide-Web to deliver content to consumers it must be pointed out that these two are rivals and basically has the same […]
- Analysis of Gender Issues in the Media The message in the advertisement simply showed that women are able to control men by using their bodies in a certain way.
- The Focus on the Importance of Symbols in Media Analysis
- Visual Media Analysis for Social Media and Other Online Platforms
- Research Methodologies for the Media Analysis
- Communications and Media Analysis
- Television Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Leadership
- Predicting Stock Market Using Social Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Television and New Media
- Media Analysis and Feminism
- Television Media Analysis: Authors and Producers
- How the Media Places Responsibility for the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Australian Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Political and Social Bias in the USA
- Collecting Data in Social Media Analysis
- The Jurisprudence and Qualitative Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Banning Beauty and the Beast in Malaysia
- Media Analysis and Understanding the Meaning of Islam
- Symbolic Interactionism and Social Networks: Media Analysis
- Television Media Analysis: The Cosby Show
- Marketing and Business Communication: Media Analysis
- The Difference Between the Quantitative and Qualitative Media Analysis
- Structuring and Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Audiences and Consumers
- Managing the News and Media Analysis
- Comparative and Critical Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Rose Petal Cottage
- Video Installation and Media Analysis
- Philosophical and Social Media Analysis
- Critical and Interdisciplinary Research in Media Analysis
- Public Relations and Media Analysis: Semantic and Social Aspects
- Functionalist Perspective for Media Analysis
- Media Analysis of Traditional Primary Documents
- Responsibility for the COVID-19 Pandemic: Media Analysis
- Qualitative Research Methods in Media Analysis
- A Visual Analytics System for Television Ratings
- Food Chain Actors’ Perceptions of and Adaptations to Volatile Markets: Results of a Media Analysis
- Religion and the Media Analysis
- Symbolic Interactionist Perspective for Media Analysis
- Employer Relation: Industrial Conflict Media Analysis
- Symbolic Interactionist Perspective Media Analysis
- Media Analysis: Overview of Media Research Methodologies and Audiences
- Patterns of Emotional Expression in Social Media Posts
- A Comparative Content Analysis of Television Shows and Gender Representation
- Environmental Sustainability Messaging in Advertisements
- Patterns of Persuasive Language in Political Debates
- News Coverage during COVID-19: Media Framing and Public Perception
- The Impact of Celebrity Endorsement on Consumer Behavior
- Analysis of Unrealistic Standards in Video Game Characters
- How Portrayal of Violence in Movies Leads to Desensitization
- Diversity of Characters and Themes in Children’s Literature
- How Fashion Magazines Affect Beauty Ideals
- Effectiveness of Educational Apps for Children
- Do Food Advertisements Promote Healthy Nutritional Choices?
- Representation of LGBTQ+ Characters in TV Series
- Environmental Messaging in Corporate Social Responsibility Reports
- Representations and Perspectives on Climate Change
- TV Show Titles
- New York Times Topics
- Radio Paper Topics
- Propaganda Topics
- Twitter Topics
- YouTube Topics
- Oprah Winfrey Topics
- Mass Communication Essay Topics
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, March 2). 100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/media-analysis-essay-topics/
"100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples." IvyPanda , 2 Mar. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/media-analysis-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples'. 2 March.
IvyPanda . 2024. "100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/media-analysis-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/media-analysis-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "100 Media Analysis Essay Topics & Examples." March 2, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/media-analysis-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
100 Best Media Topics For Research Writing

We know you need the best media topics for your next papers. Otherwise, why would you be reading this blog post? The good news is that you have picked the best place to look for topics. Our experienced writers have put together a list of the best media topics for high school and college students. Furthermore, we work hard to keep the list fresh. This means that these ideas will be most likely original. They will work great in 2023 because the list of media essay topics is updated periodically.
The Importance of Great Media Topics
You are probably wondering why we are putting so much emphasis on getting you the best media topics to write about. There are several reasons for it, but we will only tell you about 3 of them:
- Your professor will greatly appreciate your willingness to dedicate the time and effort to finding excellent topics . Trust us, professors know how to make the difference between students based solely on the topics they choose for their papers.
- It is much easier to write essays if you choose good media essays topics . A topic you know something about is the best choice. Also, a good topic enables you to quickly find plenty of information on the Internet. Following this advice you’ll easily write your literature review and the following components of your paper.
- By choosing a great topic, your essay will immediately stand out from all the rest . Your professor is surely bored of reading papers written about the same things over and over again. An interesting idea will entice him to award you at least some bonus points.
Mass Media Topics
Mass media is something of great importance in modern times, so why not write your papers on some mass media topics? Here are some great examples:
- The effect of mass media on psychological health
- Mass media and emotional health
- Mass media addiction in the US
- The role of mass media in politics
- The First Amendment in mass media
- Promoting sexuality in mass media
Media Research Topics
Did your professor ask of you to write a research paper? No problem, we have some excellent media research topics in our list. Check them out below:
- Discuss children media
- Violence in mass media in the US
- Video games in the media
- Controversial topics in the media in Europe
- Discuss post-truth in the media
- Media regulations in China
Media Analysis Essay Topics for Presentation
Would you like to write a media analysis paper for a presentation? It’s not difficult to do, if you pick the right media analysis essay topics for presentation. Here are some excellent ideas:
- Is the media creating events or reacting to them?
- Media and public relations links
- Discuss 3 major types of media
- The use of media in education (one of the most interesting mass media research paper topics)
- Influence of virtual reality on the media (one of the best media analysis essay topics)
- Discuss journalism ethics
Media Research Paper Topics for High School
Are you a high school student looking for some awesome topic for his next research paper on media? Here are some excellent examples of media research paper topics for high school:
- Major innovations in 21st century media
- Compare mainstream media in India and China
- What makes an outlet a reliable source?
- Advertisements in media
- Benefits of mass media for society
- Compare traditional media with mass media
Mass Media Research Topics
If you need to write a research paper and want to talk about something in mass media, we have some very nice ideas right here. Check out our mass media research topics:
- The right of expression in mass media
- Journalism in mass media
- Compare TV, film and radio
- Mass media in democracy
- The war against terror in mass media
- Discuss the rise of mobile media
Media Research Topics for College Students
College students who are looking to research topics about media should choose something that can bring them a top grade. Here are our best media research topics for college students:
- Influences of technology on media
- Latest innovations in media
- Discuss media censorship in China (a recommended media related topic)
- What is media propaganda?
- Mass media and its preemptive effects
Complex Media Related Research Topics
Do you want to try your hand at some difficult topics? If you want to impress your professor, we advise you to select one of these complex media related research topics:
- Mass media violating civil rights
- Does media benefit the economy of the US?
- Define media addition and discuss its effects
- Perform a qualitative analysis of 3 media outlets
- Media’s scare strategies: a case study
- Media influencing a rise in violence in the UK
Controversial Media Topics
Why should you be frightened by controversial topics? You are free to write about them, of course. Here are our best and most controversial media topics:
- Exercising the First Amendment in media in the US
- Promoting gun violence in mass media
- Mass media effects on terrorism
- Digital media is destroying traditional media
- Artificial intelligence in mass media
- Media effects on the death penalty in China
Digital Media Topics
Discussing digital media is a very good way to impress your professor. Let’s face it; the digital realm is extremely popular these days. Here are some brand new digital media topics:
- Define and discuss digital media
- Climate change in digital media
- What is mobile media?
- The fate of journalism in the 21st century (one of the best digital media research topics)
- Effects of digital media on politics
Media Analysis Topics
Writing a media analysis essay can be a very difficult task, especially if you don’t have much academic writing experience. Here are some media analysis topics that should make things easier:
- How Trump lost the media war
- Biden’s coverage in mass media in the United States
- Advertising revenue in media outlets
- Analyze screen time
- What are deepfakes and how to spot one?
- The crisis of journalism in the 21st century
Easy Media Related Topics
The perfect choice for times when you simply cannot afford to spend too much time writing your essay, our list easy media related topics is right here:
- Define mass media in the United Kingdom
- Should children watch the news?
- Promoting violence in mass media
- Spreading awareness via media
- Are newspapers still relevant today?
- The very first occurrence of mass media
Research Topics in Media and Communication
Would you like to talk about media and communication? It is not an easy subject to write about, but we can make things easier. Here are the easiest research topics in media and communication:
- Discuss body image in media
- Analyze children’s advertising tactics
- Freedom of speech in the media
- Copyright law in the media
- Define symmetrical dialogue in the media
Media Debate Topics
Are you interested in a media debate? Getting the best topics for 2023 should be your primary concern in this case. We have some very interesting media debate topics right here:
- The impact of public relations on communities
- Location-based advertising in modern media
- Analyze the concept of yellow journalism
- Good news vs bad news in the media
- Discuss the concept of proportionality in media
Brand New Media Topics
Just like you, our writers are interested in writing about the latest topics. Why don’t you pick one of our brand new media topics?
- Is radio still an important part of media?
- Newspapers going bankrupt in 2023
- Sexual content on TV shows
- Politicians’ love for the media
- Is the backing of the media important for a president?
Media Ethics Topics
Discussing ethics in relation to media is a very interesting choice. It can also get you an A+ on your next paper. Here are some exceptional media ethics topics:
- Including graphic images in media
- Depicting terrorism on TV
- Regulating newspapers in Europe
- Celebrity gossip in the media
- The influence of large media corporations
Media Law Topics
Yes, there is such a thing as media law. Would you like to write an essay about it? Here are some great ideas for media law topics:
- Discuss the First Amendment and media
- The responsibilities of journalists
- Journalists in war zones
- Fake news in the media
- Showing unsuitable content to children
Research Topics in Communication and Media Studies
Writing about communication and media studies has the potential to help you get a top grade. Here are our best research topics in communication and media studies:
- Analyze media bias in the United States
- Is digital media addictive?
- Influence of media on religion
Interesting Media Topics
We know, you want the most interesting media topics to write about. Pick one of these and write a paper that will impress your professor:
- State-controlled media in China
- Effects of media coverage on criminal trials
- The power of mass media in 2023
Trending Media Topics
You may not know which topics are trending when it comes to media, but our writers do. Here are the latest trending media topics:
- The war in Afghanistan
- Joe Biden’s rise to power
- The fall of Donald Trump
- Climate change problems
- Global warming in the media
But what if you need more topics or professional help with thesis ? What if you didn’t find the media research topic you were looking for in the list above? While this is highly unlikely, we are prepared to help you. Would you like to talk about media literacy? In case you do, our ENL writers can create a list of the most interesting (and new) media literacy topics you can find. For anything you need, just get in touch with us.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates
Media Research Paper Topics

Three main concepts of media inform communication research. The first is Harold D. Lasswell’s paradigm – “who says what, in which channel, to whom, with what effect” – which approaches media as neutral conduits of information. The second conception is the mathematical theory of communication by Claude Shannon that emphasizes technical aspects of communication systems. The third concept represents humanistic perspectives on media as cultural carriers of meaning. In this last respect, Roman Jakobson has made an important distinction between channels or contacts (concrete entities such as books, newspapers, or the internet) and codes (forms of expression such as speech, writing, music, or images).
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Much media and communication research is characterized by efforts at integrating these concepts theoretically as well as analytically. Studies commonly identify three aspects of any medium: Media are physical materials in a particular social shape that enable communication. Such materials are the vehicles of modalities – language, music, moving images, etc. Finally, media are institutions through which individuals and collectives can reflect upon themselves and the rest of society.
Digital media have stimulated renewed interest in the relationship between technologically mediated communication and face-to-face communication, and in the reshaping – remediation (Bolter & Grusin 1999) – of older media. One may distinguish between media of three degrees (Jensen 2010). Media of the first degree are humans – biologically based and culturally shaped resources of communication. Media of the second degree are mass media – from the printing press to television. Media of the third degree are digital media that recombine all previous media on single platforms.
Media Economics Research Paper Topics
Media economics is the study of economic theories and concepts applied to the media industries. Media economics is diverse and includes such topics as policy and ownership, market concentration, performance of firms, and political economy of the media. Media research paper topics related to media economics include:
- Antitrust Regulation
- Audience Commodity
- Circulation
- Commercialization of the Media
- Commodification of the Media
- Competition in Media Systems
- Concentration in Media Systems
- Consolidation of Media Markets
- Consumers in Media Markets
- Cost and Revenue Structures in the Media
- Cross-Media Marketing
- Distribution
- Diversification of Media Markets
- Economics of Advertising
- Economies of Scale in Media Markets
- Globalization of the Media
- Labor in the Media
- Labor Unions in the Media
- Markets of the Media
- Media Conglomerates
- Media Corporations, Forms of
- Media Management
- Media Marketing
- Ownership in the Media
- Political Economy of the Media
- Privatization of the Media
- Public Goods
The Development of Media Economics
The origins of media economics began with the study of economics. The classical school of economics centered on the interplay of economic forces, operation of markets, and the cost of production. The classical school would later be challenged by ‘marginalist’ economics and Marxism. The marginalists introduced demand and supply, and consumer utility. Marxism identified labor as the source of production. Marxism rejected the capitalist system and the exploitation of the working class.
By the beginning of the twentieth century, neoclassical economics was introduced, differed by its use of analytical tools and mathematics to examine market behavior and price. Later the development of macroeconomics shifted the focus to aggregate economics, encompassing the entire range of market activity. Economic theories are constantly changing and evolving. By the 1970s new approaches included monetarist theories, which re-emphasized growth in the money supply; and rational expectations, which argues that the market’s ability to anticipate government policy actions limits their effectiveness.
As the study of economics evolved, scholars began to investigate different markets and industries. Media economics emerged during the 1950s. The media industries featured all of the elements necessary for studying the economic process. Content providers represented suppliers, with consumers and advertisers forming the demand side of the market. Regulatory agencies (e.g., Federal Communications Commission (FCC)) in the US, the Federal Trade Commission, and other entities) affected macroeconomic market conditions, while the relationship among suppliers in various industries created microeconomic market conditions.
Concentration of ownership emerged as a critical topic as it impacts both regulatory and social policy. Other studies examined media competition, consumer expenditures, barriers to entry for new firms, advertiser/ownership demand, and consumer utility.
Theoretical Dimensions and Methods
Media economics utilizes many theoretical approaches: microeconomic theories, macroeconomic theories, and political economy of the media. Microeconomic studies center on specific industry and market conditions. Macroeconomic studies take a broader focus, examining such topics as labor, capital markets, and gross domestic product. Political economy emerged as a critical response to positivist approaches.
The industrial organization (IO) model offers a systematic means of analyzing a market. The model consists of market structure, conduct, and performance. The model is also called the SCP model. The model posits that if the structure of a market is known, it helps explain the likely conduct and performance among firms. Each area can be further analyzed by considering specific variables within each part of the SCP model. Critics contend that the IO model does not capture the nuances associated with new technologies. However, the model remains a key theory in microeconomics.
The theory of the firm examines the most common types of market structure: monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition, and perfect competition. Defining market structure is complicated due to consolidation across the media industries. Media concentration is examined in one of two ways. Researchers gather data on firm/ industry revenues to measure concentration by applying tools such as concentration ratios. Another method tracks concentration of ownership among the media industries. Research has shown there are a limited number of firms which control media markets. Globalization has contributed to media concentration. Competition studies draw upon niche theory, which originated in the field of biology. These studies consider competition within an industry or across industries. Indices are used to measure the breadth, overlap, and superiority of one competitor over another. Finally, macroeconomic analysis in media economics includes policy and regulatory analysis, labor and employment trends, and advertising revenues and expenditures at the national level.
Media economics embraces different methods. Many include trend studies, financial analysis, econometrics, and case studies. Trend studies are used to compare data over time for topics such as concentration and performance. Financial analysis utilizes different types of financial statements and ratios to measure performance of firms and industries. Econometric analysis uses statistical models to address its research questions. Case studies embrace different methodologies as well as data. Case studies in media economics research tend to be very targeted examinations.
Critics of media economics research contend research is too descriptive in nature, and that methodological approaches are limited. There are also concerns researchers would study only major companies, and not pay sufficient attention to new media enterprises.
Future Directions for the Study of Media Economics
There are a number of steps researchers need to address to further develop media economics. In terms of research, media economics must address how to define a media market given the convergence and consolidation across the media industries. Most media companies are now multimedia enterprises, generating content across a variety of platforms.
In addition to refining key concepts, media economics research must also expand into new arenas. Among the areas where new understanding and investigation are required are social media, and mobile markets. Media economics scholars should consider new inquiries that draw upon multiple methods of investigation. The interplay of regulation, technology, and social policy presents new opportunities for scholars to generate new theories. Scholars need to examine variables that describe evolving market structures. Improvements in methodological tools are needed to complement expansion in research and theory. New measures are needed to assess within-industry concentration and competition.
Media economics helps to understand the activities and functions of media companies as economic institutions. Media economics research continues to evolve as it analyzes and evaluates the complex and changing world in which the media industries operate.
References:
- Albarran, A. B. (2010a). The media economy. London: Routledge.
- Albarran, A. B. (2010b). The transformation of the media and communication industries. Pamplona: EUNSA.
- Albarran, A. B., Chan-Olmsted, S. M., & Wirth, M. O. (2006). Handbook of media management and economics. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Croteau, D. & Hoynes, W. (2006). The business of media: Corporate media and the public interest, 2nd edn. Thousand Oaks, CA: Pine Forge.
- Dimmick, J. W. (2003). Media competition and coexistence: The theory of the niche. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Gershon, R. A. (2013). Telecommunications and business strategy, 2nd edn. London: Routledge.
- Napoli, P. M. (2003). Audience economics. New York: Columbia University Press.
- Noam, E. M. (2009). Media ownership and concentration in America. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Picard, R. G. (2011). The economics and financing of media firms, 2nd edn. New York: Fordham University Press.
Media Effects Research Paper Topics
Mass media can produce a broad spectrum of effects – on knowledge, attitudes, emotions, social behavior, reputation of people covered by the media, etc. Effects may be the consequences of media use, but also a result of interactions with people who have used the media. Explanations are usually based on two types of theories. Learning-theory approaches address the correct reproduction of information. Therefore, divergences between beliefs and information provided by media are considered learning deficits that may also be interpreted as a lack of media effects. Cognitive-theory approaches address the processing of information triggered by media reports. Beliefs and opinions are not regarded as copies of media presentation but indicate the type of information processing. Media research paper topics related to media effects include:
- Agenda-Setting Effects
- Albert Bandura
- Appraisal Theory
- Carl I. Hovland
- Catharsis Theory
- Cognitive Availability
- Credibility Effects
- Cumulative Media Effects
- Desensitization
- Diffusion of Information and Innovation
- Direct and Indirect Media Effects
- Effects of Entertainment
- Effects of Exemplification and Exemplars
- Effects of Nonverbal Signals
- Effects of Sex and Pornography as Media Content
- Effects of Violence as Media Content
- Elaborated Models of Media Effects
- Elisabeth Noelle-Neumann
- Emotional Arousal Theory
- Excitation Transfer Theory
- Fear Induction through Media Content
- Framing Effects
- Frustration Aggression Theory
- George Gerbner
- History of Media Effects
- Intercultural Media Effects
- Knowledge Gap Effects
- Latitude of Acceptance
- Leon Festinger
- Linear and Nonlinear Models of Causal Analysis
- Mainstreaming
- Media Effects Duration
- Media Effects on Attitudes, Values, and Beliefs
- Media Effects on Emotions
- Media Effects on Public Opinion
- Media Effects on Social Behavior
- Media Effects on Social Capital
- Media System Dependency Theory
- Mediating Factors
- Mediatization of Society
- Observational Learning
- Opinion Leader
- Order of Presentation
- Physical Effects of Media Content
- Priming Theory
- Reciprocal Effects
- Schemas and Media Effects
- Secondary Victimization
- Sleeper Effect
- Social Judgment Theory
- Steven H. Chaffee
- Stimulus–Response Model
- Strength of Media Effects
- Structure of Message Effects
- Trap Effect
- Two-Step Flow of Communication
Effects on Reality Perception
Media coverage of current affairs has an influence on the public’s assessment of the significance of social problems and the urgency for solving those problems. Comparison of all issues on the media’s agenda with the population’s agenda over a short period of time, as well as comparison of the development of media coverage on single issues with the development of the population’s beliefs over a longer period of time, may indicate media effects.
The media – and above all TV – are also an important factor in cultural and political socialization. Through both information and entertainment TV conveys ideas of the state of society in which people live. The more frequently and intensely people watch TV, the stronger the influence of its presentation of reality.
Individuals generally have good judgment concerning the relative frequency of causes of death, but they typically overestimate the occurrence of rare fatalities and underestimate the occurrence of frequent causes of death. The concept of availability heuristic explains how this is related to media coverage.
Effects on Social Perception
People tend to overestimate negative media effects (perceptual hypothesis) on other people and take action (behavioral hypothesis) to prevent these negative effects. In addition, a general correlation between presumed media effects and behavior is assumed. The perceptional hypothesis has been often tested and confirmed. The behavioral hypothesis has seldom been tested and if so, subjects have been uninvolved bystanders instead of decision makers who are protagonists of media messages (Sun et al. 2009).
As ‘social beings’ people depend on the society of others. Therefore, they constantly monitor their environment in order to avoid social isolation. They draw on their interactions with other people and personal observation as well as media presentations. Each of these resources can incidentally stimulate correct or incorrect ideas about the distribution of opinions. People who consider themselves in the minority tend to withhold their opinions in public. In the process, the presumed majority opinion is artificially inflated, which in turn increases the pressure on the actual or alleged minority.
Cognitive and Emotional Effects
Citizen assessments about politicians and voting intentions are based in part on beliefs about politicians’ competence. Repeated coverage of issues sensitizes recipients to some issues and makes solutions to the issues seem especially urgent. Thus, the presumed ability of politicians to deal with the issues becomes more significant, contributing to a positive or negative image of them. Accordingly priming effects are based on agenda-setting effects.
Framing theory is based on the assumption that media recipients do not take up individual pieces of information independently of one another and derive meaning from them, but interpret them consistently according to a predetermined frame (or schema). Frame-induced information processing can be controlled by media reports that present events from a certain perspective (Entman 1991).
In the 1940s it was already known that there was a positive correlation between education and the use of information presented by the media. As consequence, in the course of time existing differences in the distribution of information can increase.
Descriptions of events trigger predictable emotional reactions. If the damage is attributed to uncontrollable natural forces, the event evokes sadness; if it is attributed to a person acting in a controlled way, it evokes anger. The extent of reactions is enforced or diminished by the interaction of emotions and cognitions. Appraisal theory combines elements of attribution theory and emotional arousal theory (Nerb & Spada 2001).
Axioms of Media-Effects Research
Most studies in the effects of mass media are based on three, mostly unspoken, axioms. The first is ‘events happen, media cover.’ According to this axiom, current events on which the media report happen independently of the media. This is doubtful because a number of events on which the media report are the result of previous coverage. Some events would happen without media coverage, but their character is modified by media coverage (mediated events). Some events happen only in order to generate media coverage (staged or pseudoevents).
The second assumption is ‘no effect without change.’ The axiom holds true only under two conditions. First, if the media did not support the existing beliefs, opinions, and behaviors of its audience, these characteristics and attributes would still exist. Second, beliefs, opinions, and behaviors have developed independently from previous media use. There is evidence that the mass media have at least partly established the information and opinions which are already held and used to interpret news on current events.
The third axiom is: ‘no effect without contact.’ This axiom is only acceptable if at least one of two conditions is fulfilled: first, existing attitudes largely prevent the reception of dissonant information; second, dissonant information will be reinterpreted according to existing attitudes. As far as conveyors or opinion leaders pass on information and opinion from the mass media unchanged, their effects have to be attributed to the media. Therefore, opinion leaders and other interlocutors do not necessarily restrain the influence of media reports, but rather extend them to those who lack direct contact with media coverage.
- Bennett, W. L. & Iyengar, S. (2008). A new era of minimal effects? The changing foundations of political communication. Journal of Communication, 58, 707–731.
- Bryant, J. & Zillmann, D. (2002). Media effects: Advances in theory and research, 2nd edn. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Entman, R. M. (1991). Framing U.S. coverage of international news: Contrasts in narratives of the KAL and Iran air incidents. Journal of Communication, 41(2), 6–27.
- Nerb, J. & Spada, H. (2001). Evaluation of environmental problems: A coherence model of cognition and emotion. Cognition & Emotion, 15(4) 521–551.
- Perloff, R. M. (2003). The dynamics of persuasion: Communication and attitudes in the twenty-first century, 2nd edn. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Sun, Y., Pan, Z., & Shen, L. (2009). Understanding the third-person perception: Evidence from a metaanalysis. Journal of Communication, 58, 280–300.
Media History Research Paper Topics
Media history as a concept in its own right possesses a relatively recent lineage. In the early decades of the twentieth century, when references to ‘the media’ – newspapers, magazines, cinema, radio, and the like – were entering popular parlance, university academics tended to be rather skeptical about whether these institutions were important enough to warrant scholarly attention. Traditional historians, in particular, were inclined to be dismissive. Matters would gradually improve over the course of the century, but even today, media history continues to occupy a contested terrain between the principal disciplines informing its development, namely media studies (broadly inclusive of communication, cultural, and journalism studies) and history. Media research paper topics related to media history include:
- Academy Awards
- Antecedents of Newspaper
- Cable Television
- Civil Rights Movement and the Media
- Coffee Houses as Public Sphere
- Collective Memory and the Media
- Electronic Mail
- Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
- Fleet Street
- Fourth Estate
- Freedom of Communication
- Historic Key Events and the Media
- History of Advertising
- History of Censorship
- History of Cinematography
- History of Citizen Journalism
- History of Digital Media
- History of Documentary Film
- History of Elections and Media
- History of Magazine
- History of News Agencies
- History of News Magazine
- History of Newspaper
- History of Postal Service
- History of Printing
- History of Public Broadcasting
- History of Sports and the Media
- History of Telegraph
- History of Violence and the Media
- Illustrated Newspapers
- Literary Journalism
- Music Videos
- Newscast, 24-Hour
- Nineteenth-Century Journalism
- Paperback Fiction
- Penny Press
- Propaganda in World War II
- Radical Media
- Radio Networks
- Radio Technology
- Satellite Television
- Social History of Radio
- Social History of Television
- Television Networks
- Television Technology
- Underground Press
- Virtual Reality
- Watergate Scandal
- Women’s Movement and the Media
Early conceptions of media history frequently accorded the commercial press a central role in promoting social change, one especially worthy of close scrutiny. These days much of this research tends to be criticized for being celebratory, however, even romanticizing the press as the pre-eminent catalyst for advancing the cause of freedom in the face of fierce government opposition. In order to overcome the limitations of this ‘Whig interpretation,’ as it has been described, media historians have begun to diversify their sources and methods. For some this has entailed looking beyond the views of the powerful and privileged so as to recover and interpret the experiences of those typically marginalized – on the basis of class, gender, ethnicity or sexuality – where the making of media history is concerned.
Serious reservations have been expressed by some historians about the very legitimacy of media history as a proper academic subject when it encompasses ostensibly trivial, ephemeral media items (advertisements, comics, graffiti, soap operas, paperback fiction, music videos, computer games, and the like) within its purview. Others have challenged this perspective, insisting that such value judgments be avoided so as to engage with the whole spectrum of emergent media in all of their complexity.
Defining Media History
Depending on how one chooses to define ‘the media,’ a case can be made that media history properly begins in the earliest days of human social life and communication. For researchers interested in the emergence of media in oral or pre-literate communities thousands of years ago, for example, the insights of archaeologists and anthropologists have proven invaluable. The advent of reading and writing is of particular significance, enabling the dissemination of news or information at a distance, and thereby helping to sustain a shared sense of social order. Studies have examined the emergence and use of various media facilitating communication, ranging from pictographs written on clay tablets, to papyrus, paper, and eventually the movable type of the printing press (Briggs and Burke 2010).
For many media historians, it is the connection between emergent media of communication and the creation of democratic society that is particularly fascinating. In this context, Anderson’s (1983) analysis of the rise of print as commodity in western Europe illuminates the emergence of nationality – “the personal and cultural feeling of belonging to a nation” – toward the end of the eighteenth century. He singles out for attention in this regard the fictional novel and the newspaper, arguing that the corresponding print languages helped to engender national consciousness in important ways.
Complementing this line of inquiry into how print enriched the ability of people to relate to themselves and to others in new ways have been efforts to understand how these media shaped the formation of public opinion. Here researchers have found the notion of a public sphere, as theorized by Jürgen Habermas (1989), to be useful, especially when investigating how spaces for public discussion and debate were initiated and sustained. Habermas identifies a range of institutions facilitating this process, with special attention devoted to coffee houses and the newspaper press (Mulhmann 2008).
Related studies have elucidated the ways in which various media forms and practices helped to give shape to new kinds of public sociability. Such studies include examinations of advertising, art, music, street literature, exhibitions in museums and galleries, as well as reading and language societies, lending libraries, and the postal system, among other concerns. Historiographies continue to rehearse contrary views on the extent to which the normative ideals of a public sphere have been realized in actual terms, a debate that continues to percolate. Nevertheless, there is general agreement that a consideration of the relative freedoms espoused by these ideals throw into sharp relief many of the factors that have acted to constrain public discussion over time.
Researching Media History
For media historians, the rationale for their craft is often expressed as a commitment to interdisciplinarity so as to situate the evolution of media forms, practices, institutions, and audiences within broader processes of societal change. Compounding this challenge, however, is the recognition that media processes can be ephemeral, and thereby elusive in conceptual and methodological terms. Often their very normality, that is, the extent to which they are simply taken for granted as a part of everyday life, means efforts to de-normalize them require considerable effort.
Media historians, it follows, must strive to be sufficiently self-reflexive about their chosen strategies when gathering source material and interpreting evidence, especially where questions related to ‘effects’ or causation are being addressed. Pertinent in this regard is the status of electronic media, for example, which may pose particular problems for the historian seeking to establish relations of significance. Not only are the actual texts under scrutiny – e.g., an early radio play or television broadcast – unlikely to be amenable to more traditional, print-based methods, but issues with regard to such logistical considerations as access, physical artifacts (microphones, receiver sets, and the like), and format-compatibility (changes in formats can make playback difficult) may surface.
The advent of digital technologies is already engendering similar types of issues for media historians. Scholarship increasingly entails finding alternative ways to manage, interpret, and preserve the extensive array of materials available across different storage systems. The sheer volume and range of these materials, coupled with continuing innovation in hardware and software (the obsolescence of technology rendering some types of data difficult to retrieve), can make for challenging decisions about how to maintain libraries, archives, databases, and other repositories of information. New questions are being posed in this regard by electronic records, including items such as electronic mail, voicemail messages, word-processing documents, Internet websites, message boards, blogs, Facebook accounts, Tweets and the like, all of which are highly perishable.
Precisely how media history research will evolve invites thoughtful consideration. Current efforts to build on the foundations set down by the press histories of the nineteenth century are making progress in enriching these traditions, while also pursuing new directions that recast familiar assumptions – sometimes in unexpected ways. The types of criticisms of ‘standard’ media history identified by Carey, namely that its arguments were based on “nothing more than speculation, conjecture, anecdotal evidence, and ideological ax grinding” (and where conclusions were not “theoretically or empirically grounded; none was supported by systematic research”), no longer aptly characterize the field (1996, 15–16). Indeed, it is reasonable to suggest that there is every indication media history will continue to develop in ever more methodologically rigorous – and intellectually exciting – directions.
- Anderson, B. (1983). Imagined communities. London: Verso.
- Briggs, A. & Burke, P. (2010). A social history of the media, 3rd edn, Cambridge: Polity.
- Carey, J. W. (1996). The Chicago School and the history of mass communication research. Repr. in James Carey: A critical reader (eds. E. S. Munson & C. A. Warren). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota Press, pp. 14–33.
- Habermas, J. (1989). The structural transformation of the public sphere. Cambridge: MIT Press.
- Mulhmann, G. (2008). A political history of journalism. Cambridge: Polity.
Media and Perceptions of Reality Research Paper Topics
Perceptions of reality, or social reality, can be conceptualized as an individual’s conception of the world (Hawkins & Pingree 1982). What intrigues many social scientists is the exploration of the specifics of these perceptions and the ways in which they are developed. Social perception has been considered from both individual- and social-level perspectives.
The individual-level conception of social reality – or, as McLeod and Chaffee (1972) refer to it, social reality – suggests that others exist in one’s mind as imaginations, and it is only in these imaginations that others have an effect on the individual. The perspective of social reality defines the social system as the unit of analysis. These scholars focus on understanding commonly held perceptions shared in society. They often base their exploration on individuals’ perceptions of what others think, or whether an individual believes that an opinion or attitude is shared by others. Because the media, in particular, provide individuals with indirect representations of reality, communication scholars have been particularly interested in how individuals develop cognitions of social reality based upon their use of and attention to the media. Media research paper topics related to perceptions of reality include:
- Behavioral Norms Perception through the Media
- Body Images in the Media Climate of Opinion
- Computer Games and Reality Perception
- Cultivation Effects
- Disowning Projection
- Entertainment Content and Reality Perception
- Extra-Media Data
- False Consensus
- False Uniqueness
- Hostile Media Phenomenon
- Media and Perceptions of Reality
- Media Campaigns and Perceptions of Reality
- Media Content and Social Networks
- Media Content in Interpersonal Communication
- Media Messages and Family Communication
- Perceived Realism as a Decision Process
- Perceived Reality as a Communication Process
- Perceived Reality as a Social Process
- Perceived Reality Meta-Analyses
- Pluralistic Ignorance
- Pluralistic Ignorance and Ideological Biases
- Social Perception
- Social Perception and Impersonal Impact
- Social Perception and Unrealistic Optimism
- Socialization by the Media
- Spiral of Silence
- Stereotyping and the Media
- Third-Person Effects
- Video Malaise
General Perception Effects
Several phenomena describing perceptions (and misperceptions) of social reality have been outlined in the literature. The term pluralistic ignorance is often used as an umbrella to describe all misperceptions of others’ opinions. Research in this area is primarily concerned with the factors that lead to individuals being more or less accurate about reality, focusing on the discrepancy between individual perceptions and actual reality.
Consensus occurs when homogeneous opinions exist across a group of individuals. Some research has suggested that an overestimate of consensus occurs when individuals perceive greater consensus on their own opinion than exists in reality. In this way, overestimation of consensus is ‘absolute’ because it is objectively false. The concept of false consensus describes the tendency to see one’s own behaviors and opinions as normal and those of others as deviant or inappropriate, which results in exaggerating the prominence of one’s own opinions.
Social projection is generally defined as the psychological phenomenon that drives several other inaccurate perceptions, including the silent majority or false idiosyncrasy effect, which occurs when some individuals support a position on an issue vocally and prominently, while those opposed to the issue – even if they are in the majority – remain silent. The disowning projection refers to the tendency toward attributing selfish motives, evil intent, or ignorance to others and denying these characteristics of oneself. The looking-glass perception occurs when people see others as holding the same view as they themselves hold.
Media-Specific Perception Effects
Another group of theories focuses on individuals’ perceptions about media content or its influence on others. The third-person effect predicts that individuals exposed to a persuasive message will perceive greater effects on others than on themselves (Davison 1981). Impersonal influence describes the influence derived from anonymous others’ attitudes, experiences, and beliefs. From this perspective, media do not need to be universally consonant or even personally persuasive in order to impact individuals’ perceptions of media influence (Mutz 1998).
The hostile media phenomenon suggests that partisans see news media coverage of controversial events as portraying a biased slant, even in news coverage that most nonpartisans label as unbiased (Vallone et al. 1985). An underlying assumption of this phenomenon is that media coverage is essentially unbiased. The persuasive press inference hypothesis draws from the hostile media phenomenon and third-person effect and places the effects into one process, i.e., people overestimate the impact of news coverage on public opinion and because of this misperception, estimates of public opinion are inaccurate (Gunther 1998).
Causal Mechanisms for Social-Reality Perceptions and Misperceptions
Some research on perceptions of social reality has emphasized mass media as the primary causal mechanism explaining perceptions of social reality. Because few people have direct personal experience with politics, mediated information has the ability to influence individuals’ perceptions of social reality at the collective level. That is, media enhance the salience of social-level judgments, in addition to influencing perceptions of public opinion.
First, spiral of silence theory suggests that because the climate of opinion is always vacillating, individuals are “scanning” their social environment for cues of what constitutes majority and minority opinion (Noelle-Neumann 1993). The media are one such source, but often present biased viewpoints. As a result of this individuals perceive a majority perspective, and this perception either promotes or prevents them from speaking out (see Schulz and Roessler 2012).
Second, cultivation implies that, over time, people are influenced by the content on television so that their perceptions of reality come to reflect those presented on television. This theory also purports that media content displays distorted estimates of social reality, e.g., the rates of crime and violence which in turn lead to the overestimation of personal risks (Shrum & Bischak 2001).
Effects of social reality perceptions can also be attributed to other causal mechanisms in three broader categories: individual, individual–other, and social explanations.
Individual explanations include cognitions and motivations. One possible mechanism in this category of cognitive explanations is the accessibility bias, or the tendency to derive estimates of others’ views based upon that information that is most accessible in one’s memory. The third-person effect also is explained by cognitive ‘errors.’ The actor– observer attributional error occurs when individuals underestimate the extent to which others account for situational factors, and overestimate their own attention to these factors. Motivational explanations can also be applied to those theories that claim media as the primary causal mechanism. For instance, Noelle-Neumann cites fear of isolation, or a motivation not to be in the minority, as a driving force behind the spiral of silence.
Social harmony and public expression mechanisms belong in the category of individual–other explanations. Because conflict is not palatable to many people, there may exist motivations to see others’ positions on issues as more like their own in order to avoid argument or dissonance (social harmony). Misperceptions of social reality at the individual–other level also can arise from either intentional or unintentional misrepresentation of one’s opinions in public. The differential interpretation hypothesis describes a conscious decision to publicly misrepresent one’s opinion, while the differential encoding hypothesis suggests that some individuals suffer from an “illusion of transparency,” mistakenly believing that their own and others’ opinions are accurately expressed publicly (Prentice and Miller 1993).
The social explanations are based upon what McLeod and Chaffee (1972) referred to as social reality, wherein a context or situation serves as the causal mechanism underlying perceptions of social reality. For instance, if an issue is particularly divisive, individuals are prone to the false consensus effect because they see one side as more similar to themselves and the other side as deviant or uncommon.
- Davison, W. P. (1981). The third-person effect in communication. Public Opinion Quarterly, 47, 1–15.
- Eveland, W. P., Jr. (2002). The impact of news and entertainment media on perceptions of social reality. In J. P. Dillard & M. Pfau (eds.), The persuasion handbook: Developments in theory and practice. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, pp. 691–727.
- Glynn, C. J., Ostman, R. E., & McDonald, D. G. (1995). Opinions, perception, and social reality. In T. L. Glasser & C. T. Salmon (eds.), Public opinion and the communication of consent. New York: Guilford, pp. 249–277.
- Gunther, A. C. (1998). The persuasive press inference: Effects of mass media on perceived public opinion. Communication Research, 25(5), 486–504.
- Hawkins, R. P. & Pingree, S. (1982). Television’s influence on social reality. In L. B. D. Pearl & J. Lazar (eds.), Television and behavior: Ten years of scientific progress and implications for the eighties. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, pp. 224–247.
- McLeod, J. M. & Chaffee, S. R. (1972). The construction of social reality. In J. T. Tedeschi (ed.), The social influence processes. Chicago, IL: Aldine-Atherton, pp. 50–99.
- Mutz, D. C. (1998). Impersonal influence: How perceptions of mass collectives affect political attitudes. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Noelle-Neumann, E. (1993). The spiral of silence: Public opinion, our social skin. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Prentice, D. A. & Miller, D. T. (1993). Pluralistic ignorance and alcohol use on campus: Some consequences of misperceiving the social norm. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 64(2), 243–256.
- Schulz, A. & Roessler, P. (2012). The spiral of silence and the Internet: Selection of online content and the perception of the public opinion climate in computer- mediated communication environments. International Journal of Public Opinion Research, 24(3), 346–367.
- Shrum, L. J. & Bischak, V. D. (2001). Mainstreaming, resonance, and impersonal impact: Testing moderators of the cultivation effect for estimates of crime risk. Human Communication Research, 27(2), 187–215.
- Vallone, R. P., Ross, L., & Lepper, M. R. (1985). The hostile media phenomenon: Biased perceptions and perceptions of media bias in coverage of the Beirut massacre. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 49(3), 577–585.
Media Production and Content Research Paper Topics
Research in the sub-field of media production and content seeks to describe and explain the symbolic world of the media with reference to a variety of contributing societal, institutional, organizational, and normative factors. It draws boundaries around a large and diverse body of research efforts, predominantly social science, but also including more interpretive cultural analysis. Media research paper topics related to media production and content include:
- Accountability of the Media
- Accountability of the News
- Bias in the News
- Commercialization Impact on Media Content
- Conflict as Media Content
- Consonance of Media Content
- Construction of Reality through the News
- Credibility of Content
- Crime Reporting
- Endorsement
- Ethics of Media Content
- Fairness Doctrine
- Fictional Media Content
- Framing of the News
- Infotainment
- Instrumental Actualization
- Internet News
- Media Performance
- Morality and Taste in Media Content
- Narrative News Story
- News Factors
- News Production and Technology
- News Values
- Objectivity in Reporting
- Quality of the News
- Quality Press
- Reality and Media Reality
- Scandalization in the News
- Sensationalism
- Separation of News and Comments
- Soap Operas
- Sound Bites
- Stereotypes
- Synchronization of the News
- Tabloid Press
- Tabloidization
- Truth and Media Content
- Violence as Media Content
Scope of the Research Area
If much of the communication field has concerned itself with the effects of media, and the process by which they are produced, this more recently emerging area has treated the media map of the world itself as problematic, something to be understood and predicted through an awareness of underlying forces. These forces provide the context of ‘media production,’ which is examined for its systematic ties to ‘content’ – particularly news and information. Given the multitude of factors influencing the media, this conceptual framework has led the field of communication to devote the same sustained research to the creation, control, and shape of the mediated environment as it has to the effects on audiences of that environment. The objects of study in this area, however, have undergone profound changes, particularly with communication technology, making it more problematic to identify ‘the media,’ ‘the profession,’ and the site of ‘production.’
This research area is often broadly referred to as ‘media sociology’ (reviewed in Berkowitz 1997). Certainly, many of the participant observation ethnographies of newsrooms and other media are so labeled, particularly given their use of traditional sociological fieldwork methods (e.g., Tuchman 1978; Gans 1979). The technology of distributed online production makes identifying the ‘sites’ where news is produced more difficult now, but the ethnography approach continues to be used. The area also encompasses studies of individual media workers, and how their personal traits affect their decisions (e.g., Weaver & Wilnat 2012). Many media critics lodge the blame for press bias squarely with individual journalists, or find fault with the entertainment industry because of ‘out-of-touch Hollywood producers, but important explanations for these communication products lie in structural bias, beyond individual prejudice. Although media organizations – including those supported by the state – employ many creative professionals, the work of those individuals is routinized and structured to yield a predictable product. Even the ‘news’ must be controlled, anticipated, and packaged to allow the organization to manage its task effectively: in Tuchman’s (1978) phrase, “routinizing the unexpected.”
Beginning in the 1950s Warren Breed (1955) and David Manning White (1950) were among the first scholars to examine the influences on content directly, with their examinations of social control in the newsroom and the story selections of an editor, described as the news ‘gatekeeper’. Reese and Ballinger (2001) observed that the gatekeepers in these studies were deemed representatives of the larger culture, and news policies were assumed to help identify as news those events of interest to the community – rendering the production and control issues unthreatening to the public interest and, as a result, of less interest to researchers. Eventually, however, these questions returned to the fore.
The hierarchy of influences model describes the multiple levels of influences – individual, routines, organizational, extra-media (social institutional), and ideological (socio system) – that impinge on media simultaneously and suggests how influence at one level may interact with that at another (Shoemaker & Reese 2014). Within the realm of newsmaking, for example, the individual- level bias of particular journalists may affect their reporting, but journalists of a particular leaning often self-select an organization because of its pre-existing policies, history, and organizational culture (routines). The news organization and its employees, in turn, must function within other institutional relationships and ideological boundaries set by the larger society. Thus, the individual functions within a web of constraints.
The compelling point of departure for this subfield is the idea that media content provides a map of the world that differs from the way that world really is, making the research task one of explaining those discrepancies. Media representations can be tied to objects in the real world, but viewed another way media content is fundamentally a ‘construction,’ and, as such, can never find its analog in some external benchmark, a ‘mirror’ of reality. This perspective directs research to understanding the construction process. Journalists, for example, ‘see’ things because their ‘news net’ is set up to allow them to be seen.
Research Findings
Given the wide variation among media round the world, generalizations about production and content must be made with caution. Now that more comparative research has begun to emerge, it is easier to distinguish between those practices common across countries and those peculiar to one or the other. Certainly, changes in technology have had widespread cross-national effects, blurring craft distinctions in the convergence of media forms.
Although broad generalizations can be made, there are also important differences across the various media. These more organizational issues involve the technological imperatives, audience considerations, economic and other dictates, as well as the regulatory environment that they all face. Each medium, whether radio, television, newspapers, or magazines, has its own unique problems to solve in providing a product to a reader, viewer, or listener. The highest level of the hierarchy of influences model, the ideological or social system, considers how the media function within a society by virtue of there being a certain kind of system – which necessarily binds them to the prevailing social order usually associated with nation-states.
Research Methods
These considerations often require a more interpretive analysis, which considers how the media reinforce the definitions of the powerful and linked to media production practices that support them. A macro level of analysis directs attention to cross-national comparisons of media production, where important patterns can be found. Shoemaker and Cohen (2006) find that news has a number of common patterns across nations, even if these are filtered through specific national cultures.
Global changes in media ownership, new ways of carrying out gatekeeping across national boundaries, and emerging shared norms of professionalism all give greater emphasis to this perspective. So, under the continuing processes of globalization, this area of research faces the challenge of identifying the universal aspects of media and social representation, the enduring particularities of individual national contexts, and the increasing interactions between these levels.
- Berkowitz, D. (1997). Social meanings of news. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
- Breed, W. (1955). Social control in the newsroom: A functional analysis. Social Forces, 33, 326–355.
- Gans, H. (1979). Deciding what’s news. New York: Pantheon.
- Reese, S. & Ballinger, J. (2001). The roots of a sociology of news: Remembering Mr Gates and social control in the newsroom. Journalism and Mass Communication Quarterly, 78(4), 641–658.
- Shoemaker, P. & Cohen, A. (2006). News around the world. London: Routledge.
- Shoemaker, P. & Reese, S. (2014). Mediating the message in the 21st Century: A media sociology perspective. London: Routledge.
- Tuchman, G. (1978). Making news. New York: Free Press.
- Weaver, D. & Wilnat, L. (2012). The global journalist in the 21st century. London: Routledge.
- White, D. (1950). The “gatekeeper”: A case study in the selection of news. Journalism Quarterly, 27, 383–396.
Back to Communication Research Paper Topics .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

100 Communication Research Topics
Table of contents
- 1 What Is Communication Research?
- 2.1 Top Research Topic Ideas
- 2.2 Research Topics for College Students
- 2.3 Business-Focused Research Topics
- 2.4 Social Media Research Topics
- 2.5 Mass Communication Research Topics
- 2.6 Interpersonal Communication Research Topics
- 2.7 Intercultural Communication Research Topics
- 2.8 Virtual Communication Research Topics
- 2.9 Health-Related Research Topics
- 2.10 Interesting Communication Research Topics
- 3 Coming up with a Thesis Statement
- 4.1 How to Create Strong Questions for Your Paper?
- 4.2 How to Find the Right Research Topics?
- 4.3 What Makes a Research Paper Topic Strong?
- 4.4 Tips for Structuring and Writing Your Paper
- 5 Conclusion
All fields of study have fresh and intriguing new research paper topics to explore. Within the subject of communication, there are loads of possibilities for research papers . This is thanks to the development of mass media and the growing popularity of various modern communication methods.
This article covers a broad range of effective research paper topics that are both interesting and relevant for this field. Any of them would make a suitable focal point for any research paper to do with how we interact with one another.
What Is Communication Research?
This is the study of how we interact with one another. It includes how the way we interact is affected by technology, culture, and individual differences. Researchers in this field use a variety of methods to study the way we converse and interact with each other, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and experiments.
Research in this area can be used to improve communication skills in personal relationships, in the workplace, and in other settings.
Writing a comprehensive research paper on communication topics can be challenging, especially when addressing complex theories and models. If you’re seeking assistance with structuring and writing your paper, professional research paper writing services can provide the guidance you need to produce high-quality academic work.
Lists of Key Communication Research Topics
The range of research paper topics in this field is extensive, to say the least. Below are 100 relevant topics that are arranged in groups of 10.
They cover a broad selection of modern communication issues and debates, from corporate and computer mediated communication to effective interpersonal communication, communication strategies, and more.

Top Research Topic Ideas
The topics in this first group mostly focus on how different factors impact the way we interact with one another. These are some of the key issues in the communication discipline today.
- The role communication plays in organizations.
- How technology influences it.
- The way globalization affects it.
- How it’s influenced by broadcast media.
- Ways in which advertising impacts it.
- The influence propaganda has on it.
- How it’s impacted by public relations.
- The effects of international journalism and journalism ethics on it.
- How the use of social media influences it.
- How it’s affected by language.
Research Topics for College Students
These topics are ideal for college students. They focus on how communication processes can influence someone’s mental health and personality traits. Both of these are important since they can influence a student’s academic progress.
- How does communication shape our identities?
- How do we use it to build relationships?
- What role does it play in influencing our emotions?
- How is our thinking influenced by it?
- In what ways do we use it to manage conflict?
- How is our behavior influenced by it?
- What factors influence the effectiveness of communication?
- In what way is it impacted by technology?
- What influences do cultural differences have on it?
- How does it shape our physical and mental health?

Business-Focused Research Topics
Having effective business communication is necessary for any sort of commercial activity to improve its marketing value. Both business to business communication and interactions with the public have to get the right message across. Below are some potential areas to do with organizational communication and public relations.
- The impact of new communication technologies.
- The use of social media and external communication.
- What effects does globalization have?
- How organizational communication is used in virtual teams.
- The impact that intercultural communication has.
- The way humor is used.
- What are the effects of gender?
- How we use non-verbal communication.
- The effect that technology has on corporate communication etiquette.
- The way we use business communication in crisis situations.
Social Media Research Topics
The focus of these topics is on social media, and it affects the way we communicate with one another. Using social media and being exposed to social media marketing can both have significant effects on practical communication skills. These topics focus on the way modern digital platforms influence our interactions.
- The effect of social media on communication practices and patterns.
- How social media changes relationship development.
- What influence does social media have on how people interact with each other?
- The effect of social media on the way people share information.
- How social media impacts the way people interact with businesses.
- The effect of social media on the way people interact with governments through proper communication channels.
- What consequences does social media have on online interactions?
- The effect that social media has on the way people interact with each other offline.
- Social media’s influence on the way people interact with each other in different cultures.
- What effects does social media have on the way people interact with each other in different age groups?
Mass Communication Research Topics
Mass communication is when you share information with a large number of people at the same time. Topics to do with mass communication are very relevant, thanks to the internet, social media platforms, and other kinds of mass media. The purpose of mass media is simply to inform loads of people about something as quickly and conveniently as possible.
- What effect do social media platforms have on mass communication?
- How does new technology affect it?
- The impact that advertising has on it.
- How news media influences it.
- Ways in which propaganda impacts it.
- The influence that public relations have on it.
- How it’s impacted by digital media and print media.
- Globalization’s impact on it.
- How new forms of media affect it.
- The ways it’s influenced by social networking.
Interpersonal Communication Research Topics
This is a broad term that refers to the exchanging of information between people. It’s when you use effective communication skills to share thoughts, ideas, and facts with at least one other person. The topics in this section look at some of the latest interpersonal communication trends.
- The effect of technology on interpersonal communication.
- The effect of culture on it.
- How gender influences it.
- The effect of age on it.
- How someone’s interaction style may impact it.
- The way context may influence it.
- How relationships can influence it.
- How it can be influenced by social apprehension.
- The effect of social competence on it.
- How it’s impacted by satisfaction.

Intercultural Communication Research Topics
This is when people from different cultures exchange information. Things like different languages, traditions, and even artifacts affect intercultural communication. The topics below look at intercultural communication and how culture shapes the many ways we interact with one another.
- How culture influences the ways we interact with one another.
- The impact of intercultural communication styles on relationships.
- How culture impacts our perceptions of interaction.
- The effect that interaction has on business relationships.
- How culture influences the way we interpret nonverbal communication.
- The impact of culture on our way of interpreting speech.
- How culture influences our information processing.
- The way culture impacts our process of making decision.
- The impact of culture on how we solve problems.
- How culture influences our interactions with others.
Virtual Communication Research Topics
Are virtual communication skills essential? You have to be just as proficient at virtual dialogue as you are at spoken words. Mastering interactive online communication is key for anyone who wants to succeed, and the topics below delve into this further.
- The impact on the development of personal relationships.
- The use of virtual dialogue in the business world.
- How it influences the way we think and learn.
- The benefits of virtual communication for people with social anxiety.
- The way it’s used in education.
- How it impacts our mental health.
- Ways in which it influences family relationships.
- How it’s used in the workplace.
- The effect it has on relationships.
- The advantages and disadvantages of virtual communication.
Health-Related Research Topics
It’s essential to have effective communication strategies in any sort of healthcare setting. Having interpersonal communication competence is vital so that practitioners can speak with patients clearly and effectively. The topics below look at how internal and external communication in the healthcare industry affects and is affected by different factors.
- The effectiveness of health communication campaigns in changing health behaviors.
- The impact of social media on interactions in the health industry.
- How humor is used in it.
- How storytelling is used in it.
- What effects it has on reducing health disparities.
- What effects it has on increasing health literacy.
- How new media technologies are used in it.
- How it influences public health outcomes.
- The role it plays in health education.
- The impact it has on patient satisfaction.
Interesting Communication Research Topics
This last batch of topics looks at how both spoken words and non-verbal communication affect different things. Some of the topics are about how we interact with one another in different areas of life.
- The impact of new communication technology on social interactions.
- The way it is used in the workplace.
- How we use it in education.
- Ways in which it is used in marketing.
- How people use it in healthcare.
- The way it affects personal relationships.
- The effects it has on organizational cultures.
- How it impacts individual productivity.
- Its effects on consumer behavior.
- The influences it has on the environment.
- Free unlimited checks
- All common file formats
- Accurate results
- Intuitive interface
Coming up with a Thesis Statement
Once you have come up with a potential research topic, you should start writing. Your first step is to write an effective thesis statement .
Your thesis statement is the argument or main point you want to make about your topic. It’s a summary of what your paper is going to be about. The purpose of it is to show the reader what you will be discussing and invite them to read your work.
Once you have your thesis statement, start writing your paper. Make sure to include evidence from scholarly sources to support your work.
Topic Selection and Writing Tips
How to create strong questions for your paper.
This question doesn’t have a single answer, as the best way to create strong questions for your paper will vary depending on the specific research project and its goals.
However, some tips on how to create strong questions include:
- Start by thinking about the specific goals of your research project. What are you trying to learn or understand?
- Draft a few potential research questions that can help you answer your goals. Be sure to make them as specific as possible.
- Test your research questions by asking them to others to see if they are clear and understandable. Are they interesting to people outside of your field of study?
- Revise and refine your research questions as needed. Be sure to keep them concise and easy to understand.
How to Find the Right Research Topics?
When writing a communication research paper, first, you should decide what topic you want to learn more about.
- Do the effects of social media and mass media on communication interest you?
- What about the role of communication in a competitive global business environment?
- What is the impact of new technology on the ways we exchange information?
- Whether effective communication is necessary to ensure credible reporting?
- How do improved relations make broadcasting media laws effective?
Once you have a general topic in mind, you can begin to narrow it down by focusing on a specific aspect of this field that interests you.
For example, if you are interested in the communication importance in a business market, you might want to focus on the impact of effective business interactions on employee productivity or customer satisfaction.
Alternatively, you could look at how private media ownership is affecting mass media, bringing journalism ethics into the discussion, and how journalists are ensuring credible reporting.
What Makes a Research Paper Topic Strong?
There is no one answer to this question, as it depends on the individual and the specific research goals. However, some factors that could make a research topic strong include its relevance to current events or real-world issues, its potential to generate new and innovative ideas, and its ability to generate interesting and valuable research findings.
Additionally, a strong topic should be interesting and engaging to read and write about, and it should be something that the researcher can be passionate about.
Tips for Structuring and Writing Your Paper
When writing communication research papers, it is important to structure your argument in a manner that’s clear and concise. Your paper should have a clear research paper introduction , body, and conclusion. Within the body of your paper, there should be a strong thesis statement, evidence that supports your argument, and a conclusion summarizing your argument.
Additionally, throughout the research paper writing process, it is significant to use clear and concise language. Use communication tips to help you put your own points across more effectively.
Deciding what to focus your research paper doesn’t have to be daunting. There are a huge number of research topics available. Finding the right one is easy.
First, think about the ideas that interest you the most. Which part of communication studies are you most passionate about? Is it media ethics, mass media, or something else?
When you’ve settled on one of the research topic ideas , start the research paper writing process. Find key sources such as books and academic articles. Think about what needs addressing in your research paper.
Now, it’s time for you to produce an excellent communication research paper.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.

Research Topics & Ideas: Journalism

PS – This is just the start…
We know it’s exciting to run through a list of research topics, but please keep in mind that this list is just a starting point . These topic ideas provided here are intentionally broad and generic , so keep in mind that you will need to develop them further. Nevertheless, they should inspire some ideas for your project.

Journalism-Related Research Topics
- Analyzing the impact of social media on news consumption patterns among millennials.
- Investigating the role of investigative journalism in combating political corruption.
- The impact of digital transformation on traditional print media business models.
- Examining the ethical challenges of undercover reporting in investigative journalism.
- The role of citizen journalism in shaping public opinion during major political events.
- Analyzing the effectiveness of fact-checking platforms in combating fake news.
- The impact of smartphone journalism on the quality of news reporting.
- Investigating the representation of minority groups in mainstream media.
- The role of photojournalism in humanizing the impacts of climate change.
- Analyzing the challenges of maintaining journalistic objectivity in conflict zones.
- The impact of artificial intelligence on newsroom operations and reporting.
- Investigating the influence of media ownership on editorial independence.
- The role of journalism in shaping public policy on environmental issues.
- Analyzing the portrayal of mental health issues in news media.
- The impact of live streaming technology on broadcast journalism.
- Investigating the challenges faced by freelance journalists in the digital era.
- The role of journalism in promoting government accountability in emerging democracies.
- Analyzing the effects of sensationalism in news reporting on public trust.
- The impact of virtual reality technology on immersive journalism.
- Investigating the role of press freedom in protecting human rights.
- The challenges of reporting on science and technology in mainstream media.
- Analyzing gender representation in sports journalism.
- The impact of media consolidation on diversity of perspectives in news.
- Investigating the ethical implications of drone journalism.
- The role of independent media in fostering democratic processes.

Journalism-Related Research Ideas (Continued)
- Analyzing the portrayal of immigration in national news outlets.
- The impact of censorship and media regulation on journalistic practices.
- Investigating the role of podcasts in the future of journalism.
- The challenges and opportunities of bilingual reporting in multicultural societies.
- Analyzing the dynamics of news reporting in authoritarian regimes.
- The impact of audience analytics on news content and presentation.
- Investigating the implications of deepfake technology for journalistic integrity.
- The role of local journalism in community engagement and development.
- Analyzing the effects of journalism on public health awareness campaigns.
- The impact of economic pressures on investigative journalism.
- Investigating the challenges of reporting in a polarized political climate.
- The role of media literacy in fostering critical thinking among audiences.
- Analyzing the influence of celebrity journalism on cultural values.
- The impact of cross-platform journalism on audience reach and engagement.
- Investigating the effects of social media algorithms on news distribution.
- The role of data journalism in enhancing transparency and public understanding.
- Analyzing the impact of crowd-sourced journalism on news authenticity.
- The challenges of balancing speed and accuracy in digital news reporting.
- Investigating the role of international correspondents in the digital age.
- The impact of public relations practices on journalistic independence.
- Analyzing the representation of LGBTQ+ issues in mainstream journalism.
- The role of journalism in addressing societal issues like homelessness and poverty.
- Investigating the effects of editorial bias in shaping public perception.
- The impact of journalism on political activism and social movements.
- Analyzing the challenges of maintaining journalistic standards in entertainment reporting.
Recent Journalism-Related Studies
While the ideas we’ve presented above are a decent starting point for finding a research topic, they are fairly generic and non-specific. So, it helps to look at actual studies in the journalism space to see how this all comes together in practice.
Below, we’ve included a selection of recent studies to help refine your thinking. These are actual studies, so they can provide some useful insight as to what a research topic looks like in practice.
- Imagination, Algorithms and News: Developing AI Literacy for Journalism (Deuze & Beckett, 2022)
- Evaluation of the Effect of a Live Interview in Journalism Students on Salivary Stress Biomarkers and Conventional Stress Scales (Roca et al., 2022)
- Professional and Personal Identity, Precarity and Discrimination in Global Arts Journalism (Sharp & Vodanovic, 2022)
- The Impact of Information and Communication Technologies on Journalism in the Digital Ara A Descriptive and Critical Approach (Chettah et al., 2022)
- Women in Mass Communication (Creedon & Wackwitz, 2022)
- Newsgames: Experiential Reality, Ludenic News Reading, Conflict of Purposes and Norms (Cengi̇z & Kaya, 2022)
- Deep Journalism and DeepJournal V1.0: A Data-Driven Deep Learning Approach to Discover Parameters for Transportation (Ahmad et al., 2022)
- A View From the Trenches: Interviews With Journalists About Reporting Science News (Anderson & Dudo, 2023)
- Understanding Journalisms: From Information to Entertainment by Persuasion and Promotion (Bernier, 2022)
- Role of educational institutions in promoting medical research and publications in Pakistan (Aslam, 2022)
- Ethics for Journalists (Keeble, 2022)
- “I Felt I Got to Know Everyone”: How News on Stage Combines Theatre and Journalism for a Live Audience (Adams & Cooper, 2022)
- Newsafety: Infrastructures, Practices and Consequences (Westlund et al., 2022)
- The Golden Age of American Journalism (Alent’eva et al., 2022)
- Advancing a Radical Audience Turn in Journalism. Fundamental Dilemmas for Journalism Studies (Swart et al., 2022)
- Mcluhan’s Theories and Convergence of Online and Papers’ Newsrooms (Barceló-Sánchez et al., 2022)
- Scientific communication after the COVID-19 crisis: TikTok publishing strategies on the transmedia board (Neira et al., 2023)
As you can see, these research topics are a lot more focused than the generic topic ideas we presented earlier. So, for you to develop a high-quality research topic, you’ll need to get specific and laser-focused on a specific context with specific variables of interest. In the video below, we explore some other important things you’ll need to consider when crafting your research topic.
Get 1-On-1 Help
If you’re still unsure about how to find a quality research topic, check out our Research Topic Kickstarter service, which is the perfect starting point for developing a unique, well-justified research topic.

Find The Perfect Research Topic

How To Choose A Research Topic: 5 Key Criteria
How To Choose A Research Topic Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + Free Topic...
Research Topics & Ideas: Automation & Robotics
A comprehensive list of automation and robotics-related research topics. Includes free access to a webinar and research topic evaluator.

Research Topics & Ideas: Sociology
A comprehensive list of sociology-related research topics. Includes free access to a webinar and research topic evaluator.

Research Topics & Ideas: Public Health & Epidemiology
A comprehensive list of public health-related research topics. Includes free access to a webinar and research topic evaluator.

Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience
Research Topics & Ideas: Neuroscience 50 Topic Ideas To Kickstart Your Research...
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 26 July 2021
Large-scale quantitative evidence of media impact on public opinion toward China
- Junming Huang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-2532-4090 1 ,
- Gavin G. Cook 1 &
- Yu Xie 1 , 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 8 , Article number: 181 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
22k Accesses
6 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Cultural and media studies
- Politics and international relations
Do mass media influence people’s opinions of other countries? Using BERT, a deep neural network-based natural language processing model, this study analyzes a large corpus of 267,907 China-related articles published by The New York Times since 1970. The output from The New York Times is then compared to a longitudinal data set constructed from 101 cross-sectional surveys of the American public’s views on China, revealing that the reporting of The New York Times on China in one year explains 54% of the variance in American public opinion on China in the next. This result confirms hypothesized links between media and public opinion and helps shed light on how mass media can influence the public opinion of foreign countries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Shifting sentiments: analyzing public reaction to COVID-19 containment policies in Wuhan and Shanghai through Weibo data
United States politicians’ tone became more negative with 2016 primary campaigns
The speed of news in Twitter (X) versus radio
Introduction.
America and China are the world’s two largest economies, and they are currently locked in a tense rivalry. In a democratic system, public opinion shapes and constrains political action. How the American public views China thus affects relations between the two countries. Because few Americans have personally visited China, most Americans form their opinions of China and other foreign lands from media depictions. Our paper aims to explain how Americans form their attitudes on China with a case study of how The New York Times may shape public opinion. Our analysis is not causal, but it is informed by a causal understanding of how public opinion may flow from the media to the citizenry.
Scholars have adopted a number of wide-ranging and even contradictory approaches to explain the relationships between media and the American mind. One school of thought stresses that media exposure shapes public opinion (Baum and Potter, 2008 ; Iyengar and Kinder, 2010 ). Another set of approaches focuses on how the public might lead the media by analyzing how consumer demand shapes reporting. Newspapers may attract readers by biasing coverage of polarizing issues towards the ideological proclivities of their readership (Mullainathan and Shleifer, 2005 ), and with the advent of social media platforms such as Facebook and Twitter, traditional media are now more responsive to audience demand than ever before (Jacobs and Shapiro, 2011 ). On the other side of this equation, news consumers generally tend to seek out news sources with which they agree (Iyengar et al., 2008 ), and politically active individuals do so more proactively than the average person (Zaller, 1992 ).
Two other approaches address factors outside the media–public binary. The first, stresses the role of elites in opinion formation. While some, famously including Noam Chomsky, argue that news media are unwitting at best and at worst complicit “shills” of the American political establishment, political elites may affect public opinion directly by communicating with the public (Baum and Potter, 2008 ). Foreign elites may also influence American opinion because American reporters sometimes circumvent domestic sources and ask trusted foreign experts and officials for opinions (Hayes and Guardino, 2011 ). The second stresses how the macro-level phenomenon of public sentiment is shaped by micro-level and meso-level processes. An adult’s opinions on various topics emerge from their personal values, many of which are set during and around adolescence from factors outside of the realm of individual control (Hatemi and McDermott, 2016 ). Social networks may also affect attitude formation (Kertzer and Zeitzoff, 2017 ).
In light of these contradictory interpretations, it is difficult to be sure whether the media shape the attitudes of consumers or, on the other hand, whether consumers shape media (Baum and Potter, 2008 ). Moreover, most of the theories summarized above are tested on relatively small slices of data. In order to offer an alternative, “big data”-based contribution to this ongoing debate, this study compares how the public views China and how the news media report on China with large-scale data. Our data set, which straddles 50 years of newspaper reporting and survey data, is uniquely large and includes more than a quarter-million articles from The New York Times.
Most extant survey data indicate that Americans do not seem to like China very much (Xie and Jin, 2021 ). Many Americans are reported to harbor doubts about China’s record on human rights (Aldrich et al., 2015 ; Cao and Xu, 2015 ) and are anxious about China’s burgeoning economic, military, and strategic power (Gries and Crowson, 2010 ; Yang and Liu, 2012 ). They also think that the Chinese political system fails to serve the needs of the Chinese people (Aldrich et al., 2015 ). Most Americans, however, recognize a difference between the Chinese state, the Chinese people, and Chinese culture, and they view the latter two more favorably (Gries and Crowson, 2010 ). In Fiske’s Stereotype Content Model (Fiske et al., 2002 ), which expresses common stereotypes as a combination of “competence” and “warmth”, Asians belong to a set of “high-status, competitive out-groups” and rank high in competence but low in warmth (Lin et al., 2005 ).
The New York Times, which calls itself the “Newspaper of Record”, is the most influential newspaper in the USA and possibly even in the Anglophonic world. It boasts 7.5 million subscribers (Business Wire, 2021 ), and while the paper’s reach may be impressive, it is yet more significant that the readership of The New York Times represents an elite subset of the American public. Print subscribers to The New York Times have a median household income of $191,000, three times the median income of US households writ large (Rothbaum and Edwards, 2019 ). Despite the paper’s haughty and sometimes condescending reporting, it “has had and still has immense social, political, and economic influence on American and the world” (Schwarz, 2012 , p. 81). The New York Times may be a paper for America’s elite, and it may be biased to reflect the tastes of its elite audience, but the paper’s ideological slant does not affect our analyses as long as the its relevant biases are consistent over the time period covered by our analyses. Our analyses support the intuition of qualitative work on The Times (Schwarz, 2012 ) and show that these biases remain more or less constant for the decades in our sample. These analyses also illuminate some of the paper’s more notable biases, including the paper’s particular predilection for globalization.
The impact of social media on traditional media is not straightforward. While new media have certainly changed old media, neither has replaced the other. It is more accurate to say that old media have been integrated into new media and, in some ways, become a form of new media themselves. Twitter has accelerated the 2000s-era trends of information access that made it possible for news readers to find their own news and also enabled readers to interact with journalists (Jacobs and Shapiro, 2011 ), and the The New York Times seems to have made a significant commitment to the Twitter ecosystem. A quick glance at the follower count of The Times’ official Twitter account shows that it is one of the most influential accounts on the site, with almost 50 million followers. For comparison, both current president Joe Biden and vice president Kamala Harris have around 10 million followers. Most New York Times reporters additionally have “verified” accounts on the platform, which means that individual reporters may be incentivized to maintain public-facing profiles more now than in the past.
The media consumption patterns that made new media possible have changed the way The New York Times interacts with its audience and how it extracts revenue. The New York Times boasts a grand total of 7.5 million subscribers, but only 800,000 of them subscribe to the print edition. The Times’ digital subscription base has boomed since the election of Donald J. Trump, growing almost sixfold from a paltry 1.3 million in 2015 to a staggering 6.7 million in 2020 (Business Wire, 2021 ). The Times increasingly relies more on digital subscriptions and less on print subscriptions and ad sales for revenue (Lee, 2020 ). Ad revenue for most papers has been in sharp decline since the early 2000s (Jacobs and Shapiro, 2011 ), and this trend has only continued into the present. The New York Times now operates almost like a direct-to-consumer, subscription tech startup. New media have not replaced but have certainly changed old media. The full impact of these changes is beyond the scope of this paper, and we suggest it as an area for further research.
A small body of prior work has studied the The New York Times and how The New York Times reports on China. Blood and Phillips use autoregression methods on time series data to predict public opinion (Blood and Phillips, 1995 ). Wu et al. use a similar autoregression technique and find that public sentiment regarding the economy predicts economic performance and that people pay more attention to economic news during recessions (Wu et al., 2002 ). Peng finds that coverage of China in the paper has been consistently negative but increasingly frequent as China became an economic powerhouse (Peng, 2004 ). There is very little other scholarship that applies language processing methods to large corpora of articles from The New York Times or other leading papers. Atalay et al. is an exception that uses statistical techniques for parsing natural languages to analyze a corpus of newspaper articles from The New York Times, the Wall Street Journal, and other leading papers in order to investigate the increasing use of information technologies in newspaper classifieds (Atalay et al., 2018 ).
We explore the impact of The New York Times on its readers by examining the general relationship between The Times and public opinion. Though some might contend that only elites read NYT, we have adopted this research strategy for two reasons. If the views of NYT only impacted the nation’s elite, the paper’s views would still propagate to the general public through the elites themselves because elites can affect public opinion outside of media channels (Baum and Potter, 2008 ). Additionally, it is a widely held belief that NYT serves as a general barometer of an agenda-setting agent for American culture (Schwarz, 2012 ). Because of these two reasons, we interpolate the relationship between NYT and public opinion from the relationship between NYT and its readers, and we extrapolate that the views of NYT are broadly representative of American media.
Our paper aims to advance understanding of how Americans form their attitudes on China with a case study of how The New York Times may shape public opinion. We hypothesize that media coverage of foreign nations affects how Americans view the rest of the world. This reduced-form model deliberately simplifies the interactions between audience and media and sidesteps many active debates in political psychology and political communication. Analyzing a corpus of 267,907 articles on China from The New York Times, we quantify media sentiment with BERT, a state-of-the-art natural language processing model with deep neural networks, and segment sentiment into eight domain topics. We then use conventional statistical methods to link media sentiment to a longitudinal data set constructed from 101 cross-sectional surveys of the American public’s views on China. We find strong correlations between how The New York Times reports on China in one year and the views of the public on China in the next. The correlations agree with our hypothesis and imply a strong connection between media sentiment and public opinion.
We quantify media sentiment with a natural language model on a large-scale corpus of 267,907 articles on China from The New York Times published between 1970 and 2019. To explore sentiment from this corpus in greater detail, we map every article to a sentiment category (positive, negative, or neutral) in eight topics: ideology, government and administration, democracy, economic development, marketization, welfare and well-being, globalization, and culture.
We do this with a three-stage modeling procedure. First, two human coders annotate 873 randomly selected articles with a total of 18,598 paragraphs expressing either positive, negative, or neutral sentiment in each topic. We treat irrelevant articles as neutral sentiments. Secondly, we fine-tune a natural language processing model Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) (Devlin et al., 2018 ) with the human-coded labels. The model uses a deep neural network with 12 layers. It accepts paragraphs (i.e., word sequences of no more than 128 words) as input and outputs a probability for each category. We end up with two binary classifiers for each topic for a grand total of 16 classifiers: an assignment classifier that determines whether a paragraph expresses sentiment in a given topic domain and a sentiment classifier that then distinguishes positive and negative sentiments in a paragraph classified as belonging to a given topic domain. Thirdly, we run the 16 trained classifiers on each paragraph in our corpus and assign category probabilities to every paragraph. We then use the probabilities of all the paragraphs in an article to determine the article’s overall sentiment category (i.e., positive, negative, or neutral) in every topic.
As demonstrated in Table 1 , the two classifiers are accurate at both the paragraph and article levels. The assignment classifier and the sentiment classifier reach classification accuracy of 89–96% and 73–90%, respectively, on paragraphs. The combined outcome of the classifiers, namely article sentiment, is accurate to 62–91% across the eight topics. For comparison, a random guess would reach an accuracy of 50% on each task (see Supplementary Information for details).
American public opinion towards China is a composite measure drawn from national surveys that ask respondents for their opinions on China. We collect 101 cross-sectional surveys from 1974 to 2019 that asked relevant questions about attitudes toward China and incorporate a probabilistic model to harmonize different survey series with different scales (e.g., 4 levels, 10 levels) into a single time series, capitalizing on “seaming” years in which different survey series overlapped (Wang et al., 2021 ). For every year, there is a single real value representing American sentiment on China relative to the level in 1974. Put another way, we use sentiment in 1974 as a baseline measure to normalize the rest of the time series. A positive value shows a more favorable attitude than that in 1974, and a negative value represents a less favorable attitude than that in 1974. Because of this, the trends in sentiment changes year-over-year are of interest, but the absolute values of sentiment in a given year are not. As shown in Fig. 1 , public opinion towards China has varied greatly from 1974 to 2019. It steadily climbed from a low of −24% in 1976 to a high of 73% in 1987, and has fluctuated between 10% and 48% in the intervening 30 years.
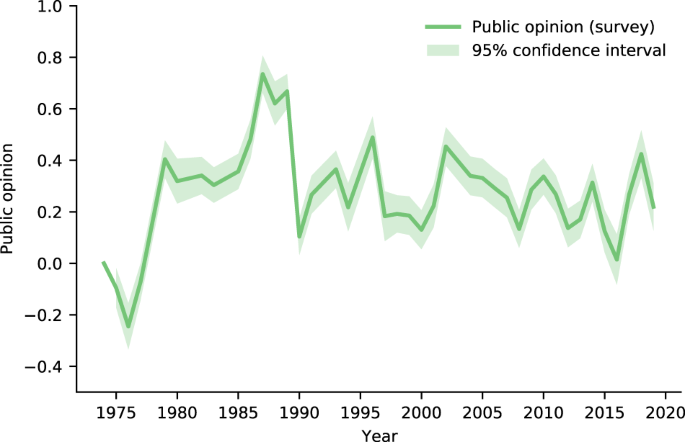
This time series is aggregated from 101 cross-sectional surveys from 1974 to 2019 that asked relevant questions about attitudes toward China with the year of 1974 as baseline. Years with attitudes above zero show a more favorable attitude than that in 1974, with a peak of 73% in 1987. Years with attitudes below zero show a less favorable attitude than that in 1974, with the lowest level of −24% in 1976. The time series is shown with a 95% confidence interval.
We begin with a demonstration of how the reporting of The New York Times on China changes over time, and we follow this with an analysis of how coverage of China might influence public opinion toward China.
Trend of media sentiment
The New York Times has maintained a steady interest in China over the years and has published at least 3,000 articles on China in every year of our corpus. Figure 2 displays the yearly volume of China-related articles from The New York Times on each of the eight topics since 1970. Articles on China increased sharply after 2000 and eventually reached a peak around 2010, almost doubling their volume from the 1970s. As the number of articles on China increased, the amount of attention paid to each of the eight topics diverged. Articles on government, democracy, globalization, and culture were consistently common while articles on ideology were consistently rare. In contrast, articles on China’s economy, marketization, and welfare were rare before 1990 but became increasingly common after 2000. The timing of this uptick coincided neatly with worldwide recognition of China’s precipitous economic ascent and specifically the beginnings of China’s talks to join the World Trade Organization.
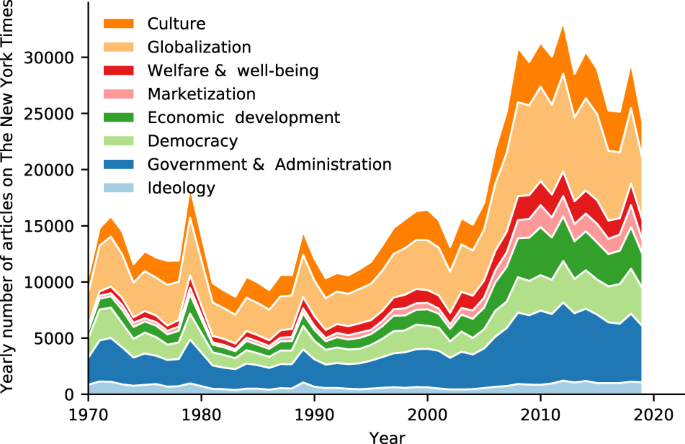
In each year we report in each topic the number of positive and negative articles while ignoring neutral/irrelevant articles. The media have consistently high attention on reporting China government & administration, democracy, globalization, and culture. There are emerging interests on China’s economics, marketization, and welfare and well-being since 1990s. Note that the sum of the stacks does not equal to the total volume of articles about China, because each article may express sentiment in none or multiple topics.
While the proportion of articles in each given topic change over time, the sentiment of articles in each topic is remarkably consistent. Ignoring neutral articles, Figure 3 illustrates the yearly fractions of positive and negative articles about each of the eight topics. We find four topics (economics, globalization, culture, and marketization) are almost always covered positively while reporting on the other four topics (ideology, government & administration, democracy, and welfare & well-being) is overwhelmingly negative.
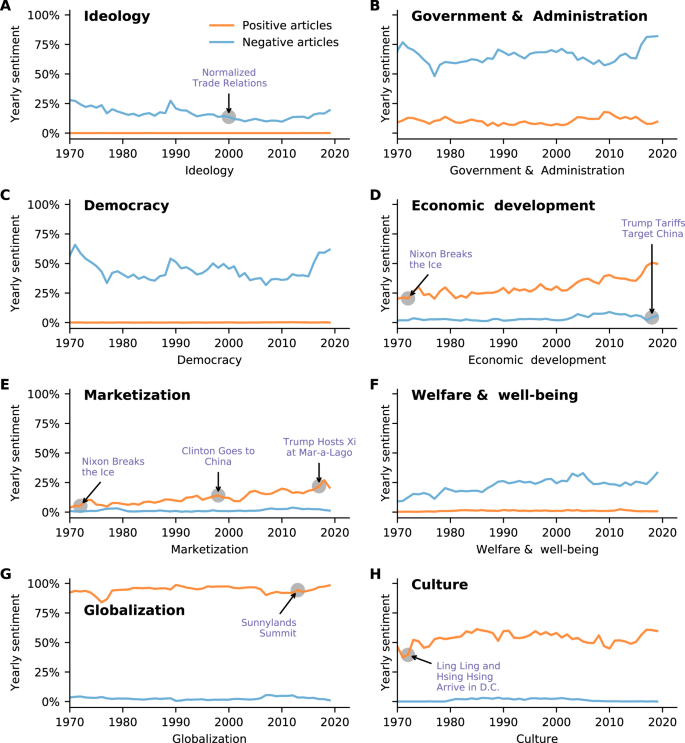
The panel reports the trend of yearly media attitude toward China in ( A ) ideology, ( B ) government & administration, ( C ) democracy, ( D ) economic development, ( E ) marketization, ( F ) welfare & well-being, ( G ) globalization, and ( H ) culture. The media attitude is measured as the percentages of positive articles and negative articles, respectively. US–China relation milestones are marked as gray dots. The New York Times express diverging but consistent attitudes in the eight domains, with negative articles consistently common in ideology, government, democracy, and welfare, and positive sentiments common in economic, globalization, and culture. Standard errors are too small to be visible (below 1.55% in all topics all years).
The NYT views China’s globalization in a very positive light. Almost 100% of the articles mentioning this topic are positive for all of the years in our sample. This reveals that The New York Times welcomes China’s openness to the world and, more broadly, may be particularly partial to globalization in general.
Similarly, economics, marketization, and culture are covered most commonly in positive tones that have only grown more glowing over time. Positive articles on these topics began in the 1970s with China–US Ping–Pong diplomacy, and eventually comprise 1/4 to 1/2 of articles on these three topics, the remainder of which are mostly neutral articles. This agrees with the intuition that most Americans like Chinese culture. The New York Times has been deeply enamored with Chinese cultural products ranging from Chinese art to Chinese food since the very beginning of our sample. Following China’s economic reforms, the number of positive articles and the proportion of positive articles relative to negative articles increases for both economics and marketization.
In contrast, welfare and well-being are covered in an almost exclusively negative light. About 1/4 of the articles on this topic are negative, and almost no articles on this topic are positive. Topics regarding politics are covered very negatively. Negative articles on ideology, government and administration, and democracy outnumber positive articles on these topics for all of the years in our sample. Though small fluctuations that coincided with ebbs in US–China relations are observed for those three topics, coverage has only grown more negative over time. Government and administration is the only negatively covered topic that does feature some positive articles. This reflects the qualitative understanding that The New York Times thinks that the Chinese state is an unpleasant but capable actor.
Despite the remarkable diversity of sentiment toward China across the eight topics, sentiment within each of the topics is startlingly consistent over time. This consistency attests to the incredible stability of American stereotypes towards China. If there is any trend to be found here, it is that the main direction of sentiment in each topic, positive or negative, has grown more prevalent since the 1970s. This is to say that reporting on China has become more polarized, which is reflective of broader trends of media polarization (Jacobs and Shapiro, 2011 ; Mullainathan and Shleifer, 2005 ).
Media sentiment affects public opinion
To reveal the connection between media sentiment and public opinion, we run a linear regression model (Eq. ( 1 )) to fit public opinion with media sentiment from current and preceding years.
where μ t denotes public opinion in year t with possible values ranging from −1 to 1. F k j s is the fraction of positive ( s = positive) or negative ( s = negative) articles on topic k in year j . Coefficient β k j s quantifies the importance of F k j s in predicting μ t .
There is inertia to public opinion. A broadly held opinion is hard to change in the short term, and it may require a while for media sentiment to affect how the public views a given issue. For this reason, j is allowed to take [ t , t − 1, t − 2, ...] anywhere from zero to a couple of years ahead of t . In other words, we inspect lagged values of media sentiment as candidate predictors for public attitudes towards China.
We seek an optimal solution of media sentiment predictors to explain the largest fraction of variance ( r 2 ) of public opinion. To reduce the risk of overfitting, we first constrain the coefficients to be non-negative after reverse-coding negative sentiment variables, which means we assume that positive articles have either no impact or positive impact and that negative articles have either zero or negative impact on public opinion. Secondly, we require that the solution be sparse and contain no more than one non-zero coefficient in each topic:
where r 2 ( μ , β , F ) is the explained variance of μ fitted with ( β , F ). The l 0 -norm ∥ β k , ⋅ , ⋅ ∥ 0 gives the number of non-zero coefficients of topic k predictors.
The solution varies with the number of topics included in the fitting model. As shown in Table 2 , if we allow fitting with only one topic, we find that sentiment on Chinese culture has the most explanatory power, accounting for 31.2% of the variance in public opinion. We run a greedy strategy to add additional topics that yield the greatest increase in explanatory power, resulting in eight nested models (Table 2 ). The explanatory power of our models increases monotonically with the number of allowed topics but reaches a saturation point at which the marginal increase in variance explained per topics decreases after only two topics are introduced (see Table 2 ). To strike a balance between simplicity and explanatory power, we use the top two predictors, which are the positive sentiment of culture and the negative sentiment of democracy in the previous year, to build a linear predictor of public opinion that can be written as
where F culture, t −1,positive is the yearly fraction of positive articles on Chinese culture in year t − 1 and F democracy, t −1,negative is the yearly fraction of negative articles on Chinese democracy in year t − 1. This formula explains 53.9% of the variance of public opinion in the time series. For example, in 1993 53.9% of the articles on culture had a positive sentiment, and 46.9% of the articles on democracy had negative sentiment ( F c u l t u r e ,1993,positive = 0.539, F democracy,1993,negative = −0.469). Substituting those numbers into Eq. ( 2 ) predicts public opinion in the next year (1994) to be 0.208, very close to the actual level of public opinion (0.218) (Fig. 4 ).

The public opinion (solid), as a time series, is well fitted by the media sentiments on two selected topics, namely “Culture” and “Democracy”, in the previous year. The dashed line shows a linear prediction based on the fractions of positive articles on “Culture” and negative articles on “Democracy” in the previous year. The public opinion is shown with a 95% confidence interval, and the fitted line is shown with one standard error.
By analyzing a corpus of 267,907 articles from The New York Times with BERT, a state-of-the-art natural language processing model, we identify major shifts in media sentiment towards China across eight topic domains over 50 years and find that media sentiment leads public opinion. Our results show that the reporting of The New York Times on culture and democracy in one year explains 53.9% of the variation in public opinion on China in the next. The conclusion that we draw from our results is that media sentiment on China predicts public opinion on China. Our analysis is neither conclusive nor causal, but it is suggestive. Our results are best interpreted as a “reduced-form” description of the overall relationship between media sentiment and public opinion towards China.
While there are a number of potential factors that may complicate our conclusions, none would change the overall thrust of our results. We do not consider how the micro-level or meso-level intermediary processes through which opinion from elite media percolates to the masses below may affect our results. We also do not consider the potential ramifications of elites communing directly with the public, of major events in US–China relations causing short-term shifts in reporting, or of social media creating new channels for the diffusion of opinion. Finally, The New York Times might have a particular bias to how it covers China.
In addition to those specified above, a number of possible extensions of our work remain ripe targets for further research. Though a fully causal model of our text analysis pipeline may prove elusive (Egami et al., 2018 ), future work may use randomized vignettes to further our understanding of the causal effects of media exposure on attitudes towards China. Secondly, our modeling framework is deliberately simplified. The state affects news coverage before the news ever makes its way to the citizenry. It is plausible that multiple state-level actors may bypass the media and alter public opinion directly and to different ends. For example, the actions and opinions of individual high-profile US politicians may attenuate or exaggerate the impact of state-level tension on public sentiment toward China. There are presumably a whole host of intermediary processes through which opinion from elite media affects the sentiment of the masses. Thirdly, the relationship between the sentiment of The New York Times and public opinion may be very different for hot-button social issues of first-line importance in the American culture wars. In our corpus, The New York Times has covered globalization almost entirely positively, but the 2016 election of President Donald J. Trump suggests that many Americans do not share the zeal of The Times for international commerce. We also plan to extend our measure of media sentiment to include text from other newspapers. The Guardian, a similarly elite, Anglophonic, and left-leaning paper, will make for a useful comparison case. Finally, our analysis was launched in the midst of heightened tensions between the US and China and concluded right before the outbreak of a global pandemic. Many things have changed since COVID-19. Returning to our analysis with an additional year or two of data will almost certainly provide new results of additional interest.
Future work will address some of these additional paths, but none of these elements affects the basic conclusion of this work. We find that reporting on China in one year predicts public opinion in the next. This is true for more than fifty years in our sample, and while knowledge of, for example, the opinion diffusion process on social media may add detail to this relationship, the basic flow of opinion from media to the public will not change. Regarding the putative biases of The New York Times, its ideological slant does not affect our explanation of trends in public opinion of China as long as the paper’s relevant biases are relatively consistent over the time period covered by our analyses.
Data availability
All data analyzed during the current study are publicly available. The New York Times data were accessed using official online APIs ( https://developer.nytimes.com/ ). We used their query API to search for 267,907 articles that mention China, Chinese, Beijing, Peking, or Shanghai. We downloaded the full text and date of each article. The survey data were obtained from three large public archives/centers, namely Roper Center for Public Opinion Research (ROPER), NORC at the University of Chicago, and Pew Research Center (Pew Research Center, 2019 ; Smith et al., 2018 ). See Supplementary Information for a full list of surveys. The source codes and pretrained parameters of the natural language processing model BERT are publicly released by Google Inc. on its github repository ( https://github.com/google-research/bert ). The finetuned BERT models and the inferred sentiment of The New York Times articles in our corpus are publicly available at Princeton University DataSpace. Please check the project webpage ( http://www.attitudetowardchina.com/media-opinion ) or the DataSpace webpage ( https://doi.org/10.34770/x27d-0545 ) to download.
Aldrich J, Lu J, Kang L (2015) How do Americans view the rising China. J Contemp China 24(92):203–221
Article Google Scholar
Atalay E, Phongthiengtham P, Sotelo S, Tannenbaum D (2018) New technologies and the labor market. J Monet Econ 97:48–67
Baum MA, Potter PB (2008) The relationships between mass media, public opinion, and foreign policy: toward a theoretical synthesis. Annu Rev Polit Sci 11(1):39–65
Blood DJ, Phillips PC (1995) Recession headline news, consumer sentiment, the state of the economy and presidential popularity: a time series analysis 1989–1993. Int J Public Opinion Res 7(1):2–22
Business Wire (2021) The New York Times company reports 2020 fourth-quarter and full-year results and announces dividend increase. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20210204005599/en/
Cao Y, Xu J (2015) The Tibet problem in the milieu of a rising China: findings from a survey on Americans’ attitudes toward China. J Contemp China 24(92):240–259
Devlin J, Chang MW, Lee K, Toutanova K (2018) BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/181004805
Egami N, Fong CJ, Grimmer J, Roberts ME, Stewart BM (2018) How to make causal inferences using texts. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/180202163
Fiske ST, Cuddy AJ, Glick P, Xu J (2002) A model of (often mixed) stereotype content: competence and warmth respectively follow from perceived status and competition. J Personal Soc Psychol 82(6):878
Gries PH, Crowson HM (2010) Political orientation, party affiliation, and American attitudes towards China. J Chin Political Sci 15(3):219–244
Hatemi PK, McDermott R (2016) Give me attitudes. Annu Rev Political Sci 19:331–350
Hayes D, Guardino M (2011) The influence of foreign voices on US public opinion. Am J Political Sci 55(4):831–851
Iyengar S, Hahn KS, Krosnick JA, Walker J (2008) Selective exposure to campaign communication: the role of anticipated agreement and issue public membership. J Politics 70(1):186–200
Iyengar S, Kinder DR (2010) News that matters: television and American opinion, Chicago studies in American politics, updated edn. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Book Google Scholar
Jacobs L, Shapiro RY (eds) (2011) Informational interdependence: public opinion and the media in the new communications era. In: The Oxford handbook of American public opinion and the media. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Kertzer JD, Zeitzoff T (2017) A bottom-up theory of public opinion about foreign policy. Am J Political Sci 61(3):543–558
Lee E (2020) New York Times hits 7 million subscribers as digital revenue rises. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/11/05/business/media/new-york-times-q3-2020-earnings-nyt.html
Lin MH, Kwan VS, Cheung A, Fiske ST (2005) Stereotype content model explains prejudice for an envied outgroup: scale of anti-Asian American stereotypes. Personal Soc Psychol Bull 31(1):34–47
Article CAS Google Scholar
Mullainathan S, Shleifer A (2005) The market for news. Am Econ Rev 95(4):1031–1053
Peng Z (2004) Representation of China: an across time analysis of coverage in the New York Times and Los Angeles Times . Asian J Commun 14(1):53–67
Article ADS Google Scholar
Pew Research Center (2019) Global attitudes & trends. https://www.pewresearch.org/global/
Rothbaum J, Edwards A (2019) U.S. median household income was $63,179 in 2018, not significantly different from 2017. https://www.census.gov/library/stories/2019/09/us-median-household-income-not-significantly-different-from-2017.html
Schwarz D (2012) Endtimes? Crises and turmoil at the New York Times, Excelsior Editions, State University of New York Press, New York.
Smith TW, Davern M, Freese J, Morgan S (2018) General social surveys, 1972–2018. NORC, University of Chicago
Wang D, Xie Y, Huang J (2021) Latent attitude method for trend analysis with pooled survey data. Preprint at SocArXiv https://doi.org/10.31235/osf.io/atsq2
Wu HD, Stevenson RL, Chen HC, Güner ZN (2002) The conditioned impact of recession news: a time-series analysis of economic communication in the United States, 1987–1996. Int J Public Opin Res 14(1):19–36
Xie Y, Jin Y (2021) Global attitudes toward China: trends and correlates. J Contemp China
Yang YE, Liu X (2012) The ‘China threat’ through the lens of US print media: 1992–2006. J Contemp China 21(76):695–711
Zaller JR et al. (1992) The nature and origins of mass opinion. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Chesley Chan (Princeton University), Wen Liu (Renmin University of China), Yichun Yang (Renmin University of China), and Emily Yin (Princeton University) for coding The New York Times articles with the topic-specific sentiment. The authors thank Chih-Jou Jay Chen (Academia Sinica), Cheng Cheng (Singapore Management University), Shawn Dorius (Iowa State University), Theodore P. Gerber (University of Wisconsin-Madison), Fengming Lu (Australian National University), Yongai Jin (Renmin University of China), Donghui Wang (Princeton University) for valuable discussions. The authors thank Xudong Guo (Tsinghua University) for helping fine-tune the BERT model and analyze the calculation results. The authors thank Tom Marling for proofreading the manuscript. The research was partially supported by the Paul and Marcia Wythes Center on Contemporary China at Princeton University and Guanghua School of Management at Peking University.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Princeton University, Princeton, NJ, USA
Junming Huang, Gavin G. Cook & Yu Xie
Peking University, Beijing, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Yu Xie .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Large-scale quantitative evidence of media impact on public opinion toward china: supplementary information, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Huang, J., Cook, G.G. & Xie, Y. Large-scale quantitative evidence of media impact on public opinion toward China. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 8 , 181 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-021-00846-2
Download citation
Received : 26 December 2020
Accepted : 22 June 2021
Published : 26 July 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-021-00846-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
EDITORIAL article
Editorial: coronavirus disease (covid-19): the impact and role of mass media during the pandemic.

- 1 Department of Social and Organizational Psychology, Iscte-University Institute of Lisbon, CIS-IUL, Lisbon, Portugal
- 2 Department of Psychology and Social Work, Mid Sweden University, Östersund, Sweden
- 3 Department of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, Medical School and University Hospital, Eberhard Karls University of Tübingen, Tübingen, Germany
Editorial on the Research Topic Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): The Impact and Role of Mass Media During the Pandemic
The outbreak of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has created a global health crisis that had a deep impact on the way we perceive our world and our everyday lives. Not only has the rate of contagion and patterns of transmission threatened our sense of agency, but the safety measures to contain the spread of the virus also required social and physical distancing, preventing us from finding solace in the company of others. Within this context, we launched our Research Topic on March 27th, 2020, and invited researchers to address the Impact and Role of Mass Media During the Pandemic on our lives at individual and social levels.
Despite all the hardships, disruption, and uncertainty brought by the pandemic, we received diverse and insightful manuscript proposals. Frontiers in Psychology published 15 articles, involving 61 authors from 8 countries, which were included in distinct specialized sections, including Health Psychology, Personality and Social Psychology, Emotion Science, and Organizational Psychology. Despite the diversity of this collective endeavor, the contributions fall into four areas of research: (1) the use of media in public health communication; (2) the diffusion of false information; (3) the compliance with the health recommendations; and (4) how media use relates to mental health and well-being.
A first line of research includes contributions examining the use of media in public health communication. Drawing on media messages used in previous health crises, such as Ebola and Zika, Hauer and Sood describe how health organizations use media. They offer a set of recommendations for COVID-19 related media messages, including the importance of message framing, interactive public forums with up-to-date information, and an honest communication about what is known and unknown about the pandemic and the virus. Following a content analysis approach, Parvin et al. studied the representations of COVID-19 in the opinion section of five Asian e-newspapers. The authors identified eight main issues (health and drugs, preparedness and awareness, social welfare and humanity, governance and institutions, the environment and wildlife, politics, innovation and technology, and the economy) and examined how e-newspapers from these countries attributed different weights to these issues and how this relates to the countries' cultural specificity. Raccanello et al. show how the internet can be a platform to disseminate a public campaign devised to inform adults about coping strategies that could help children and teenagers deal with the challenges of the pandemic. The authors examined the dissemination of the program through the analysis of website traffic, showing that in the 40 days following publication, the website reached 6,090 visits.
A second related line of research that drew the concern of researchers was the diffusion of false information about COVID-19 through the media. Lobato et al. examined the role of distinct individual differences (political orientation, social dominance orientation, traditionalism, conspiracy ideation, attitudes about science) on the willingness to share misinformation about COVID-19 over social media. The misinformation topics varied between the severity and spread of COVID-19, treatment and prevention, conspiracy theories, and miscellaneous unverifiable claims. Their results from 296 adult participants (Mage = 36.23; 117 women) suggest two different profiles. One indicating that those reporting more liberal positions and lower social dominance were less willing to share conspiracy misinformation. The other profile indicated that participants scoring high on social dominance and low in traditionalism were more willing to share both conspiracy and other miscellaneous claims, but less willing to share misinformation about the severity and spread of COVID-19. Their findings can have relevant contributions for the identification of specific individual profiles related to the widespread of distinct types of misinformation. Dhanani and Franz examined a sample of 1,141 adults (Mage = 44.66; 46.9% female, 74.7% White ethnic identity) living in the United States in March 2020. The authors examined how media consumption and information source were related to knowledge about COVID-19, the endorsement of misinformation about COVID-19, and prejudice toward Asian Americans. Higher levels of trust in informational sources such as public health organizations (e.g., Center for Disease Control) was associated with greater knowledge, lower endorsement of misinformation, and less prejudice toward Asian Americans. Media source was associated with distinct levels of knowledge, willingness to endorsement misinformation and prejudice toward American Asians, with social media use (e.g., Twitter, Facebook) being related with a lower knowledge about COVID-19, higher endorsement of misinformation, and stronger prejudice toward Asian Americans.
A third line of research addressed the factors that could contribute to compliance with the health recommendations to avoid the spread of the disease. Vai et al. studied early pre-lockdown risk perceptions about COVID-19 and the trust in media sources among 2,223 Italians (Mage = 36.4, 69.2% female). They found that the perceived usefulness of the containment measures (e.g., social distancing) was related to threat perception and efficacy beliefs. Lower threat perception was associated with less perception of utility of the containment measures. Although most participants considered themselves and others capable of taking preventive measures, they saw the measures as generally ineffective. Participants acknowledged using the internet as their main source of information and considered health organizations' websites as the most trustworthy source. Albeit frequently used, social media was in general considered an unreliable source of information. Tomczyk et al. studied knowledge about preventive behaviors, risk perception, stigmatizing attitudes (support for discrimination and blame), and sociodemographic data (e.g., age, gender, country of origin, education level, region, persons per household) as predictors of compliance with the behavioral recommendations among 157 Germans, (age range: 18–77 years, 80% female). Low compliance was associated with male gender, younger age, and lower public stigma. Regarding stigmatizing attitudes, the authors only found a relation between support for discrimination (i.e., support for compulsory measures) and higher intention to comply with recommendations. Mahmood et al. studied the relation between social media use, risk perception, preventive behaviors, and self-efficacy in a sample of 310 Pakistani adults (54.2% female). The authors found social media use to be positively related to self-efficacy and perceived threat, which were both positively related to preventive behaviors (e.g., hand hygiene, social distancing). Information credibility was also related to compliance with health recommendations. Lep et al. examined the relationship between information source perceived credibility and trust, and participants' levels of self-protective behavior among 1,718 Slovenians (age range: 18–81 years, 81.7% female). The authors found that scientists, general practitioners (family doctors), and the National Institute of Public Health were perceived as the more credible source of information, while social media and government officials received the lowest ratings. Perceived information credibility was found to be associated with lower levels of negative emotional responses (e.g., nervousness, helplessness) and a higher level of observance of self-protective measures (e.g., hand washing). Siebenhaar et al. also studied the link between compliance, distress by information, and information avoidance. They examined the online survey responses of 1,059 adults living in Germany (Mage = 39.53, 79.4% female). Their results suggested that distress by information could lead to higher compliance with preventive measures. Distress by information was also associated with higher information avoidance, which in turn is related to less compliance. Gantiva et al. studied the effectiveness of different messages regarding the intentions toward self-care behaviors, perceived efficacy to motivate self-care behaviors in others, perceived risk, and perceived message strength, in a sample of 319 Colombians (age range: 18–60 years, 69.9% female). Their experiment included the manipulation of message framing (gain vs. loss) and message content (economy vs. health). Participants judged gain-frame health related messages to be stronger and more effective in changing self-behavior, whereas loss-framed health messages resulted in increased perceived risk. Rahn et al. offer a comparative view of compliance and risk perception, examining three hazard types: COVID-19 pandemic, violent acts, and severe weather. With a sample of 403 Germans (age range: 18–89 years, 72% female), they studied how age, gender, previous hazard experience and different components of risk appraisal (perceived severity, anticipated negative emotions, anticipatory worry, and risk perception) were related to the intention to comply with behavioral recommendations. They found that higher age predicted compliance with health recommendations to prevent COVID-19, anticipatory worry predicted compliance with warning messages regarding violent acts, and women complied more often with severe weather recommendations than men.
A fourth line of research examined media use, mental health and well-being during the COVID-19 pandemic. Gabbiadini et al. addressed the use of digital technology (e.g., voice/video calls, online games, watching movies in party mode) to stay connected with others during lockdown. Participants, 465 Italians (age range: 18–73 years, 348 female), reported more perceived social support associated with the use of these digital technologies, which in turn was associated with fewer feelings of loneliness, boredom, anger, and higher sense of belongingness. Muñiz-Velázquez et al. compared the media habits of 249 Spanish adults (Mage = 42.06, 53.8% female) before and during confinement. They compared the type of media consumed (e.g., watching TV series, listening to radio, watching news) and found the increased consumption of TV and social networking sites during confinement to be negatively associated with reported level of happiness. People who reported higher levels of well-being also reported watching less TV and less use of social networking sites. Majeed et al. , on the other hand, examined the relation between problematic social media use, fear of COVID-19, depression, and mindfulness. Their study, involving 267 Pakistani adults (90 female), suggested trait mindfulness had a buffer effect, reducing the impact of problematic media use and fear of COVID-19 on depression.
Taken together, these findings highlight how using different frames for mass media gives a more expansive view of its positive and negative roles, but also showcase the major concerns in the context of a pandemic crisis. As limitations we highlight the use of cross-sectional designs in most studies, not allowing to establish true inferences of causal relationships. The outcome of some studies may also be limited by the unbalanced number of female and male participants, by the non-probability sampling method used, and by the restricted time frame in which the research occurred. Nevertheless, we are confident that all the selected studies in our Research Topic bring important and enduring contributions to the understanding of how media, individual differences, and social factors intertwine to shape our lives, which can also be useful to guide public policies during these challenging times.
Author Contributions
PA: conceptualization, writing the original draft, funding acquisition, writing—review, and editing. FE: conceptualization, writing—review, and editing. MP: writing—review and editing. NP: conceptualization, writing the original draft, writing—review, and editing. All authors approved the submitted version.
PA and NP received partial support to work on this Research Topic through Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia (FCT) with reference to the project PTDC/CCI-INF/29234/2017. MP contribution was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG, PA847/22-1 and PA847/25-1). The authors are independent of the funders.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to all the authors who proposed their work, all the researchers who reviewed the submissions to this Research Topic, and to Rob Richards for proofreading the Editorial manuscript.
Keywords: COVID-19, coronavirus disease, mass media, health communication, prevention, intervention, social behavioral changes
Citation: Arriaga P, Esteves F, Pavlova MA and Piçarra N (2021) Editorial: Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): The Impact and Role of Mass Media During the Pandemic. Front. Psychol. 12:729238. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.729238
Received: 22 June 2021; Accepted: 30 July 2021; Published: 23 August 2021.
Edited and reviewed by: Eduard Brandstätter , Johannes Kepler University of Linz, Austria
Copyright © 2021 Arriaga, Esteves, Pavlova and Piçarra. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Patrícia Arriaga, patricia.arriaga@iscte-iul.pt
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
