The impact of smartphone use on learning effectiveness: A case study of primary school students
- Published: 11 November 2022
- Volume 28 , pages 6287–6320, ( 2023 )

Cite this article
- Jen Chun Wang 1 ,
- Chia-Yen Hsieh ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5476-2674 2 &
- Shih-Hao Kung 1
90k Accesses
4 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
This study investigated the effects of smartphone use on the perceived academic performance of elementary school students. Following the derivation of four hypotheses from the literature, descriptive analysis, t testing, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Pearson correlation analysis, and one-way multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) were performed to characterize the relationship between smartphone behavior and academic performance with regard to learning effectiveness. All coefficients were positive and significant, supporting all four hypotheses. We also used structural equation modeling (SEM) to determine whether smartphone behavior is a mediator of academic performance. The MANOVA results revealed that the students in the high smartphone use group academically outperformed those in the low smartphone use group. The results indicate that smartphone use constitutes a potential inequality in learning opportunities among elementary school students. Finally, in a discussion of whether smartphone behavior is a mediator of academic performance, it is proved that smartphone behavior is the mediating variable impacting academic performance. Fewer smartphone access opportunities may adversely affect learning effectiveness and academic performance. Elementary school teachers must be aware of this issue, especially during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The findings serve as a reference for policymakers and educators on how smartphone use in learning activities affects academic performance.
Similar content being viewed by others

Smartphone Usage, Social Media Engagement, and Academic Performance: Mediating Effect of Digital Learning

Learning Hard or Hardly Learning: Smartphones in the University’s Classrooms
The smartphone in self-regulated learning and student success: clarifying relationships and testing an intervention
Kendall Hartley, Lisa D. Bendixen, … Emily Shreve
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution has stimulated interest in educational reforms for the integration of information and communication technology (ICT) into instruction. Smartphones have become immensely popular ICT devices. In 2019, approximately 96.8% of the global population had access to mobile devices with the coverage rate reaching 100% in various developed countries (Sarker et al., 2019 ). Given their versatile functions, smartphones have been rapidly integrated into communication and learning, among other domains, and have become an inseparable part of daily life for many. Smartphones are perceived as convenient, easy-to-use tools that promote interaction and multitasking and facilitate both formal and informal learning (Looi et al., 2016 ; Yi et al., 2016 ). Studies have investigated the impacts of smartphones in education. For example, Anshari et al. ( 2017 ) asserted that the advantages of smartphones in educational contexts include rich content transferability and the facilitation of knowledge sharing and dynamic learning. Modern students expect to experience multiple interactive channels in their studies. These authors also suggested incorporating smartphones into the learning process as a means of addressing inappropriate use of smartphones in class (Anshari et al., 2017 ). For young children, there are differences in demand and attributes and some need for control depending upon the daily smartphone usage of the children (Cho & Lee, 2017 ). To avoid negative impacts, including interference with the learning process, teachers should establish appropriate rules and regulations. In a study by Bluestein and Kim ( 2017 ) on the use of technology in the classroom they examined three themes: acceptance of tablet technology, learning excitement and engagement, and the effects of teacher preparedness and technological proficiency. They suggested that teachers be trained in application selection and appropriate in-class device usage. Cheng et al. ( 2016 ) found that smartphone use facilitated English learning in university students. Some studies have provided empirical evidence of the positive effects of smartphone use, whereas others have questioned the integration of smartphone use into the academic environment. For example, Hawi and Samaha ( 2016 ) investigated whether high academic performance was possible for students at high risk of smartphone addiction. They provided strong evidence of the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on academic performance. Lee et al. ( 2015 ) found a negative correlation between smartphone addiction and learning in university students. There has been a lot of research on the effectiveness of online teaching, but the results are not consistent. Therefore, this study aims to further explore the effects of independent variables on smartphone use behavior and academic performance.
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused many countries to close schools and suspend in-person classes, enforcing the transition to online learning. Carrillo and Flores ( 2020 ) suggested that because of widespread school closures, teachers must learn to manage the online learning environment. Online courses have distinct impacts on students and their families, requiring adequate technological literacy and the formulation of new teaching or learning strategies (Sepulveda-Escobar & Morrison, 2020 ). Since 2020, numerous studies have been conducted on parents’ views regarding the relationship of online learning, using smartphones, computers, and other mobile devices, with learning effectiveness. Widely inconsistent findings have been reported. For instance, in a study by Hadad et al. ( 2020 ), two thirds of parents were opposed to the use of smartphones in school, with more than half expressing active opposition ( n = 220). By contrast, parents in a study by Garbe et al. ( 2020 ) agreed to the school closure policy and allowed their children to use smartphones to attend online school. Given the differences in the results, further scholarly discourse on smartphone use in online learning is essential.
Questions remain on whether embracing smartphones in learning systems facilitates or undermines learning (i.e., through distraction). Only a few studies have been conducted on the impacts of smartphone use on academic performance in elementary school students (mostly investigating college or high school students). Thus, we investigated the effects of elementary school students’ smartphone use on their academic performance.
2 Literature review
Mobile technologies have driven a paradigm shift in learning; learning activities can now be performed anytime, anywhere, as long as the opportunity to obtain information is available (Martin & Ertzberger, 2013 ).
Kim et al. ( 2014 ) focused on identifying factors that influence smartphone adoption or use. Grant and Hsu ( 2014 ) centered their investigation on user behavior, examining the role of smartphones as learning devices and social interaction tools. Although the contribution of smartphones to learning is evident, few studies have focused on the connection between smartphones and learning, especially in elementary school students. The relationship between factors related to learning with smartphones among this student population is examined in the following sections.
2.1 Behavioral intentions of elementary school students toward smartphone use
Children experience rapid growth and development during elementary school and cultivate various aspects of the human experience, including social skills formed through positive peer interactions. All these experiences exert a substantial impact on the establishment of self-esteem and a positive view of self. Furthermore, students tend to maintain social relationships by interacting with others through various synchronous or asynchronous technologies, including smartphone use (Guo et al., 2011 ). Moreover, students favor communication through instant messaging, in which responses are delivered rapidly. However, for this type of interaction, students must acquire knowledge and develop skills related to smartphones or related technologies which has an impact on social relationships (Kang & Jung, 2014 ; Park & Lee, 2012 ).
Karikoski and Soikkeli ( 2013 ) averred that smartphone use promotes human-to-human interaction both through verbal conversation and through the transmission of textual and graphic information, and cn stimulate the creation and reinforcement of social networks. Park and Lee ( 2012 ) examined the relationship between smartphone use and motivation, social relationships, and mental health. The found smartphone use to be positively correlated with social intimacy. Regarding evidence supporting smartphone use in learning, Firmansyah et al. ( 2020 ) concluded that smartphones significantly benefit student-centered learning, and they can be used in various disciplines and at all stages of education. They also noted the existence of a myriad smartphone applications to fulfill various learning needs. Clayton and Murphy ( 2016 ) suggested that smartphones be used as a mainstay in classroom teaching, and that rather than allowing them to distract from learning, educators should help their students to understand how smartphones can aid learning and facilitate civic participation. In other words, when used properly, smartphones have some features that can lead to better educational performance. For example, their mobility can allow students access to the same (internet-based) services as computers, anytime, anywhere (Lepp et al., 2014 ). Easy accessibility to these functionalities offers students the chance to continuously search for study-related information. Thus, smartphones can provide a multi-media platform to facilitate learning which cannot be replaced by simply reading a textbook (Zhang et al., 2014 ). Furthermore, social networking sites and communication applications may also contribute to the sharing of relevant information. Faster communication between students and between students and faculty may also contribute to more efficient studying and collaboration (Chen et al., 2015 ). College students are more likely to have access to smartphones than elementary school students. The surge in smartphone ownership among college students has spurred interest in studying the impact of smartphone use on all aspects of their lives, especially academic performance. For example, Junco and Cotton ( 2012 ) found that spending a fair amount of time on smartphones while studying had a negative affect on the university student's Grade Point Average (GPA). In addition, multiple studies have found that mobile phone use is inversely related to academic performance (Judd, 2014 ; Karpinski et al., 2013 ). Most research on smartphone use and academic performance has focused on college students. There have few studies focused on elementary school students. Vanderloo ( 2014 ) argued that the excessive use of smartphones may cause numerous problems for the growth and development of children, including increased sedentary time and reduced physical activity. Furthermore, according to Sarwar and Soomro ( 2013 ), rapid and easy access to information and its transmission may hinder concentration and discourage critical thinking and is therefore not conducive to children’s cognitive development.
To sum up, the evidence on the use of smartphones by elementary school students is conflicting. Some studies have demonstrated that smartphone use can help elementary school students build social relationships and maintain their mental health, and have presented findings supporting elementary students’ use of smartphones in their studies. Others have opposed smartphone use in this student population, contending that it can impede growth and development. To take steps towards resolving this conflict, we investigated smartphone use among elementary school students.
In a study conducted in South Korea, Kim ( 2017 ) reported that 50% of their questionnaire respondents reported using smartphones for the first time between grades 4 and 6. Overall, 61.3% of adolescents reported that they had first used smartphones when they were in elementary school. Wang et al. ( 2017 ) obtained similar results in an investigation conducted in Taiwan. However, elementary school students are less likely to have access to smartphones than college students. Some elementary schools in Taiwan prohibit their students from using smartphones in the classroom (although they can use them after school). On the basis of these findings, the present study focused on fifth and sixth graders.
Jeong et al. ( 2016 ), based on a sample of 944 respondents recruited from 20 elementary schools, found that people who use smartphones for accessing Social Network Services (SNS), playing games, and for entertainment were more likely to be addicted to smartphones. Park ( 2020 ) found that games were the most commonly used type of mobile application among participants, comprised of 595 elementary school students. Greater smartphone dependence was associated with greater use of educational applications, videos, and television programs (Park, 2020 ). Three studies in Taiwan showed the same results, that elementary school students in Taiwan enjoy playing games on smartphones (Wang & Cheng, 2019 ; Wang et al., 2017 ). Based on the above, it is reasonable to infer that if elementary school students spend more time playing games on their smartphones, their academic performance will decline. However, several studies have found that using smartphones to help with learning can effectively improve academic performance. In this study we make effort to determine what the key influential factors that affect students' academic performance are.
Kim ( 2017 ) reported that, in Korea, smartphones are used most frequentlyfrom 9 pm to 12 am, which closely overlaps the corresponding period in Taiwan, from 8 to 11 pm In this study, we not only asked students how they obtained their smartphones, but when they most frequently used their smartphones, and who they contacted most frequently on their smartphones were, among other questions. There were a total of eight questions addressing smartphone behavior. Recent research on smartphones and academic performance draws on self-reported survey data on hours and/or minutes of daily use (e.g. Chen et al., 2015 ; Heo & Lee, 2021 ; Lepp et al., 2014 ; Troll et al., 2021 ). Therefore, this study also uses self-reporting to investigate how much time students spend using smartphones.
Various studies have indicated that parental attitudes affect elementary school students’ behavioral intentions toward smartphone use (Chen et al., 2020 ; Daems et al., 2019 ). Bae ( 2015 ) determined that a democratic parenting style (characterized by warmth, supervision, and rational explanation) was related to a lower likelihood of smartphone addiction in children. Park ( 2020 ) suggested that parents should closely monitor their children’s smartphone use patterns and provide consistent discipline to ensure appropriate smartphone use. In a study conducted in Taiwan, Chang et al. ( 2019 ) indicated that restrictive parental mediation reduced the risk of smartphone addiction among children. In essence, parental attitudes critically influence the behavioral intention of elementary school students toward smartphone use. The effect of parental control on smartphone use is also investigated in this study.
Another important question related to student smartphone use is self-control. Jeong et al. ( 2016 ) found that those who have lower self-control and greater stress were more likely to be addicted to smartphones. Self-control is here defined as the ability to control oneself in the absence of any external force, trying to observe appropriate behavior without seeking immediate gratification and thinking about the future (Lee et al., 2015 ). Those with greater self-control focus on long-term results when making decisions. People are able to control their behavior through the conscious revision of automatic actions which is an important factor in retaining self-control in the mobile and on-line environments. Self-control plays an important role in smartphone addiction and the prevention thereof. Previous studies have revealed that the lower one’s self-control, the higher the degree of smartphone dependency (Jeong et al., 2016 ; Lee et al., 2013 ). In other words, those with higher levels of self-control are likely to have lower levels of smartphone addiction. Clearly, self-control is an important factor affecting smartphone usage behavior.
Reviewing the literature related to self-control, we start with self-determination theory (SDT). The SDT (Deci & Ryan, 2008 ) theory of human motivation distinguishes between autonomous and controlled types of behavior. Ryan and Deci ( 2000 ) suggested that some users engage in smartphone communications in response to perceived social pressures, meaning their behavior is externally motivated. However, they may also be intrinsically motivated in the sense that they voluntarily use their smartphones because they feel that mobile communication meets their needs (Reinecke et al., 2017 ). The most autonomous form of motivation is referred to as intrinsic motivation. Being intrinsically motivated means engaging in an activity for its own sake, because it appears interesting and enjoyable (Ryan & Deci, 2000 ). Acting due to social pressure represents an externally regulated behavior, which SDT classifies as the most controlled form of motivation (Ryan & Deci, 2000 ). Individuals engage in such behavior not for the sake of the behavior itself, but to achieve a separable outcome, for example, to avoid punishment or to be accepted and liked by others (Ryan & Deci, 2006 ). SDT presumes that controlled and autonomous motivations are not complementary, but “work against each other” (Deci et al., 1999 , p. 628). According to the theory, external rewards alter the perceived cause of action: Individuals no longer voluntarily engage in an activity because it meets their needs, but because they feel controlled (Deci et al., 1999 ). For media users, the temptation to communicate through the smartphone is often irresistible (Meier, 2017 ). Researchers who have examined the reasons why users have difficulty controlling media use have focused on their desire to experience need gratification, which produces pleasurable experiences. The assumption here is that users often subconsciously prefer short-term pleasure gains from media use to the pursuit of long-term goals (Du et al., 2018 ). Accordingly, self-control is very important. Self-control here refers to the motivation and ability to resist temptations (Hofmann et al., 2009 ). Dispositional self-control is a key moderator of yielding to temptation (Hofmann et al., 2009 ). Ryan and Deci ( 2006 ) suggested that people sometimes perform externally controlled behaviors unconsciously, that is, without applying self-control.
Sklar et al. ( 2017 ) described two types of self-control processes: proactive and reactive. They suggested that deficiencies in the resources needed to inhibit temptation impulses lead to failure of self-control. Even when impossible to avoid a temptation entirely, self-control can still be made easier if one avoids attending to the tempting stimulus. For example, young children instructed to actively avoid paying attention to a gift and other attention-drawing temptations are better able to resist the temptation than children who are just asked to focus on their task. Therefore, this study more closely investigates students' self-control abilities in relation to smartphone use asking the questions, ‘How did you obtain your smartphone?’ (to investigate proactivity), and ‘How much time do you spend on your smartphone in a day?’ (to investigate the effects of self-control).
Thus, the following hypotheses are advanced.
Hypothesis 1: Smartphone behavior varies with parental control.
Hypothesis 2: Smartphone behavior varies based on students' self-control.
2.2 Parental control, students' self-control and their effects on learning effectiveness and academic performance
Based on Hypothesis 1 and 2, we believe that we need to focus on two factors, parental control and student self-control and their impact on academic achievement. In East Asia, Confucianism is one of the most prevalent and influential cultural values which affect parent–child relations and parenting practice (Lee et al., 2016 ). In Taiwan, Confucianism shapes another feature of parenting practice: the strong emphasis on academic achievement. The parents’ zeal for their children’s education is characteristic of Taiwan, even in comparison to academic emphasis in other East Asian countries. Hau and Ho ( 2010 ) noted that, in Eastern Asian (Chinese) cultures, academic achievement does not depend on the students’ interests. Chinese students typically do not regard intelligence as fixed, but trainable through learning, which enables them to take a persistent rather than a helpless approach to schoolwork, and subsequently perform well. In Chinese culture, academic achievement has been traditionally regarded as the passport to social success and reputation, and a way to enhance the family's social status (Hau & Ho, 2010 ). Therefore, parents dedicate a large part of their family resources to their children's education, a practice that is still prevalent in Taiwan today (Hsieh, 2020 ). Parental control aimed at better academic achievement is exerted within the behavioral and psychological domains. For instance, Taiwan parents tightly schedule and control their children’s time, planning private tutoring after school and on weekends. Parental control thus refers to “parental intrusiveness, pressure, or domination, with the inverse being parental support of autonomy” (Grolnick & Pomerantz, 2009 ). There are two types of parental control: behavioral and psychological. Behavioral control, which includes parental regulation and monitoring over what children do (Steinberg et al., 1992 ), predict positive psychosocial outcomes for children. Outcomes include low externalizing problems, high academic achievement (Stice & Barrera, 1995 ), and low depression. In contrast, psychological control, which is exerted over the children’s psychological world, is known to be problematic (Stolz et al., 2005 ). Psychological control involves strategies such as guilt induction and love withdrawal (Steinberg et al., 1992 ) and is related with disregard for children’s emotional autonomy and needs (Steinberg et al., 1992 ). Therefore, it is very important to discuss the type of parental control.
Troll et al. ( 2021 ) suggested that it is not the objective amount of smartphone use but the effective handling of smartphones that helps students with higher trait self-control to fare better academically. Heo and Lee ( 2021 ) discussed the mediating effect of self-control. They found that self-control was partially mediated by those who were not at risk for smartphone addiction. That is to say, smartphone addiction could be managed by strengthening self-control to promote healthy use. In an earlier study Hsieh and Lin ( 2021 ), we collected 41 international journal papers involving 136,491students across 15 countries, for meta-analysis. We found that the average and majority of the correlations were both negative. The short conclusion here was that smartphone addiction /reliance may have had a negative impact on learning performance. Clearly, it is very important to investigate the effect of self-control on learning effectiveness with regard to academic performance.
2.3 Smartphone use and its effects on learning effectiveness and academic performance
The impact of new technologies on learning or academic performance has been investigated in the literature. Kates et al. ( 2018 ) conducted a meta-analysis of 39 studies published over a 10-year period (2007–2018) to examine potential relationships between smartphone use and academic achievement. The effect of smartphone use on learning outcomes can be summarized as follows: r = − 0.16 with a 95% confidence interval of − 0.20 to − 0.13. In other words, smartphone use and academic achievement were negatively correlated. Amez and Beart ( 2020 ) systematically reviewed the literature on smartphone use and academic performance, observing the predominance of empirical findings supporting a negative correlation. However, they advised caution in interpreting this result because this negative correlation was less often observed in studies analyzing data collected through paper-and-pencil questionnaires than in studies on data collected through online surveys. Furthermore, this correlation was less often noted in studies in which the analyses were based on self-reported grade point averages than in studies in which actual grades were used. Salvation ( 2017 ) revealed that the type of smartphone applications and the method of use determined students’ level of knowledge and overall grades. However, this impact was mediated by the amount of time spent using such applications; that is, when more time is spent on educational smartphone applications, the likelihood of enhancement in knowledge and academic performance is higher. This is because smartphones in this context are used as tools to obtain the information necessary for assignments and tests or examinations. Lin et al. ( 2021 ) provided robust evidence that smartphones can promote improvements in academic performance if used appropriately.
In summary, the findings of empirical investigations into the effects of smartphone use have been inconsistent—positive, negative, or none. Thus, we explore the correlation between elementary school students’ smartphone use and learning effectiveness with regard to academic performance through the following hypotheses:
Hypothesis 3: Smartphone use is associated with learning effectiveness with regard to academic performance.
Hypothesis 4: Differences in smartphone use correspond to differences in learning effectiveness with regard to academic performance.
Hypotheses 1 to 4 are aimed at understanding the mediating effect of smartphone behavior; see Fig. 1 . It is assumed that smartphone behavior is the mediating variable, parental control and self-control are independent variables, and academic performance is the dependent variable. We want to understand the mediation effect of this model.
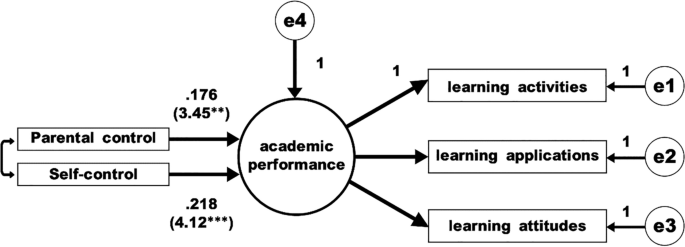
Model 1: Model to test the impact of parental control and students’ self-control on academic performance
Thus, the following hypotheses are presented.
Hypothesis 5: Smartphone behaviors are the mediating variable to impact the academic performance.
2.4 Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on smartphone use for online learning
According to 2020 statistics from the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, full or partial school closures have affected approximately 800 million learners worldwide, more than half of the global student population. Schools worldwide have been closed for 14 to 22 weeks on average, equivalent to two thirds of an academic year (UNESCO, 2021 ). Because of the pandemic, instructors have been compelled to transition to online teaching (Carrillo & Flores, 2020 ). According to Tang et al. ( 2020 ), online learning is among the most effective responses to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the effectiveness of online learning for young children is limited by their parents’ technological literacy in terms of their ability to navigate learning platforms and use the relevant resources. Parents’ time availability constitutes another constraint (Dong et al., 2020 ). Furthermore, a fast and stable Internet connection, as well as access to devices such as desktops, laptops, or tablet computers, definitively affects equity in online education. For example, in 2018, 14% of households in the United States lacked Internet access (Morgan, 2020 ). In addition, the availability and stability of network connections cannot be guaranteed in relatively remote areas, including some parts of Australia (Park et al., 2021 ). In Japan, more than 50% of 3-year-old children and 68% of 6-year-old children used the Internet in their studies, but only 21% of households in Thailand have computer equipment (Park et al., 2021 ).
In short, the COVID-19 pandemic has led to changes in educational practices. With advances in Internet technology and computer hardware, online education has become the norm amid. However, the process and effectiveness of learning in this context is affected by multiple factors. Aside from the parents’ financial ability, knowledge of educational concepts, and technological literacy, the availability of computer equipment and Internet connectivity also exert impacts. This is especially true for elementary school students, who rely on their parents in online learning more than do middle or high school students, because of their short attention spans and undeveloped computer skills. Therefore, this study focuses on the use of smartphones by elementary school students during the COVID-19 pandemic and its impact on learning effectiveness.
3.1 Participants
Participants were recruited through stratified random sampling. They comprised 499 Taiwanese elementary school students (in grades 5 and 6) who had used smartphones for at least 12 months. Specifically, the students advanced to grades 5 or 6 at the beginning of the 2018–2019 school year. Boys and girls accounted for 47.7% and 52.3% ( n = 238 and 261, respectively) of the sample.
3.2 Data collection and measurement
In 2020, a questionnaire survey was conducted to collect relevant data. Of the 620 questionnaires distributed, 575 (92.7%) completed questionnaires were returned. After 64 participants were excluded because they had not used their smartphones continually over the past 12 months and 14 participants were excluded for providing invalid responses, 499 individuals remained. The questionnaire was developed by one of the authors on the basis of a literature review. The questionnaire content can be categorized as follows: (1) students’ demographic characteristics, (2) smartphone use, (3) smartphone behavior, and (4) learning effectiveness. The questionnaire was modified according to evaluation feedback provided by six experts. Exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses were conducted to test the structural validity of the questionnaire. Factor analysis was performed using principal component analysis and oblique rotation. From the exploratory factor analysis, 25 items (15 and 10 items on smartphone behavior and academic performance as constructs, respectively) were extracted and confirmed. According to the results of the exploratory factor analysis, smartphone behavior can be classified into three dimensions: interpersonal communication, leisure and entertainment, and searching for information. Interpersonal communication is defined as when students use smartphones to communicate with classmates or friends, such as in response to questions like ‘I often use my smartphone to call or text my friends’. Leisure and entertainment mean that students spend a lot of their time using their smartphones for leisure and entertainment, e.g. ‘I often use my smartphone to listen to music’ or ‘I often play media games with my smartphone’. Searching for information means that students spend a lot of their time using their smartphones to search for information that will help them learn, such as in response to questions like this ‘I often use my smartphone to search for information online, such as looking up words in a dictionary’ or ‘I will use my smartphone to read e-books and newspapers online’.
Academic performance can be classified into three dimensions: learning activities, learning applications, and learning attitudes. Learning activities are when students use their smartphones to help them with learning, such as in response to a question like ‘I often use some online resources from my smartphone to help with my coursework’. Learning applications are defined as when students apply smartphone software to help them with their learning activities, e.g. ‘With a smartphone, I am more accustomed to using multimedia software’. Learning attitudes define the students’ attitudes toward using the smartphone, with questions like ‘Since I have had a smartphone, I often find class boring; using a smartphone is more fun’ (This is a reverse coded item). The factor analysis results are shown in the appendix (Appendix Tables 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 and 14 ). It can be seen that the KMO value is higher than 0.75, and the Bartlett’s test is also significant. The total variance explained for smartphone behavior is 53.47% and for academic performance it is 59.81%. These results demonstrate the validity of the research tool.
In this study, students were defined as "proactive" if they had asked their parents to buy a smartphone for their own use and "reactive" if their parents gave them a smartphone unsolicited (i.e. they had not asked for it). According to Heo and Lee ( 2021 ), students who proactively asked their parents to buy them a smartphone gave the assurance that they could control themselves and not become addicted, but if they had been given a smartphone (without having to ask for it), they did not need to offer their parents any such guarantees. They defined user addiction (meaning low self-control) as more than four hours of smartphone use per day (Peng et al., 2022 ).
A cross-tabulation of self-control results is presented in Table 2 , with the columns representing “proactive” and “reactive”, and the rows showing “high self-control” and “low self-control”. There are four variables in this cross-tabulation, “Proactive high self-control” (students promised parents they would not become smartphone addicts and were successful), “Proactive low self-control” (assured their parents they would not become smartphone addicts, but were unsuccessful), “Reactive high self-control”, and “Reactive low self-control”.
Regarding internal consistency among the constructs, the Cronbach's α values ranged from 0.850 to 0.884. According to the guidelines established by George and Mallery ( 2010 ), these values were acceptable because they exceeded 0.7. The overall Cronbach's α for the constructs was 0.922. The Cronbach's α value of the smartphone behavior construct was 0.850, whereas that of the academic performance construct was 0.884.
3.3 Data analysis
The participants’ demographic characteristics and smartphone use (expressed as frequencies and percentages) were subjected to a descriptive analysis. To examine hypotheses 1 and 2, an independent samples t test (for gender and grade) and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) were performed to test the differences in smartphone use and learning effectiveness with respect to academic performance among elementary school students under various background variables. To test hypothesis 3, Pearson’s correlation analysis was conducted to analyze the association between smartphone behavior and academic performance. To test hypothesis 4, one-way multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) was employed to examine differences in smartphone behavior and its impacts on learning effectiveness. To test Hypothesis 5, structural equation modeling (SEM) was used to test whether smartphone behavior is a mediator of academic performance.
4.1 Descriptive analysis
The descriptive analysis (Table 1 ) revealed that the parents of 71.1% of the participants ( n = 499) conditionally controlled their smartphone use. Moreover, 42.5% of the participants noted that they started using smartphones in grade 3 or 4. Notably, 43.3% reported that they used their parents’ old smartphones; in other words, almost half of the students used secondhand smartphones. Overall, 79% of the participants indicated that they most frequently used their smartphones after school. Regarding smartphone use on weekends, 54.1% and 44.1% used their smartphones during the daytime and nighttime, respectively. Family members and classmates (45.1% and 43.3%, respectively) were the people that the participants communicated with the most on their smartphones. Regarding bringing their smartphones to school, 53.1% of the participants indicated that they were most concerned about losing their phones. As for smartphone use duration, 28.3% of the participants indicated that they used their smartphones for less than 1 h a day, whereas 24.4% reported using them for 1 to 2 h a day.
4.2 Smartphone behavior varies with parental control and based on students' self-control
We used the question ‘How did you obtain your smartphone?’ (to investigate proactivity), and ‘How much time do you spend on your smartphone in a day?’ (to investigate the effects of students' self-control). According to the Hsieh and Lin ( 2021 ), and Peng et al. ( 2022 ), addition is defined more than 4 h a day are defined as smartphone addiction (meaning that students have low self-control).
Table 2 gives the cross-tabulation results for self-control ability. Students who asked their parents to buy a smartphone, but use it for less than 4 h a day are defined as having ‘Proactive high self-control’; students using a smartphone for more than 4 h a day are defined as having ‘Proactive low self-control’. Students whose parents gave them a smartphone but use them for less than 4 h a day are defined as having ‘Reactive high self-control’; students given smart phones and using them for more than 4 h a day are defined as having ‘Reactive low self-control’; others, we define as having moderate levels of self-control.
Tables 3 – 5 present the results of the t test and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) on differences in the smartphone behaviors based on parental control and students' self-control. As mentioned, smartphone behavior can be classified into three dimensions: interpersonal communication, leisure and entertainment, and information searches. Table 3 lists the significant independent variables in the first dimension of smartphone behavior based on parental control and students' self-control. Among the students using their smartphones for the purpose of communication, the proportion of parents enforcing no control over smartphone use was significantly higher than the proportions of parents enforcing strict or conditional control ( F = 11.828, p < 0.001). This indicates that the lack of parental control over smartphone use leads to the participants spending more time using their smartphones for interpersonal communication.
For the independent variable of self-control, regardless of whether students had proactive high self-control, proactive low self-control or reactive low self-control, significantly higher levels of interpersonal communication than reactive high self-control were reported ( F = 18.88, p < 0.001). This means that students effectively able to control themselves, who had not asked their parents to buy them smartphones, spent less time using their smartphones for interpersonal communication. However, students with high self-control but who had asked their parents to buy them smartphones, would spend more time on interpersonal communication (meaning that while they may not spend a lot of time on their smartphones each day, the time spent on interpersonal communication is no different than for the other groups). Those without effective self-control, regardless of whether they had actively asked their parents to buy them a smartphone or not, would spend more time using their smartphones for interpersonal communication.
Table 4 displays the independent variables (parental control and students' self-control) significant in the dimension of leisure and entertainment. Among the students using their smartphones for this purpose, the proportion of parents enforcing no control over smartphone use was significantly higher than the proportions of parents enforcing strict or conditional control ( F = 8.539, p < 0.001). This indicates that the lack of parental control over smartphone use leads to the participants spending more time using their smartphones for leisure and entertainment.
For the independent variable of self-control, students with proactive low self-control and reactive low self-control reported significantly higher use of smartphones for leisure and entertainment than did students with proactive high self-control and reactive high self-control ( F = 8.77, p < 0.001). This means that students who cannot control themselves, whether proactive or passive in terms of asking their parents to buy them a smartphone, will spend more time using their smartphones for leisure and entertainment.
Table 5 presents the significant independent variables in the dimension of information searching. Significant differences were observed only for gender, with a significantly higher proportion of girls using their smartphones to search for information ( t = − 3.979, p < 0.001). Parental control and students' self-control had no significance in the dimension of information searching. This means that the parents' attitudes towards control did not affect the students' use of smartphones for information searches. This is conceivable, as Asian parents generally discourage their children from using their smartphones for non-study related activities (such as entertainment or making friends), but not for learning-related activities. It is also worth noting that student self-control was not significant in relation to searching for information. This means that it makes no difference whether or not students have self-control in their search for learning-related information.
Four notable results are presented as follows.
First, a significantly higher proportion of girls used their smartphones to search for information. Second, if smartphone use was not subject to parental control, the participants spent more time using their smartphones for interpersonal communication and for leisure and entertainment rather than for information searches. This means that if parents make the effort to control their children's smartphone use, this will reduce their children's use of smartphones for interpersonal communication and entertainment. Third, student self-control affects smartphone use behavior for interpersonal communication and entertainment (but not searching for information). This does not mean that they spend more time on their smartphones in their daily lives, it means that they spend the most time interacting with people while using their smartphones (For example, they may only spend 2–3 h a day using their smartphone. During those 2–3 h, they spend more than 90% of their time interacting with people and only 10% doing other things), which is the fourth result.
These results support hypotheses 1 and 2.
4.3 Pearson’s correlation analysis of smartphone behavior and academic performance
Table 6 presents the results of Pearson’s correlation analysis of smartphone behavior and academic performance. Except for information searches and learning attitudes, all variables exhibited significant and positively correlations. In short, there was a positive correlation between smartphone behavior and academic performance. Thus, hypothesis 3 is supported.
4.4 Analysis of differences in the academic performance of students with different smartphone behaviors
Differences in smartphone behavior and its impacts on learning effectiveness with regard to academic performance were examined through. In step 1, cluster analysis was conducted to convert continuous variables into discrete variables. In step 2, a one-way MANOVA was performed to analyze differences in the academic performance of students with varying smartphone behavior. Regarding the cluster analysis results (Table 7 ), the value of the change in the Bayesian information criterion in the second cluster was − 271.954, indicating that it would be appropriate to group the data. Specifically, we assigned the participants into either the high smartphone use group or the low smartphone use group, comprised of 230 and 269 participants (46.1% and 53.9%), respectively.
The MANOVA was preceded by the Levene test for the equality of variance, which revealed nonsignificant results, F (6, 167,784.219) = 1.285, p > 0.05. Thus, we proceeded to use MANOVA to examine differences in the academic performance of students with differing smartphone behaviors (Table 8 ). Between-group differences in academic performance were significant, F (3, 495) = 44.083, p < 0.001, Λ = 0.789, η 2 = 0.211, power = 0.999. Subsequently, because academic performance consists of three dimensions, we performed univariate tests and an a posteriori comparison.
Table 9 presents the results of the univariate tests. Between-group differences in learning activities were significant, ( F [1, 497] = 40.8, p < 0.001, η 2 = 0.076, power = 0.999). Between-group differences in learning applications were also significant ( F [1, 497] = 117.98, p < 0.001, η 2 = 0.192, power = 0.999). Finally, differences between the groups in learning attitudes were significant ( F [1, 497] = 23.22, p < 0.001, η 2 = 0.045, power = 0.998). The a posteriori comparison demonstrated that the high smartphone use group significantly outperformed the low smartphone use group in all dependent variables with regard to academic performance. Thus, hypothesis 4 is supported.
4.5 Smartphone behavior as the mediating variable impacting academic performance
As suggested by Baron and Kenny ( 1986 ), smartphone behavior is a mediating variable affecting academic performance. We examined the impact through the following four-step process:
Step 1. The independent variable (parental control and students' self-control) must have a significant effect on the dependent variable (academic performance), as in model 1 (please see Fig. 1 ).
Step 2. The independent variable (parental control and students' self-control) must have a significant effect on the mediating variable (smartphone behaviors), as in model 2 (please see Fig. 2 ).
Step 3. When both the independent variable (parental control and student self-control) and the mediator (smartphone behavior) are used as predictors, the mediating variable (smartphone behavior) must have a significant effect on the dependent variable (academic performance), as in model 3 (please see Fig. 3 ).
Step 4. In model 3, the regression coefficient of the independent variables (parental control and student self-control) on the dependent variables must be less than in mode 1 or become insignificant.
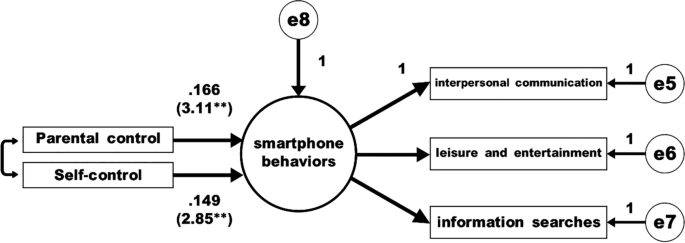
Model 2: Model to test the impact of parental control and students’ self-control on smartphone behavior
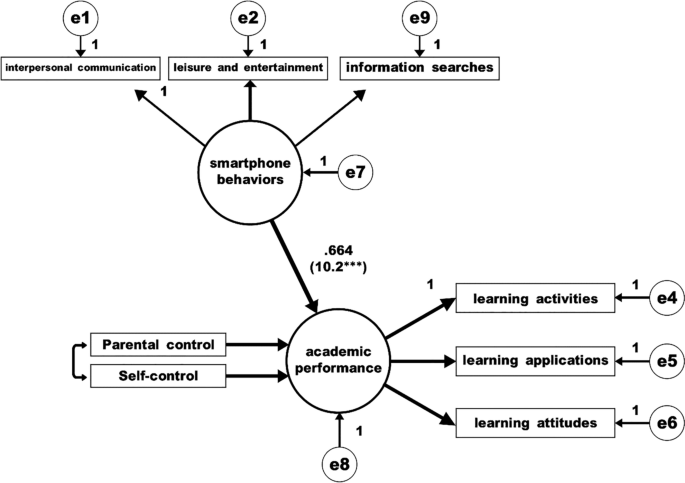
Model 3: Both independent variables (parental control and student self-control) and mediators (smartphone behavior) were used as predictors to predict dependent variables
As can be seen in Fig. 1 , parental control and student self-control are observed variables, and smartphone behavior is a latent variable. "Strict" is set to 0, which means "Conditional", with "None" compared to "Strict". “Proactive high self-control” is also set to 0. From Fig. 1 we find that the independent variables have a significant effect on the dependent variable. The regression coefficient of parental control is 0.176, t = 3.45 ( p < 0.01); the regression coefficient of students’ self-control is 0.218, t = 4.12 ( p < 0.001), proving the fit of the model (Chi Square = 13.96**, df = 4, GFI = 0.989, AGFI = 0.959, CFI = 0.996, TLI = 0.915, RMSEA = 0.051, SRMR = 0.031). Therefore, the test results for Model 1 are in line with the recommendations of Baron and Kenny ( 1986 ).
As can be seen in Fig. 2 , the independent variables have a significant effect on smartphone behaviors. The regression coefficient of parental control is 0.166, t = 3.11 ( p < 0.01); the regression coefficient of students’ self-control is 0.149, t = 2.85 ( p < 0.01). The coefficients of the model fit are: Chi Square = 15.10**, df = 4, GFI = 0.988, AGFI = 0.954, CFI = 0.973, TLI = 0.932, RMSEA = 0.052, SRMR = 0.039. Therefore, the results of the test of Model 2 are in line with the recommendations of Baron and Kenny ( 1986 ).
As can be seen in Fig. 3 , smartphone behaviors have a significant effect on the dependent variable. The regression coefficient is 0.664, t = 10.2 ( p < 0.001). The coefficients of the model fit are: Chi Square = 91.04**, df = 16, GFI = 0.958, AGFI = 0.905, CFI = 0.918, TLI = 0.900, RMSEA = 0.077, SRMR = 0.063. Therefore, the results of the test of Model 3 are in line with the recommendations of Baron and Kenny ( 1986 ).
As can be seen in Fig. 4 , the regression coefficient of the independent variables (parental control and student self-control) on the dependent variables is less than in model 1, and the parental control variable becomes insignificant. The regression coefficient of parental control is 0.013, t = 0.226 ( p > 0.05); the path coefficient of students’ self-control is 0.155, t = 3.07 ( p < 0.01).
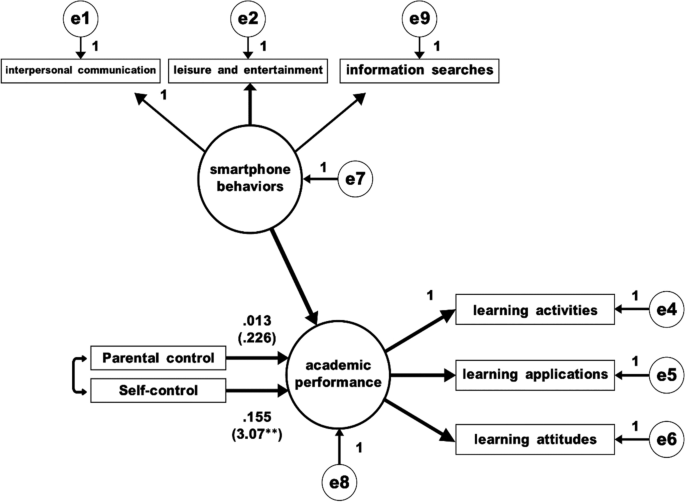
Model 4: Model three’s regression coefficient of the independent variables (parental control and student self-control) on the dependent variables
To sum up, we prove that smartphone behavior is the mediating variable to impact the academic performance. Thus, hypothesis 5 is supported.
5 Discussion
This study investigated differences in the smartphone behavior of fifth and sixth graders in Taiwan with different background variables (focus on parental control and students’ self-control) and their effects on academic performance. The correlation between smartphone behavior and academic performance was also examined. Although smartphones are being used in elementary school learning activities, relatively few studies have explored their effects on academic performance. In this study, the proportion of girls who used smartphones to search for information was significantly higher than that of boys. Past studies have been inconclusive about gender differences in smartphone use. Lee and Kim ( 2018 ) observed no gender differences in smartphone use, but did note that boys engaged in more smartphone use if their parents set fewer restrictions. Kim et al. ( 2019 ) found that boys exhibited higher levels of smartphone dependency than girls. By contrast, Kim ( 2017 ) reported that girls had higher levels of smartphone dependency than boys did. Most relevant studies have focused on smartphone dependency; comparatively little attention has been devoted to smartphone behavior. The present study contributes to the literature in this regard.
Notably, this study found that parental control affected smartphone use. If the participants’ parents imposed no restrictions, students spent more time on leisure and entertainment and on interpersonal communication rather than on information searches. This is conceivable, as Asian parents generally discourage their children from using their smartphones for non-study related activities (such as entertainment or making friends) but not for learning-related activities. If Asian parents believe that using a smartphone can improve their child's academic performance, they will encourage their child to use it. Parents in Taiwan attach great importance to their children's academic performance (Lee et al., 2016 ). A considerable amount of research has been conducted on parental attitudes or control in this context. Hwang and Jeong ( 2015 ) suggested that parental attitudes mediated their children’s smartphone use. Similarly, Chang et al. ( 2019 ) observed that parental attitudes mediated the smartphone use of children in Taiwan. Our results are consistent with extant evidence in this regard. Lee and Ogbolu ( 2018 ) demonstrated that the stronger children’s perception was of parental control over their smartphone use, the more frequently they used their smartphones. The study did not further explain the activities the children engaged in on their smartphones after they increased their frequency of use. In the present study, the participants spent more time on their smartphones for leisure and entertainment and for interpersonal communication than for information searches.
Notably, this study also found that students’ self-control affected smartphone use.
Regarding the Pearson’s correlation analysis of smartphone behavior and academic performance, except for information searches and learning attitudes, all the variables were significantly positively correlated. In other words, there was a positive correlation between smartphone behavior and academic performance. In their systematic review, Amez and Beart ( 2020 ) determined that most empirical results provided evidence of a negative correlation between smartphone behavior and academic performance, playing a more considerable role in that relationship than the theoretical mechanisms or empirical methods in the studies they examined. The discrepancy between our results and theirs can be explained by the between-study variations in the definitions of learning achievement or performance.
Regarding the present results on the differences in the academic performance of students with varying smartphone behaviors, we carried out a cluster analysis, dividing the participants into a high smartphone use group and a low smartphone use group. Subsequent MANOVA revealed that the high smartphone use group academically outperformed the low smartphone use group; significant differences were noted in the academic performance of students with different smartphone behaviors. Given the observed correlation between smartphone behavior and academic performance, this result is not unexpected. The findings on the relationship between smartphone behavior and academic performance can be applied to smartphone use in the context of education.
Finally, in a discussion of whether smartphone behavior is a mediator of academic performance, it is proved that smartphone behavior is the mediating variable impacting academic performance. Our findings show that parental control and students’ self-control can affect academic performance. However, the role of the mediating variable (smartphone use behavior) means that changes in parental control have no effect on academic achievement at all. This means that smartphone use behaviors have a full mediating effect on parental control. It is also found that students’ self-control has a partial mediating effect. Our findings suggest that parental attitudes towards the control of smartphone use and students' self-control do affect academic performance, but smartphone use behavior has a significant mediating effect on this. In other words, it is more important to understand the children's smartphone behavior than to control their smartphone usage. There have been many studies in the past exploring the mediator variables for smartphone use addiction and academic performance. For instance, Ahmed et al. ( 2020 ) found that the mediating variables of electronic word of mouth (eWOM) and attitude have a significant and positive influence in the relationship between smartphone functions. Cho and Lee ( 2017 ) found that parental attitude is the mediating variable for smartphone use addiction. Cho et al. ( 2017 ) indicated that stress had a significant influence on smartphone addiction, while self-control mediates that influence. In conclusion, the outcomes demonstrate that parental control and students’ self-control do influence student academic performance in primary school. Previous studies have offered mixed results as to whether smartphone usage has an adverse or affirmative influence on student academic performance. This study points out a new direction, thinking of smartphone use behavior as a mediator.
In brief, the participants spent more smartphone time on leisure and entertainment and interpersonal communication, but the academic performance of the high smartphone use group surpassed that of the low smartphone use group. This result may clarify the role of students’ communication skills in their smartphone use. As Kang and Jung ( 2014 ) noted, conventional communication methods have been largely replaced by mobile technologies. This suggests that students’ conventional communication skills are also shifting to accommodate smartphone use. Elementary students are relatively confident in communicating with others through smartphones; thus, they likely have greater self‐efficacy in this regard and in turn may be better able to improve their academic performance by leveraging mobile technologies. This premise requires verification through further research. Notably, high smartphone use suggests the greater availability of time and opportunity in this regard. Conversely, low smartphone use suggests the relative lack of such time and opportunity. The finding that the high smartphone use group academically outperformed the low smartphone use group also indicates that smartphone accessibility constitutes a potential inequality in the learning opportunities of elementary school students. Therefore, elementary school teachers must be aware of this issue, especially in view of the shift to online learning triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic, when many students are dependent on smartphones and computers for online learning.
6 Conclusions and implications
This study examined the relationship between smartphone behavior and academic performance for fifth and sixth graders in Taiwan. Various background variables (parental control and students’ self-control) were also considered. The findings provide new insights into student attitudes toward smartphone use and into the impacts of smartphone use on academic performance. Smartphone behavior and academic performance were correlated. The students in the high smartphone use group academically outperformed the low smartphone use group. This result indicates that smartphone use constitutes a potential inequality in elementary school students’ learning opportunities. This can be explained as follows: high smartphone use suggests that the participants had sufficient time and opportunity to access and use smartphones. Conversely, low smartphone use suggests that the participants did not have sufficient time and opportunity for this purpose. Students’ academic performance may be adversely affected by fewer opportunities for access. Disparities between their performance and that of their peers with ready access to smartphones may widen amid the prevalent class suspension and school closure during the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic.
This study has laid down the basic foundations for future studies concerning the influence of smartphones on student academic performance in primary school as the outcome variable. This model can be replicated and applied to other social science variables which can influence the academic performance of primary school students as the outcome variable. Moreover, the outcomes of this study can also provide guidelines to teachers, parents, and policymakers on how smartphones can be most effectively used to derive the maximum benefits in relation to academic performance in primary school as the outcome variable. Finally, the discussion of the mediating variable can also be used as the basis for the future projects.
7 Limitations and areas of future research
This research is significant in the field of smartphone functions and the student academic performance for primary school students. However, certain limitations remain. The small number of students sampled is the main problem in this study. For more generalized results, the sample data may be taken across countries within the region and increased in number (rather than limited to certain cities and countries). For more robust results, data might also be obtained from both rural and urban centers. In this study, only one mediating variable was incorporated, but in future studies, several other psychological and behavioral variables might be included for more comprehensive outcomes. We used the SEM-based multivariate approach which does not address the cause and effect between the variables, therefore, in future work, more robust models could be employed for cause-and-effect investigation amongst the variables.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Ahmed, R. R., Salman, F., Malik, S. A., Streimikiene, D., Soomro, R. H., & Pahi, M. H. (2020). Smartphone Use and Academic Performance of University Students: A Mediation and Moderation Analysis. Sustainability, 12 (1), 439. MDPI AG. Retrieved from https://doi.org/10.3390/su12010439
Amez, S., & Beart, S. (2020). Smartphone use and academic performance: A literature review. International Journal of Educational Research, 103 , 101618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2020.101618
Article Google Scholar
Anshari, M., Almunawar, M. N., Shahrill, M., Wicaksono, D. K., & Huda, M. (2017). Smartphones usage in the classrooms: Learning aid or interference? Education and Information Technologies, 22 , 3063–3079. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-017-9572-7
Bae, S. M. (2015). The relationships between perceived parenting style, learning motivation, friendship satisfaction, and the addictive use of smartphones with elementary school students of South Korea: Using multivariate latent growth modeling. School Psychology International, 36 (5), 513–531. https://doi.org/10.1177/0143034315604017
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator–mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51 (6), 1173–1182. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.51.6.1173
Bluestein, S. A., & Kim, T. (2017). Expectations and fulfillment of course engagement, gained skills, and non-academic usage of college students utilizing tablets in an undergraduate skills course. Education and Information Technologies, 22 (4), 1757–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-016-9515-8
Carrillo, C., & Flores, M. A. (2020). COVID-19 and teacher education: A literature review of online teaching and learning practices. European Journal of Teacher Education, 43 (4), 466–487. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2020.1821184
Chang, F. C., Chiu, C. H., Chen, P. H., Chiang, J. T., Miao, N. F., Chuang, H. T., & Liu, S. (2019). Children’s use of mobile devices, smartphone addiction and parental mediation in Taiwan. Computers in Human Behavior, 93 , 25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.11.048
Chen, R. S., & Ji, C. H. (2015). Investigating the relationship between thinking style and personal electronic device use and its implications for academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 52 , 177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.05.042
Chen, C., Chen, S., Wen, P., & Snow, C. E. (2020). Are screen devices soothing children or soothing parents?Investigating the relationships among children’s exposure to different types of screen media, parental efficacy and home literacy practices. Computers in Human Behavior, 112 , 106462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106462
Cheng, Y. M., Kuo, S. H., Lou, S. J., & Shih, R. C. (2016). The development and implementation of u-msg for college students’ English learning. International Journal of Distance Education Technologies, 14 (2), 17–29. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJDET.2016040102
Cho, K. S., & Lee, J. M. (2017). Influence of smartphone addiction proneness of young children on problematic behaviors and emotional intelligence: Mediating self-assessment effects of parents using smartphones. Computers in Human Behavior, 66 , 303–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.09.063
Cho, H.-Y., Kim, K. J., & Park, J. W. (2017). Stress and adult smartphone addiction: Mediation by self-control, neuroticism, and extraversion. Stress and Heath, 33 , 624–630. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.2749
Clayton, K., & Murphy, A. (2016). Smartphone apps in education: Students create videos to teach smartphone use as tool for learning. Journal of Media Literacy Education , 8 , 99–109. Retrieved October 13, 2021. Review from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1125609.pdf
Daems, K., Pelsmacker, P. D., & Moons, I. (2019). The effect of ad integration and interactivity on young teenagers’ memory, brand attitude and personal data sharing. Computers in Human Behavior, 99 , 245–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.05.031
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2008). Facilitating optimal motivation and psychological well-being across life’s domains. Canadian Psychology, 49 (1), 14–23. https://doi.org/10.1037/0708-5591.49.1.14
Deci, E. L., Koestner, R., & Ryan, R. M. (1999). A meta-analytic review of experiments examining the effects of extrinsic rewards on intrinsic motivation. Psychological Bulletin, 125 , 627–668. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-2909.125.6.627
Dong, C., Cao, S., & Li, H. (2020). Young children’s online learning during COVID-19 pandemic: Chinese parents’ beliefs and attitudes. Children and Youth Services Review, 118 , 105440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2020.105440
Du, J., van Koningsbruggen, G. M., & Kerkhof, P. (2018). A brief measure of social media self-control failure. Computers in Human Behavior, 84 , 68–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.02.002
Firmansyah, R. O., Hamdani, R. A., & Kuswardhana, D. (2020). IOP conference series: Materials science and engineering. The use of smartphone on learning activities: Systematic review . In International Symposium on Materials and Electrical Engineering 2019 (ISMEE 2019), Bandung, Indonesia. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/850/1/012006
Garbe, A., Ogurlu, U., Logan, N., & Cook, P. (2020). COVID-19 and remote learning: Experiences of parents with children during the pandemic. American Journal of Qualitative Research, 4 (3), 45–65. https://doi.org/10.29333/ajqr/8471
George, D., & Mallery, P. (2010). SPSS for windows step by step: A simple guide and reference. 17.0 update (10th ed.). Pearson.
Google Scholar
Grant, M., & Hsu, Y. C. (2014). Making personal and professional learning mobile: Blending mobile devices, social media, social networks, and mobile apps to support PLEs, PLNs, & ProLNs. Advances in Communications and Media Research Series, 10 , 27–46.
Grolnick, W. S., & Pomerantz, E. M. (2009). Issues and challenges in studying parental control: Toward a new conceptualization. Child Development Perspectives, 3 , 165–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-8606.2009.00099.x
Guo, Z., Lu, X., Li, Y., & Li, Y. (2011). A framework of students’ reasons for using CMC media in learning contexts: A structural approach. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 62 (11), 2182–2200. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.21631
Hadad, S., Meishar-Tal, H., & Blau, I. (2020). The parents’ tale: Why parents resist the educational use of smartphones at schools? Computers & Education, 157 , 103984. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2020.103984
Hau, K.-T., & Ho, I. T. (2010). Chinese students’ motivation and achievement. In M. H. Bond (Ed.), Oxford handbook of Chinese psychology (pp. 187–204). Oxford University Press.
Hawi, N. S., & Samaha, M. (2016). To excel or not to excel: Strong evidence on the adverse effect of smartphone addiction on academic performance. Computers & Education, 98 , 81–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.03.007
Heo, Y. J., & Lee, K. (2021). Smartphone addiction and school life adjustment among high school students: The mediating effect of self-control. Journal of Psychosocial Nursing and Mental Health Services, 56 (11), 28–36. https://doi.org/10.3928/02793695-20180503-06
Hofmann, W., Friese, M., & Strack, F. (2009). Impulse and self-control from a dual-systems perspective. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 4 (2), 162–176. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-6924.2009.01116.x
Hsieh, C. Y. (2020). Predictive analysis of instruction in science to students’ declining interest in science-An analysis of gifted students of sixth - and seventh-grade in Taiwan. International Journal of Engineering Education, 2 (1), 33–51. https://doi.org/10.14710/ijee.2.1.33-51
Hsieh, C. Y., Lin, C. H. (2021). Other important issues. Meta-analysis: the relationship between smartphone addiction and college students’ academic performance . 2021 TERA International Conference on Education. IN National Sun Yat-sen University (NSYSU), Kaohsiung.
Hwang, Y., & Jeong, S. H. (2015). Predictors of parental mediation regarding children’s smartphone use. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 18 (12), 737–743. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2015.0286
Jeong, S.-H., Kim, H. J., Yum, J.-Y., & Hwang, Y. (2016). What type of content are smartphone users addicted to? SNS vs. games. Computers in Human Behavior, 54 , 10–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2015.07.035
Judd, T. (2014). Making sense of multitasking: The role of facebook. Computers & Education, 70 , 194–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.08.013
Junco, R., & Cotton, S. R. (2012). No A 4 U: The relationship between multitasking and academic performance. Computers & Education, 59 , 505–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2011.12.023
Kang, S., & Jung, J. (2014). Mobile communication for human needs: A comparison of smartphone use between the US and Korea. Computers in Human Behavior, 35 , 376–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2014.03.024
Karikoski, J., & Soikkeli, T. (2013). Contextual usage patterns in smartphone communication services. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 17 (3), 491–502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00779-011-0503-0
Karpinski, A. C., Kirschner, P. A., Ozer, I., Mellott, J. A., & Ochwo, P. (2013). An exploration of social networking site use, multitasking, and academic performance among United States and European university students. Computers in Human Behavior, 29 , 1182–1192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.10.011
Kates, A. W., Wu, H., & Coryn, C. L. S. (2018). The effects of mobile phone use on academic performance: A meta-analysis. Computers & Education, 127 , 107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2018.08.012
Kim, K. (2017). Smartphone addiction and the current status of smartphone usage among Korean adolescents. Studies in Humanities and Social Sciences, 2017 (56), 115–142. https://doi.org/10.17939/hushss.2017.56.006
Kim, D., Chun, H., & Lee, H. (2014). Determining the factors that influence college students’ adoption of smartphones. Journal of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 65 (3), 578–588. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22987
Kim, B., Jahng, K. E., & Oh, H. (2019). The moderating effect of elementary school students’ perception of open communication with their parents in the relationship between smartphone dependency and school adjustment. Korean Journal of Childcare and Education, 15 (1), 54–73. https://doi.org/10.14698/jkcce.2019.15.01.057
Lee, J., & Cho, B. (2015). Effects of self-control and school adjustment on smartphone addiction among elementary school students. Korea Science, 11 (3), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.5392/IJoC.2015.11.3.001
Lee, E. J., & Kim, H. S. (2018). Gender differences in smartphone addiction behaviors associated with parent-child bonding, parent-child communication, and parental mediation among Korean elementary school students. Journal of Addictions Nursing, 29 (4), 244–254. https://doi.org/10.1097/JAN.0000000000000254
Lee, S. J., & Moon, H. J. (2013). Effects of self-Control, parent- adolescent communication, and school life satisfaction on smart-phone addiction for middle school students. Korean Journal of Human Ecology, 22 (6), 87–598. https://doi.org/10.5934/kjhe.2013.22.6.587
Lee, E. J., & Ogbolu, Y. (2018). Does parental control work with smartphone addiction? Journal of Addictions Nursing, 29 (2), 128–138. https://doi.org/10.1097/JAN.0000000000000222
Lee, J., Cho, B., Kim, Y., & Noh, J. (2015). Smartphone addiction in university students and its implication for learning. In G. Chen, V. K. Kinshuk, R. Huang, & S. C. Kong (Eds.), Emerging issues in smart learning (pp. 297–305). Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
Lee, S., Lee, K., Yi, S. H., Park, H. J., Hong, Y. J., & Cho, H. (2016). Effects of Parental Psychological Control on Child’s School Life: Mobile Phone Dependency as Mediator. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 25 , 407–418. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-015-0251-2
Lepp, A., Barkley, J. E., & Karpinski, A. C. (2014). The relationship between cell phone use, academic performance, anxiety, and satisfaction with life in college students. Computers in Human Behavior, 31 , 343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.10.049
Lin, Y. Q., Liu, Y., Fan, W. J., Tuunainen, V. K., & Deng, S. G. (2021). Revisiting the relationship between smartphone use and academic performance: A large-scale study. Computers in Human Behavior, 122 , 106835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2021.106835
Looi, C. K., Lim, K. F., Pang, J., Koh, A. L. H., Seow, P., Sun, D., Boticki, I., Norris, C., & Soloway, E. (2016). Bridging formal and informal learning with the use of mobile technology. In C. S. Chai, C. P. Lim, & C. M. Tan (Eds.), Future learning in primary schools (pp. 79–96). Springer.
Martin, F., & Ertzberger, J. (2013). Here and now mobile learning: An experimental study on the use of mobile technology. Computers & Education, 68 , 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.04.021
Meier, A. (2017). Neither pleasurable nor virtuous: Procrastination links smartphone habits and messenger checking behavior to decreased hedonic as well as eudaimonic well-being . Paper presented at the 67th Annual Conference of the International Communication Association (ICA), San Diego, CA.
Morgan, H. (2020). Best practices for implementing remote learning during a pandemic. The Clearing House: A Journal of Educational Strategies, Issues and Ideas, 93 (3), 135–141. https://doi.org/10.1080/00098655.2020.1751480
Park, J. H. (2020). Smartphone use patterns of smartphone-dependent children. Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing, 26 (1), 47–54. https://doi.org/10.4094/chnr.2020.26.1.47
Park, N., & Lee, H. (2012). Social implications of smartphone use: Korean college students’ smartphone use and psychological well-being. Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 15 (9), 491–497. https://doi.org/10.1089/cyber.2011.0580
Park, E., Logan, H., Zhang, L., Kamigaichi, N., & Kulapichitr, U. (2021). Responses to coronavirus pandemic in early childhood services across five countries in the Asia-Pacific region: OMEP Policy Forum. International Journal of Early Childhood, 2021 , 1–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13158-020-00278-0
Peng, Y., Zhou, H., Zhang, B., Mao, H., Hu, R., & Jiang, H. (2022). Perceived stress and mobile phone addiction among college students during the 2019 coronavirus disease: The mediating roles of rumination and the moderating role of self-control. Personality and Individual Differences, 185 , 111222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2021.111222
Reinecke, L., Aufenanger, S., Beutel, M. E., Dreier, M., Quiring, O., Stark, B., & Müller, K. W. (2017). Digital stress over the life span: The effects of communication load and Internet multitasking on perceived stress and psychological health impairments in a German probability sample. Media Psychology, 20 (1), 90–115. https://doi.org/10.1080/15213269.2015.1121832
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2000). Self-determination theory and the facilitation of intrinsic motivation, social development, and well-being. American Psychologist, 55 (1), 68–78. https://doi.org/10.1037//0003-066x.55.1.68
Ryan, R. M., & Deci, E. L. (2006). Self-regulation and the problem of human autonomy: Does psychology need choice, self-determination, and will? Journal of Personality, 74 , 1557–1585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-6494.2006.00420.x
Salvation, M. D. (2017). The relationship between smartphone applications usage and students’ academic performance. Computational Methods in Social Sciences , 5 (2), 26–39. Retrieved October 13, 2021. Review from http://cmss.univnt.ro/wp-content/uploads/vol/split/vol_V_issue_2/CMSS_vol_V_issue_2_art.003.pdf
Sarker, I. H., Kayes, A. S. M., & Watters, P. (2019). Effectiveness analysis of machine learning classification models for predicting personalized context-aware smartphone usage. Journal of Big Data, 6 , 57. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0219-y
Sarwar, M., & Soomro, T. R. (2013). Impact of smartphone’s on society. European Journal of Scientific Research, 98 (2), 219–226.
Sepulveda-Escobar, P., & Morrison, A. (2020). Online teaching placement during the COVID-19 pandemic in Chile: Challenges and opportunities. European Journal of Teacher Education, 43 (4), 587–607. https://doi.org/10.1080/02619768.2020.1820981
Sklar, A., Rim, S. Y. & Fujita, K. (2017). Proactive and reactive self-control. In D., de Ridder, M., Adriaanse, & K. Fujita (Eds). The Routledge International Handbook of Self-Control in Health and Well-Being (p. 11). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315648576
Steinberg, L., Lamborn, S. D., Dornbusch, S. M., & Darling, N. (1992). Impact of parenting practices on adolescent achievement: Authoritative parenting, school involvement, and encouragement to succeed. Child Development, 63 , 1266–1281. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1992.tb01694.x
Stice, E., & Barrera, M. (1995). A longitudinal examination of the reciprocal relations between perceived parenting and adolescents’ substance use and externalizing behaviors. Developmental Psychology, 31 , 322–334. https://doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.31.2.322
Stolz, H. E., Barber, B. K., & Olsen, J. A. (2005). Toward disentangling fathering and mothering: An assessment of relative importance. Journal of Marriage and Family, 67 , 1076–1092. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2005.00195.x
Tang, T., Abuhmaid, A. M., Olaimat, M., Oudat, D. M., Aldhaeebi, M., & Bamanger, E. (2020). Efficiency of flipped classroom with online-based teaching under COVID-19. Interactive Learning Environments . https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1817761
Troll, E. S., Friese, M., & Loschelder, D. D. (2021). How students’ self-control and smartphone-use explain their academic performance. Computers in Human Behavior, 117 , 106624. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106624
UNESCO. (2021). UNESCO figures show two thirds of an academic year lost on average worldwide due to Covid-19 school closures . Retrieved July 23, 2021. Retrieved, from https://en.unesco.org/news/unesco-figures-show-two-thirds-academic-year-lost-average-worldwide-due-covid-19-school
Vanderloo, L. M. (2014). Screen-viewing among preschoolers in childcare: A systematic review. BMC Pediatric, 14 , 205. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2431-14-205
Wang, T. H., & Cheng, H. Y. (2019). Problematic Internet use among elementary school students: Prevalence and risk factors. Information, Communication & Society, 24 (2), 108–134. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118X.2019.1645192
Wang, C. J., Chang, F. C., & Chiu, C. H. (2017). Smartphone addiction and related factors among elementary school students in New Taipei City. Research of Educational Communications and Technology, 117 , 67–87. https://doi.org/10.6137/RECT.201712_117.0005
Yi, Y. J., You, S., & Bae, B. J. (2016). The influence of smartphones on academic performance: The development of the technology-to-performance chain model. Library Hi Tech, 34 (3), 480–499. https://doi.org/10.1108/LHT-04-2016-0038
Zhang, M. W. B., Ho, C. S. H., & Ho, C. M. (2014). Methodology of development and students’ perceptions of a psychiatry educational smartphone application. Technology and Health Care, 22 , 847–855. https://doi.org/10.3233/THC-140861
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the school participants in the study.
The work done for this study was financially supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan under project No. MOST 109–2511-H-017–005.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Industry Technology Education, National Kaohsiung Normal University, 62, Shenjhong Rd., Yanchao District, Kaohsiung, 82446, Taiwan
Jen Chun Wang & Shih-Hao Kung
Department of Early Childhood Education, National PingTung University, No.4-18, Minsheng Rd., Pingtung City, Pingtung County, 900391, Taiwan
Chia-Yen Hsieh
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Kung and Wang conceived of the presented idea. Kung, Wang and Hsieh developed the theory and performed the computations. Kung and Hsieh verified the analytical methods. Wang encouraged Kung and Hsieh to verify the numerical checklist and supervised the findings of this work. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chia-Yen Hsieh .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1 Factor analysis results
Rights and permissions.
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Wang, J.C., Hsieh, CY. & Kung, SH. The impact of smartphone use on learning effectiveness: A case study of primary school students. Educ Inf Technol 28 , 6287–6320 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11430-9
Download citation
Received : 21 February 2022
Accepted : 24 October 2022
Published : 11 November 2022
Issue Date : June 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11430-9
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Smartphone use
- Learning effectiveness
- Human–computer interface
- Media in education
- Elementary education
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Smartphone Addiction among Students and its Harmful Effects on Mental Health, Oxidative Stress, and Neurodegeneration towards Future Modulation of Anti-Addiction Therapies: A Comprehensive Survey based on SLR, Research Questions, and Network Visualization Techniques
Affiliations.
- 1 School of Computer Science and Engineering, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, Chengdu, Sichuan 611731, China.
- 2 Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Jefferson College of Pharmacy, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA 19107, USA.
- 3 IoT Research Center, College of Computer Science and Software Engineering, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, Guangdong 518060, China.
- 4 School of Health Sciences, University of Management and Technology, Pakistan.
- 5 University Institute of Public Health, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, The University of Lahore, Pakistan.
- 6 Department of Public Health, North South University, Bashundhara, Dhaka 1229, Bangladesh.
- 7 Department of Information Technology, Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Bandung, Bandung, West Java 40235, Indonesia.
- 8 Department of Science and Engineering, Novel Global Community Educational Foundation, Hebersham, NSW 2770, Australia.
- 9 School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Hubei University, Wuhan 430011, China.
- 10 School of Informatics, Zhejiang Sci-Tech University, Hangzhou, Zhejiang 310018, China.
- 11 Institutes for Systems Genetics, Frontiers Science Center for Disease-related Molecular Network, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, China.
- 12 King Fahd Medical Research Center, King Abdulaziz University, Saudi Arabia.
- 13 Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Allied Health Sciences, Daffodil International University, Dhaka, Bangladesh.
- 14 Enzymoics, Novel Global Community Educational Foundation, NSW 2770, Australia.
- PMID: 35702800
- DOI: 10.2174/1871527321666220614121439
Background: Addiction is always harmful to the human body. Smartphone addiction also affects students' mental and physical health.
Aim: This study aims to determine the research volume conducted on students who are affected by smartphone addiction and design a database. We intended to highlight critical problems for future research. In addition, this paper enterprises a comprehensive and opinion-based image of smartphone-addicted students.
Methodology: We used two types of methods, such as systematic literature review and research questions based on the Scopus database to complete this study. We found 27 research articles and 11885 subjects (mean ±SD: 440.19 ± 513.58) using the PRISMA technique in this study. Additionally, we have deeply investigated evidence to retrieve the current understanding of smartphone addiction from physical changes, mental changes, behavioural changes, impact on performance, and significant concepts. Furthermore, the effect of this addiction has been linked to cancers, oxidative stress, and neurodegenerative disorders.
Results: This work has also revealed the future direction and research gap on smartphone addiction among students and has also tried to provide goals for upcoming research to be accomplished more significantly and scientifically.
Conclusion: This study suggests future analysis towards identifying novel molecules and pathways for the treatment and decreasing the severity of mobile addiction.
Keywords: Addiction; brain; education; electromagnetic field; health; mobile; nervous system; neurological disorders; oxidative stress; radiations; scopus; side effect; student; systematic literature review.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at [email protected].
Publication types
- Systematic Review
- Research Support, Non-U.S. Gov't
- Behavior, Addictive*
- Internet Addiction Disorder
- Mental Health*
- Oxidative Stress
ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Exploring the impact of smartphone addiction on decisionmaking behavior in college students: an fnirs study based on the iowa gambling task.

- Institute of Brain and Psychological Sciences, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China
The final, formatted version of the article will be published soon.
Select one of your emails
You have multiple emails registered with Frontiers:
Notify me on publication
Please enter your email address:
If you already have an account, please login
You don't have a Frontiers account ? You can register here
The pervasive use of smartphones, while enhancing accessibility to information and communication, has raised concerns about its potential negative effects on physical and mental health, including the impairment of decision-making abilities. This study investigates the influence of smartphone addiction on decision-making in college students. A sample of 80 individuals aged 17 to 26 was selected and divided into two groups based on their Smartphone Addiction Scale-Short Version (SAS-SV) scores. Participants underwent the Iowa Gambling Task (IGT) to evaluate their decision-making in risky and uncertain conditions, while fNIRS recorded their prefrontal cortex activity.The study found that individuals prone to smartphone addiction tend to make riskier choices in risky situations. However, when faced with decisions based on ambiguity, the smartphone addiction group showed increased brain activity in the dlPFC (specifically in channels 4, 9, and 11) compared to when making risky decisions. Despite this increased brain activation, there was no observable difference in behavior between the addiction-prone and control groups in ambiguous scenarios. Notably, the left dlPFC (e.g., channel 4) exhibited significantly higher activation in the addiction group compared to the control group. Findings suggest that smartphone addiction can detrimentally influence decision-making, behaviorally and neurologically, particularly in uncertain contexts. This study supports the classification of smartphone addiction as a genuine addiction and underscores its significance in psychiatric research.In essence, our research underscores the adverse effects of excessive smartphone use on decision-making processes, reinforcing the necessity to treat smartphone addiction as a pressing public health issue.
Keywords: Smartphone addiction, Decision Making, College student, IGT, fNIRS
Received: 22 Nov 2023; Accepted: 09 Apr 2024.
Copyright: © 2024 Liu, Tian, Bai, Liu, Li, Zhou and Lei. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) or licensor are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
* Correspondence: Xiaolong Liu, Institute of Brain and Psychological Sciences, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China Yi Lei, Institute of Brain and Psychological Sciences, Sichuan Normal University, Chengdu, Sichuan Province, China
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Smartphone Addiction Among the Young
More from our inbox:, cash still has a place in a digital world, i hear the birds, singing to me.

To the Editor:
Re “ The Smartphone Trap ,” by Jonathan Haidt and Jean M. Twenge (Opinion guest essay, Sunday Review, Aug. 1):
The rise of smartphone addiction among teenagers is undeniably real. However, the proposed solution of locking students’ phones up cold turkey (during school hours) may not be ideal.
My high school participated in a program that involved completely locking up students’ phones throughout the entire school day (in 2019-20). Through many conversations with my peers, I noticed that this solution — with the goal of helping students “practice the lost art of paying full attention to the people around them,” as your essay put it — produced unintended repercussions.
In fact, increased anxiety as a result of smartphone restriction often hindered students’ ability to fully engage with other students and teachers throughout the school day. Perhaps a smarter solution may include gradually weaning students off their smartphones, and increased education regarding responsible smartphone use.
Rushaad Mistry Foster City, Calif. The writer is a high school student.
Yes, face-to-face conversation among college students has declined during the time of smartphones. Fifteen years ago, I would enter a noisy college classroom to teach a class and have to draw the attention of the students, who were gabbing away with classmates. “It’s 9 o’clock; time to begin class,” I would say in a loud voice to end the student buzz.
Now I enter quiet college classrooms. The students are not speaking to each other; they have their faces buried in their cellphones. I urge them to keep their cellphones under wraps from the time that they enter the classroom and to speak to the students sitting near them. “The student sitting next to you might become your best friend, your spouse. The person might donate a kidney to you if you are in need.”
I try, but the allure of the smartphone usually triumphs.
James Tackach Narragansett, R.I. The writer is a professor of English at Roger Williams University.
Social media has many possible negative psychological and social effects. But perhaps the plunging happiness and self-esteem of teenage girls is due to another effect of smartphones: easy access to online pornography. Viewing degrading images of women in pornography can be traumatic, and the message is clear: Women are sex objects to be used for any purpose and disposed of at will.
The knowledge that the boys they know are using these images could lead to despair and cynicism among girls. The images may also encourage comparison of body type and a belief that being shaved and waxed as well as thin is necessary for attractiveness.
Anne Rettenberg San Rafael, Calif. The writer is a licensed clinical social worker.
Thank you for this all-important article. The issue of smartphones for children and teenagers does not receive the attention it needs; as your article points out, it is a serious threat to our youth.
The best practice of all is parental delay in adding full internet and social media to a young person’s phone, metering those out as the youth advances along the elementary, middle and high school years — along with weekly parental supervision of the phone.
Linda Bishop Jacksonville, Fla. The writer is a retired public-school teacher.
Re “ The United States Should Create a Digital Dollar ” (Opinion guest essay, July 26):
I couldn’t disagree more with Eswar Prasad’s views regarding the inevitable obsolescence of cash.
When power fails and towers topple (as in floods, fires, hurricanes and their aftermath), cash is king (“small bills, please”).
Mr. Prasad describes cash as being vulnerable to loss or theft. That is small change compared with what we’re seeing with digital currencies and credit card transactions.
He describes these transactions as only “relatively secure,” and while he acknowledges that electronic hacking “does pose a risk,” to say that it can be managed through more technology is a circular loop back to what makes digital transactions risky.
Bring on digital currency if you must. But leave cash in place for those of us who sensibly understand its place.
Kate Thurston Tardif Naples, Fla.
Eswar Prasad’s essay begins, “When was the last time you made a payment with dollar bills?”
The answer for me is about half an hour ago, when I bought The New York Times: $3 plus a dime, a penny and two nickels — the correct change for The Times and tax.
One morning I gave the clerk brand-new dollar bills that were stuck together, and I left the store. It was still dark. As I was about to get into my car, the clerk ran outside, calling to me, “You gave an extra dollar!”
How is digital currency going to show that kind of honesty, and from someone who may be living paycheck to paycheck?
Allen Berger Savannah, Ga.
Re “ Name That Songbird in One Click ,” by Margaret Renkl (Opinion guest essay, July 27):
The benefit of living alone as a near-nonagenarian is time for bird-watching. Thank you for reminding me of the songbird app. I look forward to knowing the identity of the avians cheering me on.
Joan May Maher Hudson, Ohio
Home — Essay Samples — Information Science and Technology — Technology in Education — Smartphone Addiction And Its Impact On A Student’S Life
Smartphone Addiction and Its Impact on a Student’s Life
- Categories: Smartphone Student Technology in Education
About this sample

Words: 632 |
Published: Apr 2, 2020
Words: 632 | Page: 1 | 4 min read
Table of contents
Physical and mental harm, social interaction, academic effect.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Information Science and Technology Education

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
5 pages / 2155 words
3 pages / 1182 words
3 pages / 1490 words
2 pages / 854 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Technology in Education
Education is a constantly evolving field, and one of the most significant drivers of change in recent years has been technology. As we enter the year 2023, the impact of technology on education is more profound than ever before. [...]
The global spread of the Internet has sparked concerns about its impact on general education and knowledge. Some worry that easy access to information may make people less intelligent, as they no longer need to engage in [...]
Technology is creeping into every aspect of our lives. From a simple smartphone that no one will leave home without, to the extremely advanced self-driving software evolving in the automobile industry, technology takes up a [...]
The education sector plays a crucial role in the growth and development of a country. Different nations employ various learning methods to ensure that students acquire the necessary skills in their chosen fields. In recent [...]
The author's passion for technology and the impact of technology on the world Interest in problem-solving and its connection to technology Pursuing a diploma course in technology after secondary school Work [...]
Nowadays, students start having cell phones to text friends and have fun but are these devices helpful, or a distraction in schools? Cell phones are an invention that starts a change in people’s lives, however, would it be [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Healthcare (Basel)

Adverse Effects of Smartphone Addiction among University Students in South Korea: A Systematic Review
Chiara achangwa.
1 Department of Public Health and Welfare, The Graduate School, Konyang University 709 Ho, Myeongkok Medical Building 158, Gwanjeodong-ro, Seo-gu, Daejeon 35365, Republic of Korea
Hyun Sik Ryu
2 Department of Emergency Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, 685 Gasuwon-Dong Seo-gu, Daejeon 35365, Republic of Korea
Jae Kwang Lee
Ju-dong jang, associated data.
This is an evidence synthesis study all articles used in this systematic review are available online from primary studies.
Background: Globally there has been an exponential increase in the penetration of smartphones among the youth population and smartphones have become indispensable in the daily lives of university students in South Korea. Several studies have associated the problematic use of smartphones or addiction with different adverse outcomes. The goal of this study was to collate empirical evidence and provides an overall synthesis of the literature about the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in South Korea. Method: We carried out a systematic review of the published literature between August and October 2022 on the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in South Korea, published between 2012 and 2022 in Pubmed/Medline, PsycInfo, Embase, Biomed-Central, Web of Science, Directory of Open Access Journals, Elsevier’s collection, Wiley Online Library, SpringerLink, Sage Journal’s collection and Cochrane Library. Results: Thirty-four articles published between 2012 and 2022 were included in the synthesis of this review. Eight studies explored the association between smartphone addiction and the psychological and mental health of university students in Korea. Smartphone addiction was associated with physical health leading to sleep disorders and musculoskeletal and neurological problems. Academic performance, procrastination, impulsivity, self-esteem, reduced social interaction, solitude, and suicide were also negatively associated with smartphone addiction. Conclusions: Our study adds to the literature regarding the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in Korea and provides more information for addiction prevention and health promotion activities.
1. Background
Globally the use of smartphones has exponentially increased becoming an inherent part of many individuals’ daily lives and has also introduced various changes in our daily activities and habits [ 1 ]. This exponential increase is because, in addition to the phone and text services provided by conventional mobile phones, smartphones contain new technology that provides an interface to make real-time broadcasts, access to a wide range of contents, and send/receive emails [ 2 ].
As of 2019, the global smartphone penetration was reported to be approximately 41.5% of the global population [ 3 ]. In 2014, the number of smartphone users in South Korea was reported to be 39 million. However, currently, the number of smartphone users is estimated to be around 53.5 million, accounting for 97% of the Korean population. Among this population, it is reported that individuals between the ages of 20–30 years have a 100% penetration rate [ 4 ]. Due to this increase in the smartphone penetration rate in the population, research shows that excessive smartphone use is problematic [ 5 , 6 , 7 , 8 , 9 , 10 ]. In the literature, the terms “problematic mobile or smartphone use” [ 11 ], “Smartphone addiction” [ 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 ] “smartphone dependence” [ 16 , 17 , 18 ], and “smartphone overuse” [ 8 , 19 ], have all been used interchangeably to express more or less the same phenomenon, which is, an individual’s inability to regulate their use of the smartphone, resulting in negative consequences in daily life.
In addition, due to the multifaceted nature of smartphone addiction, its definition still remains controversial [ 20 , 21 , 22 ]. However, according to Lee et al., smartphone addiction is a disorder involving the compulsive pathological overuse of smartphone devices. Because smartphone devices are used to access and use the internet, the term internet addiction has also been used to express some form of smartphone addiction [ 21 ]. According to Ismail et al., smartphone addiction does not differ from internet addiction in that they share common pathological manifestations [ 23 ]. Nevertheless, the standard cut-off point for determining when smartphone use has become an addiction is yet to be determined.
Smartphone addiction could be facilitated by easy access to the internet, and other popular social media apps such as Facebook, YouTube, Instagram, Twitter and other platforms that are not only designed in ways that increase the amount of time people spend on them but also monetize activities on the apps resulting in the continuous need to be online which has led to a new syndrome known as “Fear of Missing Out (FoMO)”. FoMO refers to a state in which individuals spend much of their time on social media with the fear of missing out on the latest information in social networks [ 24 ]. This desire to always be online and be up to date with information and communication has resulted in nomophobia which is defined as “the fear of lacking communication, not having contact with the mobile phone or an uncontrollable fear of leaving home without a phone [ 25 ]. This has been reported to have various health and cognitive implications [ 20 ]. Even though, some studies suggest a direct relationship between smartphone addiction and nomophobia, the relationship between them is not very clear [ 26 ]. Moreover, there are existing debates as to whether “smartphone addiction” ought to be determined based on quantity, patterns of use, or by the negative consequences of its use [ 27 , 28 , 29 ].
Attempts have been made to explain the several routes to smartphone addiction including the ability to regulate self-control and emotions, impulsivity, self-esteem, neuroticism, and distorted thinking [ 30 , 31 , 32 ]. However, based on different demographics (gender, age, socio-economic status) and personality (introvert/extrovert) characteristics individuals, have different triggers that make them use their smartphones in a problematic way [ 33 , 34 ].
University students are in the age group most interested in possessing smartphones for many different reasons [ 35 ]. They use smartphones for a variety of activities such as studying, entertaining, accessing the internet or social networks, and social communication [ 32 ]. Despite the many benefits of smartphone use, empirical research suggests that individuals are addicted to or overly dependent on smartphones, resulting in negative consequences affecting their health [ 20 ], safety [ 36 , 37 , 38 ], and daily lives [ 25 ]. The empirical literature suggests that there exist direct and indirect associations between smartphone addiction and health, and other related issues among university students in Korea [ 39 ].
After a thorough review of previous studies on smartphone addiction among university students in Korea, several issues were identified. First, there were varying reports on the negative outcomes of smartphone addiction among university students. Second, the use of different tools to evaluate smartphone addiction and its effects among university students. The literature also revealed that there is no consensus among these studies regarding the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in South Korea.
Therefore, this systematic review aimed to provide an overall synthesis of the literature regarding the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in South Korea.
We conducted a systematic review of already published literature from 1 January 2012 to 1 October 2022. Article collection and synthesis were done following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) guidelines ( Figure 1 ) [ 40 ].

PRISMA Flow diagram showing the selection of review articles.
We searched articles from major databases including Pubmed/Medline, PsycInfo, Embase, Biomed-Central, Web of Science, Directory of Open Access Journals, Elsevier’s collection, Wiley Online Library, SpringerLink, Sage Journal’s collection, and Cochrane Library. In addition, we collected additional articles from the secondary references of included studies. The databases were searched between August and October 2022. Articles were included if they were original articles with full introductions, methods, results, and discussion sections, published in a peer-reviewed journal between 2012–2022, and focused on the effect of smartphone overuse or addiction on university students in Korea. Published articles in two different languages were used: English and Korean languages (languages in which the authors are proficient). Studies were excluded if they only examined internet addiction but not in the context of smartphone use, articles focusing on the positive effects of smartphones, and if they were reviews, editorials, conference proceedings, dissertations, or commentaries without primary data or peer review. A set of search terms were created with truncations, Medical Subject Headings (MESH), and Boolean operators, as shown in Table 1 . These terms were also used in Korean, to search for articles that were published in the Korean language.
Search terms and linkage for the study.
The titles and abstracts of all included articles were reviewed independently by two authors (A.C., J.K.L.) against the above inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inter-rater reliability was calculated using Cohen’s Kappa. The full papers of all studies included after abstract screening were retrieved and reviewed for a second time based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria by the same two authors (A.C., J.K.L.). Disputes at either stage were resolved through discussion, with 2 other authors (H.S.R., J-N.J.) where necessary, until consensus was reached.
3.1. Study Characteristics
At the end of the article search from the databases, a total of 583 potential studies were identified. The final sample consisted of 34 articles. Inter-rater reliability at the screening phase was κ = 0.91 (95% CI 0.88–0.94), representing a good alignment. All studies took place primarily in South Korea with the study participants recruited from a range of universities. Smartphone addiction was directly or indirectly negatively associated with different outcomes. A heterogenous use of different tools, methods, and smartphone addiction scales was noted across the included studies. The Smartphone Addiction Scale was used in four of the studies, and the Smartphone Addiction Proneness Scale (SAPS) in two of the included studies. The remaining 28 studies each used different tools and measures.
3.2. Main Findings
3.2.1. psychological and mental health.
Smartphone addiction was reported to impact the psychological and mental health of university students in 11 studies conducted in Korea. In a study by Kim et al., students who reported poor health were significantly associated with smartphone addiction (Odds ratio (OR) = 1.98; 95% CI = 1.22–3.21). In addition, the study showed that the students with stress-related symptoms were significantly associated with smartphone addiction, depicting an approximately twofold increased risk compared to those without these symptoms [ 8 ]. Another similar study revealed that university students with smartphone addiction had higher psychiatric symptom scores compared to their counterparts with no addiction [ 41 ]. Smartphone addiction was mostly associated with anxiety and depression which are components of mental health [ 8 , 12 , 13 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 ].
3.2.2. Physical Health
Poor sleep quality.
Ten studies reported that smartphone addiction was associated with poor sleep quality in university students in South Korea. Choi et al. noted that high mobile phone addiction was correlated with poor sleep quality [ 46 ]. Another study reported that higher levels of smartphone addiction and stress were associated with lower sleep quality [ 47 ]. In addition, Kwon et al., also reported that attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms were positively correlated with smartphone addiction ( p < 0.01) and poor sleep quality ( p < 0.01) [ 9 ]. The risk of sleep problems was shown to increase in the addiction proneness groups (OR = 1.99; 95% CI: 1.33–2.98) than in the normal-user groups [ 48 ]. Many other studies reported a correlation between smartphone addiction and the quality of sleep among university students in South Korea [ 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 ].
Musculoskeletal and Neurological Problems
The extensive use of smartphones is reported to be associated with physical health–related problems, including pain in the shoulders, back, neck, legs, and wrists. According to Kim et al., back pain was found to be positively correlated with the size of the smartphone’s liquid crystal display (LCD) screen, and pain in legs and feet was found to have a negative correlation with the length of time that the smartphone was used [ 54 ]. According to a study by Paek, smartphone overuse was positively associated with dry eye syndrome ( p < 0.001), neck pain ( p < 0.05), and hand pain ( p < 0.05) [ 55 ]. In addition, uncontrollable use of smartphones for long periods exposes hands to intense stresses that may lead to pain and musculoskeletal disorders of the neck, hand, and thumb [ 56 ]. Because of the nature of smartphones, individuals usually hold the device with a single hand, which forces only the thumb to use the keys resulting in pain [ 57 ].
Two studies reported on the association between smartphone addiction and accidents. According to a study by Kwon et al., out of the 441 students who participated in the study, 57.9% experienced accidents or near misses when using smartphones while walking [ 58 ]. Another study by Kim et al., reported that compared with normal users, participants who were addicted to smartphones were more likely to experience accidents (OR = 1.90, 95% CI: 1.26–2.86), falling from height/slipping (OR = 2.08, 95% CI: 1.10–3.91), and bumps/collisions (OR = 1.83, 95% CI: 1.16–2.87) [ 15 ].
3.2.3. Effect on Academic Performance
While some studies in the literature reported that smartphone addiction had a negative effect on the academic performance of university students, others reported no effect. Winskel et al., reported that there were no significant correlations found between problematic smartphone addiction and grade point average (GPA) scores [ 59 ]. Han et al. used different models to show how smartphone addiction and college students’ behavioral intention influences academic performances by study subjects [ 60 ]. Lee and Lee found that an increase in the daily total smart device use time negatively affected students’ GPA [ 61 ]. It was also found that students with smartphone addiction were constantly interrupted by applications on their phones when they are studying and do not have enough control over their smartphone learning plan and its process [ 2 ].
3.2.4. Procrastination and Impulsivity
There was also a direct relationship between impulsivity and smartphone addiction [ 62 ]. In addition, university students with ADHD symptoms had difficulties coping with repeated cycles of negative thoughts and worries, irregular lifestyles due to poor time management, dissatisfaction with academic performance and interpersonal relationships, self-dissatisfaction, and decreased self-esteem [ 63 ].
3.2.5. Self-Esteem, Reduced Social Interaction, Solitude, and Suicide
Several studies have outlined the impact of smartphone addiction on various levels of human interactions and relationships [ 64 , 65 , 66 , 67 ]. The smartphone addiction and human relationship health results were negatively correlated ( p = 0.011). However, communication ability and human relationship health results were positively correlated ( p < 0.001) [ 68 ]. Smartphone addiction was negatively associated with interpersonal relationships [ 69 , 70 ]. Jeong et al. reported an association between internet, gaming, or smartphone addiction and suicidal ideation [ 71 ]. A summary of all the included studies is found in Table 2 .
Summary table of the studies included in the systematic review.
Note: Study details include the study design and objective of the study.
4. Discussion
The main aim of this systematic review was to identify and provide an overall synthesis of literature regarding the adverse effects of smartphone addiction on university students in South Korea. To the best of our knowledge, this present review is the first review that collates all the adverse outcomes of smartphone addiction among university students in Korea. In the past decade, smartphone penetration has greatly increased among youth groups, especially among university students, and the problem of addiction is a serious rising public health problem. Therefore, our review provides a timely and comprehensive evidence base for designing corresponding intervention measures to inform and address the adverse outcomes of smartphone addiction among university students in South Korea.
Previous literature highlighted existing discrepancies in smartphone addictive use by gender [ 46 ], the field of study [ 13 ], and level of education [ 8 ] among university students in South Korea. The main differences in these groups are the patterns of use, motivations, or purposes. However, a mixed-approach investigation including both quantitative and qualitative methods is recommended to provide a comprehensive understanding of all the facets of smartphone addiction and its impact on university students in Korea.
Throughout the reviewed literature, smartphone addiction was consistently associated with decreased psychological and mental health including stress, anxiety, and depression in university students in Korea. Due to the exponential increase in smartphone penetration rate among university students, the incidence of mental health conditions has also increased representing a significant burden on the healthcare system and a growing public health problem that should be of great concern not only to policymakers in Korea but the parents as well.
This was similar to studies in different countries, which have stated an increase in the incidence of smartphone addiction associated with mental health issues [ 69 , 70 , 71 ]. Studies have also shown that compared to the older population, younger populations are more vulnerable to developing mental conditions and harmful long-lasting behaviors and addictions which can shape their subsequent life course [ 72 ]. Therefore, policies should be developed to address and prevent the possible long-term harmful impact of smartphone addiction on future generations’ mental health and well-being.
Another aspect of concern was the impact of smartphone addiction on physical health including musculoskeletal and neurological problems, accidents, and sleep quality among university students in Korea. The poor sleep quality, reduced sleep duration, and more frequent disturbances reported could be a result of the use of different interactive apps including various social media, and gaming apps [ 73 ]. In line with these findings, smartphone addiction has also been reported to be associated with physical health in university students in different countries [ 74 , 75 ].
While empirical literature reports some positive impacts of smartphone use among students, its overuse has been reported to have a direct negative effect on academic performance. In this review, smartphone addiction was negatively associated with educational outcomes among university students implying that the greater the use of smartphones while studying, the greater the negative impact on learning. Kim et al., [ 15 ] reported that students had difficulty controlling how and when to use their smartphones, impacting their study times. To address this rising phenomenon, policymakers need to implement various cognitive-behavioral therapies, and interventions, among university students. In addition, due to the high penetration rate of smartphones among university students, educators should implement guidelines to identify the times when smartphones can or cannot be used by students in higher institutions and could also implement their use to support the curriculum [ 76 ].
Consistent with other studies [ 77 , 78 ], we found that smartphone addiction had an impact on the level of social interaction of university students. These students even in the physical presence of their friends and/or family have a strong desire to use their smartphones, and most often results in a lack of focus, engagement, and real-time involvement with their counterpart which consequently plays a negative role in interpersonal communications and connections, thereby causing considerable negative effects on relationships and social interactions [ 79 , 80 ]. In addition, during the COVID-19 period and due to the prolonged lockdown period, most lectures were switched from face-to-face to online lectures in which some students use their smartphones as well as other smart devices. This resulted in university students spending time away from their peers and educators, leading to solitude and reduced social interaction.
It is worth noting that, in this review, the reported adverse effects (depression, procrastination, health problems, self-esteem problems) found in the current study could be symptoms or antecedents of smartphone addiction rather than the consequences. For example, smartphones can act as a refuge for individuals already presenting symptoms of the above adverse effects. As such, they may be a medium that amplifies these symptoms rather than causes them. Similar outcomes have been observed in students’ social media usage where social media was not the cause of depression but rather depression was a contributing factor to social media usage [ 81 ].
Another significant direction that could be worthy of note is the impact of parenting on how students use their smartphones. Previous research in Korea has shown that, some parents to relieve themselves of parental emotional and physical exhaustion, expose their children very young to the use of smartphones [ 82 ]. Additionally, due to physical and mental immaturity, these children cannot regulate their use times and ways of use growing to be dependent on their smartphones, taking this same problematic behavior to the university [ 83 ]. However, further detailed research using a causal study design is required to properly investigate the effect of parenting on the development of smartphone addiction among university students in South Korea.
The major strength of this review is that it provides a comprehensive synthesis of the adverse effects of smartphone phone addiction among university students in South Korea. However, the authors of this study observed some limitations in the studies included in this review. Firstly, the studies used in this review all used cross-sectional data and conducted either a correlational synthesis or linear or logistic regression analyses, hence the results cannot be given a causal interpretation. To advance empirical knowledge in the literature, well-designed longitudinal and interventional research is essential for addressing the adverse effects of smartphone addiction among university students. Secondly, for all the adverse effects recorded in this study, there was a lack of research investigating theoretical mechanisms of how smartphone addiction causes these effects. Providing more detailed information on the mechanisms at work could be important in the design of policy. To implement effective and reliable policy measures concerning smartphone addiction among university students, it will be helpful to know what precisely causes the relationship between smartphone addiction and its adverse effects. Thirdly, our focus was mainly on university students limiting the application of these findings to other populations. We recommend that future research should carry out longitudinal studies to investigate the detailed relationship between smartphone addiction and different adverse outcomes.
5. Conclusions
This review shows that university students in South Korea are at risk of addiction to smartphone use. Despite heterogeneity in the reviewed studies, the studies suggest poor physical health, psychological and mental health, poor academic performance, procrastination and impulsivity, reduced social interaction, solitude, and suicide are the most observed adverse effects of smartphone addiction among university students in South Korea. These findings from this review suggest the need for larger studies that will explore different dimensions (parental, personal, institutional, and social) of smartphone addiction among university students in South Korea. This review provides significant information to parents, educators, and policymakers.
Acknowledgments
C.A. is a recipient of a Ph.D. Scholarship from the Korean Government Scholarship Program (KGSP) 2019.
Funding Statement
This research received no funding.
Author Contributions
C.A. and J.-D.J. conceptualized the study. H.S.R. and J.K.L. were involved in the search and synthesis of the articles used in this study. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Smartphone addiction has negative impacts on student learning and overall academic performance. •. The greater the use of a phone while studying, the greater the negative impact on learning. •. The skills and cognitive abilities students needed for academic success are negatively affected by excessive phone use. •.
A good sense of self-control moderated the relationship between personal growth initiative and the risk of smartphone addiction, thereby reducing the risk of smartphone addiction; this is also consistent with the results of the study of 571 college students: smartphone addiction has a negative impact on individual self-control and further leads ...
Besides the direct effect smartphone use might have on both time spent and productivity for academic-related activities, smartphone use can have an additional indirect impact on educational performance by influencing students' health. ... Depression, anxiety and smartphone addiction in university students—A cross sectional study. PloS One ...
The high use of mobile phones by young people has been predominant among female users, as a way to keep interpersonal relations, as highlighted by De-Sola et al. (2016), who also declared its use is linked to personality traits like neurosis, extroversion, impulsiveness, self-esteem, self-image and identity.
The results show that smartphone addiction negatively impacts students' learning and overall academic performance (Q (43) = 711.87, p < .001, r = −0.12). Further, findings suggest that the ...
This study investigated the effects of smartphone use on the perceived academic performance of elementary school students. Following the derivation of four hypotheses from the literature, descriptive analysis, t testing, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Pearson correlation analysis, and one-way multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA) were performed to characterize the relationship between smartphone ...
performance, this study would provide more in-depth sight on the impacts that a smartphone could have on a student's academic performance. 1.3 Research Objective: The purpose of this study is therefore to test this framework and identify the relationship and linkages between Smartphone addiction, Smartphone self-efficacy, behavioral intention and
1.1. Smartphone Addiction Prevalence Rates, Predictors and Negative Impacts among University Students. Smartphone addiction can be defined as "the inability to control the smartphone use despite negative effects on users" [].Some studies exploring the prevalence of smartphone addiction among university students have found high percentages [16,17,18,19,20,21].
The high levels of addiction to smartphones prove that it affects students' academic performance (Kibona & Mgaya, 2015). This addiction causes some concerns as ... (Ezemenaka, 2013). All these effects usually develop when students find themselves without their cell phones. Ebiye (2015) listed the rudimentary utilities of smartphones, which ...
Negi and Godiyal (2016) observed HNBUG-SRT college students while walking around the campus, along with a questionnaire and found 64 % of students used mobile phones in the campus. A randomized sample of 100 students was collected. The survey showed that there were negative psychological effects of smartphone usage on the young generation.
Abstract. Background: Smartphones play a critical role in increasing human-machine interactions, with many advantages. However, the growing popularity of smartphone use has led to smartphone overuse and addiction. This review aims to systematically investigate the impact of smartphone addiction on health outcomes.
Hence, the current study adds to the body of literature by examining students' smartphone addiction, failures of self-regulation, mind wandering, the causes of this tendency, and projections of how this process may relate to cognitive failures, which in turn may have an adverse effect on student's satisfaction with their academic lives ...
Mobile phone addiction tendency total score of between group (experimental group and control group), within group (experimental time), and interaction effect (P < 0.05), Physical exercise reduced the effect values of smartphone addiction and four dimensions in university students, and their behavior change had a significant improvement effect ...
Background: Addiction is always harmful to the human body. Smartphone addiction also affects students' mental and physical health. Aim: This study aims to determine the research volume conducted on students who are affected by smartphone addiction and design a database. We intended to highlight critical problems for future research.
The pervasive use of smartphones, while enhancing accessibility to information and communication, has raised concerns about its potential negative effects on physical and mental health, including the impairment of decision-making abilities. This study investigates the influence of smartphone addiction on decision-making in college students.
The results of this study indicate that there is an effect of smartphone addiction on students' academic procrastination with the details of the value of t = -3.177 and p = 0.002 <0.05.
Ard Su. To the Editor: Re " The Smartphone Trap ," by Jonathan Haidt and Jean M. Twenge (Opinion guest essay, Sunday Review, Aug. 1): The rise of smartphone addiction among teenagers is ...
However, results also indicate that 60.89% of participants never used smartphones for Blackboard, 66.01% students never used smartphones as a means for taking notes in a classroom and 66.89% ...
Evidence from a variety of cross-sectional, longitudinal and empirical studies implicate smartphone and social media use in the increase in mental distress, self-injurious behaviour and suicidality among youth; there is a dose-response relationship, and the effects appear to be greatest among girls. Social media can affect adolescents' self ...
Academic Effect. Finally, the last major reason a smartphone can impact a student's life is that it has a huge academic effect. When students are studying, whether at school or home, their phone is always around them which creates a big distraction and can lead to academic failure since students seem to spend more time on social media rather than studying.
In all, 366 (45.8%) students were categorized as being excessive users of smartphones. Students with excessive use of smartphones had lower scores the psychological well-being than those who did ...
Background and Aims: This present paper will review the existing evidence on the effects of excessive smartphone use on physical and mental health. Results: Comorbidity with depression, anxiety, OCD, ADHD and alcohol use disorder. Excessive smartphone use is associated with difficulties in cognitive-emotion regulation, impulsivity, impaired cognitive function, addiction to social networking ...
41%. Percentage of teens with the highest social media use who rate their overall mental health as poor or very poor, compared with 23% of those with the lowest use. For example, 10% of the highest use group expressed suicidal intent or self-harm in the past 12 months compared with 5% of the lowest use group, and 17% of the highest users expressed poor body image compared with 6% of the lowest ...
But there's a darker side to smartphone usage. The average time consumed on smartphones is increasing, and evidence reveals that smartphone addiction is connected to severe health issues. Essay on Mobile Addiction 800 words in English. Introduction. A mobile phone is expected to make things easier for us.
The full papers of all studies included after abstract screening were retrieved and reviewed for a second time based on the inclusion and exclusion criteria by the same two authors (A.C., J.K.L.). ... In addition to significant direct effects, smartphone addiction has significant indirect effects on personal relations via mental health and ...